
Packet Monitor in SonicOS 5.8
Document Contents
This document contains the following sections:
• “Packet Monitor Overview” on page 1
• “Configuring Packet Monitor” on page 5
• “Using Packet Monitor and Packet Mirror” on page 16
• “Verifying Packet Monitor Activity” on page 20
• “Related Information” on page 24
Packet Monitor Overview
This section provides an introduction to the SonicOS Enhanced packet monitor feature. This
section contains the following subsections:
• “What is Packet Monitor?” on page 1
• “Benefits of Packet Monitor” on page 2
• “How Does Packet Monitor Work?” on page 2
• “What is Packet Mirror?” on page 4
• “How Does Packet Mirror Work?” on page 4
What is Packet Monitor?
Packet monitor is a mechanism that allows you to monitor individual data packets that traverse
your SonicWALL firewall appliance. Packets can be either monitored or mirrored. The
monitored packets contain both data and addressing information. Addressing information from
the packet header includes the following:
• Interface identification
• MAC addresses
• Ethernet type
• Internet Protocol (IP) type
• Source and destination IP addresses
• Port numbers
SonicOS 5.8 Packet Monitor Feature Module
1

Packet Monitor Overview
• L2TP payload details
• PPP negotiations details
Y ou can configure the packet monitor feature in the SonicOS Enhanced management interface.
The management interface provides a way to configure the monitor criteria, display settings,
mirror settings, and file export settings, and displays the captured packets.
Benefits of Packet Monitor
The SonicOS Enhanced packet monitor feature provides the functionality and flexibility that you
need to examine network traffic without the use of external utilities, such as Wireshark (formerly
known as Ethereal). Packet monitor includes the following features:
• Control mechanism with improved granularity for custom filtering (Monitor Filter)
• Display filter settings independent from monitor filter settings
• Packet status indicates if the packet was dropped, forwarded, generated, or consumed by
the firewall
• Three-window output in the management interface:
–
List of packets
–
Decoded output of selected packet
–
Hexadecimal dump of selected packet
• Export capabilities include text or HTML format with hex dump of packets, plus CAP file
format
• Automatic export to FTP server when the buffer is full
• Bidirectional packet monitor based on IP address and port
• Configurable wrap-around of packet monitor buffer when full
How Does Packet Monitor Work?
As an administrator, you can configure the general settings, monitor filter, display filter,
advanced filter settings, and FTP settings of the packet monitor tool. As network packets enter
the packet monitor subsystem, the monitor filter settings are applied and the resulting packets
are written to the capture buffer. The display filter settings are applied as you view the buffer
contents in the management interface. You can log the capture buffer to view in the
management interface, or you can configure automatic transfer to the FTP server when the
buffer is full.
Default settings are provided so that you can start using packet monitor without configuring it
first. The basic functionality is as follows:
Start:Click Start Capture to begin capturing all packets except those used for
communication between the SonicWALL appliance and the management
interface on your console system.
Stop:Click Stop Capture to stop the packet capture.
Clear:Click Clear to clear the status counters that are displayed at the top of the
Packet Monitor page.
