Page 1
STM8L151C2/K2/G2/F2
UFQFPN28
UFQFPN32
TSSOP20
UFQFPN20
LQFP48
STM8L151C3/K3/G3/F3
8-bit ultralow power MCU, up to 8 KB Flash, up to 256 B data EEPROM,
RTC, timers, USART, I2C, SPI, ADC, comparators
Datasheet − production data
Features
■ Operating conditions
– Operating power supply: 1.65 to 3.6 V
(without BOR), 1.8 to 3.6 V (with BOR)
– Temperature range: -40 to 85 or 125 °C
■ Low power features
– 5 low power modes: Wait, Low power run,
Low power wait, Active-halt with RTC, Halt
– Ultralow leakage per I/0: 50 nA
– Fast wakeup from Halt: 5 µs
■ Advanced STM8 core
– Harvard architecture and 3-stage pipeline
– Max freq: 16 MHz, 16 CISC MIPS peak
– Up to 40 external interrupt sources
■ Reset and supply management
– Low power, ultrasafe BOR reset with 5
selectable thresholds
– Ultralow power POR/PDR
– Programmable voltage detector (PVD)
■ Clock management
– 32 kHz and 1-16 MHz crystal oscillators
– Internal 16 MHz factory-trimmed RC
– Internal 38 kHz low consumption RC
– Clock security system
■ Low power RTC
– BCD calendar with alarm interrupt
– Digital calibration with +/- 0.5 ppm accuracy
– LSE security system
– Auto-wakeup from Halt w/ periodic interrupt
■ Memories
– Up to 8 Kbytes of Flash program memory
plus 256 bytes of data EEPROM with ECC
– Flexible write/read protection modes
– 1 Kbyte of RAM
■ DMA
– 4 channels supporting ADC, SPI, I
2
USART, timers
– 1 channel for memory-to-memory
■ 12-bit ADC up to 1 Msps/28 channels
– Temp. sensor and internal ref. voltage
■ 2 ultralow power comparators
– 1 with fixed threshold and 1 rail to rail
– Wakeup capability
■ Timers
– Two 16-bit timers with 2 channels (IC, OC,
PWM), quadrature encoder (TIM2, TIM3)
– One 8-bit timer with 7-bit prescaler (TIM4)
– 1 Window and 1 independent watchdog
– Beeper timer with 1, 2 or 4 kHz frequencies
■ Communication interfaces
– One synchronous serial interface (SPI)
–Fast I
2
C 400 kHz
– One USART
■ Up to 41 I/Os, all mappable on interrupt vectors
■ Up to 20 capacitive sensing channels
supporting touchkey, proximity touch, linear
touch, and rotary touch sensors
■ Development support
– Fast on-chip programming and non-
intrusive debugging with SWIM
– Bootloader using USART
■ 96-bit unique ID
C,
July 2012 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 1/112
www.st.comThis is information on a product in full production.
1
Page 2

Contents STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
Contents
1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2 Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2.1 Device overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.2 Ultra-low-power continuum . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
3 Functional overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
3.1 Low power modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
3.2 Central processing unit STM8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
3.2.1 Advanced STM8 Core . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
3.2.2 Interrupt controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
3.3 Reset and supply management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
3.3.1 Power supply scheme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
3.3.2 Power supply supervisor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
3.3.3 Voltage regulator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
3.4 Clock management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.5 Low power real-time clock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
3.6 Memories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
3.7 DMA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
3.8 Analog-to-digital converter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
3.9 Ultra-low-power comparators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
3.10 System configuration controller and routing interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
3.11 Touchsensing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
3.12 Timers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
3.12.1 16-bit general purpose timers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
3.12.2 8-bit basic timer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
3.13 Watchdog timers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
3.13.1 Window watchdog timer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
3.13.2 Independent watchdog timer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
3.14 Beeper . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
3.15 Communication interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
3.15.1 SPI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
2/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 3

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Contents
3.15.2 I²C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
3.15.3 USART . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
3.16 Infrared (IR) interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
3.17 Development support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
4 Pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
4.1 System configuration options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
5 Memory and register map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
5.1 Memory mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
5.2 Register map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
6 Interrupt vector mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
7 Electrical parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
7.1 Parameter conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
7.1.1 Minimum and maximum values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
7.1.2 Typical values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
7.1.3 Typical curves . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
7.1.4 Loading capacitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
7.1.5 Pin input voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
7.2 Absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
7.3 Operating conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
7.3.1 General operating conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
7.3.2 Embedded reset and power control block characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . 53
7.3.3 Supply current characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
7.3.4 Clock and timing characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
7.3.5 Memory characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
7.3.6 I/O current injection characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
7.3.7 I/O port pin characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
7.3.8 Communication interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
7.3.9 Embedded reference voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
7.3.10 Temperature sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
7.3.11 Comparator characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
7.3.12 12-bit ADC1 characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
7.3.13 EMC characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 3/112
Page 4

Contents STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
7.4 Thermal characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
8 Option bytes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
9 Unique ID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
10 Package characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
10.1 ECOPACK . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
10.2 Package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
10.2.1 48-pin low profile quad flat 7x7mm package (LQFP48) . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
10.2.2 32-lead ultra thin fine pitch quad flat no-lead 5x5 mm package
(UFQFPN32) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
10.2.3 28-lead ultra thin fine pitch quad flat no-lead 4x4 mm package
(UFQFPN28) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
10.2.4 20-lead ultra thin fine pitch quad flat no-lead package (UFQFPN20) . 107
11 Device ordering information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
12 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
4/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 5

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 List of tables
List of tables
Table 1. Low density STM8L15xxx low power device features and peripheral counts. . . . . . . . . . . 12
Table 2. Timer feature comparison . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 3. Legend/abbreviation for table 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Table 4. Low density STM8L15xxx pin description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Table 5. Flash and RAM boundary addresses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Table 6. Factory conversion registers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Table 7. I/O port hardware register map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Table 8. General hardware register map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Table 9. CPU/SWIM/debug module/interrupt controller registers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Table 10. Interrupt mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Table 11. Voltage characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Table 12. Current characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Table 13. Thermal characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Table 14. General operating conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Table 15. Embedded reset and power control block characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Table 16. Total current consumption in Run mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Table 17. Total current consumption in Wait mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Table 18. Total current consumption and timing in Low power run mode at VDD = 1.65 V to
3.6 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Table 19. Total current consumption in Low power wait mode at VDD = 1.65 V to 3.6 V . . . . . . . . . 61
Table 20. Total current consumption and timing in Active-halt mode at VDD = 1.65 V to 3.6 V. . . . . 62
Table 21. Typical current consumption in Active-halt mode, RTC clocked by LSE external crystal. . 62
Table 22. Total current consumption and timing in Halt mode at VDD = 1.65 to 3.6 V . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Table 23. Peripheral current consumption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Table 24. Current consumption under external reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Table 25. HSE external clock characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Table 26. LSE external clock characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Table 27. HSE oscillator characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Table 28. LSE oscillator characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Table 29. HSI oscillator characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Table 30. LSI oscillator characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Table 31. RAM and hardware registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Table 32. Flash program and data EEPROM memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Table 33. I/O current injection susceptibility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Table 34. I/O static characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Table 35. Output driving current (high sink ports). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Table 36. Output driving current (true open drain ports) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Table 37. Output driving current (PA0 with high sink LED driver capability). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Table 38. NRST pin characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Table 39. SPI1 characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Table 40. I2C characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Table 41. Reference voltage characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Table 42. TS characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Table 43. Comparator 1 characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Table 44. Comparator 2 characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Table 45. ADC1 characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Table 46. ADC1 accuracy with VDDA = 3.3 V to 2.5 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Table 47. ADC1 accuracy with VDDA = 2.4 V to 3.6 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 5/112
Page 6

List of tables STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
Table 48. ADC1 accuracy with VDDA = VREF+ = 1.8 V to 2.4 V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Table 49. R
max for f
AIN
= 16 MHz . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
ADC
Table 50. EMS data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Table 51. EMI data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Table 52. ESD absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Table 53. Electrical sensitivities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Table 54. Thermal characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Table 55. Option byte addresses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Table 56. Option byte description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Table 57. Unique ID registers (96 bits) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Table 58. LQFP48 package mechanical data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Table 59. UFQFPN32 package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Table 60. UFQFPN28 package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Table 61. UFQFPN20 - 20-lead ultra thin fine pitch quad flat package (3x3)
package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Table 62. TSSOP20 - 20-pin thin shrink small outline package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
6/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 7

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 List of figures
List of figures
Figure 1. Low density STM8L151xx device block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Figure 2. Low density STM8L15x clock tree diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Figure 3. STM8L151Cx LQFP48 package pinout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Figure 4. STM8L151Kx UFQFPN32 package pinout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Figure 5. STM8L151Gx UFQFPN28 package pinout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Figure 6. STM8L151Fx UFQFPN20 package pinout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Figure 7. STM8L151Fx TSSOP20 package pinout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Figure 8. Memory map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Figure 9. Pin loading conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Figure 10. Pin input voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Figure 11. POR/BOR thresholds . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Figure 12. Typ. IDD(RUN) vs. VDD, fCPU = 16 MHz . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Figure 13. Typ. IDD(Wait) vs. VDD, fCPU = 16 MHz 1). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Figure 14. Typ. IDD(LPR) vs. VDD (LSI clock source) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Figure 15. Typ. IDD(LPW) vs. VDD (LSI clock source) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Figure 16. HSE oscillator circuit diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Figure 17. LSE oscillator circuit diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Figure 18. Typical HSI frequency vs V
Figure 19. Typical LSI frequency vs. VDD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Figure 20. Typical VIL and VIH vs VDD (high sink I/Os) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Figure 21. Typical VIL and VIH vs VDD (true open drain I/Os) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Figure 22. Typical pull-up resistance R
Figure 23. Typical pull-up current I
Figure 24. Typ. VOL @ VDD = 3.0 V (high sink ports) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Figure 25. Typ. VOL @ VDD = 1.8 V (high sink ports) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Figure 26. Typ. VOL @ VDD = 3.0 V (true open drain ports) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Figure 27. Typ. VOL @ VDD = 1.8 V (true open drain ports) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Figure 28. Typ. VDD - VOH @ VDD = 3.0 V (high sink ports) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Figure 29. Typ. VDD - VOH @ VDD = 1.8 V (high sink ports) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Figure 30. Typical NRST pull-up resistance R
Figure 31. Typical NRST pull-up current I
Figure 32. Recommended NRST pin configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Figure 33. SPI1 timing diagram - slave mode and CPHA=0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Figure 34. SPI1 timing diagram - slave mode and CPHA=1
Figure 35. SPI1 timing diagram - master mode
Figure 36. Typical application with I2C bus and timing diagram 1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Figure 37. ADC1 accuracy characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Figure 38. Typical connection diagram using the ADC1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Figure 39. Power supply and reference decoupling (V
Figure 40. Power supply and reference decoupling (VREF+ connected to VDDA) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Figure 41. Max. dynamic current consumption on V
conversion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Figure 42. LQFP48 package outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Figure 43. UFQFPN32 package outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Figure 44. Recommended UFQFPN32 footprint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Figure 45. UFQFPN28 package outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Figure 46. Recommended UFQFPN28 footprint (dimensions in mm) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Figure 47. UFQFPN20 - 20-lead ultra thin fine pitch quad flat package outline (3x3) . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
DD
vs VDD with VIN=VSS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
PU
vs VDD with VIN=VSS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
pu
vs VDD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
PU
vs VDD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
pu
(1)
(1)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
REF+
REF+
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
not connected to V
). . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
DDA
supply pin during ADC
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 7/112
Page 8

List of figures STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
Figure 48. UFQFPN20 recommended footprint (dimensions in mm). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Figure 49. TSSOP20 - 20-pin thin shrink small outline package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Figure 50. Low density STM8L15xxx ordering information scheme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
8/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 9

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Introduction
1 Introduction
This document describes the features, pinout, mechanical data and ordering information for
the Low density STM8L15xxx devices: STM8L151x2 and STM8L151x3 microcontrollers
with a Flash memory density of up to 8 Kbytes.
For further details on the STMicroelectronics Ultralow power family please refer to
Section 2.2: Ultra-low-power continuum on page 13.
For detailed information on device operation and registers, refer to the reference manual
(RM0031).
For information on to the Flash program memory and data EEPROM, refer to the
programming manual (PM0054).
For information on the debug module and SWIM (single wire interface module), refer to the
STM8 SWIM communication protocol and debug module user manual (UM0470).
For information on the STM8 core, refer to the STM8 CPU programming manual (PM0044).
Low density devices provide the following benefits:
● Integrated system
– Up to 8 Kbytes of low-density embedded Flash program memory
– 256 bytes of data EEPROM
– 1 Kbyte of RAM
– Internal high-speed and low-power low speed RC.
– Embedded reset
● Ultralow power consumption
– 1 µA in Active-halt mode
– Clock gated system and optimized power management
– Capability to execute from RAM for Low power wait mode and Low power run
mode
● Advanced features
– Up to 16 MIPS at 16 MHz CPU clock frequency
– Direct memory access (DMA) for memory-to-memory or peripheral-to-memory
access.
● Short development cycles
– Application scalability across a common family product architecture with
compatible pinout, memory map and modular peripherals.
– Wide choice of development tools
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 9/112
Page 10

Introduction STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
STM8L Ultralow power microcontrollers can operate either from 1.8 to 3.6 V (down to 1.65 V
at power-down) or from 1.65 to 3.6 V. They are available in the -40 to +85 °C and -40 to
+125 °C temperature ranges.
These features make the STM8L Ultralow power microcontroller families suitable for a wide
range of applications:
● Medical and handheld equipment
● Application control and user interface
● PC peripherals, gaming, GPS and sport equipment
● Alarm systems, wired and wireless sensors
● Metering
The devices are offered in five different packages from 20 to 48 pins. Different sets of
peripherals are included depending on the device. Refer to Section 3 for an overview of the
complete range of peripherals proposed in this family.
All STM8L Ultralow power products are based on the same architecture with the same
memory mapping and a coherent pinout.
Figure 1 shows the block diagram of the STM8L Low density family.
10/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 11

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Description
2 Description
The Low density STM8L15xxx Ultralow power devices feature an enhanced STM8 CPU
core providing increased processing power (up to 16 MIPS at 16 MHz) while maintaining the
advantages of a CISC architecture with improved code density, a 24-bit linear addressing
space and an optimized architecture for low power operations.
The family includes an integrated debug module with a hardware interface (SWIM) which
allows non-intrusive in-application debugging and ultrafast Flash programming.
All Low density STM8L15xxx microcontrollers feature embedded data EEPROM and low
power low-voltage single-supply program Flash memory.
The devices incorporate an extensive range of enhanced I/Os and peripherals, a 12-bit
ADC, two comparators, a real-time clock, two 16-bit timers, one 8-bit timer, as well as
standard communication interfaces such as an SPI, an I
modular design of the peripheral set allows the same peripherals to be found in different ST
microcontroller families including 32-bit families. This makes any transition to a different
family very easy, and simplified even more by the use of a common set of development
tools.
2
C interface, and one USART. The
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 11/112
Page 12
Description STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
2.1 Device overview
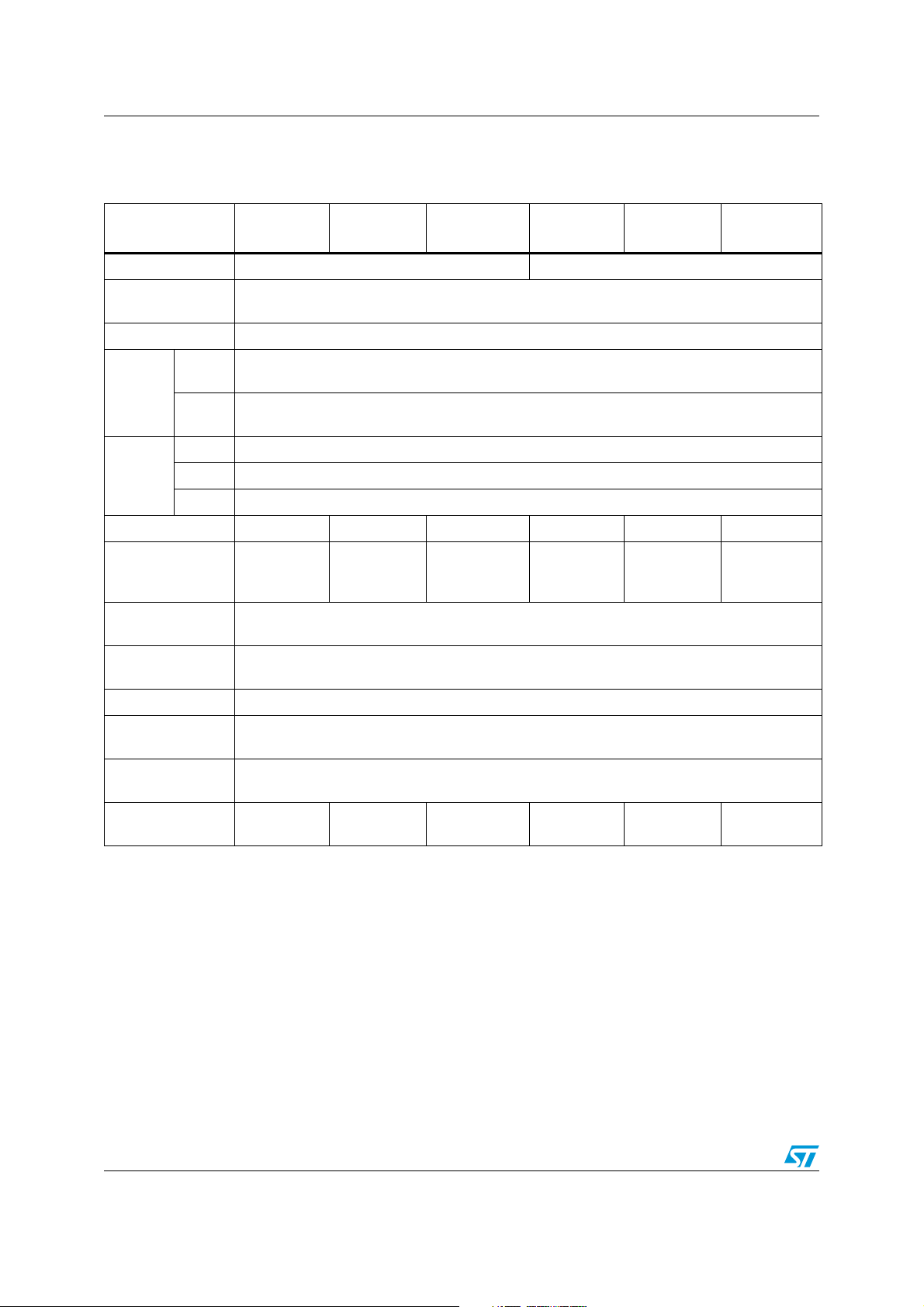
Table 1. Low density STM8L15xxx low power device features and peripheral counts
Features STM8L151F3 STM8L151G3
STM8L151K3/
STM8L151C3
STM8L151F2 STM8L151G2
STM8L151K2/
STM8L151C2
Flash (Kbytes) 8 4
Data EEPROM
(bytes)
256
RAM (Kbytes) 1
Basic
1
(8-bit)
Timers
General
purpose
Commun
-ication
interfaces
SPI 1
I2C 1
USART 1
GPIOs 18
12-bit synchronized
ADC (number of
channels)
(10)
Comparators
(COMP1/COMP2)
Others
(1)
1
26
(18)
(1)
1
30
(2)
/41
1
(23/28)
RTC, window watchdog, independent watchdog,
16-MHz and 38-kHz internal RC, 1- to 16-MHz and 32-kHz external oscillator
2
(16-bit)
(1)(2)
18
(3)
2
1
(10)
(1)
26
(18)
(1)
1
CPU frequency 16 MHz
Operating voltage
Operating
temperature
1.8 to 3.6 V (down to 1.65 V at power-down) with BOR
1.65 to 3.6 V without BOR
− 40 to +85 °C / − 40 to +125 °C
(2)
30
(23/28)
/41
1
(1)(2)
(3)
Packages
1. The number of GPIOs given in this table includes the NRST/PA1 pin but the application can use the NRST/PA1 pin as
general purpose output only (PA1).
2. 26 GPIOs in the STM8L151K3 and 40 GPIOs in the STM8L151C3.
3. 22 channels in the STM8L151K3 and 28 channels in the STM8L151C3.
TSSOP20
UFQFPN20
UFQFPN28
UFQFPN32
LQFP48
TSSOP20
UFQFPN20
UFQFPN28
UFQFPN32
LQFP48
12/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 13

