Sony MVS-6000 User Manual

MVS-6000 System
(With CCP-9000 Series Center Control Panel)
User’s Guide
Multi Format Switcher System
Volume 1 [English]
1st Edition
Software Version 8.00 and Later

NOTICE TO USERS
© 2009 Sony Corporation. All rights reserved. This
manual or the software described herein, in whole or in
part, may not be reproduced, translated or reduced to
any machine readable form without prior written approval
from Sony Corporation.
SONY CORPORATION PROVIDES NO WARRANTY
WITH REGARD TO THIS MANUAL, THE SOFTWARE
OR OTHER INFORMATION CONTAINED HEREIN AND
HEREBY EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMS ANY IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS
FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE WITH REGARD TO
THIS MANUAL, THE SOFTWARE OR SUCH OTHER
INFORMATION. IN NO EVENT SHALL SONY
CORPORATION BE LIABLE FOR ANY INCIDENTAL,
CONSEQUENTIAL OR SPECIAL DAMAGES,
WHETHER BASED ON TORT, CONTRACT, OR
OTHERWISE, ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION
WITH THIS MANUAL, THE SOFTWARE OR OTHER
INFORMATION CONTAINED HEREIN OR THE USE
THEREOF.
Sony Corporation reserves the right to make any
modification to this manual or the information contained
herein at any time without notice.
The software described herein may also be governed by
the terms of a separate user license agreement.

<Organization of This User’s Guide>
The User’s Guide for this system comprises Volumes 1 to 3.
Volume 1
This book. For the contents of this volume, see “Table of Contents” at the front.
Chapter 1 MVS-6000 Functions
Chapter 2 Menus and Control Panel
Chapter 3 Signal Selection and Transitions
Chapter 4 Keys
Chapter 5 Wipes
Chapter 6 DME Wipes
Chapter 7 Frame Memory
Chapter 8 Color Backgrounds, Copy and Swap, and Other Settings
Chapter 9 Color Corrector
Chapter 10 Special Functions
Appendix (Volume 1)
• Wipe Pattern List
• DME Wipe Pattern List
• Resizer DME Wipe Pattern List
• Menu Tree
Index
Volume 2
The volume comprises the following chapters.
Chapter 11 DME Operations
Chapter 12 External Devices
Chapter 13 Keyframe Effects
Chapter 14 Snapshots
Chapter 15 Utility/Shotbox
Chapter 16 Macros
Chapter 17 Files
Appendix (Volume 2)
• SpotLighting
• Functional Differences With Models of DME
• Macro File Editing Rules
• About the Macro Attachment List Display
• Menu Operations Not Recorded in a Menu Macro
Index
Volume 3
The volume comprises the following chapters.
Chapter 18 System Setup (System)
Chapter 19 Control Panel Setup (Panel)
Chapter 20 Switcher Setup (Switcher)
Chapter 21 DME Setup (DME)
Chapter 22 DCU Setup (DCU)
3

Chapter 23 Setup Relating to Router Interface and Tally (Router/Tally)
Chapter 24 Simple Connection of the MKS-8080/8082 AUX Bus Remote
Panel
Chapter 25 DIAGNOSIS
Appendix (Volume 3)
• Data Saved by [Setup Define] and [Initial Status Define]
• Error Messages
Index
4

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 MVS-6000 Functions
Introduction ..................................................................................................14
Features of the MVS-6000 Multi Format Switcher System......................16
Basic Video Processing.................................................................................18
Transitions.............................................................................................18
Keys.......................................................................................................22
Wipes.....................................................................................................23
DME Wipes...........................................................................................23
Frame Memory ......................................................................................24
Color Backgrounds................................................................................24
Copy and Swap......................................................................................24
Video Process........................................................................................25
Color Corrector......................................................................................25
Side Flags ..............................................................................................25
Simple P/P Software..............................................................................26
Creation of Special Effects and Management of Data and Operations...27
Digital Multi Effects (DME) .................................................................27
External Devices....................................................................................28
Keyframes .............................................................................................28
Snapshots...............................................................................................29
Utility.....................................................................................................30
Shotbox..................................................................................................30
Macros ...................................................................................................30
Files .......................................................................................................31
Setup ..............................................................................................................32
Chapter 2 Menus and Control Panel
Names and Functions of Parts of the Control Panel .................................34
Example Control Panel Configuration ..................................................34
Cross-Point Control Block ....................................................................36
Transition Control Block.......................................................................37
Device Control Block (Joystick)...........................................................42
Keyframe Control Block .......................................................................43
Numeric Keypad Control Block............................................................46
5Table of Contents

Auxiliary Bus Control Block.................................................................49
Menu Control Block..............................................................................50
Memory Card/USB Adaptor Block.......................................................51
“Memory Stick”/USB Connections Block............................................52
Key Control Block (MKS-8035 Key Control Module, Option) ...........54
Device Control Block (MKS-8031TB Trackball Module, Option) ......58
Device Control Block (MKS-8036A Search Dial Module, Option) .....61
Utility/Shotbox Control Block (MKS-8033 Utility/Shotbox Module,
Option) .......................................................................................65
Downstream Key Control Block (MKS-8032 DSK Fader Module,
Option) .......................................................................................66
Basic Menu Operations................................................................................68
Menu Organization................................................................................68
About the Top Menu List ......................................................................68
Accessing Menus...................................................................................68
Displaying a Menu ................................................................................74
Interpreting the Menu Screen................................................................75
Menu Operations ...................................................................................77
Switching Between the Main Menu Site and Subsidiary Menu Site ....89
Shortcut Menu .......................................................................................89
Chapter 3 Signal Selection and Transitions
Table of Contents
6
Video Processing Flow .................................................................................94
Signal Selection .............................................................................................96
Basics of Signal Selection .....................................................................96
Bus Selection.........................................................................................97
Signal Assignment and Selection..........................................................98
Signal Name Display...........................................................................102
Transitions...................................................................................................103
Selecting the Next Transition..............................................................103
Transition Types..................................................................................103
Procedure for Basic Transition Operation...............................................106
Key Priority Setting....................................................................................109
Setting the Key Priority in the Transition Control Block....................109
Setting the Key Priority by a Menu Operation....................................111
Display of the Key Output Status and Key Priority............................113
Selecting the Transition Type by a Menu Operation..............................114
Super Mix Settings .....................................................................................115
Color Matte Settings...................................................................................116

