Page 1

ENGLISH
HS80/HS80A
MX575C/MX575D
GPS Compass
Manual
navico.com/commercial
Page 2

Page 3

| 1
Preface | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
Preface
Disclaimer
As Navico is continuously improving this product, we retain the right to make changes to the
product at any time which may not be reflected in this version of the manual. Please contact
your nearest distributor if you require any further assistance.
It is the owner’s sole responsibility to install and use the equipment in a manner that will
not cause accidents, personal injury or property damage. The user of this product is solely
responsible for observing safe boating practices.
NAVICO HOLDING AS AND ITS SUBSIDIARIES, BRANCHES AND AFFILIATES DISCLAIM ALL
LIABILITY FOR ANY USE OF THIS PRODUCT IN A WAY THAT MAY CAUSE ACCIDENTS, DAMAGE
OR THAT MAY VIOLATE THE LAW.
Governing Language: This statement, any instruction manuals, user guides and other
information relating to the product (Documentation) may be translated to, or has been
translated from, another language (Translation). In the event of any conflict between any
Translation of the Documentation, the English language version of the Documentation will be
the official version of the Documentation.
This manual represents the product as at the time of printing. Navico Holding AS and its
subsidiaries, branches and affiliates reserve the right to make changes to specifications
without notice.
Compliance
The smart GPS compass systems complies with the following regulations:
- MX575C/HS80: Annex A.1 - 4.41 Transmitting heading device THD (GNSS method)
- Annex A.1 - 4.14 GPS equipment
Annex A.1 - 4.50 DGPS equipment
- MX575D/HS80A: Annex A.1 - 4.41 Transmitting heading device THD (GNSS method)
- Annex A.1 - 4.14 GPS equipment
Annex A.1 - 4.15 GLONASS equipment
- Annex A.1 - 4.50 DGPS equipment
Annex A.1 - 4.51 DGLONASS equipment
See also “Certifications” on page 32
For more information please refer to our website:
www.navico.com/commercial or www.simrad-yachting.com
The Wheelmark
The HS80 / MX575C systems are produced and tested in accordance with the European
Marine Equipment Directive 2010/68/EU, while the HS80A/MX575D systems are produced
and tested in accordance with the Marine Equipment Directive 96/98 EC as amended by
directive (EU) 2015/559. This means that the systems comply with the highest level of tests for
nonmilitary marine electronic navigation equipment existing today.
The Marine Equipment Directive for ships flying EU or EFTA flags, applies to all new ships, to
existing ships not previously carrying such equipment, and to ships having their equipment
replaced.
This means that all system components covered by annex A.1 must be type-approved
accordingly and must carry the Wheelmark, which is a symbol of conformity with the Marine
Equipment Directive.
Copyright
Copyright © 2016 Navico Holding AS.
Page 4
2 |
Preface | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
Warranty
The warranty card is supplied as a separate document.
In case of any queries, refer to the our website:
www.navico.com/commercial or www.simrad-yachting.com
About this manual
This manual is a reference guide for installing and using the HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D
GPS compass systems.
The latest available manual version can be downloaded from our web sites.
Important text that requires special attention from the reader is emphasized as follows:
¼ Note: Used to draw the reader’s attention to a comment or some important information.
Warning: Used when it is necessary to warn personnel that they
should proceed carefully to prevent risk of injury and/or damage to
equipment/personnel.
Page 5

| 3
Preface | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
Contents
4 Introduction
4 Overview
5 Parts list
6 Installation
6 Mounting location
8 Mounting orientation
9 Mounting options
15 Po r ts
19 Powering the Smart GPS compass
20 Connecting the Smart GPS compass to external devices
21 Default parameters
22 Operation
22 GPS overview
22 GLONASS overview
23 Smart GPS compass overview
27 Common commands and messages
31 Technical specications
31 Specifications
32 Certifications
34 Output messages
41 Proprietary Input data messages
48 Troubleshooting
50 List of abbreviations
51 Wiring Diagrams
51 MX420 CDU to GPS compass interface diagram
51 MX510/MX512 to GPS compass interface diagram
52 GPS compass interface via MX510 junction Box
53 MX512 to GPS compass interface diagram via MX512 Junction Box
54 1PPS output
54 PC to GPS compass interface diagram
55 GPS compass connection to the MX61xJB junction box.
57 HS80/HS80A connection via the NMEA 2000 network
Page 6

4 |
Introduction | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D Manual
Introduction
Overview
The HS80/HS80A GPS Compass and the MX575C/MX575D DGPS Compass are based upon a
new generation GPS engine technology.
Figure 1-1: HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D side view
¼ Note: When referring to both the HS80/HS80A GPS Compass and the MX575C/MX575D
DGPS Compass this manual uses the term smart GPS Compass. When referring to either
product, this manual uses either HS80/HS80A or MX575C/MX575D, respectively.
The smart GPS compass is a complete GPS compass and positioning system in a single
enclosure that requires only one power/data cable connection. With its NMEA 2000/NMEA
0183 support and ease of installation, it is the perfect solution for marine applications.
The HS80/MX575C is an integrated system that houses the following:
- New GPS engine technology
- Two GPS antennas
- Beacon receiver and H-Field beacon antenna (MX575C/D only)
The HS80A/MX575D is an integrated system that houses the following:
- New GPS + GLONASS engine technology
- Two Dual-Frequency GPS/GLONASS antennas
- Beacon receiver and H-field beacon antenna (MX575D only)
Common items in all the GPS compass models are:
- Power supply
- Single axis gyro
- Tilt sensor on each axis (X and Y axes)
The gyro and tilt sensors are present in all models to improve system performance and to
provide backup heading information in the event that GPS heading is not available due to
signal blockage.
¼ Note: The HS80/HS80A GPS Compass is identical to the MX575C/MX575D DGPS Compass
with the exception that it does not contain a DGPS beacon receiver and H-field antenna. If
you purchased the HS80/HS80A GPS Compass, disregard the sections of this manual that
discuss the beacon signal, receiver operation, and implications to installation relating to the
beacon signal.
The new GPS engine technology supports multiple RF front ends - enabling tighter coupling
of measurements from separate antennas for use in heading-based products. Users will
achieve excellent accuracy and stability due to the more accurate code phase measurements,
improved multipath mitigation, and fewer components.
The two smart GPS antennas are separated by 50 cm between their phase centers, resulting in
+/- 0.5° RMS heading performance. The smart GPS compass provides heading and positioning
updates of up to 20 Hz and delivers positioning accuracy of less than 1.0 m 95% of the time
when using differential GPS corrections from beacon (MX575C/MX575D only) or from Space
Based Augmentation Systems (SBAS).
Page 7

| 5
Introduction| HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D Manual
The smart GPS compass also features the GPS’ exclusive COAST™ technology that enables the
GPS receivers to utilize old differential GPS correction data for 40 minutes or more without
significantly affecting the positioning quality. The MX575C/MX575D is less likely to be
affected by differential signal outages due to signal blockages, weak signals, or interference
when using COAST.
Parts list
¼ Note: The HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D’s parts comply with IEC 60945 Section 4.4:
“exposed to the weather.”
The sections below list parts included in your HS80/HS80A kit and the MX575C/MX575D kit.
HS80/HS80A Parts list
Part Name Qty Part number
HS80 GPS Compass, or
HS80A GPS Compass
1
1
000-10938-001
000-11643-001
Serial-to-NMEA 2000 adapter 1 000-10941-001
Manual 1 988-10221-002
Kit containing the following:
• Clamp 1
• Screw 1
• Washer 1
Optional items
15 meter Power/data cable 000-10939-001
30 meter antenna cable 000-10940-001
MX575C/MX575D Parts list
Part Name Qty Part number
MX575C DGPS Compass, or
MX575D DGPS Compass
1
1
000-10747-001
000-11644-001
Power/data cable, 15 m 1 000-10939-001
Manual 1 988-10221-002
Kit containing the following:
• Clamp 1
• Screw 1
• Washer 1
Optional items
Serial-to-NMEA 2000 adapter 000-10941-001
30 meter antenna cable 000-10940-001
Page 8