2
SonicOS 5.8 Packet Monitor Feature Module
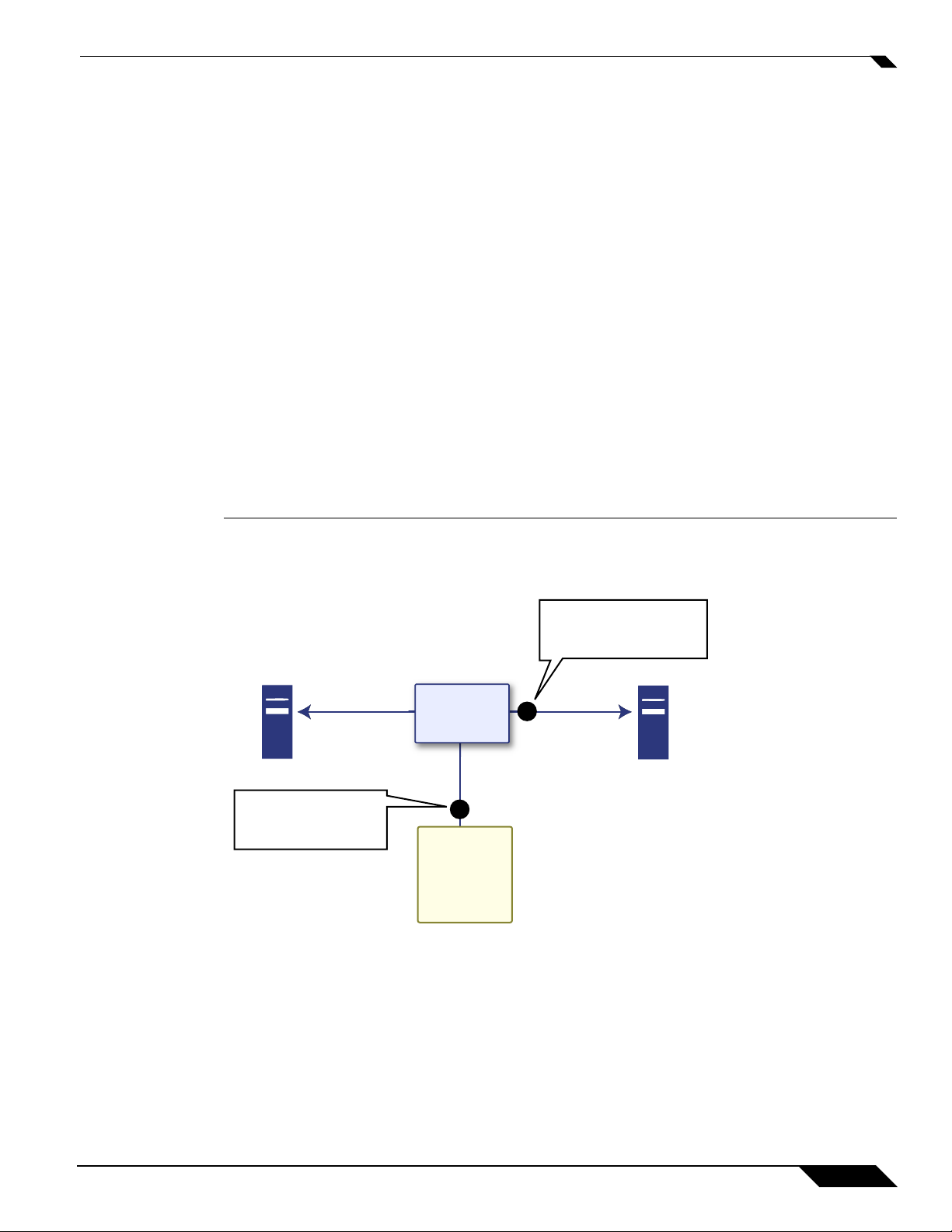
Packet Monitor Overview
Remote FTP Server
Management Host
Capture Buffer
Packets
- Incoming
- Outgoing
- Generated
- Intermediate
Monitor filter is applied
before copying the packet
into the capture buffer.
Display filter is applied
before displaying packets
to the management interface.
Refresh: Click Refresh to display new buffer data in the Captured Packets window. You
can then click any packet in the window to display its header information and
data in the Packet Detail and Hex Dump windows.
Export As: Display or save a snapshot of the current buffer in the file format that you select
from the drop-down list. Saved files are placed on your local management
system (where the management interface is running). Choose from the
following formats:
• Libpcap - Select Libpcap format if you want to view the data with the
Wireshark (formerly Ethereal) network protocol analyzer. This is also
known as libcap or pcap format. A dialog box allows you to open the buffer
file with Wireshark, or save it to your local hard drive with the extension
.pcap.
• Html - Select Html to view the data with a browser . You can use File > Save
As to save a copy of the buffer to your hard drive.
• Text - Select Text to view the data in a text editor. A dialog box allows you
to open the buffer file with the registered text editor, or save it to your local
hard drive with the extension .wri.
