Page 1

NSS evo3
Operator Manual
ENGLISH
www.simrad-yachting.com
Page 2

Page 3

Preface
Disclaimer
As Navico is continuously improving this product, we retain the right to make changes to the
product at any time which may not be reflected in this version of the manual. Please contact
your nearest distributor if you require any further assistance.
It is the owner’s sole responsibility to install and use the equipment in a manner that will not
cause accidents, personal injury or property damage. The user of this product is solely
responsible for observing safe boating practices.
NAVICO HOLDING AS AND ITS SUBSIDIARIES, BRANCHES AND AFFILIATES DISCLAIM ALL
LIABILITY FOR ANY USE OF THIS PRODUCT IN A WAY THAT MAY CAUSE ACCIDENTS, DAMAGE
OR THAT MAY VIOLATE THE LAW.
Governing Language: This statement, any instruction manuals, user guides and other
information relating to the product (Documentation) may be translated to, or has been
translated from, another language (Translation). In the event of any conflict between any
Translation of the Documentation, the English language version of the Documentation will
be the official version of the Documentation.
This manual represents the product as at the time of printing. Navico Holding AS and its
subsidiaries, branches and affiliates reserve the right to make changes to specifications
without notice.
Trademarks
Navico® is a registered trademark of Navico.
Simrad® is used by license from Kongsberg.
Navionics® is a registered trademark of Navionics, Inc.
NMEA® and NMEA 2000® are registered trademarks of the National Marine Electronics
Association.
SiriusXM® is a registered trademark of Sirius XM Radio Inc.
SimNet® is a registered trademark of Navico.
Fishing Hot Spots® is a registered trademark of Fishing Hot Spots Inc. Copyright© 2012
Fishing Hot Spots.
FUSION-Link™ Marine Entertainment Standard™ is a registered trademark of FUSION
Electronics Ltd.
C-MAP® is a registered trademark of C-MAP.
FLIR® is a registered trademark of FLIR.
Mercury® is a registered trademark of Mercury.
SmartCraft VesselView® is a registered trademark of Mercury.
Suzuki® is a registered trademark of Suzuki.
SD™ and microSD™ are trademarks or registered trademarks of SD-3C, LLC in the United
States, other countries or both.
Wi-Fi® is a registered trademark of the Wi-Fi Alliance®.
Additional mapping data: Copyright© 2012 NSI, Inc.: Copyright© 2012 by Richardson’s
Maptech.
Bluetooth® is a registered trademark of Bluetooth SIG, Inc.
HDMI® and HDMI™, the HDMI Logo, and High-Definition Multimedia Interface are trademarks
or registered trademarks of HDMI Licensing LLC in the United States and other countries.
Navico product references
This manual can refer to the following Navico products:
• Broadband Radar™ (Broadband Radar)
• Broadband 3G™ Radar (Broadband 3G Radar)
• Broadband 4G™ Radar (Broadband 4G Radar)
Preface | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
3
Page 4
• Broadband Sounder™ (Broadband Sounder)
• DownScan Imaging™ (DownScan)
• DownScan Overlay™ (Overlay)
• ForwardScan™ (ForwardScan)
• GoFree™ (GoFree)
• Halo™ Pulse Compression Radar (Halo Radar)
• INSIGHT GENESIS® (Insight Genesis)
• SonicHub® (SonicHub)
• StructureMap™ (StructureMap)
• StructureScan® (StructureScan)
• StructureScan® HD (StructureScan HD)
Copyright
Copyright © 2016 Navico Holding AS.
Warranty
The warranty card is supplied as a separate document.
In case of any queries, refer to the brand website of your display or system: www.simrad-
yachting.com.
Compliance statements
This equipment complies with:
• CE under 2014/53/EU Directive
• The requirements of level 2 devices of the Radio communications (Electromagnetic
Compatibility) standard 2008
• Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this
device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any
interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
The relevant Declaration of conformity is available in the product's section at the following
website: www.simrad-yachting.com.
Internet usage
Some features in this product use an internet connection to perform data downloads and
uploads. Internet usage via a connected mobile/cell phone internet connection or a pay-perMB type internet connection may require large data usage. Your service provider may charge
you based on the amount of data you transfer. If you are unsure, contact your service
provider to confirm rates and restrictions.
About this manual
The manual assumes that the user has basic knowledge of navigation, nautical terminology
and practices.
Important text that requires special attention from the reader is emphasized as follows:
Note: Used to draw the reader’s attention to a comment or some important information.
Ú
Warning: Used when it is necessary to warn personnel that they should
proceed carefully to prevent risk of injury and/or damage to equipment/
personnel.
Manual version
This manual is written for software version 1.0. The manual is continually updated to match
new software releases. The latest available manual version can be downloaded from
www.simrad-yachting.com.
4
Preface | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 5
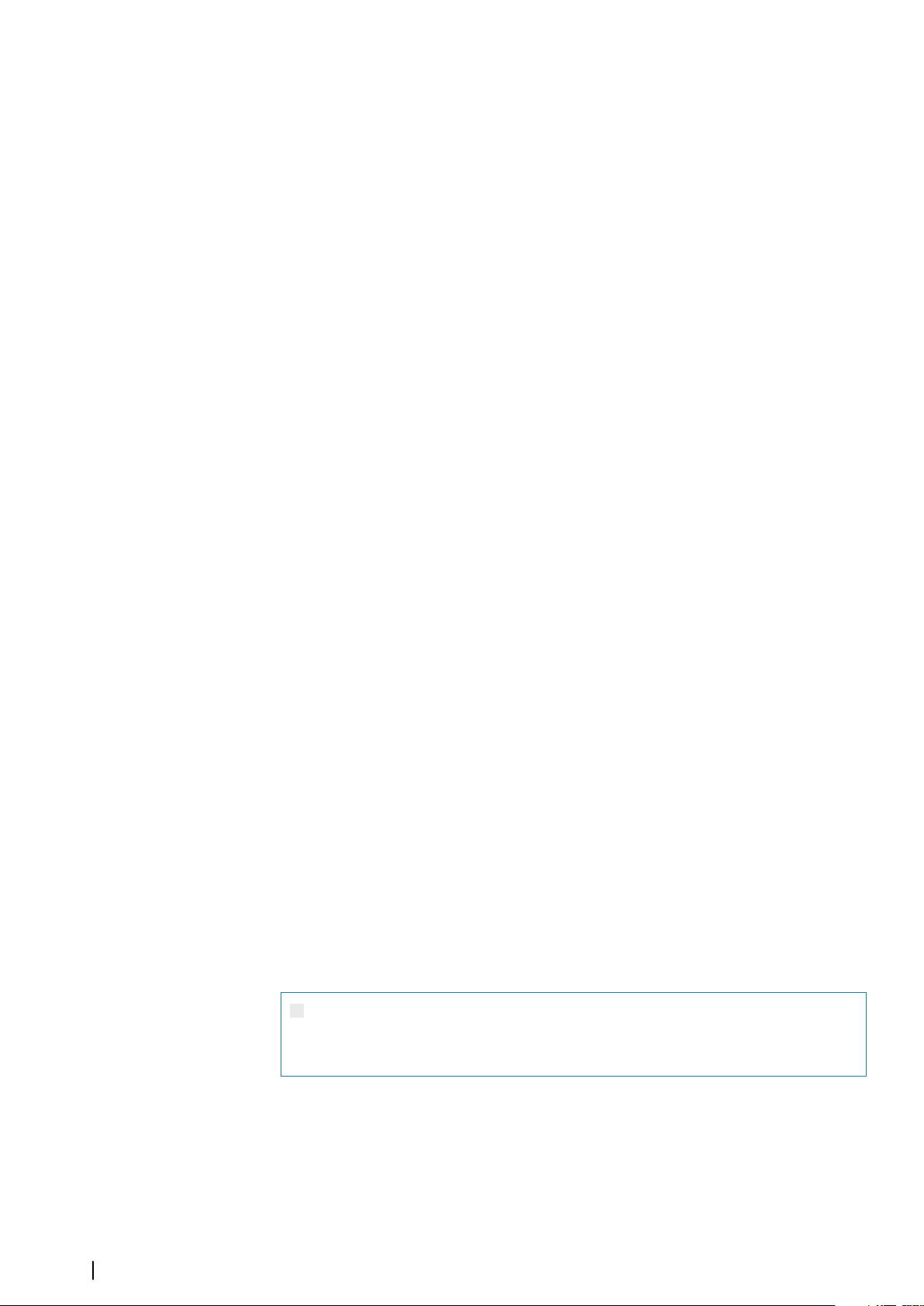
Viewing the manual on the screen
The PDF viewer included in the unit makes it possible to read the manuals and other PDF
files on the screen. Manuals can be downloaded from www.simrad-yachting.com.
The manuals can be read from a card inserted in the card reader or copied to the unit’s
internal memory.
Use the menu options or the keys and on-screen buttons to maneuver in the PDF file as
described below:
• Search, Goto page, Page Up and Down
Select the relevant panel button.
• Scroll pages
Turn the rotary knob.
• Panning on the page
Drag finger on the screen in any direction.
• Zoom In/Out
Use pinch or spread gestures.
• Exit the PDF viewer
Press the X key or select the X in the upper right corner of the panel.
The Software version
The software version currently on this unit can be found in the About dialog. The About
dialog is available in the System Settings.
For information regarding upgrading your software, refer to "Software upgrades" on page 125.
Preface | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
5
Page 6

Contents
10 Introduction
10
Front controls
11 The Home page
11 Application pages
12 Integration of 3rd party devices
14 Remote controllers
15 Basic operation
15 System Controls dialog
15 Turning the system on and off
15 Display illumination
16 Wireless
16 Locking the touchscreen
16 Instrument bar
16 Touchscreen operation
17 Using menus and dialogs
17 Selecting pages and panels
17 Displaying the Favorites panel as a pop-up on a page
18 Creating a Man Overboard waypoint
18 Screen capture
19 Customizing your system
19 Customizing the Home page wallpaper
19 Configuring the WheelKey
19 Customizing the long press feature
19 Adjusting panel size
20 Password protection
20 Adding new favorite pages
21 Edit favorite pages
21 Setting the appearance of the Instrument bar
22 Bridge Control
25 Charts
25 The Chart panel
25 Chart data
25 Showing dual chart types
26 Panning the chart
26 Chart scale
26 Vessel symbol
26 Positioning the vessel on the chart panel
27 Displaying information about chart items
27 Using the cursor on the chart panel
28 Saving waypoints
28 Creating routes
28 Find objects on chart panels
28 3D charts
29 Chart overlay
29 Insight and C-MAP charts
32 Navionics charts
35 Chart settings
37 Waypoints, Routes, and Tracks
37 Waypoints
38 Routes
40 Tracks
41 Waypoints, Routes, and Tracks dialogs
6
Contents | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 7

42 Navigating
Navigation panels
42
43 Navigate to cursor position
43 Navigate a route
44 Navigating with the autopilot
44 Navigation settings
46 TripIntel
46 Current trip statistics
46 Automatic trip recording
47 Start and stop trip recordings
47 Long-term statistics
47 Estimated fuel range ring
47 Fuel gauge
48 Tide gauge
48 View trip recordings
50 Autopilot
50 Safe operation with the autopilot
50 Activating the autopilot
50 Switching from automatic mode to manual steering
50 Autopilot indication on the pages
51 The Autopilot panel
52 Autopilot modes
52 Standby mode
52 Non-Follow Up (NFU, Power steering)
52 Follow-up steering (FU)
52 AUTO mode (auto compass)
53 NoDrift mode
53 NAV mode
54 WIND mode
55 Turn pattern steering
57 Using the NSS evo3 in an AP24/AP28 system
57 Using the autopilot in an EVC system
57 Using the NSS evo3 in an AP70/AP80 system
60 Autopilot settings
63 Radar
63 The radar panel
63 Dual radar
64 Radar overlay
64 Radar operational modes
64 Radar Range
65 Using the cursor on a radar panel
65 Saving waypoints
66 Radar sector blanking
66 Adjusting the radar image
68 Advanced radar options
69 Radar view options
70 EBL/VRM markers
71 Setting a guard zone around your vessel
71 MARPA targets
72 Recording radar data
73 Radar settings
74 Echosounder
74 The Echosounder image
74 Multiple Echosounder
Contents | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
7
Page 8

74 Zooming the image
Using the cursor on the image
75
76 Saving waypoints
76 Viewing history
76 Setting up the image
77 Advanced options
78 Start recording log data
79 Stop recording log data
79 Viewing the recorded sounder data
79 Echosounder View options
81 Echosounder settings
83 StructureScan
83 The StructureScan image
83 Zooming the StructureScan image
84 Using the cursor on the StructureScan panel
84 Saving waypoints
85 Viewing StructureScan history
85 Setting up the StructureScan image
86 Advanced StructureScan settings
87 StructureMap
87 The StructureMap image
87 Activating Structure overlay
87 StructureMap sources
88 StructureMap tips
88 Recording StructureScan data
88 Using StructureMap with mapping cards
88 Structure options
90 ForwardScan
90 The ForwardScan image
91 Setting up the ForwardScan image
91 ForwardScan view options
91 Heading extension
92 ForwardScan setup
95 Wireless connection
95 Connect and disconnect from a wireless hotspot
95 GoFree Shop
95 GoFree Link
96 Uploading log files to Insight Genesis
97 Wireless settings
98 AIS
98 AIS target symbols
98 Viewing information about AIS targets
99 Calling an AIS vessel
99 AIS SART
100 Vessel alarms
101 Vessel settings
103 Instrument panels
103 Dashboards
103 Customizing the Instruments panel
104 Audio
104 Enabling audio
8
Contents | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 9

104 SonicHub 2
The Audio panel
106
107 Setting up the audio system
107 Operating the audio system
108 Favorite channels
108 Sirius radio (North America only)
109 Weather
109 Wind barbs
109 Showing weather details
109 GRIB weather
111 SiriusXM weather
114 Weather alarms
115 Video
115 The Video panel
115 Setting up the video panel
115 FLIR camera control
117 Time plots
117 The Time plot panel
117 Selecting data
118 Alarms
118 Alarm system
118 Type of messages
118 Single alarms
118 Multiple alarms
118 Acknowledging a message
118 Alarms dialog
120 Tools
120 Waypoints
120 Tides
120 Alarms
120 Vessels
120 TripIntel
120 Sun, Moon
120 Files
121 Find
121 GoFree Shop
122 Simulator
122 Demo mode
122 Simulator source files
122 Advanced simulator settings
124 Maintenance
124 Preventive maintenance
124 Cleaning the display unit
124 Cleaning the media port door
124 Checking the keys
124 Checking the connectors
124 NMEA Data logging
125 Software upgrades
126 Backing up your system data
Contents | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
9
Page 10
Introduction
1
11
5
2
7
3
4
6
9
10
12
13
12
8
1
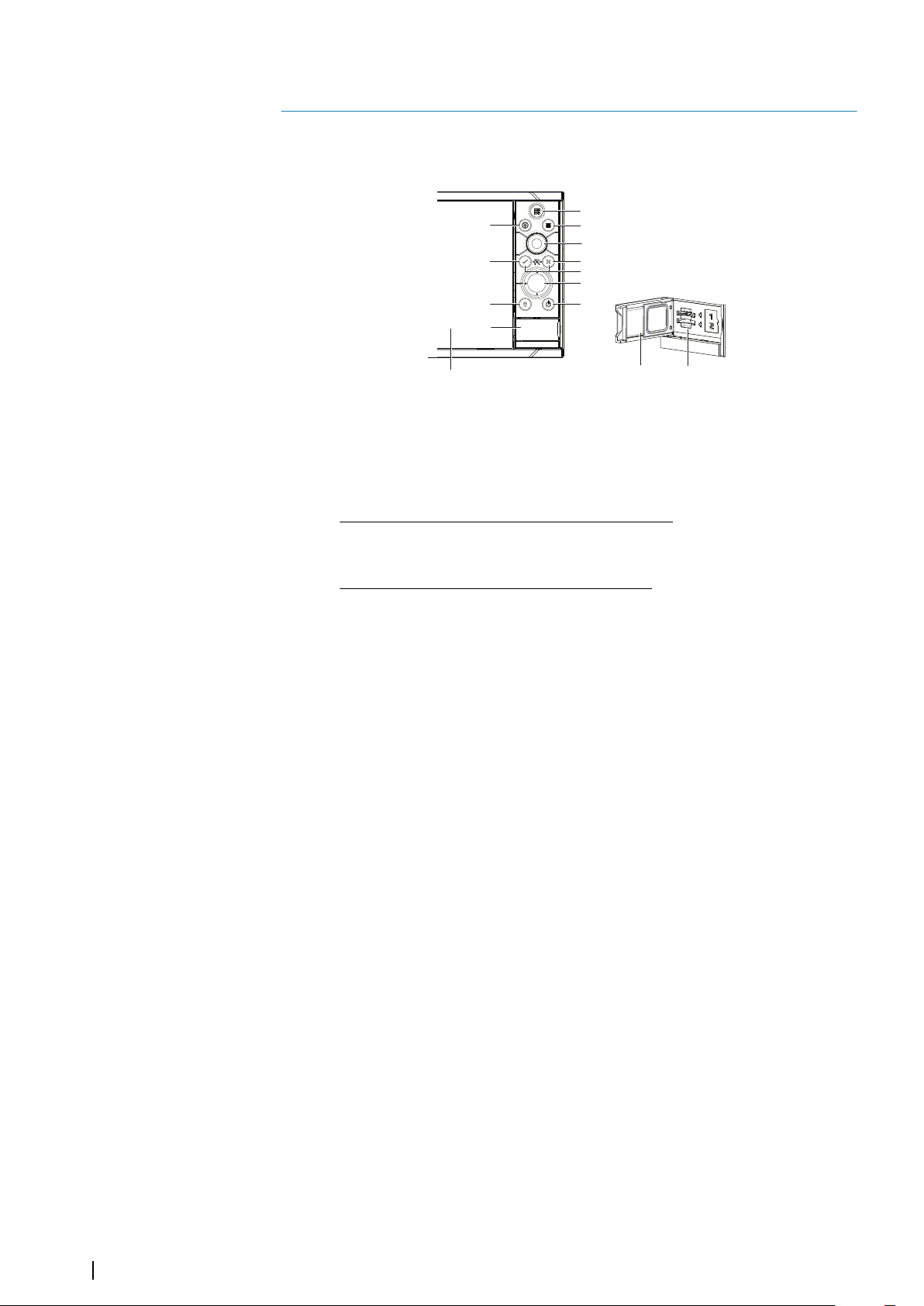
Front controls
1 Touch screen
2 Pages/Home - press to open the Home page for page selection and setup
options
3 WheelKey - user configurable key, refer to "Configuring the WheelKey" on page 19.
Default without an autopilot connected to the system:
• Short press: toggles between panels on split screen
• Long press: maximizes active panel on split screen
Default with an autopilot connected to the system:
• Short press: opens the autopilot controller and puts the autopilot in standby
mode
• Long press: toggles between panels on split screen
4 Menu key - press to display the active panel's menu
5 Rotary knob - turn to zoom or scroll the menu, press to select an option
6 Enter key - press to select an option or to save settings
7 Exit key - press to exit a dialog, return to previous menu level, and clear the cursor
from the panel
8 MOB - press simultaneously the Enter and Exit keys to create a MOB at the
vessel's position
9 Arrow keys - press to activate the cursor or to move the cursor
Menu operation: press to navigate through menu items and to adjust a value
10 Mark key - press to place waypoint at vessel position or at cursor position when
cursor is active
11 Power key - press and hold to turn the unit ON/OFF
Press once to display the System Controls dialog, additional presses to toggle
through three default dimming levels
12 Card reader door
13 Dual card reader slots
10
Introduction | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 11
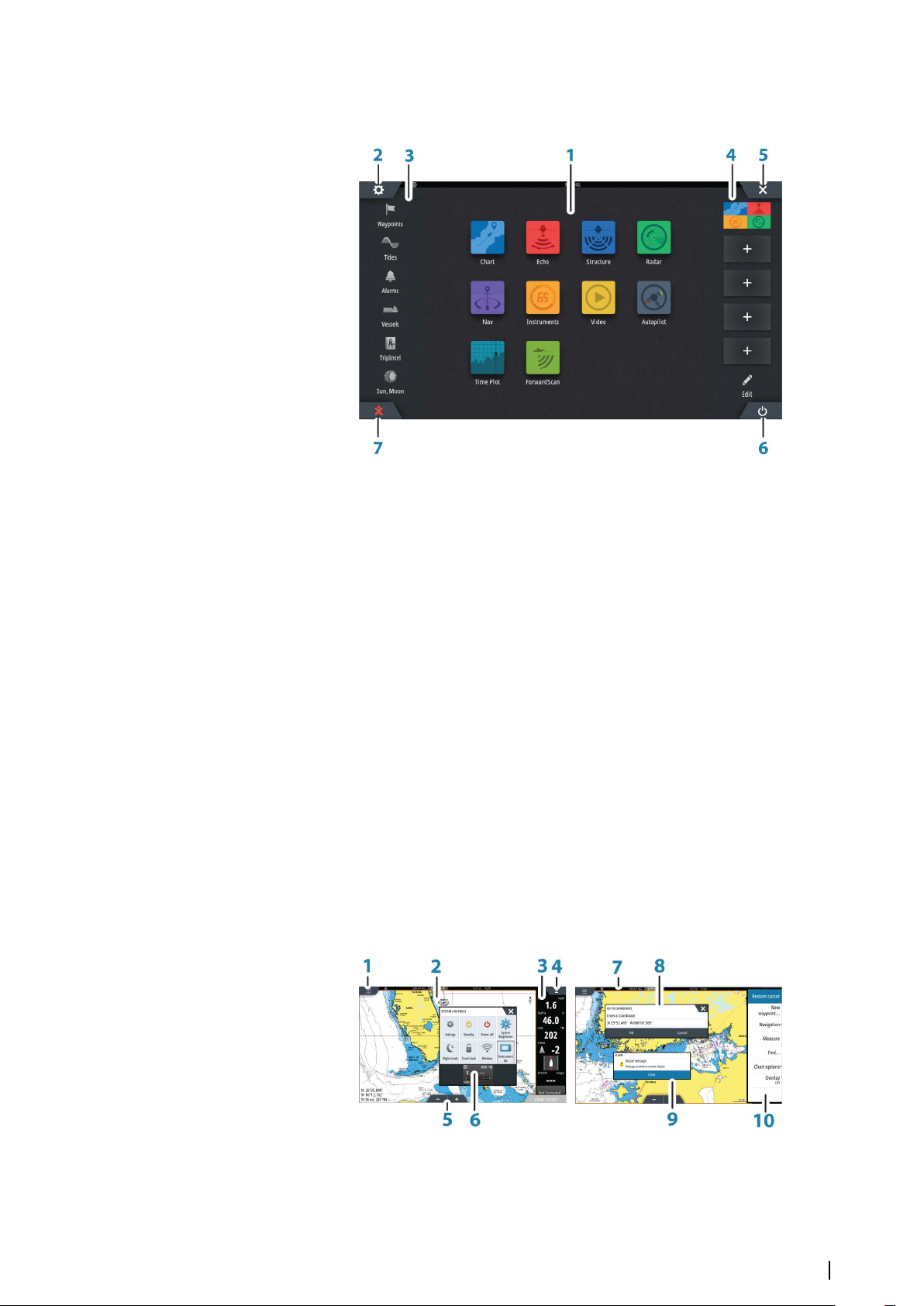
The Home page
1 Applications
Select a button to display the application as a full page panel.
Press and hold a button to display pre-configured split page options for the
application.
2 Settings button
Select to access Settings dialogs.
3 Tools
Select a button to access dialogs used for carrying out a task, or for browsing
stored information.
4 Favorites
Select a button to display the panel combination.
Press and hold a favorite button to enter edit mode for the Favorites panel.
5 Close button
Select to exit the Home page and return to the previous active page.
6 Power button
Select to power off the unit.
7 Man Over Board (MOB) button
Select to save a Man Over Board (MOB) waypoint at the current vessel position.
Application pages
Each application connected to the system is presented on panels. The application can be
presented as a full page, or in combination with other panels in a multiple panel page.
All application pages are accessed from the Home page.
Introduction | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
11
Page 12

1 Home button
2 Application panel
3 Instrument bar
Navigation and sensor information. The bar can be turned off and it can be
configured by the user.
4 Menu button
5 Zoom buttons
6 System controls dialog
Quick access to basic system settings.
Display the dialog by a short press on the Power key or by swiping down from top
of the screen.
7 Status bar
8 Dialog
Information to or input from the user.
9 Alarm message
Displayed if dangerous situations or system faults occur.
10 Menu
Panel specific menu.
Split pages
You can have up to 4 panels on each page.
2 panels page 3 panels page
Panel sizes in a split page can be adjusted from the System Controls dialog.
4 panels page
Pre-configured split pages
Each full screen application has several pre-configured split pages, featuring the selected
application combined with each of the other panels.
Note: The number of pre-configured split pages cannot be changed, and the pages
Ú
cannot be customized or deleted.
Access a pre-configured split page by pressing and holding the main panel button.
Favorite pages
All preconfigured favorite pages can be modified and deleted, and you can create your own.
You can have a total of 12 favorite pages.
For more information, refer to "Adding new favorite pages" on page 20.
12
Integration of 3rd party devices
Several 3rd party devices can be connected to the NSS evo3. The applications are displayed
on separate panels or integrated with other panels.
Introduction | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 13

A device connected to the NMEA 2000 network should automatically be identified by the
system. If not, enable the feature from the advanced option in the System settings dialog.
The 3rd party device is operated by using menus and dialogs as on other panels.
This manual does not include specific operation instructions for any 3rd party device. For
features and functionality, refer to the documentation included with the 3rd party device.
SmartCraft VesselView integration
SmartCraft data can be displayed and interaction are enabled through the unit when a
Mercury VesselView® 4, 7, 403, 502, 702, 703, or Link is present on the network.
When the features are enabled, the display may prompt the user for some basic
configuration information. Refer to the VesselView® manual or engine supplier for further
information.
The engine supplier icon appears on the Home page when a device is available.
Suzuki Engine panel
If a Suzuki C10 gauge is available on the network, a Suzuki engine icon is added to the Home
page. An icon is also added to the Page editor. You can select to display the Suzuki engine
panel as a full page panel or as part of a multi-panel page.
The layout and content of the engine panel depends on selected panel size. The digital
gauges can be customized, refer to "Customizing the panel" on page 103.
FUSION-Link integration
FUSION-Link devices connected to the NMEA 2000 network can be controlled from the NSS
evo3 system.
The FUSION-Link devices appear as additional sources when using the audio function. No
additional icons are available.
Refer to "Audio" on page 104 for more information.
FLIR camera integration
If a FLIR M-series camera is available on the Ethernet network, you can display the video and
control the camera from the NSS evo3.
The FLIR camera is controlled from the Video panel, and no additional icons appear on the
Home page.
Refer to "Video" on page 115 for more information.
BEP CZone integration
The NSS evo3 integrates with BEP’s CZone system used for controlling and monitoring a
distributed power system on your vessel.
The CZone icon is available in the Tools panel on the Home page when a CZone system is
available on the network.
A separate manual is provided with your CZone system. Refer to this documentation and to
the NSS evo3 Installation manual for how to install and configure the CZone system.
CZone dashboard
When the CZone is installed and configured, an additional CZone dashboard is added to the
Instruments panels.
Vessel dashboard Navigation dashboard Angler dashboard CZone dashboard
You switch between a panel’s dashboards by selecting the left and right arrow symbols or by
selecting the dashboard from the menu.
Introduction | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
13
Page 14