6 |
Installation | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D UserManual
Installation
Mounting location
This section provides information on determining the best location for the Smart GPS compass.
GPS reception
When considering where to mount the Smart GPS compass, consider the following GPS
reception recommendations:
• Consider GPS reception, ensuring there is a clear view of the sky available to the Smart
GPS compass so the GPS satellites are not masked by obstructions that may reduce system
performance
• Since the Smart GPS compass computes a position based on the internal primary GPS antenna
element, mount the Smart GPS compass where you desire a position with respect to the
primary GPS antenna (located on the end opposite the recessed arrow on the underside of the
enclosure).
• Locate any transmitting antennas away from the GPS Compass by at least a few meters to
ensure tracking performance is not compromised, giving you the best performance possible
• Make sure there is enough cable length to route into the vessel to reach a breakout box or
terminal strip
• Do not locate the antenna where environmental conditions exceed those specified in
“Environmental” on page 32.
Beacon reception
When using the MX575C/MX575D internal beacon receiver as the correction source, consider
the possible mounting locations from the perspective of ambient noise within the beacon
band (300 KHz).
Keep the following in mind when deciding upon a location with respect to maximizing beacon
performance:
• Ensure that the antenna is as far as possible from all other equipment that emits electromagnetic
interference (EMI) such as DC motors, alternators, solenoids, radio transmitters, power cables,
display units, and other electronic devices.
• If you are installing the antenna on a vessel, mount the MX575C/MX575D considering
maintenance and accessibility. In addition, ensure that the antenna is not obscured by the
metal mast, guy wires or metal railings on the vessel.
• If radar(s) or INMARSAT system is present, mount the GPS Compass antenna outside the path
of the transmission beam.
The MX575C/MX575D’s internal beacon receiver calculates a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR),
measured in decibels (dB) that indicates the receiver’s performance. The SNR is the height of the
signal above the noise floor: the higher the SNR, the better your beacon receiver demodulates
the signal. The optimum antenna location will be a position where your average SNR is highest.
You should turn on all accessories that you intend to use during normal operation when
locating the best position for the antenna. By monitoring the SNR, you can determine the
optimum location with respect to beacon reception. The SNR is available in the GPS6 (Beacon
Status) screen of the MX CDU.
2
Page 9
| 7
Installation | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
Environmental considerations
The Smart GPS compass is designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions; however,
adhere to the following limits when storing and using the GPS Compass:
• Operating temperature: -30°C to +70°C (-22°F to +158°F)
• Storage temperature: -40°C to +85°C (-40°F to +185°F)
• Humidity: 95% non-condensing
VHF interference
VHF interference from such devices as cellular phones and radio transmitters may interfere
with GPS operation. For example, if installing the Smart GPS compass near marine radios
consider the following:
• VHF marine radio working frequencies (Channels 1 to 28 and 84 to 88) range from 156.05 to
157.40 MHz. The GPS working center frequency is 1575.42 MHz. The bandwidth is +/- 2MHz to
+/- 10 MHz, which is dependent on the GPS antenna and receiver design
• VHF marine radios emit strong harmonics. The 10th harmonic of VHF radio, in some channels,
falls into the GPS working frequency band, which may cause the SNR of GPS to degrade
significantly
• The radiated harmonic signal strength of different brands/models varies.
• Follow VHF radio manufacturers’ recommendations on how to mount their radios and what
devices to keep a safe distance away.
• Handheld 5W VHF radios may not provide suitable filtering and may interfere with the Smart
GPS compass’s operation if too close.
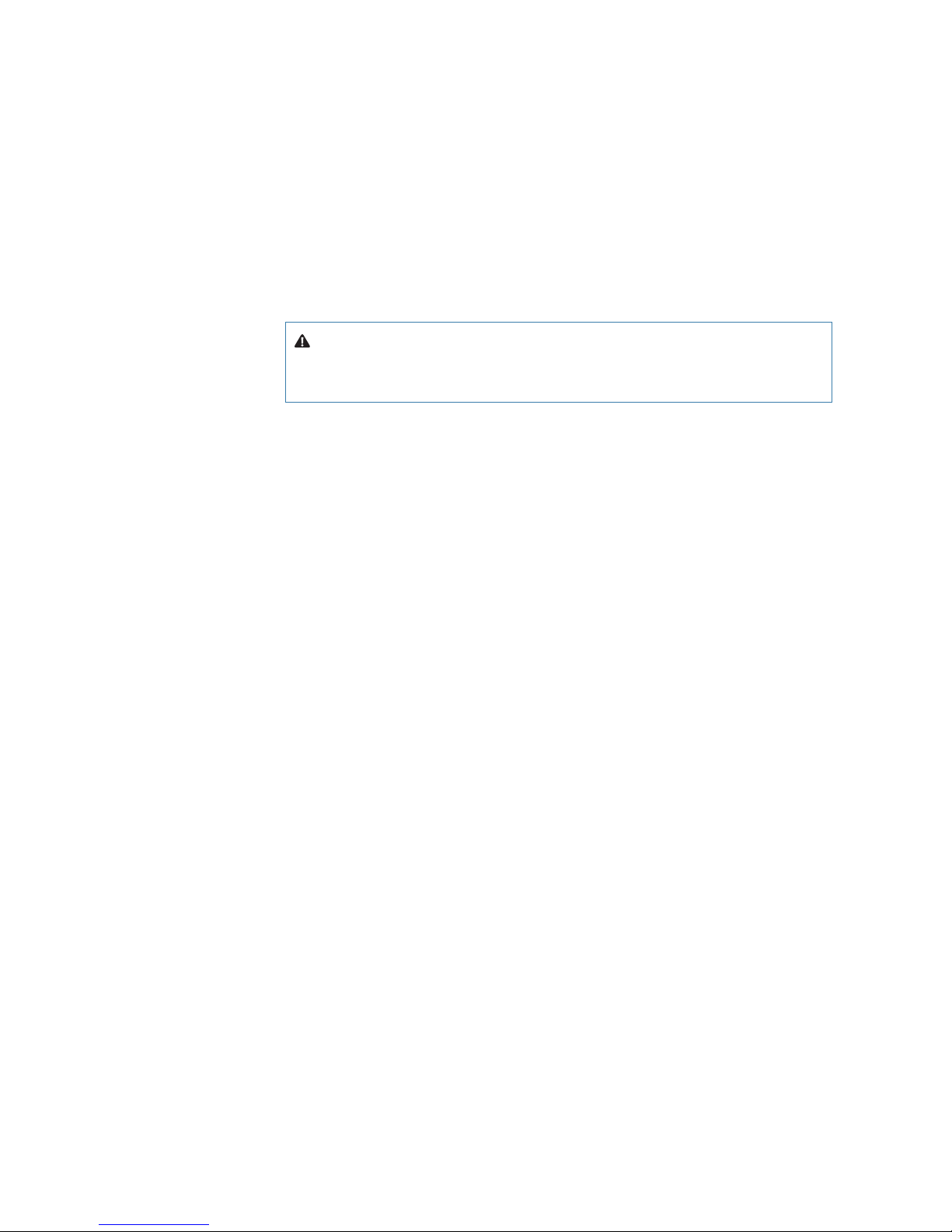
Before installing the Smart GPS compass use the following diagram to ensure there are no
nearby devices that may cause VHF interference.
Use these minimum distances
to determine where to place
the Smart GPS compass
1.5 m radius at top
(minimum)
1.0 m radius at base (minimum)
VHF antenna
Figure 2-1: Smart GPS compass minimum distance from nearby VHF radios
Page 10
8 |
Installation | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D UserManual
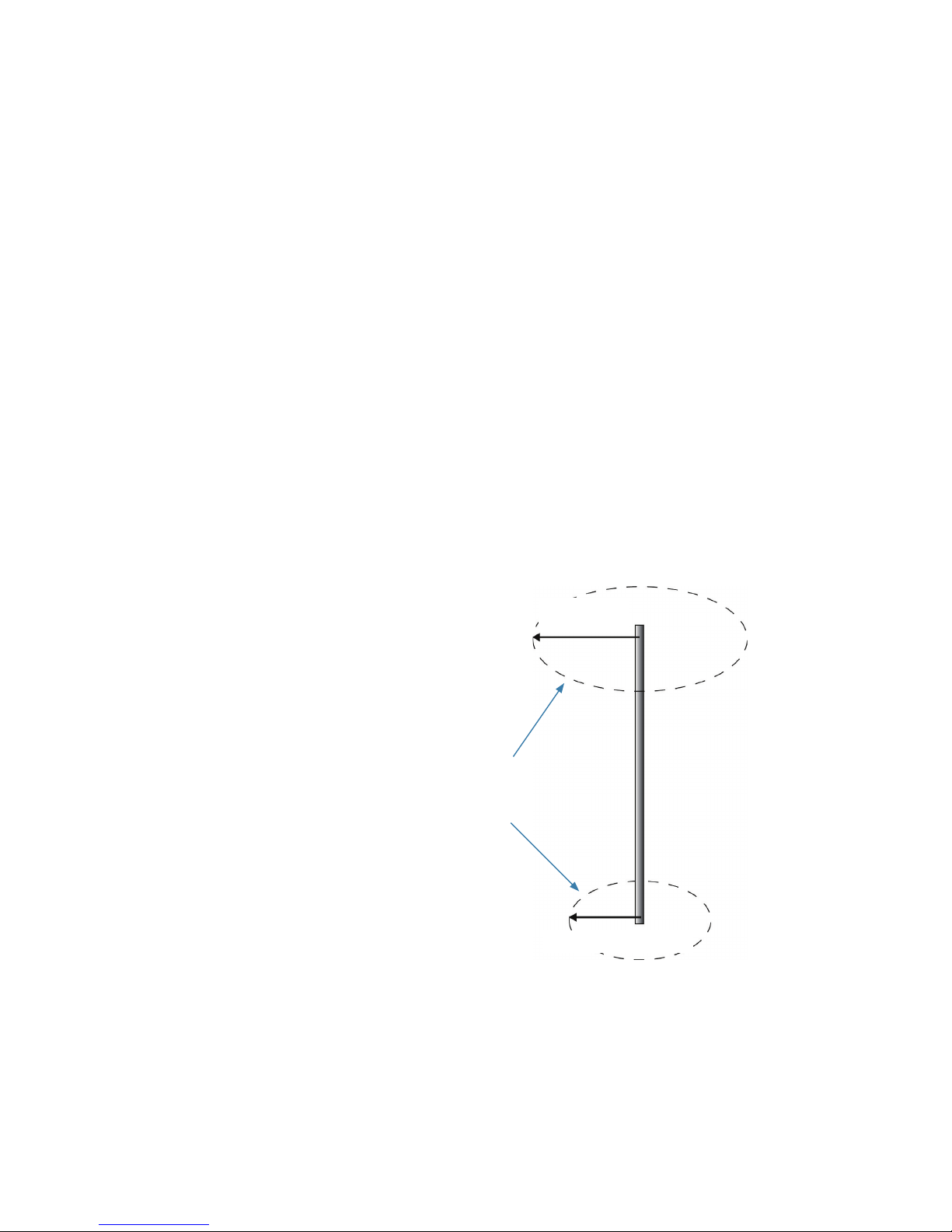
Mounting orientation
The smart GPS compass outputs heading, pitch, and roll readings regardless of the orientation
of the antennas. However, the relation of the antennas to the boat’s axis determines whether
you will need to enter a heading, pitch, or roll bias. The primary antenna is used for positioning
and the primary and secondary antennas, working in conjunction, output heading, pitch, and
roll values.
¼ Note: Regardless of which mounting orientation you use, the Smart GPS compass provides
the ability to output the heave of the vessel. This output is available via the $GPHEV message.
Parallel orientation
The most common installation is to orient the Smart GPS compass parallel to, and along the
centerline of, the axis of the boat. This provides a true heading. In this orientation:
• If you use a gyrocompass, you can enter a heading bias in the Smart GPS compass to calibrate
the physical heading to the true heading of the vessel.
• You may need to adjust the pitch/roll output to calibrate the measurement if the Vector is not
installed in a horizontal plane.
Perpendicular orientation
You can also install the antennas so they are oriented perpendicular to the centerline of the
boat’s axis. In this orientation:
• You will need to enter a heading bias of +90° if the primary antenna is on the starboard side of
the boat and -90° if the primary antenna is on the port side of the boat.
• You will need to configure the receiver to specify the GPS antennas are measuring the roll axis
using $JATT,ROLL,YES.
• You will need to enter a roll bias to properly output the pitch and roll values.
• You may need to adjust the pitch/roll output to calibrate the measurement if the Vector is not
installed in a horizontal plane.
Figure 2-2 and Figure 2-3 provide mounting orientation examples.
Recessed arrow located on
the bottom of the enclosure
Forward motion
Figure 2-2: Recommended orientation and resulting signs of HPR values
Page 11

| 9
Installation | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
Recessed arrow located on
the bottom of the enclosure
Forward motion
Figure 2-3: Alternate orientation and resulting signs of HPR values
Smart GPS compass alignment
The top of the Smart GPS compass enclosure incorporates sight design features to help you
align the enclosure with respect to an important feature on your vessel.
To use the sights, center the small post on the opposite side of the enclosure from you, within
the channel made in the medallion located in the center of the enclosure top as shown in
Figure 2-4 and Figure 2-5. Alignment accuracy when looking through the long site (Figure 2-4)
is approximately +/- 1°, while alignment through the short site (Figure 2-5) is approximately
+/- 2.5°.
Figure 2-4: Long sight alignment Figure 2-5: Short sight alignment
If you have another accurate source of heading data on your vessel, such as a gyrocompass,
you may use its data to correct for a bias in Smart GPS compass alignment within the Smart
GPS compass software configuration. Alternatively, you can physically adjust the heading of
the Smart GPS compass so that it renders the correct heading measurement; however, adding
a software offset is an easier process.
Mounting options
The Smart GPS compass allows for two different mounting options: flush mount and pole
mount.
• Flush mount - The bottom of the Smart GPS compass contains eight M8-1.25 holes for flush
mounting the unit to a flat surface (see Figure 2-6). The eight holes comprise two sets of four
holes. The inner four holes are in the same location as the HS70, allowing you to use the Smart
GPS compass as a drop-in replacement. The outer four holes provide a wider mounting option.
• Pole mount - The bottom of the Smart GPS compass contains a mounting hole (1” thread, 0.9”
depth) for easy pole mounting. Hand tighten until snug (do not over tighten). The set screws
on the long sides of the base (see middle drawing in Figure 2-6) allow you to secure the Smart
GPS compass in place (3/16” Allen wrench not included).
Page 12

10 |
Installation | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D UserManual
Smart GPS compass dimensions
Figure 2-6 illustrates the physical dimensions of the Smart GPS compass.
Figure 2-6: HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D Smart GPS compass dimensions
Page 13

| 11
Installation | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
Power/Data cable considerations
Before mounting the Smart GPS compass consider the following regarding power/data cable
routing:
• Cable must reach an appropriate power source
• Cable may connect to a data storage device, computer, or other device that accepts GPS data
• Avoid running the cable in areas of excessive heat
• Keep cable away from corrosive chemicals
• Do not run the cable through door or window jams
• Keep cable away from rotating machinery
• Do not crimp or excessively bend the cable
• Avoid placing tension on the cable
• Remove unwanted slack from the cable at the Smart GPS compass end
• Secure along the cable route using plastic wraps.
Warning: Improperly installed cable near machinery can be
dangerous.
Mounting the Smart GPS compass
This section describes how to flush mount or pole mount the Smart GPS compass. Keep the
following in mind when planning your installation:
• SIMRAD does not supply mounting surface hardware or a mounting pole. You must supply
the appropriate hardware or mounting pole required to complete Smart GPS compass
installation.
• You do not necessarily need to orient the antenna precisely as you can enter a software offset
to accommodate for a heading measurement bias due to installation.
Flush mounting the Smart GPS compass
The bottom of the Smart GPS compass contains eight holes (two sets of four holes) for
flush mounting the unit to a flat surface (Figure 2-7). The flat surface may be something you
fabricate per your installation, an off-the-shelf item (such as a radar mounting plate), or an
existing surface on your vessel.
Figure 2-7: Flush mounting holes on bottom of Smart GPS compass
Complete the following steps to flush mount the Smart GPS compass:
1. Determine the desired location and proper orientation for the Smart GPS compass.
See “Mounting orientation” on page 8 for information on determining the desired
orientation.
2. Use the supplied template or photocopy the section of the Smart GPS compass that contains
the eight mounting holes (see Figure 2-7) for use as a template to plan the mounting hole
locations. Use the inner four holes or the outer four holes per your installation.
If using a photocopy make sure it is scaled one-to-one with the mounting holes on the
bottom of the Smart GPS compass.
3. Mark the mounting hole centers on the mounting surface.
Page 14
12 |
Installation | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D UserManual
4. Place the Smart GPS compass over the marks to ensure the planned hole centers align with the
true hole centers (adjusting as necessary).
5. Use a center punch to mark the hole centers.
6. Drill the mounting holes with a 9 mm bit appropriate for the surface.
7. Place the Smart GPS compass over the mounting holes and insert the mounting screws
through the bottom of the mounting surface into the Smart GPS compass.
Warning: When installing the Smart GPS compass, hand tighten only.
Damage resulting from over tightening is not covered by the warranty.
Pole mounting the Smart GPS compass
If you need the GPS-assisted roll measurement, install the Smart GPS compass perpendicular to
the vessel’s axis. If you do not need this measurement, install the Smart GPS compass parallel
with the vessel’s axis. For more information refer to Figure 2-2 on page 8 and Figure 2-3 on
page 9.
Complete the following steps to pole mount the Smart GPS compass:
1. Determine the desired location and proper orientation for the Smart GPS compass. See
“Mounting orientation” on page 8“ for information on determining the desired orientation.
2. Hand tighten the Smart GPS compass on the pole until snug (unit is stable on pole) while
ensuring correct orientation.
Warning: Hand tighten only. Damage resulting from over tightening
is not covered by the warranty.
3. Use the set screws on the long sides of the base (see Figure 2-6 on page 10) to secure the
Smart GPS compass in place (3/16” Allen wrench not included).
Page 15

| 13
Installation | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
Connecting the serial cable or Serial-to-NMEA 2000 adapter to the Smart GPS
compass
After you mount the Smart GPS compass connect either the serial power/data cable or the
serial-to-NMEA 2000 adapter to the Smart GPS compass.
Connecting the serial Power/Data cable
1. Align the cable connector keyway with the Smart GPS compass connector key
Connect cable here
2. Rotate the cable ring clockwise until it locks. The Locking action is firm; you will feel a positive
“click” when it has locked.
Cable ring
Cable connector keyway Connector key
3. Attach the power/data cable to the cable clamp.
4. Fasten the clamp to the bottom of the Smart GPS compass using the screw and washer.
5. Attach the cable cover.
Page 16