• App Data - Sele c t A p p D a ta t o view only application data contained in the
packet. Packets cont aining no application data are skipped during th e capture.
Application data = captured packet minus L2, L3, and L4 headers.
Refer to the figure below to see a high level view of the packet monitor subsystem. This shows
the different filters and how they are applied.
SonicOS 5.8 Packet Monitor Feature Module
3

Packet Monitor Overview
What is Packet Mirror?
Packet mirroring is the process of sending a copy of packets seen on one interface to another
interface or to a remote SonicWALL appliance.
There are two aspects of mirroring:
Classification – Refers to identifying a selected set of packets to be mirrored. Incoming and
outgoing packets to and from an interface are matched against a filter. If matched, the mirror
action is applied.
Action – Refers to sending a copy of the selected packets to a port or a remote destination.
Packets matching a classification filter are sent to one of the mirror destinations. A particular
mirror destination is part of the action identifier.
Supported Platforms for Packet Mirror
On all SonicWALL NSA Series appliances running SonicOS Enhanced 5.6 or higher, packet
mirroring is fully supported.
On SonicWALL TZ Series appliances running SonicOS Enhanced 5.6 or higher, packet
mirroring is partially supported, as follows:
• Local mirroring is not supported.
• Remote mirroring is supported for both sending and receiving mirrored packets.
How Does Packet Mirror Work?
Every classification filter is associated with an action identifier . Up to two action identifiers can
be defined, supporting two mirror destinations (a physical port on the same firewall and/or a
remote SonicWALL firewall). The action identifiers determine how a packet is mirrored. The
following types of action identifiers are supported:
• Send a copy to a physical port.
• Encapsulate the packet and send it to a remote SonicWALL appliance.
• Send a copy to a physical port with a VLAN configured.
Classification is performed on the Monitor Filter and Advanced Monitor Filter tab of the
Packet Monitor Configuration window.
A SonicWALL can be configured to receive remotely mirrored traffic from a remote SonicWALL
firewall. At the local firewall, received mirrored traffic can either be saved in the capture buffer
or sent to another local interface. This is configured in the Remote Mirror Settings (Receiver)
section on the Mirror tab of the Packet Monitor Configuration window.
SonicOS Enhanced 5.6 and higher supports the following packet mirroring options:
• Mirror packets to a specified interface (Local Mirroring).
• Mirror only selected traffic.
• Mirror SSL decrypted traffic.
• Mirror complete packets including Layer 2 and Layer 3 headers as well as the payload.
• Mirror packets to a remote SonicWALL UTM appliance (Remote Mirroring Tx).
• Receive mirrored packets from a remote SonicWALL appliance (Remote Mirroring Rx).
4
SonicOS 5.8 Packet Monitor Feature Module

Configuring Packet Monitor
Y ou can access the packet monitor tool on the System > Packet Monitor p age of the SonicOS
management interface. There are six main areas of configuration for packet monitor, one of
which is specifically for packet mirror. The following sections describe the configuration options,
and provide procedures for accessing and configuring the filter settings, log settings, and mirror
settings:
• “Configuring General Settings” on page 5
• “Configuring Monitoring Based on Firewall Rules” on page 6
• “Configuring Monitor Filter Settings” on page 7
• “Configuring Display Filter Settings” on page 8
• “Configuring Logging Settings” on page 10
• “Configuring Advanced Monitor Filter Settings” on page 12
• “Configuring Mirror Settings” on page 14
Configuring General Settings
This section describes how to configure packet monitor general settings, including the number
of bytes to capture per packet and the buffer wrap option. You can specify the number of bytes
using either decimal or hexadecimal, with a minimum value of 64. The buffer wrap option
enables the packet capture to continue even when the buffer becomes full, by overwriting the
buffer from the beginning.
To configure the general settings, perform the following steps:
Configuring Packet Monitor
Step 1 Navigate to the System > Packet Monitor page and click Configure.
Step 2 In the Packet Monitor Configuration window, click the Settings tab.
