Page 1

GS64 GSM/GPRS Modem
Integrators Manual
Page 2

The information contained in this document is the proprietary information of Sony Ericsson
Mobile Communications International. The contents are confidential and any disclosure to
persons other than the officers, employees, agents or subcontractors of the owner or
licensee of this document, without the prior written consent of Sony Ericsson Mobile
Communications International, is strictly prohibited.
Further, no portion of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or
transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying
and recording, without the prior written consent of Sony Ericsson Mobile Communications
International, the copyright holder.
First Edition (March 2006)
Second Edition (May 2006)
Sony Ericsson Mobile Communications International publishes this manual without making
any warranty as to the content contained herein. Further Sony Ericsson Mobile
Communications International reserves the right to make modifications, additions and
deletions to this manual due to typographical errors, inaccurate information, or
improvements to programs and/or equipment at any time and without notice. Such changes
will, nevertheless be incorporated into new editions of this manual.
All rights reserved.
© Sony Ericsson Mobile Communications International, 2006
Publication number: LZT 123 1836
Printed in US
LZT 123 1836 2
Page 3

Revision History
Edition Change Information
First First Edition
Second Updated FCC marking requirements
Modified description of VREF function
Signal connectivity table updated
Modified description of UART1 signal behavior
LZT 123 1836 3
Page 4

Contents
Overview....................................................................................................... 9
1 Introduction.......................................................................................... 10
1.1 TARGET USERS.........................................................................................................10
1.2 PREREQUISITES.........................................................................................................10
1.3 MANUAL STRUCTURE ...............................................................................................10
1.4 NOTATION...............................................................................................................11
1.5 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ............................................................................................. 12
2 GS64 WIRELESS MODEM ........................................................................ 13
2.1 ABOUT THE GX64 FAMILY ........................................................................................ 13
2.2 WIRELESS MODEMS IN A COMMUNICATION SYSTEM.................................................. 13
2.3 FEATURES ................................................................................................................ 15
2.3.1 TYPES OF MOBILE STATION ............................................................................... 15
2.3.2 SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE.................................................................................. 16
2.3.3 VOICE CALLS..................................................................................................... 16
2.3.4 DATA................................................................................................................16
2.3.5 GPRS MULTI-SLOT SUPPORT.............................................................................. 17
2.3.6 SIM CARD ......................................................................................................... 17
2.3.7 POWER CONSUMPTION...................................................................................... 17
2.3.8 OPERATING ENVIRONMENT ............................................................................... 18
2.3.9 OTHER FEATURES.............................................................................................. 18
2.4 SERVICE AND SUPPORT ............................................................................................19
2.4.1 WEB PAGES .......................................................................................................19
2.4.2 AT COMMANDS MANUAL ..................................................................................19
2.4.3 M2MPOWER APPLICATION GUIDE....................................................................... 20
2.4.4 DEVELOPER’S KIT .............................................................................................. 20
2.5 PRECAUTIONS..........................................................................................................20
2.6 GUIDELINES FOR SAFE AND EFFICIENT USE................................................................ 20
2.6.1 GENERAL USAGE ............................................................................................... 21
LZT 123 1836 4
Page 5

2.6.2 RADIO FREQUENCY (RF) EXPOSURE AND SAR ..................................................... 21
2.6.3 PERSONAL MEDICAL DEVICES ............................................................................ 22
2.6.4 DISPOSAL OF OLD ELECTRONIC EQUIPMENT ...................................................... 23
2.7 PRODUCT MARKING.................................................................................................23
3 ABBREVIATIONS .................................................................................... 24
Integrating the Wireless Modem.................................................................. 26
4 Mechanical Description ......................................................................... 27
4.1 INTERFACE DESCRIPTION ......................................................................................... 27
4.2 PHYSICAL DIMENSIONS ............................................................................................29
5 System Connector Interface .................................................................. 30
5.1 OVERVIEW................................................................................................................ 30
5.2 SIGNAL LIST............................................................................................................. 30
5.3 DEALING WITH UNUSED PINS....................................................................................34
5.4 GENERAL ELECTRICAL AND LOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS ........................................... 35
5.5 GROUNDS................................................................................................................ 36
5.5.1 ANALOGUE GROUND (AREF) .............................................................................. 36
5.5.2 COMMON GROUND (GND).................................................................................37
5.6 REGULATED POWER SUPPLY INPUT (VCC) .................................................................. 38
5.7 VOLTAGE REFERENCE (VREF) ....................................................................................40
5.8 BATTERY CHARGING INPUT (CHG_IN) ....................................................................... 41
5.8.1 CHARGING PROCESS ......................................................................................... 42
5.8.2 SERIES DIODE....................................................................................................43
5.8.3 BATTERY SELECTION ......................................................................................... 44
5.9 POWERING THE MODULE ON AND OFF (PON_L, PON_H) ............................................47
5.9.1 VREF AS A POWER INDICATOR ........................................................................... 47
5.9.2 MODULE ON & OFF SEQUENCE ..........................................................................48
5.9.2.1 POWER ON TIMING .......................................................................................49
LZT 123 1836 5
Page 6

5.9.3 TURNING THE MODULE OFF .............................................................................. 50
5.10 ANALOGUE AUDIO................................................................................................ 52
5.10.1 AUXILIARY AUDIO TO MOBILE STATION (AUXIP, AUXIN)......................................53
5.10.2 AUXILIARY AUDIO FROM MOBILE STATION (AUXOP, AUXON).............................. 53
5.10.3 MICROPHONE SIGNALS (MICIP, MICIN) ............................................................... 54
5.10.4 SPEAKER SIGNALS (EARP, EARN).........................................................................55
5.11 PCM DIGITAL AUDIO (SSP).....................................................................................55
5.11.1 PCM DATA FORMAT .......................................................................................... 55
5.12 SERIAL DATA INTERFACES.....................................................................................57
5.12.1 UART1 .............................................................................................................. 57
5.12.2 SERIAL DATA SIGNALS (DTM1, DFM1)................................................................58
5.12.2.1 SERIAL DATA FROM WIRELESS MODEM (DFM1) ............................................... 58
5.12.2.2 SERIAL DATA TO WIRELESS MODEM (DTM1)....................................................59
5.12.3 CONTROL SIGNALS (RTS1, CTS1, DTR1, DSR1, DCD1, RI)...................................59
5.12.3.1 HARDWARE FLOW CONTROL RTS1 AND CTS1.................................................59
5.12.3.2 REQUEST TO SEND (RTS1)..............................................................................59
5.12.3.3 CLEAR TO SEND (CTS1).................................................................................. 59
5.12.3.4 DATA TERMINAL READY (DTR1) ..................................................................... 60
5.12.3.5 DATA SET READY (DSR1) ...............................................................................60
5.12.3.6 DATA CARRIER DETECT (DCD1) ..................................................................... 60
5.12.3.7 RING INDICATOR (RI) .....................................................................................60
5.12.4 UART2 (DTM2, DFM2) ....................................................................................... 61
5.12.4.1 TRANSMITTED DATA (DTM2) ......................................................................... 61
5.12.4.2 RECEIVED DATA (DFM2)................................................................................. 61
5.12.4.3 REQUEST TO SEND (RTS2)..............................................................................61
5.12.4.4 CLEAR TO SEND (CTS2).................................................................................. 61
5.12.5 USB................................................................................................................... 62
5.12.6 SIM CARD INTERFACE........................................................................................ 63
5.12.7 SIM DETECTION (SIMDET).................................................................................. 64
5.13 SYNCHRONOUS SERIAL PORT (SSP) INTERFACE [TO BE IMPLEMENTED IN A FUTURE RELEASE] 64
5.14 MEMORY CARD INTERFACE (SD/MMC) [TO BE IMPLEMENTED IN A FUTURE RELEASE] ..... 65
5.14.1 MULTIMEDIA CARD SYSTEM...............................................................................65
5.14.2 SECURE DIGITAL MEMORY CARD SYSTEM...........................................................66
5.15 SERVICE/PROGRAMMING ...................................................................................... 67
5.16 LED [TO BE IMPLEMENTED IN A FUTURE RELEASE] ............................................................... 67
5.17 GENERAL PURPOSE IO ........................................................................................... 69
LZT 123 1836 6
Page 7

5.17.1 EMBEDDED APPLICATIONS................................................................................. 70
5.18 KEYBOARD SIGNALS (KEYROW, KEYCOL)................................................................72
5.19 ANALOGUE TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS (ADIN1, ADIN2, ADIN3, ADIN4)................... 72
5.20 BURST TRANSMISSION (TX_ON)............................................................................. 74
5.21 REAL TIME CLOCK ................................................................................................ 74
5.21.1 REAL TIME CLOCK BACKUP SUPPLY (VRTC).........................................................75
5.21.2 RTC ALARM (ALARM)......................................................................................... 76
5.21.2.1 ALARM OUTPUT FROM THE MODULE.............................................................. 76
5.21.3 ALARM UTILIZATION AS A WAKE-UP.................................................................. 77
5.22 RINGER OUTPUT (BUZZER) [TO BE IMPLEMENTED IN A FUTURE RELEASE]..............................78
6 Antenna Connector ............................................................................... 79
7 Hints for Integrating the Wireless Modem ............................................. 80
7.1 SAFETY ADVICE AND PRECAUTIONS .........................................................................80
7.1.1 GENERAL ..........................................................................................................80
7.2 SIM CARD ................................................................................................................ 81
7.3 ANTENNA ................................................................................................................ 81
7.4 INSTALLATION OF THE WIRELESS MODEM.................................................................82
7.4.1 WHERE TO INSTALL THE WIRELESS MODEM........................................................ 82
7.4.1.1 ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITIONS...................................................................... 82
7.4.1.2 SIGNAL STRENGTH ........................................................................................83
7.4.1.3 CONNECTION OF COMPONENTS TO WIRELESS MODEM...................................83
7.4.1.4 NETWORK AND SUBSCRIPTION.......................................................................83
7.4.2 HOW TO INSTALL THE WIRELESS MODEM...........................................................84
7.4.2.1 POWER SUPPLY .............................................................................................. 84
7.4.2.2 GROUNDS......................................................................................................84
7.4.2.3 AUDIO........................................................................................................... 84
7.4.2.4 SOFTWARE UPGRADE ..................................................................................... 85
7.5 ANTENNA ................................................................................................................ 85
7.5.1 GENERAL ..........................................................................................................85
7.5.2 ANTENNA TYPE................................................................................................. 85
7.5.3 ANTENNA PLACEMENT ...................................................................................... 86
7.5.4 THE ANTENNA CABLE........................................................................................ 86
LZT 123 1836 7
Page 8

7.5.5 POSSIBLE COMMUNICATION DISTURBANCES ...................................................... 87
8 Embedded Applications ........................................................................ 88
8.1 FEATURES ................................................................................................................ 88
8.2 IMPLEMENTATION.................................................................................................... 88
8.2.1 LIMITATIONS.....................................................................................................88
8.2.2 M2MPOWER IDE (INTEGRATED DEVELOPMENT ENVIRONMENT)...........................89
9 TCP/IP Stack ......................................................................................... 90
9.1 IMPLEMENTATION.................................................................................................... 90
10 Technical Data ................................................................................... 91
10.1 MECHANICAL SPECIFICATIONS..............................................................................91
10.2 POWER SUPPLY VOLTAGE, NORMAL OPERATION.................................................... 92
10.3 RADIO SPECIFICATIONS ........................................................................................ 92
10.4 SIM CARD............................................................................................................. 92
10.5 ENVIRONMENTAL SPECIFICATION..........................................................................93
11 Regulatory Notices............................................................................. 95
12 Introduction to the Universal Developer’s Kit ..................................... 97
LZT 123 1836 8
Page 9

Overview
LZT 123 1836 9
Page 10

1 Introduction
1.1 Target Users
The GS64 wireless modems are designed to be integrated into machine-to-machine
or man-to-machine communications applications.
They are intended to be used by manufacturers, system integrators, applications
developers and developers of wireless communications equipment.
1.2 Prerequisites
It is assumed that the person integrating the wireless modem into an application has
a basic understanding of the following:
• GSM networking;
• Wireless communication and antennas (aerials)
• AT commands
• ITU-T standard V.24/V.28
• Micro controllers and programming
• Electronic hardware design
1.3 Manual Structure
The manual is composed of three parts:
Part 1- Overview
This section provides a broad overview of the Gx64 family and includes a list of
abbreviations used in the manual.
Part 2 - Integrating the Wireless modem
This section describes each of the signals available on the GS64 wireless modem,
along with mechanical information. The section also provides you with design
guidelines and what is needed to commercialize an application from a regulatory
point of view.
LZT 123 1836 10
Page 11
Part 3 – Developer’s Kit
R
This section lists the contents of the Developer’s Kit and provides the information to
setup and use the equipment.
1.4 Notation
The following symbols and admonition notation are used to draw the readers
attention to notable, or crucially-important information.
NOTE
Note
Draws the readers attention to pertinent, useful or interesting
information
TIP
CAUTION
!
WARNING
Tip
Provides advice, suggestions, guidance or recommendations which
augment the formal text
Caution
Cautionary information must be heeded, it draws the readers attention
to the need for understanding, care or watchfulness in relation to the
information provided
Warning
Notes marked warning must be heeded, they alert readers to
precautionary measures, risks, hazards or safety information which
directly effects equipment function, warranty or personnel safety
Danger
This information must be heeded, it identifies information and
cautionary behavior that otherwise ignored could result in catastrophic
DANGE
equipment failure, bodily injury or death
LZT 123 1836 11
Page 12

1.5 Acknowledgements
Parts of this document, including text passages, tables and illustrations, are
reproduced from copyright information by kind permission of Agere Systems Inc.
LZT 123 1836 12
Page 13