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Description
2.2 Ultra-low-power continuum
The ultra-low-power Low density STM8L15xxx devices are fully pin-to-pin, software and
feature compatible. Besides the full compatibility within the family, the devices are part of
STMicroelectronics microcontrollers ultra-low-power strategy which also includes
STM8L101xx and STM32L15xxx. The STM8L and STM32L families allow a continuum of
performance, peripherals, system architecture, and features.
They are all based on STMicroelectronics 0.13 µm ultra-low leakage process.
Note: 1 The STM8L151xx and STM8L152xx are pin-to-pin compatible with STM8L101xx devices.
Performance
All families incorporate highly energy-efficient cores with both Harvard architecture and
pipelined execution: advanced STM8 core for STM8L families and ARM Cortex™-M3 core
for STM32L family. In addition specific care for the design architecture has been taken to
optimize the mA/DMIPS and mA/MHz ratios.
This allows the ultra-low-power performance to range from 5 up to 33.3 DMIPs.
Shared peripherals
STM8L151xx/152xx and STM32L15xx share identical peripherals which ensure a very easy
migration from one family to another:
● Analog peripherals: ADC1 and comparators COMP1/COMP2
● Digital peripherals: RTC and some communication interfaces
Common system strategy
To offer flexibility and optimize performance, the STM8L151xx/152xx and STM32L15xx
devices use a common architecture:
● Same power supply range from 1.8 to 3.6 V, down to 1.65 V at power down
● Architecture optimized to reach ultra-low consumption both in low power modes and
Run mode
● Fast startup strategy from low power modes
● Flexible system clock
● Ultra-safe reset: same reset strategy for both STM8L15x and STM32L15xxx including
power-on reset, power-down reset, brownout reset and programmable voltage detector.
Features
ST ultra-low-power continuum also lies in feature compatibility:
● More than 10 packages with pin count from 20 to 100 pins and size down to 3 x 3 mm
● Memory density ranging from 4 to 128 Kbytes
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 13/112
Page 14
Functional overview STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
MS18275V2
Clock
controller
and CSS
Clocks
Address, control and data buses
8-Kbyte
1-Kbyte RAM
to core and
peripherals
IWDG
(38 kHz clock)
Port A
Port B
Port C
Power
VOLT. REG.
WWDG
256-byte
Port D
Port E
Beeper
RTC
memoryProgram
Data EEPROM
@V
DD
V
DD18
V
DD
=1.65 V
V
SS
SWIM
SCL, SDA,
SPI1_MOSI, SPI1_MISO,
SPI1_SCK, SPI1_NSS
USART1_RX, USART1_TX,
USART1_CK
ADC1_INx
COMP1_INP
COMP 1
COMP 2
COMP2_INP
V
DDA, VSSA
SMB
@V
DDA/VSSA
Temp sensor
12-bit ADC1
V
DDREF
3.6 V
NRST
PA[7:0]
PB[7:0]
PC[7:0]
PD[7:0]
PE[7:0]
PF0
BEEP
ALARM, CALIB,
POR/PDR
OSC_IN,
OSC_OUT
OSC32_IN,
OSC32_OUT
to
BOR
PVD
PVD_IN
RESET
DMA1 (4 channels)
2 channels
2 channels
COMP2_INM
Internal reference
voltage
VREFINT out
IR_TIM
1-16 MHz oscillator
16 MHz internal RC
32 kHz oscillator
STM8 Core
16-bit Timer 2
38 kHz internal RC
Interrupt controller
16-bit Timer 3
Debug module
(SWIM)
8-bit Timer 4
Infrared interface
SPI1
I²C1
USART1
V
SSREF
Port F
up to
(2)
(2)
(2)
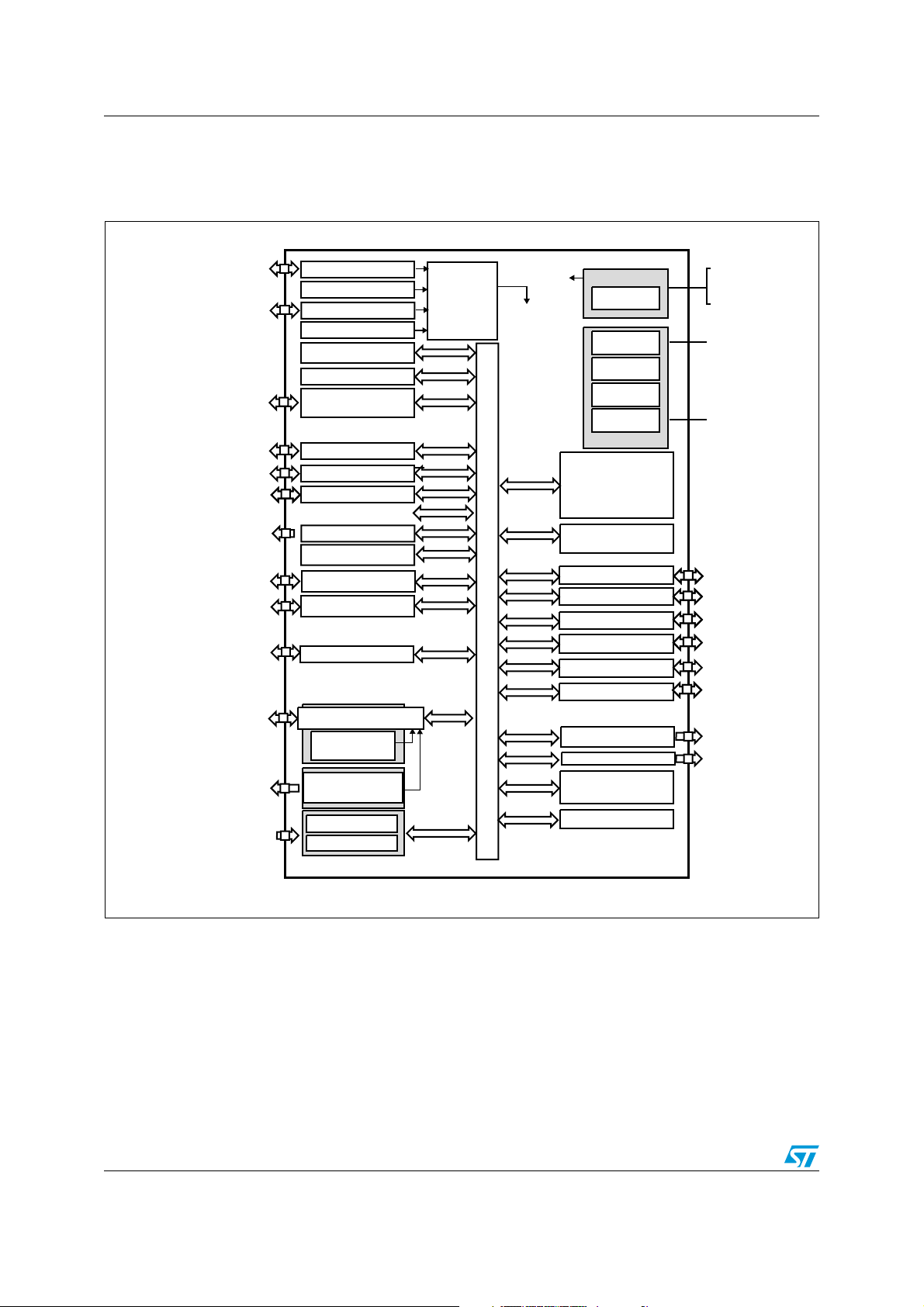
3 Functional overview
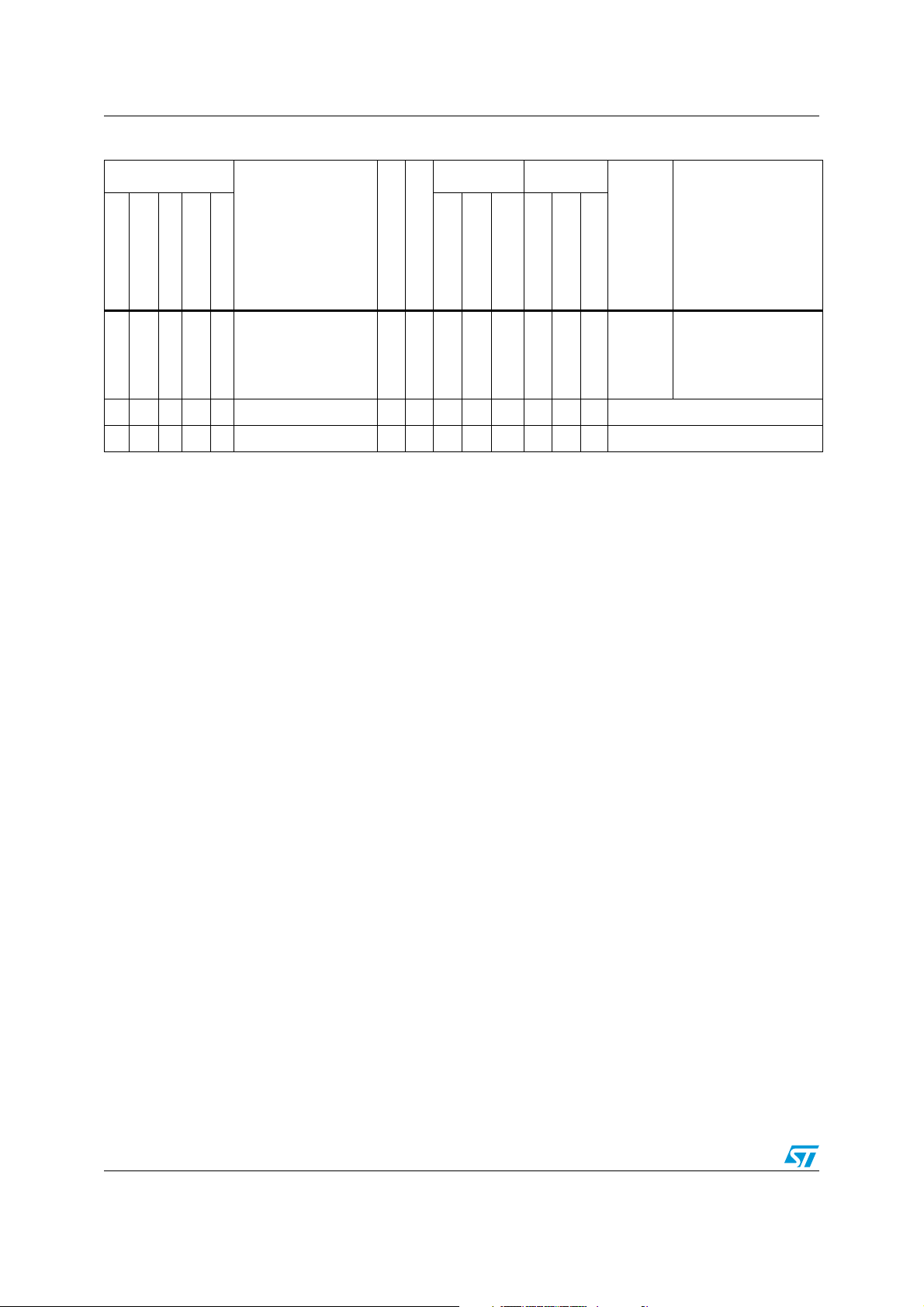
Figure 1. Low density STM8L151xx device block diagram
1. Legend:
ADC: Analog-to-digital converter
BOR: Brownout reset
DMA: Direct memory access
I²C: Inter-integrated circuit multimaster interface
IWDG: Independent watchdog
POR/PDR: Power on reset / power down reset
RTC: Real-time clock
SPI: Serial peripheral interface
SWIM: Single wire interface module
USART: Universal synchronous asynchronous receiver transmitter
WWDG: Window watchdog
2. There is no TIM1 on STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 devices.
14/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 15

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Functional overview
3.1 Low power modes
The Low density STM8L15x devices support five low power modes to achieve the best
compromise between low power consumption, short startup time and available wakeup
sources:
● Wait mode: The CPU clock is stopped, but selected peripherals keep running. An
internal or external interrupt or a Reset can be used to exit the microcontroller from
Wait mode (WFE or WFI mode). Wait consumption: refer to Tabl e 1 7.
● Low power run mode: The CPU and the selected peripherals are running. Execution
is done from RAM with a low speed oscillator (LSI or LSE). Flash and data EEPROM
are stopped and the voltage regulator is configured in ultra-low-power mode. The
microcontroller enters Low power run mode by software and can exit from this mode by
software or by a reset.
All interrupts must be masked. They cannot be used to exit the microcontroller from this
mode. Low power run mode consumption: refer to Ta bl e 1 8 .
● Low power wait mode: This mode is entered when executing a Wait for event in Low
power run mode. It is similar to Low power run mode except that the CPU clock is
stopped. The wakeup from this mode is triggered by a Reset or by an internal or
external event (peripheral event generated by the timers, serial interfaces, DMA
controller (DMA1), comparators and I/O ports). When the wakeup is triggered by an
event, the system goes back to Low power run mode.
All interrupts must be masked. They cannot be used to exit the microcontroller from this
mode. Low power wait mode consumption: refer to Tab le 1 9.
● Active-halt mode: CPU and peripheral clocks are stopped, except RTC. The wakeup
can be triggered by RTC interrupts, external interrupts or reset. Active-halt
consumption: refer to Tab l e 2 0 and Ta bl e 2 1 .
● Halt mode: CPU and peripheral clocks are stopped, the device remains powered on.
The RAM content is preserved. The wakeup is triggered by an external interrupt or
reset. A few peripherals have also a wakeup from Halt capability. Switching off the
internal reference voltage reduces power consumption. Through software configuration
it is also possible to wake up the device without waiting for the internal reference
voltage wakeup time to have a fast wakeup time of 5 µs. Halt consumption: refer to
Ta bl e 2 2 .
3.2 Central processing unit STM8
3.2.1 Advanced STM8 Core
The 8-bit STM8 core is designed for code efficiency and performance with an Harvard
architecture and a 3-stage pipeline.
It contains 6 internal registers which are directly addressable in each execution context, 20
addressing modes including indexed indirect and relative addressing, and 80 instructions.
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 15/112
Page 16

Functional overview STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
Architecture and registers
● Harvard architecture
● 3-stage pipeline
● 32-bit wide program memory bus - single cycle fetching most instructions
● X and Y 16-bit index registers - enabling indexed addressing modes with or without
offset and read-modify-write type data manipulations
● 8-bit accumulator
● 24-bit program counter - 16 Mbyte linear memory space
● 16-bit stack pointer - access to a 64 Kbyte level stack
● 8-bit condition code register - 7 condition flags for the result of the last instruction
Addressing
● 20 addressing modes
● Indexed indirect addressing mode for lookup tables located anywhere in the address
space
● Stack pointer relative addressing mode for local variables and parameter passing
Instruction set
● 80 instructions with 2-byte average instruction size
● Standard data movement and logic/arithmetic functions
● 8-bit by 8-bit multiplication
● 16-bit by 8-bit and 16-bit by 16-bit division
● Bit manipulation
● Data transfer between stack and accumulator (push/pop) with direct stack access
● Data transfer using the X and Y registers or direct memory-to-memory transfers
3.2.2 Interrupt controller
The Low density STM8L15x features a nested vectored interrupt controller:
● Nested interrupts with 3 software priority levels
● 32 interrupt vectors with hardware priority
● Up to 40 external interrupt sources on 11 vectors
● Trap and reset interrupts
16/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 17

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Functional overview
3.3 Reset and supply management
3.3.1 Power supply scheme
The device requires a 1.65 V to 3.6 V operating supply voltage (VDD). The external power
supply pins must be connected as follows:
● V
● V
● V
● V
3.3.2 Power supply supervisor
The device has an integrated ZEROPOWER power-on reset (POR)/power-down reset
(PDR), coupled with a brownout reset (BOR) circuitry. At power-on, BOR is always active,
and ensures proper operation starting from 1.8 V. After the 1.8 V BOR threshold is reached,
the option byte loading process starts, either to confirm or modify default thresholds, or to
disable BOR permanently (in which case, the V
Five BOR thresholds are available through option bytes, starting from 1.8 V to 3 V. To
reduce the power consumption in Halt mode, it is possible to automatically switch off the
internal reference voltage (and consequently the BOR) in Halt mode. The device remains
under reset when V
for any external reset circuit.
SS1
; V
= 1.8 to 3.6 V, down to 1.65 V at power down: external power supply for
DD1
I/Os and for the internal regulator. Provided externally through V
corresponding ground pin is V
SSA ; VDDA
= 1.8 to 3.6 V, down to 1.65 V at power down: external power supplies for
analog peripherals (minimum voltage to be applied to V
used). V
SS2
I/Os. V
REF+
externally through V
and V
DDA
; V
= 1.8 to 3.6 V, down to 1.65 V at power down: external power supplies for
DD2
and V
DD2
; V
(for ADC1): external reference voltage for ADC1. Must be provided
REF-
DD
must be connected to V
SSA
must be connected to V
SS2
and V
REF+
is below a specified threshold, V
SS1
REF-
.
pin.
is 1.8 V when the ADC1 is
DDA
and V
DD1
and V
DD1
min value at power down is 1.65 V).
DD
POR/PDR
, respectively.
SS1
, respectively.
SS1
or V
pins, the
DD1
, without the need
BOR
The device features an embedded programmable voltage detector (PVD) that monitors the
V
DD/VDDA
power supply and compares it to the V
levels between 1.85 V and 3.05 V, chosen by software, with a step around 200 mV. An
interrupt can be generated when V
V
DD/VDDA
is higher than the V
a warning message and/or put the MCU into a safe state. The PVD is enabled by software.
3.3.3 Voltage regulator
The Low density STM8L15x embeds an internal voltage regulator for generating the 1.8 V
power supply for the core and peripherals.
This regulator has two different modes:
● Main voltage regulator mode (MVR) for Run, Wait for interrupt (WFI) and Wait for event
(WFE) modes.
● Low power voltage regulator mode (LPVR) for Halt, Active-halt, Low power run and Low
power wait modes.
When entering Halt or Active-halt modes, the system automatically switches from the MVR
to the LPVR in order to reduce current consumption.
threshold. This PVD offers 7 different
PVD
DD/VDDA
threshold. The interrupt service routine can then generate
PVD
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 17/112
drops below the V
threshold and/or when
PVD
Page 18

Functional overview STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
3.4 Clock management
The clock controller distributes the system clock (SYSCLK) coming from different oscillators
to the core and the peripherals. It also manages clock gating for low power modes and
ensures clock robustness.
Features
● Clock prescaler: to get the best compromise between speed and current consumption
the clock frequency to the CPU and peripherals can be adjusted by a programmable
prescaler
● Safe clock switching: Clock sources can be changed safely on the fly in run mode
through a configuration register.
● Clock management: To reduce power consumption, the clock controller can stop the
clock to the core, individual peripherals or memory.
● System clock sources: 4 different clock sources can be used to drive the system
clock:
– 1-16 MHz High speed external crystal (HSE)
– 16 MHz High speed internal RC oscillator (HSI)
– 32.768 kHz Low speed external crystal (LSE)
– 38 kHz Low speed internal RC (LSI)
● RTC clock sources: the above four sources can be chosen to clock the RTC whatever
the system clock.
● Startup clock: After reset, the microcontroller restarts by default with an internal
2 MHz clock (HSI/8). The prescaler ratio and clock source can be changed by the
application program as soon as the code execution starts.
● Clock security system (CSS): This feature can be enabled by software. If a HSE clock
failure occurs, the system clock is automatically switched to HSI.
● Configurable main clock output (CCO): This outputs an external clock for use by the
application.
18/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 19

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Functional overview
Figure 2. Low density STM8L15x clock tree diagram
SWIM[3:0]
OSC_OUT
OSC_IN
OSC32_OUT
OSC32_IN
CCO
HSE OSC
1-16 MHz
HSI RC
1-16 MHz
LSI RC
38 kHz
LSE OSC
32.768 kHz
Configurable
clock output
CCO
prescaler
/1;2;4;8;16;32;64
HSE
HSI
LSI
LSE
LSE
CLKBEEPSEL[1:0]
LSI
RTCSEL[3:0]
/1;2;4;8;16;32;64
CCOSEL[3:0]
SYSCLK
prescaler
/1;2;4;8;16;32;64
RTC
prescaler
HSI
LSI
HSE
LSE
SYSCLK to core and
Peripheral
Clock
enable (13 bits)
BEEPCLK
IWDGCLK
RTCCLK
memory
PCLK to
peripherals
to
BEEP
to
IWDG
to
RTC
MS18281V1
3.5 Low power real-time clock
The real-time clock (RTC) is an independent binary coded decimal (BCD) timer/counter.
Six byte locations contain the second, minute, hour (12/24 hour), week day, date, month,
year, in BCD (binary coded decimal) format. Correction for 28, 29 (leap year), 30, and 31
day months are made automatically.
It provides a programmable alarm and programmable periodic interrupts with wakeup from
Halt capability.
● Periodic wakeup time using the 32.768 kHz LSE with the lowest resolution (of 61 µs) is
from min. 122 µs to max. 3.9 s. With a different resolution, the wakeup time can reach
36 hours
● Periodic alarms based on the calendar can also be generated from every second to
every year
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 19/112
Page 20

Functional overview STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
3.6 Memories
The Low density STM8L15x devices have the following main features:
● Up to 1 Kbyte of RAM
● The non-volatile memory is divided into three arrays:
– Up to 8 Kbytes of low-density embedded Flash program memory
– 256 bytes of data EEPROM
–Option bytes.
The EEPROM embeds the error correction code (ECC) feature.
The option byte protects part of the Flash program memory from write and readout piracy.
3.7 DMA
A 4-channel direct memory access controller (DMA1) offers a memory-to-memory and
peripherals-from/to-memory transfer capability. The 4 channels are shared between the
following IPs with DMA capability: ADC1, I2C1, SPI1, USART1, the three Timers.
3.8 Analog-to-digital converter
● 12-bit analog-to-digital converter (ADC1) with 25 channels (including 1 fast channel),
temperature sensor and internal reference voltage
● Conversion time down to 1 µs with f
● Programmable resolution
● Programmable sampling time
● Single and continuous mode of conversion
● Scan capability: automatic conversion performed on a selected group of analog inputs
● Analog watchdog
● Triggered by timer
SYSCLK
Note: ADC1 can be served by DMA1.
3.9 Ultra-low-power comparators
The Low density STM8L15x embeds two comparators (COMP1 and COMP2) sharing the
same current bias and voltage reference. The voltage reference can be internal or external
(coming from an I/O).
● One comparator with fixed threshold (COMP1).
● One comparator rail to rail with fast or slow mode (COMP2). The threshold can be one
of the following:
– External I/O
– Internal reference voltage or internal reference voltage submultiple (1/4, 1/2, 3/4)
= 16 MHz
The two comparators can be used together to offer a window function. They can wake up
from Halt mode.
20/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 21

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Functional overview
3.10 System configuration controller and routing interface
The system configuration controller provides the capability to remap some alternate
functions on different I/O ports. TIM4 and ADC1 DMA channels can also be remapped.
The highly flexible routing interface controls the routing of internal analog signals to ADC1,
COMP1, COMP2, and the internal reference voltage V
. It also provides a set of
REFINT
registers for efficiently managing the charge transfer acquisition sequence (Section 3.11:
Touchsensing).
3.11 Touchsensing
Low density STM8L15xxx devices provide a simple solution for adding capacitive sensing
functionality to any application. Capacitive sensing technology is able to detect finger
presence near an electrode which is protected from direct touch by a dielectric (example,
glass, plastic). The capacitive variation introduced by a finger (or any conductive object) is
measured using a proven implementation based on a surface charge transfer acquisition
principle. It consists of charging the electrode capacitance and then transferring a part of the
accumulated charges into a sampling capacitor until the voltage across this capacitor has
reached a specific threshold. In Low density STM8L15xxx devices, the acquisition sequence
is managed either by software or by hardware and it involves analog I/O groups, the routing
interface, and timers.Reliable touch sensing solutions can be quickly and easily
implemented using the free STM8 Touch Sensing Library.
3.12 Timers
Low density STM8L15x devices contain two 16-bit general purpose timers (TIM2 and TIM3)
and one 8-bit basic timer (TIM4).
All the timers can be served by DMA1.
Ta bl e 2 compares the features of the advanced control, general-purpose and basic timers.
Table 2. Timer feature comparison
Timer
TIM2
TIM3
TIM4 8-bit up
Counter
resolution
16-bit up/down
Counter
type
Prescaler factor
Any power of 2
from 1 to 128
Any power of 2
from 1 to 32768
DMA1
request
generation
Ye s
Capture/compare
channels
2
0
Complementary
outputs
None
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 21/112
Page 22

Functional overview STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
3.12.1 16-bit general purpose timers
● 16-bit autoreload (AR) up/down-counter
● 7-bit prescaler adjustable to fixed power of 2 ratios (1…128)
● 2 individually configurable capture/compare channels
● PWM mode
● Interrupt capability on various events (capture, compare, overflow, break, trigger)
● Synchronization with other timers or external signals (external clock, reset, trigger and
enable)
3.12.2 8-bit basic timer
The 8-bit timer consists of an 8-bit up auto-reload counter driven by a programmable
prescaler. It can be used for timebase generation with interrupt generation on timer overflow.
3.13 Watchdog timers
The watchdog system is based on two independent timers providing maximum security to
the applications.
3.13.1 Window watchdog timer
The window watchdog (WWDG) is used to detect the occurrence of a software fault, usually
generated by external interferences or by unexpected logical conditions, which cause the
application program to abandon its normal sequence.
3.13.2 Independent watchdog timer
The independent watchdog peripheral (IWDG) can be used to resolve processor
malfunctions due to hardware or software failures.
It is clocked by the internal LSI RC clock source, and thus stays active even in case of a
CPU clock failure.
3.14 Beeper
The beeper function outputs a signal on the BEEP pin for sound generation. The signal is in
the range of 1, 2 or 4 kHz.
22/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 23

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Functional overview
3.15 Communication interfaces
3.15.1 SPI
The serial peripheral interface (SPI1) provides half/ full duplex synchronous serial
communication with external devices.
● Maximum speed: 8 Mbit/s (f
● Full duplex synchronous transfers
● Simplex synchronous transfers on 2 lines with a possible bidirectional data line
● Master or slave operation - selectable by hardware or software
● Hardware CRC calculation
● Slave/master selection input pin
SYSCLK
Note: SPI1 can be served by the DMA1 Controller.
3.15.2 I²C
The I2C bus interface (I2C1) provides multi-master capability, and controls all I²C busspecific sequencing, protocol, arbitration and timing.
● Master, slave and multi-master capability
● Standard mode up to 100 kHz and fast speed modes up to 400 kHz.
● 7-bit and 10-bit addressing modes.
● SMBus 2.0 and PMBus support
● Hardware CRC calculation
Note: I
2
C1 can be served by the DMA1 Controller.
/2) both for master and slave
3.15.3 USART
The USART interface (USART1) allows full duplex, asynchronous communications with
external devices requiring an industry standard NRZ asynchronous serial data format. It
offers a very wide range of baud rates.
● 1 Mbit/s full duplex SCI
● SPI1 emulation
● High precision baud rate generator
● Smartcard emulation
● IrDA SIR encoder decoder
● Single wire half duplex mode
Note: USART1 can be served by the DMA1 Controller.
3.16 Infrared (IR) interface
The Low density STM8L15x devices contain an infrared interface which can be used with an
IR LED for remote control functions. Two timer output compare channels are used to
generate the infrared remote control signals.
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 23/112
Page 24

Functional overview STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
3.17 Development support
Development tools
Development tools for the STM8 microcontrollers include:
● The STice emulation system offering tracing and code profiling
● The STVD high-level language debugger including C compiler, assembler and
integrated development environment
● The STVP Flash programming software
The STM8 also comes with starter kits, evaluation boards and low-cost in-circuit
debugging/programming tools.
Single wire data interface (SWIM) and debug module
The debug module with its single wire data interface (SWIM) permits non-intrusive real-time
in-circuit debugging and fast memory programming.
The Single wire interface is used for direct access to the debugging module and memory
programming. The interface can be activated in all device operation modes.
The non-intrusive debugging module features a performance close to a full-featured
emulator. Beside memory and peripherals, CPU operation can also be monitored in realtime by means of shadow registers.
Bootloader
The Low density STM8L15xxx Ultralow power devices feature a built-in bootloader (see
UM0560: STM8 bootloader user manual).
The bootloader is used to download application software into the device memories,
including RAM, program and data memory, using standard serial interfaces. It is a
complementary solution to programming via the SWIM debugging interface.
24/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 25

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Pin description
12
17
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
NRST/PA1
PA2
PA3
PA4
PE0
PE1
PD1
PD2
PD3
PE3
PD0
PE5
PE4
V
DD
V
DDA
V
REF+
PE2
PB2
PC0
PC1
PC2
PC3
PC4
PC5
PC6
PC7
PE6
PE7
PB3
PB4
PB5
PB6
PB7
PF0
PD4
PD5
PD6
PD7
PA0
PA5
13 14
15
16
PA6
PA7
/V
SSA/VREF-
V
SS1
PB0
V
SSIO
V
DDIO
3738394142434445464748 40
24 23 22 21 20 19 18
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
PB1
36
Res.
(1)
MS18276V1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
13 14 15 16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
32
28 27 26 25
PA5
V
SS1
NRST/PA1
PA2
PA3
PA4
PA6
V
DD1
PD3
PB0
PB1
PD0
PD1
PD2
PB3
PB2
PB5
PB4
PD4
PB7
PB6
PD7
PD6
PD5
PC0
PC3
PC2
PC1
PC4
PC5
PC6
PA0
MS18277V1
31 30 29
1291011
PD3
PB0
PB1
PB2
PD0
PD1
PD2
PA 5
V
SS1/VSSA/VREF-
V
DD1/VDDA/VREF+
NRST/PA1
PA 2
PA 4
PB6
PB5
PB4
PB3
PC0
PD4
PB7
PC4
PC3
PC2
PC1
PA 0
PC6
PC5
2
1
3
4
5
6
7
981011121314
20
21
19
18
17
16
15
2728 26 25 24 23 22
PA 3
ai18250
4 Pin description
Figure 3. STM8L151Cx LQFP48 package pinout
Figure 4. STM8L151Kx UFQFPN32 package pinout
Figure 5. STM8L151Gx UFQFPN28 package pinout
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 25/112
Page 26

Pin description STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
2
1
3
4
5
67 8
9
11
12
13
14
15
91817161
PD0
V
DD/VDDA/VREF+
VSS/V
SSA/VREF-
PA3
PA2
PB0
NRST / PA1
PC5
PC6
PC4
PC1
PB4
PB5
PB6
PB7
PC0
PB1
PB2
10
PB3
PA0
20
MS18279V1
PA 3
PA2
VSS/V
SSA/VREF-
NRST / PA1
PC0
PC1
PB7
PB6
PB1
PB2
PB3
PB4
PB5
VDD/V
DDA/VREF+
PC4
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
10
9
8
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
11
12
13
MS18280V1
PB 0
PD0
PA0
PC6
PC5
Figure 6. STM8L151Fx UFQFPN20 package pinout
Figure 7. STM8L151Fx TSSOP20 package pinout
26/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 27

