Sony HCDHP-27 Service manual

HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
Amplifier section
For the United States model
AUDIO POWER SPECIFICATIONS
HCD-HPZ9
POWER OUTPUT AND TOTAL HARMONIC
DISTORTION:
With 6-ohm loads, both channels driven, from
120 – 10,000 Hz: rated 85 watts per channel
minimum RMS power, with no more than 10%
total harmonic distortion from 250 milliwatts to
rated output.
HCD-HPZ7
POWER OUTPUT AND TOTAL HARMONIC
DISTORTION:
With 6-ohm loads, both channels driven, from
120 – 10,000 Hz: rated 50 watts per channel
minimum RMS power, with no more than 10%
total harmonic distortion from 250 milliwatts to
rated output.
HCD-HPZ9
North American model:
Continuous RMS power output (reference):
85 + 85 W
(6 ohms at 1 kHz, 10%
THD)
Other models:
The following measured at AC 240 V, AC 220 V or AC
120 V
DIN power output (rated): 53 + 53 W
(6 ohms at 1 kHz, DIN)
Continuous RMS power output (reference):
70 + 70 W
(6 ohms at 1 kHz, 10%
THD)
HCD-HPZ7
North American model:
Continuous RMS power output (reference):
50 + 50 W
(6 ohms at 1 kHz, 10%
THD)
European model:
DIN power output (rated): 50 + 50 W (6 ohms at
1kHz, DIN)
Continuous RMS power output (reference):
60 + 60 W (6 ohms at
1kHz, 10% THD)
Music power output (reference):
100 + 100 W (6 ohms at
1kHz, 10% THD)
Other models:
The following measured at AC 220 – 240 V, 50/60 Hz
DIN power output (rated): 45 + 45 W
(6 ohms at 1 kHz, DIN)
Continuous RMS power output (reference):
50 + 50 W
(6 ohms at 1 kHz, 10%
THD)
Inputs
ANALOG IN (stereo mini jack):
Sensitivity 250 mV,
impedance 47 kilohms
Outputs
CD DIGITAL OUT: Optical Wavelength:
660 nm
PHONES (stereo mini jack):
accepts headphones with
an impedance of 8 ohms or
more
SPEAKER: accepts impedance of 6 to
16 ohms
SERVICE MANUAL
Ver. 1.5 2006.01
HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9 are the Amplifier, CD play er, T ape
Deck and Tuner section in CMT-HPZ7/HPZ9.
US and foreign patents licensed from
Dolby Laboratories.
CD CD Mechanism Type CDM82C-F1BD83 CDM82C-K6BD83
Section Base Unit Name BU-F1BD83 BU-K6BD83
TAPE Model Name Using Similar Mechanism NEW NEW
Section T ape Transport Mechanism Type CMAL5Z225A CMAL5Z225A
Photo : HCD-HPZ7
Model Name Using Similar Mechanism NEW NEW
Optical Pick-up Name KSM-215DCP KSM-213DCP/C2NP
US Model
HCD-HPZ9
Canadian Model
HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
AEP Model
UK Model
HCD-HPZ7
E Model
HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
Australian Model
HCD-HPZ9
Former T ype Models New Type Models
9-879-566-06
2006A16-1
© 2006.01
Sony Corporation
Personal Audio Division
Published by Sony Techno Create Corporation
SPECIFICATIONS
MICRO HI-FI COMPONENT SYSTEM
— Continued on next page —

HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
CD player section
System Compact disc and digital
audio system
Laser Diode Properties Emission duration:
continuous
Laser Output*:
Less than 44.6 µW
*This output is the value measurement at a distance of
200 mm from the objective lens surface on the
Optical Pick-up Block with 7 mm aperture.
Frequency response 20 Hz – 20 kHz (±0.5 dB)
Wavelength 780 – 790 nm
Tape deck section
Recording system 4-track 2-channel stereo
Frequency response 50 – 13,000 Hz (±3 dB),
using Sony TYPE I
cassettes
Tuner section
FM stereo, FM/AM superheterodyne tuner
FM tuner section
Tuning range 87.5 – 108.0 MHz
Antenna FM lead antenna
Antenna terminals 75 ohms unbalanced
Intermediate frequency 10.7 MHz
AM tuner section
Tuning range
Pan-American model: 530 – 1,710 kHz
(with the tuning interval
set at 10 kHz)
531 – 1,710 kHz
(with the tuning interval
set at 9 kHz)
European model: 531 – 1,602 kHz
(with the tuning interval
set at 9 kHz)
Other models: 530 – 1,710 kHz
(with the tuning interval
set at 10 kHz)
531 – 1,602 kHz
(with the tuning interval
set at 9 kHz)
Antenna AM loop antenna
Antenna terminals External antenna terminal
Intermediate frequency 450 kHz
General
Power requirements
North American model: 120 V AC, 60 Hz
European model: 230 V AC, 50/60 Hz
Other models: 120 V, 220 V or 230 –
240 V AC, 50/60 Hz
Adjustable with voltage
selector
Power consumption
HPZ9
North American model: 145 W
Other models: 125 W
HPZ7
North American model: 85 W
European model: 95 W
0.25 W (in Power Saving
Mode)
Other models: 90 W
Dimensions (w/h/d) (excl. speakers)
Approx. 198 × 275 ×
341 mm
Mass (excl. speakers)
Amplifier/Tuner/Tape/CD section:
HPZ9: 7.7 kg
HPZ7: 7.3 kg
Design and specifications are subject to change
without notice.
SAFETY-RELATED COMPONENT WARNING!!
COMPONENTS IDENTIFIED BY MARK 0 OR DOTTED LINE
WITH MARK 0 ON THE SCHEMATIC DIAGRAMS AND IN
THE PARTS LIST ARE CRITICAL TO SAFE OPERATION.
REPLACE THESE COMPONENTS WITH SONY PARTS WHOSE
PART NUMBERS APPEAR AS SHOWN IN THIS MANUAL OR
IN SUPPLEMENTS PUBLISHED BY SONY.
2
ATTENTION AU COMPOSANT AYANT RAPPORT
À LA SÉCURITÉ!
LES COMPOSANTS IDENTIFIÉS PAR UNE MARQUE 0 SUR
LES DIAGRAMMES SCHÉMATIQUES ET LA LISTE DES
PIÈCES SONT CRITIQUES POUR LA SÉCURITÉ DE
FONCTIONNEMENT. NE REMPLACER CES COM- POSANTS
QUE PAR DES PIÈCES SONY DONT LES NUMÉROS SONT
DONNÉS DANS CE MANUEL OU D ANS LES SUPPLÉMENTS
PUBLIÉS PAR SONY.
HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
r
Notes on chip component replacement
• Never reuse a disconnected chip component.
• Notice that the minus side of a tantalum capacitor may be
damaged by heat.
Flexible Circuit Board Repairing
• Keep the temperature of the soldering iron around 270 °C
during repairing.
• Do not touch the soldering iron on the same conductor of the
circuit board (within 3 times).
• Be careful not to apply force on the conductor when soldering
or unsoldering.
SAFETY CHECK-OUT
After correcting the original service problem, perform the following
safety check before releasing the set to the customer:
Check the antenna terminals, metal trim, “metallized” knobs, screws,
and all other exposed metal parts for AC leakage.
Check leakage as described below.
LEAKAGE TEST
The AC leakage from any exposed metal part to earth ground and
from all exposed metal parts to any exposed metal part having a
return to chassis, must not exceed 0.5 mA (500 microamperes.).
Leakage current can be measured by any one of three methods.
1. A commercial leakage tester, such as the Simpson 229 or RCA
WT-540A. Follow the manufacturers’ instructions to use these
instruments.
2. A battery-operated AC milliammeter. The Data Precision 245
digital multimeter is suitable for this job.
3. Measuring the voltage drop across a resistor by means of a
VOM or battery-operated AC voltmeter. The “limit” indication
is 0.75 V, so analog meters must have an accurate low-voltage
scale. The Simpson 250 and Sanwa SH-63Trd are examples
of a passive VOM that is suitable. Nearly all battery operated
digital multimeters that have a 2 V AC range are suitable. (See
Fig. A)
To Exposed Metal
Parts on Set
CAUTION
Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures
other than those specified herein may result in hazardous radiation
exposure.
This appliance is classified as a CLASS 1 LASER product.
The CLASS 1 LASER PRODUCT MARKING is located on the
exterior.
Laser component in this product is capable of emitting radiation
exceeding the limit for Class 1.
NOTES ON HANDLING THE OPTICAL PICK-UP
BLOCK OR BASE UNIT
The laser diode in the optical pick-up block may suffer electrostatic
break-down because of the potential difference generated by the
charged electrostatic load, etc. on clothing and the human body.
During repair, pay attention to electrostatic break-down and also
use the procedure in the printed matter which is included in the
repair parts.
The flexible board is easily damaged and should be handled with
care.
NOTES ON LASER DIODE EMISSION CHECK
The laser beam on this model is concentrated so as to be focused on
the disc reflective surface by the objective lens in the optical pickup block. Therefore, when checking the laser diode emission,
observe from more than 30 cm away from the objective lens.
LASER DIODE AND FOCUS SEARCH OPERATION
CHECK
Carry out the “S curve check” in “CD section adjustment” and check
that the S curve waveforms is output three times.
AC
0.15 µF
1.5 k
Ω
Earth Ground
voltmete
(0.75 V)
Fig. A. Using an AC voltmeter to check AC leakage.
UNLEADED SOLDER
Boards requiring use of unleaded solder are printed with the leadfree mark (LF) indicating the solder contains no lead.
(Caution: Some printed circuit boards may not come printed with
the lead free mark due to their particular size)
: LEAD FREE MARK
Unleaded solder has the following characteristics.
• Unleaded solder melts at a temperature about 40 °C higher
than ordinary solder.
Ordinary soldering irons can be used but the iron tip has to be
applied to the solder joint for a slightly longer time.
Soldering irons using a temperature regulator should be set to
about 350 °C.
Caution: The printed pattern (copper foil) may peel away if
the heated tip is applied for too long, so be careful!
• Strong viscosity
Unleaded solder is more viscou-s (sticky, less prone to flow)
than ordinary solder so use caution not to let solder bridges
occur such as on IC pins, etc.
• Usable with ordinary solder
It is best to use only unleaded solder but unleaded solder may
also be added to ordinary solder.
3

HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
Ver. 1.5
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. GENERAL ................................................................... 5
2. DISASSEMBLY
2-1. Disassembly Flow-1 ........................................................ 7
2-2. Disassembly Flow-2 ........................................................ 8
2-3. Optical Pick-up Block ..................................................... 9
2-4. Side Plate (L) (R), Top Panel Section.............................. 10
2-5. Mechanical Deck ............................................................. 10
2-6. Front Panel Section ......................................................... 11
2-7. PANEL (1), (2) Board ..................................................... 11
2-8. Main Board ...................................................................... 12
2-9. AMP Section ................................................................... 12
2-10. AMP Board...................................................................... 13
2-11. Rear Panel Section........................................................... 13
2-12. Tuner, DC Fan ................................................................. 14
2-13. POWER Board ................................................................ 14
2-14. CD Mechanism Deck (CDM82C) ................................... 15
2-15. Plate (Cover Top)............................................................. 16
2-16. Top Section...................................................................... 16
2-17. Arm Section..................................................................... 17
2-18. CD Mechanism Deck Section ......................................... 18
2-19. Sub Gear (2 Step), Sub Slider Assy................................. 19
2-20. Arm (R) ........................................................................... 20
2-21. Gear (Stock Planet) (Right) ............................................. 21
2-22. Lever (Sub Gear Back L) ................................................ 21
2-23. Arm (L)............................................................................ 22
2-24. Gear (Stock Rot Long) (Left) .......................................... 23
2-25. Gear (Stock Rot Short) (Right) ....................................... 23
2-26. Stocker (1) Assy To Stocker (5) Assy .............................. 24
2-27. Lod Motor........................................................................ 25
2-28. Slider (Push-popup)......................................................... 25
2-29. Rotary Encoder ................................................................ 26
2-30. Assembling Of The Rotary Encoder ............................... 27
2-31. Elv Motor ........................................................................ 28
2-32. Chassis (Top), Chassis (Bottom) ..................................... 29
2-33. Lever (Loading R, Loading L) ........................................ 30
2-34. Disc Stop Lever ............................................................... 31
2-35. Driver Board .................................................................... 31
2-36. BD Board (A) .................................................................. 32
2-37. Optical Pick-up (KSM-215DCP) .................................... 32
2-38. Base Unit Section ............................................................ 33
2-39. Lever (Bu Lock) .............................................................. 33
2-40. Gear (Idl-b) ...................................................................... 34
2-41. Gear (Idl-c) ......................................................................34
2-42. Spr-e (Tako-back) ............................................................35
2-43. Plate (Push) Assy............................................................. 36
2-44. Spr-p (Lock) .................................................................... 37
4. TEST MODE............................................................... 51
5. MECHANICAL ADJUSTMENTS......................... 53
6. ELECTRICAL ADJUSTMENTS.......................... 53
7. DIAGRAMS ................................................................. 55
7-1. Block Diagram — MAIN Section —............................. 57
7-2. Block Diagram — BD/DRIVER Section — .................. 58
7-3. Block Diagram — PANEL/POWER Section — ............ 59
7-4. Printed Wiring Board — BD Board — .......................... 60
7-5. Schematic Diagram — BD Board — ............................. 61
7-6. Printed Wiring Board — MOTOR Section — ............... 62
7-7. Schematic Diagram — MOTOR Section — .................. 63
7-8. Printed Wiring Board — AUDIO Section — ................. 64
7-9. Schematic Diagram — AUDIO Section — .................... 65
7-10. Printed Wiring Board — MAIN Board — ..................... 66
7-11. Schematic Diagram — MAIN Board — ........................ 67
7-12. Printed Wiring Board — AMP Section — ..................... 68
7-13. Schematic Diagram — AMP Section —........................ 69
7-14. Printed Wiring Board — PANEL (1) Board — .............. 70
7-15. Schematic Diagram — PANEL (1) Board — ................ 71
7-16. Printed Wiring Board — HEADPHONE Section — ..... 72
7-17. Schematic Diagram — HEADPHONE Section — ........ 73
7-18. Printed Wiring Board — POWER Board — .................. 74
7-19. Schematic Diagram — POWER Board —..................... 75
8. EXPLODED VIEWS
8-1. SIDE PLATE, TOP PANEL SECTION .......................... 84
8-2. FRONT PANEL SECTION............................................. 85
8-3. CHASSIS SECTION ....................................................... 86
8-4. CD MECHANISM DECK SECTION-1 (CDM82C) ..... 88
8-5. CD MECHANISM DECK SECTION-2 (CDM82C) ..... 89
8-6. CD MECHANISM DECK SECTION-3 (CDM82C) ..... 90
8-7. CD MECHANISM DECK SECTION-4 (CDM82C) ..... 91
8-8. CD MECHANISM DECK SECTION-5 (CDM82C) ..... 92
8-9. CD MECHANISM DECK SECTION-6 (CDM82C) ..... 93
8-10. CD MECHANISM DECK SECTION-7 (CDM82C) ..... 94
8-11. CD MECHANISM DECK SECTION-8 (CDM82C) ..... 95
8-12. CD MECHANISM DECK SECTION-9 (CDM82C) ..... 96
8-13. CD MECHANISM DECK SECTION-10 (CDM82C) ... 97
8-14. BASE UNIT SECTION (BU-F1BD83A) ....................... 98
9. ELECTRICAL PARTS LIST.................................. 99
3. ASSEMBLY
3-1. Disassembly Flow ........................................................... 38
3-2. Assembling Of The Stocker Section ............................... 39
3-3. Assembling Of The Gear (Stock Rot Short) (Right) ....... 40
3-4. Assembling Of The Gear (Stock Rot Long) (Left) ......... 41
3-5. Confirming The Assembling Of The Stocker Section ..... 42
3-6. Assembling Of The Gear (Stock Rotary Left) ............... 43
3-7. Assembling Of The Gear (Stock Rotary Right) .............. 44
3-8. Assembling Of The Lever (Sub Gear Back L) ................ 45
3-9. Assembling Of The Gear (Sub Gear Pin Right) .............. 46
3-10. Assembling Of The Lever (Sub Gear Back R)................ 47
3-11. Assembling Of The Sub Gear (Idler) .............................. 48
3-12. Assembling Of The Sub Gear (2 Step)............................ 49
3-13. Confirming The Assembling Of The Arm Section .......... 50
4
SECTION 1
GENERAL
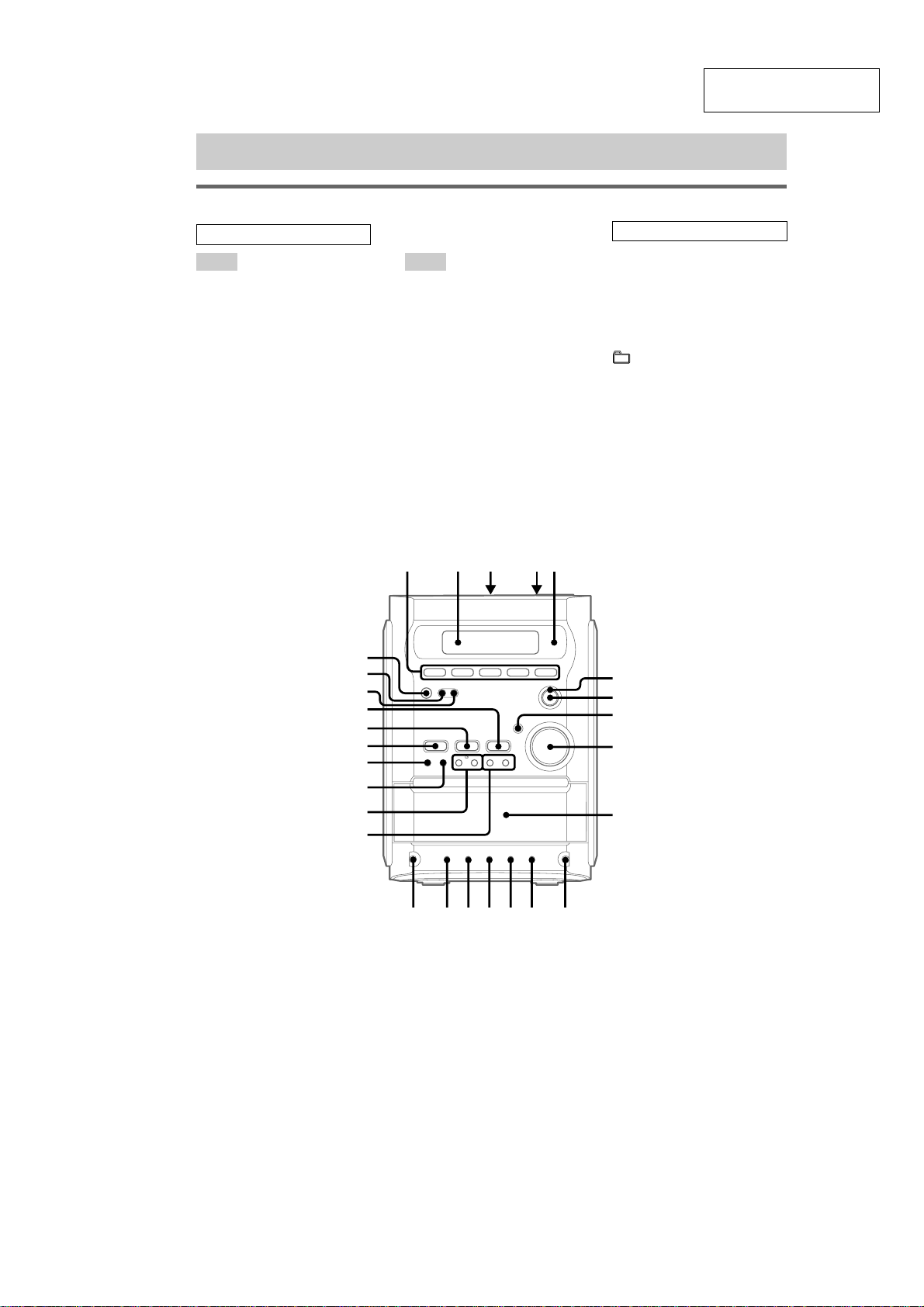
List of button locations and reference pages
Main unit
HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
This section is extracted
from instruction manual.
