查询M28256供应商
FASTACCESSTIME:
– 90ns at 5V
– 120ns at 3V
SINGLESUPPLYVOLTAGE:
–5V±10%for M28256
– 2.7V to 3.6Vfor M28256-xxW
LOWPOWER CONSUMPTION
FASTWRITECYCLE:
– 64 Bytes Page Write Operation
– Byte or Page WriteCycle
ENHANCEDEND of WRITEDETECTION:
– Data Polling
– ToggleBit
STATUSREGISTER
HIGHRELIABILITYDOUBLEPOLYSILICON,
CMOSTECHNOLOGY:
– Endurance >100,000Erase/WriteCycles
– Data Retention>10 Years
JEDECAPPROVEDBYTEWIDE PIN OUT
ADDRESS and DATALATCHEDON-CHIP
SOFTWAREDATAPROTECTION
M28256
256 Kbit (32Kb x8) Parallel EEPROM
with Software Data Protection
PRELIMINARY DATA
28
1
PDIP28 (BS) PLCC32 (KA)
28
1
SO28 (MS)
300 mils
Figure1. LogicDiagram
TSOP28 (NS)
8 x13.4mm
V
CC
DESCRIPTION
TheM28256and M28256-Ware 32Kx8lowpower
ParallelEEPROMfabricatedwithSTMicroelectronics proprietary double polysilicon CMOS technol-
A0-A14
15
8
DQ0-DQ7
ogy.
Table1. Signal Names
A0-A14 Address Input
DQ0-DQ7 Data Input / Output
W Write Enable
E Chip Enable
G Output Enable
V
CC
V
SS
January 1999 1/21
Thisis preliminaryinformationon a new product now in developmentor undergoingevaluation.Detail s aresubject to change without notice.
Supply Voltage
Ground
W
E
G
M28256
V
SS
AI01885
M28256
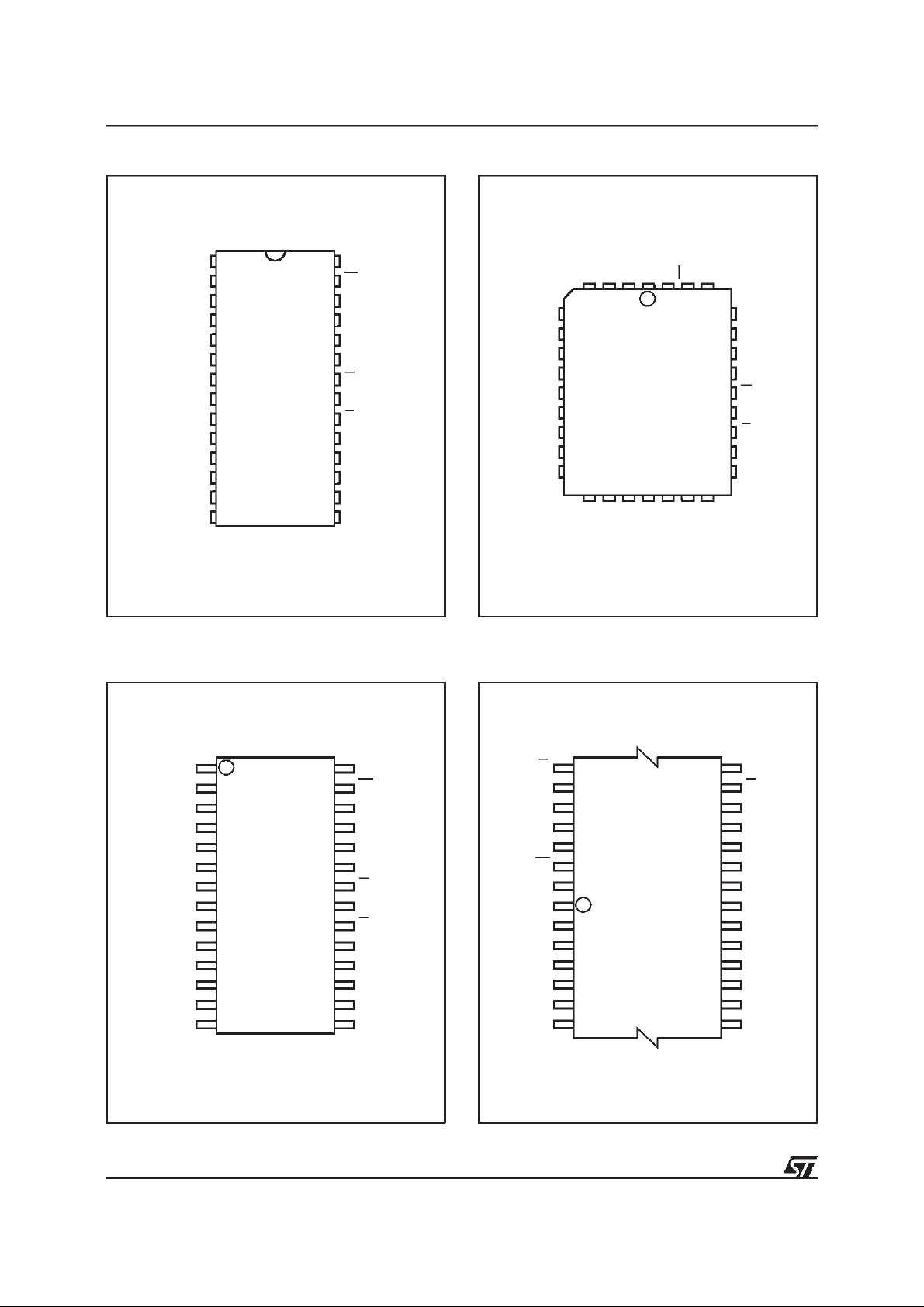
Figure2A. DIPPin Connections
A14 V
A12
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
DQ0
DQ2
SS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
M28256
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
AI01886
CC
W
A13
A8
A9
A11
G
A10
E
DQ7
DQ6
DQ5DQ1
DQ4
DQ3V
Figure2B. LCC Pin Connections
CC
DU
32
W
V
DQ4
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
NC
DQ0
A7
9
DQ1
A14
A12
1
M28256
17
SS
V
DQ2DUDQ3
A13
25
DQ5
A8
A9
A11
NC
G
A10
E
DQ7
DQ6
AI01887
Figure 2C. SOPin Connections
A14
A12
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
DQ0
DQ1
DQ2
V
SS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
M28256
