Page 1

The installation must conform to the requirements of
the authority having jurisdiction or, in the absence of
such requirements, to the National Fuel Gas Code,
ANSI Z223.1-latest edition. The installation must also
conform to the additional requirements in this Slant/Fin
Instruction Book.
In addition where required by the authority having jurisdiction, the installation must conform to American
Society of Mechanical Engineers Safety Code for
Controls and Safety Devices for Automatically Fired
Boilers, No. CSD-1.
WARNING
This boiler, gas piping and accessories must be
installed, connected, serviced and repaired by a
trained, experienced service technician, familiar with all
precautions required for gas-fired equipment and
licensed or otherwise qualified, in compliance with the
authority having jurisdiction.
WARNING
The venting system of this boiler is under positive pressure. Leakage from this system can be hazardous and if
not avoided can result in death or serious injury. In addition
to the recommendations within this manual and the User’s
Information Manual, the venting system, from the flue collector to the outdoor discharge, must be carefully checked
annually by a qualified service agency.
This manual must be left with owner and should be hung on
or adjacent to the boiler for reference.
LYNX
INSTALLATION AND OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Printed in U.S.A. 1214 Part No. 81-5001000 Publication No. LX1-40 Rev. F
Heating Contractor
Address
Phone Number
Boiler Model Number
Boiler Serial Number
Installation Date
DIRECT-VENT SEALED COMBUSTION CONDENSING BOILER
HOT WATER MODEL LX-90, LX-120 & LX-150
GAS-FIRED BOILERS FOR NATURAL AND L.P. PROPANE GASES
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Dimensions, Rating and Orifice Sizes ........................................2
Identification of Parts ........................................................................3
Installation Requirements .................................................................4
Contamination Prevention.................................................................5
Mounting the boiler on a wall............................................................6
Venting Application...........................................................................6
Boiler Room Air Supply and Ventilation............................................6
Flue Gas Venting Requirements.......................................................7
Additional Installation Requirements for Massachusetts..................7
Vent and Air Intake Material .............................................................8
PVC/CPVC Pipe General Assembly Method....................................8
Vent and Air Intake Restrictions .......................................................8
Sidewall Venting, Non-Direct Vent ..................................................10
Vent Termination Location and Clearance......................................10
Non-Direct Vent Installation ............................................................10
Direct Vent Installation....................................................................10
Sidewall Venting, Direct Vent ..........................................................10
Vent/Air Intake Termination Installation...........................................16
Direct Vent, Venting and Air Intake through a Roof........................17
Venting and Air Intake Regular Inspection .....................................18
Condensate Removal System ........................................................18
Gas Piping ......................................................................................18
Electrical Wiring ..............................................................................19
Wiring Diagram...............................................................................20
Single and Multi Zoning..................................................................22
Water Piping ...................................................................................24
Operating Instructions.....................................................................30
Boiler Control and Display..............................................................30
Boiler Operating Status ..................................................................31
Viewing and changing temperature................................................32
Viewing and changing system setting ............................................33
Initial start and operating instruction ..............................................35
Sequence of Operation...................................................................36
Combustion check and fuel input rate............................................37
Safety Check .................................................................................37
Diagnostic error codes ...................................................................38
Care and Maintenance ...................................................................41
General Troubleshooting Guide ......................................................42
WARNING
SEE “WARNING” ON PAGE 4 FOR LIQUEFIED
PETROLEUM (L.P.) PROPANE GAS-FIRED BOILERS
IMPORTANT
READ ALL OF THE FOLLOWING WARNINGS
AND STATEMENTS BEFORE READING THE
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
Page 2
Lynx
2
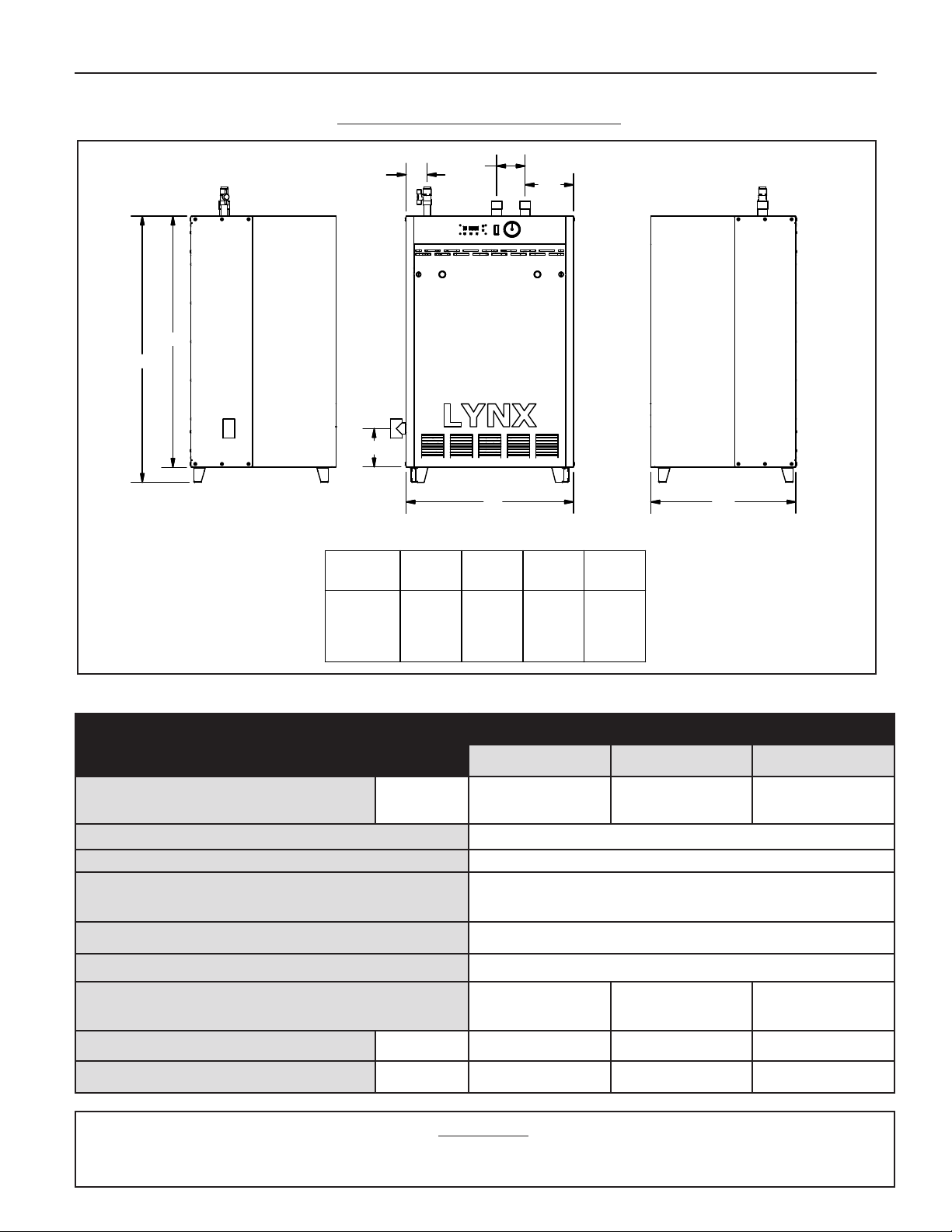
RATINGS AND DIMENSIONS
Figure 1. Dimensions data
SPECIFICATIONS
BOILER MODEL
LX-90 LX-120 LX-150
Input Rate, Btu/Hr
Max.
Min.
90,000
25,000
120,000
30,000
150,000
37,500
Water Piping Connection 1" NPT (Male)
Gas Piping Connection 1/2" NPT (Female)
Vent Connection
3" Nominal ID Pipe PVC, CPVC, Polypropylene
(solid or flexible) or SS. SEE WARNING
Air Intake Connection 3" Nominal ID PVC or CPVC
Gas Orifice Size for Natural Gas No Orifice Used
Gas Orifice Size for Propane
0.1900"
Code # C
0.2025"
Code # A
0.2200"
Code # E
Boiler Water Volume Gal. 0.4 0.6 1.1
Weight of Boiler (Uncrated) Lbs. 118 125 140
WARNING:
1. Use of cellular core PVC and CPVC or Radel for venting system is NOT allowed
2. Thermal insulation on non-metallic vent pipe and fittings is NOT allowed.
35
"C"
33
5
LEFT SIDE FRONT RIGHT SIDE
BOILER "A" "B" "C" "D"
MODEL
BOILER "A" "B" "C" "D"
LX-90 6 3/4 3 3/8 2 3/4 16 1/4
MODEL
LX-120 6 5/8 3 3/8 2 16 1/4
LX-90 6 3/4 3 3/8 2 3/4 16 1/4
LX-150 6 3/8 3 3/4 2 3/4 19
LX-120 6 5/8 3 3/8 2 16 1/4
"B"
"A"
22
"D"
Page 3
Lynx
3
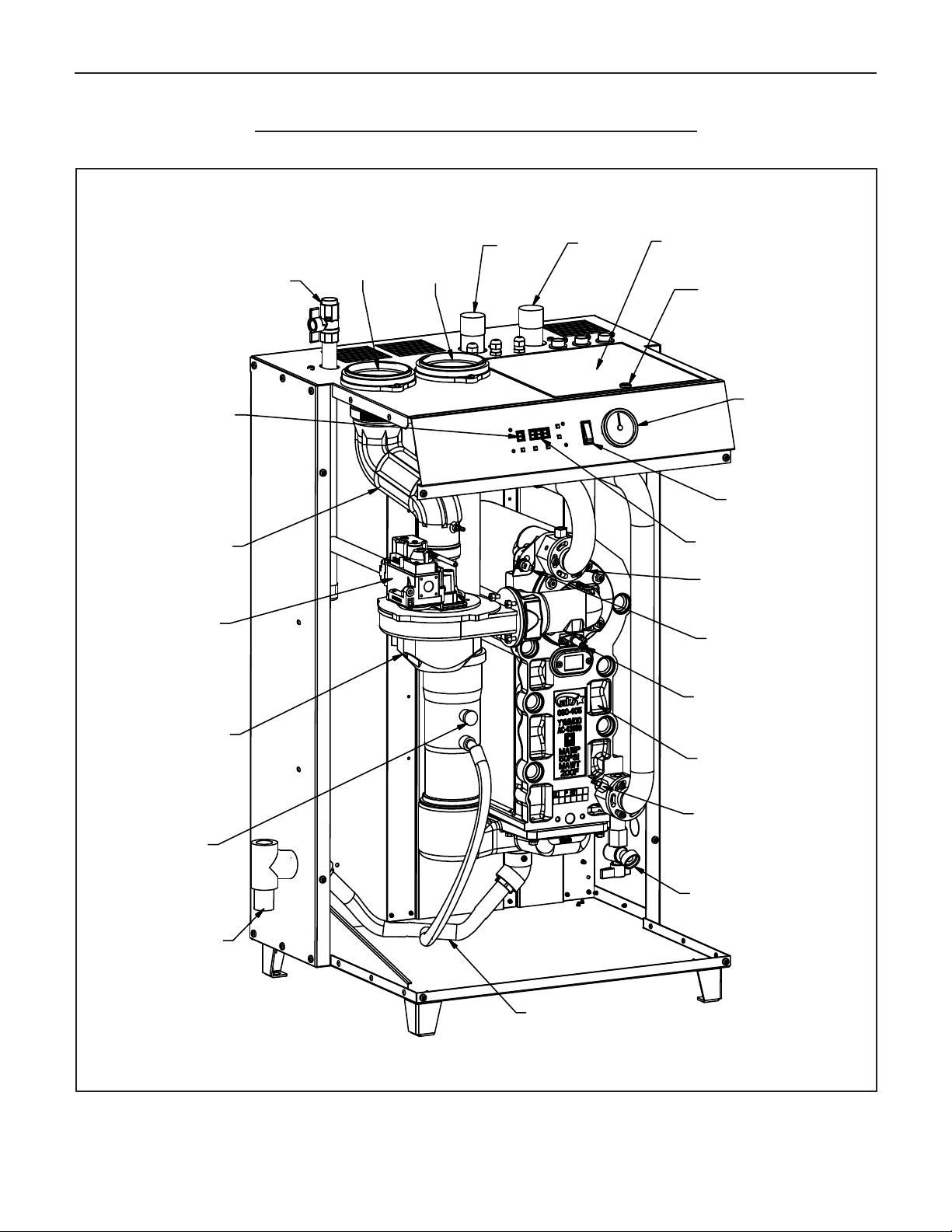
LOCATION AND IDENTIFICATION OF PARTS
Figure 2. Location and identification of parts (front and side panels are removed) model LX-150 is shown
GAS SUPPLY
VALVE
MODE
DISPLAY
AIR INTAKE
HOSE
GAS
VALVE
AIR
INTAKE
VENT
BOILER
SUPPLY
WATER
BOILER
RETURN
WATER
BOILER
CONTROL
UNDER THE COVER
TURN
BLACK SCREW
1/4 TURN
THEN LIFT
CONTROL COVER
TO REMOVE
PRESSURE
GAUGE
POWER
SWITCH
TEMPERATURE
DISPLAY
WATER
SUPPLY
SENSOR
WATER
HIGH
LIMIT
SPARK
ELECRODES
COMBUSTION
BLOWER
TEST
PORT
CONDENSATE
DRAIN
CONDENSATION
TRAP/REMOVAL
(IGNITER)
HEAT
EXCHANGER
WATER
RETURN
SENSOR
BOILER
DRAIN
VALVE
Page 4
Lynx
4
The installation must conform to the requirements of the
authority having jurisdiction or, in the absence of such
requirements, to the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1latest edition.
This installation must also conform to the additional requirements in this Slant/Fin Instruction Book.
BOILER LOCATION
Provide a level, solid foundation or vertical wall for the boiler.
Location should be as near as possible to chimney or outside
wall so that the flue pipe from boiler is short and direct. (See
paragraph heading “Vent Termination Location and Clearance” on page 9.) The location should also be such that all
boiler components are protected from water (dripping, spraying, rain, etc.) during appliance operation and service (circulator replacement, control replacement, etc.).
WARNING
SPECIAL ATTENTION FOR LIQUEFIED PETROLEUM
(L.P.) PROPANE GAS-FIRED BOILER INSTALLATIONS
LPG appliances (boilers) shall be installed in accordance
with applicable provisions of NFPA 58 ( Liquefied Petroleum
Gas Code) latest for installations in US and CAN/CGA
B149.1 latest edition for installations in Canada.
Liquefied Petroleum (LP) propane gas is heavier than air
therefore Propane gas accumulate at floor level. If you suspect a leak, do not attempt to operate boiler. A spark or
flame from the appliance (boiler) or other sources may ignite
the accumulated propane gas causing an explosion or fire.
It is recommended that inspections for gas leaks be performed periodically by licensed professional and that leak
detection devices be installed as a further safety measure.
BOILER FOUNDATION
A. Provide a solid, level foundation or vertical wall capable of
supporting the weight of the boiler filled with water, and
extending at least 2" past the jacket on all sides. See
dimensions of boilers, page 2. See also figure 4a & 4b for
mounting the boiler on the wall.
B. Boiler can be installed on both combustible and
non-combustible floors, but must NOT be installed on or
above carpeting.
C. If boiler is to be located over buried conduit containing
electric wires or telephone cables, consult local codes or
the National Board of Fire Underwriters for specific
requirements.
SAFETY
KEEP THE BOILER AREA CLEAR AND FREE FROM
COMBUSTIBLE MATERIALS, GASOLINE AND OTHER
FLAMMABLE VAPORS AND LIQUIDS.
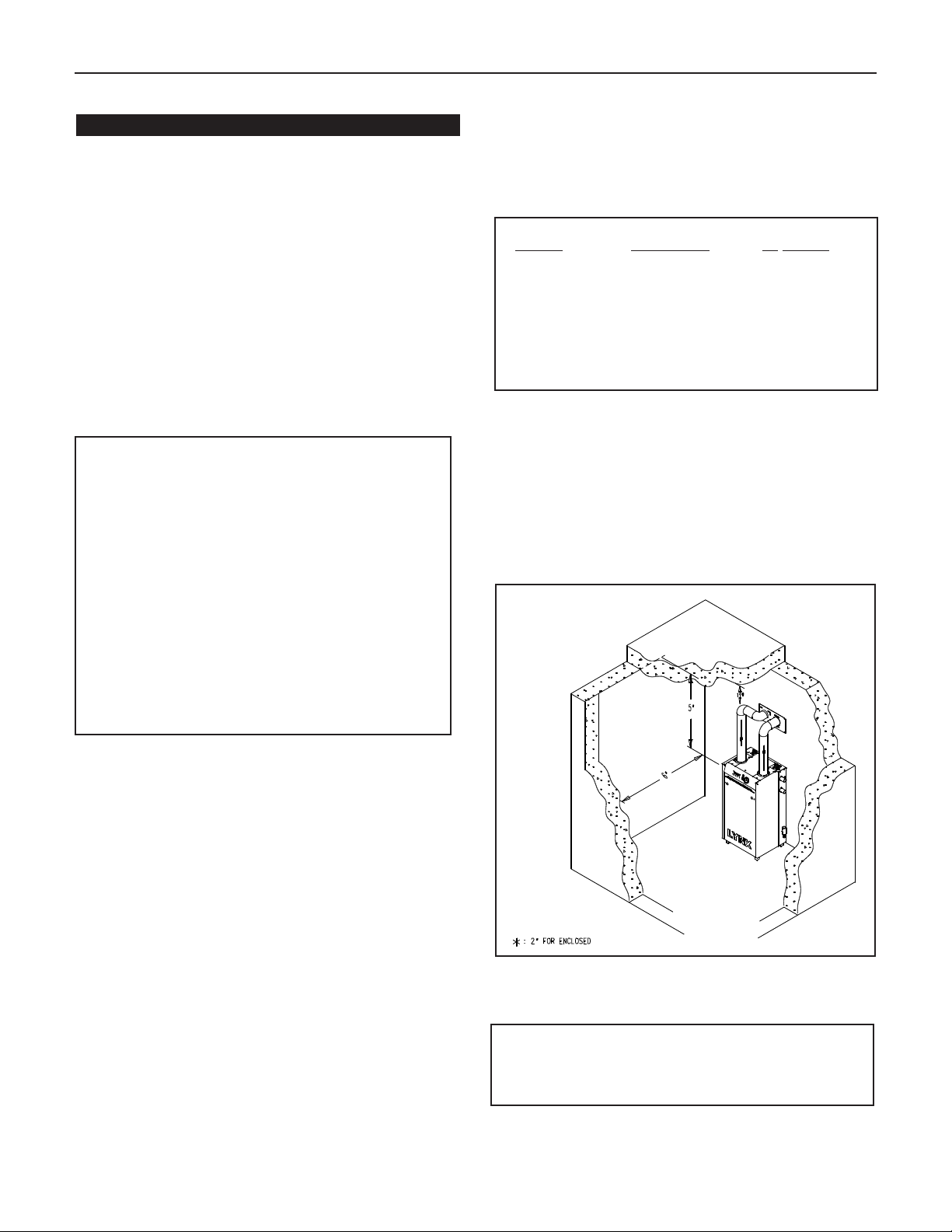
Figure 3. Lynx boiler min. clearances for combustible
construction.
INSTALLATION REQUIREMENTS
MINIMUM CLEARANCES FROM COMBUSTIBLE
CONSTRUCTIONS
A. Minimum clearances to the exterior surfaces of the boiler
shall be as follows:
MINIMUM ALCOVE AND CLOSET CLEARANCE
For Combustible Recommended
Surface
Construction for Service
Front 6" 18"
Rear 0" 0"
Left Side 0" 8"
Right Side 0" 8"
Top 5" 18"
Flue Connector:
Enclosed — 2" 6"
Uninclosed — 1" 6"
B. Provide accessibility clearance of 8" on sides requiring
servicing and 18" on sides used for passage.
C. All minimum clearances shown above must be met. This
may result in increased values of some minimum clearances in order to maintain the minimum clearances of
others.
D. Clearance from hot water pipes shall be 1 inch**.
** At points where hot water pipes emerge from a floor, wall or ceiling,
the clearance at the opening through the finished floor boards or wall
or ceiling boards may be not less than 1/2 inch. Each such opening
shall be covered with a plate of uncombustible material.
Page 5
CONTAMINATION PREVENTION
The combustion air supply must not be susceptible to contamination sources, whether the combustion air comes from the
interior or exterior of the building. Contaminated air can cause
corrosion or other damage to the heat exchanger and components of the boiler, causing failure of these parts or unsafe
operation.
Below is a list of products and areas which may cause
contaminated combustion air:
PRODUCTS TO AVOID
• Spray cans containing chloro/fluorocarbons
• Permanent wave solutions
• Chlorinated waxes/cleaners
• Chlorine-based swimming pool chemicals
• Calcium chloride used for thawing
• Sodium chloride used for water softening
• Refrigerant leaks
• Paint or varnish removers
• Hydrochloric acid/muriatic acid
• Cements and glues
• Antistatic fabric softeners used in clothes dryers
• Chlorine-type bleaches, detergents, and cleaning
solvents found in household laundry rooms
• Adhesives used to fasten building products and other
similar products
AREAS LIKELY TO HAVE CONTAMINANTS
• Dry cleaning/laundry areas and establishments
• Swimming pools
• Metal fabrication plants
• Beauty shops
• Refrigeration repair shops
• Photo processing plants
• Auto body shops
• Plastic manufacturing plants
• Furniture refinishing areas and establishments
• New building construction
• Remodeling areas
• Garages with workshops
Lynx
5
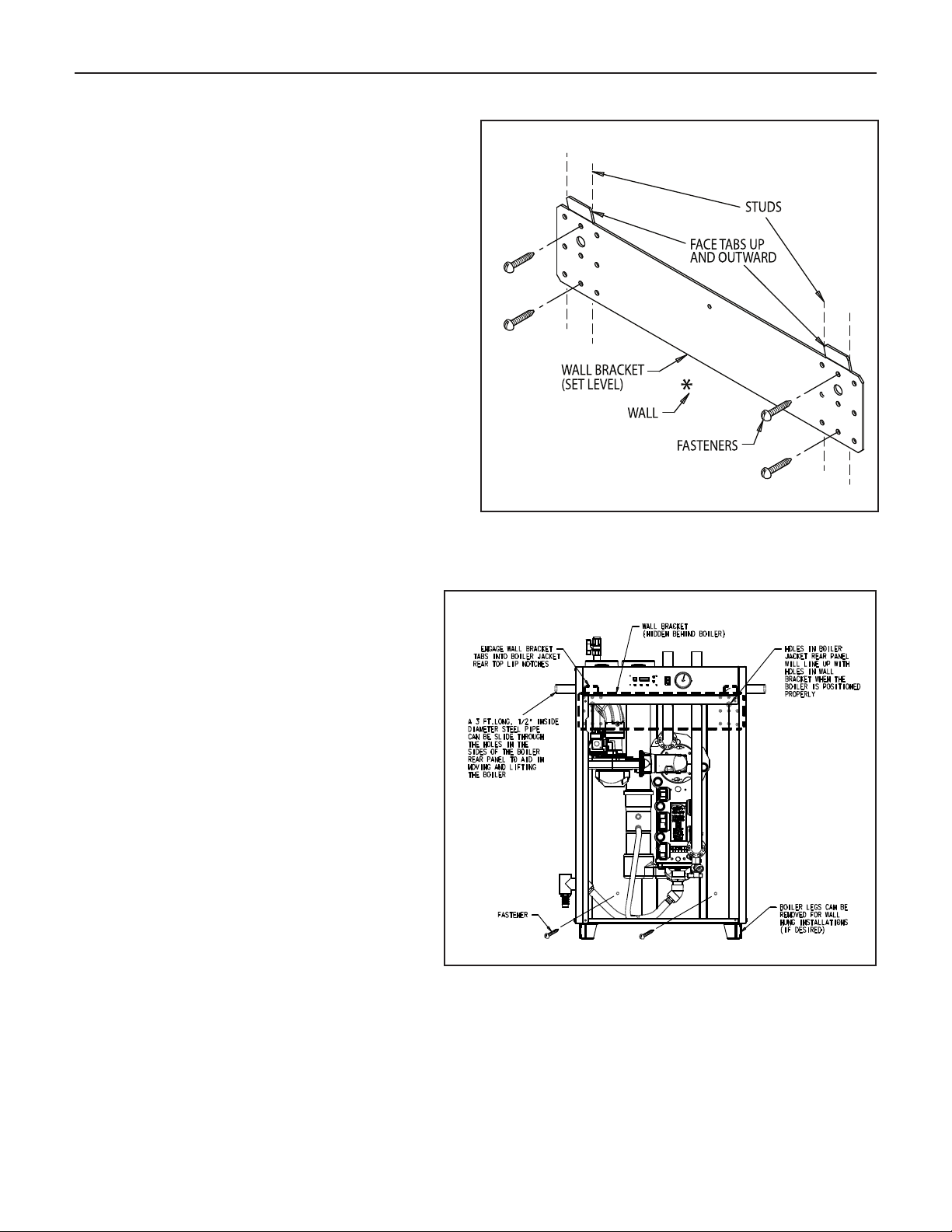
Figure 4a. Wall bracket securement
Figure 4b. Mounting boiler on the wall
Page 6

