
Automotive 128-Kbit serial I²C bus EEPROM
TSSOP8 (DW)
SO8 (MN)
169 mil width
150 mil width
Features
■ Compatible with all I
– 400 kHz Fast mode
– 100 kHz Standard mode
■ Memory array:
– 128 Kbit (16 Kbytes) of EEPROM
– Page size: 64 bytes
■ Write
– Byte Write within 5 ms
– Page Write within 5 ms
■ Single supply voltage: 2.5 V to 5.5 V
■ Operating temperature range: from -40 °C up
to +125 °C
■ Random and sequential Read modes
■ Write protect of the whole memory array
■ Enhanced ESD/Latch-Up protection
■ More than 1 million Write cycles
■ More than 40-year data retention
■ Packages
– RoHS compliant and halogen-free
(ECOPACK
2
®
)
C bus modes:
M24128-125
Datasheet − production data
March 2012 Doc ID 022581 Rev 1 1/30
This is information on a product in full production.
www.st.com
1

Contents M24128-125
Contents
1 Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2 Signal description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.1 Serial Clock (SCL) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.2 Serial Data (SDA) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.3 Chip Enable (E2, E1, E0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.4 Write Control (WC
2.5 V
(ground) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
SS
2.6 Supply voltage (V
2.6.1 Operating supply voltage V
2.6.2 Power-up conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.6.3 Device reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.6.4 Power-down conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
CC
CC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3 Memory organization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
4 Device operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
4.1 Start condition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
4.2 Stop condition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
4.3 Acknowledge bit (ACK) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
4.4 Data input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
4.5 Memory addressing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
5 Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
5.1 Write operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
5.1.1 Byte Write . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
5.1.2 Page Write . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.1.3 ECC (Error Correction Code) and Write cycling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5.1.4 Minimizing Write delays by polling on ACK . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
5.2 Read operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
5.2.1 Random Address Read . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
5.2.2 Current Address Read . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
5.2.3 Sequential Read . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
2/30 Doc ID 022581 Rev 1

M24128-125 Contents
5.2.4 Acknowledge in Read mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
6 Initial delivery state . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
7 Maximum rating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
8 DC and AC parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
9 Package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
10 Part numbering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
11 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Doc ID 022581 Rev 1 3/30

List of tables M24128-125
List of tables
Table 1. Signal names . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Table 2. Device select code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Table 3. Operating modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Table 4. Most significant address byte . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Table 5. Least significant address byte . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Table 6. Absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Table 7. Operating conditions (voltage range W) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 8. AC measurement conditions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 9. Input parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 10. Memory cell characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 11. DC characteristics (voltage range W, device grade 3) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Table 12. 400 kHz AC characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Table 13. TSSOP8 – 8-lead thin shrink small outline, package mechanical data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 14. SO8N – 8 lead plastic small outline, 150 mils body width, package data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Table 15. Ordering information scheme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Table 16. Document revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
4/30 Doc ID 022581 Rev 1

M24128-125 List of figures
List of figures
Figure 1. Logic diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Figure 2. 8-pin package connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Figure 3. Device select code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Figure 4. Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Figure 5. I
Figure 6. Write mode sequences with WC
Figure 7. Write mode sequences with WC
Figure 8. Write cycle polling flowchart using ACK . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Figure 9. Read mode sequences . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Figure 10. AC measurement I/O waveform . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Figure 11. Maximum R
Figure 12. AC waveforms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Figure 13. TSSOP8 – 8-lead thin shrink small outline, package outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Figure 14. SO8N – 8 lead plastic small outline, 150 mils body width, package outline . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
2
C bus protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
= 0 (data write enabled) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
= 1 (data write inhibited) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
value versus bus parasitic capacitance (C
2
an I
C bus at maximum frequency fC = 400 kHz . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
bus
bus
) for
Doc ID 022581 Rev 1 5/30
Description M24128-125
!)F
%% 3$!
6
##
-XXX
7#
3#,
6
33
3$!6
33
3#,
7#%
% 6
##
%
!)F
1 Description
The M24128 is a 128-Kbit I2C-compatible EEPROM (Electrically Erasable PROgrammable
Memory) organized as 16 K × 8 bits.
