Sony LCX026ALF Datasheet
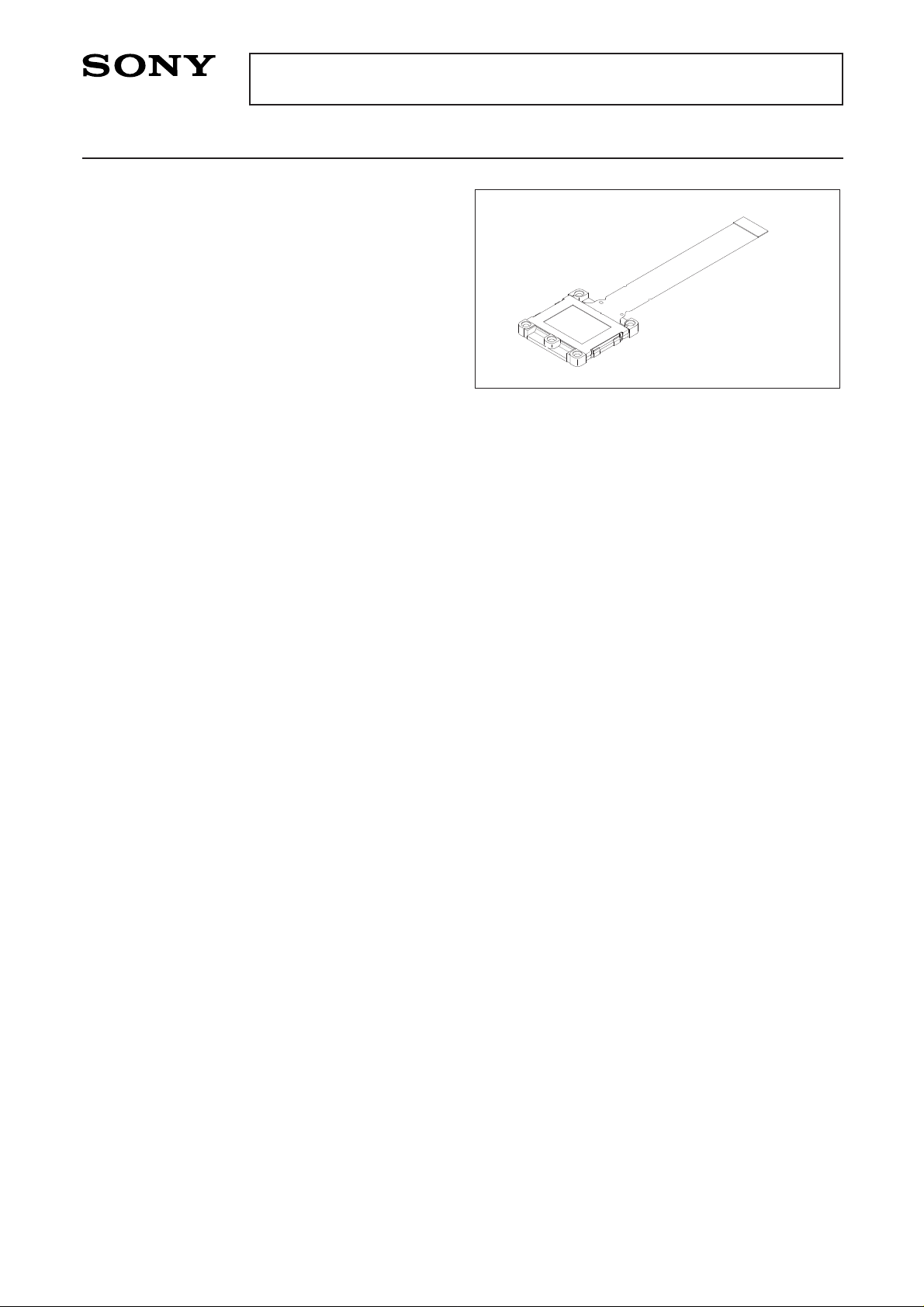
Description
The LCX026ALF is a 2.3cm diagonal active matrix
TFT-LCD panel addressed by polycrystalline silicon
super thin film transistors with a built-in peripheral
driving circuit. Use of three LCX026ALF panels
provides a full-color representation. The striped
arrangement suitable for data projectors is capable
of displaying fine text and vertical lines.
The adoption of an advanced on-chip black matrix
realizes a high luminance screen. And cross talk
free circuit and ghost free circuit contribute to high
picture quality.
This panel has a polysilicon TFT high-speed
scanner and built-in function to display images
up/down and/or right/left inverse. The built-in 5V
interface circuit leads to lower voltage of timing and
control signals.