Lynx
6
MOUNTING THE BOILER ON A WALL
Be sure that the wall is vertically plumb and capable of carrying
the weight of the boiler and the system piping, when full of
water. See page 2 for the boiler weight.
Be sure that there are studs available in the proper locations,
for securing the boiler wall bracket and back panel.
(See Figures 4a and 4b).
For wood stud walls, use lag screws or wood screws with a
coarse thread and a minimum of 3” in length.
For metal stud walls, use toggle-style bolts that are specifically
designed for such and maximum capacity exceeds the weight
of the boiler and the system piping when full of water.
DO NOT use anchors driven into sheetrock to hold the boiler
up on the wall. If mounting the boiler on a cement wall, use
anchors that are specifically designed for such, and maximum
capacity exceeds the weight of the boiler and the system
piping, when full of water.
A. INSTALL THE WALL BRACKET. SEE FIGURE 4a.
1. Remove the wall bracket from the boiler jacket rear panel,
by unfastening the single screw that holds it in place, for
shipping purposes only.
2. Select the location on the wall where the boiler will be
mounted. The upward facing tabs of the wall bracket will
align with the top surface of the boiler jacket, and 3 feet of
open wall space will be needed to accommodate the boiler
jacket rear panel below this.
3. For sheetrock and stud construction, locate the studs and
determine which set of holes in the wall bracket best align
with the center of the studs. For cement walls, determine
a location for the wall bracket to mount where the anchors
will be secure, devoid of seams or cracks.
4. Place the bracket in the selected location, with the 2 tabs
positioned up and facing outward, level it out, and mark
the holes to be used. A minimum of 4 of these holes must
be utilized, regardless of wall material.
5. Drill the appropriate diameter and depth holes for the
fasteners used in the wall, where marked.
6. Fasten the wall bracket to the wall, being sure that the
tabs face upward and outward, and the fasteners have
engaged the wall properly.
B. INSTALL THE BOILER ON THE WALL. SEE FIGURE 4b.
1. Remove the boiler jacket front cover, by turning the 2 black
screws 1/4 turn to the open position, then lifting off.
2. Remove both the boiler jacket side panels, by removing
the 2 sheetmetal screws in the top and bottom front edge,
then lift off.
3. To aid in lifting the boiler, a 3 foot long, 1/2” inside diameter
steel pipe can be slid through the holes in the sides of the
boiler rear panel. Let the pipe extend out each side of the
jacket evenly, for hand-holds, and pick up the boiler without
letting it tilt, for safety.
4. Lift the boiler up against the wall, with the top edge of the
jacket slightly above the wall bracket tabs. There are 2
holes in the upper corners of the jacket rear panel, that
can visually be aligned with the 2 larger diameter holes in
the wall bracket, to ensure that the wall bracket tabs line
up and engage with the boiler jacket near top lip notches
properly.
5. There are 2 fastener holes in the lower area of the boiler
rear panel, just below the flue collector, for insuring the
boiler does not move off the wall bracket. Mark these 2
holes, with the boiler in place, then lift the boiler off the wall
bracket.
6. Determine which fastener type will best engage with the
wall construction at the location of the 2 market holes. Drill
out the appropriate diameter and depth holes for the
fasteners, where marked.
7. Lift the boiler up onto the wall bracket again, as described
in Step 4. Secure the boiler to the wall, with the 2 fasteners
in the lower rear panel area.
8. If able to, the 1/2” diameter lifting pipe should be removed
from the boiler rear panel.
9. The 4 boiler legs may be removed at this time, if desired. 2
screws hold each leg in place, from inside the jacket
panel.
10. The boiler side panels can be replaced at this time, but the
front panel should be left off, for the startup procedure
later in the installation.
VENTING APPLICATION
Lynx boilers are sealed combustion type boilers, it may be
installed and vented either as a direct vent boiler which all air
for combustion is obtained directly from outside or as a nondirect vent boiler which air for combustion is taken from inside
the boiler room.
Lynx boilers must be vented by 3" diameter PVC/CPVC schedule 40 pipe, 3” nominal ID polypropylene pipe or the proper 3”
diameter stainless steel venting system (see “vent material” on
page 8) through the roof or sidewall.
BOILER ROOM AIR SUPPLY AND VENTILATION
An ample supply of air is required for combustion and ventilation. When buildings are insulated, caulked and weatherstripped, now or later on, direct openings to outside may be
required and should be provided. If the boiler is not near an
outside wall, air may be ducted to it from outside wall openings.
Provisions for combustion and ventilation air must be made in
accordance with section 5.3, Air for Combustion and Ventilation, of the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1-latest edition, or applicable provisions of the local building codes. The
following recommendation applies to buildings of energy-saving
construction, fully caulked and weatherstripped.
INSTALLATION IN ENCLOSED BOILER ROOM REQUIRES
TWO UNOBSTRUCTED OPENINGS FOR PASSAGE OF AIR
INTO THE BOILER ROOM:
Page 7

