Sony CFD-V77S Service Manual

CFD-V77S
SERVICE MANUAL
Ver 1.1 1999. 05
CD
Section
Tape deck Model Name Using Similar Mechanism CFD-V17
Section T ape Tr ansport Mechanism Type MF-V10-117
AEP Model
E Model
Model Name Using Similar Mechanism CFD-V17
CD Mechanism Type KSM-213CDM
Optical Pick-up Name KSS-213C
SPECIFICATIONS
CD player section
System Compact disc digital audio system
Laser diode properties Material: GaAlAs
Wavelength:780 nm
Emission duration : Continuous
Laser output : Less than 44.6 µW
(This output is the value measured at a
distance of about 200 mm from the objective
lens surface on the optical pick-up block
with 7 mm aperture.)
Spindle speed 200 r/min (rpm) to 500 r/min (rpm) (CLV)
Number of channels 2
Frequency response 20 – 20,000 Hz + 1/-2 dB
Wow and flutter Below measurable limit
Radio section
Frequency range FM Italy 87.5 – 108 MHz
Other European 87.6 – 107 MHz
models and Saudi Arabia
Other models 87.6 – 108 MHz
MW Italy 526.5 – 1,606.5 kHz
Other European 531 – 1,602 kHz
models and Saudi Arabia
Other models 530 – 1,605 kHz or
531 – 1,602 kHz
SW1 2.3 – 7 MHz
SW2 7 – 22 MHz
IF FM : 10.7 MHz
AM/MW : 455 kHz
Aerials FM : Telescopic aerial
MW : Built-in ferrite bar aerial
Cassette-corder section
Recording system 4 -track 2 channel stereo
Fast winding time Approx. 120 s (sec.) with Sony cassette C-60
Frequency response TYPE I (normal) : 70 – 10,000 Hz
General
Speakers Full range : 10 cm dia., 6 Ω, cone type (2)
Outputs Headphones jack (stereo minijack)
For 16 – 68 Ω impedance headphones
Maximum power output 4.5 W + 4.5 W
Power requirements For CD radio cassette-corder
Europe
230 V AC, 50 Hz
Other countries
110 – 120, 220 – 240 V AC selectable, 50/60
Hz or 230 V AC, 50 Hz
9 V DC, 6 R20 (size D) batteries
Power consumption AC 25 W
— Continued on next page —
CD RADIO CASSETTE-CORDER
MICROFILM
Battery life For CD radio cassette-corder:
FM recording
Sony R20P : approx. 3.5 h
Sony alkaline LR20 : approx. 10 h
Tape playback
Sony R20P : approx. 1.5 h
Sony alkaline LR20 : approx. 5 h
CD playback
Sony R20P : approx. 1 h
Sony alkaline LR20 : approx. 4 h
Dimensions Approx. 420 × 165 × 256 mm (w/h/d)
(16 5/8 × 6 1/2 × 10 1/8 inches) (incl. projecting
parts)
Mass (incl. batteries) Approx. 4.2 kg (9 lb. 4 oz)
Supplied accessories AC power cord (1)
Design and specifications are subject to change without notice.
SAFETY CHECK-OUT
After correcting the original service problem, perform the
following safety checks before releasing the set to the customer:
Check the antenna terminals, metal trim, “metallized” knobs, screws,
and all other exposed metal parts for A C leakage. Check leakage as
described below.
LEAKAGE
The AC leakage from any exposed metal part to earth ground
and from all exposed metal parts to any exposed metal part having
a return to chassis, must not exceed 0.5 mA (500 microamperes).
Leakage current can be measured by any one of three methods.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. SERVICE NOTES····························································3
2. GENERAL ··········································································4
3. DISASSEMBLY
3-1. Front Cabinet Assy ····························································· 5
3-2. Control Board ····································································· 6
3-3. Cabinet (upper) Assy ·························································· 6
3-4. Power, Battery, Half Battery, Voltage Selection Board ······ 7
3-5. Volume, Lcd, Mono st, Main Board··································· 7
3-6. Mechanism Deck, Optical Pick-up Section························ 8
4. DIAL POINTER INSTALLATION ······························· 9
5. ADJUSTMENT
5-1. Mechanical Adjustment ···················································· 10
5-2. Electrical Adjustment ······················································· 10
5-3. Tuner Section···································································· 11
5-4. Reference·········································································· 15
6. DIAGRAMS
6-1. Circuit Board Location····················································· 17
6-2. Block Diagram ································································· 18
6-3. Printed Wiring Board························································21
6-4. Schematic Diagram – Main Board(1/3) – ························ 25
6-5. Schematic Diagram – Main Board(2/3) – ························ 28
6-6. Schematic Diagram – Main Board(3/3) – ························ 31
6-7. IC Pin Function Description············································· 33
7. EXPLODED VIEWS ·················································38
8. ELECTRICAL PARTS LIST ···································44
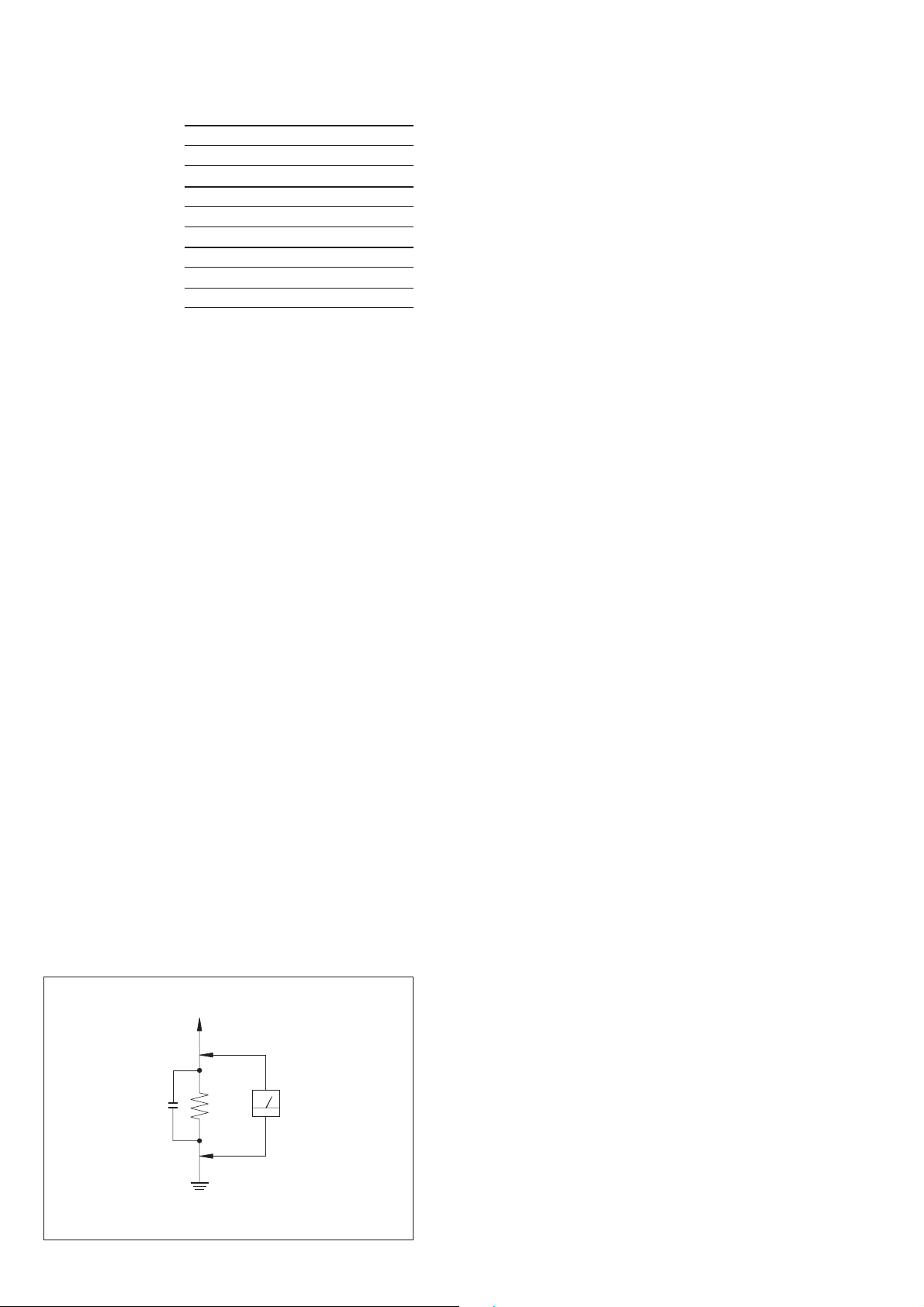
1. A commercial leakage tester, such as the Simpson 229 or RCA
WT -540A. Follo w the manufacturers’ instructions to use these
instruments.
2. A battery-operated AC milliammeter. The Data Precision 245
digital multimeter is suitable for this job.
3. Measuring the voltage drop across a resistor by means of a
VOM or battery-operated AC v oltmeter . The “limit” indication
is 0.75 V, so analog meters must have an accurate low-v oltage
scale. The Simpson 250 and Sanwa SH-63Trd are e xamples of
a passive VOM that is suitable. Nearly all battery operated
digital multimeters that have a 2V AC range are suitable. (See
Fig. A)
T o Exposed Metal
Parts on Set
AC
0.15
µ
F
Fig. A. Using an A C v oltmeter to check A C leakage.
Ω
1.5 k
Earth Ground
Voltmeter
(0.75 V)
Notes on chip component replacement
• Never reuse a disconnected chip component.
• Notice that the minus side of a tantalum capacitor may be
damaged by heat.
Flexible Circuit Board Repairing
• Keep the temperature of soldering iron around 270˚C
during repairing.
• Do not touch the soldering iron on the same conductor of the
circuit board (within 3 times).
• Be careful not to apply force on the conductor when soldering
or unsoldering.
SAFETY-RELATED COMPONENT WARNING!!
COMPONENTS IDENTIFIED BY MARK ! OR DO TTED LINE WITH
MARK ! ON THE SCHEMATIC DIAGRAMS AND IN THE PARTS
LIST ARE CRITICAL TO SAFE OPERATION. REPLACE THESE
COMPONENTS WITH SONY PARTS WHOSE PART NUMBERS
APPEAR AS SHOWN IN THIS MANUAL OR IN SUPPLEMENTS
PUBLISHED BY SONY.
— 2 —
SECTION 1
Insert a precision screw driver
and push SWITCH(S801)
SERVICE NOTES
Laser component in this product is capable
of emitting radiation exceeding the limit for
Class 1.
This appliance is classified as a CLASS 1 LASER product. The
CLASS 1 LASER PRODUCT MARKING is located on the rear
exterior.
The following caution label is located inside the unit.
NOTES ON HANDLING THE OPTICAL PICK-UP
BLOCK OR BASE UNIT
The laser diode in the optical pick-up block may suffer electrostatic
breakdown because of the potential difference generated by the
charged electrostatic load, etc., on clothing and the human body.
During repair, pay attention to electrostatic breakdown and also use
the procedure in the printed matter which is included in the repair
parts.
The flexible board is easily damaged and should be handled with
care.
NOTES ON LASER DIODE EMISSION CHECK
The laser beam on this model is concentrated so as to be focused on
the disc reflective surface by the objective lens in the optical pickup block. Therefore, when checking the laser diode emission,
observe from more than 30 cm away from the objective lens.
CHUCK PLATE JIG ON REPAIRING
On repairing CD section, playing a disc without the CD lid, use
Chuck Plate Jig.
• Code number of Chuck Plate Jig : X-4918-255-1
CAUTION
Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures
other than those specified herein may result in hazardous radiation
exposure.
LASER DIODE AND FOCUS SEARCH OPERATION
CHECK
1. Press CD open knob.
2. Open the lid for CD.
3. Push on SWITCH (S801) as following figure.
4. Confirm the laser diode emission while observing the objecting
lens. When there is no emission, Auto Po wer Control circuit or
Optical Pick-up is broken.
Objective lens moves up and down once for the focus search.