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Pin description
Table 3. Legend/abbreviation for table 4
Typ e I= input, O = output, S = power supply
Level
Output HS = high sink/source (20 mA)
FT Five-volt tolerant
Port and control
configuration
Input float = floating, wpu = weak pull-up
Output T = true open drain, OD = open drain, PP = push pull
Bold X (pin state after reset release).
Reset state
Unless otherwise specified, the pin state is the same during the reset phase (i.e.
“under reset”) and after internal reset release (i.e. at reset state).
Table 4. Low density STM8L15xxx pin description
Pin number
LQFP48
21114NRST/PA1
32225
43336
544- -
Input Output
Pin name
UFQFPN32
UFQFPN28
TSSOP20
UFQFPN20
PA2/OSC_IN/
[USART_TX]
[SPI_MISO]
PA3/OSC_OUT/[USA
RT_RX]
]
(2)
(2)
PA4/TIM2_BKIN/
[TIM2_ETR]
(1)
(2)
/
(2)
/[SPI_MOSI
(2)
Typ e
I/O level
floating
I/O X HS X Reset PA 1
I/O X XXHSXXPort A2
I/O X XXHSXXPort A3
I/O X XXHSXXPort A4
ADC1_IN2
655- -
PA5/TIM3_BKIN/
[TIM3_ETR]
(2)
/ADC1_
I/O X XXHSXXPort A5
IN1
wpu
Ext. interrupt
Default alternate
function
PP
OD
(after reset)
Main function
High sink/source
HSE oscillator input /
[USART transmit] / [SPI
master in- slave out] /
HSE oscillator output /
[USART receive]/ [SPI
master out/slave in]/
Timer 2 - break input /
[Timer 2 - external
trigger] /ADC1 input 2
Timer 3 - break input /
[Timer 3 - external
trigger] /
ADC1input 1
76- - -
PA6/ADC1_TRIG/
ADC1_IN0
I/O X XXHSXXPort A6
8----PA7 I/O X XXHSXXPort A7
24 13 12 7 10
25 14 13 8 11
26 15 14 9 12
PB0
ADC1_IN18
PB1/TIM3_CH1/
ADC1_IN17
PB2/ TIM2_CH2/
ADC1_IN16
I/O X XXHSXXPort B0
I/O X XXHSXXPort B1
I/O X XXHSXXPort B2
(3)
/TIM2_CH1/
PB3/TIM2_ETR/
27 16 15 10 13
ADC1_IN15/RTC_AL
(4)
ARM
I/O X XXHSXXPort B3
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 27/112
ADC1- trigger
/ADC1input 0
Timer 2 - channel 1 /
ADC1_IN18
Timer 3 - channel 1 /
ADC1_IN17
Timer 2 - channel 2
ADC1_IN16
Timer 2 - external
trigger / ADC1_IN15 /
RTC_ALARM
(4)
Page 28

Pin description STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
Table 4. Low density STM8L15xxx pin description (continued)
Pin number
LQFP48
UFQFPN32
UFQFPN28
UFQFPN20
Pin name
TSSOP20
Type
Input Output
I/O level
wpu
floating
OD
Ext. interrupt
High sink/source
(3)
/SPI1_NSS/
28 17 16 11 14
29 18 17 12 15
30 19 18 13 16
31 20 19 14 17
PB4
ADC1_IN14
PB5/SPI_SCK/
/ADC1_IN13
PB6/SPI1_MOSI/
ADC1_IN12
PB7/SPI1_MISO/
ADC1_IN11
37 25 21 15 18 PC0/I2C_SDA I/O FT X XT
38 26 22 16 19 PC1/I2C_SCL I/O FT X XT
41 27 23 - -
42 28 24 - -
PC2/USART_RX/ADC
1_IN6
PC3/USART_TX/
ADC1_IN5
I/O X XXHSXXPort B4
I/O X XXHSXXPort B5
I/O X XXHSXXPort B6
I/O X XXHSXXPort B7
(5)
(3)
I/O X XXHSXXPort C2
I/O X XXHSXXPort C3
PC4/USART_CK]/
43 29 25 17 20
I2C_SMB/CCO/
I/O X XXHSXXPort C4
ADC1_IN4
Default alternate
PP
(after reset)
Main function
SPI master/slave select
/ ADC1_IN14
[SPI clock] /
ADC1_IN13
SPI master out/
slave in / ADC1_IN12
SPI1 master in- slave
out/
ADC1_IN11
Port C0 I2C data
Port C1 I2C clock
USART receive /
ADC1_IN6
USART transmit /
ADC1_IN5
USART synchronous
clock / I2C1_SMB /
Configurable clock
output / ADC1_IN4
function
LSE oscillator input /
[SPI master/slave
select] / [USART
transmit]/
Timer 2 -channel 1
LSE oscillator output /
[SPI clock] / [USART
receive]/
Timer 2 -channel 2
44 30 26 18 1
45 31 27 19 2
PC5/OSC32_IN
/[SPI1_NSS]
[USART_TX]
TIM2_CH1
PC6/OSC32_OUT/
[SPI_SCK]
[USART_RX]
TIM2_CH2
(6)
(2)
(6)
(2)
(2)
/
(2)
/
/
/
I/O X XXHSXXPort C5
I/O X XXHSXXPort C6
46----PC7/ADC1_IN3 I/O X XXHSXXPort C7 ADC1_IN3
Timer 3 - channel 2 /
[ADC1_Trigger] /
ADC1_IN22
Timer 3 - external
trigger / ADC1_IN21
209869
21 10 9 - -
22 11 10 - -
PD0/TIM3_CH2/
[ADC1_TRIG]
(2)
ADC1_IN22
PD1/TIM3_ETR/
ADC1_IN21
PD2/
ADC1_IN20
/
I/O X XXHSXXPort D0
I/O X XXHSXXPort D1
I/O X XXHSXXPort D2 ADC1_IN20
28/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
(6)
(6)
Page 29
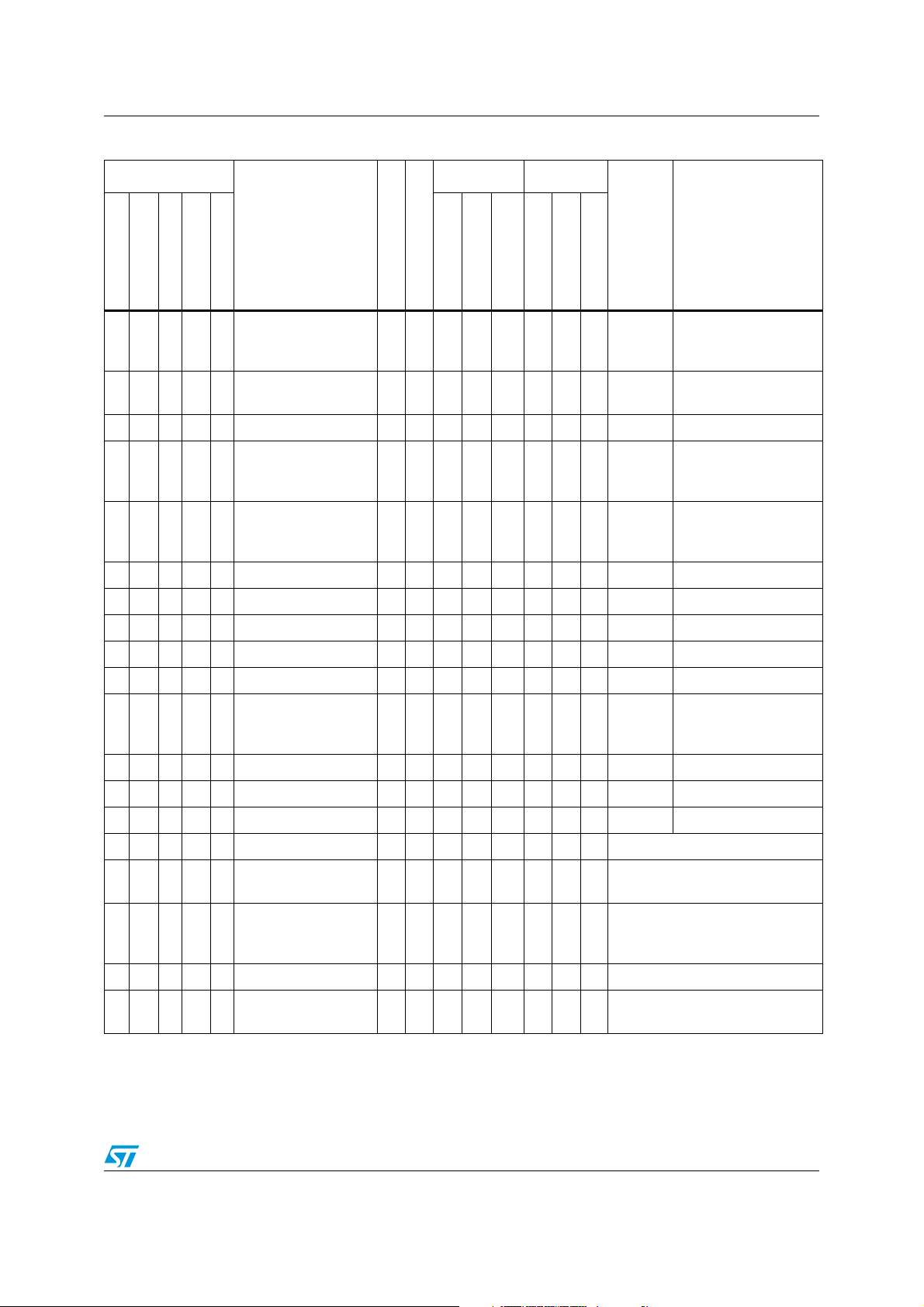
STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Pin description
Table 4. Low density STM8L15xxx pin description (continued)
Pin number
LQFP48
UFQFPN32
UFQFPN28
UFQFPN20
Pin name
TSSOP20
Type
Input Output
I/O level
wpu
floating
OD
Ext. interrupt
PP
Main function
Default alternate
function
(after reset)
High sink/source
23 12 11 - -
33 21 20 - -
PD3/
ADC1_IN19/
RTC_CALIB
PD4/
ADC1_IN10
(7)
I/O X XXHSXXPort D3
I/O X XXHSXXPort D4 ADC1_IN10
ADC1_IN19/
RTC calibration
34 22 - - - PD5/ ADC1_IN9 I/O X XXHSXXPort D5 ADC1_IN9
-23- - -
PD6/
ADC1_IN8/RTC_CALIBI/O X XXHSXXPort D6
ADC1_IN8 / RTC
calibration
PD7
36 24 - - -
/ADC1_IN7/RTC_ALARMI/O X XXHSXXPort D7 ADC1_IN7 / RTC alarm
14----PE0 I/O X XXHSXXPort E0
15----PE1 I/O X XXHSXXPort E1
16----PE2 I/O X XXHSXXPort E2
17 - - - - PE3/ADC1_IN26 I/O X XXHSXXPort E3 ADC1_IN26
(7)
18 - - - - PE4/ADC1_IN27 I/O X XXHSXXPort E4 ADC1_IN27
ADC1_IN23/
Comparator positive
input
19----
PE5/ADC1_IN23/
COMP_INP
I/O X XXHSXXPort E5
47 - - - - PE6/PVD_IN I/O X XXHSXXPort E6 PVD_IN
48 - - - - PE7/ADC1_IN25 I/O X XXHSXXPort E7 ADC1_IN25
32----PF0/ADC1_IN24 I/O X XXHSXXPort F0 ADC1_IN24
10----V
- 8758V
DD
DD /VDDA
/ V
REF+
S Digital supply voltage
S
Digital supply voltage /
ADC1 positive voltage reference
Ground voltage / ADC1 negative
97647V
SS
REF-
/ V
SSA
voltage reference / Analog ground
/ V
voltage
11----V
12----V
DDA
REF+
S Analog supply voltage
S
ADC1 positive voltage
reference
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 29/112
Page 30
Pin description STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
Table 4. Low density STM8L15xxx pin description (continued)
Pin number
LQFP48
UFQFPN32
UFQFPN28
UFQFPN20
Pin name
TSSOP20
Type
Input Output
I/O level
wpu
floating
OD
Ext. interrupt
PP
Main function
Default alternate
function
(after reset)
High sink/source
(8)
/[USART_CK]
PA 0
13228203
40----V
39----V
1. At power-up, the PA1/NRST pin is a reset input pin with pull-up. To be used as a general purpose pin (PA1), it can be
configured only as output open-drain or push-pull, not as a general purpose input. Refer to Section Configuring NRST/PA1
pin as general purpose output in the STM8L15xxx and STM8L16xxx reference manual (RM0031).
2. [ ] Alternate function remapping option (if the same alternate function is shown twice, it indicates an exclusive choice not a
duplication of the function).
3. A pull-up is applied to PB0 and PB4 during the reset phase. These two pins are input floating after reset release.
4. 20-pin and 28-pin packages only.
5. In the open-drain output column, ‘T’ defines a true open-drain I/O (P-buffer and protection diode to V
implemented).
6. 20-pin packages only.
7. 28-pin packages only
8. The PA0 pin is in input pull-up during the reset phase and after reset release.
9. High Sink LED driver capability available on PA0.
/
SWIM/BEEP/IR_TIM
(9)
SSIO
DDIO
(2)
I/O X X X
HS
XXPort A0
(9)
[USART1 synchronous
clock]
and output /
Beep output / Infrared
Timer output
I/O ground voltage
I/O supply voltage
are not
DD
(2)
/ SWIM input
Note: The slope control of all GPIO pins, except true open drain pins, can be programmed. By
default, the slope control is limited to 2 MHz.
4.1 System configuration options
As shown in Table 4: Low density STM8L15xxx pin description, some alternate functions
can be remapped on different I/O ports by programming one of the two remapping registers
described in the “ Routing interface (RI) and system configuration controller” section in the
STM8L15x and STM8L16x reference manual (RM0031).
30/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 31

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Memory and register map
GPIO and peripheral registers
0x00 0000
Low density
(up to 8 Kbyt es)
Reset and int errupt vectors
0x0 0 10 FF
RAM
0x0 0 03 F F
( Kbyte)
(512 bytes)
0x00 1100
Da t a E EP RO M
0x00 4800
0x0 0 4 87F
0x00 4880
0x00 7FFF
0x00 8000
0x00 9FFF
0x0 0 100 0
0x0 0 4 7FF
0x00 7EFF
0x00 8100
0 x00 80FF
0 x00 7F0 0
Reserved
Re se rv ed
in cl ud in g
Stack
(
256 Bytes)
Option bytes
0x00 4FFF
0x00 5000
0x0 0 5 457
0x00 5458
Re se rv ed
0x00 5FFF
Boot ROM
0x00 6000
0x0 0 6 7FF
(2 Kbytes)
0x00 6800
Re se rv ed
CPU/SWIM/Debug/ITC
Re gi st e rs
Flash program memory
0x00 4910
0x00 4911
0x00 4926
0x00 4925
0x00 4931
0x00 4932
0x00 4909
VREFINT_Factory_CONV
TS_Factory_CONV_V90
0x00 4912
Re se rv ed
Unique ID
Re se rv ed
MS18274V2
6QUP
Reserved
0x0 0 04 0 0
0x0 0 1FFF
RI
Reserved
0x00 5000
0x00 501E
0x00 5050
0x00 5055
0x00 5070
0x00 509D
0x00 50A0
0x00 50A6
0x00 50AA
0x00 50A9
0x00 50B0
0x00 50B2
0x00 50B4
0x00 50C0
0x00 50D1
0x00 50D3
0x00 50D5
0x00 50E0
0x00 50E3
0x00 50F0
0x00 50F4
0x00 5040
0x00 5191
0x00 5200
0x00 5208
0x00 5210
0x00 521F
0x00 5230
0x00 523B
0x00 5250
0x00 5267
0x00 5280
0x00 5297
0x00 52E0
0x00 52EA
0x00 52FF
0x00 5317
0x00 5340
0x00 53C8
0x00 5430
0x00 5440
0x00 5445
0x00 5450
0x00 5457
Reserved
GPIO ports
Flash
Reserved
DMA1
SYSCFG
ITC-EXT1
WFE
RST
PWR
CLK
WWDG
ITC-EXT1
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
IWDG
BEEP
RTC
SPI1
I2C1
USART1
TIM2
TIM3
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
TIM4
IRTIM
ADC1
COMP1/COMP2
RI
5 Memory and register map
5.1 Memory mapping
The memory map is shown in Figure 8.
Figure 8. Memory map
1. Table 5 lists the boundary addresses for each memory size. The top of the stack is at the RAM end
address.
2. The VREFINT_Factory_CONV byte represents the LSB of the V
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 31/112
12-bit ADC1 conversion result. The
REFINT
Page 32

Memory and register map STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
MSB have a fixed value: 0x6.
3. The TS_Factory_CONV_V90 byte represents the LSB of the V
have a fixed value: 0x3.
4. Refer to Table 8 for an overview of hardware register mapping, to Table 7 for details on I/O port hardware
registers, and to Table 9 for information on CPU/SWIM/debug module controller registers.
Table 5. Flash and RAM boundary addresses
12-bit ADC1 conversion result. The MSB
90
Memory area Size Start address End address
RAM 1 Kbyte 0x00 0000 0x00 03FF
8 Kbytes 0x00 8000 0x00 9FFF
Flash program memory
4 Kbytes 0x00 8000 0x00 8FFF
5.2 Register map
Table 6. Factory conversion registers
Address Block Register label Register name
0x00 4910 -
0x00 4911 -
Table 7. I/O port hardware register map
VREFINT_Factory_
CONV
TS_Factory_CONV_
V90
Value of the internal reference voltage
measured during the factory phase
Value of the temperature sensor output
voltage measured during the factory
phase
Address Block Register label Register name
0x00 5000
PA_ODR Port A data output latch register 0x00
0x00 5001 PA_IDR Port A input pin value register 0xXX
0x00 5002 PA_DDR Port A data direction register 0x00
Por t A
0x00 5003 PA_CR1 Port A control register 1 0x01
0x00 5004 PA_CR2 Port A control register 2 0x00
0x00 5005
PB_ODR Port B data output latch register 0x00
0x00 5006 PB_IDR Port B input pin value register 0xXX
0x00 5007 PB_DDR Port B data direction register 0x00
Por t B
Reset
status
0xXX
0xXX
Reset
status
0x00 5008 PB_CR1 Port B control register 1 0x00
0x00 5009 PB_CR2 Port B control register 2 0x00
32/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 33

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Memory and register map
Table 7. I/O port hardware register map (continued)
Address Block Register label Register name
0x00 500A
PC_ODR Port C data output latch register 0x00
Reset
status
0x00 500B PC_IDR Port C input pin value register 0xXX
0x00 500C PC_DDR Port C data direction register 0x00
Por t C
0x00 500D PC_CR1 Port C control register 1 0x00
0x00 500E PC_CR2 Port C control register 2 0x00
0x00 500F
PD_ODR Port D data output latch register 0x00
0x00 5010 PD_IDR Port D input pin value register 0xXX
0x00 5011 PD_DDR Port D data direction register 0x00
Por t D
0x00 5012 PD_CR1 Port D control register 1 0x00
0x00 5013 PD_CR2 Port D control register 2 0x00
0x00 5014
PE_ODR Port E data output latch register 0x00
0x00 5015 PE_IDR Port E input pin value register 0xXX
0x00 5016 PE_DDR Port E data direction register 0x00
Por t E
0x00 5017 PE_CR1 Port E control register 1 0x00
0x00 5018 PE_CR2 Port E control register 2 0x00
0x00 5019
PF_ODR Port F data output latch register 0x00
0x00 501A PF_IDR Port F input pin value register 0xXX
0x00 501B PF_DDR Port F data direction register 0x00
Por t F
0x00 501C PF_CR1 Port F control register 1 0x00
0x00 501D PF_CR2 Port F control register 2 0x00
Table 8. General hardware register map
Address Block Register label Register name Reset status
0x00 502E
to
Reserved area (44 bytes)
0x00 5049
0x00 5050
FLASH_CR1 Flash control register 1 0x00
0x00 5051 FLASH_CR2 Flash control register 2 0x00
0x00 5052 FLASH _PUKR
Flash
0x00 5053 FLASH _DUKR
0x00 5054 FLASH _IAPSR
Flash program memory unprotection key
register
Flash data EEPROM unprotection key
register
Flash in-application programming status
register
0x00
0x00
0x00
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 33/112
Page 34

Memory and register map STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
Table 8. General hardware register map (continued)
Address Block Register label Register name Reset status
0x00 5055
to
0x00 506F
0x00 5070
0x00 5071 DMA1_GIR1 DMA1 global interrupt register 1 0x00
0x00 5072
to
0x00 5074
0x00 5075 DMA1_C0CR DMA1 channel 0 configuration register 0x00
0x00 5076 DMA1_C0SPR DMA1 channel 0 status & priority register 0x00
DMA1_GCSR DMA1 global configuration & status register 0xFC
Reserved area (27 bytes)
Reserved area (3 bytes)
0x00 5077 DMA1_C0NDTR
0x00 5078 DMA1_C0PARH
0x00 5079 DMA1_C0PARL
0x00 507A Reserved area (1 byte)
DMA1
0x00 507B DMA1_C0M0ARH
0x00 507C DMA1_C0M0ARL
0x00 507D
to
0x00 507E
0x00 507F DMA1_C1CR DMA1 channel 1 configuration register 0x00
0x00 5080 DMA1_C1SPR DMA1 channel 1 status & priority register 0x00
0x00 5081 DMA1_C1NDTR
0x00 5082 DMA1_C1PARH
0x00 5083 DMA1_C1PARL
DMA1 number of data to transfer register
(channel 0)
DMA1 peripheral address high register
(channel 0)
DMA1 peripheral address low register
(channel 0)
DMA1 memory 0 address high register
(channel 0)
DMA1 memory 0 address low register
(channel 0)
Reserved area (2 bytes)
DMA1 number of data to transfer register
(channel 1)
DMA1 peripheral address high register
(channel 1)
DMA1 peripheral address low register
(channel 1)
0x00
0x52
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x52
0x00
34/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 35

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Memory and register map
Table 8. General hardware register map (continued)
Address Block Register label Register name Reset status
0x00 5084
0x00 5085 DMA1_C1M0ARH
0x00 5086 DMA1_C1M0ARL
0x00 5087
0x00 5088
0x00 5089 DMA1_C2CR DMA1 channel 2 configuration register 0x00
0x00 508A DMA1_C2SPR DMA1 channel 2 status & priority register 0x00
0x00 508B DMA1_C2NDTR
0x00 508C DMA1_C2PARH
0x00 508D DMA1_C2PARL
0x00 508E Reserved area (1 byte)
0x00 508F DMA1_C2M0ARH
0x00 5090 DMA1_C2M0ARL
0x00 5091
0x00 5092
0x00 5093 DMA1_C3CR DMA1 channel 3 configuration register 0x00
0x00 5094 DMA1_C3SPR DMA1 channel 3 status & priority register 0x00
DMA1
Reserved area (1 byte)
DMA1 memory 0 address high register
(channel 1)
DMA1 memory 0 address low register
(channel 1)
Reserved area (2 bytes)
DMA1 number of data to transfer register
(channel 2)
DMA1 peripheral address high register
(channel 2)
DMA1 peripheral address low register
(channel 2)
DMA1 memory 0 address high register
(channel 2)
DMA1 memory 0 address low register
(channel 2)
Reserved area (2 bytes)
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x52
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00 5095 DMA1_C3NDTR
0x00 5096
0x00 5097
0x00 5098 DMA_C3M0EAR
0x00 5099 DMA1_C3M0ARH
0x00 509A DMA1_C3M0ARL
0x00 509B
to
0x00 509C
DMA1_C3PARH_
C3M1ARH
DMA1_C3PARL_
C3M1ARL
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 35/112
DMA1 number of data to transfer register
(channel 3)
DMA1 peripheral address high register
(channel 3)
DMA1 peripheral address low register
(channel 3)
DMA channel 3 memory 0 extended
address register
DMA1 memory 0 address high register
(channel 3)
DMA1 memory 0 address low register
(channel 3)
Reserved area (3 bytes)
0x00
0x40
0x00
0x00
0x00
0x00
Page 36

Memory and register map STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
Table 8. General hardware register map (continued)
Address Block Register label Register name Reset status
0x00 509D
0x00 509E SYSCFG_RMPCR1 Remapping register 1 0x00
0x00 509F SYSCFG_RMPCR2 Remapping register 2 0x00
0x00 50A0
0x00 50A1 EXTI_CR2 External interrupt control register 2 0x00
0x00 50A2 EXTI_CR3 External interrupt control register 3 0x00
0x00 50A3 EXTI_SR1 External interrupt status register 1 0x00
0x00 50A4 EXTI_SR2 External interrupt status register 2 0x00
0x00 50A5 EXTI_CONF1 External interrupt port select register 1 0x00
0x00 50A6
0x00 50A7 WFE_CR2 WFE control register 2 0x00
0x00 50A8 WFE_CR3 WFE control register 3 0x00
0x00 50A9 WFE_CR4 WFE control register 4 0x00
0x00 50AA
0x00 50AB EXTI_CONF2 External interrupt port select register 2 0x00
0x00 50A9
to
0x00 50AF
SYSCFG
ITC - EXTI
WFE
ITC - EXTI
SYSCFG_RMPCR3 Remapping register 3 0x00
EXTI_CR1 External interrupt control register 1 0x00
WFE_CR1 WFE control register 1 0x00
EXTI_CR4 External interrupt control register 4 0x00
Reserved area (7 bytes)
0x00 50B0
RST
0x00 50B1 RST_SR Reset status register 0x01
0x00 50B2
PWR
0x00 50B3 PWR_CSR2 Power control and status register 2 0x00
0x00 50B4
to
0x00 50BF
RST_CR Reset control register 0x00
PWR_CSR1 Power control and status register 1 0x00
Reserved area (12 bytes)
36/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 37

