ST M28W320ECT, M28W320ECB User Manual

FEATURES SUMMARY
■ SUPPLY VOLTAGE
= 2.7V to 3.6V Core Power Supply
–V
DD
–V
–V
■ ACCESS TIME: 70, 85, 90,100ns
■ PROGRAMMING TIME:
= 1.65V to 3.6V for Input/Output
DDQ
= 12V for fast Program (optional)
PP
– 10µ s typical
– Double Word Programming Option
– Quadruple Word Programming Option
■ COMMON FLASH INTERFACE
■ MEMORY BLOCKS
– Parameter Blocks (Top or Bott o m location)
– Main Blocks
■ BLOCK LOCKING
– All blocks locked at Power Up
– Any combination of blocks can be locked
for Block Lock-Down
–WP
■ SECURITY
– 128 bit user Programmable OTP cells
– 64 bit unique device identifier
■ AUTOMATIC STAND-BY MODE
■ PROGRAM and ERASE SUSPEND
■ 100,000 PROGRAM/ERASE CYCLES per
BLOCK
■ ELECTRONIC SIGNATURE
– Manufacturer Code: 20h
– Top Device Code, M28W320ECT: 88BAh
– Bottom Device Code, M28W320ECB: 88BBh
M28W320ECT
M28W320E CB
32 Mbit (2Mb x16, Boot Block)
3V Supp l y Fl ash Memory
Figure 1. Packages
FBGA
TFBGA47 (ZB)
6.39 x 6.37mm
TSOP48 (N)
12 x 20mm
1/53April 2003

M28W320ECT, M28W320ECB
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SUMMARY DESCRIPTION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Figure 2. Logic Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Table 1. Signal Names . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Figure 3. TSOP Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Figure 4. TFBGA Connections (Top view through package). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Figure 5. Block Addresses. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Figure 6. Protection Register Memory Map. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
SIGNAL DESCRIPTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Address Inputs (A0-A20). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Data Input/Output (DQ0-DQ15). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Chip Enable (E). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Output Enable (G). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Write Enable (W). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Write Protect (WP). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Reset (RP). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
V
Supply Voltage. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
DD
V
Supply Voltage. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
DDQ
V
Program Supply Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
PP
V
Ground. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
SS
BUS OPERATIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Read.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Write.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Output Disable. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Standby. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Automatic Standby. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Reset. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Read Electronic Signature Comma nd . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Table 2. Bus Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
COMMAND INTERFACE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Read Memory Array Command. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Read Status Register Command. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Read Electronic Signature Comma nd . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Table 3. Command Codes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Read CFI Query Command. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Block Erase Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Program Command. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Double Word Program Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Clear Status Register Command. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Program/Erase Suspend Comm and . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Program/Erase Resume Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Protection Register Program Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2/53

M28W320ECT, M28W320ECB
Block Lock-Down Command. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Table 4. Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Table 5. Read Electronic Signature. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Table 6. Read Block Lock Signature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Table 7. Read Protection Register and Lock Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Table 8. Program, Erase Times and Program/Erase Enduranc e Cycles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
BLOCK LOCKING. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Locked State . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Unlocked State . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Lock-Down State. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Reading a Block’s Lock Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Locking Operations During Erase Suspend . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Table 9. Block Lock Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Table 10. Protection Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
STATUS REGISTER. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Program/Erase Controller Status (Bit 7) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Erase Suspend Status (Bit 6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 9
Erase Status (Bit 5). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Program Status (Bit 4). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
V
Status (Bit 3). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
PP
Program Suspend Status (Bit 2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 9
Block Protection Status (Bit 1). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Reserved (Bit 0). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Table 11. Status Register Bits. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
MAXIMUM RATING. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 12. Absolute Maximum Ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
DC and AC PARAMETERS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 13. Operating and AC Measurement Conditions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Figure 7. AC Measurement I/O Waveform . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Figure 8. AC Measurement Load Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 14. Capacitance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 15. DC Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Figure 9. Read AC Waveforms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Table 16. Read AC Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Figure 10. Write AC Waveforms, Write Enable Controlled . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Table 17. Write AC Characteristics, Write Enable Controlled . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Figure 11. Write AC Waveforms, Chip Enable Controlled . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Table 18. Write AC Characteristics, Chip Enable Controlled . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Figure 12. Power-Up and Reset AC Waveforms. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Table 19. Power-Up and Reset AC Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
3/53

M28W320ECT, M28W320ECB
PACKAGE MECHANICAL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Figure 13. TSOP48 - 48 lead Plastic Thin Small Outline, 12 x 20mm, Package Outline . . . . . . . . 30
Table 20. TSOP48 - 48 lead Plastic Thin Small Outline, 12 x 20mm, Package Mechanical Data . 30
Figure 14. TFBGA47 6.39x6.37m m - 8x6 ball array, 0.75mm pitch, Bottom View Package Out line31
Table 21. TFBGA47 6.39x6.37m m - 8x6 ball array, 0.75mm pitch, Package Mechanical Data . . . 31
Figure 15. TFBGA47 Daisy Chain - Package Connections (Top view through package) . . . . . . . . 32
Figure 16. TFBGA47 Daisy Chain - PCB Connections proposal (Top view through package). . . . 32
PART NUMBERING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Table 22. Ordering Information Scheme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Table 23. Daisy Chain Ordering Scheme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
APPENDIX A. BLOCK ADDRESS TABLES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Table 24. Top Boot Block Addresses, M28W320ECT. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Table 25. Bottom Boot Block Addresses, M28W320ECB. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
APPENDIX B. COMMON FLASH INTERFACE (CFI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Table 26. Query Structure Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
Table 27. CFI Query Identification String . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37
Table 28. CFI Query System Interface Information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Table 29. Device Geometry Definition. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
Table 30. Primary Algorithm-Specific Extended Query Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Table 31. Security Code Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
APPENDIX C. FLOWCHARTS AND PSEUDO CODES. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Figure 17. Program Flowchart and Pseudo Code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Figure 18. Double Word Program Flowchart and Pseudo Code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Figure 20. Program Suspend & Resume Flowchart and Pseudo Code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Figure 21. Erase Flowchart and Pseudo Code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Figure 22. Erase Suspend & Resume Flowchart and Pseudo Code. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Figure 23. Locking Operations Flowchart and Pseudo Code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
APPENDIX D. COMMAND INTERFACE AND PROGRAM/ERASE CONTROLLER STATE . . . . . . . 50
Table 32. Write State Machine Current/Next, sheet 1 of 2.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Table 33. Write State Machine Current/Next, sheet 2 of 2.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
REVISION HISTORY. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Table 34. Document Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
4/53
SUMMARY DESCRIPTION
The M28W320EC is a 32 Mbit (2 Mbit x 16) nonvolatile Flash memory that can b e erased electrically at the block level and programmed in-system
on a Word-by-Word basis. These operations can
be performed using a single low voltage (2.7 to
3.6V) supply. V
down to 1.65V. An optional 12V V
allows to drive the I/O pin
DDQ
power supply
PP
is provided to speed up customer programming.