Step 3 Under General Settings in the Number of Bytes T o Capture (per packet) box, type the number
of bytes to capture from each packet. The minimum value is 64.
Step 4 To continue capturing packets after the buffer fills up, select the Wrap Capture Buffer Once
Full checkbox. Selecting this option will cause packet capture to start writing captured p ackets
at the beginning of the buffer again after the buffer fills. This option has no effect if FTP server
logging is enabled on the Logging tab, because the buffer is automatically wrapped when FTP
is enabled.
SonicOS 5.8 Packet Monitor Feature Module
5
Configuring Packet Monitor
Step 5 Under Exclude Filter, select the Exclude encrypted GMS traffic to prevent capturing or
mirroring of encrypted management or syslog traffic to or from SonicWALL GMS. This setting
only affects encrypted traffic within a configured primary or secondary GMS tunnel. GMS
management traffic is not excluded if it is sent via a separate tunnel.
Step 6 Use the Exclude Management Traffic settings to prevent capturing or mirroring of
management traffic to the appliance. Select the checkbox for each type of traffic (HTTP/
HTTPS, SNMP, or SSH) to exclude. If management traffic is sent via a tunnel, the packets are
not excluded.
Step 7 Use the Exclude Syslog Traffic to settings to prevent capturing or mirroring of syslog traffic
to the logging servers. Select the checkbox for each type of server (Syslog Servers or GMS
Server) to exclude. If syslog traffic is sent via a tunnel, the packets are not excluded.