2
This I
C EEPROM can operate with a supply voltage from 2.5 V up to 5.5 V over an ambient
temperature range of -40 °C / 125 °C.
The device is compliant with the Automotive standard AEC-Q100 grade 1.
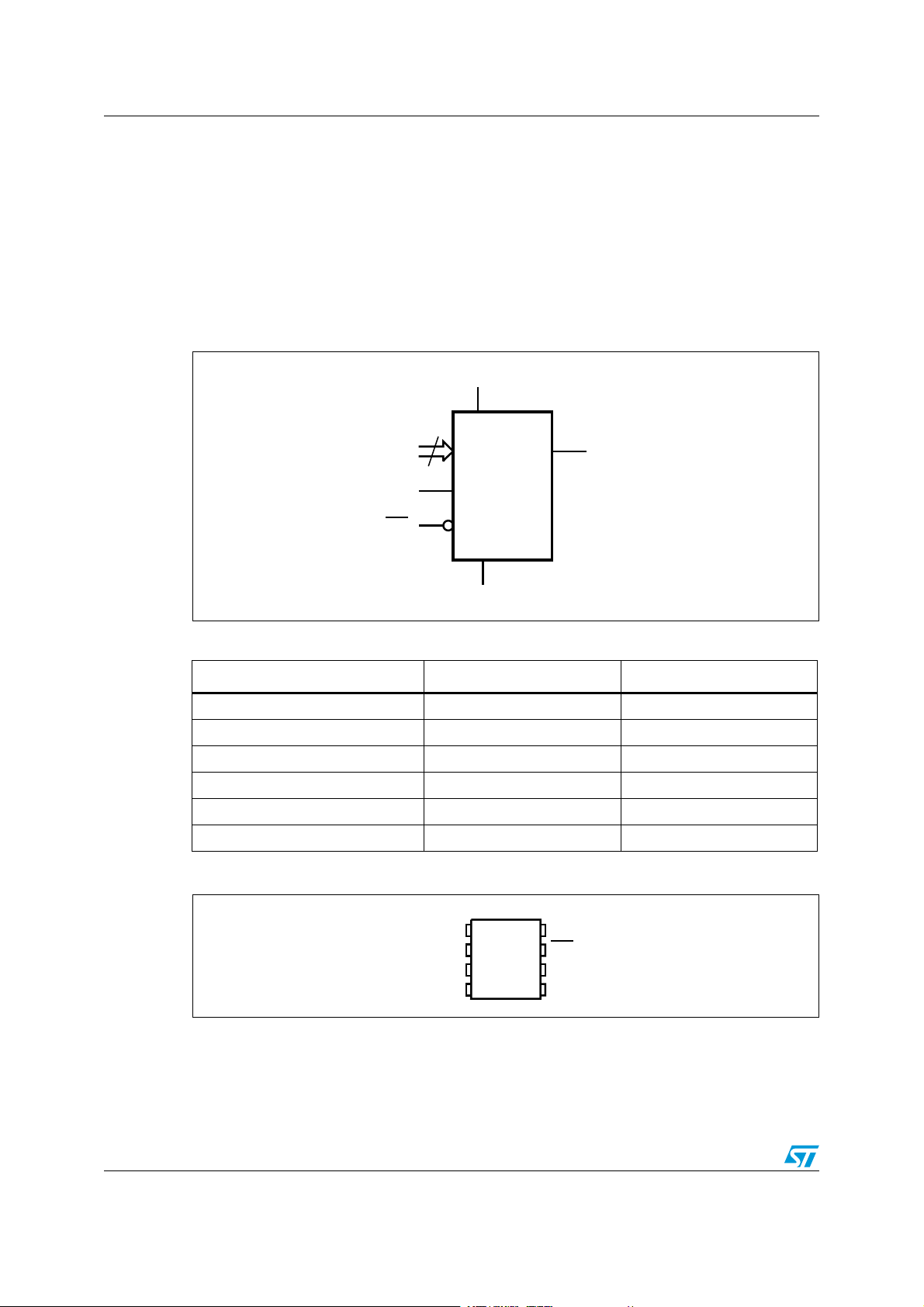
Figure 1. Logic diagram
Table 1. Signal names
Signal name Function Direction
E2, E1, E0 Chip Enable Input
SDA Serial Data I/O
SCL Serial Clock Input
WC Write Control Input
V
CC
V
SS
Supply voltage
Ground
Figure 2. 8-pin package connections
1. See Section 9: Package mechanical data for package dimensions, and how to identify pin 1.
6/30 Doc ID 022581 Rev 1
M24128-125 Signal description
Ai12806
V
CC
M24xxx
V
SS
E
i
V
CC
M24xxx
V
SS
E
i
2 Signal description
2.1 Serial Clock (SCL)
This input signal is used to strobe all data in and out of the device. In applications where this
signal is used by slave devices to synchronize the bus to a slower clock, the bus master
must have an open drain output, and a pull-up resistor must be connected from Serial Clock
(SCL) to V
applications, though, this method of synchronization is not employed, and so the pull-up
resistor is not necessary, provided that the bus master has a push-pull (rather than open
drain) output.
2.2 Serial Data (SDA)
This bidirectional signal is used to transfer data in or out of the device. It is an open drain
output that may be wire-OR’ed with other open drain or open collector signals on the bus. A
pull up resistor must be connected from Serial Data (SDA) to V
to calculate the value of the pull-up resistor).