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Memory and register map
Table 8. General hardware register map (continued)
Address Block Register label Register name Reset status
0x00 50C0
0x00 50C1 CLK_CRTCR CLK clock RTC register 0x00
0x00 50C2 CLK_ICKCR CLK internal clock control register 0x11
0x00 50C3 CLK_PCKENR1 CLK peripheral clock gating register 1 0x00
0x00 50C4 CLK_PCKENR2 CLK peripheral clock gating register 2 0x00
0x00 50C5 CLK_CCOR CLK configurable clock control register 0x00
0x00 50C6 CLK_ECKCR CLK external clock control register 0x00
0x00 50C7 CLK_SCSR CLK system clock status register 0x01
0x00 50C8 CLK_SWR CLK system clock switch register 0x01
0x00 50C9 CLK_SWCR CLK clock switch control register 0xX0
0x00 50CA CLK_CSSR CLK clock security system register 0x00
0x00 50CB CLK_CBEEPR CLK clock BEEP register 0x00
0x00 50CC CLK_HSICALR CLK HSI calibration register 0xXX
0x00 50CD CLK_HSITRIMR CLK HSI clock calibration trimming register 0x00
0x00 50CE CLK_HSIUNLCKR CLK HSI unlock register 0x00
0x00 50CF CLK_REGCSR CLK main regulator control status register 0bxx11 100X
0x00 50D0 CLK_PCKENR3 CLK peripheral clock gating register 3 0x00
0x00 50D1
to
0x00 50D2
0x00 50D3
0x00 50D4 WWDG_WR WWDR window register 0x7F
0x00 50D5
to
00 50DF
0x00 50E0
0x00 50E1 IWDG_PR IWDG prescaler register 0x00
CLK
WWDG
IWDG
CLK_CKDIVR CLK clock master divider register 0x03
(1)
Reserved area (2 bytes)
WWDG_CR WWDG control register 0x7F
Reserved area (11 bytes)
IWDG_KR IWDG key register 0x01
0x00 50E2 IWDG_RLR IWDG reload register 0xFF
0x00 50E3
to
0x00 50EF
0x00 50F0
0x00 50F1
0x00 50F2
0x00 50F3 BEEP_CSR2 BEEP control/status register 2 0x1F
0x00 50F4
to
0x00 513F
BEEP
BEEP_CSR1 BEEP control/status register 1 0x00
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 37/112
Reserved area (13 bytes)
Reserved area (2 bytes)
Reserved area (76 bytes)
Page 38

Memory and register map STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
Table 8. General hardware register map (continued)
Address Block Register label Register name Reset status
0x00 5140
RTC_TR1 RTC time register 1 0x00
0x00 5141 RTC_TR2 RTC time register 2 0x00
0x00 5142 RTC_TR3 RTC time register 3 0x00
0x00 5143 Reserved area (1 byte)
0x00 5144 RTC_DR1 RTC date register 1 0x01
0x00 5145 RTC_DR2 RTC date register 2 0x21
0x00 5146 RTC_DR3 RTC date register 3 0x00
0x00 5147 Reserved area (1 byte)
0x00 5148 RTC_CR1 RTC control register 1 0x00
0x00 5149 RTC_CR2 RTC control register 2 0x00
0x00 514A RTC_CR3 RTC control register 3 0x00
0x00 514B Reserved area (1 byte)
0x00 514C RTC_ISR1 RTC initialization and status register 1 0x01
0x00 514D RTC_ISR2 RTC initialization and Status register 2 0x00
0x00 514E
0x00 514F
Reserved area (2 bytes)
0x00 5150 RTC_SPRERH RTC synchronous prescaler register high 0x00
0x00 5151 RTC_SPRERL RTC synchronous prescaler register low 0xFF
RTC
0x00 5152 RTC_APRER RTC asynchronous prescaler register 0x7F
0x00 5153 Reserved area (1 byte)
0x00 5154 RTC_WUTRH RTC wakeup timer register high 0xFF
0x00 5155 RTC_WUTRL RTC wakeup timer register low 0xFF
0x00 5156 Reserved area (1 byte)
0x00 5157 RTC_SSRL RTC subsecond register low 0x00
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
0x00 5158 RTC_SSRH RTC subsecond register high 0x00
0x00 5159 RTC_WPR RTC write protection register 0x00
0x00 5158 RTC_SSRH RTC subsecond register high 0x00
0x00 5159 RTC_WPR RTC write protection register 0x00
0x00 515A RTC_SHIFTRH RTC shift register high 0x00
0x00 515B RTC_SHIFTRL RTC shift register low 0x00
0x00 515C RTC_ALRMAR1 RTC alarm A register 1 0x00
0x00 515D RTC_ALRMAR2 RTC alarm A register 2 0x00
0x00 515E RTC_ALRMAR3 RTC alarm A register 3 0x00
0x00 515F RTC_ALRMAR4 RTC alarm A register 4 0x00
38/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
Page 39
STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Memory and register map
Table 8. General hardware register map (continued)
Address Block Register label Register name Reset status
0x00 5160
to
0x00 5163
0x00 5164 RTC_ALRMASSRH RTC alarm A subsecond register high 0x00
0x00 5165 RTC_ALRMASSRL RTC alarm A subsecond register low 0x00
0x00 5166
RTC_ALRMASSMS
KR
0x00 5167
to
RTC
0x00 5169
0x00 516A RTC_CALRH RTC calibration register high 0x00
0x00 516B RTC_CALRL RTC calibration register low 0x00
0x00 516C
to
0x00 518F
Reserved area (4 bytes)
RTC alarm A masking register 0x00
Reserved area (3 bytes)
Reserved area (36 bytes)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
0x00 5190 CSSLSE_CSR
RTC CSS on LSE control and status
register
0x00
0x00 5191
to
Reserved area (111 bytes)
0x00 51FF
0x00 5200
SPI1_CR1 SPI1 control register 1 0x00
0x00 5201 SPI1_CR2 SPI1 control register 2 0x00
0x00 5202 SPI1_ICR SPI1 interrupt control register 0x00
0x00 5203 SPI1_SR SPI1 status register 0x02
SPI1
0x00 5204 SPI1_DR SPI1 data register 0x00
0x00 5205 SPI1_CRCPR SPI1 CRC polynomial register 0x07
0x00 5206 SPI1_RXCRCR SPI1 Rx CRC register 0x00
0x00 5207 SPI1_TXCRCR SPI1 Tx CRC register 0x00
0x00 5208
to
Reserved area (8 bytes)
0x00 520F
(1)
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 39/112
Page 40
Memory and register map STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
Table 8. General hardware register map (continued)
Address Block Register label Register name Reset status
0x00 5210
0x00 5211 I2C1_CR2 I2C1 control register 2 0x00
0x00 5212 I2C1_FREQR I2C1 frequency register 0x00
0x00 5213 I2C1_OARL I2C1 own address register low 0x00
0x00 5214 I2C1_OARH I2C1 own address register high 0x00
0x00 5215 I2C1_OAR2 I2C1 own address register for dual mode 0x00
0x00 5216 I2C1_DR I2C1 data register 0x00
0x00 5217 I2C1_SR1 I2C1 status register 1 0x00
0x00 5218 I2C1_SR2 I2C1 status register 2 0x00
0x00 5219 I2C1_SR3 I2C1 status register 3 0x0X
0x00 521A I2C1_ITR I2C1 interrupt control register 0x00
0x00 521B I2C1_CCRL I2C1 clock control register low 0x00
0x00 521C I2C1_CCRH I2C1 clock control register high 0x00
0x00 521D I2C1_TRISER I2C1 TRISE register 0x02
0x00 521E I2C1_PECR I2C1 packet error checking register 0x00
0x00 521F
to
0x00 522F
I2C1
I2C1_CR1 I2C1 control register 1 0x00
Reserved area (17 bytes)
0x00 5230
0x00 5231 USART1_DR USART1 data register 0xXX
0x00 5232 USART1_BRR1 USART1 baud rate register 1 0x00
0x00 5233 USART1_BRR2 USART1 baud rate register 2 0x00
0x00 5234 USART1_CR1 USART1 control register 1 0x00
0x00 5235 USART1_CR2 USART1 control register 2 0x00
0x00 5236 USART1_CR3 USART1 control register 3 0x00
0x00 5237 USART1_CR4 USART1 control register 4 0x00
0x00 5238 USART1_CR5 USART1 control register 5 0x00
0x00 5239 USART1_GTR USART1 guard time register 0x00
0x00 523A USART1_PSCR USART1 prescaler register 0x00
0x00 523B
to
0x00 524F
USART1
USART1_SR USART1 status register 0xC0
Reserved area (21 bytes)
40/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 41

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Memory and register map
Table 8. General hardware register map (continued)
Address Block Register label Register name Reset status
0x00 5250
0x00 5251 TIM2_CR2 TIM2 control register 2 0x00
0x00 5252 TIM2_SMCR TIM2 Slave mode control register 0x00
0x00 5253 TIM2_ETR TIM2 external trigger register 0x00
0x00 5254 TIM2_DER TIM2 DMA1 request enable register 0x00
0x00 5255 TIM2_IER TIM2 interrupt enable register 0x00
0x00 5256 TIM2_SR1 TIM2 status register 1 0x00
0x00 5257 TIM2_SR2 TIM2 status register 2 0x00
0x00 5258 TIM2_EGR TIM2 event generation register 0x00
0x00 5259 TIM2_CCMR1 TIM2 capture/compare mode register 1 0x00
0x00 525A TIM2_CCMR2 TIM2 capture/compare mode register 2 0x00
0x00 525B TIM2_CCER1 TIM2 capture/compare enable register 1 0x00
0x00 525C TIM2_CNTRH TIM2 counter high 0x00
0x00 525D TIM2_CNTRL TIM2 counter low 0x00
0x00 525E TIM2_PSCR TIM2 prescaler register 0x00
0x00 525F TIM2_ARRH TIM2 auto-reload register high 0xFF
0x00 5260 TIM2_ARRL TIM2 auto-reload register low 0xFF
0x00 5261 TIM2_CCR1H TIM2 capture/compare register 1 high 0x00
TIM2
TIM2_CR1 TIM2 control register 1 0x00
0x00 5262 TIM2_CCR1L TIM2 capture/compare register 1 low 0x00
0x00 5263 TIM2_CCR2H TIM2 capture/compare register 2 high 0x00
0x00 5264 TIM2_CCR2L TIM2 capture/compare register 2 low 0x00
0x00 5265 TIM2_BKR TIM2 break register 0x00
0x00 5266 TIM2_OISR TIM2 output idle state register 0x00
0x00 5267
to
0x00 527F
Reserved area (25 bytes)
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 41/112
Page 42

Memory and register map STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
Table 8. General hardware register map (continued)
Address Block Register label Register name Reset status
0x00 5280
0x00 5281 TIM3_CR2 TIM3 control register 2 0x00
0x00 5282 TIM3_SMCR TIM3 Slave mode control register 0x00
0x00 5283 TIM3_ETR TIM3 external trigger register 0x00
0x00 5284 TIM3_DER TIM3 DMA1 request enable register 0x00
0x00 5285 TIM3_IER TIM3 interrupt enable register 0x00
0x00 5286 TIM3_SR1 TIM3 status register 1 0x00
0x00 5287 TIM3_SR2 TIM3 status register 2 0x00
0x00 5288 TIM3_EGR TIM3 event generation register 0x00
0x00 5289 TIM3_CCMR1 TIM3 Capture/Compare mode register 1 0x00
0x00 528A TIM3_CCMR2 TIM3 Capture/Compare mode register 2 0x00
0x00 528B TIM3_CCER1 TIM3 Capture/Compare enable register 1 0x00
0x00 528C TIM3_CNTRH TIM3 counter high 0x00
0x00 528D TIM3_CNTRL TIM3 counter low 0x00
0x00 528E TIM3_PSCR TIM3 prescaler register 0x00
0x00 528F TIM3_ARRH TIM3 Auto-reload register high 0xFF
0x00 5290 TIM3_ARRL TIM3 Auto-reload register low 0xFF
0x00 5291 TIM3_CCR1H TIM3 Capture/Compare register 1 high 0x00
TIM3
TIM3_CR1 TIM3 control register 1 0x00
0x00 5292 TIM3_CCR1L TIM3 Capture/Compare register 1 low 0x00
0x00 5293 TIM3_CCR2H TIM3 Capture/Compare register 2 high 0x00
0x00 5294 TIM3_CCR2L TIM3 Capture/Compare register 2 low 0x00
0x00 5295 TIM3_BKR TIM3 break register 0x00
0x00 5296 TIM3_OISR TIM3 output idle state register 0x00
0x00 5297
to
0x00 52DF
Reserved area (72 bytes)
42/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 43
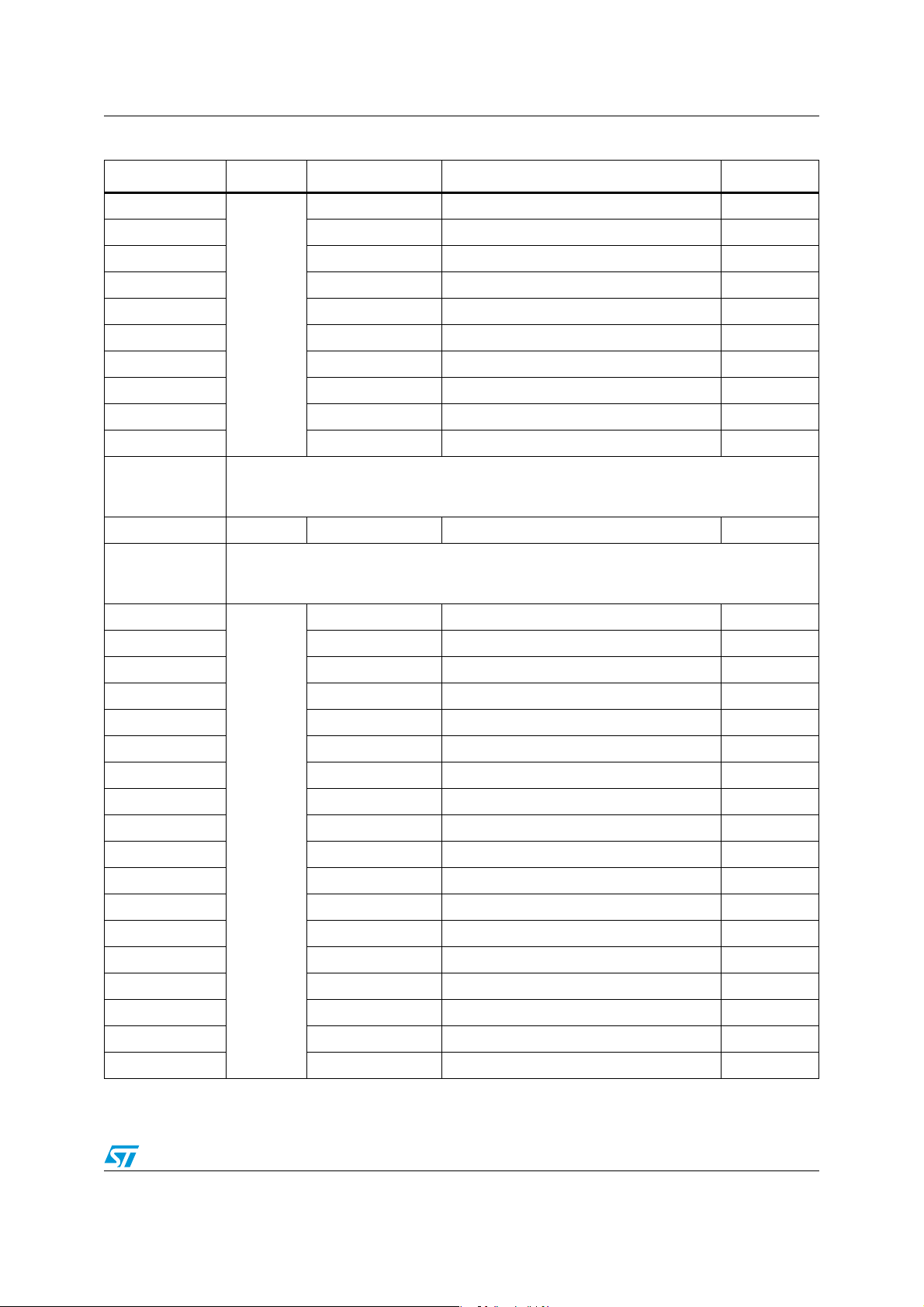
STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Memory and register map
Table 8. General hardware register map (continued)
Address Block Register label Register name Reset status
0x00 52E0
0x00 52E1 TIM4_CR2 TIM4 control register 2 0x00
0x00 52E2 TIM4_SMCR TIM4 Slave mode control register 0x00
0x00 52E3 TIM4_DER TIM4 DMA1 request enable register 0x00
0x00 52E4 TIM4_IER TIM4 Interrupt enable register 0x00
TIM4
0x00 52E5 TIM4_SR1 TIM4 status register 1 0x00
0x00 52E6 TIM4_EGR TIM4 Event generation register 0x00
0x00 52E7 TIM4_CNTR TIM4 counter 0x00
0x00 52E8 TIM4_PSCR TIM4 prescaler register 0x00
0x00 52E9 TIM4_ARR TIM4 Auto-reload register 0x00
0x00 52EA
to
0x00 52FE
0x00 52FF IRTIM IR_CR Infrared control register 0x00
0x00 5317
to
0x00 533F
0x00 5340
0x00 5341 ADC1_CR2 ADC1 configuration register 2 0x00
0x00 5342 ADC1_CR3 ADC1 configuration register 3 0x1F
0x00 5343 ADC1_SR ADC1 status register 0x00
TIM4_CR1 TIM4 control register 1 0x00
Reserved area (21 bytes)
Reserved area (41 bytes)
ADC1_CR1 ADC1 configuration register 1 0x00
0x00 5344 ADC1_DRH ADC1 data register high 0x00
0x00 5345 ADC1_DRL ADC1 data register low 0x00
0x00 5346 ADC1_HTRH ADC1 high threshold register high 0x0F
0x00 5347 ADC1_HTRL ADC1 high threshold register low 0xFF
0x00 5348 ADC1_LTRH ADC1 low threshold register high 0x00
0x00 5349 ADC1_LTRL ADC1 low threshold register low 0x00
0x00 534A ADC1_SQR1 ADC1 channel sequence 1 register 0x00
0x00 534B ADC1_SQR2 ADC1 channel sequence 2 register 0x00
0x00 534C ADC1_SQR3 ADC1 channel sequence 3 register 0x00
0x00 534D ADC1_SQR4 ADC1 channel sequence 4 register 0x00
0x00 534E ADC1_TRIGR1 ADC1 trigger disable 1 0x00
0x00 534F ADC1_TRIGR2 ADC1 trigger disable 2 0x00
0x00 5350 ADC1_TRIGR3 ADC1 trigger disable 3 0x00
0x00 5351 ADC1_TRIGR4 ADC1 trigger disable 4 0x00
ADC1
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 43/112
Page 44
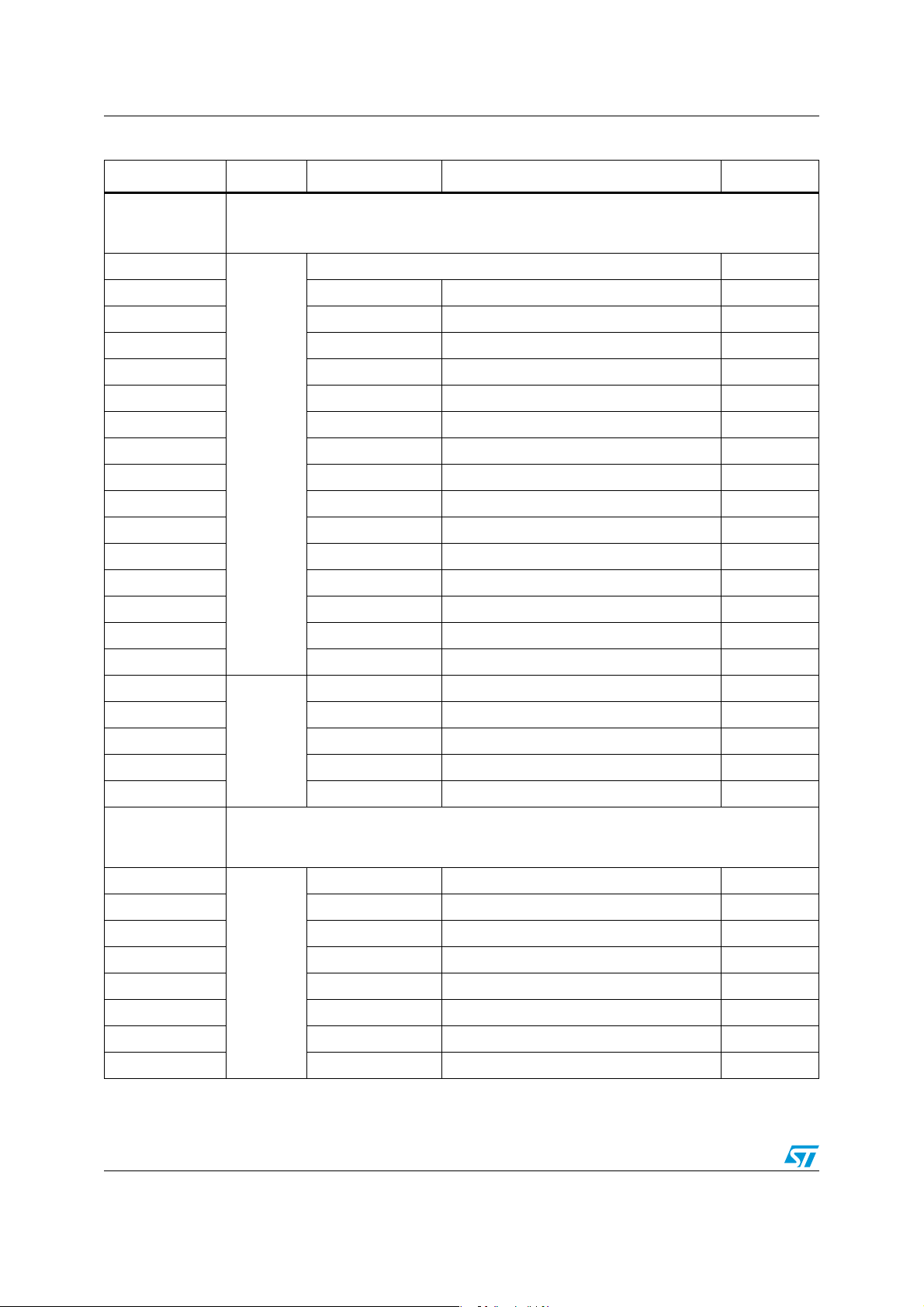
Memory and register map STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
Table 8. General hardware register map (continued)
Address Block Register label Register name Reset status
0x00 53C8
to
0x00 542F
0x00 5430
0x00 5431 RI_ICR1 RI timer input capture routing register 1 0x00
0x00 5432 RI_ICR2 RI timer input capture routing register 2 0x00
0x00 5433 RI_IOIR1 RI I/O input register 1 0xXX
0x00 5434 RI_IOIR2 RI I/O input register 2 0xXX
0x00 5435 RI_IOIR3 RI I/O input register 3 0xXX
0x00 5436 RI_IOCMR1 RI I/O control mode register 1 0x00
Reserved area (104 bytes)
Reserved area (1 byte) 0x00
0x00 5437 RI_IOCMR2 RI I/O control mode register 2 0x00
0x00 5438 RI_IOCMR3 RI I/O control mode register 3 0x00
0x00 5439 RI_IOSR1 RI I/O switch register 1 0x00
0x00 543A RI_IOSR2 RI I/O switch register 2 0x00
0x00 543B RI_IOSR3 RI I/O switch register 3 0x00
0x00 543C RI_IOGCR RI I/O group control register 0xFF
0x00 543D RI_ASCR1 RI analog switch register 1 0x00
0x00 543E RI_ASCR2 RI analog switch register 2 0x00
0x00 543F RI_RCR RI resistor control register 0x00
0x00 5440
0x00 5441 COMP_CSR2 Comparator control and status register 2 0x00
0x00 5442 COMP_CSR3 Comparator control and status register 3 0x00
0x00 5443 COMP_CSR4 Comparator control and status register 4 0x00
0x00 5444 COMP_CSR5 Comparator control and status register 5 0x00
0x00 5445
to
0x00 544F
0x00 5450
0x00 5451 RI_MASKR1 RI I/O mask register 1 0x00
0x00 5452 RI_MASKR2 RI I/O mask register 2 0x00
RI
COMP_CSR1 Comparator control and status register 1 0x00
COMP1/
COMP2
Reserved area (11 bytes)
RI_CR RI I/O control register 0x00
0x00 5453 RI_MASKR3 RI I/O mask register 3 0x00
0x00 5454 RI_MASKR4 RI I/O mask register 4 0x00
0x00 5455 RI_IOIR4 RI I/O input register 4 0xXX
0x00 5456 RI_IOCMR4 RI I/O control mode register 4 0x00
0x00 5457 RI_IOSR4 RI I/O switch register 4 0x00
1. These registers are not impacted by a system reset. They are reset at power-on.
44/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
RI
Page 45

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Memory and register map
Table 9. CPU/SWIM/debug module/interrupt controller registers
Address Block Register Label Register Name
0x00 7F00
A Accumulator 0x00
0x00 7F01 PCE Program counter extended 0x00
0x00 7F02 PCH Program counter high 0x00
0x00 7F03 PCL Program counter low 0x00
0x00 7F04 XH X index register high 0x00
(1)
0x00 7F05 XL X index register low 0x00
CPU
0x00 7F06 YH Y index register high 0x00
0x00 7F07 YL Y index register low 0x00
0x00 7F08 SPH Stack pointer high 0x03
0x00 7F09 SPL Stack pointer low 0xFF
0x00 7F0A CCR Condition code register 0x28
0x00 7F0B to
0x00 7F5F
CPU
Reserved area (85 bytes)
0x00 7F60 CFG_GCR Global configuration register 0x00
0x00 7F70
ITC_SPR1 Interrupt Software priority register 1 0xFF
0x00 7F71 ITC_SPR2 Interrupt Software priority register 2 0xFF
Reset
Status
0x00 7F72 ITC_SPR3 Interrupt Software priority register 3 0xFF
0x00 7F73 ITC_SPR4 Interrupt Software priority register 4 0xFF
ITC-SPR
0x00 7F74 ITC_SPR5 Interrupt Software priority register 5 0xFF
0x00 7F75 ITC_SPR6 Interrupt Software priority register 6 0xFF
0x00 7F76 ITC_SPR7 Interrupt Software priority register 7 0xFF
0x00 7F77 ITC_SPR8 Interrupt Software priority register 8 0xFF
0x00 7F78
to
Reserved area (2 bytes)
0x00 7F79
0x00 7F80 SWIM SWIM_CSR SWIM control status register 0x00
0x00 7F81
to
Reserved area (15 bytes)
0x00 7F8F
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 45/112
Page 46