Editing a CZone dashboard
You can customize a CZone dashboard by changing the data for each of the gauges.
Available editing options depend on the type of gauge and which data sources that are
connected to your system.
For more information, refer to "Instrument panels" on page 103.
Remote controllers
You can connect a remote controller to the network and remotely control the unit. To find
out which remote controllers can be used, refer to the product web page at:
www.simrad-yachting.com.
A separate manual is included with the remote controller.
14
Introduction | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 15
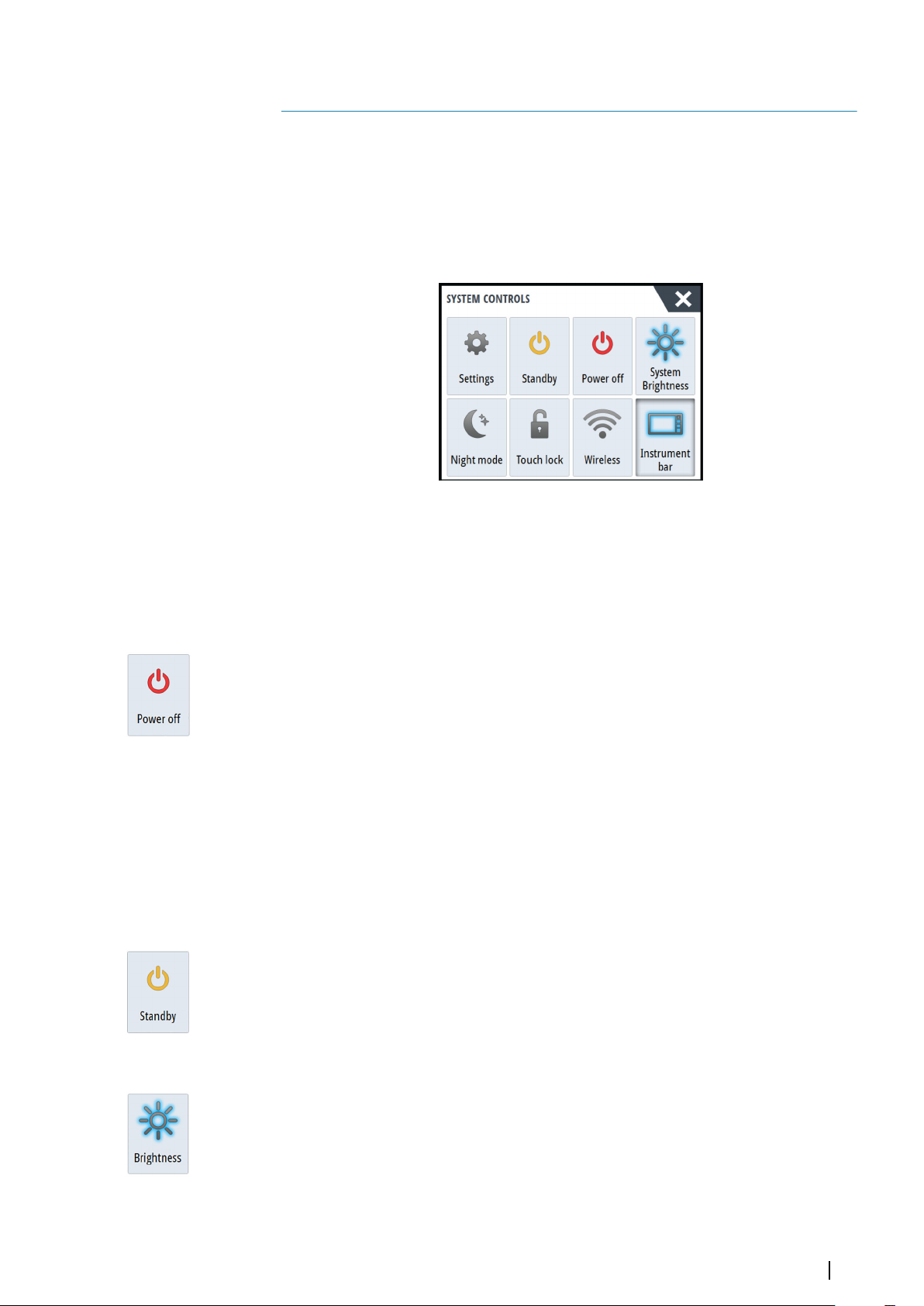
Basic operation
2
System Controls dialog
The System Controls dialog provides quick access to basic system settings. You display the
dialog by making a short press on the Power key or by swiping down from the top of the
screen.
The icons displayed on the dialog can vary. For example, the adjust splits option is only
available if you are viewing a split page when you open the System Controls dialog.
Activating functions
Select the icon of the function you want to set or toggle on or off. For those functions that
toggle on and off, a highlighted icon indicates the function is activated, as shown in the
Instrument bar icon above.
Turning the system on and off
You turn the system off by pressing the Power key, or by selecting the Power option on the
Home page or in the System Controls dialog.
If the Power key is released before the shut-down is completed, the power off process is
cancelled.
Note: If the unit is configured as a slave, you cannot power off the unit by the Power
Ú
key, and the System Controls dialog does not display the power off option.
First time startup
When the unit is started for the first time, or after a factory default, the unit displays a setup
wizard. Respond to the setup wizard prompts to select some fundamental setup options.
You can perform further setup using the system settings option and later change settings
made with the setup wizard.
Standby mode
In Standby mode, the backlight for screen and keys are turned off to save power. The system
continues to run in the background.
You select Standby mode from the System Controls dialog.
Display illumination
Brightness
The display backlighting can be adjusted at any time from the System Controls dialog.
You can also cycle the preset backlight levels by short presses on the Power key.
Night mode
The night mode option optimizes the color palette and backlight for low light conditions.
Note: Details on the chart may be less visible when the Night mode is selected!
Ú
Basic operation | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
15
Page 16
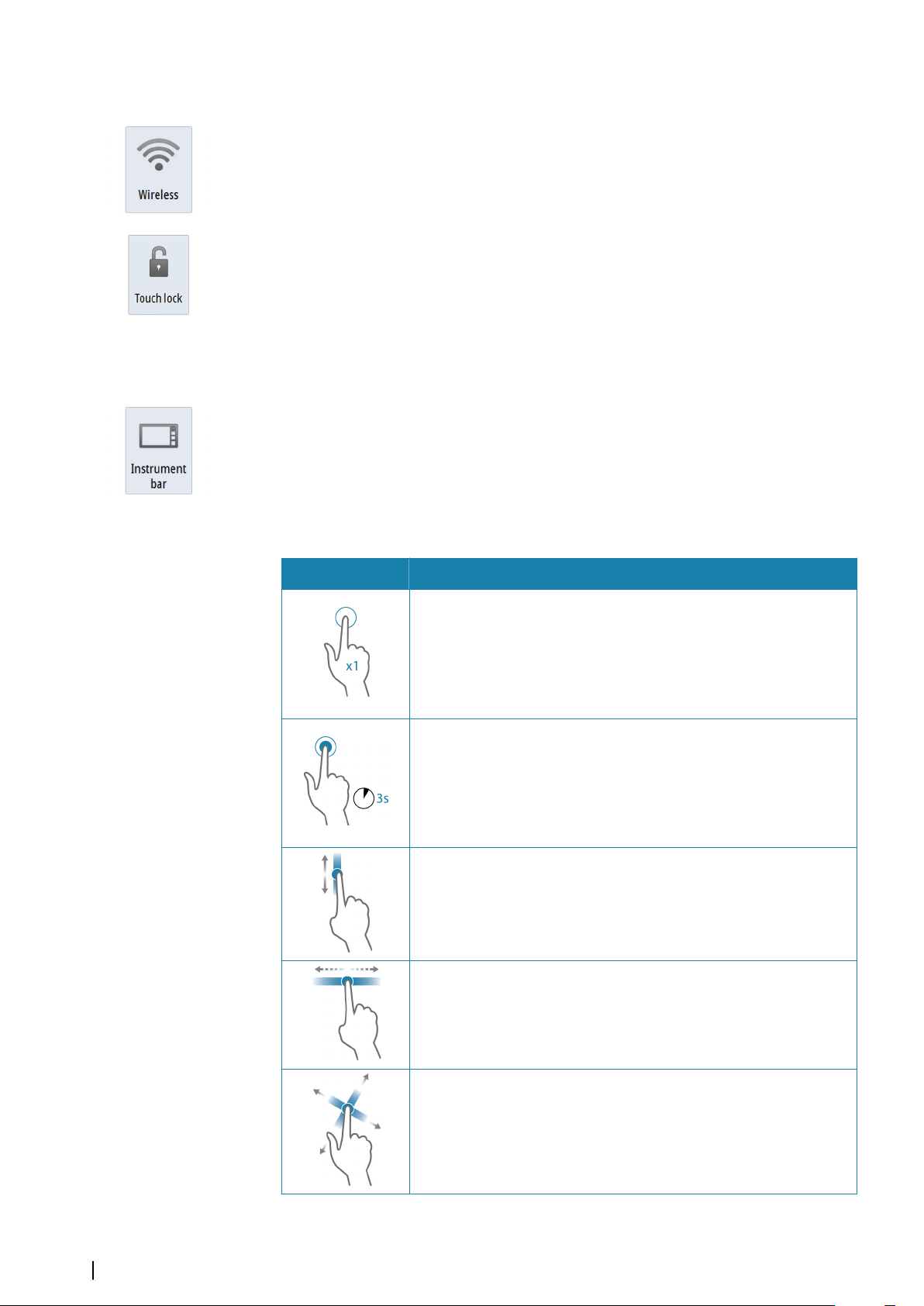
Wireless
Provides wireless connection options dependent on the status of the wireless. For example,
connect to a hotspot or change to access point. For option explanations refer to "Wireless
connection" on page 95.
Locking the touchscreen
You can temporarily lock a touchscreen to prevent accidental operation of the system. Lock
the touchscreen when large amounts of water are on the screen, for example, in heavy seas
and weather. This feature is also useful when cleaning the screen while the unit is turned on.
When the touch lock is active you can only operate the unit from the keys.
You lock the touchscreen from the System Controls dialog.
You remove the lock function by a short press on the Power key.
Instrument bar
Toggles the Instrument bar on/off for the current page only.
Touchscreen operation
Basic touchscreen operation on the different panels is shown in the table below.
The panel sections in this manual have more information about panel specific touchscreen
operation.
Icon Description
Tap to:
• Activate a panel on a multi-panel page
• Position the cursor on a panel
• Select a menu and a dialog item
• Toggle a checkbox option on or off
• Show basic information for a selected item
Press and hold:
• On any panel with a cursor to either activate the cursor assist feature
or open the menu. Refer to "Customizing the long press feature" on page 19
• On the Instrument panel to open the Choose data dialog
• On a panel button to see available split screen options
• On a favorite button to enter edit mode
Scroll through a list of available options without activating any option.
Flick to quickly scroll through e.g. the waypoint list. Tap the screen to
stop the scrolling.
16
Pan to position a chart or Echosounder image on the panel.
Basic operation | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 17

Icon Description
Pinch to zoom out on the chart or on an image.
Spread to zoom in on the chart or on an image.
Using menus and dialogs
Menus
You display a page menu by selecting the MENU button in the upper right corner of the
page.
• Activate a menu item and toggle on/off an option by selecting it
• Adjust a slide bar value by either:
dragging the slide bar
-
- selecting the + or - icons
You can also operate the menus by using the rotary knob:
• Turn the knob to scroll through menu items
• Press the knob to select a highlighted item
• Turn the knob to adjust the value of a selected item
Select the Back menu option or the X key to return to the previous menu level, and then
exit.
The status of the cursor (active vs. inactive) changes the menu options.
Dialog boxes
You select entry fields and keys in a dialog box by tapping the screen or by using the rotary
knob.
Numeric and alphanumeric keyboards are automatically displayed when required for
entering user information in dialogs. You operate the keyboard by selecting the virtual keys,
and you confirm your entry by selecting the virtual Enter key or by pressing the rotary knob.
A dialog is closed by saving or cancelling the entry.
A dialog can also be closed by selecting the X in the dialog's upper right corner or by
pressing the X key.
Selecting pages and panels
Selecting a page
• Select a full page panel by selecting the relevant application button on the Home page
• Select a favorite page by selecting the relevant favorite button
• Select a predefined split panel by pressing and holding the relevant application icon
Select active panel
In a multiple panel page, only one panel can be active at a time. The active panel is outlined
with a border.
You can only access the page menu of an active panel.
You activate a panel by tapping it.
Displaying the Favorites panel as a pop-up on a page
You can display the Favorites panel as a pop-up on any page by pressing and holding the
Home key.
Basic operation | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
17
Page 18
Select a favorites page in the pop-up to display it. The panel will switch to the selected
favorite after 3 seconds.
Creating a Man Overboard waypoint
If an emergency situation should occur, you can create a Man Overboard (MOB) waypoint at
the vessel’s current position by selecting the MOB button on the Home page.
You can also save a Man Overboard (MOB) waypoint at the vessel’s current position by
pressing the Enter and Exit keys simultaneously. Simultaneous pressing the Enter and Exit
keys creates a MOB at the vessel's location
When you activate the MOB function the following actions are automatically performed:
• a MOB waypoint is created at the vessel’s position
• the display switches to a zoomed chart panel, centered on the vessel's position
• the system displays navigation information back to the MOB waypoint
Multiple MOB waypoints are saved by repeatedly pressing the MOB buttons. The vessel
continues to show navigation information to the initial MOB waypoint. Navigation to
subsequent MOB waypoints needs to be done manually.
Cancel navigation to MOB
The system continues to display navigational information towards the MOB waypoint until
you cancel the navigation from the menu.
Delete a MOB waypoint
1. Select the MOB waypoint to activate it
2. Tap the MOB waypoint's pop-up or press the Enter key or the rotary knob to display the
MOB waypoint dialog
3. Select the delete option in the dialog.
A MOB waypoint can also be deleted from the menu when it is activated.
Screen capture
Simultaneously press the Home and Power keys to take a screen capture. Screen captures
are saved to internal memory.
You need to turn on the Screen capture option in the System Settings dialog to be able to
take a screenshot on a touch screen. When the function is activated, you can take a
screenshot on a touch screen by double-selecting the title bar of an open dialog, or by
double-selecting the status bar if no dialog is open.
To view files, refer to "Files" on page 120.
18
Basic operation | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 19
Customizing your system
3
Customizing the Home page wallpaper
The Home page's wallpaper can be customized. You can select one of the pictures included
with the system, or you can use your own picture in .jpg or .png format.
The images can be available on any location that can be seen in the files browser. When a
picture is chosen as the wallpaper, it is automatically copied to the Wallpaper folder.
Configuring the WheelKey
You can define what happens with a short or long press of the WheelKey on the front of the
unit.
To configure the Wheel key, select Configure WheelKey on the System Setting dialog.
Select the Short press option or Long press option in the WHEELKEY CONFIGURATION
dialog and then an option from the list displayed.
Customizing the long press feature
Use the Advanced settings dialog to specify if the long press on the panel opens the menu
or displays the cursor assist feature on the panel.
Adjusting panel size
You can change the panel size for an active split page. The panel size can be adjusted for
both favorite pages and for predefined split pages.
1. Activate the System Controls dialog
2. Select the adjust splits option in the dialog
3. Adjust the panel size by dragging the adjustment icon
4. Confirm your changes by tapping one of the panels, by pressing the rotary knob or the
Enter key.
Customizing your system | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
19
Page 20
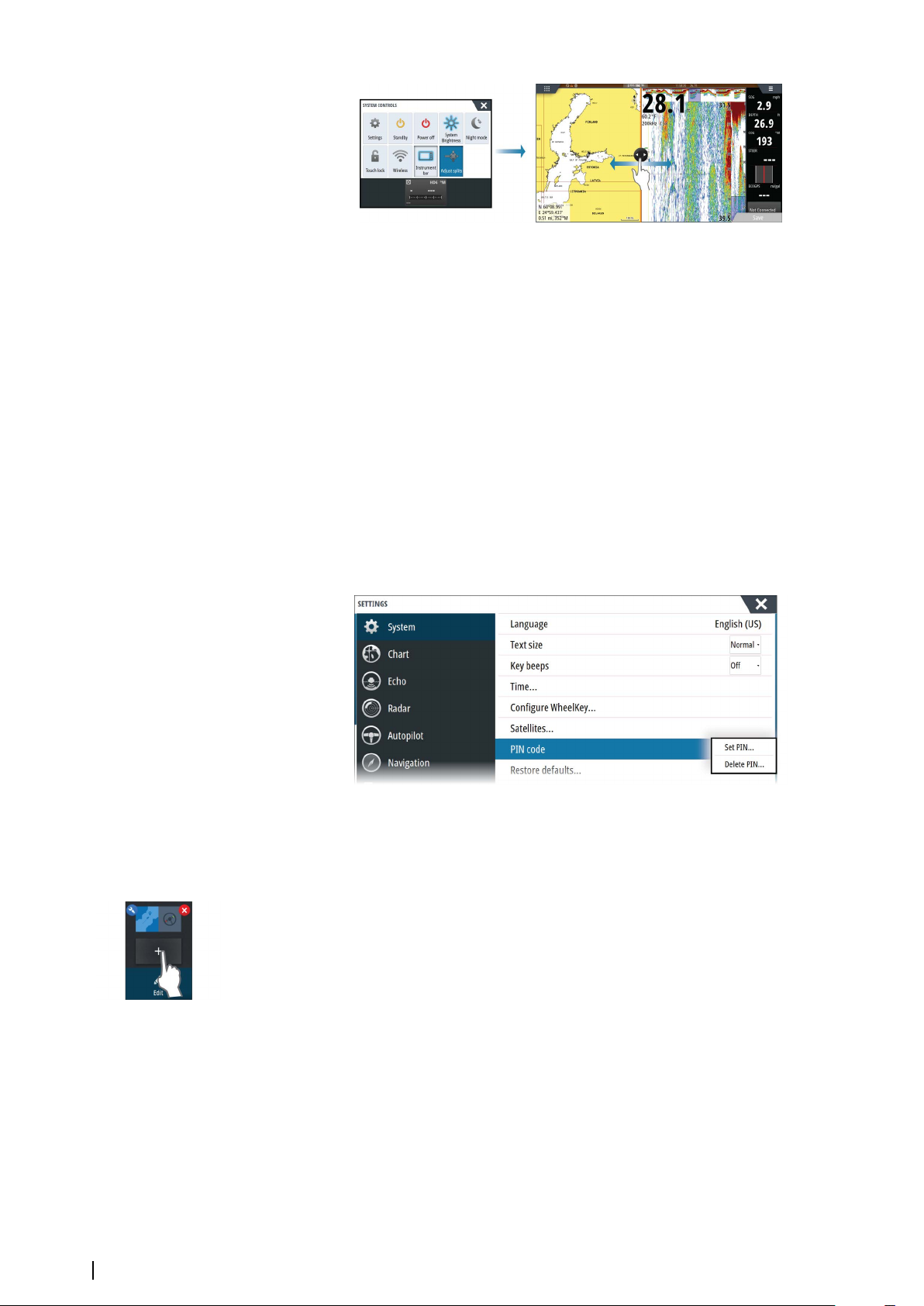
The changes are saved to the active favorite or split page.
Password protection
You can set a PIN code to prevent unauthorized access to your system settings.
Note: We recommend you record the PIN code (password) and store it in a safe place if you
use this feature.
When you establish password protection, the PIN code must be entered when any of the
following are selected. After the correct PIN code is entered, all of them can be accessed
without re-entering the PIN code.
• Settings, activated from the Tools panel or System Controls dialog
• Alarms, activated from the Tools panel
• Files, activated from the Tools panel
• GoFree Shop, activated from the Tools panel
• Settings, activated from the Chart menu under Chart Options
You set and remove password protection from the system Settings dialog.
20
Adding new favorite pages
1. Select the New icon in the favorite panel on the Home page to open the page editor
dialog
2. Drag and drop page icons to set up a new page
3. Change the panel arrangement (only possible for 2 or 3 panels), if required
4. Save the page layout.
The system displays the new favorite page, and the new page is included in the list of
favorite pages on the Home page.
Customizing your system | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 21
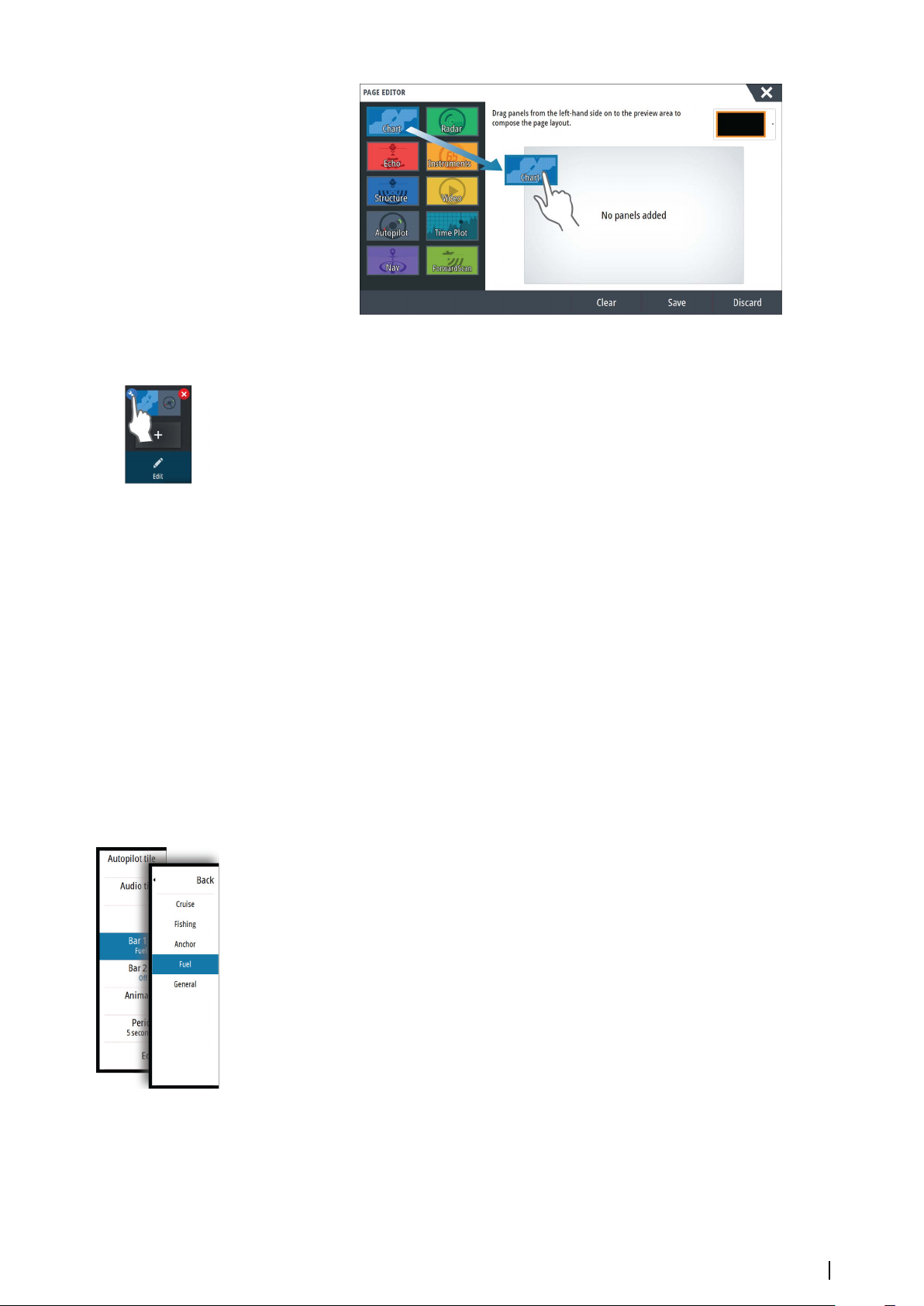
Edit favorite pages
1. Select the edit icon in the Favorite panel:
Select the X icon on a favorite icon to remove the page
-
- Select the tool icon on a favorite icon to display the page editor dialog
2. Add or remove panels in the page editor dialog
3. Save or discard your changes to leave the favorite edit mode.
Setting the appearance of the Instrument bar
Data sources connected to the system can be viewed in the Instrument bar.
You can configure the Instrument bar to display either one or two bars. If you specify to
display two bars you can set it to alternate the bars automatically. You can specify the
information displayed in the instrument bars.
Use the menu to select a predefined activity for one or both of the bars. When an activity bar
is selected, predefined instrument gauges are displayed in the instrument bar.
You can turn the Instrument bar off from the System controls dialog.
Note: This only turns the Instrument bar off for the current page.
Ú
Turning the Instrument bar on/off
1. Activate the System controls dialog
2. Deactivate/activate the instrument bar icon to toggle the bar on and off.
Select a predefined activity bar
1. Activate the Instrument bar by selecting it
2. Select the MENU button to open the menu
3. Select Bar 1 or Bar 2 and then a predefined activity bar.
Predefined gauges are displayed in the instrument bar. You can change a gauge in the
activity Instrument bar, refer to Edit the content of the Instrument bar below.
Edit the content of the Instrument bar
1. Activate the Instrument bar by selecting it
2. Select the MENU button to open the menu
3. Select Edit to change an instrument gauge followed by the gauge you want to change
4. Select the content you want to display from the Choose Data dialog
5. Select Menu and then Finish editing to save your changes.
Customizing your system | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
21
Page 22

Fuel economy gauge
You can display a fuel economy gauge in the instrument bar on application pages (Chart,
Radar, Echo, Nav, and so on). Select the predefined Fuel activity bar or change a gauge
source to Fuel Economy. To change a gauge source, refer to "Setting the appearance of the Instrument
bar" on page 21.
1 Digital readout of current economy
2 Fuel economy measurement units
3 100% efficiency, this equates to the 'nominal consumption'
4 120% efficiency
5 Average fuel economy
6 Instantaneous economy
7 Current fuel level
The fuel economy gauge displays the instantaneous versus historical average fuel efficiency.
The start of the green zone represents ‘Nominal Fuel Economy’, and it displays an additional
20% area to allow your fuel efficiency to be displayed above the nominal fuel economy.
The more efficient you consume fuel, the more the outer blue dial creeps up towards the
green portion of the scale. If you achieve the nominal efficiency of your vessel you will be at
the green zone. If you manage to achieve an efficiency better than your nominal efficiency,
you will be somewhere in the upper green zone.
Nominal fuel economy can be entered in the Vessel Setup dialog displayed from the Fuel
settings dialog.
You can reset your average fuel economy from the Reset Fuel Economy button on the Fuel
settings dialog. When you reset it, the system starts calculating the new average.
Set the measurement units for the fuel economy gauge in the Economy field in the Units
settings dialog.
Bridge Control
The Bridge Control feature allows you to control which pages are shown on several displays
at the same time. The feature is used on vessels with multiple displays mounted in the same
place to quickly configure what information is displayed.
There can be a maximum of four different bridges on your system, and you can have up to
four displays grouped into one bridge. Each display can be configured to only one bridge.
When the displays are included in a bridge, you can configure twelve page configurations
(presets) for each bridge.
22
Adding displays to a Bridge
Note: All displays must be turned on to be available for bridge configuration.
Ú
1. Open the Bridge Configuration dialog
Customizing your system | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 23
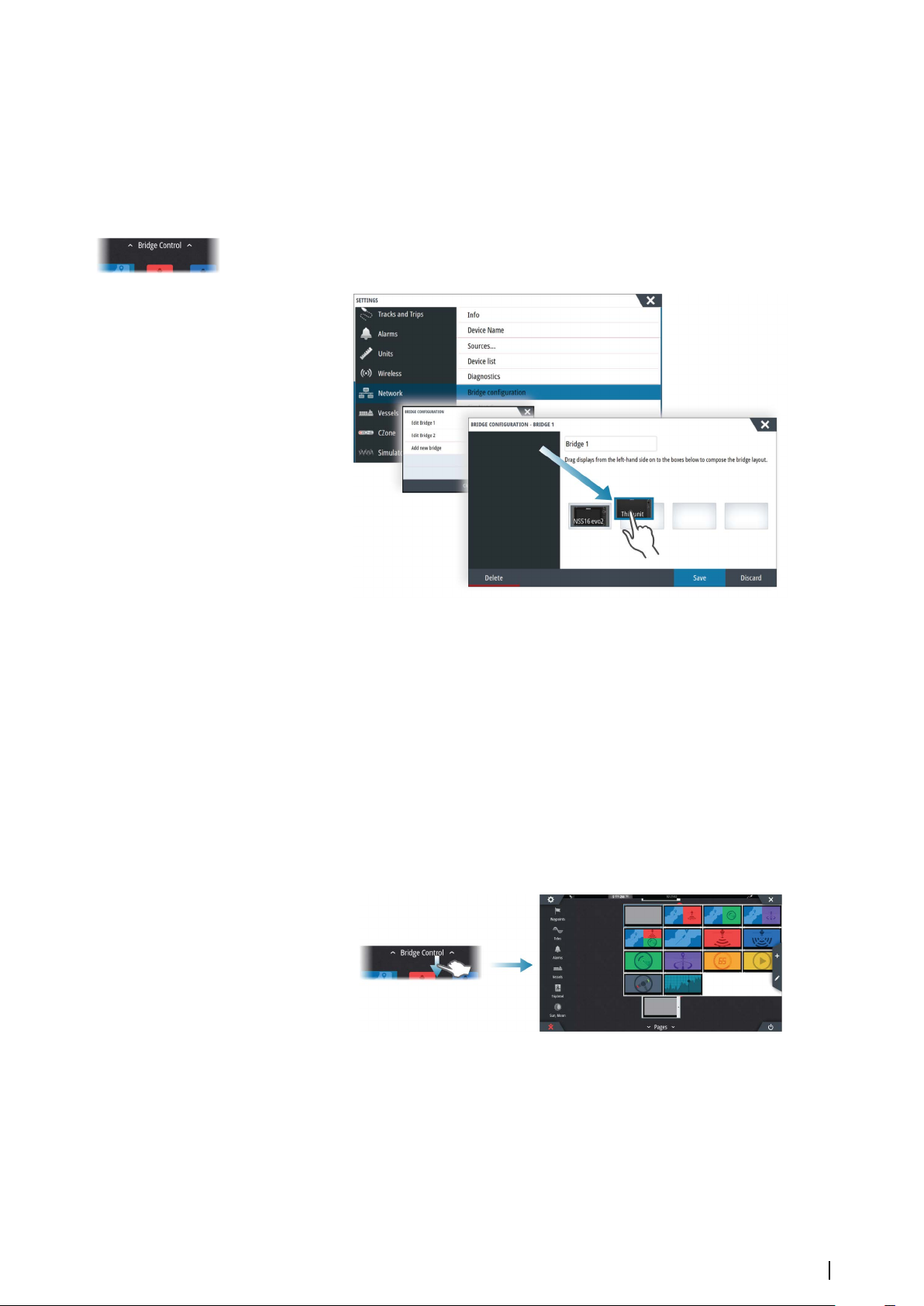
2. Select to configure a new bridge or to edit an existing
The Bridge Configuration for the selected bridge will be shown, and all displays that
are not already assigned to a bridge will be listed
3. Select the display you want to add to the bridge
- Arrange the displays from left to right in the same physical layout as the displays on
your current bridge/dashboard/helm
4. Rename the bridge if required
5. Save the configuration
Bridge Control will be displayed on the Home page of all units that are configured for a
bridge.
Configuring the preset pages for displays in a bridge
1. Activate the Bridge Control panel by swiping down on Bridge Control on the Home
page
2. Enter edit mode by selecting the edit icon
3. Select the display for which you want to define the preset page
-
The page layout option for the selected display will be read from the network, showing
main features and configured favorite pages
4. Select the preferred page
- Select the blank page if you do not want that display to be included in the selected
Bridge preset
5. Repeat step 3 and 4 until a page is configured for all displays in all Bridge presets
6. Select the edit icon again to leave the edit mode and to save your configuration
Customizing your system | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
23
Page 24