14 |
Installation | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D UserManual
Connecting the Serial-to-NMEA 2000 adapter
For more information on the serial-to-NMEA 2000 adapter see “NMEA 2000 port” on page 16.
This adapter is an optional item for the MX575C/MX575D model.
1. Align the adapter connector keyway with the Smart GPS compass connector key.
Connect adapter
here
2. Rotate the cable ring clockwise until it locks. The locking action is firm; you will feel a positive
“click” when it has locked.
Cable ring
Cable connector keyway Connector key
3. Fasten the adapter to the body of the Smart GPS compass using the provided screws and the
two slots in the adapter.
4. Attach the cable cover.
Page 17

| 15
Installation | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
Ports
The Smart GPS compass offers either NMEA 0183 serial port or NMEA 2000 port functionality.
Serial ports
The Smart GPS compass has three ports (Port A, Port B, and Port C), where:
• Port A can be both full-duplex RS-232 and half-duplex RS-422 (transmit only)
• Port B is full-duplex RS-422
• Port C is for NMEA 2000 and only available via serial-to-NMEA 2000 adapter
You can receive external differential corrections via either Port A (full-duplex RS-232) or Port
B (full-duplex RS-422). You can connect up to three devices at one time using two ports. One
device can receive data via Port A (RS-422 transmit only) while two devices can transmit and
receive data via Ports A and B (one connected to Port A RS-
232 and one connected to Port B).
¼ Notes:
1. Port A (RS-422) or Port B is required for communicating to an IMO type-approved device.
2. You can update firmware via Port A (RS-232) or Port B.
¼ Note: The MX575C/MX575D has maximum baud rate of 38400. Higher baud rates may impair
beacon signal tracking.
Serial port conguration
You may configure Port A or Port B of the GPS receiver to output any combination of data. Port
A can have a different configuration from Port B in terms of data message output, data rates,
and the baud rate of the port. This allows you to configure the ports independently based upon
your needs.
For example, if you want one generalized port and one heading-only port, you can configure
the ports as follows:
• Port A to have GPGGA, GPVTG, GPGSV, GPZDA, and GPHDT all output at 1 Hz over a 9600 baud
rate.
• Port B for GPHDT and GPROT message output at their maximum rate of 20
Hz over a 19200 baud rate.
The messages you configure each port to output and the rate of the port will be the same
for both RS-232 and RS-422 interface levels. For example, the RS-232 Port A and RS-422 Port A
output the same data messages at the same baud rate. If the baud rate or messages for the RS422 port need to be changed, this needs to be commanded through the RS-232 port.
Both RS-232 and RS-422 output signals may be used simultaneously.
¼ Note: When the smart GPS compass is connected to Port 3 & 4 of the MX line of CDUs (MX420,
MX51x and MX61xJB), the MX unit sends a setup command that configures the smart GPS
compass to adjust to 19,200 baud and turns on only the required NMEA sentences.
Selecting Baud rates and message types
When selecting your baud rate and message types use the following formula to calculate
the bits/sec for each message and then sum the results to determine the baud rate for your
required data throughput.
Message output rate * Message length (bytes) * bits in byte = Bits/second
(1 character = 1 byte, 8 bits = 1 byte, use 10 bits/byte to account for overhead)
See “Common commands and messages” on page 27 for an example of this calculation.
Page 18

16 |
Installation | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D UserManual
Recommendations for connecting to other devices
When interfacing to other devices, ensure the transmit data output from the Smart GPS
compass is connected to the data input of the other device. The signal grounds must also be
connected.
Since RS-422 is a balanced signal with positive and negative signals referenced to ground,
ensure you maintain the correct polarity. For example, when connecting the transmit data
output positive signal to the receive line of the other device, it should be connected to the
receive positive terminal. The negative transmit data signal from the Smart GPS compass is
then connected to the receive data negative input of the other device.
There is likely little reason to connect the receive data input of the Smart GPS compass to
another device unless it is able to send configuration commands to the Smart GPS compass.
Since the Smart GPS compass uses proprietary NMEA 0183 commands for control over its
configuration, the vast majority of electronics will not be able to configure its settings unless
the other device has a terminal setting where you can manually issue commands.
NMEA 2000 port
To use the HS80/HS80A for NMEA 2000 interface, you need to use the Serial-to-NMEA 2000
adapter (P/N 710-0113-000#, see Figure 2-8). This adapter is optional item for the MX575C/
MX575D model. Insert the 18-pin connector of the adapter into the male end of the 18-pin
connector on the HS80/HS80A by aligning the keys. You can then attach the adapter to the unit
using the supplied screws (machine, 8-32, ½”, PPHC, SS) and washer (washer, flat, #8, SS). The
5-pin male Micro-C connector connects to your NMEA 2000 drop cable.
Micro-C connector
18-pin Female
connector
Figure 2-8: Serial-to-NMEA 2000 adapter
The MX575C/MX575D DGPS compass model is supplied with 15 meter interface cable for
NMEA 0183 interface connection. An optional 30-meter NMEA 0183 interface cable can be
ordered separately. The NMEA 2000 interface adapter is another option for the MX575C/
MX575D.
¼ Note: The serial-to-NMEA 2000 adapter is not an IMO requirement and may not be used in
such an application.
The next section shows the requested PGNs with the Smart GPS compass in NMEA 2000
mode.
Page 19
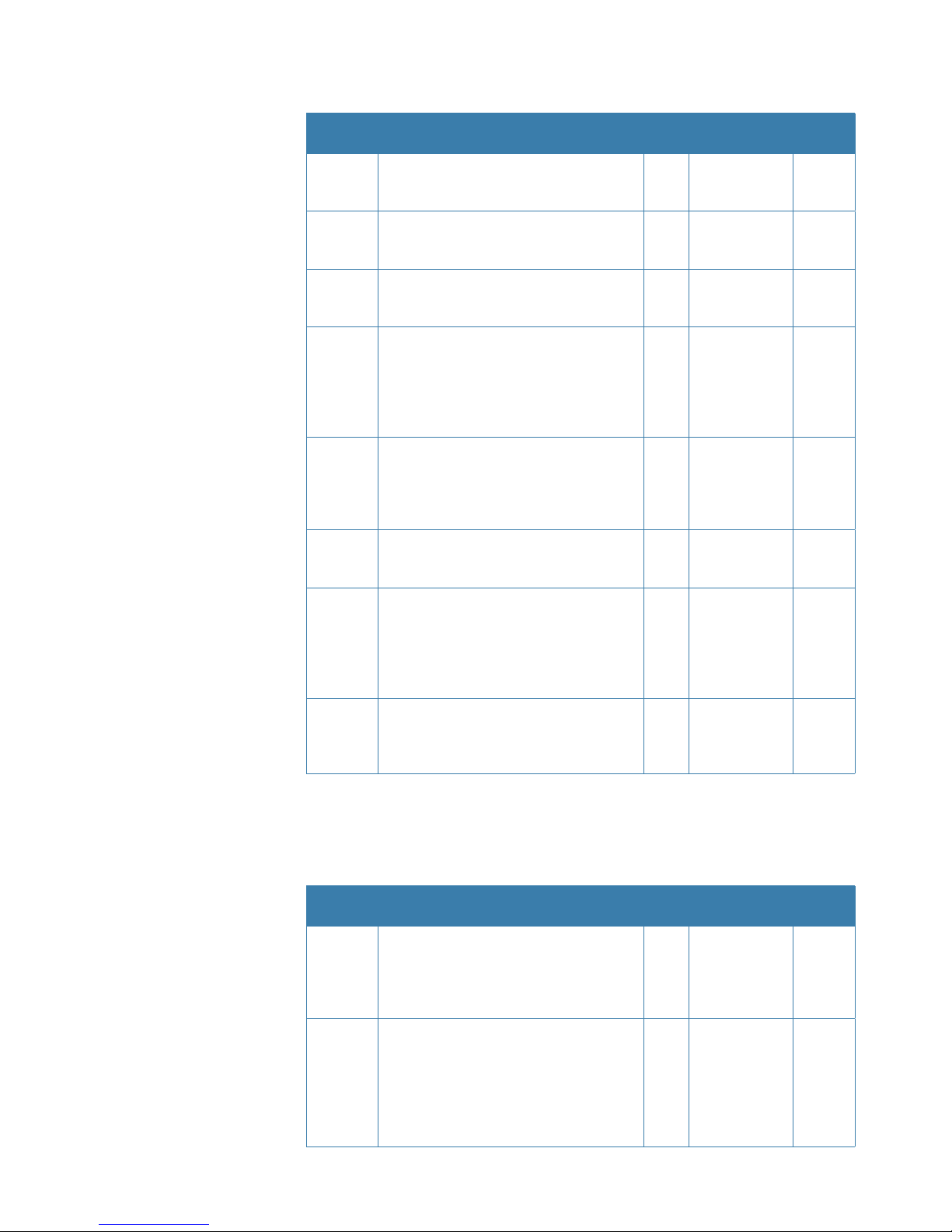
| 17
Installation | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
Received messages based on a request
PG No.
(PGN)
Description Level
Default Update
Rate (msec)
Freq
(Hz)
059392 ISO Acknowledgement
Used to acknowledge the status of certain
requests addressed to a specific ECU.
B On Request On
Request
059904 ISO Request
Request the transmission of a specific PGN,
addressed or broadcast.
B On Request On
Request
060928 ISO Address Claim
Used to identify to other ECUs the address
claimed by an ECU.
B On Request On
Request
126996 Product Information
NMEA 2000 database version supported,
manufacturer’s product code, NMEA
2000 certification level, Load Equivalency
number, and other product- specific
information.
B On Request On
Request
126464 Receive/Transmit PGNs group function
The Transmit / Receive PGN List Group
type of function is defined by first field.
The message will be a Transmit or Receive
PGN List group function.
B On Request On
Request
129538 GNSS Control Status
GNSS common satellite receiver parameter
status.
B On Request On
Request
129545 GNSS RAIM Output
Used to provide the output from a GNSS
receiver’s Receiver Autonomous Integrity
Monitoring (RAIM) process. The Integrity
field value is based on the parameters set
in PGN 129546 GNSS RAIM Settings.
B On Request On
Request
129546 GNSS RAIM Settings
Used to report the control parameters for
a GNSS Receiver Autonomous Integrity
Monitoring (RAIM) process.
B On Request On
Request
The next section shows the transmitted PGNs with their default update rate with the Smart
GPS compass in NMEA 2000 mode.
Transmitted messages
PG No.
(PGN)
Description
Level Default Update
Rate (msec)
Freq
(Hz)
126992 System Time
The purpose of this PGN is twofold: To
provide a regular transmission of UTC
time and date. To provide synchronism for
measurement data.
B 1000 1
127250 Vessel Heading
Heading sensor value with a flag for True or
Magnetic. If the sensor value is Magnetic,
the deviation field can be used to produce
a Magnetic heading, and the variation
field can be used to correct the Magnetic
heading to produce a True heading.
B 100 10
Page 20