Memory and register map STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
Table 9. CPU/SWIM/debug module/interrupt controller registers (continued)
Address Block Register Label Register Name
0x00 7F90
0x00 7F91 DM_BK1RH DM breakpoint 1 register high byte 0xFF
0x00 7F92 DM_BK1RL DM breakpoint 1 register low byte 0xFF
0x00 7F93 DM_BK2RE DM breakpoint 2 register extended byte 0xFF
0x00 7F94 DM_BK2RH DM breakpoint 2 register high byte 0xFF
0x00 7F95 DM_BK2RL DM breakpoint 2 register low byte 0xFF
0x00 7F96 DM_CR1 DM Debug module control register 1 0x00
0x00 7F97 DM_CR2 DM Debug module control register 2 0x00
0x00 7F98 DM_CSR1 DM Debug module control/status register 1 0x10
0x00 7F99 DM_CSR2 DM Debug module control/status register 2 0x00
0x00 7F9A DM_ENFCTR DM enable function register 0xFF
0x00 7F9B
to
0x00 7F9F
1. Accessible by debug module only
DM
DM_BK1RE DM breakpoint 1 register extended byte 0xFF
Reserved area (5 bytes)
Reset
Status
46/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 47

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Interrupt vector mapping
6 Interrupt vector mapping
Table 10. Interrupt mapping
IRQ
No.
Source
block
Description
Wakeup
from Halt
mode
Wakeup
from
Active-halt
mode
Wakeup
from Wait
(WFI
mode)
Wakeup
from Wait
(WFE
(1)
mode)
Vector
address
RESET Reset Yes Yes Yes Yes 0x00 8000
TRAP Software interrupt - - - - 0x00 8004
0TLI
(2)
External top level interrupt - - - - 0x00 8008
FLASH end of programing/
1 FLASH
write attempted to
- - Yes Yes 0x00 800C
protected page interrupt
DMA1 channels 0/1 half
2 DMA1 0/1
transaction/transaction
- - Yes Yes 0x00 8010
complete interrupt
DMA1 channels 2/3 half
3 DMA1 2/3
transaction/transaction
- - Yes Yes 0x00 8014
complete interrupt
RTC alarm A/
4RTC
wakeup/tamper 1/
Yes Yes Yes Yes 0x00 8018
tamper 2/tamper 3
EXTIE/
5
PVD
External interrupt port E
PVD interrupt
Yes Yes Yes Yes 0x00 801C
6 EXTIB External interrupt port B Yes Yes Yes Yes 0x00 8020
7 EXTID External interrupt port D Yes Yes Yes Yes 0x00 8024
8 EXTI0 External interrupt 0 Yes Yes Yes Yes 0x00 8028
9 EXTI1 External interrupt 1 Yes Yes Yes Yes 0x00 802C
10 EXTI2 External interrupt 2 Yes Yes Yes Yes 0x00 8030
11 EXTI3 External interrupt 3 Yes Yes Yes Yes 0x00 8034
12 EXTI4 External interrupt 4 Yes Yes Yes Yes 0x00 8038
13 EXTI5 External interrupt 5 Yes Yes Yes Yes 0x00 803C
14 EXTI6 External interrupt 6 Yes Yes Yes Yes 0x00 8040
15 EXTI7 External interrupt 7 Yes Yes Yes Yes 0x00 8044
16 Reserved 0x00 8048
CLK system clock switch/
17 CLK
CSS interrupt - - Yes Yes 0x00 804C
COMP1 interrupt
18
COMP1/
COMP2/
ADC1
COMP2 interrupt
ACD1 end of conversion/
analog watchdog/
Yes Yes Yes Yes 0x00 8050
overrun interrupt
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 47/112
Page 48

Interrupt vector mapping STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
Table 10. Interrupt mapping (continued)
IRQ
No.
Source
block
19 TIM2
20 TIM2
21 TIM3
22 TIM3
Description
TIM2 update/overflow/
trigger/break interrupt
TIM2 capture/
compare interrupt
TIM3 update/overflow/
trigger/break interrupt
TIM3 capture/
compare interrupt
Wakeup
from Halt
mode
Wakeup
from
Active-halt
mode
- - Yes Yes 0x00 8054
- - Yes Yes 0x00 8058
- - Yes Yes 0x00 805C
- - Yes Yes 0x00 8060
Wakeup
from Wait
(WFI
mode)
Wakeup
from Wait
(WFE
(1)
mode)
Vector
address
23 RI RI trigger interrupt - - Yes - 0x00 8064
24 Reserved 0x00 8068
25 TIM4
TIM4 update/overflow/
trigger interrupt
- - Yes Yes 0x00 806C
SPI1 TX buffer empty/
26 SPI1
RX buffer not empty/
Yes Yes Yes Yes 0x00 8070
error/wakeup interrupt
USART1 transmit data
27 USART1
register empty/
transmission complete
- - Yes Yes 0x00 8074
interrupt
USART1 received data
28 USART1
ready/overrun error/
idle line detected/parity
- - Yes Yes 0x00 8078
error/global error interrupt
29 I
2
C1 I2C1 interrupt
(3)
Yes Yes Yes Yes 0x00 807C
1. The Low power wait mode is entered when executing a WFE instruction in Low power run mode. In WFE mode, the
interrupt is served if it has been previously enabled. After processing the interrupt, the processor goes back to WFE mode.
When the interrupt is configured as a wakeup event, the CPU wakes up and resumes processing.
2. The TLI interrupt is the logic OR between TIM2 overflow interrupt, and TIM4 overflow interrupts.
3. The device is woken up from Halt or Active-halt mode only when the address received matches the interface address.
48/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 49

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Electrical parameters
50 pF
STM8L PIN
7 Electrical parameters
7.1 Parameter conditions
Unless otherwise specified, all voltages are referred to VSS.
7.1.1 Minimum and maximum values
Unless otherwise specified the minimum and maximum values are guaranteed in the worst
conditions of ambient temperature, supply voltage and frequencies by tests in production on
100% of the devices with an ambient temperature at T
the selected temperature range).
Data based on characterization results, design simulation and/or technology characteristics
is indicated in the table footnotes and are not tested in production. Based on
characterization, the minimum and maximum values refer to sample tests and represent the
mean value plus or minus three times the standard deviation (mean±3Σ).
7.1.2 Typical values
= 25 °C and TA = TA max (given by
A
Unless otherwise specified, typical data is based on TA = 25 °C, V
design guidelines and is not tested.
Typical ADC1 accuracy values are determined by characterization of a batch of samples
from a standard diffusion lot over the full temperature range, where 95% of the devices have
an error less than or equal to the value indicated
7.1.3 Typical curves
Unless otherwise specified, all typical curves are given only as design guidelines and are
not tested.
7.1.4 Loading capacitor
The loading conditions used for pin parameter measurement are shown in Figure 9.
Figure 9. Pin loading conditions
(mean±2Σ).
= 3 V. It is given only as
DD
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 49/112
Page 50

Electrical parameters STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
V
IN
STM8L PIN
7.1.5 Pin input voltage
The input voltage measurement on a pin of the device is described in Figure 10.
Figure 10. Pin input voltage
7.2 Absolute maximum ratings
Stresses above those listed as “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage
to the device. This is a stress rating only and functional operation of the device under these
conditions is not implied. Exposure to maximum rating conditions for extended periods may
affect device reliability.
Table 11. Voltage characteristics
Symbol Ratings Min Max Unit
- V
V
DD
SS
(2)
V
IN
(3)
V
IN
External supply voltage (including VDD,
V
, and V
DDA
DDIO
(1)
)
Input voltage on true open-drain pins
(PC0 and PC1)
Input voltage on five-volt tolerant (FT)
pins (PA7 and PE0)
Input voltage on 3.6 V tolerant (TT) pins V
Input voltage on any other pin V
Input voltage on true open-drain pins
(PC0 and PC1)
Input voltage on any other pin V
- 0.3 4.0 V
V
- 0.3 VDD + 4.0
SS
- 0.3 V
V
SS
- 0.3 4.0
SS
- 0.3 4.0
SS
V
- 0.3 VDD + 4.0
SS
- 0.3 4.0
SS
DD
+ 4.0
V
V
see Absolute maximum
V
ESD
Electrostatic discharge voltage
ratings (electrical sensitivity)
on page 94
1. All power (VDD, V
external power supply.
2. VIN maximum must always be respected. Refer to Table 12. for maximum allowed injected current values.
3. VIN maximum must always be respected. Refer to Table 12. for maximum allowed injected current values.
DDA
, V
) and ground (VSS, V
DDIO
SSA
, V
) pins must always be connected to the
SSIO
50/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 51

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Electrical parameters
Table 12. Current characteristics
Symbol Ratings Max. Unit
I
VDD
I
VSS
I
IO
Total current into V
Total current out of V
Output current sunk by IR_TIM pin (with high sink LED driver
capability)
power line (source) 80
DD
ground line (sink) 80
SS
80
Output current sunk by any other I/O and control pin 25
Output current sourced by any I/Os and control pin - 25
Injected current on true open-drain pins (PC0 and PC1)
I
INJ(PIN)
Injected current on 3.6 V tolerant pins
Injected current on any other pin
ΣI
INJ(PIN)
1. A positive injection is induced by VIN>VDD while a negative injection is induced by VIN<VSS. I
never be exceeded. Refer to Table 11. for maximum allowed input voltage values.
2. When several inputs are submitted to a current injection, the maximum ΣI
positive and negative injected currents (instantaneous values).
Table 13. Thermal characteristics
Total injected current (sum of all I/O and control pins)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(2)
is the absolute sum of the
INJ(PIN)
- 5 / +0
- 5 / +0
- 5 / +5
± 25
INJ(PIN)
Symbol Ratings Value Unit
T
STG
T
Storage temperature range -65 to +150
Maximum junction temperature 150
J
mA
mA
must
° C
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 51/112
Page 52

Electrical parameters STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
7.3 Operating conditions
Subject to general operating conditions for VDD and TA.
7.3.1 General operating conditions
Table 14. General operating conditions
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min. Max. Unit
System clock
V
V
DDA
DD
(1)
frequency
Standard operating
voltage
Analog operating
voltage
1.65 V ≤ V
ADC1 not
used
ADC1 used 1.8 3.6 V
< 3.6 V 0 16 MHz
DD
(2)
Must be at the same
potential as V
DD
1.65
1.65
(2)
3.6 V
3.6 V
f
SYSCLK
LQFP48 288
Power dissipation at
TA= 85 °C for suffix 3
and suffix 6
devices
(3)
P
D
Power dissipation at
= 125 °C for suffix 3
T
A
devices
UFQFPN32 288
UFQFPN28 250
UFQFPN20 196
TSSOP20 181
LQFP48 77
UFQFPN32 185
UFQFPN28 62
UFQFPN20 49
TSSOP20 45
T
A
T
J
1. f
SYSCLK
2. 1.8 V at power-up, 1.65 V at power-down if BOR is disabled
3. To calculate P
characteristics” table.
max is given by the test limit. Above this value, the product behavior is not guaranteed.
4. T
J
Temperature range
Junction temperature
range
= f
CPU
), use the formula P
Dmax(TA
1.65 V ≤ V
=(T
Dmax
1.65 V ≤ V
< 3.6 V (6 suffix version) -40 85
DD
< 3.6 V (3 suffix version) -40 125
DD
-40 °C ≤ T
< 85 °C
A
(6 suffix version)
-40 °C ≤ TA < 125 °C
(3 suffix version)
-TA)/ΘJA with T
Jmax
in this table and Θ
Jmax
-40 105
-40 130
in “Thermal
JA
(4)
(4)
mW
°C
52/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 53

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Electrical parameters
7.3.2 Embedded reset and power control block characteristics
Table 15. Embedded reset and power control block characteristics
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min
t
VDD
t
TEMP
V
PDR
V
BOR0
V
BOR1
V
BOR2
V
BOR3
V
BOR4
VDD rise time rate
VDD fall time rate
Reset release delay
BOR detector
enabled
BOR detector
enabled
rising
V
DD
0
20
Power-down reset threshold Falling edge 1.30
Brown-out reset threshold 0
(BOR_TH[2:0]=000)
Brown-out reset threshold 1
(BOR_TH[2:0]=001)
Brown-out reset threshold 2
(BOR_TH[2:0]=010)
Brown-out reset threshold 3
(BOR_TH[2:0]=011)
Brown-out reset threshold 4
(BOR_TH[2:0]=100)
Falling edge 1.66 1.70 1.74
Rising edge 1.39 1.75 1.81
Falling edge 1.89 1.93 1.97
Rising edge 1.98 2.03 2.07
Falling edge 2.25 2.30 2.35
Rising edge 2.35 2.40 2.44
Falling edge 2.50 2.55 2.60
Rising edge 2.59 2.65 2.70
Falling edge 2.74 2.79 2.85
Rising edge 2.83 2.89 2.95
(1)
(1)
(2)
Typ
(1)
3
1.50 1.65 V
Max Unit
(1)
∞
µs/V
(1)
∞
ms
V
V
PVD0
PVD threshold 0
Rising edge 1.89 1.94 1.97
Falling edge 2.04 2.05 2.08
Falling edge 2.82 1.85 1.88
V
PVD1
PVD threshold 1
Rising edge 2.12 2.14 2.17
Falling edge 2.21 2.24 2.28
V
PVD2
PVD threshold 2
Rising edge 2.31 2.33 2.37
Falling edge 2.41 2.44 2.48
V
PVD3
PVD threshold 3
Rising edge 2.51 2.53 2.57
Falling edge 2.61 2.64 2.69
V
PVD4
PVD threshold 4
Rising edge 2.71 2.74 2.79
Falling edge 2.79 2.83 2.88
V
PVD5
PVD threshold 5
Rising edge 2.90 2.94 2.99
Falling edge 3.01 3.04 3.09
V
PVD6
1. Data guaranteed by design, not tested in production.
2. Data based on characterization results, not tested in production.
PVD threshold 6
Rising edge 3.12 3.15 3.20
V
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 53/112
Page 54

Electrical parameters STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
1.8 V
Vdd
Internal NRST
VBOR0
BOR threshold
BOR Threshold_0
PDR Threshold
with
BOR
without
BOR
Time
with
BOR
Safe Reset
Reset
at power up
BOR activated by user for
power down detection
Vdd
Vdd
Operating power supply
3.6 V
without BOR = Batte ry lif e exten sion
VPDR
Safe Reset release
BOR always active
Figure 11. POR/BOR thresholds
7.3.3 Supply current characteristics
Total current consumption
The MCU is placed under the following conditions:
● All I/O pins in input mode with a static value at V
● All peripherals are disabled except if explicitly mentioned.
In the following table, data is based on characterization results, unless otherwise specified.
Subject to general operating conditions for V
DD
and TA.
or VSS (no load)
DD
54/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 55
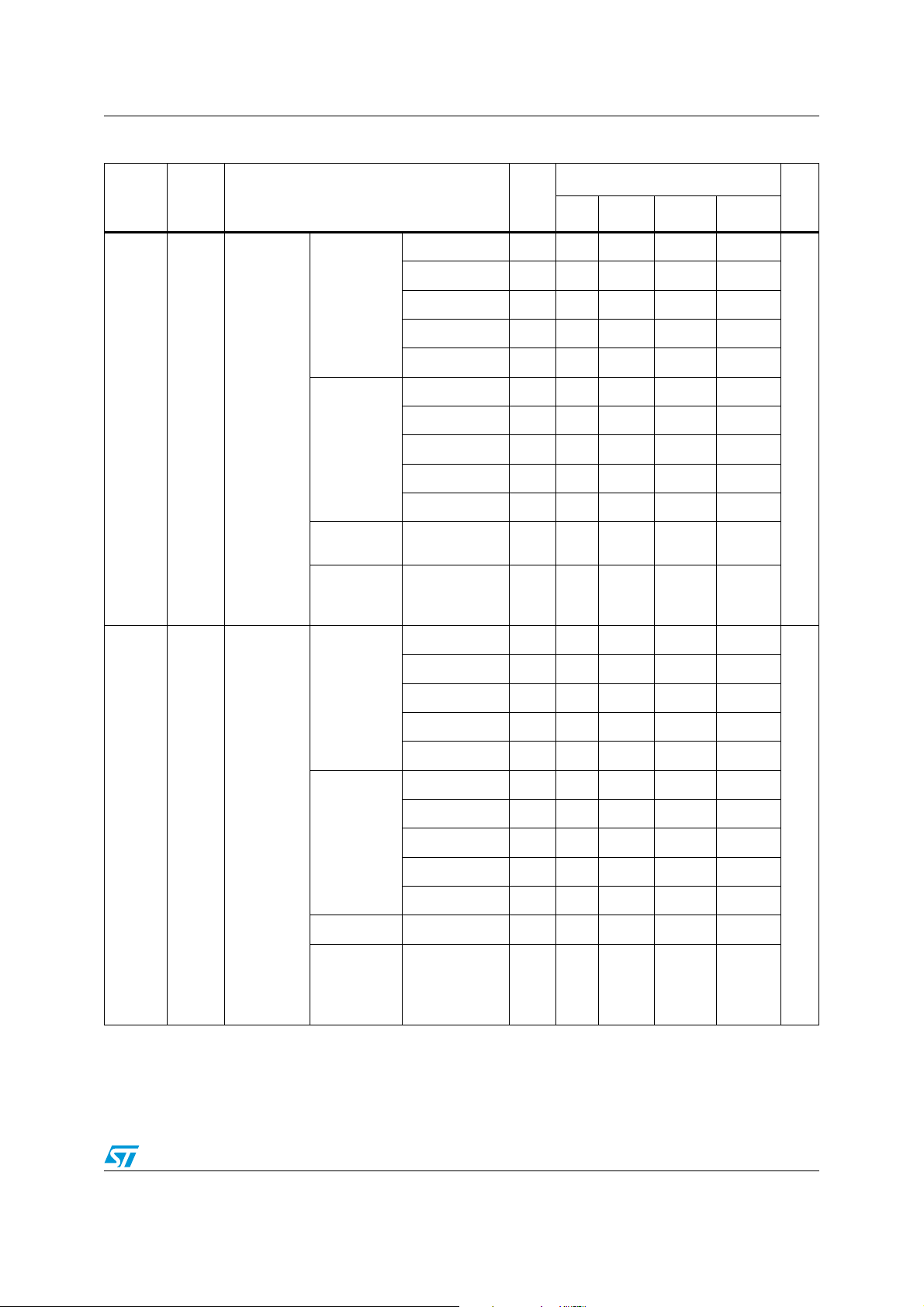
STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Electrical parameters
Table 16. Total current consumption in Run mode
Symbol
I
DD(RUN)
Para
meter
Supply
current
in run
(3)
mode
All
peripherals
OFF,
code
executed
from RAM,
from
V
DD
1.65 V to
3.6 V
Conditions
HSI RC osc.
(16 MHz)
(4)
HSE external
clock
(5)
(f
CPU=fHSE
)
LSI RC osc.
(typ. 38 kHz)
(1)
f
CPU
f
CPU
f
CPU
f
CPU
f
CPU
f
CPU
f
CPU
f
CPU
f
CPU
f
CPU
f
CPU
= 125 kHz
= 1 MHz
= 4 MHz
= 8 MHz
= 16 MHz
= 125 kHz
= 1 MHz
= 4 MHz
= 8 MHz
= 16 MHz
= f
LSI
LSE external
= f
clock
f
CPU
LSE
(32.768 kHz)
f
= 125 kHz
CPU
f
= 1 MHz
CPU
I
DD(RUN)
Supply
current
in Run
mode
All
peripherals
OFF, code
executed
from Flash,
from
V
DD
1.65 V to
HSI RC
(7)
osc.
HSE external
clock
(f
CPU=fHSE
(5)
)
= 4 MHz
f
CPU
= 8 MHz
f
CPU
f
= 16 MHz
CPU
f
= 125 kHz
CPU
f
= 1 MHz
CPU
f
= 4 MHz
CPU
f
= 8 MHz
CPU
3.6 V
= 16 MHz
f
CPU
= f
LSI RC osc.
f
CPU
LSI
LSE ext.
clock
(32.768
(8)
kHz)
f
CPU
= f
LSE
Max
Typ
55 °C
85 °C 105°C
(2)
125 °C
0.39 0.47 0.49 0.52 0.55
0.48 0.56 0.58 0.61 0.65
0.75 0.84 0.86 0.91 0.99
1.10 1.20 1.25 1.31 1.40
1.85 1.93 2.12
(6)
2.29
(6)
2.36
0.05 0.06 0.09 0.11 0.12
0.18 0.19 0.20 0.22 0.23
0.55 0.62 0.64 0.71 0.77
0.99 1.20 1.21 1.22 1.24
1.90 2.22 2.23
(6)
2.24
(6)
2.28
0.040 0.045 0.046 0.048 0.050
0.035 0.040 0.048
(6)
0.050 0.062
0.43 0.55 0.56 0.58 0.62
0.60 0.77 0.80 0.82 0.87
1.11 1.34 1.37 1.39 1.43
1.90 2.20 2.23 2.31 2.40
3.8 4.60 4.75 4.87 4.88
0.30 0.36 0.39 0.44 0.47
0.40 0.50 0.52 0.55 0.56
1.15 1.31 1.40 1.45 1.48
2.17 2.33 2.44 2.56 2.77
4.0 4.46 4.52 4.59 4.77
0.110 0.123 0.130 0.140 0.150
0.100 0.101 0.104 0.119 0.122
Unit
(2)
(6)
mA
(6)
mA
1. All peripherals OFF, VDD from 1.65 V to 3.6 V, HSI internal RC osc. , f
2. For devices with suffix 3
3. CPU executing typical data processing
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 55/112
CPU=fSYSCLK
Page 56

Electrical parameters STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
4. The run from RAM consumption can be approximated with the linear formula:
I
(run_from_RAM) = Freq * 90 µA/MHz + 380 µA
DD
5. Oscillator bypassed (HSEBYP = 1 in CLK_ECKCR). When configured for external crystal, the HSE consumption
(I
) must be added. Refer to Table 27.
DD HSE
6. Tested in production.
7. The run from Flash consumption can be approximated with the linear formula:
(run_from_Flash) = Freq * 195 µA/MHz + 440 µA
I
DD
8. Oscillator bypassed (LSEBYP = 1 in CLK_ECKCR). When configured for extenal crystal, the LSE consumption
) must be added. Refer to Table 28.
(I
DD LSE
Figure 12. Typ. I
DD(RUN)
vs. VDD,f
= 16MHz
CPU
3.00
2.75
2.50
2.25
2.00
IDD(RUN)HSI [mA]
1.75
1.50
1.6 2.1 2.6 3.1 3.6
[V]
V
DD
1. Typical current consumption measured with code executed from RAM
-40°C
25°C
90°C
130°C
ai18213
56/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 57

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Electrical parameters
In the following table, data is based on characterization results, unless otherwise specified.
Table 17. Total current consumption in Wait mode
Symbol Parameter
I
DD(Wait)
Supply
current in
Wait mode
CPU not
clocked,
all peripherals
OFF,
code executed
from RAM
with Flash in
(3)
mode
I
DDQ
from
V
DD
1.65 V to 3.6 V
Conditions
HSI
HSE external
clock
(f
CPU=fHSE
,
(4)
Max
(1)
= 125 kHz
f
CPU
f
= 1 MHz
CPU
= 4 MHz
f
CPU
f
= 8 MHz
CPU
f
= 16 MHz
CPU
f
= 125 kHz
CPU
f
= 1 MHz
CPU
= 4 MHz
f
CPU
)
f
CPU
f
CPU
= 8 MHz
= 16 MHz
Typ
55°C
85 °C
105 °C
(2)
125 °C
(2)
0.33 0.39 0.41 0.43 0.45
0.35 0.41 0.44 0.45 0.48
0.42 0.51 0.52 0.54 0.58
0.52 0.57 0.58 0.59 0.62
0.68 0.76 0.79
0.82
(5)
0.85
(5)
0.032 0.056 0.068 0.072 0.093
0.078 0.121 0.144 0.163 0.197
0.218 0.26 0.30 0.36 0.40
0.40 0.52 0.57 0.62 0.66
0.760 1.01 1.05
1.09
(5)
1.16
(5)
Unit
mA
= f
LSI
(6)
LSE
external clock
(32.768
f
CPU
f
CPU
= f
LSI
LSE
kHz)
f
= 125 kHz
CPU
f
= 1 MHz
CPU
f
CPU
f
CPU
f
CPU
f
CPU
f
CPU
f
CPU
f
CPU
f
CPU
f
CPU
f
CPU
= 4 MHz
= 8 MHz
= 16 MHz
= 125 kHz
= 1 MHz
= 4 MHz
= 8 MHz
= 16 MHz
= f
LSI
= f
LSE
I
DD(Wait)
Supply
current in
Wait
mode
CPU not
clocked,
all peripherals
OFF,
code executed
from Flash,
from
V
DD
1.65 V to 3.6 V
HSI
(4)
HSE
external clock
(f
=HSE)
CPU
LSI
(6)
LSE
external clock
(32.768 kHz)
1. All peripherals OFF, VDD from 1.65 V to 3.6 V, HSI internal RC osc. , f
0.035 0.044 0.046 0.049 0.054
0.032 0.036 0.038 0.044 0.051
0.38 0.48 0.49 0.50 0.56
0.41 0.49 0.51 0.53 0.59
0.50 0.57 0.58 0.62 0.66
0.60 0.66 0.68 0.72 0.74
0.79 0.84 0.86 0.87 0.90
0.06 0.08 0.09 0.10 0.12
0.10 0.17 0.18 0.19 0.22
0.24 0.36 0.39 0.41 0.44
0.50 0.58 0.61 0.62 0.64
1.00 1.08 1.14 1.16 1.18
0.055 0.058 0.065 0.073 0.080
0.051 0.056 0.060 0.065 0.073
= f
CPU
SYSCLK
mA
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 57/112
Page 58

Electrical parameters STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
500
550
600
650
700
750
800
850
900
950
1000
1.6 2.1 2.6 3.1 3.6
V
DD
[V]
IDD(WAIT)HSI [μA]
-40°C
25°C
90°C
130°C
ai18214
2. For temperature range 3.
3. Flash is configured in I
4. Oscillator bypassed (HSEBYP = 1 in CLK_ECKCR). When configured for external crystal, the HSE consumption
(I
) must be added. Refer to Table 27.
DD HSE
5. Tested in production.
6. Oscillator bypassed (LSEBYP = 1 in CLK_ECKCR). When configured for extenal crystal, the LSE consumption
) must be added. Refer to Table 28.
(I
DD HSE
mode in Wait mode by setting the EPM or WAITM bit in the Flash_CR1 register.
DDQ
Figure 13. Typ. I
1. Typical current consumption measured with code executed from Flash memory.
DD(Wait)
vs. VDD,f
CPU
=16MHz
1)
58/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 59