Selecting Bridge presets
You display an overview of available Bridge presets by swiping down on Bridge Control
on the Home page.
When you select one of the preset configurations all devices included in that bridge will
switch to the pre-configured pages.
24
Customizing your system | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 25
4
Charts
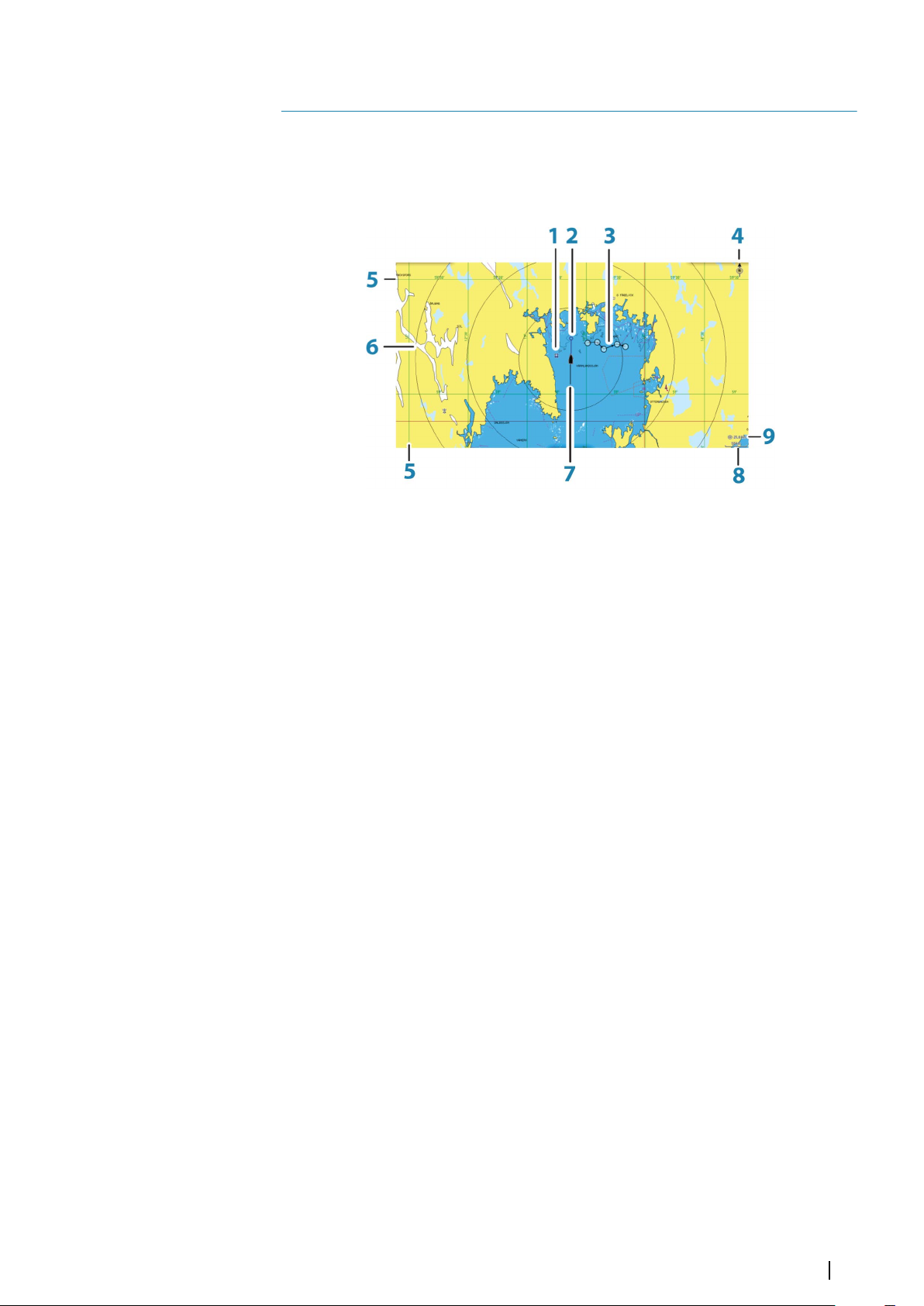
The chart function displays your vessel’s position relative to land and other chart objects. On
the chart panel you can plan and navigate routes, place waypoints, and display AIS targets.
The Chart panel
1 Waypoint*
2 Vessel with extension line (extension line is optional)
3 Route*
4 North indicator
5 Grid lines*
6 Range rings*
7 Track*
8 Chart range scale
9 Range rings interval (only displayed when Range rings are turned on)
* Optional chart items. You turn the optional chart items on/off individually from the Chart
settings dialog.
Chart data
The system is delivered with different embedded cartography depending on region.
All units support Insight charts from Navico including Insight Genesis. The system also
supports charts from Navionics and C-MAP as well as content created by a variety of third
party mapping providers in the AT5 format. For a full selection of available charts, visit
www.gofreeshop.com, www.c-map.com, or www.navionics.com.
Note: In this manual, all possible chart menu options are described. These options vary
Ú
depending on the chart you are using.
Charts on chart cards are shared over the Ethernet network, so only one chart card per vessel
is required.
Note: The system does not automatically switch to embedded cartography if the chart
Ú
card is removed. A low-resolution chart will be displayed until you re-insert the card or
manually switch back to the embedded cartography.
Showing dual chart types
If you have different chart types available - embedded, in the card slot, or on the Ethernet
network - you can show two different chart types simultaneously on a page with two chart
panels.
Charts | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
25
Page 26
You can select a dual chart panel by pressing and holding the Chart application button on
the Home page, or by creating a favorite page with two chart panels.
Selecting chart type
You specify the chart type in the Chart panel by selecting one of the available chart types in
the chart source menu option.
If you have a multiple Chart panel, the chart type is set individually for each chart panel.
Activate one of the chart panels, and then select one of the available chart types in the chart
source menu option. Repeat the process for the second chart panel, and select an alternative
chart type for this panel.
If you have identical charts available - built in, in the card slot or on the Ethernet network the system automatically selects the chart with most chart details for your displayed region.
Panning the chart
You can move the chart in any direction by dragging your finger on the screen.
Select the Clear cursor menu option or press the X key to remove the cursor and cursor
window from the panel. This also centers the chart to the vessel position.
Chart scale
You zoom in and out on the chart by using the zoom panel icons, the rotary knob, or by
using 2 fingers to pinch (zoom out) and spread (zoom in).
Chart range scale and range rings interval (when turned on) are shown in the lower right
corner of the chart panel.
Vessel symbol
When the system has a valid GPS position lock, the vessel symbol indicates vessel position. If
no GPS position is available, the vessel symbol includes a question mark.
Positioning the vessel on the chart panel
Chart orientation
Several options are available for how the chart is rotated in the panel. The chart orientation
symbol in the panel’s upper right corner indicates the north direction.
North up Heading up
North up
Displays the chart with north upward.
Heading up
Displays the chart with the vessel’s heading directed upward. Heading information is
received from a compass. If heading is not available, then the COG from the GPS is used.
Course up
26
Course up
Displays the chart with the direction the vessel is ACTUALLY traveling directed upward,
which in some cases is not the direction the vessel is headed.
Look ahead
Moves the vessel icon closer to the bottom of the screen so that you can maximize your view
ahead.
Charts | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 27

Displaying information about chart items
When you select a chart item, a waypoint, a route, or a target, basic information for the
selected item is displayed. Select the chart item's pop-up to display all available information
for that item. You can also activate the detailed information dialog from the menu.
Note: If you are viewing applicable C-MAP charts on your system, you can select marine
Ú
objects to display information about services and available multimedia (photos)
associated with the location or object.
Note: Pop-up information has to be enabled in chart settings to see basic item
Ú
information.
Using the cursor on the chart panel
By default, the cursor is not shown on the chart panel.
When you activate the cursor, the cursor position window is displayed. When the cursor is
active, the chart does not pan or rotate to follow the vessel.
Press the X key or select the Clear cursor menu option to remove the cursor and the cursor
window from the panel. This also centers the chart to the vessel position.
Select the Restore cursor menu option to display the cursor in its previous location. The
Clear cursor and Restore cursor options are useful features for toggling between the
vessel's current location and the cursor position.
GoTo cursor
You can navigate to a selected position on the image by positioning the cursor on the panel,
then using the Goto Cursor option in the menu.
The cursor assist function
Note: The cursor assist function is available if it is enabled. Refer to "Customizing the long press
Ú
feature" on page 19.
The cursor assist function allows for fine tuning and precision placement of the cursor
without covering details with your finger.
Activate the cursor on the panel, then press and hold your finger on the screen to switch the
cursor symbol to a selection circle, appearing above your finger.
Without removing your finger from the screen, drag the selection circle to the desired
position.
When you remove your finger from the screen the cursor reverts to normal cursor operation.
Measuring distance
The cursor can be used to measure the distance between your vessel and a selected position,
or between 2 points on the chart panel.
1. Position the cursor on the point from where you want to measure the distance. Start the
measure function from the menu
-
The measuring icons appear with a line drawn from the vessel center to the cursor
position, and the distance is listed in the cursor information window.
2. You can reposition the measuring points by dragging either icon as long as the
measuring function is active
Note: The bearing is always measured
Ú
Charts | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
from the grey icon to the blue icon.
27
Page 28
You can also start the measuring function without an active cursor. Both measuring icons are
then initially located at the vessel position. The grey icon follows the vessel as the vessel
moves, while the blue icon remains at the position given when you activated the function.
You terminate the measuring function by selecting the Finish measuring option or by
pressing the X key.
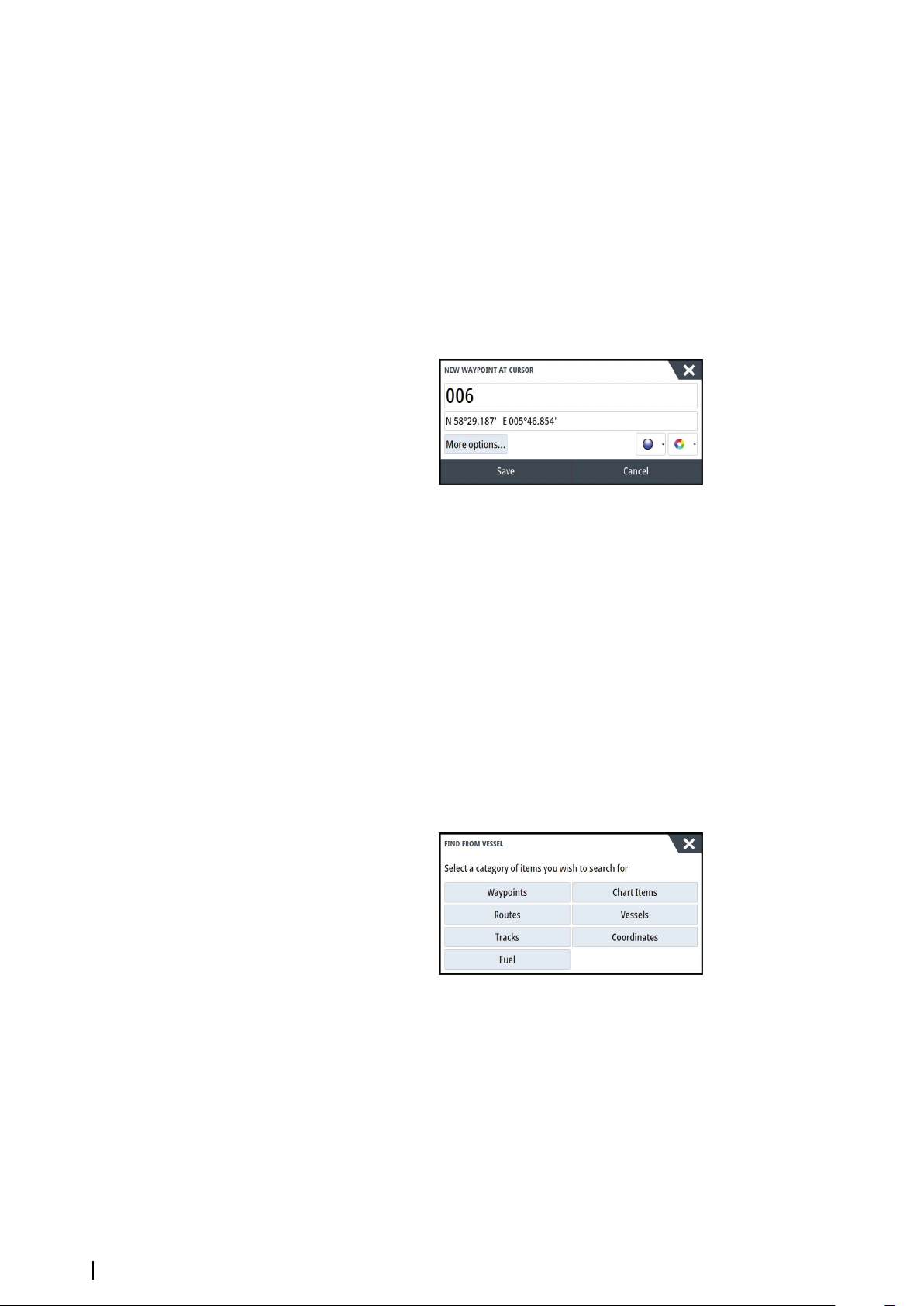
Saving waypoints
A waypoint is saved at the cursor position if active or at the vessel's position if the cursor is
not active on the panel, by doing the following:
• Pressing the rotary knob
• Pressing the Mark key
• Using the new waypoint option in the menu
Creating routes
You can create routes as follows on the chart panel.
1. Position the cursor on the chart panel
2. Select New followed by New route in the menu
3. Tap the chart panel to position the first routepoint
4. Continue positioning the remaining routepoints
5. Save the route by selecting the save option in the menu.
Note: For more information, refer to "Waypoints, Routes, and Tracks" on page 37.
Ú
Find objects on chart panels
You can search for other vessels or various chart items from a chart panel.
Activate the cursor on the panel to search from the cursor position. If the cursor is not active,
the system searches for items from the vessel's position.
28
Note: You must have a SIRIUS data package subscription to search for fueling stations
Ú
and an AIS receiver connected to search for vessels.
3D charts
The 3D option provides a three dimensional graphical view of land and sea contours.
Note: All chart types work in 3D mode, but without 3D cartography for the appropriate
Ú
area the chart appears flat.
When the 3D chart option is selected, the Pan and the Rotate icons appear on the chart
panel.
Charts | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 29
Panning the 3D chart
You can move the chart in any direction by selecting the Pan icon and then panning in the
desired direction.
Press the X key or select the Return to vessel menu option to stop panning, and to center
the chart to vessel position.
Controlling the view angle
You can control the view angle by selecting the Rotate icon and then panning the chart
panel.
• To change the direction you are viewing, pan horizontally
• To change the tilt angle of the view, pan vertically
Note: When centered on the vessel position, only the tilt angle can be adjusted. The
Ú
view direction is controlled by the chart orientation setting. See "Positioning the vessel on the
chart panel" on page 26.
Zooming a 3D chart
You zoom in and out on a 3D chart by using the zoom panel icons or the rotary knob.
Chart overlay
Radar, structure, SonarChart Live (Navionics charts only) and weather data can be displayed
as overlay on your chart panel.
When an overlay is selected, the chart menu expands to include basic menu functions for the
selected overlay.
Radar, structure and weather functions are described in separate sections in this manual. For
more information about SonarChart Live, see section "SonarChart Live" on page 32.
Insight and C-MAP charts
All possible menu options for Insight and C-MAP charts are described below. The features
and menu options available can vary depending on the charts you use. This section shows
menus from an Insight chart.
Note: A menu option is greyed out if it is not available on the chart displayed. For
Ú
example, raster charts are not available with Insight, so the Raster charts menu option is
greyed out when Insight charts are displayed.
Insight and C-MAP tides and currents
The system can display Insight and C-MAP tides and currents. With this information it is
possible to predict the time, level, direction and strength of currents and tides. This is an
important tool when considering planning and navigation of a trip.
In large zoom ranges the tides and currents are displayed as a square icon including the
letter T (Tides) or C (Current). When you select one of the icons, tidal or current information
for that location are displayed.
Dynamic current data can be viewed by zooming inside a 1-nautical mile zoom range. At
that range, the Current icon changes to an animated dynamic icon that shows the speed and
direction of the current. Dynamic icons are colored in black (greater than 6 knots), red
(greater than 2 knots and less than or equal to 6 knots), yellow (greater than 1 knot and less
than or equal to 2 knots) or green (equal to or less than 1 knot), depending on the current in
that location.
If there is no current (0 knots) this will be shown as a white, square icon.
Charts | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
29
Page 30

Static Current and Tide icons Dynamic Current icons
Insight and C-MAP specific chart options
Orientation, Look ahead, 3D, and change Chart source (previously described in this section)
are common for all chart types.
Presentation
The charts can be displayed in different imagery styles.
Shaded relief No contours
Raster imagery
Shaded relief
Shades seabed terrain.
No contours
Removes contour lines from the chart.
Raster charts
Changes the view to that of a traditional paper chart.
Raster transparency
Controls the transparency of raster imagery.
High resolution bathymetry
Enables and disables higher concentration of contour lines.
High resolution bathymetry
30
Charts | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 31

Insight and C-MAP view options
Chart detail
• Full
All available information for the chart in use.
• Medium
Minimum information sufficient for navigation.
• Low
Basic level of information that cannot be removed, and includes information that is
required in all geographic areas. It is not intended to be sufficient for safe navigation.
Insight and C-MAP chart categories
Insight and C-MAP charts include several categories and sub-categories that you can turn
on/off individually depending on which information you want to see.
Photo overlay
Photo overlay enables you to view satellite photo images of an area as an overlay on the
chart. The availability of such photos is limited to certain regions, and cartography versions.
You can view photo overlays in either 2D or 3D modes.
No Photo overlay Photo overlay, land only Full Photo overlay
Photo transparency
The Photo transparency sets the opaqueness of the photo overlay. With minimum
transparency settings the chart details are almost hidden by the photo.
Minimum transparency Transparency at 80
Depth palette
Controls the Depth palette used on the map.
Paper chart
Changes the appearance of the map to a paper chart style.
Safety depth
Insight and C-MAP charts use different shades of blue to distinguish between shallow (lighter
shades) and deep (darker shades) water. After enabling Safety depth, specify the
desired safety depth limit. The Safety depth sets the limit at which depths will be
drawn without blue shading.
Depth filter
Filters out depth values shallower than the selected depth filter limit.
Charts | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
31
Page 32

Shading
Shades different areas of the seabed, depending on the selected Shading category.
Note: Composition and Vegetation shading are not applicable to C-MAP charts.
Ú
Depth 1 and Depth 2
Depth presets that shade different depths in different colors.
Custom
You can adjust the depth threshold, color and opacity (transparency) of color shading for
Depth 1 and Depth 2.
3D exaggeration
Graphical settings that are available in 3D mode only. Exaggeration is a multiplier applied to
the drawn height of hills on land, and troughs in water to make them look taller or deeper.
Note: This option is grayed out if the data is not available in the map card inserted.
Ú
Navionics charts
Some Navionics features require the most current data from Navionics. For those features, a
message is displayed stating that the feature is unavailable if you do not have the
appropriate Navionics charts or chart card inserted. For more information on what is required
for these features, refer to www.navionics.com
Navionics specific chart options
Orientation, Look ahead, 3D and change Chart source (previously described in this section)
are common for all chart types.
Community edits
Toggles on the chart layer including Navionics edits. These are user information or edits
uploaded to Navionics Community by users, and made available in Navionics charts.
For more information, refer to Navionics information included with your chart, or to
Navionics website: www.navionics.com.
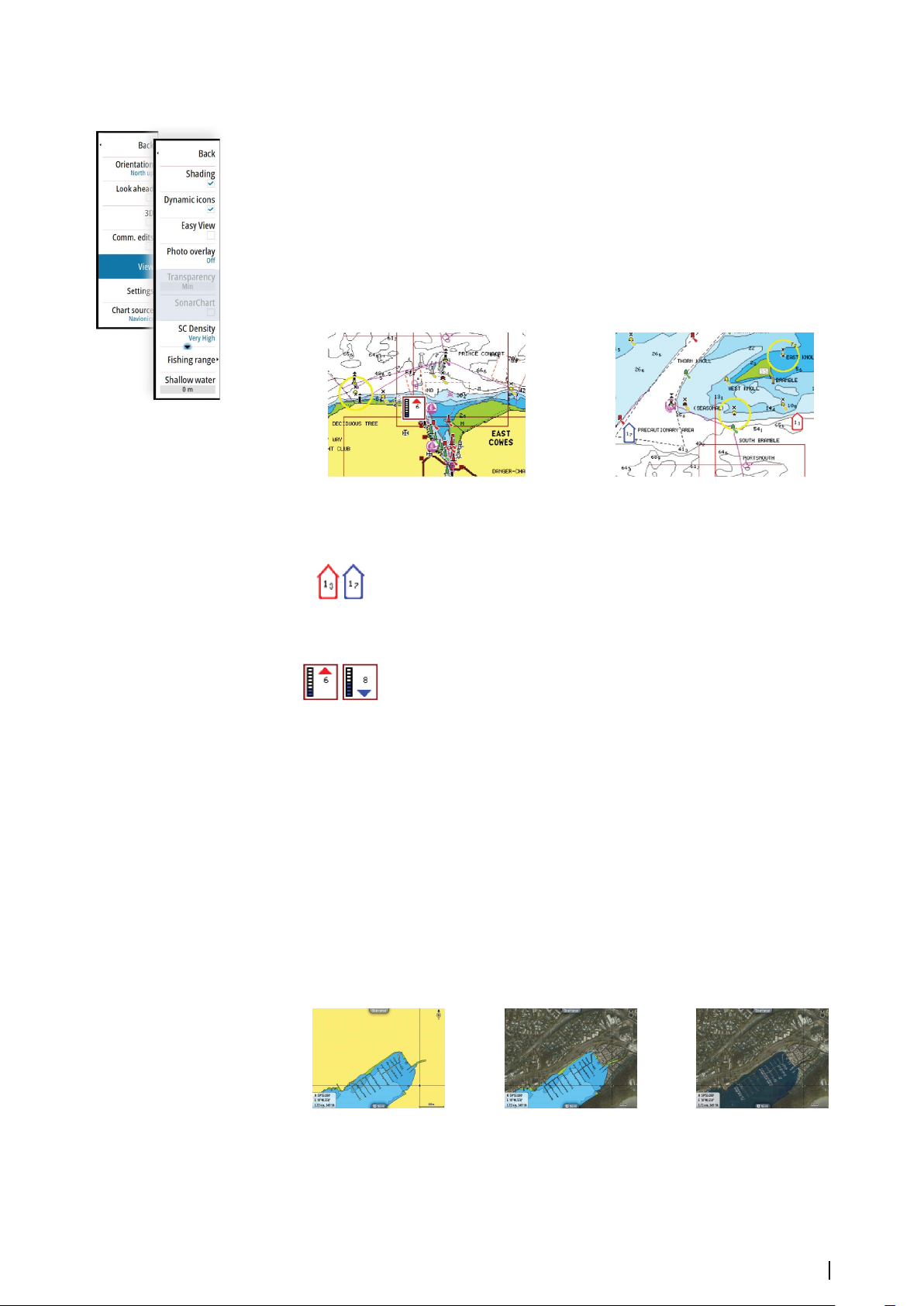
SonarChart Live
SonarChart Live is a real-time feature where the device creates an overlay of depth contours
based on your own live sonar soundings.
In the Navionics chart menu, select Overlay and then SonarChart Live to display it as an
overlay on the chart.
When you select SonarChart Live overlay the menu expands to display SonarChart Live
Options. Use the options to set the transparency and minimum depth.
Transparency
The SonarChart Live overlay is drawn on top of other chart data. The chart data is completely
covered at minimum transparency. Adjust the transparency to allow the chart details to be
seen.
32
Minimum depth
Adjusts what SonarChart Live rendering treats as the safety depth. This affects the coloring of
the SonarChart Live area. As the vessel approaches the safety depth, the SonarChart Live area
will gradually change from a simple grey/white to red.
Charts | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 33
Navionics view options
Chart shading
Shading adds terrain information to the chart.
Navionics dynamic tide and current icons
Shows tides and currents with a gauge and an arrow instead of the diamond icons used for
static tides and current information.
The tide and current data available in Navionics charts are related to a specific date and time.
The system animates the arrows and/or gauges to show the tides and currents evolution
over time.
Dynamic tide information Dynamic current information
The following icons and symbology are used:
Current speed
The arrow length depends on the rate, and the symbol is rotated
according to flow direction. Flow rate is shown inside the arrow symbol.
The red symbol is used when current speed is increasing, and the blue
symbol is used when current speed is decreasing.
Tide height
The gauge has 8 labels and is set according to absolute max/min value
of the evaluated day. The red arrow is used when tide is rising, and the
blue arrow is used when tide is falling.
Note: All numeric values are shown in the relevant system units (unit of measurement)
Ú
set by user.
Easy View
Magnifying feature that increases the size of chart items and text.
Note: There is no indication on the chart showing that this feature is active.
Ú
Photo overlay
Photo overlay enables you to view satellite photo images of an area as an overlay on the
chart. The availability of such photos is limited to certain regions, and cartography versions.
You can view photo overlays in either 2D or 3D modes.
No Photo overlay Photo overlay, land only Full Photo overlay
Photo transparency
The Photo transparency sets the opaqueness of the photo overlay. With minimum
transparency settings the chart details are almost hidden by the photo.
Charts | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
33
Page 34

Minimum transparency Maximum transparency
SonarChart
The system supports the Navionics SonarChart feature.
SonarChart displays a bathymetry map showing high resolution contour detail and standard
navigational data. For more information, refer to www.navionics.com.
SC Density
Controls the density of the SonarChart and SonarChart Live contours.
Fishing range
Select a range of depths between which Navionics fills with a different color.
This allows you to highlight a specific range of depths for fishing purposes. The range is only
as accurate as the underlying chart data, meaning that if the chart only contains 5 meter
intervals for contour lines, the shading is rounded to the nearest available contour line.
No Depth highlight range Depth highlight range: 6 m - 12 m
Shallow water highlight
Highlights areas of shallow water.
This allows you to highlight areas of water between 0 and the selected depth (up to 10
meters/30 feet).
No shallow water highlighted Shallow water highlight: 0 m - 3 m
34
Charts | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 35
Navionics chart settings
Colored seabed areas
Used for displaying different depth areas in different shades of blue.
Presentation type
Provides marine charting information such as symbols, colors of the navigation chart and
wording for either International or U.S. presentation types.
Annotation
Determines what area information, such as names of locations and notes of areas, is available
to display.
Chart details
Provides you with different levels of geographical layer information.
Safety depth
The Navionics charts use different shades of blue to distinguish between shallow and deep
water.
Safety depth, based on a selected limit, is drawn without blue shading.
Note: The built in Navionics database features data down to 20 m, after which it is all
Ú
white.
Contours depth
Determines which contours you see on the chart down to the selected safety depth value.
Rock filter level
Hides rock identification on the chart beneath a given depth.
This helps you to declutter charts in areas where there are many rocks located at depths well
below your vessel's draught.
Chart settings
Settings and display options made in the Chart settings page are common for all chart
panels.
3D boat selection
Determines which icon to use on 3D charts.
Boat settings
The boat settings are used when calculating an automatic route. The boat's draught, width
and height must be input to use Navionics Dock-to-dock autorouting and easy routing
features.
Charts | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
35
Page 36

Note: Dock-to-doc Autorouting is not available in units used in U.S. territorial waters.
Ú
Range Rings
The range rings can be used to present the distance from your vessel to other chart objects.
The range scale is set automatically by the system to suit the chart scale.
Extension lines
Sets the lengths of the extension lines for your vessel and for other vessels shown as AIS
targets.
A: Heading
B: Course Over Ground (COG)
The lengths of the extension lines are either set as a fixed distance, or to indicate the distance
the vessel moves in the selected time period. If no options are turned on for the vessel then
no extension lines are shown for your vessel.
Your vessel heading is based on information from the active heading sensor and the COG is
based on information from the active GPS sensor.
For other vessels, COG data is included in the message received from the AIS system.
ForwardScan
If you have ForwardScan and this option is selected, the ForwardScan heading extension is
shown on the chart. Refer to "Heading extension" on page 91.
SonarChart Live tide correction
When selected, the tide correction feature uses information from nearby tide stations (if
available) to adjust the depth values used by SonarChart Live as the sonar is recorded.
Synchronize 2D/3D chart
Links the position shown on one chart with the position shown on the other chart when a
2D and a 3D chart are shown side by side.
Pop-up information
Selects whether basic information for chart items is displayed when you select the item.
Grid lines
Turns on/off viewing of longitude and latitude grid lines on the chart.
Waypoints, Routes, Tracks
Turns on/off displaying of these items on chart panels. Also opens the Waypoints, Routes and
Tracks dialogs you can use to manage them.
36
Charts | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 37

Waypoints, Routes, and Tracks
5
Waypoints
A waypoint is a user generated mark positioned on a chart, on a radar image or on the
Echosounder image. Each waypoint has an exact position with latitude and longitude
coordinates. A waypoint positioned on the Echosounder image has a depth value, in
addition to position information. A waypoint is used to mark a position you later may want to
return to. Two or more waypoints can also be combined to create a route.
Saving waypoints
A waypoint is saved at the cursor position if active or at the vessel's position if the cursor is
not active on the panel, by doing the following:
• Pressing the rotary knob
• Pressing the Mark key
• Using the new waypoint option in the menu
Moving a waypoint
1. Select the waypoint you want to move. The waypoint icon expands to indicate that it is
active.
2. Activate the menu and select the waypoint in the menu
3. Select the move option
4. Select the new waypoint position
5. Press the Enter key or the rotary knob to confirm the new position.
The waypoint is now automatically saved at the new position.
Edit a waypoint
You can edit all information about a waypoint from the Edit Waypoint dialog.
This dialog is activated by selecting the waypoint's pop-up, by pressing the rotary knob, or
from the menu when the waypoint is activated.
The dialog can also be accessed from the Waypoints tool on the Home page.
Waypoint alarm settings
You can set an alarm radius for each individual waypoint you create. The alarm is set in the
Edit Waypoint dialog.
Note: The waypoint radius alarm must be toggled ON in the alarm dialog to activate an
Ú
alarm when your vessel comes within the defined radius. For more information, refer to
"Alarms dialog" on page 118.
Waypoints, Routes, and Tracks | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
37
Page 38

