3000-pixel CCD Linear Image Sensor (B/W)
Description
The ILX103A is a rectangular reduction type CCD
linear image sensor designed for bar code POS
hand scanner and optical measuring equipment use.
A built-in timing generator and clock-drivers ensure
single 5V power supply for easy use.
Features
• Number of effective pixels: 3000 pixels
• Pixel size: 7µm × 200µm (7µm pitch)
• S/H output
• Built-in timing generator and clock-drivers
• Output amplifier gain switching function
(2-level: switching gain ratio 1:4)
• SIP small package
• Clock frequency: 500kHz (Typ.),
100kHz (Min.), 1MHz (Max.)
Absolute Maximum Ratings
• Supply voltage VDD 6V
•Operating temperature –10 to +60 °C
• Storage temperature –30 to +80 °C
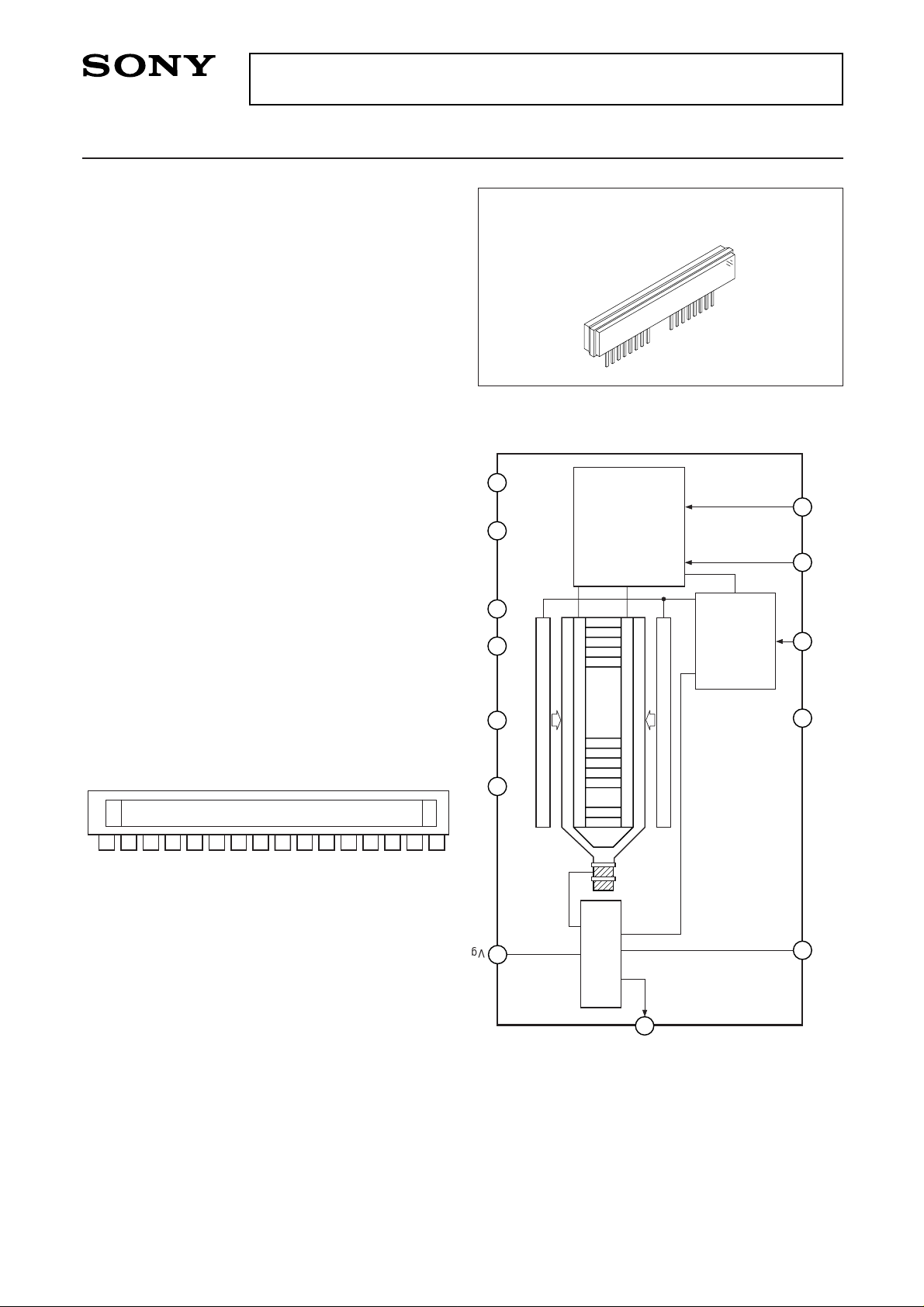
Pin Configuration (Top View)
Internal Structure
– 1 –
E98X48A91-PS
Sony reserves the right to change products and specifications without prior notice. This information does not convey any license by
any implication or otherwise under any patents or other right. Application circuits shown, if any, are typical examples illustrating the
operation of the devices. Sony cannot assume responsibility for any problems arising out of the use of these circuits.
ILX103A
1
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
1
VDD
GND
Vout
Vgg
φCLK
SWG
NC
NC
φROG
φSHUT
GND
V
DD
T1
V
DD
GND
NC
3000
Vgg
GND
V
DD
VDD
GND
VDD
GND
D24
D25
D54
D55
S1
S2
S3
S2999
S3000
D56
D65
Output Amplifier
Driver
Readout gate
Readout gate
CCD analog shift register
CCD analog shift register
Driver
Readout gate pulse
generator
Shutter pulse
generator
Timing generator
4
2
1 12 11 14 15
6 13 5 9 10
φSHUT
φROG
φCLK
T1
SWG
Vout
3
16 pin SIP (Ceramic)