The panel contains an active area variable circuit
which supports SVGA/VGA/PC98∗1data signals by
changing the active area according to the type of
input signal. In addition, double-speed processed
NTSC/PAL can also be supported.
∗1
“PC98” is a treadmark of NEC Corporation.
Features
• Number of active dots: 485,000 (0.9-inch, 2.3cm in diagonal)
• Accepts the computer requirements of SVGA (804 × 604), VGA (644 × 484) and PC98 (644 × 404) platforms
• Supports NTSC (644 × 484) and PAL (762 × 572) by processing the video signal at double speed
• High optical transmittance: 17% (typ.)
• Built-in cross talk free circuit and ghost free circuit
• High contrast ratio with normally white mode: 350 (typ.)
• Built-in H and V drivers (built-in input level conversion circuit, 5V driving possible)
• Up/down and/or right/left inverse display function
• High durable polarizer used
• Built-in λ/2 retardation film for red light (V)
Element Structure
• Dots: 804 (H) × 604 (V) = 485,616
• Built-in peripheral driver using polycrystalline silicon super thin film transistors
Applications
• Liquid crystal data projectors
• Liquid crystal projectors, etc.
– 1 –
LCX026ALF
E98536-PS
2.3cm (0.9-inch) Black-and-White LCD Panel
Sony reserves the right to change products and specifications without prior notice. This information does not convey any license by
any implication or otherwise under any patents or other right. Application circuits shown, if any, are typical examples illustrating the