A. NON-DIRECT VENT INSTALLATION
1. Air drawn horizontally from outdoors DIRECTLY through
an outside wall; one louvered opening near the floor and
one louvered opening near the ceiling, each opening with a
minimum FREE air passage area of 1 square inch per 4000
Btuh of total appliances’ input.
2. Air drawn horizontally through HORIZONTAL DUCTS;
one opening near the floor and one opening near the ceiling,
each opening with a minimum FREE air passage area of 1
square inch per 2000 Btuh of total appliances’ input.
3. Air drawn VERTICALLY from outdoors; one opening at the
floor and one opening at the ceiling, each opening with a
minimum FREE air passage area of 1 square inch per 4000
Btuh of total appliances’ input.
4. Air drawn from inside the building; one opening near the
floor and one opening near the ceiling, each opening with a
minimum FREE air passage area of 1 square inch per 1000
Btuh of total appliances’ input.
IF BOILERS ARE INSTALLED ADJACENT TO OTHER FUEL
BURNING EQUIPMENT, THE AREA OF FREE OPENINGS
MUST BE APPROPRIATELY INCREASED TO ACCOMMODATE
THE ADDITIONAL LOAD.
B. DIRECT VENT INSTALLATION
Adequate air supply should be provided to prevent overheating of
the boiler controls and boiler room. Openings for passage of air
into the boiler room for direct-vent installation must be at least
1
⁄2
of the openings required for the non-direct vent as
mentioned above.
If additional non-direct vent appliances are installed in the same
space and adequate air openings are provided for them, there
are no additional air openings required for the Lynx boiler.
For both direct and non-direct installation, the following must be
considered:
- Openings must never be reduced or closed. If doors or
windows are used for air supply, they must be locked
open.
- Protect against closure of openings by snow and debris.
Inspect frequently.
- No mechanical draft exhaust or supply fans are to be
used in or near the boiler area.
- Boiler area must never be under negative pressure. The
flow of combustion and ventilating air to the boiler must
not be obstructed.
FLUE GAS VENTING REQUIREMENTS
The Lynx boiler is a high efficiency, mechanically forced draft
boiler and, therefore, require different venting arrangements than
natural draft, lower efficiency boilers.
THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS MUST BE CAREFULLY
READ AND FOLLOWED IN ORDER TO AVOID ANY HAZARDOUS CONDITIONS DUE TO IMPROPER INSTALLATION
OF THE AIR INTAKE AND FLUE GAS VENTING SYSTEM.
The vent piping installation MUST be in accordance with these
instructions and with ANSI Z223.1-latest edition NATIONAL
FUEL GAS CODE, Part 7, Venting of Equipment. Other local
codes may also apply and must be followed. Where there is a
conflict between these requirements, the more stringent case
shall apply. The use of a vent damper is NOT permitted on this
boiler series.
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS FOR THE COMMONWEALTH
OF MASSACHUSETTS
When the Bobcat is installed and used in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, the following additional
requirements pursuant to Massachusetts
code 248 CMR MUST be met:
(1). Exisiting chimneys shall be permitted to have their use continued
when a gas conversion burner is installed, and shall be equipped with a
manual reset device that will automatically shut off gas to the burner in the
event of a sustained back-draft.
(2)(a). For all side wall horizontally vented gas fueld equipment installed in
every dwelling, building or structure used in whole or part for residential
purposes, including those owned or operated by the Commonwealth and
where the side wall exhaust vent termination is less than seven (7) feet
above finsihed grade in the area of the venting, including but not limited to
decks and porches, the following requirements shall be satisfied:
1. INSTALLATION OF CARBON MONOXIDE DETECTORS. At the time
of installation of the side wall horizontal vented fueled equipment, the
installing plumber or gasfitter shall observe that a hard wired carbon
monoxide detector with an alarm and battery back-up is installed on the
floor level where the gas equipment is to be installed. In addition, the
installing plumber or gasfitter shall observe that a battery operated or hard
wired carbon monoxide detector with an alarm is installed on each additional level of the dwelling, building or structure served by the side wall
horizontal vented gas fueled equipment. It shall be the responsibility of the
property owner to secure the services of qualified licensed professionals
for the installation of hard wired carbon monoxide detectors.
a. In the event that the side wall horizontally vented gas fueld equipment
is installed in a crawl space or an attic, the hard wired carbon monoxide
detector with alarm and battery back up may be installed on the next adjacent floor level.
b. In th event that the requirements of this subdivision can not be met at
the time of completion of installation, the owner shall have a period of thirty (30) days to comply with the above requirements; provided, however,
that during said thirty (30) day period, a battery operated carbon monoxide
detector with an alarm shall be installed.
2. APPROVED CARBON MONOXIDE DETECTORS. Each carbon
monoxide detector as required in accordance with the above provisions
shall comply with NFPA 720 and be ANSI/UL 2034 listed and IAS certified.
3. SIGNAGE. A metal or plastic identification plate shall be permanently
mounted to the exterior of the building at a minimum height of eight (8)
feet above grade directly in line with the exhaust vent terminal for the horizontally vented gas fueled heating appliance or equipment. The sign shall
read, in print size no less that one-half (1/2) inch in size, “GAS VENT
DIRECTLY BELOW, KEEP CLEAR OF ALL OBSTRUCTIONS”.
4. INSPECTION. The state or local gas inspector of the side wall horizontally vented gas fueled equipment shall not approve the installation unless,
upon inspection, the inspector observes carbon monoxide detectors and
signage installed in accordance with the provisions of 248 CMR
5.08(2)(a)1 through 4.
(b) EXEMPTIONS. The following equipment is exempt from 248 CMR
5.08(2)(a)1 through 4:
1. The equipment listed in Chapter 10 entitled “Equipment Not
Required TO Be Vented” in the most current edition of NFPA 54 as
adopted by the Board; and
2. Product Approved side wall horizontally vented gas fueled equipment installed in a room or structure separate from the dwelling, building or structure used in whole or part for residential purposes.
Lynx
7
Page 8
Lynx
8
VENT AND AIR INTAKE MATERIALS
The vent and air intake system for direct or non-direct vent installation must be 3” diameter PVC/CPVC schedule. 40 pipe, 3”
nominal polypropylene (solid or flexible) or UL listed single wall 3”
diameter AL29-4C* stainless steel material. The following manufacturers’ systems are approved for use within a specified minimum and maximum equivalent vent length in this manual.
When joining the various components of the listed stainless
steel vent systems, the manufacturers’ instructions should be
closely followed to insure proper sealing. Use sealant specified
by vent system manufacturer for sealing of pipe and fittings, if
required. When joining the PVC/CPVC pipe and fittings, follow
the instructions provided in this manual. All connections must be
liquid and pressure tight. DO NOT use galvanized flue pipe or
any plastic-type materials other than specified above.
The integral flue adapter on the boiler is designed to accommodate either PVC/CPVC Schedule 40 pipe, polypropylene or
the listed stainless steel vent systems. This adapter has built-in
sealing rings, so no additional sealant is required. Make sure
the pipes are round and burr-free, and push down into the
appropriate step of the adapter, until snug. (See Figure 5).
Apply liquid soap to the outer end of the vent pipe and air
intake pipe for easy insertion.
The integral air intake adapter on the boiler is designed to take
PVC/CPVC pipe.
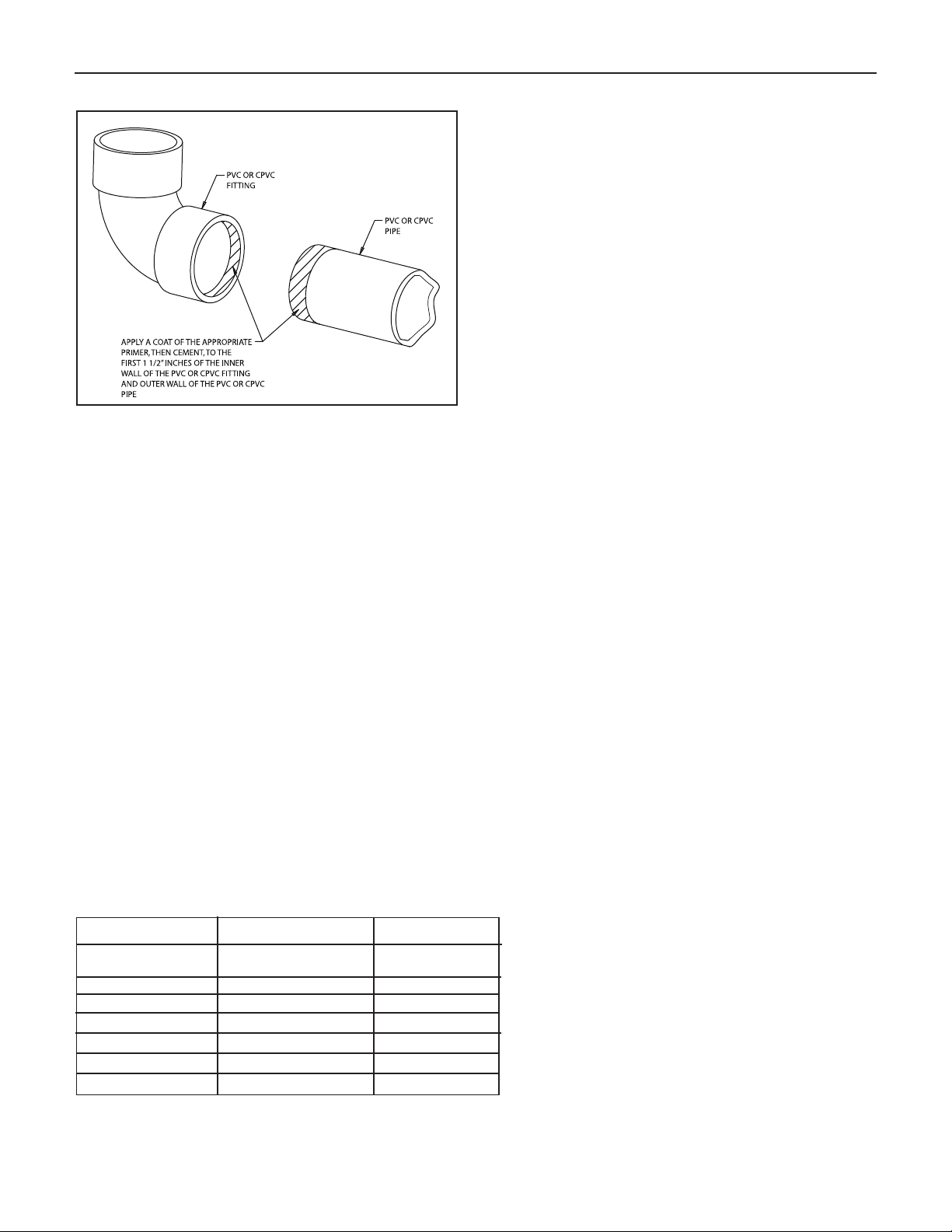
PVC/CPVC PIPE GENERAL ASSEMBLY METHOD
The following are the recommended methods for cutting,
cleaning and connecting PVC and CPVC pipe, for both the
vent and air intake piping system:
1. When laying out the piping system, work from the boiler
vent and air intake adapter to the point of outside
termination.
2. Cut the PVC/CPVC pipe to the required lengths, and
pre-assemble the entire system, before sealing.
Disassembly after sealing, to make any corrections, will not
be possible.
3. Once the pre-assembled PVC/CPVC pipe vent and air
intake system is verified to be of the proper length pipe and
fitting orientation, begin disassembling and preparing the
pipes and fittings for the sealing process. This can be done
section by section, or the complete vent and air intake
system can be disassembled. It is recommended to mark
the various parts, before complete disassembly, to
eliminate the possibility of errors during re-assembly.
4. De-burr the inside and outside of every PVC/CPVC pipe, to
ensure that they engage fully into the fittings, and flow is
not compromised. A small chamfer on the outside of each
pipe can particularly aid in the final assembly process.
5. Wipe or knock out any debris from inside the PVC or
CPVC pipe, which may have accumulated there from the
cutting process or storage. Debris can cause operational
problems with the boiler combustion components.
6. Thoroughly clean the outside ends of each pipe, and the
inside of each fitting. The surfaces must be dry for the
sealing agents to work properly. Handle the prepared pipe
lengths away from the cleaned ends, and handle the
cleaned fittings, from the outside, to avoid contamination.
7. Re-assembly of the PVC or CPVC pipe should be done in
sections, to avoid the primer and cement drying before the
parts are engaged.
8. For each joint, first apply a coat of primer to the outside
sealing surface of the pipe and the inside sealing surface of
each fitting. Use only the primer type that is specified for
either the PVC or CPVC pipe that is bing utilized.
9. Before the primer dries, apply a coat of cement over it. A
second coat of cement can be applied, if necessary, but
must be done quickly and in a manner that avoids
unnecessary build-up that would cause obstruction inside
the system. Use only the cement type that is specified for
either the PVC or CPVC pipe that is being utilized.
10. Before the cement dries, insert the pipe into the fitting. A
slight twisting motion while pushing the pipe into the fitting
will aid in distributing the cement evenly and ensuring the
parts fully engage.
11. Quickly wipe the excess cement from the outside areas of
the joint. Discard any rags used to avoid later getting the
cement on hands, clothes and equipment.
Note: Polypropylene pipe, follow manufacturers instructions.
VENT AND AIR INTAKE RESTRICTIONS
1. Maximum allowed equivalent vent and air intake length for
all of the approved vent and air intake materials is 100 feet.
2. Equivalent of vent or air intake length is sum of the
straight pipe lengths and equivalent length of elbows as
shown in the table on page 9.
*AL29-4C is a registered Trademark of Allegheny Ludlum Corp
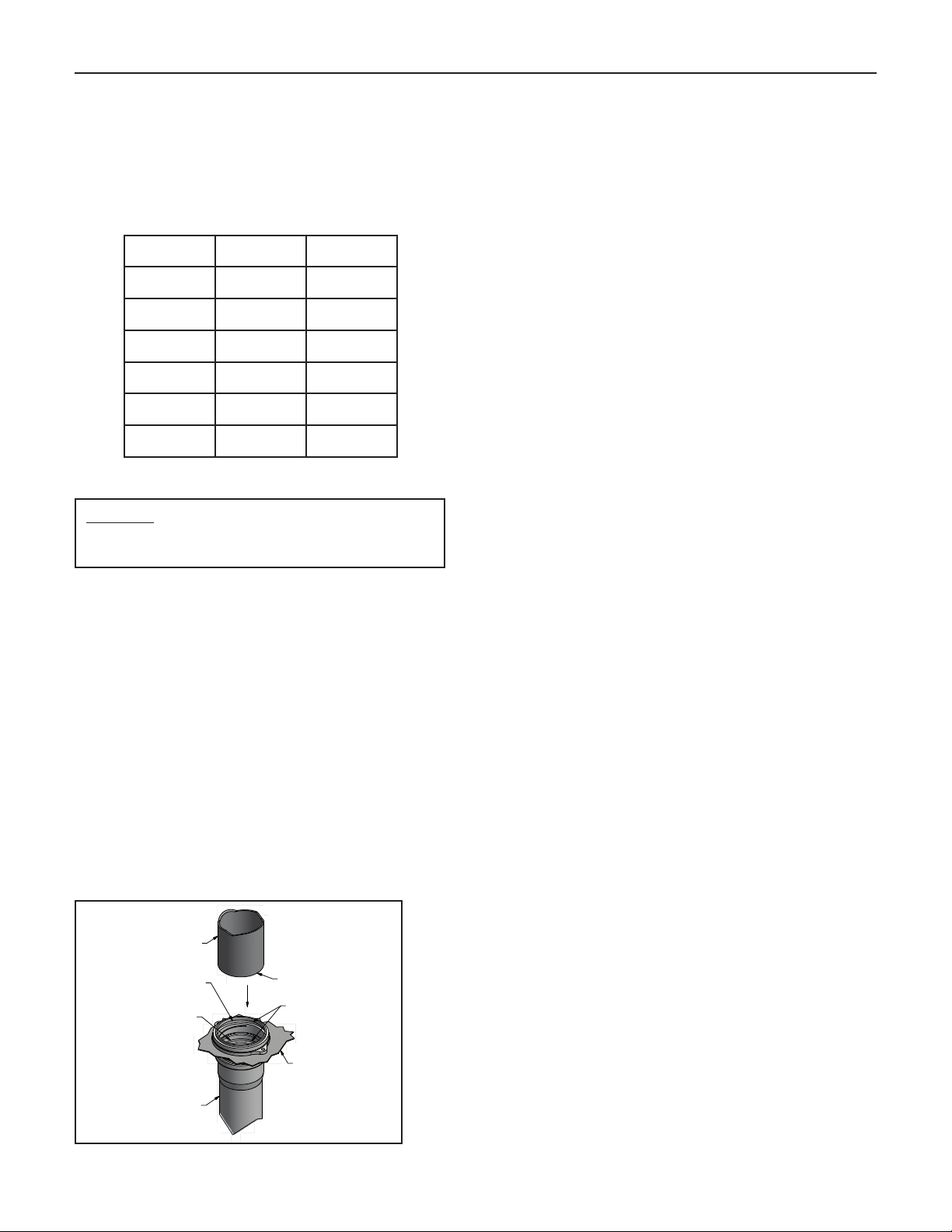
Figure 5. Vent Pipe installation into Boiler Adapter.
Manufacturer Type/System Sealant
Heat-Fab. Inc.
Saf-T Vent
EZ Seal
Not Required
ProTech Sys-
tem, Inc.
FasNSeal Not Required
Flex-L Interna-
tional, Inc.
StaR-34 GE-IS806
N/A
PVC pipe,
Schedule 40
PVC primer and
cement
N/A
CPVC pipe,
Schedule 40
CPVC primer
and cement
Centrotherm
Eco System
Polypropylene Not required
WARNING: 1. Use of cellular core PVC and CPVC or Radel
for venting system is NOT allowed 2. Thermal insulation on
non-metallic vent pipe and fittings is NOT allowed.
VENT PIPE
(PVC SHOWN)
INSTALL PVC/CPVC PIPE
DOWN TO THIS LIP
INSTALL STAINLESS
STEEL PIPE OR
POLYPROPYLENE
PIPE DOWN TO
THIS LIP
BOILER UPPER
VENT PIPE
CHECK EDGES
FOR BURRS
SEALING
RINGS
TOP OF BOILER
JACKET
Page 9
Lynx
9
3. The vent termination is in addition to the allowed
equivalent lengths.
4. Minimum vent length is 2 feet of straight pipe, plus one
90˚ elbow that is required.
5. Vent length restriction is for both direct and non-direct
vent installations.
EXAMPLE: The combustion air is provided by air intake
piping directly to the boiler (direct-vent installation). The vent
piping will be PVC and installation location will require the
use of 4 elbows for the vent to run the termination. The air
intake piping will also be PVC, and also will require the use
of 4 elbows.
In this case, the maximum straight pipe vent length that can
be utilized with the 4 elbows would be: 100' - (4 x 5') = 80'.
Since the air intake pipe also is PVC and requires the use of
4 elbows, the maximum straight pipe air intake length that
can be utilized is also 80 feet.
If the air for combustion were taken from the boiler room
(non-direct vent installation), still the maximum straight vent
length would be 80 feet.
6. The Lynx boiler is equipped with a built-in condensation
drain and trap. The trap must be filled with water. DO NOT
operate the boiler without filling the trap with water to
prevent flue gas discharge into space. The drain must
dispose of possibly large quantities of condensate, which
may require a neutralizing system. Refer to the “Condensate
Drainage” section of this manual. No additional condensation drain and trap is required on the vent piping
system itself.
7. The horizontal vent pipe must be sloped upward from the
boiler at a pitch of at least 1/4” per 1 foot of run, so that
the condensate from the vent system runs to the boiler
vent adapter pipe, then out the built-in condensation drain
and trap.
8. The horizontal vent and air intake pipes must be supported
with pipe straps, at intervals no greater than 5 feet, when
polypropylene, PVC/CPVC pipe is utilized. This support
spacing applies also to stainless steel vent pipe, unless the
manufacturer’s instructions permit otherwise. The vertical
vent and air intake pipes also must be supported, wherever
the building construction provides allowance for it, such as
ceiling or roof passage openings where a firestop and
support or braces can be affixed.
9. Minimum clearances of vent pipes from combustible
constructions must be maintained (see Page 4). No
clearance is required between the vent and air intake pipes
of this boiler.
10. Common venting with other appliances or another Lynx
boiler is not allowed.
11. DO NOT install a vent damper or similar devices in vent
system or on the boiler.
12. DO NOT insulate venting system.
Figure 6.
Heat-Fab, Inc. Saf-T Standard 3
elbow
Heat-Fab, Inc. Saf-T, tight radius elbow 6
ProTech System, Inc. FasNseal 6
Flex-L International, Inc. StaR-34 6
N/A PVC, Schedule 40 5
N/A CPVC, Schedule 40 5
Centrotherm Eco Systems
Polypropylene 5
Manufacturer
Type/System
Equivalant length (Ft.)
Equivalent Length of Various 90-Degree Elbows
Page 10

