Features
■ High output power
(50 W music power IEC 268.3 rules)
■ High operating supply voltage (50 V)
■ Single or split supply operations
■ Very low distortion
■ Short-circuit protection (OUT to GND)
■ Thermal shutdown
Description
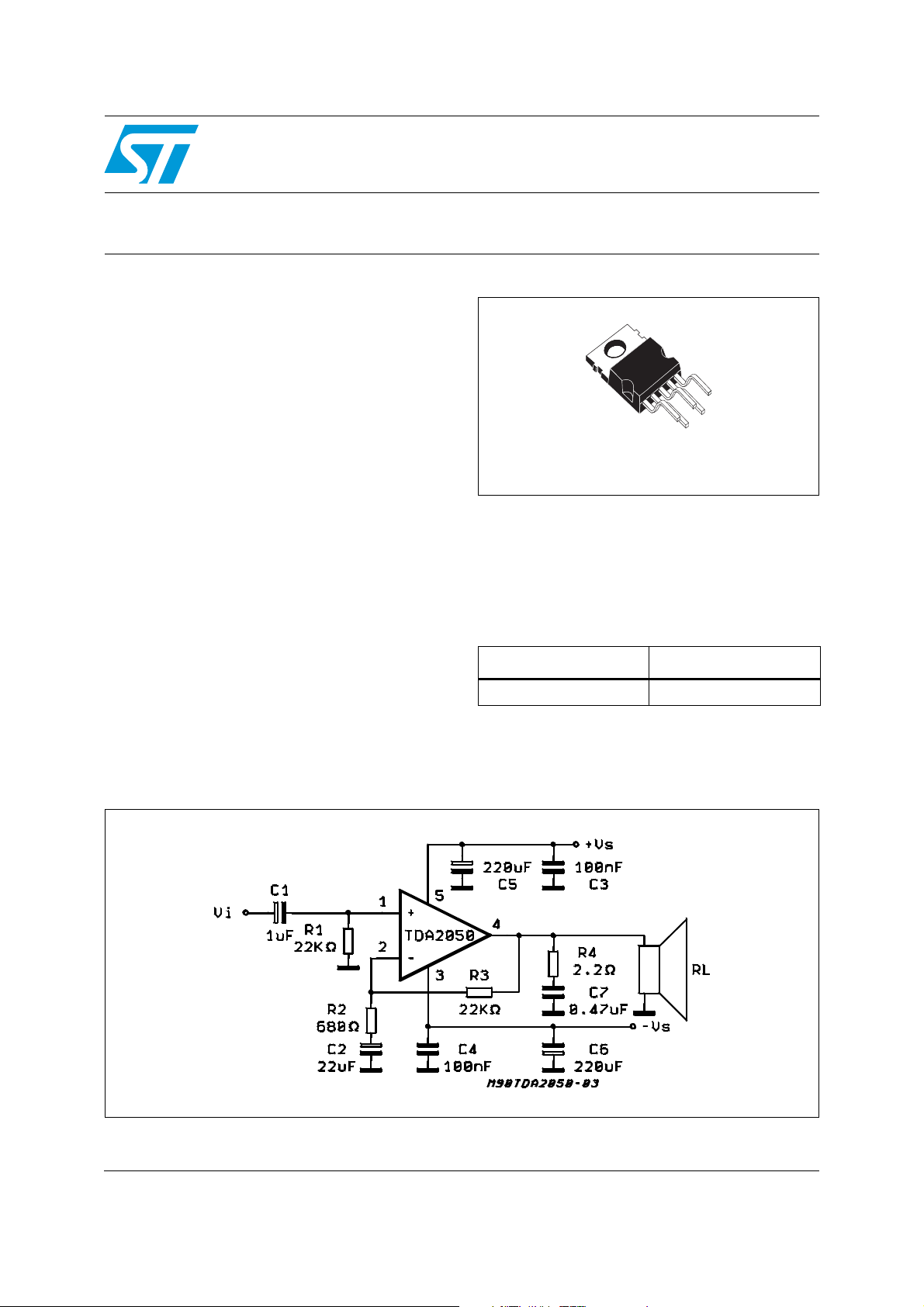
The TDA 2050 is a monolithic integrated circuit in
a Pentawatt package, intended for use as an
audio class-AB audio amplifier.
Thanks to its high power capability the TDA2050
is able to provide up to 35 W true RMS power into
a 4 ohm load at THD = 0%, V
and up to 32 W into an 8 ohm load at THD = 10%,
V
= ±22 V, f = 1 kHz.