Executing a Transition...............................................................................119
Transition Preview .....................................................................................131
Independent Key Transitions ....................................................................133
Chapter 4 Keys
Overview......................................................................................................141
Key Setting Operations Using Menus.......................................................148
Key Setting Operations With the Cross-Point Control Block................173
Key Setting Operations With the Key Control Block.............................175
Transition Indicator Function..............................................................119
Setting the Transition Rate..................................................................120
Pattern Limit........................................................................................122
Executing an Auto Transition..............................................................126
Executing a Transition With the Fader Lever (Manual Transition)....127
Combinations of Auto and Manual Transitions ..................................127
Non-Sync State....................................................................................127
Fader Lever Operation in Bus Fixed Mode.........................................128
Basic Independent Key Transition Operations....................................136
Setting the Independent Key Transition Type by a Menu Operation..136
Setting the Independent Key Transition Rate......................................137
Key Types............................................................................................141
Key Modifiers......................................................................................143
Key Memory........................................................................................146
Key Default .........................................................................................147
Key Setting Menus ..............................................................................148
Key Type Setting.................................................................................149
Chroma Key Composition...................................................................151
Chroma Key Adjustments ...................................................................152
Selecting Key Fill and Key Source .....................................................158
Key Edge Modifications......................................................................160
Masks...................................................................................................167
Applying a DME Effect to a Key........................................................169
Key Modify Clear................................................................................171
Blink Function.....................................................................................171
Video Processing.................................................................................172
Applying a DME Effect to a Key........................................................173
Operations in the Key Control Block..................................................175
Key Edge Modifications......................................................................179
Masks...................................................................................................183
7Table of Contents

Resizer .........................................................................................................186
Key Snapshots.............................................................................................196
Chapter 5 Wipes
Overview......................................................................................................200
Basic Procedure for Wipe Settings ...........................................................201
Wipe Settings for Independent Key Transitions .....................................213
Wipe Snapshots...........................................................................................218
Applying a DME Effect to a Key........................................................184
Other Key Setting Operations .............................................................185
Two-Dimensional Transformations of Keys.......................................186
Resizer Interpolation Settings .............................................................191
Resizer Crop/Border Settings..............................................................191
Applying Resizer Effects.....................................................................194
Key Snapshot Operations ....................................................................196
Wipe Settings Menu ............................................................................201
Wipe Pattern Selection ........................................................................201
Setting Wipe Modifiers .......................................................................201
Wipe Modify Clear..............................................................................212
Basic Procedure for Independent Key Transition Wipe Settings........213
Setting Independent Key Transition Wipe Modifiers .........................214
Wipe Snapshot Operations With the Menus .......................................218
Chapter 6 DME Wipes
Overview......................................................................................................222
Basic Procedure for DME Wipe Settings .................................................232
DME Wipe Settings for Independent Key Transitions ...........................242
Resizer DME Wipe Setting ........................................................................246
DME Wipe Snapshots ................................................................................248
Table of Contents
8
Types of DME Wipe Pattern...............................................................222
DME Wipe Pattern Variation and Modifiers.......................................229
Relation Between DME Wipes and Other Effects..............................230
DME Wipe Settings Menu ..................................................................232
DME Wipe Pattern Selection ..............................................................232
Setting DME Wipe Modifiers .............................................................234
DME Wipe Modify Clear....................................................................241
Basic Procedure for Independent Key Transition DME Wipe Settings
..................................................................................................242
Setting Independent Key Transition DME Wipe Modifiers................243

DME Snapshot Operations With the Menus.......................................248
Creating User Programmable DME Patterns .........................................249
User Programmable DME Transition Mode .......................................249
Chapter 7 Frame Memory
Overview......................................................................................................256
Still Image Operations ...............................................................................259
Preparations .........................................................................................259
Interpreting the Frame Memory Menu................................................260
Selecting an Input Image.....................................................................263
Selecting Outputs and Target Frame Memory ....................................264
Capturing and Saving an Input Image.................................................265
Recalling Still Images .........................................................................269
Image Processing.................................................................................271
Image Output.......................................................................................276
Continuously Capturing Still Images (Record)...................................277
Recalling a Continuous Sequence of Still Images (Animation)..........279
Frame Memory Clip Function ..................................................................282
Frame Memory Clip Operations...............................................................284
Preparations for Operation ..................................................................284
Recalling Clips ....................................................................................284
Clip Playback ......................................................................................286
Clip Creation .......................................................................................290
Creating and Handling Frame Memory Folders..................................292
Clip Output..........................................................................................293
Recording and Playback of Ancillary Data.........................................293
Clip Transition Operations........................................................................296
Image Data Management...........................................................................299
Pair File Processing .............................................................................299
Moving Files........................................................................................300
Deleting Files ......................................................................................301
Renaming Files....................................................................................302
External Hard Disk Drive Access .............................................................303
Hard Disk Formatting..........................................................................303
Saving Files .........................................................................................304
Recalling Files.....................................................................................305
Chapter 8 Color Backgrounds, Copy and Swap, and Other Settings
Color Background ......................................................................................308
9Table of Contents

Color Background Settings Menu.......................................................308
Basic Color Background Setting Operations.......................................308
Copy and Swap ...........................................................................................312
Copy and Swap Operations .......................................................................316
Copy and Swap Menu Operations.......................................................316
Copy by Button Operation ..................................................................317
Misc Menu Operations...............................................................................318
Port Settings for Control From an External Device ............................318
Editing Keyboard Settings...................................................................319
Safe Title Settings ...............................................................................320
Displaying a List of Transition Rates and Changing the Settings.......321
AUX Menu Operations ..............................................................................323
AUX Bus Settings ...............................................................................323
Status Menu ................................................................................................324
Router Control Menu Operations.............................................................325
Checking the List of Inputs for Each Destination...............................325
Switching the Source for Each Destination.........................................326
Video Process ..............................................................................................327
Video Process Adjustments of a Primary Input Signal .......................327
Video Process Adjustments on a Particular Bus .................................327
Video Process Memory .......................................................................328
Video Process Settings................................................................................329
Chapter 9 Color Corrector
Preparations................................................................................................332
Overall Color Corrector Operations ........................................................334
Enabling Color Corrector ....................................................................334
Copy and Swap Operations .................................................................334
Color Corrector Functions ........................................................................336
Input Video Processing Operations.....................................................336
Primary Color Correction Operations .................................................337
Secondary Color Correction Operations .............................................340
RGB Clip Operations ..........................................................................341
Luminance Processing Operations ......................................................342
Spot Color Adjustment........................................................................345
Output Video Processing Operations ..................................................347
YUV Clip Operations..........................................................................348
Table of Contents
10

