Ultra compact high performance e-Compass
LGA-16
(3x3x1 mm)
3D accelerometer and 3D magnetometer module
Features
■ 3 magnetic field channels and 3 acceleration
channels
■ ±2/±4/±8/±12 gauss dynamically selectable
magnetic full-scale
■ ±2/±4/±6/±8/±16 g dynamically selectable
linear acceleration full-scale
■ 16-bit data output
■ SPI / I
■ Analog supply voltage 2.16 V to 3.6 V
■ Power-down mode / low-power mode
■ Programmable interrupt generators for free-
■ Embedded temperature sensor
■ Embedded FIFO
■ ECOPACK
Applications
■ Tilt compensated compass
■ Map rotation
■ Position detection
■ Motion activated functions
■ Free-fall detection
■ Click/double click recognition
■ Pedometer
■ Intelligent power saving for handheld devices
■ Display orientation
■ Gaming and virtual reality input devices
■ Impact recognition and logging
■ Vibration monitoring and compensation
2
C serial interfaces
fall, motion detection and magnetic field
detection
®
, RoHS and “Green” compliant
LSM303D
Datasheet — preliminary data
Description
The LSM303D is a system-in-package featuring a
3D digital linear acceleration sensor and a 3D
digital magnetic sensor.
The LSM303D has linear acceleration full-scales
of ±2g / ±4g / ±6g / ±8g / ±16g and a magnetic
field full-scale of ±2 / ±4 / ±8 / ±12 gauss. All fullscales available are fully selectable by the user.
The LSM303D includes an I
that supports standard and fast mode 100 kHz
and 400 kHz and SPI serial standard interface.
The system can be configured to generate an
interrupt signal for free-fall, motion detection and
magnetic field detection. Thresholds and timing of
interrupt generators are programmable by the end
user on the fly.
Magnetic and accelerometer parts can be
enabled or put into power-down mode separately.
The LSM303D is available in plastic land grid
array package (LGA) and is guaranteed to
operate over an extended temperature range from
-40 °C to +85 °C.
Table 1. Device summary
Part number
Temperature
range [°C]
2
C serial bus interface
Package Packaging
LSM303D -40 to +85 LGA-16 Tray
LSM303DTR -40 to +85 LGA-16
June 2012 Doc ID 023312 Rev 1 1/54
This is preliminar y information on a new product now in development or undergoing evaluation. Details are subject to
change without notice.
Tape and
reel
www.st.com
54

Contents LSM303D
Contents
1 Block diagram and pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.1 Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.2 Pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2 Module specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2.1 Sensor characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2.2 Temperature sensor characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2.3 Electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.4 Communication interface characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2.4.1 SPI - serial peripheral interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2.4.2 Sensor I2C - inter IC control interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2.5 Absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
3 Terminology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
3.1 Set/reset pulse . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
3.2 Sensitivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
3.2.1 Linear acceleration sensor sensitivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
3.2.2 Magnetic sensor sensitivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
3.3 Zero-g level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
3.4 Zero-gauss level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
4 Functionality . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
4.1 Self-test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
4.2 Temperature sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
4.3 FIFO . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
4.4 Factory calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
5 Application hints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
5.1 External capacitors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
5.2 Pull-up resistors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
5.3 Digital Interface power supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
5.4 Soldering information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
2/54 Doc ID 023312 Rev 1

LSM303D Contents
5.5 High-current wiring effects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
6 Digital interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
6.1 I2C serial interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
6.1.1 I2C operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
6.2 SPI bus interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
6.2.1 SPI read . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
6.2.2 SPI write . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
6.2.3 SPI read in 3-wire mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
7 Output register mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
8 Register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
8.1 TEMP_OUT_L (05h), TEMP_OUT_H (06h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
8.2 STATUS_M (07h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
8.3 OUT_X_L_M (08h), OUT_X_H_M (09h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
8.4 OUT_Y_L_M (0Ah), OUT_X_H_M (0Bh) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
8.5 OUT_X_L_M (0Ch), OUT_X_H_M (0Dh) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
8.6 WHO_AM_I (0Fh) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
8.7 INT_CTRL_M (12h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
8.8 INT_SRC_M (13h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
8.9 INT_THS_L_M (14h), INT_THS_H_M (15h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
8.10 OFFSET_X_L_M (16h), OFFSET_X_H_M (17h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
8.11 OFFSET_Y_L_M (18h), OFFSET_Y_H_M (19h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
8.12 OFFSET_Z_L_M (1Ah), OFFSET_Z_H_M (1Bh) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
8.13 REFERENCE_X (1Ch) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
8.14 REFERENCE_Y (1Dh) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
8.15 REFERENCE_Z (1Eh) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
8.16 CTRL0 (1Fh) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
8.17 CTRL1 (20h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
8.18 CTRL2 (21h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
8.19 CTRL3 (22h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
8.20 CTRL4 (23h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
8.21 CTRL5 (24h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Doc ID 023312 Rev 1 3/54

Contents LSM303D
8.22 CTRL6 (25h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
8.23 CTRL7 (26h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
8.24 STATUS_A (27h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
8.25 OUT_X_L_A (28h), OUT_X_H_A (29h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
8.26 OUT_Y_L_A (2Ah), OUT_X_H_A (2Bh) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
8.27 OUT_X_L_A (2Ch), OUT_X_H_A (2Dh) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
8.28 FIFO_CTRL (2Eh) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
8.29 FIFO_SRC (2Fh) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
8.30 IG_CFG1 (30h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
8.31 IG_SRC1 (31h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
8.32 IG_THS1 (32h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
8.33 IG_DUR1 (33h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
8.34 IG_CFG2 (34h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
8.35 IG_SRC2 (35h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
8.36 IG_THS2 (36h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
8.37 IG_DUR2 (37h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
8.38 CLICK_CFG (38h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
8.39 CLICK_SRC (39h) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
8.40 CLICK_THS (3Ah) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
8.41 TIME_LIMIT (3Bh) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
8.42 TIME_LATENCY (3Ch) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
8.43 TIME WINDOW (3Dh) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
8.44 Act_THS (3Eh) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
8.45 Act_DUR (3Fh) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
9 Package Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
10 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
4/54 Doc ID 023312 Rev 1

LSM303D List of tables
List of tables
Table 1. Device summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Table 2. Pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Table 3. Sensor characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Table 4. Temperature sensor characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Table 5. Electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Table 6. SPI slave timing values. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Table 7. I2C slave timing values. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Table 8. Absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Table 9. Serial interface pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 10. I2C terminology. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 11. SAD+read/write patterns. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 12. Transfer when master is writing one byte to slave . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 13. Transfer when master is writing multiple bytes to slave . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Table 14. Transfer when master is receiving (reading) one byte of data from slave . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Table 15. Transfer when master is receiving (reading) multiple bytes of data from slave . . . . . . . . . 23
Table 16. Register address map. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Table 17. STATUS_M register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Table 18. STATUS_M description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Table 19. WHO_AM_I register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Table 20. INT_CTRL_M register. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Table 21. INT_CTRL_M description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Table 22. INT_SRC_M register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Table 23. INT_SRC_M description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Table 24. INT_THS_L_M . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Table 25. INT_THS_H_M . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Table 26. OFFSET_X_L_M . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Table 27. OFFSET_X_H_M . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Table 28. OFFSET_Y_L_M . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Table 29. OFFSET_Y_H_M . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Table 30. OFFSET_Z_L_M . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Table 31. OFFSET_Z_H_M . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Table 32. CTRL0 register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Table 33. CTRL0 description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Table 34. CTRL1 register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Table 35. CTRL1 description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Table 36. Acceleration data rate configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Table 37. CTRL2 register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Table 38. CTRL2 register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Table 39. Acceleration anti-alias filter bandwidth . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Table 40. Acceleration full-scale selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Table 41. CTRL3 register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Table 42. CTRL3 register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Table 43. CTRL4 register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Table 44. CTRL4 register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Table 45. CTRL5 register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Table 46. CTRL5 register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Table 47. Magnetic data rate configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Table 48. CTRL6 register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Doc ID 023312 Rev 1 5/54

List of tables LSM303D
Table 49. CTRL6 register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Table 50. Magnetic full-scale selection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Table 51. CTRL7 register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Table 52. CTRL7 register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Table 53. High-pass filter mode selection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Table 54. Magnetic sensor mode selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Table 55. STATUS_A register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Table 56. STATUS_A description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Table 57. FIFO_CTRL register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Table 58. FIFO_CTRL register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Table 59. FIFO mode configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Table 60. FIFO_SRC register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Table 61. FIFO_SRC description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Table 62. IG_CFG1 register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Table 63. IG_CFG1 register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Table 64. Interrupt mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Table 65. IG_SRC1 register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Table 66. IG_SRC1 register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Table 67. IG_THS1 register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Table 68. IG_THS1 description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Table 69. IG1_DUR1 register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Table 70. IG1_DUR1 register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Table 71. IG_CFG2 register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Table 72. IG_CFG2 register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Table 73. Interrupt mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Table 74. IG_SRC2 register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Table 75. IG_SRC2 register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Table 76. IG2_THS register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Table 77. IG2_THS register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Table 78. IG_DUR2 register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Table 79. IG_DUR2 register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Table 80. CLICK_CFG register. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Table 81. CLICK_CFG description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Table 82. CLICK_SRC register. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Table 83. CLICK_SRC register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Table 84. CLICK_THS register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Table 85. CLICK_SRC register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Table 86. TIME_LIMIT register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Table 87. TIME_LIMIT description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Table 88. TIME_LATENCY register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Table 89. TIME_LATENCY description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Table 90. TIME_WINDOW register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Table 91. TIME_WINDOW description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Table 92. Act_THS register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Table 93. Act_THS register description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Table 94. Act_DUR register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Table 95. Act_DUR description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Table 96. TFLGA 3x3x1.0 16L mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Table 97. Document revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
6/54 Doc ID 023312 Rev 1