18 |
Installation | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D UserManual
PG No.
(PGN)
Description
Level Default Update
Rate (msec)
Freq
(Hz)
127251 Rate of Turn
Rate of change of the Heading.
B 100 10
127257 Attitude
Provides a single transmission that
describes the position of a vessel relative
to both horizontal and vertical planes.
This would typically be used for vessel
stabilization, vessel control and onboard
platform stabilization.
B 1000 1
127258 Magnetic Variation
Message for transmitting variation. The
message contains a sequence number to
allow synchronization of other messages
such as Heading or Course over Ground.
The quality of service and age of service
are provided to enable recipients to
determine an appropriate level of service if
multiple transmissions exist.
1000 1
129025 Position, Rapid Update
Provides latitude and longitude referenced
to WGS84. Being defined as single frame
message, as opposed to other PGNs that
include latitude and longitude and are
defined as fast or multi- packet, this PGN
lends itself to being transmitted more
frequently without using up excessive
bandwidth on the bus for the benefit of
receiving equipment that may require
rapid position updates.
B 100 10
129026 COG & SOG, Rapid Update
Single frame PGN that provides Course
Over Ground (COG) and Speed Over
Ground (SOG).
B 250 4
129027 Position Delta, High Precision Rapid Update
The “Position Delta, High Precision Rapid
Update” Parameter Group is intended for
applications where very high precision
and very fast update rates are needed for
position data. This PGN can provide delta
position changes down to 1 mm with a
delta time period accurate to 5 msec.
B 100 10
129028 Altitude Delta, High Precision Rapid Update
The “Altitude Delta, High Precision Rapid
Update” Parameter Group is intended for
applications where very high precision
and very fast update rates are needed for
altitude and course over ground data.
This PG can provide delta altitude changes
down to 1 millimeter, a change in direction
as small as 0.0057°, and with a delta time
period accurate to 5 msec.
B 100 10
129029 GNSS Position Data
Conveys a comprehensive set of Global
Navigation Satellite System (GNSS)
parameters, including position information.
B 1000 1
Page 21

| 19
Installation | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
PG No.
(PGN)
Description
Level Default Update
Rate (msec)
Freq
(Hz)
129033 Time & Date
Single transmission that provides UTC
time, UTC Date, and Local Offset.
B 1000 1
129539 GNSS DOPs
Provides a single transmission containing
GNSS status and dilution of precision
components (DOP) that indicate the
contribution of satellite geometry to the
overall positioning error. There are three
DOP parameters reported: horizontal
(HDOP), Vertical (VDOP), and time (TDOP).
B 1000 1
129540 GNSS Sats in View
GNSS information on current satellites in
view tagged by sequence ID. Information
includes PRN, elevation, azimuth, SNR,
defines the number of satellites; defines
the satellite number and the information.
B 1000 1
Powering the Smart GPS compass
Power considerations
For best performance use a clean and continuous 12-24 VDC power supply. The Smart GPS
compass power supply circuit features reverse polarity protection but will not operate with
reverse polarity.
See “Power” on page 32 for complete power specifications.
Connecting to a power source
¼ Note: This section refers to powering the MX575C/MX575D unit via the serial cable
connection. The HS80/HS80A power is taken from the NMEA 2000 main buss. Follow the
standard procedure for powering up via NMEA 2000.
Before you power up the Smart GPS compass you must terminate the wires of the power
cable as required. There are a variety of power connectors and terminals on the market from
which to choose, depending on your specific requirements.
Warning: Do not apply voltage higher than 36 VDC. This will damage the receiver and void the
warranty.
To interface the Smart GPS compass power cable to the power source:
• Connect the red wire of the cable’s power input to DC positive (+)
• Connect the black wire of the cable’s power input to DC negative (-)
The Smart GPS compass will start when an acceptable voltage is applied to the power leads
of the extension cable.
Electrical isolation
The Smart GPS compass’s power supply circuit is isolated from the communication lines and
the PC-ABS plastic enclosure isolates the electronics mechanically from the vessel (addressing
the issue of vessel hull electrolysis).
Page 22

20 |
Installation | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D UserManual
Connecting the Smart GPS compass to external devices
¼ Note: This section refers to a serial connection. For connecting external NMEA 2000 devices,
plug the serial-to-NMEA 2000 adapter into the HS80/HS80A and then attach a standard
NMEA 2000 drop line cable to the adapter.
¼ Note: The NMEA (N2K) adapter is not included as standard accessory of the MX575C/MX575D
model.
Power/Data cable considerations
The MX575C/MX575D uses a single 15 m (49 ft) or optional 30 m (98 ft) cable for power and
data input/output. This cable is optional for HS80/HS80A
J1
50 mm
P1
Cover drain wire
with black shrink
tube
Shrink tubes
15 m / 30 m
100 mm
Figure 2-9: Power/Data cable, 15m or 30m
The receiver end of the cable is terminated with an environmentally sealed 18-pin connector
while the opposite end is not terminated and requires field stripping and tinning.
Depending on the application and installation needs, you may need to shorten this cable.
However, if you require a longer cable run than 30 m, you can bring the cable into a break-out
box that incorporates terminal strips.
When lengthening the cable keep the following in mind:
• To lengthen the serial lines inside the vessel, use 20-gauge twisted pairs and minimize the
additional wire length.
• When lengthening the power input leads to the Smart GPS compass, ensure the additional
voltage drop is small enough that your power system can continue to power the system
above the minimum voltage of the system. Wire of 18-gauge or larger should also be used.
• Minimize RS-232 cable length to ensure reliable communication.
• Use similar color-coded wires whenever possible.
Power/Data cable pin out specications
Figure 2-10 shows the power/data cable pin out, and the table shows the cable’s pin out
specifications.
Figure 2-10: Power/data cable pin assignment
Page 23

| 21
Installation | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
Pin Function Wire Color
1 Power (+) Red
2 Power (-) Black
3 Port A Tx RS-232 Blue
4 Port A Rx RS-232 Black/blue stripe
5 Reserved
6 Port A Tx RS-422 (+) Green
7 Port B Rx RS-422 (+) Brown
8 Port B Rx RS-422 (-) Black/brown stripe
9 Reserved
10 Drain Bare wire
11 Port A Tx RS-422 (-) Green/black stripe
12 Signal ground Grey
13 Alarm White
14 Alarm White/red stripe
15 1 PPS (+) Orange
16 Port B Tx RS-422 (+) Yellow
17 Port B Tx RS-422 (-) Yellow/black stripe
18 1 PPS (-) Orange/black stripe
Default parameters
The table below provides details on certain default parameters. Contact your dealer for
default port settings for your unit.
¼ Note: Use the $JSAVE command to save changes you make to the Smart GPS compass’s
configuration for the changes to be present in subsequent power cycles.
Unit Parameter Specification
HS80/HS80A and MX575C/
MX575D
Max DGPS age (correction age) 2700 seconds
Elevation mask 5°
Differential mode
HS80/HS80A: SBAS
MX575C/MX575D: Beacon
MX575C/MX575D (internal
beacon parameters)
Frequency selection Automatic
MSK rate selection Automatic
Page 24

22 |
Operation | HS80/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
Operation
GPS overview
When referring to the four D/GPS compass models, namely: HS80, HS80A, MX575C and
MX575D this manual uses the general term “smart GPS compass”. Specific model number
will be called when describing a particular feature or operation that is unique to that model.
The HS80/HS80A compass GPS compass models are GPS only receiver, while the MX575C/
MX575D models are GPS + GLONASS receivers.
When the smart GPS compass is powered for the first time, it performs a ‘cold start’ that
involves acquiring the available GPS satellites in view and the land-based beacon DGPS
service for the MX575C/MX575D. External source of RTCM SC-104 differential corrections can
also be used in lieu of the built-in beacon receiver. If you use an external source of correction
data, it must support an eight data bit, no parity, one stop bit configuration (8-N-1).
GPS operation
The GPS receiver is always operating, regardless of the DGPS operation mode. The following
sections describe general operation of the Smart GPS compass’s internal GPS receiver.
¼ Note: Differential source and status have no impact on heading, pitch, or roll. They only have
an impact on positioning and heave.
GLONASS overview
The GLONASS receiver technology is only available in the HS80A and the MX575D models.
GLONASS is a global satellite navigation system developed by the Soviet Union, providing
real-time position and velocity determination for military and civilian users. The GLONASS
satellites are located in orbits at 25,510 km altitude with a 64.8 degree inclination. GLONASS’
orbit makes it especially suited for use in high latitudes (north or south), where getting a
GPS signal can be problematic. The constellation operates in three orbital planes, with 8
evenly spaced satellites on each plane. A fully operational constellation with global coverage
consists of 24 satellites. To get a position fix the receiver must be in the range of at least four
satellites.
Combining the GPS and GLONASS system provides the following advantages:
• Better signal acquisition times
• Better position and time accuracy
• Reduces the physical blocking of signal in urban cities where tall buildings are the norms.
• Better satellite geometry resulting in better HDOP
Automatic tracking
The Smart GPS compass receiver automatically searches for GPS (and GLONASS) satellites,
acquires the signals, and manages the navigation information required for positioning and
tracking.
Receiver performance
The Smart GPS compass works by finding four or more GPS satellites in the visible sky. It uses
information from these satellites to compute a position within 4.0 m. Since there is some
error in the GPS data calculations, the Smart GPS compass also tracks a differential correction.
The Smart GPS compass uses these corrections to improve its position accuracy to better
than 1.0 m.
The two main aspects of GPS receiver performance are:
1. Satellite acquisition, and
2. Positioning and heading calculation.
When the Smart GPS compass is properly positioned, the satellites transmit coded
information to the antennas on a specific frequency. This allows the receiver to calculate a
range to each satellite from both antennas. GPS/GLONASS is essentially a timing system. The
ranges are calculated by timing how long it takes for the signal to reach the antenna. The
3
Page 25

| 23
Operation | HS80/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
GPS receiver uses a complex algorithm incorporating satellite locations and ranges to each
satellite to calculate the geographic location and heading. Reception of any four or more GPS
signals allows the receiver to compute three-dimensional coordinates and a valid heading.
Dierential operation
The purpose of differential GPS (DGPS) is to remove the effects of selective availability (SA),
atmospheric errors, timing errors, and satellite orbit errors, while enhancing system integrity.
Autonomous positioning capabilities of the Smart GPS compass will result in positioning
accuracies of 4.0 m 95% of the time. In order to improve positioning quality to better than 1.0
m 95%, the Smart GPS compass is able to use differential corrections received through the
internal beacon receiver (for MX575C/MX575D), SBAS demodulator or through externallysupplied RTCM corrections.
SBAS tracking
The HS80/HS80A can scan and track SBAS signals without the need to tune the receiver. The
HS80/HS80A features two-channel tracking that provides an enhanced ability to maintain
a lock on an SBAS satellite when more than one satellite is in view. This redundant tracking
approach results in more consistent tracking of an SBAS signal in areas where signal blockage
of a satellite is possible. The MX575C/MX575D is configured to receive beacon DGPS
corrections. However, it can also be configured to receive SBAS or external RTCM corrections
from the SIMRAD-MX CDU.
Beacon operation
Many marine authorities, such as the U.S. coast guard, have installed networks of radio beacon
stations that broadcast DGPS corrections to users of this system. With the increasing utility of
these networks for terrestrial applications, there is an increasing trend toward densification
of these networks inland. The dual channel beacon receiver in the MX575C/MX575D can
operate in manual or automatic tuning mode, or, using database mode, will select the closest
station in compliance with IEC 61108-4 standards. The MX575C/MX575D is configured to
receive DGPS corrections from beacon stations by default.
Smart GPS compass overview
The Smart GPS compass provides accurate and reliable heading and position information at
high update rates. To accomplish this task, the Smart GPS compass uses a high performance
GPS receiver and two antennas for GPS signal processing. One antenna is designated as the
primary GPS antenna and the other is the secondary GPS antenna. Positions computed by
the Smart GPS compass are referenced to the phase center of the primary GPS antenna.
Heading data references the vector formed from the primary GPS antenna phase center to
the secondary GPS antenna phase center.
The heading arrow located on the bottom of the Smart GPS compass enclosure defines
system orientation. The arrow points in the direction the heading measurement is computed
(when the antenna is installed parallel to the fore-aft line of the vessel). The secondary
antenna is directly above the arrow.
Fixed baseline moving base station RTK
The Smart GPS compass’s internal GPS receiver uses both the L1 GPS C/A code and carrier
phase data to compute the location of the secondary GPS antenna in relation to the primary
GPS antenna with a very high sub-centimeter level of precision. The technique of computing
the location of the secondary GPS antenna with respect to the primary antenna, when the
primary antenna is moving, is often referred to as moving base station Real Time Kinematic
(or moving base station RTK).
Generally, RTK technology is very sophisticated and requires a significant number of possible
solutions to be analyzed where various combinations of integer numbers of L1 wavelengths
to each satellite intersect within a certain search volume. The integer number of wavelengths
is often referred to as the “ambiguity” as they are initially ambiguous at the start of the RTK
solution.
The Smart GPS compass restricts the RTK solution. It does this knowing that the secondary
GPS antenna is 50 cm from the primary GPS antenna. This is called a fixed baseline and it
defines the search volume of the secondary antenna as the surface of a sphere with radius 50
Page 26