S
Moreover, the TDA2050 delivers typically 50 W
music power into a 4 ohm load over 1 sec at
V
= 22.5 V, f = 1 kHz.
S
= ±18 V, f = 1 kHz
S
TDA2050
32 W hi-fi audio power amplifier
Pentawatt V
The high power and very low harmonic and
crossover distortion (THD = 0.05% typ, at
V
= ±22 V, PO = 0.1 to 15 W, RL= 8 ohm,
S
f = 100 Hz to 15 kHz) make the device most
suitable for both hi-fi and high-end TV sets.
Table 1. Device summary
Order code Package
TDA2050V Pentawatt vertical
Figure 1. Test and application circuit
August 2011 Doc ID 1461 Rev 3 1/18
www.st.com
18
Device overview TDA2050
1 Device overview
Table 2. Absolute maximum ratings
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
s
V
i
V
i
I
o
P
tot
T
, T
stg
Table 3. Thermal data
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
Supply voltage ±25 V
Input voltage V
s
Differential input voltage ±15 V
Output peak current (internally limited) 5 A
Power dissipation at T
Storage and junction temperature -40 to 150 °C
j
= 75 °C 25 W
CASE
R
th j-case
Thermal resistance junction-case 3 (max) °C
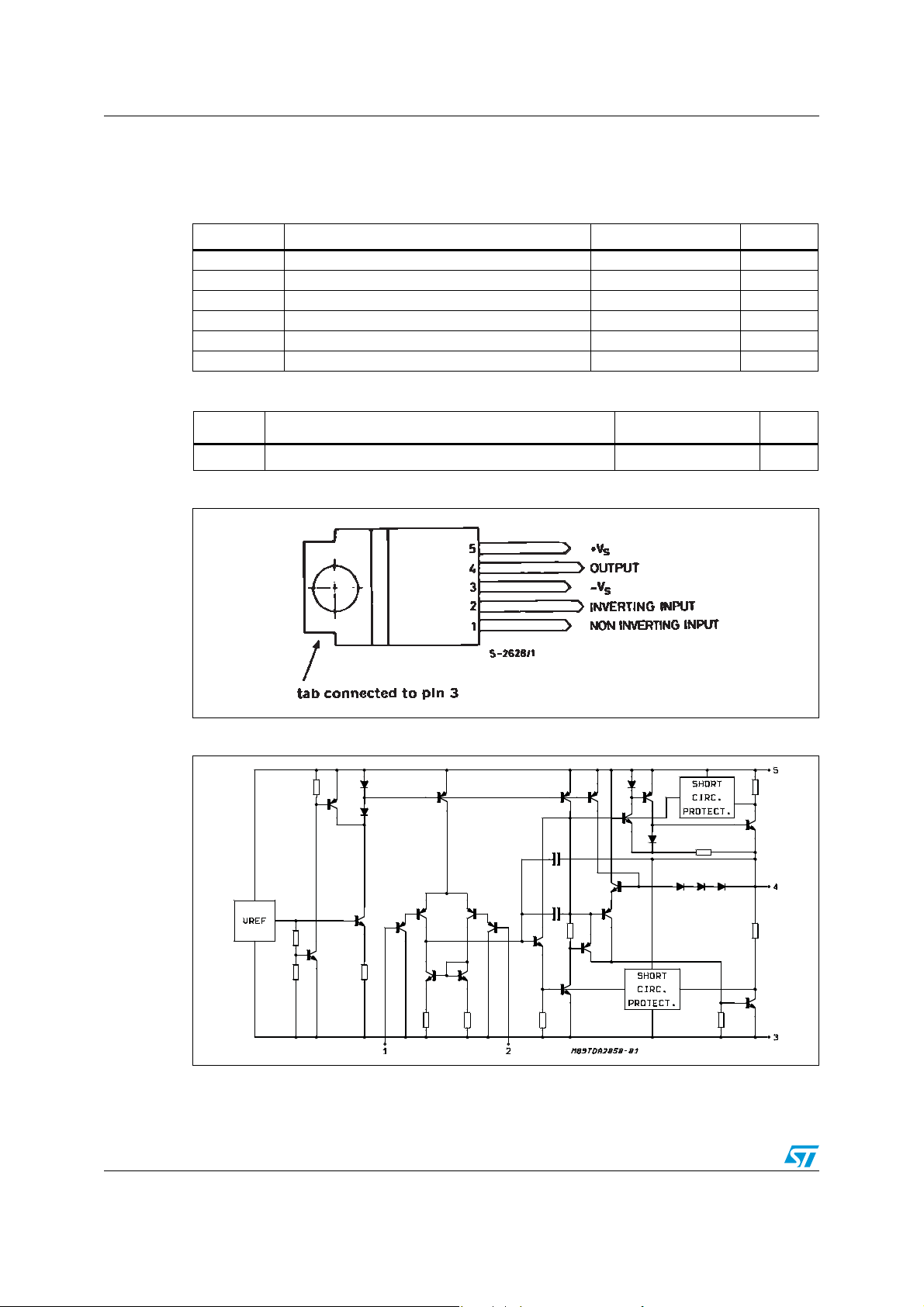
Figure 2. Pin connections (top view)
Figure 3. Schematic diagram
2/18 Doc ID 1461 Rev 3

TDA2050 Device overview
The values given in the following table refer to the test circuit VS = ±18 V, T
= 25 °C,
amb
f = 1 kHz, unless otherwise specified.
