Page 1

EliteView
The easy way to manage your network
SNMP-Based
Network Management Software
for Windows
Managing SMC’s TigerSwitch™100
TM
User Guide
Page 2

ELITEVIEW™
ETWORK MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE
N
MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH™100
SMC6608T
SMC6608M
SMC
350 Kennedy Drive
Hauppauge, New York 11788
Publication 900.10908, Rev. B
Page 3

Information furnished by SMC Networks, Inc. (SMC) is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by SMC for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties
which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent
rights of SMC. SMC reserves the right to change specifications at any time without notice.
Copyright © 1998 by
SMC Networks, Inc.
Hauppauge, New York.
All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A.
Trademarks:
SMC is a registered trademark; and TigerSwitch, EliteView and EliteFax are trademarks of SMC
Networks, Inc. Other product and company names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their
respective holders.
Page 4

CONTENTS
Introduction .......................................................................................................................1
Accessing the TigerSwitch 100 .........................................................................................2
Accessing TigerSwitch 100 Summary Screens..........................................................3
TigerSwitch 100 Front Panel Description..................................................................3
Switch Summary................................................................................................................6
Accessing the Switch Summary.................................................................................6
Switch Summary Guidelines......................................................................................7
Modifying Switch Summary parameter fields ....................................................7
Switch Statistics.................................................................................................................9
Accessing Switch Statistics........................................................................................9
Switch Statistics Guidelines .......................................................................................10
Modifying Switch Statistics parameter fields .....................................................10
IP Statistics ........................................................................................................................11
Accessing IP Statistics................................................................................................11
IP Statistics Guidelines...............................................................................................12
Modifying IP Statistics parameter fields.............................................................12
Corresponding MIB Variables ............................................................................13
SNMP Statistics.................................................................................................................14
Accessing SNMP Statistics ........................................................................................14
SNMP Statistics Guidelines .......................................................................................15
Modifying SNMP Statistics parameter fields .....................................................15
Corresponding MIB Variables ............................................................................16
ICMP Statistics..................................................................................................................17
Accessing ICMP Statistics .........................................................................................17
ICMP Statistics Guidelines ........................................................................................18
Modifying ICMP Statistics parameter fields.......................................................18
Corresponding MIB Variables ............................................................................19
i
Page 5

CONTENTS
Health Statistics .................................................................................................................20
Accessing Health Statistics ........................................................................................20
Health Statistics Guidelines........................................................................................21
Modifying Health Statistics parameter fields......................................................21
Corresponding MIB II Variables ........................................................................22
Spanning Tree....................................................................................................................23
Accessing Spanning Tree ...........................................................................................23
Spanning Tree Guidelines ..........................................................................................24
Modifying Spanning Tree parameters.................................................................24
VLAN Groups ...................................................................................................................25
Accessing VLAN Groups...........................................................................................25
VLAN Groups Guidelines..........................................................................................26
Modifying VLAN Groups...................................................................................26
Port Summary....................................................................................................................27
Accessing Port Summary ...........................................................................................28
Port Summary Guidelines ..........................................................................................28
Modifying Port Summary parameter fields.........................................................28
Port Statistics.....................................................................................................................30
Accessing Port Statistics ............................................................................................30
Port Statistics Guidelines............................................................................................31
Modifying Port Statistics parameter fields..........................................................31
Configuring Traps..............................................................................................................32
Accessing Trap Configuration....................................................................................32
Trap Configuration Guidelines...................................................................................32
Modifying Trap Configuration parameter fields.................................................33
Index ..................................................................................................................................I-1
ii
Page 6

Introduction
SMC’s TigerSwitch 100 units are high-performance, Fast Ethernet switches that are perfect
for high-traffic environments. Depending on the model, the TigerSwitch 100 features either
8 fixed 100BASE-TX ports with Auto-Negotiation (automatic selection of data rate and
operating mode based on attached device) or various combinations of 100BASE-TX and
100BASE-FX ports distributed among two 4-port replaceable modules.
An SNMP Agent is also included so that SMC’s EliteView or other SNMP-based
management applications can collect and display status and performance information about
the switch and perform needed configuration and control functions.
Supported TigerSwitch 100 models include:
• SMC6608T
• SMC6608M
Some of the real-time management functions that EliteView allows you to perform for the
TigerSwitch 100 include:
• Viewing Status LEDs
• Viewing Switch Summary and Statistics
• Viewing a Port Summary and Port Statistics
• Obtaining performance statistics for IP, SNMP and ICMP protocols
• Configuring and viewing statistics for the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
• Configuring trap tables
• VLAN Groups
Refer to your TigerSwitch 100 documentation for a full description of the TigerSwitch 100
switch and the MIB variables used to manage it.
Note: For general instructions about how to install and use EliteView, refer to the
EliteView User Guide.
1
Page 7
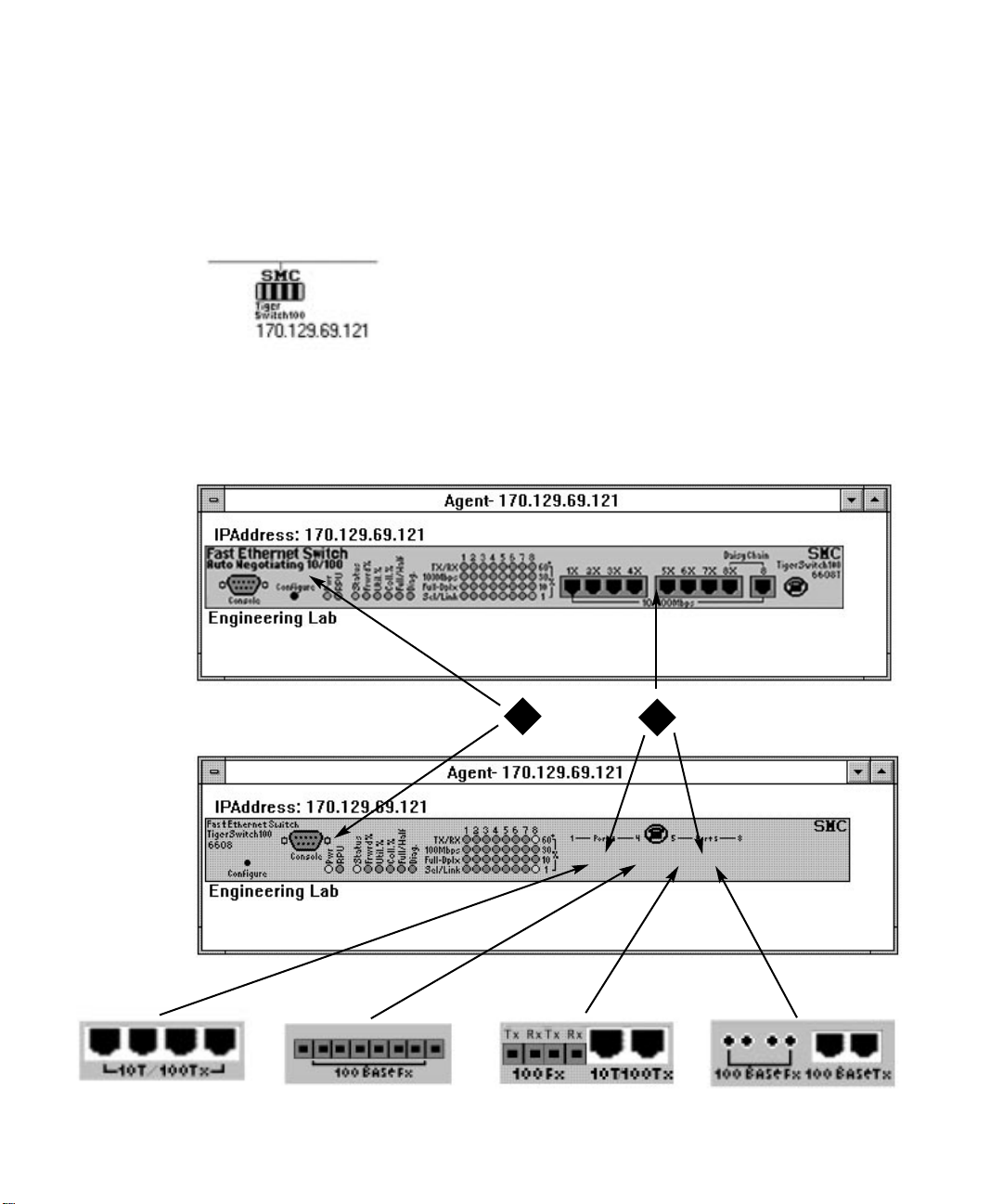
MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
Accessing the TigerSwitch 100
On the Subnet map, double-click the TigerSwitch 100 icon representing the switch you wish
to manage.
Note: You can also select a TigerSwitch 100 from the Node list,
or you may use the pull-down menus. Under Object,
choose Manage Device, click on IP and enter the IP
address of the switch you wish to manage.
A zoomed-in graphic of the front-panel of the TigerSwitch 100 unit you are accessing,
similar to one of those illustrated below, will appear showing the node address and location.
The front panel LEDs are also displayed (Refer to the TigerSwitch 100 user guide for a
complete description of the front panel LEDs).
SMC6608T
SMC6608M
SMC6600T
2
SMC6600F
1
SMC6600FSCT
2
SMC6600FSTT
Page 8

MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
Accessing TigerSwitch 100 Summary Screens
The diagrams on the previous page represent the front-panels of the two TigerSwitch 100
units. Please note that the front-panel representation of the TigerSwitch 100M (SMC6608M)
is dependent upon the module(s) installed in the switch. Any one (or two) of the modules
shown below the graphic will appear as part of the graphic (in the general area marked by the
arrows), if installed in the switch.
Switch and Port Summary screens are accesible through the front-panel graphic. To access
either of these screens, double-click on the corresponding zone (see previous page):
Displays Switch Summary screen
1
Displays Port Summary screen. (When the cursor is passed over a port, the port
2
outline changes color to red. Double-click on the port after it changes to red to
access the Port Summary screen for that port.)
Almost all of the subsequent management screens are accessible through either the Switch
Summary or Port Summary screen. The Trap Table configuration screen, however, must be
accessed by way of the pull-down menus (See the chapter entitled “Configuring Traps” for
specific information).
TigerSwitch 100 Front Panel Description
The Configure button is used to toggle the display mode to access various configuration
functions:
Port Status Display Mode (“Status”)
Displays the status of each port (transmission mode, transmit, receive, and link) during normal operation.
System Performance Display Mode (“Frwrd%”, “Util%”, Coll%”)
Displays system performance data (forwarding ratio, bandwidth utilization, collision ratio)
during normal operation.
Full/Half Duplex Display Mode (“Full/Half”)
Sets port communication mode to full-duplex or half-duplex operation.
Diagnostics Display Mode (“Diag”)
Tests the status of various system components. A “long press’ on the Configure button is
used to initiate basic configuration. A “short press” switches from one function to the next,
and another “long press” implements the selection.
3
Page 9
MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
Front Panel LEDs
LED Condition Status
Power
PWR Off No AC power .
RPU Off
PWR Green Internal power supply is operating properly; redundant
RPU Off power supply is not present or has been disconnected
PWR Green Both internal and redundant power supplies are operating
RPU Green properly
PWR Red Internal power supply has failed; device is being powered
RPU Green by redundant power supply
PWR Red Redundant power supply has failed; device is being
RPU Off powered by internal power supply
Port Status Display Mode
Status On Port status display mode active
Off Port status display mode inactive
TX/RX Green - Blinking Port is transmitting/receiving packets; blinking is
proportional to the rate of traffic passing through the port
Off No packets are traversing this port
100Mbps On Port is set at 100 Mbps
Off Port is set at 10 Mbps
Full-Dplx On Port is set for full-duplex operation
Off Port is set for half-duplex operation
Sel/Link On A valid link exists on this port
Off No valid link has been established on this port
Statistical Display for System Performance Display Mode
60+ Green Forward % Display Mode: The percentage of packets that
are forwarded to another port .
30 Green Utilization % Display Mode: The utilization percentage of
LAN bandwidth
10 Green Collision % Display Mode: The percentage of packet
1 Green collisions in the port’s segment
4
Page 10
MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
LED Condition Status
Port Forwarding Ratio (System Performance Display Mode)
Frwrd% On Port forward display mode active
Off Port forward display mode is inactive
Port Utilization Rate (System Performance Display Mode)
Util% On Port utilization display mode active
Off Port utilization display mode is inactive
Port Collision Ratio (System Performance Display Mode)
Coll% On Port collision display mode active
Off Port collision display mode is inactive
Full/Half Duplex Display Mode
Full/Half On Transmission mode selection enabled
Off Transmission mode selection disabled
Port On Port selected
Selection Off Port not selected
LED
Port On Port is set for full-duplex operation
Status Off Port is set for for half-duplex operation
LED
Diagnostics Display Mode*
Diag On Diagnostics mode selection enabled
Off Diagnostics mode selectin disabled
* Diagnostics are performed in two stages: the System Diagnostic and Port Diagnostic tests.
Results are provided in the Port Status display area. Please refer to the TigerSwitch 100 user
guide for a detailed explanation of results.
5
Page 11
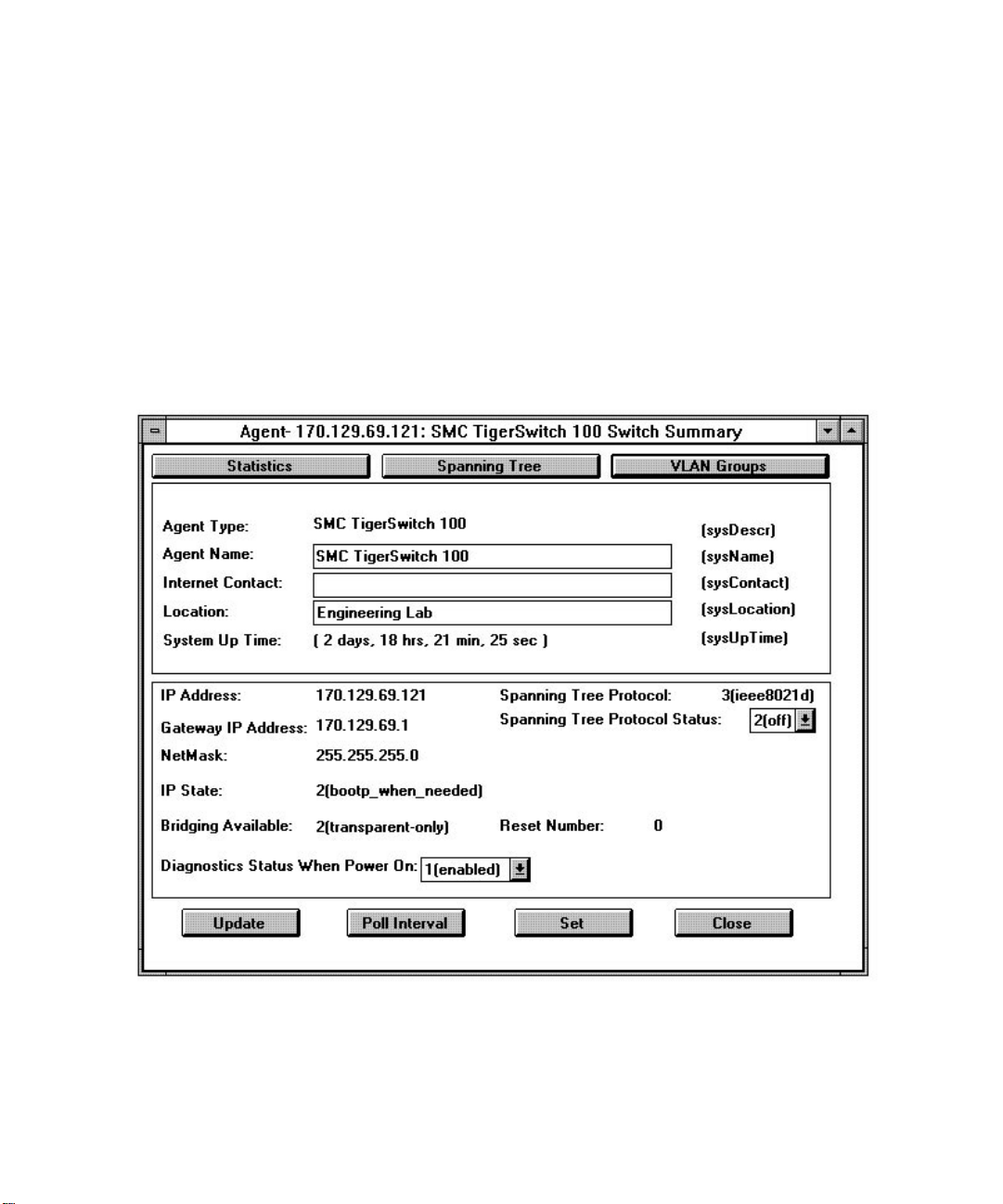
Switch Summary
The Switch Summary screen allows you to set parameters, change the poll interval for
collecting statistics, and update or halt the gathering of statistics. It also contains buttons for
accessing Switch Statistics, Spanning Tree and VLAN Group screens.
Accessing the Switch Summary
Double-click anywhere in Zone 1 (See page 2) to display the Switch Summary screen for the
TigerSwitch 100.
6
Page 12