ALPHABETICAL ORDER
A – I J – Z
ANALOG IN jack qs (22, 24, 28)
CANCEL wa (15)
Cassette compartment 4 (21)
CD SYNC qg (22)
DISC 1 – 5 2 (13, 14, 16, 22)
DISC SKIP/EX-CHANGE wh
(13, 14, 17, 22)
Disc tray qa (13)
Display window 3
DSGX 9 (23)
FM MODE qh (20)
FUNCTION ws (14, 16, 18, 19,
21, 22, 29)
ILLUMINATION qd (12)
Jog dial 7 (15, 17)
PHONES jack qk
PLAY MODE qj (14, 16, 22)
PUSH ENTER 8 (15, 17)
REC PAUSE/START (record) qf
(22)
Remote sensor 6
REPEAT qh (16)
TUNER/BAND wg (18, 19)
TUNING MODE qj (18, 19)
TUNE +/– ql (18, 19)
VOLUME control 0
23 64 5
1
wj
wh
wg
wf
wd
ws
wa
w;
ql
BUTTON DESCRIPTIONS
?/1 (power) 1 (11, 19, 32)
Z
PUSH OPEN/CLOSE (tape
open/close) 5 (21)
lj/JL (rewind/fast
forward, go back/go forward)
ql (14, 21, 23)
+/– (select group) w; (14, 22)
x (stop) wa (12, 19, 22)
TAPE H (play) wd (21)
CD HS (play) wf (14)
(CD open/close) wj (13, 21)
Z
+/1
A
7
8
9
HS
HS
lj JL
s
0
qa
i
qk
qh
qf
qgqj
qsqd
5
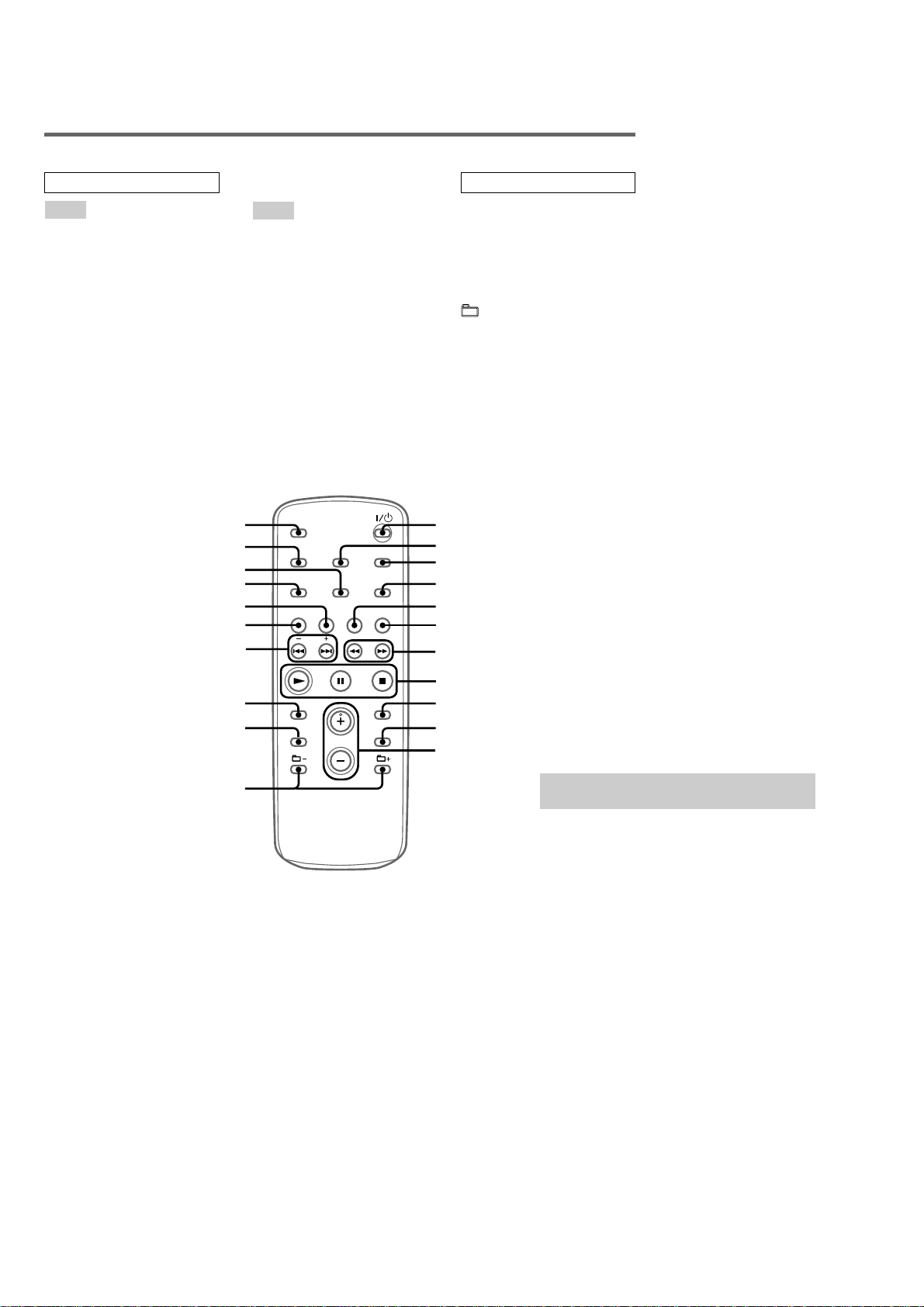
HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
Remote control
ALPHABETICAL ORDER
A – E
CD qj (14, 16)
CLEAR qf (17)
CLOCK/TIMER SELECT 2
(24, 25)
CLOCK/TIMER SET 3 (12, 24,
25)
DISC SKIP 0 (14, 16)
DISPLAY w; (20, 26, 27)
ENTER 9 (12, 16, 18, 24, 25)
EQ qd (23)
F – Z
FM MODE 4 (20)
FUNCTION 6 (14, 16, 18, 19,
21, 22, 29)
PLAY MODE ql (14, 16, 22)
REPEAT 4 (16)
SLEEP wa (23)
TAPE qh (21)
TUNER BAND 5 (18, 19)
TUNER MEMORY qk (18)
TUNING MODE ql (18, 19)
VOLUME +/– qa (24)
wa 1
w;
ql
qk
qj
qh
qg
2
3
4
5
6
7
BUTTON DESCRIPTIONS
?/1 (power) 1 (12, 24)
m/M (rewind/fast forward)
7 (14, 21)
N (play) 8 (14, 21)
X (pause) 8 (14, 21)
x (stop) 8 (14, 21)
+/– (select group) qs (14, 16)
./> (go back/go forward)
qg (12, 14, 23, 24)
+/– (tuning) qg (18)
qf
qd
qs
8
9
0
qa
Setting the clock
Use buttons on the remote for the operation.
1
Press ?/1 to turn on the system.
2
Press CLOCK/TIMER SET.
3
Press . or > repeatedly to set the
hour.
4
Press ENTER.
5
Press . or > repeatedly to set the
minute.
6
Press ENTER.
The clock starts working.
To adjust the clock
1
Press CLOCK/TIMER SET.
2
Press . or > repeatedly to select
“CLOCK SET”, then press ENTER.
3
Do the same procedures as step 3 to 6
above.
Note
The clock is not displayed in Power Saving Mode
(page 26).
6
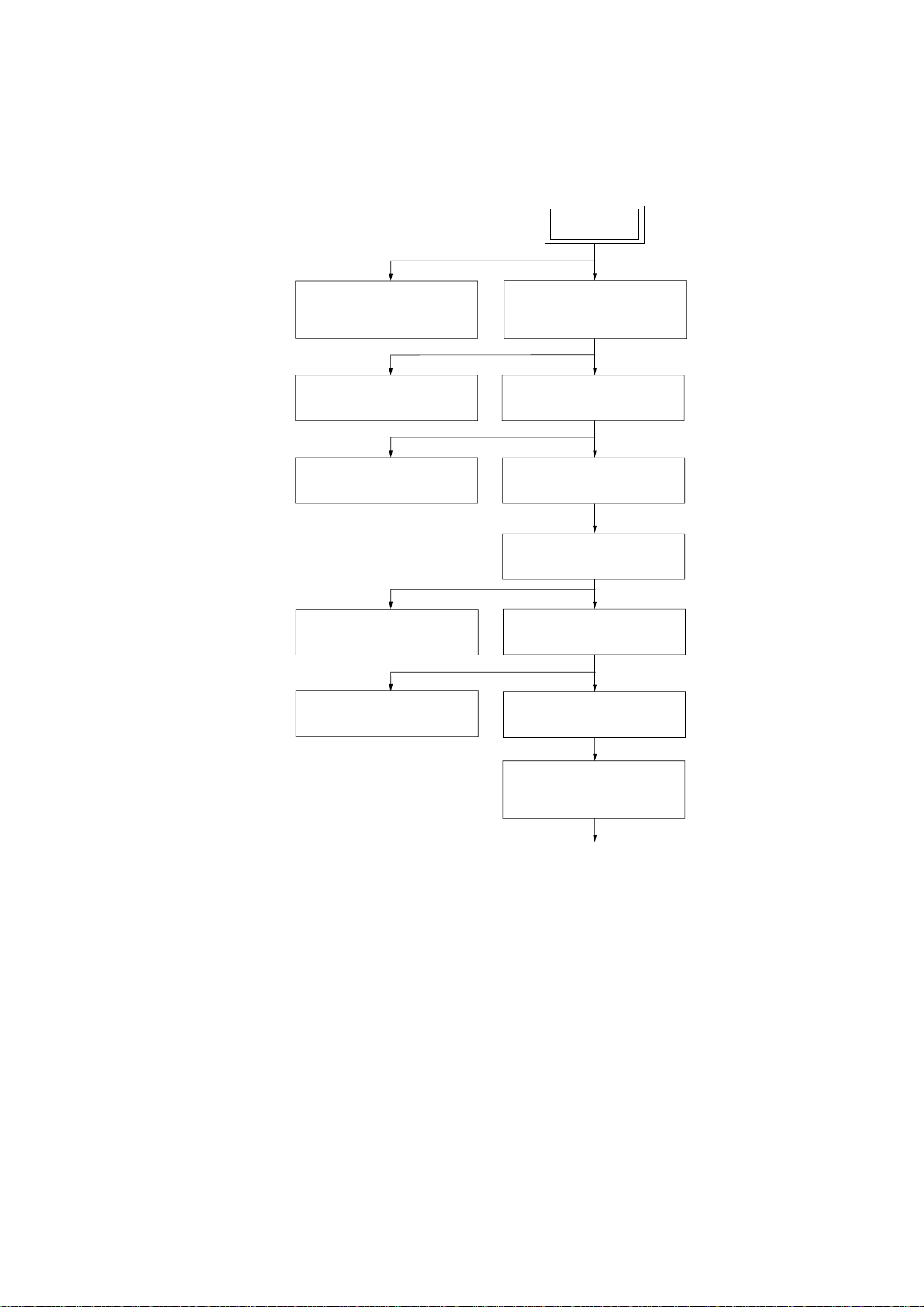
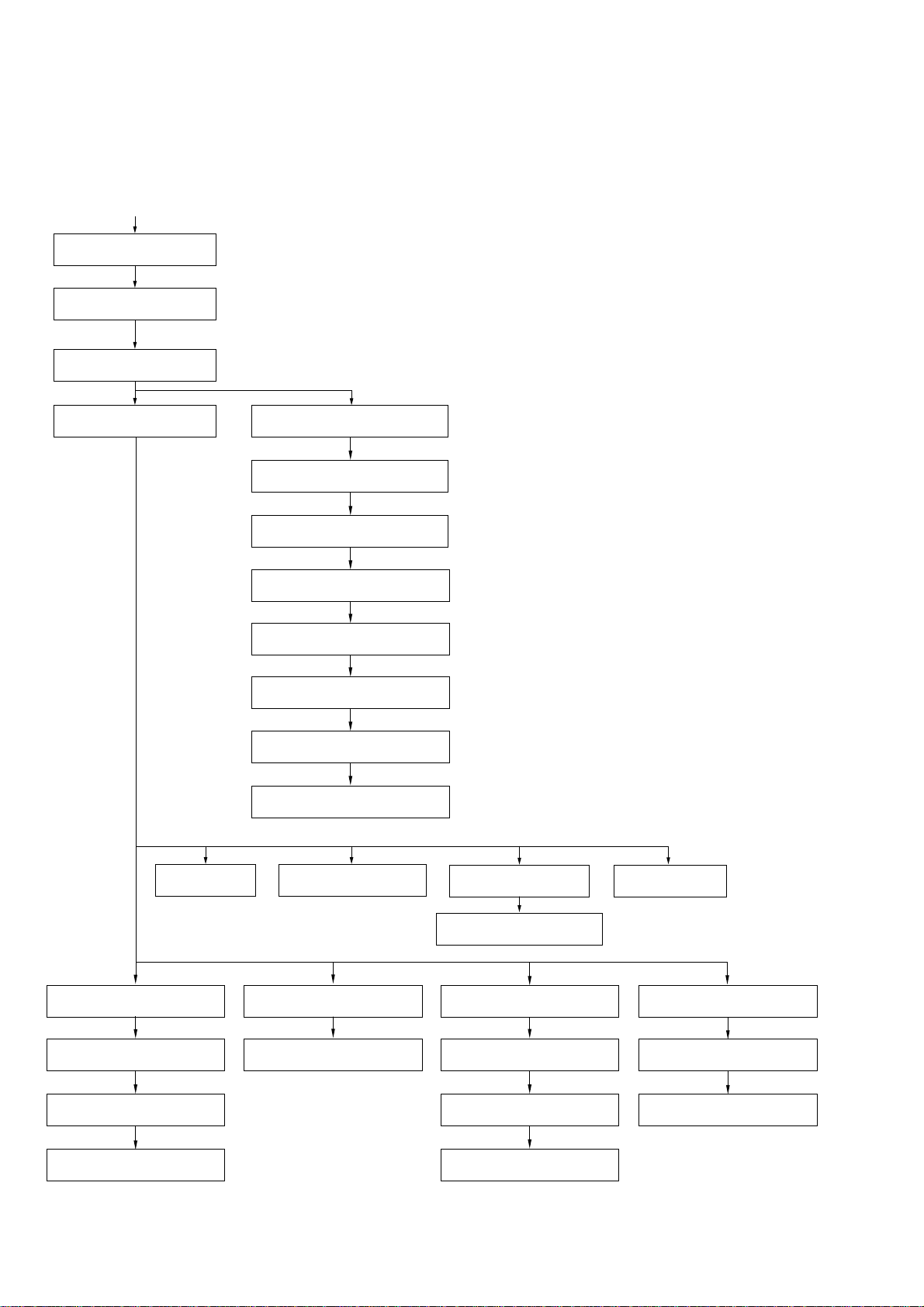
2-1. DISASSEMBLY FLOW-1
•This set can be disassembled in the order shown below.
HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
SECTION 2
DISASSEMBLY
SET
2-3.OPTICAL PICK-UP
BLOCK
(Page 9)
2-5.MECHANICAL DECK
(Page 10)
2-7.PANEL (1), (2) BOARD
(Page 11)
2-10.AMP BOARD
(Page 13)
2-12.TUNER, DC FAN
(Page 14)
2-4.SIDE PLATE (L) (R),
TOP PANEL SECTION
(Page 10)
2-6.FRONT PANEL SECTION
(Page 11)
2-8.MAIN BOARD
(Page 12)
2-9.AMP SECTION
(Page 12)
2-11.REAR PANEL SECTION
(Page 13)
2-13.POWER BOARD
(Page 14)
2-14.CD MECHANISM DECK
(CDM82C)
(Page 15)
to DISASSEMBLY FLOW-2
7
HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
2-2. DISASSEMBLY FLOW-2
•This set can be disassembled in the order shown below.
from DISASSEMBLY FLOW-1
2-15. PLATE (COVER TOP)
(Page 16)
2-16. T OP SECTION
(Page 16)
2-17. ARM SECTION
(Page 17)
2-18. CD MECHANISM DECK
SECTION (Page 18)
2-19. SUB GEAR (2 STEP),
SUB SLIDER ASSY (Page 19)
2-20. ARM (R)
(Page 20)
2-21. GEAR (STOCK PLANET)
(RIGHT) (Page 21)
2-22. LEVER (SUB GEAR BACK L)
(Page 21)
2-23. ARM (L)
(Page 22)
2-24. GEAR (STOCK ROT LONG)
(LEFT) (Page 23)
2-25. GEAR (STOCK ROT SHORT)
(RIGHT) (Page 23)
2-26. STOCKER (1) ASSY TO
STOCKER (5) ASSY (Page 24)
2-27. LOD MOTOR
(Page 25)
2-32. CHASSIS (TOP),
CHASSIS (BOTTOM) (Page 29)
2-33. LEVER
(LOADING R, LOADING L) (Page 30)
2-34. DISC STOP LEVER
(Page 31)
2-35. DRIVER BOARD
(Page 31)
8
2-28. SLIDER (PUSH-POPUP)
(Page 25)
2-36. BD BOARD (A)
(Page 32)
2-37. OPTICAL PICK-UP
(KSM-215DCP) (Page 32)
2-29. ROTARY ENCODER
(Page 26)
2-30. ASSEMBLING OF THE
ROTARY ENCODER (Page 27)
2-38. BASE UNIT SECTION
(Page 33)
2-39. LEVER (BU LOCK)
(Page 33)
2-40. GEAR (IDL-B)
(Page 34)
2-41. GEAR (IDL-C)
(Page 34)
2-31. ELV MOTOR
(Page 28)
2-42. SPR-E (TAKO-BACK)
(Page 35)
2-43. PLATE (PUSH) ASSY
(Page 36)
2-44. SPR-P (LOCK)
(Page 37)
Note: Follow the disassembly procedure in the numerical order given.
k
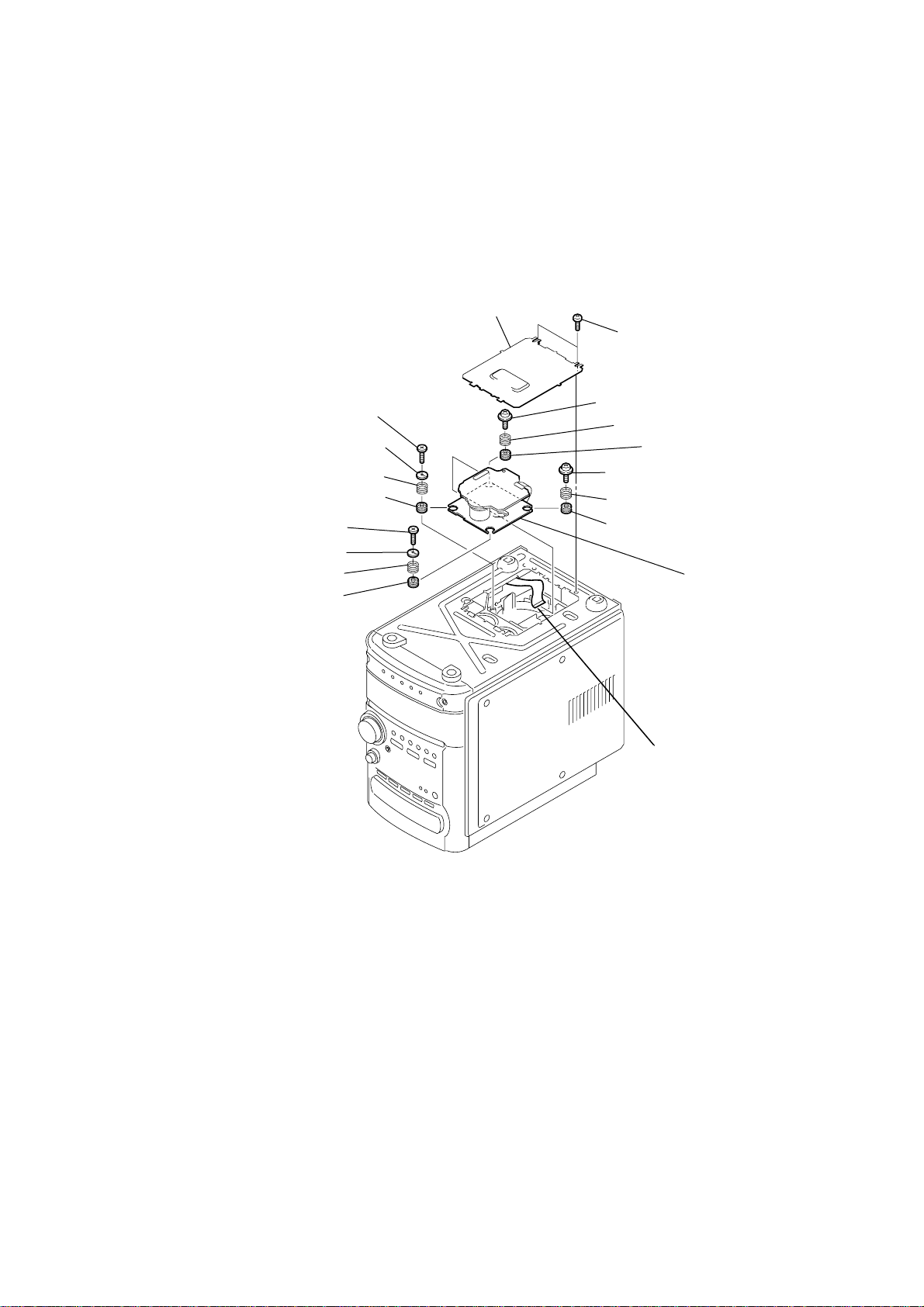
2-3. OPTICAL PICK-UP BLOCK
2
bottom cover plate
4
screw
(BTTP M2.6)
5
BU stopper
6
insulator spring (coil)
qf
insulator
7
screw
(BTTP M2.6)
8
BU stopper
9
insulator spring (coil)
qg
insulator
1
two screws
(BVTT3
0
floating screw
(+PTPWH M2.6)
qa
insulator spring (coil)
qh
qs
floating screw
(+PTPWH M2.6)
qd
insulator spring (coil)
qj
insulator
×
6
)
insulator
qk
optical pick-up bloc
HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
3
w
ire (flat type)
23p(CN102)
9
HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
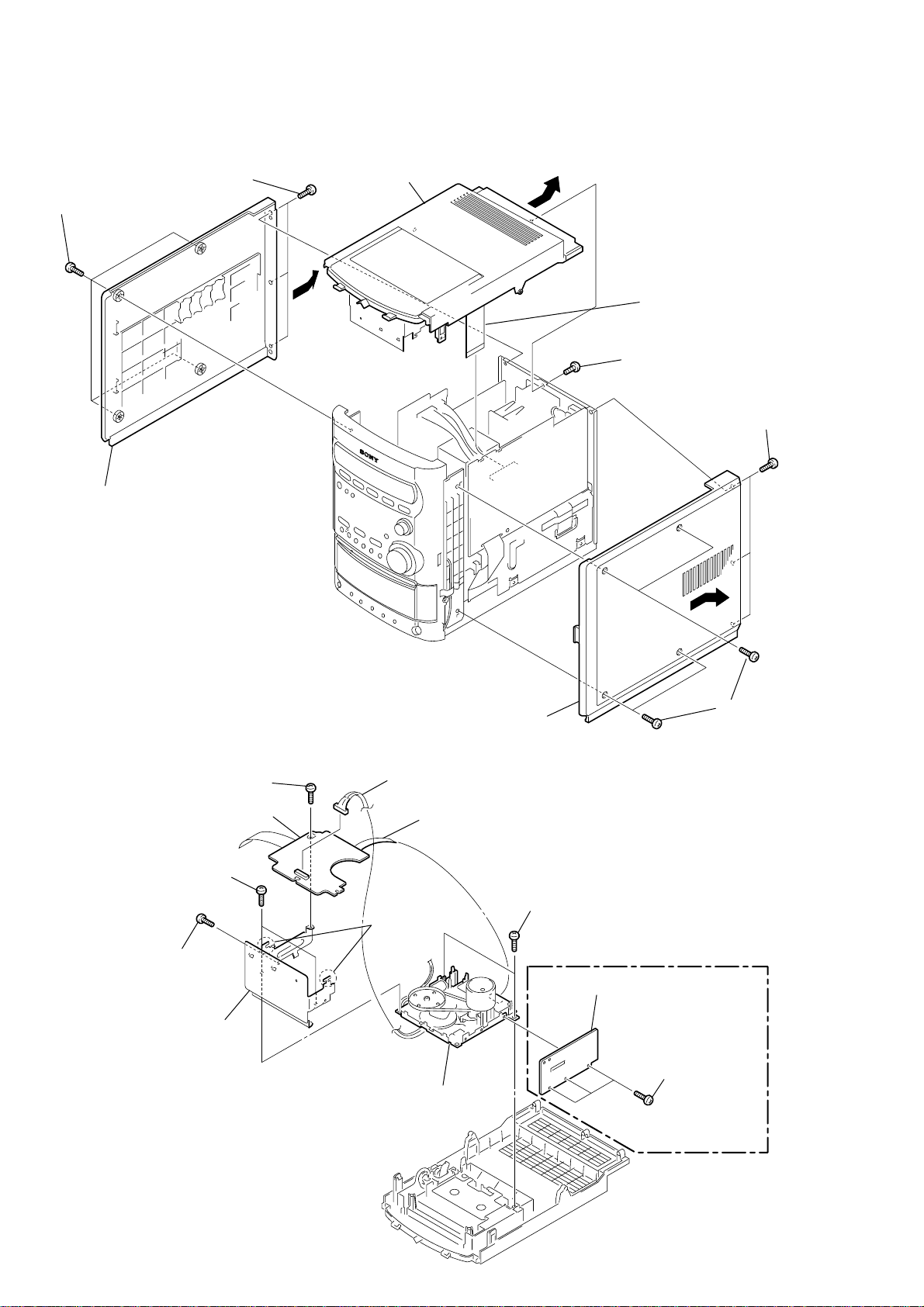
2-4. SIDE PLATE (L) (R), TOP PANEL SECTION
9
top panel section
5
four screws
(BVTP3
4
three screws
(BVTP3
×
8
)
×
8
)
8
w
ire (flat type)
23p(CN307)
7
screw
(BVTP3
×
8
)
1
three screws
(BVTP3
×
8
)
6
side plate (L)
2-5. MECHANICAL DECK
5
screw
(BVTP2.6
9
AU-TC board
4
two screws
(BVTP2.6
×
8
2
3
side plate (R)
6
×
8
)
)
(CN301)
8
two hooks
connector
7
w
ire (flat type)
(7p)
3
two screws
(BVTP2.6
•Abbreviation
CET : East European and Russian model.