Table 4. Electrical characteristics
Symbol Parameter Test conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
V
s Supply voltage range ± 4.5 ± 25 V
I
Quiescent drain current
d
I
Input bias current Vs = ± 22 0.1 0.5 µA
b
V
I
Input offset voltage Vs = ± 22 ± 15 mV
OS
Input offset current ± 200 nA
OS
Vs = ± 4.5
Vs = ± 25
d = 0.5%,
R
P
o
Output power
= 4 Ω
L
= 8 Ω
R
L
= ± 22 V, RL = 8 Ω
V
s
d = 10%,
= 4 Ω
R
L
= 8 Ω
R
L
24
22
Vs = ± 22 V, RL = 8 Ω
Music power IEC268.3 rules
d = 10%, T = 1s
R
= 4 Ω; Vs = ± 22.5 V
L
= 0.1 to 24W, RL = 4 Ω, f = 1 kHz
P
o
f = 100 to 10 kHz, Po = 0.1 to 18 W
30
5090mA
55
28
18
25
35
22
32
50 W
0.03
0.5
0.5%%
mA
W
W
W
W
W
W
d Distortion
Vs = ± 22 V, R
f = 1 kHz, Po = 0.1 to 20 W,
f = 100 Hz to 10 kHz;
= 0.1 to 15 W
P
o
= 8 Ω,
L
0.02
0.5%%
SR Slew rate 5 8 V/µs
G
v Voltage gain (open loop) f = 1 kHz 80 dB
G
v Voltage gain (closed loop) f = 1 kHz 30 30.5 31 dB
BW Power bandwidth (-3dB) V