operation of the devices. Sony cannot assume responsibility for any problems arising out of the use of these circuits.
For the availability of this product, please contact the sales office.
– 2 –
LCX026ALF
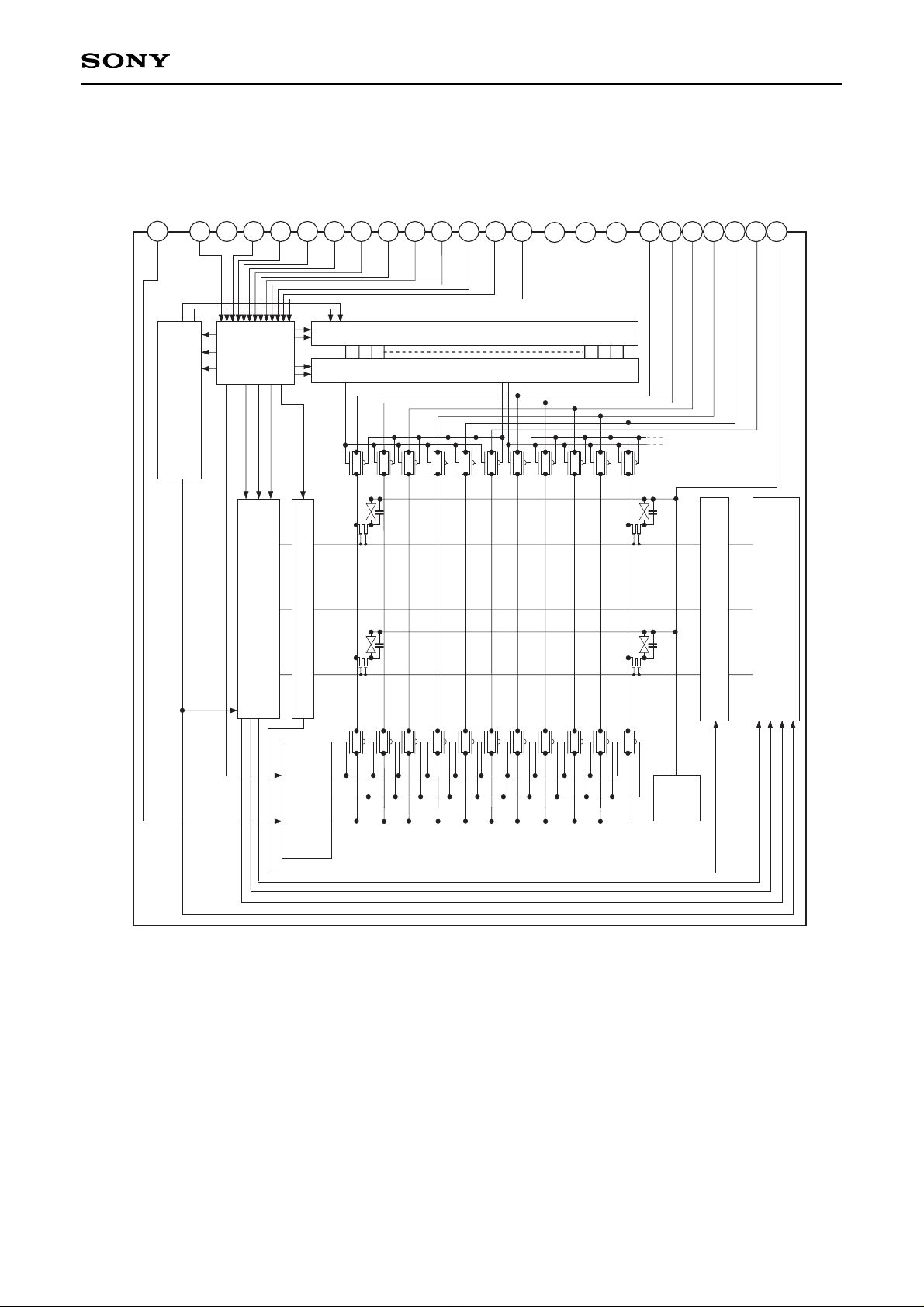
Block Diagram
1
18
H Shift Register (Bidirectional Scanning)
Up/Down and/or Right/Left
Inversion Control Circuit
V Shift Register
(Bidirectional Scanning)
Precharge Control
Circuit
COM
PAD
V Shift Register
(Bidirectional Scanning)
COM
SIG6
SIG5
SIG4
SIG3
SIG2
SIG1
Vss
VV
DD
HV
DD
MODE1
ENB
DWN
PCG
VCK
VST
RGT
BLK
HCK2
HCK1
HST
PSIG
14 15
17
9
20
19
21
22
12
11
10
8
23
16
7
6
4
3
5
2
24
Black Frame Control Circuit
Black Frame Control Circuit
13
Black Frame Control Circuit
MODE2
MODE3
Input Signal
Level Shifter
Circuit
– 3 –
LCX026ALF
Absolute Maximum Ratings (VSS = 0V)
• H driver supply voltage HVDD –1.0 to +20 V
• V driver supply voltage VVDD –1.0 to +20 V
• Common pad voltage COM –1.0 to +17 V
• H shift register input pin voltage HST, HCK1, HCK2, –1.0 to +17 V
RGT
• V shift register input pin voltage VST, VCK, PCG, –1.0 to +17 V
BLK, ENB, DWN
MODE1, MODE2, MODE3
• Video signal input pin voltage SIG1, SIG2, SIG3, SIG4, –1.0 to +15 V
SIG5, SIG6, PSIG
• Operating temperature Topr –10 to +70 °C
• Storage temperature Tstg –30 to +85 °C
Operating Conditions (VSS = 0V)
• Supply voltage
HVDD 15.5 ± 0.5V
VVDD 15.5 ± 0.5V