Switch Summary Guidelines
Gray fields display data collected from discovered devices. These fields may not be
modified. Note: You can only set parameters and/or change the poll interval when the
polling process is stopped (i.e., when the Halt/Update button is toggled to Update).
Modifying Switch Summary parameter fields
1. Click on Halt.
2. Enter or change the following parameters to desired values:
• Agent Name — This field, which displays the name of the device, can be up to 256
characters in length. It corresponds to the MIB II variable sysName.
• Internet Contact — This field, which displays the name and/or phone number of a
contact person (e.g., the network manager or technical support department), can be a
maximum of 32 characters. It corresponds to the MIB II variable sysContact.
• Location — This field, which displays the location of the TigerSwitch 100, can be up to
256 characters in length. It corresponds to the MIB II variable sysLocation.
• Spanning Tree Protocol Status — This field displays the switch's Spanning Tree status,
ON or OFF. The Spanning Tree Protocol, when enabled, allows redundant paths to be
created between LAN segments. The default factory setting for Spanning Tree Protocol
is enabled. It can be disabled using this drop-down list.*
MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
• Diagnostic Status When Power On — This field displays the status of the option to
enable a diagnostic status test upon power on (off or on).
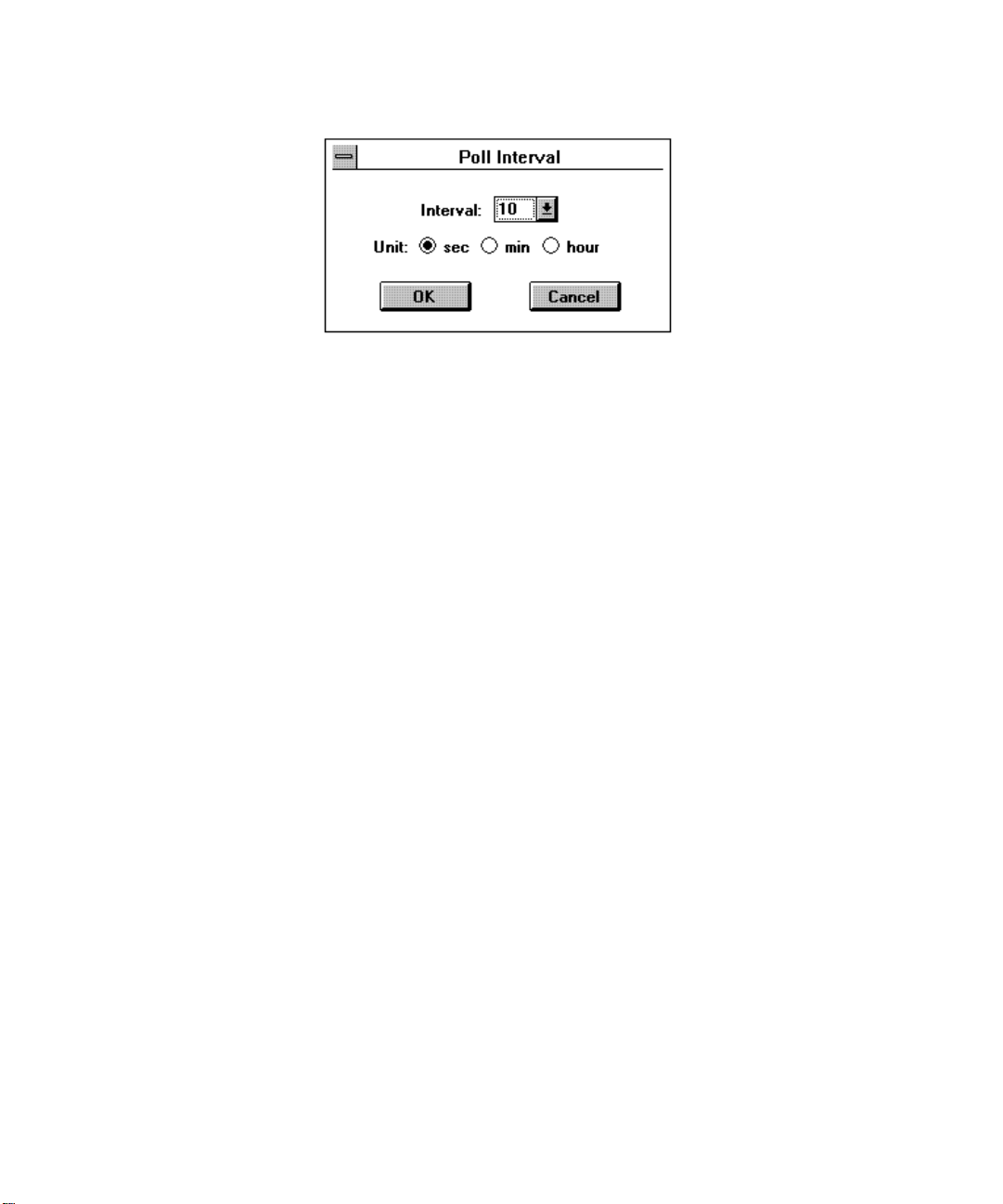
• Poll Interval — Poll Interval — This is the time interval during which EliteView reads
the status of the TigerSwitch 100. The interval may be set to between 0 seconds (no
polling) and 60 hours. The default value is 10 seconds. To change the interval, click on
the Poll Interval button to display the Poll Interval dialog box (see figure on page 8).
You can adjust the time interval by changing the Interval and Unit settings. Then, click
OK to initiate the new settings.
*Note: In the event that any port is configured as a member of multiple VLAN groups, Spanning Tree Protocol
will be disabled. Therefore, the drop-down list will be deactivated and the user will no longer be able to
turn on Spanning Tree.
7
Page 13
MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
3. Click on Set to save the changes.
4. Click on Update to initiate the changes.
5. Click on Close to close the window.
The following is a list of parameters which are displayed only. They cannot be changed
from the Switch Summary screen:
• IP Address— This field displays the IP Address of the TigerSwitch 100.
• Gateway IP Address — This field displays the address of the default gateway (or router)
to which the switch sends IP packets destined for a different subnet.
• NetMask— This field displays the IP subnet mask of the switch that corresponds to the
assigned IP address.
• IP State — This field specifies whether the IP address is set by the Boot Protocol
(BOOTP). Options include IP Disabled (switch will not process any IP or Address
Resolution Protocol [ARP] frames it receives), BOOTP When Needed (default, if a
non-zero IP address has been stored in EEPROM, IP is enabled, if the IP address is zero,
the switch will broadcast BOOTP requests to try to learn its IP address), and BOOTP
Always (IP is enabled but will not function until a BOOTP reply is received).
• Bridging Available — This field indicates the type of bridging this bridge can perform.
The TigerSwitch 100 supports transparent-only (2).
• Spanning Tree Protocol — This field displays the version of Spanning Tree Protocol
being run. The TigerSwitch 100 supports ANSI/IEEE 8021d (3).
• Reset Number — This field displays the reset count, or the number of times the switch
has been reset.
8
Page 14