2 GS64 WIRELESS MODEM
2.1 About the Gx64 Family
The Sony Ericsson Gx64 family of devices are Quad Band GSM/GPRS wireless modems
operating in the GSM 850/900/1800/1900 bands.
The products belong to a new generation of Sony Ericsson wireless modems, and are
intended to be used in machine-to-machine applications and man-to-machine
applications. They are used when there is a need to send and receive data (by SMS,
CSD, or GPRS), and make voice calls over the GSM network.
Two software variants of the Gx64 devices exist. One variant is designed to be
controlled from a micro-controller situated on the host application. The other variant
offers the option to run applications embedded onto the module itself. When using
the embedded application version the controlling script can be run internal to the
module, with or without the use of an external control.
A typical application, involves a micro-controller and a wireless modem, in which the
micro-controller sends AT commands to the wireless modem via an RS232
communications link.
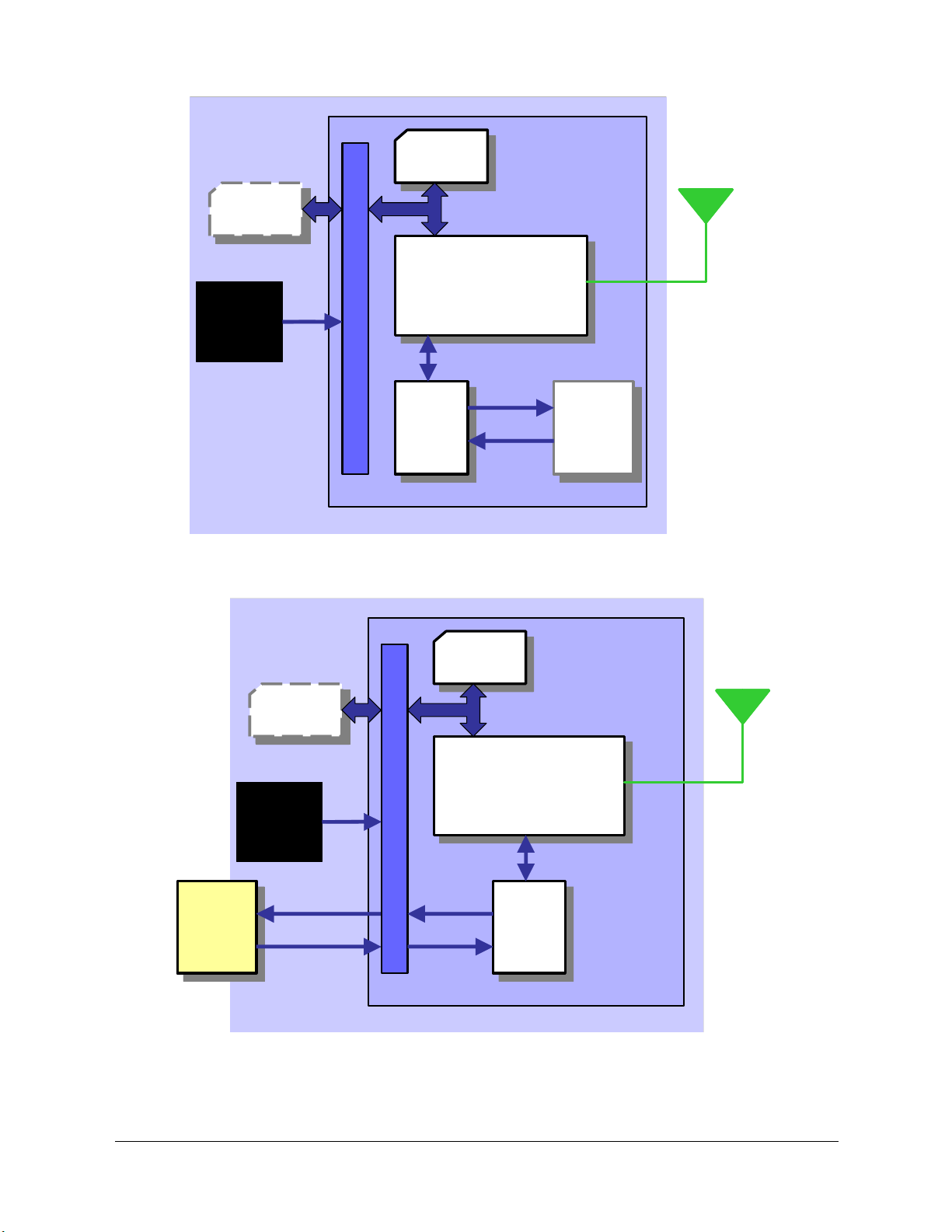
2.2 Wireless modems in a Communication System
Figure
system using the wireless modem.
when the script is embedded on the wireless modem and
communication system when a micro-controller is used. They also show the
communication principles of the system and the interface between the wireless
modem and the application. The definitions in the figures, as used elsewhere in this
manual, are in accordance with the recommendations of 3GPP TS 27.007.
The MS (mobile station) represents the wireless modem and SIM card. The wireless
modem excluding SIM card, is known as the ME (mobile equipment).
The DTE (data terminal equipment) is the controlling application. This can be either
an external host or an internal embedded application
2.2-1 and
Figure
2.2-2 illustrate the main blocks of a wireless communication
Figure
2.2-1 shows the communication system
Figure
2.2-2 shows the
The DCE (data circuit terminating equipment) is the serial communication interface of
the MS.
LZT 123 1836 13
Page 14
MS
MS
SIM
SIM
DC
DC
POWER
POWER
SYSTEM INTERFACE
SYSTEM INTERFACE
DCE
DCE
SIM
SIM
DCE
DCE
GSM
GSM
GSM
GSM
ENGINE
ENGINE
ENGINE
ENGINE
STATUS &
STATUS &
RESPONSE
RESPONSE
COMMAND
COMMAND
& CONTROL
& CONTROL
EMBEDDED
EMBEDDED
APPLICATION
APPLICATION
DTE
DTE
DTE
DTE
GSM
GSM
NETWORK
NETWORK
Figure 2.2-1 Main Blocks in a Wireless System (embedded application)
MS
MS
SIM
DTE
DTE
DTE
DTE
SIM
SIM
DC
DC
POWER
POWER
STATUS &
STATUS &
RESPONSE
RESPONSE
COMMAND
COMMAND
& CONTROL
& CONTROL
SIM
SYSTEM INTERFACE
SYSTEM INTERFACE
GSM
GSM
GSM
GSM
ENGINE
ENGINE
ENGINE
ENGINE
DCE
DCE
DCE
DCE
GR64
GR64
GSM
GSM
NETWORK
NETWORK
Figure 2.2-2 Main Blocks in a Wireless System (external micro-controller)
LZT 123 1836 14
Page 15

In accordance with the recommendations of ITU-T (International Telecommunication
Union - Telecommunications Standardization Sector) V.24, the TE communicates with
the MS over a serial interface.
The functions of the wireless modem follow the recommendations provided by 3GPP
(3rd Generation Partnership Project) and ITU-T. 3GPP is a collaboration agreement
that was established in December 1998. The collaboration agreement brings
together a number of telecommunications standards bodies which are known as
Organizational Partners
ATIS, TTA, and TTC.
3GPP specifies a set of AT commands for controlling the GSM element of the wireless
modem; these commands are supplemented by Sony Ericsson specific commands.
To find out how to work with AT commands, see the AT Commands Manual.
2.3 Features
. The current Organizational Partners are ARIB, CCSA, ETSI,
The wireless modem performs a set of telecom services (TS) according to 3GPP
release 99 and ITU-T. The functions of the wireless modem are implemented by
issuing AT commands over a serial interface.
2.3.1 Types of Mobile Station
The GS64 is a fully Quad Band capable GSM/GPRS mobile station with the
characteristics shown in the table below.
Feature GSM850 E-GSM900 GSM1800 GSM1900
Frequency range (MHz)
Channel spacing 200kHz 200kHz 200kHz 200kHz
Number of channels 124 174 374 299
Number of Time Division slots 8 8 8 8
Duplex spacing 45MHz 45MHz 95MHz 80MHz
GSM power class 4 (2W) 4 (2W) 1 (1W) 1 (1W)
Tx 824-849 880-915 1710-1785 1850-1910
Rx 869-894 925-960 1805-1880 1930-1990
Modulation GMSK
Receive sensitivity <-102dBm at antenna connector
GPRS multi-slot class Class 10
LZT 123 1836 15
Page 16

2.3.2 Short Message Service
The wireless modem supports the following SMS services:
Sending; MO (mobile-originated) with both PDU (protocol data unit) and text mode
supported
Receiving; MT (mobile-terminated) with both PDU and text mode supported
CBM (cell broadcast message); a service in which a message is sent to all subscribers
located in one or more specific cells in the GSM network (for example, traffic reports)
SMS status report according to 3GPP TS 23.40
The maximum length of a text mode SMS message is 160 characters using 7-bit
encoding. The wireless modem supports up to six concatenated messages to extend
this function. Concatenation is performed by the host application.
2.3.3 Voice Calls
The wireless modem offers the capability of MO (mobile originated) and MT (mobile
terminated) voice calls, as well as supporting emergency calls. Multi-party, call
waiting and call divert features are available. Some of these features are networkoperator specific.
For the inter-connection of audio, the wireless modem offers both single ended and
balanced analogue input and output lines. Direct interface to the digital PCM (pulse
code modulation) bus used within the wireless modem is available, thus by-passing
the internal analogue circuitry. The wireless modems support HR, FR, EFR and AMR
vocoders.
2.3.4 Data
The wireless modem supports the following data protocols:
GPRS (General Packet Radio Service)
The wireless modem is a Class B terminal. The wireless modem is GPRS multislot
class10 enabled, capable of receiving at a maximum of four timeslots per frame
(down link), and transmitting in two timeslots per frame (up link). See section 2.3.5
for multi-slot allocation by class.
LZT 123 1836 16
Page 17

CSD (Circuit Switched Data)
The GS64 wireless modem is capable of establishing a CSD communication at 9.6
kbps over the air.
2.3.5 GPRS Multi-Slot Support
GSM Multi-slot classes supported by Gx64 devices
Multislot
Class
8 4 1 5 1 up; 4 down
10 4 2 5
2.3.6 SIM Card
The GS64 supports an external SIM card through its system connector. Both 3V and
1.8V SIM technology is supported. Older, 5V SIM technology is not supported.
A mechanical variant of the GS64 also supports an on-card SIM. For dual SIM
support, automated SIM-switching is available. Only one SIM is active at any one
time, it is not possible to concurrently register on more than one network.
Maximum slot allocation
Downlink Uplink Active
Allowable
Configuration
1 up; 4 down
2 up; 3 down
Max data rate
8-12Kbps Send
32-48Kbps Receive
8-12Kbps Send
32-48Kbps Receive
16-24Kbps Send
24-36Kbps Receive
2.3.7 Power Consumption
Feature
Sleep Mode
DRX 8
Idle Mode
Voice/CSD
GSM850 & E-GSM900
1.6 mA 17 mA 2000 mA
Data (GPRS)
Voice/CSD
GSM1800 & GSM1900
1.6 mA 16 mA 1450 mA
Data (GPRS)
LZT 123 1836 17
Transmit
Operation
Page 18

The power consumption figures shown represent average current for maximum
transmitted power, single uplink (transmit) slot, single downlink (receive) slot. The
module will consume more average power in different multi-slot configurations, the
worst case being that of two uplink and three downlink slots.
2.3.8 Operating Environment
Parameter Min Max Units
Operating Temperature -30 +75 °C
Humidity 95 %RH
Storage Temperature -40 +85 °C
For complete details of the environmental specification please refer to Para. 10.5.
2.3.9 Other Features
The GS64 supports many other features, including :
• multiplexing in accordance with 3GPP TS 27.010
• GPS interoperability
• SIM application tool kit, class 2 release 99 compliant
• On board TCP/IP stack
• In addition, customers have the option of a GS64 software variant which adds
embedded application functionality.
LZT 123 1836 18
Page 19
2.4 Service and Support
2.4.1 Web Pages
Visit the Sony Ericsson M2M extranet web site for the following information:
where to buy wireless modems or for recommendations concerning accessories and
components
local contact details for customer support in your region
FAQs (frequently asked questions)
documentation related to integrating the module, including application notes, design
guides and AT command manuals
Access to the Sony Ericsson extranet site requires a user account and password.
Accounts can be arranged through your local account manager.
The extranet web site address is:
https://extranet.sonyericsson.com/collaborationarea/m2m/default.aspx
2.4.2 AT Commands Manual
The AT Commands Manual provides users with all the AT commands that can be used
with the wireless modem. AT commands appear in logical groups and contain the
command, a description of its functionality and an example of use.
LZT 123 1836 19
Page 20

2.4.3 M2mpower Application Guide
The M2mpower Application Guide provides users with all the information they need
to build an application using the M2mpower support environment. This manual is
supplied as part of the M2mpower package.
2.4.4 Developer’s Kit
Sony Ericsson provides the developer’s kit to get you started quickly. The kit includes
the necessary hardware required to begin the development of an application. It
includes the following:
This Integrator’s Manual
Developer’s kit hardware
Developer’s kit accessories
Power supply
User need to order the M2M module(s) of their choice, and provide a computer or
micro-controller. The AT command manual provides the necessary command and
control reference to drive the module.
2.5 Precautions
The wireless modems are ESD protected up to ±2kV on all pins other than the SIM
interface. The SIM interface is protected up to ±15kV. Integrators must follow
electronic device handling precautions when working with any electronic device
system to ensure no damage occurs to the host or the wireless modem. In the section
‘Integrating the Wireless modem’, users will find more information about safety and
product care. Do not exceed the environmental and electrical limits as specified in
‘Technical Data’ section.
RS232 cable
Headset
Antenna
2.6 Guidelines for Safe and Efficient Use
Users must follow the general usage outlined in this chapter before using the GS64
for any purpose.
LZT 123 1836 20
Page 21

2.6.1 General Usage
Always treat the product with care and keep it in a clean and dust-free place
Do not expose the product to liquid
Avoid exposing the product to moisture or high humidity environments
Do not expose the product to extreme high or low temperatures beyond those
specified for operation and storage
Do not expose the product to open flames or lit tobacco products
Do not drop, throw or try to bend the product
Do not paint the product
Do not use the product near medical equipment without requesting permission
Do not use the product when in, or around aircraft, or areas posted “turn off two-way
radio”
Do not use the product in an area where a potentially explosive atmosphere exists
Do not place the product or install wireless equipment in the area above a vehicle’s
air bag
Do not attempt to disassemble the product; only Sony Ericsson authorized personnel
should perform servicing
2.6.2 Radio Frequency (RF) exposure and SAR
Your wireless modem device is a low-power radio transmitter and receiver
(transceiver). When it is turned on, it emits low levels of radio frequency energy (also
known as radio waves or radio frequency fields).
LZT 123 1836 21
Page 22

Governments around the world have adopted comprehensive international safety
guidelines, developed by scientific organizations, e.g. ICNIRP (International
Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection) and IEEE (The Institute of Electrical
and Electronics Engineers Inc.), through periodic and thorough evaluation of scientific
studies. These guidelines establish permitted levels of radio wave exposure for the
general population. The levels include a safety margin designed to assure the safety
of all persons, regardless of age and health, and to account for any variations in
measurements.
Specific Absorption Rate (SAR) is the unit of measurement for the amount of radio
frequency energy absorbed by the body when using a transceiver. The SAR value is
determined at the highest certified power level in laboratory conditions, but the
actual SAR level of the transceiver while operating can be well below this value. This is
because the transceiver is designed to use the minimum power required to reach the
network.
The GS64 wireless modem device has been approved for applications where the
antenna is located >20cm from the body. In all other configurations the integrator is
responsible for meeting the local SAR regulations.
Integrators of the GS64 wireless modem device are responsible for ensuring that they
meet the SAR regulatory requirements of the countries in which they intend to
operate the device, and that their documentation contains the relevant SAR
declaration, certification information, and user guidance as appropriate.
More information on radio frequency exposure and SAR can be found at
www.sonyericsson.com
.
2.6.3 Personal Medical Devices
Wireless modem devices may affect the operation of cardiac pacemakers, hearing aids
and certain other implanted equipment. If a minimum distance of 15 cm (6 inches) is
maintained between the GS64 module’s radiating antenna and a pacemaker, the risk
of interference is limited. If the integrator’s application is likely to be situated in the
vicinity of personnel, a suitable warning should be contained in the equipment
manual to this effect.
LZT 123 1836 22
Page 23

2.6.4 Disposal of Old Electronic Equipment
This symbol on the product or on its packaging indicates that this product shall not
be treated as household waste. Instead it shall be handed over to an appropriate
collection point for the recycling of electrical and electronic equipment. By ensuring
this product is disposed of correctly, you will help prevent potential negative
consequences for the environment and human health, which could otherwise be
caused by inappropriate waste handling of this product. The recycling of materials
will help to conserve natural resources. For more detailed information about recycling
of this product, please contact your local city office, your household waste disposal
service or the Sony Ericsson regional sales office.
2.7 Product Marking
Your attention is drawn to the Regulatory Notices contained in Section 11, specifically
the paragraph pertaining to the FCC marking requirements for devices in which the
GS64 is installed. Any device that integrates the GS64, which is subject to FCC
regulatory approval, must have an exterior label identifying the GR64 FCC ID number.
LZT 123 1836 23
Page 24