Lynx
10
VENTING INSTALLATION
Only the PVC/CPVC, polypropylene and approved stainless
steel materials listed on page 8 may be used for the venting
system installation. If stainless steel vent systems are used, follow the manufacturer’s instructions, in conjunction with these
instructions.
I. Non-Direct Vent Installation
The air for combustion is taken from the ambient air
surrounding the boiler; therefore, ample supply of air is required
for combustion and ventilation (see page 7.)
DO NOT use this installation method if the surrounding of the
boiler is contaminated. See page 5 for the list of harmful
contaminants and their sources, to avoid.
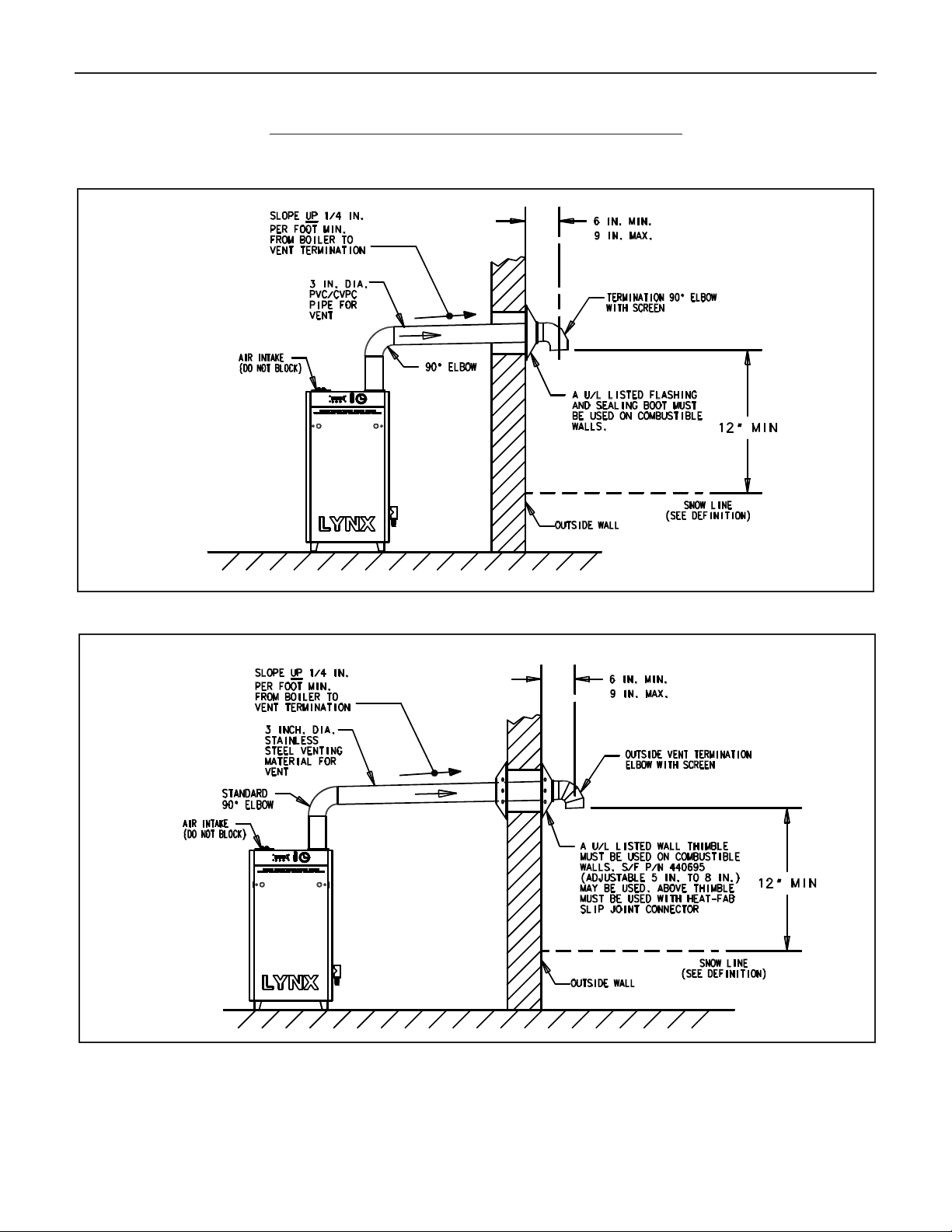
A. SIDEWALL VENTING - NON-DIRECT VENT
Figures 7 and 8 show typical horizontal sidewall venting. For
combustible wall passage of vent piping, a UL listed thimble
or flashing and sealing boot must be used, providing the wall
thickness from 3" minimum up to 12" maximum. The vent
piping must terminate with a screened tee or elbow termination
facing down.
CAUTION: Flue gasses exiting from the vent terminal will
condense. Building materials in the area of the vent terminal
should be protected from discoloration and degradation.
VENT TERMINATION LOCATION AND CLEARANCES
1. The venting system shall terminate at least 3 feet above
any forced air inlet located within 10 feet.
2. The venting system shall terminate at least 12 inches
below, or 12 inches horizontally from, any door, window
or gravity air inlet into any building. The bottom of the vent
terminal or air intake terminal shall be at least 12 inches
above grade or the normal snow level whichever is
greater.
3. Through the wall vents shall not terminate over public
walkways or over areas where condensate or vapor could
create a nuisance or hazard or could be detrimental to
the operation of regulators, relief valves or other equipment. Minimum clearance of 4 feet horizontal distance is
maintained, from electric meters, gas meters, regulators
and relief equipment.
4. Vent termination must not be located in any confined
space (i.e. window wells, alcoves, narrow alleys) or under
any overhang or deck. Vent termination should not allow
flue gas discharge towards neighbor’s windows or where
personal injury or property damages can occur.
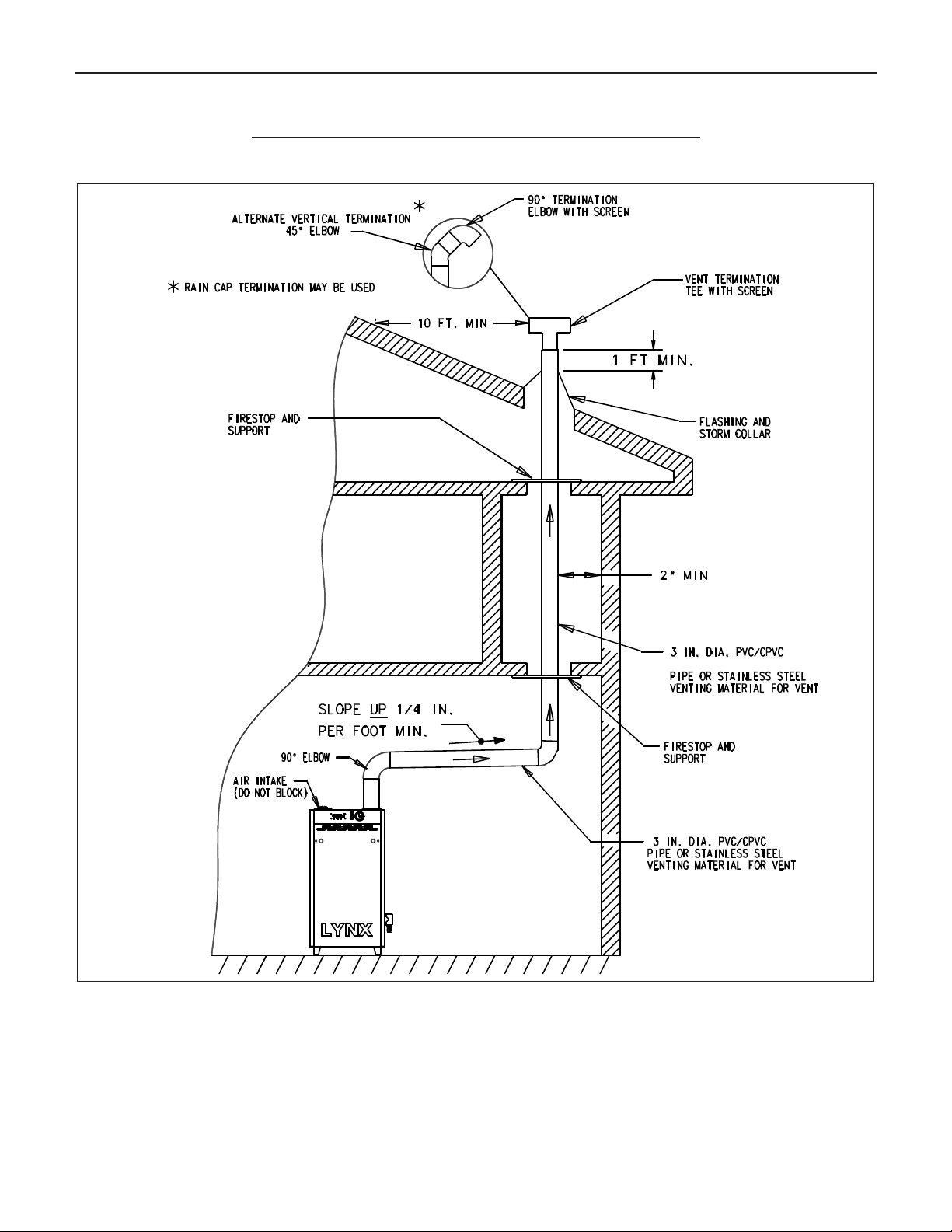
B. NON-DIRECT VENT - VERTICAL VENTING
Figure 9 shows typical venting through the roof. The vent pipe
must pass through the ceiling, floor and the roof vertically
through a 6" minimum diameter cutout. A fire stop is required
for each ceiling and floor penetration. For roof passage, an
appropriate UL listed roof flashing must be used.
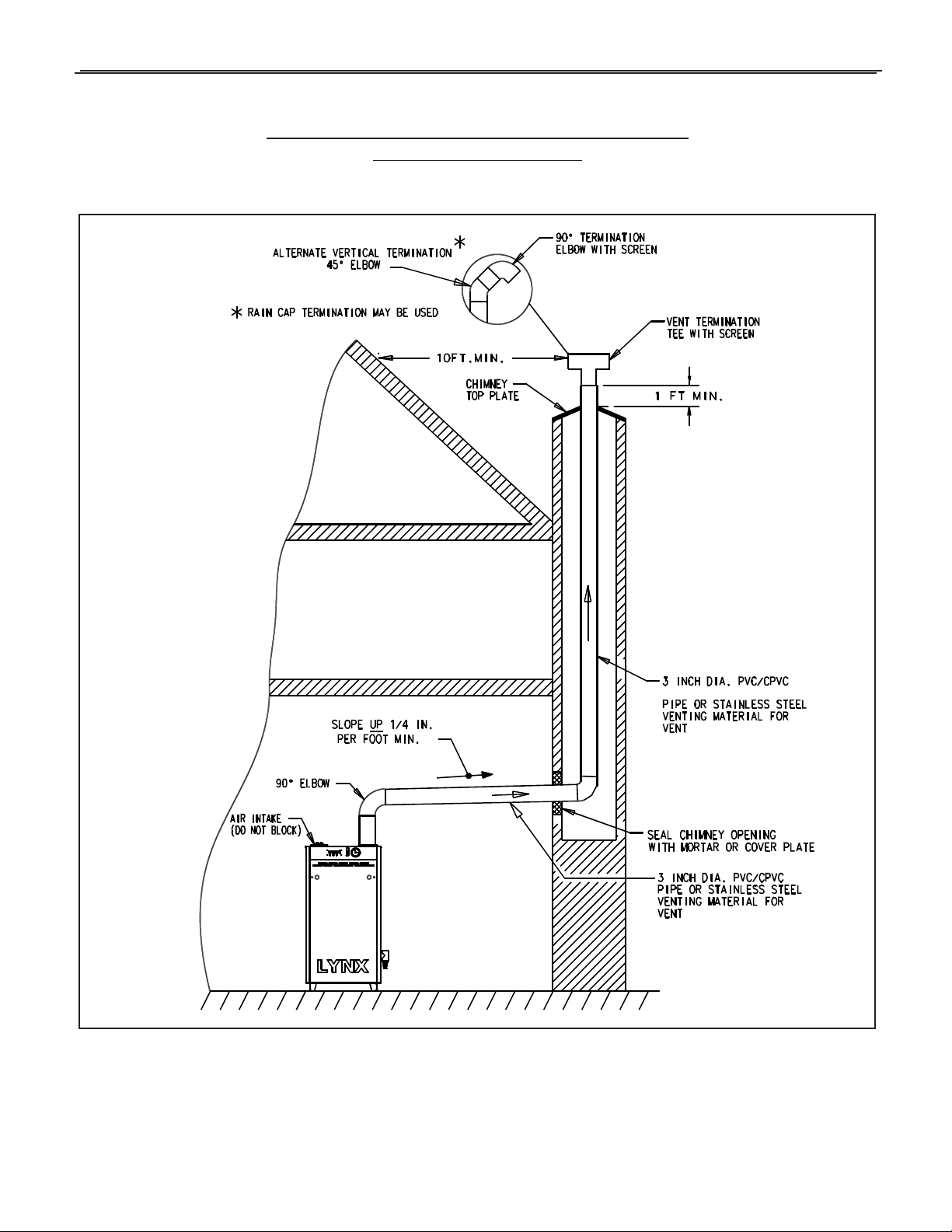
An existing chimney (see Figure 10) may be used as a chase
for vertical venting. Other appliances CANNOT be vented into
the same chimney or vent pipe within the chimney.
The vertical vent piping must terminate with a screened tee,
combination of 45˚ elbow and a 90˚ screened elbow termination or a rain cap termination.
II. Direct Vent Installation
Air intake piping from outside to the boiler air intake adapter
provides the air for combustion. The boiler surrounding may be
contaminated (See page 5). Piping the air intake to the outside
can prevent contaminants from the boiler surrounding from
entering the combustion air supply.
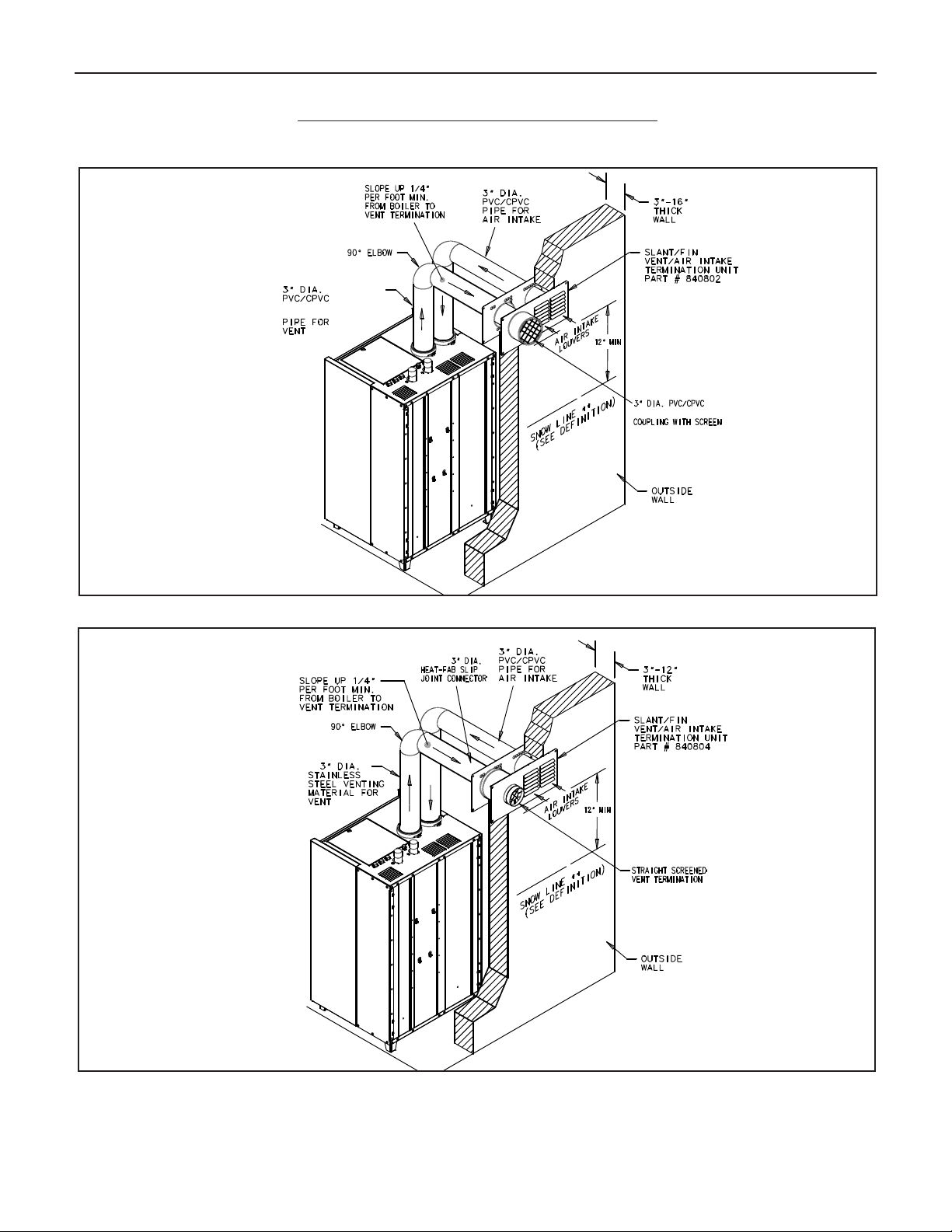
A. SIDEWALL DIRECT VENTING
Figures 11 and 12 show typical sidewall direct venting, using a
Slant/Fin vent/air intake termination. There are 2 different models of vent/air intake termination available. One is designed
specifically for PVC/CPVC or polypropylene venting, and the
other is designed specifically for stainless steel venting systems. Only these 2 models of vent/air intake termination are
approved for this method of installation. Refer to the Slant/Fin
boilers Parts List (publication number LXA-10PL) for the appropriate model for the vent material to be used.
CAUTION: Flue gasses existing from the vent terminal will condense. Building materials in the area of the terminal should be
protected from discoloration and degradation.
Vent termination location and clearances for non-direct vent
stated on Paragraph I, also applies to sidewall direct venting.
Alternate Sidewall venting for direct or non-direct venting:
Vent and/or air intake piping may be installed per figure 12a in
order to provide enough clearance from snow line. The total
vent/air intake equivalent length must not exceed 100 ft.
In cold climates, install an insolated enclosure around the vent
piping to protect from freezing.
Page 11
Lynx
11
NON-DIRECT VENT, SIDEWALL VENTING
All joints must be liquid and pressure tight. Use 3” dia. PVC/CPVC schedule 40 pipe, 3” nominal ID polypropylene pipe
or U/L listed single wall 3" dia. AL29-4C S.S.*. venting materials (See page 7).
Figure 7. Non-direct vent, side wall venting - utilizing PVC/CPVC or polypropylene pipe for venting.
Figure 8. Non-direct vent, side wall venting - utilizing stainless steel vent materials for venting.
*
AL 29-4C IS A REGISTERED TRADEMARK OF ALLEGHENY LUDLUM CORP.
** Definition of Snow Line: Knowledge of local conditions will reveal the maximum height that repeated snowfalls accumulate to.
The height should be used as the SNOW LINE.
Page 12
Lynx
12
NON-DIRECT VENT, VENTING THROUGH A ROOF
All joints must be liquid and pressure tight. Use 3” dia. PVC/CPVC schedule 40 pipe, 3” nominal polypropylene pipe
or U/L listed single wall 3" dia. AL29-4C S.S.*. venting materials (See page 7).
Figure 9. Lynx - non-direct vent, venting through the roof
*
AL 29-4C IS A REGISTERED TRADEMARK OF ALLEGHENY LUDLUM CORP.
POLYPROPYLENE
,
Page 13
Lynx
13
NON - DIRECT VENT, UTILIZING AN EXISTING
CHIMNEY AS A CHASE
All joints must be liquid and pressure tight. Use 3” dia. PVC/CPVC schedule 40 pipe, 3” ID polypropylene or U/L listed single wall
3" dia. AL29-4C S.S.*. venting materials (See page 7).
Figure 10. Lynx - non-direct vent, utilizing an existing chimney as a chase.
*
AL 29-4C IS A REGISTERED TRADEMARK OF ALLEGHENY LUDLUM CORP.
POLYPROPYLENE
,
Page 14
Lynx
14
DIRECT VENT, SIDEWALL VENTING
All joints must be liquid and pressure tight. Use 3” dia. PVC/CPVC schedule 40 pipe, 3” nominal ID polypropylene or U/L listed single wall
3" dia. AL29-4C S.S.*. venting materials (See page 7).
Figure 11. Direct vent, sidewall venting illustration; utilizing PVC/CPVC or polypropylene pipe for venting
Figure 12. Direct vent, sidewall venting illustration; utilizing stainless steel vent materials for venting.
*
AL 29-4C IS A REGISTERED TRADEMARK OF ALLEGHENY LUDLUM CORP.
** Definition of Snow Line: Knowledge of local conditions will reveal the maximum height that repeated snowfalls accumulate to.
The height should be used as the SNOW LINE.
OR POLYPROPYLENE
OR POLYPROPYLENE
Page 15