— 3 —
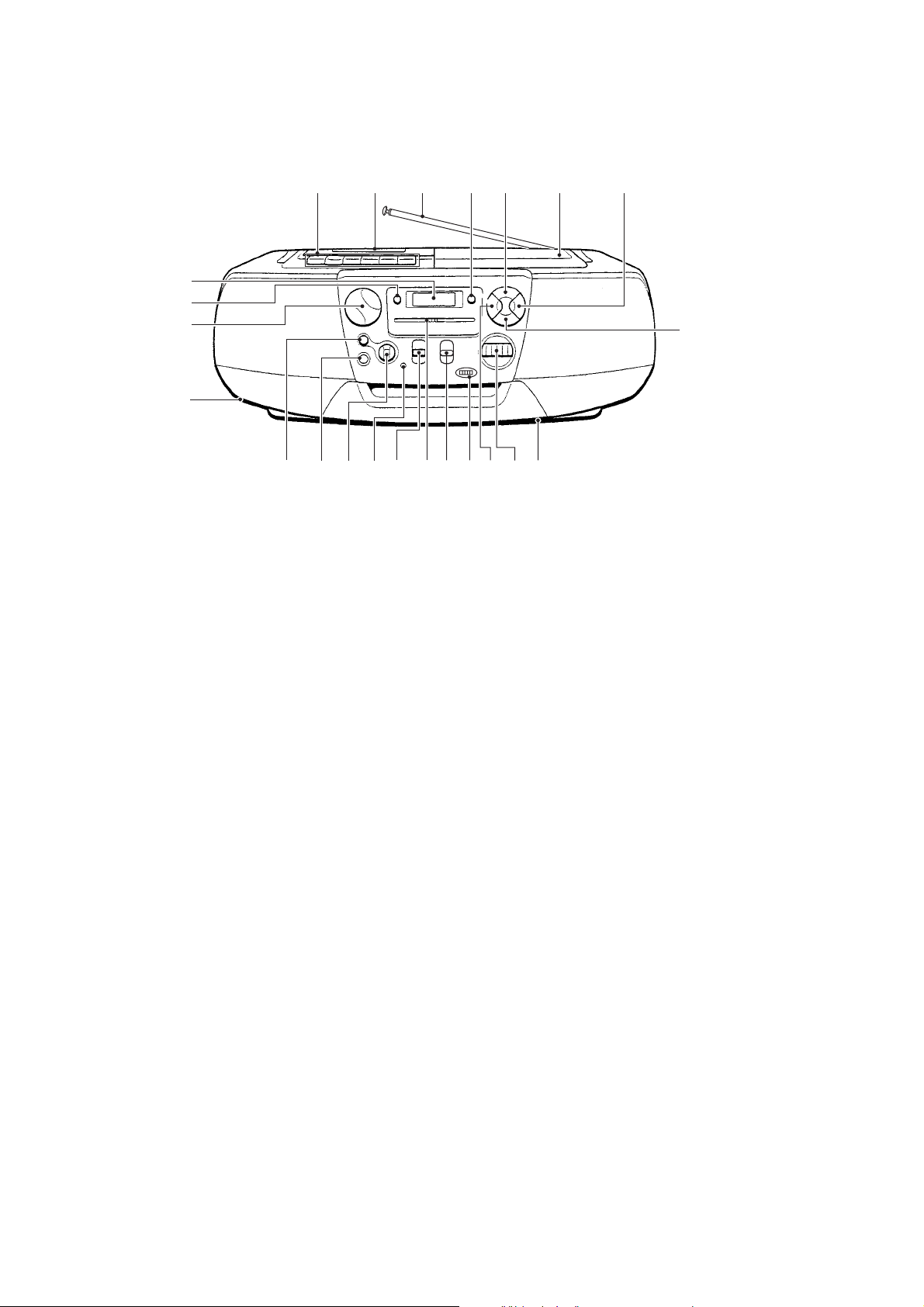
LOCATION AND FUNCTION OF CONTROLS
MAIN UNIT
SECTION 2
GENERAL
1
23
@™
@¡
@º
!ª
1 Tape operation buttons
r button
· button
0 button
) button
p, 6 button
P button
2 CASSETE LID
3 FM rod antenna
4 DISPLAY ENTER button
5 CD ^ button
6 CD 6 PUSH OPEN/CLOSE button
7 CD + button
8 CD p button
4
56
0
@£
!™!¢ !£!∞!§!¶!•
!¡
9 Battery compartment
!º TUNE knob
!¡ CD = button
!™ DIAL
!£ BAND switch
!¢ FUNCTION switch
!∞ OPR/BATT indicator
!§ TONE knob
!¶ 2 Phones jack
!• MEGA BASS knob
!ª AC IN jack
@º VOLUME knob
@¡ PLAY MODE button
@™ Information display
@£ FINE TUNING knob
9
7
8
— 4 —
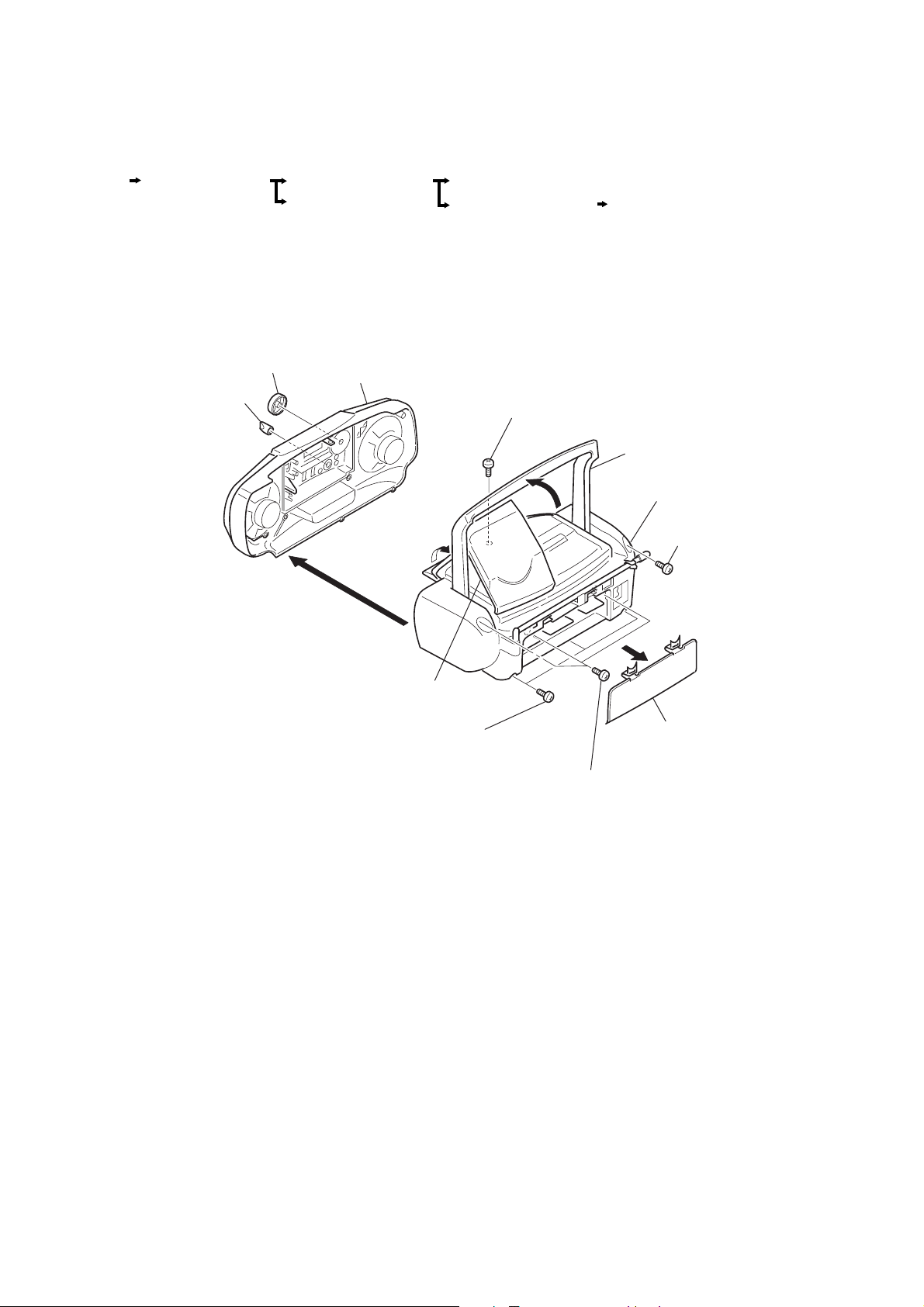
SECTION 3
DISASSEMBLY
• The equipment can be removed using the following procedure.
Set
Front cabinet assy
Cabinet (upper) assy
Control board
Power, battery, half battery, voltage selection board
Volume, lcd,
mono st, main board
Note : Follow the disassembly procedure in the numerical order given.
3-1. FRONT CABINET ASSY
8
9
Tone knob
Vol knob
0
Front cabinet assy
7
+BVTP 3
Screw
Mechanism deck, optical pick-up section
×
12
5
Remove the Handle
in the direction of the arrow.
Rear cabinet assy
3
Screw
+BVTP 3
×
10
6
Open the CD lid in
the direction of the arrow.
4
Three screws
+BVTP 3
×
12
2
Three screws
+BVTP 3
×
1
10
Lid battery case
— 5 —
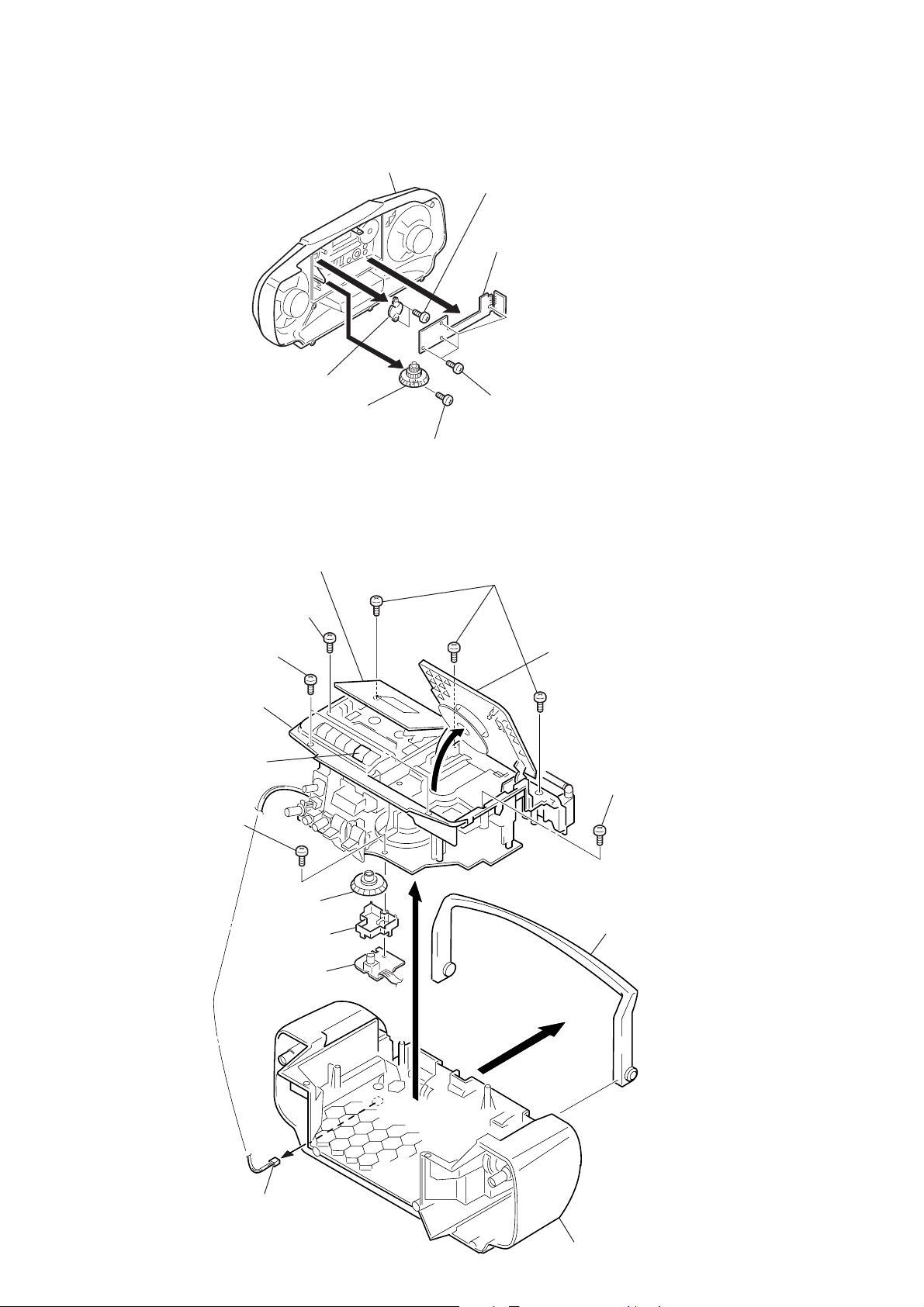
3-2. CONTROL BOARD
d
3-3. CABINET (UPPER) ASSY
2
Open the cassette holder assy by
pressing STOP/EJECT button.
Screw
6
+BVTP 3
6
CD button
4
Knob (TU)
×
12
Front cabinet assy
3
Screw
+BVTP 2.6 × 8
5
T wo screws
+BVTP 2.6 × 8
2
CONTROL boar
1
Four screws
+BVTP 2.6 × 8
1
Three screws
+BVTP 3
×
12
5
T wo screws
+BVTP 3
9
Cabinet (upper) assy
STOP/EJECT
button
!¡
Screw
+BVTP 2.6
×
8
×
10
Knob(FT)
Chassis(FT)
FINE TUNING
board
3
Open the CD lid in
the direction of the arrow.
4
Screw
+BVTP 3
8
0
Open the Handle in
the direction of the arrow.