The device features an asymmetrical blocked ar-
chitecture. The M28W320E C has an array of 71
blocks: 8 Parameter Blocks of 4 KWord and 63
Main Blocks of 32 KWord. M28W320ECT has the
Parameter Blocks at the top of the memory address space while the M28W320ECB locates the
Parameter Blocks starting from the bottom. The
memory maps are shown in Figure 5, Block Addresses.
The M28W320EC features an instant, individual
block locking scheme that allo ws any block to be
locked or unlocked with no latency, enabling instant code and data protection. All blocks have
three levels of protection. They can be locked and
locked-down individually preventing any accidental programming or erasure. There is an additional
hardware protection against program and erase.
When V
PP
≤ V
all blocks are protected against
PPLK
program or erase. All blocks are locked at Power
Up.
Each block can be erased separately. Erase can
be suspended in order to perform either read or
program in any other block and then resumed.
Program can be s uspended to read data in any
other block and then resumed. Each block can be
programmed and erased over 100,000 cycles.
The device includes a Protection Register to increase the pro tection of a syste m design. The Protection Register is divided into two segments, t he
first is a 64 bit area which contains a unique device
number written by ST, while the second is a 128 bit
area, one-time-programmable by the user. The
user programmable segment can be permanent ly
protected. Figure 6, shows the Protection Register
Memory Map.