e
Input noise voltage
N
Input resistance (pin 1) 500 kΩ
R
i
SVR Supply voltage rejection
h Efficiency
T
Thermal shutdown junction
sd-j
temperature
= 200 mW, RL = 4 Ω; 20 to 80.000 Hz
i
B = Curve A
B = 22 Hz to 22 kHz
R
= 22 kΩ, f = 100 Hz;
g
V
= 0.5 V
ripple
P
= 28 W, RL = 4 Ω 65 %
o
= 25 W, RL = 8 Ω,Vs = ± 22 V, 67 %
P
o
RMS
4
510µVµV
45 dB
150 °C
Doc ID 1461 Rev 3 3/18
Device overview TDA2050
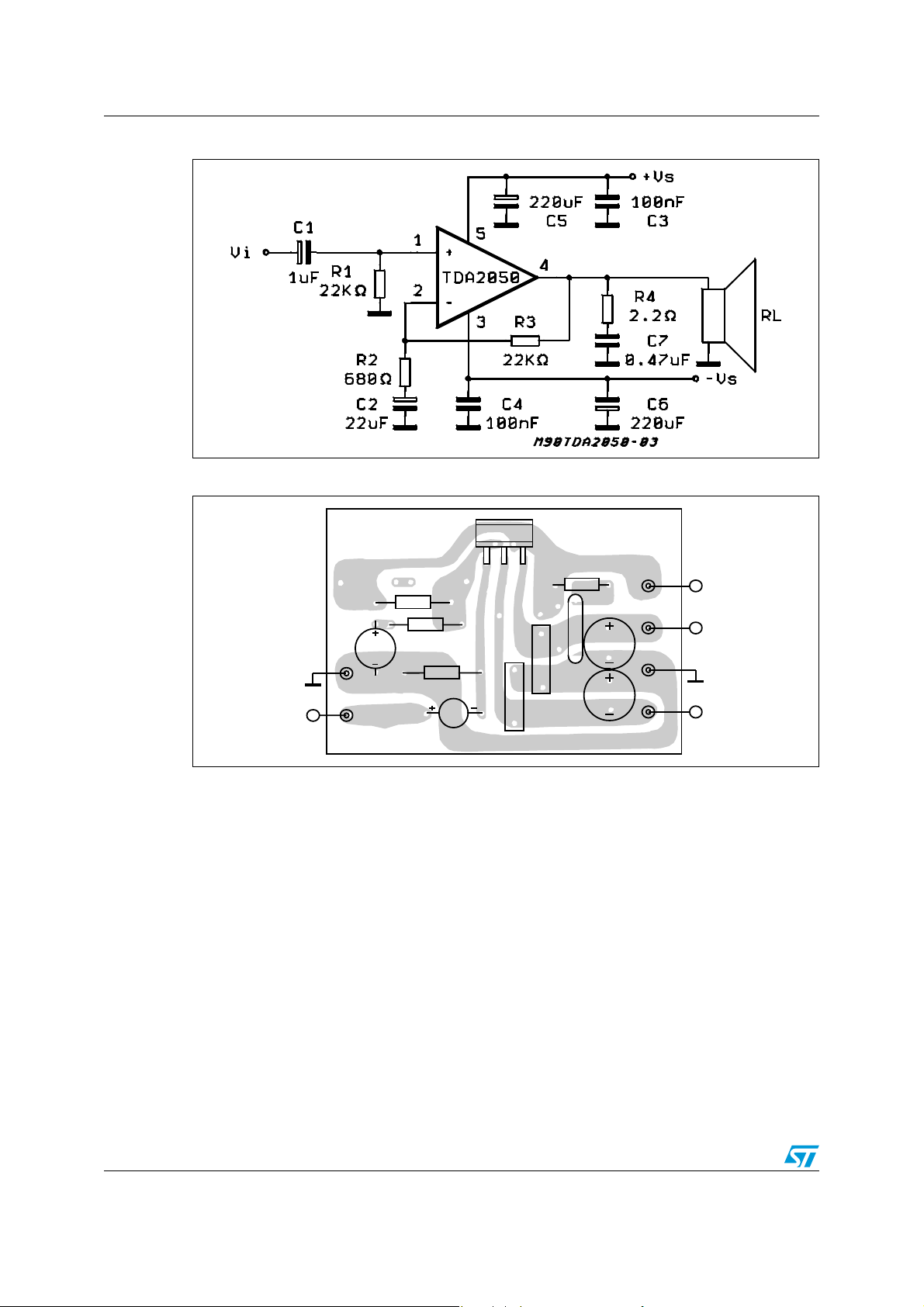
Figure 4. Split-supply typical application circuit
Figure 5. PC board and component layout of split-supply typical application circuit
TDA2050
L
R4
R3
R2
C2
R1
C4
C1
Vi
C7
C5
C3
C6
R
+Vs
-Vs
4/18 Doc ID 1461 Rev 3
TDA2050 Split-supply application suggestions
2 Split-supply application suggestions
The recommended values of the external components are those shown on the application
circuit of Figure 5. Different values can be used. The following table can help the designer.