×
12
7
Connector
Rear cabinet
— 6 —
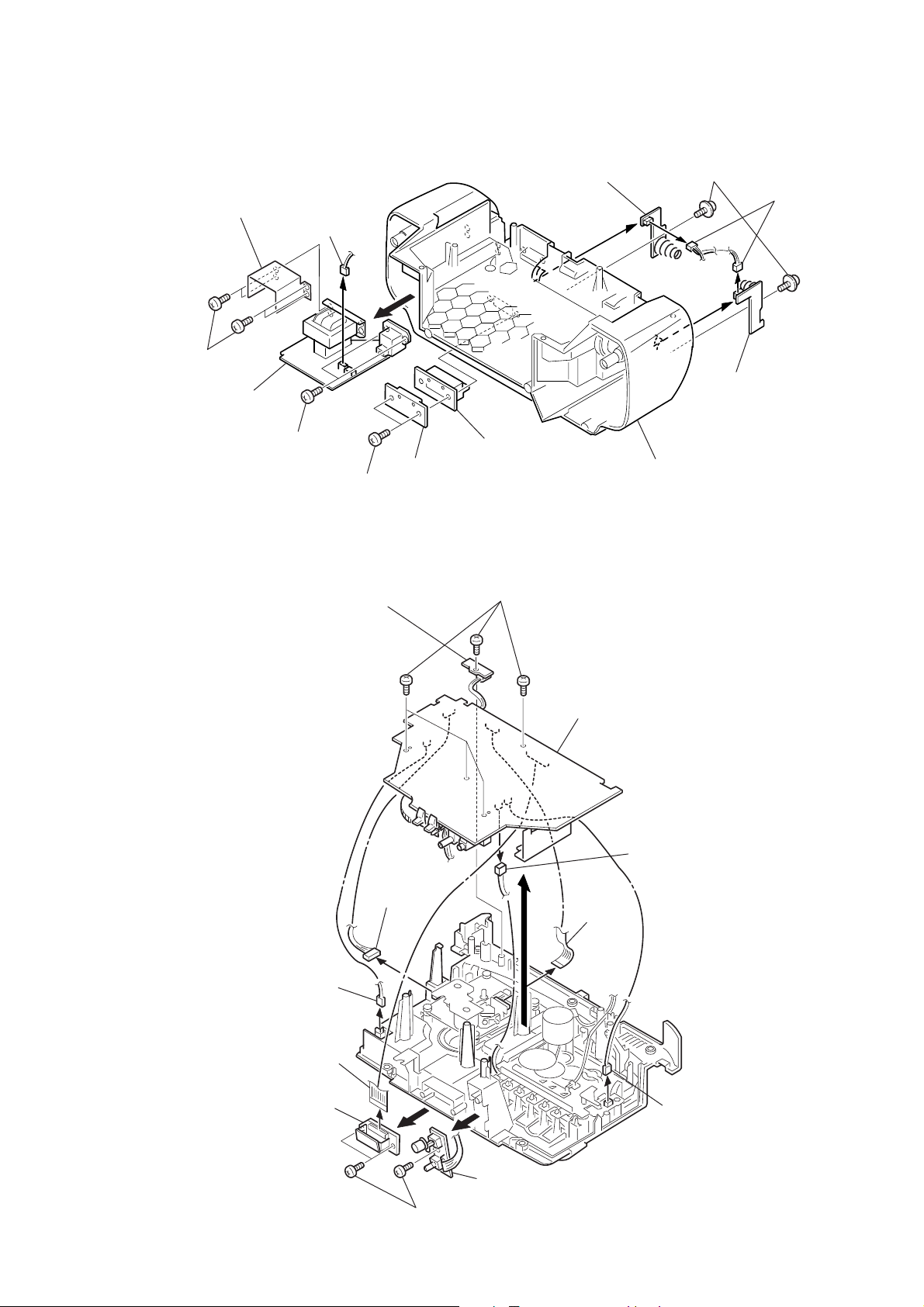
3-4. POWER, BATTERY, HALF BATTERY, VOLTAGE SELECTION BOARD
r
8
BATTERY board
2
Plate(Transformer 4.5W), shield
4
Connector
1
Four screws
+BVTP 3 × 10
5
POWER board
3
T wo screws
+BVTP 3 × 10
!¡
Cover(VOL SEL)
0
T wo screws
+BVTP 3 × 10
!™
VOLTA GE SELECTION
board
Rear cabinet assy
3-5. VOLUME, LCD, MONO ST, MAIN BOARD
6
T wo screws
+BVTP 3 × 8
9
HALF BATTERY
board
7
T wo connectors
!¡
Connector
!™
MONO ST board
0
Connector
5
Five screws
+BVTP 3 × 10
6
!£
MAIN board
8
Flexible
9
Connector
3
Flexible
4
LCD board
2
1
Three Screws
+BVTP 3 × 10
— 7 —
VOLUME board
7
Connecto
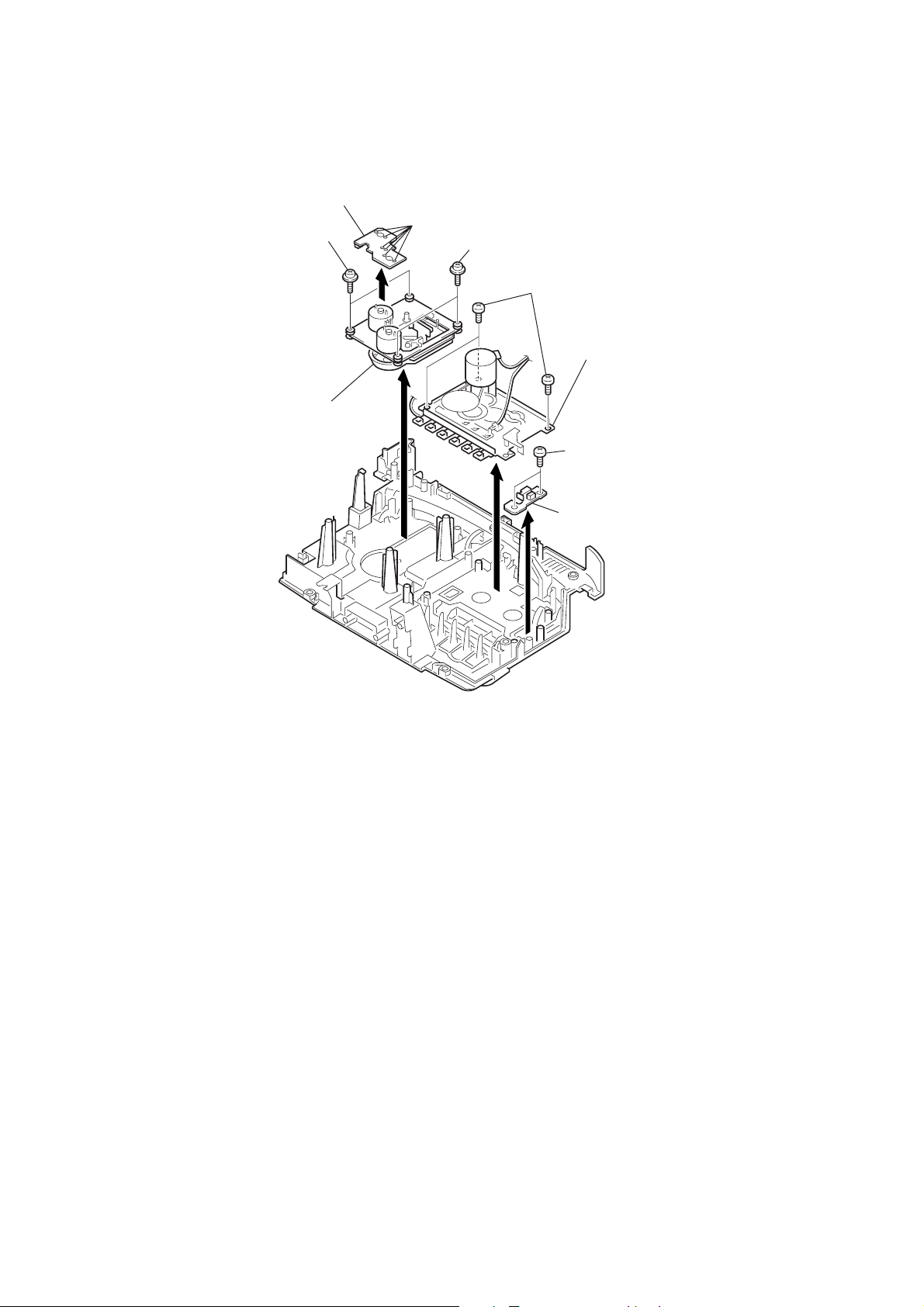
3-6. MECHANISM DECK, OPTICAL PICK-UP SECTION
0
8
CD MOTOR board
7
6
Two screws
9
Optical pick-up section
Remove solder
5
Two screws
3
+BVTP 3
Three screws
×
10
4
Mechanism deck
1
+BVTP 3
2
RECORD
switch board
Two screws
×
1
— 8 —
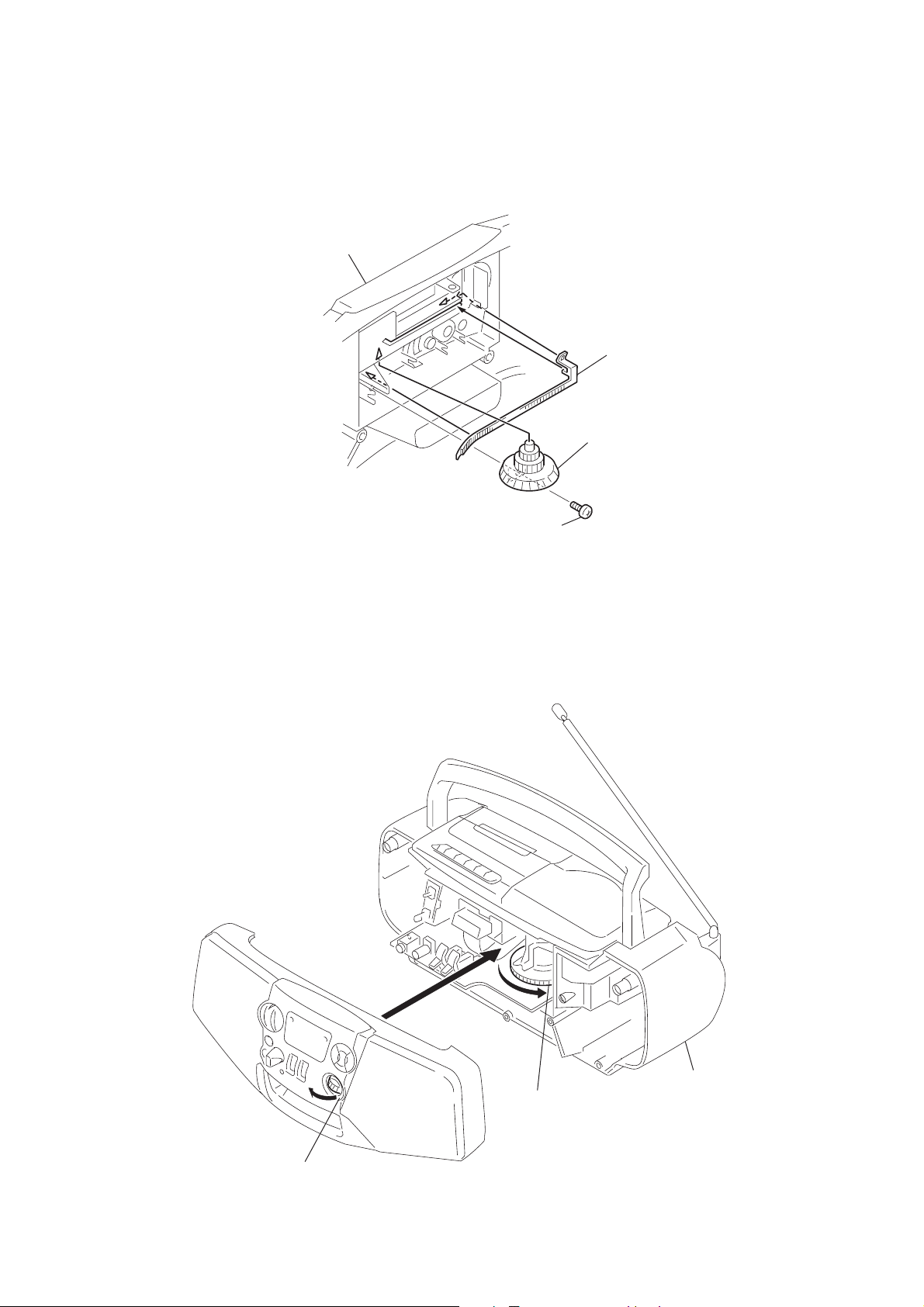
SECTION 4
r
DIAL POINTER INSTALLATION
Note : Follow the installation procedure in the numerical order given.
1 Align the pointer with the groove of front cabinet assy and insert it as shown in the illustration.
2 Align Knob (TU) with front cabinet and fasten the screw.
Front Cabinet assy
1
Pointe
Knob (TU)
2
Screw
+BVTP 2.6
×
8
3 Turn the Knob (TU) in the direction of the arrow as shown in the illustration until pointer agrees with scale “ 0 ” (at leftmost end of
scale).
4 Turn the tuning capacitor gear fully in the direction of the arrow as shown in the illustration.
5 Fasten the front cabinet assy and rear cabinet assy with the screws.
3
Knob (TU)
5
Rear cabinet assy
4
Tuning capacitor gear
— 9 —
SECTION 5
ADJUSTMENTS
5-1. MECHANICAL ADJUSTMENT
PRECAUTION
1. Clean the following parts with a denatured-alchool-moistened
swab:
record/playback head pinch roller
erase head rubber belts
capstans
2. Demagnetize the record/playback head with a head
demagnetizer. (Do not bring the head demagnetizer close to
the erase head.)
3. Do not use a magnetized screwdriver for the adjustments.
4. After the adjustments, apply suitable locking compound to the
parts adjusted.
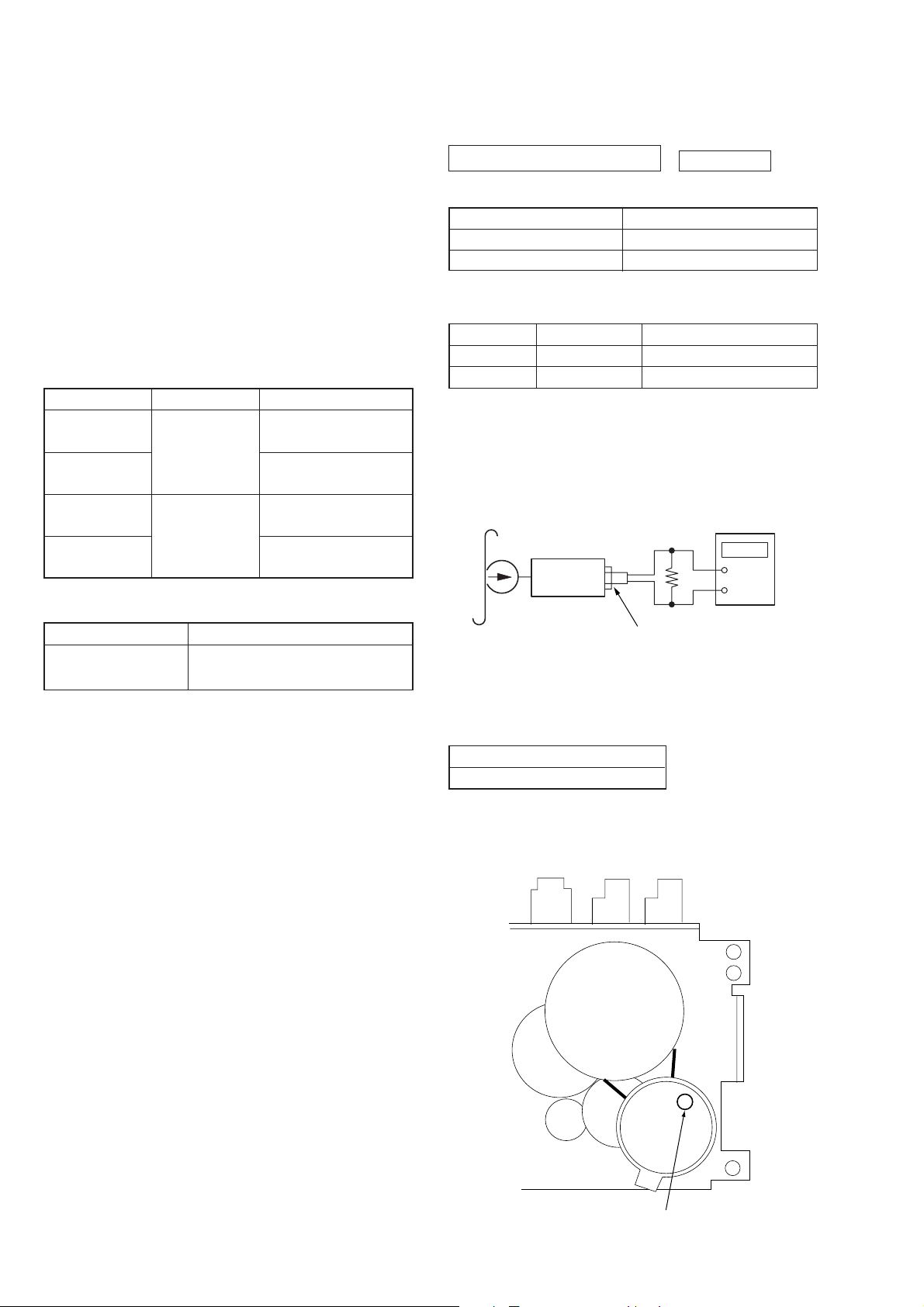
Torque Measurement
Mode
FWD
FWD
back tension
Fast Forward
Rewind
T ape Tension Measurement
Torque Meter
CQ-102C
CQ-201B
Meter Reading
18 – 60 g•cm
(0.25 – 0.83 oz•inch)
1.0 – 5.0 g•cm
(0.014 – 0.069 oz•inch)
45 – 95 g•cm
(0.62 – 1.32 oz•inch)
45 – 95 g•cm
(0.62 – 1.32 oz•inch)
5-2. ELECTRICAL ADJUSTMENT
TAPE RECODER SECTION
Standard output level
Output
Load impedance
Output signal level
Test tape
T est Tape
WS-48A
P-4-A063
Tape Speed Adjustment
Procedure :
Mode : Playback
test tape
WS-48A
(3kHz, 0dB)
Signal
3 kHz, 0 dB
6.3 kHz, –10 dB
set
0dB = 0.775V
0.25 V (–10 dB)
Tape speed adjustment
Head azimuth adjustment.