Lynx
15
Figure 13a. Vent/Air intake termination; utilizing
PVC/CPVC pipe for venting.
Figure 13b. Vent/Air intake termination; utilizing stainless
steel venting materials.
Figure 12a. Sidewall venting and air intake piping (snorkel style)
Figure 13c. Vent/Air intake termination; utilizing
polypropylene pipe for venting.
FLUE PIPE
BIRD
SCREEN
AIR INTAKE
PIPE
12" MIN.
16" MAX.
12" MIN.
12" MAX.
L
W
O
N
S
BIRD
SCREEN
L
L
A
W
*
E
N
I
Page 16

Lynx
16
VENT/AIR INTAKE TERMINATION FOR PVC/CPVC, OR
POLYPROPYLENE VENTING INSTALLATION (P# 840802000)
This termination is designed specifically for 3” diameter PVC,
CPVC Schedule 40 or polypropylene pipe to be used as the
vent and air intake piping material, only. It can be used on a
combustible wall, provided the 1” minimum clearance of the
vent pipe to any combustible surface is maintained.
1. Termination must be installed horizontally.
2. Refer to Figure 13a or 13c for installation details.
3. Wall thickness should be 3” to 18” thick.
4. Follow instruction for “vent termination location and
clearances” explained on page 10.
5. Cut a rectangular opening with the following dimensions in
the wall.
Height: 5
1
⁄4”
Width: 123⁄4”
6. From outside of the wall, install outside termination plate
using 4 screws. Make sure the louvers are at right side.
Seal the plate perimeter with silicon.
7. Apply a bead of silicon around the outer surface of the out
side termination plate air intake collar, about 1/2” from the
edge. This will seal the air intake pipe to the air intake
collar, in step #9.
8. From inside, install the inside termination plate, using 4
screws. Make sure that the holes for the vent and air intake
pipe visually line up with the vent passage hole and air
intake collar on the outside termination plate.
9. Cut the PVC or CPVC air intake pipe to the proper
dimension to fit onto the air intake collar of the terminal.
Slide the air intake pipe through the inside termination
plate and onto the air intake collar, where the sealant was
pre-applied in Step #7.
10. Cut the vent pipe so that it will extend out at least 2" from
outside termination plate and 2" from the inside
termination plate.
11. Cement a 3” diameter PVC or CPVC coupling onto the
PVC or CPVC vent pipe, and install stainless steel
screen into the coupling (supplied with the boiler).
12. From outside the wall, insert the bare end of the PVC or
CPVC vent pipe through the outside and inside terminal
plates, until the coupling is flush with the outside wall plate.
13. From inside, proceed with the air intake and vent pipe
installation. Follow the proper PVC/CPVC assembly
practices specified on page 8, and venting system
restrictions specified on page 8 of this manual.
Note: For venting with polypropylene pipe, special gasket
(P# 813005000) must be added to inside and outside plate
as shown on figure 13c.
VENT/AIR INTAKE TERMINATION FOR STAINLESS STEEL
VENTING INSTALLATION (P# 840804000)
This termination is designed specifically for Heat-Fab Saf-T
vent 3” diameter stainless steel venting system to be used as
the vent, and 3” diameter PVC or CPVC schedule 40 pipe to
be used as the air intake piping material, only. It can be used
on a combustible wall, provided a length of 4” diameter galvanized pipe is installed as a thimble around the vent pipe, for the
wall passage.
1. Termination must be installed horizontally.
2. Refer to Figure 13b for installation details.
3. Wall thickness should be 3” to 12” thick.
4. Follow instruction for “vent termination location and
clearances” explained on page 10.
5. Cut a rectangular opening with the following dimensions in
the wall.
Height: 5
1
⁄4”
Width: 12
3
⁄4”
6. From outside of the wall, install outside termination plate
using 4 screws. Make sure the louvers are at right side.
Seal the plate perimeter with silicon.
7. Apply a bead of silicon around the outer surface of the
outside termination plate air intake collar, about 1/2” from
the edge. This will seal the air intake pipe to the air intake
collar, in step #11.
8. For combustible wall a 4” galvanized pipe must be used as
a wall thimble.The length of the 4” galvanized pipe should
be approximately 1” shorter than the wall thickness.
9. From inside the building, fit galvanized pipe over 4” collar of
the outside plate.
10. From inside, install inside termination plate using 4 screws.
Make sure the 4” collar on the plate, penetrated into the
galvanized pipe.
11. Cut the PVC or CPVC air intake pipe to the proper
dimension to fit onto the air intake collar of the terminal.
Slide the air intake pipe through the inside termination
plate and onto the air intake collar, where the sealant was
pre-applied in Step #7.
12. Assemble and seal straight screened termination to the slip
joint connector.
13. From outside of the building, insert vent pipe (slip joint
connector and termination assembly) through the 3” holes
of the outside and inside termination plate.
14. From inside, proceed with air intake and vent pipe
installation. Follow vent manufacturer’s instructions and
restrictions specified on page 8 of this manual.
Page 17

Lynx
17
B. DIRECT VENT - VENTING AND AIR INTAKE
THROUGH A ROOF
Figure 14 shows typical vertical venting. The vent pipe must
pass through the ceiling, floor and the roof vertically through a
6” minimum diameter cutout. A fire stop is required for each
ceiling and floor penetration. For roof passage an appropriate
UL listed roof flashing must be used.
The vertical vent piping must terminate with a screened
straight termination. The air intake termination should be a
screened 180˚ elbow facing down. The air intake opening must
be at least 1 foot below the vent opening.
For PVC/CPVC pipe, follow the proper assembly practices
specified on page 8, and venting system restrictions specified
on page 8 of this manual. For stainless steel venting systems,
follow the vent manufacturer’s instructions and the restrictions
specified on page 8 of this manual.
Alternate air intake for venting through a roof (see fig. 14) or utilizing an existing chimney as a chase (see fig. 10): Air intake
may be piped to the boiler from the sidewall as shown on
figure 14a.
DIRECT VENT, VENTING AND AIR INTAKE
THROUGH A ROOF
All joints must be liquid and pressure tight. Use 3” dia. PVC/CPVC schedule 40 pipe, 3” nominal polypropylene pipe or
U/L listed single wall 3" dia. AL29-4C S.S.*. venting materials (See page 7).
*
AL 29-4C IS A REGISTERED TRADEMARK OF ALLEGHENY LUDLUM CORP.
** Definition of Snow Line: Knowledge of local conditions will reveal the maximum height that repeated snowfalls accumulate to.
The height should be used as the SNOW LINE.
Figure 14. Direct vent, venting and air intake through a roof.
Figure 14a. Direct vent, venting through a roof and air
intake sidewalls.
POLYPROPYLENE
,
Page 18