×
8
)
four screws
(BVTP3
×
8
)
10
0
screw
(BVTP2.6
qa
×
8
)
bracket (CST)
qs
mechanical deck
(HPZ7:AEP, UK, CET model)
2
shield board
1
three screws
(BVTP2.6
×
8
)
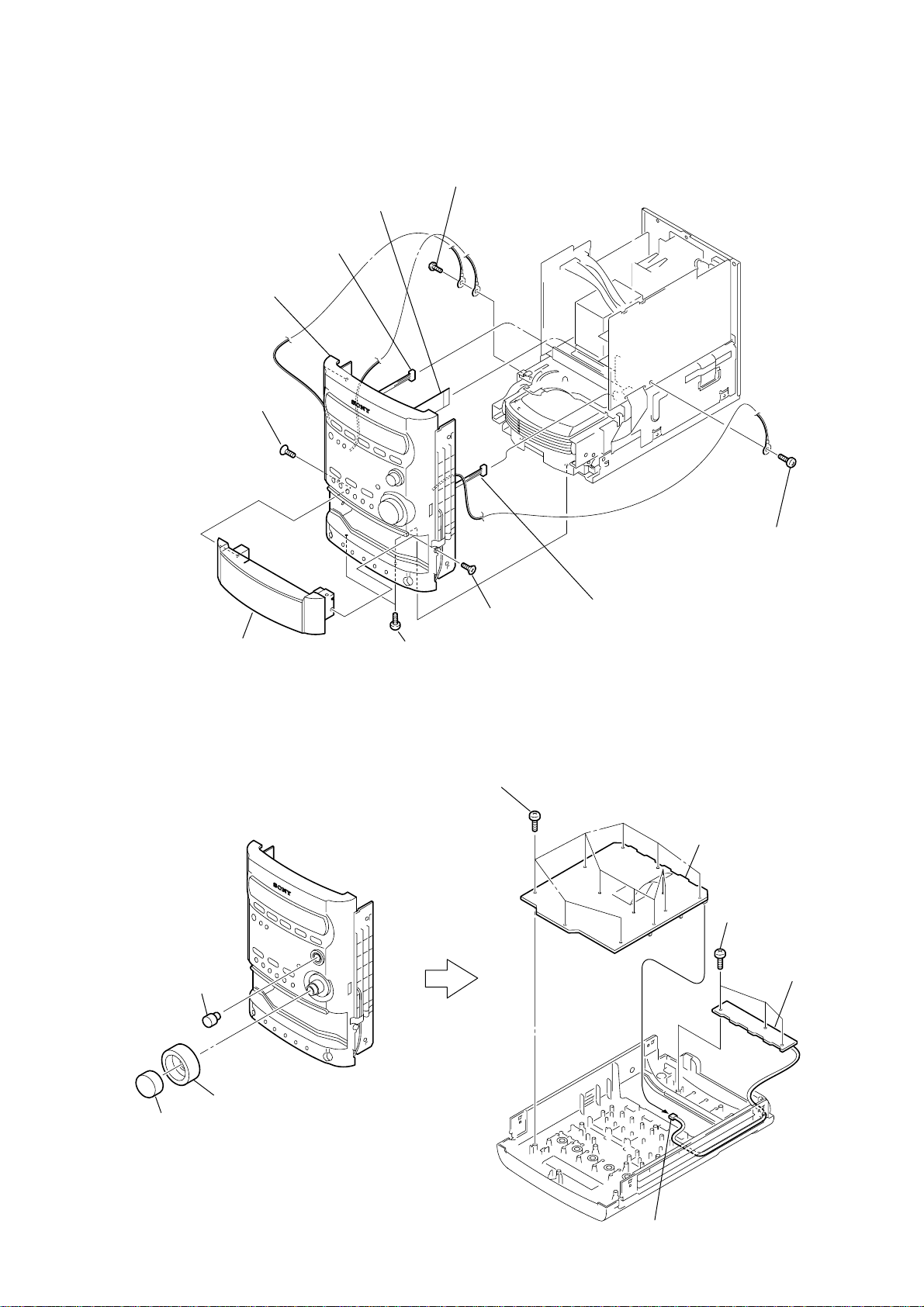
2-6. FRONT PANEL SECTION
8
25p(CN312)
9
connector
q;
front panel section
2
screw
(KTP3
×
8
)
w
ire (flat type)
(CN302)
6
screw
(BV 3
HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
×
6
)
3
CD lid
2-7. PANEL (1), (2) BOARD
3
knob
(JOG)
4
two screws
(BV 3
×
6
)
4
twelve screws
(BVTP2.6
1
screw
(KTP3
×
8
5
screw
(BVTP3
×
8
)
7
connector
×
8
)
)
(CN308)
6
PANEL (1) board
7
three screws
(BVTP2.6
8
×
PANEL (2) board
8
)
1
knob
2
(VOL)
ornament
(VOL)
5
connector
(CN802)
11
HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
)
2-8. MAIN BOARD
9
w
ire (flat type)
(11p)(CN305)
6
two screws
(BVTP3
×
8
)
2
connector
(CN306)
3
connector
(CN314)
4
(CN309)
connector
qa
MAIN board
1
w
ire (flat type)
(11p)(CN313)
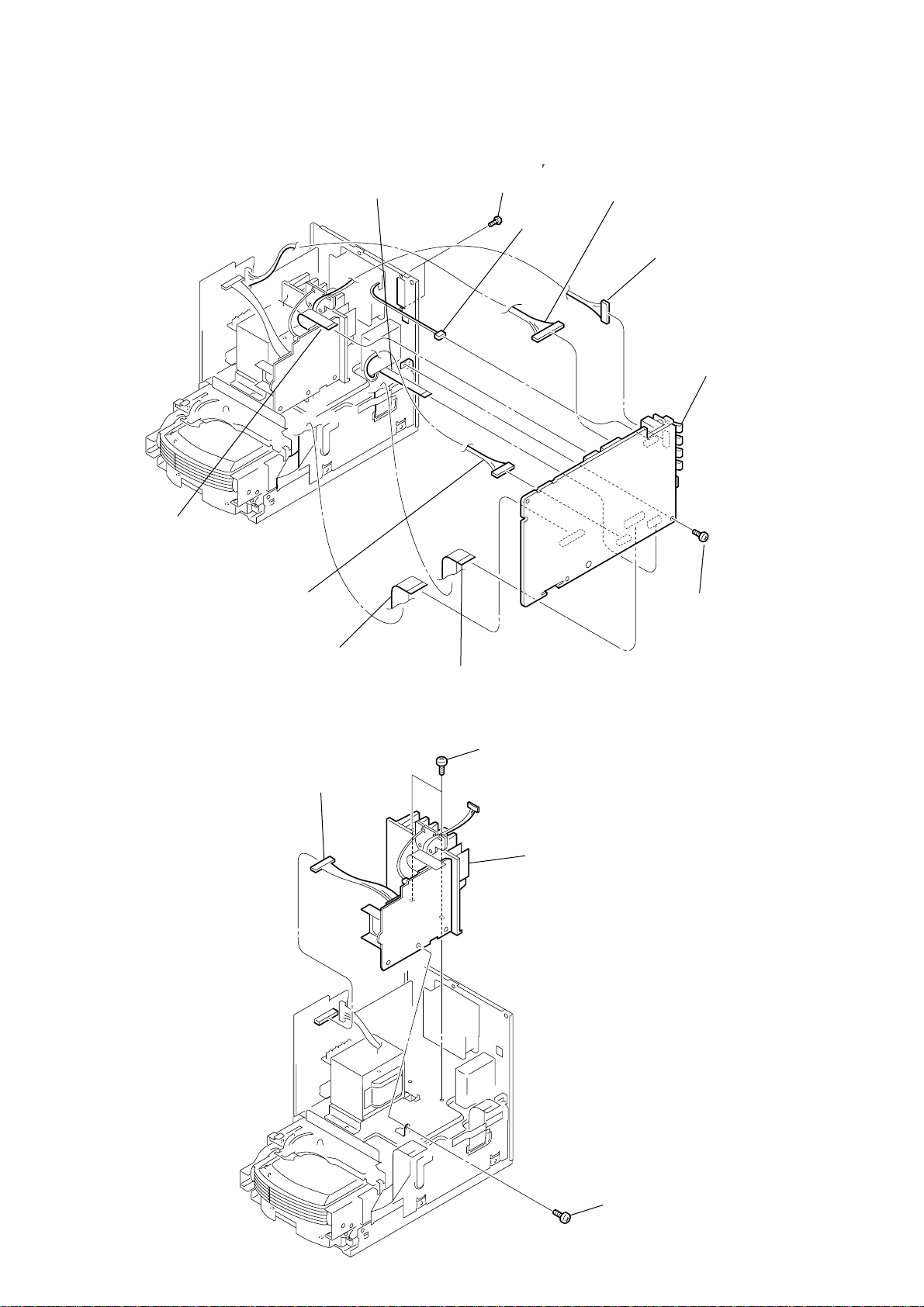
2-9. AMP SECTION
7
connector
(CN303)
8
w
ire (flat type)
(21p)(CN311)
1
(CN902)
connector
q;
w
ire (flat type)
(23p)(CN304)
2
two screws
(BV2.6
×
4
10
)
AMP section
5
screw
(BVTP3
×
8
)
12
3
screw
(BVTP3
×
8
2-10. AMP BOARD
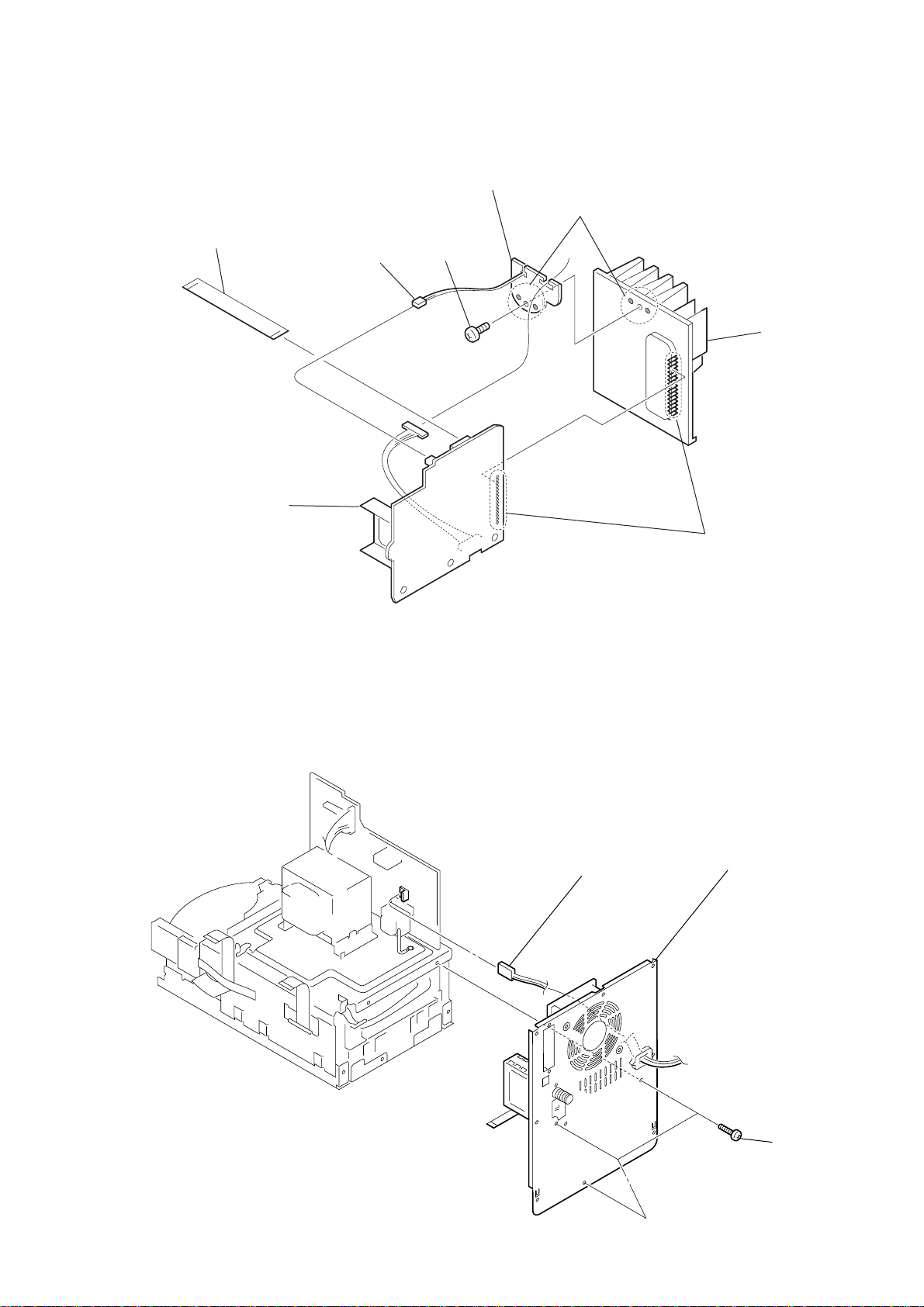
k
5
w
ire (flat type)
11p (CN601)
1
connector
(CN991)
4
thermistor board
2
screw
(BVTP3
HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
3
Remove soldering
from the two points.
×
8
)
7
heat sin
8
AMP board
2-11. REAR PANEL SECTION
1
connector
(CN905)
6
Remove soldering
from the 15 points.
3
rear panel section
2
three screws
(BVTP3
×
8
)
13
HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
)
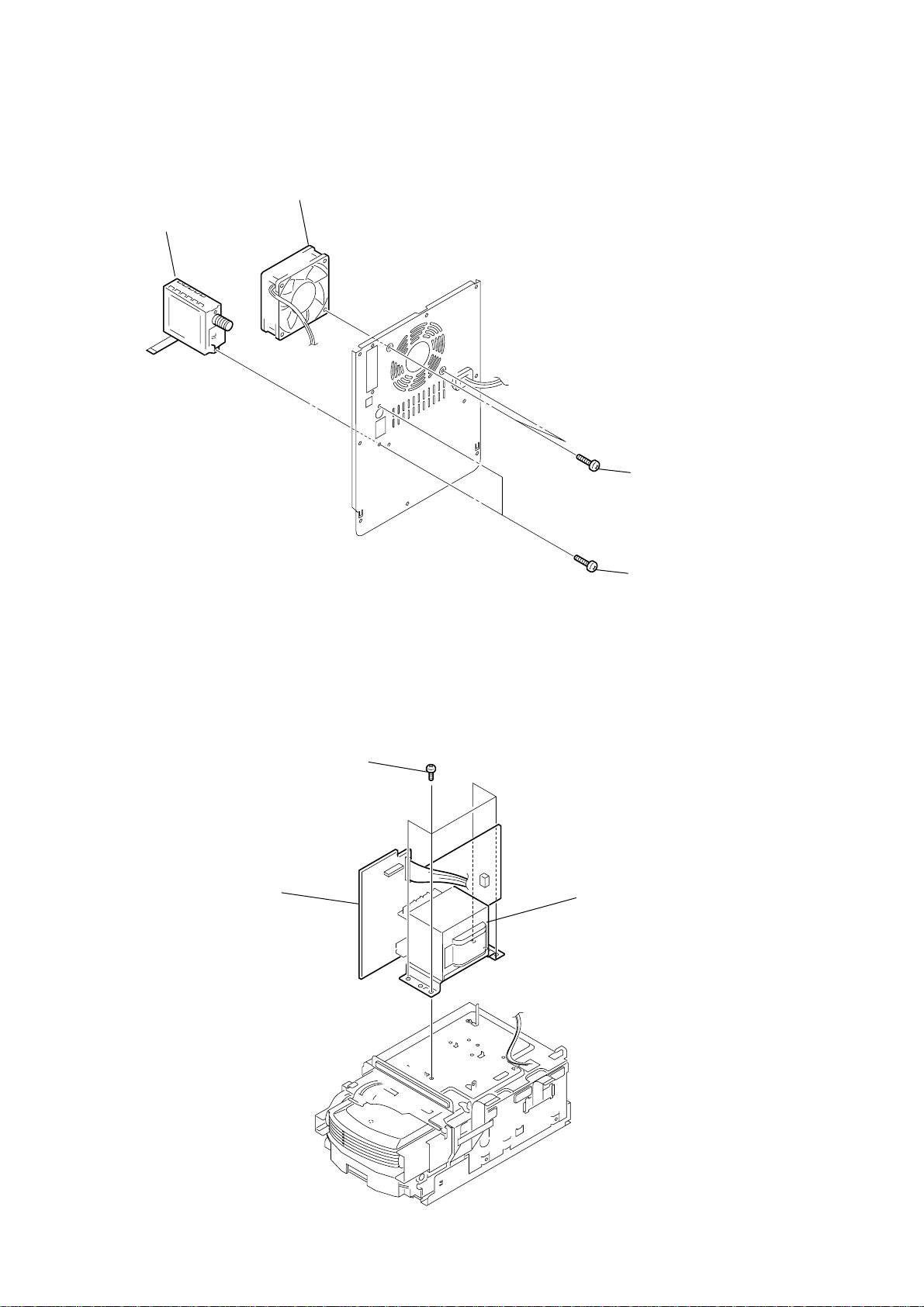
2-12. TUNER, DC FAN
4
tuner
2
DC fan
1
two screws
(BVTP3
×
8
2-13. POWER BOARD
2
POWER board
1
four screws
(BVTT4
3
two screws
(BVTP3
×
8
)
×
6
)
T901
14
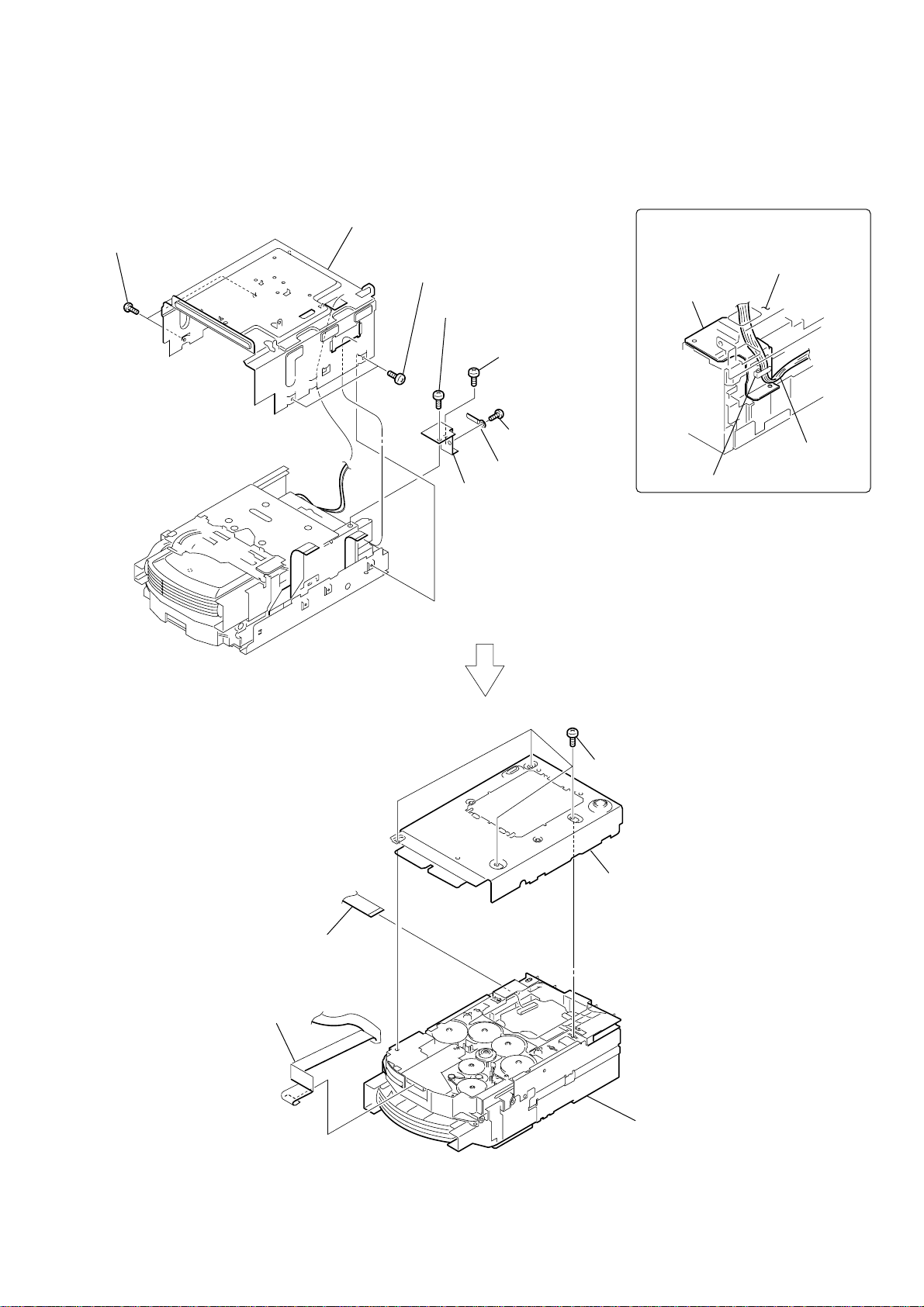
2-14. CD MECHANISM DECK (CDM82C)
HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
1
two screws
(BV 3
3
sub chassis
×
6
)
2
two screws
(BV 3
×
6
)
6
screw
(BVTP2.6
8
5
plate
7
×
screw
4
clamp
8
)
(BVTT3
screw
(BVTP2.6
×
6
)
×
8
Please attach connector,
as shown in a figure.