Table 5. Recommended values of external components
Component
R1 22 kΩ Input impedance
R2 680 Ω
R3 22 kΩ Increase of gain Decrease of gain
R4 2.2 Ω Frequency stability Danger of oscillations
C1 1 µF Input decoupling DC Higher low-frequency cutoff
C2 22 µF
C3, C4 100 nF Supply voltage bypass Danger of oscillation
C5, C6 220 µF Supply voltage bypass Danger of oscillation
C7 0.47 µF Frequency stability Danger of oscillation
1. The gain must be higher than 24 dB
Recommended
value
Purpose
Feedback resistor
Inverting input DC
decoupling
Larger than
recommended value
Increase of input
impedance
Decrease of gain
Increase of switch
ON/OFF noise
(1)
Smaller than
recommended value
Decrease of Input
Impedance
Increase of gain
(1)
Higher low-frequency cutoff
Doc ID 1461 Rev 3 5/18
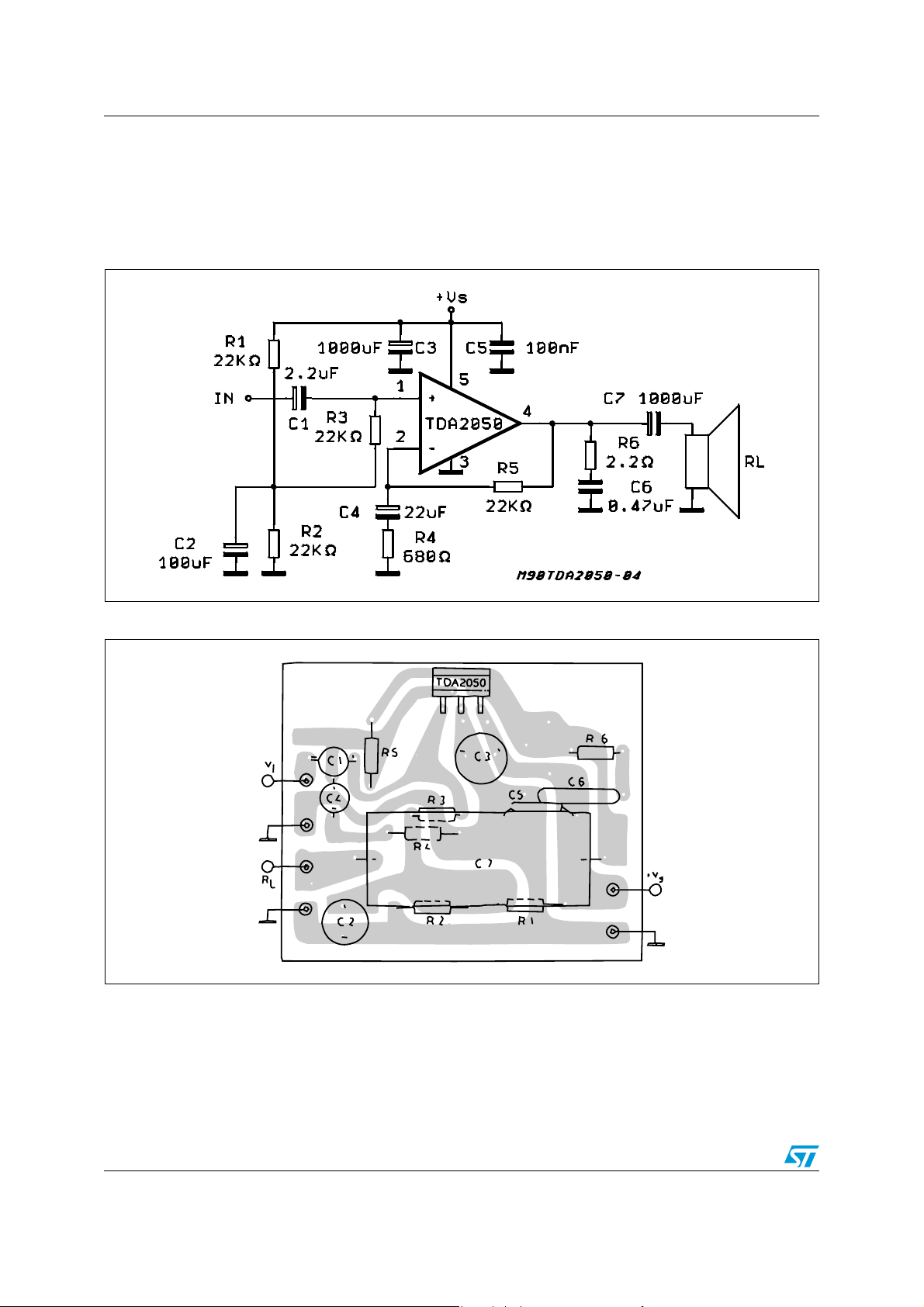
Split-supply application suggestions TDA2050
2.1 Printed circuit board
The layout shown in Figure 5 should be adopted by the designers. If different layouts are
used, the ground points of input 1 and input 2 must be well decoupled from the ground
return of the output in which a high current flows.
Figure 6. Single-supply typical application circuit
Figure 7. PC board and component layout of single-supply typical application circuit
6/18 Doc ID 1461 Rev 3
TDA2050 Single-supply application suggestions
3 Single-supply application suggestions
The recommended values of the external components are those shown in the application
circuit of Figure 6. Different values can be used. The following table can help the designer.
