Page 1
Data
Projector
4-409-080-11 (1)
Operating Instructions
Before operating the unit, please read this manual and supplied Quick Reference Manual
thoroughly and retain it for future reference.
VPL-CX235
VPL-CW255
Not all models are available in all countries and area. Please check
with your local Sony Authorized Dealer.
© 2011 Sony Corporation
Page 2

Table of Contents
Overview
Location and Function of Controls .... 3
Main unit ...................................... 3
Connector Panel ...........................4
Remote Commander and Control
Panel ..........................................5
Preparation
Connecting the Projector ................... 7
Connecting a Computer ................7
Connecting a Video equipment .... 8
Connecting an External Monitor and
Audio Equipment .................... 10
Projecting/Adjusting an
Image
Projecting an Image ......................... 11
Adjusting the Projected image ... 12
Turning Off the Power ................18
Adjustments and Settings
Using a Menu
Using a MENU ................................19
The PICTURE SETTING Menu ...... 20
The INPUT SETTING Menu .......... 21
The SET SETTING Menu ............... 24
The MENU SETTING Menu .......... 26
The INSTALL SETTING Menu ...... 27
The INFORMATION Menu ............29
Network
Using Network Features ...................30
Displaying the Control Window of
the Projector with a Web
Browser ...................................30
Confirming the Information
regarding the Projector ............31
Operating the Projector from a
Computer .................................31
Making the Network Settings .....31
Using the e-mail report
Function ...................................32
Others
Indicators ..........................................33
Messages List ...................................34
Troubleshooting ................................35
Replacing the Lamp ..........................37
Cleaning the Air Filter ......................39
Specifications ...................................40
Projection Distance and Lens Shift
Range ............................................45
Dimensions .......................................49
Index .................................................51
2
Table of Contents
Page 3

B Overview
q
q
Location and Function of Controls
Main unit
0
9
8
7
qg
qh
qd
2
qj
1
3
a
qd
5
qd
6
f
a Projection lens
b Focus ring (page 12)
c Zoom lever (page 12)
d Lamp cover (page 37)
e Air filter cover/Ventilation holes
(intake) (page 39)
f Ventilation holes (intake)
g Ventilation holes (exhaust)
Overview
qa
qs
4
i LAMP/COVER indicator
(page 33)
j Control panel (page 5)
k Connector panel (page 4)
l Remote control detector
m Adjuster (page 14)
n Speaker
o Security lock
Connects to an optional security cable
manufactured by Kensington.
For details, visit Kensington’s web site.
http://www.kensington.com/
p Security bar
Connects to a commercially available
security chain or wire.
If it is difficult to pull out, pull out the
Security bar using a screwdriver.
Caution
Do not place anything near the ventilation
holes as this may cause internal heat
buildup. Do not place your hand or
deformable items (plastic, etc.) near the
ventilation holes or around the projector, as
it may cause damage or personal injury.
h ON/STANDBY indicator
(page 33)
Security bar
q Lens shift cover (page 13)
For lens shift adjusting, remove this to
access the lens shift screws inside the
unit.
Location and Function of Controls
3
Page 4
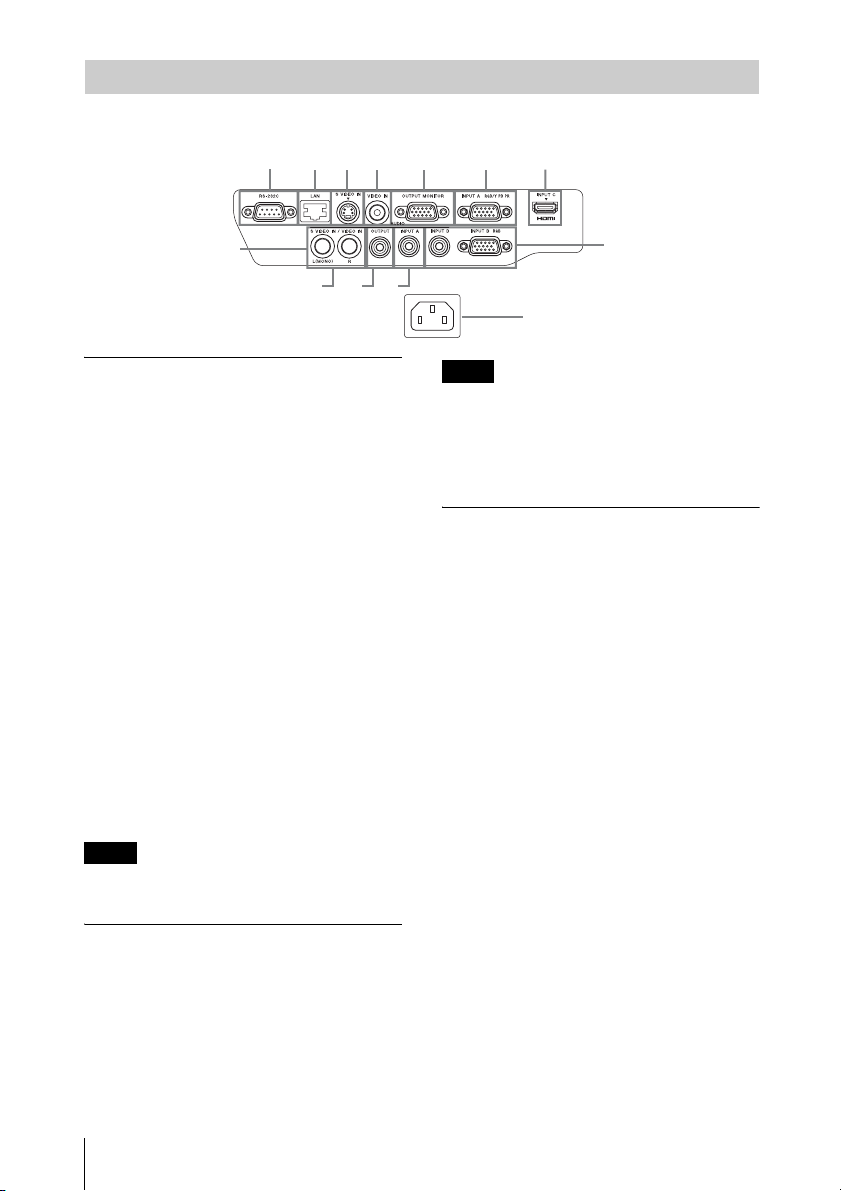
Connector Panel
VPL-CX235/VPL-CW255
4
Input (pages 7, 8)
a INPUT A
Video: RGB/YPBPR input connector
(RGB/Y PB PR)
Audio: Audio input connector (AUDIO)
b INPUT B
Video: RGB input connector (RGB)
Audio: Audio input connector (AUDIO)
c INPUT C
Video: HDMI input connector (HDMI)
Audio: HDMI input connector (HDMI)
d S VIDEO (S VIDEO IN)
Video: S video input connector
Audio: Audio input connector (L
[MONO] AUDIO/R)
5874
165
6 1
3
2
9
Note
This connector outputs the projected image or
audio. The image is output as a computer signal
input from the RGB input connector (INPUT
A/INPUT B) or a video signal input from the
YP
BPR input connector (INPUT A).
Others
g RS-232C connector
RS-232C compatible control connector.
Connects the computer’s RS-232C
connector and the RS-232C cross cables.
h LAN connector (page 30)
i AC IN (∼) socket
Connects the supplied AC power cord.
e VIDEO (VIDEO IN)
Video: Video input connector
Audio: Audio input connector (L
[MONO] AUDIO/R)
Note
The audio inputs of S VIDEO and VIDEO are
shared.
Output (page 10)
f OUTPUT
Video: Monitor output connector
(MONITOR)
Audio: Audio output connector
(AUDIO)
4
Location and Function of Controls
Page 5

Remote Commander and Control Panel
7
21336
Remote Commander
4
2
3
4
INPUT
MENU
RETURN
ASPECT
D ZOOM
APA ECO MODE
ENTER
KEYSTONE
VOLUME
PATTERN
FREEZE
RESET
PIC MUTING
AUDIO MUTING
1
6
5
Control Panel
a Turning on the power/Going to
standby mode
?/1 (On/Standby) key
b Selecting an input signal
(page 11)
INPUT key
c Operating a menu (page 19)
MENU key
RESET key
ENTER /V/v/B/b (arrow) keys
RETURN key
This function is not provided in this
projector.
d Adjusting the image (page 12)
ASPECT key
KEYSTONE key
PATTERN key
APA (Auto Pixel Alignment) key
Note
*
* Use this key when inputting a computer
signal via the RGB input connector
(INPUT A/INPUT B).
e Using various functions during
projecting
D ZOOM (Digital Zoom) +/– key
*1
Enlarges a portion of the image while
projecting.
1 Press the D ZOOM + key to display
the digital zoom icon on the projected
image.
2 Press the V/v/B/b keys to move the
digital zoom icon to the point on the
image you wish to enlarge.
3 Press the D ZOOM + key or the D
ZOOM – key repeatedly to change the
enlargement ratio. The image can be
enlarged up to 4 times.
Press the RESET key to restore the
previous image.
PIC MUTING key
Cuts off the image. Press again to restore
the image.
AUDIO MUTING key
Mutes the audio output. Press again to
restore the previous volume.
VOLUME +/– key
For adjusting the volume output.
FREEZE key
*2
Pauses a projected image. Press again to
restore the image.
Notes
*1: Use this key when inputting a
computer signal. But it may not be
used depending on the resolution of
the input signal.
*2: Use this key when inputting a
computer signal.
Overview
Location and Function of Controls
5
Page 6
f Setting the energy–saving mode
easily
ECO MODE key
Energy-saving mode can be set easily.
Energy-saving mode consists of “Lamp
Mode,” “Standby Mode”, “With Static
Signal” and “With No Input.”
1 Press the ECO MODE key to display
the ECO Mode menu.
ECO Mode Menu
ECO Mode
ECO
User
Sel: Exit:
2 Press the V/v key or ECO MODE key
to select ECO or User mode.
ECO: Sets each mode to the optimum
energy-saving value.
Lamp Mode: Low
With No Input: Standby
With Static Signal: Lamp
Dimming
Standby Mode: Low
(go to step 6)
User: Sets each item of the energy-
saving mode menu as you desire
(go to step 3).
3 Select “User” then press the b key.
The setting items appear.
For details on ECO Mode settings, see
“Lamp Mode” (page 27) and “Standby
Mode” (page 28) on the INSTALL
SETTING menu and “With No Input”
(page 24), “With Static Signal”
(page 24) on the SET SETTING menu.
Others
g Infrared transmitter
About Remote Commander operation
• Direct the Remote Commander toward the
remote control detector.
• The shorter the distance between the
Remote Commander and the projector is,
the wider the angle within which the
Remote Commander can control the
projector becomes.
• Make sure that nothing obstructs the
infrared beam between the Remote
Commander and the remote control
detector on the projector.
User
Lamp Mode Standard
AUTO POWER SAVING
With No Input Off
With Static Signal
Standby Mode Standard
Sel: Set: Exit:
Off
4 Press the V/v key to select the item
then press the ENTER key.
5 Press the V/v key to select the setting
value.
6 Press the ENTER key to restore the
User screen.
6
Location and Function of Controls
Page 7