Lynx
18
VENTING AND AIR INTAKE SYSTEM REGULAR INSPECTION
A. Inspect the system regularly for condensation, corrosion,
sagging and/or physical damage. A qualified professional
should service the boiler annually and include such an
inspection at that time. The homeowner should look over the
system monthly for damage, water stains, any signs of rust,
other corrosions or separation of the vent and air intake piping
(if direct-vent).
B. Should an inspection turn up signs of condensation, corrosion,
sagging or damage, the boiler should be shut down immediately and the condition should be corrected by a qualified
professional.
CONDENSATE REMOVAL SYSTEM
Lynx boilers are equipped with a built-in condensation drain and
trap. The trap must be filled with water. DO NOT operate the boiler
without filling the trap with water to prevent flue gas discharge into
space. Periodic inspection should be made of this assembly for
deterioration of the tubing and to insure that the trap is not
plugged. If it is plugged or appears to have excessive sediment in
it, it should be removed from the drain assembly, straightened out
to clear the obstruction, reformed, filled with water and reinstalled
as before.
A 3/4” PVC tee, located on the right side of the boiler jacket, is
provided to run the condensate liquid from the boiler. Connect the
plastic tubing that will be run to the drain to the bottom take-off of
the tee. Leave the top take-off of the tee open, to act as a vacuum
breaker. If the building drain is above the bottom portion of the tee,
a condensate removal pump will be required. This pump must
have an overflow switch, and be compatible with the acidic condensate liquid, as must all fittings and the tubing used in this condensate removal system. (See Figure 15).
No part of the condensate removal system can be exposed to
freezing temperatures, or any other conditions that could cause
blockage. DO NOT run drain tubing to the outside of the building.
In addition, certain jurisdictions or drain pipe materials may require
a neutralization unit to be installed in the condensate removal system. Any piping other than plastic types will be subject to corrosion
or deterioration from the acidic condensate, which may have a pH
level as low as 3.0. A condensate filter containing lime, marble, or
phosphate chips can neutralize the condensate to a pH level
above 6.5, which is safe for all drain piping materials. (See Figure
15). The neutralizing filter medium will require periodic changing,
to ensure it’s affectiveness. Replacing the medium on an annual
basis is recommended, or refer to the manufacturer’s instructions
for systems that are available for neutralizing condensate.
COMMONWEALTH OF MASSACHUSETTS SPECIAL
REQUIREMENT
When the Lynx is installed and used in the Commonwealth of
Massachusetts, a neutralization unit MUST be installed in the
condensate removal system.
GAS PIPING
A. Local installation codes apply. The pipe joint compound used
on threads must be resistant to the action of liquefied petroleum gases.
B. The gas supply line to the boiler should run directly from the
meter for natural gas or from the fuel tank for L.P. propane gas.
A manual gas supply shut-off valve is provided on the boiler’s
gas supply pipe. (See Figure 2, on page 3). Local codes may
specify a manual main gas supply shut-off valve to be 5’ above
the floor, and a disconnection union at the gas piping entrance
to the boiler. In this case, unless the boiler is wall mounted at
the right height, the gas supply shut-off valve must be relocated
to the specified location. If the gas supply pipe must be upsized
for flow considerations, then the same size main gas supply
shut-off valve must be used.
Selecting pipe size for natural gas:
1. Measure or estimate the length of piping from the meter to
the installation site.
2. Consult gas supplier for heating value of gas (Btu/cu. ft.).
3. Divide boiler rated input by heating value to find gas flow in
piping (cu. ft. per hour).
4. Use table below to select proper pipe size.
EXAMPLE: Boiler model LX-120 is to be installed. Distance from
gas meter to the boilers is 30ft. Heating value of natural gas is
1020 Btu/cu. Ft. Select proper pipe size.
Gas flow = 120,000 Btu/hour
= 118 cu. ft. per hour
1020 Btu/cu. ft.
Figure 15. Condensate disposal system
Page 19

Lynx
19
At 30 ft. length of pipe, match required capacity from table on
this page (choose higher capacity, in this case is 152 cu. ft. per
hour). Required pipe size is
3
⁄4".
Improper gas pipe sizing will result in flame outages, insufficient heat and other installation difficulties. For more information and also if other appliances are to be attached to the
piping system, see Appendix C of National Fuel Gas Code
ANSI Z223.1-latest edition.
C. The boiler and its gas connection must be leak tested
before replacing the boiler in operation. Use liquid soap
solution for all gas leak testing. DO NOT use open flame.
This boiler and it’s individual shutoff valve must be
disconnected from the gas supply piping system during and
pressure testing of that system at test pressures in excess
of
1
⁄2 PSIG. This boiler must be isolated from the gas supply
piping system by closing its individual manual shutoff valve
during any pressure testing of the gas supply piping system
at test pressures equal to or less than
1
⁄2 PSIG.
D. All gas piping used should be inspected thoroughly for
cleanliness before makeup. A sediment trap is integrally
provided, as illustrated on page 3.
E. The minimum and maximum gas supply pressure (at the
inlet of gas valve) are shown on the boiler rating plate for
the type of gas used. Gas supply pressure should never be
less than minimum or more than maximum pressure when
the boiler or any other appliance is turned on or off.
ELECTRICAL WIRING
All field wiring to the boiler is connected to the 2 sets of
terminal strips, located under the jacket top panel.
(See Figure 2, on page 3)
DANGER: Before wiring always turn off electric power supply.
Otherwise, shock or death can result.
1. Power Supply
A separately fused circuit is recommended. Use standard
15 Amp. fuse or breaker and 14 gage conductors in BX
cable or conduit.
Provide disconnect means and overload protection as
required. See boiler wiring diagram (Figure 16a) boiler
control (Figure16b) and ladder diagram (Figure 16c).
Boiler must be electrically grounded in accordance with the
requirements of the authority having jurisdiction, or, in the
absence of such requirements, with the National Electrical
Code, ANSI/NFPA 70-latest edition.
Proper polarity is critical for the power supply connections.
Reversed polarity will cause system lockout. Proper grounding is critical for boiler operation, connect the ground wire to
the green ground screw next to the line voltage terminal
strip.
2. Circulator(s)
A set of terminals are provided for the boiler (primary loop)
circulator. Only wire this circulator to these terminals,
additional (secondary loop) circulators for space heating
require the use of relays and a separate power source.
For multiple zoning, either zone valves or circulators maybe
used.
For zone valve system (See Figure 17a).
For pump zoning system (See Figure 17b and 17c).
DO NOT use boiler transformer to power external
accessories like zone valve and relays, overload and/or
burned out transformer and boiler malfunction can result.
Use separate transformer to power such components.
A second set of terminals are provided for the domestic hot
water tank circulator (if used). The primary loop circulator is
always de-energized when the DHW tank circulator is
energized, for priority.
3. SPACE HEATING THERMOSTAT(S)
Install thermostat on an inside wall and away from any heat
sources, sunshine and drafts. A set of terminals are provided for connection of 24 volt style thermostats, relays or zone
valve end switches (isolated contacts). (See wiring diagram
Figure 16a).
Thermostat heat anticipator: For a non-zoned system set
thermostat heat anticipator to 0.1 Amps, for zoned system
set to match power requirements of zone valves or relays.
Refer to manufacturer’s instructions and specifications. Also
see instructions with thermostat.
4. DOMESTIC HOT WATER TANK THERMOSTAT
A set of terminals are provided for connection of the DHW
tank thermostat (if used). (See wiring diagram Figure 16a).
5. OUTDOOR AIR SENSOR
A set of terminals are provided for connection of an outdoor
air sensor (if this method is used). (See wiring diagram
Figure 16a).
The outdoor air sensor must be a 12k ohm type. Mount on
an outside wall, shielded from direct sunlight or flow of heat
or cooling form other sources. See instructions provided
with sensor.
6. LOW WATER CUTOFF
A set of terminals are provided for connection of a LWCO. If
this device is used, remove the factory installed jumper from
these terminals. (See wiring diagram Figure 16a).
Length
of pipe
in Feet
1/2
3
/4 11
1
/4
11/2
Gas Flow In piping -- cu. ft. per hr.
Iron Pipe Size (IPS) — inches
10 132 278 520 1050 1600
20 92 190 350 730 1100
30 73 152 285 590 890
40 63 130 245 500 760
50 56 115 215 440 670
60 50 105 195 400 610
70 46 96 180 370 560
80 43 90 170 350 530
90 40 84 160 320 490
100 38 79 150 305 460
At pressure drop of 0.3 in. water, specific gravity = 0.6.
Page 20

Lynx
20
Figure 16a. Schematic wiring diagram.
Page 21

Lynx
21
Figure 16b. Boiler Control.
Figure 16c. Ladder wiring diagram.
SPARK
CABLE
BOILER CONTROL
SPARK
IGNITOR
GROUND
T2
J12
J9
J13
J5
ARGUS VISION CONTROL
L1
HOT
DISCONNECT
BOILER ON/OFF
120V SECTION OF
CONTROL BOARD
120V
10V
PROCESSOR
ON CONTROL
120V/60HZ
SWITCH
SWITCH
WATER HIGH
MICRO
BOARD
J6
NOT
USED
M
LIMIT
120V
COMBUSTION
BLOWER
FUSE
NEUTRAL
BOILER
CIRCULATOR
M
24V
DHW THERMOSTAT
(IF USED) OR SENSOR
SUPPLY WATER
SENSOR
OUTDOOR SENSOR
(IF USED)
J2
NOT
USED
L2
DHW CIRCULATOR
(IF USED)
GAS
VALVE
SPARK
ELECRODE
"CALL FOR HEAT"
24V ROOM THERMOSTAT
OR ISOLATED CONTACT
FLUE GAS
SENSOR
GND
CHASSIS
GND
LOW WATER CUT OFF
(IF USED) OR JUMPER
RETURN WATER
SENSOR
DISPLAY
Page 22

Lynx
22
Figure 17a. Multizoning of Lynx boiler; zone valve system.
Figure 17b. Multizoning of Lynx boiler; pump zoning system using R845A relay.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
FIELD WIRING
TERMINALS
ON BOILER
1
2
TT
3456
TT TT
LI
L2
DISCONNECT
SWITCH
1
R845A
RELAY ZONE 3
CIRC.
ZONE 3
R845A
RELAY ZONE 2
CIRC.
ZONE 2
R845A
RELAY ZONE 1
CIRC.
ZONE 1
ZONE 3
THERMOSTAT
ZONE 2
THERMOSTAT
ZONE 1
THERMOSTAT
POWER SUPPLY, PROVIDE DISCONNECT
MEANS AND OVERLOAD PROTECTION
AS REQUIRED.
MULTIZONING OF "LYNX" BOILER;
PUMP ZONING SYSTEM USING R845A RELAY
1
23456
1
23456
MULTIZONING OF "LYNX" BOILER;
ZONE VALVE SYSTEM USING V8043E/F ZONE VALVES AND R845A RELAY
ZONE 1
THERMOSTAT
V8043E/F
END
SWITCH
TT T TT TT TT TT T TT
TH-TR
MOTOR
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
V8043E/F
SWITCH
FIELD WIRING
TERMINALS
ON BOILER
END
TH-TR
ZONE 2
THERMOSTAT
V8043E/F
MOTOR
T
R845A
RELAY
END
SWITCH
1
TH-TR
JUMPER
2
3456
ZONE 3
THERMOSTAT
MOTOR
T
DISCONNECT
SWITCH
LI
1
120V/24V
TRANSFORMER
SPACE
HEATING
SYSTEM
T
CIRCULATOR
1
POWER SUPPLY, PROVIDE DISCONNECT
MEANS AND OVERLOAD PROTECTION
AS REQUIRED.
L2
Page 23

Lynx
23
Figure 17c. Multizoning of Lynx boiler; pump zoning system using R882A/B relays.
Figure 17d. Single zoning of Lynx boiler; pump
zoning system using R845A relay.
Figure 17e. Single zoning of Lynx boiler; pump zoning system
using R882A/B relay.
R882A/B
ZONE 3
THERMOSTAT
MULTIZONING OF "LYNX" BOILER;
PUMP ZONING SYSTEM USING R882A/B RELAYS
R882A/B
ZONE 2
THERMOSTAT
R882A/B
ZONE 1
THERMOSTAT
TRANSFORMER
120V/24V
DISCONNECT
SWITCH
LI
L2
120V/60HZ
1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
CIRC.
ZONE 3
FIELD WIRING
TERMINALS
ON BOILER
CIRC.
ZONE 2
1
POWER SUPPLY, PROVIDE DISCONNECT
MEANS AND OVERLOAD PROTECTION
AS REQUIRED.
CIRC.
ZONE 1
THERMOSTAT
THERMOSTAT
TT
R845A
RELAY
1
DISCONNECT
SWITCH
1
LI
L2
1
POWER SUPPLY, PROVIDE DISCONNECT
MEANS AND OVERLOAD PROTECTION
AS REQUIRED.
3
2
CIRCULATOR
4
56
R 882A/B
RELAY
CIRCULATOR
1
POWER SUPPLY, PROVIDE DISCONNECT
MEANS AND OVERLOAD PROTECTION
AS REQUIRED.
120 V / 24 V
TRANSFORMER
DISCONNECT
SWITCH
LI
L2
1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
FIELD WIRING
TERMINALS
ON BOILER
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
FIELD WIRING
TERMINALS
ON BOILER
Page 24

Lynx
24
WATER PIPING
A. Connection of system to boiler:
Primary/secondary piping should be used to ensure the
proper flow through the boiler. (See Figures 20 through 22). The
boiler loop piping must be the same diameter as the water
outlet (supply) and inlet (return) piping connections
provided on the boiler, particularly on longer loops. See page 2
for piping connection size.
B. Circulator Pumps:
The boiler loop piping must utilize the Taco 0011 or Grundfos
UPS 26-99F circulator that is supplied with the boiler, to
ensure the proper flow through the boiler. Refer to Figure 19
for the boiler water side pressure drop and Table 2 for the
recommended pump models for the domestic hot water
system. Install the pumps in the orientation shown in
Figures 20 through 22.
C. Relief Valve(supplied with boiler):
Tee the relief valve into the boiler water outlet (supply) piping
as close to the water outlet (supply) connection as possible.
(See Figure 18). The relief valve’s discharge piping must be the
same size or larger than the relief valve’s outlet, and must
terminate 6” minimum from floor with a plain (no threads) end.
Place a bucket under pressure relief valve discharge. Make
sure discharge is always visible. DO NOT hard-pipe to drain
piping, or any place where freezing could occur. No shut-off
valve is permitted between the relief valve and boiler, or in the
discharge line.
D. Air Control System:
An appropriately sized diaphragm-type expansion tank must be
used to control the system pressure. See boiler volume data on
page 2, and the recommended location in Figures 20 through
22. An air vent is recommended to be installed on an air
separator in close proximity to the expansion tank.
E. Cold Water Fill:
A pressure reducing (fill) valve, with a shut-off valve upstream
of it, should be installed in close proximity of the expansion
tank. (See Figures 20 through 22). Use a back flow check valve
in the cold water supply as required by local codes.
F. Low Water Cutoff:
On a hot water boiler installed above radiation level, the boiler
must be provided with a low water cutoff device at the time of
installation by the installer (see Figure 18 for piping arrangement).
G. Water Treatment and Freeze Protection:
A good water treatment program will not only extend the useful
life of this boiler but it will also save much of the time and
expense of repairs made necessary by preventable
occurrences. A reputable water treatment company that has
experience with aluminum boilers should be consulted to
evaluate and determine the best overall treatment program for
your boiler.
The heat exchanger of this boiler is made of aluminum, so the
system water PH must be maintained between 7.5 and 8.5 level.
Procedure:
1. Thoroughly drain and flush the system (new or used)
with fresh water before connecting the boiler to the
system to remove any sediment or glycol.
2. Install the boiler per instructions in this manual.
3. It is recommended to clean the heating system with
proper cleaner. Do not use phosphate-based (TSP)
cleaners, as they will harm aluminum heat exchanger.
Follow manufacturer instruction. Rhomar Hydro-Solv
9100 is recommended (add approximately 1 gallon
per 50 gallon of system water). Circulate cleaner for
minimum of 1/2 hour, and then thoroughly flush until
the water runs clear.
4. It is recommended to add system treatment
(inhibitor). Do not use phosphate, nitrate or high pH
products. Follow manufacturer instructions. Rhomar
Pro-Tek 922 is recommended at the rate of 1 gallon
per 50 gallon of system water.
Note: Extra inhibitor may not be needed if using the
approved antifreeze containing inhibitor additive as
listed below.
Test the PH of the water system annually, if the PH is
out of the range (7.5-8.5), the inhibitor level may not
be sufficient, add inhibitor to the system.
5. Anti-freeze is sometimes used in hydronic systems to
protect against freeze-up in the event of power failure
or boiler shut down in the cold winter.
Approved anti-freeze is RhoGard (propylene glycol
with Pro-Tek 922 inhibitor) by Rhomar Water
Management Inc. or Noburst AL by Noble. Follow the
manufacturer’s instructions for proper application and
proper mixture for the minimum ambient temperature.
Any use of anti-freeze other than that supplied by
Slant/Fin or approved will void the warranty.
Notice: When adding less than 50% RhoGard
antifreeze to a system, additional inhibitor should be
added to ensure adequate corrosion protection.
Keep water hardness less than 7 grains/gallon. It is
recommended to use water softener for hard water
areas or if well water is used.
Never use Ethylene glycol, as it is toxic to humans. Never
use any type of automotive or standard glycol freeze
protection fluid. Do not exceed 50% by volume concentrate of anti-freeze. Check anti-freeze concentration annually.
H. Piping a heating - cooling system to a water boiler
and chiller:
Figure 22 illustrates a method of piping a heating-cooling
system to a water boiler and a chiller. Hand valves (shown)
or automatic valves must be installed to prevent circulation
of chilled water in the boiler or hot water in the chiller.
The air control system and pressure control system must
operate with chiller only, or the boiler only, being valved to
the piping system. Separate control devices on the boiler
and chiller may be used, or a single set of air and pressure
controls on the common piping may be preferred.
If the boiler is used to supply hot water to heating coils in air
handling units, flow control valves or other devices must be
installed to prevent gravity circulation of water in the coils
during the cooling cycle.
Page 25