28
27
26
25
24
23 A11
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
AI01888
V
CC
W
A13
A8
A9
G
A10
E
DQ7
DQ6
DQ5
DQ4
DQ3
Warning:
NC = Not Connected, DU = Don’t Use.
Figure2D. TSOPPin Connections
G
A11
A13
V
A14
A12
A9
A8
W
CC
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
22
28
M28256
1
78
21
15
14
AI01889
A10
E
DQ7
DQ6
DQ5
DQ4
DQ3
V
SS
DQ2
DQ1
DQ0
A0
A1
A2
2/21

M28256
Table2. Absolute Maximum Ratings
(1)
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
T
T
STG
V
CC
V
IO
V
V
ESD
Notes:
1. Except for therating ”Operating Temperature Range”, stresses above those listed in the Table ”Absolute Maximum Ratings”may
2. Depends on range.
3. 100pF through 1500Ω; MIL-STD-883C, 3015.7
Ambient Operating Temperature
A
Storage TemperatureRange – 65 to 150
Supply Voltage – 0.3 to 6.5 V
Input/Output Voltage – 0.3 to VCC+0.6 V
Input Voltage – 0.3 to 6.5 V
I
Electrostatic Discharge Voltage (Human Body model)
cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation of the device at these or any other conditions
above those indicated in the Operating sections of this specification is not implied.Exposure to Absolute Maximum Rating
conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.Refer also to the STMicroelectronicsSUREProgram and other
relevant quality documents.
(2)
(3)
–40to85 °C
4000 V
Figure3. Block Diagram
EGW
C
°
A6-A14
(Page Address)
A0-A5
VPPGEN RESET
ADDRESS
LATCH
ADDRESS
LATCH
Y DECODE
X DECODE
CONTROL LOGIC
256K ARRAY
SENSE AND DATA LATCH
I/O BUFFERS
DQ0-DQ7
PAGE
LOAD
TIMER STATUS
TOGGLE BIT
DATA POLLING
AI01697
3/21

M28256
Table3. Operating Modes
Mode E G W DQ0 - DQ7
Read V
Write V
Standby / Write Inhibit V
Write Inhibit X X V
Write Inhibit X V
Output Disable X V
Notes: 1. X = VIHor V
DESCRIPTION
IL.
(Cont’d)
The devices offer fast access timewith low power
dissipationand requires a 5V or 3Vpower supply.