B Preparation
Connecting the Projector
Notes
• Make sure all the equipment is powered off when connecting the projector.
• Use the proper cables for each connection.
• Insert the cable plugs firmly; Loose connections may reduce performance of picture signals or
cause a malfunction. When pulling out a cable, be sure to grip it by the plug, not the cable itself.
• For more information, refer also to the instruction manuals of the equipment you are connecting.
• Use a no-resistance audio cable.
Connecting a Computer
Connection with a computer is explained for each input signal.
INPUT A/INPUT B
For connecting a computer with an RGB output connector.
Mini D-sub 15-pin cable (supplied)
RGB output
Computer
connector
Audio output
connector
Preparation
Audio cable (Stereo mini plug) (not supplied)
Note
It is recommended that you set the resolution of your computer to 1024 × 768 pixels (VPL-CX235)
or 1280 × 800 pixels (VPL-CW255) for the external monitor.
INPUT C
For connecting video equipment with an HDMI output connector.
HDMI output
connector
Computer
Notes
• Use HDMI-compatible equipment and cable(s) that have an HDMI logo on them.
• The HDMI connector of this projector is not compatible with DSD (Direct Stream Digital) Signal
or CEC (Consumer Electronics Control) Signal.
• For a PC with DVI-D output connector, use an HDMI-DVI-D cable (not supplied).
HDMI cable
(not supplied)
Connecting the Projector
7
Page 8

Connecting a Video equipment
Connections with a VHS video deck, DVD player, or BD player are explained for each input
signal.
S VIDEO IN
For connecting video equipment with an S-video output connector.
S video cable
(not supplied)
S video output
connector
Video equipment
VIDEO IN
For connecting video equipment with a video output connector.
Video equipment
Audio output
connector
Audio cable (Phono plug × 2) (not supplied)
Video cable (not supplied)
Video output
connector
Audio output
connector
Audio cable (Phono plug × 2) (not supplied)
INPUT A
For connecting video equipment with a YPBPR output connector.
Component – Mini D-sub 15-pin cable (not supplied)
YP
BPR output
connector
Audio output
Video equipment
8
Connecting the Projector
connector
Audio cable (Phono plug × 2 – stereo mini plug) (not supplied)
Page 9

INPUT C
For connecting video equipment with an HDMI output connector.
HDMI output
connector
Video equipment
Notes
HDMI cable
(not supplied)
• Use HDMI-compatible equipment and cable(s) that have an HDMI logo on them.
• The HDMI connector of this projector is not compatible with DSD (Direct Stream Digital) Signal
or CEC (Consumer Electronics Control) Signal.
To attach the HDMI cable
Fix the cable to the cable tie holder at the bottom of the projector, using a commercially
available cable tie, as in the illustration.
Use a cable tie of less than 1.9 mm × 3.8 mm in thickness.
Bottom of the projector
Cable tie holder
Preparation
Cable tie
(commercially
available)
Connecting the Projector
9
Page 10

Connecting an External Monitor and Audio Equipment
OUTPUT
Projected images and input audio can be output to display equipment such as a monitor and
audio equipment such as speakers with a built-in amplifier. When an audio cable is connected
to the audio output connector, no sound will be heard from the built-in speaker.
Display equipment
Audio equipment
Note
RGB input
connector
Audio input
connector
Mini D-sub 15-pin
cable (supplied)
Audio cable
(stereo mini plug)
(not supplied)
Projected images and audio can be output. The image is output only as a computer signal input from
the RGB input connector (INPUT A/INPUT B) or a video signal input from the YP
BPR input
connector (INPUT A).
10
Connecting the Projector
Page 11

B Projecting/Adjusting an Image
Projecting an Image
The size of a projected image depends on the distance between the projector and screen. Install
the projector so that the projected image fits the screen size. For details on projection distances
and projected image sizes, see
“Projection Distance and Lens Shift Range” (page 45).
5
35
4
Computer
Video equipment
6
1 Plug the AC power cord into the wall
outlet.
2 Connect all equipment to the projector
(page 7).
3 Press ?/1 to turn on the unit.
4 Turn on the connected equipment.
5 Select the input source.
Each time you press the INPUT key on
the projector, the input signal switches.
Press the INPUT key repeatedly to select
an image to be projected.
2
Projector
1
Wall outlet
6 To project an image from a computer,
set your computer to output to external
display.
How to switch the computer to output to
the projector varies, depending on the
type of computer.
(Example)
+
7 Adjust the focus and position of the
projected image (page 12).
Projecting/Adjusting an Image
Projecting an Image
11
Page 12
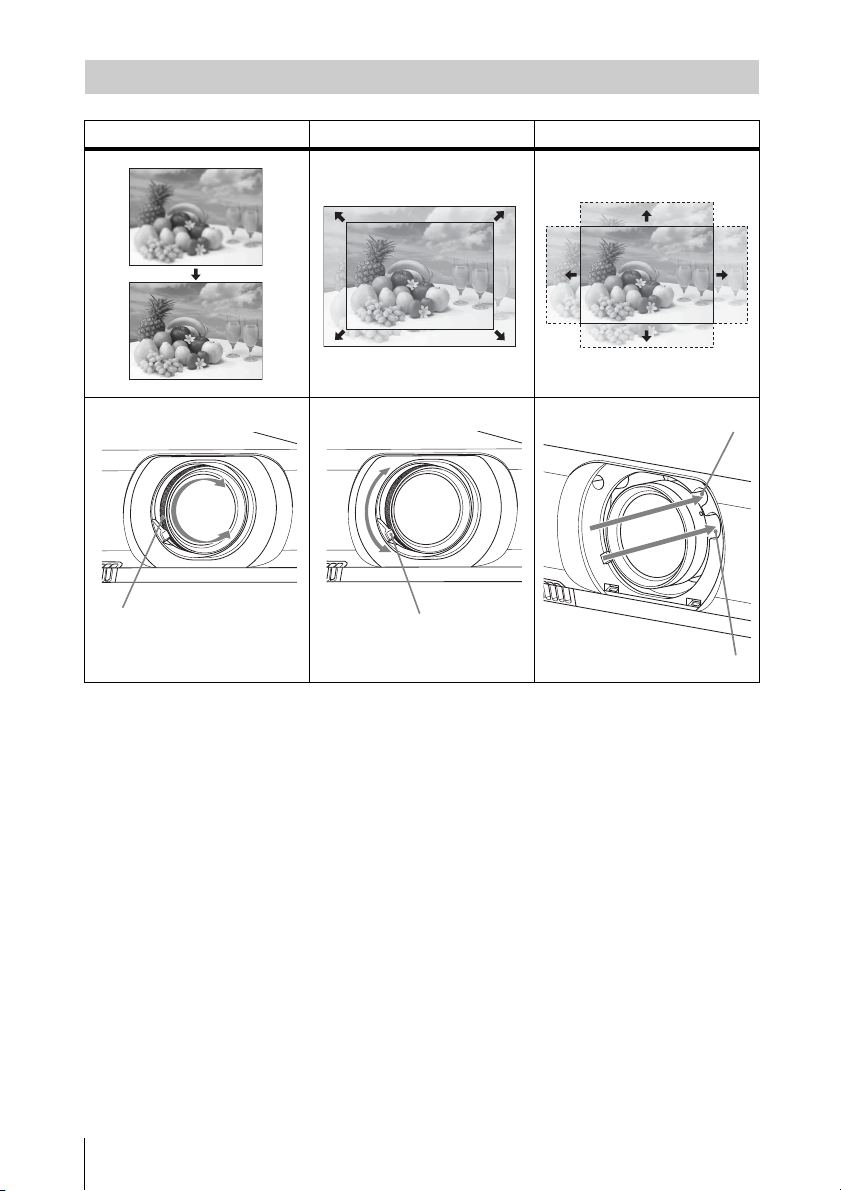
Adjusting the Projected image
Focus Size (Zoom) Position (Lens shift)
2V shift screw
Focus ring
12
Projecting an Image
Zoom lever
1H shift screw
Page 13