24 |
Operation | HS80/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
cm centered on the location of the primary antenna (see Figure 3-1).
Primary Antenna
50 cm
Baseline
Figure 3-1: Secondary antenna’s search volume
¼ Note: The Smart GPS compass moving base station algorithm only uses GPS to calculate
heading. Differential corrections are not used in this calculation and will not affect heading
accuracy.
Supplemental sensors
The Smart GPS compass has three supplemental sensors (gyro and two tilt sensors) that are
integrated into the unit’s main PCB. The supplemental sensors are enabled by default. You
can enable/disable the gyro and both tilt sensors (you cannot enable/disable each tilt sensor
separately).
The sensors act to reduce the RTK search volume, which improves heading startup and reacquisition times. This improves the reliability and accuracy of selecting the correct heading
solution by eliminating other possible, erroneous solutions.
Sensor operation summary
Feature Normal Operation Coasting (no GPS)
Heading GPS Gyro
Heave GPS None
Pitch GPS Inertial tilt sensor
Roll Inertial sensor Inertial tilt sensor
Tilt aiding
The Smart GPS compass’s accelerometers (internal tilt sensors) are factory calibrated and
enabled by default. This constrains the RTK heading solution beyond the volume associated
with just a fixed antenna separation. This is because the Smart GPS compass knows the
approximate inclination of the secondary antenna with respect to the primary antenna. The
search space defined by the tilt sensor will be reduced to a horizontal ring on the sphere’s
surface by reducing the search volume.
Page 27

| 25
Operation | HS80/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
This considerably decreases instances of incorrect headings as well as startup and
reacquisition times (see Figure 3-2).
Tilt angle
Figure 3-2: Smart GPS compass’s tilt aiding
Gyro aiding
The Smart GPS compass’s internal gyro offers several benefits. It reduces the sensor volume
for an RTK solution. This shortens reacquisition times when a GPS heading is lost because
the satellite signals were blocked. The gyro provides a relative change in angle since the last
computed heading, and, when used in conjunction with the tilt sensor, defines the search
space as a wedge-shaped location (see Figure 3-3).
Figure 3-3: Smart GPS compass’s gyro aiding
The gyro aiding accurately smooth the heading output and the rate of turn. It provides a
substitute heading for a short period, accurate to within 1º per minute for up to three
minutes, in times of GPS loss for either antenna. If the outage lasts longer than three minutes,
the gyro will have drifted too far and the Smart GPS compass begins outputting null fields in
the heading output messages. There is no user control over the timeout period of the gyro.
Calibration, which is set at the factory, is required for the gyro to remove latency from the
heading solution as well as provide backup heading when GPS is blocked. The receiver
will calibrate itself after running for a while but it may be important to follow the manual
calibration instructions if you want to guarantee performance quickly after powering up the
receiver.
The gyro initializes itself at power up and during initialization. There is no need for manual
calibration. When the gyro is first initializing, it is important that the dynamics that the
gyro experiences during this warm up period are similar to the regular operating dynamics.
For example, if you use the Smart GPS compass on a high speed, maneuverable craft, it is
recommended that when gyro aiding in the Smart GPS compass is first turned on, use it in
an environment that has high dynamics for the first five to ten minutes instead of sitting
stationary.
With the gyro enabled, the gyro is also used to update the post HTAU smoothed heading
output from the moving base station RTK GPS heading computation. This means that if the
HTAU value is increased while gyro aiding is enabled, there will be little to no lag in heading
output due to vehicle maneuvers.
Page 28

26 |
Operation | HS80/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
Time constants
The Smart GPS compass incorporates user-configurable time constants that can provide a
degree of smoothing to the heading, pitch, rate of turn (ROT), course over ground (COG),
and speed measurements. You can adjust these parameters depending on the expected
dynamics of the vessel. For example, increasing the time is reasonable if the vessel is very large
and is not able to turn quickly or would not pitch quickly. The resulting values would have
reduced ‘noise,’ resulting in consistent values with time. However, if the vessel is quick and
nimble, increasing this value can create a lag in measurements. The level of smoothing maybe
adjusted manually but if you are unsure on how to set this value, it is best to be conservative
and leave it at the default setting.
¼ Note: For heading and rate of turn there is no lag once the gyro is calibrated and enabled.
Heading time constant
Use the $JATT,HTAU command to adjust the level of responsiveness of the true heading
measurement provided in the $GPHDT message. The default value of this constant is 10.0
seconds of smoothing when the gyro is enabled. The gyro is enabled by default, but can be
turned off. By turning the gyro off, the equivalent default value of the heading time constant
would be 0.5 seconds of smoothing. This is not automatically done and therefore you must
manually enter it. Increasing the time constant increases the level of heading smoothing and
increases lag only if the gyro is disabled.
Pitch time constant
Use the $JATT,PTAU command to adjust the level of responsiveness of the pitch
measurement provided in the $PSAT,HPR message. The default value of this constant is 0.5
seconds of smoothing. Increasing the time constant increases the level of pitch smoothing
and increases lag.
Rate of Turn (ROT) time constant
Use the $JATT,HRTAU command to adjust the level of responsiveness of the ROT
measurement provided in the $GPROT message. The default value of this constant is 2.0
seconds of smoothing. Increasing the time constant increases the level of ROT smoothing.
Course Over Ground (COG) time constant
Use the $JATT,COGTAU command to adjust the level of responsiveness of the COG
measurement provided in the $GPVTG message. The default value of this constant is 0.0
seconds of smoothing. Increasing the time constant increases the level of COG smoothing.
COG is computed using only the primary GPS antenna and its accuracy depends upon the
speed of the vessel (noise is proportional to 1/speed). This value is invalid when the vessel
is stationary, as tiny movements due to calculation inaccuracies are not representative of a
vessel’s movement.
Speed time constant
Use the $JATT,SPDTAU command to adjust the level of responsiveness of the speed
measurement provided in the $GPVTG message. The default value of this constant is
0.0 seconds of smoothing. Increasing the time constant increases the level of speed
measurement smoothing.
Alarm functionality
¼ Note: Alarm functionality is only valid for serial communication.
A relay is located on the Transmit Heading Device (THD) circuit board. The relay contacts are
isolated from all circuitry in the THD. The THD is connected to the coil side of the relay, but
not to the contacts that are connected to the external pins through the main IO connector.
If the THD loses power or heading, the coil voltage is lost and the relay opens and activates
the notification method employed by the user. When the heading is output, the relay
contacts remain closed, completing the circuit as an indication that the Smart GPS compass is
operational.
¼ Note: Alarm pins must be connected to an IMO type-approved device.
Page 29

| 27
Operation | HS80/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
Alarm signal
There are two wires (24 AWG multi-strands) on the output cable that are used for the external
alarm function. The color codes for the two wires are white and white/red stripe and are the
output of a relay. When this relay closes, the connection is complete on the user-defined
external notification device.
Watchdog
The watchdog is a timer that is controlled by the software that monitors if the heading is lost.
The watchdog software is compliant with IEC 60495.
Common commands and messages
¼ Note: When selecting your baud rate and message types use the following formula and
example to calculate the bits/sec for each message and then sum the results to determine
the baud rate for your required data throughput. Transmitting the commands listed
in “Commands” on page 27 and monitoring the messages in “NMEA 0183 and other
messages” on page 28 requires that the PC serial communication port be connected to the
RS-232 interface wires of the 18-Pin antenna cable of the MX575C/MX575D (see “PC to GPS
compass interface diagram” on page 54). The HS80/HS80A requires this optional cable.
Message output rate * Message length (bytes) * bits in byte = Bits/second
(1 character = 1 byte, 8 bits = 1 byte, use 10 bits/byte to account for overhead)
Example:
Message Rate Bytes Bits in byte Bits/sec
GPHDT 10 20 10 2000
GPROT 5 18 10 900
GPHDG 1 33 10 330
GPGGA 1 83 10 830
GPZDA 1 38 10 380
Total 4440
The next sections provides brief descriptions of common commands and messages for the
Smart GPS compass.
Commands
Command Description
$GPMSK Tune beacon to specific frequency
$JAGE Specify maximum DGPS (COAST) correction age (6 to 8100 seconds)
$JAPP Query or specify receiver application firmware
$JASC
Specify ASCII messages to output to specific ports (see ASCII
messages in Table 3-3)
$JBAUD Specify RS-232, RS-422 (output) communication rate
$JBIN Specify binary messages to output to specific ports (see Table 3-4)
$JDIFF Query or specify differential correction mode
$JGEO Query or specify SBAS for current location and SBAS satellites
$JI Query unit’s serial number and firmware versions
$JOFF Turn off all data messages
$JQUERY,GUIDE Query accuracy suitability for navigation
Page 30

28 |
Operation | HS80/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
Command Description
$JRESET
Reset unit’s configuration to firmware defaults
¼ Note: $JRESET clears all parameters. For the Smart GPS compass
you will have to issue the $JATT, FLIPBRD, YES command to
properly redefine the circuitry orientation inside the product
once the receiver has reset. Failure to do so will cause radical
heading behavior.
You can also issue the $JRESET command with an optional field
as follows:
• $JRESET,ALL does everything $JRESET does, plus it clears
almanacs
• $JRESET,BOOT does everything $JRESET,ALL does, plus clears
use of the real-time clock at startup, clears use of backed-up
ephemeris and almanacs, and reboots the receiver when done
$JSAVE Save session’s configuration changes
In Table 3-3 the Info Type value is one of the following:
- P = Position
- V = Velocity, Time
- H = Heading, Attitude
- S = Sats, Stats, Quality
NMEA 0183 and other messages
Message
Info
Type
Max Output
Rate
Description
IEC Approved
Message
$GPDTM P 1 Hz Datum reference Yes
$GPGGA P 20 Hz GPS position and fix data Yes
$GPGLL P 20 Hz Geographic position - lat/long Yes
$GPGNS P 20 Hz GNSS position and fix data Yes
$GPGRS S 1 Hz GNSS range residual (RAIM) Yes
$GPGSA S 1 Hz GNSS DOP and active satellites Yes
$GPGST S 1 Hz
GNSS pseudo range error statistics and
position accuracy
Yes
$GPGSV S 1 Hz GNSS satellites in view Yes
*$GPHDG H 20 Hz
Provides magnetic deviation and
variation for calculating magnetic or
true heading
*see last bullet in Note at end of this
table
Yes
*$GPHDM H 20 Hz
Magnetic heading (based on GPSderived heading and magnetic
declination)
*see last bullet in Note at end of this
table
No
*$GPHDT H 20 Hz
GPS-derived true heading
*see last bullet in Note at end of this
table
Yes
$GPHEV H 20 Hz Heave value (in meters) Yes
$GPRMC P 20 Hz
Recommended minimum specific GNSS
data
Yes
Page 31

| 29
Operation | HS80/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
*$GPROT H 20 Hz
GPS-derived rate of turn (ROT)
*see last bullet in Note at end of this
table
Yes
$GPRRE S 1 Hz
Range residual and estimated position
error
Yes
$GPVTG V 20 Hz COG and ground speed Yes
$GPZDA V 20 Hz Time and date Yes
$PASHR H 20 Hz
Time, heading, roll, and pitch data in one
message
No
$PSAT,GBS S 1 Hz Satellite fault detection (RAIM) Ye s
$PSAT,HPR H 20 Hz
Proprietary NMEA message that
provides heading, pitch, roll, and time in
single message
No
$PSAT,INTLT H 1 Hz
Proprietary NMEA message
that provides the pitch and roll
measurements from the internal
inclinometers (in degrees)
Yes
$RD1 S 1 Hz SBAS diagnostic information Yes
$TSS1 H 20 Hz
Heading, pitch, roll, and heave message
in the commonly used TSS1 message
format
No
¼ Notes:
- The “GP” of the message is the talker ID.
- GPGRS, GPGSA, GPGST, and GPGSV support external integrity checking. They are to be
synchronized with corresponding fix data (GPGGA or GPGNS).
- You can change the message header for the HDG, HDM, HDT, and ROT messages to either
GP or HE using the $JATT,NMEAHE command.
- To preface these messages with GP, issue the following command:
$JATT,NMEAHE,0<CR><LF>
- To preface these messages with HE, issue the following command:
$JATT,NMEAHE,1<CR><LF>
Binary messages
$JBIN Message Description
1 GPS position
2 GPS DOPs
80 SBAS
93 SBAS ephemeris data
94 Ionosphere and UTC conversion parameters
95 Satellite ephemeris data
96 Code and carrier phase
97 Processor statistics
98 Satellites and almanac
99 GPS diagnostics
Page 32