Step 8 Use the Exclude Internal Traffic for settings to prevent capturing or mirroring of internal traf fic
between the SonicWALL appliance and its High Availability partner or a connected SonicPoint.
Select the checkbox for each type of traffic (HA or SonicPoint) to exclude.
Step 9 To save your settings and exit the configuration window, click OK.
Configuring Monitoring Based on Firewall Rules
The Packet Monitor and Flow Reporting features allow traffic to be monitored based on firewall
rules for specific inbound or outbound traffic flows. This feature set is enabled by choosing to
monitor flows in the Firewall > Access Rules area of the SonicOS management interface.
To configure the general settings, perform the following steps:
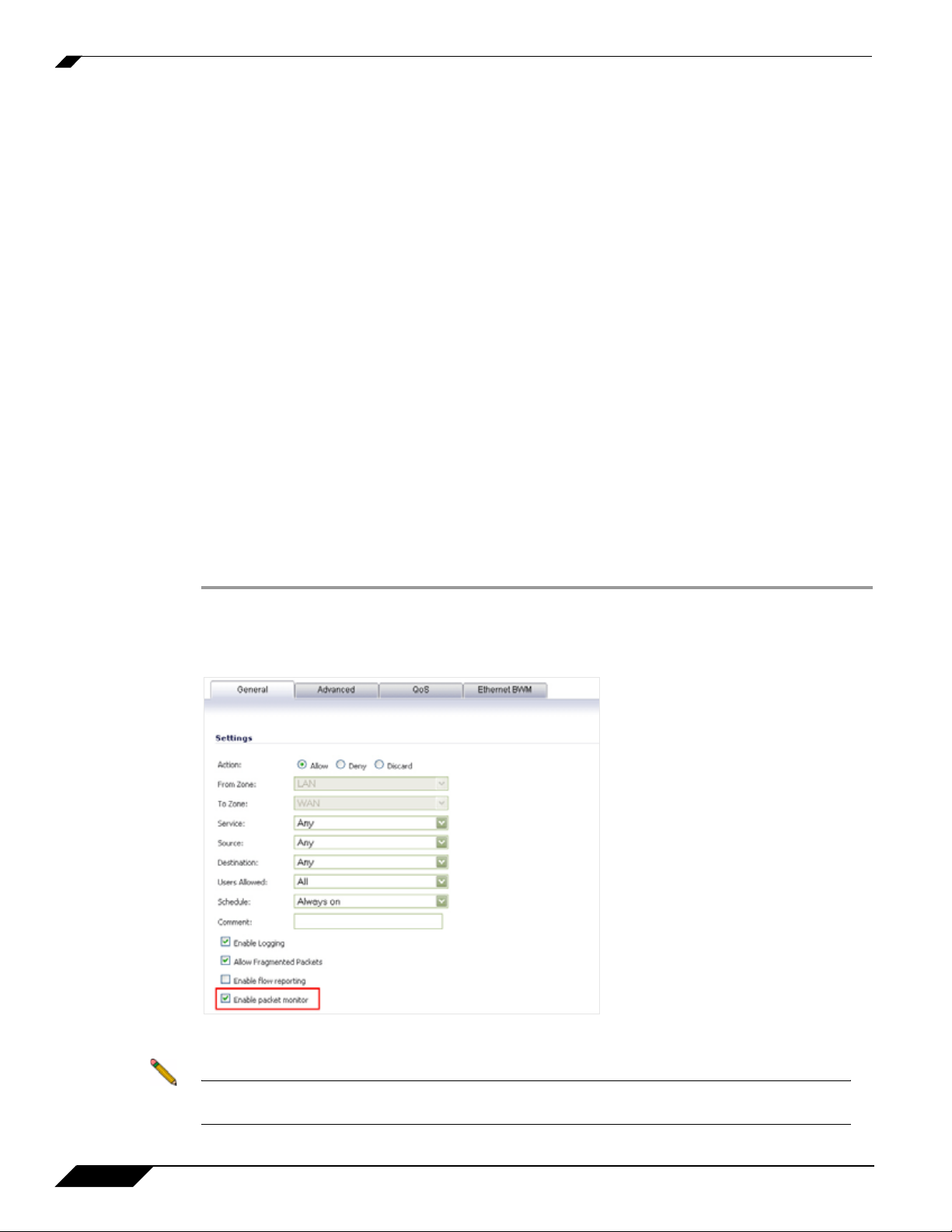
Step 1 Navigate to the Firewall > Access Rules page and click Configure icon for the rule(s) you wish
to enable packet monitoring or flow reporting on.
Step 2 Select the Enable packet monitor checkbox to send packet monitoring statistics for this rule.
Step 3 Click the OK button to save your changes.
Note Further monitor filter settings are required on the System > Packet Monitor page to enable
monitoring based on firewall rules.
6
SonicOS 5.8 Packet Monitor Feature Module
Configuring Monitor Filter Settings
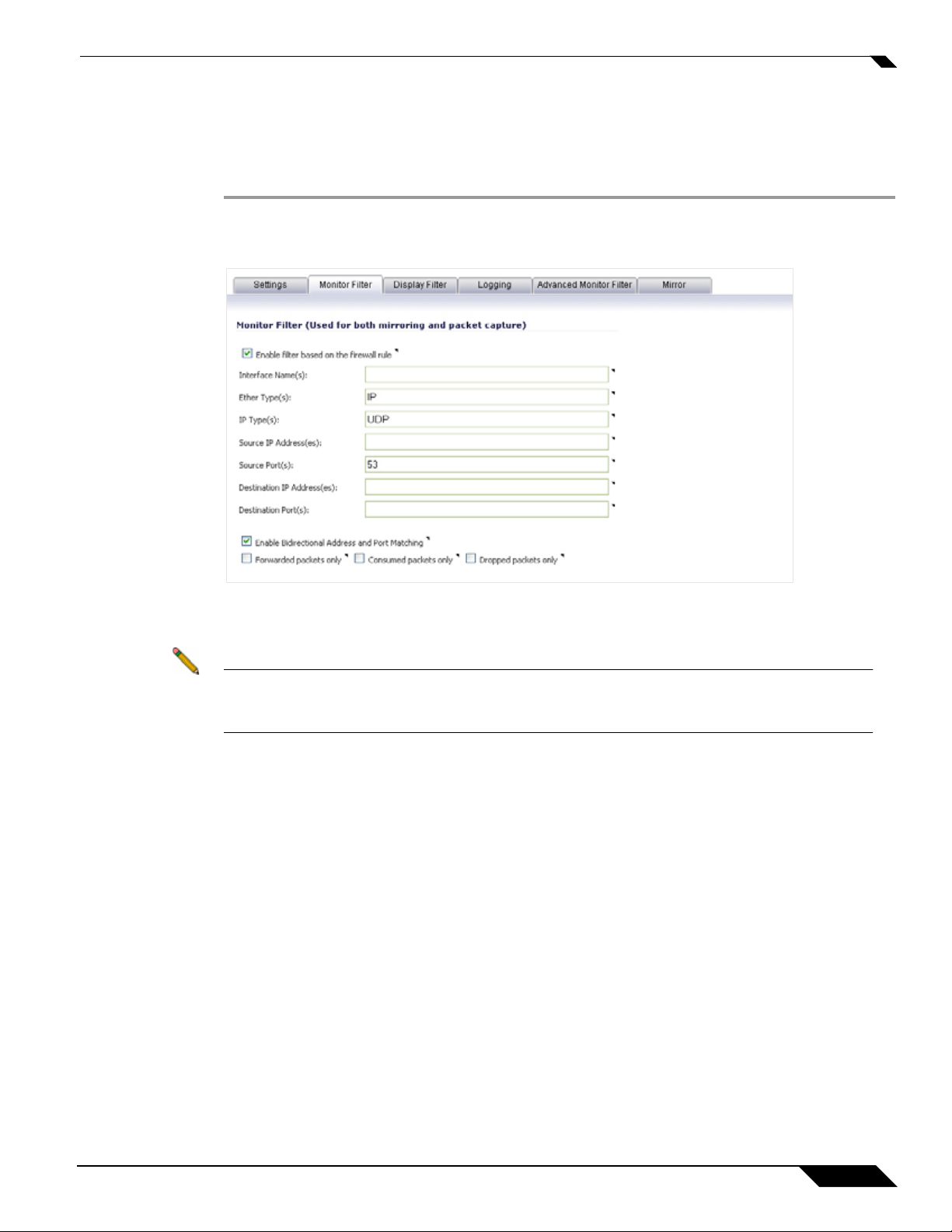
All filters set on this page are applied to both packet capture and p acket mirroring. To configure
Monitor Filter settings, complete the following steps:
Step 1 Navigate to the System > Packet Monitor page and click Configure.
Step 2 In the Packet Monitor Configuration window, click the Monitor Filter tab.