Adjusting the tilt of the projector by lens shift
You can adjust the position of the projected
image by turning the screws for lens shift
(V shift screw and H shift screw).
1 Lift up the lower end of the lens shift cover
with your finger to remove it.
2 Insert a Philips screwdriver to the 1H
shift screw inside the unit and turn it to
adjust right or left, and to the 2V shift
screw to adjust up or down. Be careful not
to look into the lens.
Continued turning of these screws will
return the lens shift to its original position.
Adjust the screws to set the lens shift to the
optimum position. For details on the
adjustment range, see the “Lens shift
range” (page 48).
Lens shift cover
Projecting/Adjusting an Image
2V shift screw
3 Return the lens shift cover to the unit.
1H shift screw
Projecting an Image
13
Page 14
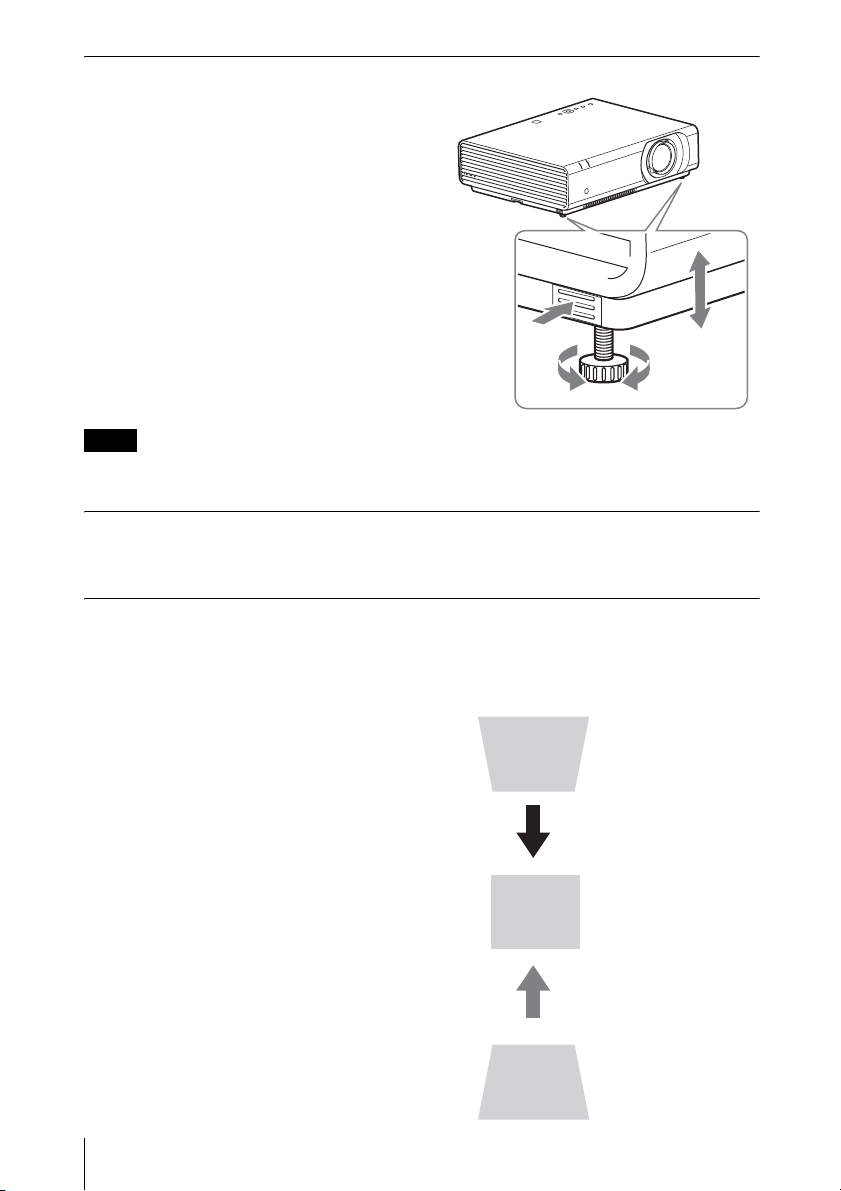
Adjusting the tilt of the projector with the adjusters
You can adjust the height of the projector
pushing the side button on this unit.
By changing the slope of the projector with
adjusters, you can adjust the position of the
projected image.
How to alter the angle
1 Push in the adjuster button at the side of
the unit.
2 Keeping the button pushed in, raise the
main unit to the desired angle.
3 Release the adjuster button.
4 For fine positioning, turn the right and left
adjusters beneath the unit.
1
3
2
4
Notes
• Be careful not to let the projector down on your fingers.
• Do not push hard on the top of the projector with the adjuster extended. It may cause malfunction.
Changing the aspect ratio of the projected image
Press ASPECT on the remote commander to change the aspect ratio of the projected image.
You can also change the setting in Aspect of the INPUT SETTING menu (pages 21, 22).
Correcting trapezoidal distortion of the projected image (Keystone feature)
When the projected image is a trapezoid, tapering to the top or bottom
Keystone feature may not work automatically when the screen is tilted. In this case, set
keystone manually.
1 Press KEYSTONE on the remote
commander once or select V Keystone in
the INSTALL SETTING menu.
2 Use V/v/B/b to set the value. The higher
the setting, narrower the top of the
projected image. The lower the setting, the
narrower the bottom.
Increase the number
towards plus
14
Projecting an Image
Increase the number
towards minus
Page 15
When the projected image a trapezoid, tapering to the right or left
1 Press KEYSTONE on the remote
commander twice or select H Keystone in
the INSTALL SETTING menu.
2 Use V/v/B/b to set the value. The higher
the setting, the narrower the right part of
the projected image. The lower the setting,
the narrower the left part.
Increase the num ber
towards minus
Notes
• Since the Keystone adjustment is an electronic correction, the image may be deteriorated.
• Depending on the position adjusted with the lens shift feature, the aspect ratio of the image may
change from the original or projected image may be distorted with Keystone adjustment.
Increase the number
towards plus
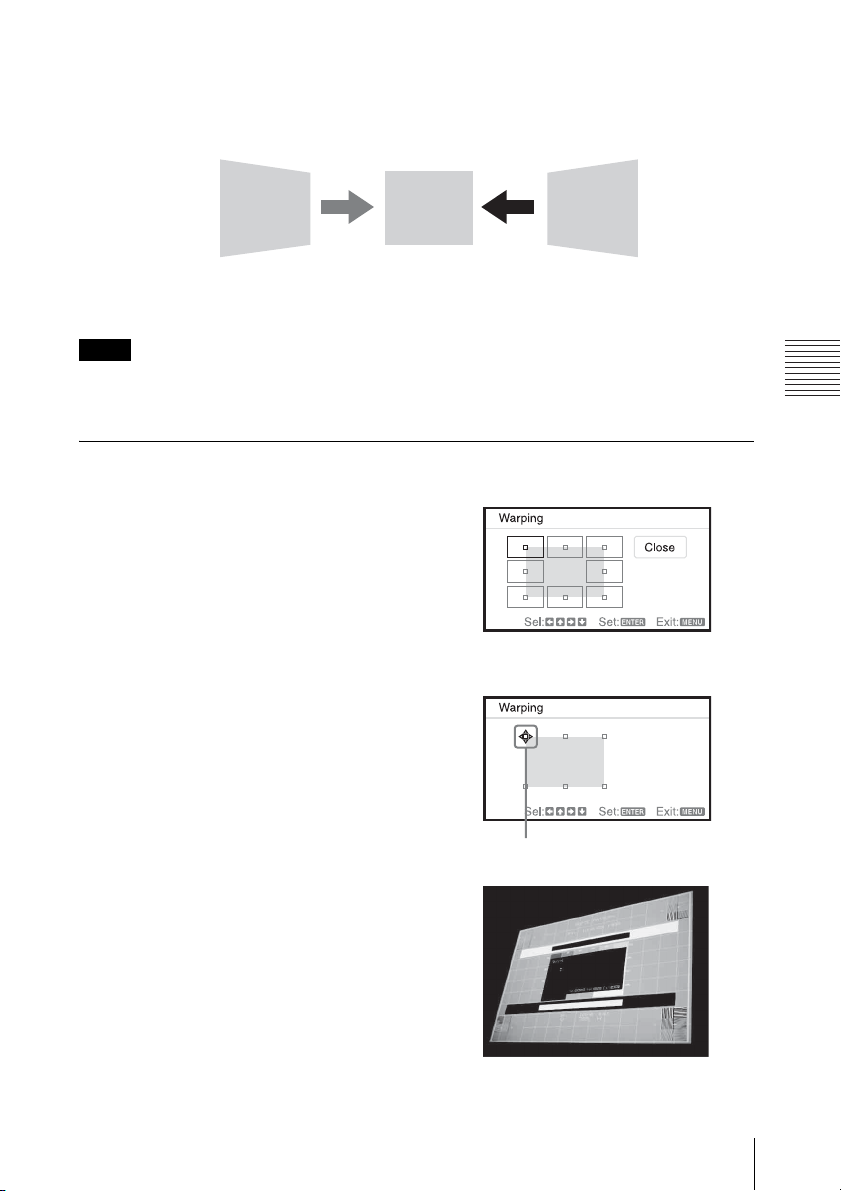
Correcting the image twist (Warp correction feature)
You can correct the image twist by the warp correction feature
1 Select “Warping” in the INSTALL
SETTING menu, and select “Adjust.”
2 The guide is displayed.
The corners of the image to be corrected
1 Move the s by using V/v/B/b to select
the corner you want to correct.
If you press ENTER, you will go back to
the cursor display.
Adjust using this cursor.
Projecting/Adjusting an Image
2 Adjust the position of the corner you want
to correct by using V/v/B/b.
Projecting an Image
15
Page 16
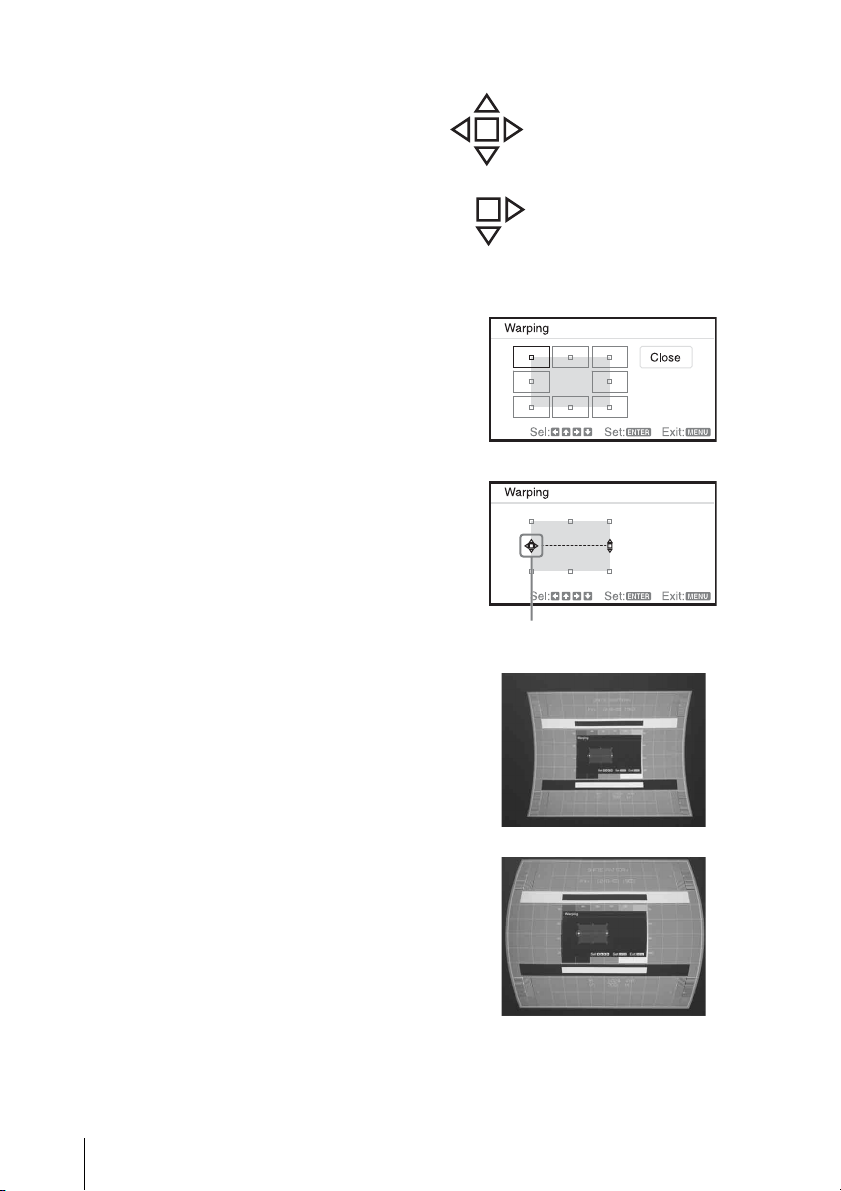
3 The cursor will disappear if the deflection
range limit is reached.
Example of cursor display:
You can adjust in all directions.
You can adjust only towards the
right and downwards.
Correcting deflection 1-The right/left edges of the image
1 Move the s by using V/v/B/b to select
the corner you want to correct.
If you push the ENTER, you can switch to
the cursor display.
2 You can adjust the deflection of the edges
by using V/v/B/b.
You can adjust the central position of the
edges by using V/v. For the range of
deflection, use B/b.
Adjust using this cursor.
16
Projecting an Image
Page 17
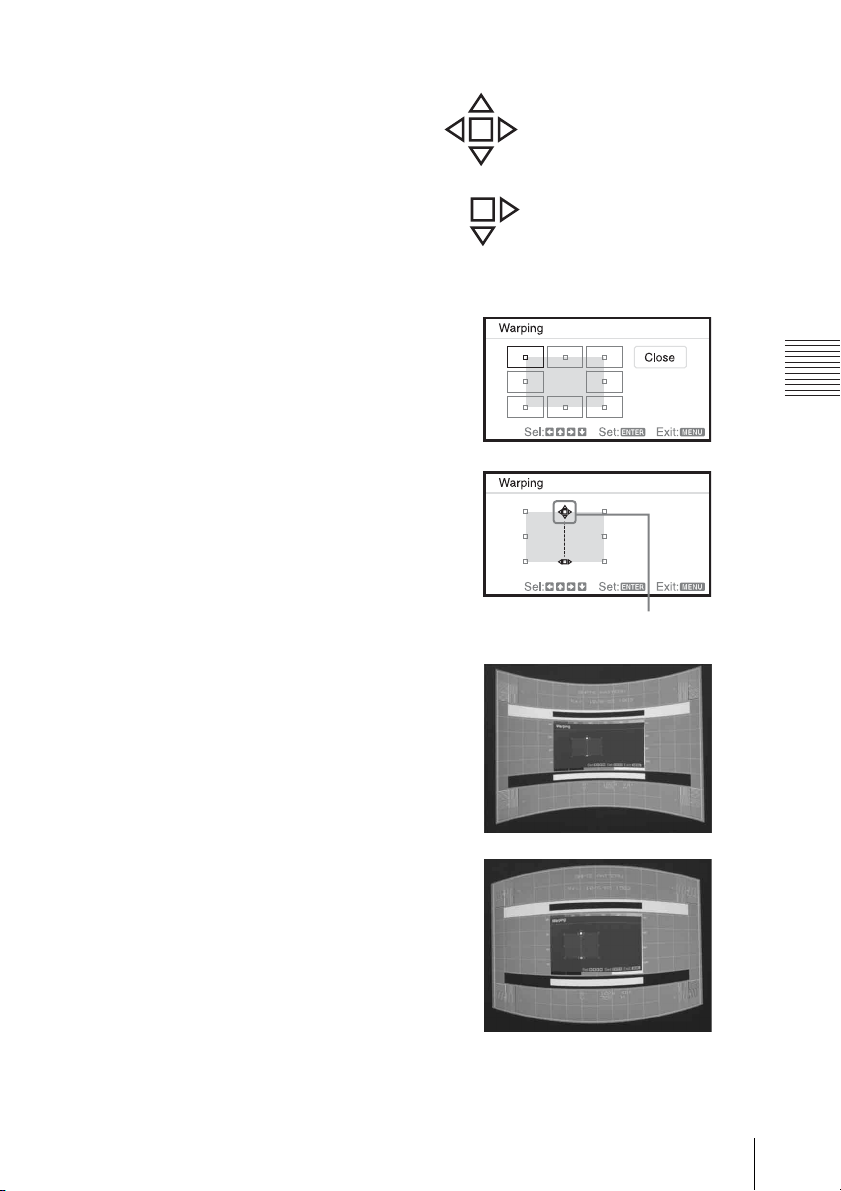
3 The cursor will disappear if the deflection
range limit is reached.
Example of cursor display:
You can adjust in all directions.
You can adjust only towards the
right and downwards.
Correcting deflection 2-The top/bottom edges of the image
1 Move the s by using V/v/B/b to select
the corner you want to correct.
If you push the ENTER, you can switch to
the cursor display.
Adjust using this cursor.
Projecting/Adjusting an Image
2 You can adjust the deflection of the edges
by using V/v/B/b.
You can adjust the top position of the
edges by using B/b. For the range of
deflection, use V/v.
Projecting an Image
17
Page 18