32
Ω
HP OUT
32 Ω
Used for
digital frequency
counter
+
–
Torque Meter
CQ-403A
Meter Reading
more than 60 g
(more than 2.12 oz)
J301 (phones)
Adjustment V alue : normal tape speed
Adjust the tape speed adjustment control inside motor, so that the
frequency counter reading becomes 3,000 Hz.
Specification Value :
Digital frequency counter
2,910 – 3,090Hz
Frequency difference between the beginning and the end of the
tape should be within 1.5% (45 Hz).
Adjustment Location :
— 10 —
Tape speed adjustment
control inside motor
5-3. TUNER SECTION
r
a
r
• Switch Location
VOLUME : MAX
MEGA BASS : OFF
PRESET SOUND MODE : OFF
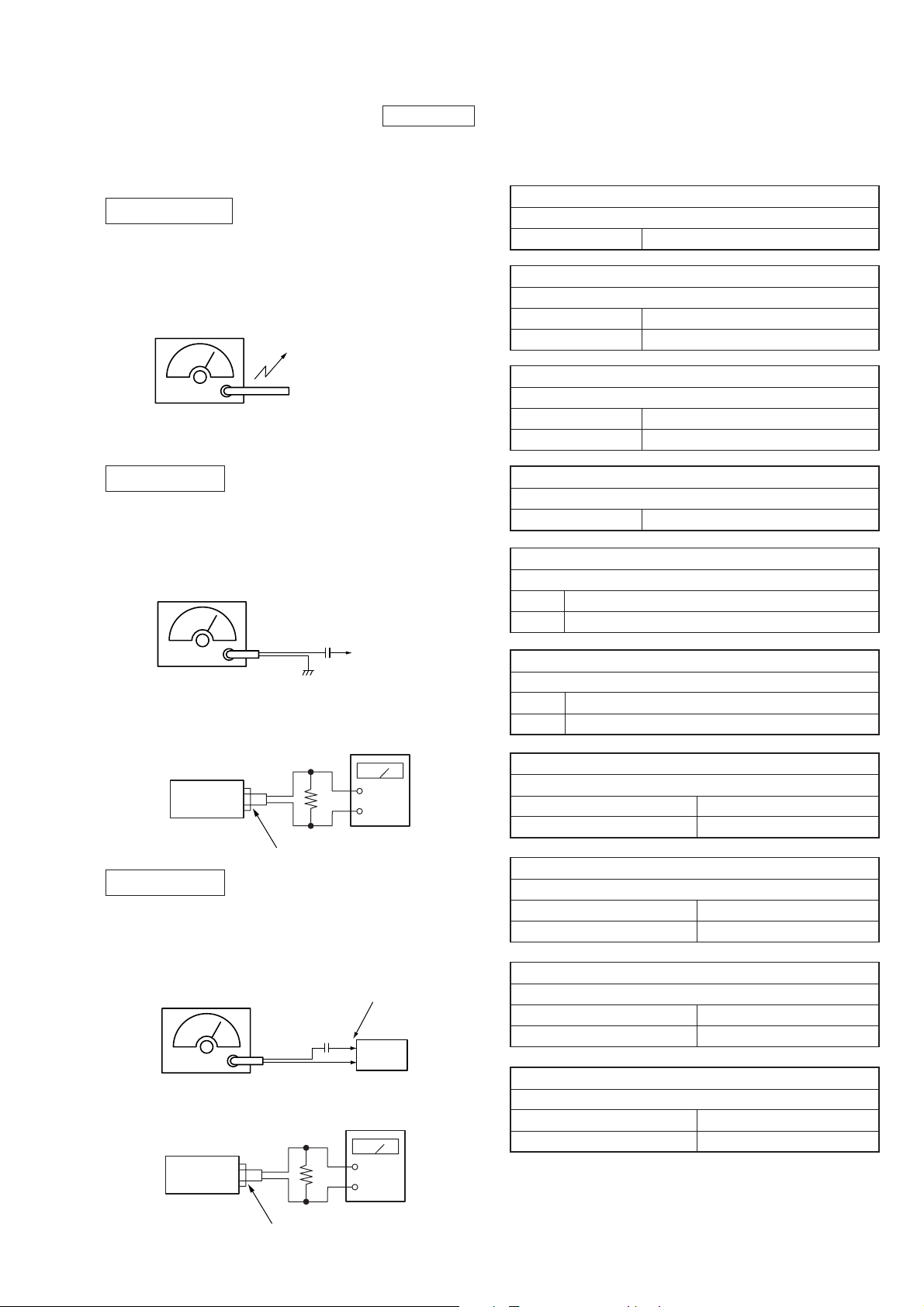
MW SECTION
Setting :
FUNCTION switch : RADIO
BAND : MW
Signal generator
MW RF signal
generator
30% amplitude modulation by 400Hz
signal.
Output level : as low as possible
Put the lead-wire
antenna close to
the set.
0 dB = 1 µV
• Repeat the procedures in each adjustment several times for the
maximum level meter indication.
• The frequency coverage and tracking adjustments should be
finally done by the trimmer capacitors.
MW IF ADJUSTMENT
Adjust for a maximum reading on level meter.
T2 455 kHz
MW TRACKING ADJUSTMENT
Adjust for a maximum reading on level meter.
L3 620 kHz
CT3 1,400 kHz
MW FREQUENCY COVERAGE ADJUSTMENT
Adjust for a maximum reading on level meter.
L4 520 kHz (516 kHz)<516 kHz>
CT4 1,680 kHz (1,630 kHz)<1,630 kHz>
FM SECTION
Setting :
FUNCTION switch : RADIO
BAND : FM
Signal generator
FM RF signal
generator
0.01µF
75kHz (100%) amplitude modulation
by 1kHz signal.
Output level : as low as possible
32
set
J301 (phones)
SW SECTION
Setting :
FUNCTION switch : RADIO
BAND : SW1/SW2
FINE TUNING knob : mechanical mid
AM rf signal
generator
30% amplitude modulation by 400 Hz
signal output level : as low as possible
32
set
J301 (phones)
telescopic
antenna
input
level mete
Ω
+
–
telescopic antenn
input
10 pF
set
level mete
Ω
+
–
FM IF ADJUSTMENT
Adjust for a maximum reading on level meter.
T1 10.7 MHz
FM TRACKING ADJUSTMENT
Adjust for a maximum reading on level meter.
L1 86.5 MHz(87.35 MHz )[87.0 MHz]<87.35 MHz>
CT1 109.5 MHz(108.25 MHz )[108.3 MHz]<108.25 MHz>
FM FREQUENCY COVERAGE ADJUSTMENT
Adjust for a maximum reading on level meter.
L2 86.5 MHz (87.35 MHz )[87.0 MHz]<87.35MHz>
CT2 109.5 MHz (107.8 MHz)[108.3 MHz]<108.25 MHz>
SW1 FREQUENCY COVERAGE ADJUSTMENT
Adjust for a maximum reading on level meter.
L6 CT6
2.2 MHz 7.3 MHz
SW1 TRACKING ADJUSTMENT
Adjust for a maximum reading on level meter.
L5 CT5
2.2 MHz 7.3 MHz
SW2 FREQUENCY COVERAGE ADJUSTMENT
Adjust for a maximum reading on level meter.
L8 CT10
6.8 MHz 22.5 MHz
SW2 TRACKING ADJUSTMENT
Adjust for a maximum reading on level meter.
L7 CT9
6.8 MHz 22.5 MHz
( ) : Saudi Arabia model
[ ] : AEP model
< > : Italian model
Adjustment Location : Main board (See page 13)
— 11 —
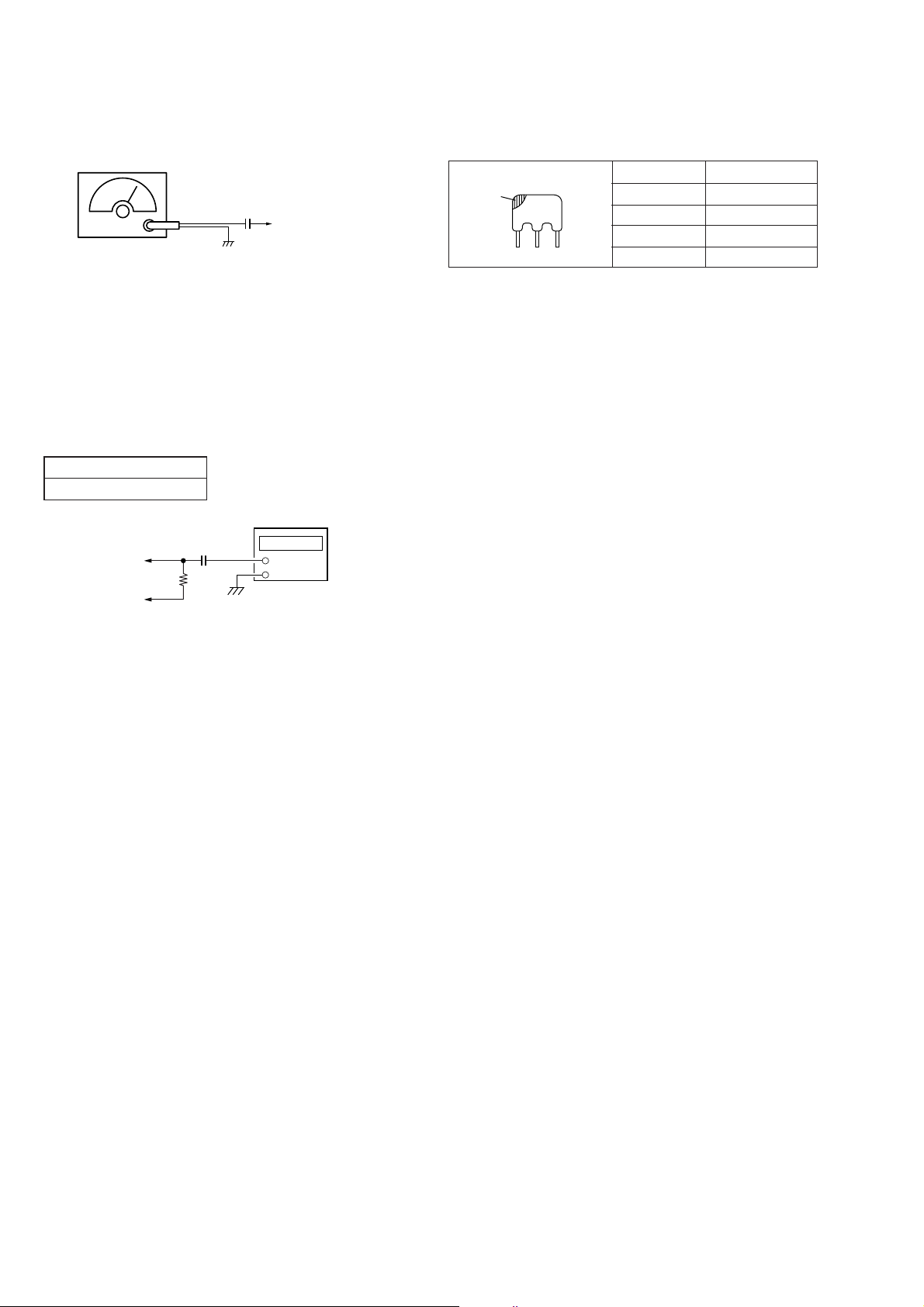
FM VCO Adjustment
color
mark
CF1
r
Procedure :
FM RF SSG
0.01µF
to FM ANT IN terminal
Carrier frequency : 98MHz
IF frequency : According to
the color of CF1.
Modulation : no modulation
Output level : 0.1V (100dB)
1. Connect frequency counter to the positions shown below.
2. Tune the set to 98MHz.
3. Adjust RV1 so that the frequency counter reading becomes
76,000 Hz.