3 ABBREVIATIONS
Abbreviation Explanation
ADC Analogue to Digital Converter
AMR Adaptive Multi Rate
ATMS Audio to Mobile Station
AFMS Audio from Mobile Station
CBM Cell Broadcast Message
CBS Cell Broadcast Service
CSD Circuit Switched Data
DCE Data Circuit Terminating Equipment
DK Developer’s Kit
DTE Data Terminal Equipment
DTMF Dual Tone Multi Frequency
EA Embedded Application
EFR Enhanced Full Rate
EMC Electro-Magnetic Compatibility
ETSI European Telecommunication Standards Institute
FR Full Rate
GPRS General Packet Radio Service
GPS Global Positioning System
GSM Global System for Mobile Communication
HR Half Rate
IDE Integrated Development Environment
IP Internet Protocol
ITU-T
International Telecommunication Union –
Telecommunications (Standardisation Sector)
LDO Low Drop Out (voltage regulator)
M2mpower Sony Ericsson’s powerful support environment
ME Mobile Equipment
MMCX Micro Miniature Coax
MO Mobile Originated
LZT 123 1836 24
Page 25

Abbreviation Explanation
MS Mobile Station
MT Mobile Terminated
PCM Pulse Code Modulation
PDU Protocol Data Unit
RF Radio Frequency
RFU Reserved for Future Use
RLP Radio Link Protocol
RTC Real Time Clock
SDP Service Discovery Protocol
SIM Subscriber Identity Module
SMS Short Message Service
TCP Transport Control Protocol
UDP User Datagram Protocol
LZT 123 1836 25
Page 26

Integrating the Wireless
Modem
LZT 123 1836 26
Page 27
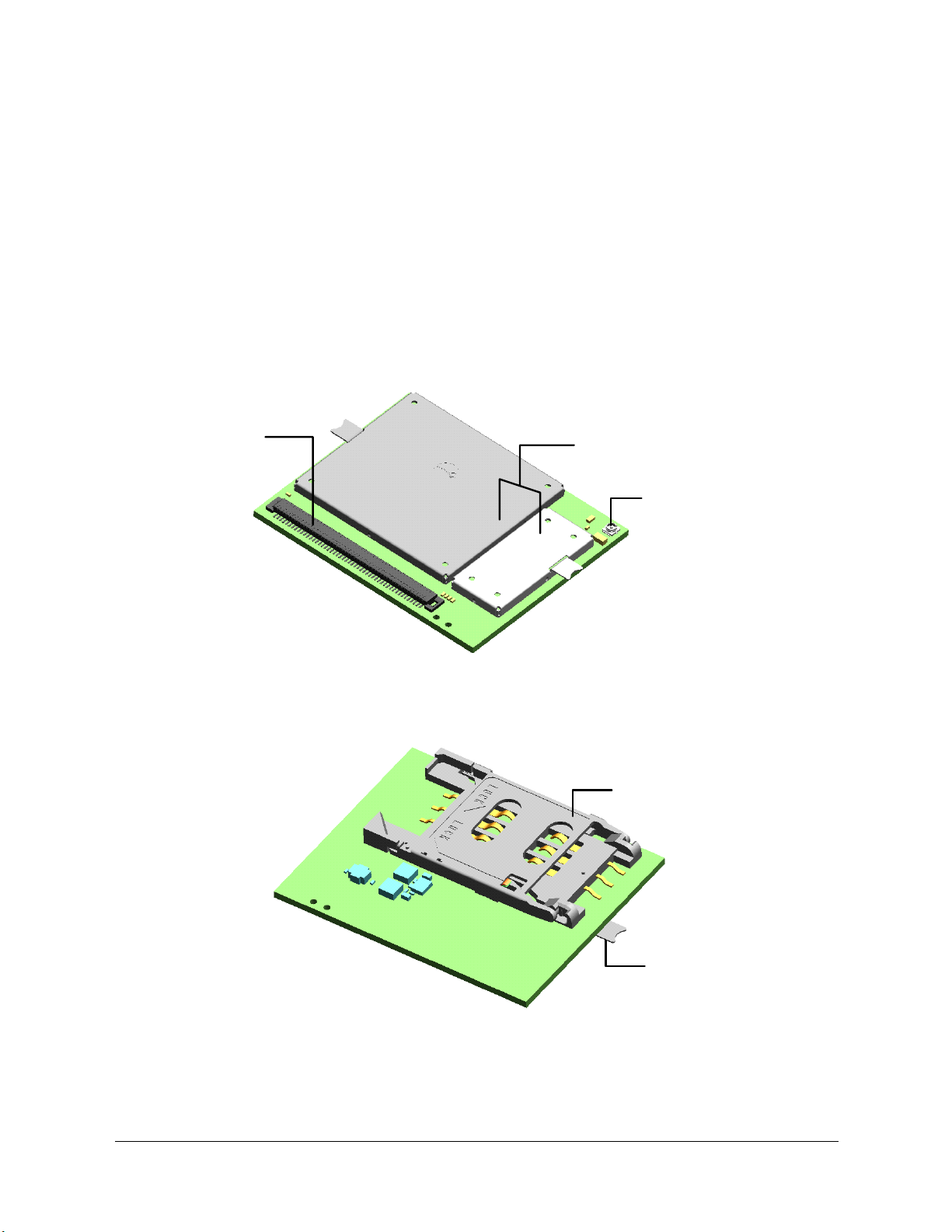
4 Mechanical Description
4.1 Interface Description
The pictures below show the mechanical design of the wireless modem along with the
positions of the different connectors and mounting holes. The wireless modem is
protected with tin coated steel ASI 1008/1010 covers that meet the environmental
and EMC requirements.
system connector
system connector
wireless modem
wireless modem
shielded circuits
shielded circuits
antenna
antenna
connector
connector
Figure 4.1-1 Wireless modem viewed from below
integrated SIM holder
integrated SIM holder
integrated SIM holder
solder tab
solder tab
solder tab
Figure 4.1-2 Wireless modem, viewed from above (Integrated SIM holder version)
LZT 123 1836 27
Page 28

Please note the following:
Keypad, display, microphone, speaker and battery are not part of the wireless modem
For the GS64 variant without an integrated SIM holder, the SIM card is mounted in the
user application, external to the wireless modem (this is also an option for the
integrated SIM holder variant)
The GS64 variant without an integrated SIM holder has no components mounted on
the top-side
The System Connector is a 100-pin, narrow (0.5 mm) pitch type designed for boardto-board mating. The pins and their electrical characteristics are described in Section
5, together with the System Connector Interface.
Information about the Antenna Connector is found in Section 6.
Antenna Connector details are found in Section 6.
LZT 123 1836 28
Page 29
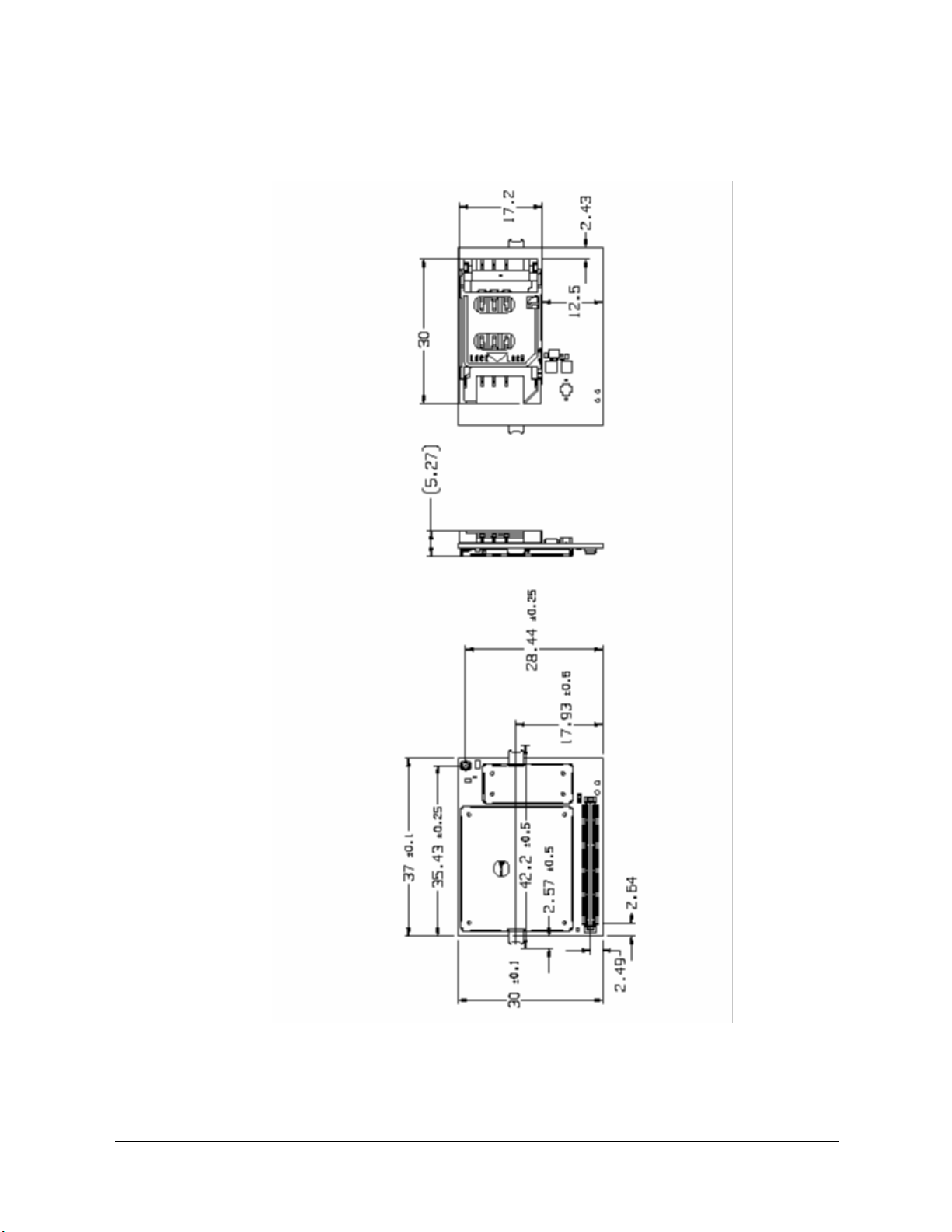
4.2 Physical Dimensions
Figure 4.2-1 Dimensions of the Wireless modem (Integrated SIM variant)
Measurements are given in millimeters. See also Technical Data, in Section 10 .
LZT 123 1836 29
Page 30
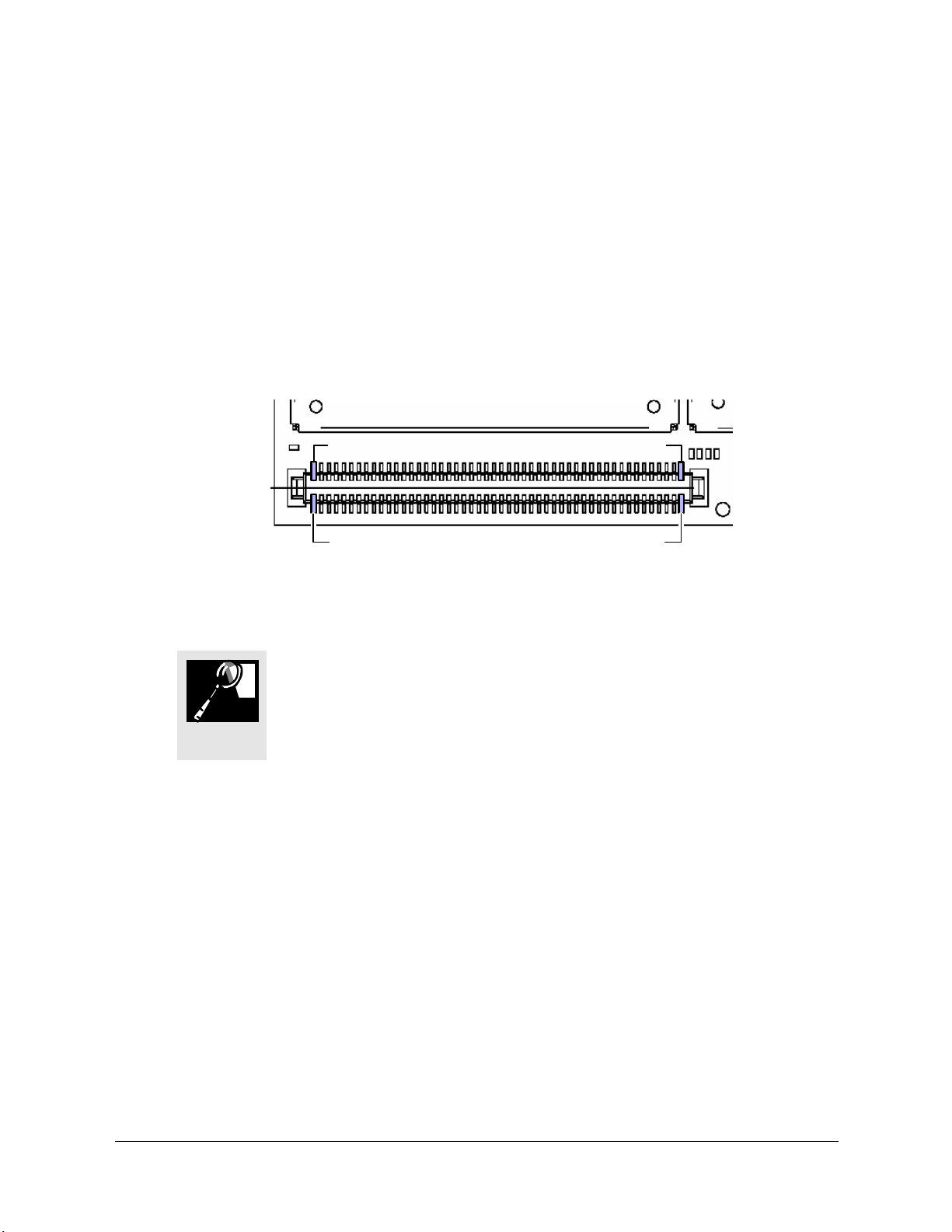
5 System Connector Interface
5.1 Overview
Electrical connections to the wireless modem (except the antenna), are made through
the System Connector Interface. The system connector is a 100-pin, narrow (0.5 mm)
pitch device designed for board-to-board connectivity.
Figure 5.1-1 below shows the numbering of the connector pins.
Pin 100
Pin 100
Pin 2
Pin 2
Figure 5.1-1 Wireless modem, viewed from underneath
TIP
5.2 Signal List
The following table gives the pin assignments for the system connector interface and
a short description for each signal.
Pin 1
Pin 99
Pin 99
Pin 1
A mating (host circuit board) connector can be obtained from Panasonic
by ordering the following part
100 PIN SOCKET AXK5F00547YG
LZT 123 1836 30
Page 31

Table 5.2-1 Pin Assignments
PIN
Pin Name Direction Function
1 GND - Ground Yes
2 VCC Input DC power Yes
3 GND - Ground Yes
4 VCC Input DC power Yes
5 GND - Ground Yes
6 VCC Input DC power Yes
7 GND - Ground Yes
8 VCC Input DC power Yes
9 GND - Ground Yes
10 VCC Input DC power Yes
11 GND - Ground Yes
12 VCC Input DC power Yes
13 CHG_IN Input Battery charger power
14 SIMVCC Output 1.8V or 3.0V SIM card supply Yes1
15 SIMRST Output SIM card reset signal Yes1
16 SIMCLK Output SIM card clock signal Yes1
17 SIMDAT In/Out SIM card data Yes1
18 SIMDET Input SIM presence detection Yes1
19 Reserved - -
20 SERVICE Input Flash programming enable signal
21 PON_H Input Device on control Yes2
22 Reserved - -
23 Reserved - -
24 Reserved - -
25 Reserved - -
26 Reserved - -
27 ADIN1 Input ADC Input 1
28 ADIN2 Input ADC Input 2
29 ADIN3 Input ADC Input 3
30 ADIN4 Input ADC Input 4
31 VRTC Input DC supply for real time clock
32 ALARM Output RTC alarm
Connection
Required
LZT 123 1836 31
Page 32