Configuring Packet Monitor
Step 3 Choose to Enable filter based on the firewall rule if you are using firewall rules to capture
specific traffic.
Note Before the “Enable filter based on the firewall rule” option is selected, be certain you have
selected one or more access rules on which to monitor packet traffic. This configuration is
done from the Firewall > Access Rules page of the SonicOS management interface.
Step 4 Specify how Packet Monitor will filter packets using these options:
• Interface Name(s) - You can specify up to ten interfaces separated by commas. Refer to
the Network > Interfaces screen in the management interface for the available interface
names. Y ou can use a negative value to configure all interfaces except the one(s) specified;
for example: !X0, or !LAN.
• Ether T ype(s) - You can specify up to ten Ethernet types separated by commas. Currently,
the following Ethernet types are supported: ARP, IP, PPPoE-SES, and PPPoE-DIS. The
latter two can be specified by PPPoE alone. This option is not case-sensitive. For example,
to capture all supported types, you could enter: ARP, IP, PPPOE. You can use one or more
negative values to capture all Ethernet types except those specified; for example: !ARP,
!PPPoE. You can also use hexadecimal values to represent the Ethernet types, or mix hex
values with the standard representations; for example: ARP, 0x800, IP. Normally you would
only use hex values for Ethernet types that are not supported by acronym in SonicOS
Enhanced. See “Supported Packet Types” on page 24.