• Input pulse voltage (Vp-p of all input pins except video signal and uniformity improvement signal input pins)
Vin 5.0 ± 0.5V
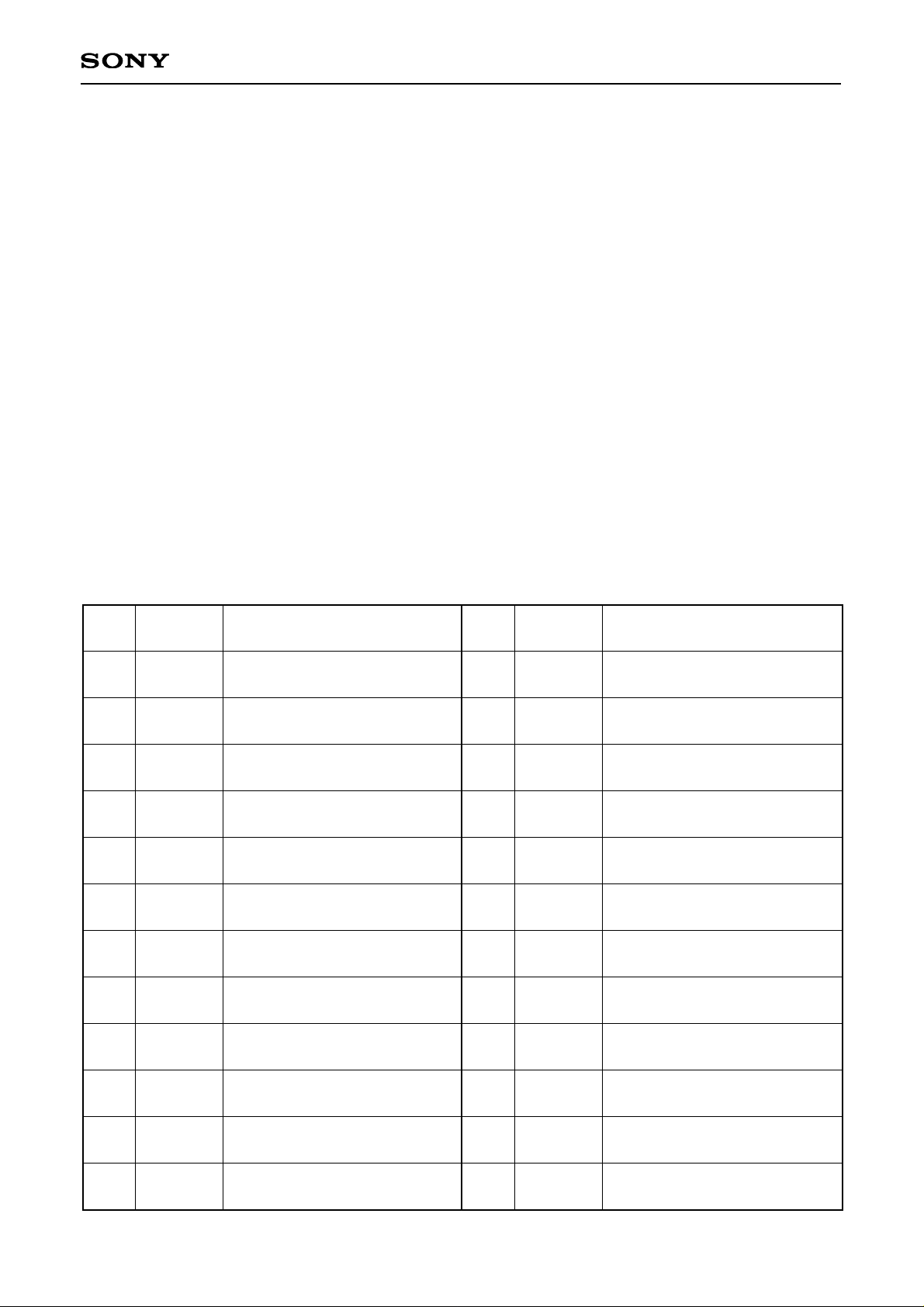
Pin Description
Pin
No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
PSIG
SIG4
SIG3
SIG5
SIG2
SIG6
SIG1
HVDD
RGT
MODE3
MODE2
MODE1
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
HST
HCK1
HCK2
Vss
BLK
ENB
VCK
VST
PCG
DWN
VVDD
COM
Start pulse for H shift register
drive
Clock pulse for H shift register
drive
Clock pulse for H shift register
drive
GND (H, V drivers)
Black Frame display pulse
Enable pulse for gate selection
Clock pulse for V shift register
drive
Start pulse for V shift register
drive
Improvement pulse for uniformity
Drive direction pulse for V shift
register (H: normal, L: reverse)
Power supply for V driver
Common voltage of panel
Symbol Description
Pin
No.
Symbol Description
Uniformity improvement signal
Video signal 4 to panel
Video signal 3 to panel
Video signal 5 to panel
Video signal 2 to panel
Video signal 6 to panel
Video signal 1 to panel
Power supply for H driver
Drive direction pulse for H shift
register (H: normal, L: reverse)
Display area switching 3
Display area switching 2
Display area switching 1
– 4 –
LCX026ALF
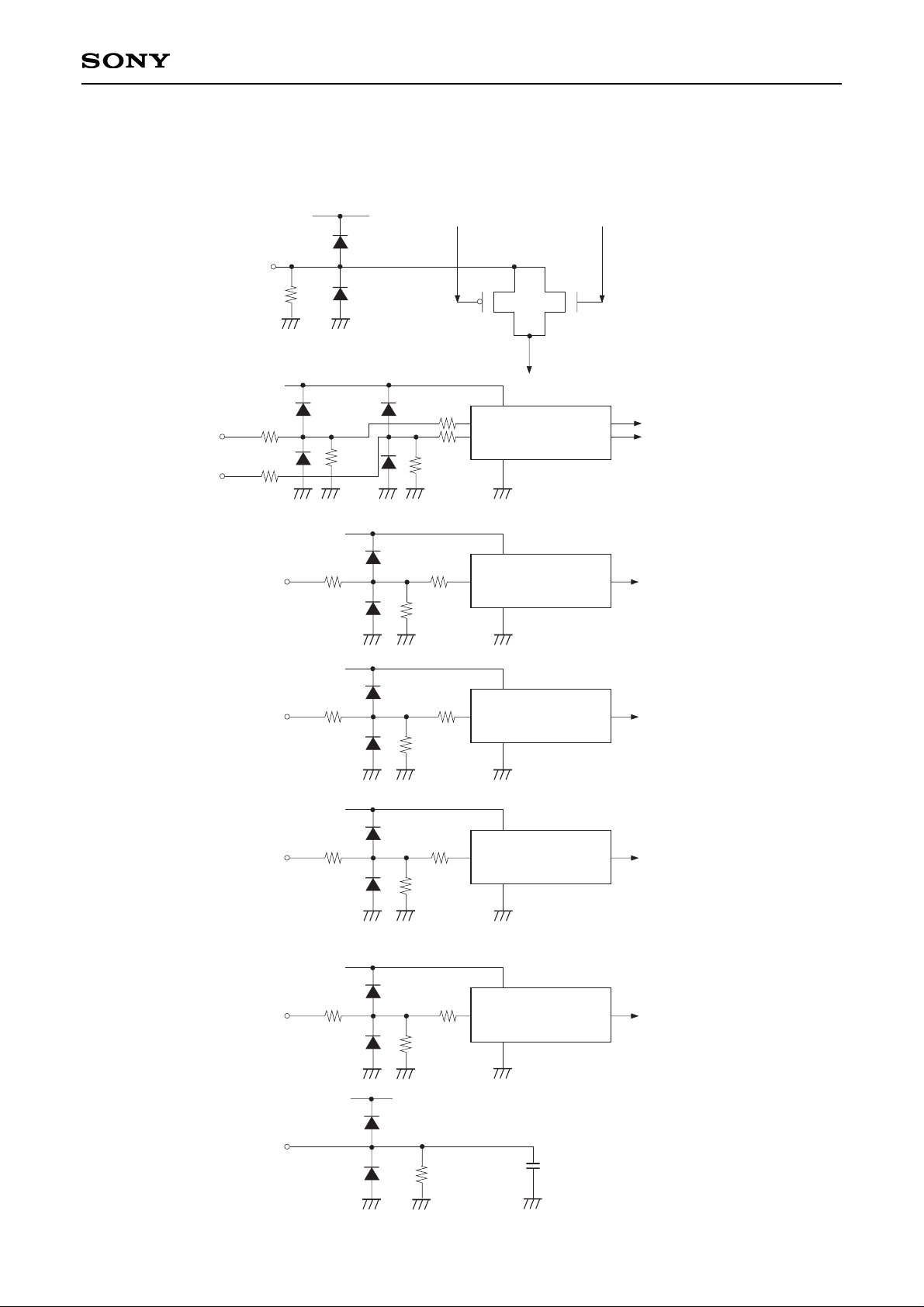
Input Equivalent Circuit
To prevent static charges, protective diodes are provided for each pin except the power supplies. In addition,
protective resistors are added to all pins except the video signal inputs. All pins are connected to VSS with a