PIN
Pin Name Direction Function
33 PON_L Input Device on/off control Yes2
34 VUSB Output USB DC power Yes3
35 USBDP In/Out USB data positive Yes3
36 USBDN In/Out USB data negative Yes3
37 LED1 Output LED control
38 LED2 Output LED control
39 TX_ON Output Transmit indication
40 GPIO1 In/Out General purpose IO
41 GPIO2 In/Out General purpose IO
42 Reserved - -
43 GPIO3 In/Out General purpose IO
44 GPIO4 In/Out General purpose IO
45 GPIO5 In/Out General purpose IO
46 Reserved - -
47 Reserved - -
48 GPIO6 In/Out General purpose IO
49 GPIO7 In/Out General purpose IO
50 GPIO8 In/Out General purpose IO
51 GPIO9 In/Out General purpose IO
52 BUZZER Output Buzzer Output
53 RI Output Ring Indicator
54 DCD1 Output Data Carrier Detect (UART1)
55 DTR1 Input Data Terminal Ready (UART1) Yes5
56 DSR1 Output Data Set Ready (UART1) Yes5
57 RTS1 Input Ready To Send (UART1) Yes5
58 CTS1 Output Clear To Send (UART1) Yes5
59 DTM1 Input Data To Module from host (UART1) Yes4
60 DFM1 Output Data From Module to host (UART1) Yes4
61 RTS2 Input Ready To Send (UART2)
62 CTS2 Output Clear To Send (UART2)
63 DTM2 Input Data To Module from host (UART2)
64 DFM2 Output Data From Module to host (UART2)
65 VREF Output Core voltage reference Yes
66 PCMCLK In/Out Serial PCM clock
67 PCMFS In/Out Serial PCM frame synchronization
68 PCMDTM Input Serial PCM data to module from host
Connection
Required
LZT 123 1836 32
Page 33

PIN
Pin Name Direction Function
Connection
Required
69 PCMDFM Output Serial PCM data from module to host
70 SSPCLK In/Out SPI clock
71 SSPFS In/Out SPI frame synchronization
72 SSPDTM Input SPI data to module from host
73 SSPDFM Output SPI data to host from module
74 MMCCLK Output
75 MMCCMD In/Out
76 MMCDAT0
77 MMCDAT1
78 MMCDAT2
79 MMCDAT3
80 MMCMD_EN
In/Out SD/MMC card data 0
In/Out SD/MMC card data 1
In/Out SD/MMC card data 2
In/Out SD/MMC card data 3
Output SD/MMC card command enable
81 MMCDAT_EN Output
MMCDAT_EN0 Output SD/MMC card data enable (data 0)
82
83
KEYROW1 Input
84
KEYROW2 Input
85
KEYROW3 Input
86
KEYROW4 Input
87
KEYROW5 Input
SD/MMC card clock
SD/MMC card command/response
SD/MMC card data enable (data 1-3)
Keyboard row 1
Keyboard row 2
Keyboard row 3
Keyboard row 4
Keyboard row 5
88 KEYCOL1 Output Keyboard row 1
89 KEYCOL2 Output Keyboard row 2
90 KEYCOL3 Output Keyboard row 3
91 KEYCOL4 Output Keyboard row 4
92 AUXIP Input Aux audio to module from host (pos)
93 AUXIN Input Aux audio to module from host (neg)
94 AUXOP Output Aux audio from module to host (pos)
95 AUXON Output Aux audio from module to host (neg)
96 AREF - Analogue reference
97 MICIP Input Microphone input positive
98 MICIN Input Microphone input negative
99 EARP Output Earpiece output positive
100 EARN Output Earpiece output negative
LZT 123 1836 33
Page 34

1
- These signals are required if the external SIM interface is used
2
- At least one of these interfaces is required to be connected
3, 4
NOTE
- At least one of these interfaces is required to be connected
5
- These pin connections are required for sleep mode operation
5.3 Dealing with Unused pins
Integrators applications may connect all of the GS64 signals pins, or just those
necessary for minimal operation, or most commonly some other permutation. If
GR64 signal pins are not connected to the host application you should terminate
them in the following manner.
Table 5.3-1 Unused Pin Termination
Pin Name Unused pins
1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11 GND Must be connected
2, 4, 6, 8, 10,12 VCC Must be connected
27 ADIN1 Ground
28 ADIN2 Ground
29 ADIN3 Ground
30 ADIN4 Ground
65 VREF Must be connected
92 AUXIP Connect to AREF
93 AUXIN Connect to AREF
97 MICIP Connect to AREF
98 MICIN Connect to AREF
All other signal pin may be left open (un-terminated)
LZT 123 1836 34
Page 35

5.4 General Electrical and Logical Characteristics
The electrical characteristics in this document refer to the behavior of the device
under specified conditions. Electrical requirements refer to conditions imposed on the
user for proper operation of the device.
All IO to and from the GS64 is 1.8V unless otherwise stated. For user applications
employing other logic voltage technology it may be necessary to implement level
translators on the host-side circuitry in order to achieve level compatibility. To
facilitate ease of level conversion the GS64 provides a 1.8V reference on the VREF pin.
The VREF voltage from which all 1.8V logic is derived is covered in section 5.7
All input buffers are of the same type and they offer hysteresis of 200 mV—380 mV
The electrical characteristics for 1.8V IO signals are shown in Table 5.4-1
Table 5.4-1 1.8V IO Characteristics
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
Input Voltage Low (VIL) –0.3 0.45 V
Input Voltage High (VIH) 1.16 VREF+0.3 V
Input Current (no pull-up) Low (VIL) 1.0
Input Current (no pull-up) High (VIH) 1.0
Output Low Voltage, 2 mA (VOL) 0.25 x VREF V
Output High Voltage, –2 mA (VOH) 0.75 x VREF V
Output 3-State Current Low (IOZL) 10
Input Voltage Low (VIL) –0.3 0.45 V
Input Voltage Low (VIH) 1.16 VREF+0.3 V
µA
µA
µA
Table 5.4-2 1.8V IO Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
Input Withstanding Voltage Low –0.5 V
Input Withstanding Voltage High 2.3 V
Stresses in excess of the voltage withstanding limits can cause
!
WARNING
permanent damage to the device. These are absolute stress ratings only.
Functional operation of the device is not implied at these or any other
conditions in excess IO characteristics table. Exposure to absolute
maximum ratings for extended periods can adversely affect device
reliability.
LZT 123 1836 35
Page 36

5.5 Grounds
Pin Name Direction Function
1 GND - Ground
3 GND - Ground
5 GND - Ground
7 GND - Ground
9 GND - Ground
11 GND - Ground
96 AREF - Analogue reference
There are two ground connections in the wireless modem, AREF (analogue ground)
and GND (digital ground). Pin assignments are shown in the table above.
AREF and GND are connected at a single point inside the wireless
modem, however they must not be joined together in the user
application.
NOTE
5.5.1 Analogue Ground (AREF)
AREF is the return signal, or analogue audio reference, for AUXI and AUXO. These
two signals provide a single-ended auxiliary audio input (host to module) and output
(module to host). AREF is connected to the common GND inside the wireless modem
only. The application must not connect GND and AREF.
Parameter Limit Unit
Maximum current (I
) 12.5 mA
MAX
LZT 123 1836 36
Page 37

5.5.2 Common Ground (GND)
GND is the reference, or return signal, for all system interface digital signals, radio
section power, and is also the DC return for the power supply, VCC.
User application circuitry should connect all GND pins together in order to carry the
high current drawn by the wireless modem.
Parameter Per Pin Total Unit
Maximum current (I
) 600 3600 mA
MAX
Maximum average current (I
) 100 600 mA
AVG
LZT 123 1836 37
Page 38

5.6 Regulated Power Supply Input (VCC)
Pin Name Direction Function
2 VCC Input DC power
4 VCC Input DC power
6 VCC Input DC power
8 VCC Input DC power
10 VCC Input DC power
12 VCC Input DC power
Power is supplied to the wireless modem VCC pins, from an external source.
User application circuitry should connect all VCC pins together in to carry the current
drawn by the wireless modem.
The electrical characteristics for VCC are shown in the following table.
Parameter Mode Limit
VCC Supply voltage
Nominal 3.6 V
Min 3.2 V
Max 4.5 V
Absolute maximum limit -0.3V to 6.5V
<100mV @<200kHz
Maximum supply ripple
<20mV @>200kHz
Maximum allowable voltage drop Transmission burst 200mV
2100 mA peak
Maximum current consumed Full power (2W) transmit
340 mA average
Stresses in excess of the absolute maximum limits can cause permanent
!
WARNING
damage to the device. These are absolute stress ratings only. Functional
operation of the device is not implied at these or any other conditions in
excess of those given in the normal Min & Max values stated. Exposure
to absolute maximum ratings for extended periods can adversely affect
device reliability.
LZT 123 1836 38
Page 39

The wireless modem has insufficient internal capacitance to supply the
large current peaks during GSM burst transmission - use the following
general guidelines in designing the application power supply.
TIP
Fit a low ESR electrolytic capacitor close to the wireless modem (>1,000
µF, with an ESR < 100 m)
Ensure power supply to wireless modem line resistance is < 200 m
The module has approximately 40µF of internal capacitance across the
VCC pins. During initial power-up the host power supply will have to
CAUTION
charge this capacitance to the operating voltage. This initial in-rush
current may exceed the module’s normal peak current, sometimes
greater than an order of magnitude higher (depending upon the power
supply design) for a short duration (generally a few microseconds).
LZT 123 1836 39
Page 40

5.7 Voltage Reference (VREF)
Pin Name Direction Function
65 VREF Input Host application voltage reference
The GS64 has level shifter circuits on each digital IO interface. This allows
applications with different logic technology to interface to the module without having
to perform voltage level-shifting on the host circuitry. VREF is connected to the hostside level-shifters. This pin must be connected to your digital IO voltage source.
VREF Input
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
VREF input voltage 1.8 5.2 V
VREF load current 0.1 50
µA
Figure 5.7-1 Level shifter arrangement
LZT 123 1836 40
Page 41

5.8 Battery Charging Input (CHG_IN)
Pin Name Direction Function
11 CHG_IN Input Battery charger power
For battery powered applications, the GS64 provides a charge input (CHG_IN) pin to
aid and support battery charging. A typical application would power the wireless
modem directly from a battery source connected to VCC (pins 2, 4, 6, 8, 10) then
provide a dc power source to the CHG_IN connection (pin 11). The GS64 can control
an internal switching FET which creates a charging pathway to the battery. While
power is provided at CHG_IN, the battery charge can be maintained. If the power
should fail or be removed at CHG_IN, the application will be supported by the battery
alone. When CHG_IN voltage returns, the battery charging and maintenance will
commence once more.
The GS64 module supports only one mode of charging, microprocessor supervised
pulsed-charging. Also, the module only supports one battery cell type as standard.
Users may, if they wish, develop charging algorithms and control through the Sony
Ericsson M2mpower Embedded Applications. Users wishing to attempt charging of
battery types not supported by the standard type, indicated in this document, do so
at their own risk.
Battery charging algorithms are unique to different battery types. Sony
Ericsson Mobile Communications will not accept any responsibility or
liability for damage, product failures, even death or injury occurring as
DANGER
a result of incompatible battery and charging algorithms being
applied.
Safety considerations must be taken into account when using the battery charge
function of the GS64; for example, monitoring the temperature of the battery. If the
temperature of the battery exceeds its specification limits, battery charging must be
stopped immediately. If the battery temperature continues to rise the application
should be suspended or the battery disconnected. Battery temperature can be
monitored with a suitable detection circuit, using the GS64 ADC inputs.
When charging Lithium batteries, the battery pack must have an
internal protection circuit in accordance with the manufacturer's
instructions.
CAUTION
LZT 123 1836 41
Page 42

During microprocessor supervised mode, the GS64 takes a current-limited voltage
source at the CHG_IN pin to implement constant-current charging of a single Li-Ion
cell connected to the VCC pins.
CHG_IN
D1
D1
VOLTAGE
VOLTAGE
SOURCE
SOURCE
CHG_IN
C1
C1
TO
TO
uPC
uPC
TIMER
TIMER
TIMER
TIMER
V
V
SUI
SUI
SUI
SUI
REF1
REF1VREF1
CHARGE FET
CHARGE FET
+
+
-
-
BATTERY
BATTERY
BATTERY
BATTERY
CHARGER
CHARGER
CHARGER
CHARGER
CONTROL
CONTROL
CONTROL
CONTROL
3.6V
3.6V
3.6V
3.6V
50mA
50mA
50mA
50mA
MAX CURRENT
MAX CURRENT
DETECTION
DETECTION
ADC
ADC
VCC
VCC
SINGLE
SINGLE
CELL Li-ION
+
+
-
-
V
V
REF2
REF2VREF2
ADIN1
ADIN1
CELL Li-ION
Figure 5.8-1 Typical application for pulse charging a battery
5.8.1 Charging Process
Figure 5.8-1 shows a typical battery charging implementation. The voltage source
must be current limited (500 mA max). A reverse current protection diode prevents
external fault conditions from draining the battery. A small (typ 10µF) capacitor
should be placed close to the CHG_IN pin.
In the application shown, a conditioning phase slowly raises the voltage of a deeply
discharged cell to a level suitable for fast-charging. After cell conditioning is
complete, the microprocessor uses the GS64’S ADC converter to monitor the battery
cell’s status and uses the power management block to control the charge-FET.
LZT 123 1836 42
Page 43

A charge request is initiated when an external voltage source is applied to the CHG_IN
pin. However, before this request is passed to the microprocessor, CHG_IN is verified
to be greater than VCC by 150 mV, and at least 3.7 V. If the latter criteria is not met,
the module limits charging to the conditioning phase. If the former criteria is not met,
the charge request is ignored and all charging is disabled. If the CHG_IN voltage
exceeds the upper limit of 6.3 V it will be detected by the module, but charging is not
inhibited. In this case, however, CHG_IN is outside the normal operating range of the
device, so the software will not initiate charging if CHG_IN > 6.3 V is detected.
The delta between CHG_IN and VCC is continuously monitored; however, the valid to
invalid detection has a delay of 46 ms. When CHG_IN exceeds VCC by 150 mV, it is
considered to be at a valid relative level. It is considered to have an invalid relative
level if it subsequently falls below VCC by 50 mV. If the relative voltage of CHG_IN
goes invalid and remains invalid for the duration of the detection delay, charging is
terminated.
As a safety precaution, the battery cell voltage must be at least 2.5 V before fastcharge is allowed to take place. If the battery cell voltage is less than 2.5 V, it is
considered either deeply discharged or shorted. To protect a Li-ion cell from the
damage that may occur if it is fast-charged from this state, a 3.6 V trickle-charge
source is used to safely condition the battery cell. The conditioning charge current is
limited to 50 mA, which for most Li-ion cells is 10% or less of the recommended CC
fast-charge current. In most instances, the battery cell voltage will be greater than
2.5 V at the time the charge request is initiated, resulting in the conditioning phase
being skipped.
There is always a small chance that the charge management block in
the GS64 power management ASIC will malfunction or fail, which
could lead to over-charging of the battery. It is strongly
CAUTION
recommended that any battery chosen for use with your application
has its own additional integrated over-current and over-voltage
protection.
5.8.2 Series Diode
When charging is disabled, the potential for rapid cell discharge through the body
diode inherent in the Enhancement-mode charging FET, a Schottky diode must be
placed in between the external source and the CHG_IN pin. The diode should have a
forward current and power dissipation rating consistent with its intended use, and a
maximum forward voltage drop of 0.6V.
LZT 123 1836 43
Page 44