plate
)
sub chassis
connector
clamp
qs
w
23p (CN102)
qa
w
ire (flat type)
21p (CN801)
ire (flat type)
9
four screws
(BV 3
0
chassis
×
6
)
qd
CD mechanism deck
(CDM82C)
15
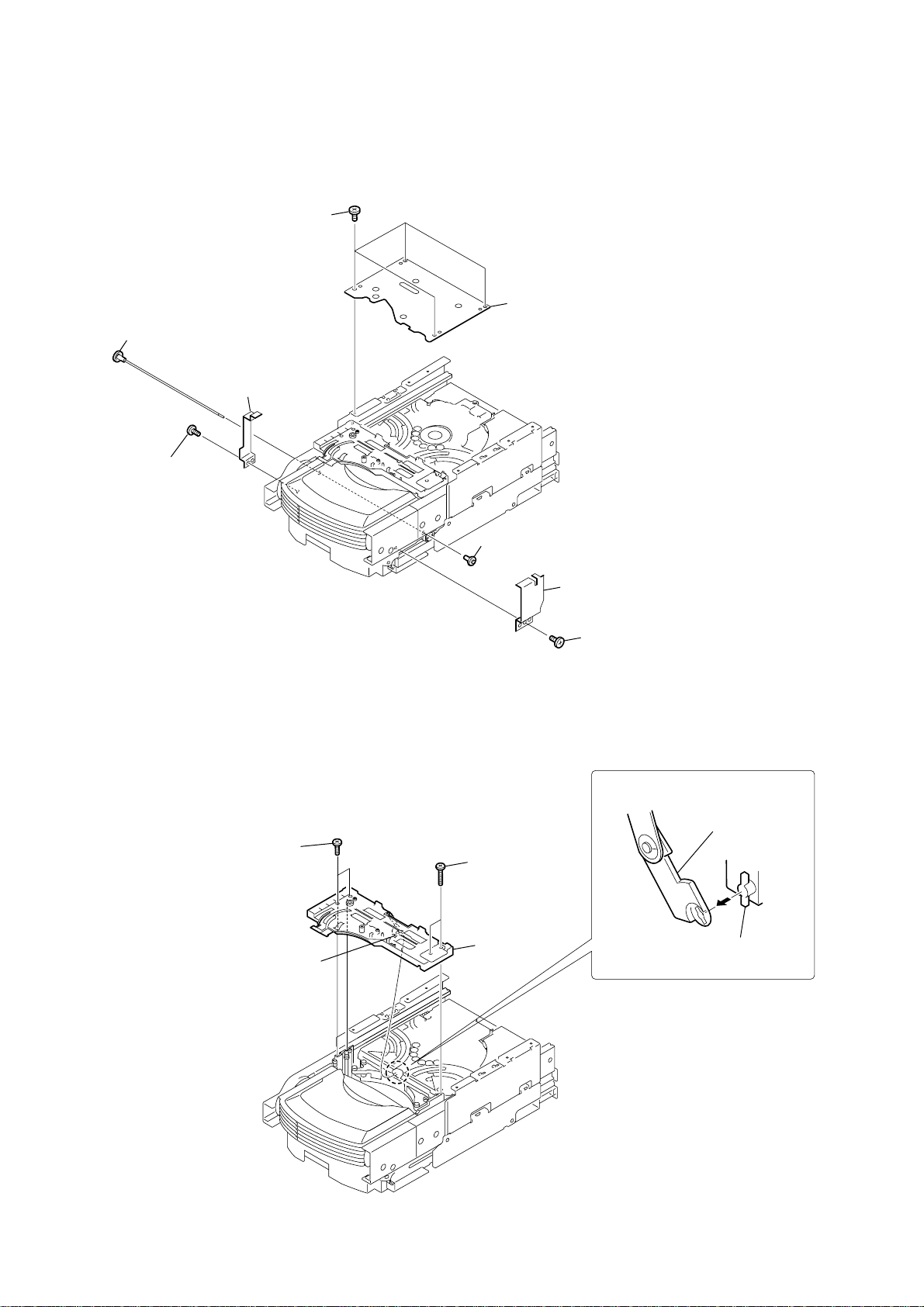
HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
)
2-15. PLATE (COVER TOP)
3
(BTTPM 2.6
2
gear (joint op), shaft (stock)
8
plate (cam R)
7
screw
(BTTPM 2.6
×
8)
four screws
×
8)
4
plate (cover top)
2-16. TOP SECTION
1
two screws
(BTP 2
shock guard
(lower)
×
1
gear (joint op)
6
plate (cam L)
5
screw
(BTTPM 2.6
8)
2
two screws
(PTPWH 2
5
top
×
14)
×
8
4
shock guard
(lower)
3
claw
16
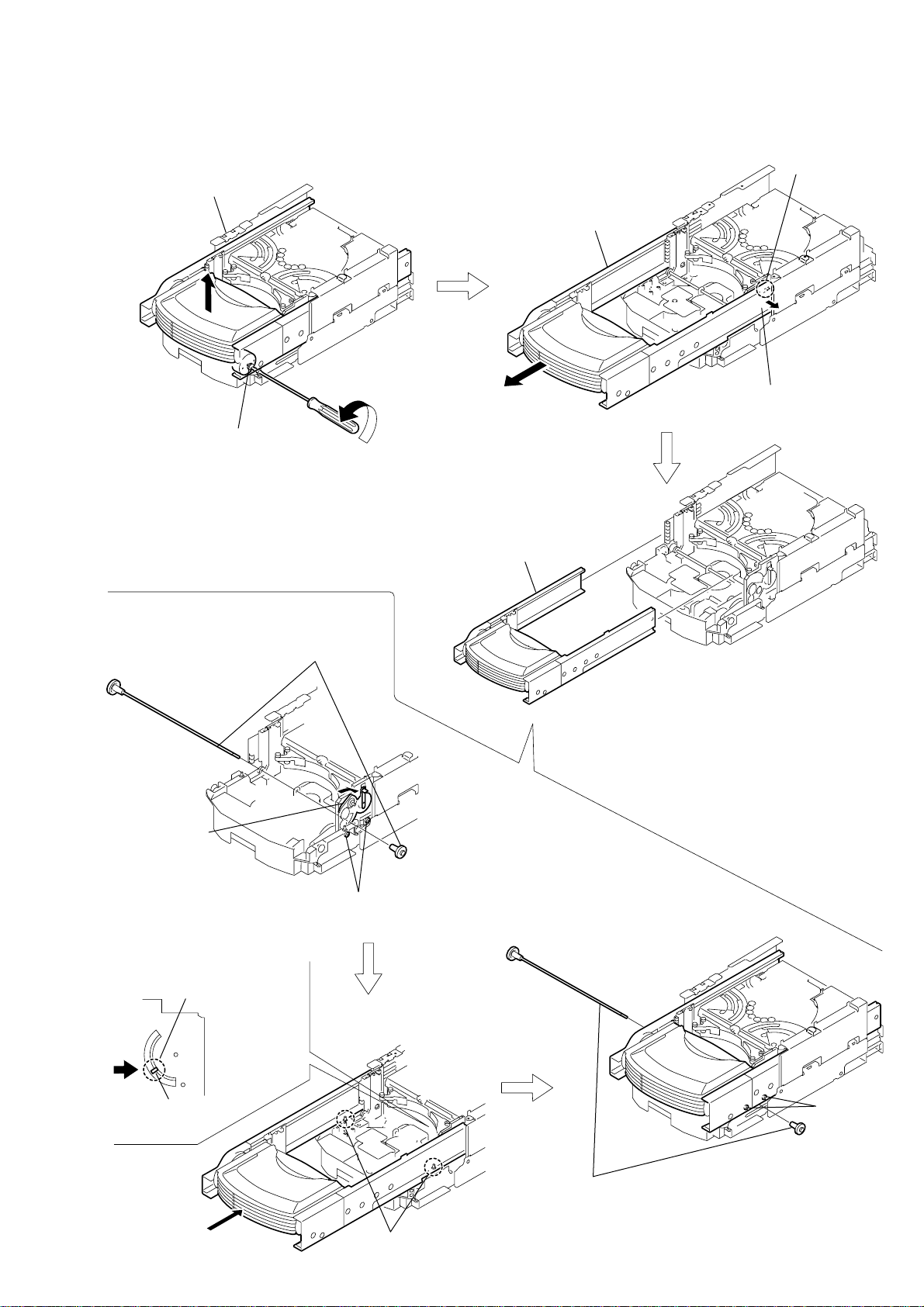
2-17. ARM SECTION
B
A
1
T
urn over the
pulley (LOD motor)
in the direction of the arrow A.
2
Slide the arm section in the
direction of the arrow B.
4
Push this portion with a finger
in the direction of the arrow C.
3
claw
6
arm section
5
Remove the
arm section
in the direction of the arrow D.
C
D
1
gear (joint op),
two shaft (shaft) stocks
8
gear (joint op), two shaft (shaft) stocks
2
loosen two
screws
4
two claws
5
arm section
3
turn over the
gear (swing)
in the direction
of the arrow.
7
two
screws
6
Push this portion with a finger
in the direction of the arrow C.
gear (swing)
PRECAUTION DURING ARM SECTION
INSTALLATION
HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
17
HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
2-18. CD MECHANISM DECK SECTION
pulley (ELV motor)
A
2
Slide the
in the direction of the arrow
B
CD mechanism deck section
B
.
1
T
urn over the
in the direction of the arrow
pulley (ELV motor)
plate (cam L)
A
.
3
four
claws
4
Remove the CD mechanism deck section
in the direction of the arrow
C
C
.
18
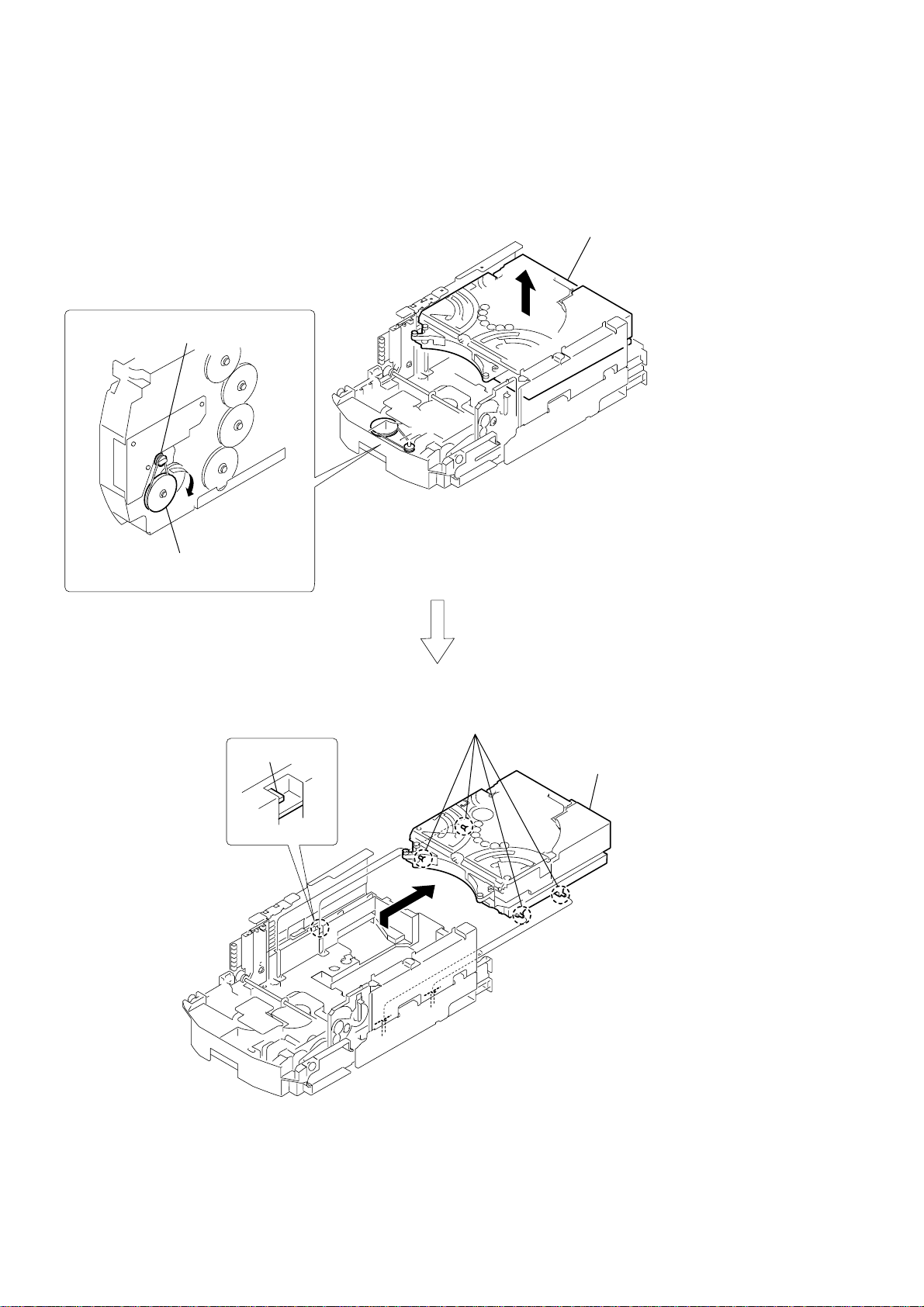
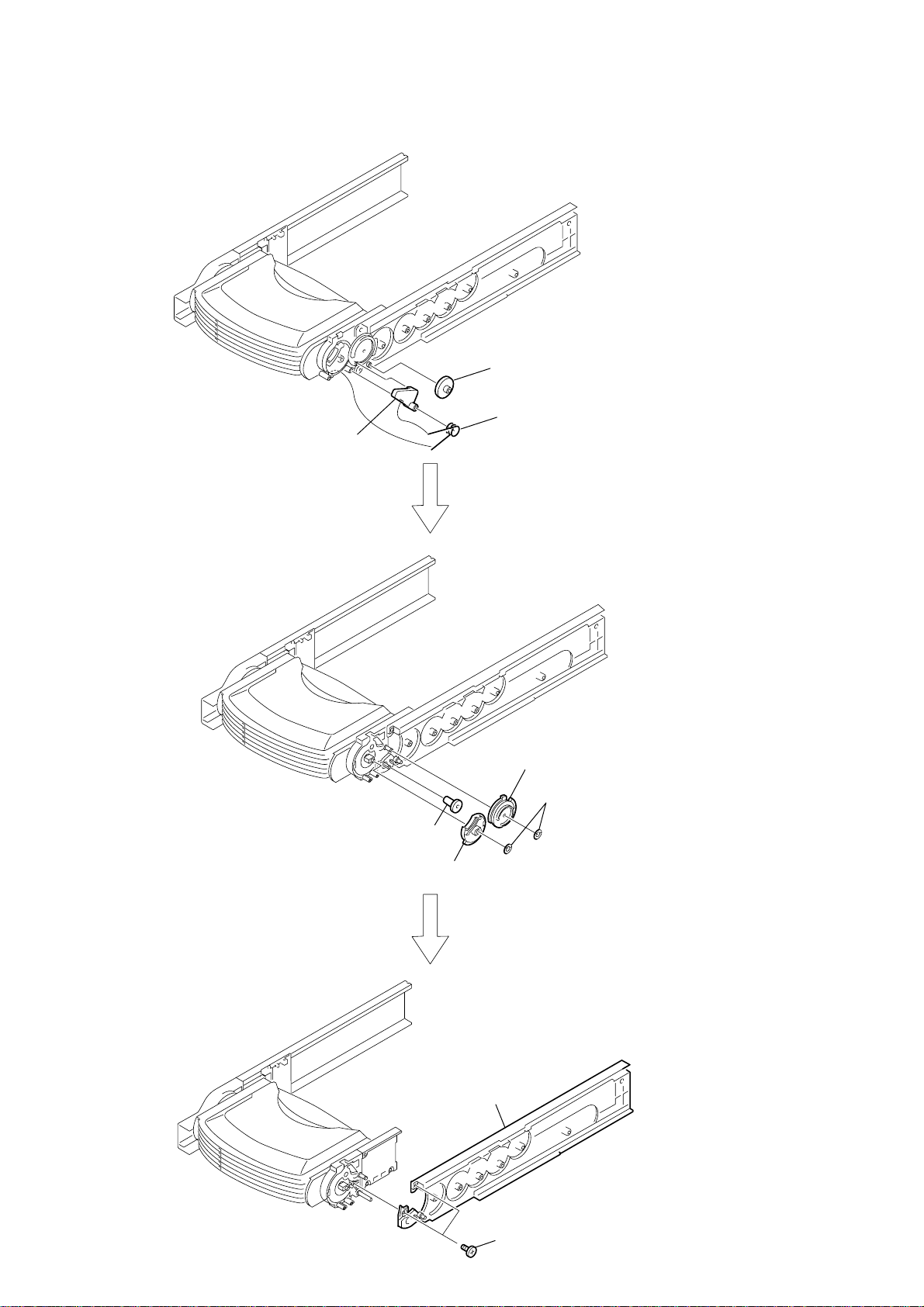
2-19. SUB GEAR (2 STEP), SUB SLIDER ASSY
9
Remove the
in the direction of the arrow.