LSM303D List of figures
List of figures
Figure 1. Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Figure 2. Pin connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Figure 3. SPI slave timing diagram (2). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Figure 4. I2C slave timing diagram (3) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Figure 5. LSM303D electrical connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Figure 6. Read and write protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Figure 7. SPI read protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Figure 8. Multiple byte SPI read protocol (2-byte example) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Figure 9. SPI write protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Figure 10. Multiple byte SPI write protocol (2-byte example). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Figure 11. SPI read protocol in 3-wire mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Figure 12. TFLGA 3x3x1.0 16L mechanical drawing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Doc ID 023312 Rev 1 7/54
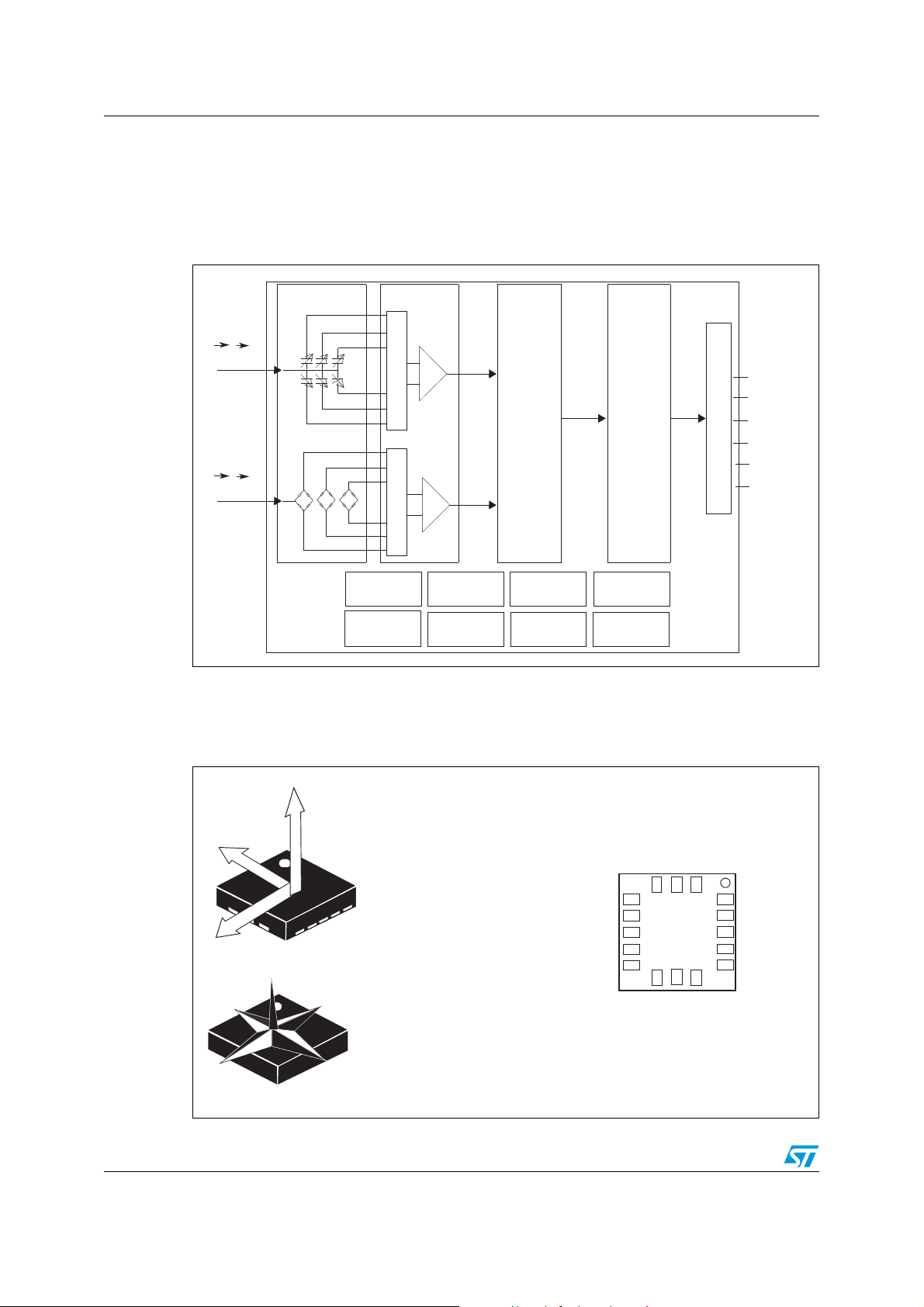
Block diagram and pin description LSM303D
Y+
Z+
Y-
Z-
X+
X-
MUX
CS
SCL/SPC
I (a)
+
-
CHARGE
AMPLIFIER
Sensing Block Sensing Interface
A/D
Control
Logic
converter
DI
SPI / I2C
SDA/SDI/SDO
SDO/SA0
MUX
I (M)
+
-
CHARGE
AMPLIFIER
Y+
Z+
Y-
Z-
X+
X-
INTERRUPT GEN.
CLOCK
TRIMMING
CIRCUITS
REFERENCE
OFFSET
CIRCUITS
BUILT-IN
CIRCUITS
SET/RESET
TEMPERATURE
FIFO
SENSOR
INT1
INT2
AM12676V1
DIRECTION OF
DETECTABLE
MAGNETIC FIELDS
DIRECTION OF
DETECTABLE
ACCELERATIONS
TOP VIEW
1
5
9
13
(BOTTOM VIEW)
Y
1
X
Z
Pin 1 indicator
X
Z
Y
TOP VIEW
AM12677V1
1 Block diagram and pin description
1.1 Block diagram
Figure 1. Block diagram
1.2 Pin description
Figure 2. Pin connection
8/54 Doc ID 023312 Rev 1
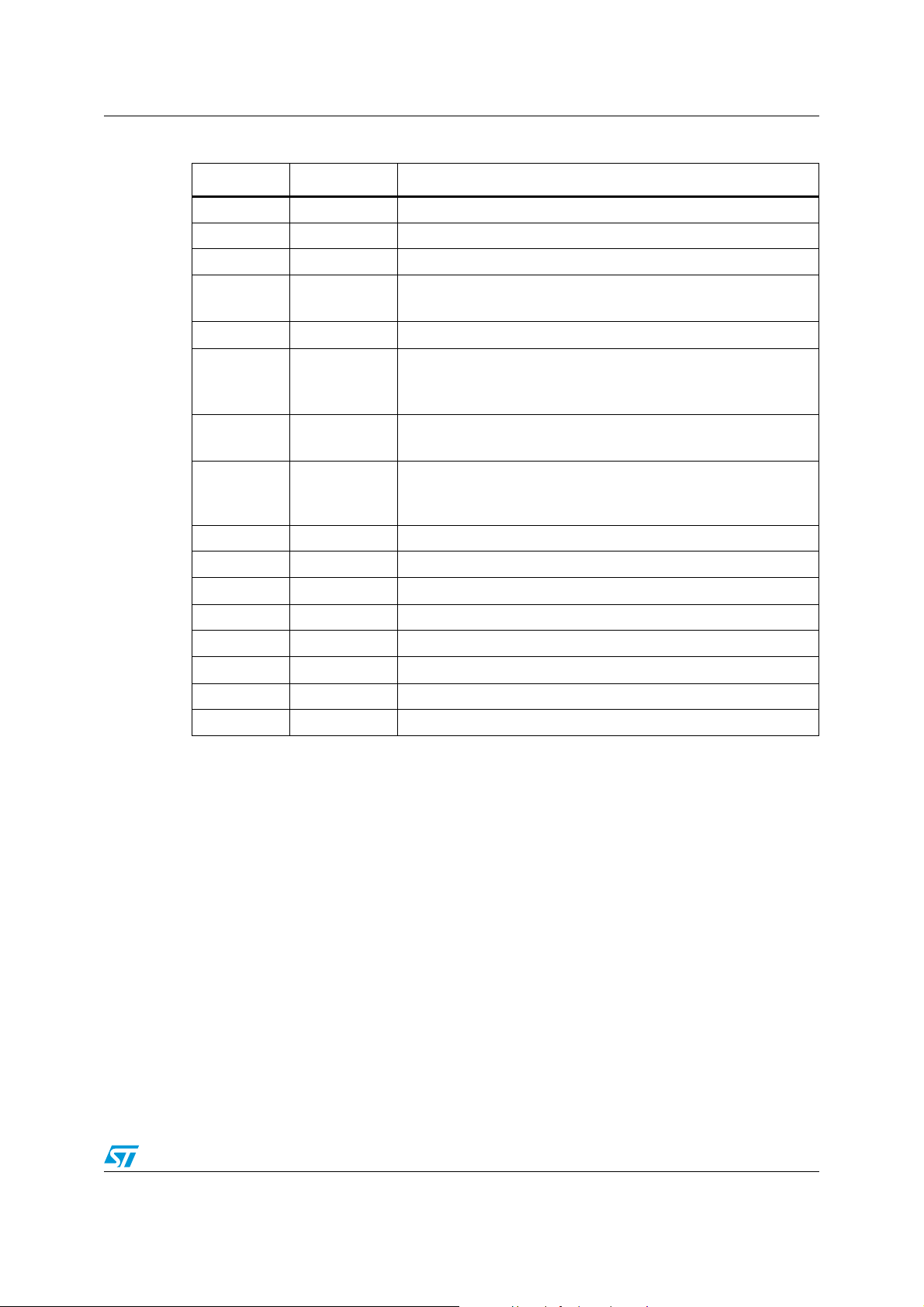
LSM303D Block diagram and pin description
Table 2. Pin description
Pin# Name Function
1 Vdd_IO Power supply for I/O pins
2 SETC S/R capacitor connection (C2)
3 SETP S/R capacitor connection (C2)
4
SCL
SPC
5GND0 V supply
SDA
6
SDI
SDO
2
I
C serial clock (SCL)
SPI serial port clock (SPC)
2
I
C serial data (SDA)
SPI serial data input (SDI)
3-wire interface serial data output (SDO)
7
SDO
SA0
SPI serial data output (SDO)
2
I
C less significant bit of the device address (SA0)
SPI enable
8CS
2
C/SPI mode selection (1: SPI idle mode / I2C communication
I
enabled; 0: SPI communication mode / I
9 INT 2 Interrupt 2
10 Reserved Connect to GND
11 INT 1 Interrupt 1
12 GND 0 V supply
13 GND 0 V supply
14 Vdd Power supply
15 C1 Capacitor connection (C1)
16 GND 0 V supply
2
C disabled)
Doc ID 023312 Rev 1 9/54
Module specifications LSM303D
2 Module specifications
2.1 Sensor characteristics
@ Vdd = 2.5 V, T = 25 °C unless otherwise noted
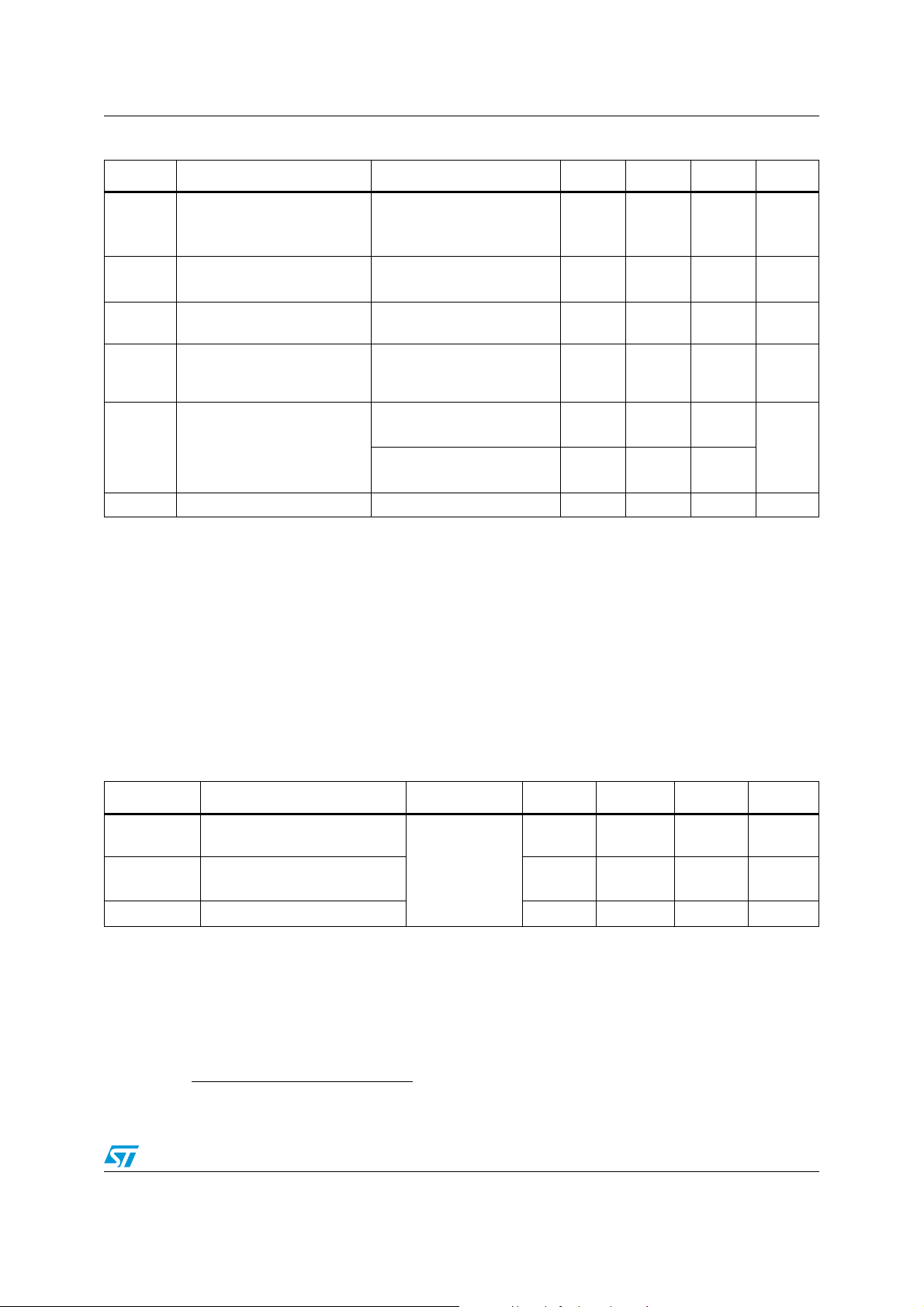
Table 3. Sensor characteristics
Symbol Parameter Test conditions Min. Typ.
LA_FS
M_FS Magnetic measurement range
LA_So Linear acceleration sensitivity
M_GN Magnetic sensitivity
LA_TCSo
M_TCSo
LA_TyOff
LA_TCOff
LA_An
Linear acceleration
measurement range
Linear acceleration sensitivity
change vs. temperature
Magnetic sensitivity change
vs. temperature
Linear acceleration typical
zero-g level offset
accuracy
Linear acceleration zero-g
level change vs. temperature
Linear acceleration noise
density
(3),(4)
(2)
Linear acceleration FS=±2g 0.061
Linear acceleration FS=±4g 0.122
Linear acceleration FS=±6g 0.183
Linear acceleration FS=±8g 0.244
Linear acceleration FS=±16g 0.732
Magnetic FS=±2gauss 0.080
Magnetic FS=±4gauss 0.160
Magnetic FS=±8gauss 0.320
Magnetic FS=±12gauss 0.479
Max. delta from 25 °C ±0.5 m
Linear acceleration FS=2g;
ODR = 100 Hz
(a)
.
(1)
Max. Unit
±2
±4
±6
±8
±16
±2
±4
±8
±12
±0.01 %/°C
±0.05 %/°C
±60 mg
g
gauss
mg/LSB
mgauss/
LSB
g/°C
150
ug/
sqrt(Hz)
a. The product is factory calibrated at 2.5 V. The operational power supply range is from 2.16 V to 3.6 V.
10/54 Doc ID 023312 Rev 1
LSM303D Module specifications
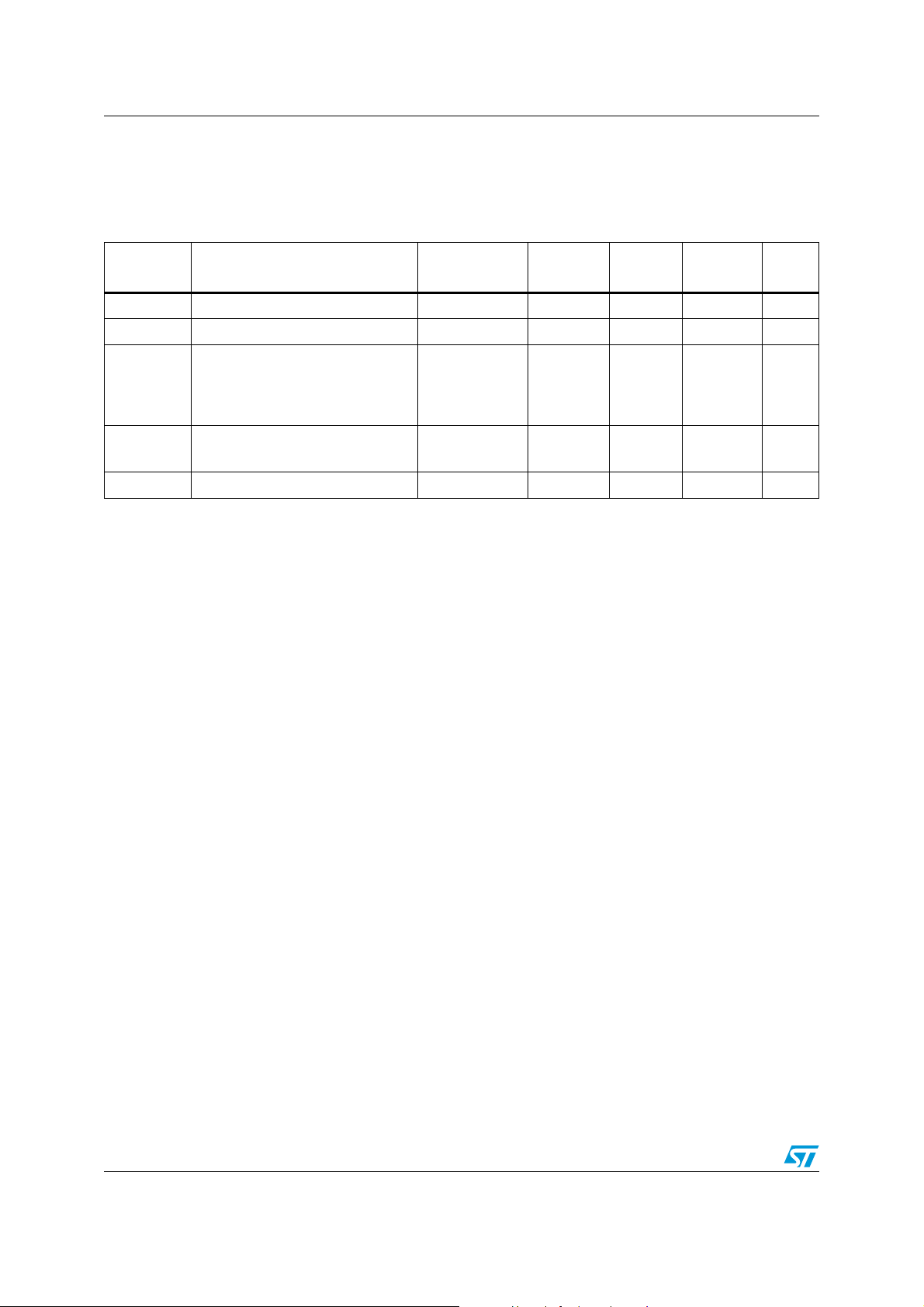
Table 3. Sensor characteristics (continued)
Symbol Parameter Test conditions Min. Typ.
(1)
Max. Unit
M_R Magnetic noise density
M_CAS
Magnetic cross-axis
sensitivity
M_EF Maximum exposed field
Magnetic FS = 2gauss;
LR setting
CTRL5 (M_RES [1,0]) = 00b
Cross field = 0.5 gauss
Applied = ±3 gauss
No permitting effect on zero
reading
5
±1
10000 gauss
mgauss/
RMS
%FS/
gauss
Sensitivity starts to degrade.
M_DF Magnetic disturbing field
LA_ST
Linear acceleration self-test
positive difference
(6)
Automatic S/R pulse restores
the sensitivity
(5)
±2g range, X, Y-axis
AST = 1 see Table 37
±2g range, Z-axis
AST = 1 see Table 37
70
70
20 gauss
1700
1700
Top Operating temperature range -40 +85 °C
1. Typical specifications are not guaranteed.
2. Verified by wafer level test and measurement of initial offset and sensitivity.
3. Typical zero-g level offset value after MSL3 preconditioning.
4. Offset can be eliminated by enabling the built-in high-pass filter.
5. Set/reset pulse is automatically applied at each conversion cycle.
“Self-test output change” is defined as: OUTPUT[mg]
6.
(CTRL5 AST bit =1)
- OUTPUT[mg]
(
CTRL5 AST bit =0
.
)
mg
2.2 Temperature sensor characteristics
@ Vdd = 2.5 V, T = 25 °C unless otherwise noted
Table 4. Temperature sensor characteristics
Symbol Parameter Test conditions Min. Typ.
TSDr
TODR Temperature refresh rate
Top Operating temperature range -40 +85 °C
1. Typical specifications are not guaranteed.
2. Refer to Table 47: Magnetic data rate configuration.
Temperature sensor output
change vs. temperature
-
b. The product is factory calibrated at 2.5 V.
(b)
.
(1)
8 LSB/°C
M_ODR
(2)
[2:0]
Max. Unit
Hz
Doc ID 023312 Rev 1 11/54
Module specifications LSM303D
2.3 Electrical characteristics
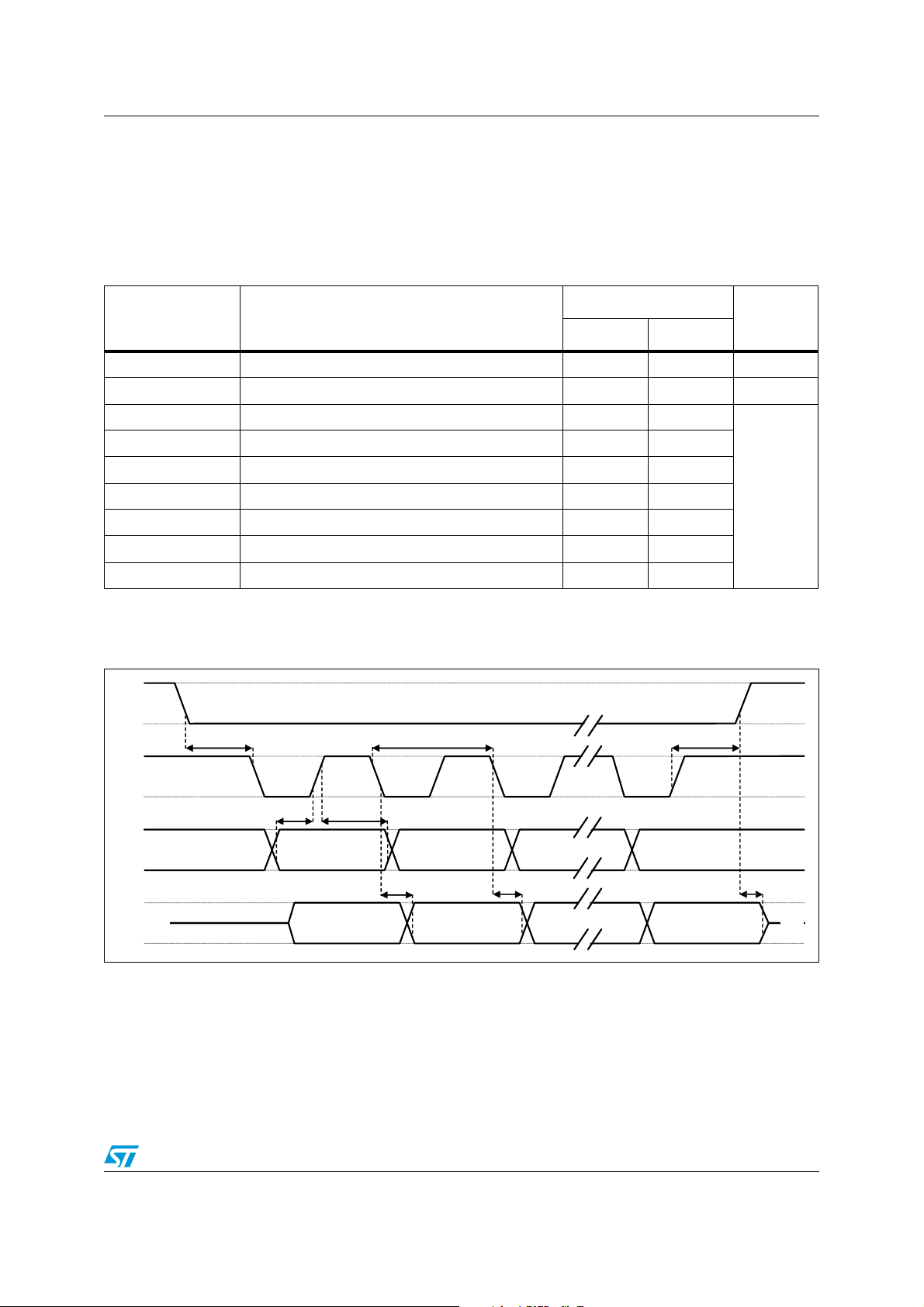
@ Vdd = 2.5 V, T = 25 °C unless otherwise noted.
Table 5. Electrical characteristics
Symbol Parameter
Tes t
conditions
Min. Typ.
(1)
Max. Unit
Vdd Supply voltage 2.16 3.6 V
Vdd_IO Module power supply for I/O 1.71 1.8 Vdd+0.1
LR setting
Idd
eCompass
in normal mode
(2)
current consumption
(3)
CTRL5 (M_RES
[1,0]) = 00b, see
300 µA
Ta bl e 4 5
IddSL
Current consumption in
power-down
(4)
1µA
Top Operating temperature range -40 +85
1. Typical specifications are not guaranteed.
2. eCompass
3. Magnetic sensor setting ODR =6.25 Hz, accelerometer sensor ODR = 50 Hz and magnetic high resolution setting.
4. Linear accelerometer and magnetic sensor in power-down mode.
: accelerometer - magnetic sensor.
°C
12/54 Doc ID 023312 Rev 1
LSM303D Module specifications
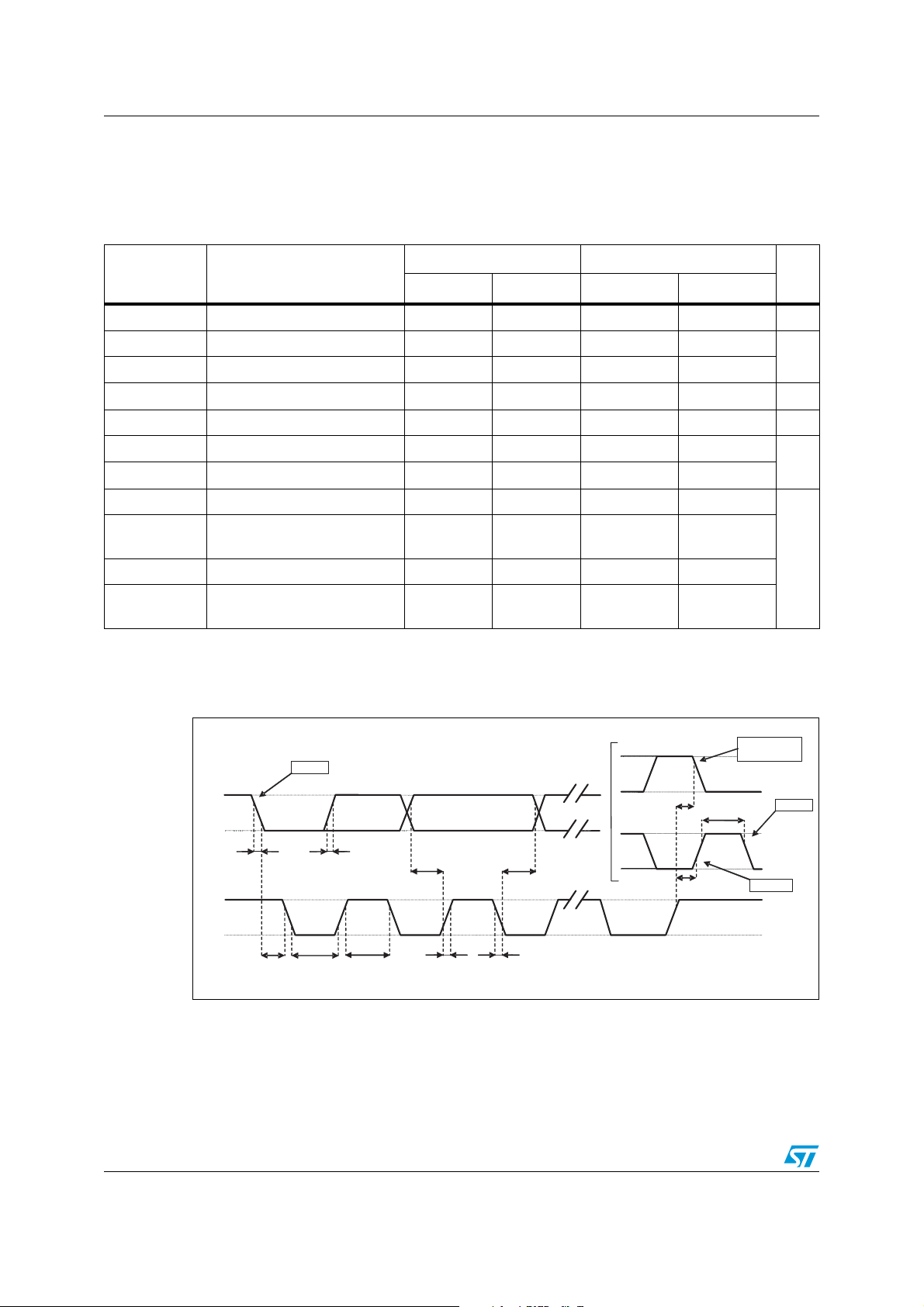
SPC
CS
SDI
SDO
t
su(CS)
t
v(SO)
t
h(SO)
t
h(SI)
t
su(SI)
t
h(CS)
t
dis(SO)
t
c(SPC)
MSB IN
MSB OUT
LSB OUT
LSB IN
(3)
(3)
(3)
(3)
(3)
(3)
(3)
(3)
2.4 Communication interface characteristics
2.4.1 SPI - serial peripheral interface
Subject to general operating conditions for Vdd and Top.
Table 6. SPI slave timing values
(1)
Val ue
Symbol Parameter
Min. Max.
tc(SPC) SPI clock cycle 100 ns
fc(SPC) SPI clock frequency 10 MHz
tsu(CS) CS setup time 5
th(CS) CS hold time 20
tsu(SI) SDI input setup time 5
th(SI) SDI input hold time 15
tv(SO) SDO valid output time 50
th(SO) SDO output hold time 5
tdis(SO) SDO output disable time 50
Unit
ns
1. Values are guaranteed at 10 MHz clock frequency for SPI with both 4 and 3 wires, based on characterization results, not
tested in production.
(2)
Figure 3. SPI slave timing diagram
2. Measurement points are done at 0.2·Vdd_IO and 0.8·Vdd_IO, for both input and output ports.
Doc ID 023312 Rev 1 13/54
Module specifications LSM303D
SD A
SCL
t
f(SD A )
t
su(SP)
t
w(SCLL)
t
su(SD A)
t
r(SDA )
t
su(SR)
t
h(ST)
t
w(SCLH )
t
h(SDA )
t
r(SCL)
t
f(SCL)
t
w(SP:SR)
STAR T
REPEATED
STA RT
STO P
STA RT
2.4.2 Sensor I2C - inter IC control interface
Subject to general operating conditions for Vdd and Top.
Table 7. I2C slave timing values
Symbol Parameter
I2C standard mode
(1)
I2C fast mode
Min. Max. Min. Max.
(1)
Unit
f
(SCL)
t
w(SCLL)
t
w(SCLH)
t
su(SDA)
t
h(SDA)
t
r(SDA) tr(SCL)
t
f(SDA) tf(SCL)
t
h(ST)
t
su(SR)
t
su(SP)
t
w(SP:SR)
SCL clock frequency 0 100 0 400 kHz
SCL clock low time 4.7 1.3
SCL clock high time 4.0 0.6
SDA setup time 250 100 ns
SDA data hold time 0 3.45 0 0.9 µs
SDA and SCL rise time 1000 20 + 0.1C
SDA and SCL fall time 300 20 + 0.1C
START condition hold time 4 0.6
Repeated START condition
setup time
4.7 0.6
STOP condition setup time 4 0.6
Bus free time between STOP
and START condition
4.7 1.3
1. Data based on standard I2C protocol requirement, not tested in production.
2. Cb = total capacitance of one bus line, in pF.
Figure 4. I
2
C slave timing diagram
(3)
µs
(2)
b
(2)
b
300
ns
300
µs
3. Measurement points are done at 0.2·Vdd_IO and 0.8·Vdd_IO, for both ports.
14/54 Doc ID 023312 Rev 1
LSM303D Module specifications
This is a mechanical shock sensitive device, improper handling can cause permanent
damage to the part
This is an ESD sensitive device, improper handling can cause permanent damage to
the part
2.5 Absolute maximum ratings
Stresses above those listed as “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage
to the device. This is a stress rating only and functional operation of the device under these
conditions is not implied. Exposure to maximum rating conditions for extended periods may
affect device reliability.
Table 8. Absolute maximum ratings
Symbol Ratings Maximum value Unit
Vdd Supply voltage -0.3 to 4.8 V
Vdd_IO I/O pins supply voltage -0.3 to 4.8 V
Vin
Input voltage on any control pin (SCL/SPC,
SDA/SDI/SDO, SDO/SA0, CS)
-0.3 to Vdd_IO +0.3 V
A
A
T
POW
UNP
T
OP
STG
Acceleration (any axis, powered, Vdd = 2.5 V)
Acceleration (any axis, unpowered)
Operating temperature range -40 to +85 °C
Storage temperature range -40 to +125 °C
Note: Supply voltage on any pin should never exceed 4.8 V.
3,000 for 0.5 ms g
10,000 for 0.1 ms g
3,000 for 0.5 ms g
10,000 for 0.1 ms g
Doc ID 023312 Rev 1 15/54