30 |
Operation | HS80/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
Parameters specic to $JATT command
Parameter Description Query Specify
COGTAU Set/query COG time constant (0.0 to 3600.0 sec) X X
CSEP Query antenna separation X
EXACT
Enable/disable internal filter reliance on the
entered antenna separation
X X
FLIPBRD
Turn the flip feature on/off. Default is Yes (On). If
performing a factory reset verify this is on.
X X
GYROAID Enable/disable gyro X X
HBIAS Set/query heading bias (-180.0º to 180.0º) X X
HELP
Show the available commands for GPS heading
operation and status
X
HIGHMP
Set/query the high multipath setting for use in
poor
GPS environments X X
HRTAU Set/query ROT time constant (0.0 to 3600.0 sec) X X
HTAU
Set/query heading time constant (0.0 to 3600.0
sec)
X X
LEVEL Enable/disable level operation X X
MSEP Manually set or query antenna separation X X
NEGTILT Enable/disable negative tilt X X
NMEAHE
Change the HDG, HDM, HDT, and ROT message
headers between GP and HE
X X
PBIAS Set/query pitch/roll bias (-15.0º to 15.0º) X X
PTAU Set/query pitch time constant (0.0 to 3600.0 sec) X X
ROLL Configure for roll or pitch GPS orientation X X
SEARCH Force a new GPS heading search X
SPDTAU Set/query speed time constant (0.0 to 3600.0 sec) X X
SUMMARY Display current Crescent Vector settings summary X
TILTAID Enable/disable accelerometer, pre-calibrated X
TILTCAL Calibrate accelerometers X
Page 33

| 31
Technical specications | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
Technical specications
Specications
GPS sensor
Item Specification
Model# HS80/MX575C HS80A/MX575D
Receiver type
GPS L1, C/A code with
carrier phase smoothing
L1 GPS and GLONASS C/A
code
Channels
Two 12-channel, parallel
tracking
Two 270-channel, parallel
tracking
SBAS tracking 2-channel, parallel tracking
Update rate 1-20 Hz (position and heading)
Horizontal accuracy
< 1.0 m 95% confidence (DGPS)
< 4.0 m 95% confidence (autonomous, no SA)
Heading accuracy
< 0.5° RMS
Normal operation: GPS Coasting (no GPS): Gyro
Heave accuracy
< 30 cm RMS
Normal operation: GPS Coasting (no GPS): None
Pitch accuracy
< 1° RMS
Normal operation: GPS
Coasting (no GPS): Inertial sensor
Roll accuracy
< 1° RMS using accelerometer
Normal operation: Inertial sensor
Coasting (no GPS): Inertial sensor
Rate of turn 90°/s maximum
Cold start < 60 s typical (no almanac or RTC)
Warm start < 20 s typical (almanac and RTC)
Hot start < 10 s typical (almanac, RTC, and position)
Heading fix < 10 s typical (valid position)
Compass safe distance 75 cm (29.5 in)4
Maximum speed 1,850 kph (999 kts)
Maximum altitude 18,288 m (60,000 ft)
Timing ( 1PPS) Accuracy 50 ns
Communication
Item Specification
HS80/MX575C HS80A/MX575D
Serial ports 1 RS-232 (full-duplex)
2 RS-422 (1 full duplex, 1 half duplex)
Baud rates HS80/HS80A: 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200
MX575C/MX575D: 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400
Correction I/O protocol RTCM SC-104
Data I/O protocol NMEA 0183, NMEA 2000
4
Page 34

32 |
Technical specications | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
Power
Item Specification
HS80/MX575C HS80A/MX575D
Input voltage 6 to 36 VDC
Power consumption 3 W nominal
Current consumption HS80/HS80A MX575C/MX575D
320 mA @ 9 VDC 350 mA @ 9 VDC
240 mA @ 12 VDC 265 mA @ 12 VDC
180 mA @ 16 VDC 200 mA @ 16 VDC
Power isolation Isolated to enclosure
Reverse polarity protection Yes
Mechanical
Item Specification
Enclosure UV resistant, white plastic, AES HW 600G, non-corrosive,
self-extinguishing
Dimensions 209.16 W x 668.54 L x 122.32 H (mm)
8.234 W x 26.320 L x 4.815 H (in)
Weight HS80/HS80A
2.131 kg (4.70 lb)
MX575C/MX575D
2.44 kg (5.38 lb)
Environmental
Item Specification
Operating temperature -30°C to +70°C (-22°F to +158°F)
Storage temperature -40°C to +85°C (-40°F to +185°F)
Humidity 95% non-condensing
Vibration IEC 60945
EMC FCC Part 15, Subpart B; CISPR22; IEC 60945 (CE)
Certications
Heading Device (HS80 & MX575C)
IMO Resolution MSC.116(73) ISO 22090-3 Ed.1.0, 2004 incl. Corr. 1,2005
IMO Resolution A.694(17) IEC 60945 Ed.4.0, 2002 incl. Corr.1, 2008
IMO Resolution MSC.191(79) IEC 61162-2 Ed.1.0, 1998
IEC 61162-1 Ed.4.0, 2010
IMO Wheelmarked for Annex A.1 item 4.41 Transmitting heading device THD (GNSS method.
Based on the Directive 2009/26/EC.
Page 35

| 33
Technical specications | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
Navigation Equipment (HS80 & MX575C)
IMO Resolution MSC.112(73) IEC 61108-1 Ed.2.0 2003
IMO Resolution MSC.114(73) IEC 61108-4 Ed.1.0 2004
IMO Resolution A.694(17) IEC 60945 Ed.4.0, 2002 incl. Corr.1, 2008
IMO Resolution MSC.191(79) IEC 61162-1 Ed.4.0, 2010
Heading Device (HS80A & MX575D)
IMO Resolution MSC.116(73) ISO 22090-3 Ed.1.0, 2004 incl. Corr. 1,2005
IMO Resolution A.694(17) IEC 60945 Ed.4.0, 2002 incl. Corr.1, 2008
IMO Resolution MSC.191(79) IEC 61162-1 Ed.4.0, 2010
IEC 61162-2 Ed1.0, 1998
IEC 61162-3. 1.1, 2010 (NMEA 2000)
IMO Wheelmarked for Annex A.1 item 4.41 Transmitting heading device THD (GNSS method.
Based on the Directive 2012/32/EU, additional applied version: Directive 2013/52/EU.
Navigation Equipment (HS80A & MX575D)
IMO Resolution MSC.112(73) IEC 61108-1 Ed.2.0 2003
IMO Resolution MSC.113(73) IEC 61108-2 Ed. 1.0, 1998
IMO Resolution MSC.114(73) IEC 61108-4 Ed.1.0 2004
IMO Resol;ution MSC.115(73) IEC 60945 Ed.4.0, 2002 incl. Corr. 1, 2008
IMO Resolution A.694(17) IEC 61162-1 Ed. 4.0, 2010
IMO Resolution MSC.191(79) IEC 61162-3 Ed. 1.1, 2010 (NMEA2000)
1
Depends on multipath environment, number of satellites in view, satellite geometry,
ionospheric activity, and use of SBAS
2
Depends on multipath environment, number of satellites in view, satellite geometry, and
ionospheric activity
* SIMRAD GPS proprietary
4
IEC 60945 Standard
5
Based on a 40 second time constant
Page 36

34 |
Technical specications | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
Output messages
The smart GPS compass data output conforms to the NMEA 0183 V4.0 at 4800, 9600, or 19200
baud. Below is a list of the NMEA sentences output:
NMEA 0183 data output sentences
(1) GBS - GNSS Satellite Fault Detection (Modied MX Marine version)
This message is used to support Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring (RAIM) feature in
the MX CDU. A special character flag was added for proper RAIM status determination
$PMVXG,GBS,hhmmss.ss,x.x,x.x,x.x,xx,x.x,x.x,x.x,x,x,x*hh<CR><LF>
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
¼ Notes:
1 UTC time of the GGA or GNS fix associated with this sentence.
2 Expected error in Latitude (meters)
3 Expected error in Longitude (meters)
4 Expected error in Altitude (meters)
5 ID number of most likely failed satellite
6 Probability of missed detection for most likely failed satellite
7 Estimate of bias in meters on most likely failed satellite
8 Standard deviation of bias estimate
9 RAIM: 0=safe, 1=caution, 2=unsafe
10 GNSS signal ID: 0 = All, 1 = GPS
11 GNSS system ID; 1 = GPS, 2 = GLONASS, 3 = GALILEO, 4 = RESERVED
(2) GGA – Global Positioning System Fix Data
Time, position and fix related data for a GPS receiver.
$GPGGA,hhmmss,llll.llll,a,yyyyy.yyyy,a,x,xx,x.x,x.x,M,x.x,M,x.x,xxxx*hh<CR><LF>
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
¼ Notes:
1 UTC of position
2, 3 Latitude, N/S
4, 5 Longitude, E/W
6 GPS Quality Indicator
0 = Fix not available or invalid
1 = GPS SPS Mode, fix valid
2 = Differential GPS, SPS Mode, fix valid
3 = GPS PPS Mode, fix valid
7 Number of Satellites in use, 00-12, may be different from the number in view
8 Horizontal Dilution of Precision (HDOP)
9 Antenna altitude/mean-sea-level (geoid)
10 Units of antenna altitude, Meters
11, 12 Geoidal Height, Meters
13 Age of Differential GPS Data
14 Differential Reference Station ID
Page 37

| 35
Technical specications | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
(3) GNS-GNSS Fix Data
Fix data for single or combined satellite navigation systems (GNSS). This sentence provides fix
data for GPS, GLONASS, possible future satellite systems and systems combining these. This
sentence could be used with the talker identification of GP, GPS, GL for GLONASS, GN for GNSS
combined system.
If a GNSS receiver is capable simultaneously of producing a position using combined satellite
systems, as well as a position using only one of the satellite systems, then separate $GPGNS
and $GLGNS sentences may be used to report the data calculated from the individual systems.
If a GNSS receiver is set up to use more than one satellite system, but for some reason one
or more of the systems are not available, then it may continue to report the positions using
$GNGNS, and use the mode indicator to show which satellite systems are being used
$GNGNS,hhmmss,llll.llll,a,yyyyy.yyyy,a,x,xx,x.x,x.x,M,x.x,M,x.x,xxxx,x*hh<CR><LF>
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
¼ Notes:
1 UTC of position
2, 3 Latitude, N/S
4, 5 Longitude, E/W
6
Mode Indicator
N = No Fix available or invalid
A = Autonomous. Satellite system used is non-differential mode in position
fix
D = Differential. GPS, SPS Mode, fix valid
P = Precise. Satellite system used in precision mode.
R = Real Time Kinematic
F = Float RTK
E = Estimated (DR) mode
M = Manual Input Mode
S = Simulator Mode
7 Number of Satellites in use, 00-99, may be different from the number in view
8 Horizontal Dilution of Precision (HDOP)
9 Antenna altitude/mean-sea-level (geoid)
10 Units of antenna altitude, Meters
11, 12 Geoidal Height, Meters
13 Age of Differential GPS Data
14 Differential Reference Station ID
15 RAIM indicator
S = Safe
U = Unsafe
C = Caution
N = None
Page 38