Program and Erase command s are written to the
Command Interface of the memory. An on-chip
Program/Erase Controller takes care of the timings necessary for program and erase operations.
The end of a program or erase operation can be
detected and any error conditions identified. The
command set required to control the memory is
consistent with JEDEC standards.
M28W320ECT, M28W320ECB
The memory is of fered in TSOP48 (10 X 20mm)
and TFBGA47 (6.39 x 6.37mm, 0.75mm pitch)
packages and is supplied with all the bits erased
(set to ’1’).
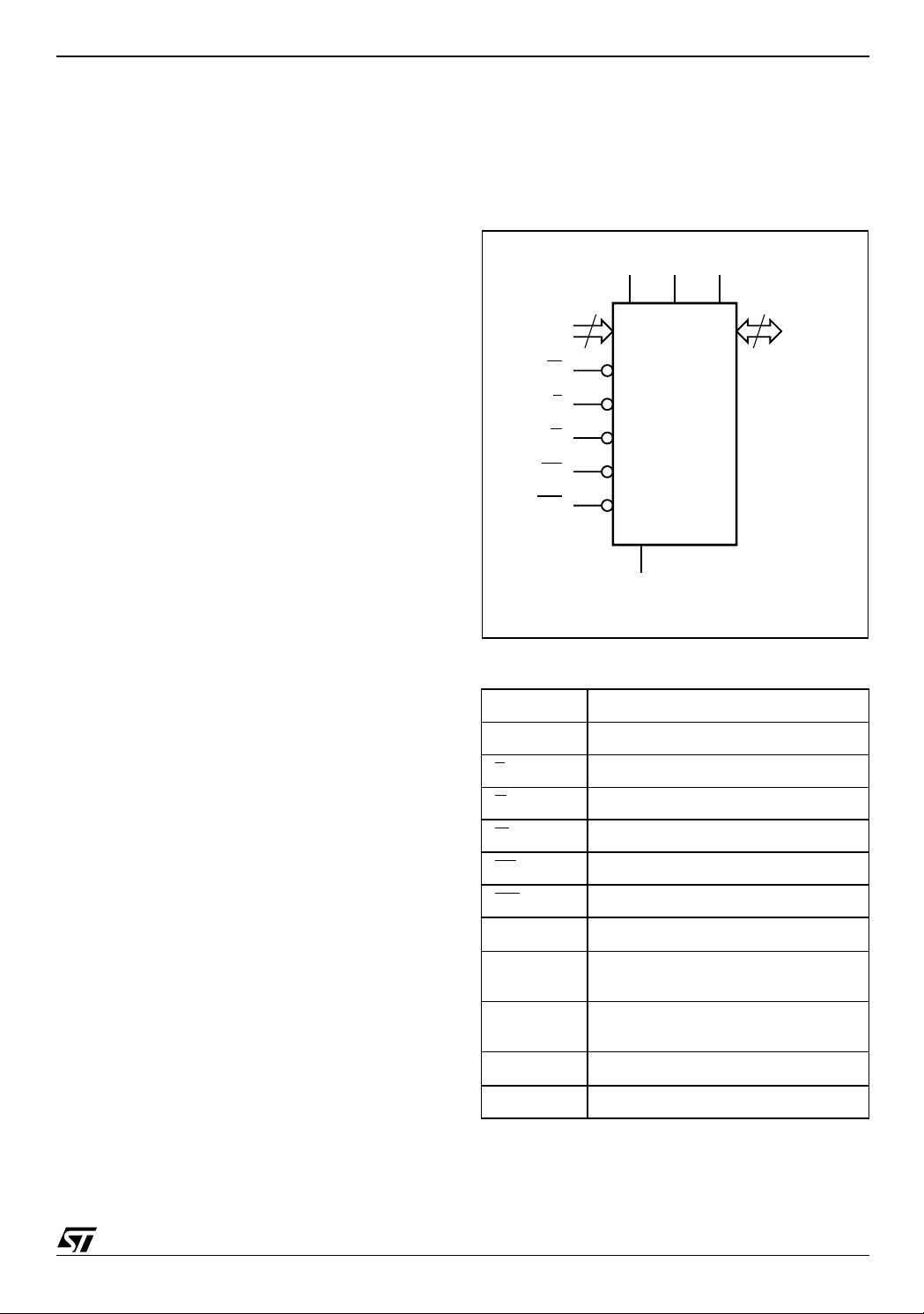
Figure 2. Logic Diagram
V
V
DD
DDQVPP
21
A0-A20
W
E
G
RP
WP
M28W320ECT
M28W320ECB
V
SS
Table 1. Signal Names
A0-A20 Address Inputs
DQ0-DQ15 Data Input/Output
E
G
W
RP
WP
V
DD
V
DDQ
V
PP
V
SS
NC Not Connected Internally
Chip Enable
Output Enable
Write Enable
Reset
Write Protect
Core Power Supply
Power Supply for
Input/Output
Optional Supply Voltage for
Fast Program & Erase
Ground
16
DQ0-DQ15
AI05517
5/53
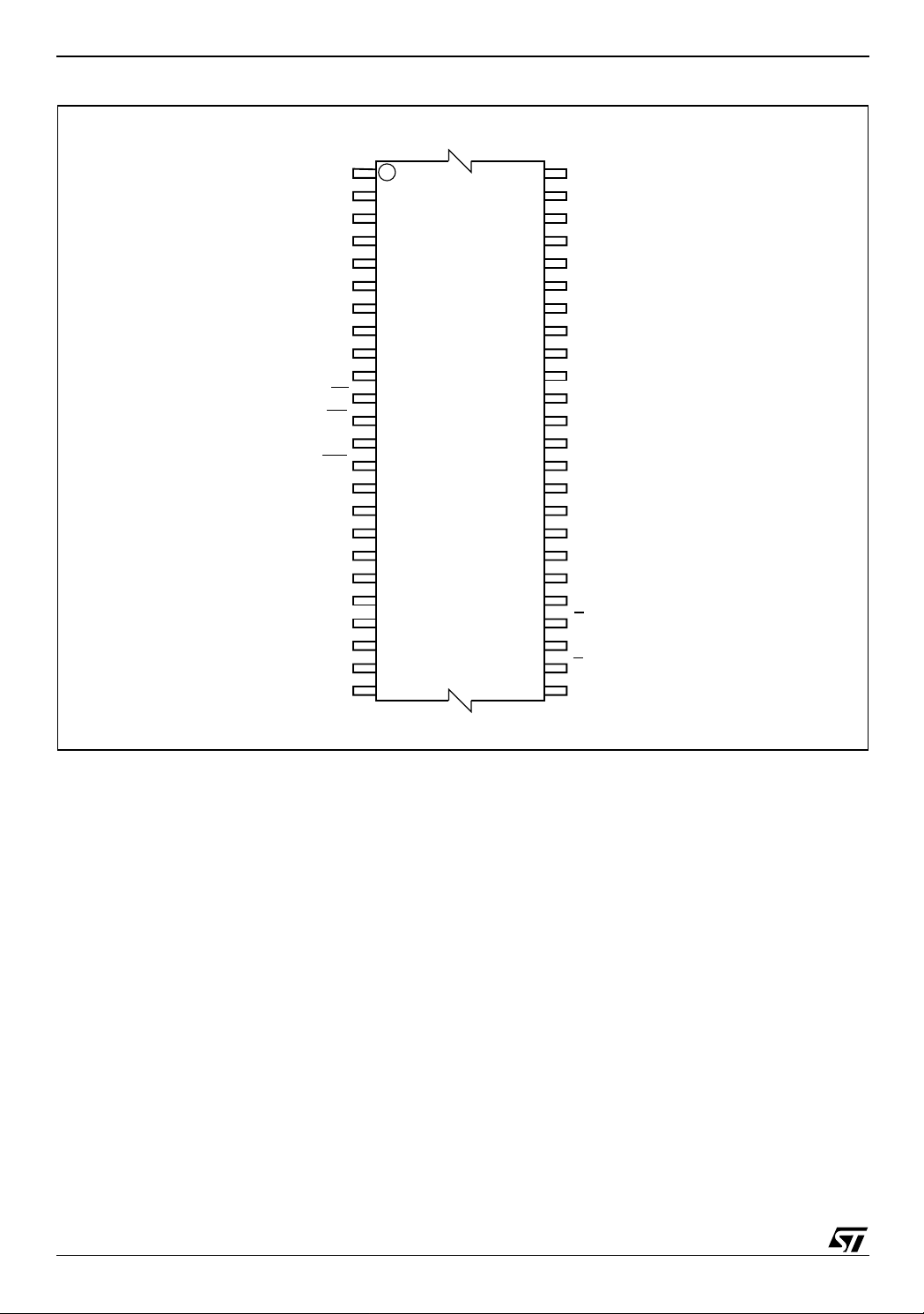
M28W320ECT, M28W320ECB
Figure 3. TSOP Connections
A15
A14
A13
A12
A11
1
48
A16
V
DDQ
V
SS
DQ15
DQ7
A10 DQ14
37
36
DQ6
DQ13
DQ5
DQ12
DQ4
V
DD
DQ11
DQ3
DQ10
DQ2
DQ9
DQ1
DQ8
DQ0
G
V
SS
E
A0
NC
A20
RP
V
PP
WP
A19
A18
A17
A9
A8
W
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
12
M28W320ECT
M28W320ECB
13
24 25
AI05518
6/53
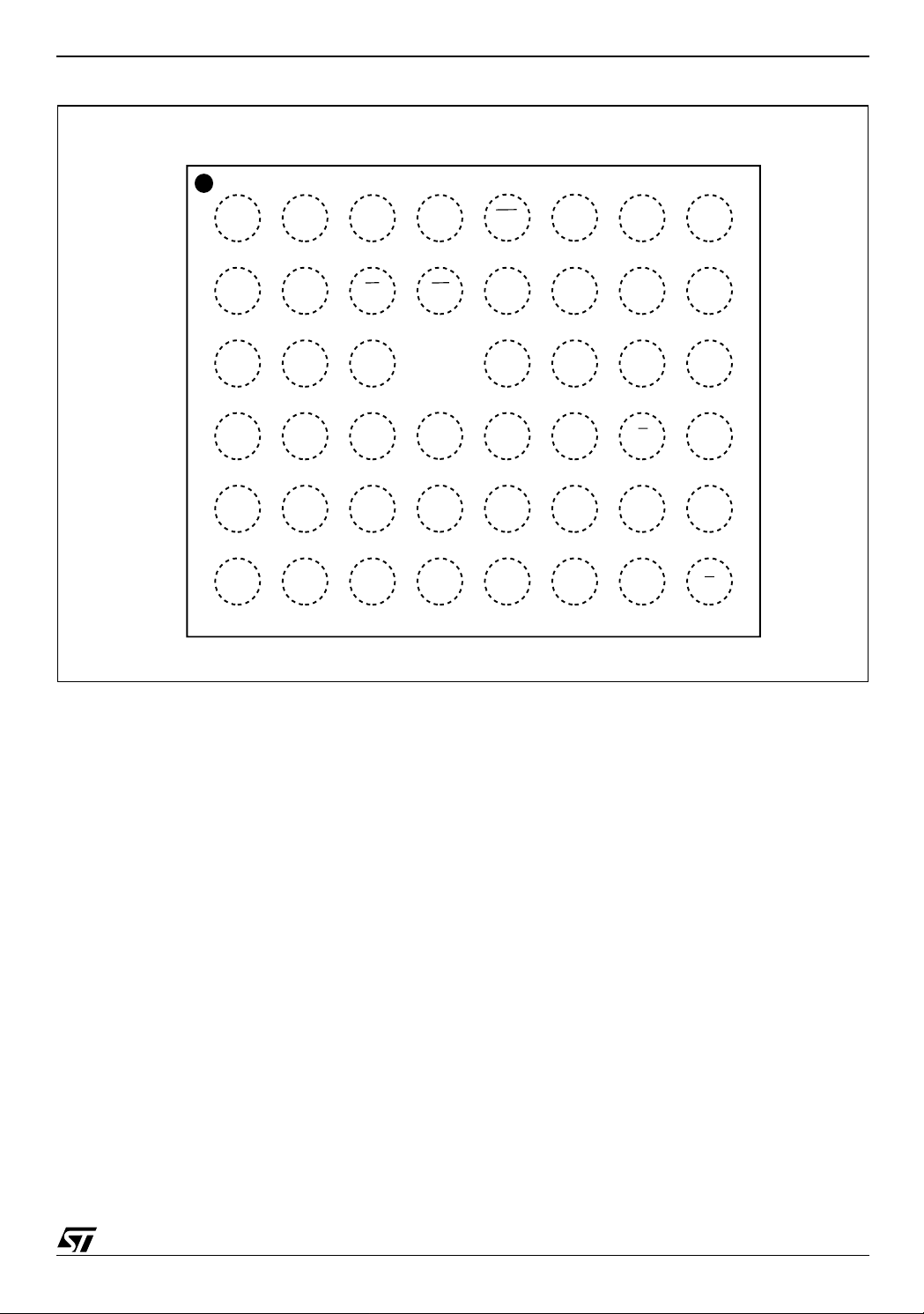
Figure 4. TFBGA Connections (Top view through package)
M28W320ECT, M28W320ECB
87654321
A
B
C
D
E
F
DDQ
SS
DQ7V
A8A11A13
DQ13
PP
RP A18
DQ11
DQ12
DQ4