Chapter 10 Special Functions
Side Flags.....................................................................................................352
Overview .............................................................................................352
Side Flag Settings................................................................................352
Wipe Action on Images With Side Flags............................................354
DME Wipe Action for an Image With Side Flags ..............................355
Simple P/P Software ...................................................................................357
Overview .............................................................................................357
Restrictions on Use..............................................................................357
Simple P/P Output Signal Selection on an M/E..................................360
Appendix (Volume 1)
Wipe Pattern List .......................................................................................362
DME Wipe Pattern List .............................................................................363
DME Wipe Patterns Available in One-Channel Mode .......................363
DME Wipe Patterns Available in Two-Channel Mode.......................367
Resizer DME Wipe Pattern List ...............................................................370
Menu Tree ...................................................................................................372
Recalling Menus..................................................................................372
M/E-1 to M/E-3 Menus .......................................................................372
PGM/PST Menu ..................................................................................375
Frame Memory Menu..........................................................................377
Color Bkgd Menu................................................................................378
AUX/MON Menu................................................................................378
CCR Menu...........................................................................................379
Copy/Swap Menu................................................................................380
Misc Menu...........................................................................................380
Status Menu.........................................................................................380
DME Menu..........................................................................................381
Global Effect Menu .............................................................................382
Device Menu .......................................................................................382
Macro Menu ........................................................................................383
Key Frame Menu.................................................................................384
Effect Menu.........................................................................................385
Snapshot Menu....................................................................................386
Shotbox Menu .....................................................................................387
File Menu ............................................................................................388
Engineering Setup Menu.....................................................................389
11Table of Contents

Diagnostic Menu .................................................................................393
Index ............................................................................................................394
12
Table of Contents

Chapter 1 MVS-6000 Functions
Introduction ................................................................................................14
Features of the MVS-6000 Multi Format Switcher System ....................16
Basic Video Processing ...............................................................................18
Transitions ...........................................................................................18
Keys .....................................................................................................22
Wipes ...................................................................................................23
DME Wipes .........................................................................................23
Frame Memory ....................................................................................24
Color Backgrounds ..............................................................................24
Copy and Swap ....................................................................................24
Video Process ......................................................................................25
Color Corrector ....................................................................................25
Side Flags ............................................................................................25
Simple P/P Software ............................................................................26
Creation of Special Effects and Management of Data and Operations .27
Digital Multi Effects (DME) ...............................................................27
External Devices ..................................................................................28
Keyframes ...........................................................................................28
Snapshots .............................................................................................29
Utility ...................................................................................................30
Shotbox ................................................................................................30
Macros .................................................................................................30
Files .....................................................................................................31
Setup ............................................................................................................32
Chapter 1 MVS-6000 Functions
Introduction
This manual is the User’s Guide for the MVS-6000 Multi Format Switcher
system.
This manual describes principally the operation of the system using the CCP9000 series of center control panels.
The User’s Guide for this system comprises three volumes.
For the contents of each volume, see the section “Organization of This User’s
Guide” at the front of this volume.
Devices and system nomenclature
In this manual, when discussing the principal components of the MVS-6000
system, in place of the formal product names, abbreviated names
characterizing the functions and features are sometimes used. When
distinctions between system configurations must be drawn, the terms in the
following table are used.
Principal components and naming
The formal product names of the principal components of the MVS-6000
system, and the terms used in this manual are as follows.
Formal product name Term used in this manual
MVS-6000 Multi Format Switcher Processor Switcher or switcher processor
MKS-6470 Board Set DME or DME board set or MKS-6470
MVE-8000A Multi Format DME Processor DME or DME processor or MVE-
8000A
MVE-9000 Multi Format DME Processor DME or DME processor or MVE-9000
CCP-9000/9000A-series Center Control Panel Control panel or center control panel
DCU-8000 (MKS-8700) Device Control Unit DCU or MKS-8700
DCU-2000 (MKS-2700) Device Control Unit DCU or MKS-2700
14
Introduction
System nomenclature
The following terms are used for systems, depending on the combination of
installed options, and the signal format.
System configuration and features Term for system
System with installed option boards and
settings to support HDTV format
System with installed option boards and
settings to support SDTV format
HD system
SD system

System configuration and features Term for system
A system in which the center control panel has
two M/E banks
A system in which the center control panel has
one M/E bank
2M/E system
1M/E system
Related manuals
The following manuals are supplied with the individual products of the MVS6000 Multi Format Switcher system.
MVS-6000 Switcher Processor Pack
• MVS-6000 Operation Manual
• MVS-6000/8000 Installation Manual
MVE-8000A DME Processor Pack
• MVE-8000A Operation Manual
• MVE-8000A Installation Manual
MKS-6470 DME Board Set
• MKS-6470 Operation Manual
• MKS-6470 Installation Manual
MVE-9000-C DME Processor Pack
• MVE-9000-C Operation Manual
• MVE-9000-C Installation Manual
CCP-9000-C Center Control Panel Pack
• CCP-9000-C Operation Manual
• CCP-9000-C Installation Manual
• CCP-9000A-C Operation Manual
• CCP-9000A-C Installation Manual
Chapter 1 MVS-6000 Functions
DCU-8000 Device Control Unit Pack
• DCU-8000 Operation Manual
• DCU-8000 Installation Manual
DCU-2000 Device Control Unit Pack
• DCU-2000-C Operation Manual
• DCU-2000-C Installation Manual
15Introduction

Features of the MVS-6000 Multi Format Switcher System
Chapter 1 MVS-6000 Functions
The MVS-6000 Multi Format Switcher System boasts high performance and
multifunctionality. The following are some of the principal features of this
system.
System configuration flexibility
Multiformat support
This system supports both HDTV and SDTV signal formats. The format
selection can be switched by a simple control panel operation.
For the signal formats that can be selected, see “Setting the Signal Format” in
Chapter 18 (Volume 3).
Extensible system configuration
By suitable combination of options, the switcher can be configured with
various inputs and outputs, and different numbers of M/E banks. The system
offers the flexibility to change and expand as required.
Additionally, by installing the optional MKS-6470 DME Board Set, you can
obtain the functionality of two DME channels.
Powerful external device interfaces
By connecting to a Sony routing switcher or similar, a large system can be
built. From the control panel, it is also possible to operate other equipment,
including VTRs and disk recorders.
Powerful tally system
The complete system including routing switcher provides an all-inclusive tally
system. The system can be adapted to different applications and settings, using
multiple tally outputs, including both on-air and recording tallies.
Comprehensive video manipulation
M/E banks
Each mix/effects bank (M/E bank) is equipped with four keyers, and each
keyer is capable not only of chroma keying, but also independent key
transitions separate from the background transitions. The four keys can be
freely combined, to carry out four different program outputs.
Features of the MVS-6000 Multi Format Switcher System
16