high resistor of 1MΩ (typ.). The equivalent circuit of each input pin is shown below: (Resistance value: typ.)
Input
LC
Level conversion circuit
(single-phase input)
2.5kΩ2.5kΩ
VV
DD
Input
Level conversion circuit
(single-phase input)
250Ω250Ω
HV
DD
Input
Level conversion circuit
(single-phase input)
2.5kΩ2.5kΩ
HV
DD
Input
HV
DD
250Ω
250Ω
250Ω
250Ω
Level conversion circuit
(2-phase input)
Input
HV
DD
Signal line
(1) SIG1, SIG2, SIG3, SIG4, SIG5, SIG6, PSIG
(2) HCK1, HCK2
(3) RGT
(4) HST
(5) PCG, VCK
(6) VST, BLK, ENB, DWN, MODE1, MODE2, MODE3
(7) COM
1MΩ
Input
1MΩ
1MΩ
1MΩ
Level conversion circuit
(single-phase input)
250Ω250Ω
VV
DD
Input
1MΩ
1MΩ
1MΩ
VVDD
1MΩ
– 5 –
LCX026ALF
Input Signals
1. Input signal voltage conditions (VSS = 0V)
Item
H shift register input voltage
HST, HCK1, HCK2, RGT
(Low)
(High)
(Low)
(High)
VHIL
VHIH
VVIL
VVIH
VVC
Vsig
Vcom
Vpsig
–0.5
4.5
–0.5
4.5
6.8
VVC – 4.5
VVC – 0.5
VVC ± 4.3
0.0
5.0
0.0
5.0
7.0
7.0
VVC – 0.4
VVC ± 4.5
0.4
5.5
0.4
5.5
7.2
VVC + 4.5
VVC – 0.3
VVC ± 4.7
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V shift register input voltage
MODE1, MODE2, MODE3,
BLK, VST, VCK, PCG,
ENB, DWN
Video signal center voltage
Video signal input range
∗1
Common voltage of panel
∗2
Uniformity improvement signal
input voltage (PSIG)
∗3
Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit
∗1
Input video signal shall be symmetrical to VVC.