Specification Value :
Frequency counter
75,950 – 76,050 Hz
Frequency counte
IC1 Pin
IC1 Pin
4
7
0.01µF
33k
Ω
+
–
BLACK 10.64MHz
BLUE 10.67MHz
RED 10.70MHz
ORANGE 10.73MHz
WHITE 10.76MHz
Adjustment Location : MAIN board (See page 13)
— 12 —
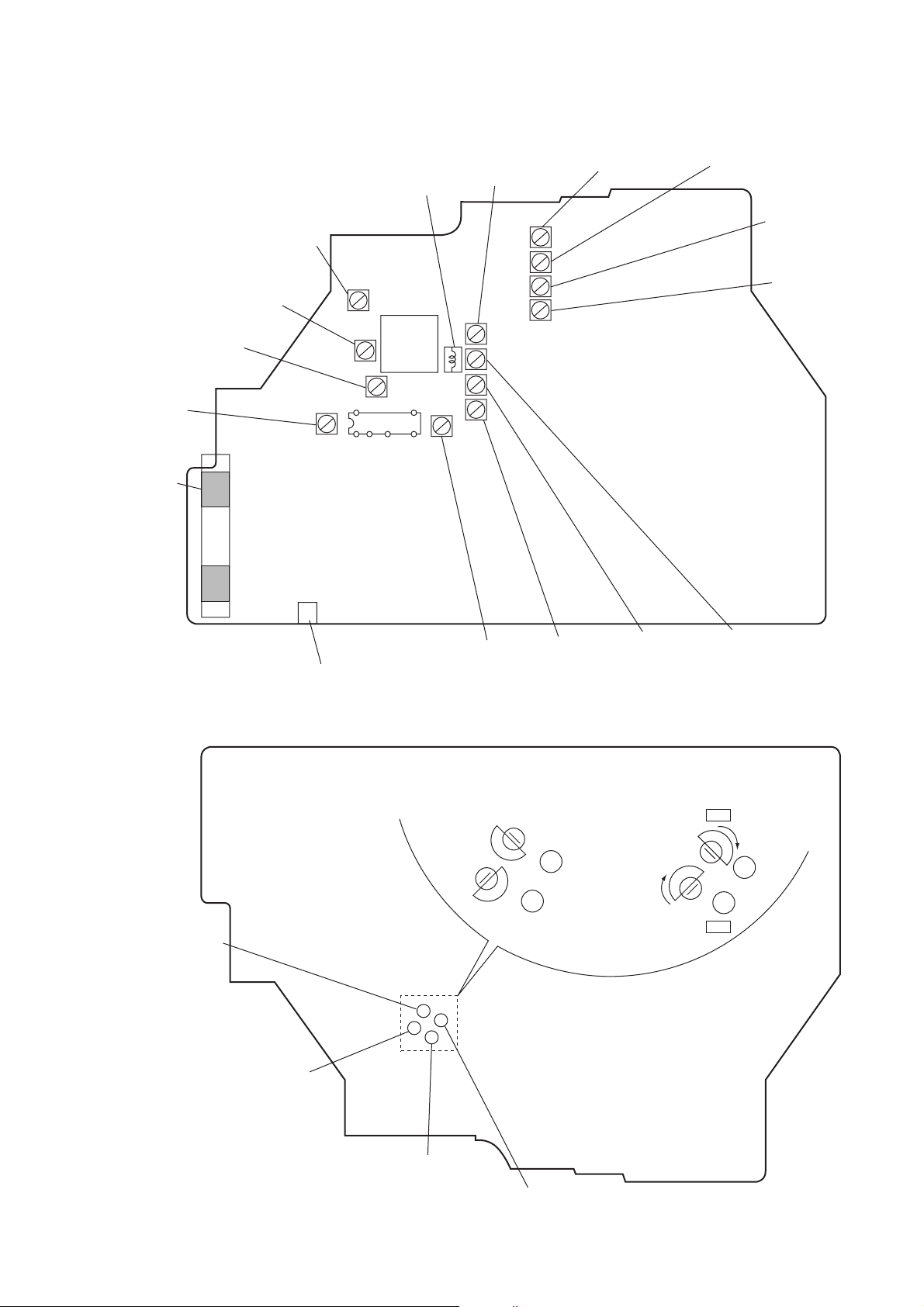
Adjustment Location : MAIN board (Component side)
L1
FM T rac king
L4
MW Frequency
Coverage
Adjustment
RV1
FM VCO
Adjustment
L2
FM Frequency
Coverage
Adjustment
Adjustment
CV1
L5
SW1 T rac king
Adjustment
CT6
SW1 Frequency
Coverage
Adjustment
L6
SW1 Frequency
Coverage
Adjustment
CT10
SW2 Frequency
Coverage
Adjustment
L8
SW2 Frequency
Coverage
Adjustment
T1
FM IF
30
Adjustment
74
1
IC1
L3
MW T rac king
Adjustment
FM ANT IN terminal
Adjustment Location : MAIN board (Conductor side)
16
15
T2
MW IF
Adjustment
CT9
SW2 T rac king
Adjustment
L7
SW2 T rac king
Adjustment
Set the CT2 (FM OSC) and CT4 (MW OSC)
trimmers to their extreme outside.
FM OSC
MW OSC
CT5
SW1 T rac king
Adjustment
FM OSC
CT2
FM Frequency
Coverage
Adjustment
CT4
MW Frequency
Coverage
Adjustment
CT3
MW T rac king
Adjustment
— 13 —
Inside NG
CT1
FM T rac king
Adjustment
MW OSC
Outside OK
CD SECTION
V
s
Notes on Check
1. Perform the traverse check in the CD test mode.
After check, be sure to exit the test mode.
2. Perform check in the order given.
3. Use the disc (YEDS-18, Parts No. 3-702-101-01) only when
so indicated.
Before Check
Put the set into test mode and perform the following checks.
Repair if there are any problems.
• Sled Motor Check
Press + , = keys and confirm that the Optical pick-up moves
smoothly from the innermost to outermost circumference and back
smoothly and with no catching or abnormal noises.
(Cancellation of BTL mute)
+ : Optical pick-up moves to the outer circumference.
= : Optical pick-up moves to the inner circumference.
• Focus Search Check
1. Press the CD ^ key. (Focus search operation is performed
continuously.)
2. Look at the Optical pick-up objective lens and confirm that it
moves up and down smoothly, with no catching or abnormal
noises.
3. Press p button.
Confirm that focus search operation stops. If it does not, press
p button again longer.
How to Enter the Set into Test Mode
1. Set the function switch to power off.
2. Set the function switch to CD while = key and p key
pressing.
The set is into CD test mode (88 is displayed).
3. Turn the power off to release test mode.
How to Exit the Test Mode
Turn the POWER OFF.
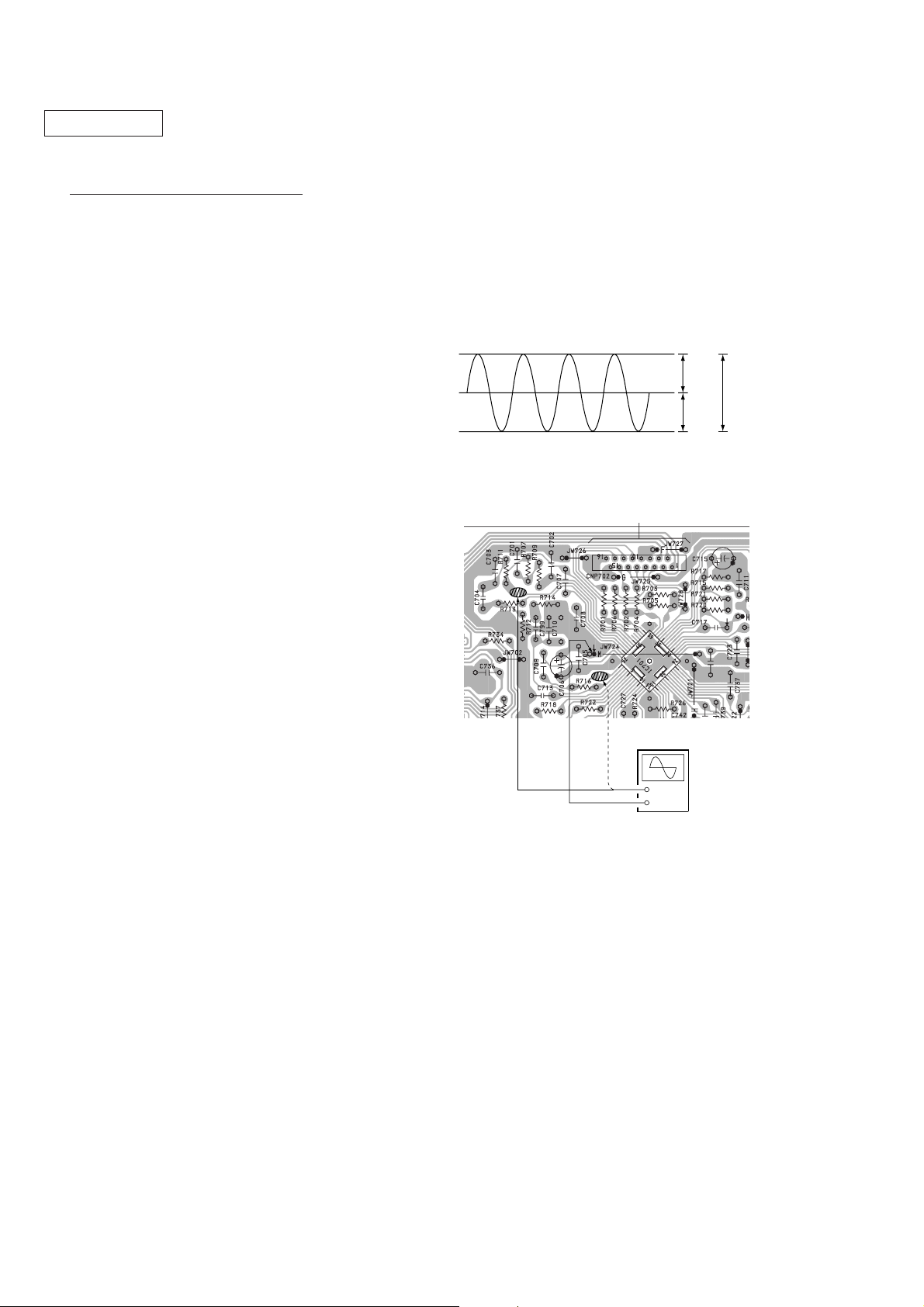
TRAVERSE Check
This check is to be done when the optical pick-up block is replaced.
Check Procedure:
1. Connect the oscilloscope to test point TP (VC) and TP (TE) on
MAIN board.
2. Put the set into test mode.
3. Optical pick-up setting to the center by + or = button
pushing.
4. Insert disk (YEDS-18) and press ^ button.
5. Check that the oscilloscope traverse waveform is symmetrical,
as shown in the figure below.
6. Release test mode after adjustment is completed.
A
VOLT/DIV : 0.1
0V
TIME/DIV : 1m
B
A = B C = 300mV – 700mV
C
[MAIN BOARD] (Conductor side)
TP(TE)
TP(RF)
TP(VC)
TP(FE)
Oscilloscope
(DC range)
TP (TE)
TP (FE)
TP (VC)
+
–
— 14 —
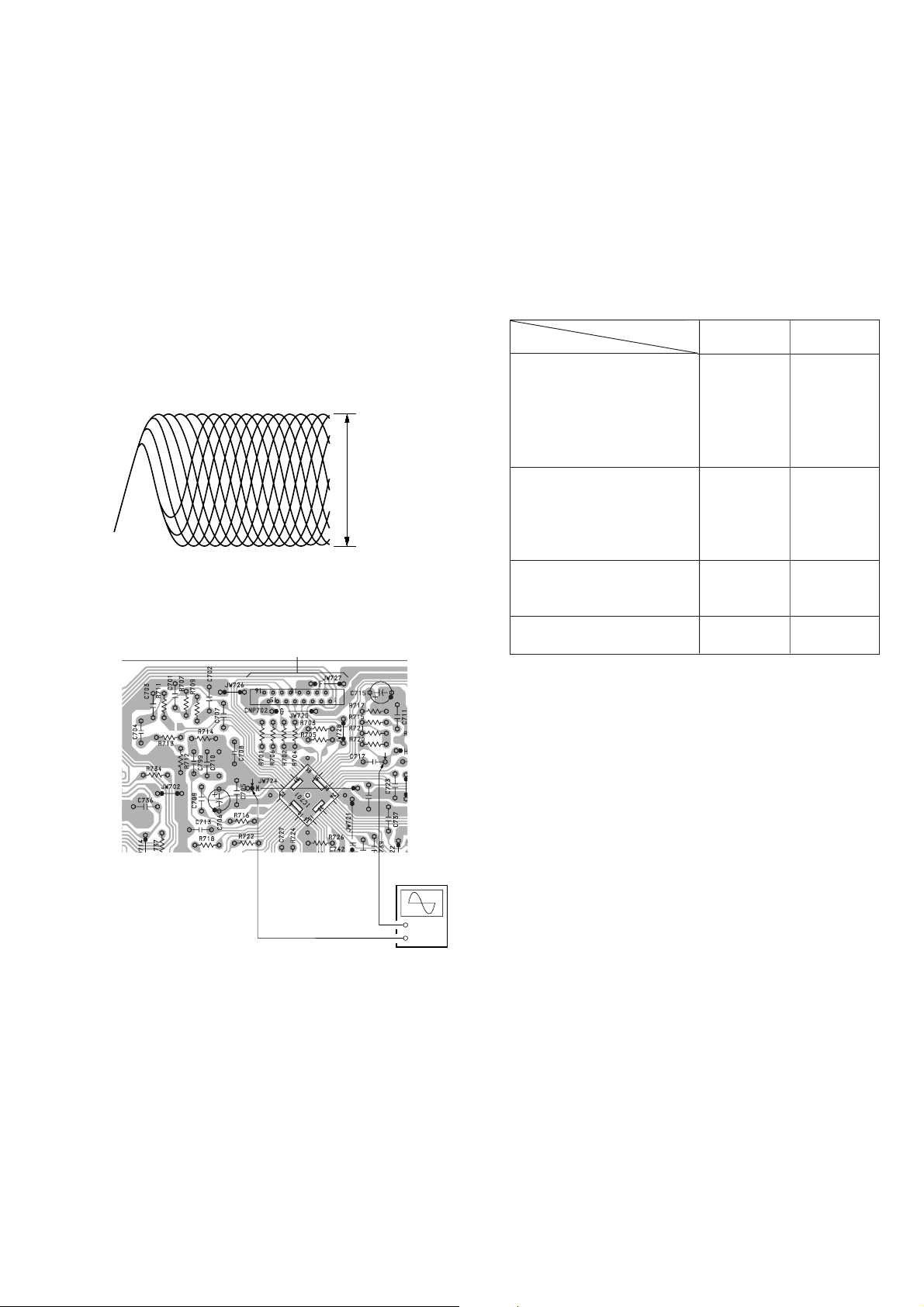
Focus Bias Check
s
This check is to be done when the optical block replaced.