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Electrical parameters
In the following table, data is based on characterization results, unless otherwise specified.
Table 18. Total current consumption and timing in Low power run mode at V
= 1.65 V to
DD
3.6 V
Symbol Parameter
I
DD(LPR)
Supply current in Low
power run mode
LSI RC osc.
(at 38 kHz)
(4)
external
LSE
clock
(32.768 kHz)
Conditions
all peripherals OFF
with TIM2 active
all peripherals OFF
(1)(2)
(3)
Typ Ma x Un it
= -40 °C
T
A
to 25 °C
T
= 55 °C 5.7 6
A
= 85 °C 6.8 7.5
T
A
T
= 105 °C 9.2 10.4
A
= 125 °C 13.4 16.6
T
A
= -40 °C
T
A
to 25 °C
T
= 55 °C 6.0 6.3
A
= 85 °C 7.2 7.8
T
A
= 105 °C 9.4 10.7
T
A
T
= 125 °C 13.8 17
A
TA = -40 °C
to 25 °C
= 55 °C 5.67 6.1
T
A
T
= 85 °C 5.85 6.3
A
= 105 °C 7.11 7.6
T
A
= 125 °C 9.84 12
T
A
TA = -40 °C
to 25 °C
5.1 5.4
5.4 5.7
5.25 5.6
5.59 6
μA
T
= 55 °C 6.10 6.4
A
with TIM2 active
1. No floating I/Os
> 85 °C is valid only for devices with suffix 3 temperature range.
2. T
A
3. Timer 2 clock enabled and counter running
4. Oscillator bypassed (LSEBYP = 1 in CLK_ECKCR). When configured for extenal crystal, the LSE consumption
) must be added. Refer to Table 28
(I
DD LSE
(3)
= 85 °C 6.30 7
T
A
T
= 105 °C 7.55 8.4
A
= 125 °C 10.1 15
T
A
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 59/112
Page 60

Electrical parameters STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
Figure 14. Typ. I
18
16
14
12
10
[μA]
8
DD(LPR)LSI
I
6
4
2
0
DD(LPR)
1.6 2. 1 2.6 3.1 3.6
vs. V
(LSI clock source)
DD
V
DD
–40° C
25° C
90° C
130° C
[V]
ai18216
60/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 61

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Electrical parameters
0.00
2.00
4.00
6.00
8.00
10.00
12.00
14.00
16.00
1.6 2.1 2.6
3.1 3.6
V
DD
[V]
I
DD(LPW )LSI
[µA]
-40°C
25°C
90°C
130°C
ai18217
In the following table, data is based on characterization results, unless otherwise specified.
Table 19. Total current consumption in Low power wait mode at V
Symbol Parameter
I
DD(LPW)
Supply current in
Low power wait mode
LSI RC osc.
(at 38 kHz)
LSE external
(4)
clock
(32.768 kHz)
Conditions
(1)(2)
all peripherals OFF
with TIM2 active
(3)
all peripherals OFF
with TIM2 active
(3)
T
A
T
A
T
A
T
A
T
A
T
A
T
A
T
A
T
A
T
A
TA = -40 °C to 25 °C
T
A
T
A
T
A
T
A
TA = -40 °C to 25 °C
T
A
T
A
T
A
T
A
1. No floating I/Os.
> 85 °C is valid only for devices with suffix 3 temperature range.
2. T
A
3. Timer 2 clock enabled and counter is running.
4. Oscillator bypassed (LSEBYP = 1 in CLK_ECKCR). When configured for extenal crystal, the LSE consumption
) must be added. Refer to Table 28.
(I
DD LSE
= 1.65 V to 3.6 V
DD
Typ Max Uni t
= -40 °C to 25 °C
33.3
= 55 °C 3.3 3.6
= 85 °C 4.4 5
= 105 °C 6.7 8
= 125 °C 11 14
= -40 °C to 25 °C
3.4 3.7
= 55 °C 3.7 4
= 85 °C 4.8 5.4
= 105 °C 7 8.3
= 125 °C 11.3 14.5
2.35 2.7
= 55 °C 2.42 2.82
= 85 °C 3.10 3.71
= 105 °C 4.36 5.7
= 125 °C 7.20 11
2.46 2.75
= 55 °C 2.50 2.81
= 85 °C 3.16 3.82
= 105 °C 4.51 5.9
= 125 °C 7.28 11
μA
Figure 15. Typ. I
DD(LPW)
vs. V
(LSI clock source)
DD
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 61/112
Page 62

Electrical parameters STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
In the following table, data is based on characterization results, unless otherwise specified.
Table 20. Total current consumption and timing in Active-halt mode at V
Symbol Parameter
I
DD(AH)
I
DD(WUFAH)
t
WU_HSI(AH)
t
WU_LSI(AH)
1. No floating I/O, unless otherwise specified.
> 85 °C is valid only for devices with suffix 3 temperature range.
2. T
A
3. Oscillator bypassed (LSEBYP = 1 in CLK_ECKCR). When configured for extenal crystal, the LSE consumption
(I
DD LSE
4. Wakeup time until start of interrupt vector fetch.
The first word of interrupt routine is fetched 4 CPU cycles after t
5. ULP=0 or ULP=1 and FWU=1 in the PWR_CSR2 register.
Supply current in
Active-halt mode
Supply current during
wakeup time from
Active-halt mode
(using HSI)
Wakeup time from
(4)(5)
Active-halt mode to
Run mode (using HSI)
Wakeup time from
(4)
(5)
) must be added. Refer to Table 28
Active-halt mode to
Run mode (using LSI)
Conditions
LSI RC (at 38 kHz)
LSE external clock (32.768
(3)
kHz)
.
WU
= 1.65 V to 3.6 V
DD
(1)(2)
T
= -40 °C to 25 °C
A
= 55 °C 1.2 3
T
A
= 85 °C 1.5 3.4
T
A
= 105 °C 2.6 6.6
T
A
= 125 °C 5.1 12
T
A
TA = -40 °C to 25 °C
= 55 °C 0.62 1.4
T
A
= 85 °C 0.88 2.1
T
A
= 105 °C 2.1 4.85
T
A
= 125 °C 4.8 11
T
A
Typ Max Unit
0.9 2.1
0.5 1.2
2.4 mA
4.7 7 μs
150 μs
μA
Table 21. Typical current consumption in Active-halt mode, RTC clocked by LSE external crystal
Symbol Parameter Condition
(1)
Typ Uni t
LSE 1.15
V
= 1.8 V
I
DD(AH)
(2)
Supply current in Active-halt
mode
DD
V
DD
= 3 V
(3)
LSE/32
LSE 1.30
(3)
LSE/32
1.05
µA
1.20
LSE 1.45
V
= 3.6 V
DD
1. No floating I/O, unless otherwise specified.
2. Based on measurements on bench with 32.768 kHz external crystal oscillator.
3. RTC clock is LSE divided by 32.
LSE/32
(3)
1.35
62/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 63

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Electrical parameters
In the following table, data is based on characterization results, unless otherwise specified.
Table 22. Total current consumption and timing in Halt mode at V
Symbol Parameter Condition
(1)(2)
= 1.65 to 3.6 V
DD
Typ Max Unit
Supply current in Halt mode
I
DD(Halt)
(Ultra-low-power ULP bit =1 in
PWR_CSR2 register)
the
Supply current during wakeup
I
DD(WUHalt)
time from Halt mode (using
HSI)
t
WU_HSI(Halt)
t
WU_LSI(Halt)
1. TA = -40 to 125 °C, no floating I/O, unless otherwise specified.
> 85 °C is valid only for devices with suffix 3 temperature range.
2. T
A
3. Tested in production.
4. ULP=0 or ULP=1 and FWU=1 in the PWR_CSR2 register.
5. Wakeup time until start of interrupt vector fetch.
The first word of interrupt routine is fetched 4 CPU cycles after t
(4)(5)
(4)(5)
Wakeup time from Halt to Run
mode (using HSI)
Wakeup time from Halt mode
to Run mode (using LSI)
= -40 °C to 25 °C 350
T
A
= 55 °C 580 2000
T
A
TA = 85 °C 1160
TA = 105 °C 2560
TA = 125 °C 4.4
2.4 mA
4.7 7 µs
150 µs
.
WU
1400
2800
6700
13
(3)
(3)
(3)
(3)
nA
µA
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 63/112
Page 64

Electrical parameters STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
Current consumption of on-chip peripherals
Table 23. Peripheral current consumption
Symbol Parameter
I
DD(TIM2)
I
DD(TIM3)
I
DD(TIM4)
I
DD(USART1)
I
DD(SPI1)
I
DD(I2C1)
I
DD(DMA1)
I
DD(WWDG)
I
DD(ALL)
I
DD(ADC1)
I
DD(COMP1)
I
DD(COMP2)
I
DD(PVD/BOR)
I
DD(BOR)
I
DD(IDWDG)
TIM2 supply current
TIM3 supply current
TIM4 timer supply current
USART1 supply current
SPI1 supply current
I2C1 supply current
DMA1 supply current
WWDG supply current
Peripherals ON
ADC1 supply current
Comparator 1 supply current
Comparator 2 supply current
Power voltage detector and brownout Reset unit supply current
(6)
Brownout Reset unit supply current
Independent watchdog supply current
(1)
(1)
(1)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(5)
Slow mode 2
Fast mode 5
(6)
including LSI supply
current
excluding LSI
supply current
Typ.
= 3.0 V
V
DD
8
8
3
6
3
5
3
2
38 µA/MHz
1500 µA
0.160
2.6
2.4
0.45
0.05
Unit
µA/MHz
µA
1. Data based on a differential IDD measurement between all peripherals OFF and a timer counter running at 16 MHz. The
CPU is in Wait mode in both cases. No IC/OC programmed, no I/O pins toggling. Not tested in production.
2. Data based on a differential I
the on-chip peripheral when clocked and not kept under reset. The CPU is in Wait mode in both cases. No I/O pins
toggling. Not tested in production.
3. Peripherals listed above the I
4. Data based on a differential I
5. Data based on a differential I
enabled with static inputs. Supply current of internal reference voltage excluded.
6. Including supply current of internal reference voltage.
measurement between the on-chip peripheral in reset configuration and not clocked and
DD
parameter ON: TIM2, TIM3, TIM4, USART1, SPI1, I2C1, DMA1, WWDG.
DD(ALL)
measurement between ADC1 in reset configuration and continuous ADC1 conversion.
DD
measurement between COMP1 or COMP2 in reset configuration and COMP1 or COMP2
DD
64/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 65

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Electrical parameters
Table 24. Current consumption under external reset
Symbol Parameter Conditions Typ Unit
V
= 1.8 V 48
I
DD(RST)
1. All pins except PA0, PB0 and PB4 are floating under reset. PA0, PB0 and PB4 are configured with pull-up under reset.
Supply current under
external reset
(1)
All pins are externally
tied to V
DD
DD
= 3 V 76
DD
= 3.6 V 91
V
DD
7.3.4 Clock and timing characteristics
HSE external clock (HSEBYP = 1 in CLK_ECKCR)
Subject to general operating conditions for VDD and TA.
Table 25. HSE external clock characteristics
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
f
HSE_ext
V
HSEH
V
HSEL
External clock source
frequency
(1)
OSC_IN input pin high level
voltage
OSC_IN input pin low level
voltage
116MHz
0.7 x V
V
SS
DD
V
DD
0.3 x V
DD
µAV
V
C
in(HSE)
I
LEAK_HSE
1. Data guaranteed by Design, not tested in production.
OSC_IN input
capacitance
(1)
OSC_IN input leakage
current
2.6 pF
V
< V
IN
< V
DD
SS
LSE external clock (LSEBYP=1 in CLK_ECKCR)
Subject to general operating conditions for VDD and TA.
in(LSE)
(2)
(2)
External clock source frequency
(1)
OSC32_IN input pin high level voltage 0.7 x V
OSC32_IN input pin low level voltage V
OSC32_IN input capacitance
(1)
SS
32.768 kHz
DD
0.3 x V
0.6 pF
V
DD
OSC32_IN input leakage current ±1 µA
Table 26. LSE external clock characteristics
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
f
LSE_ext
V
LSEH
V
LSEL
C
I
LEAK_LSE
1. Data guaranteed by Design, not tested in production.
2. Data based on characterization results, not tested in production.
±1 µA
V
DD
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 65/112
Page 66

Electrical parameters STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
OSC_OUT
OSC_IN
f
HSE
to core
C
L1
C
L2
R
F
STM8
Resonator
Consumption
control
g
m
R
m
C
m
L
m
C
O
Resonator
g
mcrit
2 Π× f
HSE
×()
2
Rm× 2Co C+()
2
=
HSE crystal/ceramic resonator oscillator
The HSE clock can be supplied with a 1 to 16 MHz crystal/ceramic resonator oscillator. All
the information given in this paragraph is based on characterization results with specified
typical external components. In the application, the resonator and the load capacitors have
to be placed as close as possible to the oscillator pins in order to minimize output distortion
and startup stabilization time. Refer to the crystal resonator manufacturer for more details
(frequency, package, accuracy...).
Table 27. HSE oscillator characteristics
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
f
HSE
R
C
I
DD(HSE)
g
t
SU(HSE)
1. C=
2. The oscillator selection can be optimized in terms of supply current using a high quality resonator with small R
Refer to crystal manufacturer for more details
High speed external oscillator
frequency
Feedback resistor 200 kΩ
F
(1)
Recommended load capacitance
(2)
C = 20 pF,
f
= 16 MHz
HSE oscillator power consumption
OSC
C = 10 pF,
=16 MHz
f
OSC
Oscillator transconductance 3.5
m
(4)
Startup time VDD is stabilized 1 ms
C
=
C
is approximately equivalent to 2 x crystal C
L1
L2
LOAD
.
116MHz
20 pF
2.5 (startup)
0.7 (stabilized)
2.5 (startup)
0.46 (stabilized)
(3)
3. Data guaranteed by Design. Not tested in production.
4. t
is the startup time measured from the moment it is enabled (by software) to a stabilized 16 MHz oscillation. This
SU(HSE)
value is measured for a standard crystal resonator and it can vary significantly with the crystal manufacturer.
Figure 16. HSE oscillator circuit diagram
value.
m
(3)
mA
(3)
mA/V
HSE oscillator critical g
Rm: Motional resistance (see crystal specification), Lm: Motional inductance (see crystal specification),
: Motional capacitance (see crystal specification), Co: Shunt capacitance (see crystal specification),
C
m
=C: Grounded external capacitance
C
L1=CL2
>> g
g
m
mcrit
66/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
formula
m
Page 67
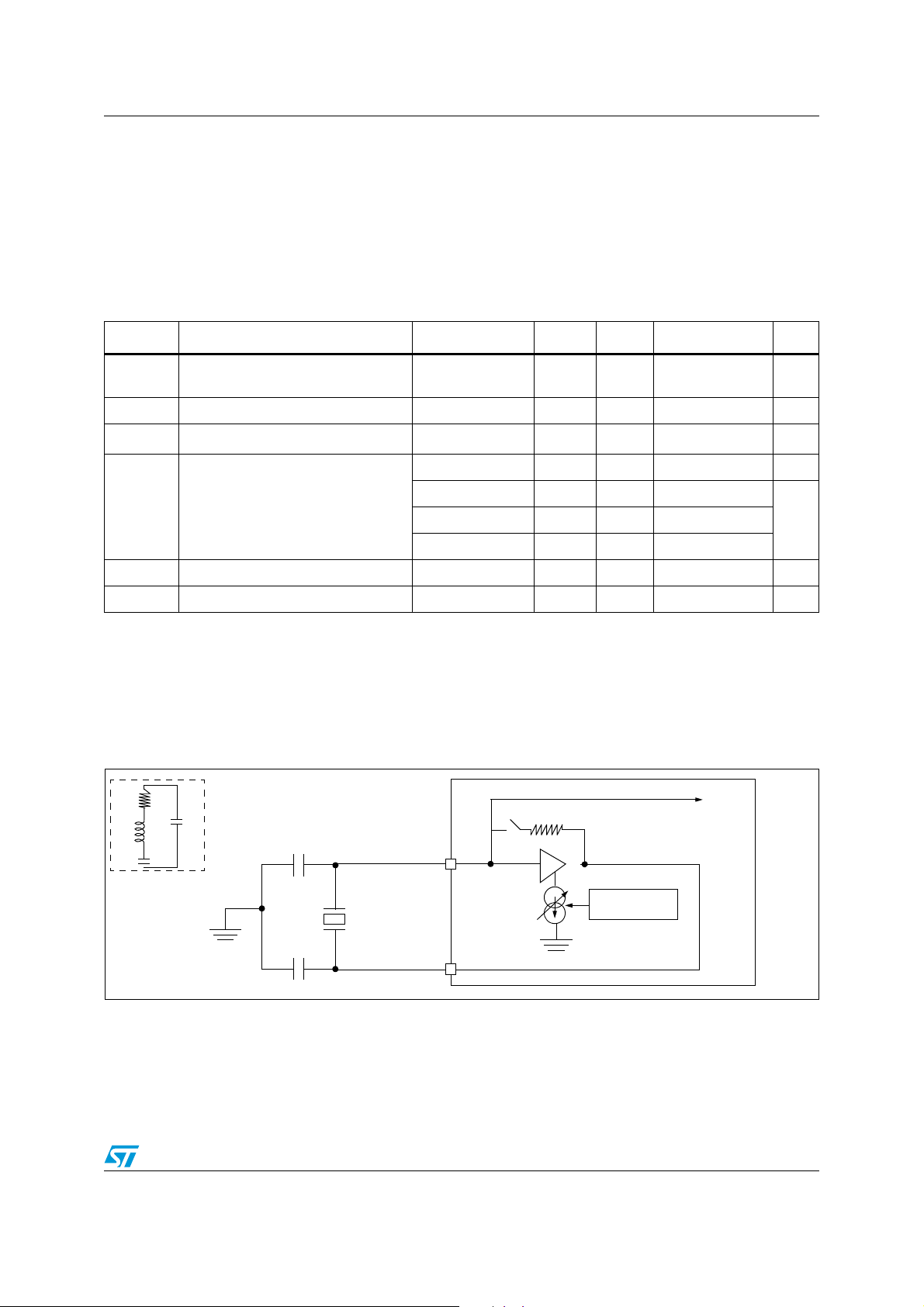
STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Electrical parameters
OSC_OUT
OSC_IN
f
LSE
C
L1
C
L2
R
F
STM8
Resonator
Consumption
control
g
m
R
m
C
m
L
m
C
O
Resonator
LSE crystal/ceramic resonator oscillator
The LSE clock can be supplied with a 32.768 kHz crystal/ceramic resonator oscillator. All
the information given in this paragraph is based on characterization results with specified
typical external components. In the application, the resonator and the load capacitors have
to be placed as close as possible to the oscillator pins in order to minimize output distortion
and startup stabilization time. Refer to the crystal resonator manufacturer for more details
(frequency, package, accuracy...).
Table 28. LSE oscillator characteristics
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
f
LSE
R
C
I
DD(LSE)
g
t
SU(LSE)
1. C=
2. The oscillator selection can be optimized in terms of supply current using a high quality resonator with a small R
Refer to crystal manufacturer for more details.
Low speed external oscillator
frequency
Feedback resistor ΔV = 200 mV 1.2 MΩ
F
(1)
Recommended load capacitance
(2)
32.768 kHz
8pF
1.4
V
= 1.8 V 450
LSE oscillator power consumption
Oscillator transconductance 3
m
(4)
Startup time VDD is stabilized 1 s
C
=
C
is approximately equivalent to 2 x crystal C
L1
L2
DD
= 3 V 600
DD
= 3.6 V 750
V
DD
.
LOAD
(3)
(3)
3. Data guaranteed by Design. Not tested in production.
4. t
is the startup time measured from the moment it is enabled (by software) to a stabilized 32.768 kHz oscillation.
SU(LSE)
This value is measured for a standard crystal resonator and it can vary significantly with the crystal manufacturer.
Figure 17. LSE oscillator circuit diagram
value.
m
µA
nAV
µA/V
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 67/112
Page 68

Electrical parameters STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
Internal clock sources
Subject to general operating conditions for VDD, and TA.
High speed internal RC oscillator (HSI)
In the following table, data is based on characterization results, not tested in production,
unless otherwise specified.
Table 29. HSI oscillator characteristics
Symbol Parameter
Conditions
(1)(2)
Min Typ Max Unit
f
HSI
ACC
TRIM
t
su(HSI)
I
DD(HSI)
1. VDD = 3.0 V, TA = -40 to 125 °C unless otherwise specified.
> 85 °C is valid only for devices with suffix 3 temperature range.
2. T
A
3. Tested in production.
4. The trimming step differs depending on the trimming code. It is usually negative on the codes which are multiples of 16
(0x00, 0x10, 0x20, 0x30...0xE0). Refer to the AN3101 “STM8L15x internal RC oscillator calibration” application note for
more details.
5. Guaranteed by design, not tested in production.
Frequency VDD = 3.0 V 16 MHz
(3)
-4.5 3 %
3.7 6
100 140
Accuracy of HSI
oscillator (factory
HSI
calibrated)
HSI user trimming
(4)
step
HSI oscillator setup
time (wakeup time)
HSI oscillator power
consumption
= 3.0 V, TA = 25 °C -1
V
DD
= 3.0 V, 0 °C ≤ TA ≤ 55 °C -1.5 1.5 %
V
DD
= 3.0 V, -10 °C ≤ TA ≤ 70 °C -2 2 %
V
DD
= 3.0 V, -10 °C ≤ TA ≤ 85 °C -2.5 2 %
V
DD
= 3.0 V, -10 °C ≤ TA ≤ 125 °C -4.5 2 %
V
DD
1.65 V ≤ V
≤ 3.6 V,
DD
-40 °C ≤ TA ≤ 125 °C
Trimming code ≠ multiple of 16 0.4 0.7 %
Trimming code = multiple of 16 ± 1.5 %
(3)
1
(5)
(5)
%
µs
µA
68/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 69

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Electrical parameters
13.0
13.5
14.0
14.5
15.0
15.5
16.0
16.5
17.0
17.5
18.0
1.65 1.8 1.95 2.1 2.25 2.4 2.55 2.7 2.85 3 3.15 3.3 3.45 3.6
V
DD
[V]
HSI frequency [MHz]
-40°C
25°C
90°C
130°C
Figure 18. Typical HSI frequency vs V
DD
Low speed internal RC oscillator (LSI)
In the following table, data is based on characterization results, not tested in production.
Table 30. LSI oscillator characteristics
Symbol
Parameter
(1)
Conditions
(1)
Min Typ Max Unit
f
t
su(LSI)
I
DD(LSI)
1. VDD = 1.65 V to 3.6 V, TA = -40 to 125 °C unless otherwise specified.
2. Guaranteed by design, not tested in production.
3. This is a deviation for an individual part, once the initial frequency has been measured.
Frequency 26 38 56 kHz
LSI
LSI oscillator wakeup time 200
LSI oscillator frequency
(3)
drift
0 °C ≤ TA ≤ 85 °C -12 11 %
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 69/112
(2)
µs
Page 70

Electrical parameters STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
25
27
29
31
33
35
37
39
41
43
45
1.6 2.1 2.6 3.1 3.6
V
DD
[V]
LSI frequency [kHz]
-40°C
25°C
90°C
130°C
Figure 19. Typical LSI frequency vs. V
DD
70/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 71

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Electrical parameters
7.3.5 Memory characteristics
TA = -40 to 125 °C unless otherwise specified.
Table 31. RAM and hardware registers
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
V
RM
1. Minimum supply voltage without losing data stored in RAM (in Halt mode or under Reset) or in hardware
registers (only in Halt mode). Guaranteed by characterization, not tested in production.
Data retention mode
Flash memory
Table 32. Flash program and data EEPROM memory
(1)
Halt mode (or Reset) 1.65 V
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ
V
Operating voltage
DD
(all modes, read/write/erase)
f
SYSCLK
= 16 MHz 1.65 3.6 V
Programming time for 1 or 64 bytes (block)
erase/write cycles (on programmed byte)
t
prog
Programming time for 1 to 64 bytes (block)
write cycles (on erased byte)
T
=+25 °C, VDD = 3.0 V
I
prog
Programming/ erasing consumption
Data retention (program memory) after 10000
erase/write cycles at TA= –40 to +85 °C
A
=+25 °C, VDD = 1.8 V
T
A
T
= +85 °C 30
RET
(1)
Max
(1)
6ms
3ms
0.7 mA
(3 and 6 suffix)
t
RET
Data retention (program memory) after 10000
erase/write cycles at T
(3 suffix)
(2)
= –40 to +125 °C
A
Data retention (data memory) after 300000
erase/write cycles at TA= –40 to +85 °C
T
= +125 °C 5
RET
T
= +85 °C 30
RET
(1)
years
(1)
(3 and 6 suffix)
Data retention (data memory) after 300000
erase/write cycles at TA= –40 to +125 °C
T
= +125 °C 5
RET
(1)
(3 suffix)
Erase/write cycles (program memory) TA = –40 to +85 °C
10
(1)
(3 and 6 suffix),
= –40 to +105 °C
(3)
N
RW
Erase/write cycles (data memory)
T
A
(3 suffix) or
= –40 to +125 °C
T
A
300
(4)
(1)
kcycles
(3 suffix)
1. Data based on characterization results, not tested in production.
2. Conforming to JEDEC JESD22a117
3. The physical granularity of the memory is 4 bytes, so cycling is performed on 4 bytes even when a write/erase operation
addresses a single byte.
4. Data based on characterization performed on the whole data memory.
Unit
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 71/112
Page 72