∗2
The typical value of the common pad voltage may lower its suitable voltage according to the set
construction to use. In this case, use the voltage of which has maximum contrast as typical value.
When the typical value is lowered, the maximum and minimum values may lower.
∗3
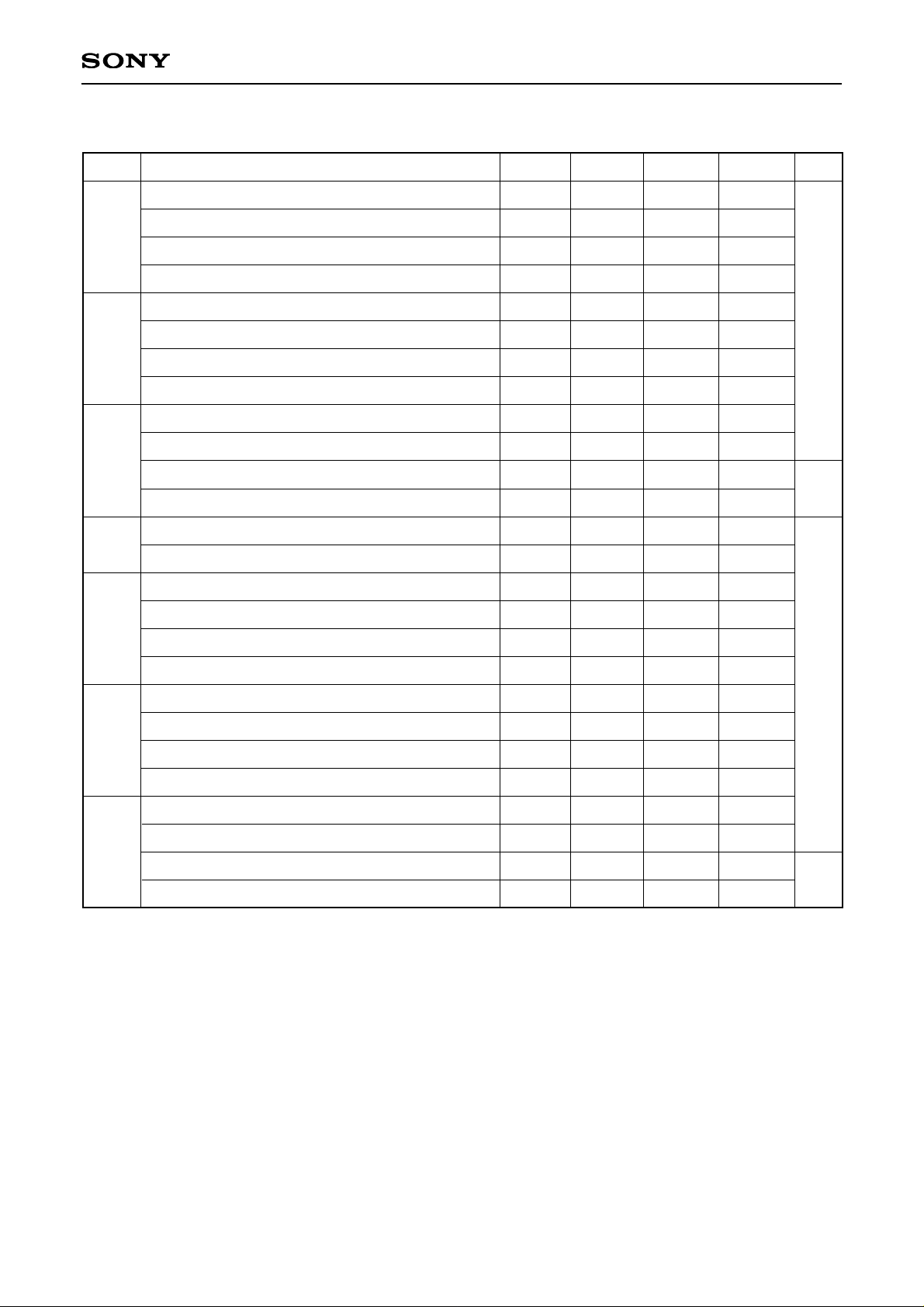
Input a uniformity improvement signal PSIG in the same polarity with video signals SIG1 to 6 and which is
symmetrical to VVC. Also, the rising and falling of PSIG are synchronized with the rising of PCG pulse, and
the rise time trPSIG and fall time tfPSIG are suppressed within 800ns (as shown in a diagram below).