36 |
Technical specications | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
(4) GLL – Geographic Position - Latitude/Longitude
Latitude and Longitude of vessel position, time of position fix and status.
$GPGLL,llll.ll,a,yyyyy.yy,a,hhmmss.ss,A,a*hh<CR><LF>
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
¼ Notes:
1, 2 Latitude, N/S
3, 4 Longitude, E/W
5 UTC of position
6 Status
V - Invalid
A - Autonomous Mode
D - Differential Mode
7 Mode indicator
(5) GSA – GPS DOP and Active Satellites
GPS receiver operating mode, satellites used in the navigation solution reported by the
$GPGGA sentence, and DOP values.
$GPGSA,a,x,xx,xx,xx,xx,xx,xx,xx,xx,xx,xx,xx,xx,x.x,x.x,x.x,x*hh<CR><LF>
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
¼ Notes:
1 Mode:
M = Manual, forced to operate in 2D or 3D Mode
A = Automatic, allowed to automatically switch 2D/3D
2 Mode:
1 = Fix not available
2 = 2D
3 = 3D
3-14 PRN numbers of satellites used in solution (null
for unused fields)
15 PDOP
16 HDOP
17 VDOP
18 Signal type 1 for L1/CA
Page 39

| 37
Technical specications | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
(6) GST - GNSS Pseudorange Error Statistics
This message is used to support Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring (RAIM).
Pseudorange measurement error statistics can be translated in the position domain in order
to give statistical measures of the quality of the position solution.
If only GPS, GLONASS, etc. is used for the reported position solution, the talker ID is GP, GL, etc.,
and the error data pertains to the individual system. If satellites from multiple systems are
used to obtain the reported position solution, the talker ID is GN and the errors pertain to the
combined solution.
$GPGST,hhmmss.ss,x.x,x.x,x.x,x.x,x.x,x.x,x.x*hh<CR><LF>
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
¼ Notes:
1 UTC time of the GGA or GNS fix associated with this sentence
2 RMS value of the standard deviation of the range inputs to the navigation
process. Range inputs include preudoranges & DGNSS corrections
3 Standard deviation of semi-major axis of error ellipse (meters)
4 Standard deviation of semi-minor axis of error ellipse (meters)
5 Orientation of semi-major axis of error ellipse (degrees from true north)
6 Standard deviation of latitude error (meters)
7 Standard deviation of longitude error (meters)
8 Standard deviation of altitude error (meters)
(7) GSV - GNSS Satellite in View
Number of satellites (SV) in view, PRN numbers, elevation, azimuth and SNR values. Four
satellites maximum per transmission, additional satellite data sent in second or third message.
Total number of messages being transmitted and the number of the message transmitted are
indicated in the first two fields.
$GPGSV,x,x,xx,xx,xx,xxx,xx,....................,xx,xx,xxx,xx,x*hh<CR><LF>
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 1213
¼ Notes:
1 Total number of messages, 1 to 3
2 Message number, 1 to 3
3 Total number of satellites in view
4 Satellite PRN number
5 Elevation, degrees, 90 degrees maximum
6 Azimuth, degrees True, 000 to 359
7 SNR (C/No) 00-99 dB, null when not tracking
8 2nd and 3rd SV
9, 10, 11, 12 4th SV
13 Signal ID: 1 = GPS L1/CA, 2 = GLONASS L1, 3 = GALILEO, 4 = RESERVE
Page 40

38 |
Technical specications | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
8) HDT – Heading, True
Actual vessel heading in degrees (True) produced by any device or system producing true
heading.
$GPHDT,x.x,T*hh<CR><LF>
1 2
¼ Notes:
1 Heading
2 Degrees True
(9) RMC - Recommended Minimum Specic GPS Data
Time, date, position, course and speed data provided by a GPS navigation receiver. This
sentence is transmitted at intervals not exceeding 2 seconds. All data fields must be
provided: null fields used only when data is temporarily unavailable.
$GPRMC,hhmmss.ss,A,llll.llll,a,yyyyy.yyyy,a,x.x,x.x,xxxxxx,x.x,a,a,a*hh<CR><LF>
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11-12-13
¼ Notes:
1 UTC of Position fix
2 Status
A = data valid
V = Navigation receiver warning
3, 4 Latitude, N/S
5, 6 Longitude, E/W
7 Speed over ground, knots
8 Course Over Ground, True
9 Date: dd/mm/yy
10, 11 Magnetic variation, degrees E/W:
Easterly variation (E) subtracts from True course
Westerly variation (W) add to True course
12 Mode indicator:
A = Autonomous mode
D = Differential mode
E = Estimated (DR)
M = Manual input mode
S = Simulator mode
N = Data not valid
13 RAIM Status:
S=RAIM Safe
U=RAIM Unsafe
C= Caution
V=Not Valid
Page 41

| 39
Technical specications | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
(10) ROT – Rate Of Turn
Rate of turn and direction of turn.
$GPROT,x.x,A*hh<CR><LF>
1 2
¼ Notes:
1 Rate of turn, degrees/minute, “-“ = bow turns to port
2 Status: (A = Data valid, V = Data invalid)
(11) VTG - Course Over Ground and Ground Speed
The actual course and speed relative to the ground.
$GPVTG,x.x,T,x.x,M,x.x,N,x.x,K,a*hh<CR><LF>
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
¼ Notes:
1, 2 Course over ground, degrees True
3, 4 Course over ground, degrees Magnetic
5, 6 Speed over ground, knots
7, 8 Speed over ground, km/hr
9 Mode indicator:
A = Autonomous mode
D = Differential mode
E = Estimated (DR)
M = Manual input mode
S = Simulator mode
N = Data not valid
(12) ZDA - Time and Date
UTC, day, month, year and local time zone
$GPZDA,hhmmss,xx,xx,xxxx,xx,xx*hh<CR><LF>
1 2 3 4 5 6
¼ Notes:
1 UTC
2, 3, 4 Day, month & year
5 Local zone hours, 00 to + 13 hrs
6 Local zone in minutes, 00 to +59.
Page 42

40 |
Technical specications | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
(13) PCSI - Beacon Status Message
This message contains a variety of information relating to the status of Beacon engine
inside the MX575C/MX575D. The $PCSI,1 output message from the SBX beacon module
is intelligently routed through the MX575C/MX575D to the port from which the $PCSI,1
message was requested.
$PCSI,CS0,PXXX-Y.YYY,SN,fff.f,M,ddd,R,SS,SNR,MTP,Q,ID,H,T
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1314
¼ Notes:
1 Channel 0
2 Resident SBX-3 firmware version
3 SBX-3 receiver serial number
4 Channel 0 current frequency
5 Frequency Mode (‘A’ - Auto or ‘M’ - Manual)
6 MSK bit rate
7 RTCM rate
8 Signal strength
9 Signal to noise ratio
10 Message throughput
11 Quality number {0-25} - number of successive good 30 bit RTCM words
received
12 Beacon ID to which the receiver’s primary channel is tuned
13 Health of the tuned beacon [0-7]
14 $PCSI,1 status output period {0-99}
Page 43

| 41
Technical specications | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
Proprietary Input data messages
The table below gives a list of the available proprietary input messages and their description:
Message type Description
$PMVXG,303 RESET CONTROL
$PMVXG,026 NMEA MESSAGE SCHEDULE
$PMVXG,200 SET PORT CONFIGURATION
$PCSI BEACON PCB CONTROL
$GPMSK,305 BEACON AUTO/MANUAL CONTROL
$JSAVE SAVES ALL CHANGED PARAMETERS
$JDIFF CONTROLS THE DIFFERENTIAL BEACON RECEIVER
$JSHOW SHOWS ALL GPS AND BEACON PARAMETERS
Sentence type - $PMVXG,303
Description: Reset Control
This message allows the user to command various types of resets to the Smart GPS compass.
Flow: Input
$PMVXG,303 – Reset Control
Field Description Units Format Range
1 Reset Control Int
0. No Action
1. Reset Serial I/O to Factory Default
Settings.
2. Resets GPS Parameters to Factory
Default settings, User I/O Settings
Remain
3. Resets GPS Parameters to Factory
Default Settings, I/O Settings Return to
Factory Defaults.
4. Reset All Parameters Except the
Oscillator Model
2 NULL
Example:
$PMVXG,303,3*57
$PMVXG,303,4*50
Sentence type - $PMVXG,026
Description: NMEA Message Schedule
This message enables/disables output of the specified sentence to the NMEA port and
defines the output rate.
Flow: Input
$PMVXG,026 – NMEA Schedule
Field Description Units Format Range
1
Equipment Port
Output Block
Example “GGA”
Char Default = None
Page 44

42 |
Technical specications | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
2 Clear Current List Int
0 = NO
1 = YES
Default = None
3
Add/Delete Sentence
From List
Int
1 = Append Sentence to Output List
2 = Delete Sentence From Output List
Default = None
4
Sentence Output
Rate
Sec Float
>0 = Output Period
-1 = When new Data is Available
5
Position Precision
(number of decimal
units in position
output)
Int
2-6
Default = 2
6 Null
Example:
$PMVXG,026,HDT,0,1,1,,,*
$PMVXG,026,ROT,0,1,1,,,*
$PMVXG,026,VTG,0,1,5,5,*
Sentence type: $PMVXG,200
Description: Set Port Configuration
This message sets the transmission rate, number of data bits, and parity convention for each
of the serial interface ports.
Flow: Input
$PMVXG,200 – PORT CONFIGURATION
Field Description Units Format Range
1 Serial Port Int
0 = Current Port
1 = Port 1
2 = Port 2
Default:
2 Baud Rate Int
5 = 4800
6 = 9600
7 = 19200
Default:
3 Stop Bits Int
1 = 1 Stop Bit
2 = 2 Stop Bits
Default:
4 Pacing Mode Int
0 = None
1 = XON/XOFF
2 = CTS/RTS
Default:
5 Parity Int
0 = No Parity
1 = Even Parity
2 = Odd Parity
Default:
Page 45

| 43
Technical specications | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
6
Serial Port Output
Format
Int
0 = None
1 = MX LB2
2 = Auxiliary LB2
4 = RTCM Output
10 = Primary NMEA
11 = Auxiliary NMEA
Default:
7
Serial Port Input
Format
Int
1 = MX LB2
2 = Aux. LB2
4 = RTCM Input
10 = NMEA Input
11 = Aux NMEA
Default:
Example:
$PMVXG,200,1,6,,,,10,10*61
$PMVXG,200,1,7,,,,,*60
Sentence type: $GPMSK
Description: Beacon tune command
There are three main derivatives of this command that affects the method of beacon receiver
tuning, and each are described in the following sections.
Full manual command ($GPMSK):
This command instructs the MX575C/MX575D’s internal beacon receiver to tune to a
specified frequency and MSK Rate.
It has the following form:
$GPMSK,fff.f,M,ddd,M,n<CR><LF>
The internal SBX will reply with the following response:
$PCSI,ACK,GPMSK,fff.f,M,ddd,M,n<CR><LF>
When this message is acknowledged by the internal beacon receiver, it will immediately tune
to the frequency specified and demodulate at the rate specified.
Field Description
fff.f Frequency in kHz (283.5 to 325)
M Designates manual frequency selection
ddd MSK bit rate (100 or 200 bps)
M Designates manual MSK bit rate selection
n
Period of output of performance status message, 0 to 100 seconds
($CRMSS)
Example:
$GPMSK,305,M,,A,,,*
$GPMSK,305,,A,,A,,,*
Page 46

44 |
Technical specications | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
Partial manual tune command ($GPMSK):
This command instructs the internal beacon receiver to tune to a specified frequency and
automatically select the correct MSK rate.
It has the following form:
$GPMSK,fff.f,M,,A,n<CR><LF
The internal SBX will reply with the following response:
$PCSI,ACK,GPMSK,fff.f,M,,A,n<CR><LF>
When this message is acknowledged by the internal beacon receiver, it will immediately tune
to the frequency specified and demodulate at the rate specified.
Field Description
fff.f Frequency in kHz (283.5 to 325)
M Designates manual frequency selection
ddd MSK bit rate (100 or 200 bps)
A Designates Automatic MSK bit rate selection
n
Period of output of performance status message, 0 to 100 seconds
($CRMSS)
Automatic beacon search command ($GPMSK,305):
This command initiates the beacon receiver to automatic mode of operation in which the
receiver operates without operator intervention, selecting the most appropriate beacon station.
This command has the following format:
$GPMSK,305,A,,A,,,<CR><LF>
The internal beacon receiver will reply with the following response:
$PCSI,ACK,GPMSK,,A,,A,n<CR><LF>
Field Description
A1 Automatic Frequency selection Mode
A2 Designates Automatic rate selection
null
The Smart GPS compass provides the above response to this variety of $GPMSK message,
and immediately tunes to the optimum beacon station in automatic mode, provided a
valid beacon almanac is present in receiver memory. Without a valid almanac, the beacon
receiver will perform a Global Search to identify candidate stations in the area, followed by the
acquisition phase of the initial search.
Beacon database search mode ($GPMSK,305):
This operating mode has been added to the MX575C/MX575D beacon receiver in order to
be compliant with the specification IEC 61108-4 for ship borne DGPS maritime radio beacon
receiver equipment.
The basic operation is outlined below.
1. The receiver will determine the 10 closest beacon stations after the GPS receiver has
calculated a valid position fix. The list can be accessed using the command $PCSI,3,2*.
2. The primary beacon channel tries to tune to the closest available station, using the frequency
and bit rate specified in the station database.
3. The background channel tunes to the frequency of the closest station using an alternate bit
rate.
Page 47