Table 6. Recommonded values
Component
R1, R2, R3 22 kΩ Biasing resistor
R4 680 Ω
R5 22 kΩ Decrease of gain
R6 2.2 Ω Frequency stability Danger of oscillations
C1 2.2 µF Input decoupling DC Higher low-frequency cutoff
C2 100 µF Supply voltage rejection
C3 1000 µF Supply voltage bypass
C4 22 µF
C5 100 nF Supply voltage bypass Danger of oscillations
C6 0.47 µF Frequency stability Danger of oscillations
C7 1000 µF Output DC decoupling Higher low-frequency cutoff
Recommended
value
Purpose
Feedback resistor
Inverting input DC
decoupling
Increase of gain Decrease of gain
Worse turn-off transient
Worse turn-on delay
Increase of switching
ON/OFF
Larger than
recommended value
(1)
Increase of gain
Smaller than
recommended value
(1)
Danger of oscillations
Worse turn-off transient
Higher low-frequency cutoff
1. The gain must be higher than 24 dB
Note: If the supply voltage is lower than 40 V and the load is 8 ohm (or more), a lower value of C2
can be used (i.e. 22 mF). C7 can be larger than 1000 µF only if the supply voltage does not
exceed 40 V.
Doc ID 1461 Rev 3 7/18

Typical characteristics (split-supply test circuit unless otherwise specified) TDA2050
4 Typical characteristics (split-supply test circuit
unless otherwise specified)
Figure 8. Output power vs. supply voltage Figure 9. Distortion vs. output power
Figure 10. Output power vs. supply voltage Figure 11. Distortion vs. output power
8/18 Doc ID 1461 Rev 3

TDA2050 Typical characteristics (split-supply test circuit unless otherwise specified)
Figure 12. Distortion vs. frequency Figure 13. Distortion vs. frequency
Figure 14. Quiescent current vs. supply
voltage
Figure 15. Supply voltage rejection vs.
frequency
Doc ID 1461 Rev 3 9/18

Typical characteristics (split-supply test circuit unless otherwise specified) TDA2050
Figure 16. Supply voltage rejection vs.
frequency (single-supply) for
different values of C2 (Figure 6)
Figure 18. Total power dissipation and
efficiency vs. output power
Figure 17. Supply voltage rejection vs.
frequency (single-supply) for
different values of C2 (Figure 6)
Figure 19. Total power dissipation and
efficiency vs. output power
10/18 Doc ID 1461 Rev 3

TDA2050 Short-circuit protection
5 Short-circuit protection
The TDA2050 has an original circuit which limits the current of the output transistors. The
maximum output current is a function of the collector emitter voltage, hence the output
transistors work within their safe operating area. This function can therefore be considered
as being peak power limiting rather than simple current limiting. It reduces the possibility
that the device gets damaged during an accidental short-circuit from AC output to ground.
Doc ID 1461 Rev 3 11/18

Thermal shutdown TDA2050
6 Thermal shutdown
The presence of a thermal limiting circuit offers the following advantages:
1. An overload on the output (even if it is permanent), or an above-limit ambient
temperature can be easily tolerated since Tj cannot be higher than 150 °C.
2. The heatsink can have a smaller factor of safety compared with that of a conventional
circuit. There is no possibility of device damage due to high junction temperature. If for
any reason, the junction temperature increases up to 150 °C, the thermal shutdown
simply reduces the power dissipation and the current consumption.
The maximum allowable power dissipation depends upon the thermal resistance junctionambient. Figure 20 shows this dissipable power as a function of ambient temperature for
different thermal resistances.
Figure 20. Maximum allowable power dissipation vs. ambient temperature
6.1 Mounting instructions
The power dissipated in the circuit must be removed by adding an external heatsink. Thanks
to the pentawatt package, the heatsink mounting operation is very simple, a screw or a
compression spring (clip) being sufficient. Between the heatsink and the package it is better
to insert a layer of silicon grease, to optimize the thermal contact; no electrical isolation is
needed between the two surfaces. Figure 21 shows an example of a heatsink.
12/18 Doc ID 1461 Rev 3

TDA2050 Thermal shutdown
6.2 Dimension recommendations
The following table shows the length that the heatsink in Figure 21 must have for several
values of P
Table 7. Dimension recommendations
P
(W) 12 8 6
tot
Length of heatsink (mm) 60 40 30
of heatsink (°C/W) 4.2 6.2 8.3
R
th
Figure 21. Example of heatsink
and Rth.
tot
Doc ID 1461 Rev 3 13/18

Appendix A
A.1 Music power concept
Music power is (according to the IEC clauses n.268-3 of Jan. 83) the maximum power which
the amplifier is capable of producing across the rated load resistance (regardless of nonlinearity) 1 sec after the application of a sinusoidal input signal of frequency 1 kHz.