• IP Type(s) - You can specify up to ten IP types separated by commas. The following IP
types are supported: TCP, UDP, ICMP, GRE, IGMP, AH, ESP. This option is not casesensitive. You can use one or more negative values to capture all IP types except those
SonicOS 5.8 Packet Monitor Feature Module
7
Configuring Packet Monitor
specified; for example: !TCP, !UDP. You can also use hexadecimal values to represent the
IP types, or mix hex values with the standard representations; for example: TCP, 0x1, 0x6.
See “Supported Packet Types” on page 24.
• Source IP Address(es) - You can specify up to ten IP addresses separated by commas;
for example: 10.1.1.1, 192.2.2.2. You can use one or more negative values to capture
packets from all but the specified addresses; for example: !10.3.3.3, !10.4.4.4.
• Source Port(s) - You can specify up to ten TCP or UDP port numbers separated by
commas; for example: 20, 21, 22, 25. You can use one or more negative values to capture
packets from all but the specified ports; for example: !80, !8080.
• Destination IP Address(es) - You can specify up to ten IP addresses separated by
commas; for example: 10.1.1.1, 192.2.2.2. You can use one or more negative values to
capture packets destined for all but the specified addresses; for example: !10.3.3.3,
!10.4.4.4.
• Destination Port(s) - You can specify up to ten TCP or UDP port numbers separated by
commas; for example: 20, 21, 22, 25. You can use one or more negative values to capture
packets destined for all but the specified ports; for example: !80, !8080.
• Bidirectional Address and Port Matching - When this option is selected, IP addresses
and ports specified in the Source or Destination fields on this page will be matched against
both the source and destination fields in each packet.
• Forwarded packets only - Select this option to monitor any packets which are forwarded
by the firewall.
• Consumed packets only - Select this option to monitor all packets which are consumed
by internal sources within the firewall.
• Dropped packets only - Select this option to monitor all p acket s which are dropped at the
perimeter.
Note If a field is left blank, no filtering is done on that field. Packets are captured or mirrored
without regard to the value contained in that field of their headers.
Step 5 To save your settings and exit the configuration window, click OK.
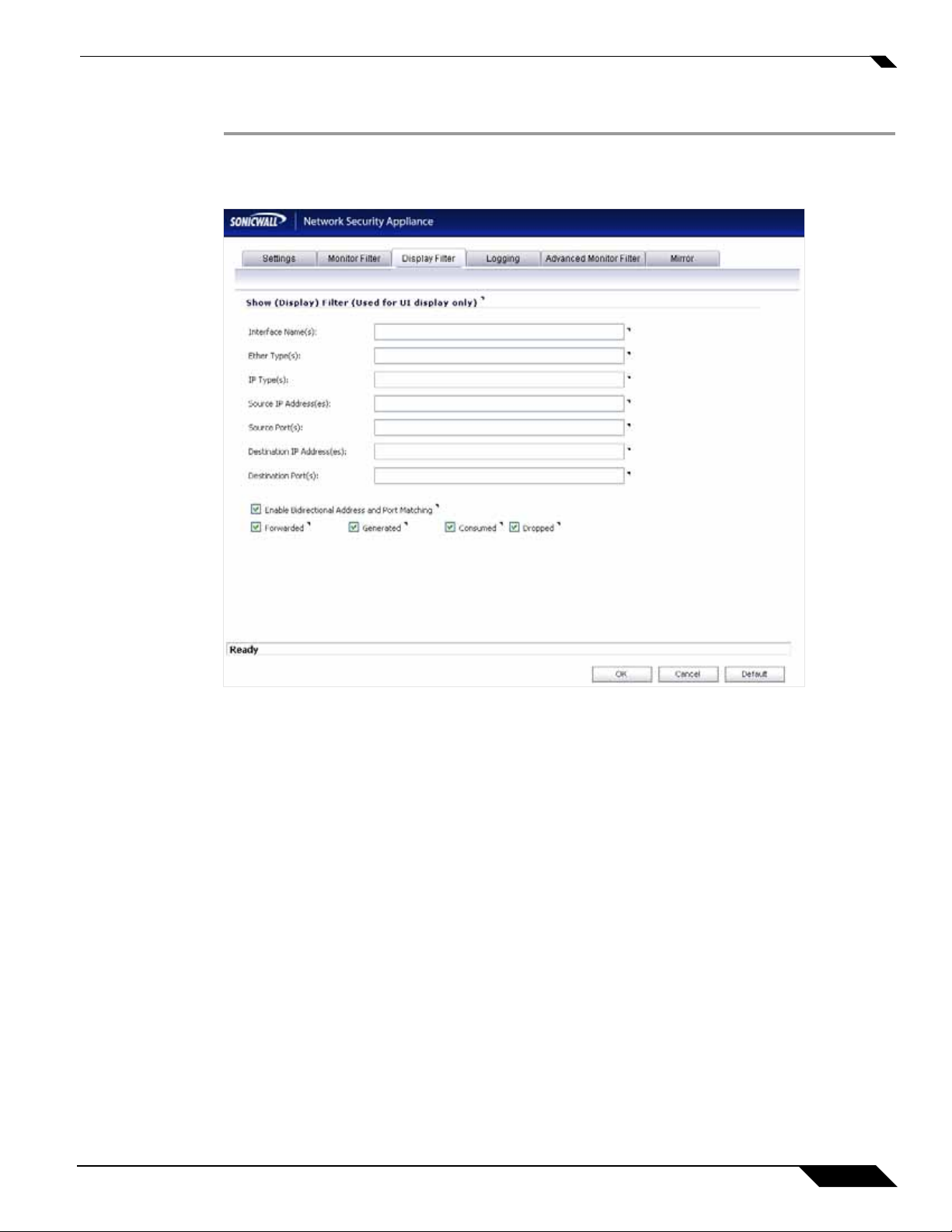
Configuring Display Filter Settings
This section describes how to configure packet monitor display filter settings. The values that