Terminology LSM303D
3 Terminology
3.1 Set/reset pulse
The set/reset pulse is an automatic operation performed before each magnetic acquisition
cycle to de-gauss the sensor and to ensure alignment of the magnetic dipoles and therefore
the linearity of the sensor itself.
3.2 Sensitivity
3.2.1 Linear acceleration sensor sensitivity
Sensitivity describes the gain of the sensor and can be determined, for example, by applying
1 g acceleration to it. As the sensor can measure DC accelerations this can be done easily
by pointing the axis of interest towards the center of the earth, noting the output value,
rotating the sensor by 180 degrees (pointing to the sky) and noting the output value again.
By doing so, ±1 g acceleration is applied to the sensor. Subtracting the larger output value
from the smaller one, and dividing the result by 2, leads to the actual sensitivity of the
sensor. This value changes very little over temperature and also time. The sensitivity
tolerance describes the range of sensitivities of a large population of sensors.
3.2.2 Magnetic sensor sensitivity
Sensitivity describes the gain of the sensor and can be determined, for example, by applying
a magnetic field of 1 gauss to it.
3.3 Zero-g level
Zero-g level offset (TyOff) describes the deviation of an actual output signal from the ideal
output signal if no acceleration is present. A sensor in a steady-state on a horizontal surface
measures 0 g in X-axis and 0 g in Y-axis, whereas the Z-axis measures 1 g. The output is
ideally in the middle of the dynamic range of the sensor (content of OUT registers 00h, data
expressed as 2’s complement). A deviation from the ideal value in this case is called Zero-g
offset. Offset is, to some extent, a result of stress to MEMS sensor and therefore the offset
can slightly change after mounting the sensor onto a printed circuit board or exposing it to
extensive mechanical stress. Offset changes little over temperature, see “Zero-g level
change vs. temperature”. The Zero-g level tolerance (TyOff) describes the standard
deviation of the range of Zero-g levels of a population of sensors.
3.4 Zero-gauss level
Zero-gauss level offset describes the deviation of an actual output signal from the ideal
output if no magnetic field is present. Thanks to the set/reset pulse and to the magnetic
sensor read-out chain, the offset is dynamically cancelled. The Zero-gauss level does not
show any dependencies from temperature and power supply.
16/54 Doc ID 023312 Rev 1