Lynx
25
Figure 18. Relief Valve and Low Water Cutoff Installation
Page 26

Lynx
26
Table 2. Recommended pump models for domestic hot water tank piping.
Figure 19. Boiler water side pressure drop
5
Notes:
* This is the minimum flow rate recommended for the boiler.
** Domestic water tank piping head is based on 1” inside diameter piping and full port valves.
*** Refer to the DHW Tank Manufacturer’s water flow rate requirements and associated pressure drop head loss, to select
the appropriate circulator.
▲ Or Grundfos UPS 26-99F.
Boiler
Model
No.
Flow
Rate
(gpm)
Temp
Rise
(˚F)
Boiler
Head
Loss
(Feet w.c.)
Domestic
Water
Tank Piping
Head Loss **
(Feet w.c.)
Available Head Capability Left for Various
Model Circulators to Overcome DHW Tank
Head Loss (Feet w.c.) ***
Taco 0014
Taco 0011
▲
Taco 0013
8.1 20 8.2 2.5 7.3 14.1 17.5
6.5 25 5.4 2.2 10.9 18.2 22.2
5.4 30 3.5 2.0 14.0 21.3 25.2
4.0* 40 2.1 1.5 16.4 23.9 28.2
10.8 20 9.5 3.0 4.5 11.4 13.4
8.6 25 6.6 2.7 8.5 14.8 18.7
7.2 30 4.2 2.5 11.5 18.3 22.2
5.4* 40 2.5 1.5 15.5 23.0 27.0
13.5 20 9.0 3.5 2.7 7.5 11.5
10.8 25 6.0 3.0 8.0 13.5 17.5
9.0 30 4.2 2.5 11.0 17.0 20.5
6.8* 40 2.5 2.0 14.0 21.5 24.5
LX-90LX-120LX-150
10
8
Head
6
(feet w.c.)
4
2
0
0
2
4
L
6
Flow Rate (GPM)
0
9
-
X
8
0
2
1
-
X
L
10
0
5
-1
LX
12
14
1
Page 27

Lynx
27
Figure 20. Zoning with circulators.
Page 28

Lynx
28
Figure 21. Zoning with zone valves.
Page 29

Lynx
29
Figure 22. Piping a heating-cooling system to the boiler and a chiller.
Page 30

Lynx
30
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
I. FILLING AND VENTING WATER SYSTEMS
A. Fill the system with water. Vent or purge of air.
B. Fire the boiler as soon as possible (see following warning
and instructions) and bring water temperature in the
system.
C. Vent air and add water as needed to achieve operating
pressure on boiler gauge. Pressure must be between
approximately 12 psi (cold water) and 25 psi at water
temperature setting of high limit control, for boilers
equipped with 30 psi relief valves. Boilers rated for a higher
pressure and equipped with a matching relief valve may
operate at a higher pressure, but no higher than 5 psi
below the relief valve opening pressure.
D. Check for and repair any leaks before placing system in
service.
BEFORE FIRING BOILER, make these checks:
Before firing boiler, review the “Boiler Control and Display
Features” section of this manual. Understanding the features and
programming the applicable parameters is essential for setting up
the boiler to operate properly on the heating system it is installed
on.
1. System is full of water. Air is vented or purged.
2. Relief valve is installed in accordance with ASME Boiler
and Pressure Vessel Code, Section IV. Valve opening is
not closed or reduced in size.
3. Venting is installed according to instructions under “FLUE
GAS VENTING REQUIREMENTS”.
4. All wiring is completed, following applicable wiring
diagrams.
5. Using soap solution, check for gas leaks in all gas piping
from meter to boiler gas supply pipe. DO NOT use open
flame.
II. BOILER CONTROL AND DISPLAY FEATURES
(See Figure 23)
A. Boiler Operation Status:
“Mode Display” shows status of boiler operation
(see table 3).
B. View and Changing Temperatures:
Setting boiler supply water temperature and water tank
temperature (see table 4).
Press “Select” button for viewing following different modes
on “Mode Display”
1. While “c” is blinking, boiler supply water temperature
for space heating may be set to desired temperature
The setting range is between 90˚ to 185˚F.
2. While “d” is blinking, boiler supply water temperature
for DHW may be set to desired temperature. The
setting range is between 104˚ to 185˚F.
3. While “t” is blinking, DHW tank temperature may be
set to desired temperature (if tank is equipped with
sensor). The setting range is between 104˚ to 185˚F.
4. View actual boiler supply & return water temperature, domestic hot water tank temperature (if tank
equipped with sensor), flue temperature and outside
temperature (if outside sensor is used) on
“Temperature Display” by selecting 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5 on
“Mode Display”.
• These numbers are steady on display and are
not settable.
• All sensor inputs to the control must be
connected to a 12k ohm sensor.
C. Viewing and changing system setting:
A trained, experienced service technician or installer should
perform following adjustments. See table 5 for details.
1. Space heating and DHW post pump time may be
changed.
2. Space heating and DHW modes may be chosen.
3. Weather compensation slope and set point temperature
may be changed (if outside sensor is used).
(See Figure 24 for graph).
4. Read actual blower RPM
5. Adjust blower RPM for high and low input adjustment.
6. Read flame current in micro amp.
7. Run boiler on high, low or ignition input steady for 20
minutes for test purposes.
D. Display and push buttons:
1. Reset - Used to clear a Lock out error (indicated with an
“A” in the “Mode Display”).
2. Select - Used to scroll through the modes in the “View
and Changing Temperatures” and “Viewing and Changing
System Setting” menus.
3. Enter - Used to store values that are changed in the “View
and Changing Temperatures” and “Viewing and Changing
System Setting” menus.
4. Up- Used to increase values in the “View and Changing
Temperatures” and “Viewing and Changing System
Setting” menus.
5. Down - Used to decrease values in the “View and
Changing Temperatures” and “Viewing and Changing
System Setting” menus.
Page 31

Lynx
31
Figure 23. Display Board
MODE
DISPLAY
DESCRIPTION & TEMPERATURE DISPLAY
Boiler is on stand-by mode.
Temperature display shows supply water Temp.
Space heating mode.
Temperature display shows supply water Temp.
Domestic hot water mode.
Temperature display shows supply water Temp.
Frost protection mode. **
Temperature display shows supply water Temp.
Lockout (Alarm) condition.
Temperature Display indicates the lockout code
Reset button must be pressed to resume normal operation.
Error Condition. *
Temperature display indicates the error code.
Warning Condition. ***
Temperature display indicates the error code.
NOTE: Blinking dot on “Mode Display” indicates active heating control, burner off.
Steady dot indicates burner is on.
*: Error must be corrected to resume boiler operation. Pressing the “Reset” button is not required.
**: The boiler loop circulator is energized, if the boiler water temperature drops below 50˚F.
***: Error must be corrected to resume DHW operation. Space heating not affected. Pressing
the “Reset” button is not required.
Table 3
LYNX BOILER DISPLAY BOARD
“Boiler Operation Status”
"MODE" DISPLAY
"RESET" PUSH BUTTON
"BURNER STATUS"
STEADY DOT = BURNER ON
BLINKING DOT = BURNER OFF
"TEMPERATURE" DISPLAY (3 DIGITS)
"UP" PUSH BUTTON
*
"DOWN" PUSH BUTTON
"ENTER" PUSH BUTTON
"SELECT" PUSH BUTTON
Page 32

Lynx
32
MODE
DISPLAY
DESCRIPTION & TEMPERATURE DISPLAY
Space heating supply water temperature could be changed by
pressing “Up/Down” button. Settable from 90˚F to 185˚F
(steps of 1 F). The default value is 176˚F.
Press “Enter” button to store.
(see note 1)
Domestic hot water supply temperature could be changed by
pressing”Up/Down” button. Settable from 104˚F to 185˚F
(steps of 1 F). The default value is 176˚F.
Press “Enter” button to store.
(see note 2)
Domestic hot water tank temperature could be changed by
pressing “Up/Down” button. Settable from 104˚F to 160˚F
(steps of 1 F). The default value is 140˚F.
Press “Enter” button to store.
(see note 3)
Temperature display shows actual supply water temperature.
Temperature display shows actual return water temperature.
Temperature display shows actual DHW tank temperature.
(if the water tank is equipped with sensor).
Temperature display shows actual flue gas temperature.
Temperature display shows actual outside temperature.
(if outdoor sensor is used)
NOTE:
1- For space heating mode “0” (boilers not utilizing outdoor sensor))
2- For DHW mode “2” (storage tank with Aquastat)
3- For DHW mode “1” (storage tank with sensor)
Table 4
VIEWING AND CHANGING TEMPERATURES
Press “SELECT” button for viewing different modes on “MODE DISPLAY”
blinking
blinking
blinking
Page 33

Lynx
33
MODE DISPLAY
DESCRIPTION
Changing space heating post pump time. Settable from 10 to 900 seconds.
(steps of 10 seconds). The default value is 30 seconds.
Changing DHW post pump time. Settable from 1 to 255 seconds.
(steps of 1 seconds). The default value is 15 seconds.
Changing space heating control mode
0: Thermostat only (default) - boiler without outdoor sensor
1: Outdoor sensor and Thermostat
2: Outdoor sensor only
3: Permanent heat demand (boiler circulator always on)
Changing domestic hot water (DHW) mode
0: No DHW
1: Storage tank with sensor
2: Storage tank with thermostat (default value)
Changing DHW or space heating priority mode
0: DHW priority (no time limit)
1: Space heating priority (no time limit)
2: DHW priority for limited time (default)
3: Space heating priority for limited time
Changing priority limited time. Settable from 20 to 80 minutes.
The default value is 30 minutes.
Boiler model selection, values are:
2 for model LX-90
3 for model LX-120
6 for model LX-150
Boiler model confirmation, values are:
2 for model LX-90
3 for model LX-120
6 for model LX-150
Natural or Propane gas selection
0: for natural gas (default)
1: for propane
Weather compensation supply water reference temperature
(space heating mode 1 or 2). Settable from 16˚F to 122˚F (steps of 1 F).
The default value is 86˚F.
Changing compensation slope (space heating mode 1 or 2).
Settable from 0.1 to 5.0 (steps of 0.1).
The default value is 1.0.
Not Utilized
Changing weather compensation set point (space heating mode 2 only).
Settable from 32˚F to 122˚F (steps of 1˚F).
The default value is 68˚F.
Display shows blower RPM (mutiply reading by 10 for actual RPM)
Change blower RPM for high input (steps of 30 RPM, limit +/- 480 RPM).
Change blower RPM for low input (steps of 30 RPM, limit +/- 120 RPM).
Display shows flame current in micro amps
System test – Display shows flame current
0: System test off
L: Steady low input (20 minutes)
I: Steady ignition input (20 minutes)
H: Steady high input (20 minutes)
NOTE: *: Alternating **: Steady
VIEWING AND CHANGING SYSTEM SETTING -
Table 5
“To change system setting or perform system test”
The menu is accessed by pressing and holding “SELECT” and “ENTER” buttons for 10 seconds. To access different modes,
press “SELECT” button To change system setting: Press “UP or DOWN” button, then press “ENTER”
WARNING: Only a trained, experienced service technician or installer should use this table.
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
**
*
*
**
*
*
Page 34

Lynx
34
Figure 24. Space Heating mode with outside sensor water set point graph.
Maximum
water target
temp.
185 °F
Water
Supply
Target Temp.
(°F)
200
190
180
170
160
150
140
130
120
)
.
x
a
m
(
0
0
.
5
=
e
e
p
p
o
o
l
l
S
S
0
.
.
4
3
=
=
e
p
o
l
S
0
.
8
.
2
1
=
=
e
e
p
p
o
o
l
l
S
S
5
.
1
=
e
p
o
l
S
2
.
1
=
e
p
o
l
S
=
e
p
o
l
S
e
p
o
l
S
)
t
l
u
a
f
e
d
(
0
.
1
5
.
0
=
110
Minimum
water target
temp.
100
90
Water
reference
80
temp. (default
of 86°F)
70
70 60 -20-10 -3001020304050
68°F
Outdoor Temp. (°F)
)
.
n
i
m
(
1
.
0
=
e
p
o
l
S
-40
Page 35

Lynx
35
III. INITIAL START
Safe lighting and other performance criteria were met when testing
various gas manifold and control assemblies used on the Lynx
boiler under the ANSI Z21.13 - latest edition.
Instructions
Follow the lighting instructions in this manual. These instructions
are also attached to the boiler.
SAFETY INFORMATION
For Your Safety Read Before Operating
WARNING: If you do not follow these instructions exactly, a fire
or explosion may result causing property damage, personal
injury or loss of life.
A. This appliance does not have a pilot. It is equipped with
an ignition device which automatically lights the burner.
DO NOT try to light the burner by hand.
B. BEFORE OPERATING smell all around the appliance area
for gas. Be sure to smell next to the floor because some gas
is heavier than air and will settle on the floor.
WHAT TO DO IF YOU SMELL GAS:
• DO NOT try to light any appliance.
• DO NOT touch any electric switch: DO NOT use any
phone in your building.
• Immediately call you gas supplier from a neighbor’s
phone. Follow the gas supplier’s instructions.
• If you cannot reach your gas supplier, call the fire
department.
C. Use only your hand to turn the gas supply shut-off valve.
Never use tools. If the supply shut-off valve will not turn by
hand, don’t try to repair it, call a qualified service technician.
Force or attempted repair may result in a fire or explosion.
D. DO NOT use this appliance if any part has been under
water. Immediately call a qualified service technician to
inspect the appliance and to replace any part of the
control system and any gas control which has been under
water.
1. STOP! Read the safety information above.
2. Set the thermostat to lowest setting.
3. Turn off all electric power to the appliance.
4. This appliance is equipped with an ignition device which
automatically lights the burner. D
O NOT try to light the
burner by hand.
5. Open the gas supply shut-off valve, by turning the handle to
be parallel to the gas piping (See Figure 25).
6. Wait five (5) minutes (longer for propane) to clear out any
gas, then smell for gas, including near the floor. If you then
smell gas, STOP! Follow “B” in the safety information
above on this page. If you don’t smell gas, go to next step.
7. Turn on all electric power to the appliance.
8. Set thermostat to desired setting.
If the appliance will not operate, follow the instructions
“To Turn Off Gas to Appliance” and call your service
technician or gas supplier.
TO TURN OFF GAS TO APPLIANCE
1. Set thermostat to lowest setting.
2. Turn off all electric power to the appliance if service is to
be performed.
3. Close the gas supply shut off valve, by turning the handle
to be perpendicular to the gas piping. (See Figure 25).
Figure 25. Gas supply shutoff valve operation.
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
TURN 90˚
TO OPEN
TURN 90˚
TO CLOSE
GAS SUPPLY SHUTOFF VALVE
IN "OPEN" POSITION
GAS SUPPLY SHUTOFF VALVE
IN "CLOSED" POSITION
Page 36