Powerful frame memory functions
An HDTV system can hold approximately 1,000 still image frames or 2,000
frames in 720P/59.94 format, and an SDTV system can hold approximately
5,000 frames in 480i/59.94 format or 4,000 frames in 576i/50 format in
memory, and up to eight frames can be recalled and used simultaneously.
Link operation with DME
Using the MKS-6470 DME Board Set (option), a range of DME functions
including DME wipes and processed keys can be handled as switcher
functions.
You can use a maximum of two DME channels.
Designed for use in a live broadcasting environment
High-performance user interface
The menu control block provides a large color LCD panel, with rapid touchpanel menu selection.
The source name displays have color backlit LCD displays. The signal names,
and graphical representations of the patterns associated with buttons provide
intuitive feedback, and allow the immediate decisions that are required in a live
operating environment.
Chapter 1 MVS-6000 Functions
17Features of the MVS-6000 Multi Format Switcher System

Chapter 1 MVS-6000 Functions
Basic Video Processing
This section introduces basic functions used for video processing on the
switcher.
Transitions
In the M/E banks and PGM/PST bank, the switch from the current video stream
(appearing on the corresponding program monitor) to a new video stream is
referred to as a transition.
In the M/E banks and PGM/PST bank, you can change one of the images, the
background, and keys 1 to 4 (downstream keys 1 to 4 in the PGM/PST bank),
and also vary combinations of these simultaneously.
The following are examples of transition.
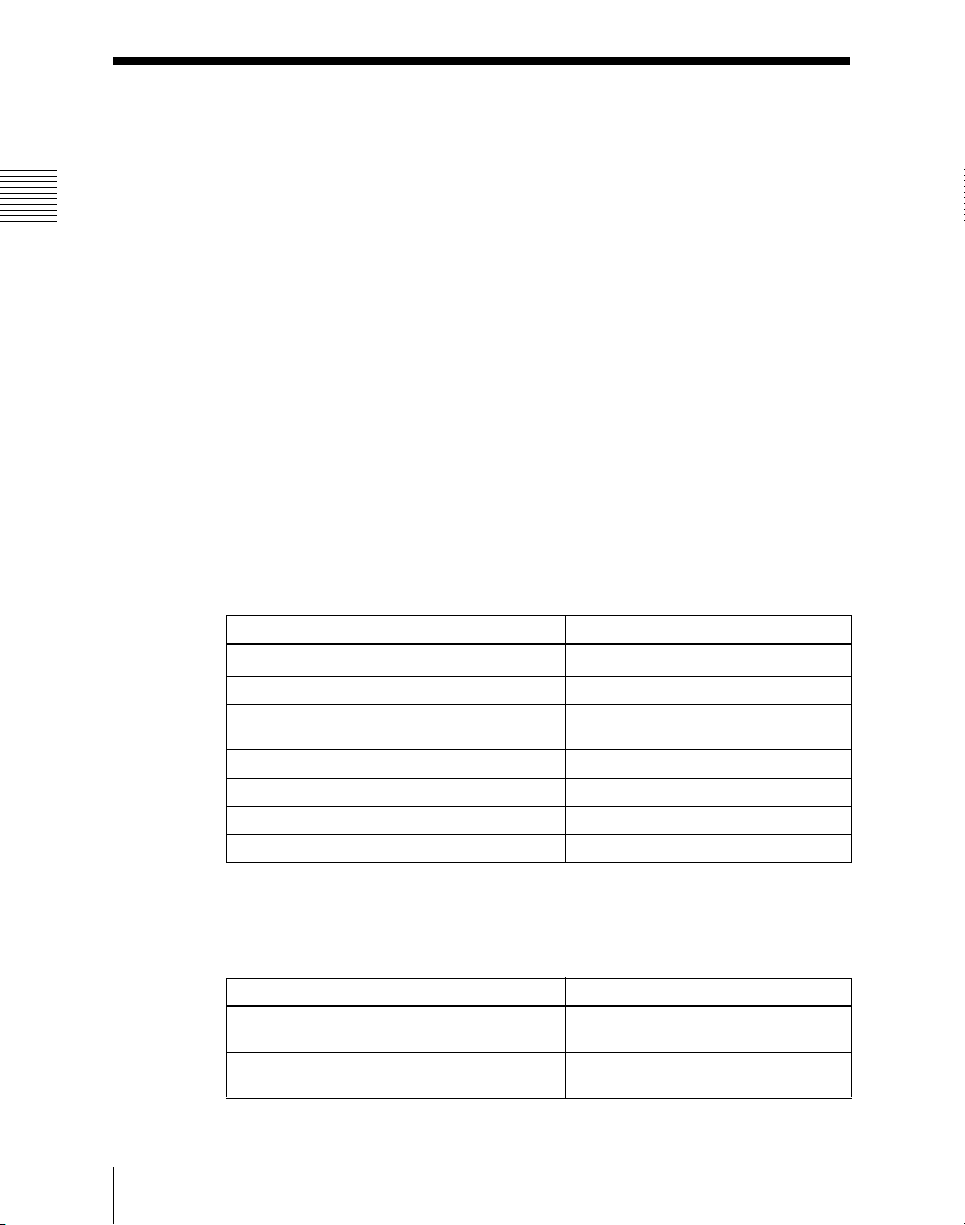