LSM303D Functionality
4 Functionality
4.1 Self-test
Self-test allows to check the linear acceleration sensor functionality without moving it. The
self-test function is off when the self-test bit (ST) is programmed to ‘0‘. When the self-test bit
is programmed to ‘1’, an actuation force is applied to the sensor, simulating a definite input
acceleration. In this case the sensor outputs exhibit a change in their DC levels which are
related to the selected full-scale through the device sensitivity. When self-test is activated,
the device output level is given by the algebraic sum of the signals produced by the
acceleration acting on the sensor and by the electrostatic test-force. If the output signals
change within the amplitude specified inside Section 2.1, then the sensor is working
properly and the parameters of the interface chip are within the defined specifications.
4.2 Temperature sensor
The LSM303D features an internal temperature sensor. Temperature data can be enabled
by setting the TEMP_EN bit on the CTRL5 (24h) register to 1.
Both TEMP_OUT_H and TEMP_OUT_L registers must be read.
Temperature data is stored inside TEMP_OUT_L (05h), TEMP_OUT_H (06h) as 2’s
complement data in 12-bit format, right justified.
The output data rate of the temperature sensor is set by M_ODR [2:0] in CTRL5 (24h) and is
equal to the magnetic sensor output data rate.
4.3 FIFO
The LSM303D embeds an acceleration data FIFO for each of the three output channels, X,
Y and Z. This allows a consistent power saving for the system, as the host processor does
not need to continuously poll data from the sensor, but it can wake up only when needed
and burst the significant data out from the FIFO. This buffer can work according to four
different modes: Bypass mode, FIFO mode, Stream mode and Stream-to-FIFO mode. Each
mode is selected by the FIFO_MODE bits. Programmable threshold level, FIFO_empty or
FIFO_Full events can be enabled to generate dedicated interrupts on the INT1/2 pin.
Bypass mode
In Bypass mode, the FIFO is not operational and for this reason it remains empty. As
described in Figure 5, for each channel only the first address is used. The remaining FIFO
slots are empty.
FIFO mode
In FIFO mode, data from X, Y and Z channels are stored in the FIFO. A FIFO threshold
interrupt can be enabled in order to be raised when the FIFO is filled to the level specified by
the internal register. The FIFO continues filling until it is full. When full, the FIFO stops
collecting data from the input channels.
Doc ID 023312 Rev 1 17/54

Functionality LSM303D
Stream mode
In Stream mode, data from X, Y and Z measurements are stored in the FIFO. A FIFO
threshold interrupt can be enabled and set as in FIFO mode.The FIFO continues filling until
it’s full. When full, the FIFO discards the older data as the new arrive.
Stream-to-FIFO mode
In Stream-to-FIFO mode, data from X, Y and Z measurements are stored in the FIFO. A
FIFO threshold interrupt can be enabled in order to be raised when the FIFO is filled to the
level specified by the internal register. The FIFO continues filling until it’s full. When full, the
FIFO discards the older data as the new arrive. Once a trigger event occurs, the FIFO starts
operating in FIFO mode.
Bypass-to-Stream mode
In Bypass-to-Stream mode, the FIFO starts operating in Bypass mode and once a trigger
event occurs (related to IG_CFG1 (30h) register events), the FIFO starts operating in
Stream mode.
Retrieve data from FIFO
FIFO data is read through OUT_X_A, OUT_Y_A and OUT_Z_A registers. When the FIFO is
in Stream, Trigger or FIFO mode, a read operation to the OUT_X_A, OUT_Y_A or
OUT_Z_A registers provides the data stored in the FIFO. Each time data is read from the
FIFO, the oldest X, Y and Z data are placed in the OUT_X_A, OUT_Y_A and OUT_Z_A
registers and both single read and read_burst operations can be used.
4.4 Factory calibration
The IC interface is factory calibrated. The trimming values are stored inside the device by a
non-volatile memory. Anytime the device is turned on, the trimming parameters are
downloaded into the registers to be used during normal operation. This allows the user to
use the device without further calibration.
18/54 Doc ID 023312 Rev 1

LSM303D Application hints
CS
C3= 10µF
Vdd
C4 = 100nF
GND
Vdd_IO
SDO/SA0
SDA/SDI/SDO
INT 1
SCL/SPC
Digital signal from/to signal controller. Signal’s levels are defined by proper selection of Vdd_IO
1
5
8
13
TOP VIEW
6
9
1416
9
5
INT 2
C1= 4.7µF
C2=0.22µF
AM12678V1
5 Application hints
Figure 5. LSM303D electrical connection
5.1 External capacitors
The C1 and C2 external capacitors should be low SR value ceramic type construction (typ.
suggested value 200 mΩ). Reservoir capacitor C1 is nominally 4.7 µF in capacitance, with
the set/reset capacitor C2 nominally 0.22 µF in capacitance.
The device core is supplied through the Vdd line. Power supply decoupling capacitors
(C4=100 nF ceramic, C3=10 µF Al) should be placed as near as possible to the supply pin
of the device (common design practice). All the voltage and ground supplies must be
present at the same time to have proper behavior of the IC (refer to Figure 5).
The functionality of the device and the measured acceleration/magnetic field data is
selectable and accessible through the I
5.2 Pull-up resistors
The functions, the threshold and the timing of the two interrupt pins (INT1 and INT2) can be
completely programmed by the user through the I
If an I2C interface is used, pull-up resistors (suggested value 10 kΩ) must be placed on the
2
two I
C bus lines.
2
C/SPI interfaces.
Doc ID 023312 Rev 1 19/54
2
C/SPI interfaces.