3 The cursor will disappear if the deflection
range limit is reached.
Example of cursor display:
You can adjust in all directions.
You can adjust only towards the
right and downwards.
Automatically adjusts Phase, Pitch and Shift of projected image while a
signal is input from a computer (APA (Auto Pixel Alignment))
Press APA on the remote commander. Press again to cancel during the setting.
If Smart APA is set to On, executes APA automatically when a signal is input (page 24).
Turning Off the Power
1 Press the ?/1 key on the main unit or the Remote Commander.
The shutdown message appears.
If you do not press any of the keys for a while, the projector will turn off.
If you press ?/1 on the projector or remote commander while the shutdown message is on
the screen, the projector will restart.
2 Unplug the AC power cord from the wall outlet.
After step 1, the fan continues to run for a while to reduce internal heat, however, you may
also unplug the AC power cord before the fan stops.
To turn off without displaying confirmation message
Hold the ?/1 key on the main unit pressed for a few seconds.
18
Projecting an Image
Page 19

B Adjustments and Settings Using a Menu
Using a MENU
Note
The menu displays used for the explanation below may be different depending on the model you are
using.
1 Press the MENU key to display the
menu.
2 Select the setting menu.
Use the V or v key to select the setting
menu then press b or ENTER
Setting menu
PICTURE SETTING Input-A
Picture Mode Presentation
Adjust Picture...
Volume 30
Sel: Set: Back: Eixt:
key.
3 Select the setting item.
Use the V or v key to select the setting
menu then press b or ENTER key.
To return to the selection screen of the
setting menu, press the B key.
Setting items
PICTURE SETTING Input-A
Picture Mode Presentation
Adjust Picture...
Volume 30
factory preset value, press the RESET
key during setting or adjusting.
Selecting items
PICTURE SETTING Input-A
Picture Mode Standard
Adjust Picture...
Volume 30
Sel: Set: Back: Eixt:
Dynamic
Standard
Presentation
Using the setting menu
Press the V or v key to select the item.
Press the ENTER key to restore the
previous screen.
Using the adjustment menu
To increase the number, press the V or b
key and to decrease the number, press
the v or B key. Press the ENTER key to
register the setting. The previous screen
is restored.
90
5 Press the MENU key to clear the
menu.
The menu disappears automatically if no
key is pressed for a while.
Adjustments and Settings Using a Menu
Sel: Set: Back: Eixt:
4 Make the setting or adjustment for the
selected item.
Menu operation differs depending on the
setting item. If the next menu window is
displayed, select the item according to
the operations in step 3.
To return to the selection screen of the
setting items, press the B key. Also, to
reset the setting value of an item to its
Using a MENU
19
Page 20

The PICTURE SETTING Menu
For adjusting the picture for each input signal.
Items Item descriptions
Picture Mode
Adjust Picture... The unit can store the setting values of the following sub menu items for each
Contrast The higher the setting, the greater the contrast. The lower the setting, the
Brightness The higher the setting, the brighter the picture. The lower the setting, the
*2*4
Color
*2*4*5
Hue
Sharpness
Color Temp.*3High/Middle/Low: The higher the temperature, the more bluish the picture.
DDE
(Dynamic
Detail
Enhancer)
*2*6
Gamma
*1
Mode
Volume The higher the setting, the higher an audio volume and the lower the setting,
Dynamic:
Standard: Makes the picture be natural and well balanced.
Presentation
picture mode separately.
lower the contrast.
darker the picture.
The higher the setting, the greater the intensity. The lower the setting, the
lower the intensity.
The higher the setting, the more greenish the picture becomes. The lower the
setting, the more reddish the picture becomes.
*2*8
The higher the setting, the sharper the picture. The lower the setting, the
softer the picture.
The lower the temperature, the more reddish the picture.
Off: Plays back the interlace format without conversion.
Progressive: Plays back the video signal of the interlace format converting to
progressive.
Film: Precisely reproduces the image from a film source to suit the original
film source.
Graphics1*7: Gamma correction to make halftones brighter. This setting is
suitable when projecting highly colorful images, such as photos, in a bright
place.
Graphics2: Gamma correction to improve the reproduction of halftones.
Highly colorful images, such as photos, can be reproduced in natural tones.
Text: Contrasts black and white. Suitable for images that contain lots of text.
the lower the audio volume. The audio output level will work simultaneously.
Emphasizes the contrast to produce a “dynamic and vivid” picture.
*1
: Makes the picture bright to suit for a presentation.
Notes
*1: When a computer signal is input, this option is available.
*2: When a video signal is input, this option is available.
*3: When “Picture Mode” is set to the item other than “Presentation,” this option is available.
*4: When a B & W signal is input, this option is not available.
*5: When an analog TV signal is input, this option may not available, depending on the color system.
*6: When a progressive signal or a 1080i signal is input, this option is not available.
*7: When “Presentation” is set in the PICTURE SETTING menu, this option is available.
*8: This is not available when the input signal is HD(1080i/720p).
20
The PICTURE SETTING Menu
Page 21

The INPUT SETTING Menu
For adjusting the size, position, and aspect ratio of the projected image for each input signal.
Items Item descriptions
Adjust Signal Adjusts the image of computer signal. Use this item if the edge of the image
Dot Phase
H Size
*2
Shift
*3
Aspect
When the
computer
signal is
input
When the
video signal
is input
(VPLCX235)
When the
video signal
is input
(VPLCW255)
Over Scan
*4
is cut and reception is bad.
*1
Adjusts the dot phase of the display pixel and the input signal. Set to the
value where looks clearest.
*1
The higher the setting, the wider the horizontal image elements (pitch). The
lower the setting, the narrower the horizontal image elements (pitch).
H: The higher the setting, the farther right the image is projected on the
screen. The lower the setting, the image farther left.
V: The higher the setting, the farther up the image is projected on the screen.
The lower the setting, the image farther down.
Changes the aspect ratio of the projected image (page 22).
Normal: Displays the image on the center point of the projected image
without changing the resolution of the input signal or enlarging the image.
Full1: Displays the image to fit the maximum projected image size without
changing the aspect ratio of the input signal.
Full2: Displays the image to fit the maximum projected image size.
*5
Full3
: Displays a 1280 × 760 dot picture on the screen without changing
the aspect ratio of the original image.
4:3: Displays the image to fit the maximum projected image size with an
aspect ratio fixed to 4:3.
16:9: Displays the image to fit the maximum projected image size with an
aspect ratio fixed to 16:9.
Zoom: Display the center point of the projected image to zoom.
4:3: Displays the image with an aspect ratio fixed to 4:3.
16:9: Displays the image with an aspect ratio fixed to 16:9.
Zoom: Displays the image to enlarge without changing the aspect
ratio of the original image.
Wide Zoom: Displays the image to enlarge with minimum distortion.
On/Off: When set to “On”, the outer edges of the picture will be hidden.
Select this setting when noise appears along the edge of the picture.
Adjustments and Settings Using a Menu
Notes
*1: Available when a computer signal is input from the RGB input connector (INPUT A/INPUT B).
*2: Available when a computer signal is input from the RGB input connector (INPUT A/INPUT B)
or a video signal is input from the YP
BPR input connector (INPUT A).
*3: • Note that if the projector is used for profit or for public viewing, modifying the original picture
by switching to the aspect mode may constitute an infringement of the rights of authors or
producers, which are legally protected.
• Depending on the input signal, setting items for aspect ratio or some other setting items cannot
be set in some cases, or changing the aspect ratio setting may have no effect.
• A part of the image may be displayed in black, depending on the setting item.
*4: Available when a video signal is input from the YP
BPR input connector (INPUT A) or the HDMI
input connector (INPUT C).
*5: VPL-CW255 only.
The INPUT SETTING Menu
21
Page 22