Check Procedure:
1. Connect the oscilloscope to test point TP (VC) and TP (RF) on
MAIN board.
2. Put the set into test mode.
3. Opitical pick-up setting to the center by + or – button pushing.
4. Insert disk (YEDS-18) and press ^ button.
5. Press the MODE button. (Tracking servo ON)
6. Check that the oscilloscope wavewform is as sho wn in the figure
below (eye pattern).
A good eye pattern means that the diamond shape (◊) in the
center of the waveform can be clearly distinguished.
7. Release test mode after adjustment is completed.
• RF signal reference waveform (eye pattern)
VOLT/DIV : 0.2V
TIME/DIV : 500n
0.9Vp-p – 1.3Vp-p
When observing the eye pattern, set the oscilloscope for AC range
and raise vertical sensivity.
[MAIN BOARD] (Conductor side)
5-4. REFERENCE
Focus/Tracking Gain Check
Adjustment Location : MAIN board (Component side)
(See page 16)
A frequency response analyzer is necessary in order to perform this
check exactly.
However , this gain has a mar gin, so e ven if it is slightly of f, there is
no problem.
Focus/Tracking gain determines the pick-up follo w-up (vertical and
horizontal) relative to mechanical noise and mechanical shock when
the 2-axis device operate.
Symptoms
Gain
• The time until music starts
becomes longer for STOP ➡
CD ^ or automatic
selection (0 , ) buttons
pressed). (Normally takes
about 2 seconds.)
• Music does not start and disc
continues to rotate for STOP
➡ CD ^ or automatic
selection (0 , ) buttons
pressed.)
• Sound is interrupted during
PLAY. Or time counter
display stops progressing.
• More noise during 2-axis
device operation.
Focus
low
—
—
high
Tracking
low or high
low
low
high
TP(VC)
TP
(RF)
TP(VC)
TP(RF)
Oscilloscope
(DC range)
+
–
Check Procedure:
1. Keep the set horizontal.
2. Inset disk (YEDS-18) and press ^ button.
3. Connect an oscilloscope to TP (FE) and TP (VC) on the MAIN
board.
4. Check that the waveform is as shown in the f igure below . (Focus
waveform)
— 15 —
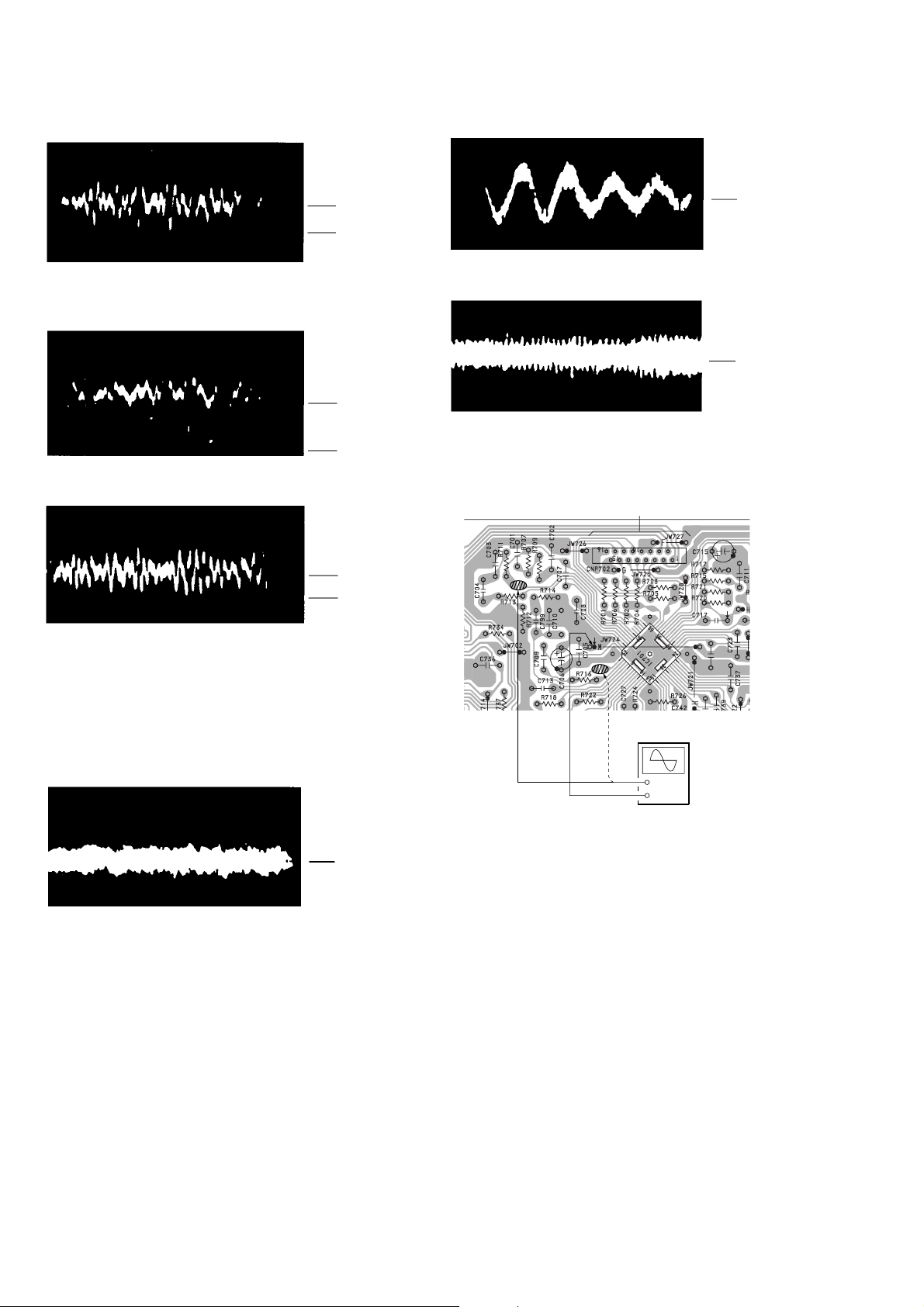
• Good Example
V
V
V
V
V
V
• Incorrect Examples (Fundamental wave appears)
VOLT/DIV : 100m
TIME/DIV : 1ms
100mV
0V
• Incorrent Examples (DC level changes more than on adjusted
waveform)
VOLT/DIV : 100m
TIME/DIV : 2ms
200mV
0V
low focus gain
VOLT/DIV : 100m
TIME/DIV : 2ms
75mV
0V
high focus gain
VOLT/DIV : 0.2
TIME/DIV : 2ms
0V
low tracking gain
VOLT/DIV : 0.2
TIME/DIV : 2ms
0V
high tracking gain
(high fundamental wave than for low gain)
[MAIN BOARD] (Conductor side)
TP(TE)
TP(RF)
TP(VC)
TP(FE)
5. Connect an oscilloscope between TP (TE) and TP (VC).
6. Insert disc (YEDS-18) and press the CD ^ button.
7. Check that the waveform is as shown in the figure below.
(tracking waveform)
VOLT/DIV : 0.2
TIME/DIV : 2ms
0V
TP (TE)
TP (FE)
TP (VC)
Oscilloscope
(DC range)
+
–
— 16 —
SECTION 6
DIAGRAMS
CFD-V77S
6-1. CIRCUIT BOARDS LOCATION
RECORD SWITCH board
POWER board
VOLUME board
LCD board
CONTROL board
CONNECTOR board
VOLTAGE
SELECTION
board
BATTERY board
FINE TUNING
board
MONO ST board
HALF BATTERY board
CD MOTOR board
MAIN board
6-2. BLOCK DIAGRAM
3
AEP, CEF, CET MODEL
MONO ST
BOARD
Note on Printed Wiring Board:
• X : parts extracted from the component side.
• Y : parts extracted from the conductor side.
• b : Pattern from the side which enables seeing.
Note on Schematic Diagrams:
• All capacitors are in µF unless otherwise noted. pF: µµF
50 WV or less are not indicated except for electrolytics
CNB907
VOLTAGE
SELECTION
BOARD
E,EA,SP MODELSAEP, CEF, CET MODELS
and tantalums.
• All resistors are in Ω and 1/
specified.
¢
•
• 2 : nonflammable resistor.
• C : panel designation.
• H : adjustment for repair.
• U : B+ Line.
• Po wer voltage is dc 9 V and f ed with regulated dc power
• Voltages and waveforms are dc with respect to ground
– For MAIN BOARD (1/3) –
– For MAIN BOARD (2/3) –
– For MAIN BOARD (3/3) –
• V oltages are taken with a V OM (Input impedance 10 MΩ).
• Signal path.
• Abbreviation
: internal component.
supply from battery terminal.
under no-signal (detuned) conditions.
The components identified by mark ! or dotted
line with mark ! are critical for safety.
Replace only with part number specified.
no mark : PLAY (TAPE SECTION)
CD STOP
( ) : REC (TAPE SECTION)
no mark : CD PLAY
TAPE STOP
no mark : FM
( ) : MW
[ ] : SW
Voltage variations may be noted due to normal production tolerances.
F : FM
E : PB
a : REC
J : CD
EA : Saudi Arabia model
SP : Singapore model
CEF : Italian model
CET : East European and Russian models
4
W or less unless otherwise
— 17 — — 18 — — 19 — — 20 —
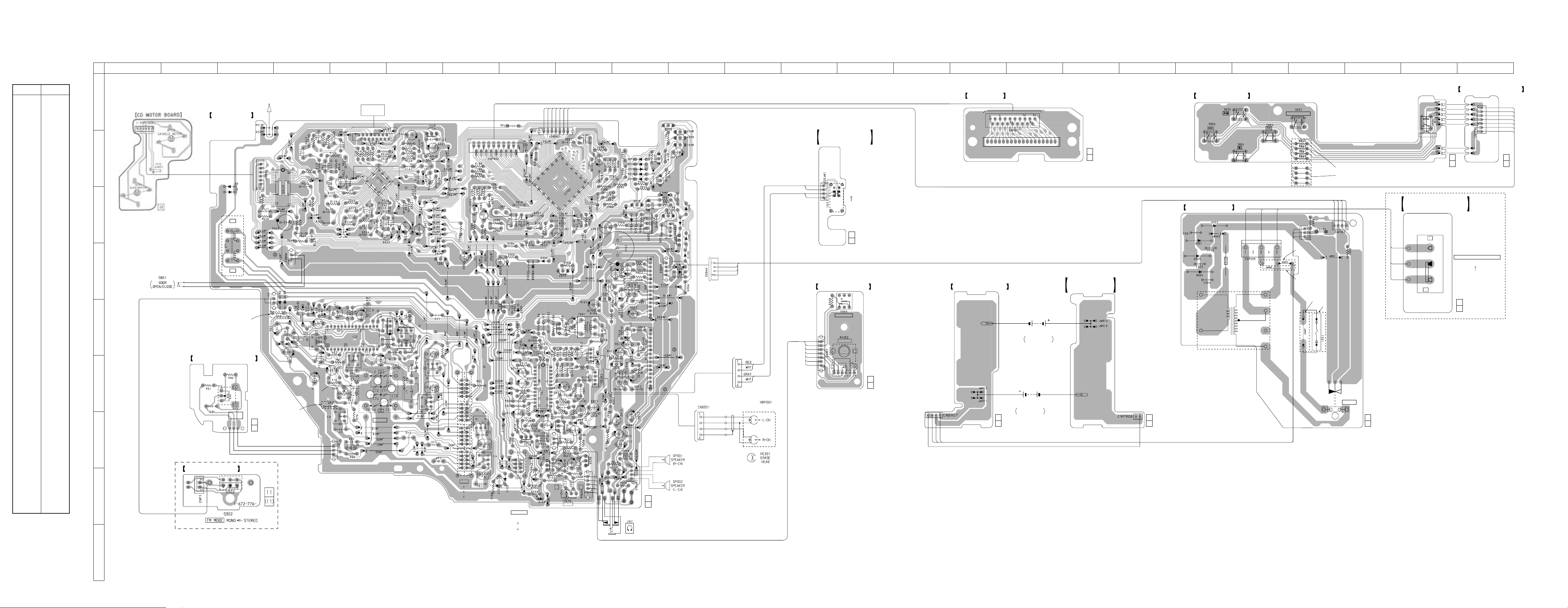
CFD-V77S
6-3. PRINTED WIRING BOARD • Refer to page 20 for Note on Printed Wiring Board. • Refer to page 17 for Circuit Boards Location.