The circuit has been designed to offer a flexible
microcontroller interface featuring both hardware
and software handshaking with Data Polling and
Toggle Bit and access to a status register. The
devicessupport a 64 byte page write operation.A
Software Data Protection (SDP) is also possible
using the standardJEDECalgorithm.
(1)
IL
IL
IH
V
IL
V
IH
X X Hi-Z
IL
IH
Read
Thedevice is accessedlike a staticRAM. WhenE
and G are low with W high, the data addressedis
presented on the I/O pins. The I/O pins are high
impedancewhen either G or E is high.
Write
Writeoperations are initiated when both W and E
are low and G is high.Thedevice supportsboth E
and W controlled write cycles. The Address is
latched by the falling edge of E or W which ever
occurslast and the Data on the risingedge of E or
PIN DESCRIPTION
Addresses (A0-A14).
The address inputs select
an 8-bit memory location during a read or write
operation.
Chip Enable (E).
The chip enable input must be
lowto enableall read/writeoperations.When Chip
Enableis high, power consumptionis reduced.
OutputEnable (G).
The Output Enable input controls the dataoutput buffers and is usedto initiate
readoperations.
DataIn/ Out(DQ0-DQ7).
Datais writtento orread
fromthe memorythrough the I/O pins.
WriteEnable(W).
TheWriteEnable inputcontrols
the writingof datato thememory.
W which ever occurs first. Once initiated the write
operation is internally timed until completion and
the status of the Data Polling and the Toggle Bit
functions on DQ7 and DQ6 is controlled accordingly.
Page Write
Page write allows up to 64 bytes within the same
page to be consecutivelylatched into the memory
prior to initiating a programming cycle. All bytes
must be located in a single page address, that is
A14-A6 mustbe the same forall bytes;if not,the
Page Write instruction is not executed. The page
writecan be initiatedby any byte write operation.
A page write is composed of successive Write
instructions which have to be sequenced with a
specific period of time between two consecutive
OPERATIONS
WriteProtection
In orderto preventdata corruptionand inadvertent
writeoperations;an internalV
its Write operationsif V
CC
comparatorinhib-
CC
is below VWI (see Table
7andTable9).Accesstothememoryinwrite mode
is allowed after a power-upas specifiedin Table7
and Table 9.
Write instructions, period of time which has to be
smaller than the t
Table13).
If thisperiod of time exceedsthet
internalprogrammingcycle will start.Onceinitiated
thewrite operationis internallytimed until completion and the status of the Data Polling and the
ToggleBit functionson DQ7and DQ6 is controlled
accordingly.
V
IH
V
IL
IH
X Data Out or Hi-Z
X Hi-Z
value (see Table 12 and
WHWH
Data Out
Data In
Data Out or Hi-Z
value, the
WHWH
4/21

M28256
StatusRegister
Thedevicesprovide severalWriteoperationstatus
flags that can beused to minimize the application
writetime. These signals are available on the I/O
portbits during programming cycleonly.
Data Polling bit (DQ7).
During the internal write
cycle,any attemptto read the last bytewrittenwill
produceon DQ7 the complementary value of the
previously latched bit. Once the write cycle is finished the true logic value appears on DQ7 in the
readcycle.
Toggle bit (DQ6). The devices offer another way
for determining when the internal write cycle is
completed.During theinternal Erase/Write cycle,
DQ6 will toggle from ”0” to ”1” and ”1” to ”0” (the
first read value is ”0”) on subsequent attempts to
read any byte of the memory. When the internal
cycle is completed the toggling will stop and the
data read on DQ7-DQ0is the addressed memory
byte.The deviceisnow accessiblefor a newRead
or Write operation.
PageLoadTimerStatusbit(DQ5).DuringaPage
Writeinstruction,the devicesexpectto receivethe
stream of data with a minimum period of time
between each data byte. This period of time
(t
) isdefined by theon-chip Page Loadtimer
WHWH
whichrunning/overflowstatusis availableonDQ5.
DQ5 Low indicates that the timeris running, DQ5
Highindicatesthe time-outafter which the internal
writecycle will start.
Figure4. StatusBit Assignment
DQ7 DQ6 DQ5 DQ4 DQ3 DQ2 DQ1 DQ0
DP TB PLTS X X X X X
DP = Data Polling
TB = ToggleBit
PLTS = Page Load Timer Status
Software Data Protection
The devices offer a software controlled write protectionfacility thatallowstheuser to inhibitallwrite
modesto the device.This can be usefulin protecting the memory from inadvertentwrite cycles that
may occur due to uncontrolledbus conditions.