Switch Statistics
The Switch Statistics screen allows you to view more detailed status information and statistics about the TigerSwitch 100. It also contains buttons for accessing IP Statistics, SNMP
Statistics, ICMP Statistics, and Health Statistics screens.
Accessing Switch Statistics
Click the Statistics button on the Switch Summary screen to access the Switch Statistics
screen illustrated below.
MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
9
Page 15

MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
Switch Statistics Guidelines
Gray fields display data collected from discovered devices. These fields may not be
modified. Note: You can only set parameters and/or change the poll interval when the
polling process is stopped (i.e., when the Halt/Update button is toggled to Update).
Modifying Switch Statistics parameter fields
1. Click on Halt.
2. Enter or change the following parameters to desired values:
• Agent Name — This field, which displays the name of the device, can be up to 256
characters in length. It corresponds to the MIB II variable sysName.
• Internet Contact — This field, which displays the name and/or phone number of a
contact person (e.g., the network manager or technical support department), can be a
maximum of 32 characters. It corresponds to the MIB II variable sysContact.
• Location — This field, which displays the location of the TigerSwitch 100, can be up to
256 characters in length. It corresponds to the MIB II variable sysLocation.
• Poll Interval — This is the time interval during which EliteView reads the status of the
TigerSwitch 100. The interval may be set to between 0 seconds (no polling) and 60
hours. The default value is 10 seconds. To change the interval, click on the Poll Interval
button to display the Poll Interval dialog box (See page 7). You can adjust the time
interval by changing the Interval and Unit settings. Then, click OK to initiate the new
settings.
10
3. Click on Set to save the changes.
4. Click on Update to initiate the changes.
5. Click on Close to close the window.
Page 16

IP Statistics
This window provides information about IP packets received and transmitted by the
TigerSwitch 100.
Accessing IP Statistics
Click the IP button on the Switch Statistics screen to display the IP Statistics screen
illustrated below.
MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
11
Page 17

MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
IP Statistics Guidelines
Gray fields display data collected from discovered devices. These fields may not be
modified. Note: You can only set parameters and/or change the poll interval when the
polling process is stopped (i.e., when the Halt/Update button is toggled to Update).
Modifying IP Statistics parameter fields
1. Click on Halt.
2. Enter or change the following parameters to desired values:
• Agent Name — This field, which displays the name of the device, can be up to 256
characters in length. It corresponds to the MIB II variable sysName.
• Location — This field, which displays the location of the TigerSwitch 100, can be up to
256 characters in length. It corresponds to the MIB II variable sysLocation.
• Poll Interval — This is the time interval during which EliteView reads the status of the
TigerSwitch 100. The interval may be set to between 0 seconds (no polling) and 60
hours. The default value is 10 seconds. To change the interval, click on the Poll Interval
button to display the Poll Interval dialog box (See page 7). You can adjust the time
interval by changing the Interval and Unit settings. Then, click OK to initiate the new
settings.
12
3. Click on Set to save the changes.
4. Click on Update to initiate the changes.
5. Click on Close to close the window.
Page 18

MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
Corresponding MIB Variables
The statistics displayed correspond to the following MIB II variables.
• Packets Received — ipInReceives
• Header Errors — ipInHdrErrors
• Invalid Address Errors — ipInAddrErrors
• Packets Routed — ipForwDatagrams
• Unknown Protocol Errors — ipInUnknownProtos
• In Discards — ipInDiscards
• Packets Delivered OK — ipInDelivers
• Packets Transmitted — ipOutRequests
• Out Discards — ipOutDiscards
• No Route Errors — ipOutNoRoutes
• IP Fragments Received — ipReasmReqds
• Datagrams Reassembled — ipReasmOKs
• Reassembly Errors — ipReasmFails
• Datagrams Fragmented — ipFragOKs
• Fragmentation Errors — ipFragFails
• Fragments Generated — ipFragCreates
• Routing Entry Discards — ipRoutingDiscards
For more information about these standard MIB II variables, refer to RFC 1213.
13
Page 19

MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
SNMP Statistics
This window displays the most recently retrieved statistics for SNMP PDUs, requests and
errors.
Accessing SNMP Statistics
Click the SNMP button on the Switch Statistics screen to display the SNMP Statistics screen
illustrated below.
14
Page 20

SNMP Statistics Guidelines
Gray fields display data collected from discovered devices. These fields may not be
modified. Note: You can only set parameters and/or change the poll interval when the
polling process is stopped (i.e., when the Halt/Update button is toggled to Update).
Modifying SNMP Statistics parameter fields
1. Click on Halt.
2. Enter or change the following parameters to desired values:
• Agent Name — This field, which displays the name of the device, can be up to 256
characters in length. It corresponds to the MIB II variable sysName.
• Location — This field, which displays the location of the TigerSwitch 100, can be up to
256 characters in length. It corresponds to the MIB II variable sysLocation.
• Poll Interval — This is the time interval during which EliteView reads the status of the
TigerSwitch 100. The interval may be set to between 0 seconds (no polling) and 60
hours. The default value is 10 seconds. To change the interval, click on the Poll Interval
button to display the Poll Interval dialog box (See page 7). You can adjust the time
interval by changing the Interval and Unit settings. Then, click OK to initiate the new
settings.
MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
3. Click on Set to save the changes.
4. Click on Update to initiate the changes.
5. Click on Close to close the window.
15
Page 21

MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
Corresponding MIB Variables
The statistics displayed correspond to the following MIB II variables.
• PDU’s Received — snmpInPkts
• PDU’s Transmitted — snmpOutPkts
• Bad Version Received — snmpInBadVersions
• Bad Community Name Received — snmpInBadCommunityNames
• Authentication Failures — snmpInBadCommunityUses
• ASN.1 Parsing Errors — snmpInASNParseErrs
• MIB Objects Retrieved — snmpInTotalReqVars
• MIB Objects Changed — snmpInTotalSetVars
• Total Get Requests — snmpInGetRequests
• Total GET NEXT Requests — snmpInGetNexts
• Total Set Requests — snmpInSetRequests
16
• Too Big Errors — snmpOutTooBigs
• No Such Name Errors — snmpOutNoSuchName
• Bad Value Errors — snmpOutBadValues
• General Errors — snmpOutGenErrs
• Get Responses — snmpOutGetResponses
• Traps Transmitted — snmpOutTraps
For more information about these standard MIB II variables, refer to RFC 1213.
Page 22

ICMP Statistics
This window displays statistics relating to ICMP messages (ping packets).
Accessing the ICMP Statistics
Click the ICMP button on the Switch Statistics screen to display the ICMP Statistics screen
illustrated below.
MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
17
Page 23

MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
ICMP Statistics Guidelines
Gray fields display data collected from discovered devices. These fields may not be
modified. Note: You can only set parameters and/or change the poll interval when the
polling process is stopped (i.e., when the Halt/Update button is toggled to Update).
Modifying ICMP Statistics parameter fields
1. Click on Halt.
2. Enter or change the following parameters to desired values:
• Agent Name — This field, which displays the name of the device, can be up to 256
characters in length. It corresponds to the MIB II variable sysName.
• Location — This field, which displays the location of the TigerSwitch 100, can be up to
256 characters in length. It corresponds to the MIB II variable sysLocation.
• Poll Interval — This is the time interval during which EliteView reads the status of the
TigerSwitch 100. The interval may be set to between 0 seconds (no polling) and 60
hours. The default value is 10 seconds. To change the interval, click on the Poll Interval
button to display the Poll Interval dialog box (See page 7). You can adjust the time
interval by changing the Interval and Unit settings. Then, click OK to initiate the new
settings.
18
3. Click on Set to save the changes.
4. Click on Update to initiate the changes.
5. Click on Close to close the window.
Page 24

MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
Corresponding MIB Variables
The statistics displayed correspond to the following MIB II variables.
Receive Transmit
• Messages — icmpInMsgs — icmpOutMsgs
• Errors — icmpInErrors — icmpOutErrors
• Destination Unreachables — icmpInDestUnreachs — icmpOutDestUnreachs
• Time Exceeds — icmpInTimeExcds — icmpOutTimeExcds
• Parameter Problems — icmpInParmProbs — icmpOutParmProbs
• Source Quenches — icmpInSrcQuenchs — icmpOutSrcQuenchs
• Redirects — icmpInRedirects — icmpOutRedirects
• Echo Requests — icmpInEchos — icmpOutEchos
• Echo Replies — icmpInEchoReps — icmpOutEchoReps
• Timestamp Requests — icmpInTimestamps — icmpOutTimestamps
• Timestamp Replies — icmpInTimestampReps — icmpOutTimestampReps
• Address Mask Requests — icmpInAddrMasks — icmpOutAddrMasks
• Address Mask Replies — icmpInAddrMaskReps — icmpOutAddrMaskReps
For more information about these standard MIB II variables, refer to RFC 1213.
19
Page 25
MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
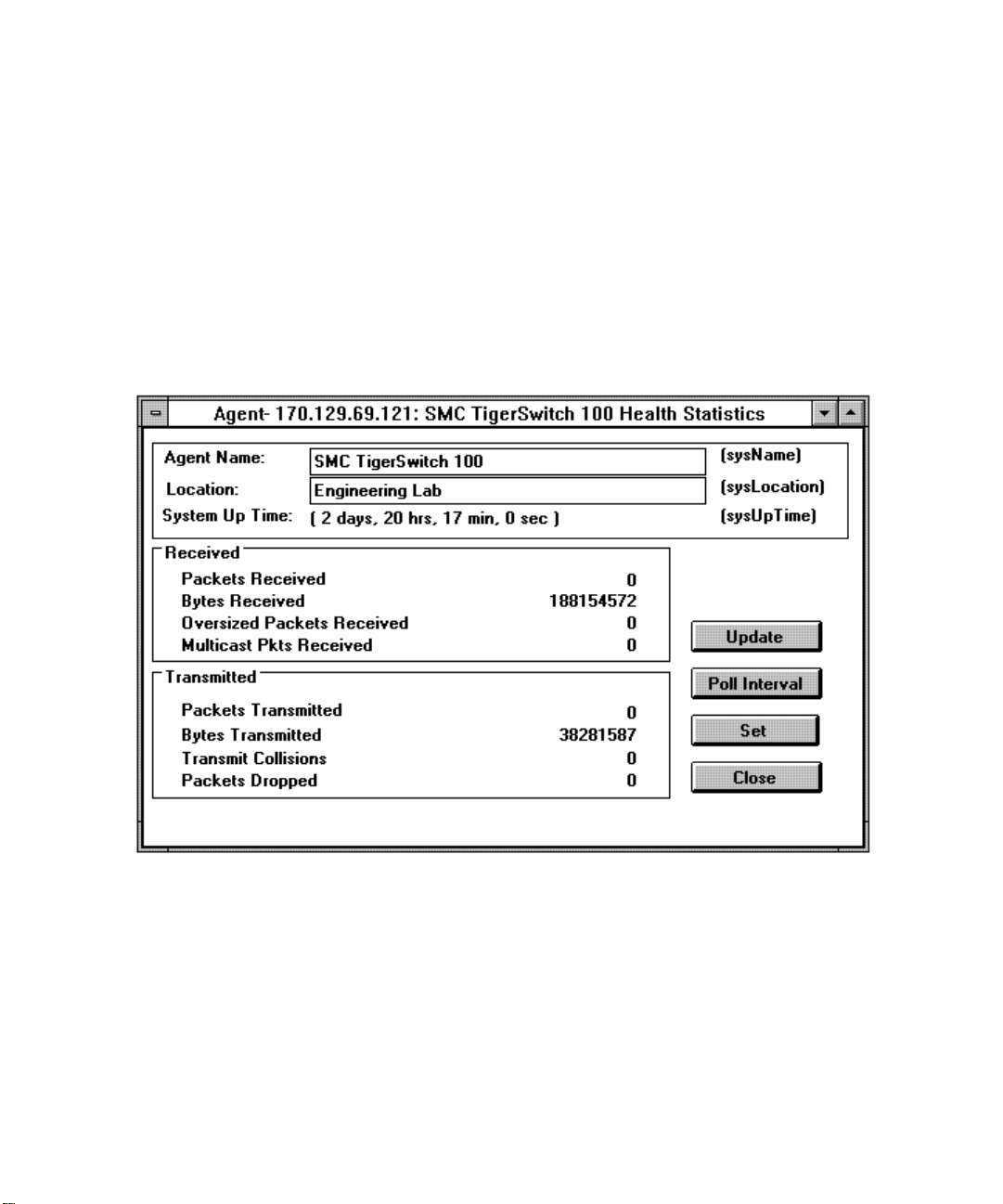
Health Statistics
This window includes information that reflects packet transmit and receive activity across the
entireTigerSwitch 100.
Accessing Health Statistics
Click the Health button on the Switch Statistics screen to display the Health Statistics
screen illustrated below.
20
Page 26

Health Statistics Guidelines
Gray fields display data collected from discovered devices. These fields may not be
modified. Note: You can only set parameters and/or change the poll interval when the
polling process is stopped (i.e., when the Halt/Update button is toggled to Update).
Modifying Health Statistics parameter fields
1. Click on Halt.
2. Enter or change the following parameters to desired values:
• Agent Name — This field, which displays the name of the device, can be up to 256
characters in length. It corresponds to the MIB II variable sysName.
• Location — This field, which displays the location of the TigerSwitch 100, can be up to
256 characters in length. It corresponds to the MIB II variable sysLocation.
• Poll Interval — This is the time interval during which EliteView reads the status of the
TigerSwitch 100. The interval may be set to between 0 seconds (no polling) and 60
hours. The default value is 10 seconds. To change the interval, click on the Poll Interval
button to display the Poll Interval dialog box (See page 7). You can adjust the time
interval by changing the Interval and Unit settings. Then, click OK to initiate the new
settings.
MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
3. Click on Set to save the changes.
4. Click on Update to initiate the changes.
5. Click on Close to close the window.
21
Page 27

MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
Corresponding MIB Variables
The statistics displayed correspond to the following MIB II variables.
• Packets Received — sum of ifInUcastPkts and ifInNUcastPkts
• Packets Transmitted — sum of ifOutUcastPkts and ifOutNUcastPkts
• Bytes Received — sum of ifOutUcastPkts and ifOutNUcastPkts
• Bytes Transmitted — sum of ifOutOctets for all 8 ports
• Oversized Packets Received — sum of dot3StatsFramesTooLongs for all 8 ports
• Multicast Packets Received — sum of ifInNUcastPkts for all 8 ports
• Transmit Collision — sum of dot3StatsMultipleCollisionFrames
• Packets Dropped — sum of ifInUnknownProtos for all 8 ports
for all 8 ports
for all 8 ports
for all 8 ports
for all 8 ports
22
For more information about these standard MIB II variables, refer to RFC 1213 and RFC 1643.
Page 28

Spanning Tree
The Spanning Tree dialog box allows you to configure and modify Spanning Tree
parameters.
Accessing Spanning Tree
Click the Spanning Tree button on the Switch Summary screen to display the Spanning
Tree dialog box illustrated below.
MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
23
Page 29

MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
Spanning Tree Guidelines
Gray fields display data collected from discovered devices. These fields may not be
modified.
Modifying Spanning Tree parameters
1. Enter or change the following parameters, according to the guidelines provided:
Bridge Data:
• MAC Address — The MAC address of port 1 on the TigerSwitch 100
• Priority — This can have any value from 0 to 65535. This is used by the Spanning Tree
Protocol, along with the MAC address, to uniquely identify the TigerSwitch 100.
Spanning Tree Configuration:
• Max Age Time — The value that all bridges use for MaxAge when this bridge is acting
as the root. The value must be a whole number, at least 6 seconds, and must adhere to
the following equations:
2 x (Forward Delay Time - 1) ≥ Max Age Time (1)
Max Age Time ≥ 2 x (Hello Time + 1) (2)
24
• Hello Time — The value that all bridges use for HelloTime when this bridge is acting as
the root. The value must be a whole number, and adhere to the above equations.
• Forward Delay Time — The value that all bridges use for ForwardDelay when this
bridge is acting as the root. The value must be a whole number, at least 4 seconds, and
adhere to the above equations.
• Database Aging Time — The time in which the TigerSwitch 100 discards inactive
addresses.
2. When all information has been entered, click on Set to change the associated MIB II
variables within the TigerSwitch 100.
3. Click on Close to close the window.
Page 30

VLAN Groups
This window displays current VLAN group information. It allows VLAN grouping status for
all ports to be modified.
Each row corresponds to the port listed on the left-hand side. Each column represents the
group number that each port can be associated with. Each port can be included in up to 8
groups, but each port must be included in at least one group. Otherwise, an error will be
generated.
Accessing VLAN Groups
Click the VLAN Groups button on the Switch Summary screen to display the VLAN
Groups screen illustrated below.
MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
25
Page 31

MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
VLAN Groups Guidelines
Modifying VLAN Groups
1. Click on Halt.
2. To add a port to a VLAN group, click the empty box at the intersection of the
row and column corresponding to the appropriate port and VLAN group,
respectively. A check mark will appear in the box to indicate that the port is now
included in the VLAN group.
3. To remove a port from a VLAN group, click the checked box at the intersection
of the row and column corresponding to the appropriate port and VLAN group,
respectively. The check mark will disappear from the box to indicate that the port is
not included in the VLAN group.
4. The VLAN Groups screen has extra Set and Clear buttons located at the
bottom of each column. These buttons allow the user to check or uncheck an entire
column all at once.
5. Click on Set to save the changes.
26
6. Click on Update to initiate the changes.*
7. Click on Close to close the window.
8. The following parameters may also be set from this screen:
• Poll Interval — This is the time interval during which EliteView reads the status of the
TigerSwitch 100. The interval may be set to between 0 seconds (no polling) and 60
hours. The default value is 10 seconds. To change the interval, click on the Poll Interval
button to display the Poll Interval dialog box (See page 7). You can adjust the time
interval by changing the Interval and Unit settings. Then, click OK to initiate the new
settings.
* Note: When changes are updated, EliteView must send a command frame to the SNMP
agent in the TigerSwitch 100 and a response frame must be received back for the changes to
take effect. The result is a slight delay between the updating of VLAN information and the
actual activation of changes. If further changes are required, it is recommended that you exit
the VLAN Groups screen, and then re-enter it after several seconds to insure that the
previously input changes have taken effect before making any new modifications.
Page 32

Port Summary
The Port Summary screen allows you to set parameters, change the poll interval for collecting
statistics, update or halt the gathering of statistics for the selected port, modify the VLAN
group membership for the selected port and access the Port Statistics screen.
MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
27
Page 33

MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
Accessing Port Summary
Double-click on a port box (Zone 2 - See page 2) and the Port Summary screen will be
displayed for that port. (When the cursor is passed over a port of the TigerSwitch 100 graph-
ic, the port outline changes color to red. Double-click on the port after it changes to red to
access the Port Summary screen.)
Port Summary Guidelines
Gray fields display data collected from discovered devices. These fields may not be
modified. Note: You can only set parameters and/or change the poll interval when the
polling process is stopped (i.e., when the Halt/Update button is toggled to Update).
Modifying Port Summary parameter fields
1. Click on Halt.
2. Enter or change the following parameters to desired values:
• Agent Name — This field, which displays the name of the device, can be up to 256
characters in length. It corresponds to the MIB II variable sysName.
28
• Internet Contact — This field, which displays the name and/or phone number of a
contact person (e.g., the network manager or technical support department), can be a
maximum of 32 characters. It corresponds to the MIB II variable sysContact.
• Location — This field, which displays the location of the TigerSwitch 100, can be up to
256 characters in length. It corresponds to the MIB II variable sysLocation.
• Poll Interval — This is the time interval during which EliteView reads the status of the
TigerSwitch 100. The interval may be set to between 0 seconds (no polling) and 60
hours. The default value is 10 seconds. To change the interval, click on the Poll Interval
button to display the Poll Interval dialog box (See page 7). You can adjust the time
interval by changing the Interval and Unit settings. Then, click OK to initiate the new
settings.
• Operation Status — This field displays the port status (enabled or disabled).
• Port Duplex — This field displays the communication mode of the port. Options include
auto-negotiation, full-duplex, and half-duplex.
• Switch Mode — This field displays the method to be used for forwarding packets. Options include cut-through (CT), fragment-free cut-through (FgFree), adaptive cut-
through (A-CT), and store-and-forward (S&F).
Page 34

MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
• Flow Control — This field displays the flow control status (enabled or disabled).
• VLAN Groups — This section displays the port’s VLAN group membership status. To
modify the port’s VLAN status, click the empty check box under the desired group to
add the port to that group. To remove the port from a VLAN group, click the checkmarked box under the group to remove the check mark. (See pages 25-26 for
additional information regarding VLAN groups)
3. Click on Set to save the changes.
4. Click on Update to initiate the changes.
5. Click on Close to close the window.
29
Page 35

MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
Port Statistics
The Port Statistics screen allows you to view more detailed status information and statistics
regarding the selected port.
Accessing Port Statistics
Click the Statistics button on the Port Summary screen to access the Port Statistics screen
illustrated below.
30
Page 36