Changing the background
A background transition switches from the video currently selected on the
background A bus (the current video) to the video selected on the background
B bus (the new video).
Basic Video Processing
18
Transition
Background BBackground A
In the default selection of flip-flop mode (see page 128), the background
always switches in the direction from the A bus to the B bus. When the
transition completes, the cross-point selections on the A and B buses are
interchanged.
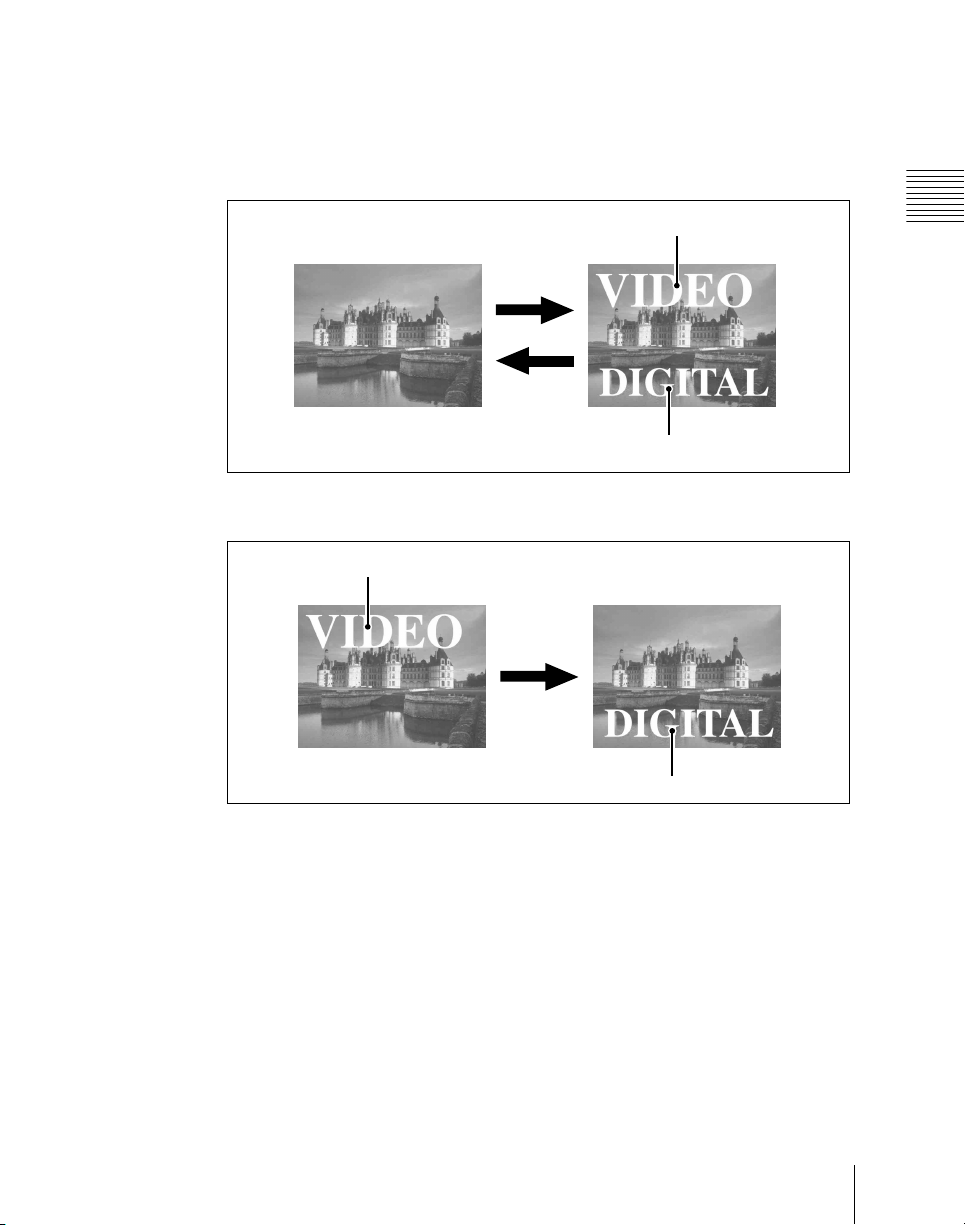
Inserting and deleting a key
You can insert one or more of the four keys (downstream keys on the PGM/
PST bank).
If you select a key which is already inserted, the transition will delete the key.
A simultaneous combination of deleting and inserting keys is also possible.
Key 1
Insert
Delete
Inserting or deleting key 1 and key 2
Transition
Key 1
Key 2
Key 2
Chapter 1 MVS-6000 Functions
Deleting key 1 and inserting key 2
19Basic Video Processing
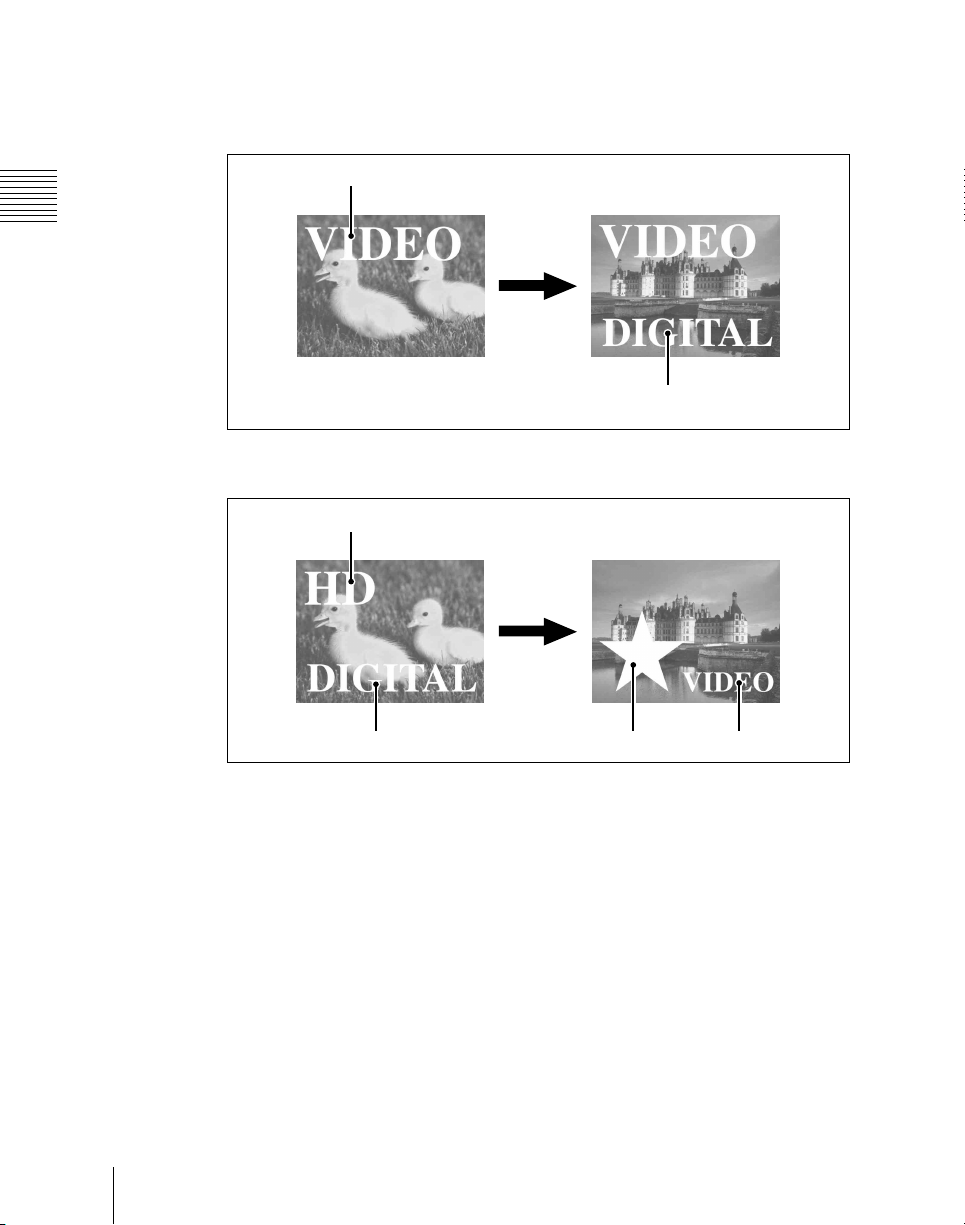
Chapter 1 MVS-6000 Functions
Simultaneously changing the background and keys
You can change any of the four keys (downstream keys on the PGM/PST bank)
and the background at the same time.
Key 1
Transition
Key 2
Changing the background and key 2 simultaneously
Key 1
Basic Video Processing
20
Transition
Key 2
Changing the background and keys 1 to 4 simultaneously
Key 3
Key 4
Selecting the transition type determines the way in which the transition occurs.
The following are the transition type.
•Mix
• NAM (non-additive mix)
• Super mix
• Preset color mix (color matte)
•Wipe
•DME wipe
• Clip transition
•Cut