Aspect
VPL-CX235
Input signal Recommended
Computer signal
setting value and
projected image
(4:3) (Full1)
(16:9) (Full1)
(16:10) (Full1)
(4:3) (4:3)*3
*1
*1 *2
*1 *2
*1: If you select “Normal,” the image is
projected in the same resolution as the
input signal without changing the aspect
ratio of the original image.
*2: If you select “Full2,” the image is projected
to fit the projected image size, regardless
of the aspect ratio of the image.
*3: Depending on the input signal, the
projected image may be projected as
illustrated below. In this a case, select
“16:9.”
*4: Depending on the input signal, the image
may be projected as illustrated below. In
this a case, select “Zoom.”
(16:9) (16:9)
Video signal
22
The INPUT SETTING Menu
*4
Page 23

VPL-CW255
Input signal Recommended
setting value and
projected image
(4:3) (Full1)
(16:9) (Full1)
*1 *2 *3
*1 *2 *3
*1: If you select “Normal,” the image is
projected in the same resolution as the
input signal without changing the aspect
ratio of the original image.
*2: If you select “Full2,” the image is projected
to fit the projected image size, regardless
of the aspect ratio of the image.
Computer signal
(16:10) (Full1)
*3
*3: If you adjust the projected image position
using an image with 16:9 aspect ratio and
then switch the input source to 4:3 image,
the top and bottom edge of the image may
be hidden. In this a case, select “Full3.”
Adjustments and Settings Using a Menu
(4:3) (4:3)
*4 *5
*4: Depending on the input signal, the
projected image may be projected as
illustrated below. In this a case, select
“16:9.”
(16:9) (16:9)
Video signal
*5: Depending on the input signal, the image
may be projected as illustrated below. In
this a case, select “Zoom.”
The INPUT SETTING Menu
23
Page 24

The SET SETTING Menu
The SET SETTING menu is used for setting various functions of the projector.
Items Item descriptions
AUTO P OW ER
SAVING
With No Input Lamp Cutoff: The lamp turns off automatically and power
With Static Signal Lamp Dimming/Off: If “Lamp Dimming” is selected, the lamp
Smart APA On/Off: When set to “On,” executes APA automatically when a signal
Auto Input Search On/Off: When set to “On,” the projector detects input signals in the
Input-A Signal Sel. Auto/Computer/Component/Video GBR: When set to “Auto,”
Color System Auto/NTS C3.58/PAL/PAL-60/SECAM/NTSC4.43/PAL-M/PAL-N:
IR Receiver The front and rear remote control detectors of the projector.
Panel Key Lock On/Off: When set to “On,” locks all the control panel keys of the
You can make various power reduction settings.
consumption is reduced if no signal is input for 10 minutes. The lamp
lights again when a signal is input or any key is pressed. In Lamp
Cutoff, the ON/STANDBY indicator lights in orange. (page 33)
Standby: If no signal is input to the unit for more than 10 minutes, the
power turns off automatically, and the unit enters standby mode.
Off: You can deactivate the With No Input.
slowly dims when the image has not changed for a period of time. You
can choose the period before the image darkens from “5,” “10,” “15,”
“20” minutes or “Demo..” If you select “Demo.,” the image will
darken about 30 seconds later.
*1*2
is input.
following order: Input-A/Input-B/Input-C/Video/S Video. It indicates
the input channel when the power is turned on or the INPUT key is
pressed.
selects the type of video signal input automatically when “Input-A” is
selected with the INPUT key.
When set to “Auto,” selects the color system automatically when “S
Video” or “Video” is selected with the INPUT key.
Front & Rear: The IR receivers on the front and rear of the unit are
available.
Front: The IR receiver on the front is available.
Rear: The IR receiver on the rear is available.
projector. However, you can operate the following when set to “On”:
• Press and hold the ?/1 key for approximately 10 seconds during
Standby mode.
c The projector turns on.
• Press and hold the ?/1 key for approximately 10 seconds during
power on.
c The projector goes to Standby mode.
• Press and hold the MENU key for approximately 10 seconds during
power on.
c “Panel Key Lock” is set to “Off” and enables operation of all keys
on the projector.
*3
*3
24
The SET SETTING Menu
Page 25

Items Item descriptions
CC Display
*5
CC1/CC2/CC3/CC4/Text1/Text2/Text3/Text4: Select the closed
caption service (Captions or Text).
Off: Closed caption does not appear.
Network Setting
*4
IP Address Setup Auto (DHCP): The IP address is assigned automatically from the
DHCP server such as a router.
Manual: To specify the IP Address manually.
IP Address/Subnet
Mask/Default
Gateway/DNS
Server/Apply
When “Manual” is selected for “IP Address Setup,” select the item
with the B or b key and input the value with V or v key. When all
items are entered, select “Apply” then press the ENTER key. The
entered settings will be registered.
Lamp Timer Reset When replacing the lamp, resets the lamp timer (page 37).
Notes
*1: Executes APA when a computer signal is input via the RGB input connector (INPUT A/INPUT
B).
*2: If the projected image includes large amount of black portion around it, the APA function will
not work properly and a part of the image may not be displayed on the screen and also optimum
image cannot be obtained, depending on the type of input signal. In this case, adjust the “Dot
Phase,” “H size,” and “Shift” items manually.
*3: The image may not be adjusted properly depending on the type of input signal. In such a case,
adjust it manually to suit to the connected equipment.
*4: “Network Setting” is not displayed while “REMOTE” is selected from “External Control” in the
INSTALL SETTING menu.
*5: This is available only when the video signal is NTSC.
Adjustments and Settings Using a Menu
The SET SETTING Menu
25
Page 26

The MENU SETTING Menu
The MENU SETTING menu is used for setting for the operations by using the menu or the
Remote Commander.
Items Item descriptions
Status On: All on-screen statuses are enabled.
Language Selects the language used in the menu and on-screen displays.
Menu Position Top Left/Bottom Left/Center/Top Right/Bottom Right: Selects the display
Start Up Image On/Off: When set to “On,” the Start Up Image is displayed on the screen upon
Off: Turn off the on-screen displays except for the menus, message when
turning off the power, and warning messages.
position of the menu.
startup of the projector.
26
The MENU SETTING Menu
Page 27

The INSTALL SETTING Menu
The INSTALL SETTING menu is used for installing the projector.
Items Item descriptions
Screen Fitting HV Keystone/ Warping: You can choose how to correct image twist.
V Keystone
H Keystone
Warping This is displayed when “Warping” is selected in the “Screen Fitting”.
Image Flip HV/H/V/Off: Flips the projected image horizontally and/or vertically
Background Black/Blue: Selects the background color of the projected image when no
Lamp Mode High/Standard/Low: When set to “High,” the image becomes brighter,
High Altitude
Mode
Security Lock
Direct Power On On/Off: When set to “On,” you can turn the power on without going to
External Control REMOTE: Select to control the projector using RS-232C.
*1*5
*1*5
*2
This is displayed when “HV Keystone” is selected in the “Screen Fitting.”
Auto: The Keystone adjustment is done automatically. If the screen is
tilted, this function may not work properly. In that case, select “Manual”
for Keystone adjustment.
Manual: The higher the setting, the narrower the top of the projected
image. The lower the setting, the narrower the bottom.
This is displayed when “HV Keystone” is selected in the “Screen Fitting.”
The higher the setting, the narrower the right part of the projected image.
The lower the setting, the narrower the left part.
Adjust: You can correct image twist.
Reset: You can reset adjusted values back to the default values.
according to the installation method.
signal is input.
and power consumption becomes higher.
On/Off: Set to “On” when using the projector at an altitude of 1,500 m or
higher. Continuing to use the wrong setting may affect component
reliability.
*3
On/Off: This function enables restriction of the projector to authorized
users by password. The setting procedures for security locking are as
follows:
1 Select “On” and press ENTER to display the setting menu.
2 Input the password with the MENU, V/v/B/b, and ENTER keys. (The
default password setting is “ENTER, ENTER, ENTER, ENTER.”)
3 Input a new password with the MENU, V/v/B/b, and ENTER keys.
4 Enter the password again to confirm.
Enter the password when you turn on the projector after disconnecting and
reconnecting the AC power cord.
When it is set to “Off,” you can cancel the security lock. You are required to
input the password again.
If you fail to enter the correct password after three consecutive times, the
projector cannot be used. In this case, press the ?/1 key to go Standby
mode then turn on the power again.
Standby mode when the AC power cord is connected to a wall outlet.
Regardless of the Direct Power On setting, you can disconnect the AC
power cord to turn off the power without going to the Standby mode.
NETWORK: Select to control the projector via network.
Adjustments and Settings Using a Menu
The INSTALL SETTING Menu
27
Page 28

Items Item descriptions
Standby Mode Standard/Low: When set to “Low,” lowers power consumption in Standby
Notes
*1: Since the Keystone adjustment is an electronic correction, the image may be deteriorated.
*2: When “High Altitude Mode” is set to “On,” the speed of the fan increases, and the fan noise
becomes slightly louder.
*3: You will not be able to use the projector if you forget your password. If you call qualified Sony
personnel because you have forgotten the password, you will be asked to verify the projector’s
serial number and your identity. (This process may differ in other countries/regions.) Once your
identity has been confirmed, we will provide you with the password.
*4: When “Standby Mode” is set to “Low,” the network and network control function cannot be
operated while the projector is in standby mode.
*5: Depending on the position adjusted with the lens shift feature, the aspect ratio of the image may
change from the original or projected image may be distorted with Keystone adjustment.
*4
mode.
28
The INSTALL SETTING Menu
Page 29