sub slider assy
HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
0
sub slider assy
5
sub gear (2 step)
sub slider assy
4
sub gear (idler)
1
k tapping screw (K2.6
3
2
two screws (M2
×
8)
cover (R)
×
5)
6
7
sub gear (idler)
8
sub gear (idler)
sub gear (idler)
19
HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
)
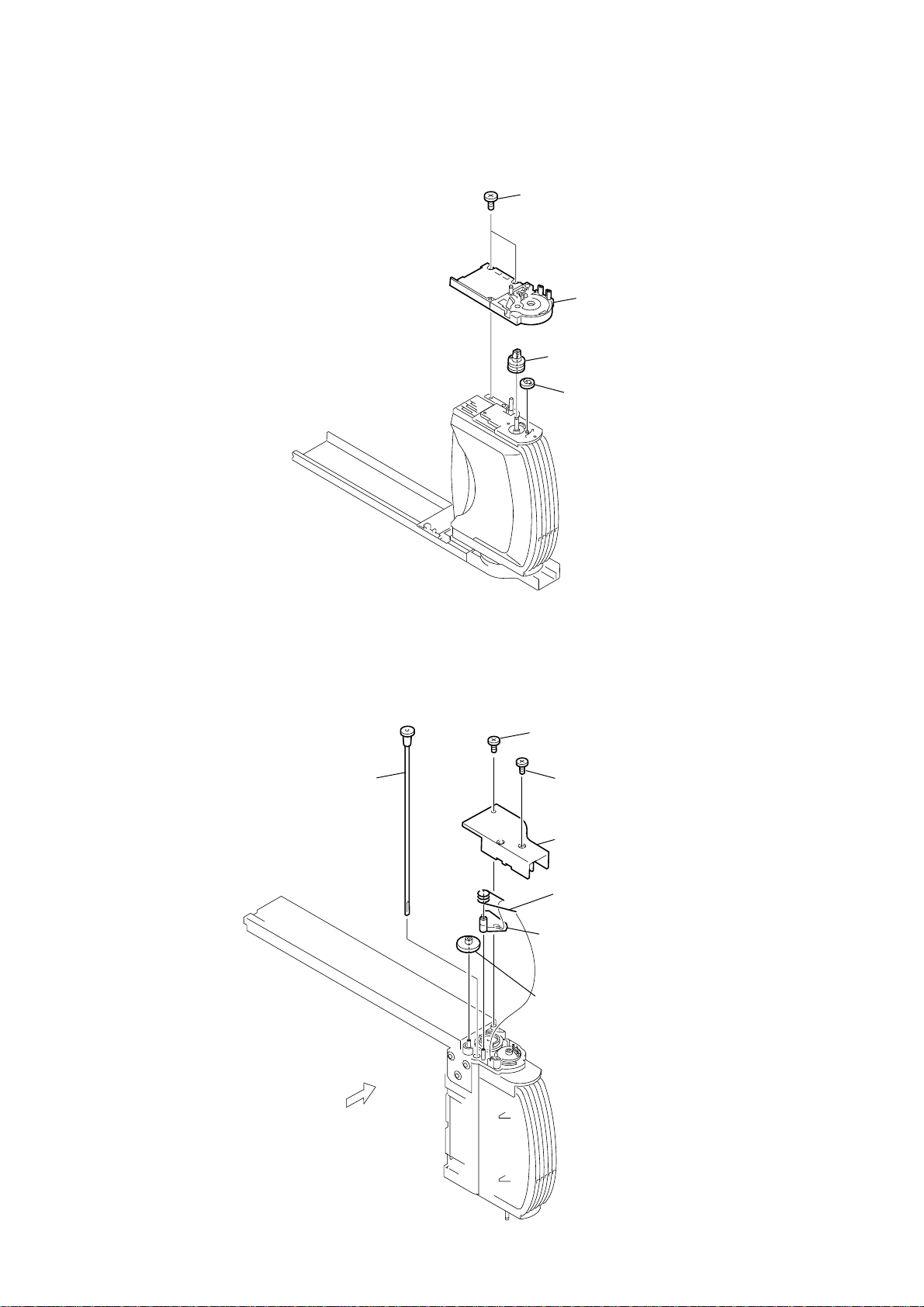
2-20. ARM (R)
3
lever (sub gear back R)
1
sub gear (joint just front)
2
SPR-T (sub gear back R)
7
gear (stock joint)
6
gear (stock rotary right)
9
arm (R)
5
gear (sub gear pin right
4
two washers (5.5)
20
8
two screws
× 5
(K2
)
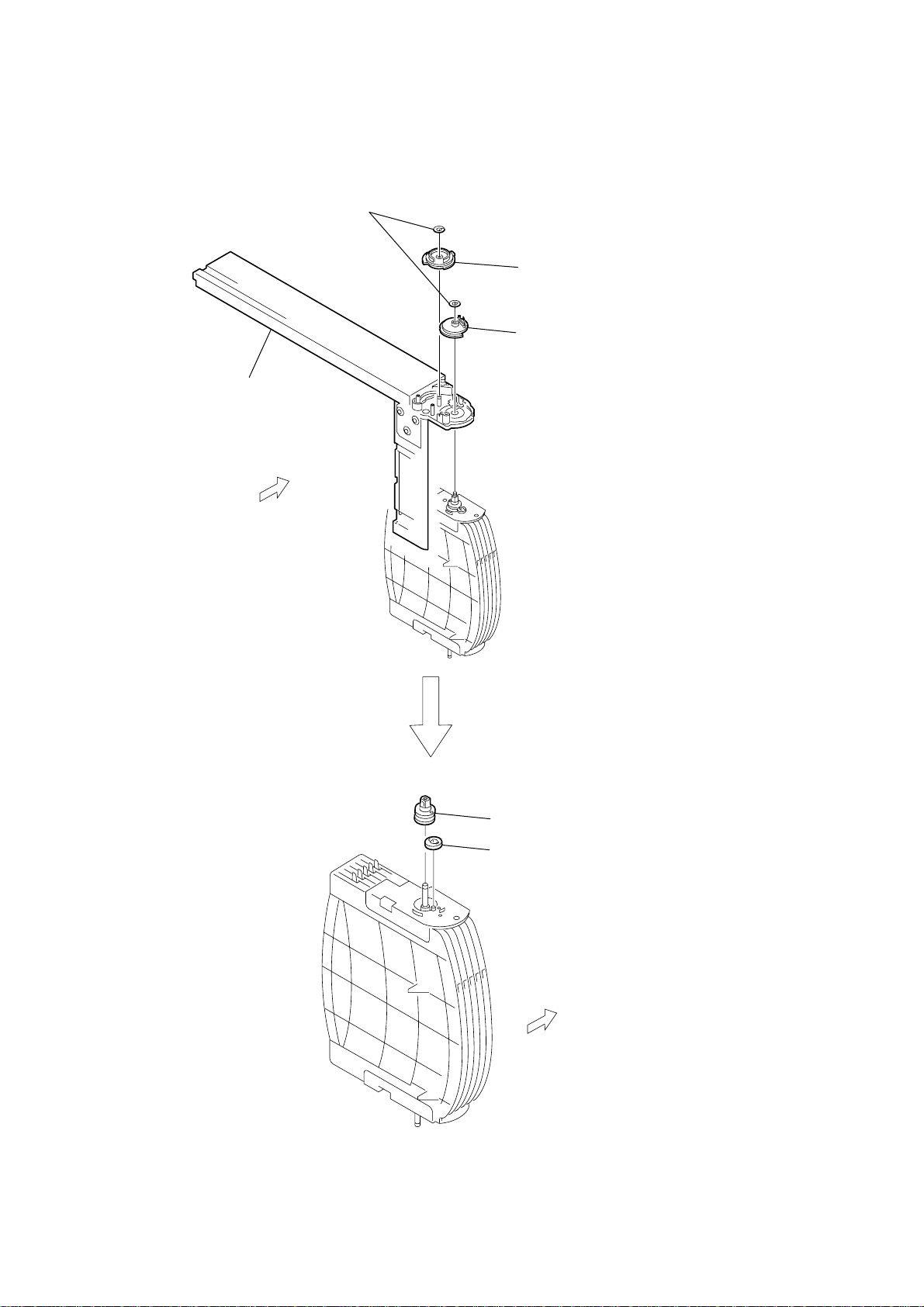
2-21. GEAR (STOCK PLANET) (RIGHT)
)
)
1
two screws (BTTP M2.6
2
stock base (A)
3
gear (stock sun)
4
gear (stock planet)
×
HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
6
2-22. LEVER (SUB GEAR BACK L)
5
gear (stock joint),
shaft (stock)
UPPER
SIDE
2
screw (M2
1
3
6
7
lever (sub gear back L)
4
sub gear (joint just front)
×
5)
screw (K2.6
cover (L)
SPR-T (sub gear back L
×
8)
21
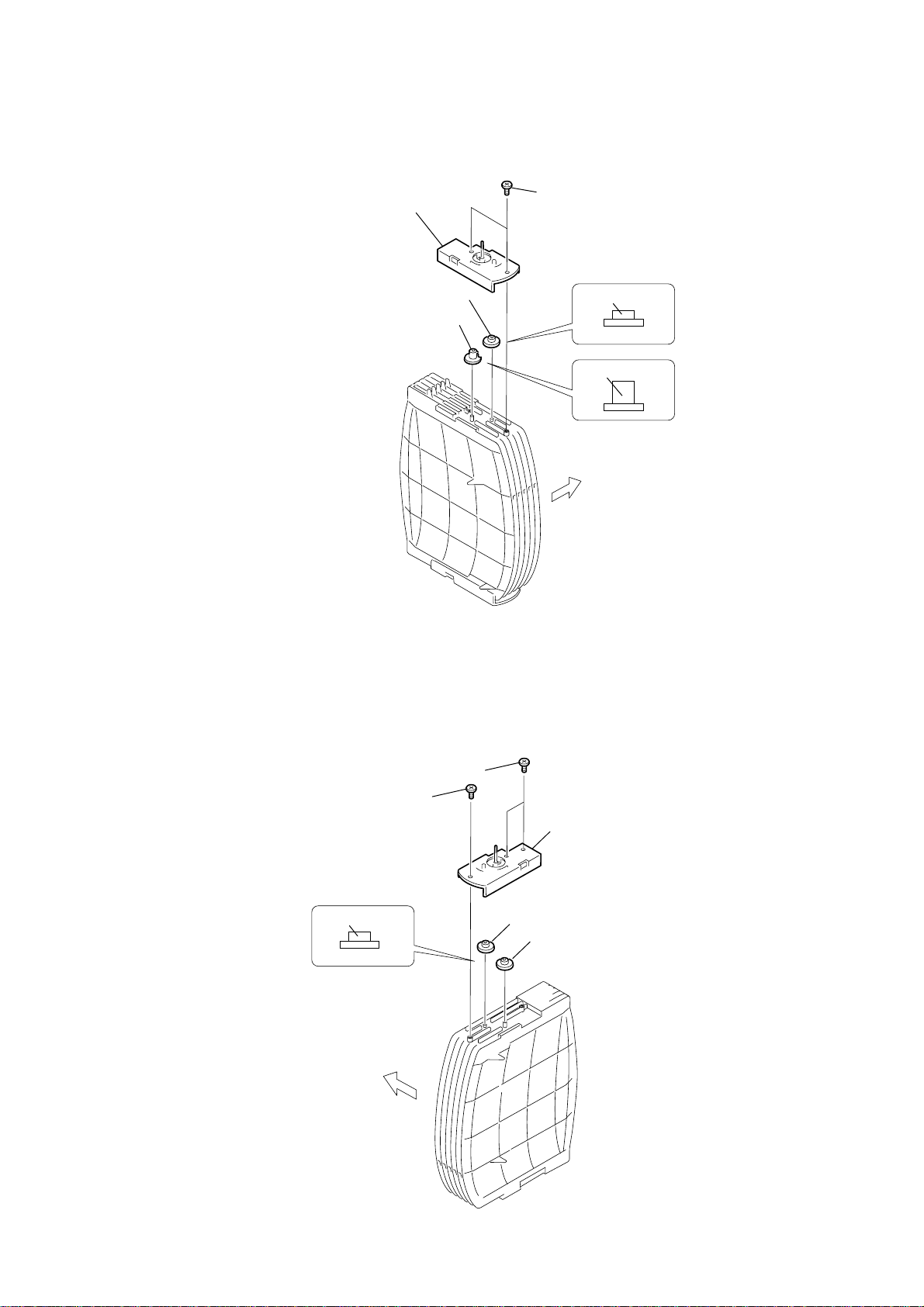
HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
)
2-23. ARM (L)
4
arm (L), stock base (B)
1
two washers (5.5)
UPPER
SIDE
2
gear (sub gear pin right
3
gear (stock rotary right)
6
gear (stock sun)
5
gear (stock planet)
UPPER
SIDE
22
2-24. GEAR (STOCK ROT LONG) (LEFT)
)
2
stock box (L)
3
gear (stock rot short)
4
gear (stock rot long)
1
two screws (2
short
long