Routes
A route consists of a series of routepoints entered in the order that you want to navigate
them.
When you select a route on the chart panel it turns green, and the route name is displayed.
The system includes support for Navionics Autorouting and C-MAP Easy Routing. This feature
automatically suggests routepoints between the first and last routepoint of a route, or
between selected routepoints in a complex route. You can use the feature when you create a
new route, or you can use it to edit already saved routes.
Creating a new route on the chart panel
1. Activate the cursor on the chart panel
2. Select the new route option from the menu
3. Position the first waypoint on the chart panel
4. Continue positioning new routepoints on the chart panel until the route is completed
5. Save the route by selecting the save option in the menu.
Edit a route from the chart panel
1. Select the route to make it active
2. Select the route edit option in the menu
3. Position the new routepoint on the chart panel:
-
If you set the new routepoint on a leg, a new point is added between existing
routepoints
- If you set the new routepoint outside the route, the new routepoint is added after the
last point in the route
4. Drag a routepoint to move it to a new position
5. Save the route by selecting the save option in the menu.
Note: The menu changes depending on the selected edit option. All edits are confirmed
Ú
or cancelled from the menu.
Dock-to-dock Autorouting and Easy Routing
The Dock-to-dock Autorouting and Easy Routing suggest new routepoint positions based on
information in the map and on your boat's size. Before you can start using this feature the
boat draught, width and height must be entered into the system. The boat settings dialog is
automatically displayed if the information is missing when you start the feature.
Note: Units designed for sale in the U.S. region do not have Autorouting capabilities.
Ú
Autorouting features are disabled on all non-U.S. units when they are used in U.S.
territorial waters.
Note: It is not possible to start the Dock-to-dock Autorouting or Easy Routing if one of
Ú
the selected routepoints is located in an unsafe area. A warning dialog is displayed, and
you have to move the relevant routepoint(s) to a safe area to proceed.
Note: If no compatible cartography is available, the Dock-to-dock Autorouting or Easy
Ú
Routing menu option is not available. Compatible cartography includes C-MAP MAX-N+,
Navionics+ and Navionics Platinum. For a full selection of available charts, visit
www.gofreemarine.com, www.c-map.com or www.navionics.com.
1. Position at least two routepoints on a new route, or open an existing route for editing.
2. Select Dock-to-dock Autorouting, followed by:
- Entire Route if you want the system to add new routepoints between the first and the
last routepoint of the open route.
- Selection if you want to manually select the routepoints that define the limits for the
autorouting, then select the relevant routepoints. Selected routepoints are colored red.
Only two routepoints can be selected, and the system discards any routepoints
between your selected start and end points.
3. Select Accept to start the automatic routing.
38
Waypoints, Routes, and Tracks | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 39
- When the automatic routing is completed the route appears in preview mode, and the
legs are color coded to indicate safe or unsafe areas. Navionics uses red (unsafe) and
green (safe), while C-MAP uses red (unsafe), yellow (dangerous) and green (safe).
4. Move any routepoints if required when the route is in preview mode.
5. Select Keep to accept the routepoints positions.
6. Eventually repeat step 2 (Selection) and step 3 if you want the system to automatically
position routepoints for other parts of the route.
7. Select Save to complete the automatic routing and save the route.
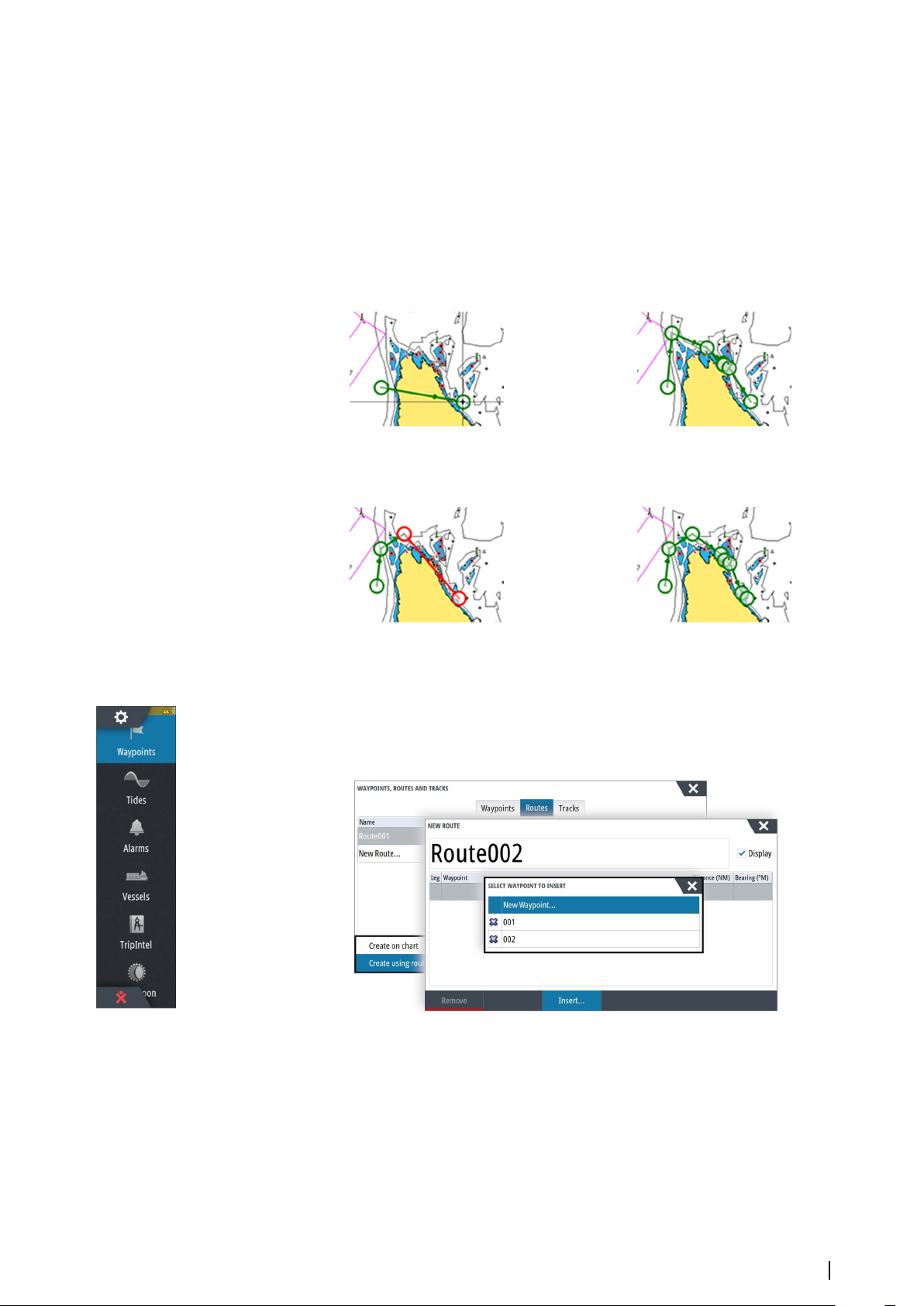
Dock-to-dock Autorouting and Easy Routing examples
• Entire route option used when first and last route points are selected.
First and last routepoint Result after automatic routing
• Selection option used for autorouting part of a route.
Two routepoints selected Result after automatic routing
Creating routes using existing waypoints
You can create a new route by combining existing waypoints from the Routes dialog. The
dialog is activated by using the Waypoints tool on the Home page and then selecting the
Routes tab.
Converting Tracks to Routes
You can convert a track to a route from the Edit Track dialog. The dialog is activated by
activating the track, then selecting the track's pop-up, pressing the rotary knob or selecting
the info options from the menu.
You can convert a track to a route from the Edit Track dialog. The dialog is activated by
activating the track, then selecting the track's pop-up, pressing the rotary knob or selecting
the info options from the menu.
The Edit Tracks dialog can also be accessed by selecting the Tracks tool on the Home page.
Waypoints, Routes, and Tracks | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
39
Page 40
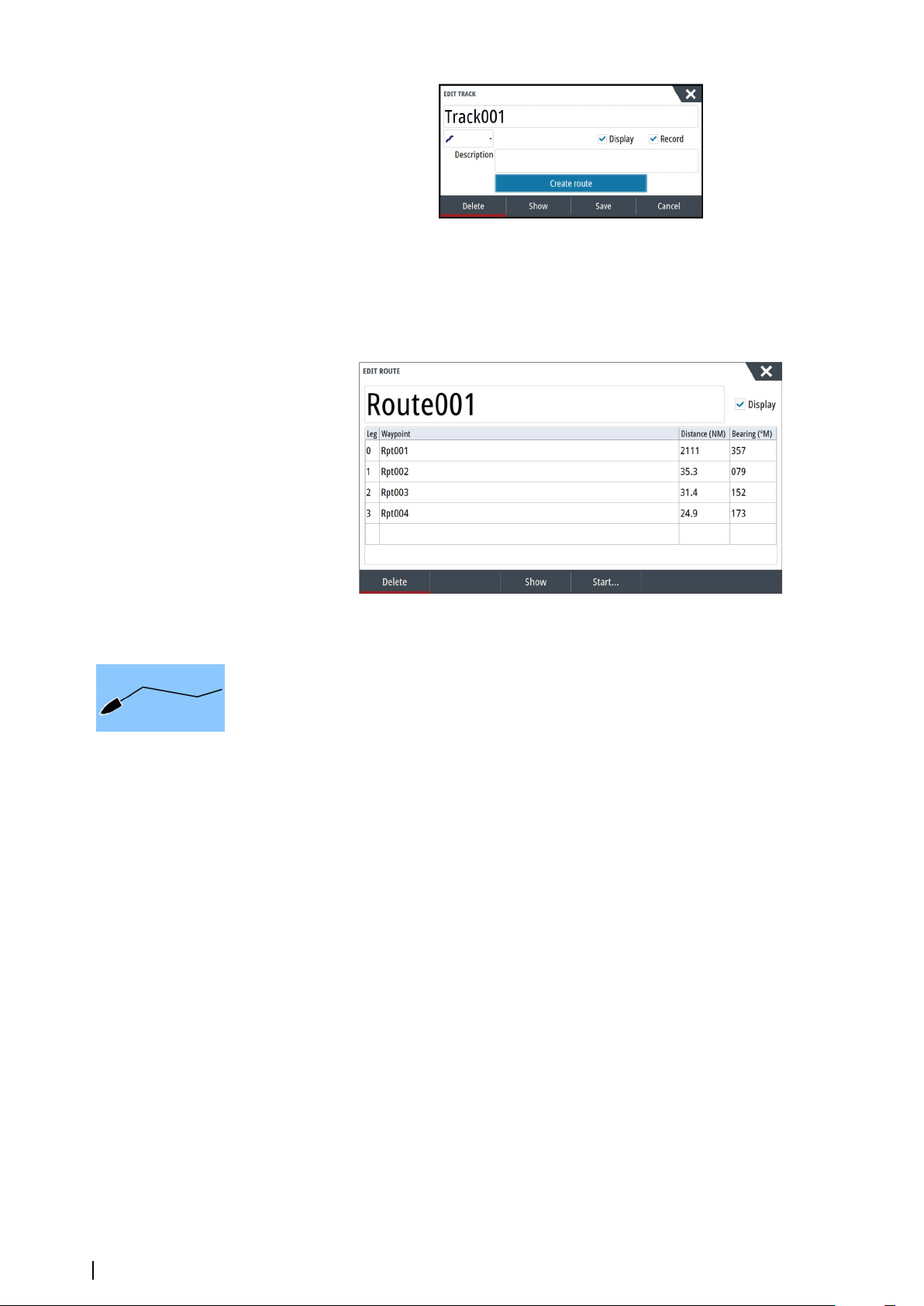
The Edit Route dialog
You can add and remove routepoints from the Edit Route dialog. This dialog is activated by
selecting an active route's pop-up, by pressing the rotary knob, or from the menu.
The dialog can also be accessed by using the Waypoints tool on the Home page.
Tracks
Tracks are a graphical presentation of the historical path of the vessel, allowing you to retrace
where you have travelled. Tracks can be converted to routes from the Edit dialog.
From the factory, the system is set to automatically track and draw the vessel's movement on
the chart panel. The system continues to record the Tracks until the length reaches the
maximum points, and then automatically begins overwriting the oldest points.
The automatic tracking function can be turned off from the Tracks dialog.
Creating new Tracks
You can start a new trail from the Trails dialog, activated by using the Waypoints tool on the
Home page.
Tracks settings
Tracks are made up of a series of points connected by line segments whose length depends
on the frequency of the recording.
Note: The Tracks option must also be turned ON in the chart settings to be visible.
Ú
40
Waypoints, Routes, and Tracks | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 41
Waypoints, Routes, and Tracks dialogs
The Waypoints, Routes, and Tracks dialogs give access to advanced edit functions and
settings for these items.
The dialogs are accessed by selecting the Waypoints button on the Tools panel on the
Home page.
Waypoints, Routes, and Tracks | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
41
Page 42
6
Navigating
The navigation function included in the system allows you to navigate to the cursor position,
to a waypoint, or along a predefined route.
If autopilot functionality is included in your system, the autopilot can be set to automatically
navigate the vessel.
For information about positioning waypoints and creating routes, refer to "Waypoints, Routes, and
Tracks" on page 37.
Navigation panels
The Nav and Position panels can be used to display information when you are navigating.
The Nav panel
The Nav panel is activated from the Home page, either as a full page panel or as part of a
multiple panel page.
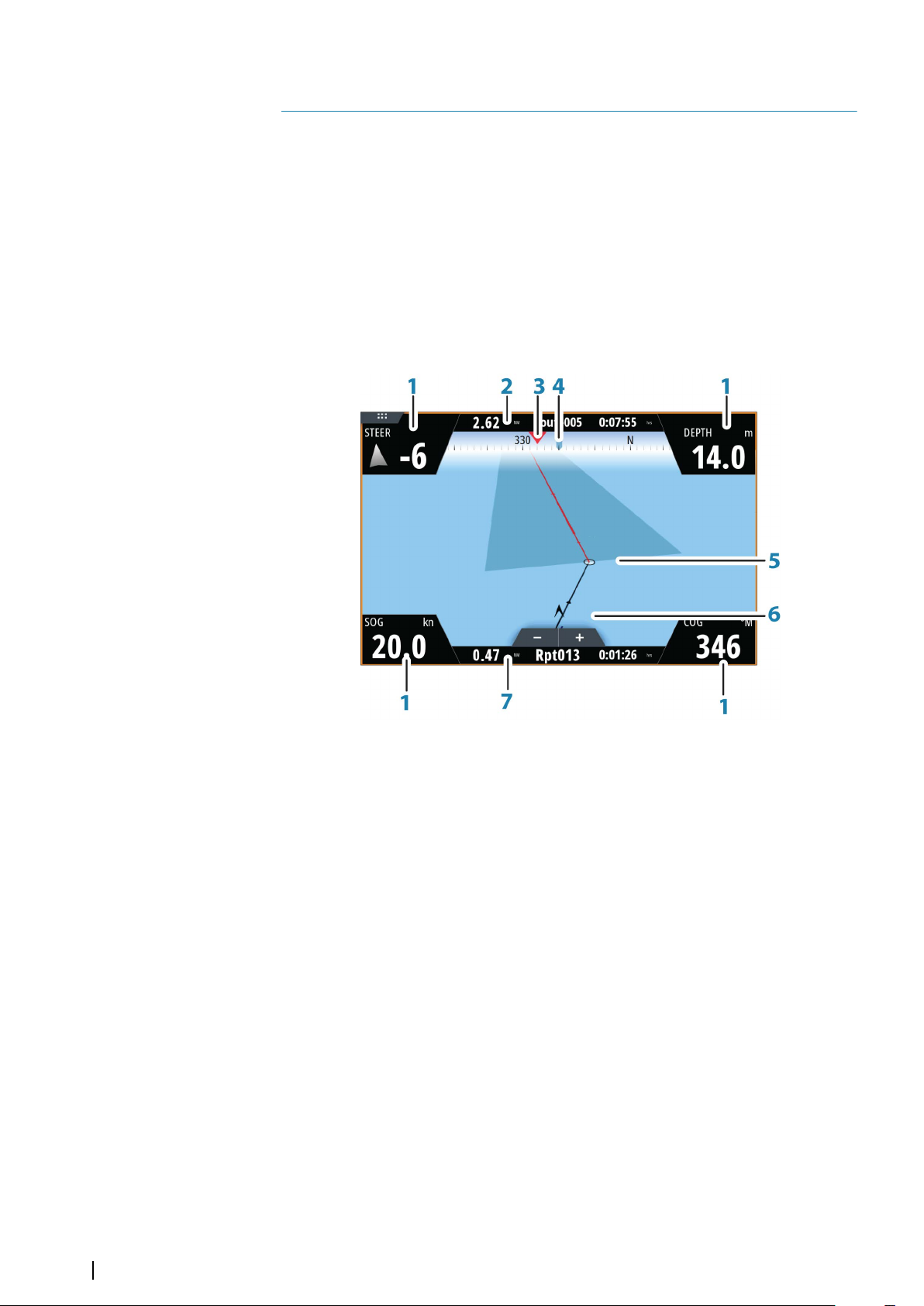
1 Data fields
2 Route information
3 Vessel heading
4 Bearing to next routepoint
5 Bearing line with allowed off course limit
When travelling on a route the bearing line shows the intended course from one
waypoint towards the next. When navigating towards a waypoint (cursor position,
MOB or an entered lat/lon position), the bearing line shows the intended course
from the point at which navigation was started towards the waypoint.
6 Vessel symbol
Indicates distance and bearing relative to the intended course. If the XTE (Cross
Track Error) exceeds the defined XTE limit, this is indicated with a red arrow
including the distance from the track line. Refer to "XTE limit" on page 45.
7 Routepoint information
Position panels
You can switch between displaying the Nav panel or the Position panel. The Position panel is
activated from the menu.
By default, there is one position panel available showing GPS position.
42
Navigating | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 43

If Loran is enabled, there are two position panels. This is indicated with arrow symbols on left
and right side of the panel.
You toggle between the panels by selecting the left or right arrow symbols, or by using the
arrow keys.
GPS position info Loran position info
Edit data fields
To change the data fields displayed on the Navigation panels:
1. Activate the menu
2. Select the edit option from the menu
3. Activate the field you want to edit
4. Select the information type
5. Save your changes.
Navigate to cursor position
You can start navigating to a cursor position on any chart, radar, or Echosounder panel.
Position the cursor at the selected destination on the panel, and then select the Goto
Cursor option in the menu.
Note: The Goto Cursor menu option is not available if you are already navigating.
Ú
Navigate a route
You can start navigating a route from the chart panel or from the Route dialog.
When route navigation is started, the menu expands and shows options for canceling the
navigation, for skipping a waypoint, and for restarting the route from current vessel position.
Starting a route from the chart panel
Activate a route on the panel, and then select the route navigation option from the menu.
You can select a routepoint to start navigating from a selected position.
Start navigating a route from the Route dialog
You can start navigating from the Route dialog, activated by:
• Selecting the Waypoint tool from the Home page and then the Routes tab
• Selecting the route details from the menu
Navigating | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
43
Page 44

Cancel navigation
When you are navigating, the menu includes an option for cancelling the navigation.
Navigating with the autopilot
When you start navigation on a system with autopilot functionality, you are prompted to set
the autopilot to navigation mode.
Note: The prompt to set the autopilot to navigation mode is disabled if the boat type is
Ú
set to SAIL in the Autopilot Commissioning dialog.
If you choose not to engage the autopilot or if your boat is set to SAIL, the autopilot can be
set to navigation mode from the Autopilot Controller later on. For more information about
autopilot functionality, refer to "Autopilot" on page 50.
Navigation settings
44
Navigation method
Different methods are available for calculating the distance and bearing between any two
points on a chart.
The Great circle route is the shortest path between two points. However, if you are to travel
along such a route, it would be difficult to steer manually as the heading would constantly
be changing (except in the case of due north, south, or along the equator).
Rhumb lines are tracks of constant bearing. It is possible to travel between two locations
using Rhumb line computation, but the distance would usually be greater than if Great circle
is used.
Arrival radius
Sets an invisible circle around the destination waypoint.
Navigating | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 45

The vessel is considered arrived at the waypoint when it is within this radius.
XTE limit
This setting defines how far the vessel can deviate from the selected route, if the vessel goes
beyond this limit, an alarm is activated.
Arrival alarm
When the arrival alarm is enabled, an alarm is activated when the vessel reaches the
waypoint or when it is within the specified arrival radius.
Magnetic variation
Magnetic variation is the difference between true bearings and magnetic bearings, caused
by different locations of the Geographic and the Magnetic north poles. Any local anomalies
such as iron deposits might also affect the magnetic bearings.
When set to Auto, the system automatically converts magnetic north to true north. Select
manual mode if you need to enter your own local magnetic variation.
Datum
Most paper charts are made in the WGS84 format, which also is used by the NSS evo3.
If your paper charts are in a different format, you can change the datum settings accordingly
to match your paper charts.
Coordinate system
Several coordinate systems can be used to control the format for latitude and longitude
coordinates displayed on the chart panel.
Phantom Loran
Enables use of Phantom Loran positioning system.
Loran settings
Defines Loran chains (GRI) and preferred station for waypoint entry, cursor position and
position panel.
The graphic example shows a cursor position window with Loran position information.
For more information refer to your Loran system documentation.
Navigating | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
45
Page 46

7
TripIntel
TripIntel lets you store and recall information on trips. You can use the information to make
informed decisions prior to commencing a trip, or when a trip is underway.
Note: Vessel Fuel setup is required for this feature. Refer to the unit's separate installation
Ú
manual.
Note: For best results, it is recommended to run software version 2.4.0 or newer in your
Ú
EP-85R Storage Device or latest software in your Fuel Data manager.
Select the TripIntel button on the Tool panel to display the TripIntel page.
Current trip statistics
The Information tab on the TripIntel page shows current trip statistics:
• Distance traveled
• Time traveled
• Average speed
• Maximum speed
• Fuel economy
• Fuel used
Automatic trip recording
There is an automatic trip detection feature. When you start navigating you are prompted to
start recording the trip if no trip is currently underway and your speed has been more than 2
knots for 20 seconds. You will be prompted to continue a trip or start a new trip if the trip
was not explicitly saved before a power off.
You can manually start the recording later from the TripIntel page.
You can turn off the automatic trip detection feature from the Tracks and Trip settings dialog.
46
TripIntel | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 47

Start and stop trip recordings
If you have selected to not start recording a trip from the automatic trip detection prompt,
you can manually start a recording from the TripIntel page.
The Start and Stop trip options let you specify a trip recording. You can use them to
segment a single passage into multiple trips providing a finer level of control of the
information that is logged for a journey.
Long-term statistics
Select Long Term Statistics to view seasonal trip information such as engine running hours,
total distance traveled, and fuel economy.
Adjust total distance
Select the Adjust total distance button to change the Total distance. Use this option if you
have not recorded a trip or part of a trip that you have taken and want to include the
distance in the Total distance statistic.
Reset fuel economy
Select Reset fuel economy to reset the fuel economy in the Fuel economy gauge on the
Instrument bar.
Estimated fuel range ring
The Estimated fuel range ring on the TripIntel page represents the estimated total distance
that the boat can travel based on historical consumption, and the amount of fuel left in the
tanks.
Note: The Estimated fuel range ring represents fuel consumption on a one way trip only,
Ú
it does not include fuel estimates for the return trip to your current location. It represents
the distance in which your boat will completely run out of fuel.
Note: The Estimated fuel range ring is calculated from the Vessel Fuel Remaining only,
Ú
not level sensors. When recording your refueling, you must 'Set to full' or 'Add fuel' for
the range ring to be accurate.
Fuel gauge
The Fuel Gauge on the TripIntel page, and on the economy gauge is displayed based on the
setting in the Vessel Setup page. You must select the Fuel Remaining measurement type.
• Fuel consumed by engine(s)
• Fuel tank level sensor(s)
Note: This is only for the TripIntel page and the economy graph.
Ú
TripIntel | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
47
Page 48
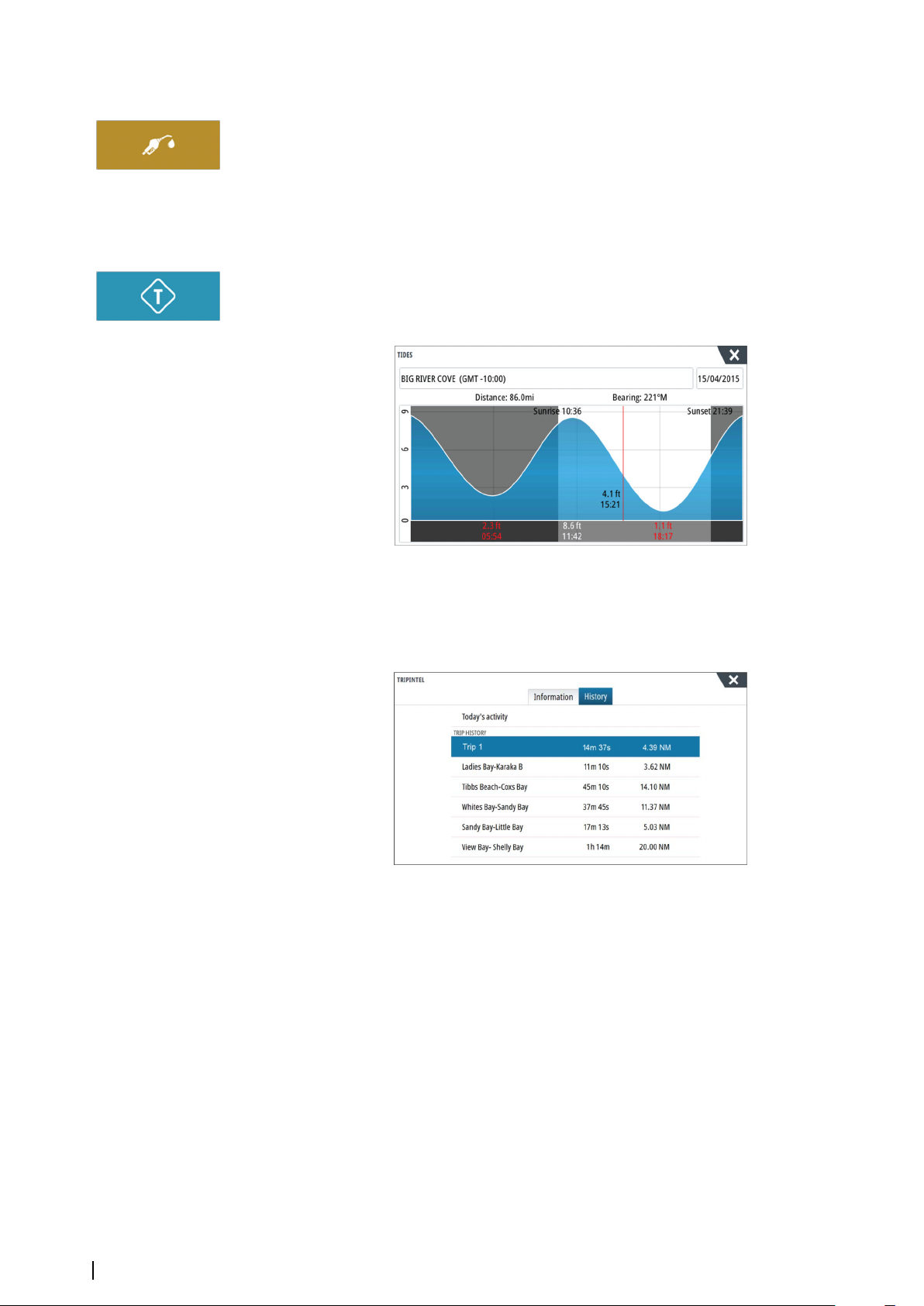
Record your refueling
Select the Fuel button to record the amount of your refuel. The refuel information is used for
calculating the Vessel Fuel Remaining amount.
Tide gauge
The Tide gauge on the TripIntel page shows the tide height at the selected tide station.
Tide graphs and stations
Tide stations on Chart cards provide tide information. Select the Tide button to view tide
graphs and specify which Tide station provides tide information. If no tide station is chosen,
tide information from the nearest tide station is used.
View trip recordings
Recorded trips are listed in the History tab on the TripIntel page. To view detailed trip
information select a trip in the list.
Change trip recording names
Trips are given generic names when they are created. You can change the trip name to a
more meaningful one by selecting it on the History list and then select the name in the Trip
History details dialog. This opens the Trip name dialog where you can change the trip name.
48
TripIntel | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 49

TripIntel | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
49
Page 50

8
Autopilot
If a compatible autopilot computer is connected to the system, autopilot functionality is
available in the system.
The system does not allow for more than one autopilot computer on the network.
The display unit automatically detects the autopilot computer available on the network and
presents settings, configuration and user options for the connected computer.
For details about installing and configuring an autopilot computer, refer to the separate
manuals that come with the autopilot computer.
Safe operation with the autopilot
Warning: An autopilot is a useful navigational aid, but DOES NOT replace
a human navigator.
Activating the autopilot
You activate the autopilot from any panel by selecting the autopilot tile in the Instrument
bar, followed by selecting a mode in the Autopilot Controller.
Switching from automatic mode to manual steering
You switch the autopilot to STBY mode from any automatic operation mode from the
autopilot pop-up or using a physical standby key.
Autopilot indication on the pages
1 Autopilot indication in Status bar
2 Autopilot pop-up
3 Autopilot tile in Instrument bar
Autopilot mode indication in the Status bar
The Status bar shows autopilot information as long as an autopilot computer is connected to
the network.
Icons are included if the autopilot is passive or locked by another autopilot control unit.
50
Autopilot pop up
You control the autopilot from the autopilot pop-up.
The pop-up has a fixed position on the page, and it is available for all pages except when an
Autopilot panel is active.
Autopilot | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 51

As long as the autopilot pop-up is active, you cannot operate the background panel or its
menu.
You remove the pop-up from a page by selecting the X in the upper right corner, or by
pressing the X key. You turn it on again by selecting the autopilot tile in the instrument bar.
The following pop-ups are available:
• Autopilot controller, showing active mode, heading, rudder and various steering
information depending on active autopilot mode. Manual adjustments to the set heading
can only be made when the port and starboard arrow indicators are illuminated red and
green.
• Mode selection, includes access to turn pattern selection.
• Turn pattern selection
Note: The turn steering option is not available if the boat type is set to SAIL in the
Ú
Autopilot Commissioning dialog, instead the tack/gybe feature is implemented. Refer to
"Tacking in AUTO mode" on page 52 and "Tacking in WIND mode" on page 55.
Autopilot controller Mode selection Turn pattern selection
Autopilot tile in Instrument bar
You can select to show the autopilot tile in the Instrument bar.
If the autopilot pop-up is turned off you can turn it on by selecting the tile in the Instrument
bar.
The Autopilot panel
The autopilot panel is used to display navigation data. It can be shown as a full screen panel,
or in a multi-panel page.
The number of data fields included in the autopilot panel is dependent on available panel
size.
Data fields
The following abbreviations are used in the autopilot panel:
CTS Course to steer
DTD Distance to destination
DTW Distance to next waypoint
SOG Speed over ground
COG Course over ground
XTE Cross track error (L: left or R: right)
Autopilot | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
51
Page 52
Autopilot modes
The autopilot has several steering modes. The number of modes and features within the
mode depend on the autopilot computer, the boat type and available inputs, as explained in
the description of the following steering modes.
Standby mode
Standby mode is used when you steer the boat at the helm. Switch the autopilot to Standby
mode from any operation by selecting the Standby mode button in the autopilot pop-up or
using a physical standby key.
Non-Follow Up (NFU, Power steering)
In NFU mode you use the port and starboard arrow buttons in the autopilot pop-up to
control the rudder. The rudder will move as long as the button is pressed.
• Activate NFU mode by selecting the port or starboard arrow button in the pop-up when
the autopilot is in Standby or FU mode.
You return to Standby mode by selecting the Standby mode button in the autopilot popup or using a physical standby key.
Follow-up steering (FU)
In FU mode you use the rotary knob to control the rudder angle. Press the rotary knob, then
turn the knob to set the rudder angle. The rudder moves to the commanded angle and then
stop.
• You select FU mode from the autopilot pop-up
Note: If the autopilot pop-up is closed or if an alarm dialog is activated on the unit
Ú
controlling the autopilot in FU mode, the autopilot automatically changes to Standby
mode.
Warning: While in FU mode you cannot take manual control of the wheel.
AUTO mode (auto compass)
In AUTO mode the autopilot issues rudder commands required to steer the vessel
automatically on a set heading.
• You select AUTO mode from the autopilot pop-up. When the mode is activated, the
autopilot selects the current boat heading as the set heading.
Changing set heading in AUTO mode
You adjust the set heading by using the rotary knob, the Port/Starboard arrow buttons in the
autopilot pop-up, or by selecting the Heading tile in the autopilot pop-up and then entering
the desired heading value.
An immediate heading change takes place. The new heading is maintained until a new
heading is set.
Heading capture
When the vessel is turning in AUTO mode, an instant reset of the mode activates the heading
capture function. This automatically cancels the turn, and the vessel continues on the
heading read from the compass the very moment you re-activated the mode.
52
Tacking in AUTO mode
Note: The tack function is only available when the system is set up for boat type SAIL in
Ú
the Autopilot Commissioning dialog and is not available for NAC-1 autopilot computers.
Autopilot | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 53