Port Statistics Guidelines
Gray fields display data collected from discovered devices. These fields may not be
modified. Note: You can only set parameters and/or change the poll interval when the
polling process is stopped (i.e., when the Halt/Update button is toggled to Update).
Modifying Port Statistics parameter fields
1. Click on Halt.
2. Enter or change the following parameters to desired values:
• Agent Name — This field, which displays the name of the device, can be up to 256
characters in length. It corresponds to the MIB II variable sysName.
• Location — This field, which displays the location of the TigerSwitch 100, can be up to
256 characters in length. It corresponds to the MIB II variable sysLocation.
• Poll Interval — This is the time interval during which EliteView reads the status of the
TigerSwitch 100. The interval may be set to between 0 seconds (no polling) and 60
hours. The default value is 10 seconds. To change the interval, click on the Poll Interval
button to display the Poll Interval dialog box (See page 7). You can adjust the time
interval by changing the Interval and Unit settings. Then, click OK to initiate the new
settings.
MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
3. Click on Set to save the changes.
4. Click on Update to initiate the changes.
5. Click on Close to close the window.
31
Page 37

MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
Configuring Traps
The Trap Configuration table lets you configure the sending of trap alert notifications.
Accessing Trap Configuration
Select the TigerSwitch 100 Agent and then select the Configure pull-down menu. Choose
Trap Table from the pull-down menu selection list shown below. The Trap Configuration
dialog box (illustrated on the following page) will then be displayed.
Trap Configuration Guidelines
The information in the top portion of the screen is automatically read by EliteView. If this is
the first time you are configuring the trap table, the Destination Addresses are all set to zero.
The trap destination address and community string must be entered.
The following parameters may be set:
• Agent Name — This field, which displays the name of the device, can be up to 256 characters in length. It reflects the MIB II variable sysName.
• Location — This field, which displays the location of the TigerSwitch XE, can be up to
256 characters in length. It corresponds to the MIB II variable sysLocation.
• SNMP Trap Destination — You can configure up to 8 destination addresses. Enter the
IP address, following the format shown, for the stations to be sent trap alerts.
32
Page 38

MANAGING SMC’S TIGERSWITCH 100
Modifying Trap Configuration parameter fields
1. Enter the destination IP Address(es) and choose the Community String.
2. Change the Status to 2(valid) to add this row to the Trap Table. (Changing the
Status to 1(invalid) removes the specified row from the Trap Table.)
3. When all information has been entered, click on Set to save the trap configuration.
4. Click on Close to close the window.
33
Page 39

INDEX
100Mbps LED 4
A
Accessing
Health Statistics 20
ICMP Statistics 17
IP Statistics 11
Port Statistics 30
Port Summary 27
SNMP Statistics 14
Spanning Tree 23
Summary screens 2
Switch Statistics 9
Switch Summary 6
TigerSwitch 100 2
Trap Configuration 29
VLAN Membership 25
Auto-negotiation 28
B
Boot Protocol (BOOTP) 8
Bridge data 24
Bridging Available 8
C
Coll% LED 5
Collision% Display Mode 4
Configure button 3
Configuring Traps 32
D
Database Aging Time 24
Diag LED 5
Diagnostics Display Mode 3
Diagnostic status when power on 8
Display modes 3
Displaying Port Summary 3
Displaying Switch Summary 3
F
Features 1
Flow Control 29
Forward Delay Time 24
Forward% Display Mode 4
Front panel 3
Frwrd% LED 4
Full-Dplx LED 4
Full-duplex 28
Full/Half Duplex Display Mode 3
G
Gateway IP Address 8
H
Half-duplex 28
Health Statistics 20
MIB variables 22
Hello Time 24
I
ICMP Statistics 17
MIB variables 19
Icon 2
Internal power supply 4
IP Address 8
IP State 8
IP Statistics 11
MIB variables 13
L
LEDs 3
I-1
Page 40

INDEX
M
MAC Address 24
Max Age Time 24
N
NetMask 8
O
Operation Status 28
P
Port collision ratio 5
Port Duplex 28
Port forwarding ratio 5
Port Statistics 30
Port Status Display Mode 3
Port Summary 27
Port utilization rate 5
Priority 24
PWR LED 4
R
S
Sel/Link LED 4
SNMP Statistics 14
MIB variables 16
Spanning Tree 23
Configuration 24
Protocol status 8
Statistical display 4
Status LED 4
Supported models 1
Switch Mode 28
Switch Statistics 9
Switch Summary screen 6
System Performance Display Mode 4
T
TigerSwitch icon 2
TX/RX LED 4
U
Utilization % Display Mode 4
Util% LED 4
Redundant power supply 4
Reset Number 8
RPU LED 4
V
VLAN membership 25
Port Summary 29
I-2
Page 41

FOR TECHNICAL SUPPORT, CALL:
From U.S.A. and Canada (8:30 AM - 8:00 PM Eastern Time)
(800) SMC-4-YOU; (516) 435-6250; (516) 434-9314 (Fax)
From Europe (8:00 AM - 5:30 PM UK Greenwich Mean Time)
44 (0) 1344 420068; 44 (0) 1344 418835 (Fax)
Bulletin Board Services (BBS)
Modem settings: 9600,8,n,1 unless otherwise noted
New York: (516) 434-3162 (connect speed up to 14,400)
Southern Europe: 33 (1) 39.73.57.00
United Kingdom: 44 (0) 1344 418838
INTERNET
e-mail addresses:
techsupport@smc.com; european.techsupport@smc.com
Driver updates:
Host name info.smc.com
SMC Forum on CompuServe:
At the prompt (!) type: GO SMC
World Wide Web: http://www.smc.com/
FTP Site: ftp.smc.com
FOR LITERATURE OR ADVERTISING RESPONSE, CALL:
U.S.A. and Canada: (800) SMC-4-YOU; Fax (516) 273-1803
New York: (516) 435-6000; Fax (516) 273-1803
Latin America: (630) 916-7007; Fax (630) 916-6304
Southern Europe: 33 (0) 1.41.38.32.32; Fax 33 (0) 1.41.38.01.58
Europe: 44 (0) 1344 418800; Fax 44 (0) 1344 418828
Northern Europe: 44 (0) 1344 418820; Fax 44 (0) 1344 418826
Central Europe: 49 (0) 89 92861-0; Fax 49 (0) 89 92861-230
Eastern Europe/Middle East: 49 (0) 89 92861-142; Fax 49 (0) 89 9101934
South Africa: 27 (0) 11 784-0414; Fax 27 (0) 11 784-0363
Asia Pacific: (65) 336 1800; Fax (65) 339 6625
South Asia: (65) 336 1800; Fax (65) 336 3955
Korea: 82-2-551-2751; Fax 82-2635-7730
Japan: 81 (3) 57212271; Fax 81 (3) 57212270
Australia: 61-2-9929-9159; Fax 61-2-9929-9140
EliteFax
™
(SMC's Fax-on-Demand System):
U.S.A. and Canada: (800) SMC-8329
Elsewhere: (516) 435-6107
Publication Number: 900.10908, Rev. B
 Loading...
Loading...