According to this definition our method of measurement comprises the following steps:
● Set the voltage supply at the maximum operating value
● Apply a input signal in the form of a 1 kHz tone burst of 1 sec duration: the repetition
period of the signal pulses is 60 sec
● The output voltage is measured 1 sec from the start of the pulse
● Increase the input voltage until the output signal shows a THD=10%
● The music power is then V
condition of point 4 and R
The target of this method is to avoid excessive dissipation in the amplifier.
A.2 Instantaneous power
2
/RL, where V
out
is the rated load impedance
L
is the output voltage measured in the
out
TDA2050
Another power measurement (maximum instantaneous output power) was proposed by the
IEC in 1988 (IEC publication 268-3 subclause 19.A). We give here only a brief extract of the
concept, and a circuit useful for the measurement. The supply voltage is set at the maximum
operating value.
The test signal consists of a sinusoidal signal whose frequency is 20 Hz, to which are added
alternate positive and negative pulses of 50 µs duration and 500 Hz repetition rate. The
amplitude of the 20 Hz signal is chosen to drive the amplifier to its voltage clipping limits,
while the amplitude of the pulses takes the amplifier alternately into its current-overload
limits. A circuit for generating the test signal is given in Figure 22.
The load network consists of a 40 µF capacitor, in series with a 1 ohm resistor. The
capacitor limits the current due to the 20 Hz signal to a low value, whereas for the short
pulses the effective load impedance is of the order of 1 ohm, and a high output current is
produced.
Using this signal and load network the measurement may be made without causing
excessive dissipation in the amplifier. The dissipation in the 1 ohm resistor is much lower
than a rated output power of the amplifier, because the duty-cycle of the high output current
is low. By feeding the amplifier output voltage to the Xplates of an oscilloscope, and the
voltage across the 1 ohm resistor (representing the output current) to the Y=plates, it is
possible to read on the display the value of the maximum instantaneous output power.
The result of this test applied on the TDA2050 is:
Peak power = 100 W typ
14/18 Doc ID 1461 Rev 3

TDA2050
Figure 22. Test circuit for peak power measurement
Doc ID 1461 Rev 3 15/18