There are two modes for carrying out a transition: auto transitions are carried
out by a button operation, and manual transitions are carried out using the fader
lever. It is also possible to combine these two modes.
Independent Key Transitions
In addition to common transitions, it is possible to carry out independent
transitions on the keyers of the M/E banks and PGM/PST bank. These are
called “independent key transitions.”
By carrying out an independent key transition in combination with a common
transition, different transition types can be used for the background and keys.
The following description compares the independent key transition with a
common transition, taking a simultaneous change of the background and key
as an example.
Video used in the transition
Chapter 1 MVS-6000 Functions
Background A
Background B
Key to insert
Effect of a common transition
In the case shown in the previous illustration, carrying out a common transition
produces the following change in the image.
Transition type: wipe
Effect of a common transition
Same wipe is applied to
background and key.
21Basic Video Processing
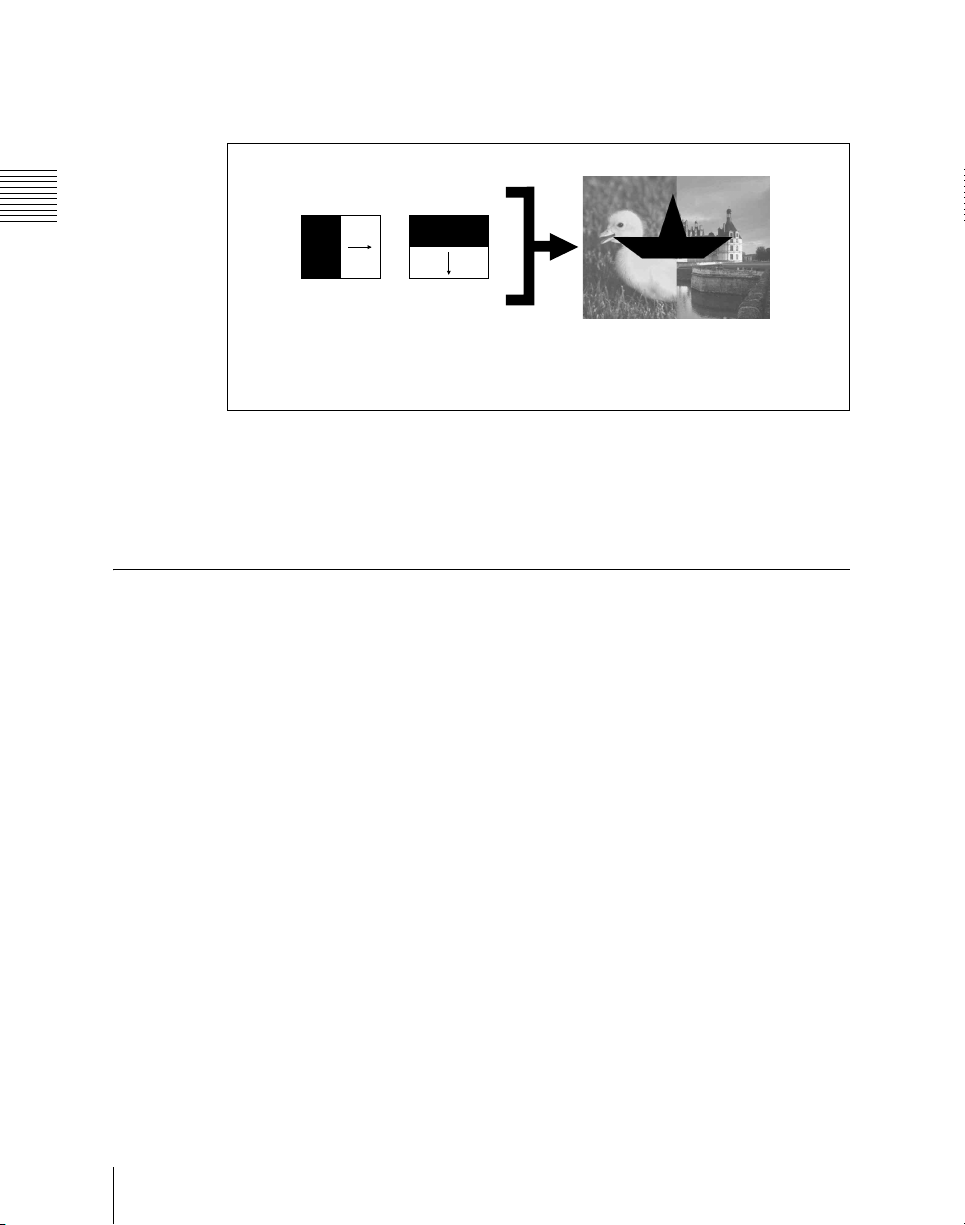
Chapter 1 MVS-6000 Functions
Effect of use with an independent key transition
The key is inserted with an independent key transition as the background
changes with a common transition, providing the following result.
Keys
Transition type:
wipe
Effect of a background transition and independent key transition
Independent key
transition type:
wipe
Different wipe patterns are applied to
the background and key transitions.
For details of transitions, see Chapter 3 “Signal Selection and Transitions”
(page 93).
A key is an effect in which a part of the background image is replaced by an
image or superimposed text. The signal determining how the background is cut
out is termed “key source,” and the signal that replaces the cut-out part is
termed “key fill.” The system component responsible for processing a key is
referred to as a keyer.
Each switcher bank has four keyers.
On each switcher bank, you can use the following key types (methods of
processing the key source).
• Luminance key
• Linear key
• Color vector key
• Chroma key
• Key wipe pattern key
Key modifiers
Basic Video Processing
22
You can apply borders and other modifiers to the edge of the key image.