WP A19
A20
DQ2
DD
A7V
A5A17WA10A14
DQ0DQ9DQ3DQ6DQ15V
DQ1DQ10V
A4
A2
A1A3A6A9A12A15
A0EDQ8DQ5DQ14A16
V
SS
G
AI03847
7/53
M28W320ECT, M28W320ECB
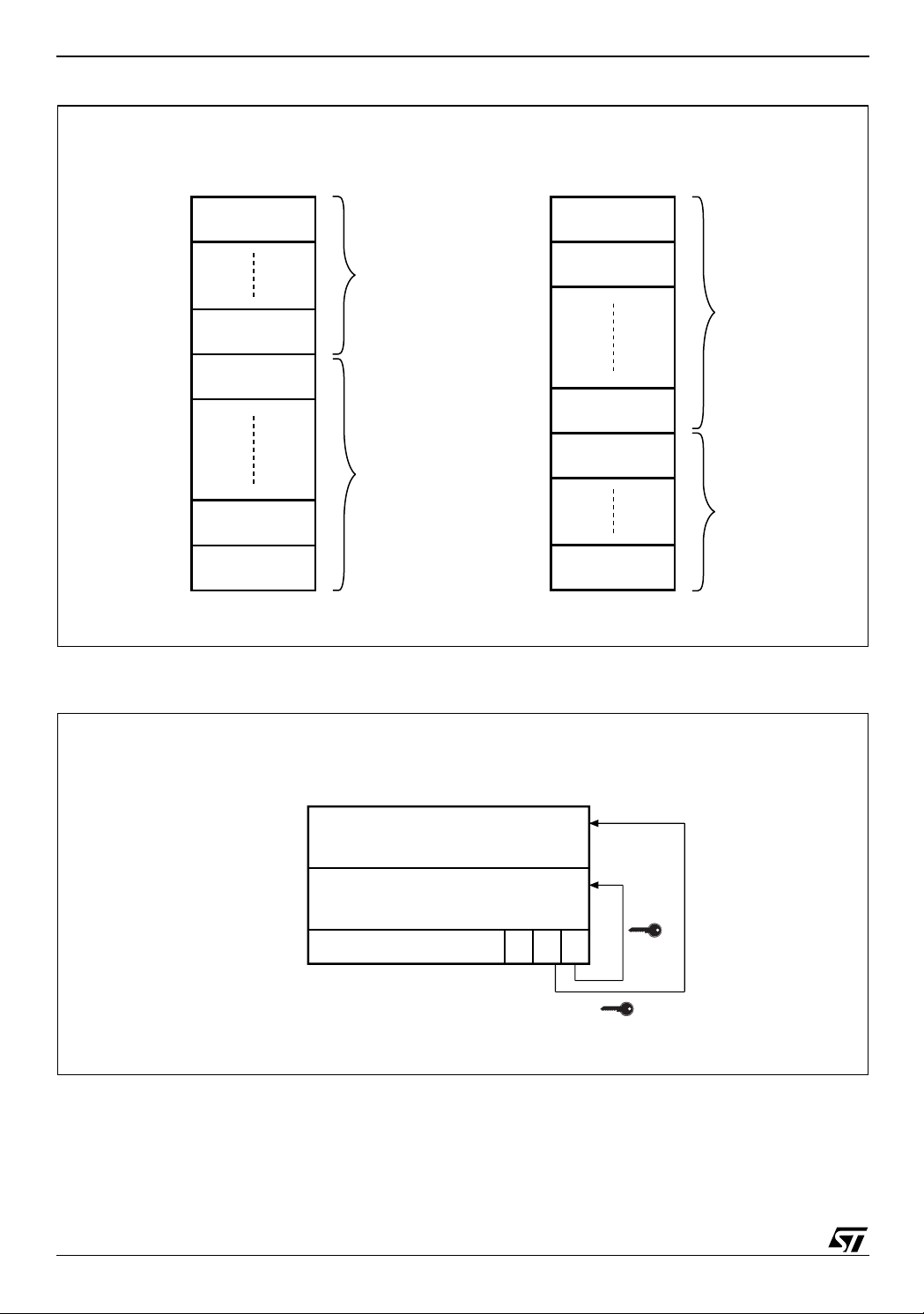
Figure 5. Block Addresses
M28W320ECT
Top Boot Block Addresses
1FFFFF
1FF000
1F8FFF
1F8000
1F7FFF
1F0000
00FFFF
008000
007FFF
000000
Note: Also see Appendix A, Tables 24 and 25 f or a full listing o f the Block Addres ses.
4 KWords
Total of 8
4 KWord Blocks
4 KWords
32 KWords
Total of 63
32 KWord Blocks
32 KWords
32 KWords
Bottom Boot Block Addresses
1FFFFF
1F8000
1F7FFF
1F0000
00FFFF
008000
007FFF
007000
000FFF
000000
M28W320ECB
32 KWords
32 KWords
Total of 63
32 KWord Blocks
32 KWords
4 KWords
Total of 8
4 KWord Blocks
4 KWords
AI05519
Figure 6. Prot ect i on Register Mem o ry Map
PROTECTION REGISTER
8Ch
User Programmable OTP
85h
84h
81h
80h
Note1. Bit 2 of the Protection Register Lock must not be programmed to 0.
Unique device number
Protection Register Lock 2
(1)
10
AI05520
8/53

SIGNAL DESCRIPTIONS
See Figure 2 Logic Diagram and Table 1,Signal
Names, for a brief overview of the signals connected to this device.
Address Inputs (A0-A20). The Address Inputs select the cells i n the memory array to a ccess during Bus Read operations. During Bus Write operations they control the commands sent to the Command Interface of the internal state machine.
Data Input/Output (DQ0-DQ15). The Data I/O outputs the data stored at the selected address during a Bus Read operation or inputs a command or the data to be programmed durin g a Write Bus operation.