Tacking should only be performed into the wind and must be tried out in calm sea
conditions with light wind to find out how it works on your boat. Due to a wide range of
boat characteristics (from cruising to racing boats) the performance of the tack function may
vary from boat to boat.
Tacking in AUTO mode is different from tacking in WIND mode. In AUTO mode the tack angle
is fixed and as defined by the user. For more details, refer to "Tacking in WIND mode" on page 55.
You initiate the tack function from AUTO mode.
When tacking direction is selected the autopilot changes the current set course according to
the set fixed tacking angle.
You can interrupt the tack operation as long as the tack dialog is open by selecting the
opposite tacking direction. When interrupted the boat returns to the previous set heading.
NoDrift mode
NoDrift mode combines the autopilot and the positioning information from the GPS.
In NoDrift mode the vessel is steered along a calculated track line in a direction set by the
user. If the vessel's heading is drifting away from the original heading due to current and/or
wind, the vessel follows the line with a crab angle.
1. Turn the vessel to the desired heading
2. Activate the NoDrift mode. The autopilot draws an invisible bearing line based on current
heading from the boat’s position
Unlike in AUTO (compass) mode, the autopilot now uses the position information to
calculate the cross track error, and automatically keeps your track straight.
You use the port/starboard arrow panel buttons in the autopilot pop-up or the rotary knob
to reset the bearing line while in NoDrift mode.
Dodging
If you need to avoid an obstacle when using NoDrift mode, you can set the autopilot to
Standby mode and power steer or use the helm until the obstacle is passed.
If you return to NoDrift mode within 60 seconds you can select to continue on previous set
bearing line.
If you do not respond, the dialog disappears and the autopilot goes to NoDrift mode with
current heading as set bearing line.
NAV mode
Warning: NAV mode should only be used in open waters.
You can use the autopilot to automatically steer the boat to a specific waypoint location, or
along a pre-defined route. The position information from the GPS is used to change the
course to steer to keep the boat on the track line and to the destination waypoint.
Note: To obtain satisfactory navigation steering, the NSS evo3 must have valid position
Ú
input. Autosteering must be tested and determined satisfactory prior to entering the
NAV mode.
Start automatic navigating
When you start navigating a route or to a waypoint from the chart panel, you are prompted
to set the autopilot to NAV mode. If you reject this request, you can start NAV mode from the
Autopilot controller.
Note: The prompt to set the autopilot to navigation mode is disabled if the boat type is
Ú
set to SAIL in the Autopilot Commissioning dialog. To start navigating, you must select
NAV mode from the Autopilot controller.
When NAV mode is initiated, the autopilot automatically keeps the vessel on the leg.
When the vessel reaches the arrival circle for a routepoint, the autopilot gives an audible
warning and displays a dialog with the new course information. If the required course
change to the next waypoint is less than the Navigation change limit, the autopilot
automatically changes the course. If the required course change to next waypoint in a route
Autopilot | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
53
Page 54
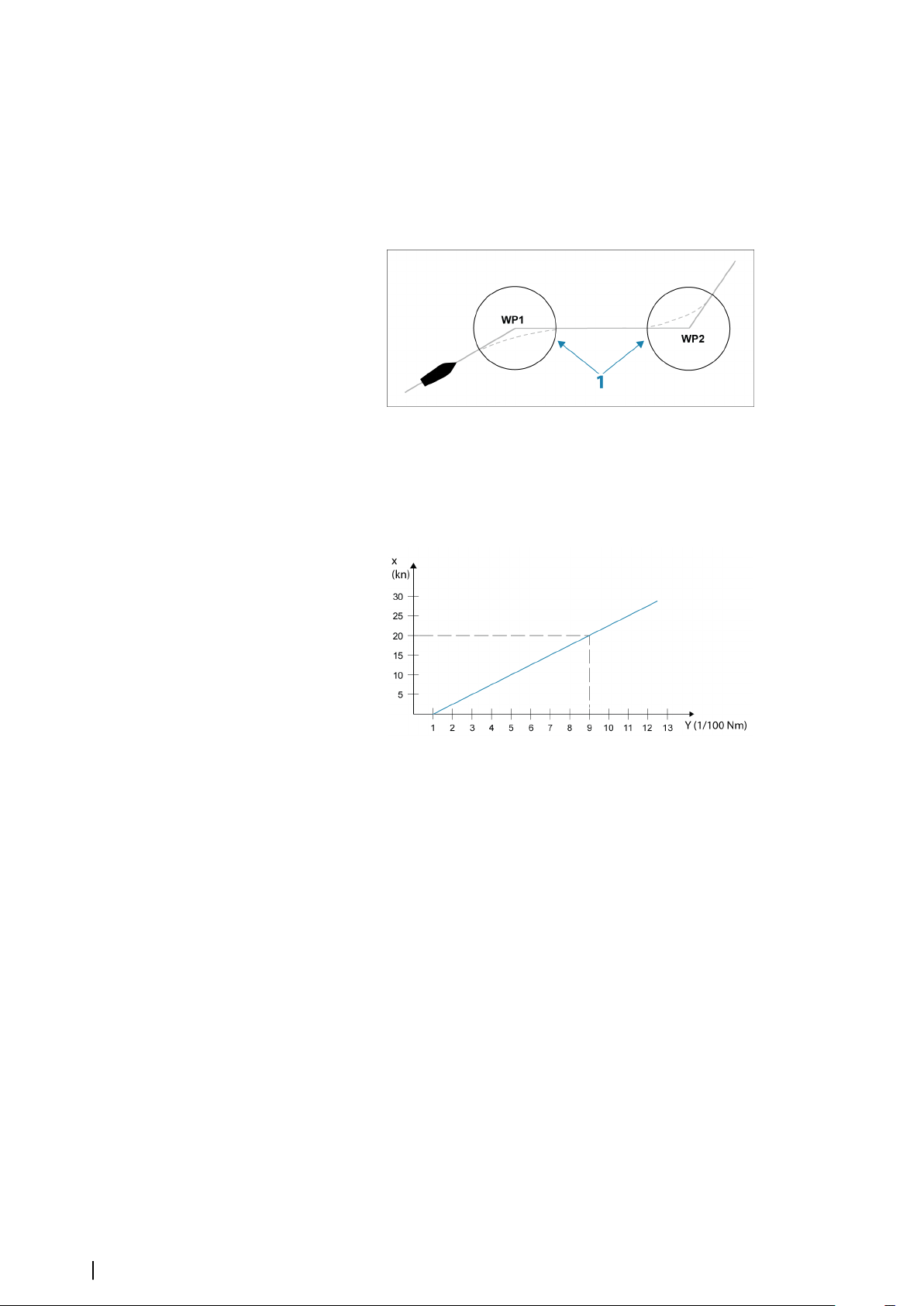
is more than the set limit, you are prompted to verify that the upcoming course change is
acceptable.
Note: For information about navigation settings, refer to "Navigation settings" on page 44.
Ú
Waypoint arrival circle
The Arrival radius defines the point at which a turn is initiated when you are navigating a
route.
The arrival circle (1) should be adjusted according to boat speed. The higher the speed, the
wider the circle. The intention is to make the autopilot start the heading change in due time
to make a smooth turn onto the next leg.
The figure below may be used to select the appropriate waypoint circle when creating the
route.
X axis = Boat speed in knots
Y axis = Arrival circle, radius in 1/100 Nm
Example: With the speed of 20 knots you should use a waypoint circle with radius 0.09 Nm.
Note: The distance between any waypoints in a route must not be smaller than the
Ú
radius of the waypoint arrival circle.
WIND mode
Note: The WIND mode is only available if the system has been set up for sailboat in the
Ú
Autopilot Commissioning dialog. This mode is not available for NAC-1 autopilot
computers.
Before the WIND mode is started it must be verified that valid input from wind transducer is
available.
Initiate wind steering as follows;
1. Switch the Autopilot to AUTO mode
2. Adjust the boat heading until wind angle is according to the angle you want to maintain
3. Select the mode indication in the autopilot controller to activate the autopilot menu, and
select WIND mode
The set course to steer (CTS) and set wind angle are entered from the compass heading and
the wind transducer at the moment the WIND mode is selected. From that point the
autopilot changes the course to maintain the wind angle as the wind direction may change.
54
Autopilot | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 55

Tacking in WIND mode
Note: The tack function is only available when the system is set up for boat type SAIL in
Ú
the Autopilot Commissioning dialog and is not available for NAC-1 autopilot computers
Tacking should only be performed into the wind and must be tried out in calm sea
conditions with light wind to find out how it works on your boat. Due to a wide range of
boat characteristics (from cruising to racing boats) the performance of the tack function may
vary from boat to boat.
Tacking in WIND mode as compared to AUTO mode is performed when sailing with
apparent or true wind as the reference. The true wind angle should be less than 90 degrees.
The rate of turn during the tack will be given by the Tack time defined in the sailing
parameter setup. The tack time is also controlled by the speed of the boat to prevent loss of
speed during a tack.
You can initiate the tack function from WIND mode.
When you initiate the tacking, the autopilot immediately mirrors the set wind angle to the
opposite side of the bow.
You can interrupt the tack operation as long as the tack dialog is open by selecting the
opposite tacking direction. When interrupted, the boat returns to the previous set heading.
Gybing
Gybing is possible when the true wind angle is larger than 120°.
The time to make a gybe is determined by the speed of the boat to make it as quick as
possible within control.
Turn pattern steering
The autopilot includes a number of automatic turn steering features when the autopilot is in
AUTO mode.
Note: The turn steering option is not available if the boat type is set to SAIL in the
Ú
Autopilot Commissioning dialog, instead the tack/gybe feature is implemented.
Initiating a turn
You start the turn by selecting the relevant turn icon, followed by selecting the port or
starboard options in the turn dialog to select the turn direction.
Stopping the turn
You can stop the turn from within the turn dialog.
At any time during a turn you can select Autopilot standby in the System Controls dialog
to return to Standby mode and manual steering.
You can also stop a turn by pressing a physical standby key to return to Standby mode and
manual steering.
Turn variables
The turn steering options, except the C-turn, have settings that you can adjust before you
start a turn and at any time when the boat is in a turn.
U-turn
U-Turn changes the current set heading to be 180° in the opposite direction.
The turn rate is identical to Rate limit settings. This cannot be changed during the turn.
Note: Refer to the separate NSS evo3 Installation manual for information about Rate limit
Ú
settings.
C-turn
Steers the vessel in a circle.
You can adjust the Rate of turn from the turn dialog before the turn is initiated and during
the turn. Increasing the turn rate makes the vessel turn a smaller circle.
Autopilot | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
55
Page 56
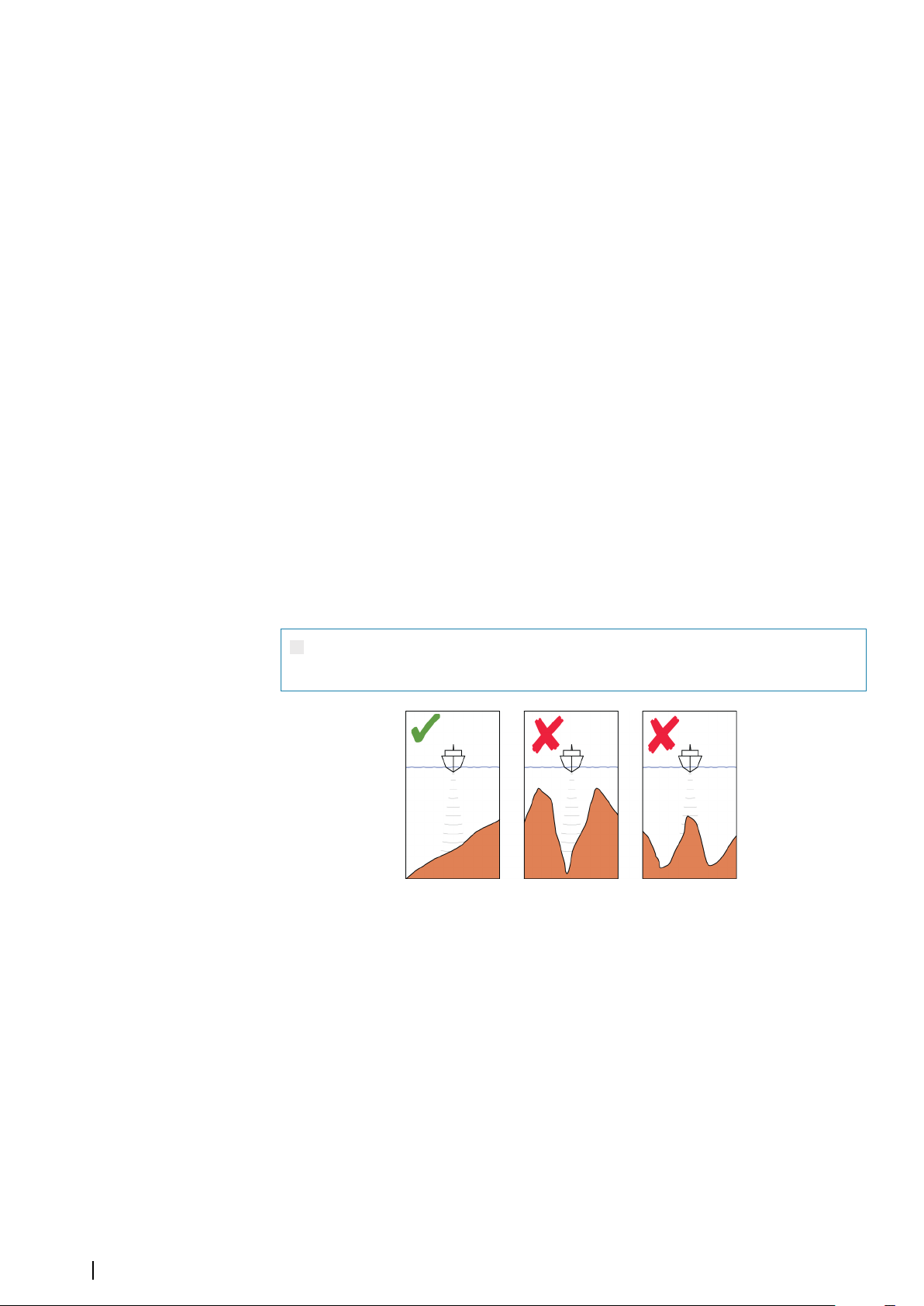
Spiral turn
Spiral-turn makes the vessel turn in a spiral with a decreasing or increasing radius. You set the
initial radius before the turn is initiated, and the change per turn during the turn. If the
change per turn is set to zero, the vessel turns in a circle. Negative values indicate decreasing
radius while positive values indicate increasing radius.
Zigzag turns
Steers the vessel in a zigzag pattern.
For navigating in a zigzag pattern, you set the initial heading change before the turn is
started.
During the turn you can alter the main heading, the heading change, and the leg distance.
Square turn
Makes the vessel automatically turn 90° after having travelled a defined leg distance.
At any time during the turn you can change the main heading and the distance of the leg
until the vessel makes a new 90° turn.
Lazy S-turn
Makes the vessel yaw around the main heading.
You set the selected heading change before the turn is started.
During the turn you can alter the main heading, the heading change and the turn radius
from within the turn dialog.
Depth contour tracking, DCT
If the system has Echosounder input, the autopilot can be set to follow a depth contour.
TM
Warning: Do not use this feature unless the seabed is suitable. Do not use
it in rocky waters where the depth is varying significantly over a small area.
Use the following process to initiate DCT steering:
1. Ensure that you have depth reading on the panel or on a separate depth instrument.
2. Steer the boat to the depth you want to track, and in the direction of the depth contour.
3. Activate AUTO mode, select depth contour steering and monitor the depth reading.
4. Select the port or starboard option in the turn dialog to initiate the depth contour
steering to follow the bottom sloping to starboard or to port:
56
Autopilot | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 57

Port option
(depth decreases to port)
The following parameters are available for depth contour tracking:
Depth gain
This parameter determines the ratio between commanded rudder and the deviation from
the selected depth contour. The higher depth gain value the more rudder is applied.
If the value is too small, it takes a long time to compensate for drifting off the set depth
contour, and the autopilot fails to keep the boat on the selected depth.
If the value is set too high, the overshoot increases and the steering is unstable.
Contour Cross Angle (CCA)
The CCA is an angle that is added to or subtracted from the set course.
With this parameter you can make the boat yaw around the reference depth with lazy-s
movements.
The larger the CCA, the bigger yawing is allowed. If you the CCA set to zero there are no lazy-
s movements.
Starboard option
(depth decreases to starboard)
Using the NSS evo3 in an AP24/AP28 system
Command transfer
If your NSS evo3 is connected to an autopilot system including an AP24 or AP28 control unit,
only one control unit can be active at the same time. An inactive control unit is indicated
with a square with a cross symbol in autopilot controller pop-up.
Locking remote stations
The AP24/AP28 includes a Remote Lock function that disables autopilot control from other
units. A locked control unit is indicated with a key symbol in autopilot controller pop-up.
When the remote lock function is enabled on an AP24/AP28 control unit, only the active
control unit stays in command. No transfer of command to NSS evo3 or other autopilot
control units on the system can take place.
You can only unlock the remote stations from the AP24/AP28 unit in command.
Using the autopilot in an EVC system
When the NSS evo3 is connected to an EVC system via the SG05, you can take manual
control of the steering regardless of the autopilot mode.
The mode indicator on the pilot pop-up is replaced by a dash to indicate EVC override.
The system returns to NSS evo3 control in standby mode if no rudder command is given
from the EVC system within a predefined period.
Using the NSS evo3 in an AP70/AP80 system
If your MFD is connected to an AP70/AP80 autopilot system, the MFD can be used to operate
the autopilot.
In an AP70/AP80 autopilot system, only one control unit can be active at the same time.
Note: The MFD cannot be used to configure or commission an AP70/AP80 system.
Ú
The thruster symbol on the MFD Mode button indicates thrusters are defined in
the AP70/AP80 autopilot system.
Autopilot | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
57
Page 58
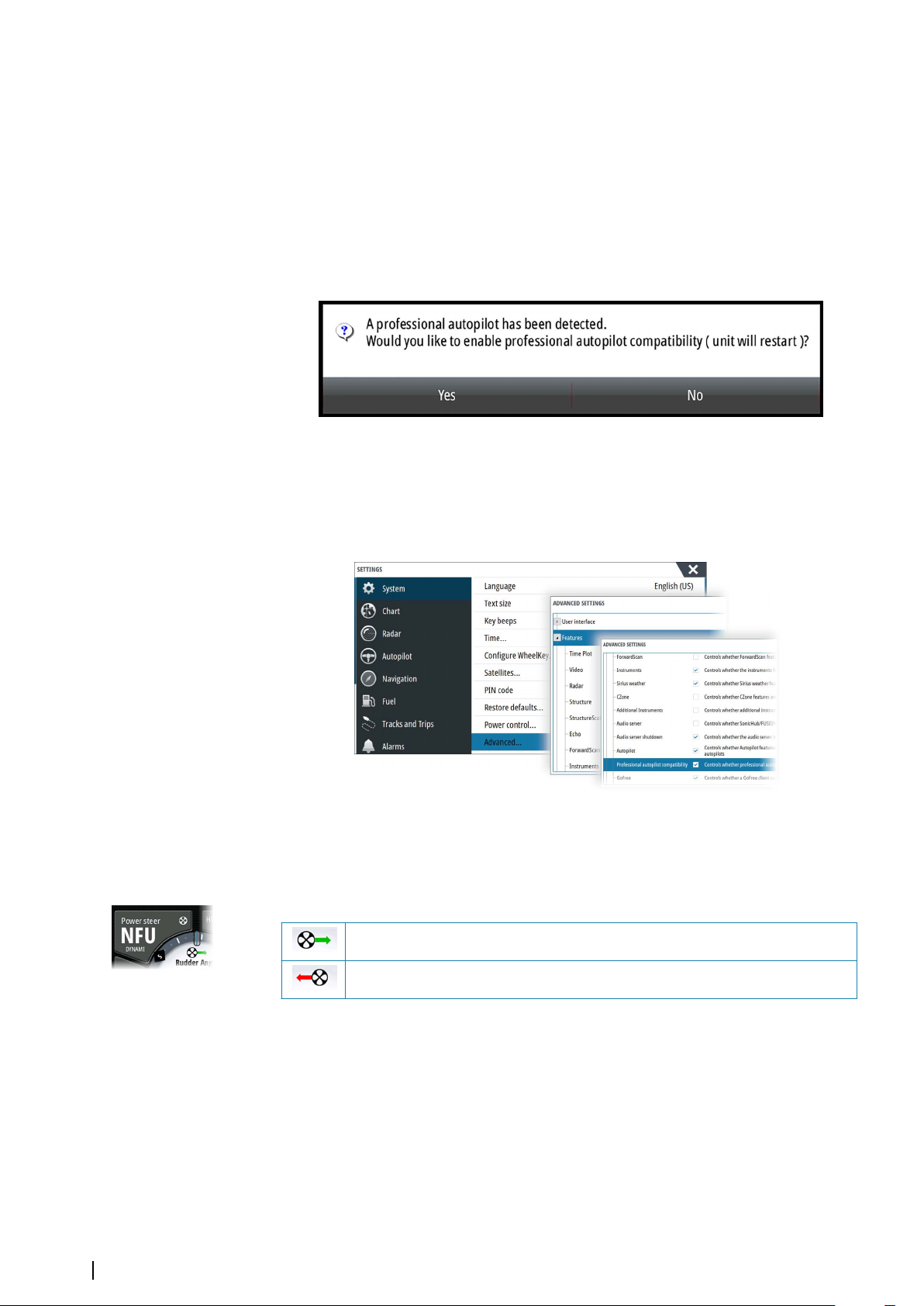
For more information about AP70/AP80 autopilot system, refer to the separate AP70/AP80
documentation.
Autopilot detection
The AP70/AP80 system has its own source groups. For compatibility reasons if the MFD is
going to be used to run the AP70/AP80 system, the MFD must use the same source groups
as the AP70/AP80 system.
When a MFD is connected to an AP70/AP80 system, it detects the AP70/AP80 system and a
prompt is displayed asking if the MFD should restart and use the AP70/AP80 system source
groups (restart in professional autopilot compatibility mode).
If yes is selected, then the MFD restarts using the same source groups as the AP70/AP80
system. If No is selected then the question is not asked again and the MFD cannot be used to
operate the AP70/AP80 system.
This setting can be changed by selecting Professional autopilot compatibility in the
Advanced settings dialog.
58
Running thruster symbols
When thrusters are running in an AP70/AP80 system, thruster symbols are displayed in the
MFD Autopilot controller pop-up.
Clockwise thrust rotation.
Counter-clockwise thrust rotation.
Command transfer
An AP70/AP80 system can be set up as a Master system or an Open system.
In a Master setup, the master controller gives control to other control units. An MFD cannot
be the master controller in a Master setup. In a Master setup, the MFD can request to control
the autopilot and the MFD must accept control from the master controller after the master
controller approves transfer of control to the MFD. Once control is accepted, the MFD is
active and can be used to operate the autopilot.
In an Open system setup, the MFD can take control of the autopilot by selecting the Mode
button on the Autopilot controller pop-up and then selecting Take cmd in the CMD transfer
Autopilot | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 59
dialog. When this occurs the MFD becomes active and the other control units become
passive.
In an Open system, control stations can be temporarily locked to avoid accidental control
from another control unit. When the MFD has control in an Open system, the MFD can lock
and unlock all passive control units. If the MFD is passive and locked, it can request control of
the autopilot from the active control unit. The MFD must accept control from the active
controller after the active controller approves transfer of control to the MFD.
The following indicators are displayed in the Mode button of the Autopilot controller popup:
Passive - MFD does not have control of the autopilot. If only the passive
icon is displayed, it means it is an Open unlocked system and selecting
the Mode button takes control of the autopilot.
Locked system - The key icon indicates it can be a Master system or a
locked Open system.
If the key icon is displayed, and the <10, <1, 10>, 1> buttons are enabled
(red or green colored arrows and white numbers) then the MFD is active
and controls the autopilot.
If the key icon is displayed, and the <10, <1, 10>, 1> buttons are disabled
(black arrows and numbers) then the MFD is passive and does not
control the autopilot. Select the Mode button to request control from
the active control unit if it is a locked Open system, or the master
controller if it is a Master system.
none
Active in Open system - the MFD has control of the autopilot in an Open
system.
Locking and un-locking other control units
Select the Cmd/Thruster option in the Mode selection pop-up to open the Cmd/Thruster
selection pop-up.
Unlock other stations - allows other control units to take control of the autopilot without
requesting permission.
Lock other stations - locks other control units from taking control of the autopilot. When
other control units are locked, they must request control of the autopilot from the MFD.
When control of the autopilot is requested from another control unit, a prompt is displayed
in the MFD to authorize command transfer.
Autopilot | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
59
Page 60

Selecting the work profile
The AP70/AP80 can be set up with 6 different work profiles associated with different work
modes or preferences. Use the AP70/AP80 controller to set up the different work profiles. In
the MFD, the active work profile is displayed in the Mode button of the MFD Autopilot
controller pop-up and the Mode selection pop-up. If the MFD has control of the autopilot,
you can use it to select which work profile is active.
To change the work profile using the MFD, the autopilot must be in standby mode.
1. Select the Mode button in the Autopilot controller pop-up to display the Mode selection
pop-up
2. Select the Work profiles button to display defined work profiles in the Work profiles
selection pop-up
3. Select the work profile you want to activate
4. Select Close to close the Work profiles selection pop-up.
Enabling and disabling thrusters
Select the Cmd/Thrusters button in the Modes selection pop-up to open the Cmd/Thrusters
selection pop-up.
The Cmd/Thrusters selection pop-up provides options to enable or disable thrusters.
Autopilot settings
The autopilot settings can be split between settings done by the user, and settings done
during installation and commissioning of the autopilot system.
• User settings can be changed for various operational conditions or user preferences
• Installation settings are defined during commissioning of the autopilot system. No
changes should later be done to these settings
Both user settings and installation settings depends on which autopilot computer that is
connected to the system.
60
Autopilot | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 61

The following sections describe the settings that can be changed by the user. The settings
are described per autopilot computer.
Installation settings are available in the documentation following the autopilot computers.
Chart compass
You can select to show a compass symbol around your boat on the chart panel. The
compass symbol is off when the cursor is active on the panel.
Locking autopilot operation from a unit
You can lock a unit to prevent unauthorized operation of the autopilot. When the unit is
locked, it is indicated with a lock symbol and with text in the pop up. No automatic modes
can be selected from a locked display.
Note: The lock function is not available on a unit which has autopilot control!
Ú
If the NSS evo3 is part of an AP24/AP28 system, all other autopilot control units can be locked
for autopilot control from the AP24/ AP28 control unit.
NAC-2/NAC-3 Autopilot computer
Steering (NAC-2/NAC-3)
These options allow for manually changing parameters that were set during the
commissioning of the autopilot computer. For more details, refer to the separate
documentation for the autopilot computer.
• Turn rate: Preferred turn rate used while turning in degrees per minute
• Rudder gain: This parameter determines the ratio between commanded rudder and the
heading error. The higher rudder value the more rudder is applied. If the value is too small
it will take a long time to compensate for a heading error, and the autopilot will fail to
keep a steady course. If the value is set too high the overshoot will increase and the
steering will be unstable.
• Counter rudder: Relation between change in heading error and applied rudder. Higher
counter rudder will reduce applied rudder faster when approaching the set heading
• Autotrim: Controls how aggressively the autopilot will apply rudder to compensate for a
constant heading offset, e.g. when external forces such as wind or current affects the
heading. Lower autotrim will give faster elimination of a constant heading offset
Note: In VRF mode this parameter controls the time constant of the rudder estimate. A
Ú
lower value makes the rudder estimate faster, i.e. that it will more quickly catch up with
the boat's movements.
• Init rudder: Defines how the system moves the rudder when switching from manual
steering to an automatic mode.
- Center: Moves the rudder to zero position
- Actual: Maintains the rudder offset
• Rudder limit: Determines the maximum rudder movement in degrees from midship
position that the autopilot can command the rudder in the automatic modes. The Rudder
Autopilot | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
61
Page 62

limit setting is only active during autosteering on straight courses, NOT during course
changes. Rudder limit does not affect Non-Follow-up steering
• Off heading limit: Sets the limit for the off heading alarm. An alarm occurs when the actual
heading deviates from the set heading more than the selected limit
• Track response: Defines how fast the autopilot shall respond after having registered a
cross track distance
• Track approach angle: Defines the angle used when the vessel is approaching a leg. This
setting is used both when you start navigating and when you use track offset
• Course change confirm angle: Defines the limits for course change to next waypoint in a
route. If the course change is more than this set limit, you are prompted to verify that the
upcoming course change is acceptable.
Sailing (NAC-2/NAC-3)
Note: Sailing parameters are only available when the boat type is set to Sail.
Ú
• Wind mode: Select what wind function the autopilot will use when in wind mode
-
Auto:
If TWA is <70º: Wind mode will use AWA
If TWA is ≥70º: Wind mode will use TWA
- Apparent
- True
• Tack time: Controls the rate of turn (tack time) when performing a tack in wind mode.
• Tack angle: Controls the angle that the boat will tack to between 50º - 150º in AUTO mode
• Manual speed: If neither boat speed or SOG data is available and or deemed reliable a
manual value for speed source can be entered and used by the autopilot to aid steering
calculations
Steering response
Note: Only available for NAC-1 autopilot computers.
Ú
Used to increase or decrease the steering sensitivity. A low response level reduces the rudder
activity and provides a more loose steering. A high response level increases the rudder activity
and provides more tight steering. Too high a response level will cause the boat to make S
movements.
Installation
Used for autopilot installation and commissioning. See the separate NSS evo3 Installation
manual.
Commissioning
Note: Only available for NAC-1 autopilot computers.
Ú
Used for commissioning the rudder or virtual rudder feedback. See the separate NSS evo3
Installation manual.
62
Autopilot | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 63