Masks
A mask allows a part of the image to be replaced by the background or a key.
To prevent unwanted holes in the background, or if a key is not the desired
shape, you can correct this with a mask.
Resizer
Wipes
This function allows you to apply effects, similar to a DME, such as zoom,
movement, or aspect ratio change to a part of a created key. You can use the
following operations.
• Two-dimensional transform of a key
• Resizer interpolation settings
• Resizer crop/border settings
• Resizer effect settings (mosaic, defocus)
For details, see Chapter 4 “Keys” (page 139).
A wipe is a transition from the current video stream to a new video stream,
using a wipe pattern.
Changing the background by means of a wipe is referred to as a “background
wipe,” and inserting or deleting a key with a wipe is termed a “key wipe.”
There are two types of wipe: those that can be selected in a common transition,
and those that can be selected in an independent key transition.
You can also specify the wipe direction, or set the pattern position, applying
various changes and modifiers to the selected wipe pattern.
For details, see Chapter 5 “Wipes” (page 199).
Chapter 1 MVS-6000 Functions
DME Wipes
A DME wipe is a wipe transition that uses a DME effect to change from one
video image to the next.
There are two types of DME wipe: those which can be selected for a normal
transition, and those which can be selected for an independent key transition.
The patterns that can be used for a DME wipe are as follows.
Slide, Squeeze, Door, Flip tumble, Frame in-out, Picture-in-picture, 2D
trans, 3D trans, Mosaic, Defocus, Brick, and User programmable DME
23Basic Video Processing

You can also specify the wipe direction, or set the pattern position, applying
various changes and modifiers to the selected DME wipe pattern.
Resizer DME wipes
Using the resizer, you can carry out key DME wipes.
Chapter 1 MVS-6000 Functions
For details, see Chapter 6 “DME Wipes” (page 221).
Frame Memory
Frame memory is a function for using a still image or video (frame memory
clip) as material for editing.
You can create a still image by capturing a frame of input video or a clip by
specifying a range of input video. The created images and clips can be written
to memory for playback, editing, and output.
For details, see Chapter 7 “Frame Memory” (page 255).
Color Backgrounds
This function can be used to obtain color background video.
One color signal generated from the dedicated generators can be output.
For details, see “Color Background” (page 308).
Copy and Swap
Basic Video Processing
24
This function can be used to copy and swap the settings among the M/E-1 to
M/E-3, and PGM/PST banks or between keyers.
The following settings can be copied or swapped.
• Overall settings for the M/E and PGM/PST banks
• Keyer settings
• Wipe settings in a transition control block
• Wipe settings in an independent key transition control block
• DME wipe settings in a transition control block
• DME wipe settings in an independent key transition control block
• Matte data (color 1, color 2, and how to compose them)
• Color settings
• DME channel settings
• Format converter input settings (copy only)
• Format converter output settings (copy only)

For details, see “Copy and Swap” (page 312).
Video Process
The term “video process” is applied to adjustments to the gain, hue, black level
of the input video signal. There are two types of adjustment; adjustment of an
individual primary input signal and adjustment as image effects on a particular
bus
For details, see “Video Process” (page 327).
Color Corrector
The color corrector enables video signal color correction (black balance/white
balance adjustment, gamma correction, knee correction, etc.).
The color corrector includes the following adjustments.
• Input video processing
• Primary color correction
• Secondary color correction
• RGB clip
• Luminance processing
• Spot color adjustment
• Output video processing
• YUV clip
For details, see Chapter 9 “Color Corrector” (page 331).
Chapter 1 MVS-6000 Functions
Side Flags
The term “side flags” refers to the areas to left and right of an image with aspect
ratio 4:3 embedded within a 16:9 frame, when these areas are filled with a
separate image selected from the utility bus.
25Basic Video Processing
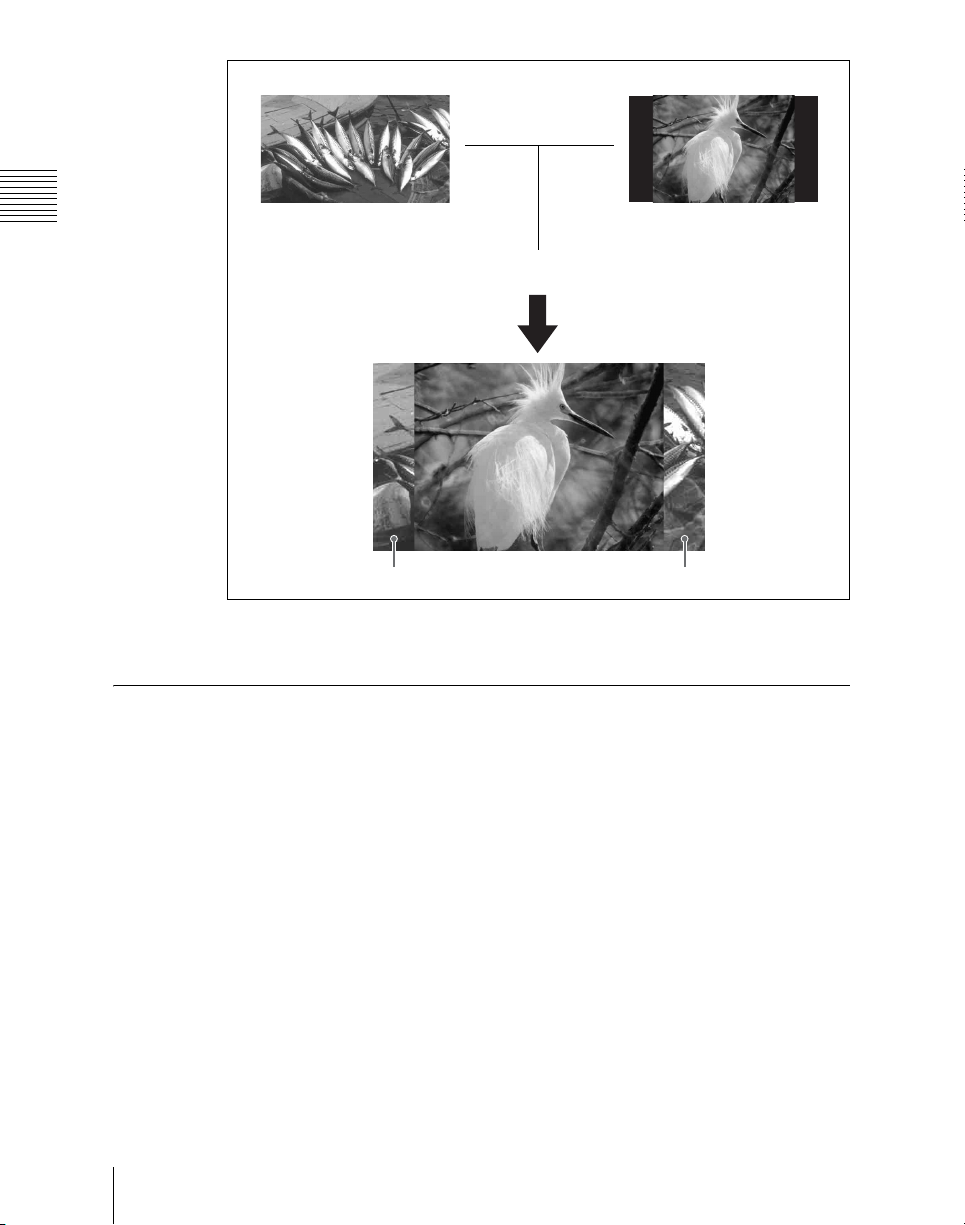
Chapter 1 MVS-6000 Functions
areas (selected from utility
bus)
Input source with aspect ratioImage to fill the side flag
Turn the side flag
function on
Side flag area
For details, see “Side Flags” (page 352).
Simple P/P Software
By installing the BZS-6250 Simple P/P Software in the MVS-6000 Switcher
Processor, you can use a separate program/preset function without using the M/
E hardware.
For details, see “Simple P/P Software” (page 357).
Side flag area
Basic Video Processing
26