Application hints LSM303D
5.3 Digital Interface power supply
This digital interface, dedicated to the linear acceleration and to the magnetic field signal, is
capable of operating with a standard power supply (Vdd) or using a dedicated power supply
(Vdd_IO).
5.4 Soldering information
The LGA package is compliant with ECOPACK®, RoHS and “Green” standards.
It is qualified for soldering heat resistance according to JEDEC J-STD-020.
Leave “Pin 1 Indicator” unconnected during soldering.
Land pattern and soldering recommendations are available at www.st.com/mems
5.5 High-current wiring effects
High current in wiring and printed circuit trace can be the cause of errors in magnetic field
measurements for compassing.
Conductor generated magnetic fields add to the earth’s magnetic field creating errors in
compass heading computations.
Keep currents higher than 10 mA a few millimeters further away from the sensor IC.
.
20/54 Doc ID 023312 Rev 1

LSM303D Digital interfaces
6 Digital interfaces
The registers embedded in the LSM303D may be accessed through both the I2C and SPI
serial interfaces. The latter may be SW-configured to operate either in 3-wire or 4-wire
interface mode.
The serial interfaces are mapped onto the same pins. To select/exploit the I
CS line must be tied high (i.e connected to Vdd_IO).
Table 9. Serial interface pin description
Pin name Pin description
2
C interface, the
CS
SCL/SPC
SDA/SDI/SDO
SDO/SA0
I2C/SPI mode selection (1: SPI idle mode / I2C communication enabled; 0: SPI
communication mode / I
2
I
C serial clock (SCL)
SPI serial port clock (SPC)
2
I
C serial data (SDA)
SPI serial data input (SDI)
3-wire interface serial data output (SDO)
SPI serial data output (SDO)
2
I
C less significant bit of the device address (SA0)
6.1 I2C serial interface
The LSM303D I2C is a bus slave. The I2C is employed to write data into registers whose
content can also be read back.
The relevant I
Table 1 0 . I2C terminology
Transmitter The device which sends data to the bus
Receiver The device which receives data from the bus
2
C terminology is given in the table below.
Term Description
2
C disabled)
Master
Slave The device addressed by the master
The device which initiates a transfer, generates clock signals and terminates a
transfer
There are two signals associated with the I2C bus: the serial clock line (SCL) and the serial
data line (SDA). The latter is a bi-directional line used for sending and receiving the data
to/from the interface. Both lines must be connected to Vdd_IO through external pull-up
resistors. When the bus is free, both lines are high.
2
The I
C interface is compliant with fast mode (400 kHz) I2C standards as well as with normal
mode.
Doc ID 023312 Rev 1 21/54

Digital interfaces LSM303D
6.1.1 I2C operation
The transaction on the bus is started through a START (ST) signal. A START condition is
defined as a HIGH to LOW transition on the data line while the SCL line is held HIGH. After
this has been transmitted by the master, the bus is considered busy. The next byte of data
transmitted after the START condition contains the address of the slave in the first 7 bits and
the eighth bit tells whether the master is receiving data from the slave or transmitting data to
the slave. When an address is sent, each device in the system compares the first seven bits
after a START condition with its address. If they match, the device considers itself
addressed by the master.
The slave address (SAD) associated to the LSM303D is 00111xxb, whereas the xx bits are
modified by the SDO/SA0 pin in order to modify the device address. If the SDO/SA0 pin is
connected to the voltage supply, the address is 0011101b, otherwise, if the SDO/SA0 pin is
connected to ground, the address is 0011110b. This solution permits the connection and
addressing of two different accelerometers to the same I
Data transfer with acknowledge is mandatory. The transmitter must release the SDA line
during the acknowledge pulse. The receiver must then pull the data line low so that it
remains stable low during the high period of the acknowledge clock pulse. A receiver which
has been addressed is obliged to generate an acknowledge after each byte of data
received.
2
The I
C embedded in the LSM303D behaves as a slave device and the following protocol
must be adhered to. After the START condition (ST) a slave address is sent, once a slave
acknowledge (SAK) has been returned, an 8-bit sub-address is transmitted: the 7 LSb
represent the actual register address while the MSb enables address auto-increment. If the
MSb of the SUB field is 1, the SUB (register address) is automatically incremented to allow
multiple data read/write.
2
C lines.
The slave address is completed with a read/write bit. If the bit is ‘1’ (read), a repeated
START (SR) condition must be issued after the two sub-address bytes; if the bit is ‘0’ (write)
the master transmits to the slave with direction unchanged. Ta b le 1 1 explains how the
SAD+read/write bit pattern is composed, listing all the possible configurations.
Table 11. SAD+read/write patterns
Command SDO/SA0 pin SAD[6:2] SAD[1:0] R/W SAD+R/W
Read 0 00111 10 1 3D
Write 0 00111 10 0 3C
Read 1 00111 01 1 3B
Write 1 00111 01 0 3A
Table 12. Transfer when master is writing one byte to slave
Master ST SAD + W SUB DATA SP
Slave SAK SAK SAK
22/54 Doc ID 023312 Rev 1

LSM303D Digital interfaces
Table 13. Transfer when master is writing multiple bytes to slave
Master ST SAD + W SUB DATA DATA SP
Slave SAK SAK SAK SAK
Table 14. Transfer when master is receiving (reading) one byte of data from slave
Master ST SAD + W SUB SR SAD + R NMAK SP
Slave SAK SAK SAK DATA
Table 15. Transfer when master is receiving (reading) multiple bytes of data from slave
Master ST SAD+W SUB SR SAD+R MAK MAK NMAK SP
Slave SAK SAK SAK DATA DATA DATA
Data is transmitted in byte format (DATA). Each data transfer contains 8 bits. The number of
bytes sent per transfer is unlimited. Data is transferred with the most significant bit (MSb)
first. If a receiver cannot receive another complete byte of data until it has performed some
other function, it can hold the clock line, SCL, LOW to force the transmitter into a wait state.
Data transfer only continues when the receiver is ready for another byte and releases the
data line. If a slave receiver does not acknowledge the slave address (i.e. it is not able to
receive because it is performing some real-time function) the data line must be left HIGH by
the slave. The master can then abort the transfer. A low to high transition on the SDA line
while the SCL line is HIGH is defined as a STOP condition. Each data transfer must be
terminated by the generation of a STOP (SP) condition.
In order to read multiple bytes, it is necessary to assert the most significant bit of the subaddress field. In other words, SUB(7) must be equal to ‘1’ while SUB(6-0) represents the
address of the first register to be read.
In the communication format presented, MAK is master acknowledge and NMAK is no
master acknowledge.
6.2 SPI bus interface
The SPI is a bus slave. The SPI allows writing and reading the registers of the device.
The serial interface interacts with the outside world through 4 wires: CS, SPC, SDI and
SDO.
Doc ID 023312 Rev 1 23/54

Digital interfaces LSM303D
CS
SPC
SDI
SDO
RW
AD5 AD4 AD3 AD2 AD1 AD0
DI7 DI6 DI5 DI4 DI3 DI2 DI1 DI0
DO7 DO6 DO5 DO4 DO3 DO2 DO1 DO0
MS
AM10129V1
Figure 6. Read and write protocol
CS is the serial port enable and is controlled by the SPI master. It goes low at the start of the
transmission and goes back high at the end. SPC is the serial port clock and it is controlled
by the SPI master. It is stopped high when CS is high (no transmission). SDI and SDO are
respectively the serial port data input and output. These lines are driven at the falling edge
of SPC and should be captured at the rising edge of SPC.
Both the read register and write register commands are completed in 16 clock pulses or in
multiples of 8 in the case of multiple byte read/write. Bit duration is the time between two
falling edges of SPC. The first bit (bit 0) starts at the first falling edge of SPC after the falling
edge of CS while the last bit (bit 15, bit 23, ...) starts at the last falling edge of SPC just
before the rising edge of CS.
bit 0: RW
bit. When 0, the data DI(7:0) is written to the device. When 1, the data DO(7:0)
from the device is read. In the latter case the chip drives SDO at the start of bit 8.
bit 1: MS
bit. When 0, the address remains unchanged in multiple read/write commands.
When 1, the address is auto-incremented in multiple read/write commands.
bit 2-7: address AD(5:0). This is the address field of the indexed register.
bit 8-15: data DI(7:0) (write mode). This is the data that is written to the device (MSb first).
bit 8-15: data DO(7:0) (read mode). This is the data that is read from the device (MSb first).
In multiple read/write commands, further blocks of 8 clock periods are added. When the MS
bit is 0, the address used to read/write data remains the same for every block. When the MS
bit is 1, the address used to read/write data is incremented at every block.
The function and the behavior of SDI and SDO remain unchanged.
24/54 Doc ID 023312 Rev 1

LSM303D Digital interfaces
CS
SPC
SDI
SDO
RW
DO7 DO6 DO5DO4 DO3 DO2 DO1 DO0
AD5 AD4 AD3 AD2 AD1 AD0
MS
AM10130V1
C S
SPC
SDI
SDO
RW
DO7DO6DO5DO4DO3 DO 2 DO1 DO 0
AD5 AD4AD3 AD2 AD1 AD0
DO15 DO 14 DO 13 DO 12 DO11 DO 10 D O9 D O8
M S
AM10131V1
6.2.1 SPI read
Figure 7. SPI read protocol
The SPI read command is performed with 16 clock pulses. The multiple byte read command
is performed by adding blocks of 8 clock pulses to the previous one.
bit 0: READ bit. The value is 1.
bit 1: MS
bit. When 0, do not increment address; when 1, increment address in multiple
reading.
bit 2-7: address AD(5:0). This is the address field of the indexed register.
bit 8-15: data DO(7:0) (read mode). This is the data that is read from the device (MSb first).
bit 16-... : data DO(...-8). Further data in multiple byte reading.
Figure 8. Multiple byte SPI read protocol (2-byte example)
Doc ID 023312 Rev 1 25/54

Digital interfaces LSM303D
CS
SPC
SDI
RW
DI7 DI6 DI5 DI4 DI3 DI2 DI 1 DI0
AD5 AD 4 AD 3 AD2 AD 1 AD0MS
AM10132V1
CS
SPC
SDI
RW
AD5 AD4 AD3 AD2 AD1 AD0
DI7 DI6 DI5 DI4 DI3 DI 2 DI1 DI0 DI15 D I1 4 DI13 DI12 DI 11 DI10 DI 9 DI8
MS
AM10133V1
6.2.2 SPI write
Figure 9. SPI write protocol
The SPI write command is performed with 16 clock pulses. The multiple byte write
command is performed by adding blocks of 8 clock pulses to the previous one.
bit 0: WRITE bit. The value is 0.
bit 1: MS
bit. When 0, do not increment address; when 1, increment address in multiple
writing.
bit 2 -7: address AD(5:0). This is the address field of the indexed register.
bit 8-15: data DI(7:0) (write mode). This is the data that is written to the device (MSb first).
bit 16-... : data DI(...-8). Further data in multiple byte writing.
Figure 10. Multiple byte SPI write protocol (2-byte example)
6.2.3 SPI read in 3-wire mode
3-wire mode is entered by setting the bit SIM (SPI serial interface mode selection) to ‘1’ in
CTRL2 (21h).
26/54 Doc ID 023312 Rev 1

LSM303D Digital interfaces
CS
SPC
SDI/O
RW
DO7 DO6 DO5 DO4 DO3 DO 2 DO 1 DO 0
AD5 AD 4 AD3 AD2 AD1 AD 0MS
AM10134V1
Figure 11. SPI read protocol in 3-wire mode
The SPI read command is performed with 16 clock pulses:
bit 0: READ bit. The value is 1.
bit 1: MS
bit. When 0, do not increment address; when 1, increment address in multiple
reading.
bit 2-7: address AD(5:0). This is the address field of the indexed register.
bit 8-15: data DO(7:0) (read mode). This is the data that is read from the device (MSb first).
Multiple read command is also available in 3-wire mode.
Doc ID 023312 Rev 1 27/54