UPPER
SIDE
×
HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
6)
2-25. GEAR (STOCK ROT SHORT) (RIGHT)
1
two screws (2
2
screw (1.7 )
short
UPPER
SIDE
×
6)
3
stock box (R)
4
gear (stock rot short)
5
gear (stock rot short
23
HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
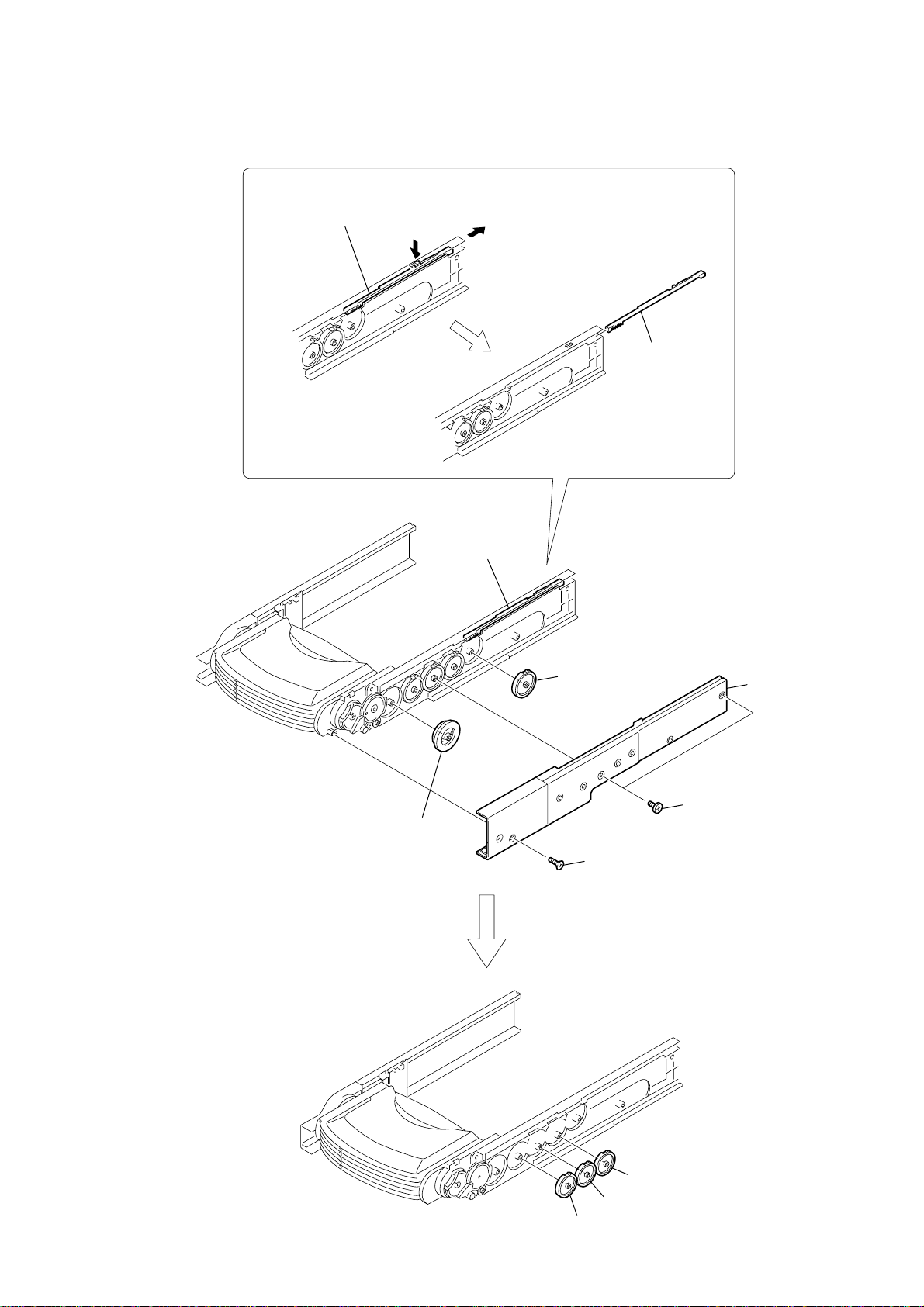
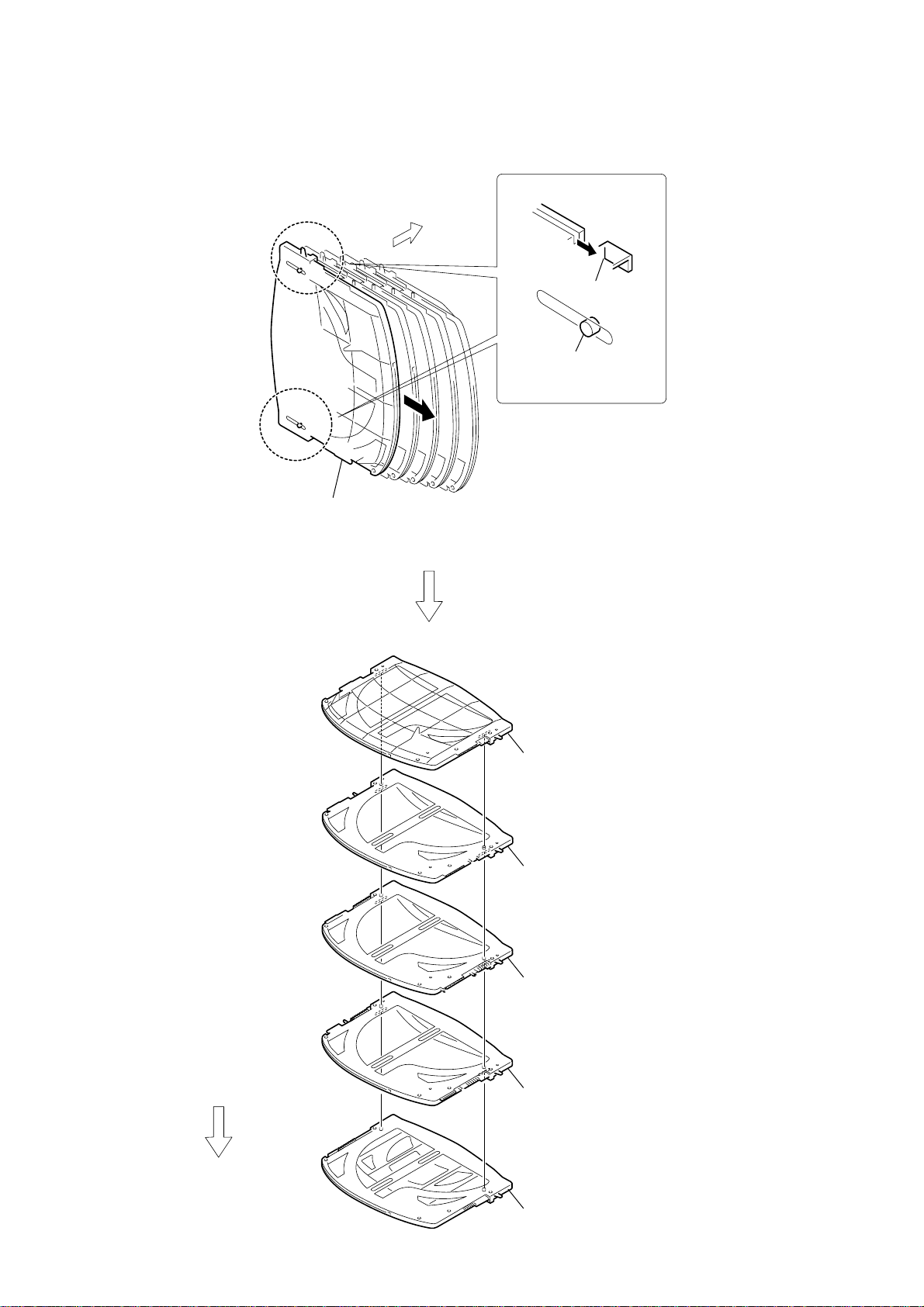
2-26. STOCKER (1) ASSY TO STOCKER (5) ASSY
UPPER
SIDE
1
dowel
2
claw
3
Remove the stocker
in the direction of the arrow.
(1) assy
Repeat the steps 1 to 1, when removing the part
(2), (3), (4) and (5) of the stocker assy.
4
stocker (1) assy
5
stocker (2) assy
24
UPPER
SIDE
6
stocker (3) assy
7
stocker (4) assy
8
stocker (5) assy
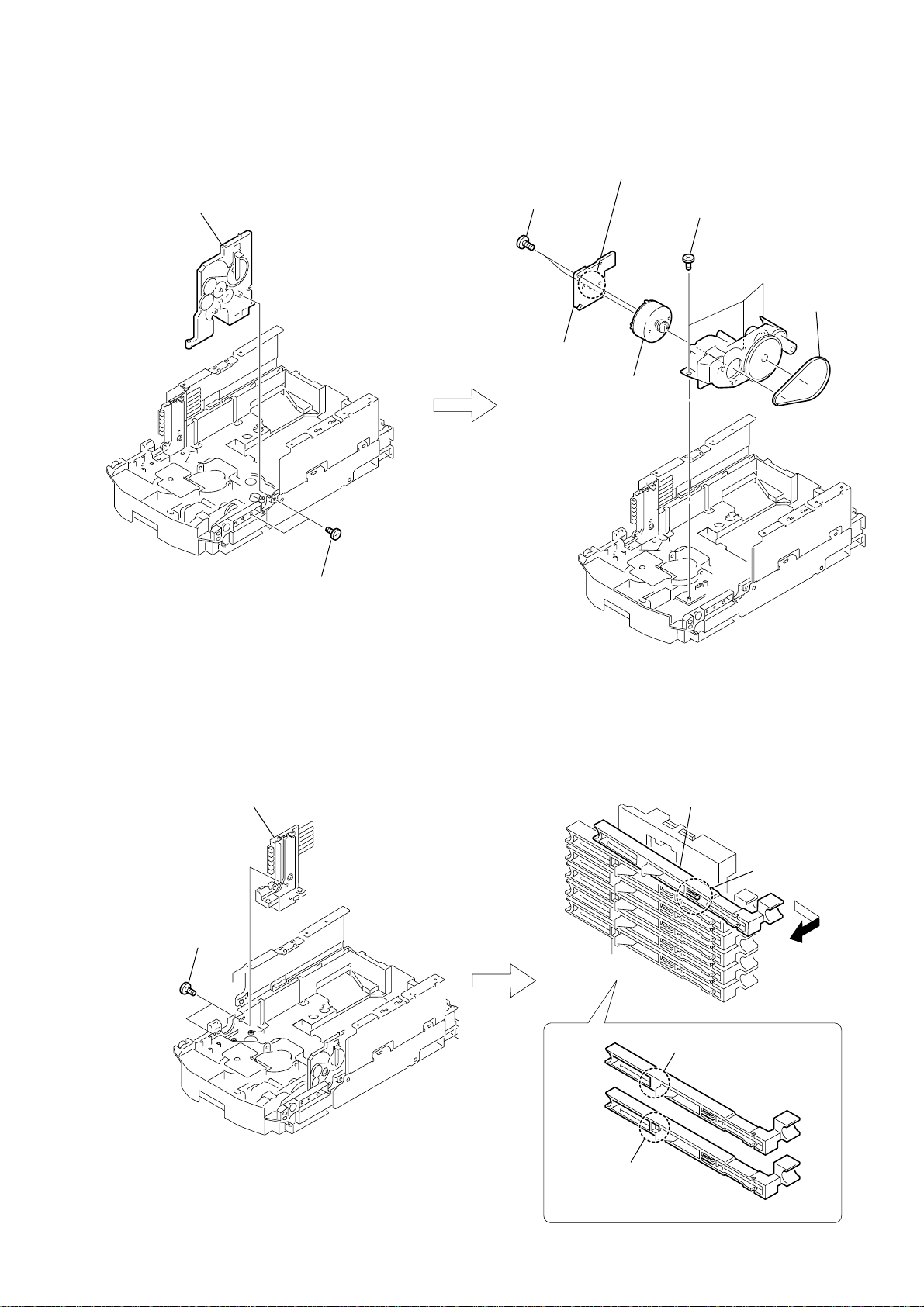
2-27. LOD MOTOR
)
2
sub chassis assy (R)
5
two screws
(BTTP M2.6
7
LOD MOTOR board
×
HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
6
Remove soldering from the two points
3
8)
8
LOD motor
three screws
(BTTP M2.6
×
8)
4
belt (MOT-OP
1
two screws
(BTTP M2.6
2-28. SLIDER (PUSH-POPUP)
2
sub chassis assy (L)
1
two screws
(BTTP M2.6
×
8)
×
8)
4
Remove the slider (push-popup1)
in the direction of the arrow.
3
claw
slider (push-popup 1)
slider (push-popup 2)
25
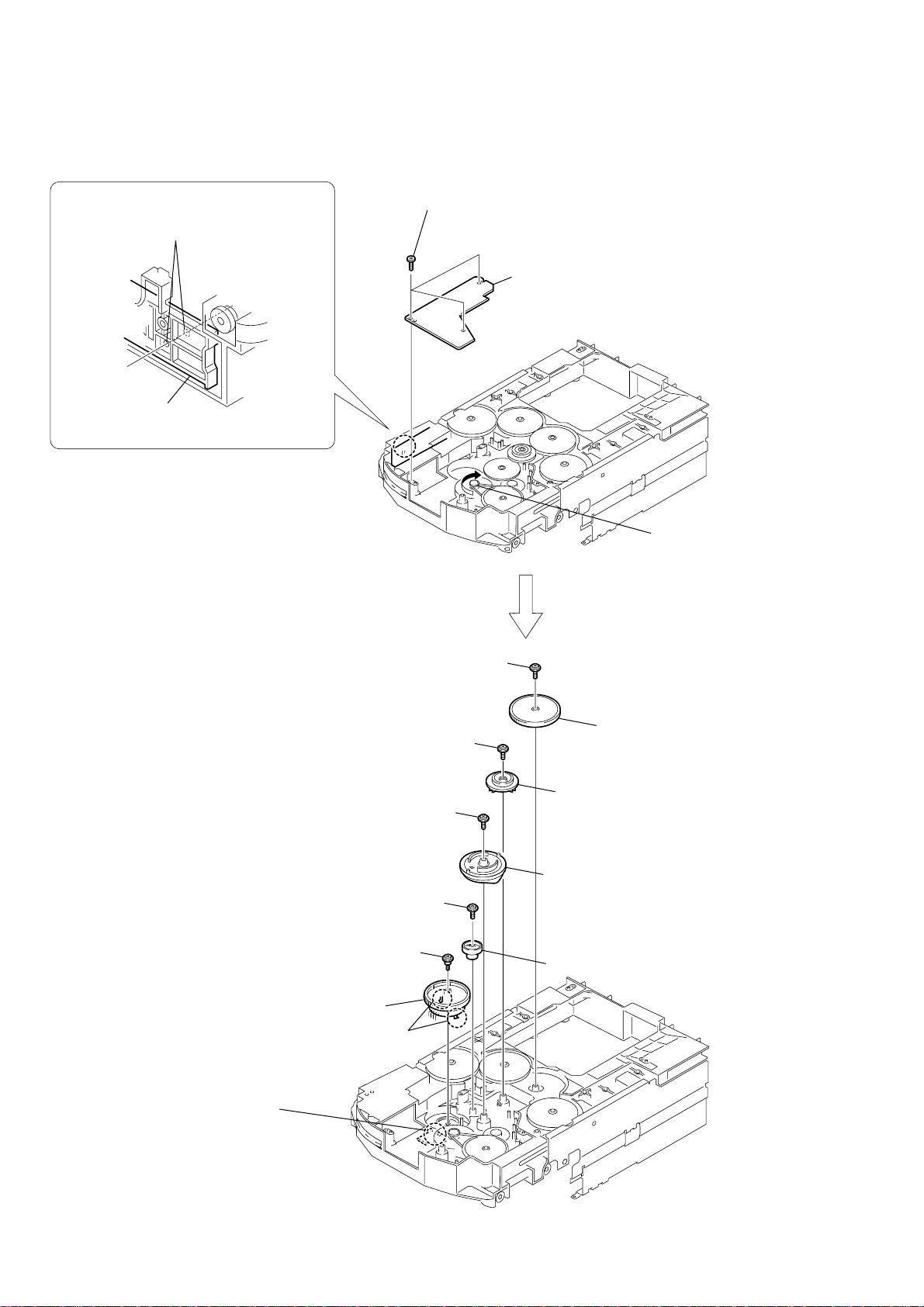
HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
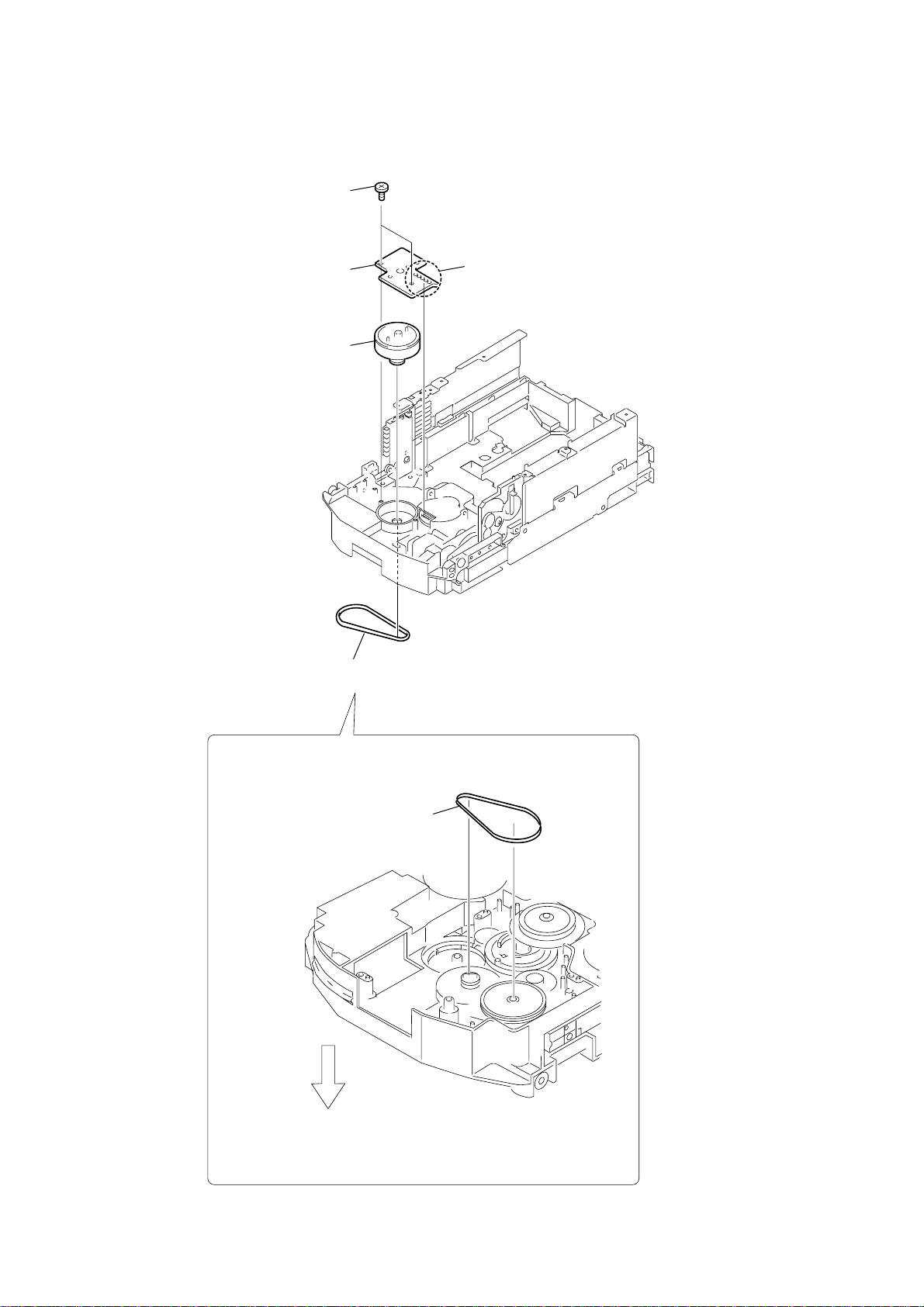
2-29. ROTARY ENCODER
4
Rotate the
the hole on the chassis can be seen
through the plate (comR).