Chip Enable (E
). The Chip Enable input acti-
vates the memory control logic, input buffers, decoders and sense amplifiers. When Chip Enable is
and Reset is at VIH the device is in active
at V
IL
mode. When Chi p E nable i s at V
the memory is
IH
deselected, the outputs are high impedan ce and
the power consumption is reduced to the stand-by
level.
Output Enable (G
). The Output Enable controls
data outputs during the Bus Read operation of the
memory.
Write Enable (W
). The Write Enable controls the
Bus Write operation of the memory’s Command
Interface. The data and address inputs are latched
on the rising edge of Chip Enable, E, or Write Enable, W
Write Protect (WP
, whichever occurs first.
). Write Protect is an input
that gives an additional hardware protection for
each block. When Write Protect is at V
, the Loc k-
IL
Down is enabled and the prote ction status of t he
block cannot be changed. When Write Protect is at
, the Lock-Down is disabled and the block can
V
IH
be locked or unlocked. (refer to Table 7, Read Protection Register and Protection Register Lock).
Reset (RP
ware reset of the memory. W hen Reset is at V
). The Reset input provides a hard-
IL
the memory is in reset mode: the outputs are high
impedance and the current consumption is minimized. After Reset all blocks are in the Locked
M28W320ECT, M28W320ECB
state. When Reset is at V
operation. Exiting reset mode the device enters
read array mode, but a negative transition of Chip
Enable or a change of the addres s is required t o
ensure valid data outputs.
Supply Voltage. VDD provides the power
V
DD
supply to the internal core of the memory device.
It is the main power supply for all operations
(Read, Program and Erase).
Su pp ly V olt ag e . V
V
DDQ
power supply to the I/O pins a nd ena bles all Ou tputs to be powered independently from V
can be tied to VDD or can use a separate supply.
Program Supply Voltage. VPP is both a
V
PP
control input and a power supply pin. The two
functions are selected by the voltage range applied to the pin. The Supply Voltage V
Program Supply Voltage V
any order.
If V
is kept in a low voltage range (0V to 3.6V)
PP
V
is seen as a control input. In this case a volt-
PP
age lower than V
PPLK
against program or erase, whi le V
ables these functions (see Table 15, DC Characteristics for the relevant values). V
sampled at the beginning of a Program or Erase;
a change in its value after the operation has started does not have any effect on Program or Erase,
however for Double or Q uadruple Word Program
the results are uncertain.
If V
is in the range 11.4V to 12.6V it acts as a
PP
power supply pin. In this condition V
stable until the Program/Erase algorit hm is completed (see Table 17 and 18).
Ground. VSS is the reference for all voltage
V
SS
measurements.
Note: Each device in a system should have
V
DD, VDDQ
pacitor close to the pin. See Figure 8, AC Mea-
,
and VPP decoupled wi th a 0.1 µF ca-
surement Load Circu it. The PCB trace widths
should be sufficient to carry the required V
program and erase currents.
, the device is in normal
IH
provides the
DDQ
can be applied in
PP
gives an absolute protection
PP
DD
and the
DD
> V
is only
PP
must be
PP
. V
PP1
DDQ
en-
PP
9/53
M28W320ECT, M28W320ECB
BUS OPERATIONS
There are six standard bus operations that control
the device. These are Bus Read, Bus Wri te, Output Disable, Standby, Automatic Standby and Reset. See Table 2, Bus Operations, for a summary.
Typically glitches of less than 5ns on Chip Enable
or Write Enable are ignored by the memory and do
not affect bus operations.
Read. Read Bus operations are used to output the contents of the Memory Array, the Electronic Signature, the Status Register and the Common Flash Interface. Both Chip Enable and Output Enable must be at V eration. The Chip Enable in put should be us ed to enable the device. Out put E nable shoul d be used to gate data onto the output. The data read depends on the previous command written to the memory (see Command Interface section). See Figure 9, Read Mode AC Wa veforms, and Table 16, Read AC Characteristics, for details of when the output becomes valid.
Read mode is the default state of the device when
exiting Reset or after power-up.
Write. Bus Write operations write Commands to the memory or latch Input Data to be programmed. A write operation is initiated when Chip Enable and Write Enable are at V V
. Commands, Input Data and Addresses are
IH
latched on the rising edge of Write Enable or Chip
Enable, whichever occurs first.
in order to perform a read op-
IL
with Output Enable at
IL
See Figures 10 and 11, Write AC Waveforms, and
Tables 17 and 18, Write AC Characteristics, for
details of the timing requirements.
Output Disa bl e . The data outputs are high impedance when the Output Enable is at V
.
IH
Standby. Stan dby disables most of the inte rnal circuitry allowing a substantial reduction of the current consumption. The memory is in stand-by when Chip Enable is at V
and the device is in
IH
read mode. The power consumption is reduced to
the stand-by level and the o utputs are set to high
impedance, independently from the Output Enable
or Write Enable inputs. If Chip Enable switches to
V
during a program or erase operation, t he de-
IH
vice enters Standby mode when finished. Automatic Standby. Automatic Standby pro-
vides a low power consumption state during Read
mode. Following a read operation, the device enters Automatic Standby after 150ns of bus inactivity even if Chip Enable is Low, V
current is reduced to I
. The data I nputs/Out-
DD1
, and the supply
IL
puts will still output data if a bus Read operation is
in progress.
Reset. During Reset mode when Output Enable is Low, V
, the memory is deselected and the out-
IL
puts are high impedance. The memory is in Reset
mode when Reset is at V
. The power consump-
IL
tion is reduced to the Standby level, independently
from the Chip Enable, Output Enable or Write Enable inputs. If Reset is pulled to V
during a Pro-
SS
gram or Erase, this operation is aborted and the
memory content is no longer valid.
Table 2. Bus Operations
Operation E G W RP WP
Bus Read
Bus Write
Output Disable
Standby
Reset X X X
Note: X = VIL or VIH, V
10/53
V
V
V
V
= 12V ± 5%.
PPH
IL
IL
IL
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IH
XX
V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IH
V
IH
V
IH
V
IH
V
IL
V
PP
X Don’t Care Data Output
V
X
X Don’t Care Hi-Z
X Don’t Care Hi-Z
X Don’t Care Hi-Z
DD
or V
PPH
DQ0-DQ15
Data Input
COMMAND INTERFACE
All Bus Write operations t o the me mory are in terpreted by the Command Interface. Commands
consist of one or more sequential Bus Write operations. An internal Program/Erase Controller handles all timings and verifies the correct execution
of the Program and Erase commands. The Program/Erase Controller provides a S tatus Register
whose output may be read at any time during, to
monitor the progress of the operation, or the P rogram/Erase states. See Table 3, Command
Codes, for a summary o f the c ommands and see
Appendix 22, Table 32, Write State Machine Current/Next, for a summa ry of the Command Interface.
The Command Interface is reset to Read mode
when power is first applied, when exiting from Reset or whenever V
is lower than V
DD
LKO
. Command sequences must be followed exactly. Any
invalid combination of commands will reset the device to Read mode. Refer to Table 4, Commands,
in conjunction with the text descriptions below.