Output register mapping LSM303D
7 Output register mapping
The table below provides a listing of the 8-bit registers embedded in the device, and the
related addresses:
Table 16. Register address map
Register address
Name Type
Hex Binary
Reserved -- 00-04 -- -- Reserved
TEMP_OUT_L r 05 000 0101 Output
TEMP_OUT_H r 06 000 0110 Output
STATUS_M r 07 000 0111 Output
OUT_X_L_M r 08 000 1000 Output
OUT_X_H_M r 09 000 1001 Output
OUT_Y_L_M r 0A 000 1010 Output
OUT_Y_H_M r 0B 000 1011 Output
Default Comment
OUT_Z_L_M r 0C 000 1100 Output
OUT_Z_H_M r 0D 000 1101 Output
Reserved -- 0E 000 1110 -- Reserved
WHO_AM_I r 0F 000 1111 01001001
Reserved -- 10-11 -- -- Reserved
INT_CTRL_M rw 12 001 0010 11101000
INT_SRC_M r 13 001 0011 Output
INT_THS_L_M rw 14 001 0100 00000000
INT_THS_H_M rw 15 001 0101 00000000
OFFSET_X_L_M rw 16 001 0110 00000000
OFFSET_X_H_M rw 17 001 0111 00000000
OFFSET_Y_L_M rw 18 001 01000 00000000
OFFSET_Y_H_M rw 19 001 01001 00000000
OFFSET_Z_L_M rw 1A 001 01010 00000000
OFFSET_Z_H_M rw 1B 001 01011 00000000
REFERENCE_X rw 1C 001 01100 00000000
REFERENCE_Y rw 1D 001 01101 00000000
REFERENCE_Z rw 1E 001 01110 00000000
CTRL0 rw 1F 001 1111 00000000
CTRL1 rw 20 010 0000 00000111
CTRL2 rw 21 010 0001 00000000
28/54 Doc ID 023312 Rev 1

LSM303D Output register mapping
Table 16. Register address map (continued)
Register address
Name Type
Hex Binary
CTRL3 rw 22 010 0010 00000000
CTRL4 rw 23 010 0011 00000000
CTRL5 rw 24 010 0100 00011000
CTRL6 rw 25 010 0101 00100000
CTRL7 rw 26 010 0110 00000001
STATUS_A r 27 010 0111 Output
OUT_X_L_A r 28 010 1000 Output
OUT_X_H_A r 29 010 1001 Output
OUT_Y_L_A r 2A 010 1010 Output
OUT_Y_H_A r 2B 010 1011 Output
OUT_Z_L_A r 2C 010 1100 Output
OUT_Z_H_A r 2D 010 1101 Output
Default Comment
FIFO_CTRL rw 2E 010 1110 00000000
FIFO_SRC r 2F 010 1111 Output
IG_CFG1 rw 30 011 0000 00000000
IG_SRC1 r 31 011 0001 Output
IG_THS1 rw 32 011 0010 00000000
IG_DUR1 rw 33 011 0011 00000000
IG_CFG2 rw 34 011 0100 00000000
IG_SRC2 r 35 011 0101 Output
IG_THS2 rw 36 011 0110 00000000
IG_DUR2 rw 37 011 0111 00000000
CLICK_CFG rw 38 011 1000 00000000
CLICK_SRC r 39 011 1001 Output
CLICK_THS rw 3A 011 1010 00000000
TIME_LIMIT rw 3B 011 1011 00000000
TIME _LATENCY rw 3C 011 1100 00000000
TIME_WINDOW rw 3D 011 1101 00000000
Act_THS rw 3E 011 1110 00000000
Act_DUR rw 3F 011 1111 00000000
Registers marked as Reserved must not be changed. Writing to these registers may cause
permanent damage to the device.
Doc ID 023312 Rev 1 29/54

Output register mapping LSM303D
The content of the registers that are loaded at boot should not be changed. They contain the
factory calibration values. Their content is automatically restored when the device is
powered up.
30/54 Doc ID 023312 Rev 1

LSM303D Register description
8 Register description
The device contains a set of registers which are used to control its behavior and to retrieve
acceleration and magnetic data. The register address, consisting of 7 bits, is used to identify
them and to write the data through the serial interface.
8.1 TEMP_OUT_L (05h), TEMP_OUT_H (06h)
Temperature sensor data. Temperature data is stored as 2’s complement data in 12-bit
format, right justified.
Refer to Section 4.2 for details on how to enable and read the temperature sensor output
data.
8.2 STATUS_M (07h)
Table 1 7 . STATU S _M regist e r
ZYXMOR/ Tempor ZMOR YMOR XMOR ZYXMDA / Tempda ZMDA YMDA XMDA
Table 18. STATUS_M description
ZYXMOR/
Te mp o r
ZMOR Z-axis data overrun. Default value: 0
YMOR Y-axis data overrun. Default value: 0
XMOR X-axis data overrun. Default value: 0
ZYXMDA /
Te mp d a
ZMDA Z-axis new data available. Default value: 0
YMDA Y-axis new data available. Default value: 0
Magnetic X, Y and Z-axis and temperature data overrun. Default value: 0
(0: no overrun has occurred; 1: a new set of data has overwritten the previous ones)
Temperature data overrun if T_ONLY bit in CTRL7 (26h) is set to ‘1’. Default value: 0.
(0: no overrun has occurred; 1: a new data for the Z-axis has overwritten the previous
one)
(0: no overrun has occurred; 1: a new data for the Y-axis has overwritten the previous
one)
(0: no overrun has occurred; 1: a new data for the X-axis has overwritten the previous
one)
X, Y and Z-axis and temperature new data available. Default value: 0
(0: a new set of data is not yet available; 1: a new set of data is available)
Temperature new data available if the T_ONLY bit in CTRL7 (26h) is set to ‘1’.
(0: a new data for the Z-axis is not yet available; 1: a new data for the Z-axis is available)
(0: a new data for the Y-axis is not yet available; 1: a new data for the Y-axis is available)
XMDA X-axis new data available. Default value: 0
(0: a new data for the X-axis is not yet available; 1: a new data for the X-axis is available)
Doc ID 023312 Rev 1 31/54

Register description LSM303D
8.3 OUT_X_L_M (08h), OUT_X_H_M (09h)
X-axis magnetic data. The value is expressed in 16-bit as 2’s complement.
8.4 OUT_Y_L_M (0Ah), OUT_X_H_M (0Bh)
Y-axis magnetic data. The value is expressed in 16-bit as 2’s complement.
8.5 OUT_X_L_M (0Ch), OUT_X_H_M (0Dh)
Z-axis magnetic data. The value is expressed in 16-bit as 2’s complement.
8.6 WHO_AM_I (0Fh)
Table 19. WHO_AM_I register
0 1 0 01001
Device identification register.
8.7 INT_CTRL_M (12h)
Table 20. INT_CTRL_M register
XMIEN YMIEN ZMIEN PP_OD MIEA MIEL 4D MIEN
Table 21. INT_CTRL_M description
XMIEN Enable interrupt recognition on X-axis for magnetic data. Default value: 0.
(0: disable interrupt recognition; 1: enable interrupt recognition)
YMIEN Enable interrupt recognition on Y-axis for magnetic data. Default value: 0.
(0: disable interrupt recognition; 1: enable interrupt recognition)
ZMIEN Enable interrupt recognition on Z-axis for magnetic data. Default value: 0.
(0: disable interrupt recognition; 1: enable interrupt recognition)
PP_OD Interrupt pin configuration. Default value: 0.
(0: push-pull; 1: open drain)
MIEA Interrupt polarity. Default value: 0.
(0: interrupt active low; 1: interrupt active high)
MIEL Latch interrupt request on INT_SRC_M (13h) register. Default value: 0.
(0: interrupt request not latched; 1: interrupt request latched)
Once the MIEL is set to ‘1’, the interrupt is cleared by reading the INT_SRC_M (13h)
register.
32/54 Doc ID 023312 Rev 1

LSM303D Register description
Table 21. INT_CTRL_M description (continued)
4D 4D enable: 4D detection on acceleration data is enabled when 6D bit in IG_CFG1
(30h) is set to 1. Default value: 0.
MIEN Enable interrupt generation for magnetic data. Default value: 0.
(0: disable interrupt generation; 1: enable interrupt generation)
8.8 INT_SRC_M (13h)
Table 22. INT_SRC_M register
M_PTH_X M_PTH_Y M_PTH_Z M_NTH_X M_NTH_Y M_NTH_Z MROI MINT
Table 23. INT_SRC_M description
M_PTH_X Magnetic value on X-axis exceeds the threshold on the positive side.
Default value: 0.
M_PTH_Y Magnetic value on Y-axis exceeds the threshold on the positive side.
Default value: 0.
M_PTH_Z Magnetic value on Z-axis exceeds the threshold on the positive side.
Default value: 0.
M_NTH_X Magnetic value on X-axis exceeds the threshold on the negative side.
Default value: 0.
M_NTH_Y Magnetic value on Y-axis exceeds the threshold on the negative side.
Default value: 0.
M_NTH_Z Magnetic value on Z-axis exceeds the threshold on the negative side.
Default value: 0.
MROI Internal measurement range overflow on magnetic value.
Default value: 0.
MINT Magnetic interrupt event. The magnetic field value exceeds the threshold.
Default value: 0.
8.9 INT_THS_L_M (14h), INT_THS_H_M (15h)
Magnetic interrupt threshold. Default value: 0.
The value is expressed in 16-bit unsigned.
Even if the threshold is expressed in absolute value, the device detects both positive and
negative thresholds.
Table 24. INT_THS_L_M
THS7 THS6 THS5 THS4 THS3 THS2 THS1 THS0
Doc ID 023312 Rev 1 33/54

Register description LSM303D
Table 25. INT_THS_H_M
0 THS14 THS13 THS12 THS11 THS10 THS9 THS8
8.10 OFFSET_X_L_M (16h), OFFSET_X_H_M (17h)
Magnetic offset for X-axis. Default value: 0.
The value is expressed in 16-bit as 2’s complement.
Table 26. OFFSET_X_L_M
OFF_X_7 OFF_X_6 OFF_X_5 OFF_X_4 OFF_X_3 OFF_X_2 OFF_X_1 OFF_X_0
Table 27. OFFSET_X_H_M
OFF_X_15 OFF_X_14 OFF_X_13 OFF_X_12 OFF_X_11 OFF_X_10 OFF_X_9 OFF_X_8
8.11 OFFSET_Y_L_M (18h), OFFSET_Y_H_M (19h)
Magnetic offset for Z-axis. Default value: 0.
The value is expressed in 16-bit as 2’s complement.
Table 28. OFFSET_Y_L_M
OFF_Y_7 OFF_Y_6 OFF_Y_5 OFF_Y_4 OFF_Y_3 OFF_Y_2 OFF_Y_1 OFF_Y_0
Table 29. OFFSET_Y_H_M
OFF_Y_15 OFF_Y_14 OFF_Y_13 OFF_Y_12 OFF_Y_11 OFF_Y_10 OFF_Y_9 OFF_Y_8
8.12 OFFSET_Z_L_M (1Ah), OFFSET_Z_H_M (1Bh)
Magnetic offset for Y-axis. Default value: 0.
The value is expressed in 16-bit as 2’s complement.
Table 30. OFFSET_Z_L_M
OFF_Z_7 OFF_Z_6 OFF_Z_5 OFF_Z_4 OFF_Z_3 OFF_Z_2 OFF_Z_1 OFF_Z_0
Table 31. OFFSET_Z_H_M
OFF_Z_15 OFF_Z_14 OFF_Z_13 OFF_Z_12 OFF_Z_11 OFF_Z_10 OFF_Z_9 OFF_Z_8
34/54 Doc ID 023312 Rev 1

LSM303D Register description
8.13 REFERENCE_X (1Ch)
Reference value for high-pass filter for X-axis acceleration data.
8.14 REFERENCE_Y (1Dh)
Reference value for high-pass filter for Y-axis acceleration data.
8.15 REFERENCE_Z (1Eh)
Reference value for high-pass filter for Z-axis acceleration data.
8.16 CTRL0 (1Fh)
Table 32. CTRL0 register
BOOT FIFO_EN FTH_EN 0
1. These bits must be set to ‘0’ for the correct working of the device.
(1)
(1)
0
HP_Click HPIS1 HPIS2
Table 33. CTRL0 description
BOOT Reboot memory content. Default value: 0
(0: normal mode; 1: reboot memory content)
FIFO_EN FIFO enable. Default value: 0
(0: FIFO disable; 1: FIFO enable)
FTH_EN FIFO programmable threshold enable. Default value: 0
(0: disable; 1: enable)
HP_Click High-pass filter enabled for click function. Default value: 0
(0: filter bypassed; 1: filter enabled)
HPIS1 High-pass filter enabled for interrupt generator 1. Default value: 0
(0: filter bypassed; 1: filter enabled)
HPIS2 High-pass filter enabled for interrupt generator 2. Default value: 0
(0: filter bypassed; 1: filter enabled)
8.17 CTRL1 (20h)
Table 34. CTRL1 register
AODR3 AODR2 AODR1 AODR0 BDU AZEN AYEN AXEN
Doc ID 023312 Rev 1 35/54