The INFORMATION Menu
The INFORMATION menu enables you to confirm various information on the projector, such
as the total usage hours of a lamp.
Items Item descriptions
Model Name Displays the model name.
Serial No. Displays the serial number.
*1
fH
*1
fV
Signal Type Displays the type of the current input signal.
IP Address
Lamp Timer Indicates the total usage time of a lamp.
Note
*1: These items may not be displayed depending on the input signal.
*2: Not displayed when “REMOTE” is selected in “External Control” in the INSTALL SETTING
*3: If “000.000.000.000” is displayed as the IP Address, select the Information menu again.
*2*3
menu.
Displays the horizontal frequency of the current input signal.
Displays the vertical frequency of the current input signal.
Displays IP address.
Adjustments and Settings Using a Menu
The INFORMATION Menu
29
Page 30

B Network
Using Network Features
Connection to the network allows you to operate the following features:
• Checking the current status of the projector via a Web browser.
• Remotely controlling the projector via a Web browser.
• Receiving the e-mail report for the projector.
• Making the network settings for the projector.
• Supports network monitoring, control protocol (Advertisement, PJ Talk, PJ Link, AMX
DDDP [Dynamic Device Discovery Protocol]).
Notes
• The menu displays used for the explanation below may be different depending on the model you
are using.
• Supported Web browsers are Internet Explorer 6/7/8.
• The menu displays only English.
• If the browser of your computer is set to [Use a proxy server] when you have access to the projector
from your computer, click the check mark to set accessing without using a proxy server.
Displaying the Control Window of the Projector with a Web Browser
1 Connect the LAN cable.
LAN cable
(straight type)
(not supplied)
Hub, router, etc
LAN Connector
2 Set the network settings for the
projector using “Network Setting” on
the SET SETTING menu (page 25).
3 Start a web browser on the computer,
enter the following in the address field,
then press the Enter key on your
computer.
http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
(xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx: IP address for the
projector)
You can confirm the IP address of the
projector under “Network Setting” on
the SET SETTING menu.
The following window appears in the
Web b r owser :
Once you make the network settings, you
can open the Control window only by
performing step 3 of this procedure.
30
Using Network Features
Page 31

How to operate the Control window
Switching the page
Click one of the Page Switching buttons to
display the desired setting page.
Page Switching buttons
Confirming the Information regarding the Projector
You can confirm the current settings for the
projector on the Information page.
Information area
Operating the Projector from a Computer
You can control the projector from the
computer on the Control page.
Making the Network Settings
Setting the network password
The log-in screen appears after the Network
page is selected.
No password is set by default. The user name
is preset to “root.” Input required
information after logging in.
Changing the password
Enable: Select to set a new password.
Disable: Select not to change the
password.
Network
Note
If you forget your password, consult with
qualified Sony personnel.
Operation area
The functions of the keys shown in the
operation area are the same as those of the
keys on the supplied Remote Commander.
Setting the location
Location: Input information on where
the projector is installed.
Using Network Features
31
Page 32

Using the e-mail report Function
Set the e-mail report function on the Mail
Report page. Entered values will not be
applied unless you click on [Apply].
1 Set the e-mail report function.
Enable: Select to activate the e-mail
report function.
Disable: Select to deactivate the e-mail
report function.
1
2
3
4
5
2 Enter the outgoing e-mail address in
the Send To box then check the Report
Timing check box of the e-mail report
to be sent.
A massage will be sent simultaneously
to secondary recipients by entering their
e-mail addresses in the CC box.
5 Send the test mail.
Check on the Send test mail check box
then click on [Apply] to send your test
mail to the e-mail address you set.
Notes
• The e-mail report function is not available
because the network which Outbound Port25
Blocking is used cannot be connected to the
SMTP server.
• You cannot use the following characters to
enter the characters in the text box: “ ' ”, “ “
”, “ & ”, “ < ”, “ > ”
3 Set the timing to send e-mail report.
Over Lamp Usage Time: Tick the box
to send a report that indicates the time
for lamp replacement.
Error: Tick the box to send a report that
indicates an error occurring.
4 Set the mail account for sending e-
mail reports.
User Name: Enter the allocated user
name. Up to 64 characters can be
input.
Password: Enter the e-mail password.
SMTP Server: Enter the address of
outgoing mail server (SMTP). Up to
64 characters can be input.
32
Using Network Features
Page 33

B Others
Indicators
The indicators allow checking the status and notify you of abnormal operation of the projector.
If the projector exhibits abnormal status, address the problem in accordance with the table
below.
ON/STANDBY indicator
Status Meaning/Remedies
Lights in red The projector is in Standby mode.
Flashes in green • The projector is ready to operate after having been turned on.
Lights in green The projector’s power is on.
Lights in orange The projector is in AUTO POWER SAVING (lamp cut off). (page 24)
Flashes in red The projector is in abnormal status. Symptoms are indicated by
Flashes twice The internal temperature is unusually high. Check the items below.
Flashes six times Unplug the AC power cord from a wall outlet. After checking that the
Other number of
flashes
• The lamp cools after the projector is turned off.
number of flashes. Address the problem in accordance with the
following. If the symptom is shown again, consult with qualified Sony
personnel.
• Check to see if nothing is blocking the ventilation holes.
• Check to see if the air filter is not clogged. (pages 3, 39)
ON/STANDBY indicator goes out, plug the power cord to a wall
outlet again then turn on the projector.
Consult with qualified Sony personnel.
LAMP/COVER indicator
Status Meaning/Remedies
Flashes in red Symptoms are indicated by number of flashes. Address the problem in
accordance with the following.
Flashes twice The lamp cover or air filter cover is not attached securely. (pages 37,
39)
Flashes three times The temperature of lamp is unusually high. Turn off the power and
wait for lamp to cool then turn on the power again. If the symptom is
shown again, the lamp may be burnt out. In such a case, replace the
lamp with a new one (page 37).
Indicators
Others
33
Page 34

Messages List
When any of the messages listed below appears on the projected image, address the problem in
accordance with the table below.
Message Meaning/Remedy Page
High temp.! Lamp off in
1 min.
Frequency is out of
range!
Please check Input-A
Signal Sel.
Please replace the Lamp
and clean the Filter.
Not applicable! Invalid key pressed. –
The panel keys are
locked!
Check the items below.
• Check to see if nothing is blocking the ventilation holes.
• Check to see if the air filter is not clogged.
Change the output setting of the connected equipment to one
for signals supported by the projector.
Set “Input-A Signal Sel.” to “Auto” or select the input signal
type to suit to the input signal.
Replace the lamp with a new one and clean the air filter. The
message appears whenever you turn on the power until you
replace the lamp and reset the lamp timer.
“Panel Key Lock” is set to “On.” 24
3, 39
44
24
37, 39
34
Messages List
Page 35

Troubleshooting
Before asking to have the projector repaired, try to diagnose the problem, following the
instructions below.
Symptom Remedy Page
The power is not turned
on.
No image. Check if the connecting cable is connected to external
On-screen display does
not appear.
The aspect ratio of the
display is not right/the
image is displayed
smaller /a portion of
image does not appear.
The image is a
trapezoid.
The image is dark/too
bright.
The image is not clear. Check if the projector is in focus. 12
Check if the AC power cord is firmly connected. –
When the “Panel Key Lock” is set to “On,” you cannot turn on
the projector using the ?/1 key on the projector.
If the lamp or lamp cover is not attached securely, the projector
cannot be turned on.
equipment firmly.
Check if the computer signal is set for output to an external
monitor. If you set your computer, such as a notebook
computer, to output the signal to both your computer’s display
and an external monitor, the picture of the external monitor
may not appear properly. Set your computer to output the
signal to only an external monitor.
Check if the input source is correctly selected. 11
Check if the picture is muted. 5
The on-screen display does not appear when “Status” in the
MENU SETTING menu is set to “Off.”
Set “Aspect” manually. 5, 21,
The images become trapezoidal because of the projection
angle. In such a case, you can correct the trapezoidal
distortion, using a Keystone feature.
When the “V Keystone” is set to “Manual,” the keystone
feature does not work automatically. Set “V Keystone” to
“Auto” or “Manual” to set manually.
When the projector is installed on an uneven surface, the
feature may not work properly. In this case, select “Manual” to
set “V Keystone” manually.
The settings for “Brightness,” “Contrast,” and “Lamp Mode”
affect brightness of the image. Check if the value is
appropriate.
The image will be dark when the lamp is burnt out. Check
“Lamp Timer,” and replace the lamp with a new one if
necessary.
The picture will not be clear if condensation has accumulated
on the lens. In such a case, let the projector sit for about two
hours with the power on.
22
5, 14,
27
5, 14,
27
5, 14,
27
20, 27
24
37
–
11
26
Others
29
–
Troubleshooting
35
Page 36

Symptom Remedy Page
The image is noisy. Check if the connecting cable is connected to external
No sound. Check that the connecting cables between the projector and
The Remote
Commander does not
work.
The fan is noisy. The sound from the fan is often greater than normal to cool the
equipment properly.
external video or audio equipment are securely connected.
Check if the output setting of connected external audio
equipment is set to output the audio signal from the projector.
Check if the connecting cable is connected to external
equipment firmly.
Audio is not output if audio muting is activated. 5
Check if “Volume” is not set to minimum. 5, 20
Check that the batteries are installed correctly. –
Check that the batteries are not exhausted. –
lamp, etc. in the following cases.
• “Lamp Mode” is set to “High.”
• “High Altitude Mode” is set to “On.”
• The unit is used in the location where the temperature is high.
If the ventilation holes are blocked, the internal temperature of
the projector rises and the fan noise becomes larger.
7
7
–
–
27
3
36
Troubleshooting
Page 37

Replacing the Lamp
Replace the lamp with a new one if a message displayed on the projected image or the LAMP/
COVER indicator notifies you to replace the lamp (pages 33, 34).
Use an LMP-C240 projector lamp (not supplied) for replacement.
Caution
• The lamp remains hot after the projector is
turned off. If you touch the lamp, you may
burn your finger. When you replace the
lamp, wait for at least an hour after
turning off the projector for the lamp to
cool sufficiently.
• Do not allow any metallic or inflammable
objects into the lamp replacement slot after
removing the lamp, otherwise it may cause
electrical shock or fire. Do not put your
hands into the slot.
Notes
• If the lamp breaks, contact qualified
Sony personnel. Do not replace the lamp
yourself.
• When removing the lamp, be sure to pull it
out straight, by holding the designated
location. If you touch a part of the lamp other
than the designated location, you may be
burned or injured. If you pull out the lamp
while the projector is tilted, the pieces may
scatter if the lamp breaks any may cause
injury.
1 Turn off the projector, and disconnect
the AC power cord from a wall outlet.
2 When the lamp has cooled
sufficiently, open the lamp cover by
loosening 3 screws.
You can remove the lamp cover for a
while when installing on the ceiling.
Take care to prevent the lamp cover from
falling down, as it is not fixed.
Do not apply pressure to the lamp cover
while it is open.
Others
Replacing the Lamp
37
Page 38