Read Memory Array Command
The Read command returns the memory to its
Read mode. One Bus Write cycle is required to issue the Read Memory Array command and return
the memory to Read mode. Subsequ ent read operations will read the addressed locat ion and output the data. When a device Reset occurs, the
memory defaults to Read mode.
Read Status Register Command
The Status Register indicates when a program or
erase operation is complete and the success or
failure of the operation itself. Issue a Read Status
Register command to rea d the Status Register’s
contents. Subsequent Bus Read op erations read
the Status Register at any address, u ntil another
command is issued. See Table 11, Status Register
Bits, for details on the definitions of the bits.
The Read Status Register command m ay be issued at any time, even during a Program/Erase
operation. Any Read attempt during a Program/
Erase operation will automatically output the content of the Status Register.
Read Electronic Signature Command
The Read Electronic Signature command reads
the Manufacturer and Device Codes and the Block
Locking Status, or the Protection Register.
The Read Electronic Signature command consists
of one write cycle, a subsequent read will output
the Manufacturer Code, the Device Code, the
Block Lock and Lock-Down Status, or the Protection and Lock Register. See Tables 5, 6 and 7 for
the valid address.
M28W320ECT, M28W320ECB
Table 3. Command Codes
Hex Code Command
01h Block Lock confirm
10h Program
20h Erase
2Fh Block Lock-Down confirm
30h
40h Program
50h Clear Status Register
55h Reserved
56h
60h
70h Read Status Register
90h Read Electronic Signature
98h Read CFI Query
B0h Program/Erase Suspend
C0h Protection Register Program
D0h
FFh Read Memory Array
Read CFI Query Command
The Read Query Command is used to read dat a
from the Common Flash Interface (CFI) Me mory
Area, allowing programming equi pment or applications to automatically match their interface to
the characteristics of the device. One Bus Write
cycle is required to issue the Read Query Command. Once the command is issued subsequent
Bus Read operations read from the Common
Flash Interface Memory Area. See Appendix B,
Common Flash Inte rface, Tables 26, 27, 28, 29,
30 and 31 for details on the information contained
in the Common Flash Interface memory area.
Block Erase Command
The Block Erase com mand can be used to erase
a block. It sets all the bits within the selected block
to ’1’. All previous d ata in th e block is lost. If th e
block is protected then the Erase operation will
abort, the data in the block will not be changed and
the Status Register will output the error.
Two Bus Write cycles are required to issue the
command.
■ The first bus cycle sets up the Erase command.
Double Word Program
Quadruple Word Program
Block Lock, Block Unlock, Block Lock-
Down
Program/Erase Resume, Block Unlock
confirm
11/53

M28W320ECT, M28W320ECB
■ The second latches the block address in the
internal state machine and starts the Program/
Erase Controller.
If the second bus cycle is not Write Erase Confirm
(D0h), Status Register bits b4 and b5 are s et and
the command aborts.
Erase aborts if Reset turns to V
. As data integrity
IL
cannot be guaranteed when the Erase operation is
aborted, the block must be erased again.
During Erase operations the memory will accept
the Read Status Re gister com mand and the P rogram/Erase Suspend command, all other commands will be ignored. Typical Erase times are
given in Table 8, Program, Erase Times and P rogram/Erase Endurance Cycles.
See Appendix C, Figure 21 , Erase Flowchart and
Pseudo Code, for a suggested flowchart for using
the Erase command.
Program Command
The memory array can be programmed word-byword. Two bus write cycles are required to issue
the Program Command.
■ The first bus cycle sets up the Program
command.
■ The second latches the Address and the Data to
be written and starts the Program/Erase
Controller.
During Program operations the memory will accept the Read Status Register command and the
Program/Erase Suspend command. Typical Program times are g iven in Tab le 8, P rogram, E rase
Times and Program/Erase Endurance Cycles.
Programming aborts if Reset goe s to V
. As data
IL
integrity cannot be guaranteed when the program
operation is aborted, the block containing the
memory location must be erased and reprogrammed.
See Appendix C, Figure 17, Program Flowchart
and Pseudo Code, for the f lowchart for using the
Program command.
Double Word Program Command
This feature is offered to improve the programming
throughput, writing a page of two adjacent words
in parallel.The two words m ust differ only for the
address A0. Programm ing should not be att emp ted when V
is not at V
PP
PPH
.
Three bus write cycles are necessary to issue the
Double Word Program command.
■ The first bus cycle sets up the Double Word
Program Command.
■ The second bus cycle latches the Address and
the Data of the first word to be written.
■ The third bus cycle latches the Address and the
Data of the second word to be written and starts
the Program/Erase Controller.
Read operations output the Status Register content after the programming has s tarted. Programming aborts if Reset goes to V
. As data integrity
IL
cannot be guaranteed when the program operation is aborted, the block containing the memory
location must be erased and reprogrammed.
See Appendix C, Figure 18, Double Word Program Flowchart and Pseudo Code, for the flowchart for using the Double Word Program
command.
Quadruple Word Program Command
This feature is offered to improve the programming
throughput, writing a page of four adjacent words
in parallel.The four words must differ only for the
addresses A0 and A1. Programming should not be
attempted when V
is not at V
PP
PPH
.
Five bus write cycles are necessary to issue the
Quadruple Word Program command.
■ The first bus cycle sets up the Quadruple Word
Program Command.
■ The second bus cycle latches the Address and
the Data of the first word to be written.
■ The third bus cycle latches the Address and the
Data of the second word to be written.
■ The fourth bus cycle latches the Address and
the Data of the third word to be written.
■ The fifth bus cycl e latches the Addres s and th e
Data of the fourth word to be written and starts
the Program/Erase Controller.
Read operations output the Status Register content after the programming has s tarted. Programming aborts if Reset goes to V
. As data integrity
IL
cannot be guaranteed when the program operation is aborted, the block containing the memory
location must be erased and reprogrammed.
See Appendix C, Figure 19, Quadruple Word Program Flowchart and Pseudo Code, for the flowchart for using the Quadruple Word Program
command.
Clear Status Register Command
The Clear Status Register comm and c an b e us ed
to reset bits 1, 3, 4 and 5 in the Status Register to
‘0’. One bus write cycle is required to issue the
Clear Status Register command.
The bits in the Status Register do not automatically return to ‘0’ when a new Program or Erase command is issued. The error bits in the Status
Register should be cleared before attempting a
new Program or Erase command.
Program/Erase Suspend Command
The Program/Erase Suspend command is used to
pause a Program or Erase operation. One bus
write cycle is required to issue the Program/Erase
command and pau se the Prog ram/Erase controller.
12/53

M28W320ECT, M28W320ECB
During Program/Erase Suspend the Command Interface will accept the Program/Erase Resume,
Read Array, Read Status Register, Read Electronic Signature and Read CFI Query commands. Additionally, if the suspend operation was Erase then
the Program, Double Word Program, Quadruple
Word Program, Block Lo ck, Block Lock-Down or
Protection Program commands will also be accepted. The block being erased may be protected
by issuing the Block Protect, Block Lock or Protection Program commands. When the Program/
Erase Resume com mand is issued the operation
will complete. Only the blocks not being erased
may be read or programmed correctly.