5.8.3 Battery Selection
Whilst there are several rechargeable battery technologies commercially available,
including Nickel Cadmium (NiCd), Nickel Metal Hydride (Ni-MH), Lithium-Polymer (LiPolymer) and Lithium-Ion (Li-Ion), the only technology recommended and supported
for use with the GR64 is Li-Ion. Li-Ion provides a good combination of high energy
(3.7v) and long cycle life, which lead to low overall energy cost.
The weight of lithium ion batteries is approximately one half compared with a nickel
cadmium or nickel metal hydride battery of similar capacity. The volume of lithium
ion batteries is 40 to 50% smaller than that of nickel cadmium, and 20 to 30% smaller
than that of a nickel metal hydride.
The lithium ion battery is free from the so-called memory effect, a phenomenon
associated with nickel cadmium in which the apparent battery capacity decreases
when shallow charge and discharge cycles are repeated.
A single lithium ion cell has a voltage of 3.7V (mean value), which is equal to either
three nickel cadmium or nickel-metal hydride cells connected in series. This voltage
is close to the nominal VCC of the GS64 device.
Li-Ion batteries generally provide long storage life with few limiting condition, and
offer problem-free charge after long storage. Under normal conditions, the lithium
ion battery has a life of more than 500 charge/discharge cycles. Also, Li-Ion
batteries have a slow self-discharge rate (typically 1.3% per month, compared with
Ni-MH batteries which can exceed 50% per month).
Lithium ion batteries are environmentally friendly, inasmuch as they do not contain
any heavy metal pollution substances such as cadmium, lead, or mercury.
There are many manufacturers of Li-Ion batteries worldwide. Sony Ericsson make no
recommendations with regard to specific vendors, but here are some considerations
for GS64 users which may prove to be useful in the selection process and
implementation:
Li-Ion batteries marketed for cellular (mobile) phone use may make a good choice
battery manufacturers with heritage in supplying the cellular (mobile) phone industry
could make a good choice, especially for high-volume requirements
look carefully for batteries which are rated at temperatures that the GS64 is likely to
operate at (many batteries are only specified for -20°C to +65°C operation which may
not be sufficient)
LZT 123 1836 44
Page 45

small form-factor (typically handset-sized) Li-Ion battery capacity varies
considerably, some batteries are rated as high as 3200mAh (600mAh to 1800mAH
are more commonly available)
weight is generally not a problem with typical GS64 user application, even so small
form-factor Li-Ion batteries (up to 1800mAh) can vary between 10 to 40 grams
size is generally a factor of capacity, since larger capacity batteries naturally have
more material/cells, and will range between 2750mm
factor Li-Ion batteries
the speed by which lithium-ion ages is governed by temperature and state-ofcharge; high temperatures and deep discharge will effect useful life
if possible avoid frequent full discharges because this puts additional strain on the
battery, partial discharges with frequent recharges are better
never short circuit the terminals of a Li-Ion battery
3
to 18000mm3 for small form-
do not expose Li-Ion batteries to moisture or rain
monitor battery temperature during charging using a thermistor placed on or near the
battery wired to an ADC input on the module
Li-Ion batteries have a higher ESR (compared to Ni-Cd or Ni-MH), although this
should not be a limiting factor for peak current delivery, any battery should be
capable of at least 50% greater than the GS64 demands (~3A pk)
To determine battery life, on a full charge, the following rule of thumb can be
applied:
Standby time = Battery Capacity (mAh) / Idle current (mA)
Call time (voice or data) = Battery Capacity (mAh) / Call current (mA)
Example 1 – Standby time:
A 600mAh rated Li-Ion battery, from fully charged (around 4.2V) to the module cutoff point (3.2V) will provide around 95% of its total charge capacity. For a standby
(idle) current of 18mA, the module will typically provide
600*0.95/18 = 32 hours standby time
LZT 123 1836 45
Page 46

Example 2 – Call time:
An 1800mAh rated Li-Ion battery fully charged, transmitting maximum power on a
low-band (850/900MHz) channel may consume an average 320mA, therefore the
module would typically provide
1800*0.95/320 = 5 hours 20 mins call time
Example 3 – Typical Operation:
A module performing periodic network data transfers and communicating intervallic
status information to its host would spend its non-active periods in sleep mode. If
the module spends 30 mins each day on call (320mA), 30 second each hour
performing housekeeping, monitoring and status tasks (110mA), and sleeps (2.1mA)
during the intervening periods, an 1800mAh rated Li-Ion battery fully charged would
typically provide
1800*0.95/([0.5hr*320]+[0.2hr*110]+[23.3hr*2.1]) = 7 days 6 hrs operation
The above examples are given for guidance, the actual battery life will
depend upon variables such as battery condition, number of previous
charge/discharge cycles, operating temperature, series resistance
CAUTION
between battery and the module, and manufacturing tolerances
LZT 123 1836 46
Page 47

5.9 Powering the Module ON and OFF (PON_L, PON_H)
Pin Name Direction Function
21 PON_H Input Device On/Off control
33 PON_L Input Device On/Off control
The GS64 offers two hardware methods to power up and down the module.
The PON_L signal utilizes a momentary switching mechanism to alternate between
power-on and power-off sequences. PON_L is held high to VCC by an internal pullup resistor. The user asserts PON_L by pulling this signal low for a pre-defined
period to initiate powering-on of the module. The user re-asserts PON_L with a
subsequent low transition, which is held low for a pre-defined period, to power-off
the module.
The PON_H signal is designed to be pulled high and maintained high for the power on
period. PON_H is held low by an internal pull-down resistor. The user asserts PON_H
by pulling this signal high to VCC in order to initiate powering-on of the module,
then maintains it constantly high during normal use. A subsequent de-assertion,
marked by a transition of PON_H from high to low, and then maintaining the signal
low, will initiate the power-off process.
Only one input should be exercised for each Power-on to Power-off event.
5.9.1 VREF as a Power Indicator
Presence of the VREF signal can be used as a useful indicator that power-on has been
successfully initiated. The absence of VREF can be used a successful indicator that
the power-off sequence is complete.
The initial presence of VREF indicates that the LDOs are powered, however the
module will be establishing network connectivity and registration at this point.
Communications between the host application and the module can commence shortly
thereafter, however completion of the network registration will be sometime
afterwards (the period is dependent upon network loading at the time of attempted
registration).
Once the power-off sequence has been initiates, shutting-down the LDOs is the last
action in the process. The absence of VREF is an indication that network deregistration and shut-down is complete.
LZT 123 1836 47
Page 48

5.9.2 Module On & Off Sequence
Figure 5.9-1 shows typical powering-on and powering-off sequences, using the two
optional hardware interfaces.
Figure 5.9-1 Typical Power-On & Power-Off Sequences
Event Description
A VCC is applied to the module, PON_L is pulled high internally
B PON_L is pulled low by the user application, initiating a power-on sequence
C VREF presence indicates a successful power-on initialization
D PON_L is pulled low by the user application, initiating a power-off sequence
E VREF absence indicates network de-registration and shut-down complete
F VCC can be safely removed
G VCC is applied to the module, PON_H is pulled low internally
H PON_H is pulled high & retained high, initiating a power-on sequence
I VREF presence indicates a successful power-on initialization
J PON_H is released, initiating a power-off sequence
K VREF absence indicates network de-registration and shut-down complete
L VCC can be safely removed
LZT 123 1836 48
Page 49

5.9.2.1 Power On Timing
Figure 5.9-2 Power On timing using PON_L as an example
The GS64 power On sequence is shown above using PON_L as an example. The
significant signals are VCC, P_ON and VREF, shown by solid lines. The other signals
(in dashed lines) are internal to the module and are shown for reference purposes
only.
Initially, power is supplied to the VCC pins. The presence of power raises the PON_L
through a pull-up resistor to VCC potential. In order to power the module, PON_L is
pulled to ground. Once PON_L has been held low for 125ms (denoted by t
primary LDOs power up, including the VREF output. VREF exceeds it’s reset threshold
approx 500µs later, then 250ms afterwards (denoted by t
) the
2
RESET
line goes high.
The microprocessor can latch the power-on state by setting the power keep
(PWR_KEEP)
high after the
RESET
goes high and before the power on (PON_L) signal is
released.
It is recommended that P_ON is held low for at least 450ms to guarantee completion
of the power up sequence.
) the
1
LZT 123 1836 49
Page 50

The PON_H signal has a similar effect at the point of assertion. The power-on timing
sequence is the same, provided PON_H remains high. PON_H has to remain high in
order for the module to function.
5.9.3 Turning the Module Off
Figure 5.9-3 Power Down timing
The GS64 power down sequence is shown above. The significant signals are VCC,
PON_L and VREF, shown by solid lines. The other signals (in dashed lines) are internal
to the module and are shown for reference purposes only.
With the module powered normally, PON_L is pulled-up to VCC potential. In order to
power down the module, PON_L is pulled to ground. Once PON_L has been held low
for at least 125ms the shut-down procedure begins. Although PON_L can be held
low for longer, it will delay completion of the shut-down event. If the module is
registered on a GSM network, the de-registration process will complete; this may last
between 3 to 30 seconds. The power latch (PWR_KEEP) is released and approximately
70ms later the LDO outputs fall, as indicated by the removal of the VREF output.
Once VREF is no longer present, the application can safely remove VCC.
In order to turn the module off using the PON_H signal, the signal is released. The
power-off timing sequence is the same, provided PON_H remains low.
LZT 123 1836 50
Page 51

The RTC can continue to operate even though VCC is removed,
provided that a sufficiently charged backup device is connected to the
VRTC. Refer to section 5.21.1 for details.
NOTE
The relevant characteristics of the ON/OFF Power control interface are shown in the
table below.
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Input current
PON_L
PON_H
Input low=0V, VCC=3.6V -60 -25 -12
Input high =VCC, VCC=3.6V 0 1
Input low=0V, VCC=3.6V -1 0
Input high =VCC, VCC=3.6V 8 20 60
µA
µA
µA
µA
LZT 123 1836 51
Page 52

5.10 Analogue Audio
Pin Name Direction Function
92 AUXIP Input Differential auxiliary audio to module from host (pos)
93 AUXIN Input Differential auxiliary audio to module from host (neg)
94 AUXOP Output Differential auxiliary audio to host from module (pos)
95 AUXON Output Differential auxiliary audio to host from module (neg)
96 AREF - Analogue reference
97 MICIP Input Microphone input positive
98 MICIN Input Microphone input negative
99 EARP Output Earpiece output positive
100 EARN Output Earpiece output negative
The analogue audio signals comprise of two audio inputs to the module, and two
audio outputs from the module. Both sets of audio interfaces are differential.
Analogue audio can be used for various configurations, including a car kit mode,
portable hands free and speakerphone (with an additional output gain stage).
Five audio profiles are available for GS64 users to configure various modes of
operation. Each profile is factory set to represent different modes, typical of general
usage. The customer can modify profiles to optimize acoustic performance to their
specific application.
The analogue inputs and outputs share common uplink and downlink chains which
are multiplexed, and selectively switched by the user through AT-commands.
There are five factory-set audio profiles as follows:
• portable hands free
• handset
• car kit
• speakerphone
• headset
Portable hands free is the factory-set default profile. The modification, configuration,
manipulation and storage of audio profiles is achieved with the AT*E2EAMS (Audio
Profile Modification) and AT*E2APR (Audio Profile).
LZT 123 1836 52
Page 53

5.10.1 Auxiliary Audio To Mobile Station (AUXIP, AUXIN)
AUXI is a differential auxiliary analogue audio input to the wireless modem.
Internally, the signal is routed to the CODEC (COder/DECoder), where it is converted
to digital audio and mapped to an internal bus.
All sources must be AC-coupled to avoid attenuation of low frequencies. Use a
capacitor greater than the value shown in the table below.
The AUXI input is a passive network followed by the transmit part of the CODEC.
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Input voltage full scale
max input gain 142 158 178 mVrms
min input gain 447 501 564 mVrms
Frequency response -3dB cut-off 300 3400 Hz
Output dc bias level 2.16 2.4 2.64 V
AC coupling capacitance 1
5.10.2 Auxiliary Audio From Mobile Station (AUXOP, AUXON)
The auxiliary output is a differential analogue audio output from the wireless modem
and may be used to drive a speaker or an earpiece. The interface has an internal
100nF coupling capacitor; a load of 10kohm will provide a near full-scale output
capability between 300 to 4300 Hz.
The table below shows the audio signal levels for AUXO.
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Output voltage full scale RL =10k 670 750 840 mVrms
Frequency response -3dB cut-off (RL =10k) 225 Hz
µF
LZT 123 1836 53
Page 54

5.10.3 Microphone Signals (MICIP, MICIN)
MICP and MICN are balanced differential microphone input pins. These inputs are
compatible with an electret microphone. The microphone contains a FET buffer with
an open drain output, which is supplied with at 2.4V ±10% relative to ground by the
wireless modem as shown below.
Figure 5.10-1 Microphone connections to the wireless modem
The input low-noise amplifier stage is constructed out of standard low-noise op
amps. External resistors set the gain of this stage.
The input gain is scaled by the input resistors to be around 18, which provides
optimal performance for many standard types of electret microphones. The module
provides a microphone bias at 2.4V, and can supply at least 1mA of current.
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
max input gain 14 16 18 mVrms
Input voltage full scale
min input gain 45 50 56 mVrms
Frequency response -3dB cut-off 300 3400 Hz
Output dc bias level 2.16 2.4 2.64 V
LZT 123 1836 54
Page 55

5.10.4 Speaker Signals (EARP, EARN)
EARP and EARN are the speaker output signals. These are differential-mode outputs.
With a full-scale PCM input to the CODEC, 0 dB audio output gain setting, and a
differential load RL = 30Ω, the output voltage between EARP and EARN is 1.5 V rms.
For load resistances less than 30Ω, the full-scale output needs is limited using the
modules internal programmable gain attenuator.
The electrical characteristics are given in the table below.
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
RL = 30 1.34 1.5 1.68 Vrms
Input voltage full scale
Frequency response -3dB cut-off 300 3400 Hz
5.11 PCM Digital Audio (SSP)
Pin Name Direction Function
66 PCMCLK In/Out Serial PCM clock
67 PCMFS In/Out Serial PCM frame synchronization
68 PCMDTM Input Serial PCM data to module from host
69 PCMDFM Output Serial PCM data from module to host
The SSP (Synchronous Serial Port) digital interface is configured to provide a PCM
(digital) audio interface. This interface can be used to process PCM digital audio
signals as an alternative to routing signals to the CODECs through the analogue
uplink and downlink chains.
RL = 16 1.41 Vrms
RL = 8
1.24 Vrms
5.11.1 PCM Data Format
The PCM digital audio interface for GS64 is based upon the Texas Instruments SSI
standard. The SSP is a versatile interface which can be programmed for different
clock rates and data frame sizes between 4 to 16 bits.
LZT 123 1836 55
Page 56

PCMCLK (bit clock) and PCMSYNC (frame synchronization) are both generated by the
DSP within the wireless modem. The DSP within the wireless modem in this instance
is the master for all external PCM, so clocks and data from external devices must be
synchronized to it.
For standard GSM voice a 13-Bit PCM data word is embedded in a 16-bit word frame,
as shown in Figure 5.11-1 below.
sample LSB justified
sample LSB justified
LSBMSB
LSBMSB
D15
D15
13-bit sample occupies these frame bits
13-bit sample occupies these frame bits
Figure 5.11-1 Typical 16-bit PCM Voice Sample Word Format
Typical PCM data transfer is shown in the following figures.
D0
D0
SSPCLK
SSPCLK
SSPFS
SSPFS
SSPDTM
SSPDTM
SSPDFM
SSPDFM
SSPCLK
SSPCLK
SSPFS
SSPFS
SSPDTM
SSPDTM
SSPDFM
SSPDFM
Q
Q
LSB
MSB
MSB
Q
Q
MSB
MSB
LSB
LSB
LSB
Figure 5.11-2 PCM Frame format for a single transfer
LSB
LSB
LSB
LSB
LSB
MSB
MSB
MSB
MSB
LSB
LSB
LSB
MSB
MSB
MSB
MSB
Frame nFrame n-1 Frame n+1
Frame nFrame n-1 Frame n+1
Figure 5.11-3 PCM Frame format for a continuous transfer
LZT 123 1836 56
Page 57