Register description LSM303D
Table 35. CTRL1 description
AODR [3:0]
BDU Block data update for acceleration and magnetic data. Default value: 0
AZEN Acceleration Z-axis enable. Default value: 1
AYEN Acceleration Y-axis enable. Default value: 1
AXEN Acceleration X-axis enable. Default value: 1
Acceleration data rate selection. Default value: 000
(0000: Power-down mode; Others: Refer to Ta bl e 3 6)
(0: continuous update; 1: output registers not updated until MSB and LSB have been
read)
(0: Z-axis disabled; 1: Z-axis enabled)
(0: Y-axis disabled; 1: Y-axis enabled)
(0: X-axis disabled; 1: X-axis enabled)
AODR [3:0] is used to set power mode and ODR selection. In the following table all
frequencies resulting in a combination of AODR [3:0] are shown:
Table 36. Acceleration data rate configuration
AODR3 AODR2 AODR1 AODR0 Power mode selection
0000Power-down mode
00013.125 Hz
00106.25 Hz
001112.5 Hz
010025 Hz
010150 Hz
0110100 Hz
0111200 Hz
1000400 Hz
1001800 Hz
10101600 Hz
8.18 CTRL2 (21h)
Table 37. CTRL2 register
ABW1 ABW0 AFS2 AFS1 AFS0 0
(1)
AST SIM
1. This bit must be set to ‘0’ for the correct working of the device.
36/54 Doc ID 023312 Rev 1

LSM303D Register description
Table 38. CTRL2 register description
ABW [1:0] Accelerometer anti-alias filter bandwidth. Default value:0
Refer to Table 3 9
AFS Acceleration full-scale selection. Default value: 0
Refer to Table 4 0
AST Acceleration self-test enable. Default value: 0
(0: self-test disabled; 1: self-test enabled)
SIM SPI Serial Interface mode selection. Default value: 0
(0: 4-wire interface; 1: 3-wire interface).
Table 39. Acceleration anti-alias filter bandwidth
ABW1 ABW0 Anti-alias filter bandwidth
00773 Hz
01194 Hz
10362 Hz
1150 Hz
Table 40. Acceleration full-scale selection
AFS2 AFS1 AFS0 Acceleration full-scale
000± 2g
001± 4g
010± 6g
011± 8g
100± 16g
8.19 CTRL3 (22h)
Table 41. CTRL3 register
INT1
_BOOT
Table 42. CTRL3 register description
INT1_BOOT
INT1_Click
INT1
_Click
INT1
_IG1
Boot on INT1 enable. Default value: 0
(0: disable; 1: enable)
Click generator interrupt on INT1. Default value: 0
(0: disable; 1: enable)
_IG2
INT1
INT1
_IGM
INT1
_DRDY_A
INT1
_DRDY_M
INT1
_EMPTY
Doc ID 023312 Rev 1 37/54

Register description LSM303D
Table 42. CTRL3 register description (continued)
INT1_IG1
INT1_IG2
INT1_IGM
Inertial interrupt generator 1 on INT1. Default value: 0
(0: disable; 1: enable)
Inertial interrupt generator 2 on INT1. Default value: 0
(0: disable; 1: enable)
Magnetic interrupt generator on INT1. Default value: 0
(0: disable; 1: enable)
INT1_DRDY_A
INT1_DRDY_M
INT1_EMPTY
8.20 CTRL4 (23h)
Table 43. CTRL4 register
INT2
_Click
Table 44. CTRL4 register description
INT2
_Click
INT2
_IG1
INT2
_INT1
Click generator interrupt on INT2. Default value: 0
(0: disable; 1: enable)
Inertial interrupt generator 1 on INT2. Default value: 0
(0: disable; 1: enable)
Accelerometer data-ready signal on INT1. Default value: 0
(0: disable; 1: enable)
Magnetometer data-ready signal on INT1. Default value: 0
(0: disable; 1: enable)
FIFO empty indication on INT1. Default value: 0
(0: disable; 1: enable)
INT2
_INT2
INT2
_INTM
INT2
_DRDY_A
INT2
_DRDY_M
INT2
_Overrun
INT2
_FTH
INT2
_IG2
INT2
_IGM
INT2
_DRDY_A
INT2
_DRDY_M
INT2
_Overrun
INT2
_FTH
38/54 Doc ID 023312 Rev 1
Inertial interrupt generator 2 on INT2. Default value: 0
(0: disable; 1: enable)
Magnetic interrupt generator on INT2. Default value: 0
(0: disable; 1: enable)
Accelerometer data-ready signal on INT2. Default value: 0
(0: disable; 1: enable)
Magnetometer data-ready signal on INT2. Default value: 0
(0: disable; 1: enable)
FIFO overrun interrupt on INT2. Default value: 0
(0: disable; 1: enable)
FIFO threshold interrupt on INT2. Default value: 0
(0: disable; 1: enable)

LSM303D Register description
8.21 CTRL5 (24h)
Table 45. CTRL5 register
TEMP_EN M_RES1 M_RES0 M_ODR2 M_ODR1 M_ODR0 LIR2 LIR1
Table 46. CTRL5 register description
TEMP_EN Temperature sensor enable. Default value: 0
(0: temperature sensor disabled; 1: temperature sensor enabled)
M_RES [1:0] Magnetic resolution selection. Default value: 00
(00: low resolution, 11: high resolution)
M_ODR [2:0]
LIR2 Latch interrupt request on INT2_SRC register, with INT2_SRC register cleared by
LIR1 Latch interrupt request on INT1_SRC register, with INT1_SRC register cleared by
Magnetic data rate selection. Default value: 110
Refer to Table 4 7
reading INT2_SRC itself. Default value: 0.
(0: interrupt request not latched; 1: interrupt request latched)
reading INT1_SRC itself. Default value: 0.
(0: interrupt request not latched; 1: interrupt request latched).
Table 47. Magnetic data rate configuration
MODR2 MODR1 MODR0 Power mode selection
0003.125 Hz
0016.25 Hz
01012.5 Hz
01125 Hz
10050 Hz
101100 Hz
1 1 0 Do not use
111Reserved
1. Available only for accelerometer ODR > 50 Hz or accelerometer in power-down mode (refer to Table 36,
AODR setting).
8.22 CTRL6 (25h)
Table 48. CTRL6 register
(1)
0
1. These bits must be set to ‘0’ for the correct working of the device.
MFS1 MFS0 0
(1)
(1)
(1)
0
(1)
0
(1)
0
(1)
0
Doc ID 023312 Rev 1 39/54

Register description LSM303D
Table 49. CTRL6 register description
MFS [1:0] Magnetic full-scale selection. Default value: 01
Refer to Table 5 0
Table 50. Magnetic full-scale selection
MFS1 MFS0 Magnetic full-scale
0 0 ± 2 gauss
0 1 ± 4 gauss
1 0 ± 8 gauss
1 1 ± 12 gauss
8.23 CTRL7 (26h)
Table 51. CTRL7 register
AHPM1 AHPM0 AFDS T_ONLY 0
(1)
MLP MD1 MD0
1. This bit must be set to ‘0’ for the correct working of the device.
Table 52. CTRL7 register description
AHPM [1:0] High-pass filter mode selection for acceleration data. Default value: 00
Refer to Tabl e 5 3
AFDS Filtered acceleration data selection. Default value: 0
(0: internal filter bypassed; 1: data from internal filter sent to output register and FIFO)
T_ONLY Temperature sensor only mode. Default value: 0
If this bit is set to ‘1’, the temperature sensor is on while the magnetic sensor is off.
MLP Magnetic data low-power mode. Default value: 0
If this bit is ‘1’, the M_ODR [2:0] is set to 3.125 Hz independently from the MODR settings. Once the bit is set to ‘0’, the magnetic data rate is configured by MODR bits in
CTRL5 (24h) register.
MD [1:0] Magnetic sensor mode selection. Default 10
Refer to Tabl e 5 4
Table 53. High-pass filter mode selection
AHPM1 AHPM0 High-pass filter mode
0 0 Normal mode (reset X, Y and Z-axis reading REFERENCE_X
(1Ch), REFERENCE_Y (1Dh) and REFERENCE_Y (1Dh) registers
respectively)
0 1 Reference signal for filtering
40/54 Doc ID 023312 Rev 1

LSM303D Register description
Table 53. High-pass filter mode selection (continued)
AHPM1 AHPM0 High-pass filter mode
1 0 Normal mode
1 1 Auto-reset on interrupt event
Table 54. Magnetic sensor mode selection
MD1 MD0 Magnetic sensor mode
0 0 Continuous-conversion mode
0 1 Single-conversion mode
1 0 Power-down mode
1 1 Power-down mode
8.24 STATUS_A (27h)
Table 55. STATUS_A register
ZYXAOR ZAOR YAOR XAOR ZYXADA ZADA YADA XADA
Table 56. STATUS_A description
ZYXAOR Acceleration X, Y and Z-axis data overrun. Default value: 0
(0: no overrun has occurred; 1: a new set of data has overwritten the previous ones)
ZAOR Acceleration Z-axis data overrun. Default value: 0
(0: no overrun has occurred; 1: a new data for the Z-axis has overwritten the previous
one)
YAOR Acceleration Y-axis data overrun. Default value: 0
(0: no overrun has occurred; 1: a new data for the Y-axis has overwritten the previous
one)
XAOR Acceleration X-axis data overrun. Default value: 0
(0: no overrun has occurred; 1: a new data for the X-axis has overwritten the previous
one)
ZYXADA Acceleration X, Y and Z-axis new value available. Default value: 0
(0: a new set of data is not yet available; 1: a new set of data is available)
ZADA Acceleration Z-axis new value available. Default value: 0
(0: a new data for the Z-axis is not yet available; 1: a new data for the Z-axis is available)
YADA Acceleration Y-axis new value available. Default value: 0
(0: a new data for the Y-axis is not yet available; 1: a new data for the Y-axis is available)
XADA Acceleration X-axis new value available. Default value: 0
(0: a new data for the X-axis is not yet available; 1: a new data for the X-axis is available)
Doc ID 023312 Rev 1 41/54

Register description LSM303D
8.25 OUT_X_L_A (28h), OUT_X_H_A (29h)
X-axis acceleration data. The value is expressed in 16-bit as 2’s complement.
8.26 OUT_Y_L_A (2Ah), OUT_X_H_A (2Bh)
Y-axis acceleration data. The value is expressed in 16-bit as 2’s complement.
8.27 OUT_X_L_A (2Ch), OUT_X_H_A (2Dh)
Z-axis acceleration data. The value is expressed in 16-bit as 2’s complement.
8.28 FIFO_CTRL (2Eh)
Table 57. FIFO_CTRL register
FM2 FM1 FM0 FTH4 FTH3 FTH2 FTH1 FTH0
Table 58. FIFO_CTRL register description
FM [2:0] FIFO mode selection. Default value: 000
Refer to Ta bl e 5 9
FTH [4:0] FIFO threshold level. Default value: 00000
Table 59. FIFO mode configuration
FM2 FM1 FM0 FIFO mode
000Bypass mode
001FIFO mode
010Stream mode
011Stream-to-FIFO mode
100Bypass-to-Stream mode
Interrupt generator 2 can change the FIFO mode.
8.29 FIFO_SRC (2Fh)
FiFO status register.
Table 60. FIFO_SRC register
FTH OVRN EMPTY FSS4 FSS3 FSS2 FSS1 FSS0
42/54 Doc ID 023312 Rev 1

LSM303D Register description
Table 61. FIFO_SRC description
FTH FIFO threshold status.
FTH bit is set to ‘1’ when FIFO content exceeds threshold level.
OVRN FIFO overrun status.
OVRN bit is set to ‘1’ when FIFO buffer is full.
EMPTY Empty status.
EMPTY bit is set to ‘1’ when all FIFO samples have been read and FIFO is empty.
FSS [4:0] FIFO stored data level.
FSS4-0 bits contain the current number of unread FIFO levels.
8.30 IG_CFG1 (30h)
Inertial interrupt generator 1 configuration register.
Table 62. IG_CFG1 register
AOI 6D ZHIE/
ZUPE
ZLIE/
ZDOWNE
YHIE/
YUPE
YLIE/
YDOWNE
XHIE/
XUPE
XLIE/
XDOWNE
Table 63. IG_CFG1 register description
AOI And/Or combination of interrupt events. Default value: 0.
Refer to Ta bl e 6 4
6D 6-direction detection function enabled. Default value: 0.
Refer to Ta bl e 6 4
ZHIE/
ZUPE
ZLIE/
ZDOWNE
YHIE/
YUPE
YLIE/
YDOWNE
XHIE/
XUPE
XLIE/
XDOWNE
Enable interrupt generation on Z high event or on direction recognition. Default
value: 0 (0: disable interrupt request; 1: enable interrupt request)
Enable interrupt generation on Z low event or on direction recognition. Default
value: 0 (0: disable interrupt request; 1: enable interrupt request)
Enable interrupt generation on Y high event or on direction recognition. Default
value: 0 (0: disable interrupt request; 1: enable interrupt request.)
Enable interrupt generation on Y low event or on direction recognition. Default
value: 0 (0: disable interrupt request; 1: enable interrupt request.)
Enable interrupt generation on X high event or on direction recognition. Default
value: 0 (0: disable interrupt request; 1: enable interrupt request.)
Enable interrupt generation on X low event or on direction recognition. Default
value: 0 (0: disable interrupt request; 1: enable interrupt request.)
Content of this register is loaded at boot.
Write operation at this address is possible only after system boot.
Doc ID 023312 Rev 1 43/54