Lynx
36
LYNX BOILER SEQUENCE OF OPERATION
THERMOSTAT CALLS FOR HEAT
CIRCULATOR(S) ON
5 SECOND PRE-PURGE PERIOD
GAS VALVE REMAINS OPEN. CONTROL
CONTINUOUSLY MONITORS
THERMOSTAT, HIGH LIMIT, WATER
SENSORS, BLOWER SPEED, FLAME
SIGNAL, AND LWCO (IF USED).
THERMOSTAT CALL FOR HEAT ENDS
GAS VALVE CLOSES
10 SECOND BLOWER POST PURGE.
15 SECOND CIRCULATOR POST PURGE.
CONTROL LOCKOUT
DISPLAY SHOWS
ERROR “A 33”
YES
NO
NO
COMBUSTION BLOWER ON
(AT MEDIUM SPEED)
TRIAL FOR IGNITION
SPARK IGNITOR ENERGIZED
FOR 3.5 SECONDS
YES
GAS VALVE OPENS
FOR 2.5 SECONDS
SPARK CONTINUES FOR
2.5 SECONDS
SPARK IGNITOR DE-ENERGIZED
GAS VALVE REMAINS OPEN FOR
3.5 SECONDS
YES
2 TIMES RETRIALS
FOR IGNITION
GAS VALVE CLOSED.
BLOWER POST PURGE
10 SECONDS.
NO
CONTROL LOCKOUT
DISPLAY SHOWS
ERROR “A 01”
YES
CONTROL LOCKOUT
DISPLAY SHOWS
ERROR “A 03”
NO
WATER HIGH LIMIT
CLOSED?
BLOWER SPEED CONFIRMED?
3 TRIALS FOR
IGNITION WITH NO
FLAME SENSED?
FLAME SIGNAL SENSED?
Page 37

Lynx
37
IV. Check combustion and fuel input rate
A. Remove the boiler jacket front panel by turning the black
screws 1/4 turn to the open position. Lift off the panel.
B. Start and run the boiler in the “System Test” mode in the
“VIEWING AND CHANGING SYSTEM SETTING” menu.
Refer to table 5 on page 33. Use the p or q push button to
choose first the high (alternating S-H on mode display) and
then the low (alternating S-L on mode display) firing rate.
C. Check the fuel input rate on the gas meter (for natural gas
boilers).
BTUH INPUT= cu.ft. metered in 3 minutes X heating value of
the gas* X 20
*The higher heating value of the gas can vary for different
localities. Consult the gas supplier for this value in
BTU/cu.ft.
If the fuel input is not at the rate specified on page 2 at the high
or low firing rate, then the blower speed should be adjusted to
attain the specified input rate. This can be done by using the
“Change blower RPM for high or low input” mode in the
“VIEWING AND CHANGING SYSTEM SETTING” menu.
Refer to Table 5 on page 33. Increasing the blower RPM will
increase the fuel input rate, and decreasing the blower RPM
will decrease the fuel input rate.
D. Measure the CO and CO2 of the flue gas at high and low
firing rate using a calibrated combustion test instrument. A
flue sample port is provided in the vent pipe (See Figure 2
on page 3). The CO should not exceed 100 PPM at high
input and 50 PPM at low input when the combustion is
correct. The CO2 should be in the range listed in Table 6.
E. If the combustion (CO2 and CO measurement) at either
high or low input rate is out of the range, shut down the
boiler and contact Slant/Fin Tech. service department at
1-800-873-4346.
F. Exit the “System Test” mode (Push “ENTER” button).
V. SAFETY CHECK
A. Check for gas leaks:
Using soap solution, check for gas leaks from meter to gas
valve including all pipes and fittings and gas valve
connections. Use liquid soap solution for all gas testing. DO
NOT use open flame.
B. Thermostat Test:
Set thermostat setting to low enough to end call for heat.
Gas valve should close and burner should stop firing.
Blower and circulator pump should go into a post purge,
then shut off.
C. Control Safety Shutdown test:
With the burner firing, disconnect the spark cable from the
spark ignitor. Gas valve should close and burner should
stop firing. The boiler will try for ignition three times after
this, then should lock out with an “A 01” error shown on the
display. Reconnect the spark cable to the spark ignitor, and
press the “Reset” button to return to normal operation.
Warning: Only a trained and qualified service technician must
do the adjustment to the input of the boiler.
Warning: Failure to comply with the above mentioned
requirement might result in property damage,
personal injury or loss of life.
Fuel
Firing
Rate
CO2%
Minimum Nominal Maximum
Natural
Gas
High 9.2% 9.5% 9.8%
Low 8.7% 9.0% 9.3%
Propane
High 10.7% 11.0% 11.3%
Low 10.2% 10.5% 10.7%
Table 6. Combustion values for natural gas and propane.
Page 38

Lynx
38
ERROR CODE INDICATION REMEDY
01
Ignition Failure - 3 unsuccessful
ignition attempts in a row.
Check for steady sparking at electrodes. If spark not
steady - check spark gap to be .125”, clean or replace
spark ignitor, check power supply voltage and grounding.
If spark is steady - check for proper gas supply pressure.
Check combustion, if able to ignite, or replace gas valve.
02
Flame Failure - 3 losses of flame
signal during one demand.
Check for proper combustion, at both max. and min.
input firing rates. If combustion is within the range
specified in Table 6 on page 36, clean or replace spark
ignitor, check power supply voltage and grounding.
03
Water High Limit Open
Check to see if the water outlet temperature reaches
203˚F. If it does, replace the water outlet 12k ohm
sensor. If it does not, replace the water high limit switch.
04, 05, 09, 10,
12, 13, 14, 15,
16, 18, 32
Control Failure
Replace control board. Make sure the proper boiler
model selection and confirmation code is entered.
See Table 5 on page 32.
19, 20
Flame Detected at Wrong Time
If a flame is still observed after a call for heat is stopped,
replace the gas valve. If the burner seems to be shutting
down properly, replace the spark ignitor.
33
Fan Failure - RPM error
Check wire harness connections going to the blower.
Replace blower.
A. LOCKOUT ERRORS: Indicated by an “A” in the mode display. The reset button must be pressed to clear the error
and retry operation. The temperature display shows the error code.
VI. DIAGNOSTIC ERROR CODES
WARNING: Only a trained, experienced service technician
should perform troubleshooting. Turn off all electric power to
the boiler before service.
Page 39

Lynx
39
B. BLOCKING ERRORS: Indicated by an “E” in the mode display. Operation is automatically restored, once the
condition returns to normal or is fixed. The temperature display shows the error code. Pressing the “Reset”
button is not required.
ERROR CODE INDICATION REMEDY
01
Water Outlet Sensor Open
Check wire harness connections going to the
sensor.
Replace the sensor.
02
Water Inlet Sensor Open
Check wire harness connections going to the
sensor.
Replace the sensor.
03
Flue Gas Sensor Open
Check wire harness connections going to the
sensor.
Replace the sensor.
11
Water Outlet Sensor Shorted Replace the sensor.
12
Water Inlet Sensor Shorted Replace the sensor.
13
Flue Gas Sensor Shorted Replace the sensor.
19, 42, 45,
46, 47, 48
Control Failure
Replace control board. Make sure the proper
boiler model selection and confirmation code is
entered. See Table 5 on page 33.
20
Flame Detected at Wrong Time
If a flame is still observed after a call for heat is
stopped, replace the gas valve, If the burner
seems to be shutting down properly, replace the
spark ignitor.
21
Polarity Error Reverse the hot and neutral power supply wires.
22
Frequency Error
Check power supply frequency to be 60 hz,
certain power supplies may not provide the
proper frequency.
24
Earth Connection Faulty Check grounding of control and boiler chassis.
continued on page 40
Page 40

Lynx
40
ERROR CODE INDICATION REMEDY
30
Excess Flue Temperature
Check flue gas temperature, at the maximum firing
rate and high water temperature. If the flue gas
temperature reaches 212˚F, check the fuel input
rate and combustion. Check the condition of the
heat exchanger. If the flue gas temperature does
not reach 212˚F, replace the flue sensor.
31
Low Water Cutoff Error
If a low water cutoff is installed, check the system
water pressure and content. Check the condition of
the LWCO. If no LWCO is installed, check the
jumper is in place at the wiring terminal board.
See Figure 16a on page 20.
32
Excess Water Inlet Temperature
Check that the wire harnesses to the water inlet
and outlet sensors are not reversed. The water
inlet sensor harness should have a blue colored
connector, the water outlet sensor harness should
have a red colored connector. Check that the
pumping flow direction is correct.
51
Reset Button Error
Try turning power supply off and on again. If error
returns, replace the display board.
52
Boiler Model Selection Error
Check that the proper boiler model selection and
confirmation code is entered in the display.
See Table 5 on page 33.
continued from page 39
04
Domestic Hot Water Tank Sensor Open
If sensor is utilized, check wire harness connections
going to the sensor, or replace the sensor. If no sensor is utilized, check the proper DHW mode is programmed. See Table 5 on page 33.
14
Domestic Hot Water Tank
Sensor Shorted
If sensor is utilized, replace the sensor. If no sensor
is utilized, check the proper DHW mode is programmed. See Table 5 on page 33.
C. WARNING ERRORS: Indicated by an “H” in the mode display. Operation of the space heating mode is not affect-
ed, and the warning is displayed intermittently. Operation of the DHW mode is automatically restored, once the
condition is fixed. The temperature display shows the error code. Pressing the “reset” button is not required.
Page 41

Lynx
41
CARE AND MAINTENANCE
This section must be brought to the attention of the owner by the
installer so that the owner can make the necessary arrangements with a qualified service agency for the periodic care and
maintenance of the boiler. The installer must also inform the
owner that the lack of proper care and maintenance of this boiler
and any fuel burning equipment may result in a hazardous condition. Installer should discuss contents of the User’s Information
Manual (Publication LXA-UIM) with the owner.
A trained and qualified service technician should perform the
inspection listed in these instructions before each heating season
and at regular intervals.
I. GENERAL MAINTENANCE
A. Safety check, see page 38.
B. Vent and air intake system inspection
1. Check for obstruction, condensation, corrosion and
physical damage.
2. Check outside termination. Screen and louvers should be
free of any debris and must be cleaned as required.
3. Perform “Venting and Air intake System Regular
Inspection”, see page 18.
C. Piping
Check the following:
1. Water piping and accessories for leaks. Slightest leaks
should be corrected.
2. System to be full of water and pressure to remain stable at
correct setting on gauge.
3. Air-control system. Noise and air binding in radiation
should not occur.
4. Low water cutoff for operation (see instruction furnished
with unit).
D. Boiler Room Air Supply
Check air vents for continuous positive supply of air as
required. Air needs are greatest in cold weather if boiler
installation is non-direct vent method. Air vents must open and
free of obstruction.
WARNING: The flow of combustion and ventilating air to the
boiler should not be obstructed.
II. ANNUAL MAINTENANCE
It is recommended that the igniter be inspected annually and
cleaned of all contaminents and if necessary replaced.
III. INSPECTION DURING HEATING SEASON
A. Check water pressure regularly and add water slowly to
system when needed. If much water is added, venting may be
necessary. Regular loss of water from boiler system may
indicate either a system leak, or a faulty air control system, or
a faulty automatic fill valve.
B. Check venting system. See “Venting and Air Intake System
Regular Inspection” on page 18.
C. Check condensation drain trap to be full of water. Check for
deterioration of the tubing. Check that the trap is not plugged.
D. The combustion blower does not require or have provisions
for lubrication.
E. If required, lubricate the circulator as per the manufacturer’s
instruction.
IV. CLEANING
A. Heat Exchanger: In the unlikely event of flue passage or
water passage blockage, service to remedy situation must be
performed only by an authorized Slant/FIn representative.
B. Burner: In the unlikely event of blockage or deterioration,
service to remedy situation must be performed only by an
authorized Slant/Fin representative.
IF REPLACEMENT PARTS ARE NEEDED
When parts are needed, refer to boiler model and serial number
shown on the boiler name/rating plate. Refer to publication
number LX1-10PL replacement parts for part numbers. Whenever possible refer to the original order by number and date.
Control identification and replacement should not be attempted
by unskilled personnel. Only, simple easily - identified controls
and parts may be obtained locally. All other control and parts
should be identified by and ordered form Slant./Fin. Relief/Safety
valves must be ASME rated for the pressure and gross output of
the boiler.
For replacement parts, heating contractors should contact their
Slant/Fin boiler distributor.
Page 42

Lynx
42
GENERAL TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE FOR SERVICE PERSONNEL
WARNING: Only a trained, experienced service technician should perform troubleshooting.
Turn off all electrical power to the boiler before servicing.
A. BURNER FAILS TO OPERATE - NO HEAT
CAUSE
REMEDY
1. No power, display off, power switch off. Main electric 1. Close switch. Check or replace fuse.
switch open. Blown or defective line fuse.
2. Gas supply valve shut off. 2. Open gas supply valve. Check gas pressure.
3. Harnesses plug-in connectors are not securely connected. 3. Check connectors on boiler control.
4. Operational problem, detected by control. 4. Error code on display can be correlated to
specific problems and remedy. Refer to page
38-40 for error codes.
B. NOT ENOUGH HEAT
1. Thermostat setting is too low. 1. Set thermostat at higher setting.
2. Boiler water maintained at too low temperature. 2. Increase space heating set point temperature.
Refer to Table 4 on page 32.
3. Circulator not running. 3. With thermostat calling for heat, check for power
to circulator. If power is O.K. but circulator is not
running, replace circulator.
4. Boiler water level too low. 4. Carefully snap open relief valve handle to
determine if boiler is full of water, if not full of
water, check for system leaks and check water
pressure regulator. Repair any system leaks.
Adjust or replace water pressure reducing valve.
5. Fuel input rate too low. 5. Check the maximum fuel input firing rate.
Refer to page 37 for the procedure.
C. FUMES AND GAS ODORS
1. Leaks in gas piping or accessories. 1. Locate leaks and repair.
2. Gas leaks in service line or meter connections. 2. Close service supply valve - shut down boiler
and notify utility.
3. Condensation trap is not full of water. 3. Check and fill with water
4. Venting system is physically damaged. 4. Check carefully and repair. Also, see “Venting
System Regular Inspection”.
5. Over - firing or poor combustion. 5. Check the maximum fuel input firing rate and
combustion. Refer to page 37 for procedure.
Page 43

Lynx
43
NOTES:
Page 44

SLANT/FIN CORPORATION, Greenvale, N.Y. 11548 • Phone: (516) 484-2600
FAX: (516) 484-5921 • Canada: Slant/Fin LTD / LTE E , Mississauga, Ontario
www.slantfin.com
©Slant/Fin Corp. 2014.
 Loading...
Loading...