9
Radar
The radar panel can be set up as a full screen view or combined with other panels.
The radar image can also be displayed as an overlay on a chart panel. For more information,
see "Chart overlay" on page 29.
Note: Radar overlay requires data from a heading sensor or compass to ensure proper
Ú
orientation with the chart.
The radar panel
1 Range
2 Orientation
3 Motion
4 Compass*
5 Heading line*
6 Rotary controls
7 Range rings*
8 Range markers*
9 Data bar
* Optional radar symbology.
Radar symbology can be turned ON/OFF collectively from the Radar menu, or individually as
described in "Radar settings panel" on page 73.
Dual radar
You can connect to any combination of two supported radars and see both radar images at
the same time.
Note: Interference will be seen on the Broadband Radar on most ranges when a pulse or
Ú
Halo radar, and a Broadband radar are transmitting at the same time on the same boat.
We recommend to only transmit on one radar at a time. For example, transmit
Broadband radar for typical navigational usage, or pulse or Halo radar to locate weather
cells, defined coastlines at a distance and to trigger Racons.
You can select a dual radar panel by pressing and holding the Radar application button on
the Home page, or by creating a favorite page with two radar panels.
Radar | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
63
Page 64
Selecting the radar source
You specify the radar in the Radar panel by selecting one of the available radars in the radar
source menu option. If you have a multiple Radar panel, the radar is set individually for each
radar panel. Activate one of the radar panels, and then select one of the available radars in
the radar source menu option. Repeat the process for the second radar panel, and select an
alternative radar for this panel.
Note: The 3-digit radar source number is the last 3 digits of the radar's serial number.
Ú
Radar overlay
You can overlay the Radar image on the Chart. This can help you to easily interpret the radar
image by correlating the radar targets with charted objects.
Note: A heading sensor must be present in the system for radar overlay.
Ú
When the radar overlay is selected, basic radar operational functions are available from the
Chart panel’s menu.
Selecting radar overlay source on chart panels
To select the radar source of the radar overlay displayed on the chart panel, use the Radar
options and then Source chart panel menu options to select the radar source.
For chart pages with more than one chart with radar overlay, it is possible to set up different
radars sources for each chart panel. Activate one of the chart panels and then select one of
the available radars in the radar source menu option. Repeat the process for the second chart
panel with radar overlay, and select an alternative radar for this panel.
Radar operational modes
The radar’s operational modes are controlled from the Radar menu. The following modes are
available:
Power off
The power to the radar scanner is turned off. Power off is only available when radar is in
standby mode.
Standby
The power to the radar scanner is on, but the radar is not transmitting.
Note: You can also put the radar in standby mode from the System Controls dialog.
Ú
Halo light
Controls the levels of the Halo Radar pedestal blue accent lighting. There are four levels
possible for the lighting. The accent lighting can only be adjusted when the radar is in
standby mode.
Note: The blue accent pedestal lighting might not be approved for use in your boating
Ú
location. Check your local boating regulations before turning the blue accent lights ON.
Transmit
The scanner is on and transmitting. Detected targets are drawn on the radar PPI (Plan
Position Indicator).
64
Note: You can also put the radar in transmit mode from the System Controls dialog.
Ú
Radar Range
You adjust radar range by turning the rotary knob or by selecting the zoom icons on the
radar panel.
Radar | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 65

Dual range
(Broadband 4G and Halo Radar only)
When connected to a Broadband 4G or Halo radar, it is possible to run the radar in Dual
Range mode.
The radar appears in the radar sources menu as two virtual radar sources A and B. Range and
radar controls for each virtual radar source are fully independent and the source can be
selected for a particular chart or radar panel in the same manner as dual radar described in
"Selecting the radar source" on page 64.
Note: Some controls that are related to physical properties of the radar itself are not
Ú
independent of source. These are Fast Scan, Antenna Height and Bearing alignment.
MARPA is fully independent and up to 10 targets may be tracked for each virtual radar
source.
Up to two independent Guard Zones may also be defined for each virtual radar source.
Using the cursor on a radar panel
By default, the cursor is not shown on a radar panel.
When you position the cursor on the radar panel, the cursor position window is activated
and the cursor menu options are displayed.
To remove the cursor and cursor elements from the panel, select Clear cursor or press the X
key.
GoTo cursor
You can navigate to a selected position on the image by positioning the cursor on the panel,
then using the Goto Cursor option in the menu.
The cursor assist function
Note: The cursor assist function is available if it is enabled. Refer to "Customizing the long press
Ú
feature" on page 19.
The cursor assist function allows for fine tuning and precision placement of the cursor
without covering details with your finger.
Activate the cursor on the panel, then press and hold your finger on the screen to switch the
cursor symbol to a selection circle, appearing above your finger.
Without removing your finger from the screen, drag the selection circle to the desired
position.
When you remove your finger from the screen the cursor reverts to normal cursor operation.
Saving waypoints
A waypoint is saved at the cursor position if active or at the vessel's position if the cursor is
not active on the panel, by doing the following:
• Pressing the rotary knob
• Pressing the Mark key
• Using the new waypoint option in the menu
Radar | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
65
Page 66

Radar sector blanking
(Halo Radar only)
You can define up to four sectors on the PPI inside which no radar data is transmitted. This
enables you to blank-out interference caused by features on your boat or from a secondary
radar. The blanking occurs on the main radar image and radar overlay on a chart. An enabled
sector is shown as a magenta outline with 3 arcs crossing the blanking area. To specify radar
sector blanking, refer to the Halo Radar Installation Manual.
Note: Radar sector blanking is only available for Halo radars.
Ú
Main radar PPI Radar overlay on a chart
Adjusting the radar image
You may be able to improve the radar image by adjusting the radar sensitivity, and by
filtering out the random echoes from sea and weather conditions.
The radar control images are located in the upper right corner of the radar panel. You can
adjust the image settings by selecting the radar control image or by pressing the rotary knob.
The selected control expands and displays its name in full and a slide bar is displayed. You
can then adjust the value by turning the rotary know or by using the slide bar.
You can also adjust the image settings from the radar menu.
Radar use modes
(Halo Radar only)
Radar modes are available with default optimal control settings for different environments.
The following modes are available:
• Custom - In this mode all radar controls can be adjusted and will be retained after a mode
change or radar power cycle. Radar defaults are set for general purpose use.
• Harbor - In this mode the radar settings are optimized for areas such as busy waterways
and large man-made structures where good target discrimination and rapid image
updates are needed.
• Offshore - In this mode the radar settings are optimized for offshore sea conditions and
making isolated targets larger and easy to see.
• Weather - In this mode the radar settings are optimized for best detection and
presentation of rain clutter. Image update rate is slowed and color depth is increased.
• Bird - In this mode the radar settings are optimized for best detection of birds. The radar is
set up for maximum sensitivity. This mode is not recommended for use in congested
harbor environments.
Not all controls are adjustable in each mode. The following list shows preset controls and
adjustability for each control.
Range
Custom: Adjustable
Harbor: Full*
Offshore: Full*
Weather: Full*
Bird: Up to 24nm
Threshold
Custom: Adjustable
Harbor: 30%
Offshore: 30%
Weather: 0%
Bird: 0%
66
Radar | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 67

Gain
Custom: Adjustable
Harbor: Adjustable
Offshore: Adjustable
Weather: Adjustable
Bird: Adjustable
Sea
Custom: Adjustable
Harbor: Adjustable
Offshore: Adjustable
Weather: Adjustable
Bird: Adjustable
Rain
Custom: Adjustable
Harbor: Adjustable
Offshore: Adjustable
Weather: Adjustable
Bird: Adjustable
Noise Rejection
Custom: Adjustable
Harbor: Medium
Offshore: High
Weather: Medium
Bird: High
Target Expansion
Custom: Adjustable
Harbor: Low
Offshore: Medium
Weather: OFF
Bird: OFF
Interference Reject
Custom: Adjustable
Harbor: Adjustable
Offshore: Adjustable
Weather: Adjustable
Bird: Adjustable
Target Separation
Custom: Adjustable
Harbor: Medium
Offshore: OFF
Weather: OFF
Bird: OFF
Fast scan
Custom: Adjustable
Harbor: High
Offshore: High
Weather: OFF
Bird: OFF
* Maximum range is dependent on antenna length.
Modes in dual ranges
(Halo Radar only)
Modes can be set independently for each range. For example, you can have Offshore mode
for range A and Weather mode for range B. However, interaction between ranges occurs in
some cases:
• When using Bird mode for both ranges, maximum range is restricted to 24 NM and range
resolution is reduced.
• Fast scan - The antenna rotation speed is set to the slower of the two modes selected. For
example, Fast Scan is disabled when using Harbor and Weather modes because Fast Scan
is Off in Weather mode.
• The Interference reject setting can affect the interference seen or removed on both
ranges.
Directional clutter rejection
(Broadband 4G Radar only)
This mode automatically works when GAIN = AUTO and SEA = HARBOR or OFFSHORE. The
purpose is to allow smaller vessels to be seen in the leeward direction of the sea clutter. The
GAIN of the radar receiver is increased dynamically during the sweep, in the leeward
direction, for increased target sensitivity in heavier sea states.
When GAIN or SEA = MANUAL, the Directional Clutter Rejection mode will be OFF (nondirectional).
In addition, CALM, MODERATE or ROUGH STC Curve settings are available in the Radar
options menu to better optimize the radar image to your liking.
Gain
The gain controls the sensitivity of the radar receiver.
A higher gain makes the radar more sensitive to radar returns, allowing it to display weaker
targets. If the gain is set too high, the image might be cluttered with background noise.
Gain has a manual and an automatic mode. You toggle between automatic and manual
mode in the slide bar, or by pressing and holding the rotary knob.
Radar | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
67
Page 68
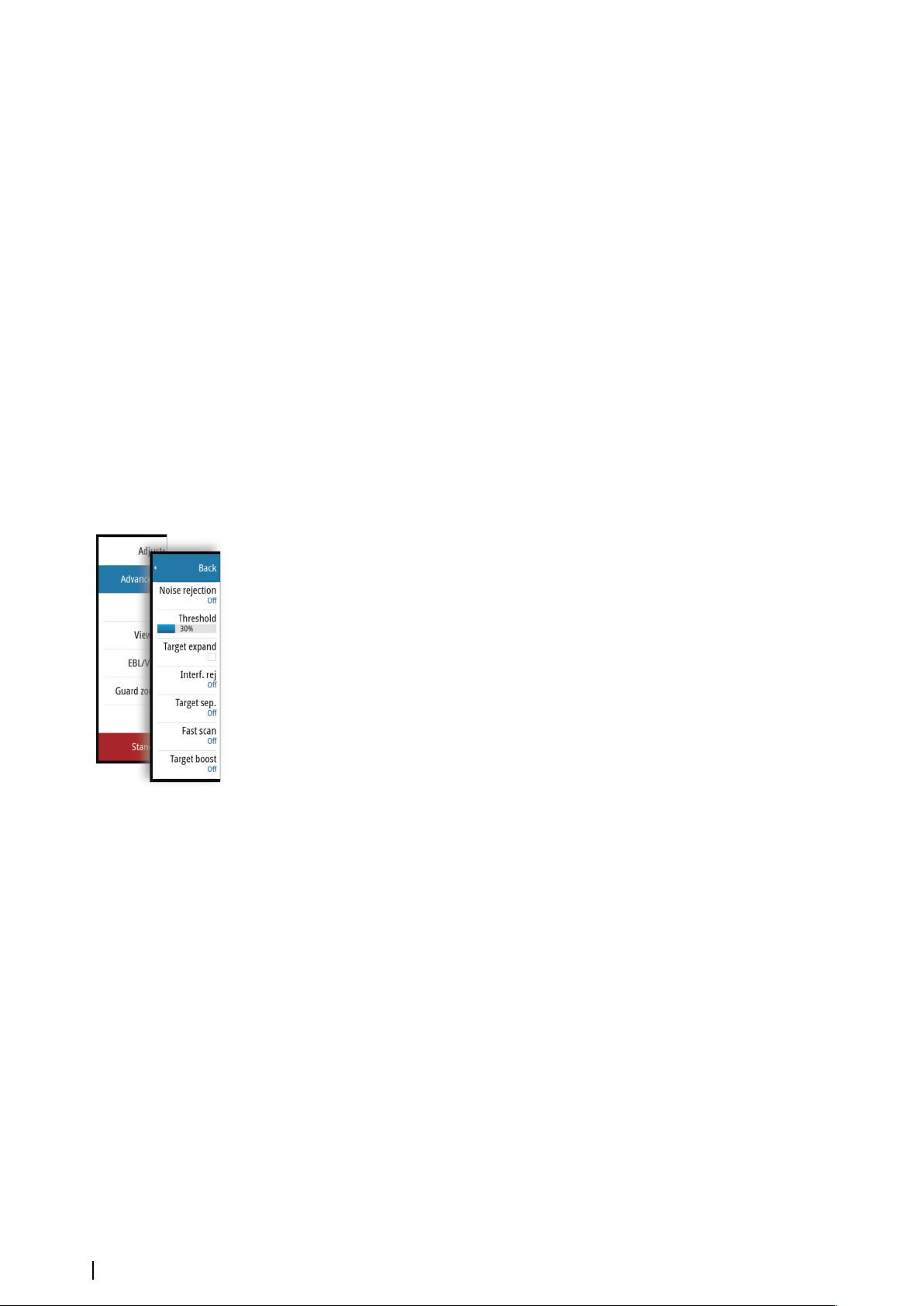
Sea clutter
Sea clutter is used to filter the effect of random echo returns from waves or rough water near
the vessel.
When you increase Sea clutter, filtering the on-screen clutter caused by the echoes of waves
is reduced.
The system includes predefined Sea clutter settings for harbor and offshore conditions for all
radar systems except Halo, in addition to the manual mode where you can adjust the
settings. For all radar systems except Halo, you select Sea clutter modes from the menu, or by
a long press on the rotary knob. You can only adjust the Sea clutter value in manual mode.
Auto Sea Offset
(Halo Radar only)
To allow fine tuning of the Sea control while in Auto mode (Auto uses directional adaptive
clutter rejection), the Auto setting may be offset.
Rain clutter
Rain clutter is used to reduce the effect of rain, snow or other weather conditions on the
radar image.
The value should not be increased too much as this may filter out real targets.
Advanced radar options
Noise Rejection
(Broadband 4G and Halo radar only)
The Noise Rejection control sets the amount of noise filtering applied by the radar. Target
sensitivity is increased at longer ranges when this control is set to Low or High, but does
cause some loss of target discrimination.
Tip: To get maximum range performance from Broadband 4G Radar, transmit on one range
only, set the Noise Reject control to High and the threshold as low as possible. The default is
30% for less clutter on the screen. If OFF is selected for the NSS evo3, the range performance
is about equal to 3G radar. In some areas where extreme high interference may exist, try OFF
for best radar image.
Radar threshold
The threshold sets required signal strength for the lowest radar signals. Radar returns below
this limit are filtered and are not displayed.
Default value: 30%.
Target expansion
Target expansion increases the length of targets in range, making them easier to see.
Rejecting radar interference
Interference could be caused by radar signals from other radar units operating in the same
frequency band.
A high setting reduces the interference from other radars.
In order not to miss weak targets, the interference rejection should be set to low when no
interference exists.
68
Target separation
(Broadband 4G and Halo Radar only)
The Target separation control allows you to control the target discrimination of the radar
(separation between objects is more prominent).
Radar | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 69
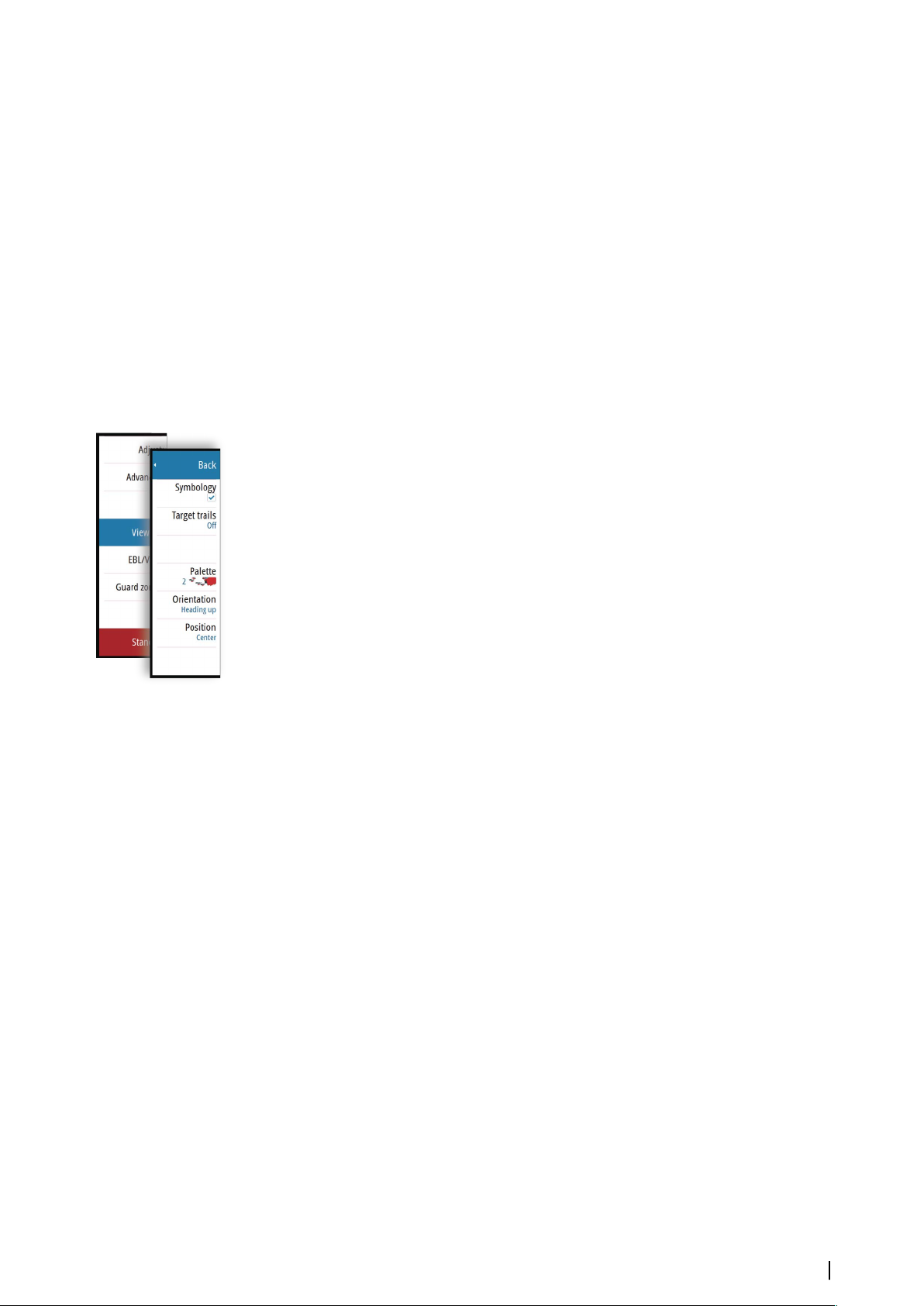
Fast scan
(Broadband and Halo radar only).
Sets the speed of the radar antenna rotation. This option gives faster target updates.
Note: Maximum speed may not be achieved depending on the radar Settings, Mode,
Ú
and Range selected. The radar will only rotate as fast as the current control settings allow.
Sea State
Set the Sea State control according to current sea conditions for best sea clutter rejection.
Target boost
(3G and 4G Broadband, and Pulse Radar only)
The target boost control increases pulse length or reduces radar bandwidth to make targets
appear larger in range and increase radar sensitivity.
Radar view options
Radar symbology
Radar symbology defined in the Radar Settings panel can be turned on/off collectively. See
the radar panel illustration showing optional radar items.
Target trails
You can set how long the trails generated from each target on your radar panel remain. You
can also turn OFF target trails.
Note: True motion is recommended when using Target trails
Ú
Clearing target trails from the panel
When target trails are displayed on the panel, the radar menu expands to include an option
where you can clear target trails from your radar panel temporarily. The target trails start to
appear again unless you switch them off as described above.
The radar palette
Different colors (palettes) can be used to represent detail on your radar panel.
Radar orientation
Radar orientation is indicated on the upper left corner of the radar panel as either HU
(Heading UP), NU (North Up) or CU (Course up).
Heading up
Rotates the radar image to display the current heading directly up on the radar image.
North up
Rotates the radar image with the north direction upwards.
Course up
Rotates the radar image to display the current navigation course directly up.
This option works only when the system is navigating an active route. If you are not
navigating an active route, the heading up orientation is used until the navigation function is
started.
Positioning the radar center
You can move the radar PPI (Plan Position Indicator) center to different positions within the
radar panel, and select how your vessel symbol moves on the radar image.
Radar motion is indicated on the upper left corner of the radar panel as either TM (True
motion) or RM (Relative motion).
The radar position can only be changed when the radar is transmitting.
Radar | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
69
Page 70
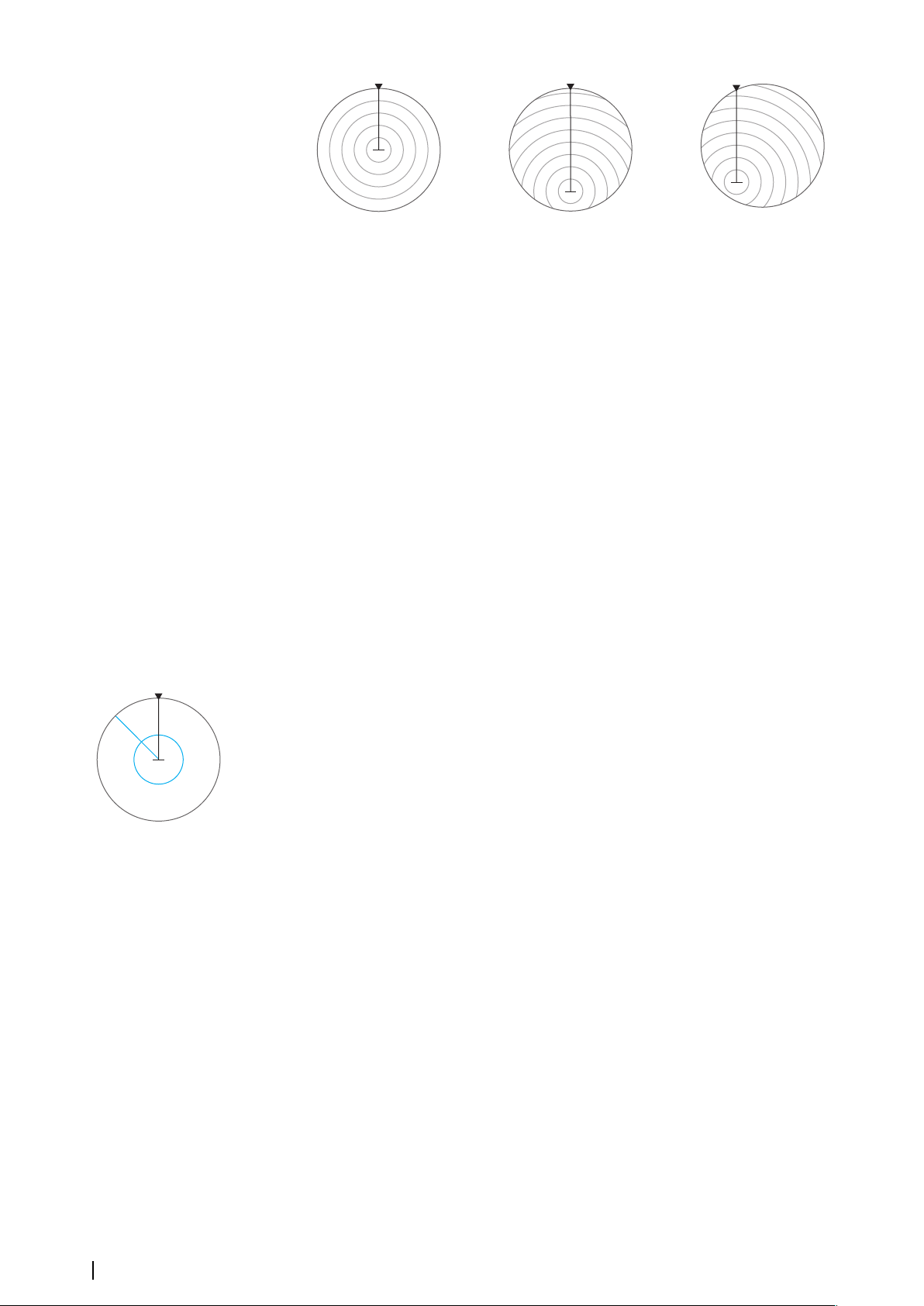
Center
Center
Default setting. The radar PPI center is centered on the radar panel.
Look Ahead
Moves the radar PPI center to the bottom of the panel to maximize the view ahead.
Offset
Allows you to move the PPI center to any location on the radar panel.
1. Select the offset option from the menu
2. Move the cursor to where you want to position the radar center
3. Confirm the setting by selecting the Save offset button in the bottom right corner of the
panel.
True motion
In True motion, your vessel and moving targets move across the Radar screen as you travel.
All stationary objects remain in a fixed position. When the vessel’s symbol reaches the edge
of the screen, the radar image is redrawn with the vessel symbol repositioned in the center of
the screen.
When True motion is selected, the menu expands to include a reset true motion option. This
allows for manually resetting the radar image and vessel symbol to the center of the screen.
Look ahead
Custom offset
EBL/VRM markers
The electronic bearing line (EBL) and variable range marker (VRM) allows quick
measurements of range and bearing to vessels and landmasses within radar range. Two
different EBL/VRMs can be placed on the radar image.
The EBL/VRMs are by default positioned from the center of the vessel. It is, however, possible
to offset the reference point to any selected position on the radar image.
When positioned, you can turn the EBL/VRM on/off by selecting the relevant markers on the
data bar, or by deselecting the marker from the menu.
Defining an EBL/VRM marker
1. Ensure that the cursor is not active
2. Activate the menu, select EBL/VRM, then select EBL/VRM 1 or EBL/VRM 2
-
The EBL/VRM is now positioned on the radar image
3. Select the adjustment option from the menu if you need to reposition the marker, then
adjust the marker by dragging it into position on the radar image
4. Select the save option to save your settings
Placing EBL/VRM markers by using the cursor
1. Position the cursor on the radar image
2. Activate the menu
3. Select one of the EBL/VRM markers
- The EBL line and the VRM circle are positioned according to the cursor position.
70
Offsetting an EBL/VRM marker
1. Ensure that the cursor is not active
2. Activate the menu, select EBL/VRM, then select the marker you wish to offset
3. Select the set offset option
4. Position the cursor on the radar panel to set the offset position
Radar | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 71
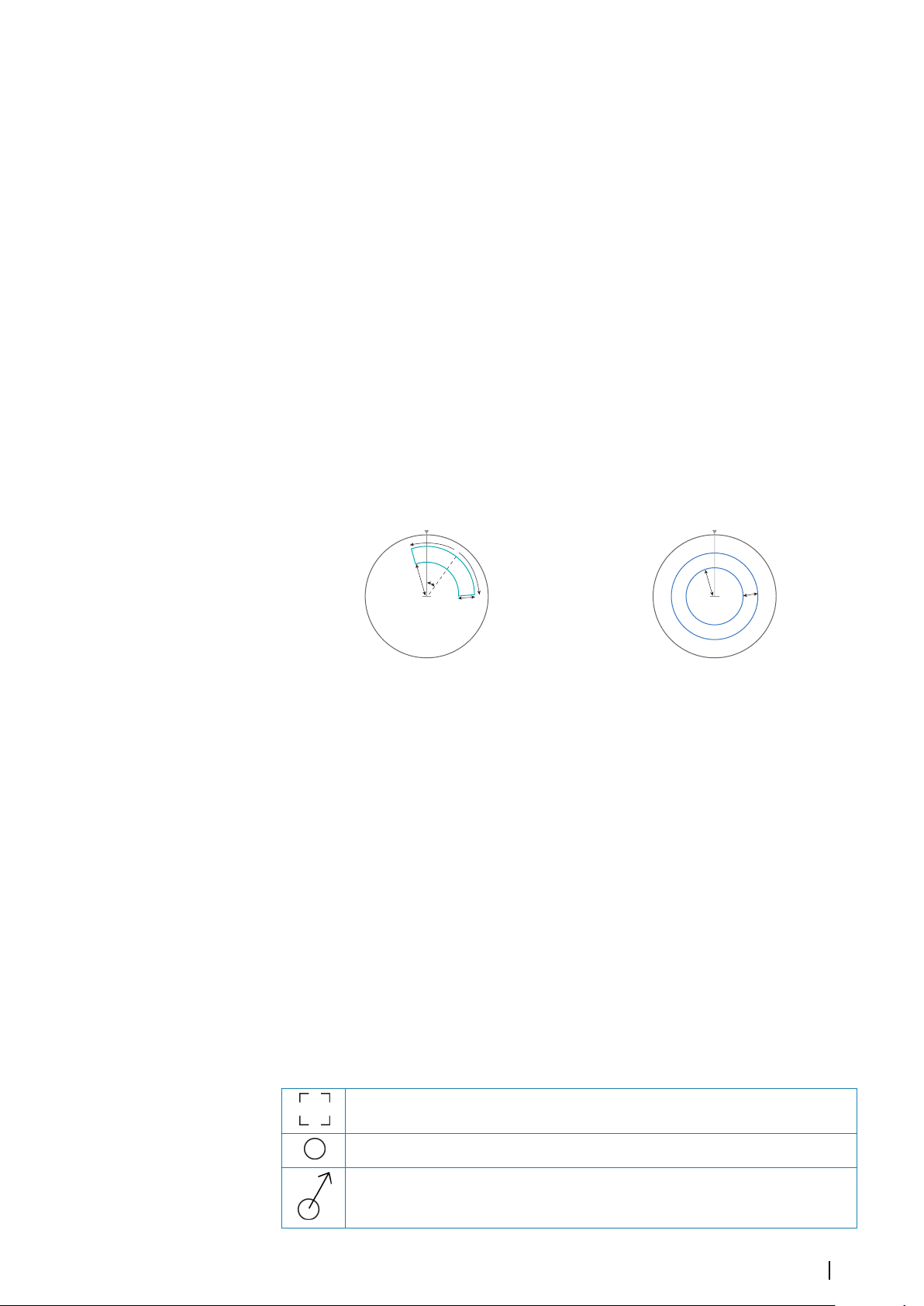
5. Select the save option to save your settings.
C
B
A
D
B
C
You can reset the EBL/VRM center to vessel position from the menu.
Setting a guard zone around your vessel
A guard zone is an area (either circular or a sector) that you can define on the radar image.
When activated, an alarm alerts you when a radar target enters or exits the zone.
Defining a guard zone
1. Ensure that the cursor is not active
2. Activate the menu, select Guard zones, then select one of the guard zones
3. Select the shape for the zone
-
The adjustment options depend on the guard zone shape
4. Select Adjust to define the settings for the guard zone. The values can be set from the
menu or by dragging on the radar panel.
- A: Bearing, relative to the vessel heading
- B: Depth
- C: Range, relative to vessel center
- D: Width
5. Select the save option to save your settings.
When positioned, you can turn the guard zones on/off by selecting the relevant section on
the data bar.
Shape: Sector
Shape: Circle
Alarm settings
An alarm is activated when a radar target breaches the guard zone limits. You can select if
the alarm is activated when the target enters or exits the zone.
Sensitivity
The guard zone sensitivity can be adjusted to eliminate alarms for small targets.
MARPA targets
If the system includes a heading sensor, the MARPA function (Mini Automatic Radar Plotting
Aid) can be used to track up to ten radar targets.
You can set alarms to notify you if a target gets too close. Refer to "Radar settings"
MARPA tracking is an important tool for collision avoidance.
Note: MARPA requires heading data for both the radar and the NSS evo3.
Ú
MARPA target symbols
The system uses the target symbols shown below.
Acquiring MARPA target. Typically it takes up to 10 full rotations of the scanner.
on page 73.
Tracking MARPA target, not moving or at anchor.
Radar | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Tracking and safe MARPA target with extension lines.
71
Page 72
Dangerous MARPA target.
A target is defined as dangerous when it enters the guard zone defined on the
radar panel.
When no signals have been received within a time limit a target will be defined
as lost.
The target symbol represents the last valid position of the target before the
reception of data was lost.
Selected MARPA target, activated by positioning the cursor on the target icon.
The target returns to the default target symbol when the cursor is removed.
Tracking MARPA targets
1. Position the cursor on the target on the radar image
2. Select Acquire targets from the menu
3. Repeat the process if you want to track more targets
After your targets are identified, it may take up to 10 radar sweeps to acquire and then track
the target.
Cancelling MARPA target tracking
When targets are being tracked, the radar menu expands to include options for cancelling
individual targets or to stop the tracking function.
Cancel tracking individual targets by selecting the target icon before activating the menu.
Viewing MARPA target information
If the pop-up is activated, you can select a MARPA target to display basic target information.
Information for the 3 MARPA targets closest to the vessel is also displayed in the data bar.
When a target is selected, detailed information for the target can be displayed from the
menu.
You can display information about all MARPA targets by using the Vessels option on the
Home page.
MARPA alarm settings
You can define the following MARPA alarms:
• MARPA target lost
Controls whether an alarm is activated when a MARPA target is lost.
• MARPA unavailable
Controls whether an alarm is activated if you do not have the required inputs for MARPA
to work (valid GPS position and heading sensor connected to the radar server).
Recording radar data
You can record radar data and save the file internally in the NSS evo3 unit, or save it onto a
memory card inserted into the unit’s card reader.
A recorded radar file can be used for documenting an event or an operational error. A logged
radar file can also be used by the simulator.
If more than one radar is available, you can select which source you want to record.
72
Radar | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 73