Thedevicesare shippedas standardinthe”unprotected” state meaning thatthe memory contents
canbe changedas required by the user. After the
Software Data Protection enable algorithm is issued, the device enters the ”Protect Mode” of
operationwhere no further write commands have
anyeffect on the memorycontents.
The devices remain in this mode until a valid
SoftwareData Protection(SDP) disablesequence
is received whereby the device reverts to its ”unprotected”state. TheSoftware Data Protection is
fully non-volatile and is not changed by power
on/off sequences. To enable the Software Data
Protection (SDP) the device requires the user to
write(with a PageWrite addressing three specific
databytestothreespecificmemorylocations,each
locationin a different page) as per Figure 6. Similarly to disable the Software Data Protection the
userhas to write specific data bytes intosix different locations as per Figure 5 (with a Page Write
adressingdifferent bytes in differentpages).
Thiscomplexseriesensuresthattheuserwillnever
enable or disable the Software Data Protection
accidentally.
To write into the devices when SDP is set, the
sequence shown in Figure 6 must be used. This
sequence provides an unlock key to enable the
writeaction, and at the same time SDP continues
to be set.
Anextension to this is whereSDPis required to be
set,and data is to be written.
Using the same sequenceas above, the datacan
be written and SDP is set at the same time, giving
boththese actions in thesame Write cycle (t
WC
).
5/21

M28256
Figure5. SoftwareData Protection Enable Algorithmand Memory Write
WRITE AAh in
Address 5555h
Page
Write
Instruction
WRITE 55h in
Address 2AAAh
WRITE A0h in
Address 5555h
SDP is set
SDP ENABLE ALGORITHM
Page
Write
Instruction
Figure6. SoftwareData Protection Disable Algorithm
SDP
Set
WRITE AAh in
Address 5555h
WRITE 55h in
Address 2AAAh
WRITE A0h in