3 Loosen the 3 screws on the lamp then
pull out the lamp by its grab.
Grab
4 Insert the new lamp all the way in until
it is securely in place. Tighten the
3 screws.
7 Reset the lamp timer for notification of
the next replacement time.
Select “Lamp Timer Reset” on the SET
SETTING menu then press the ENTER
key. When a message appears, select
“Yes” to reset the lamp timer (page 25).
Caution
Disposal of the used lamp
For the customers in the USA
Lamp in this product contains mercury.
Disposal of these materials may be
regulated due to environmental
considerations. For disposal or
recycling information, please contact
your local authorities or the
Telecommunications Industry
Association (www.eiae.org).
5 Close the lamp cover and tighten the
3 screws.
Note
Be sure to install the lamp and Lamp cover
securely as it was. If not, the projector
cannot be turned on.
6 Connect the AC power cord to a wall
outlet and turn on the projector.
38
Replacing the Lamp
Page 39

Cleaning the Air Filter
When a message appears on the projected image, clean the air filter (page 34).
If the dust cannot be removed from the air filter even after cleaning, replace the air filter with
a new one. For details on a new air filter, consult with qualified Sony personnel.
Caution
If you neglect to clean the air filter, dust may accumulate, clogging it. As a result, the
temperature may rise inside the unit, leading to a possible malfunction or fire.
1 Turn off the projector, and disconnect
the AC power cord from the AC outlet.
2 Draw out the air filter cover.
Air filter cover
Note
If you remove the air filter cover when
power is turned on and the AC power cord
is not removed from the AC outlet, avoid
touching the fan inside the unit, as it may
cause injury.
3 Clean the air filter with a vacuum
cleaner.
Remove the filter holder to remove the
air filter.
Claws
Filter
holder
The air filter consists of 2 filters.
Upper filter: Black
Lower filter: Gray
4 Attach the air filter cover to the unit.
Note
Be sure to attach the air filter cover firmly.
Incorrect attachment of the cover may
cause a malfunction.
Others
Air
filter
Cleaning the Air Filter
39
Page 40

Specifications
Item Description
Model VPL-CX235/VPL-CW255
Projection system 3 LCD system
Display device Effective display
Projection lens Focus Manual
Light source High-pressure mercury lamp, 245 W type
Projected image
size
Luminous flux
(Brightness)
Speaker 10 W × 1 (monaural)
Applicable
scanning
frequency
Resolution When a computer
Color system NTSC
*1
size
Effective picture
elements
Zoom Manual
signal is input
When a video
signal is input
VPL-CX235: 0.63 inch (16.0 mm), 3 plate, Aspect ratio
4:3
VPL-CW255: 0.75-inch (19.1 mm), 3 plate, Aspect ratio
16:10
VPL-CX235: 2,359,296 pixels (1024 × 768 pixels, 3
plate panels)
VPL-CW255: 3,072,000 pixels (1280 × 800 pixels, 3
plate panels)
40 inches to 300 inches (1.02 m to 7.62 m)
VPL-CX235: 4200 lm
VPL-CW255: 4500 lm
(when “Lamp Mode” is set to “High”)
Horizontal: 19 kHz to 92 kHz, Vertical: 48 Hz to 92 Hz
Maximum display resolution: 1600 × 1200 pixels (resize)
Panel display resolution:
VPL-CX235: 1024 × 768 pixels
VPL-CW255: 1280 × 800 pixels
NTSC, PAL, SECAM, 480/60i, 576/50i, 480/60p,
576/50p, 720/60p, 720/50p, 1080/60i, 1080/50i
3.58, PAL, SECAM, NTSC4.43, PAL-M, PAL-N,
PA L6 0
40
Specifications
Page 41

Item Description
Model VPL-CX235/VPL-CW255
INPUT OUTPUT
(Computer/video)
INPUT A RGB/YPBPR input connector: Mini D-sub 15 pin
female, G with sync/Y: 1 Vp-p ± 2 dB, sync negative,
75 ohms terminated, RGB/P
BPR: 0.7 Vp-p ± 2 dB, 75
ohms terminated, Sync signal: TTL level high
impedance, positive/negative
Audio input connector: Stereo mini jack, rated input
500 mVrms, input impedance more than 47 kohms
INPUT B RGB input connector: Mini D-sub 15-pin female,
RGB: 0.7 Vp-p ± 2 dB, 75 ohms terminated, Sync signal:
TTL level high impedance, positive/negative
Audio input connector: Stereo mini jack, rated input
500 mVrms, input impedance more than 47 kohms
INPUT C HDMI input connector: HDMI 19-pin, HDCP support,
Audio input connector: HDMI audio support
S VIDEO IN S video input connector: Mini DIN 4-pin, Y: 1 Vp-p
± 2 dB, sync negative, 75 ohmes terminated, C: (burst
signal) 0.286 (NTSC)/0.3 (PAL/SECAM) Vp-p ± 2 dB,
75 ohms terminated
Audio input connector: Phono jack × 2, rated input
500 mVrms, Input impedance more than 47 kohms
VIDEO IN Video input connector: Phono jack, 1 Vp-p ± 2 dB,
sync negative, 75 ohmes terminated
Audio input connector: Shared with S VIDEO IN
OUTPUT MONITOR output connector: Mini D-sub 15-pin
female, G with sync/Y: 1 Vp-p ± 2 dB, sync negative,
75 ohms terminated, RGB/P
BPR: 0.7 Vp-p ± 2 dB,
75 ohms terminated, Sync signal: HD, VD 4 V (open),
1 Vp-p (75 ohms), positive/negative
Audio output connector: Stereo mini jack, stereo,
1 Vrms (maximum volume, when inputting 500 mVrms),
output impedance 5 kohms
Others connector RS-232C connector: D-Sub 9 pin female
LAN connector: RJ45, 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX
Operating
temperature/
0 °C to 40 °C (32 °F to 104 °F)/20% to 80% (no
condensation)
Operating
humidity
Storage
temperature/
–10 °C to +60 °C (14 °F to 140 °F)/ 20% to 80% (no
condensation)
Storage humidity
Power
100 V to 240 V AC, 3.6 A-1.4 A, 50/60 Hz
requirements
Power
consumption
100 V AC: 350 W
240 V AC: 330 W
Others
Specifications
41
Page 42

Item Description
Model VPL-CX235/VPL-CW255
Standby power 100 V AC: 3 W (when “Standby Mode” is set to
Heat dissipation 100 V AC: 1195 BTU
Standard
dimensions
(W/H/D)
Mass Approx. 5.4 kg (11 lb 15 oz)
Supplied
accessories
Optional
accessories
Notes
*1: For details, refer to “Acceptable Input Signals” on page 44.
*2: Information on accessories in this manual is current as of December 2011.
Design and specifications of the unit, including the optional accessories, are subject to change
without notice.
*2
“Standard”)/0.5 W (when “Standby Mode” is set to
“Low”)
240 V AC: 3 W (when “Standby Mode” is set to
“Standard”)/0.5 W (when “Standby Mode” is set to
“Low”)
240 V AC: 1126 BTU
Approx. 406 × 122.3 × 330.5 mm (15
13 inches)
Approx. 406 × 113 × 330.5 mm (15
13 inches) (without projecting parts)
See “Checking the Supplied Accessories” in the supplied
Quick Reference Manual.
Projector Lamp LMP-C240 (for replacement)
31
/32 × 413/16 ×
31
/32 × 47/16 ×
Always verify that the unit is operating properly before use. SONY WILL NOT BE LIABLE
FOR DAMAGES OF ANY KIND INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO,
COMPENSATION OR REIMBURSEMENT ON ACCOUNT OF THE LOSS OF PRESENT
OR PROSPECTIVE PROFITS DUE TO FAILURE OF THIS UNIT, EITHER DURING
THE WARRANTY PERIOD OR AFTER EXPIRATION OF THE WARRANTY, OR FOR
ANY OTHER REASON WHATSOEVER.
42
Specifications
Page 43

Pin assignment
RGB input connector (Mini D-sub
15-pin, female)
1 Video input
(red) R
2 Video input
9 Power supply
input for DDC
10 GND
(green) G
3 Video input
11 GND
(blue) B
4 GND 12 DDC/SDA
5 RESERVE 13 Horizontal sync
signal
6 GND (R) 14 Vertical sync
signal
7 GND (G) 15 DDC/SCL
8 GND (B)
RS-232C connector (D-Sub 9-pin,
female)
51
9
6
1NC 6NC
2RXDA 7RTS
3TXDA 8CTS
4DTR 9NC
5 GND
Others
Specifications
43
Page 44

Acceptable Input Signals
Computer signal
Resolution
fH [kHz]/
fV [Hz]
Input connector
RGB HDMI
640 × 350 31.5/70
37.9/85
640 × 400 24.8/56
31.5/70
37.9/85
640 × 480 31.5/60
35.0/67
37.9/73
37.5/75
43.3/85
800 × 600 35.2/56
37.9/60
48.1/72
46.9/75
53.7/85
832 × 624 49.7/75
1024 × 768 48.4/60
56.5/70
60.0/75
68.7/85
1152 × 864 64.0/70
67.5/75
77.5/85
1152 × 900 61.8/66
1280 × 960 60.0/60
75.0/75
1280 × 1024 64.0/60
80.0/75
91.1/85
1400 × 1050 65.3/60
1280 × 768 47.8/60
1280 × 720 44.8/60
1360 × 768 47.7/60
z
z
z
z
z
zz
z
z
z
z
z
zz
z
z
z
z
zz
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
zz
z
zz
z
z
zz
zz
zz
zz
Resolution
fH [kHz]/
fV [Hz]
1440 × 900 55.9/60
1280 × 800 49.7/60
1600 × 1200 75/60
1920 × 1200 74.0/59.95
Input connector
RGB HDMI
zz
zz
z
z
Digital TV signal
Input connector
Signal fV [Hz]
480i 60
576i 50
480p 60
576p 50
1080i 60
1080i 50
720p 60
720p 50
RGB/
YP
BPR
zz
zz
zz
zz
zz
zz
zz
zz
HDMI
Analog TV signal
Input
Signal fV [Hz]
connector
VIDEO /
S VIDEO
NTSC 60
PA L/ SE CA M 50
z
z
Notes
• When a signal other than the signals listed in
table is input, the picture may not be
displayed properly.
• An input signal meant for screen resolution
different from that of the panel will not be
displayed in its original resolution. Text and
lines may be uneven.
44
Specifications
Page 45