During a Program/Erase Suspend, the device can
be placed in a pseudo-standby mode by taking
Chip Ena ble to V
Reset turns to V
. Program/Erase is aborted if
IH
.
IL
See Appendix C, Figure 20, Program or Double
Word Program Suspend & Resume Flowchart and
Pseudo Code, an d Figure 22, Erase Sus pend &
Resume Flowchart and Pseudo Code for flowcharts for using the Program/Erase Suspend command.
Program/Erase Resume Command
The Program/Erase Resume command can be
used to restart the Program/Erase Controller after
a Program/Erase Suspend o peration has paused
it. One Bus Write cycle is required to issue the
command. Once the command is issued subsequent Bus Read operations read the Status Register.
See Appendix C, Figure 20, Program or Double
Word Program Suspend & Resume Flowchart and
Pseudo Code, an d Figure 22, Erase Sus pend &
Resume Flowchart and Pseudo Code for flowcharts for using the Program/Erase Resume command.
Protectio n Register Program Comm and
The Protection Register Program command is
used to Program the 128 bit user O ne-Time-Programmable (OTP) segment of the Protection Register. The segment is programmed 16 bits at a
time. When shipped all bits in the segment are set
to ‘1’. The user can only program the bits to ‘0’.
Two write cycles are required to issue the Protec-
tion Register Program command.
■ The first bus cycle sets up the Protection
Register Program command.
■ The second latches the Address and the Data to
be written to the Protection Register and starts
the Program/Erase Controller.
Read operations output the Status Register content after the programming has started.
The segment can be protected by programming bit
1 of the Protection Lock Register (see Figure 6,
Protection Register Memory Map). Attempting to
program a previously prot ected Protection Register will result in a Status Register error. The protection of the Protection Register is not reversible.
The Protection Register Program cannot be suspended.
Block Lock Command
The Block Lock command is used to lock a block
and prevent Program or Erase operations from
changing the data in it. All blocks are locked at
power-up or reset.
Two Bus Write cycles are required to issue the
Block Lock command.
■ The first bus cycle sets up the Block Lock
command.
■ The second Bus Write cycle latc hes the block
address.
The lock status can be monitored for each block
using the Read Electronic Signature command.
Table. 10 shows the protection status after issuing
a Block Lock command.
The Block Lock bits are vo latile, once set they remain set until a hardware reset or power-down/
power-up. They are cleared by a Blocks Unlock
command. Refer to the section, Block Locking, for
a detailed explanation.
Block Unlock Command
The Blocks Unlock command i s used to unlock a
block, allowing the block to be programmed or
erased. Two Bus Write cycles are requ ired to issue the Blocks Unlock command.
■ The first bus cycle sets up the Block Unlock
command.
■ The second Bus Write cycle latc hes the block
address.
The lock status can be monitored for each block
using the Read Electronic Signature command.
Table. 10 shows the protection status after issuing
a Block Unlock command. Refer to the section,
Block Locking, for a detailed explanation.
Block Lock-Down Command
A locked block cannot be Programmed or Erased,
or have its protection status changed when WP
low, V
. When WP is high, V
IL
the Lock-Down
IH,
is
function is disabled and the locked blocks can be
individually unlocked by the Block Unlock command.
Two Bus Write cycles are required to issue the
Block Lock-Down command.
■ The first bus cycle sets up the Block Lock
command.
■ The second Bus Write cycle latc hes the block
address.
13/53
M28W320ECT, M28W320ECB
The lock status can be monitored for each block
using the Read Electronic Signature command.
Locked-Down blocks revert to the locked (and not
locked-down) state when the device is reset on
power-down. Table. 10 sho ws the protection status after issuing a Block Lock-Down command.
Refer to the section, Block Locking, for a detailed
explanation.
Table 4. Commands
Bus Write Operations
Commands
Read Memory
Array
Read Status
Register
Read Electronic
Signature
Read CFI Query 1+ Write X 98h Read QA QD
Erase 2 Write X 20h Write BA D0h
Program 2 Write X
Double Word
Program
Quadruple Word
Program
Clear Status
Register
Program/Erase
Suspend
Program/Erase
Resume
Block Loc k 2 Write X 60h Write
Block Unlock 2 Write X 60h Write
Block Loc k-Down 2 Write X 60h Write
Protection
Register Program
Note: 1. X = D on’t Car e, RA= Read Ad dress, RD=Rea d Data, SRD=St atus R egister Data, I D=Iden tifier (M anufa cture a nd De vice Cod e),
(3)
(4)
QA=Query Address, QD=Query Data, BA=Block Address, PA=Program Address, PD=Program Data, PRA=Protection Register Address, PRD=Protection Register Data.
2. The signa tu re addresses are listed in Tabl es 5, 6 and 7.
3. Program A ddresses 1 and 2 must be consecutive Address es differing onl y for A0.
4. Program A ddresses 1,2,3 and 4 must be cons ecutive Addresses differing only for A0 and A1.
5. 55h is reserved.
6. To be charac terized.
1+ Write X FFh
1+ Write X 70h Read X SRD
1+ Write X 90h Read
1st Cycle 2nd Cycle 3rd Cycle 4th Cycle 5th Cycle
Cycles
Op. Add Data Op. Add Data Op. Add Data Op. Add Data Op. Add Data
RA RD
Read
(2)
IDh
SA
40h
or
Write PA PD
10h
3 Write X 30h Write PA1 PD1 Write PA2 PD2
5Write X
1 Write X 50h
1Write X B0h
1Write X D0h
(6)
Write PA1 PD1 Write PA2 PD2 Write PA3 PD3 Write PA4 PD4
56h
BA 01h
BA D0h
2Fh
BA
2 Write X C0h Write
PRA PRD
14/53
M28W320ECT, M28W320ECB
Table 5. Read Electronic Signature
Code Device E G W A0 A1 A2-A7 A8-A20 DQ0-DQ7 DQ8-DQ15
Manufacture.
Code
M28W320ECT
Device Code
M28W320ECB
Note: RP = VIH.
Table 6. Read Block Lock Signature
Block Status E
Locked Block
Unlocked Block
Locked-Down
Block
Note: 1. A Lo ck ed-Down Block can be locked "DQ0 = 1" or unlocked "DQ0 = 0"; see Bl ock Locking sec tion.
G W A0 A1 A2-A7 A8-A11 A12-A20 DQ0 DQ1 DQ2-DQ15
V
VILVIHVILV
IL
V
VILVIHVILV
IL
V
VILVIHVILV
IL
Table 7. Read Protection Register and Lock Register
Word E
Lock
Unique ID 0
Unique ID 1
Unique ID 2
Unique ID 3
OTP 0
OTP 1
OTP 2
OTP 3
OTP 4
OTP 5
OTP 6
OTP 7
Note: 1. DQ2 in the Protection Lock Register must not be programmed to 0.