Electrical parameters STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
7.3.6 I/O current injection characteristics
As a general rule, current injection to the I/O pins, due to external voltage below VSS or
above V
in order to give an indication of the robustness of the microcontroller in cases when
abnormal injection accidentally happens, susceptibility tests are performed on a sample
basis during device characterization.
Functional susceptibilty to I/O current injection
While a simple application is executed on the device, the device is stressed by injecting
current into the I/O pins programmed in floating input mode. While current is injected into the
I/O pin, one at a time, the device is checked for functional failures.
The failure is indicated by an out of range parameter: ADC1 error, out of spec current
injection on adjacent pins or other functional failure (for example reset, oscillator frequency
deviation, etc.).
The test results are given in the following table.
Table 33. I/O current injection susceptibility
Symbol Description
(for standard pins) should be avoided during normal product operation. However,
DD
Functional susceptibility
Negative
injection
Positive
injection
Unit
Injected current on true open-drain pins (PC0 and
PC1)
I
INJ
Injected current on all five-volt tolerant pins -5 +0
Injected current on all 3.6 V tolerant pins -5 +0
Injected current on any other pin -5 +5
7.3.7 I/O port pin characteristics
General characteristics
Subject to general operating conditions for VDD and TA unless otherwise specified. All
unused pins must be kept at a fixed voltage: using the output mode of the I/O for example or
an external pull-up or pull-down resistor.
-5 +0
mA
72/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 73

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Electrical parameters
Table 34. I/O static characteristics
Symbol Parameter
Input voltage on true open-drain
pins (PC0 and PC1)
V
Input low level voltage
IL
(2)
Input voltage on any other pin
Input voltage on true open-drain
pins (PC0 and PC1)
with VDD < 2 V
V
Input high level voltage
IH
(2)
Input voltage on true open-drain
pins (PC0 and PC1)
with V
Input voltage on any other pin
V
Schmitt trigger voltage
hys
hysteresis
(3)
I/Os 200
True open drain I/Os 200
V
High sink I/Os
I
Input leakage current
lkg
(4)
V
True open drain I/Os
V
PA0 with high sink LED driver
capability
≤ VIN≤ V
SS
≤ VIN≤ V
SS
≤ VIN≤ V
SS
Conditions
≥ 2 V
DD
DD
DD
DD
(1)
Min
Typ
Max Unit
VSS-0.3 0.3 x V
VSS-0.3 0.3 x V
5.2 V
0.70 x V
DD
5.5
0.70 x V
DD
VDD+0.3
--50
- - 200
- - 200
(5)
(5)
(5)
DD
DD
V
mV
nA
R
C
1. VDD = 3.0 V, TA = -40 to 125 °C unless otherwise specified.
2. Data based on characterization results, not tested in production.
3. Hysteresis voltage between Schmitt trigger switching levels. Based on characterization results, not tested.
4. The max. value may be exceeded if negative current is injected on adjacent pins.
5. Not tested in production.
6. R
Figure 23).
Weak pull-up equivalent
PU
IO
pull-up equivalent resistor based on a resistive transistor(corresponding I
PU
(2)(6)
resistor
I/O pin capacitance 5 pF
V
IN=VSS
30 45 60 kΩ
current characteristics described in
PU
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 73/112
Page 74

Electrical parameters STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
1.6 2.1
2.6 3.1
3.6
V
DD
[V]
V
IL
and V
IH
[V]
-40°C
25°C
90°C
130°C
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
1.6 2.1 2.6 3.1 3.6
V
DD
[V]
V
IL
and V
IH
[V]
-40°C
25°C
90°C
130°C
Figure 20. Typical VIL and V
Figure 21. Typical V
and V
IL
vs VDD (high sink I/Os)
IH
vs VDD (true open drain I/Os)
IH
74/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 75

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Electrical parameters
30
35
40
45
50
55
60
1.6 1.8 2 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 3 3.2 3.4 3.6
V
DD
[V]
Pull-Up resistance [k
Ω
]
-40°C
25°C
90°C
130°C
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
1.65 1.8 1.95 2.1 2.25 2.4 2.55 2.7 2.85 3 3.15 3.3 3.45 3.6
V
DD
[V]
Pull-Up current [μA]
-40°C
25°C
90°C
130°C
Figure 22. Typical pull-up resistance RPU vs VDD with VIN=V
Figure 23. Typical pull-up current Ipu vs VDD with VIN=V
SS
SS
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 75/112
Page 76

Electrical parameters STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
Output driving current
Subject to general operating conditions for V
Table 35. Output driving current (high sink ports)
I/O
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Max Unit
Type
(1)
V
OL
High sink
V
OH
1. The IIO current sunk must always respect the absolute maximum rating specified in Table 12 and the sum
of I
(I/O ports and control pins) must not exceed I
IO
2. The IIO current sourced must always respect the absolute maximum rating specified in Table 12 and the
sum of I
IO
Output low level voltage for an I/O pin
(2)
Output high level voltage for an I/O pin
(I/O ports and control pins) must not exceed I
and TA unless otherwise specified.
DD
= +2 mA,
I
IO
= 3.0 V
V
DD
= +2 mA,
I
IO
= 1.8 V
V
DD
= +10 mA,
I
IO
= 3.0 V
V
DD
= -2 mA,
I
VSS
.
VDD
.
IO
= 3.0 V
V
DD
= -1 mA,
I
IO
= 1.8 V
V
DD
I
= -10 mA,
IO
V
= 3.0 V
DD
VDD-0.45
V
-0.45
DD
V
DD
0.45 V
0.45 V
0.7 V
-0.7 V
V
V
Table 36. Output driving current (true open drain ports)
I/O
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Max Unit
Type
= +3 mA,
I
IO
V
= 3.0 V
(1)
V
OL
Output low level voltage for an I/O pin
Open drain
1. The IIO current sunk must always respect the absolute maximum rating specified in Table 12 and the sum
of I
(I/O ports and control pins) must not exceed I
IO
VSS
.
DD
I
= +1 mA,
IO
V
DD
= 1.8 V
0.45
0.45
Table 37. Output driving current (PA0 with high sink LED driver capability)
I/O
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Max Unit
Type
= +20 mA,
I
(1)
V
IR
OL
1. The IIO current sunk must always respect the absolute maximum rating specified in Table 12 and the sum
of IIO (I/O ports and control pins) must not exceed I
Output low level voltage for an I/O pin
.
VSS
V
IO
DD
= 2.0 V
0.45 V
V
76/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 77

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Electrical parameters
0
0.25
0.5
0.75
1
0 2 4 6 8 101214161820
L
OL
25
90
ai18226
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0123456 78
L
OL
25
90
ai18227
ai18228
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
01234567
L
OL
25
90
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
01234567
L
OL
25
90
BJ
0
0.25
0.5
0.75
1
1.25
1.5
1.75
2
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
I
OH
[mA]
V
DD
- V
OH
[V]
-40°C
25°C
90°C
130°C
ai12830
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
01234567
H
DD
- V
OH
25
90
BJ
Figure 24. Typ. VOL @ VDD = 3.0 V (high sink
ports)
-40°C
°C
°C
[V]
V
130°C
I
[mA]
O
Figure 26. Typ. VOL @ VDD = 3.0 V (true open
drain ports)
-40°C
°C
°C
[V]
V
130°C
Figure 25. Typ. VOL @ VDD = 1.8 V (high sink
ports)
-40°C
°C
°C
[V]
V
130°C
I
[mA]
O
Figure 27. Typ. VOL @ VDD = 1.8 V (true open
drain ports)
-40°C
°C
[V]
V
°C
130°C
Figure 28. Typ. V
sink ports)
I
[mA]
O
DD - VOH
@ VDD = 3.0 V (high
Figure 29. Typ. V
sink ports)
-40°C
°C
°C
130°C
[V]
V
I
[mA]
O
DD - VOH
I
[mA]
O
@ VDD = 1.8 V (high
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 77/112
Page 78

Electrical parameters STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
30
35
40
45
50
55
60
1.6 1.8 2 2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 3 3.2 3.4 3.6
V
DD
[V]
Pull-up resistance [k
Ω
]
-40°C
25°C
90°C
130°C
NRST pin
Subject to general operating conditions for VDD and TA unless otherwise specified.
Table 38. NRST
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min
pin characteristics
Typ
Max Unit
V
IL(NRST)
V
IH(NRST)
NRST input low level voltage
NRST input high level voltage
(1)
(1)
IOL = 2 mA
for 2.7 V ≤ V
V
(3)
(3)
(1)
I
= 1.5 mA
OL
for V
DD
V
OL(NRST)
V
HYST
R
PU(NRST)
V
F(NRST)
V
NF(NRST)
1. Data based on characterization results, not tested in production.
2. 200 mV min.
3. Data guaranteed by design, not tested in production.
NRST output low level voltage
NRST input hysteresis
(3)
NRST pull-up equivalent resistor
(1)
NRST input filtered pulse
NRST input not filtered pulse
Figure 30. Typical NRST pull-up resistance RPU vs VDD
DD
< 2.7 V
≤ 3.6
V
1.4
SS
0.8
V
DD
0.4
10%V
DD
(2)
30 45 60 kΩ
50
300
V
mV
ns
78/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 79

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Electrical parameters
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
1.65 1.8 1.95 2.1 2.25 2.4 2.55 2.7 2.85 3 3.15 3.3 3.45 3.6
V
DD
[V]
Pull-U
p current [μA]
-40°C
25°C
90°C
130°C
EXTERNAL
RESET
CIRCUIT
STM8
Filter
R
PU
V
DD
INTERNAL RESET
NRST
0.1 µF
(Optional)
Figure 31. Typical NRST pull-up current Ipu vs VDD
The reset network shown in Figure 32 protects the device against parasitic resets. The user
must ensure that the level on the NRST pin can go below the V
IL(NRST)
max. level specified
in Ta bl e 3 8 . Otherwise the reset is not taken into account internally.
For power consumption sensitive applications, the external reset capacitor value can be
reduced to limit the charge/discharge current. If the NRST signal is used to reset the
external circuitry, attention must be paid to the charge/discharge time of the external
capacitor to fulfill the external devices reset timing conditions. The minimum recommended
capacity is 10 nF.
Figure 32. Recommended NRST pin configuration
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 79/112
Page 80

Electrical parameters STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
7.3.8 Communication interfaces
SPI1 - Serial peripheral interface
Unless otherwise specified, the parameters given in Ta bl e 3 9 are derived from tests
performed under ambient temperature, f
conditions summarized in Section 7.3.1. Refer to I/O port characteristics for more details on
the input/output alternate function characteristics (NSS, SCK, MOSI, MISO).
Table 39. SPI1 characteristics
Symbol Parameter Conditions
SYSCLK
frequency and VDD supply voltage
(1)
Min Max Unit
f
SCK
1/t
c(SCK)
t
r(SCK)
t
f(SCK)
t
su(NSS)
t
h(NSS)
t
w(SCKH)
t
w(SCKL)
t
su(MI)
t
su(SI)
t
h(MI)
t
h(SI)
t
a(SO)
t
dis(SO)
t
v(SO)
t
v(MO)
t
h(SO)
t
h(MO)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)(3)
(2)(4)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
SPI1 clock frequency
Master mode 0 8
Slave mode 0 8
SPI1 clock rise and fall
time
NSS setup time Slave mode 4 x 1/f
Capacitive load: C = 30 pF - 30 ns
SYSCLK
NSS hold time Slave mode 80 -
(2)
SCK high and low time
Master mode,
f
MASTER
= 8 MHz, f
SCK
= 4 MHz
105 145
Master mode 30 -
Data input setup time
Slave mode 3 -
Master mode 15 -
Data input hold time
Slave mode 0 -
Data output access time Slave mode - 3x 1/f
Data output disable time Slave mode 30 -
Data output valid time Slave mode (after enable edge) - 60
Data output valid time
Master mode (after enable
edge)
-20
Slave mode (after enable edge) 15 -
Data output hold time
Master mode (after enable
edge)
1-
MHz
-
SYSCLK
1. Parameters are given by selecting 10 MHz I/O output frequency.
2. Values based on design simulation and/or characterization results, and not tested in production.
3. Min time is for the minimum time to drive the output and max time is for the maximum time to validate the data.
4. Min time is for the minimum time to invalidate the output and max time is for the maximum time to put the data in Hi-Z.
80/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 81

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Electrical parameters
ai14134
SCK Input
CPHA=0
MOSI
INPUT
MISO
OUT PUT
CPHA=0
MS B O U T
MSB IN
BI T6 O UT
LSB IN
LSB OUT
CPOL=0
CPOL=1
BIT1 IN
NSS input
t
SU(NSS)
t
c(SCK)
t
h(NSS)
t
a(SO)
t
w(SCKH)
t
w(SCKL)
t
v(SO)
t
h(SO)
t
r(SCK)
t
f(SCK)
t
dis(SO)
t
su(SI)
t
h(SI)
ai14135
SCK Input
CPHA=1
MOSI
INPUT
MISO
OUT PUT
CPHA=1
MS B O U T
MSB IN
BI T6 O UT
LSB IN
LSB OUT
CPOL=0
CPOL=1
BIT1 IN
t
SU(NSS)
t
c(SCK)
t
h(NSS)
t
a(SO)
t
w(SCKH)
t
w(SCKL)
t
v(SO)
t
h(SO)
t
r(SCK)
t
f(SCK)
t
dis(SO)
t
su(SI)
t
h(SI)
NSS input
Figure 33. SPI1 timing diagram - slave mode and CPHA=0
Figure 34. SPI1 timing diagram - slave mode and CPHA=1
1. Measurement points are done at CMOS levels: 0.3V
and 0.7V
DD
DD
.
(1)
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 81/112
Page 82

Electrical parameters STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
ai14136
SCK output
CPHA=0
MOSI
OUTUT
MISO
INP UT
CPHA=0
MSBIN
M SB OUT
BIT6 IN
LSB OUT
LSB IN
CPOL=0
CPOL=1
B I T1 OUT
NSS input
t
c(SCK)
t
w(SCKH)
t
w(SCKL)
t
r(SCK)
t
f(SCK)
t
h(MI)
High
SCK output
CPHA=1
CPHA=1
CPOL=0
CPOL=1
t
su(MI)
t
v(MO)
t
h(MO)
Figure 35. SPI1 timing diagram - master mode
(1)
1. Measurement points are done at CMOS levels: 0.3V
and 0.7V
DD
DD
.
82/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 83

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Electrical parameters
I2C - Inter IC control interface
Subject to general operating conditions for V
The STM8L I
2
C interface (I2C1) meets the requirements of the Standard I2C communication
DD
, f
SYSCLK
, and TA unless otherwise specified.
protocol described in the following table with the restriction mentioned below:
Refer to I/O port characteristics for more details on the input/output alternate function
characteristics (SDA and SCL).
Table 40. I2C characteristics
Symbol Parameter
t
w(SCLL)
t
w(SCLH)
t
su(SDA)
t
h(SDA)
t
r(SDA)
t
r(SCL)
t
f(SDA)
t
f(SCL)
t
h(STA)
t
su(STA)
t
su(STO)
t
w(STO:STA)
C
1. f
SYSCLK
Data based on standard I
2.
SCL clock low time 4.7 1.3
SCL clock high time 4.0 0.6
SDA setup time 250 100
SDA data hold time 0 0 900
SDA and SCL rise time 1000 300
SDA and SCL fall time 300 300
START condition hold time 4.0 0.6
Repeated START condition setup
time
STOP condition setup time 4.0 0.6 μs
STOP to START condition time (bus
free)
Capacitive load for each bus line 400 400 pF
b
must be at least equal to 8 MHz to achieve max fast I2C speed (400 kHz).
2
C protocol requirement, not tested in production.
Standard mode
I2C
(2)
Min
Max
(2)
Fast mode I
(2)
Min
4.7 0.6
4.7 1.3 μs
2C(1)
Max
(2)
Unit
μs
ns
μs
Note: For speeds around 200 kHz, the achieved speed can have a± 5% tolerance
For other speed ranges, the achieved speed can have a± 2% tolerance
The above variations depend on the accuracy of the external components used.
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 83/112
Page 84

Electrical parameters STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
REPEATED START
START
STOP
START
t
f(SDA)
t
r(SDA)
t
su(SDA)th(SDA)
t
f(SCL)
t
r(SCL)
t
w(SCLL)
t
w(SCLH)
t
h(STA)
t
su(STO)
t
su(STA)tw(STO:STA)
SDA
SCL
4.7kΩ
SDA
STM8L
SCL
V
DD
100Ω
100Ω
V
DD
4.7kΩ
I2CBUS
2
Figure 36.
Typical application with I
C bus and timing diagram
1. Measurement points are done at CMOS levels: 0.3 x VDD and 0.7 x V
1)
DD
84/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 85

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Electrical parameters
7.3.9 Embedded reference voltage
In the following table, data is based on characterization results, not tested in production,
unless otherwise specified.
Table 41. Reference voltage characteristics
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max. Unit
I
REFINT
T
S_VREFINT
I
BUF
V
REFINT out
I
LPBUF
I
REFOUT
C
REFOUT
t
VREFINT
t
BUFEN
ACC
VREFINT
STAB
STAB
(1)(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
VREFINT
VREFINT
Internal reference voltage
consumption
ADC1 sampling time when reading
the internal reference voltage
Internal reference voltage buffer
consumption (used for ADC1)
Reference voltage output 1.202
1.4 µA
510µs
13.5 25 µA
(3)
1.224 1.242
(3)
Internal reference voltage low
power buffer consumption (used for
730 1200 nA
comparators or output)
Buffer output current
(4)
1µA
Reference voltage output load 50 pF
Internal reference voltage startup
time
Internal reference voltage buffer
startup time once enabled
Accuracy of V
REFINT
VREFINT_Factory_CONV byte
Stability of V
REFINT
over
(1)
stored in the
(5)
temperature
Stability of V
REFINT
over
temperature
Stability of V
REFINT
after 1000
hours
-40 °C ≤ TA ≤
125 °C
0 °C ≤ TA ≤ 50
°C
23ms
10 µs
± 5 mV
20 50 ppm/°C
20 ppm/°C
TBD ppm
V
1. Defined when ADC1 output reaches its final value ±1/2LSB
2. Data guaranteed by Design. Not tested in production.
3. Tested in production at V
4. To guaranty less than 1%
5. Measured at V
= 3 V ±10 mV. This value takes into account VDD accuracy and ADC1 conversion accuracy.
DD
= 3 V ±10 mV.
DD
V
REFOUT
deviation.
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 85/112
Page 86
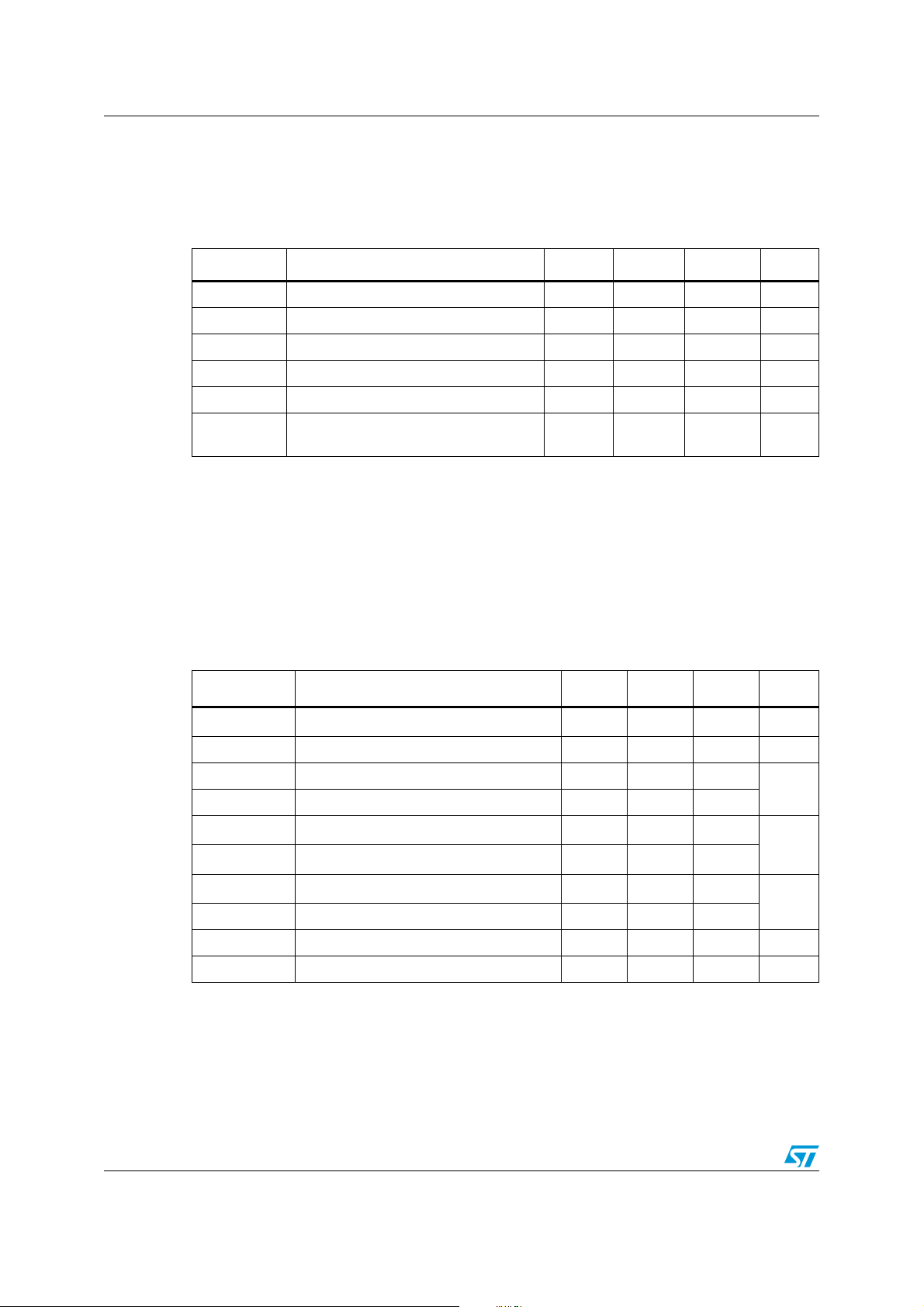
Electrical parameters STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
7.3.10 Temperature sensor
In the following table, data is based on characterization results, not tested in production,
unless otherwise specified.
Table 42. TS characteristics
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max. Unit
(1)
V
90
T
L
Avg_slope
I
DD(TEMP)
T
START
T
S_TEMP
1. Tested in production at VDD = 3 V ±10 mV. The 8 LSB of the V90 ADC1 conversion result are stored in the
TS_Factory_CONV_V90 byte.
2. Data guaranteed by design, not tested in production.
3. Defined for ADC1 output reaching its final value ±1/2LSB.
Sensor reference voltage at 90°C ±5 °C, 0.580 0.597 0.614 V
(2)(3)
(2)
V
SENSOR
(2)
(2)
ADC1 sampling time when reading the
linearity with temperature ±1 ±2 °C
Average slope 1.59 1.62 1.65 mV/°C
Consumption 3.4 6 µA
Temperature sensor startup time 10 µs
temperature sensor
10 µs
7.3.11 Comparator characteristics
In the following table, data is guaranteed by design, not tested in production, unless
otherwise specified.
Table 43. Comparator 1 characteristics
Symbol Parameter Min Typ
V
DDA
T
A
R
400K
R
10K
V
IN
V
REFINT
t
START
t
d
V
offset
I
COMP1
1. Based on characterization, not tested in production.
2. Tested in production at VDD = 3 V ±10 mV.
3. The delay is characterized for 100 mV input step with 10 mV overdrive on the inverting input, the noninverting input set to the reference.
4. Comparator consumption only. Internal reference voltage not included.
Analog supply voltage 1.65 3.6 V
Temperature range -40 125 °C
R
value 300 400 500
400K
R
value 7.5 10 12.5
10K
Comparator 1 input voltage range 0.6
Internal reference voltage
Comparator startup time 7 10
Propagation delay
(3)
Comparator offset error ±3 ±10 mV
Current consumption
(1)
Max
Unit
kΩ
V
(2)
DDA
1.202 1.224 1.242
V
µs
(4)
310
160 260 nA
86/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 87

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Electrical parameters
In the following table, data is guaranteed by design, not tested in production.
Table 44. Comparator 2 characteristics
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ
Max
(1)
Unit
V
DDA
T
V
t
START
t
d slow
t
d fast
V
offset
I
COMP2
1. Based on characterization, not tested in production.
2. The delay is characterized for 100 mV input step with 10 mV overdrive on the inverting input, the noninverting input set to the reference.
3. Comparator consumption only. Internal reference voltage not included.
Analog supply voltage 1.65 3.6 V
Temperature range -40 125 °C
A
Comparator 2 input voltage range 0
IN
Fast mode 15 20
Comparator startup time
Slow mode 20 25
Propagation delay in slow mode
Propagation delay in fast mode
(2)
(2)
1.65 V ≤ V
≤ 2.7 V
2.7 V ≤ V
3.6 V
1.65 V ≤ V
≤ 2.7 V
2.7 V ≤ V
3.6 V
DDA
DDA
DDA
DDA
≤
≤
1.8 3.5
2.5 6
0.8 2
1.2 4
Comparator offset error ±4 ±20 mV
Current consumption
(3)
Fast mode 3.5 5
Slow mode 0.5 2
V
DDA
V
µs
µA
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 87/112
Page 88

Electrical parameters STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
7.3.12 12-bit ADC1 characteristics
In the following table, data is guaranteed by design, not tested in production.
Table 45. ADC1 characteristics
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
V
DDA
V
REF+
V
REF-
I
VDDA
I
VREF+
V
AIN
T
A
R
AIN
C
ADC1
f
ADC1
f
CONV
Analog supply voltage 1.8 3.6 V
Reference supply
voltage
Lower reference voltage
Current on the VDDA
input pin
Current on the VREF+
input pin
Conversion voltage
range
2.4 V ≤ V
1.8 V ≤ V
≤ 3.6 V
DDA
≤ 2.4 V V
DDA
2.4
0
(2)
V
DDA
SSA
V
DDA
V
V
V
1000 1450 µA
700
(peak)
(1)
µA
400
450
(average)
V
REF+
(1)
µA
Temperature range -40 125 °C
External resistance on
V
AIN
Internal sample and
hold capacitor
ADC1 sampling clock
frequency
on PF0 fast channel
on all other channels
on PF0 fast channel
on all other channels
2.4 V≤ V
DDA
≤ 3.6 V
without zooming
1.8 V≤ V
DDA
≤ 2.4 V
with zooming
V
on PF0 fast
AIN
channel
50
(3)
kΩ
16 pF
0.320 16 MHz
0.320 8 MHz
(4)(5)
1
MHz
12-bit conversion rate
V
on all other
AIN
channels
760
(4)(5)
kHz
f
TRIG
t
LAT
External trigger
frequency
External trigger latency 3.5 1/f
88/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
t
conv
1/f
ADC1
SYSCLK
Page 89