5.12 Serial Data Interfaces
The serial channels consist of two UARTs and a USB port. These provide
communication links to the application or accessory units.
The serial channels can be used in differing configurations, depending upon the users
requirements and application. In practice, both UARTs can be configured as either
the control interface or the logging interface. Similarly, control and logging can be
carried out simultaneously on the USB interface. However, the common (default)
configuration options are described:
UART1 has full RS-232 functionality and is used for all on- and off –line
communication (modem sleep & wake functional control is an integral component of
this interface). Its intended use is that of the primary command (AT) interface.
UART2 behaves as a general-purpose serial data link. It can be used for data logging
and de-bugging purposes. It can also be used as a data interface to peripheral
devices, such as a GPS receiver.
The USB port provides a convenient general purpose peripheral (slave) port for use
with host devices which have USB controllers.
5.12.1 UART1
Pin Name Direction Function
53 RI Output Ring Indicator
54 DCD1 Output Data Carrier Detect (UART1)
55 DTR1 Input Data Terminal Ready (UART1)
57 RTS1 Input Ready To Send (UART1)
58 CTS1 Output Clear To Send (UART1)
59 DTM1 Input Data To Module from host (UART1)
60 DFM1 Output Data From Module to host (UART1)
56 DSR1 Output Data Set Ready (UART1)
UART1 is a full featured Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter providing fullduplex asynchronous communication.
LZT 123 1836 57
Page 58

UART1 has the following features :
• 32 bytes of FIFO for both receive and transmit
• FIFO threshold interrupts
• 1 start bit, 7 or 8 data bits, 1 optional parity bit, 1 or 2 stop bits
• Programmable baud rate
• Auto-configuration mode with auto-baud and auto-format operation
• Hardware flow control
• Software flow control.
UART1 signals replicate a 9-pin RS232 (V.24) serial port. However, UART1 signal
levels are not compliant with the RS232 (V.28) standard. Conversion between the
wireless modem CMOS levels and RS232 levels can be achieved using a standard
interface IC, such as the Maxim Integrated Products MAX3237. The relationship
between the levels is shown in the table below.
DTM, DFM RI,RTS,CTS,DSR,DTM,DCD RS232 level GS64 level
1 OFF <-3V VREF-0.4V
0 ON >+3V 0.4V
5.12.2 Serial Data Signals (DTM1, DFM1)
The default baud rate of the UARTs is auto-baud. Baud rates of between 600 bauds
to 460 kbauds are possible. The wireless modem also supports 3GPP TS27.010
multiplexing protocol, which starts when the appropriate command is sent.
5.12.2.1 Serial Data From Wireless modem (DFM1)
DFM1 is an output signal that the wireless modem uses to send data via UART1 to the
host application.
LZT 123 1836 58
Page 59

5.12.2.2 Serial Data To Wireless modem (DTM1)
DTM1 is an input signal, used by the application to send data via UART1 to the
wireless modem.
5.12.3 Control Signals (RTS1, CTS1, DTR1, DSR1, DCD1, RI)
Depending upon the user application, some, all, or none of the control signals may be
needed. Each of the control signals can alternatively be configured as a general
purpose IO. When hardware flow control is not used in communications between the
application and the wireless modem, some applications may require RTS and CTS to
be connected to each other at the wireless modem. Users should familiarize
themselves with the specific implementation of their UART.
The GS64 has a feature in which sleep (lower power) mode can be controlled through
a special handshake protocol using hardware flow control. Details of this protocol
and the AT commands associated with it are contained in a special Application Note,
obtainable through your normal customer support channel.
UART1 converted signals, together with GND, DTM1 and DFM1 form a 9-pin RS232
data port.
5.12.3.1 Hardware flow control RTS1 and CTS1
RTS and CTS provide a hardware flow control mechanism.
5.12.3.2 Request to Send (RTS1)
RTS is used to condition the DCE for data transmission. The default level is high by
internal pull up. The application must pull RTS low to enable data transmission from
the wireless modem. Similarly, the wireless modem asserts CTS low, indicating it is
ready to receive data transmission from the host.
5.12.3.3 Clear To Send (CTS1)
CTS is asserted by the DCE to indicate that the host (DTE) may transmit data. When
CTS is high, the host (DTE) is not permitted to transmit data. The table below shows
the load characteristics for this signal.
LZT 123 1836 59
Page 60

5.12.3.4 Data Terminal Ready (DTR1)
DTR indicates that the DTE is ready to receive data. It also acts as a hardware ‘hangup’, terminating calls when switched high. The signal is active low. Users can define
the exact behavior of DTR with an the AT&D command. DTR1 is used as an optional
sleep control mechanism when the module is configured appropriately.
5.12.3.5 Data Set Ready (DSR1)
DSR indicates that the DCE is ready to receive data. The signal is active low. Behavior
is controlled using the AT&S command. DSR1 is used as an optional sleep control
mechanism when the module is configured appropriately
5.12.3.6 Data Carrier Detect (DCD1)
DCD indicates that the DCE is receiving a valid carrier (data signal) when low.
Behavior is controlled using the AT&C command.
5.12.3.7 Ring Indicator (RI)
RI indicates that a ringing signal is being received by the DCE when toggled low.
Users can define the exact behavior of RI with an AT command, including the option
of asserting the RI signal to flag an incoming SMS by using the AT*E2SMSRI
command.
LZT 123 1836 60
Page 61

5.12.4 UART2 (DTM2, DFM2)
Pin Name Direction Function
61 RTS2 Input Request To Send (UART2)
62 CTS2 Output Clear To Send (UART2)
63 DTM2 Input Data To Module from host (UART2)
64 DFM2 Output Data From Module to host (UART2)
UART 2 consists of a full duplex serial communication port with transmission,
reception lines and hardware flow control.
Timing and electrical signals characteristics are the same as for UART1, DTM1 and
DFM1, including the baud rate range and the capability to auto-baud.
5.12.4.1 Transmitted Data (DTM2)
DTM2 is used by the application to send data to the wireless modem via UART2. It
has the same electrical characteristics the equivalent signal in UART1.
5.12.4.2 Received Data (DFM2)
DFM2 is used to send data to the application via UART2. It has the same electrical
characteristics as the equivalent signal in UART1.
5.12.4.3 Request to Send (RTS2)
RTS is used to condition the DCE for data transmission. It has the same electrical
characteristics as the equivalent signal in UART1.
5.12.4.4 Clear To Send (CTS2)
CTS is asserted by the DCE to indicate that the host (DTE) may transmit data. It has
the same electrical characteristics as the equivalent signal in UART1.
LZT 123 1836 61
Page 62

5.12.5 USB
Pin Name Direction Function
35 USBDP In/Out USB data positive
36 USBDN In/Out USB data negative
34 VUSB Input USB DC power
The USB interface is compliant with the USB2.0 standard for a full speed (12Mbps)
endpoint device. Together with VUSB (the USB transceiver DC power) and GND it
creates a standard USB 4-pin interface. VUSB (VBUS in the USB standard) is nominally
5.0V.
The USB interface has the following features
• Full-speed (12 Mbits/s) device operation
• 16 unidirectional endpoints
• Each endpoint capable of supporting control, interrupt, isochronous and bulk
transfer
• Programmable endpoint types and FIFO sizes and internal 1120-byte logical
(2240-byte physical for dual-packet mode) shared FIFO storage allow a wide
variety of configurations.
• Dual-packet mode of FIFOs reduces latency
• USB reset can be programmed to clear device address.
• Firmware ability to wake up and reset a suspended device
• 8, 16, 32, and 64-byte FIFO sizes for non-isochronous transfers
• 64, 256, 512, and 1024-byte FIFO sizes for isochronous transfers
• Firmware downloading
• Trace debug port for module diagnostics
The USB interface supports 3GPP TS 27.010 multiplexing, and may be used as the
primary AT-command interface.
Internally, the USBDP line is pulled up by a 1.5K resistor, in accordance with the USB
standard, to indicate that it’s a full-speed capable device to the USB controller.
To implement successful applications using the GS64 USB interface, users should
familiarize themselves with the USB specification.
LZT 123 1836 62
Page 63

5.12.6 SIM Card Interface
Pin Name Direction Function
14 SIMVCC Output 1.8V or 3.0V SIM card supply
15 SIMRST Output SIM card reset signal
16 SIMCLK Output SIM card clock signal
17 SIMDAT In/Out SIM card data
18 SIMDET Input SIM presence detection
This interface allows the user to communicate with the smart (SIM) card in the user
application. The GS64 offers alternative arrangements for accessing the SIM
depending on which variant of the GS64 is used. Both variants provide this interface
through the system connector, referred to as the
distinguish it from the integrated SIM interface.
The maximum distance between the SIM card holder and the wireless modem is
70cm. SIM holders placed further than this distance may not meet the SIM interface
performance specification.
external
or
remote
SIM interface to
This SIM interface allows the use of 3 V and 1.8 V SIM cards. The module does not
support 5V SIM cards. The wireless modem automatically detects the SIM type,
switching the signal voltages accordingly. SIM voltage levels, as shown in the
following table, are dependent on the type of SIM card detected by the wireless
modem.
Signal Parameter Mode
SIM supply voltage
1.8V 1.71 1.8 1.89 V
Min Typ Max Unit
3.0V 2.75 2.9 3.05 V
SIMVCC
Short circuit current 10 50 mA
Quiescent Supply Current 3.0V 20
Output Capacitance 0.3 2
µA
µF
Output Capacitor ESR 0.01 1.0
High level input voltage (VIH)
1.8V 0.7xSIMVCC V
3.0V 0.7xSIMVCC V
Low level input voltage (VIL)
SIMDAT
High level output voltage (VOH)
1.8V 0.2xSIMVCC V
3.0V 0.4 V
1.8V 0.8xSIMVCC V
3.0V 0.8xSIMVCC V
Low level output voltage (V
1.8V 0.4 V
)
OL
3.0V 0.4 V
LZT 123 1836 63
Page 64

Signal Parameter
High level output voltage (VOH)
SIMCLK
SIMRST
Low level output voltage (V
5.12.7 SIM Detection (SIMDET)
SIMDET is used to determine whether a SIM card has been inserted into or removed
from the SIM card holder. You should normally wire it to the ‘card inserted switch’ of
the SIM card holder, but different implementations are possible.
When left open, an internal pull-up resistor maintains the signal high and means ‘SIM
card missing’ to the wireless modem. When pulled low the radio device assumes a
SIM card is inserted. SIMDET is a Digital IO signal.
In order to meet regulatory approval requirements, the SIMDET
function must be implemented in the host application.
Mode Min Typ Max Unit
1.8V 0.9xSIMVCC V
3.0V 0.9xSIMVCC V
1.8V 0.4 V
)
OL
3.0V 0.4 V
NOTE
5.13 Synchronous Serial Port (SSP) Interface [to be implemented in a future release]
Pin Name Direction Function
70 SSPCLK In/Out SPI clock
71 SSPFS In/Out SPI frame synchronization
72 SSPDTM Input SPI data to module from host
73 SSPDFM Output SPI data to host from module
The SSP interface provides a synchronous serial peripheral interface based on the
Motorola SPI protocol.
The SSPI interface operates in a single master mode only, with the module acting as
master. Four clock rates are supported through programming; 1.5MHz, 800kHz,
400kHz, 200kHz. The interface supports a variable word size, between 4bits to 16
bits. Continuous Transfer modes are not supported.
The SSP supports programmable data sizes of 4 bits to 16 bits, in addition to which
the polarity of the clock signal to the SPCLK pin is programmable through a register.
LZT 123 1836 64
Page 65

5.14 Memory Card Interface (SD/MMC) [to be implemented in a future release]
Pin Name Direction Function
74 MMCCLK Output SD/MMC card clock
75 MMCCMD In/Out SD/MMC card command/response
76 MMCDAT0 In/Out SD/MMC card data 0
77 MMCDAT1 In/Out SD/MMC card data 1
78 MMCDAT2 In/Out SD/MMC card data 2
79 MMCDAT3 In/Out SD/MMC card data 3
80 MMCMD_EN Output SD/MMC card command enable
81 MMCDAT_EN Output SD/MMC card data enable (data 1-3)
82 MMCDAT_EN0 Output SD/MMC card data enable (data 0)
SD/MMC interface module acts as either a multimedia card bus host or a secure
digital memory card bus host. The interface conforms to the following standards:
• Multimedia Card Specification v2.11
• Secure Digital Memory Card Physical Layer Specification v0.96
The SD/MMC interface provides around 800kbps net throughput.
The SD/MMC interface, like all IO in the module, is 1.8V. In order to interface to
some SD/MMC devices based on 3V technology it is necessary to level shift these
signals for compatibility purposes. The MMC MD & DAT enable signals (pins 80, 81,
82) are provided to configure level shifters for directivity, which may be used with the
Agere PSC2217 level shifter for example. There are other means of level shifting
using bi-directional level shifters which do not require direction pins, such as:
• Philips GTL2002, 2-bit bidirectional low voltage translators
• Maxim MAX3001E, 8-channel bidirectional level translators
5.14.1 Multimedia Card System
The multimedia card system transfers commands and data using three signal lines on
a single physical bus:
LZT 123 1836 65
Page 66

• MMCCLK: One bit is transferred on both command and data lines with each clock
cycle. The clock frequency varies between 0 MHz and 20 MHz for a multimedia
card.
• MMCCMD: Bidirectional command channel that initializes a card and transfers
commands. CMD has two operational modes; open-drain for initialization and
push-pull for command transfer. This depends on speed requirements for the
command channel during the initialization phase; external open-drain pull-up
resistor may be needed if the 200 k internal pull-up resistor is too large.
• MMCDAT: Bidirectional data channel, operating in push-pull mode.
5.14.2 Secure Digital Memory Card System
The secure digital memory card system consists of the host and cards connected in a
star topology. Multimedia cards and secure digital memory cards can be used in the
same system. The power supply can be provided by the host or level-shifter devices
such as Agere’s PSC2217.
The following signals are used on the secure digital memory card bus:
• MMCCLK: Host to card clock signal.
• MMCCMD: Bidirectional command/response signal (one per card if multiple cards
are connected to the bus, in which case, bus multiplexing logic is required).
• MMCDAT[3:0]: Bidirectional data signals (one set per card).
• VDD, VSS: Power and ground signals provided by the host or level translator
product.
The MCI (Multimedia Card Interface) does not contain bus multiplexing logic. If more
than one secure digital memory cards needs to be supported, the user must
implement bus multiplexing logic with external components.
LZT 123 1836 66
Page 67

5.15 Service/Programming
Pin Name Direction Function
20 SERVICE Input Flash programming enable signal
The SERVICE interface is a standard IO, configured internally as an Input. This input is
activated in order to enable flash memory programming. The SERVICE interface is
normally pulled HIGH and is made active by the host application pulling it LOW.
There are two methods for updating the firmware in the GR64: Sony
Ericsson Emma III and Updater. The Emma III system is a web based
tool that accesses a Sony Ericsson server from which signed software
NOTE
can be downloaded. The Updater is a local application that downloads
a signed image provided by SEMC.
5.16 LED [to be implemented in a future release]
Pin Name Direction Function
37 LED1 Output LED control signal
38 LED2 Output LED control signal
The LED driver interface is able to operate single LEDs or a series of LEDs (such as
LED backlighting). The LED interfaces are driven by programmable current sources,
designed to control the brightness of the LEDs connected to them (typical of
keyboard or LCD illumination).
LED1 can be programmed to sink up to 75mA or 150mA in nonlinear steps over two
ranges of output. LED2 can be programmed to sink from up to 50mA or 100mA in
nonlinear step over two ranges of outputs. Both LED drivers are capable of sinking
their maximum output current at a worst-case maximum output voltage of 0.4 V. For
efficient use, the LEDs should be forward connected between the main battery and
their corresponding LED driver output.
LZT 123 1836 67
Page 68