Radar settings
Radar symbology
You can select which optional radar items that should be turned on/off collectively from the
menu. Refer to the Radar panel illustration.
Bearings
Used for selecting whether the radar bearing should be measured in relation to True/
Magnetic North (°T/°M) or to your relative heading (°R).
Data bar
Turns on/off the radar data bar. Refer to the radar panel illustration.
The data bar can show up to 3 targets, arranged with the most dangerous targets on top.
You can select to show MARPA targets on top and before any AIS targets, even if the AIS
targets are closer to your vessel.
MARPA settings
You can define the length of the MARPA trail making it easier to follow target movement.
A circle can be added around your vessel to present the danger zone. The radius of the ring is
the same as the closest point of approach as set in the Dangerous Vessels dialog. Refer to
"Defining dangerous vessels" on page 102. An alarm triggers if a vessel is tracking into your safe
zone.
Installation
The Installation option is used for radar installation, described in the separate Radar or NSS
evo3 Installation manuals.
Radar | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
73
Page 74
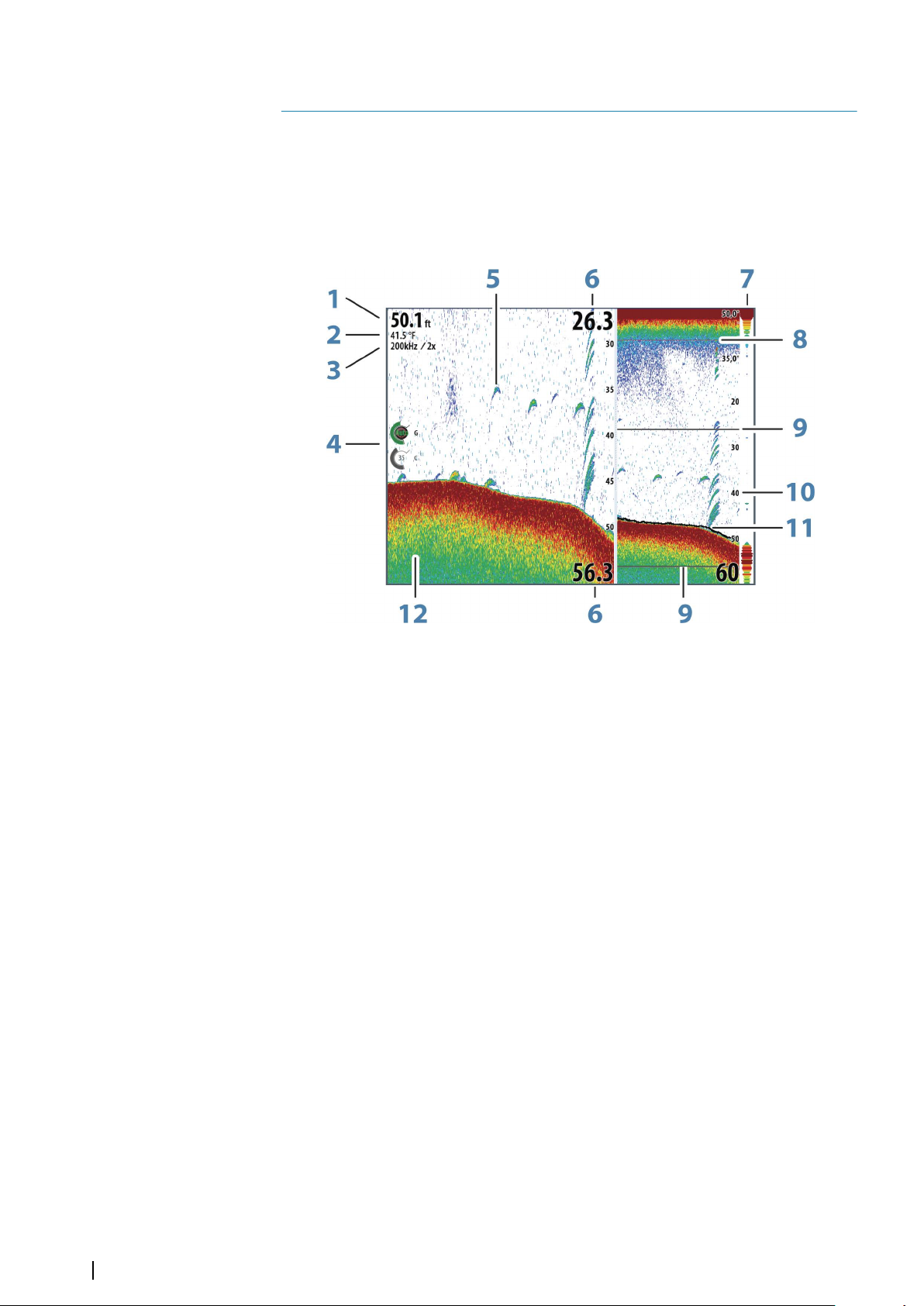
10
Echosounder
The Echosounder function provides a view of the water and bottom beneath your vessel,
allowing you to detect fish and examine the structure of the sea floor.
The unit has internal CHRIP, Broadband, StructureScan, TotalScan, and ForwardScan
Echosounder.
The Echosounder image
1 Depth
2 Temperature
3 Frequency / Zoom
4 Gain / Color adjustment icons
5 Fish arches
6 Upper and Lower range
7 A-Scope*
8 Temperature graph*
9 Zoom bars*
10 Range scale
11 Depth line*
12 Bottom
* Optional Echosounder items.
Note: You turn the optional Echosounder items on/off individually. Refer to "Echosounder
Ú
View options" on page 79.
Multiple Echosounder
You can specify the Echosounder source for the image in the Echosounder panel. You can
display two different sources simultaneously, using a split panel configuration. For more
information how to select the source for a panel, refer to "Source" on page 77.
74
Zooming the image
You can zoom the image by:
Echosounder | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 75

• turning the rotary knob
• using the panel zoom icons
• pinching or spreading on the screen
Zoom level is shown on the upper left side of the image.
When zooming in, the sea floor is kept near the bottom of the screen, irrespective of whether
it is in auto-range or manual range.
If the range is set considerably less than the actual depth, the unit is not able to find the
bottom when zooming.
If the cursor is active, the unit zooms in where the cursor is pointed.
Zoom bar
The zoom bar is displayed when you zoom the image.
Drag the zoom bar vertically to view different parts of the water column.
Using the cursor on the image
The cursor can be used to measure a distance to a target, to mark a position, and to select
targets.
By default, the cursor is not shown on the image.
When you position the cursor on the image; the screen pauses, the depth at the cursor
position is shown, and the information window and the history bar are activated.
To remove the cursor and cursor elements from the panel, select Clear cursor or press the X
key.
GoTo cursor
You can navigate to a selected position on the image by positioning the cursor on the panel,
then using the Goto Cursor option in the menu.
The cursor assist function
Note: The cursor assist function is available if it is enabled. Refer to "Customizing the long press
Ú
feature" on page 19.
The cursor assist function allows for fine tuning and precision placement of the cursor
without covering details with your finger.
Activate the cursor on the panel, then press and hold your finger on the screen to switch the
cursor symbol to a selection circle, appearing above your finger.
Without removing your finger from the screen, drag the selection circle to the desired
position.
When you remove your finger from the screen the cursor reverts to normal cursor operation.
Measuring distance
The cursor can be used to measure the distance between the position of two observations
on the image.
1. Position the cursor on the point from where you want to measure the distance
2. Start the measuring function from the menu
3. Position the cursor on the second measuring point
A line is drawn between the measuring points, and the distance is listed in the Cursor
Information panel
4. Continue selecting new measuring points if required
You can use the menu to re-position the start point and the end point as long as the
measuring function is active.
When you select Finish measuring or press the X key, the image resumes to normal
scrolling.
Echosounder | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
75
Page 76

Saving waypoints
You can save a waypoint at a selected location by positioning the cursor on the panel, and
then doing one of the following:
• Pressing the rotary knob
• Pressing the Mark key
• Using the new waypoint option in the menu
Viewing history
Whenever the cursor is shown on the Echosounder panel, the scroll bar is shown at the top
of the panel. The scroll bar shows the image you are currently viewing in relation to the total
Echosounder image history stored.
If the scroll bar is on the far right side, it indicates that you are viewing the latest soundings. If
you position the cursor to the left side of the screen, the history bar starts scrolling towards
the left, and the automatic scrolling as new soundings are received is turned off.
You can view echosounder history by panning the image.
To resume normal scrolling, select Clear cursor or press the X key.
76
Setting up the image
Use the Echosounder menu options to set up the image. When the cursor is active, some
options on the Echosounder menu are replaced with cursor mode features. Select Clear
cursor to return to the normal Echosounder menu.
The range
The range setting determines the water depth that is visible on the screen.
Frequency
The unit supports several transducer frequencies. Available frequencies depend on the
transducer model that is connected.
You can view two frequencies at the same time by selecting dual Echosounder panels from
the Home page.
Frequency is the ‘tone’ the transducer transmits. Transducers are designed to operate on
different frequencies as the various frequencies have different qualities.
• A low frequency, for example 50 kHz, will go deep. It generates a wide cone but is
somewhat more sensitive to noise. It is good for bottom discrimination and wide area
search.
• A high frequency, for example 200 kHz, offers higher discrimination and is less sensitive to
noise. It is good for separating targets and for higher speed vessels.
Echosounder | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 77

Color and gain settings
You can also adjust the image settings from the Echosounder menu.
Gain
The gain controls the sensitivity of the Echosounder.
The more you increase the gain, the more details are shown on the image. However, a higher
gain setting may introduce more background clutter on the image. If the gain is set too low,
weak echoes might not be displayed.
Auto gain
The Auto gain option keeps the sensitivity at a level that works well under most conditions.
With the gain in auto mode, you can set a positive or negative offset that gets applied to the
auto gain.
Color
Strong and weak echo signals have different colors to indicate the different signal strengths.
The colors used depend on which palette you select.
The more you increase the Color setting, the more echoes is displayed in the color at the
strong return end of the scale.
Structure options
When a StructureScan source is connected to your system, you can overlay a DownScan
image on the regular echo image.
Provides options for specifying the DownScan image. This menu option is available when
Overlay downscan is selected in Echo settings dialog. For more information see "settings" on
page 81.
Source
Select to specify the source for the image in the selected panel.
You can display two different sources simultaneously, using a split panel configuration. Menu
controls for each panel are independent.
The source can be the internal Echosounder, another MFD on the Ethernet network, or a
Echosounder module. To define sources, refer to the separate NSS evo3 Installation manual.
Note: Using two transducers at the same frequency ranges can cause interference
Ú
between the two, and they can show up on the image as vertical lines. To avoid this, set
one transducer at one frequency range (such as Medium CHIRP) and the other
transducer at a different frequency range (such as High CHIRP) using the Frequency
menu option.
Pausing the image
You can pause the image, allowing you to examine it.
This function is useful when you need to position a waypoint exactly on the image, and if
you are using the cursor to measure a distance between 2 elements on the image.
The pause function stops the Echosounder from pinging the transducer. The system is not
collecting Echosounder data when paused in this manner.
Advanced options
The Advanced option is only available when the cursor is not active.
Noise rejection
Signal interference from bilge pumps, engine vibration and air bubbles can clutter the
image.
The noise rejection option filters the signal interference and reduces the on-screen clutter.
Echosounder | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
77
Page 78

TVG
Wave action and boat wakes can cause onscreen clutter near the surface. The TVG (Time
Variable Gain) option reduces surface clutter by decreasing the sensitivity of the receiver near
the surface.
Note: For optimal image return and clarity in most conditions, the default value is set to
Ú
3, the maximum (range is 0-3).
Scroll speed
You can select the scrolling speed of the image on the screen. A high scroll speed updates
the image fast, while a low scroll speed presents a longer history.
Note: In certain conditions it may be necessary to adjust the scroll speed to get a more
Ú
useful image. Such as adjusting the image to a faster speed when vertically fishing
without moving.
Ping speed
Ping speed controls the rate the transducer transmits the signal into the water. By default,
the ping speed is set to max. It may be necessary to adjust the ping speed to limit
interference or to adjust for specific fishing conditions.
Start recording log data
You can start recording log data and save the file internally in the unit, or save it onto a card
inserted into the unit’s card reader.
The record function is activated from the Advanced menu option.
When the data is being recorded, there is a flashing red symbol in the top left corner and a
message appears periodically at the bottom of the screen.
78
Filename
Specify the name of the recording (log).
File format
Select a file format from the drop-down, slg (Echosounder only), xtf (Structure only*), sl2
(Echosounder and Structure) or sl3 (includes ForwardScan).
Note: XTF format is for use only with select 3rd party Echosounder viewing tools.
Ú
Save to
Select whether the recording is to be saved internally or to a memory card in the card reader.
Echosounder | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 79
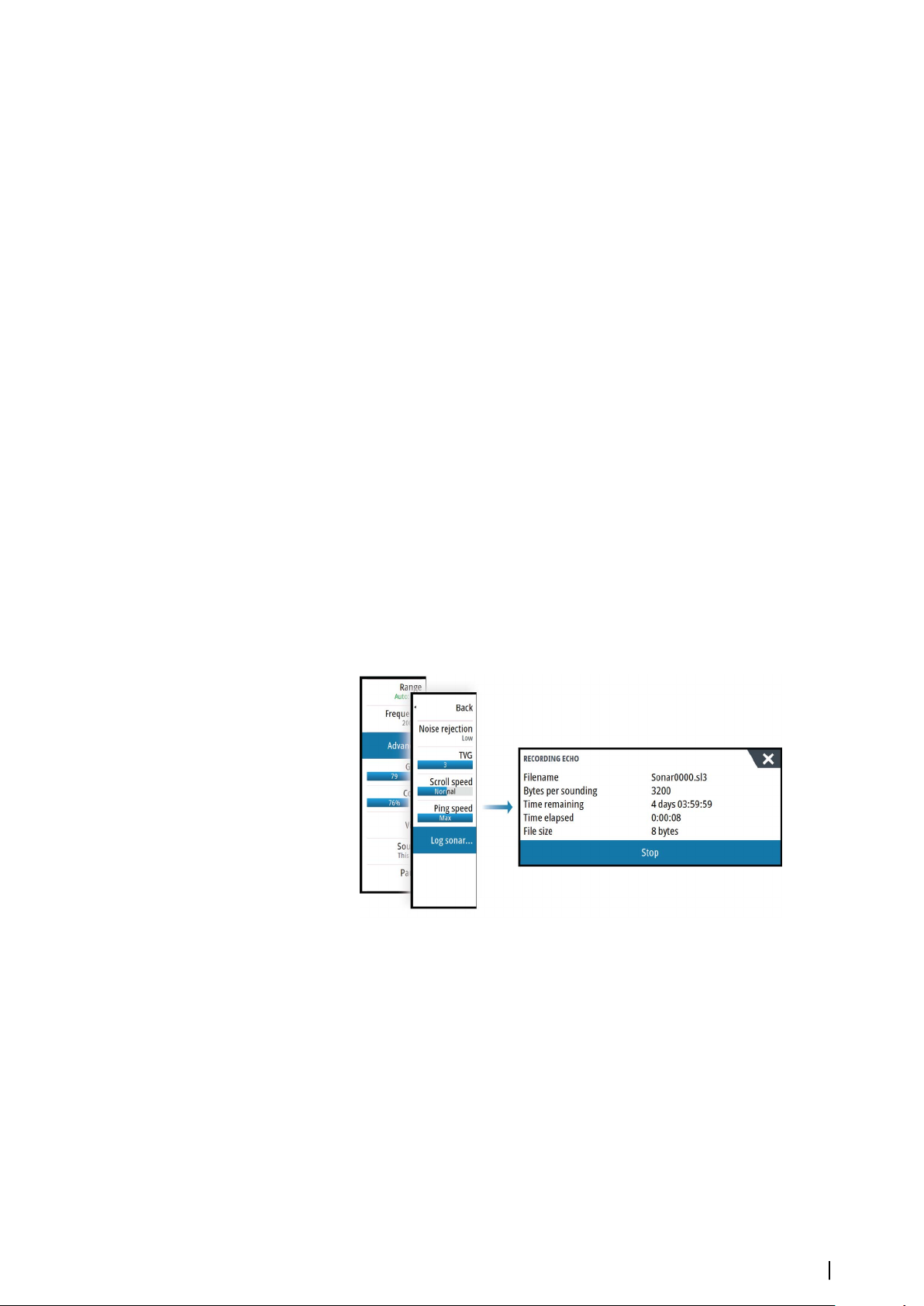
Bytes per sounding
Select how many bytes per seconds that are to be used when saving the log file. More bytes
yield better resolution, but cause the record file to increase in size compared to using lower
byte settings.
Create StructureMap
If StructureScan is available on the network, you can convert the .sl2 logs to StructureMap
format (.smf) when recording completes. The log file can also be converted to StructureMap
format from the Files option.
Upload to Insight Genesis
Files are transmitted to Insight Genesis when recording completes, if you are connected to a
wireless hotspot. For information about wireless hotspots, refer to "Wireless connection"
95.
on page
Privacy
If allowed by your selected Insight Genesis account, you can choose between setting the
recorded log files as Private or Public at Insight Genesis.
Time remaining
Shows the remaining allocated space available for recordings.
Stop recording log data
Select Stop in the Recording Echo dialog to fully stop the recording of all echosounder data.
Note: If you have selected the Upload to Insight Genesis option and are connected to
Ú
a wireless hotspot, your recorded files are transmitted to Insight Genesis when you select
Stop.
Viewing the recorded sounder data
Both internally and externally stored sounder records may be reviewed when the view sonar
log option is selected in the Echo settings dialog. Refer to "Echosounder settings" on page 81.
The log file is displayed as a paused image, and you control the scrolling and display from the
replay menu option.
You can use the cursor on the replay image, and pan the image as on a normal echo image.
If more than one channel was recorded in the selected echo file, you can select which
channel to display.
You exit the replay mode by pressing the X key or by selecting the X symbol in the upper
right corner of the replay image.
Echosounder View options
Echosounder | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
79
Page 80

Split screen options
Zoom
The Zoom mode presents a magnified view of the sounder image on the left side of the
panel.
By default the zoom level is set to 2x. You can select up to 8x zoom from the drop-down
menu, using the +/- keys, or the zoom (+ or -) buttons.
The range zoom bars on the right side of the display shows the range that is magnified. If you
increase the zooming factor the range is reduced. You see this as reduced distance between
the zoom bars.
Bottom lock
The bottom lock mode is useful when you want to view echoes close to the bottom. In this
mode, the left side of the panel shows an image where the bottom is flattened. The range
scale is changed to measure from the seabed (0) and upwards. The bottom and the zero line
are always shown on the left image, independent of the range scale. The scaling factor for
the image on the left side of the panel is adjusted as described for the Zoom option.
Palettes
You can select between several display palettes optimized for a variety of fishing conditions.
Temperature graph
The temperature graph is used to illustrate changes in water temperature.
When toggled on, a colored line and temperature digits are shown on the Echosounder
image.
Depth line
A depth line can be added to the bottom surface to make it easier to distinguish the bottom
from fish and structures.
A-Scope
The A-scope is a display of real-time echoes as they appear on the panel. The strength of the
actual echo is indicated by both width and color intensity.
Zoom bars
The zoom bars shows the range that is magnified on a split panel with zoom views.
The range zoom bars on the right side of the display shows the range that is magnified and
displayed on the left side. If you increase the zooming factor, the range is reduced. You see
this as reduced distance between the zoom bars.
You can move the zoom bars on the right side up or down to cause the left side image to
show different depths of the water column.
Fish ID
You can select how you want the echoes to appear on the screen. You can also select if you
want to be notified by a beep when a fish ID appears on the panel.
80
Traditional fish echoes Fish symbols Fish symbols and depth indication
Note: Not all fish symbols are actual fish.
Ú
Echosounder | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 81
Echosounder settings
Internal Echosounder
Select to make the internal Echosounder available for selection in the Echosounder menu.
For more information about panel source selection, refer to the Operator manual.
When set to off, this option disables the internal
as a Echosounder source for any unit on the network. Select this option on a unit which does
not have a transducer connected.
Echosounder in the unit. It will not be listed
Network Echosounder
You can share the Echosounder images from this unit with other units connected on the
Ethernet network.
For more information about how to setup Echosounder, refer to the separate NSS evo3
Installation manual.
Overlay downscan
When a DownScan source is connected to your system, you can overlay DownScan images
on the regular Echosounder image.
When activated, the Echosounder menu expands to include basic DownScan options.
View Echosounder log
Used to view Echosounder recordings. The log file is displayed as a paused image, and you
control the scrolling and display from the menu.
You can use the cursor on the image, measure distance, and set view options as on a live
Echosounder image. If more than one channel was recorded in the selected Echosounder
file, you can select which channel to display.
You exit the view function by selecting the X in the upper right corner.
Structure depth offset
Setting for Structure transducers.
All transducers measure water depth from the transducer to the bottom. As a result, water
depth readings do not account for the distance from the transducer to the lowest point of
the boat in the water or from the transducer to the water surface.
To show the depth from the lowest point of the boat to the bottom, do the following. Before
setting the Structure offset, measure the distance from the structure transducer to the lowest
point of the boat in the water. If, for example, the distance is 0.3 m (1 ft), it will be input as
(minus) - 0.3 m (-1 ft).
To show the depth from the water surface to the bottom, do the following. Before setting
the Structure offset, measure the distance from the structure transducer to the water surface.
If, for example, the distance is 0.3 m (1 ft), it will be input as (plus) 0.3 m (1 ft).
Echosounder | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
81
Page 82

A setting of 0 (zero) causes the depth displayed to be the distance from the transducer to the
bottom.
Installation
Used for defining Echosounder sources available for selection in the Source menu option. For
information about defining sources, refer to the separate NSS evo3 Installation manual. For
information about Source selection, refer to "Source" on page 77.
ForwardScan Installation
Used for ForwardScan installation and setup. Refer to the "ForwardScan setup" on page 92.
82
Echosounder | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 83
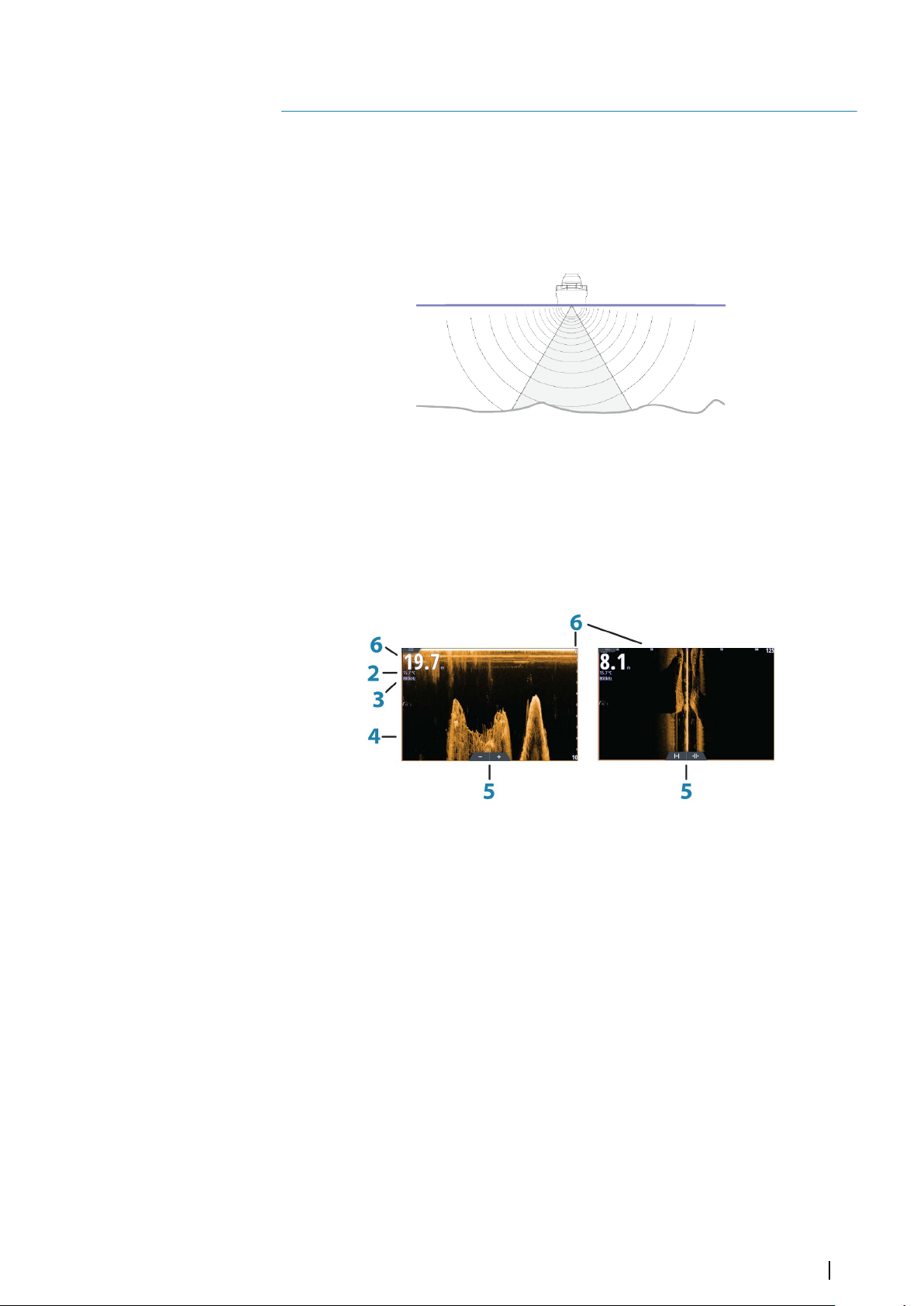
11
StructureScan
StructureScan uses high frequencies to provide a high resolution, picture-like image of the
seabed.
The unit has built-in StructureScan.
Note: You must have a StructureScan HD, TotalScan or StructureScan 3D transducer
Ú
installed to use StructureScan features.
Note: Connect StructureScan transducers to the Sonar2 port only.
Ú
The StructureScan image
The view
The StructureScan panel can be set up as a DownScan image, or showing left/right side
scanning.
The DownScan image can also be added as an overlay to the traditional Echosounder image.
1 Depth
Note: The depth reading depends on the Structure depth offset setting,
Ú
refer to "Structure depth offset" on page 81
2 Temperature
3 Frequency
4 Bottom
5 Zoom (downscan) / Range (sidescan) icons
6 Range scale
Zooming the StructureScan image
You can zoom a StructureScan image by:
• turning the rotary knob when the cursor is not active
• using the panel zoom icons
• by pinching or spreading on the screen
Zoom level is shown on the upper left side of the panel.
StructureScan | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
83
Page 84