Address 5555h
WRITE Data
be Written in
any Address
Write
in Memory
SDP
not Set
to
Write
Data
+
SDP Set
after tWC
AI01698B
WRITE
is enabled
Page
Write
Instruction
WRITE AAh in
Address 5555h
WRITE 55h in
Address 2AAAh
WRITE 80h in
Address 5555h
WRITE AAh in
Address 5555h
WRITE 55h in
Address 2AAAh
WRITE 20h in
Address 5555h
Unprotected
tWC (Write Cycle time)
State
after
AI01699B
6/21
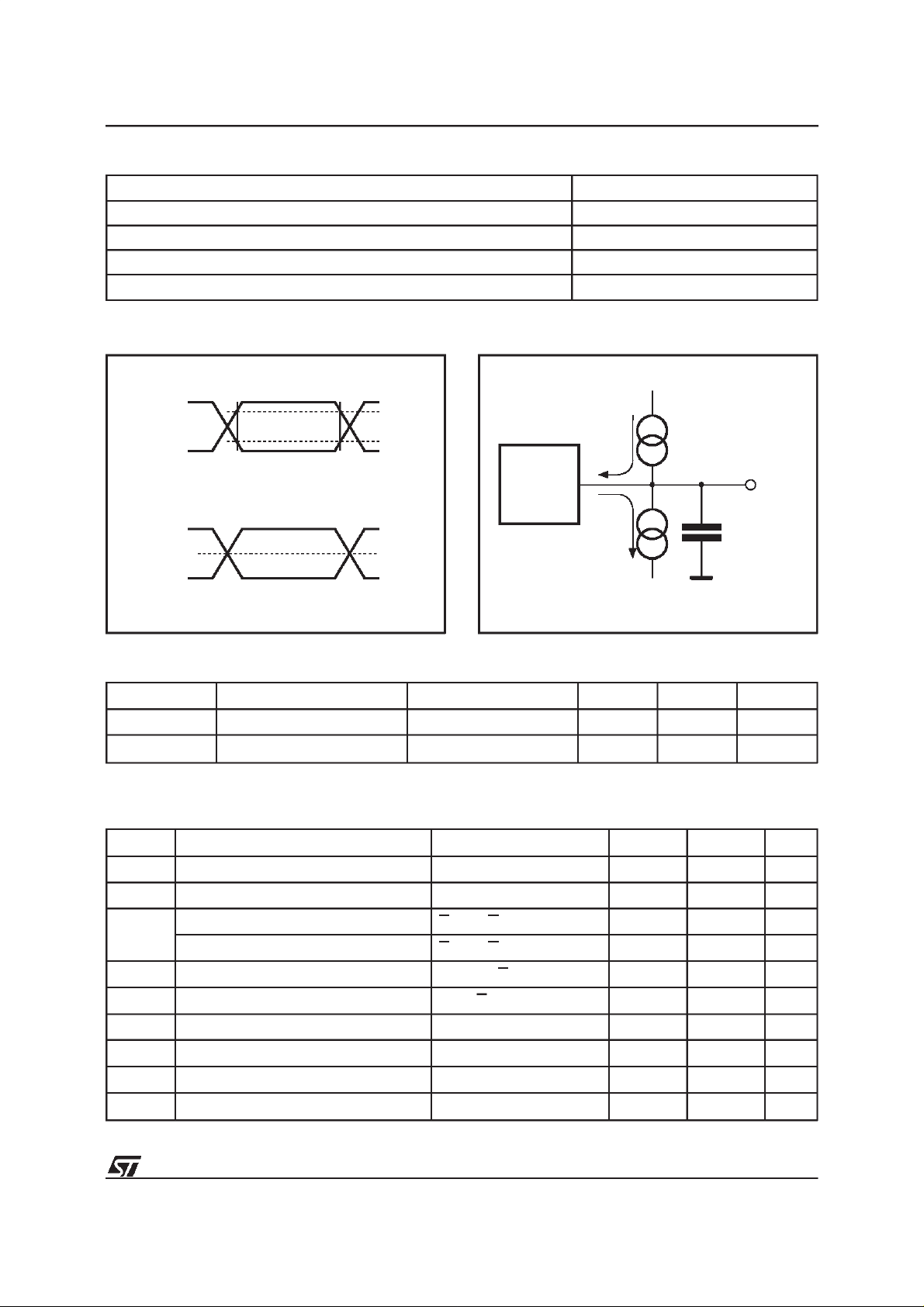
Table4. AC MeasurementConditions
Input Rise and FallTimes ≤ 20ns
Input Pulse Voltages(M28256) 0.4V to 2.4V
Input Pulse Voltages(M28256-W) 0V toV
Input and Output Timing Ref. Voltages(M28256) 0.8V to 2.0V
Input and Output Timing Ref. Voltages(M28256-W) 0.5 V
CC
CC
M28256
–0.3V
Figure7. AC TestingInput Output Waveforms
4.5V to 5.5V Operating Voltage
2.4V
0.4V
2.7V to 3.6V Operating Voltage
VCC– 0.3V
0V
Table5. Capacitance
(1)
(TA=25°C, f = 1 MHz )
2.0V
0.8V
0.5 V
CC
AI02101B
Figure8. AC TestingEquivalent LoadCircuit
I
OL
DEVICE
UNDER
TEST
I
OH
CLincludes JIG capacitance
Symbol Parameter Test Condition Min Max Unit
C
IN
C
OUT
Note:
1. Sampled only, not 100% tested.
Input Capacitance VIN=0V 6 pF
Output Capacitance V
=0V 12 pF
OUT
Table6. Read Mode DC Characteristicsfor M28256
(T
=0 to 70°C or –40 to85°C;VCC= 4.5V to 5.5V)
A
OUT
CL= 100pF
AI02102B
Symbol Parameter TestCondition Min Max Unit
I
I
LO
I
CC
I
CC1
I
CC2
V
V
V
V
Note: 1. All I/O’s open circuit.
Input Leakage Current 0V ≤ VIN≤ V
LI
Output Leakage Current 0V ≤ VIN≤ V
Supply Current (TTLinputs) E = VIL,G=VIL,f=5MHz 30 mA
(1)
Supply Current (CMOS inputs) E = V
(1)
Supply Current (Standby) TTL E = V
(1)
Supply Current (Standby) CMOS E > VCC–0.3V 100 µA
Input Low Voltage – 0.3 0.8 V
IL
Input High Voltage 2 VCC+ 0.5 V
IH
Output Low Voltage IOL= 2.1 mA 0.4 V
OL
Output High Voltage IOH= –400 µA 2.4
OH
,G=VIL,f=5MHz 25 mA
IL
CC
CC
IH
10 µA
10 µA
1mA
7/21
 Loading...
Loading...