The LED drivers require no supporting components, eliminating the need for currentlimiting resistors. The LED outputs should be programmed to values consistent with
their rated values. If desired, both LED outputs can be ganged together to provide a
maximum single LED driver sink capability of 250mA.
Figure 5.16-1 Typical circuit for LEDs
LZT 123 1836 68
Page 69

5.17 General Purpose IO
All general purpose IO (GPIO) is programmable by the user. Some GPIO signals are
dedicated, other GPIO can be configured as an alternative to other signal functionality
if it is not required by the user. GPIO which has alternate functionality is effectively
multiplexed, so that the user chooses through AT commands the appropriate
configuration for their application.
Dedicated IO
Pin Name Default Alternate Function
40 GPIO1 GPIO1 None
41 GPIO2 GPIO2 None
43 GPIO3 GPIO3 None
44 GPIO4 GPIO4 None
45 GPIO5 GPIO5 None
48 GPIO6 GPIO6 None
49 GPIO7 GPIO7 None
50 GPIO8 GPIO8 None
51 GPIO9 GPIO9 None
Configurable IO
Pin Name Default Alternate function
74 GPIO10 MMCCLK SD/MMC card clock
75 GPIO11 MMCCMD SD/MMC card command
76 GPIO12 MMCDAT0 SD/MMC card data
77 GPIO13 MMCDAT1 SD/MMC card data
78 GPIO14 MMCDAT2 SD/MMC card data
79 GPIO15 MMCDAT3 SD/MMC card data
80 GPIO16 MMCMD_EN SD/MMC card command enable
81 GPIO17 MMCDAT_EN SD/MMC card data enable (1-3)
82 GPIO18 MMCDAT_EN0 SD/MMC card data enable (0)
83 GPIO19 KEYROW1 Keyboard row 1
84 GPIO20 KEYROW2 Keyboard row 2
85 GPIO21 KEYROW3 Keyboard row 3
86 GPIO22 KEYROW4 Keyboard row 4
87 GPIO23 KEYROW5 Keyboard row 5
88 GPIO24 KEYCOL1 Keyboard row 1
89 GPIO25 KEYCOL2 Keyboard row 2
90 GPIO26 KEYCOL3 Keyboard row 3
LZT 123 1836 69
Page 70

91 GPIO27 KEYCOL4 Keyboard row 4
Regular (dedicated) IO and alternate function IO have exactly the same characteristics
and can be programmed in the same way. The use of alternate function IO is subject
to some degree of limitation:
Signals which are assigned SD/MMC functionality are controlled by a single register
bit so that all nine signals are allocated to either memory card or GPIO; it not possible
individually allocate function.
Signals which are assigned keyboard functionality can be re-allocated GPIO
functionality on a pin-by-pin basis, providing anything from 1 to 9 additional GPIO.
Signals defined as keyboard functions are programmed to generate interrupts,
however the same pins programmed as GPIO do not have interrupt capability
associated with them.
GPIO is programmable for the following features
• either an input or output
• level-sensitive or transition-sensitive
• open drain or direct drive
• polarity (inversion)
• internal pull-up resistors
Signal labeled in the
Configurable IO
table which are not being used for the indicated
alternative function be used as general purpose inputs or outputs; they are not
constrained to work in only one direction.
GPIO has a number of sharing (configuration) options. Sharing means that it is not
feasible to operate all the alternative features concurrently, however, with care,
dynamic switching from one feature to another is possible.
5.17.1 Embedded Applications
When a particular IO feature is required, the user sets the state of the relevant IO
blocks by disabling one set before enabling others.
LZT 123 1836 70
Page 71

The wireless modem checks the state of the IO when the user requests a new
function. The new function is rejected if the current function is not released first.
The states of GPIO
n
to GPIOm are retained for the next power up. For example,
inputs remain as inputs and outputs remain as outputs. The voltage of a defined
output pin will still drop to 0 Volts in the wireless modem power down state.
LZT 123 1836 71
Page 72

5.18 Keyboard Signals (KEYROW, KEYCOL)
Pin Name Direction Default Function
83
84
85
86
87
KEYROW1 Input
KEYROW2 Input
KEYROW3 Input
KEYROW4 Input
KEYROW5 Input
Keyboard row 1
Keyboard row 2
Keyboard row 3
Keyboard row 4
Keyboard row 5
88 KEYCOL1 Output Keyboard row 1
89 KEYCOL2 Output Keyboard row 2
90 KEYCOL3 Output Keyboard row 3
91 KEYCOL4 Output Keyboard row 4
The keyboard interface consists of 9 programmable IO pins that are configured for
use in scanning a keyboard/keypad. The maximum sized keyboard matrix achievable
is 5 x 4. Keyboard inputs must be active for a selectable minimum pulse-width
before interrupt generation occurs in the key-press detection process.
Pins that are not needed for the keyboard can be used as programmable IO, as
described in section 0.
The default keyboard configuration is shown in the
Default Function
column of the
table above. Users wishing to configure the keyboard interface differently or as GPIO
should obtain a separate Application Note describing keyboard and GPIO
programming from Sony Ericsson through Customer Support.
5.19 Analogue to Digital Converters (ADIN1, ADIN2, ADIN3, ADIN4)
Pin Name Direction Function
27 ADIN1 Input ADC Input 1
28 ADIN2 Input ADC Input 2
29 ADIN3 Input ADC Input 3
30 ADIN4 Input ADC Input 4
LZT 123 1836 72
Page 73

The module has a single precision 10-bit ADC, shared by a number of functions
within the module and also through the external interface connections. The ADC
sharing arrangement is shown below.
Figure 5.19-1 ADC sharing arrangement
ADC sampling frequency and sampling source selection can be set up and controlled
with AT-commands by the user. ADC samples requires up to 5 clock (ADCLK) cycles
to process. The ADC also performs some system-level sampling. These two factors
limit the maximum practical sampling rate to around 12ksps.
Table 5.19-1 ADC Interface Characteristics
Parameter Condition
Min Typ Max Unit
Resolution 10 bit
Coding: Unsigned Magnitude 000 3FF Hex
Differential Nonlinearity –1 1 lsb
Integral Nonlinearity –10 10 lsb
Full-scale Error –3 3 %
Offset Error –14 14 lsb
Conversion Gain* 421 lsb/V
Conversion Intercept* –9 lsb
Low-level Input Voltage ADC output=000h
High-level Input Voltage ADC output=3FFh 2.45 2.59 V
ADC Clock (ADCLK) 260 325 390 kHz
ADC Conversion Time 12 ADCLK
ADC Sample Delay 5 ADCLK
LZT 123 1836 73
Page 74

5.20 Burst Transmission (TX_ON)
Pin Name Direction Function
39 TX_ON Output Transmit indication
Burst transmission is the period during which the GSM transceiver is transmitting RF
signals. TX_ON is an indicator that the module is transmitting.
A typical application may use TX_ON to blank adjacent receiver circuitry as a means of
protecting sensitive input stages.
5.21 Real Time Clock
The real-time clock (RTC) is driven by a 32.768 kHz clock from an internal crystal
oscillator. The clock is divided by 32,768 to generate a clock with a 1 second period
that increments a 29-bit seconds counter. In addition, it can generate interrupts at a
programmed time. The following are the features of RTC:
• 17-year time interval with 1 second resolution.
• Programmed time alarm interrupt
• Alarm output pin
An RTC alarm can be set by using the AT-command AT+CALA.
The RTC relies on an uninterrupted 1.5 V (nominal) power supply (VRTC), whether the
module is powered off or on. The RTC alarm operates from the VRTC supply, and
therefore utilize 1.5 V logic. Users have the responsibility to provide a backup
battery to provide uninterrupted VRTC function when the module is powered down.
RTC Accuracy
Parameter
RTC accuracy Ambient (+25±2°C) operation
RTC accuracy Extreme temperatures
Condition Max Unit
52.6
65.2
Secs/month
Secs/month
LZT 123 1836 74
Page 75

5.21.1 Real Time Clock Backup Supply (VRTC)
Pin Name Direction Function
31 VRTC Input DC supply for real time clock
VRTC provides an input connection to the module which allows the user to power the
real time clock (RTC) within the GS64 by way of a coin cell or charged capacitor.
When the module is powered, an internal LDO regulator provides a 200µA source
designed to supply the microprocessor’s RTC block. It is also intended to recondition
a rechargeable coin cell that supplies the RTC module when the main battery is
removed, or has insufficient energy. Because this LDO is always on, even when the
module is powered down, it features very low quiescent current. It also offers reverse
current protection, with low leakage, when the coin cell is powering the RTC block.
The RTC LDO is primarily designed to charge manganese-silicon lithium batteries.
Rechargeable coin cells with different chemical composition may also be charged,
provided their charging requirements are consistent with the RTC LDO’s electrical
characteristics. The VRTC output is nominally 1.5 V.
VRTC LDO characteristics
Parameter Condition
IOUT
Output Voltage Tolerance
= 10 µA
Maximum Output Current 200
Min Typ Max Unit
1.45 1.5 1.55 V
µA
Short-circuit Current Limit VRTC to GND 0.7 1.6 2.9 mA
Output Resistance
Line Regulation
Off Reverse Leakage Current 0.1 1
IOUT = 10 µA
IOUT = 10 µA
75 100 150
5 mV
µA
In the backup condition the RTC block will function to as low as 1.1V on the VRTC
pin. The RTC draws 10µA typically during powered backup (15µA max).
Figure 5.21-1 shows the VRTC connectivity arrangement.
LZT 123 1836 75
Page 76

5.21.2 RTC Alarm (ALARM)
Figure 5.21-1 VRTC connection
Pin Name Direction Function
32 ALARM Output RTC Alarm
The Alarm output is logic output from the module which is supplied from the RTC
circuitry block. This block is in turn supplied either from the main supply of the
module or from a backup battery if the main supply is not available.
5.21.2.1 ALARM Output from the Module
The ALARM time is set by the use of an AT-command. The output is normally at
VRTC level and will go low for one second when the ALARM becomes active.
Since the VRTC interface is operable down to 1.1V, transistor circuitry must be used
on the host side. It is recommended that integrators use an FET to minimize current
consumption. If a suitable FET, operating at the low voltage necessary, cannot be
found then bi-polar must be used. The resistors shall be kept as high impedance as
possible to minimize current consumption.
LZT 123 1836 76
Page 77

Figure 5.21-2 Typical host-side circuit for ALARM output
VRTC is specified to work down to 1.1V across the environmental operating
conditions of the GS64. Integrators may discover in controlled environments that the
VRTC interface will function reliably as low as 0.8V, so best practice would be to
design the circuitry to operate down to 0.7V.
5.21.3 ALARM Utilization as a Wake-up
The ALARM output can be used by the host application to wake up from standby or
hibernation mode, but it can also be used to completely power up the host
application. The example below shows how the ALARM output (marked
5.21-2, and
application. The application has a parallel hold transistor (V4), and a Start Button.
In
on Figure 5.21-3) triggers the enabling of the main power to the
Out
on Figure
Figure 5.21-3 Example of host wake-up circuit
LZT 123 1836 77
Page 78

5.22 Ringer Output (BUZZER) [to be implemented in a future release]
Pin Name Direction Function
52 BUZZER Output Buzzer output
Connecting the BUZZER signal to an inverting transistor-buffer followed by a
piezoelectric transducer enables the wireless modem to play pre-programmed
melodies or sounds.
LZT 123 1836 78
Page 79

6 Antenna Connector
The wireless modem’s antenna connector allows transmission of the radio frequency
(RF) signals from the wireless modem to an external customer supplied antenna. The
connector is a micro-miniature coaxial WFL surface mounted component. Suitable
WFL type mating plug are available from the following manufacturers;
Hirose
The nominal impedance of the antenna interface is 50 ohms.
Feature GSM850 E-GSM900 GSM1800 GSM1900
Frequency range (MHz)
Maximum power 33dBm(2W)
Antenna Connector impedance 50 ohms
Antenna VSWR 2.5:1 max
824-894 880-960 1710-1880 1850-1990
33dBm(2W)
30dBm(1W)
30dBm(1W)
LZT 123 1836 79
Page 80

7 Hints for Integrating the Wireless Modem
This chapter gives you advice and helpful hints on how to integrate the wireless
modem into your application from a hardware perspective.
Please read and consider the information under the following headings before
starting your integration work:
• Safety advice and precautions.
• Installation of the wireless modem.
• Antenna.
7.1 Safety Advice and Precautions
7.1.1 General
Always ensure that use of the wireless modem is permitted. The radio device may
present a hazard if used in proximity to personal medical electronic devices. As a
rule, the wireless modem must not be used in hospitals or onboard aircraft.
You are responsible for observing your country’s safety standards, and where
applicable the relevant wiring rules.
Never use the wireless modem at a gas station, refueling point, blasting area or in any
other environment where combustible vapors or explosives may be present.
Operating the wireless modem close to other electronic devices, such as antennas,
television sets, and radios may cause electromagnetic interference.
Never try to dismantle the wireless modem yourself. There are no components inside
the wireless modem that can be serviced by the user. If you attempt to dismantle the
wireless modem, you may invalidate the warranty.
To protect the power supply cables and meet the fire safety requirements, it is
recommended that the electrical circuits are supplied with a power regulator. The
power regulator should be placed as close to the terminals of the power supply as
possible.
LZT 123 1836 80
Page 81

Do not connect any incompatible component or product to the module.
NOTE
The connection/disconnection method for the development board is by means of the
DC power jack. For this reason, the mains supply should be situated close to the
development board and be easily accessible.
7.2 SIM Card
Sony Ericsson does not warrant against defects, malfunction, nonconformities or deviation caused by the connection of incompatible
components or products to the GS64.
Before handling any SIM card, users should ensure that they are not charged with
static electricity. Use proper precautions to avoid electrostatic discharges. The
wireless modem must be switched off before the SIM card is installed or uninstalled.
When the SIM card holder is opened, the SIM card connections lie exposed under the
SIM card holder. CAUTION: Do not touch these connections! Failure to heed this
advice may release an electrical discharge that could damage the wireless modem or
the SIM card.
When designing applications, the SIM card’s accessibility should be taken into
account. Sony Ericsson recommends that users protect SIM card access by a PIN
code. This will ensure that the SIM card cannot be used by an unauthorized person.
7.3 Antenna
If the antenna is to be mounted outside, consider the risk of lightning.
Always follow the instructions provided by the antenna manufacturer.
Never connect more than one wireless modem to a single antenna.
The wireless modem can be damaged by radio frequency energy from the transmitter
of another adjacent wireless transmitter.
LZT 123 1836 81
Page 82

Like any mobile station, the antenna of the wireless modem emits radio frequency
energy. To avoid EMI (electromagnetic interference), users must determine whether
the application itself, or equipment in the application’s proximity, requires further
protection against radio emission and the disturbances it might cause. Protection is
secured either by shielding the surrounding electronics or by moving the antenna
away from the electronics and the external signals cable.
The wireless modem and antenna may be damaged if either come into contact with
ground potentials other than the one in the users application. Beware, ground
potential are not always what they appear to be.
In the final application, the antenna must be positioned more than 20 cm away from
human bodies. When this rule cannot be applied, the application designer is
responsible for providing the SAR measurement test report and declaration.
Even if SAR measurements are not required, it is considered good practice to insert a
warning in any manual produced, indicating it is a radio product and that care should
be taken.
7.4 Installation of the Wireless modem
7.4.1 Where to Install the Wireless modem
There are several conditions which need to be taken into consideration when
designing your application as they might affect the wireless modem and its function.
They are:
7.4.1.1 Environmental Conditions
The wireless modem must be installed so that the environmental conditions stated in
the Technical Data chapter, such as temperature, humidity and vibration are satisfied.
Additionally, the electrical specifications in the Technical Data section must not be
exceeded.
LZT 123 1836 82
Page 83