• Semiconductor
Location
Ref. No. Location
D1 C-3
D2 C-3
D3 E-4
D4 E-4
D301 G-9
D302 D-9
D307 E-8
D308 D-8
D310 H-9
D311 C-10
D312 G-8
D314 H-8
D401 C-11
D402 C-11
D403 B-10
D404 B-10
D406 B-10
D407 B-10
D408 B-10
D409 D-11
D410 D-11
D411 D-11
D801 D-7
D901 D-20
D902 C-20
D903 D-20
D904 D-20
IC1 E-5
IC301 F-9
IC303 D-10
IC304 F-10
IC701 B-5
IC702 C-9
IC703 C-4
Q1 E-6
Q2 G-5
Q101 F-10
Q102 G-8
Q103 H-8
Q201 E-9
Q202 G-8
Q203 G-9
Q301 E-9
Q307 C-11
Q308 C-10
Q309 C-10
Q310 E-8
Q401 B-11
Q402 B-11
Q403 B-10
Q404 B-10
Q405 B-11
Q406 C-10
Q407 D-9
Q408 A-10
Q409 D-11
Q701 B-6
Q801 D-6
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
12
MAIN BOARD
L3
FERRITEROD
ANTENNA
(MW)
AEP, CEF, CET
MODELS
FINE TUNING BOARD
FINE
TUNING
1-672-961-
AEP, CEF, CET MODELS
MONO ST BOARD
16
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10111213141516171819202122232425
CONNECTOR BOARD
11
(11)
1-673-261-
S901
VOLTAGE SELECTOR
110 - 120V
220 - 240V
11
(11)
11
(11)
FM TELESCOPIC
ANTENNA
11
(11)
ANT1
AEP, CEF, CET
MODELS
EA MODEL
OPTICAL
PICK-UP BLOCK
ASSY
E, EA, SP
MODELS
CV1
TUNING
-7 -8
-5 -6
-3 -4
-1 -2
S1
BAND
MW
SW2
SW1
FM
S351
FUNCTION
TAPE
(CD/RADIO OFF)
RADIO
CD
D310
(OPR/BATT)
RED
WHT
TONE
BLU
YEL
BLK
BRO
VIO
R251
11
(11)
RED
WHT
BLU
YEL
REC/PB
HEAD
RECORD SWITCH
BOARD
RED
WHT
GRY
WHT
1-672-955-
MEGA BASS
RED
WHT
BLU
YEL
BLK
BRO
VIO
VOLUME
S301
REC
PB
11
(11)
1-672-959-
11
(11)
RED
WHT
CONTROL BOARDLCD BOARD
DISPLAY/ENTER
PLAY MODE
LCD800
(LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY)
1-672-957-
BATTERY BOARDVOLUME BOARD
DRY BATTERY
SIZE "D"
IEC DESIGNATION
R20 3PCS. 4.5V
DRY BATTERY
SIZE "D"
IEC DESIGNATION
1-672-302-
BLK
11
(11)
R20 3PCS. 4.5V
11
(11)
HALF BATTERY
BOARD
1-672-358-
11
(11)
POWER BOARD
PS901
T901
POWER
TRANSFORMER
1 3
5
BLU
WHT
RED
AEP, CEF, CET
MODELS
E, EA, SP MODELS
AEP, CEF, CET MODELS
E, EA, SP MODELS
E, EA, SP MODELS
AEP, CEF, CET MODELS
WHT
BLU
YEL
RED
J901
~ AC IN
1-672-956-
1-672-958-
E, EA, SP MODELS
VOLTAGE SELECTION
BOARD
S901
1
3
5
1-672-960-
11
(11)
I
— 21 — — 22 — — 23 — — 24 —
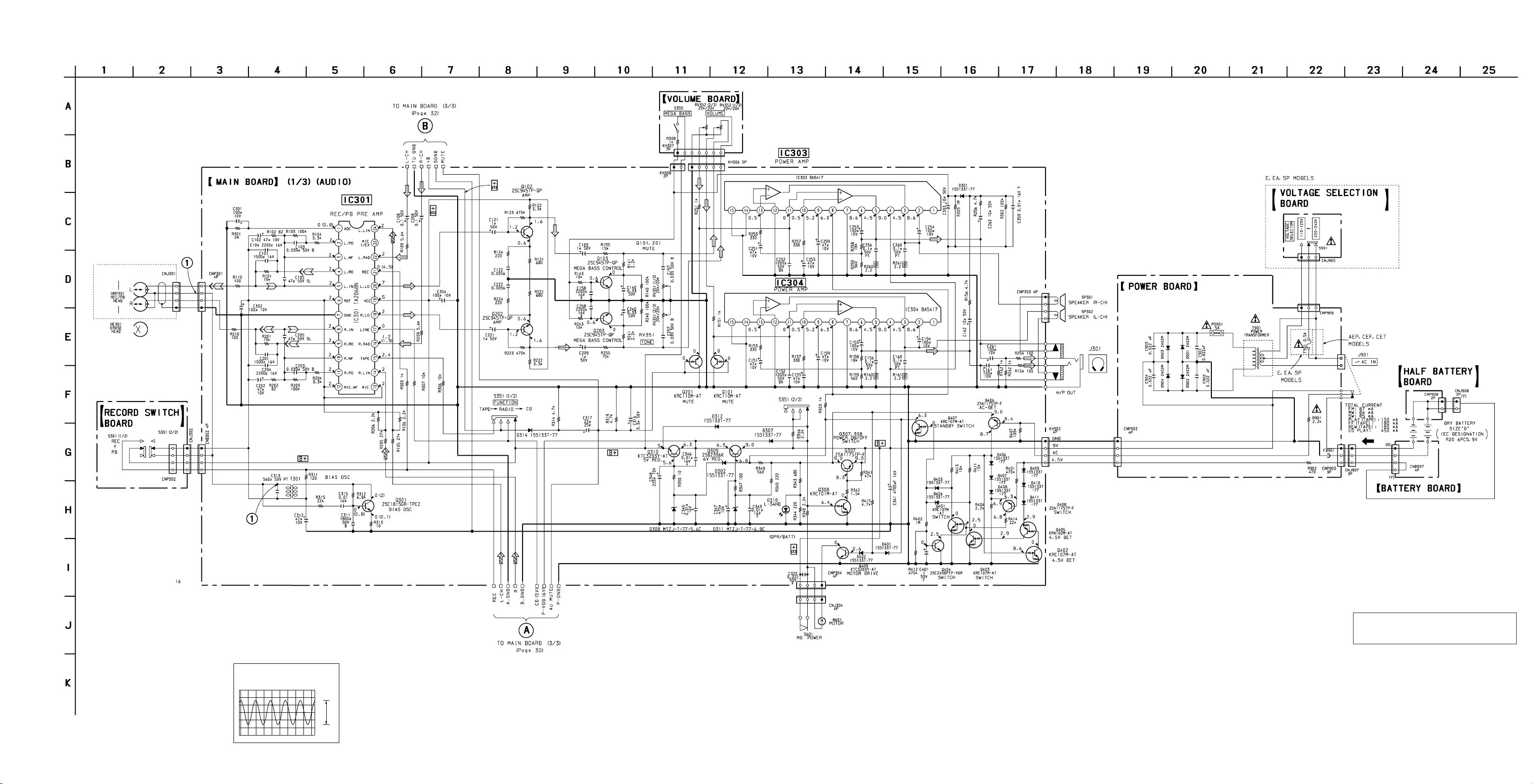
6-4. SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM – MAIN BOARD (1/3) – • Refer to page 20 for Note on Schematic Diagram. • Refer to page 35 for IC Block Diagrams.
CFD-V77S
1
CN 301 2 REC MODE
C313
55.2kHz
— 25 — — 26 — — 27 —
10V/div
10µsec/div
30Vp-p
The components identified by mark ! or dotted
line with mark ! are critical for safety.
Replace only with part number specified.
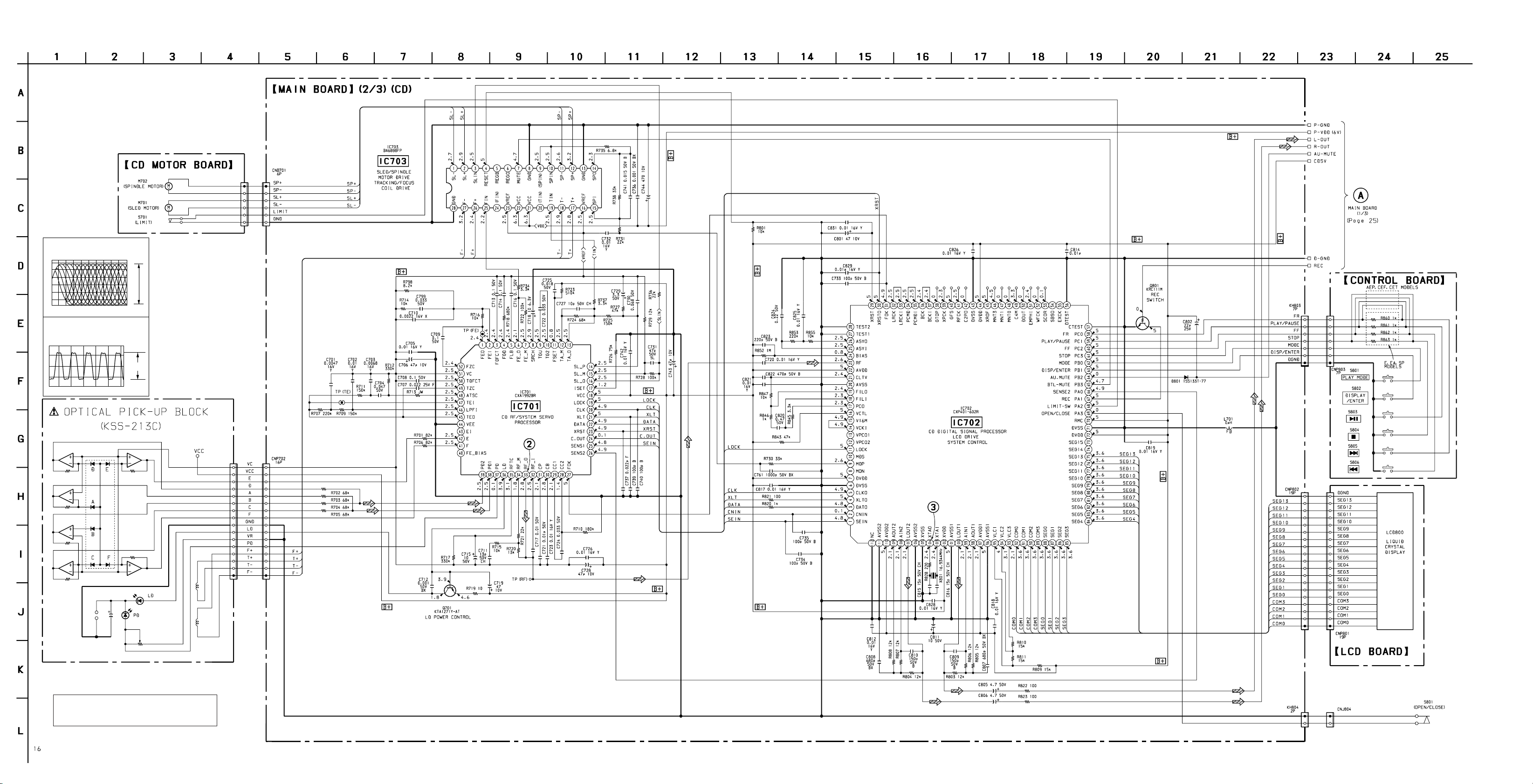
CFD-V77S
6-5. SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM – MAIN BOARD (2/3) – • Refer to page 20 for Note on Schematic Diagram. • Refer to page 35 for IC Block Diagrams.
2
IC701 #£ RFO
3
IC702 ` XTAO
104
16.9 MHz
0.2V/div
0.5µsec/div
1.0 Vp-p
2V/div
50µsec/div
5 Vp-p
The components identified by mark ! or dotted
line with mark ! are critical for safety.
Replace only with part number specified.
— 28 — — 29 — — 30 —
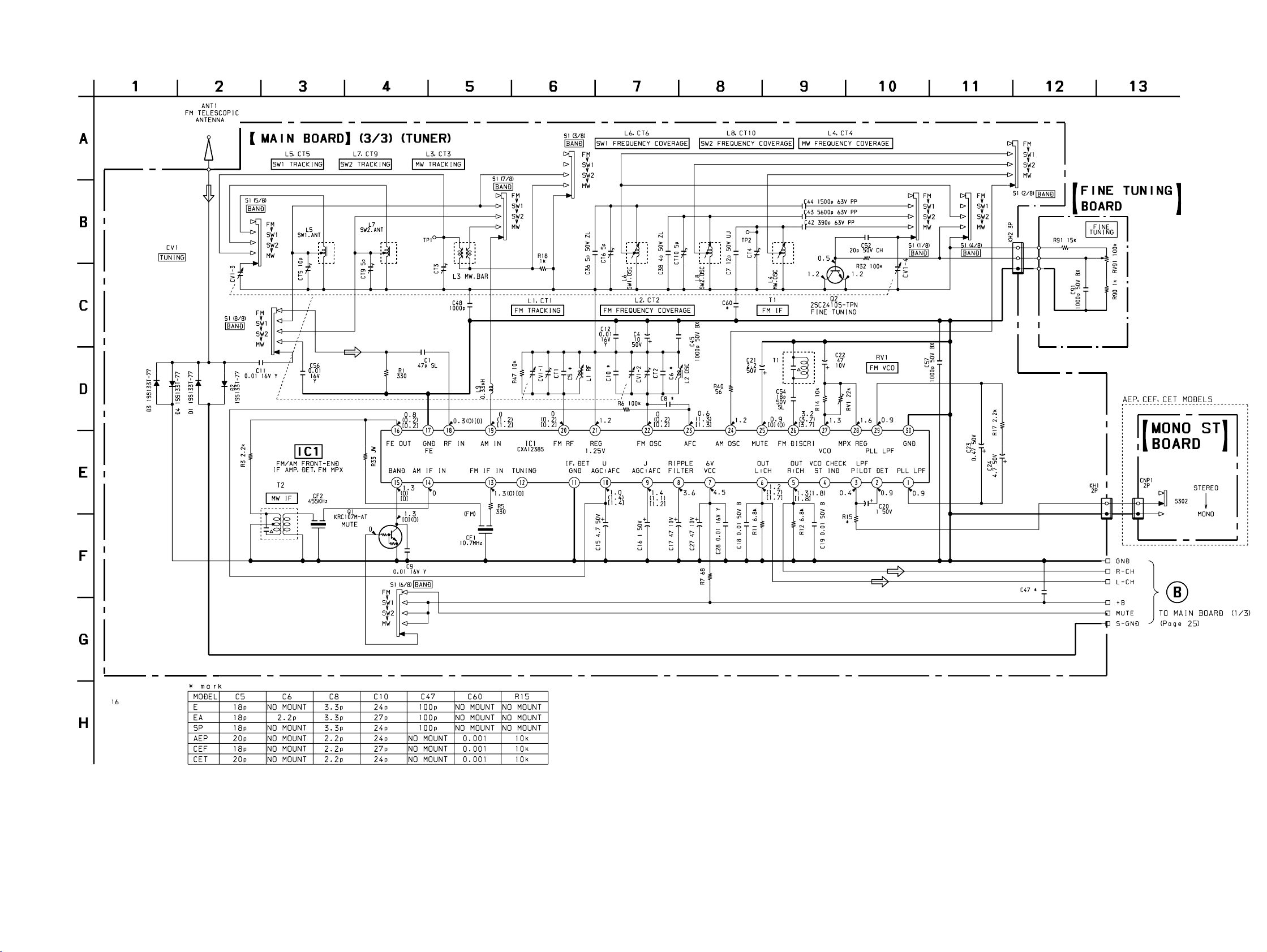
6-6. SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM – MAIN BOARD (3/3) – • Refer to page 20 for Note on Schematic Diagram.
• Refer to page 35 for IC Block Diagrams.