The optimum input voltage of PSIG may be changed according as drive conditions of the drive side.
Level Conversion Circuit
The LCX026ALF has a built-in level conversion circuit in the clock input unit on the panel. The input signal
level increases to HVDD or VVDD. The VCC of external ICs are applicable to 5 ± 0.5V.
trPSIG
tfPSIG
VVC
PSIG
PCG
90%
10%
Input waveform of uniformity improvement signal PSIG
– 6 –
LCX026ALF
2. Clock timing conditions (Ta = 25°C) (SVGA mode: fHCKn = 4.0MHz, fVCK = 24.0kHz)
∗4
Hckn means Hck1 and Hck2.
∗5
Blk is the timing during SVGA mode (fHckn = 4.0MHz, fVck = 24.0kHz).
Hst rise time
Hst fall time
Hst data set-up time
Hst data hold time
Hckn rise time
∗4
Hckn fall time
∗4
Hck1 fall to Hck2 rise time
Hck1 rise to Hck2 fall time
Vst rise time
Vst fall time
Vst data set-up time
Vst data hold time
Vck rise time
Vck fall time
Enb rise time
Enb fall time
Vck rise/fall to Enb rise time
Enb pulse width
Pcg rise time
Pcg fall time
Pcg rise to Vck rise/fall time
Pcg pulse width
Blk rise time
Blk fall time
Blk fall to Vst rise time
Blk pulse width
trHst
tfHst
tdHst
thHst
trHckn
tfHckn
to1Hck
to2Hck
trVst
tfVst
tdVst
thVst
trVck
tfVck
trEnb
tfEnb
tdEnb
twEnb
trPcg
tfPcg
toVck
twPcg
trBlk
tfBlk
toVst
twBlk
—
—
50
50
—
—
–15
–15
—
—
5
5
—
—
—
—
400
2400
—
—
900
1100
—
—
32
20
—
—
60
60
—
—
0
0
—
—
10
10
—
—
—
—
500
2500
—
—
1000
1200
—
—
33
21
30
30
70
70
30
30
15
15
100
100
15
15
100
100
100
100
600
2600
30
30
1100
1300
100
100
34
22
ns
µs
ns
Item Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit
HST
HCK
VST
VCK
ENB
PCG
BLK
∗5
µs
– 7 –
LCX026ALF
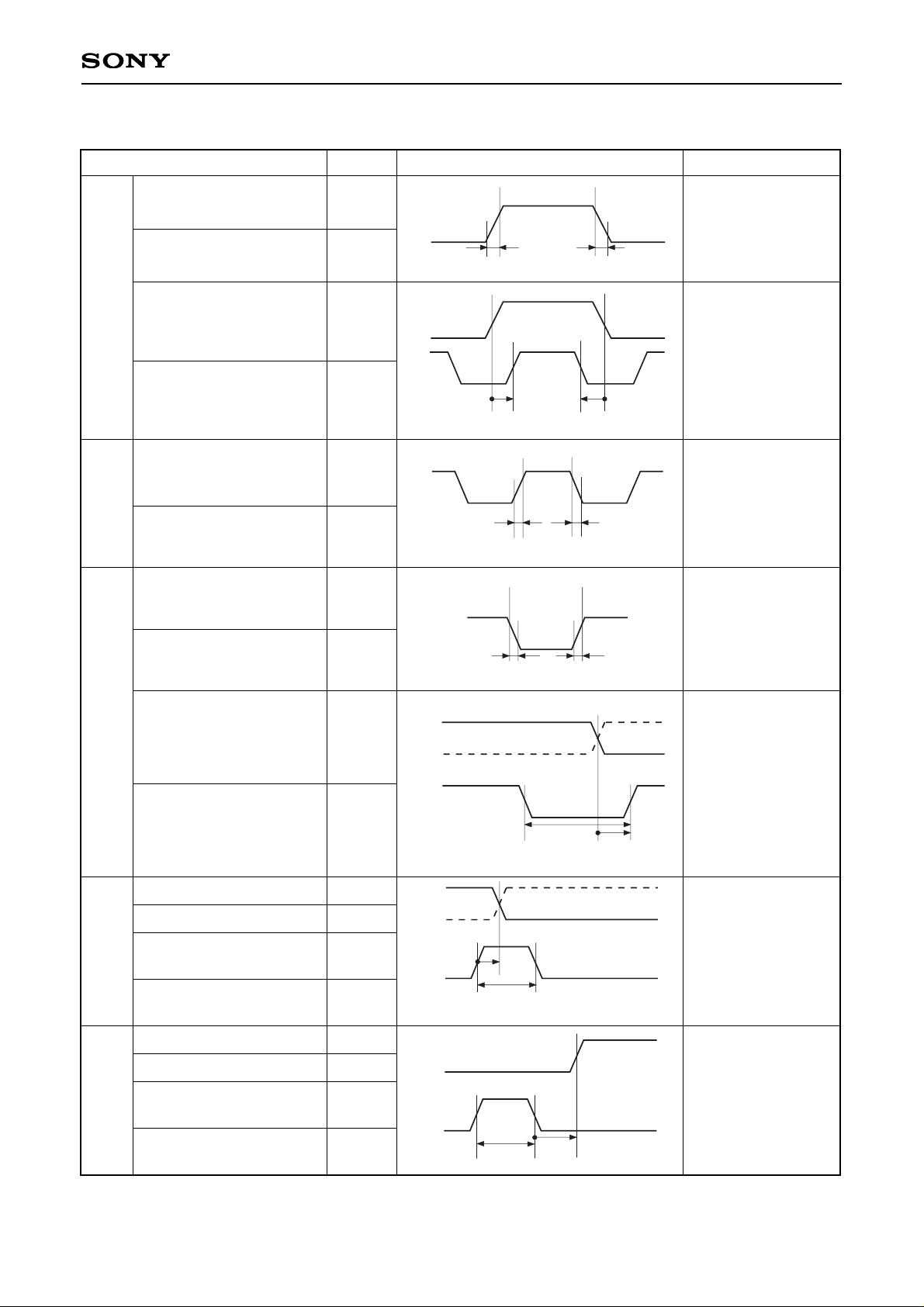
∗6