you provide here are compared to corresponding fields in the captured packet s, and only those
packets that match are displayed. These settings apply only to the display of captured p ackets
on the management interface, and do not affect packet mirroring.
Note If a field is left blank, no filtering is done on that field. Packets are displayed without regard
to the value contained in that field of their headers.
8
SonicOS 5.8 Packet Monitor Feature Module
Configuring Packet Monitor
To configure Packet Monitor display filter settings, complete the following steps:
Step 1 Navigate to the System > Packet Monitor page and click Configure.
Step 2 In the Packet Monitor Configuration window, click the Display Filter tab.
Step 3 In the Interface Name(s) box, type the SonicWALL appliance interfaces for which to display
packets, or use the negative format (!X0) to display packet s captured from all interfaces except
those specified. You can specify up to ten interfaces separated by commas. Refer to the
Network > Interfaces screen in the management interface for the available interface names.
Step 4 In the Ether Type(s) box, enter the Ethernet types for which you want to display packets, or
use the negative format (!ARP) to display packets of all Ethernet types except those specified.
You can specify up to ten Ethernet types separated by commas. Currently, the following
Ethernet types are supported: ARP, IP, PPPoE-SES, and PPPoE-DIS. The latter two can be
specified by PPPoE alone. You can also use hexadecimal values to represent the Ethernet
types, or mix hex values with the standard representations; for example: ARP, 0x800, IP.
Normally you would only use hex values for Ethernet types that are not supported by acronym
in SonicOS Enhanced. See “Supported Packet Types” on page 24.
Step 5 In the IP Type( s) box, enter the IP packet types for which you want to display packets, or use
the negative format (!UDP) to display packets of all IP types except those specified. You can
specify up to ten IP types separated by commas. The following IP types are supported: TCP,
UDP, ICMP, GRE, IGMP, AH, ESP. You can also use hexadecimal values to represent the IP
types, or mix hex values with the standard representations; for example: TCP, 0x1, 0x6. See
“Supported Packet Types” on page 24. To display all IP types, leave blank.
Step 6 In the Source IP Address(es) box, type the IP addresses from which you want to display
packets, or use the negative format (!10.1.2.3) to display packets captured from all source
addresses except those specified.
SonicOS 5.8 Packet Monitor Feature Module
9
 Loading...
Loading...