Creation of Special Effects and Management of Data and Operations
This section introduces functions used for creation of special effects, control of
external devices or switcher operations, and data management.
Digital Multi Effects (DME)
When used with the switcher, DME allows you to add three-dimensional
effects such as image movement, rotation, magnification and shrinking, as well
as a wide variety of special effects.
Each channel can be used on its own or in combination with other channels,
which allows you to create advanced effects with more complexity.
The following types of DME special effects are available.
• Edge effects: Border, Crop, Beveled Edge, Key Border, Art Edge, Flex
Shadow, Drop Shadow
• Effects for entire image: Defocus, Blur, Multi Move
• Effects for video image: Sepia, Mono, Posterization, Solarization, Nega,
Contrast, Mosaic, Mask, Sketch, Metal, Dim and Fade, Glow
• Freeze effects
• Nonlinear effects: Wave, Mosaic Glass, Flag, Twist, Ripple, Rings, Broken
Glass, Flying Bar, Blind, Split, Split Slide, Mirror, Multi Mirror,
Kaleidoscope, Lens, Circle, Panorama, Page Turn, Roll, Cylinder, Sphere,
Explosion, Swirl, Melt, Character Trail
• Lighting effects: Lighting, Spotlighting
• Recursive effects: Trail, Motion Decay, Keyframe Strobe
• Background color
• Separate Sides (effects for front and back sides)
• Signal inversion (Invert effect)
• Key density adjustment
• Key source selection
Chapter 1 MVS-6000 Functions
Global effects
Global effects are special effects created by combining the images of
successive channels. The following types of global effects are available.
• Combiner
•Brick
• Shadow
For details, see Chapter 11 “DME” (Volume 2).
27Creation of Special Effects and Management of Data and Operations

Chapter 1 MVS-6000 Functions
External Devices
In this system, you can operate while controlling the following types of
external device:
• Devices supporting P-Bus (Peripheral II protocol)
• Devices supporting GPI
•VTRs
• Disk recorder (Sony disk 9-pin protocol and video disk communications
protocol)
• Extended VTR (Abekas A53 protocol)
For details on the devices that can be connected, consult your Sony
representative.
You can control an external device by previously registering timeline
keyframes.
For details, see Chapter 12 “External Devices” (Volume 2).
Keyframes
A keyframe represents an instantaneous state of an image; it can be saved in a
register (see “Register” in Chapter 13 (Volume 2)) and recalled for reuse.
By arranging a number of keyframes on the time axis, and interpolating
between successive keyframes, you can create an effect in which there is a
continuous change from each keyframe to the next.
Creation of Special Effects and Management of Data and Operations
28

The following figure shows three keyframes created with a wipe pattern (the
circle) in different positions. This is interpolated to create the effect shown.
Background A
Background B
Keyframe 1 Keyframe 2 Keyframe 3
Example of keyframes and effect execution
Interpolated images
Effect execution
You can save the sequence of keyframes representing a single effect in a
register. Then by recalling this register, you can replay the same effect.
For details, see Chapter 13 “Keyframe Effects” (Volume 2).
Chapter 1 MVS-6000 Functions
Snapshots
The term “snapshot” refers to a function whereby the various settings required
to apply a particular effect to an image are saved in a register as a set of data,
for recall as required, to recover the original state.
Snapshots are divided as follows.
• Snapshots applying to a particular region (functional block of the switcher or
• Master snapshot
• Key snapshot
• Wipe snapshot
• DME wipe snapshot:
An individual snapshot may also have attached special conditions relating to
switcher or DME operation when the snapshot is recalled.
DME)
29Creation of Special Effects and Management of Data and Operations

These conditions are called “attributes” of the snapshot, and can be added when
the snapshot is saved or recalled.
For details, see Chapter 14 “Snapshots” (Volume 2).
Chapter 1 MVS-6000 Functions
Utility
The utility function refers to a function whereby you can assign an arbitrary
action or a shortcut for frequently used menu to a particular button, then
instantly recall the action or menu by pressing the button.
For details, see “Utility Execution” in Chapter 15 (Volume 2).
Shotbox
The term “shotbox” refers to a function whereby for each specified region (see
“Region” in Chapter 13 (Volume 2)) any snapshot or keyframe effect can be
recalled simultaneously.
For details, see “Shotbox” in Chapter 15 (Volume 2).
Macros
The term “macro” refers to the function whereby a sequence of signal
selections and other operations on the control panel is saved as data in memory,
so that it can be recalled as required to automatically execute the same
sequence of operations.
The individual control panel operations constituting a macro are termed
“events.
Macros also provide the following functions.
Menu macros
The term “menu macro” refers to the function whereby a sequence of menu
operations is saved as data in memory, so that it can be recalled as required to
automatically execute the same sequence of operations.
Macro timeline
By recording macro recall and execute action on a timeline, in the same way as
for keyframes in an effect, you can automatically execute them in a sequence.
Creation of Special Effects and Management of Data and Operations
30
 Loading...
Loading...