– 2 –
ILX103A
Pin Description
Pin No. Symbol Description
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
VDD
GND
Vout
Vgg
φCLK
SWG
NC
NC
φROG
φSHUT
GND
VDD
T1
VDD
GND
NC
Power supply
GND
Signal output
Output circuit gate bias
Clock pulse input
Control (Output circuit amplification factor ×4/×1)
NC
NC
Readout gate pulse input
Electrical shutter pulse input
GND
Power supply
TEST (Connect to GND with 1000pF capacitor)
Power supply
GND
NC
Recommended Voltage
Item
VDD
Min.
4.5
Mode Description
Output circuit gain
High
Low
Pin 6 SWG
VDD
GND
Typ.
5.0
Max.
5.5
Unit
V
Input Pin Capacity
Symbol
CφCLK
CφROG
CφSHUT
Min.
—
—
—
Typ.
10
10
10
Max.
—
—
—
Unit
pF
pF
pF
Item
Input capacity of φCLK pin
Input capacity of φROG pin
Input capacity of φSHUT pin

– 3 –
ILX103A
Electro-optical Characteristics (Analog Characteristic) (Note 1)
Ta = 25°C, VDD = 5V, Clock frequency: 500kHz, Light source = 3200K,
IR cut filter: CM-500S (t = 1.0mm), Output circuit gain low mode
Item Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit Remarks
Sensitivity 1
Sensitivity 2
Sensitivity nonuniformity
Saturation output voltage
Dark voltage average
Dark signal nonuniformity
Image lag
Dynamic range
Saturation exposure
5V current consumption
Total transfer efficiency
Output impedance
Offset level
R1
R2
PRNU
VSAT
VDRK
DSNU
IL
DR
SE
IVDD
TTE
ZO
VOS
52.5
—
—
0.6
—
—
—
—
—
—
92.0
—
—
75
925
5.0
0.8
2.5
5.0
5.0
320
0.01
7.0
97.0
250
2.5
97.5
—
10.0
—
6.0
12.0
—
—
—
17.0
—
—
—
V/(lx · s)
V/(lx · s)
%
V
mV
mV
%
—
lx · s
mA
%
Ω
V
Note 2
Note 3
Note 4
—
Note 5
Note 6
Note 7
Note 8
Note 9
—
—
—
Note 10
Note)
1. In accordance with the given electro-optical characteristics, the even black level is defined as the average
value of D24, D25 to D53.
2. For the sensitivity test light is applied with a uniform intensity of illumination.
3. Light source: LED λ = 660nm
4. PRNU is defined as indicated below. Ray incidence conditions are the same as for Note 2.
PRNU = × 100 [%]
The maximum output of the effective pixels is set to VMAX, the minimum output to VMIN and the average
output to VAVE.
5. Integration time is 10ms.
6. The difference between the maximum and average values and the difference between the minimum and
average values of the dark output voltage is calculated. The larger value is defined as dark signal
nonuniformity. Integration time is 10ms.
7. Typical value is used for clock pulse and readout pulse. VOUT = 500mV.
8. DR = VSAT/VDRK
When optical integration time is shorter, the dynamic range sets wider because dark output voltage is in
proportion to optical integration time.
9. SE = VSAT/R1
10. Vos is defined as indicated below.
(VMAX – VMIN)/2
VAVE
D51 D52
Vout
V
OS
GND
D53 D54 D55 S1

– 4 –
ILX103A
–1
D1
D0
5
0
5
0
5
φROG
φSHUT
φCLK
V
OUT
Optical
black
(30 pixels)
Dummy signal (55 pixels)
1-Line output period (3066 pixels)
3100 or more clock pulses are required.
Effective picture
elements signal
(3000 pixels)
Dummy signal
(10 pixels)
0
D2
D3
D4
D21
D22
D23
D24
0
1
2
D53
D54
D55
S1
S2
S3
S4
S2998
S2997
S2999
S3000
D56
D57
D58
D59
D61
D60
D62
D63
D64
D65
Clock Timing Diagram
 Loading...
Loading...