Definitions: The right-pointing arrow ( ) means +.
The left-pointing arrow ( ) means –.
The black dot at an arrow ( ) indicates the start of measurement.
<Horizontal Shift Register Driving Waveform>
Hst rise time
HST
HCK
Hst fall time
Hst data set-up time
Hst data hold time
Hckn rise time
∗3
Hckn fall time
∗3
Hck1 fall to Hck2 rise time
Hck1 rise to Hck2 fall time
• Hckn
∗3
duty cycle 50%
to1Hck = 0ns
to2Hck = 0ns
• Hckn
∗3
duty cycle 50%
to1Hck = 0ns
to2Hck = 0ns
• Hckn
∗3
duty cycle 50%
to1Hck = 0ns
to2Hck = 0ns
trHst
tfHst
tdHst
thHst
trHckn
tfHckn
to1Hck
to2Hck
Item Symbol Waveform Conditions
90%
10%
10%
90%
Hst
trHst tfHst
50%
50%
∗
6
Hst
Hck1
tdHst thHst
50%
50%
∗
3
Hckn
10%
10%
90%
90%
trHckn tfHckn
50%
50%
∗
6
Hck1
to2Hck to1Hck
50%
50%
Hck2
– 8 –
LCX026ALF
<Vertical Shift Register Driving Waveform>
VCK
ENB
Vck rise time
Vck fall time
Enb rise time
Enb fall time
Vck rise/fall to Enb rise
time
Enb pulse width
trVck
tfVck
trEnb
tfEnb
tdEnb
twEnb
Item Symbol Waveform Conditions
Vck
10%
10%
90%
90%
trVckn tfVckn
90%
90%
10%
10%
tfEn trEn
Enb
Enb
50%
50%
50%
twEnb
tdEnb
Vck
∗
6
PCG
∗7
Pcg rise time
trPcg
Pcg fall time
tfBlk
Pcg rise to Vck rise/fall
time
toVst
Pcg pulse width
twBlk
BLK
Blk rise time
trPcg
Blk fall time
tfPcg
Blk fall to Vst rise time
Blk pulse width
toVck
twBlk
Pcg
50%
50%
50%
twPcg
toVck
Vck
∗
6
Blk
50%
50%
toVst
Vst
∗
6
50%
twBlk
∗7
Input the pulse obtained by taking the OR of the above pulse (PCG) and BLK to the PCG input pin.
Vst rise time
VST
Vst fall time
Vst data set-up time
Vst data hold time
trVst
tfVst
tdVst
thVst
90%
10%
10%
90%
Vst
trVst tfVst
50%
50%
∗
6
Vst
Vck
tdVst thVst
50%
50%
 Loading...
Loading...