. (Figure 11 indicates how to calculate the value of the pull-up resistor). In most
CC
. (Figure 11 indicates how
CC
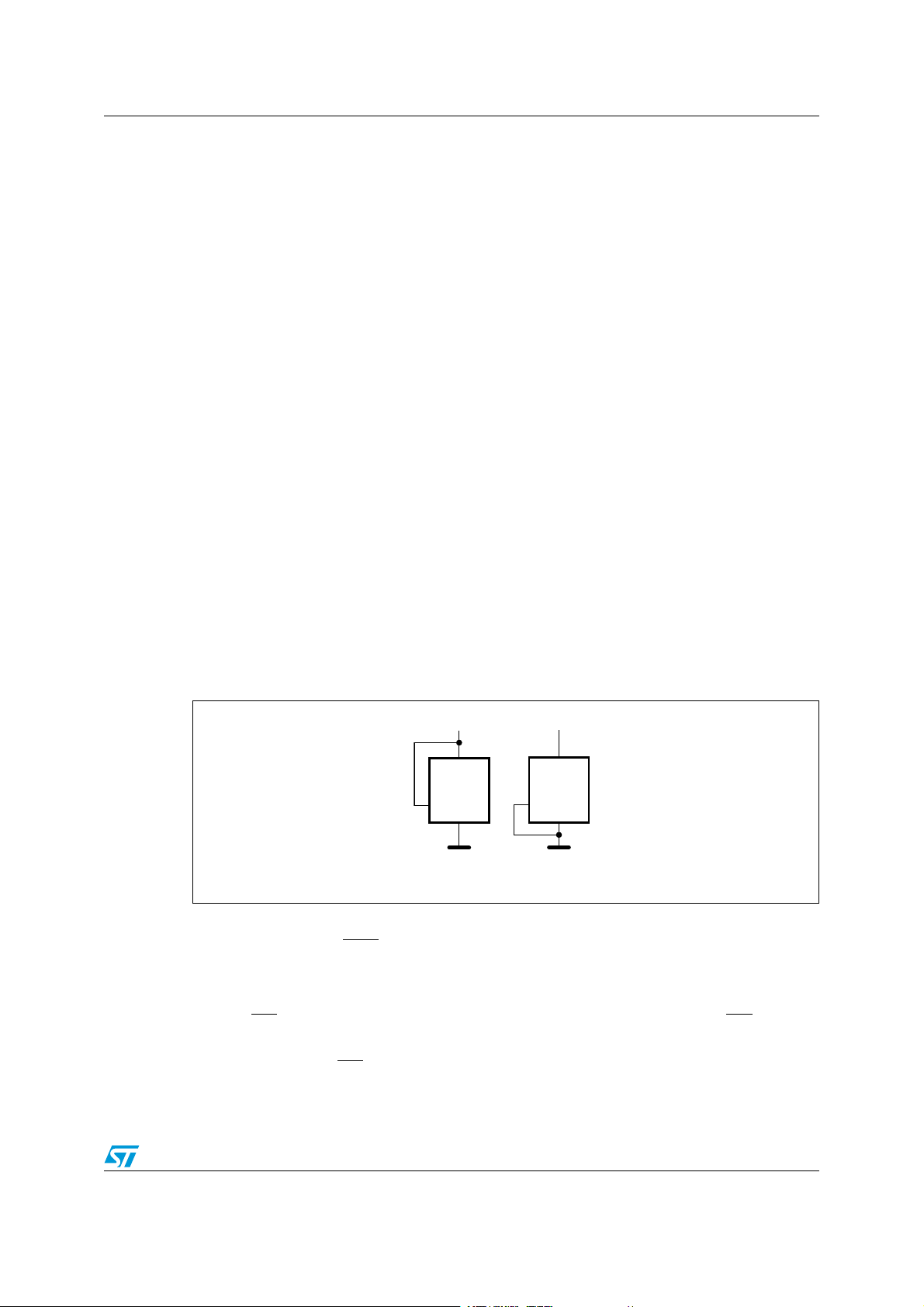
2.3 Chip Enable (E2, E1, E0)
(E2,E1,E0) input signals are used to set the value that is to be looked for on the three least
significant bits (b3, b2, b1) of the 7-bit device select code (see Ta b le 2 ). These inputs must
be tied to V
or VSS, as shown in Figure 3. When not connected (left floating), these inputs
CC
are read as low (0).
Figure 3. Device select code
2.4 Write Control (WC)
This input signal is useful for protecting the entire contents of the memory from inadvertent
write operations. Write operations are disabled to the entire memory array when Write
Control (WC
driven low or left floating.
) is driven high. Write operations are enabled when Write Control (WC) is either
When Write Control (WC
) is driven high, device select and address bytes are
acknowledged, Data bytes are not acknowledged.
Doc ID 022581 Rev 1 7/30

Signal description M24128-125
2.5 VSS (ground)
VSS is the reference for the VCC supply voltage.
2.6 Supply voltage (VCC)
2.6.1 Operating supply voltage V
Prior to selecting the memory and issuing instructions to it, a valid and stable VCC voltage
within the specified [V
(min), VCC(max)] range must be applied (see Operating conditions
CC
in Section 8: DC and AC parameters). In order to secure a stable DC supply voltage, it is
recommended to decouple the V
nF to 100 nF) close to the V
CC
CC/VSS
This voltage must remain stable and valid until the end of the transmission of the instruction