Package mechanical data TDA2050
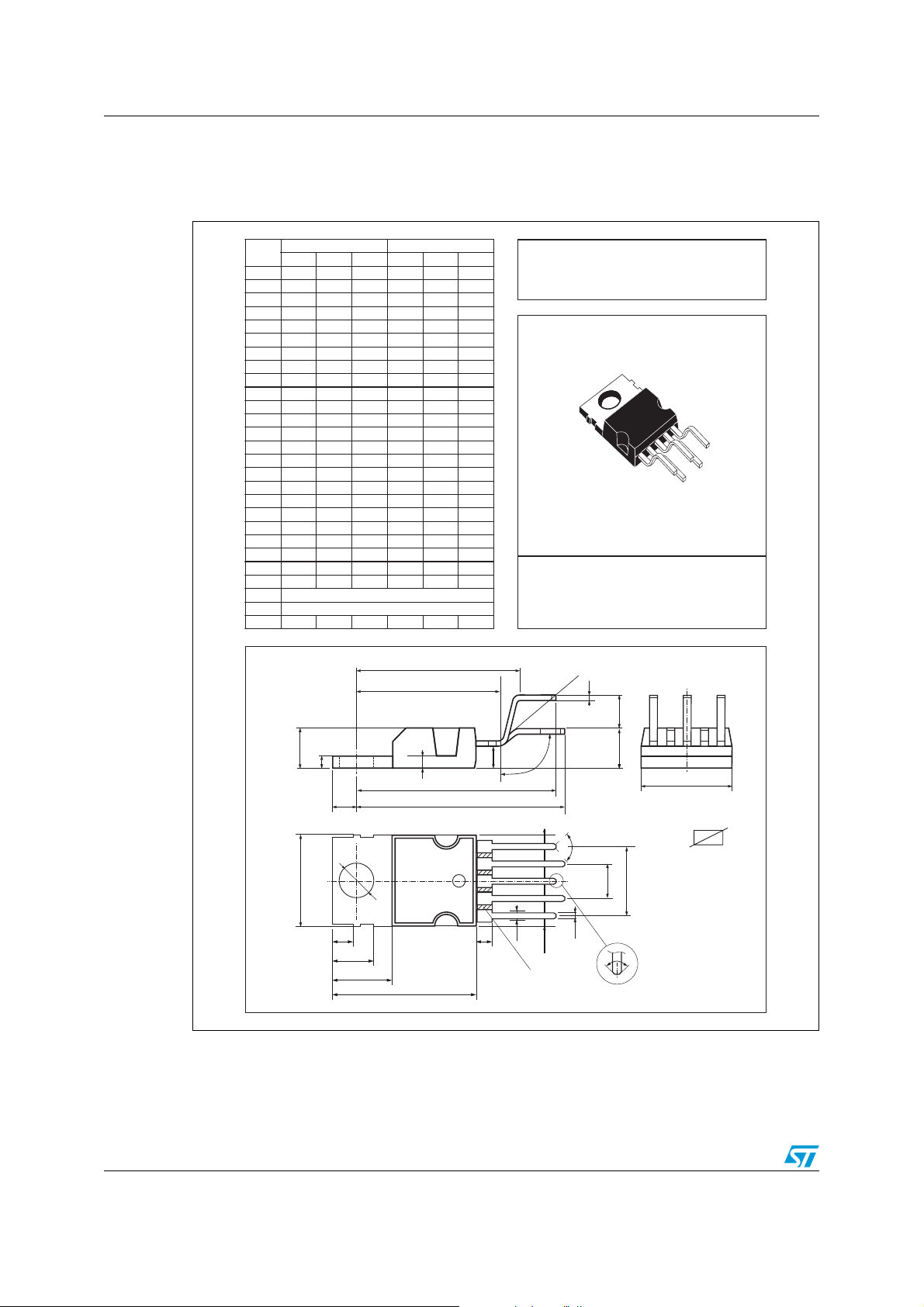
7 Package mechanical data
Figure 23. Pentawatt V package
DIM.
A 4.80 0.188
C 1.37 0.054
D 2.40 2.80 0.094 0. 11
D1 1.20 1.35 0.047 0.053
E 0.35 0.55 0.014 0.022
E1 0.76 1.19 0.030 0.047
F 0.80 1.05 0.031 0.041
F1 1.00 1.40 0.039 0.055
G 3 .20 3.40 3.60 0.126 0.134 0.142
G1 6.60 6.80 7.00 0.260 0.267 0.275
H2 10.40 0.41
H3 10.40 0.409
L 17.55 17.85 18.15 0.691 0 .703 0.7 15
L1 15.55 15.75 15.95 0.612 0.620 0.628
L2 21.2 21 .4 21.6 0.831 0.843 0.850
L3 22.3 22 .5 22.7 0.878 0.886 0.894
L4 1.29 0.051
L5 2.60 3.00 0.102 0.118
L6 15.10 15.80 0.594 0.622
L7 6.00 6.60 0.236 0.260
L9 2.10 2.70 0.083 0.106
L10 4 .30 4.80 0.170 0.189
M 4.23 4.5 4.75 0.167 0.178 0.187
M1 3.75 4.0 4.25 0.148 0.157 0.187
V4 40° (Typ.)
V5 90° (Typ.)
DIA 3 .65 3.85 0.143 0.151
mm inch
MIN. TYP. MAX. MIN. TYP. MAX.
L
L1
OUTLINE AND
MECHANICAL DATA
Weight: 2.00gr
Pentawatt V
E
M1
H3
A
C
D1
L5
Dia.
L9
L10
L7
L6
D
L2
L3
L4
V5
V4
F1
H2
RESIN BETWEEN
LEADS
M
H2
F
E1
E
GG1
F
V4
PENTVME
0015981 F
In order to meet environmental requirements, ST offers these devices in different grades of
®
ECOPACK
packages, depending on their level of environmental compliance. ECOPACK®
specifications, grade definitions and product status are available at: www.st.com.
ECOPACK
®
is an ST trademark.
16/18 Doc ID 1461 Rev 3

TDA2050 Revision history
8 Revision history
Table 8. Document revision history
Date Revision Changes
Removed minimum value from Pentawatt (vertical) package
31-Aug-2011 3
dimension H3 in Figure 23: Pentawatt V package
Revised general presentation, minor textual updates
Doc ID 1461 Rev 3 17/18

TDA2050
Please Read Carefully:
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY TWO AUTHORIZED ST REPRESENTATIVES, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT
RECOMMENDED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING
APPLICATIONS, NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY,
DEATH, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE. ST PRODUCTS WHICH ARE NOT SPECIFIED AS "AUTOMOTIVE
GRADE" MAY ONLY BE USED IN AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AT USER’S OWN RISK.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2011 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Philippines - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
18/18 Doc ID 1461 Rev 3
 Loading...
Loading...