Using the cursor on the StructureScan panel
By default, the cursor is not shown on the StructureScan image.
When you position the cursor on a DownScan image, the screen pauses, the cursor
information window and the history bar are activated. On a DownScan image, the depth is
shown at cursor position.
When you position the cursor on a SideScan image, the screen pauses, and the cursor
information window is activated. On a SideScan image, the left/right distance from the vessel
to the cursor are shown at the cursor position.
GoTo cursor
You can navigate to a selected position on the image by positioning the cursor on the panel,
then using the Goto Cursor option in the menu.
The cursor assist function
Note: The cursor assist function is available if it is enabled. Refer to "Customizing the long press
Ú
feature" on page 19.
The cursor assist function allows for fine tuning and precision placement of the cursor
without covering details with your finger.
Activate the cursor on the panel, then press and hold your finger on the screen to switch the
cursor symbol to a selection circle, appearing above your finger.
Without removing your finger from the screen, drag the selection circle to the desired
position.
When you remove your finger from the screen the cursor reverts to normal cursor operation.
Measuring distance
The cursor can be used to measure the distance between the position of two observations
on the image.
1. Position the cursor on the point from where you want to measure the distance
2. Start the measuring function from the menu
3. Position the cursor on the second measuring point
-
A line is drawn between the measuring points, and the distance is listed in the Cursor
Information panel
4. Continue selecting new measuring points if required
You can use the menu to re-position the start point and the end point as long as the
measuring function is active.
When you select Finish measuring or press the X key, the image resumes to normal
scrolling.
Saving waypoints
You can save a waypoint at a selected location by positioning the cursor on the panel, and
then doing one of the following:
• Pressing the rotary knob
• Pressing the Mark key
• Using the new waypoint option in the menu
84
StructureScan | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 85

Viewing StructureScan history
Whenever the cursor is active on a StructureScan panel, the scroll bar is shown on the panel.
The scroll bar shows the image you are currently viewing in relation to the total
StructureScan image history stored. Depending on the view selected, the scroll bar is on the
far right side (SideScan) or at the top of the screen (DownScan).
You can pan the image history by dragging up/down (SideScan) or left/right (DownScan).
To resume normal StructureScan scrolling, press Clear cursor.
Setting up the StructureScan image
Range
The range setting determines the water depth and SideScan range that is visible on the
screen.
Auto range
When the range is set to Auto the system automatically sets the range depending on the
water depth.
Preset range levels
You can select between several preset range levels.
Custom range
This option allows you to manually set both upper and lower range limits.
StructureScan frequencies
StructureScan supports two frequencies. 455 kHz provides ideal range and image quality in
most situations, while 800kHz is used to provide higher detail in shallow water.
Contrast
Determines the brightness ratio between light and dark areas of the screen.
To adjust the contrast setting:
1. Select the contrast icon or activate the contrast option in the menu to display the color
adjustment bar
2. Drag the bar or use the rotary knob to set the value.
Palettes
You can select between several display palettes optimized for a variety of fishing conditions.
View
You can set up the StructureScan page as a DownScan image, left only, right only, or left/
right side scanning.
Pausing the StructureScan image
You can pause the StructureScan image, allowing you to examine the structures and other
images in more depth and detail.
This function is useful when you need to position a waypoint exactly on the StructureScan
image, and if you are using the cursor to measure a distance between 2 elements on the
image.
StructureScan | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
85
Page 86

Advanced StructureScan settings
TVG
Wave action and boat wakes can cause onscreen clutter near the surface. The TVG (Time
Variable Gain) option reduces surface clutter by decreasing the sensitivity of the receiver near
the surface.
Note: For optimal image return and clarity in most conditions, the default value is set to
Ú
3, the maximum (range is 0-3).
Flipping the Structure image left/right
If required, the left/right SideScanning images can be flipped to match the direction of the
transducer installation.
Range Lines
Range lines can be added to the image to make it easier to estimate depth (Downscan) and
distance (SideScan).
Recording StructureScan data
You can record StructureScan data and save the file internally in the NSS evo3 unit, or onto
memory card as described in "Start Recording echosounder data" on page 78.
86
StructureScan | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 87

12
StructureMap
The StructureMap feature overlays SideScan images from a StructureScan source on the map.
This makes it easier to visualize the underwater environment in relation to your position, and
aids in interpreting SideScan images.
The StructureMap image
The example below shows a chart panel with Structure overlay, combined with a traditional
SideScan panel.
You move around in the chart as usual when you have a Structure overlay:
• zoom the chart and the scanned image by turning the rotary knob, by using the zoom
icons, or by pinching or spreading on the screen
• move the chart to view the scanned image by dragging it in the desired direction
Pressing the X key or selecting the Clear cursor option removes the cursor from the panel,
and the chart center is positioned at the vessel.
Activating Structure overlay
1. Turn on Structure overlay from the chart menu
-
The chart menu is increased to show Structure options
- Structure data starts to appear on the chart screen as soon as Structure overlay is
enabled
2. Select Structure source
- Live data is default
Note: Structure overlay can also be activated by selecting a saved StructureMap file in
Ú
the files browser.
StructureMap sources
Two sources can be used to overlay Structure logs on the charts, but only one can be viewed
at a time:
• Live data - Used when StructureScan data is available on the system.
• Saved files - These are recorded StructureScan (*.sl2) data that are converted to
StructureMap (*.smf) format. Saved *.smf files can be used even if no StructureScan
sources are connected.
Live source
When live data is selected, the SideScan imaging history is displayed as a trail behind the
vessel icon. The length of this trail varies depending on available memory in the unit and
range settings. As the memory fills up, the oldest data is automatically deleted as new data is
added. When increasing the search range, the ping speed of the StructureScan transducer is
reduced, but the width and the length of the image history is increased.
Note: Live mode does not save any data. If the unit is turned off, all recent data is lost.
Ú
StructureMap | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
87
Page 88

Saved files
When Saved files are selected, the StructureMap file is overlaid on the map based on position
information in the file.
If the chart scale is large, the StructureMap area is indicated with a boundary box until the
scale is large enough to show Structure details.
Saved mode is used to review and examine StructureMap files, and to position the vessel on
specific points of interest on a previous scanned area.
Note: When saved files are used as the source, all StructureMap files found on the
Ú
memory card and in the system’s internal memory are displayed. If there is more than
one StructureMap of the same area, the images overlap and clutter the chart. If several
logs of the same area are required, the maps should be put on separate memory cards.
StructureMap tips
• To get a picture of taller structures (a wreck, etc.) — do not drive over it, instead, steer the
boat so the structure is on the left or right side of your vessel.
• Do not use Autorange when using StructureScan. Set your structure range to a
significantly greater level (two-to-three times) than the water depth to ensure a complete
scan and to maximize conversion accuracy.
• Do not overlap history trails when conducting a side-by-side scan of an area.
Recording StructureScan data
StructureScan data can be recorded from a chart panel with Structure overlay enabled.
StructureScan recordings can also be started from a StructureScan panel.
When StructureScan data is being recorded, there is a flashing red symbol and a message
appears periodically at the bottom of the screen.
Note: The message includes information about file size. Keep the size of your logs to
Ú
100MB or less to allow for faster file conversion.
The recording is stopped by re-selecting the record function.
Converting StructureScan data to StructureMap format
A StructureScan log file (.sl2) is converted to StructureMap format (.smf ) after recording from
the recording dialog, or from the files browser.
You can create standard or high resolution files. High resolution .smf files capture more detail,
but take longer to convert and are larger than standard resolution files.
To save disc space it is recommended to remove the StructureScan (.sl2) files after
conversion.
Using StructureMap with mapping cards
StructureMap allows you to maintain full chart capability and can be used with embedded
cartography as well as Navionics, Insight and other third-party charting cards compatible
with the system.
When using StructureMap with mapping cards, copy the StructureMap (.smf ) files to the
unit’s internal memory. We recommend keeping copies of StructureMap files on external
mapping cards.
Structure options
You adjust the StructureMap settings from the Structure options menu. The menu is
available when Structure overlay is enabled.
Not all options are available when saved StructureMap files are used as the source.
Unavailable options are greyed.
88
Range
Sets the search range.
StructureMap | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 89

Transparency
Sets the opaqueness of the Structure overlay. With minimum transparency settings, the chart
details are almost hidden by the StructureMap overlay.
Palette
Selects Structure palette.
Contrast
Determines the brightness ratio between light and dark areas of the screen.
Water column
Shows/hides the water column in Live mode.
If turned OFF schools of bait fish might not be seen on the SideScan image.
If turned ON the accuracy of the SideScan image on the map might be affected by the water
depth.
Frequency
Sets the transducer frequency used by the unit. 800 kHz offers the best resolution, while 455
kHz has greater depth and range coverage.
Noise rejection
Signal interference from bilge pumps, engine vibration and air bubbles can clutter the sonar
screen. The noise rejection option filters the signal interference and reduces on-screen
clutter.
Clear live history
Clears existing live history data from the screen and begins showing only the most current
data.
Record data
Records StructureScan data.
Source
Selects StructureMap source.
StructureMap | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
89
Page 90
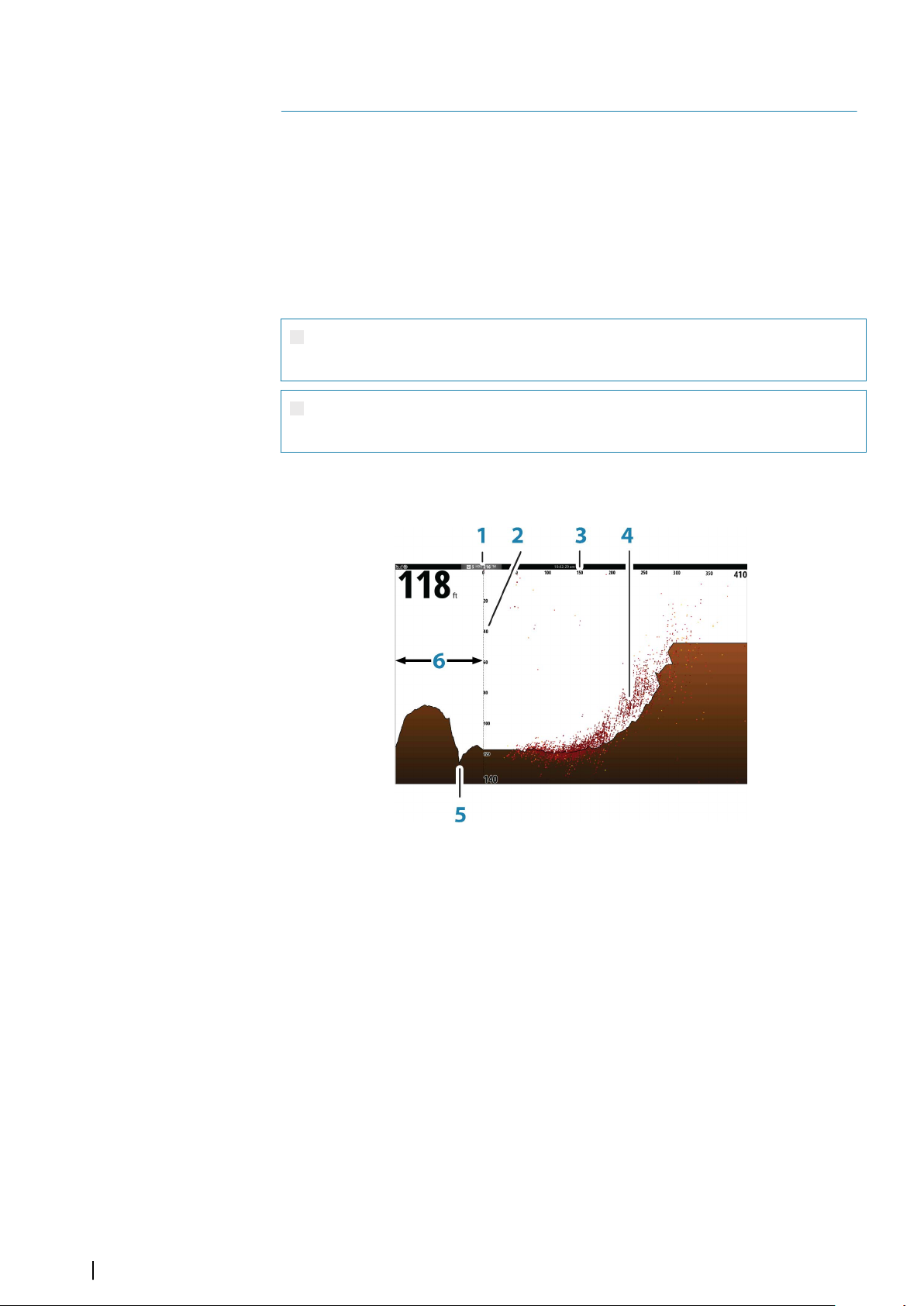
13
ForwardScan
ForwardScan sonar is a navigational aid that helps you monitor the underwater environment
in front of your vessel while carrying out slow speed maneuvers.
To use the ForwardScan feature you must have a ForwardScan transducer mounted on your
vessel. For installation instructions, refer to the ForwardScan transducer installation manual.
The ForwardScan transducer can be connected to a SonarHub and shared over the Ethernet
network. You can also connect the ForwardScan transducer to the Sonar2 port on your NSS
evo3 unit, leaving the Sonar1 port available for a CHIRP transducer.
Note: When a ForwardScan transducer connected to the NSS evo3 is in use. Transducers
Ú
connected to Sonar1 port will be paused.
Warning: Do not rely on this equipment as your principle source of
navigation or hazard detection.
Warning: Do not use this equipment to gauge depth or other conditions
for swimming or diving.
The ForwardScan image
90
1 Transducer location shown as the origin on the page
2 Depth range scale and vessel position
3 Forward range scale
4 Point data
5 Bottom
6 Depth history
ForwardScan | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 91

Setting up the ForwardScan image
Depth
Controls depth range. Depth range is set to auto mode by default.
Forward range
Controls the forward looking search range. Maximum Forward range is 91 meters (300 feet).
Noise Rejection
Filters out signal interference and reduces on-screen clutter.
Record
Records ForwardScan sonar logs.
Pause
Pauses forward-looking Echosounder transmissions.
ForwardScan view options
Palette
Several display palettes are available for a variety of water conditions.
History ratio
Controls how much Echosounder history is shown behind the boat. The higher the ratio, the
more history will be shown.
Point data
By default, ForwardScan only shows the bottom. Select the Point data menu option to
specify to view no sonar data points, all sonar data points, or only points (Objects) in the
water column.
Show zones
Displays warning zones (yellow) and critical zones (red) on the screen. Refer to "Critical forward
range and Critical depth" on page 92.
Depth lines
Displays lines on the screen that make it easier to quickly estimate depth and the underwater
objects.
Heading extension
You can use the heading extension to monitor ForwardScan on the chart panel. Heading
extension colors are based on the ForwardScan alarm values.
ForwardScan | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
91
Page 92

ForwardScan extension
1 Red - Critical
2 Yellow - Warning
3 Green - Safe
Select ForwardScan in the Chart Settings dialog to view the ForwardScan heading extension
on the chart panel.
ForwardScan setup
Specify the setup in the ForwardScan installation dialog.
Critical forward range and Critical depth
Critical Forward Range and Critical Depth are user-selected thresholds that define a critical
zone forward of your vessel.
If you travel into water shallow enough to cross into the critical zone, the Critical Zone alarm
is activated. You can display the critical warning zones by activating the Show zones menu
option.
92
ForwardScan | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 93

ForwardScan image with Show zones active
A
B
1 Critical zone
2 Warning zone
Warning Forward Range and Warning Depth values are based on the selected Critical
Forward Range and Critical Depth values.
Note: To receive Critical Zone alerts, enable ForwardScan alarm in the Alarm settings
Ú
dialog. For more information about enabling alarms, refer to Alarms.
Transducer angle
We recommend installing the transducer vertical to the waterline. In cases where that is not
possible, the Transducer Angle setting helps offset the difference between the transducer
angle and the waterline.
The angle can be adjusted from 0 (vertical) to 20 degrees.
Warning: Adjustments to the transducer angle value should be done with
caution. Large variations in the transducer angle value can distort depth
data, increasing the risk of striking underwater obstructions.
Depth offset
All transducers measure water depth from the transducer to the bottom. As a result, water
depth readings do not account for the distance from the transducer to the lowest point of
the boat (for example; bottom of the keel, rudder, or skeg) in the water or from the
transducer to the water surface.
Before setting the offset, measure the distance from the transducer to the lowest point of the
boat in the water or from the transducer to the water surface.
ForwardScan | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
93
Page 94

A Lowest point of vessel offset: Set the distance from the transducer to the lowest
point of the boat in the water - this should be set as a negative value. For example,
- 0.3 m (-1 ft).
B Depth below surface (waterline) offset: Set the distance from the transducer to the
surface - this should be set as a positive value. For example, +0.5 m (+1.77 ft).
For depth below transducer, set the offset to 0.
94
ForwardScan | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 95
14
Wireless connection
GoFree wireless connectivity gives you the ability to:
• Use a wireless device to remotely view (smartphone and tablet) and control the system
(tablet only).
• Access the GoFree Shop.
• Upload your Echosounder logs to create custom maps at Insight Genesis.
• Download software updates
• Connect to third party applications
Note: Maps, charts, software updates, and other data files can be large. Your data
Ú
provider may charge you based on the amount of data you transfer. If you are unsure
contact the service provider for information.
The unit includes Built-in wireless functionality for connecting to the internet and wireless
devices such as smartphones and tablets.
Initial configuration and setup of the built-in wireless functionality is described in your
system's Installation Manual.
Connect and disconnect from a wireless hotspot
To connect to a wireless hotspot, select the Wireless option in the System Controls dialog
and then select Not Connected. This opens the Wireless Devices dialog. Use this dialog to
select the desired hotspot, enter the login information and then select Connect. Connecting
to a wireless hotspot changes the wireless mode to Client mode. In this mode, you can
access the GoFree Shop.
To disconnect from a wireless hotspot, select the Wireless option in the System Controls
dialog, then select Connected hotspot_name, and then Disconnect. This changes the wireless
mode to Access point mode. In this mode, you can connect a wireless device so that Apps
such as GoFree Link can access the vessel's navigation information.
GoFree Shop
The wireless must be connected to an external wireless hotspot in order to access the
GoFree Shop.
At the GoFree Shop you can browse, purchase and download compatible content for your
system including navigation charts and Insight Genesis Maps. When you log on, the system
automatically gives you a notification if a new software version is available for your system. If
an update is available, you can download it to a card slot or defer the download until later. If
you defer the download until later, the notification is available in the About dialog accessible
from the System Settings.
GoFree Link
The wireless functionality lets you use a wireless device to remotely view (smartphone and
tablet) and control the system (tablet only). The system is viewed and controlled from the
wireless device by the GoFree Link Apps downloaded from their relevant Application store.
When remote control is accepted, the active page is mirrored to the wireless device.
Note: To use smartphones and tablets to view and control the system, wireless
Ú
functionality must be disconnected from the wireless hotspot (in Access point mode).
Note: For safety reasons, Autopilot and CZone functions cannot be controlled from a
Ú
wireless device.
Connecting a tablet
Install the GoFree App on the tablet before following this procedure.
Wireless connection | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
95
Page 96

1. Set the internal wireless to Access Point mode. To do this, select the Wireless devices
page in the Wireless settings dialog and then select the Internal wireless. Next, select the
Mode option and then select Internal Access Point.
2. Select a device on the Wireless devices page to view its network key.
3. Navigate to the wireless network connection page on the tablet, and find the unit or
GoFree wireless xxxx network. If more than one is in range, review the Wireless devices
page on the unit to confirm which wireless device is connected to the unit.
4. Enter the Network Key in the tablet to connect to the network.
5. Open the GoFree application - the unit should be automatically detected. The name
displayed will be either the default, or that assigned in the Device Name setting. If the unit
does not appear, follow the on screen instructions to manually find the device.
6. Select the graphic icon of the unit. The unit displays a prompt similar to the following:
7. Select Yes for one-time connection, or Always if device is to be remembered for regular
connection. This setting can be changed later if required.
Note: The internal wireless module only supports GoFree connection to itself. Other
Ú
units connected on the network are not visible.
Connecting a smartphone
Install the GoFree App on the smartphone before following this procedure.
1. Set the internal wireless to Access Point mode. To do this, select the Wireless devices
page in the Wireless settings dialog and then select the unit's Internal Wireless. Next,
select the Mode option and then select Internal Access Point.
2. Select a device on the Wireless devices page to view its Network Key.
3. Navigate to the wireless network connection page on the smartphone, and find the unit
or GoFree wireless xxxx network. If more than one is in range, review the Wireless devices
page from the unit's Wireless settings dialog to confirm which wireless device is
connected to the unit.
4. Enter the Network Key in the smartphone to connect to the network.
5. Open the GoFree application on the smartphone, the unit should be automatically
detected. The name displayed will be either the default, or that assigned in the Device
Name setting. If the unit does not appear, follow the on screen instructions to manually
find the device.
The MFD's display is shown on the smartphone. To change the MFD's display on the
smartphone, use the MFD to change the display on the MFD. The display change on the
MFD is reflected on the smartphone.
96
Uploading log files to Insight Genesis
To upload a recorded Echosounder log file to Insight Genesis, select the file you want to
upload from the Files panel and select the upload to Insight Genesis option.
Note: You must be connected to a wireless hotspot to upload recorded log files to
Ú
Insight Genesis.
Note: Recorded log files can also be uploaded to Insight Genesis if you have specified
Ú
Upload to Insight Genesis in the Record Echo dialog. For more information, refer to
"Start Recording log data" on page 78.
Wireless connection | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 97

Wireless settings
Provides configuration and setup options for the wireless functionality.
For more information, refer to the NSS evo3 Installation Manual.
Connect to a wireless hotspot
Displays the Wireless device dialog that you can use to connect the wireless functionality to a
wireless hotspot.
Remote controllers
When a wireless device (smart phone or tablet) is connected, it should appear in the Remote
controllers list. Selecting Always allow means the device can automatically connect without
needing a password each time. This menu also allows you to disconnect devices that no
longer require access.
Wireless devices
This dialog shows the internal wireless and any connected WIFI-1 devices, as well as their IP
and channel number. Selecting the internal wireless or a WIFI-1 device provides additional
detail.
To view and change internal wireless detail values (Network Name (SSID), Network Key, or
Channel) the internal wireless must be in Access Point (Internal Wifi) mode. To select a
network (hotspot) to connect to, the internal wireless must be in Client Mode. Use the
Mode option to change modes.
Client settings
Displays information about the wireless hotspot your unit is connected to or the last one
your unit was connected to. You can select the hotspot in the dialog to set it as a hotspot
you want to always connect to when in range or you can select to delete it.
Advanced
Initiates the Iperf and DHCP Probe tools that help in fault-finding and setting up the wireless
network.
Note: Iperf and DHCP Probe are tools provided for diagnostic purposes by users familiar
Ú
with network terminology and configuration. Navico is not the original developer of
these tools, and does not provide support related to their use.
Wireless connection | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
97
Page 98

15
AIS
If a compatible AIS (Automatic Identification System) source is connected to the system, then
any targets detected by these devices can be displayed and tracked. You can also see
messages and position for DSC transmitting devices within range.
AIS targets can be displayed as overlay on radar and chart images, making this feature an
important tool for safe travelling and collision avoidance.
You can set alarms to notify you if an AIS target gets too close or if the target is lost.
AIS vessels on a chart panel
AIS target symbols
The system uses the AIS target symbols shown below:
Sleeping AIS target (not moving or at anchor).
Moving and safe AIS target with course extension line.
Dangerous AIS target, illustrated with bold line.
A target is defined as dangerous based on the CPA and TCPA settings. Refer
to "Defining dangerous vessels" on page 102.
Lost AIS target.
When no signals have been received within a time limit, a target is defined
as lost.
The target symbol represents the last valid position of the target before the
reception of data was lost.
Selected AIS target, activated by selecting a target symbol.
The target returns to the default target symbol when the cursor is removed
from the symbol.
AIS vessels on a radar panel
98
AIS SART (AIS Search And Rescue Transmitter).
Viewing information about AIS targets
Searching for AIS items
You can search for AIS targets by using the Find option in the Tools panel.
From a chart panel you can search for AIS targets by using the Find option in the menu. If
the cursor is active, the system searches for vessels around the cursor position. Without an
active cursor, the system searches for vessels around your vessel's position.
AIS | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
Page 99

Viewing information about single AIS targets
When you select an AIS icon on the chart or radar panel the symbol changes to Selected
target symbol, and the vessel's name is displayed.
You can display detailed information for a target by selecting the AIS pop-up, or from the
menu when the target is selected.
AIS information on radar panels
The radar data bar includes information on up to 3 AIS targets.
The targets are listed with the closest target on top, and are color coded to indicate target
status.
Calling an AIS vessel
If the system includes a VHF radio supporting DSC (Digital Select Calling) calls over NMEA
2000, you can initiate a DSC call to other vessels from the NSS evo3.
The call option is available in the AIS Vessel Details dialog, and in the Vessel status dialog
activated from the Tools panel.
From the Call dialog you can change channel or cancel the call. The Call dialog is closed
when the connection is established.
AIS SART
When an AIS SART (Search and Rescue beacon) is activated, it starts transmitting its position
and identification data. This data is received by your AIS device.
If your AIS receiver is not compliant with AIS SART, it interprets the received AIS SART data as
a signal from a standard AIS transmitter. An icon is positioned on the chart, but this icon is an
AIS vessel icon.
If your AIS receiver is compliant with AIS SART, the following takes place when AIS SART data
is received:
AIS | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
99
Page 100
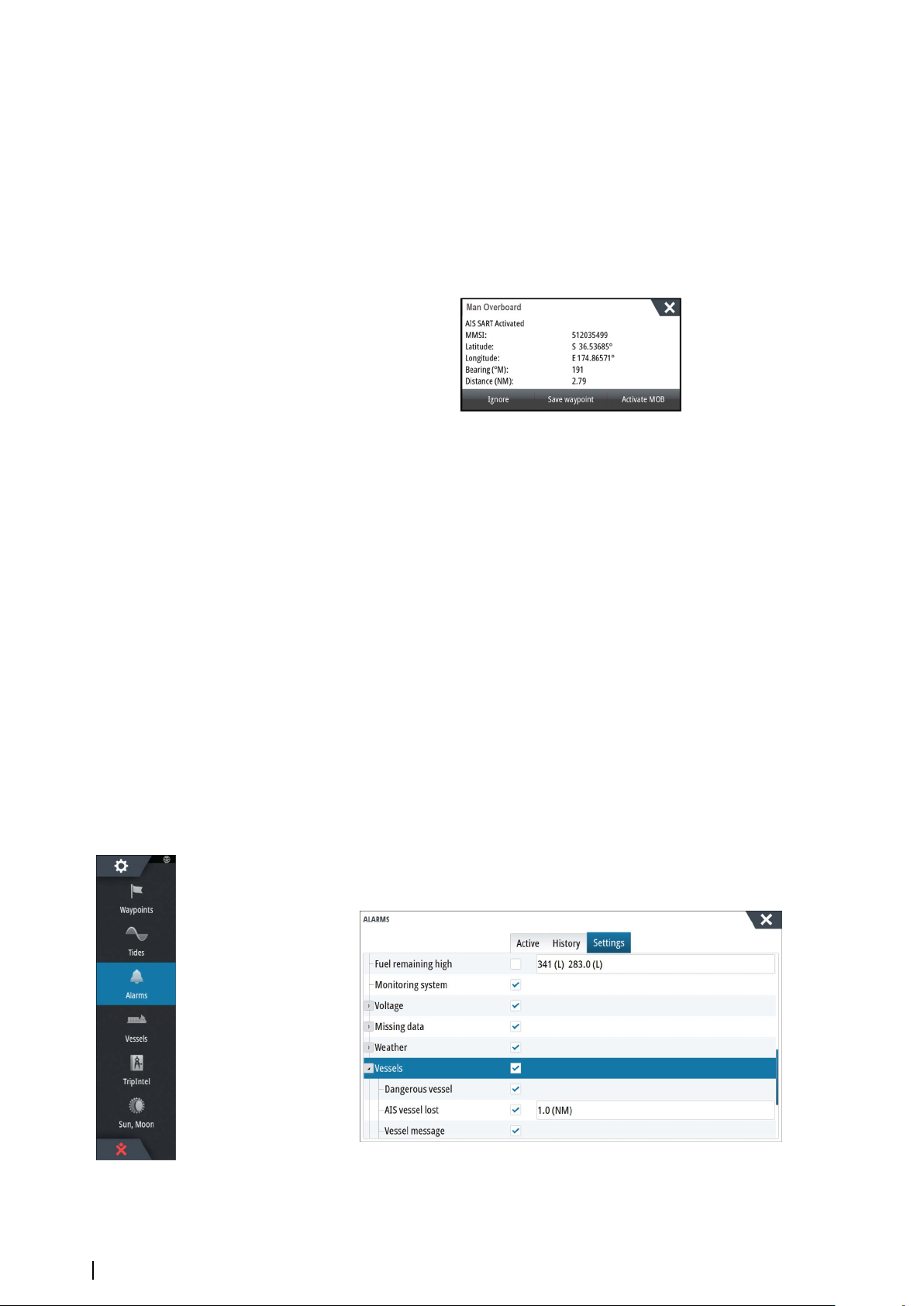
• An AIS SART icon is located on the chart in the position received from the AIS SART
• An alarm message is displayed
If you have enabled the siren, the alarm message is followed by an audible alarm.
Note: The icon is green if the received AIS SART data is a test and not an active message.
Ú
AIS SART alarm message
When data is received from an AIS SART, an alarm message is displayed. This message
includes the AIS SART’s unique MMSI number, and its position, distance, and bearing from
your vessel.
You have the following options:
• Ignore the alarm
The alarm is muted and the message closed. The alarm does not reappear
-
Note: If you ignore the alarm, the AIS SART icon remains visible on your chart, and the
Ú
AIS SART remains in the Vessels list.
• Save the waypoint
The waypoint is saved to your waypoint list. This waypoint name is prefixed with MOB
AIS SART - followed by the unique MMSI number of the SART. For example, MOB AIS
SART - 12345678.
• Activate the MOB function
- The display switches to a zoomed chart panel, centered on the AIS SART position
- The system creates an active route to the AIS SART position
Note: If the MOB function is already active, this will be terminated and replaced by the
Ú
new route towards the AIS SART position!
Note: If the AIS stops receiving the AIS SART message, the AIS SART remains in the
Ú
Vessels list for 10 minutes after it receives the last signal.
If you select the AIS SART icon on the chart panel, then you can see the AIS MOB details.
Vessel alarms
You can define several alarms to alert you if a target shows up within predefined range limits,
or if a previously identified target is lost.
100
AIS | NSS evo3 Operator Manual
 Loading...
Loading...