G W A0-A7 A8-A20 DQ0 DQ1 DQ2 DQ3-DQ7 DQ8-DQ15
V
ILVILVIH
V
ILVILVIH
V
ILVILVIH
V
ILVILVIH
V
ILVILVIH
V
ILVILVIH
V
ILVILVIH
V
ILVILVIH
V
ILVILVIH
V
ILVILVIH
V
ILVILVIH
V
ILVILVIH
V
ILVILVIH
VILV
V
IL
V
VILV
IL
V
VILV
IL
80h Don’t Care Don’t Care
V
IH
IHVIH
IHVIH
IH
IH
IH
V
IL
V
V
0 Don’t Care Block Address 1 0 00h
0 Don’t Care Block Address 0 0 00h
0 Don’t Care Block Address
0 Don’t Care 20h 00h
IL
0 Don’t Care BAh 88h
IL
0 Don’t Care BBh 88h
IL
(1)
X
OTP Prot.
data
Don’t Care
See note (1)
1 00h
Don’t
Care
81h Don’t Care ID data ID data ID data ID data ID data
82h Don’t Care ID data ID data ID data ID data ID data
83h Don’t Care ID data ID data ID data ID data ID data
84h Don’t Care ID data ID data ID data ID data ID data
85h Don’t Care OTP data OTP data OTP data OTP data OTP data
86h Don’t Care OTP data OTP data OTP data OTP data OTP data
87h Don’t Care OTP data OTP data OTP data OTP data OTP data
88h Don’t Care OTP data OTP data OTP data OTP data OTP data
89h Don’t Care OTP data OTP data OTP data OTP data OTP data
8Ah Don’t Care OTP data OTP data OTP data OTP data OTP data
8Bh Don’t Care OTP data OTP data OTP data OTP data OTP data
8Ch Don’t Care OTP data OTP data OTP data OTP data OTP data
Don’t Care
15/53
M28W320ECT, M28W320ECB
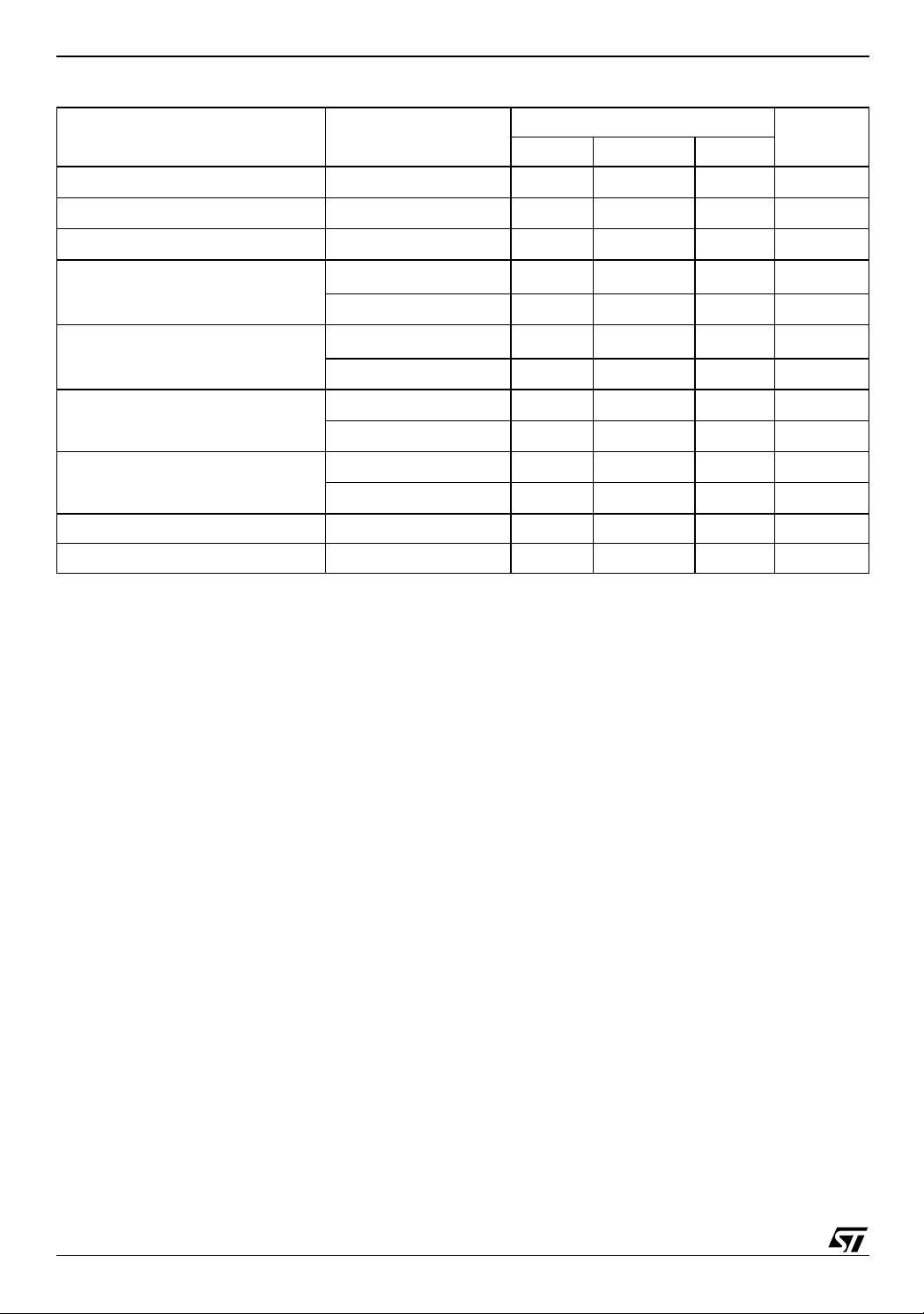
Table 8. Program, Erase Times and Progra m /Erase Endura nce Cycl es
Parameter Test Conditions
Min Typ Max
V
Word Program
Double Word Program
Quadruple Word Program
Main Block Program
Parameter Block Program
Main Block Erase
Parameter Block Erase
= V
PP
V
= 12V ±5%
PP
V
= 12V ±5%
PP
V
= 12V ±5%
PP
= V
V
PP
= 12V ±5%
V
PP
= V
V
PP
= 12V ±5%
V
PP
= V
V
PP
V
= 12V ±5%
PP
V
= V
PP
DD
DD
DD
DD
DD
Program/Erase Cycles (per Block) 100,000 cycles
Data Retention 20 years
Note: 1. Typical time to program a Main or Parameter Block using the Double Word Program and the Quadruple Word Program commands
respectively.
M28W320EC
10 200 µs
10 200 µs
10 200 µs
0.16/0.08
(1)
5s
0.32 5 s
0.02/0.01
(1)
4s
0.04 4 s
110s
110s
0.4 10 s
0.4 10 s
Unit
16/53
 Loading...
Loading...