ELV
motor until the position for
plate (com R)
1
three screws
(BTTP M2.6
×
6)
2
RELAY board
5
screw
(PTPWH2.6
7
screw
(PTPWH2.6
9
screw
(PTPWH2.6
qa
screw
(PTPWH2.6
qd
step tapping screw
(PWH2
×
×
6)
8)
×
3
Rotate the ELV motor in
the direction of the arrow.
×
8)
6
×
8)
8)
8
0
gear (geneva 1)
qs
gear (encoder)
gear (pulley UD)
gear (geneva 2)
26
qf
Remove soldering
from the five points
qh
rotary encoder
qg
two claws
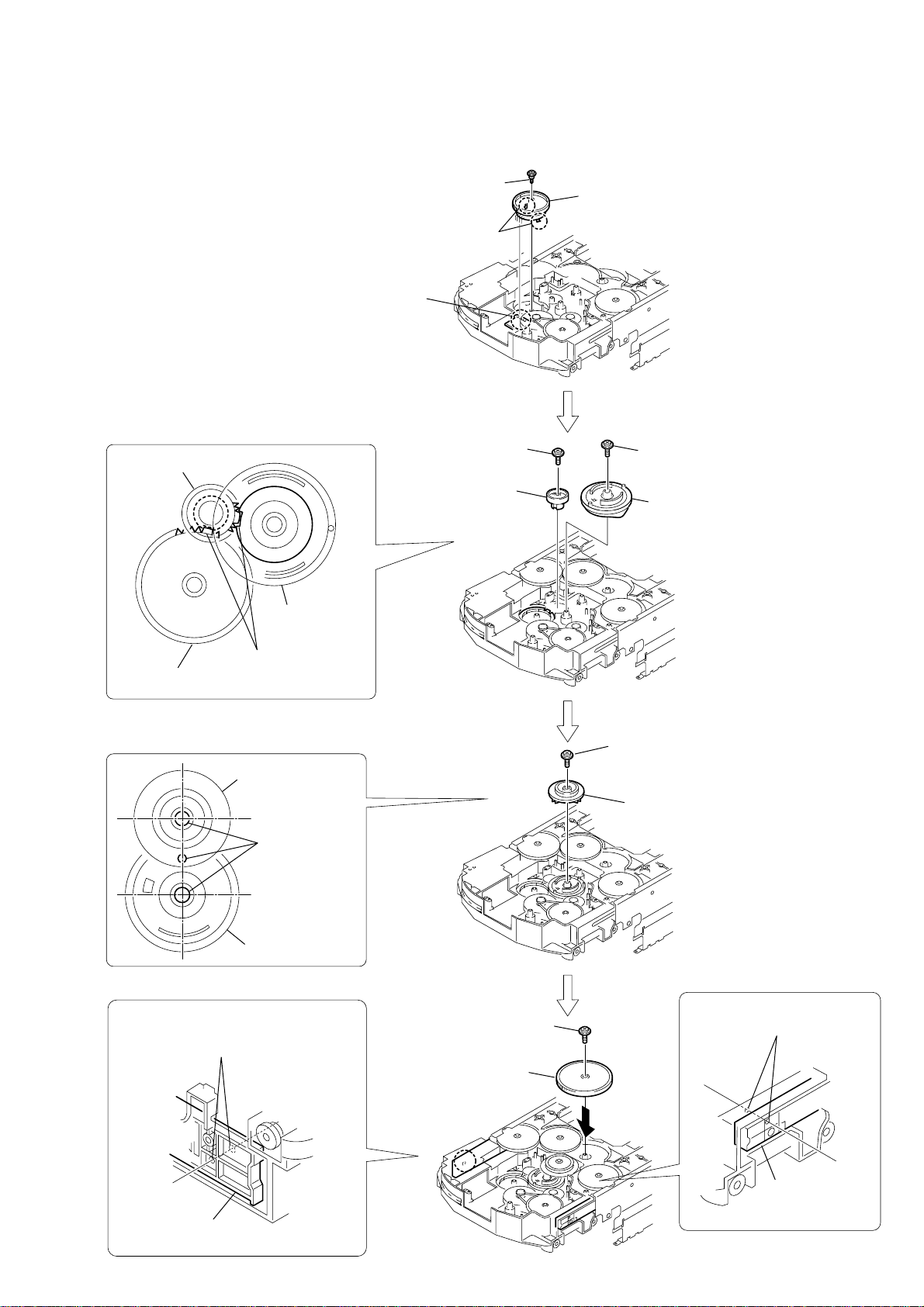
4
screw
(PTPWH2.6
×
8)
1
rotary encoder
2
two claws
3
Apply the soldering
in five points.
9
screw
(PTPWH2.6
×
8)
8
screw
(PTPWH2.6
×
8)
qa
Adjust phases.
7
Adjust phases.
6
gear (geneva 1)
5
gear (encoder)
gear
(geneva 1)
gear (geneva 1)
gear (geneva 2)
rotary encoder
gear (encoder)
qs
screw
(PTPWH2.6
×
8)
0
gear (geneva 2)
qh
screw
(PTPWH2.6
×
8)
qg
gear (pulley UD)
plate (com R)
plate (com L)
qd
Align the plate (com R)
and the chassis hole.
qf
Align the plate (com L)
and the chassis hole.
2-30. ASSEMBLING OF THE ROTARY ENCODER
HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
27
HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
2-31. ELV MOTOR
2
two screws
(BTTP M2.6
4
ELV MOTOR board
5
ELV
×
8)
motor
3
Remove soldering
from the five points
1
belt (MOT-UD)
belt (MOT-UD)
UPPER
SIDE
28
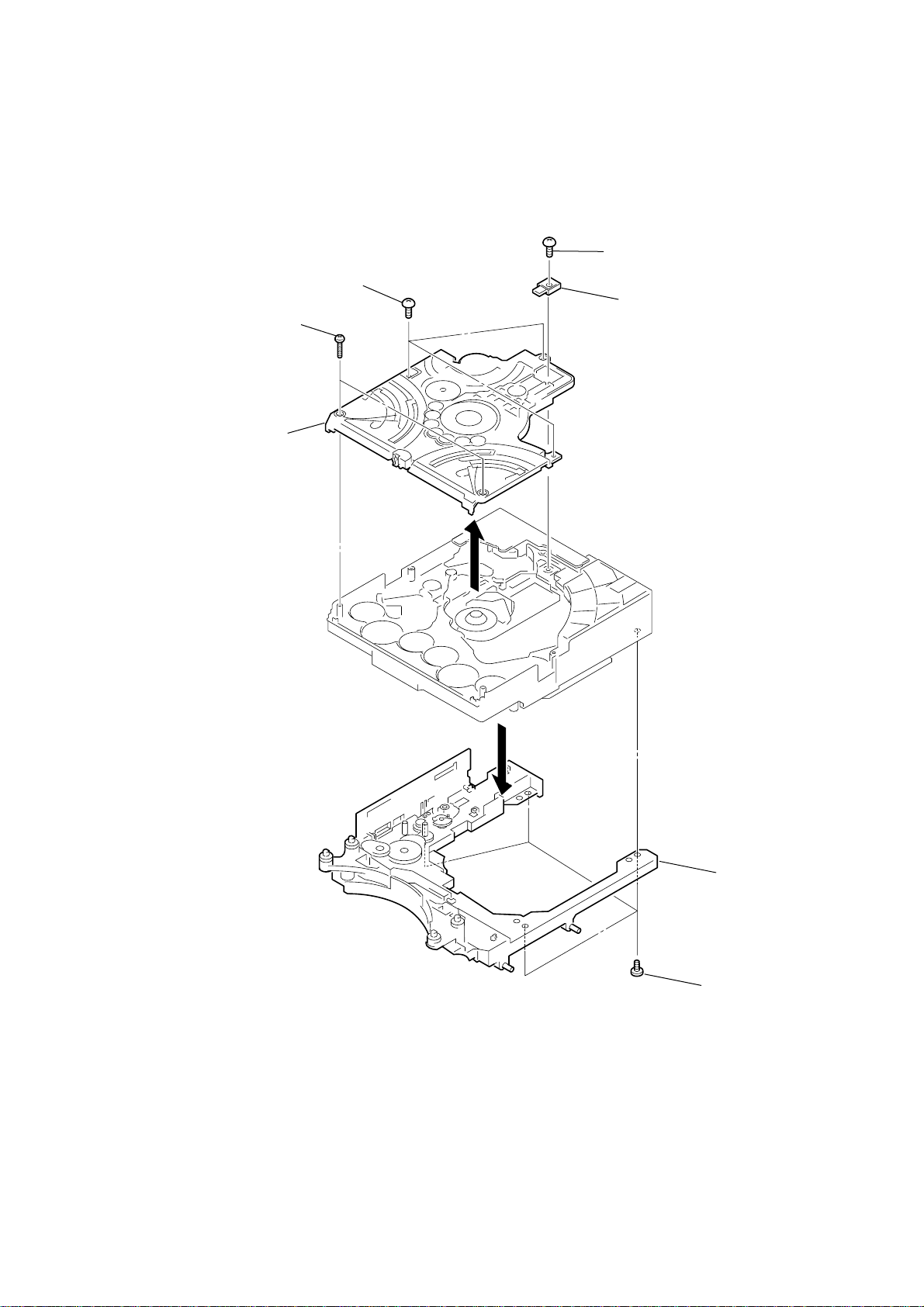
2-32. CHASSIS (TOP), CHASSIS (BOTTOM)
)
4
3
two screws
(P2
5
chassis (top)
three screws
(BVTP2.6
×
10)
×
8)
1
screw
(BVTP2.6
2
lever (CL UP2)
HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
×
8)
7
chassis (bottom
6
four screws
×
(P3
12)
29
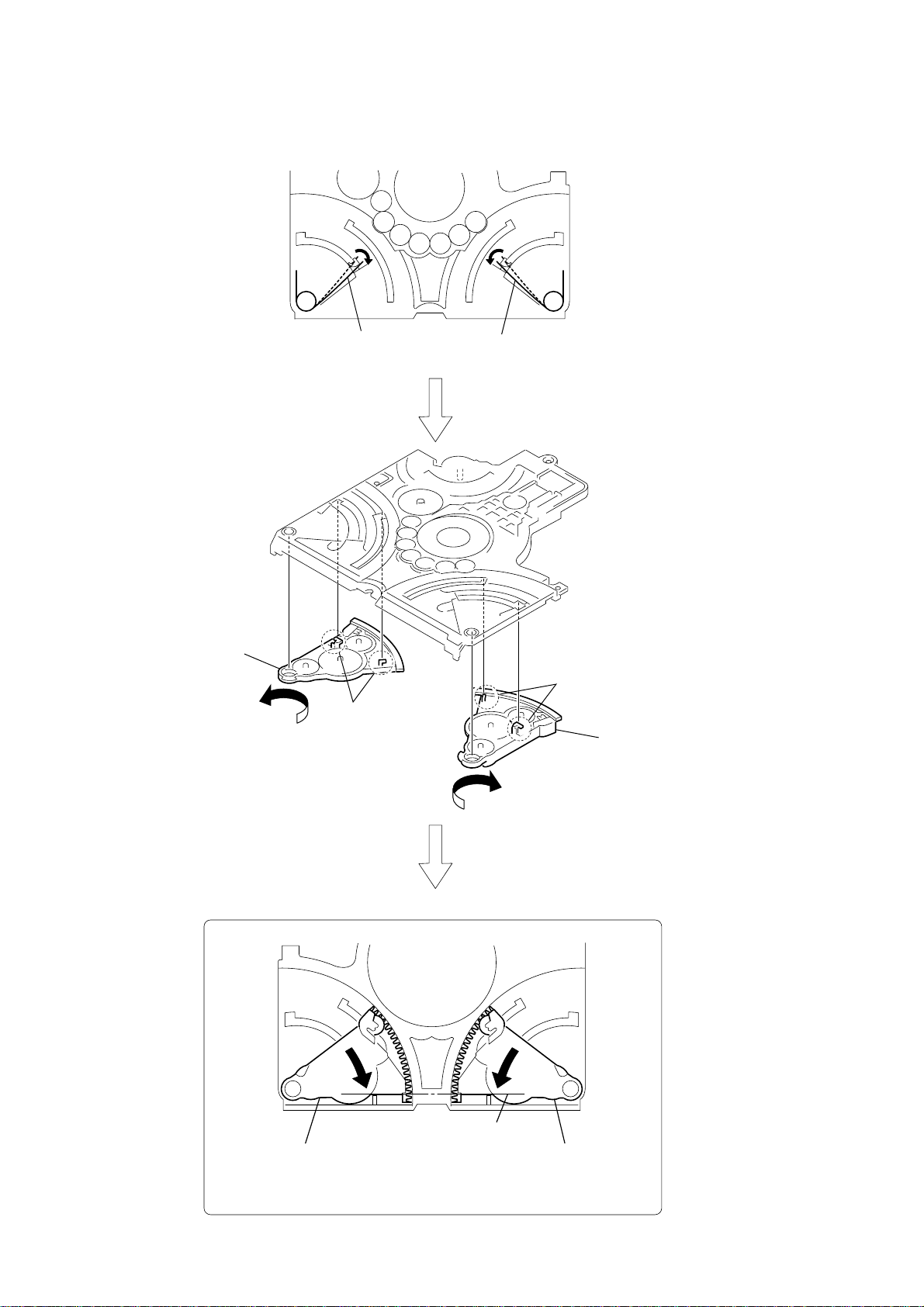
HCD-HPZ7/HPZ9
)
2-33. LEVER (LOADING R, LOADING L)
6
lever (loading R),
gear (IDL-G),
gear (IDL-H)
2
SPR-T (loading L) SPR-T (loading R)
5
two hooks
1
3
two hooks
PRECAUTION DURING LEVER (LOADING R/L) INSTALLATION
Align the horizontal position.
lever (loading L)
Install the
both levers so that they move symmetrically.
lever (loading R)
4
lever (loading L
30
 Loading...
Loading...