Projection Distance and Lens Shift Range
The following describes the projection distance and height from lens center to bottom of screen
by each projected screen size.
The projection distance is the distance between the front of the lens and the surface of the
projected image.
Height H is the height from the bottom of the projected image (top for ceiling mount) to A
(determined by drawing a perpendicular line from lens center to projected image surface). For
this unit, the same projection distance calculations apply to both floor and ceiling installation.
Caution
Never mount the projector on the ceiling or move it by yourself. Be sure to consult with
qualified Sony personnel (charged).
Floor Installation/Ceiling Installation (Top side parallel to ceiling)
Projection distance L
Height H from
lens center to
bottom of screen
Height H from
lens center to
top of screen
Projected
image
A
A
Projected
image
Projection distance L
Front of the lens
Front of the lens
Others
Top side
Projection Distance and Lens Shift Range
45
Page 46

The lens shift range represents the distance in percent (%) by which the lens can be shifted from
the initial position of the projected image, with full width or full height of the projected image
regarded as 100%.
Projected image
50%
50%
Center of the
projected
image
Lens shift range
HSL
Center of the lens
Shaded region: Lens shift range
Side of the projector
Projected image
Center of the
50%
50%
UP: Vertical lens shift range (up) [%]
VS
DN: Vertical lens shift range (down) [%]
VS
projected
image
Lens shift range
Center of the lens
Top of the projector
HSR: Horizontal lens shift range (right) [%]
L: Horizontal lens shift range (left) [%]
HS
Projection distance/Projection distance formula
Projection distance (VPL-CX235)
Projected image size
Projection Distance L
Diagonal D Width × Height
80 inch (2.03 m) 1.63
100 inch (2.54 m) 2.03
120 inch (3.05 m) 2.44
150 inch (3.81 m) 3.05
200 inch (5.08 m) 4.06
×
1.22 (64 × 48) 2.65 – 3.88 (105 – 152) 0.03 (1) 0.03 (1)
×
1.52 (80 × 60) 3.33 – 4.86 (131 – 191) 0.04 (2) 0.04 (2)
×
1.83 (96 × 72) 4.00 – 5.84 (158 – 230) 0.05 (2) 0.05 (2)
×
2.29 (120 × 90) 5.01 – 7.32 (198 – 288) 0.06 (2) 0.06 (2)
×
3.05 (160 × 120) 6.70 – 9.77 (264 – 384) 0.08 (3) 0.08 (3)
UP
VS
VSDN
Center of the
image
HSR
Projected
image
Unit: m (inches)
Height H from lens center
to bottom of screen
Projection
Distance L
(min.)
Projection
Distance L
(max.)
Projection distance formula (VPL-CX235)
D: Projected image size (Diagonal)
H: Distance between the bottom edge of the image and the center of the lens
46
Projection Distance and Lens Shift Range
Page 47

Expression#1 Unit: m (inches)
Projection Distance L (min.) Projection Distance L (max.)
L=0.033708 × D – 0.0490
(L=1.327085 × D – 1.9300)
L=0.049125 × D – 0.0482
(L=1.934037 × D – 1.8982)
Expression#2
Height H from lens center to bottom of screen
Projection Distance L (min.) Projection Distance L (max.)
H=0.00038 × D+0.00000
(H=0.01500 × D+0.00000)
H=0.00038 × D+0.00000
(H=0.01500 × D+0.00000)
Projection distance (VPL-CW255)
Unit: m (inches)
Projected image size
Diagonal D Width × Height
80 inch (2.03 m) 1.72
100 inch (2.54 m) 2.15
120 inch (3.05 m) 2.58
150 inch (3.81 m) 3.23
200 inch (5.08 m) 4.31
×
1.08 (68
×
1.35 (85
×
1.62 (102
×
2.02 (127
×
2.69 (170
×
42) 2.22
×
53) 2.79
×
64) 3.36
×
79) 4.21
×
106) 5.63
Throw Distance L
–
3.25 (88
–
–
4.08 (110
–
4.91 (133
–
6.15 (166
–
8.21 (222
Height H from lens center
to bottom of screen
Projection
Distance L
(min.)
128) 0.00 (0) 0.00 (0)
–
160) 0.00 (0) 0.00 (0)
–
193) 0.00 (0) 0.00 (0)
–
242) 0.00 (0) 0.00 (0)
–
323) 0.00 (0) 0.00 (0)
Projection
Distance L
(max.)
Projection distance formula (VPL-CW255)
D: Projected image size (Diagonal)
H: Distance between the bottom edge of the image and the center of the lens
Expression#1 Unit: m (inches)
Projection Distance L (min.) Projection Distance L (max.)
L=0.028357 × D – 0.0490
(L=1.116434 × D – 1.9300)
L=0.041327 × D – 0.0482
(L=1.627044 × D – 1.8982)
Expression#2
Height H from lens center to bottom of screen
Projection Distance L (min.) Projection Distance L (max.)
H=0.00000
(H=0.00000
×
D+0.00000
×
D+0.00000)
H=0.00000
(H=0.00000
Projection Distance and Lens Shift Range
×
D+0.00000
×
D+0.00000)
Others
47
Page 48

Lens shift range
VPL-CX235 VPL-CX255
5%
4% 4%
5%
VSUP=VSDN=5[%]
R=HSL=4[%]
HS
5%
3% 3%
5%
VS
UP=VSDN=5[%]
R=HSL=3[%]
HS
48
Projection Distance and Lens Shift Range
Page 49

Dimensions
Front
Center of the lens
Side
406.0 (15 31/32)
330.5 (13)
104.5 (4
1
/8)
/32)
15
63.0 (2
Unit: mm (inches)
/16)
7
/16)
13
113.0 (4
122.3 (4
Others
Unit: mm (inches)
Dimensions
49
Page 50

Bottom
368.0 (14
Center of the lens
1
/2)
45.3 (1
25
/32)
Edge of the lens
3
19.0 (
/4)
/16)
7
/16)
3
36.5 (1
4.7 (
/16)
7
88.4 (3 15/32)
102.7 (4
/32)
23
18.4 (
203.1 (8)
1
/32)
13.9 (9/16)
46.1 (1 13/16)
/32)
31
/8) 138.5 (5
1
278.5 (10
104.5 (4
Unit: mm (inches)
50
Dimensions
Page 51

Index
A
AC IN ........................................................4
Acceptable input signal ........................... 44
Adjust Signal ........................................... 21
Adjuster ...............................................3, 14
Adjusting lens shift ..................................13
Air filter ...................................................39
Air filter cover/Ventilation holes
(intake) ...............................................3
APA ...........................................................5
Aspect ............................................5, 21, 22
Audio muting .............................................5
Auto Input Search ....................................24
B
Background .............................................27
Brightness ................................................20
C
CC Display ..............................................25
Color ........................................................20
Color System ........................................... 24
Color Temp. .............................................20
Connecting a computer ..............................7
Connecting a Video equipment .................8
Connecting an external monitor and audio
equipment ........................................10
Connector panel .....................................3, 4
Contrast ...................................................20
Control panel ............................................. 5
D
DDE .........................................................20
Default Gateway ...................................... 25
Digital Zoom .............................................5
Direct Power On ...................................... 27
DNS Server .............................................25
Dot Phase .................................................21
E
ECO MODE (Energy-saving mode) .........6
e-mail report ............................................32
External Control ......................................27
F
fH ............................................................ 29
Focus ....................................................... 12
Focus ring ................................................. 3
Freeze ........................................................ 5
fV ............................................................ 29
G
Gamma Mode ......................................... 20
H
H Size ...................................................... 21
High Altitude Mode ................................ 27
Hue .......................................................... 20
I
Image Flip ............................................... 27
Information menu ................................... 29
Input .......................................................... 4
INPUT SETTING menu ......................... 21
Input-A Signal Sel. ................................. 24
INSTALL SETTING menu ..................... 27
IP Address ............................................... 29
IP Address Setup ..................................... 25
IR Receiver ............................................. 24
K
Keystone ................................................... 5
L
Lamp cover ............................................... 3
Lamp Mode ............................................. 27
Lamp Timer ............................................ 29
Lamp Timer Reset ................................... 25
LAMP/COVER indicator .................... 3, 33
LAN connector ......................................... 4
Language ................................................. 26
Lens shift cover ................................... 3, 13
Location and function of controls ............. 3
M
Main unit ................................................... 3
MENU SETTING menu ......................... 26
Messages list ........................................... 34
Model Name ........................................... 29
N
Network Features .................................... 30
Network Setting ...................................... 25
Others
Index
51
Page 52

O
ON/STANDBY indicator .................... 3, 33
Output .......................................................4
Over Scan ................................................ 21
W
Warping .............................................15, 27
With No Input ..........................................24
With Static Signal ....................................24
P
Panel Key Lock ....................................... 24
Picture mode ........................................... 20
Picture muting ........................................... 5
PICTURE SETTING menu .................... 20
Pin assignment ........................................43
Projecting an image ................................. 11
Projection distance ..................................45
R
Remote commander .................................. 5
Remote control detector ............................3
Replacing the lamp .................................37
RS-232C ....................................................4
S
Security bar ...............................................3
Security Lock ...................................... 3, 27
Selecting an input signal ...........................5
Serial No. ................................................ 29
SET SETTING menu ..............................24
Sharpness ................................................ 20
Shift .........................................................21
Smart APA .............................................. 24
Specifications ..........................................40
Standby Mode .........................................28
Start Up Image ........................................26
Status .......................................................26
Subnet Mask ............................................25
Z
Zoom ........................................................12
Zoom lever .................................................3
T
Troubleshooting ...................................... 35
Turn off ............................................... 5, 18
Turn on ................................................5, 11
U
Using a menu .......................................... 19
V
V Keystone .................................... 5, 14, 27
Ventilation holes ........................................ 3
Volume ......................................................5
52
Index
Page 53

About Trademarks
• Adobe Acrobat is a trademark of Adobe
Systems Incorporated.
• Kensington is a registered trademark of
Kensington Technology Group.
• HDMI, HDMI logo, and High-Definition
Multimedia Interface are trademarks or
registered trademarks of HDMI Licensing
LLC in the United States and other
countries.
• Internet Explore is registered trademarks
of Microsoft Corporation in the United
States and/or other countries.
• PJLink is a registered trademark of Japan
Business Machine and Information
System Industries Association.
• AMX is a trademark of AMX Corporation.
• All other trademarks and registered
trademarks are trademarks or registered
trademarks of their respective holders. In
this manual,
specified.
™
and ® marks are not
Index
Others
53
Page 54

Sony Corporation
 Loading...
Loading...