7.4.1.2 Signal Strength
The wireless modem has to be placed in a way that ensures sufficient signal strength.
To improve signal strength, the antenna can be moved to another position. Signal
strength may depend on how close the wireless modem is to a radio base station. You
must ensure that the location at which you intend to use the wireless modem, is
within the network coverage area.
Degradation in signal strength can be the result of a disturbance from another
source, for example an electronic device in the immediate vicinity. More information
about possible communication disturbances can be found in section 8.3.5, page 59.
When an application is completed, you can verify signal strength by issuing the AT
command AT+CSQ or AT*E2EMM. See the AT Commands Manual for further details.
Before installing the wireless modem, use an ordinary mobile telephone
to check a possible location for it. In determining the location for the
radio device and antenna, you should consider signal strength as well
TIP
as cable length.
7.4.1.3 Connection of Components to Wireless modem
The integrator is responsible for the final integrated system. Incorrectly designed or
installed, external components may cause radiation limits to be exceeded. For
instance, improperly made connections or improperly installed antennas can disturb
the network and lead to malfunctions in the wireless modem or equipment.
7.4.1.4 Network and Subscription
Before the integrator’s application is used, the user must ensure that their chosen
network provides the necessary telecommunication services. Integrators should
contact their service provider to obtain the necessary information.
Integrators intending to use SMS in the application should ensure this is included in
their (voice) subscription.
Similarly, integrators intending to use GPRS for data services should also ensure that
this service is available on their network and in their account plan.
LZT 123 1836 83
Page 84

Users should consider the choice of the supplementary services described in section
2.3.2Short Message Service, page 16.
7.4.2 How to Install the Wireless modem
7.4.2.1 Power Supply
Use a high-quality power supply cable with low resistance. This ensures that the
voltages at the connector pins are within the allowed range, even during the
maximum peak current. An electrolytic capacitor should be placed close to the power
supply pins of the wireless modem to supply the peak currents during burst
transmission. See 5.6 Regulated Power Supply Input (VCC), page 38.
7.4.2.2 Grounds
A ground connection is provided at the mounting hole next to the RF connector on
the wireless modem (see Figure 5.1, page 19). Connect this ground point to the GND
pins of the wireless modem by the shortest, low impedance path possible. The
purpose of this connection is to allow any ESD picked up by the antenna to bypass the
wireless modem’s internal ground path.
Note! It is recommended that you use a cable with a maximum resistance of 5
milliohm for the ground connection.
Note! AREF and GND are connected at a single point inside the wireless modem. They
must not be joined together in your application.
7.4.2.3 Audio
Use a coupling capacitor in AUXI line if the application does not use the wireless
modem’s bias voltage. See also Figure 5.10-1 Microphone connections to the
wireless modem, page 54.
LZT 123 1836 84
Page 85

7.4.2.4 Software Upgrade
There are two ways of updating the firmware in the GS64. There is a web based tool
that can access a Sony Ericsson server from where SW can be downloaded. There is
also an Updater, which is a local application that downloads an image provided by
SEMC.
7.5 Antenna
7.5.1 General
The antenna is the component in the users system that maintains the radio link
between the network and the wireless modem. Since the antenna transmits and
receives electromagnetic energy, its efficient function will depend on:
the type of antenna (for example, circular or directional)
the placement of the antenna
communication disturbances in the vicinity in which the antenna operates
In the sections below, issues concerning antenna type, antenna placement, antenna
cable, and possible communication disturbances are addressed.
In any event, users should contact their local antenna manufacturer for additional
information concerning antenna type, cables, connectors, antenna placement, and the
surrounding area. Users should also determine whether the antenna needs to be
grounded or not. Usually, a local antenna manufacturer should be able to design a
special antenna suitable for the integrators application and environment.
7.5.2 Antenna Type
Users should ensure that they choose the right type of antenna for the wireless
modem.
LZT 123 1836 85
Page 86

The antenna must be designed for the frequency bands deployed in the regions that
the wireless modem is being used. For fixed locations this may be dual bands (for
example E-GSM900/GSM1800 in Europe; GSM850/GSM1900 in North America). For
applications which are mobile, users should consider whether three or all four GSM
bands could be encountered.
Other factors in choosing antenna are equally important:
the impedance of the antenna and antenna cable must be 50 ohms at all frequencies
being used
the antenna output-power handling capability must be a minimum of 2 W
the antenna VSWR value should be less than 3:1 to avoid damage to the radio device
7.5.3 Antenna Placement
The antenna should be placed away from electronic devices or other antennas. The
recommended minimum distance between adjacent antennas, operating in a similar
radio frequency band, is at least 50 cm.
If signal strength is weak, it is useful to face a directional antenna at the closest radio
base station. This can increase the strength of the signal received by the wireless
modem.
The wireless modem’s peak output power can reach 2 W. RF field strength varies with
antenna type and distance. At 10 cm from the antenna the field strength may be up
to 70 V/m and at 1m it will have reduced to 7 V/m.
In general, CE-marked products for residential and commercial areas, and light
industry can withstand a minimum of 3 V/m.
7.5.4 The Antenna Cable
Use 50 ohm impedance low-loss cable and high-quality 50 ohm impedance
connectors (frequency range up to at least 2 GHz) to avoid RF losses. Ensure that the
antenna cable is as short as possible.
The effectiveness of the antenna, cable and connectors is determined by their quality.
All connectors, adaptors and cables should be of the highest quality, lowest loss,
lowest VSWR rating that is affordable to the user.
LZT 123 1836 86
Page 87

Minimize the use of extension cables, connectors and adapters. Each additional
cable, connector or adapter will result in additional loss of signal power.
7.5.5 Possible Communication Disturbances
Communication disturbances can adversely effect the quality of wireless links,
including the following causes:
Noise can be caused by electronic devices and radio transmitters.
Path-loss occurs as the strength of the received signal steadily decreases in
proportion to the distance from the transmitter.
Shadowing is a form of environmental attenuation of radio signals caused by hills,
buildings, trees or even vehicles. This can be a particular problem inside buildings,
especially if the walls are thick and reinforced.
Multi-path fading is a sudden decrease or increase in the signal strength. This is the
result of interference caused when direct and reflected signals reach the antenna
simultaneously. Surfaces such as buildings, streets, vehicles, etc., can reflect signals.
LZT 123 1836 87
Page 88

8 Embedded Applications
The wireless modem has the capability to store and run customer written code in the
form of a script during the processor’s idle time, through the use of an on board
interpreter.
8.1 Features
Main features of embedded applications are as follows:
C based scripting language (Sony Ericsson specific)
Over the air upgrade of scripts (NOT GSM software)
Library of intrinsic functions
2 scripts can be stored in the memory at any time (but only 1 can be active)
8.2 Implementation
The wireless modem has up to 256k of space available for storage of two scripts in
the scripting language and TBD of operating RAM. Structures included in this
language are:
If - else statements
While loops
For loops
All hardware interfaces that are normally available to the wireless modem through the
AT commands are available to the embedded application.
Further drivers have been written such as M bus, keypad, SPI and I2C for use by the
embedded application (EA) through the use of the I/O pins.
8.2.1 Limitations
Since the wireless modem is processing the script using its own memory, limitations
are placed onto the scripts that are run.
LZT 123 1836 88
Page 89

A direct comparison cannot be made to a fully compiled C program in terms of size,
but a gauge of script size is that if each line were 128 characters long in the script
then the script could be about 16,000 lines long.
Processing power is something that needs to be considered as the script is run as a
low priority process within the software. However, controller mode stops GSM
operation and provides all the processing power for the script to be run. See the
M2mpower Application Guide
for more details.
Code cannot be ported directly from an existing application and loaded directly onto
the wireless modem. It must be re-written in the Sony Ericsson Mobile script
language so that the wireless modem interpreter can function correctly.
8.2.2 M2mpower IDE (Integrated Development Environment)
The IDE is a Windows based package which allows the user to write, simulate, debug
and download the application into a wireless modem with the embedded application
(EA) software. The standard version is designed to run on Windows XP and 2000.
The M2mpower Application Guide is available for implementing applications using the
developer’s kit and the embedded application (EA) functionality.
This is a required package to be able to implement an embedded application (EA).
For further information please contact Sony Ericsson Mobile Communications
customer support.
LZT 123 1836 89
Page 90

9 TCP/IP Stack
An on board IP/TCP/UDP stack has been integrated into the software negating the
need for the customer to implement one in their own code base.
This is accessible by using an embedded applications (see section 9) using intrinsic
functions or through AT commands.
9.1 Implementation
The following types of commands allow various functions:
Open/closing IP connection - Negotiates/closes a dynamic IP address with the web
server.
Send/Receive TCP packets - Performs all TCP operations to send and receive packets.
Send/Receive UDP packets - Performs all UDP operations to send and receive packets.
Resolve URL to an IP address - Similar to nslookup command in DOS When the unit is
set up and controlled using the embedded applications
LZT 123 1836 90
Page 91

10 Technical Data
10.1 Mechanical Specifications
Refer to Figure 4.2-1 Dimensions of the Wireless modem for reference to mechanical
features.
Mechanical Feature
Variant
Value
Length 37 mm
Width 30 mm
without SIM holder 2.67 mm
Thickness (see illustration below)
with SIM holder 5.27 mm
Weight
Figure 10.1-1 GS64 module with thickness dimensions
LZT 123 1836 91
Page 92

10.2 Power supply voltage, normal operation
Parameter Mode Limit
VCC Supply voltage
Maximum allowable voltage drop Transmission burst 200mV
Maximum current consumed Full power (2W) transmit
Nominal 3.6 V
Min 3.2 V
Max 4.5 V
Absolute maximum limit -0.3V to 6.5V
<100mV @<200kHz
Maximum supply ripple
<20mV @>200kHz
2250 mA (peak)
2100 mA (avg)
Stresses in excess of the absolute maximum limits can cause
!
WARNING
permanent damage to the device. These are absolute stress ratings
only. Functional operation of the device is not implied at these or any
other conditions in excess of those given in the operational sections of
the data sheet. Exposure to absolute maximum ratings for extended
periods can adversely affect device reliability.
10.3 Radio specifications
Feature GSM850 E-GSM900 GSM1800 GSM1900
Frequency range (MHz) 824-894 880-960 1710-1880 1850-1990
Maximum power 33dBm (2W)
Antenna impedance 50 ohms
33dBm (2W)
30dBm (1W)
30dBm (1W)
10.4 SIM card
Parameter 1.8V 3.0V 5.0V
External SIM support Yes Yes No
Integrated SIM support (optional) Yes Yes No
LZT 123 1836 92
Page 93

10.5 Environmental Specification
Test Case Test Summary Ref Standard
Temp: max storage
Heat Test
Cold Test
Temperature Cycling
Thermal Shock Test
Humidity: nominal
Duration: 16 hours
Temp: min storage
Duration: 16 hours
Temp (low) : min storage
Temp (high) : max storage
2 hrs dwell at each extreme
6 hrs transition between temps
Duration: 5 cycles x 16 hours
(80 hrs total)
Temp (low) : min storage
Temp (high) : max storage
6 min dwell at each extreme
0.5 to 3 min transition
Duration: 30 cycles (Group 2,3)
IEC 60068-2-2
IEC 60068-2-1
IEC 60068-2-14
IEC 60068-2-14
Temp (low) : nominal ambient
Temp (high) : max operating
Humidity (high) : 95% ±5% RH
Humidity (low) : 93% ±5% RH
Moist Heat Cyclic Test
9 hr dwell at each temperature
IEC 60068-2-30
3 hr transition between temps
Duration: 6 cycles x 24 hours
(144 hrs total)
SIM insertion : 500 cycles
System connector : 10,000 cycles
Operational Durability
Flips/Hinges : 1,000 cycles
1/52 41-FEA 202 8370
RF connector : 5,000
1m drop height on to concrete
- all sides
Free Fall Test
- all faces
IEC 60068-2-32 Test Ed
- all corners
- any extended features
LZT 123 1836 93
Page 94

Test Case Test Summary Ref Standard
Freq: 10-60 Hz, constant
displacement ±0.35mm
Freq : 60-500 Hz, constant
Sinusoidal Vibration
Random Vibration
acceleration 5 g
Sweep velocity: 1 oct/min
Sweeps: 5 per axis
Axis: 3 axis (x, y, z) per device
Power Spectral Density:
5 Hz 0.10 m
12 Hz 2.20 m
20 Hz 2.20 m
200 Hz 0.04 m
500 Hz 0.04 m
2/s3
2/s3
2/s3
2/s3
2/s3
Duration : 2 hrs each axis
Axis : 3 axis (x, y, z) per device
IEC 60068-2-6
IEC 60068-2-34
Pulse shape: Half-sine
Amplitude: 30 g±15%
Mechanical Shock Test
Duration: 6 ms
Axis: ±x, ±y, ±z
IEC 60068-2-27
Test Ea
No. shocks: 3 each direction
(18 total)
Mechanical force :
Mixed Plug-in
Connector
50 N in ±x, -y, ±z directions
100 N in +y (mating axis)
1/152 41-FEA 202 8370
LZT 123 1836 94
Page 95

11 Regulatory Notices
The GS64 described in this manual conforms to the Radio and Telecommunications Terminal
Equipment (R&TTE) directive 99/5/EC with requirements covering EMC directive 89/336/EEC
and Low Voltage directive 73/23/EEC. The product fulfils the requirements according to
3GPP TS 51.010-1, EN 301 489-7 and EN60950.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions:
(1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and
(2) The device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
The GS64 modular transmitter is labelled with its own FCC ID number. In the normal method
of mounting the GS64 in a customer application the label is not visible to an end-user.
Similarly, the customer application itself may obscure the GS64 module entirely. If the FCC
ID is not visible when the module is installed inside another device, then the outside of the
device into which the module is installed must display a label referring to the enclosed
module. This exterior label can use wording such as the following: “Contains Transmitter
Module FCC ID: PY7BC051022” or “Contains FCC ID: PY7BC051022”. Any similar wording
that expresses the same meaning may be used.
FCC ID PY7BC051022
This product has not yet received GCF or FCC approval
IC: 4170B-BC051022
Append Declaration
LZT 123 1836 95
Page 96

Developers Kit
LZT 123 1836 96
Page 97

12 Introduction to the Universal Developer’s Kit
The Sony Ericsson M2M universal developer’s kit (UDK) is designed to get you started
quickly. It contains all the hardware you will need to begin the development of an
application.
The only items you need to provide are; a wireless modem, a computer, a SIM card
with a network subscription, and a knowledge of programming with AT commands.
The main hardware of the UDK is an open board onto which you plug the wireless
modem, using an adaptor board where necessary. Connectors, switches, jumpers
and SIM card holder are provided to allow you to configure and access all the
functions of the radio device.
Two version of the UDK exists; the first-generation UDK is designed for legacy M2M
products available during 2003 to 2005; a second-generation Universal Developers
Kit Mk 2 is available for M2M products from 2006 onwards. Components, adaptor
boards and peripheral interfaces are not inter-changeable between the two UDK
products.
A separate user manual describes the set-up and use of the UDK. This can be
downloaded from the Sony Ericsson M2M Extranet web pages or obtained from your
local sales support representative upon request.
LZT 123 1836 97
 Loading...
Loading...