Register description LSM303D
Table 64. Interrupt mode
AOI 6D Interrupt mode
0 0 OR combination of interrupt events
0 1 6-direction movement recognition
1 0 AND combination of interrupt events
1 1 6-direction position recognition
Difference between AOI-6D = ‘01’ and AOI-6D = ‘11’.
AOI-6D = ‘01’ is movement recognition. An interrupt is generated when orientation moves
from an unknown zone to a known zone. The interrupt signal stays for a duration ODR.
AOI-6D = ‘11’ is direction recognition. An interrupt is generated when orientation is inside a
known zone. The interrupt signal stays until orientation is inside the zone.
8.31 IG_SRC1 (31h)
Inertial interrupt generator 1 status register.
Table 65. IG_SRC1 register
0 IA ZHZLYHYLXHXL
Table 66. IG_SRC1 register description
IA
ZH
ZL
YH
YL
XH
XL
Interrupt status. Default value: 0
(0: no interrupt has been generated; 1: one or more interrupts have been generated)
Z high. Default value: 0
(0: no interrupt; 1: Z high event has occurred)
Z low. Default value: 0
(0: no interrupt; 1: Z low event has occurred)
Y high. Default value: 0
(0: no interrupt; 1: Y high event has occurred)
Y low. Default value: 0
(0: no interrupt; 1: Y low event has occurred)
X high. Default value: 0
(0: no interrupt; 1: X high event has occurred)
X low. Default value: 0
(0: no interrupt; 1: X low event has occurred)
Reading at this address clears the IG_SRC1 (31h) IA bit (and the interrupt signal on the
corresponding interrupt pin) and allows the refreshment of data in the IG_SRC1 (31h)
register if the latched option was chosen.
44/54 Doc ID 023312 Rev 1

LSM303D Register description
8.32 IG_THS1 (32h)
Table 67. IG_THS1 register
0 THS6 THS5 THS4 THS3 THS2 THS1 THS0
Table 68. IG_THS1 description
THS [6:0] Interrupt generator 1 threshold. Default value: 000 0000
8.33 IG_DUR1 (33h)
Table 69. IG1_DUR1 register
0 D6D5D4D3D2D1D0
Table 70. IG1_DUR1 register description
D [6:0] Duration value. Default value: 000 0000
D6 - D0 bits set the minimum duration of the interrupt 1 event to be recognized. Duration
steps and maximum values depend on the ODR chosen.
8.34 IG_CFG2 (34h)
This register contains the settings for the inertial interrupt generator 2.
Table 71. IG_CFG2 register
AOI 6D ZHIE/
Table 72. IG_CFG2 register description
AOI And/Or combination of interrupt events. Default value: 0. Refer to Ta bl e 7 3
6D 6-direction detection function enabled. Default value: 0. Refer to Ta bl e 7 3
ZHIE/
ZUPE
ZLIE/
ZDOWNE
YHIE/
YUPE
YLIE/
YDOWNE
Enable interrupt generation on Z high event or on direction recognition. Default
value: 0 (0: disable interrupt request; 1: enable interrupt request)
Enable interrupt generation on Z low event or on direction recognition. Default
value: 0 (0: disable interrupt request; 1: enable interrupt request)
Enable interrupt generation on Y high event or on direction recognition. Default
value: 0 (0: disable interrupt request; 1: enable interrupt request.)
Enable interrupt generation on Y low event or on direction recognition. Default
value: 0 (0: disable interrupt request; 1: enable interrupt request.)
ZUPE
ZLIE/
ZDOWNE
YHIE/
YUPE
YLIE/
YDOWNE
XHIE/
XUPE
XLIE/
XDOWNE
Doc ID 023312 Rev 1 45/54

Register description LSM303D
Table 72. IG_CFG2 register description (continued)
XHIE/
XUPE
XLIE/
XDOWNE
Enable interrupt generation on X high event or on direction recognition. Default
value: 0 (0: disable interrupt request; 1: enable interrupt request.)
Enable interrupt generation on X low event or on direction recognition. Default
value: 0 (0: disable interrupt request; 1: enable interrupt request.)
Content of this register is loaded at boot.
Write operation at this address is possible only after system boot.
Table 73. Interrupt mode
AOI 6D Interrupt mode
0 0 OR combination of interrupt events
0 1 6-direction movement recognition
1 0 AND combination of interrupt events
1 1 6-direction position recognition
Difference between AOI-6D = ‘01’ and AOI-6D = ‘11’.
AOI-6D = ‘01’ is movement recognition. An interrupt is generated when orientation moves
from an unknown zone to a known zone. The interrupt signal stays for a duration ODR.
AOI-6D = ‘11’ is direction recognition. An interrupt is generated when orientation is inside a
known zone. The interrupt signal stays until orientation is inside the zone.
8.35 IG_SRC2 (35h)
This register contains the status for the inertial interrupt generator 2.
Table 74. IG_SRC2 register
0 IA ZHZLYHYLXHXL
Table 75. IG_SRC2 register description
IA
ZH
ZL
Interrupt generator 2 status. Default value: 0
(0: no interrupt has been generated; 1: one or more interrupts have been generated)
Z high. Default value: 0
(0: no interrupt; 1: Z high event has occurred)
Z low. Default value: 0
(0: no interrupt; 1: Z low event has occurred)
YH
YL
46/54 Doc ID 023312 Rev 1
Y high. Default value: 0
(0: no interrupt; 1: Y high event has occurred)
Y low. Default value: 0
(0: no interrupt; 1: Y low event has occurred)

LSM303D Register description
Table 75. IG_SRC2 register description (continued)
XH
X high. Default value: 0
(0: no interrupt; 1: X high event has occurred)
XL
Reading at this address clears the IG_SRC2 (35h) IA bit (and the interrupt signal on the
corresponding interrupt pin) and allows the refreshment of data in the IG_SRC2 (35h)
register if the latched option was chosen.
X low. Default value: 0
(0: no interrupt; 1: X low event has occurred)
8.36 IG_THS2 (36h)
Table 76. IG2_THS register
0 THS6 THS5 THS4 THS3 THS2 THS1 THS0
Table 77. IG2_THS register description
THS [6:0] Interrupt generator 2 threshold. Default value: 000 0000
8.37 IG_DUR2 (37h)
Table 78. IG_DUR2 register
0 D6D5D4D3D2D1D0
Table 79. IG_DUR2 register description
D6 - D0 Duration value. Default value: 000 0000
D6 - D0 bits set the minimum duration of the interrupt 2 event to be recognized. Duration
steps and maximum values depend on the ODR chosen.
8.38 CLICK_CFG (38h)
Table 80. CLICK_CFG register
-- -- ZD ZS YD YS XD XS
Doc ID 023312 Rev 1 47/54

Register description LSM303D
Table 81. CLICK_CFG description
ZD Enable interrupt double click-click on Z-axis. Default value: 0
(0: disable interrupt request; 1: enable interrupt request on measured accel. value
higher than preset threshold)
ZS Enable interrupt single click-click on Z-axis. Default value: 0
(0: disable interrupt request; 1: enable interrupt request on measured accel. value
higher than preset threshold)
YD Enable interrupt double click-click on Y-axis. Default value: 0
(0: disable interrupt request; 1: enable interrupt request on measured accel. value
higher than preset threshold)
YS Enable interrupt single click-click on Y-axis. Default value: 0
(0: disable interrupt request; 1: enable interrupt request on measured accel. value
higher than preset threshold)
XD Enable interrupt double click-click on X-axis. Default value: 0
(0: disable interrupt request; 1: enable interrupt request on measured accel. value
higher than preset threshold)
XS Enable interrupt single click-click on X-axis. Default value: 0
(0: disable interrupt request; 1: enable interrupt request on measured accel. value
higher than preset threshold)
8.39 CLICK_SRC (39h)
Table 82. CLICK_SRC register
-- IA DClick SClick Sign Z Y X
Table 83. CLICK_SRC register description
IA Interrupt active. Default value: 0
(0: no interrupt has been generated; 1: one or more interrupts have been generated)
DClick Double click-click enable. Default value: 0
(0: double click-click detection disable; 1: double click-click detection enable)
SClick Single click-click enable. Default value: 0
(0: single click-click detection disable; 1: single click-click detection enable)
Sign Click-click sign. 0: positive detection; 1: negative detection
Z Z click-click detection. Default value: 0
(0: no interrupt; 1: Z high event has occurred)
Y Y click-click detection. Default value: 0
(0: no interrupt; 1: Y high event has occurred)
X X click-click detection. Default value: 0
(0: no interrupt; 1: X high event has occurred)
48/54 Doc ID 023312 Rev 1

LSM303D Register description
8.40 CLICK_THS (3Ah)
Table 84. CLICK_THS register
- Ths6Ths5Ths4Ths3Ths2Ths1Ths0
Table 85. CLICK_SRC register description
Ths [6:0] Click-click threshold. Default value: 000 0000
8.41 TIME_LIMIT (3Bh)
Table 86. TIME_LIMIT register
- TLI6TLI5TLI4TLI3TLI2TLI1TLI0
Table 87. TIME_LIMIT description
TLI [6:0] Click-click time limit. Default value: 000 0000
8.42 TIME_LATENCY (3Ch)
Table 88. TIME_LATENCY register
TLA7 TLA6 TLA5 TLA4 TLA3 TLA2 TLA1 TLA0
Table 89. TIME_LATENCY description
TLA [7:0] Click-click time latency. Default value: 000 0000
8.43 TIME WINDOW (3Dh)
Table 90. TIME_WINDOW register
TW7 TW6 TW5 TW4 TW3 TW2 TW1 TW0
Table 91. TIME_WINDOW description
TW [7:0] Click-click time window
Doc ID 023312 Rev 1 49/54

Register description LSM303D
8.44 Act_THS (3Eh)
Table 92. Act_THS register
-- ACTH6 ACTH5 ACTH4 ACTH3 ACTH2 ACTH1 ACTH0
Table 93. Act_THS register description
ACTH [6:0] Sleep to Wake, Return to Sleep activation threshold
1LSb = 16mg
8.45 Act_DUR (3Fh)
Table 94. Act_DUR register
ActD7 ActD6 ActD5 ActD4 ActD3 ActD2 ActD1 ActD0
Table 95. Act_DUR description
ActD [7:0] Sleep to Wake, Return to Sleep duration
DUR = (Act_DUR + 1)*8/ODR
50/54 Doc ID 023312 Rev 1

LSM303D Package Information
9 Package Information
In order to meet environmental requirements, ST offers these devices in different grades of
ECOPACK
specifications, grade definitions and product status are available at: www.st.com.
ECOPACK is an ST trademark.
®
packages, depending on their level of environmental compliance. ECOPACK
Doc ID 023312 Rev 1 51/54

Package Information LSM303D
7983231_M
Table 96. TFLGA 3x3x1.0 16L mechanical data
mm
Dim.
Min. Typ. Max.
A1 1
A2 0.785
A3 0.200
D1 2.850 3.000 3.150
E1 2.850 3.000 3.150
L1 1.000 1.060
L2 2.000 2.060
N1 0.500
N2 1.000
M 0.040 0.100
P1 0.875
P2 1.275
T1 0.290 0.350 0.410
T2 0.190 0.250 0.310
d0.150
k0.050
Figure 12. TFLGA 3x3x1.0 16L mechanical drawing
52/54 Doc ID 023312 Rev 1

LSM303D Revision history
10 Revision history
Table 97. Document revision history
Date Revision Changes
22-Jun-2012 1 Initial release.
Doc ID 023312 Rev 1 53/54

LSM303D
Please Read Carefully:
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY TWO AUTHORIZED ST REPRESENTATIVES, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT
RECOMMENDED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING
APPLICATIONS, NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY,
DEATH, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE. ST PRODUCTS WHICH ARE NOT SPECIFIED AS "AUTOMOTIVE
GRADE" MAY ONLY BE USED IN AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AT USER’S OWN RISK.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2012 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Philippines - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
54/54 Doc ID 023312 Rev 1
 Loading...
Loading...