and, for a write instruction, until the completion of the internal write cycle (t
2.6.2 Power-up conditions
The VCC voltage has to rise continuously from 0 V up to the minimum VCC operating voltage
(see Operating conditions in Section 8: DC and AC parameters) and the rise time must not
vary faster than 1 V/µs.
2.6.3 Device reset
In order to prevent inadvertent write operations during power-up, a power-on-reset (POR)
circuit is included.
At power-up, the device does not respond to any instruction until V
internal reset threshold voltage. This threshold is lower than the minimum V
voltage (see Operating conditions in Section 8: DC and AC parameters). When V
over the POR threshold, the device is reset and enters the Standby Power mode; however,
the device must not be accessed until V
specified [V
parameters).
(min), VCC(max)] range (see Operating conditions in Section 8: DC and AC
CC
CC
line with a suitable capacitor (usually of the order of 10
package pins.
).
W
has reached the
CC
reaches a valid and stable DC voltage within the
CC
operating
CC
CC
passes
In a similar way, during power-down (continuous decrease in V
accessed when V
drops below VCC(min). When VCC drops below the power-on-reset
CC
threshold voltage, the device stops responding to any instruction sent to it.
2.6.4 Power-down conditions
During power-down (continuous decrease in VCC), the device must be in the Standby Power
mode (mode reached after decoding a Stop condition, assuming that is there is no internal
write cycle in progress).