CFD-V77S
— 31 — — 32 —
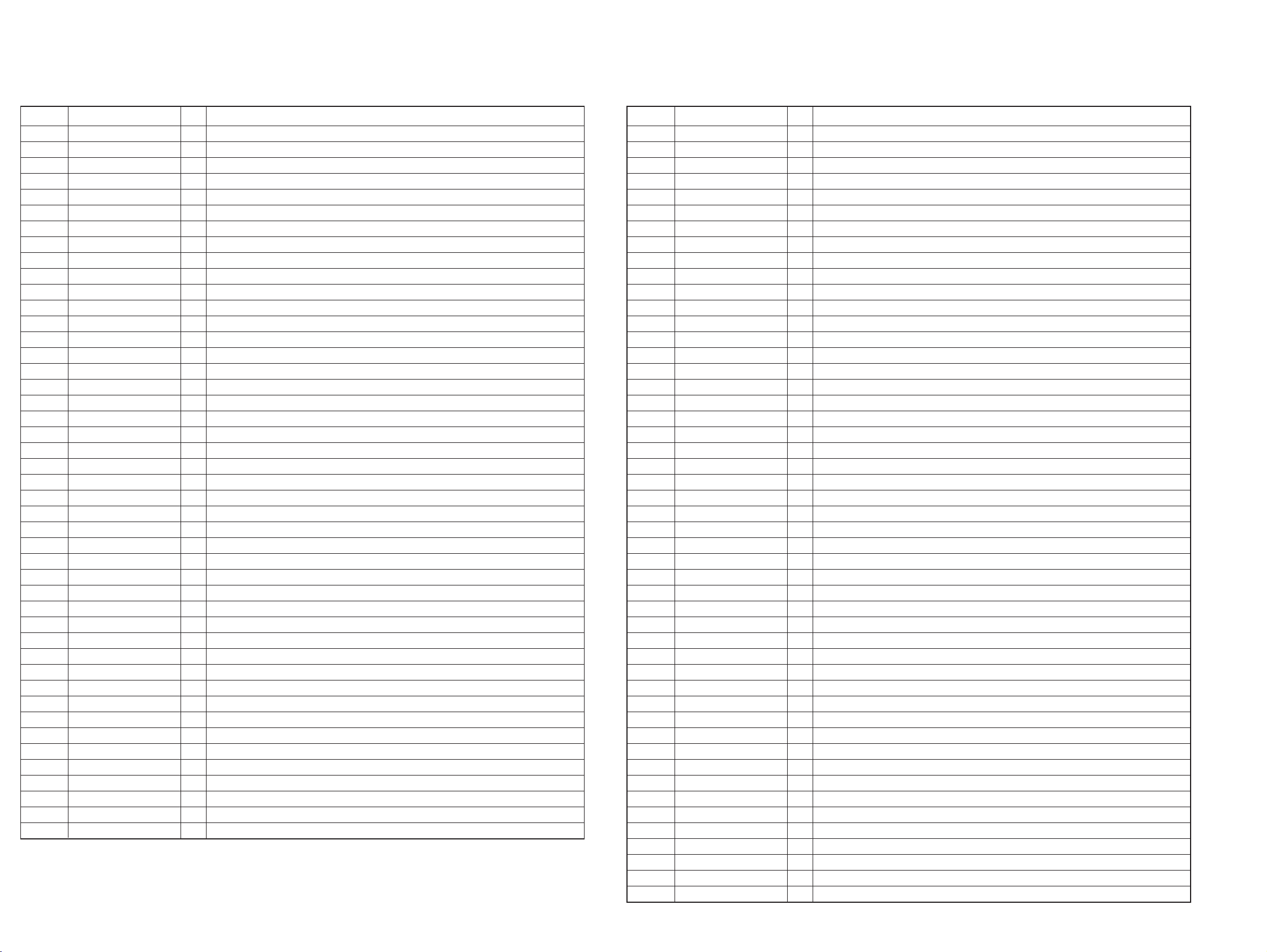
6-7. IC PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
IC702 CD DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSOR, LED DRIVE, SYSTEM CONTROL (CXP401-602R)
Pin No. Pin name I/O Description
1 SEIN I CD SENS input.
2 CNIN I CD SENS input.
3 DATO O CD DSP command data output.
4 XLTO O Latch output.
5 CLKO O Clock output for CD DSP command.
6DVSS– Digital ground.
7DVDD– Digital power supply (+5V).
8 MON – Not used (Open).
9 MDP O Spindle motor drive control.
10 MDS – Not used (Open).
11 LOCK O Lock signal output.
12 VPCO2 – Not used (Open).
13 VPCO1 – Not used (Open).
14 VCKI – Not used (Connect to !∞ pin).
15 V16M – Not used (Connect to !¢ pin).
16 VCTL – Not used (“H” level).
17 PCO O Decoder PLL phase comparator output.
18 FILI I Decoder PLL filter input.
19 FILO O Decoder PLL filter output.
20 AV
21 CLTV I Decoder PLL VCO control voltage input.
22 AV
23 RF I CD RF signal input.
24 BIAS I Playback EFM asymmetry current constant input.
25 ASYI I Playback EFM asymmerty comparater voltage input.
26 ASYO O Playback EFM full swing output.
27 TEST1 I Test terminal (Fixed at “L”).
28 TEST2 I Test terminal (Fixed at “L”).
29 XRST I CD reset input.
30 XRSTO O CD reset output. “L” : Reset
31 FOK I FOK signal input.
32 LRCK O L/R clock signal output. (Connect to #£ pin)
33 LRCKI I L/R clock signal input. (Connect to #™ pin)
34 PCMD O PCM data output. (Connect to #∞ pin)
35 PCMDI I PCM data input. (Connect to #¢ pin)
36 BCK O Bit clock signal output. (Connect to #¶ pin)
37 BCKI I Bit clock signal input. (Connect to #§ pin)
38 GTOP – Not used (Open).
39 XPCK – Not used (Open).
40 GFS – Not used (Open).
41 RFCK – Not used (Open).
42 C2PO – Not used (Open).
43 DV
44 DV
45 XROF – Not used (Open).
DD
SS
DD
– Analog ground.
– Analog power supply (+5V).
SS
– Digital ground.
– Digital power supply (+5V).
Pin No. Pin name I/O Description
46 MNT3 – Not used (Open).
47 MNT1 – Not used (Open).
48 MNT0 – Not used (Open).
49 C4M – Not used (Open).
50 DOUT – Not used (Open).
51 EMPHI – Not used (Open).
52 WFCK – Not used (Open).
53 SCOR – Not used (Open).
54 SBSO – Not used (Open).
55 EXCK – Not used (Open).
56 DTEST I Test terminal (Fixed at “L”).
57 CTEST I Test terminal (Fixed at “L”).
58 FR I = key input.
59 PLAY/PAUSE I ^ key input.
60 FF I
+
key input.
61 STOP I p key input.
62 MODE I PLAY MODE key input.
63 DISP/ENTER I DISPLAY/ENTER key input.
64 AU MUTE O Audio mute signal output.
65 BTL MUTE O BTL mute signal output.
66 SENCE2 I CD SENCE input.
67 REC I Function REC input.
68 LIMIT SW I LIMIT switch input.
69 OPEN/CLOSE I CD door open/close switch input.
70 RMC – Not used (Fixed at “H”).
71 DV
72 DV
DD
SS
– Digital ground.
– Digital power supply (+5V).
73 SEG 15 – Not used (Open).
74 SEG 14 – Not used (Open).
75 – 88 SEG 0 – 13 O LCD segment output.
89 – 92 COM 0 – 3 O LCD common output.
93 – 95 VCL 1 – 3 I LCD drive device voltage input.
96 AVSS1 – Analog ground.
97 AVDD1 – Analog power supply (+5V).
98 AOUT1 O Audio output.
99 AIN1 I Audio input.
100 LOUT1 O L-CH audio output.
101 AVSS1 – Analog ground.
102 XV
DD
– Oscillator power supply (+5V).
103 XTAI I Oscillator connect terminal (16.9344MHz).
104 XTAO O Oscillator connect terminal (16.9344MHz).
105 XV
SS
– Oscillator ground.
106 AVSS2 – Analog ground.
107 LOUT2 O R-CH audio output.
108 AIN2 I Audio input.
109 AOUT2 O Audio output.
110 AVDD2 – Digital power supply (+5V).
111 AVSS2 – Ground terminal.
112 NC – Not used (Connect to ground).
— 33 — — 34 —
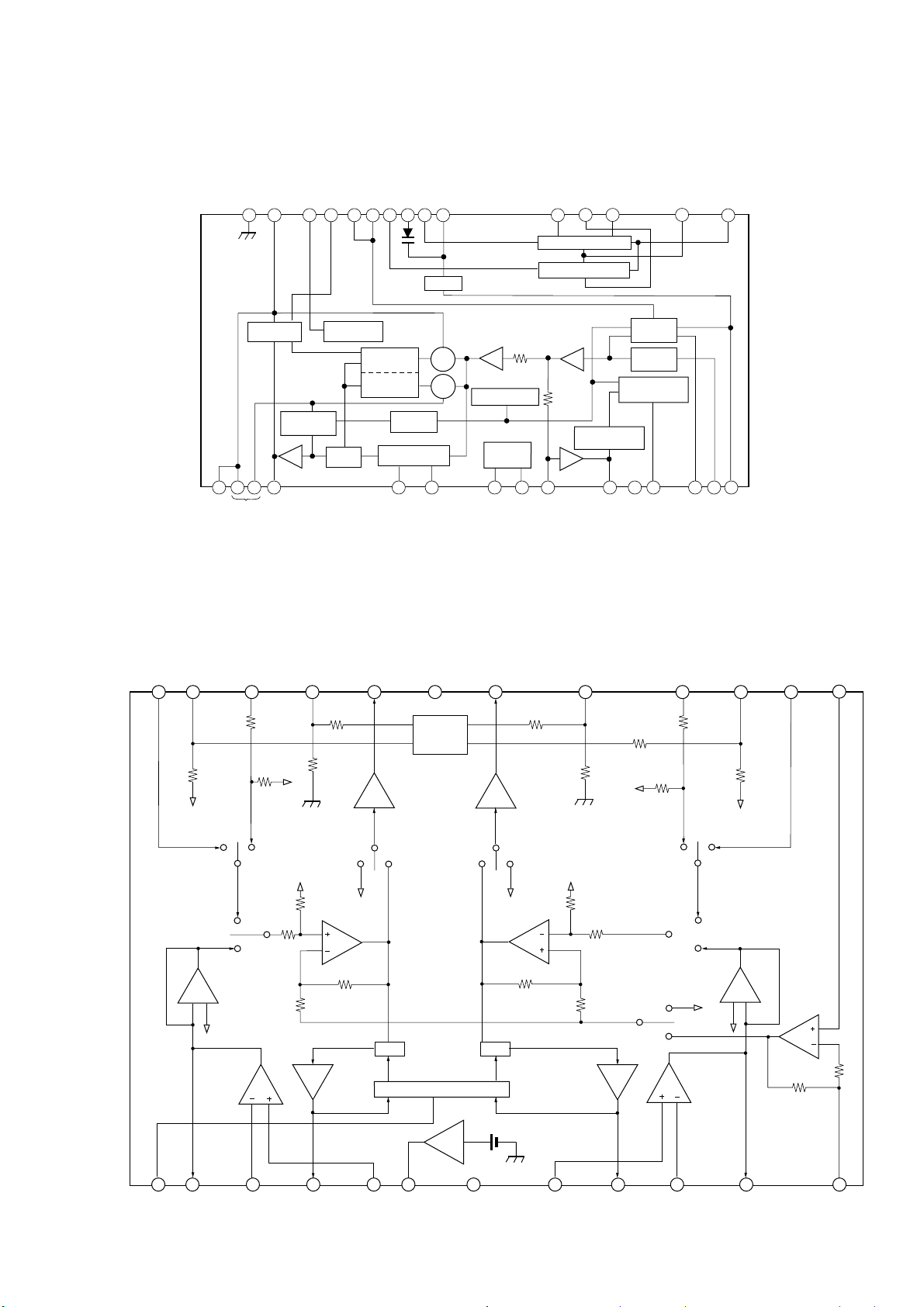
• IC BLOCK DIAGRAMS
IC1 CXA1538S
GND
PLL LPF
MPX REG
VCOFMDISCRI
MUTE
AM OSC
AFC
FM OSC
REG
FM RF
AM IN
19
2030 29 28 27 262524 23 22 21
FM FRONT-END
RF IN
18
GND_FE
17
IF OUT
16
IC301 T A2068N
LIN
MIC
2324
15k
LINE
I/EX
1
PLL LPF 1
3
2
PILOT DET
22
RADOI
VCO
LPF
L. RAD
10k
6k
MONO/ST
SELECT
4
ST IND
VCO CHECK
21
REC
10k
MONITOR
MPX REG.
1k
AMP
1/2
COUNTER
1/2
COUNTER
DECORD AMP
L. LO
7dB
MUTING
5
R_ch
REG
REG
PD 1
PD 2
6
L_ch
VCC
LOGIC
AUTOBLEND
RIPPLE
FILTER
7
VCC
R. LO
181920
7dB
MONITOR
8
FILTER
RIPPLE
1k
AMP
AM FRONT-END
9
J AGC : AFC
17
10k
BAND PASS
MUTE
10
U AGC : AFC
LINE
FM IF /
DISCRI
AM
IF / DET
TUNING
INDICATOR
11
12
TUN
IF, DET GND
10k
1k
6k
16
13
FM IF IN
R. RAD
RADIO
14
15
AM IF IN
BAND SELE
15
LINE
TAPE
10k
14
R. LIN
MIC
13
IN
MUTE
TAPE
10k
–––––
TAPE
BUF AMP
A1
NAB
AMP1
1
2
AGC
L. PO
10k
10k
3
L. NF
BUF AMP
B1
10k
26dB 26dB
REC
AMP1
4
L. RO
ON
ALC1
REF AMP
5
6
L. IN
DET
REF
ON
7
GND
BUF AMP
B2
ALC2
2.1
10k
MUTE
8
R. IN
10k
REC
AMP2
10k
10k
9
R. RO
–––––
BUF AMP
MUTE
ON
AMP2
10
R. NF
TAPE
NAB
TAPE
A2
11
R. PO
AMP1
10k
MIC
1k
12
NF
MIC
— 35 —
 Loading...
Loading...