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Electrical parameters
Table 45. ADC1 characteristics (continued)
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
V
on PF0 fast
AIN
channel
< 2.4 V
V
DDA
on PF0 fast
V
AIN
t
S
t
conv
t
WKUP
Sampling time
12-bit conversion time
Wakeup time from OFF
state
channel
2.4 V ≤ V
on slow channels
V
AIN
V
DDA
V
on slow channels
AIN
2.4 V ≤ V
≤ 3.6 V
DDA
< 2.4 V
≤ 3.6 V
DDA
16 MHz 1
TA = +25 °C 1
Time before a new
(6)
t
IDLE
t
VREFINT
1. The current consumption through V
- one constant (max 300 µA)
- one variable (max 400 µA), only during sampling time + 2 first conversion pulses.
So, peak consumption is 300+400 = 700 µA and average consumption is 300 + [(4 sampling + 2) /16] x 400 = 450 µA at
1Msps
2. V
REF-
3. Guaranteed by design, not tested in production.
4. Minimum sampling and conversion time is reached for maximum Rext = 0.5 kΩ.
5. Value obtained for continuous conversion on fast channel.
6. The time between 2 conversions, or between ADC1 ON and the first conversion must be lower than t
7. The t
conversion
Internal reference
voltage startup time
REF
or V
must be tied to ground.
DDA
maximum value is ∞ on the “Z” revision code of the device.
IDLE
T
= +70 °C 20
A
= +125 °C 2
T
A
is composed of two parameters:
0.43
0.22
0.86
0.41
(4)(5)
(4)(5)
(4)(5)
(4)(5)
12 + t
(4)
S
µs
µs
µs
µs
1/f
ADC1
µs
3µs
(7)
(7)
(7)
refer to
Ta bl e 4 1
IDLE.
s
ms
ms
ms
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 89/112
Page 90

Electrical parameters STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
In the following three tables, data is guaranteed by characterization result, not tested in
production.
Table 46. ADC1 accuracy with V
Symbol Parameter Conditions Typ Max Unit
DNL Differential non linearity
INL Integral non linearity
TUE Total unadjusted error
Offset Offset error
Gain Gain error
= 3.3 V to 2.5 V
DDA
= 16 MHz 1 1.6
f
ADC1
f
= 8 MHz 1 1.6
ADC1
= 4 MHz 1 1.5
f
ADC1
= 16 MHz 1.2 2
f
ADC1
f
= 8 MHz 1.2 1.8
ADC1
= 4 MHz 1.2 1.7
f
ADC1
= 16 MHz 2.2 3.0
f
ADC1
f
= 8 MHz 1.8 2.5
ADC1
= 4 MHz 1.8 2.3
f
ADC1
f
= 16 MHz 1.5 2
ADC1
= 8 MHz 1 1.5
f
ADC1
= 4 MHz 0.7 1.2
f
ADC1
f
= 16 MHz
ADC1
= 8 MHz
ADC1
= 4 MHz
f
ADC1
LSB
LSB
11.5f
Table 47. ADC1 accuracy with V
Symbol Parameter Typ Max Unit
DNL Differential non linearity 1 2 LSB
INL
TUE
Integral non linearity
Total unadjusted error
Offset Offset error 1 2 LSB
Gain Gain error 1.5 3 LSB
Table 48. ADC1 accuracy with V
Symbol Parameter Typ Max Unit
DNL Differential non linearity 1 2 LSB
INL
TUE
Integral non linearity
Total unadjusted error
Offset Offset error 2 3 LSB
Gain Gain error 2 3 LSB
= 2.4 V to 3.6 V
DDA
= V
DDA
REF
+
= 1.8 V to 2.4 V
1.7 3 LSB
24LSB
23LSB
35LSB
90/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 91

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Electrical parameters
E
O
E
G
1LSB
IDEAL
(1) Example of an actual transfer curve
(2) The ideal transfer curve
(3) End point correlation line
E
T
=Total Unadjusted Error: maximum deviation
between the actual and the ideal transfer curves.
E
O
=Offset Error: deviation between the first actual
transition and the first ideal one.
E
G
=Gain Error: deviation between the last ideal
transition and the last actual one.
E
D
=Differential Linearity Error: maximum deviation
between actual steps and the ideal one.
E
L
=Integral Linearity Error: maximum deviation
between any actual transition and the end point
correlation line.
4095
4094
4093
5
4
3
2
1
0
7
6
1234567
4093 4094 4095 4096
(1)
(2)
E
T
E
D
E
L
(3)
V
DDA
V
SSA
ai14395b
V
REF+
4096
(or depending on package)]
V
DDA
4096
[1LSB
IDEAL =
ai17090c
STM8L15xxx
V
DD
AINx
IL±50 nA
0.6 V
V
T
R
AIN
(1)
C
parasitic
V
AIN
0.6 V
V
T
R
ADC
C
ADC
(1)
12-bit
converter
Sample and hold ADC
converter
Figure 37. ADC1 accuracy characteristics
Figure 38. Typical connection diagram using the ADC1
1. Refer to Ta b l e 4 5 for the values of R
2. C
represents the capacitance of the PCB (dependent on soldering and PCB layout quality) plus the
parasitic
pad capacitance (roughly 7 pF). A high C
this, f
should be reduced.
ADC1
AIN
and C
parasitic
.
ADC1
value will downgrade conversion accuracy. To remedy
General PCB design guidelines
Power supply decoupling should be performed as shown in Figure 39 or Figure 40,
depending on whether V
is connected to V
REF+
or not. Good quality ceramic 10 nF
DDA
capacitors should be used. They should be placed as close as possible to the chip.
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 91/112
Page 92

Electrical parameters STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
V
REF+
S
STM8L
V
DDA
V
SSA/VREF-
1 μF // 10 nF
F
1 μF // 10 nF
Supply
External
reference
ai17031b
V
REF+/VDDA
STM8L
1 μF // 10 nF
V
REF–/VSSA
ai17032b
Supply
Figure 39. Power supply and reference decoupling (V
// 10 n
Figure 40. Power supply and reference decoupling (V
not connected to V
REF+
TM8L
connected to V
REF+
DDA
DDA
)
)
92/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 93

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Electrical parameters
A
Figure 41. Max. dynamic current consumption on V
supply pin during ADC
REF+
conversion
Sampling
(n cycles)
DC clock
I
ref+
700μA
300μA
Table 49. R
tS
(cycles)
AIN
tS
(µs)
max for f
2.4 V < V
= 16 MHz
ADC
Slow channels Fast channels
< 3.6 V 1.8 V < V
DDA
DDA
4 0.25 Not allowed Not allowed 0.7 Not allowed
9 0.5625 0.8 Not allowed 2.0 1.0
16 1 2.0 0.8 4.0 3.0
Conversion (12 cycles)
R
max (kohm)
AIN
< 2.4 V 2.4 V < V
< 3.3 V 1.8 V < V
DDA
MS18181V1
< 2.4 V
DDA
24 1.5 3.0 1.8 6.0 4.5
48 3 6.8 4.0 15.0 10.0
96 6 15.0 10.0 30.0 20.0
192 12 32.0 25.0 50.0 40.0
384 24 50.0 50.0 50.0 50.0
7.3.13 EMC characteristics
Susceptibility tests are performed on a sample basis during product characterization.
Functional EMS (electromagnetic susceptibility)
Based on a simple running application on the product (toggling 2 LEDs through I/O ports),
the product is stressed by two electromagnetic events until a failure occurs (indicated by the
LEDs).
● ESD: Electrostatic discharge (positive and negative) is applied on all pins of the device
until a functional disturbance occurs. This test conforms with the IEC 61000 standard.
● FTB: A burst of fast transient voltage (positive and negative) is applied to V
through a 100 pF capacitor, until a functional disturbance occurs. This test conforms
with the IEC 61000 standard.
A device reset allows normal operations to be resumed. The test results are given in the
table below based on the EMS levels and classes defined in application note AN1709.
and VSS
DD
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 93/112
Page 94
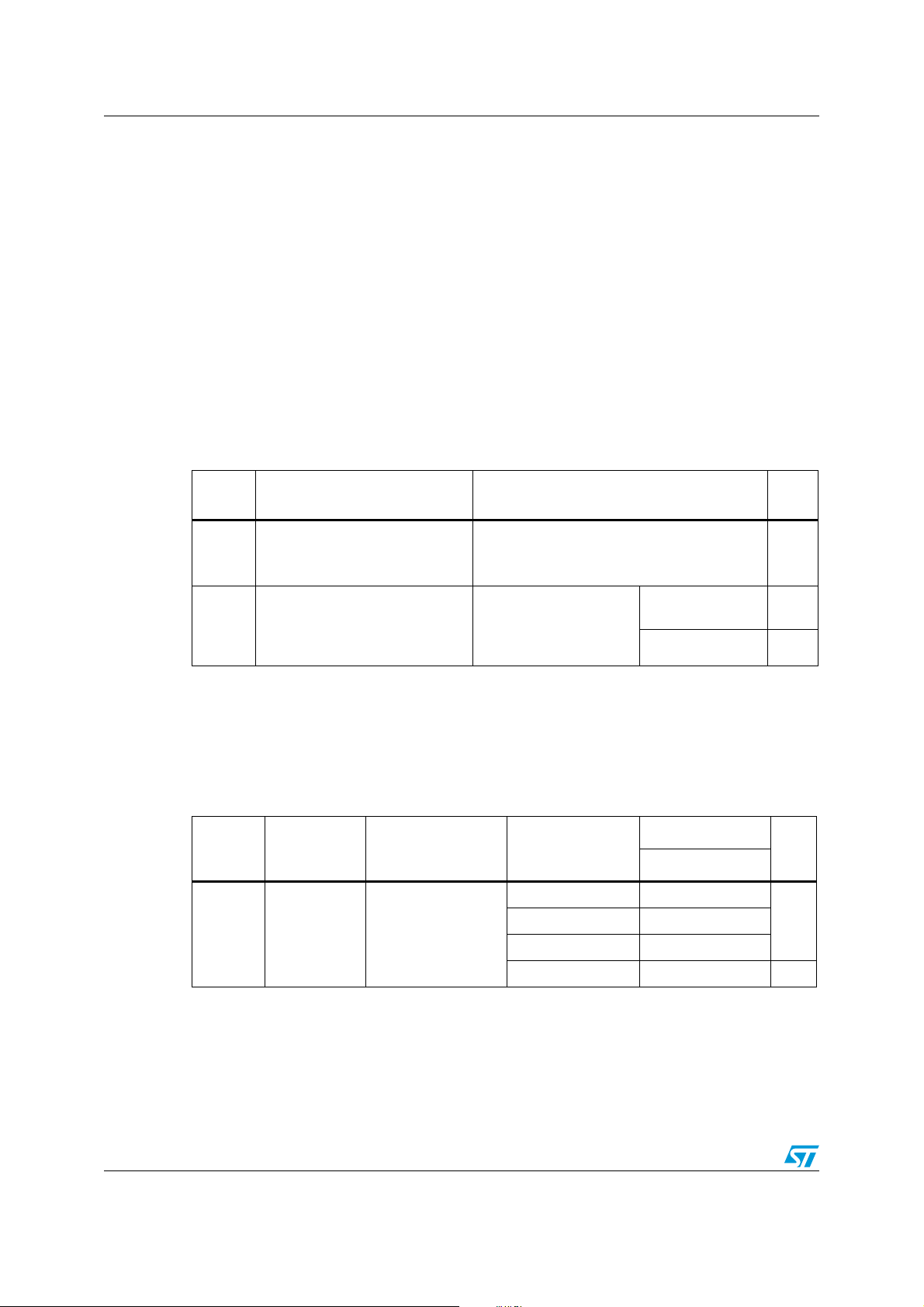
Electrical parameters STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
Designing hardened software to avoid noise problems
EMC characterization and optimization are performed at component level with a typical
application environment and simplified MCU software. It should be noted that good EMC
performance is highly dependent on the user application and the software in particular.
Therefore it is recommended that the user applies EMC software optimization and
prequalification tests in relation with the EMC level requested for his application.
Prequalification trials
Most of the common failures (unexpected reset and program counter corruption) can be
reproduced by manually forcing a low state on the NRST pin or the Oscillator pins for 1
second.
To complete these trials, ESD stress can be applied directly on the device, over the range of
specification values. When unexpected behavior is detected, the software can be hardened
to prevent unrecoverable errors occurring (see application note AN1015).
Table 50. EMS data
Symbol Parameter Conditions
V
= 3.3 V, TA = +25 °C,
DD
= 16 MHz,
f
CPU
conforms to IEC 61000
= 3.3 V, TA = +25 °C,
V
DD
= 16 MHz,
f
CPU
conforms to IEC 61000
V
V
Voltage limits to be applied on
any I/O pin to induce a functional
FESD
disturbance
Fast transient voltage burst limits
to be applied through 100 pF on
EFTB
V
DD
and V
pins to induce a
SS
functional disturbance
Using HSI
Using HSE 2B
Level/
Class
2B
4A
Electromagnetic interference (EMI)
Based on a simple application running on the product (toggling 2 LEDs through the I/O
ports), the product is monitored in terms of emission. This emission test is in line with the
norm IEC61967-2 which specifies the board and the loading of each pin.
Table 51. EMI data
Symbol Parameter Conditions
S
EMI
1. Not tested in production.
Peak leve l
(1)
V
DD
= +25 °C,
T
A
LQFP48
conforming to
IEC61967-2
= 3.6 V,
Monitored
frequency band
Max vs.
Unit
16 MHz
0.1 MHz to 30 MHz -3
dBμV30 MHz to 130 MHz 9
130 MHz to 1 GHz 4
SAE EMI Level 2 -
Absolute maximum ratings (electrical sensitivity)
Based on two different tests (ESD and LU) using specific measurement methods, the
product is stressed in order to determine its performance in terms of electrical sensitivity.
For more details, refer to the application note AN1181.
94/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 95

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Electrical parameters
Electrostatic discharge (ESD)
Electrostatic discharges (a positive then a negative pulse separated by 1 second) are
applied to the pins of each sample according to each pin combination. The sample size
depends on the number of supply pins in the device (3 parts*(n+1) supply pin). Two models
can be simulated: human body model and charge device model. This test conforms to the
JESD22-A114A/A115A standard.
Table 52. ESD absolute maximum ratings
Symbol Ratings Conditions
V
ESD(HBM)
V
ESD(CDM)
1. Data based on characterization results, not tested in production.
Electrostatic discharge voltage
(human body model)
Electrostatic discharge voltage
(charge device model)
= +25 °C
T
A
Maximum
(1)
value
2000
500
Static latch-up
● LU: 3 complementary static tests are required on 6 parts to assess the latch-up
performance. A supply overvoltage (applied to each power supply pin) and a current
injection (applied to each input, output and configurable I/O pin) are performed on each
sample. This test conforms to the EIA/JESD 78 IC latch-up standard. For more details,
refer to the application note AN1181.
Table 53. Electrical sensitivities
Symbol Parameter Class
LU Static latch-up class II
Unit
V
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 95/112
Page 96
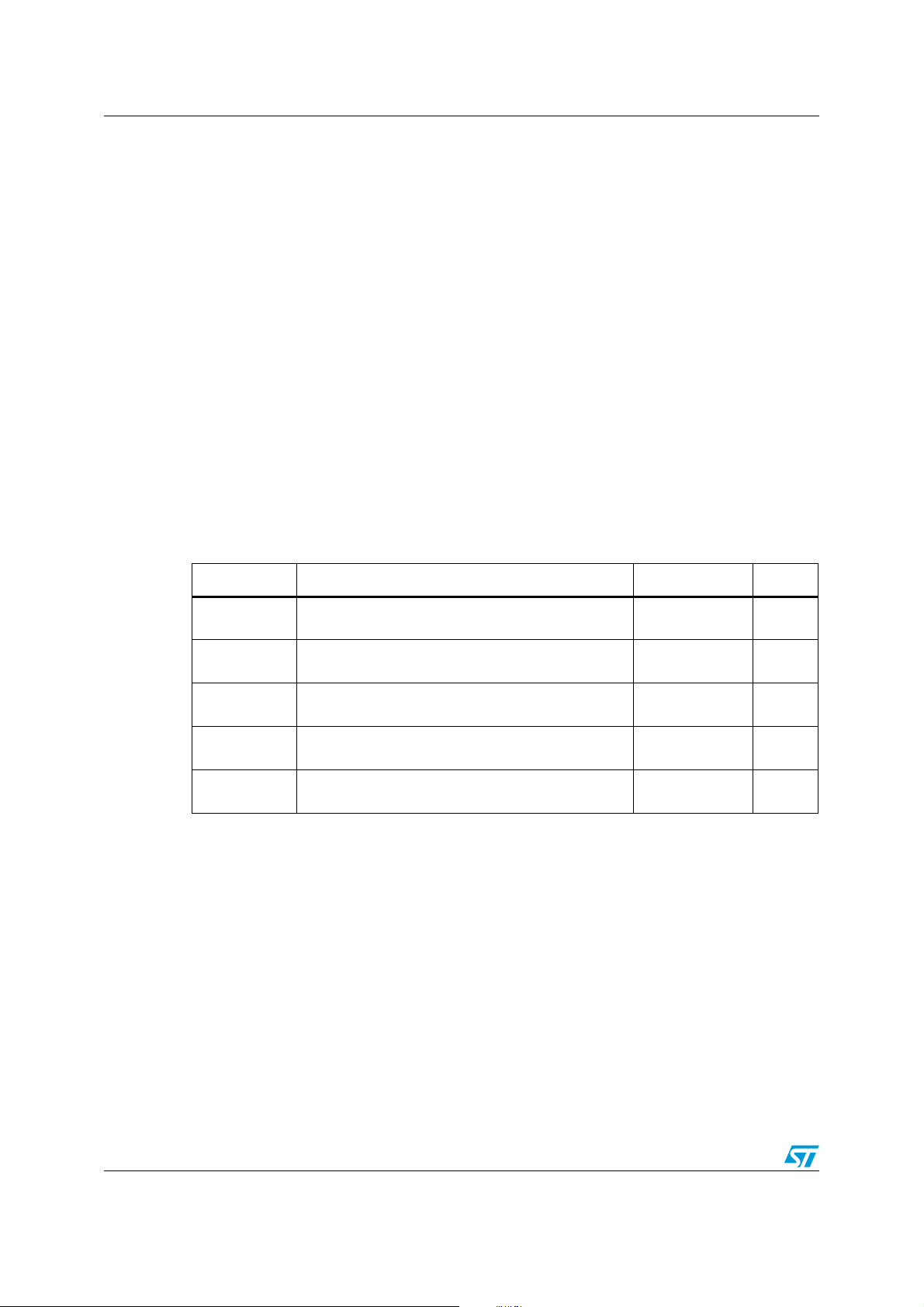
Electrical parameters STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
7.4 Thermal characteristics
The maximum chip junction temperature (T
) must never exceed the values given in
Jmax
Table 14: General operating conditions on page 52.
The maximum chip-junction temperature, T
, in degree Celsius, may be calculated using
Jmax
the following equation:
T
Jmax
= T
Amax
+ (P
Dmax
x ΘJA)
Where:
● T
● Θ
● P
● P
is the maximum ambient temperature in °C
Amax
is the package junction-to-ambient thermal resistance in °C/W
JA
is the sum of P
Dmax
is the product of I
INTmax
INTmax
DD
and P
I/Omax (PDmax
= P
INTmax
+ P
and VDD, expressed in Watts. This is the maximum chip
I/Omax
)
internal power.
● P
represents the maximum power dissipation on output pins
I/Omax
Where:
P
I/Omax =
taking into account the actual V
Σ (VOL*IOL) + Σ((VDD-VOH)*I OH),
and VOH/IOH of the I/Os at low and high level in
OL/IOL
the application.
Table 54. Thermal characteristics
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
Θ
JA
Thermal resistance junction-ambient
LQFP 48- 7 x 7 mm
(1)
65 °C/W
Θ
JA
Θ
JA
Θ
JA
Θ
JA
1. Thermal resistances are based on JEDEC JESD51-2 with 4-layer PCB in a natural convection
environment.
Thermal resistance junction-ambient
UFQFPN 32 - 5 x 5 mm
Thermal resistance junction-ambient
UFQFPN28 - 4 x 4 mm
Thermal resistance junction-ambient
UFQFPN20 - 3 x 3 mm
Thermal resistance junction-ambient
TSSOP20
38 °C/W
80 °C/W
102 °C/W
110 °C/W
96/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 97

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Option bytes
8 Option bytes
Option bytes contain configurations for device hardware features as well as the memory
protection of the device. They are stored in a dedicated memory block.
All option bytes can be modified in ICP mode (with SWIM) by accessing the EEPROM
address. See Tabl e 5 5 for details on option byte addresses.
The option bytes can also be modified ‘on the fly’ by the application in IAP mode, except for
the ROP and UBC values which can only be taken into account when they are modified in
ICP mode (with the SWIM).
Refer to the STM8L15x Flash programming manual (PM0054) and STM8 SWIM and Debug
Manual (UM0470) for information on SWIM programming procedures.
Table 55. Option byte addresses
Option
Addr. Option name
Read-out
0x00 4800
0x00 4802
0x00 4807 Reserved 0x00
0x00 4808
0x00 4809
0x00 480A
0x00 480B Bootloader
0x00 480C 0x00
protection
(ROP)
UBC (User
Boot code size)
Independent
watchdog
option
Number of
stabilization
clock cycles for
HSE and LSE
oscillators
Brownout reset
(BOR)
option bytes
(OPTBL)
byte
No.
OPT0 ROP[7:0] 0xAA
OPT1 UBC[7:0] 0x00
OPT3
[3:0]
OPT4 Reserved LSECNT[1:0] HSECNT[1:0] 0x00
OPT5
[3:0]
OPTBL
[15:0]
76543210
Reserved
Reserved BOR_TH
Option bits Factory
default
setting
WWDG
_HALT
OPTBL[15:0]
WWDG
_HW
IWDG
_HALT
IWDG
_HW
BOR_
ON
0x00
0x01
0x00
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 97/112
Page 98

Option bytes STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
Table 56. Option byte description
Option
byte
No.
ROP[7:0] Memory readout protection (ROP)
OPT0
0xAA: Disable readout protection (write access via SWIM protocol)
Refer to Readout protection section in the STM8L15x and STM8L16x reference manual (RM0031).
UBC[7:0] Size of the user boot code area
0x00: UBC is not protected.
0x01: Page 0 is write protected.
OPT1
0x02: Page 0 and 1 reserved for the UBC and write protected. It covers only the interrupt vectors.
0x03: Page 0 to 2 reserved for UBC and write protected.
0x7F to 0xFF - All 128 pages reserved for UBC and write protected.
The protection of the memory area not protected by the UBC is enabled through the MASS keys.
Refer to User boot code section in the STM8L15x and STM8L16x reference manual (RM0031).
OPT2 Reserved
IWDG_HW: Independent watchdog
0: Independent watchdog activated by software
1: Independent watchdog activated by hardware
IWDG_HALT: Independent window watchdog off on Halt/Active-halt
0: Independent watchdog continues running in Halt/Active-halt mode
1: Independent watchdog stopped in Halt/Active-halt mode
OPT3
WWDG_HW: Window watchdog
0: Window watchdog activated by software
1: Window watchdog activated by hardware
WWDG_HALT: Window window watchdog reset on Halt/Active-halt
0: Window watchdog stopped in Halt mode
1: Window watchdog generates a reset when MCU enters Halt mode
HSECNT: Number of HSE oscillator stabilization clock cycles
0x00 - 1 clock cycle
0x01 - 16 clock cycles
0x10 - 512 clock cycles
0x11 - 4096 clock cycles
OPT4
LSECNT: Number of LSE oscillator stabilization clock cycles
0x00 - 1 clock cycle
0x01 - 16 clock cycles
0x10 - 512 clock cycles
0x11 - 4096 clock cycles
Refer to Table 28: LSE oscillator characteristics on page 67.
Option description
98/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
Page 99

STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3 Option bytes
Table 56. Option byte description (continued)
Option
byte
No.
OPT5
OPTBL
Option description
BOR_ON:
0: Brownout reset off
1: Brownout reset on
BOR_TH[3:1]: Brownout reset thresholds. Refer to Ta b le 1 9 for details on the thresholds according to
the value of BOR_TH bits.
OPTBL[15:0]:
This option is checked by the boot ROM code after reset. Depending on
content of addresses 00 480B, 00 480C and 0x8000 (reset vector) the
CPU jumps to the bootloader or to the reset vector.
Refer to the UM0560 bootloader user manual for more details.
Doc ID 018780 Rev 4 99/112
Page 100

Unique ID STM8L151x2, STM8L151x3
9 Unique ID
STM8 devices feature a 96-bit unique device identifier which provides a reference number
that is unique for any device and in any context. The 96 bits of the identifier can never be
altered by the user.
The unique device identifier can be read in single bytes and may then be concatenated
using a custom algorithm.
The unique device identifier is ideally suited:
● For use as serial numbers
● For use as security keys to increase the code security in the program memory while
using and combining this unique ID with software cryptographic primitives and
protocols before programming the internal memory.
● To activate secure boot processes
Table 57. Unique ID registers (96 bits)
Address
0x4926
0x4927 U_ID[15:8]
0x4928
0x4929 U_ID[31:24]
0x492A Wafer number U_ID[39:32]
0x492B
0x492C U_ID[55:48]
0x492D U_ID[63:56]
0x492E U_ID[71:64]
0x492F U_ID[79:72]
0x4930 U_ID[87:80]
0x4931 U_ID[95:88]
Content
description
X co-ordinate on
the wafer
Y co-ordinate on
the wafer
Lot number
76543 2 1 0
Unique ID bits
U_ID[7:0]
U_ID[23:16]
U_ID[47:40]
100/112 Doc ID 018780 Rev 4
 Loading...
Loading...