8/30 Doc ID 022581 Rev 1
), the device must not be
CC
M24128-125 Memory organization
AI06899
WC
E1
E0
Control Logic
High Voltage
Generator
I/O Shift Register
Address Register
and Counter
Data
Register
1 Page
X Decoder
Y Decoder
SCL
SDA
E2
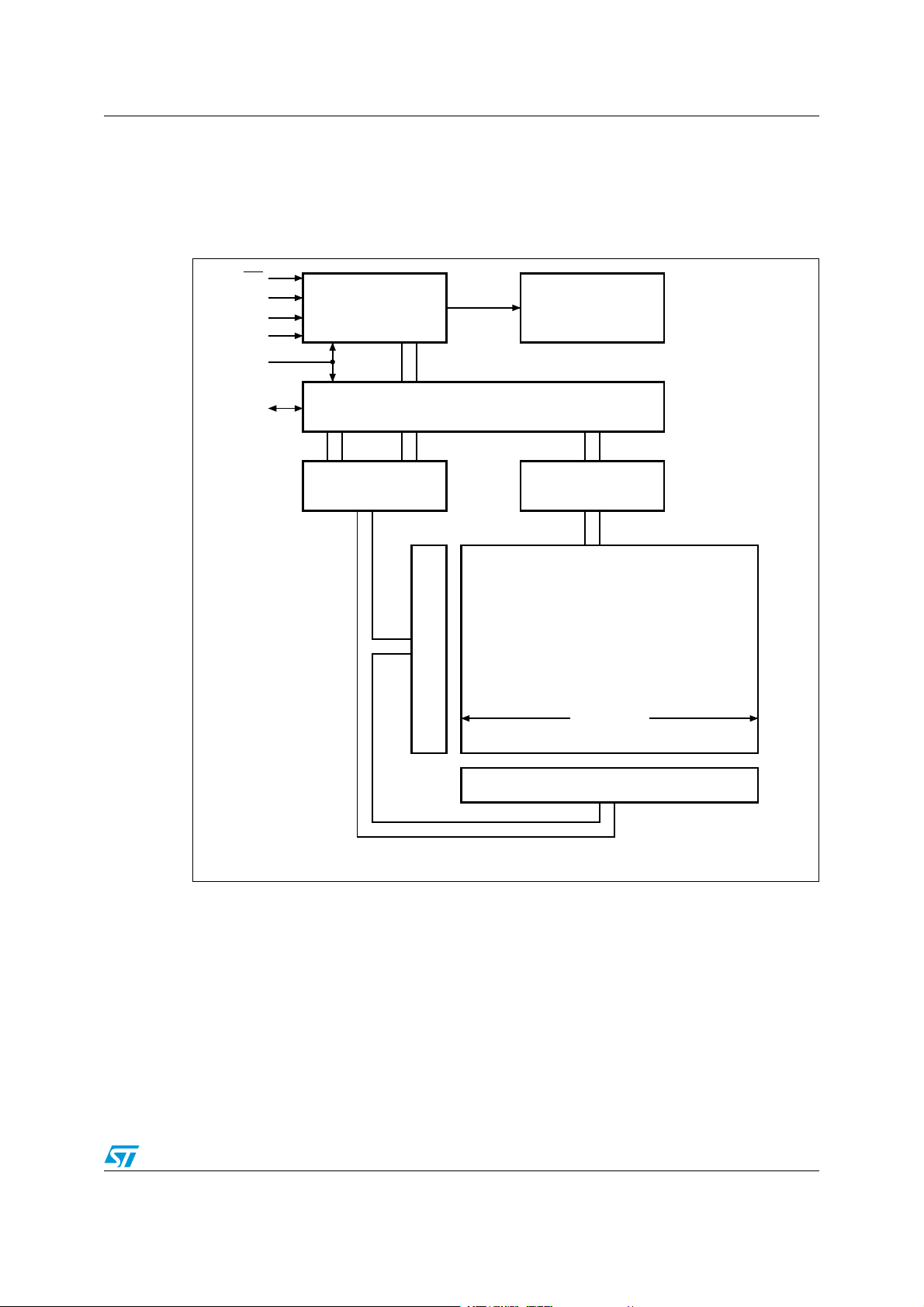
3 Memory organization
The memory is organized as shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4. Block diagram
Doc ID 022581 Rev 1 9/30
 Loading...
Loading...