| 45
Technical specications | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
4. The primary channel retunes to the alternate bit rate if lock is achieved on the background
channel (with acceptable station health and WER).
5. The background channel continually searches for a closer station using the station database
once a lock is achieved on the primary channel.
6. The primary channel will remain tuned to the same station unless one of the following
occurs:
- Word error rate (WER) drops below 10%
- Station becomes unhealthy or unmonitored
- Background channel finds a closer station
- Position changes enough to affect station list.
This command has the following format:
$GPMSK,305,D,,D<CR><LF>
Sentence type: $JSHOW
Description: Command to show its current configuration.
This command is used to poll the Smart GPS compass receiver for its current configuration.
This command has the following structure.
$JSHOW[,subset] <CR><LF>
Using the $JSHOW command without the optional ‘,subset’ field will provide a complete
response from the receiver. An example of this response follows.
$>JSHOW,BAUD,9600 (1)
$>JSHOW,BAUD,9600,OTHER (2)
$>JSHOW,ASC,GPGGA,1.0,OTHER (3)
$>JSHOW,ASC,GPVTG,1.0,OTHER (4)
$>JSHOW,ASC,GPGSV,1.0,OTHER (5)
$>JSHOW,ASC,GPGST,1.0,OTHER (6)
$>JSHOW,ASC,D1,1,OTHER (7)
$>JSHOW,DIFF,WAAS (8)
$>JSHOW,ALT,NEVER (9)
$>JSHOW,LIMIT,10.0 (10)
$>JSHOW,MASK,5 (11)
$>JSHOW,POS,51.0,-114.0 (12)
$>JSHOW,AIR,AUTO,OFF (13)
$>JSHOW,FREQ,1575.4200,250 (14)
$>JSHOW,AGE,1800 (15)
This example response is summarized in the following table.
Line Description
1 This line indicates that the current port is set to a baud rate of 9600
2 This line indicates that the other port is set to a baud rate of 9600
3 This line indicates that GPGGA is output at a rate of 1 Hz from the other port
4 This line indicates that GPVTG is output at a rate of 1 Hz from the other port
5 This line indicates that the GPGSV is output at a rate of 1 Hz from the other port
Page 48

46 |
Technical specications | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
Line Description
6 This line indicates that GPGST is output at a rate of 1 Hz from the other port
7 This line indicates that D1 is output at a rate of 1 Hz from the other port
8 This line indicates that the current differential mode is WAAS
9 This line indicates the status of the altitude aiding feature
10
This line indicates the threshold of estimated differential performance that allows
the green DGPS LED to illuminate (on the Mini MAX only)
11 This line indicates the current elevation mask cutoff angle, in degrees
12 This line indicates the current seed position used for startup, in decimal degrees
13 This line indicates the current status of the AIR mode
14 This line indicates the current frequency of the L-band receiver
15 This line indicates the current maximum acceptable differential age in seconds
When issuing this command with the optional, ‘subset’ data field (without the square
brackets), a one-line response is provided. The subset field maybe either CONF or GP.
When CONF is specified for ‘subset’, the following response is provided.
$>JSHOW,CONF,N,0.0,10.0,5,A,60W
This response is summarized in the following table.
Message
Component
Description
$>JSHOW,CONF Message header
N N ‘N’ indicates no altitude aiding
0.0
‘0.0’ indicates the aiding value, if specified (either specified height or
PDOP threshold)
10.0 Residual limit for the $JLIMIT command
5 Elevation mask cutoff angle, in degrees
A AIR mode indication
60 Maximum acceptable age of correction data in seconds
W Current differential mode, ‘W’ indicates WAAS mode
When GP is specified for ‘subset’, the following is an example response provided:
$>JSHOW,GP,GGA,1.0
This response will provide the >$JSHOW,GP message header, followed by each message
currently being output through the current port and also the update rate for that message.
Sentence type: $JDIFF
Description: Beacon receiver differential mode
This command is used to change the differential mode of the receiver. The default differential
mode is Auto/Database.
This command has the following structure.
$JDIFF,diff<CR><LF>
Where the differential mode variable, ‘diff’, has one of the following values:
$JDIFF,diff<CR><LF>
Page 49

| 47
Technical specications | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
Values Description
OTHER
Specifying OTHER instructs the receiver to use external corrections input
through the opposite port from which you are communicating
BEACON
Specifying BEACON instructs the receiver to use corrections from the
internal SBX beacon engine
WAAS Specifying WAAS instructs the receiver to use SBAS corrections
LBAND Specifying LBAND instructs the receiver to use OmniSTAR corrections.
AUTODIFF Specifying AUTODIFF instructs the receiver to use eDif mode
NONE
In order for the receiver to operate in autonomous mode, the NONE
argument may be specified in this command.
Example:
$JDIFF,BEACON*
$JDIFF,LBAND*
$JDIFF,WAAS*
Page 50

48 |
Troubleshooting | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
Troubleshooting
Table A-1 provides troubleshooting for common problems.
Table A-1: Troubleshooting
Symptom Possible Solution
Receiver fails to power • Verify polarity of power leads
• Check integrity of power cable connectors
• Check power input voltage (6 to 36 VDC)
• Check current restrictions imposed by power source
(minimum available should be > 1.0 A)
No data from HS80/HS80A
(N2K Network connection)
• Check N2K connectivity using the Device List from the
CDU.
• Check integrity and connectivity of power and data
cable connections
No data from MX575C/
MX575D (NMEA -0183
connection)
• Check receiver power status to ensure the receiver is
powered (an ammeter can be used for this)
• Verify desired messages are activated (using the CDU or
$JSHOW command in any terminal program)
• Ensure the baud rate of the smart GPS compass matches
that of the receiving device
• Check integrity and connectivity of power and data
cable connections
Random data from
smart GPS compass
• Verify the RTCM or binary messages are not being output
accidentally (send a $JSHOW command)
• Ensure the baud rate of the smart GPS compass matches
that of the remote device
• Potentially, the volume of data requested to be output
by the smart GPS compass could be higher than the
current baud rate supports (try using 19200 as the baud
rate for all devices or reduce the amount of data being
output)
No GPS lock • Verify the smart GPS compass has a clear view of the sky
• Verify the lock status of GPS satellites (this can be done
with using the MFD or CDU)
No SBAS lock • Verify the smart GPS compass has a clear view of the sky
• Verify the lock status of SBAS satellites (this can be done
using the CDU)
• Set SBAS mode to automatic with the $JWAASPRN,AUTO
command
• Note: SBAS lock is only possible if you are in an
appropriate SBAS region; currently, there is limited SBAS
availability in the southern hemisphere.
5
Page 51

| 49
Troubleshooting | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
Symptom Possible Solution
No heading or incorrect
heading value
• Check CSEP value is fairly constant without varying more
than 1 cm (0.39 in)—larger variations may indicate a
high multipath environment and require moving the
receiver location
• Heading is from primary GPS antenna to secondary GPS
antenna, so the arrow on the underside of the smart
GPS compass should be directed to the bow side
• $JATT,SEARCH command forces the smart GPS compass
to acquire a new heading solution (unless gyro is
enabled)
• Enable GYROAID to provide heading for up to three
minutes during GPS signal loss
• Enable TILTAID to reduce heading search times
• Monitor the number of satellites and SNR values for both
antennas using the CDU—at least four satellites should
have strong SNR values
• Potentially, the volume of data requested to be output
by the smart GPS compass could be higher than the
current baud rate supports (try using 19200 as the baud
rate for all devices or reduce the amount of data being
output)
No DGPS position in external
RTCM mode
• Verify the baud rate of the RTCM input port matches the
baud rate of the external source
• Verify the pinout between the RTCM source and the
RTCM input port (transmit from the source must go to
receive of the RTCM input port and grounds must be
connected)
• Ensure corrections are being transmitted to the correct
port—using the $JDIFF,PORTB command on Port A will
cause the receiver to expect the corrections to be input
through Port B
No Beacon lock (MX575C &
D only)
• Verify the MX575C/MX575D has no obstructions from
large metal objects and railings.
• Verify the Beacon status in the GPS6 screen of the CDU.
Select a known beacon station frequency using manual
mode.
¼ Note: Beacon lock is only possible if you are in areas
where the land-based beacons cover. There are many
areas of the world where beacon signal is not available.
Page 52

50 |
Troubleshooting | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
List of abbreviations
CDU Control Display Unit
COG Course Over Ground
DGPS Differential Global Positioning System
GLONASS Global Orbiting Navigation Satellite System
GNSS Global Navigation Satellite System
GPS Global Positioning System
HDOP Horizontal Dilution Of Precision
IMO International Maritime Organization
NMEA National Marine Electronic Association
PDOP Positional Dilution Of Precision
RAIM Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring
ROT Rate Of Turn
RTK Real Time Kinematic
SBAS Satellite Based Augmentation System
SOG Speed Over Ground
THD Transmitting Heading Device
VDOP Vertical Dilution Of Precision
Page 53

| 51
Wiring Diagrams | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
Wiring Diagrams
MX420 CDU to GPS compass interface diagram
RL1
RL2
RS232 enable
J1
UPPER LOWER
Rs232
PORT 2
Tx
Rx
GND
MX420/2 JUNCTION BOX
CABLE A
MX ANTENNA
PORT
PORT1
DUAL CONTROL
EXT. ALARM
POWER FAIL
PWR INPUT
IN +
GND
U1
U2
U7
U4
U9
U5
U6
2 AMP
B IN
A IN
B OUT
A OUT
BRN
ORG
GRN
BLK
RED
GREY
PURPLE
YEL
WHT
BLU
B IN
A IN
B OUT
A OUT
NO
NC
C
NO
NC
C
IN -
12-32 VDC
POWER INPUT
1
18
MX420/2
HS80/HS80A
MX575C/MX575D
BLK (GND)
RED (12 VDC)
YEL
YEL/BL K
BLK/B RN
BRN
GRN
GRN/BLK
ORG*
ORG/BLK *
1PPS+
1 PPS-
MX510/MX512 to GPS compass interface diagram
RED (+12 VDC)
BLK (NEG)
BLK
GRN (NMEA3 RX+)
ORG (NMEA3 RX-)
BRN (NMEA3 TX+)
BLU (NMEA3 TX -)
YEL/BL K
YEL
BLK/BRN
BRN
MX510/MX512 CDU
HS80/HS80A
MX575C/MX575D
10-PIN CABLE ASSY.
P/N 3508 102 70150
(3-METERS)
WHT (BEACON IN +)
YEL (BEACON IN -)
GRN/BLK
GRN
*ORG (1 PPS+)
*ORG/BL K (1 PPS-)
6
Page 54

52 |
Wiring Diagrams | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
GPS compass interface via MX510 junction Box
Page 55

| 53
Wiring Diagrams | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
MX512 to GPS compass interface diagram via MX512 Junction Box
Page 56

54 |
Wiring Diagrams | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
1PPS output
BLK (-)
YEL/BL K (Port B TX-)
YEL (Port B TX+)
BLK/ BRN (Port B RX-)
BRN (Port B RX+
HS80/HS80A
MX575C/MX575D
BLK/GRN (Port A TX-)
GRN (Port A TX+)
ORG (1 PPS+)
*ORG/BLK (1 PPS-)
+
12-24 VDC
GND
To 1 PPS
Load
PC to GPS compass interface diagram
BLK (-)
YEL/BLK (Port B TX-)
YEL (P ort B T X+ )
BLK/B RN (Port B RX-)
BRN (P ort B RX+
HS 80/HS80A
M X575C/MX575D
BLK/G RN (Por t A TX -)
GR Y (G ND)
+12-24 VDC
GND
2
3
5
d
B-9
C
onnector
Page 57

| 55
Wiring Diagrams | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
GPS compass connection to the MX61xJB junction box.
T
T
12/24V DC
MX61xJB
Junction Box
12/24V DC
Where:
N2K Backbone
Drop line
NMEA 0183 line
GN70/MX610/MX612
MX575C/MX757D
HS80/HS80A
GPS Compass
Ports 3&4
Port 2
Port 1
Page 58

56 |
Wiring Diagrams | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
REMOTE
PORT1 PORT2
PORT3 PORT4 SUPPLY
+ -
TERMINATION
SIMNET
SIMNET
BRN
BLK/BRN
YEL
YEL/BLK
GRN
BLK/GRN
RED
BLK
MX575C/MX575D
GPS Compass
MX61xJB PCB Terminals
ANTENNA CABLE
000-10939-001 (15 m)
000-10940-001 (30 m)
Speed Log+
Speed Log -
RX+
RX-
TX+
TX-
NMEA 0183 CONNECTOR
TERMINALS
RED
BLK
WHT
BLU
N2K
NEG
12-24 VDC
Page 59

| 57
Wiring Diagrams | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
HS80/HS80A connection via the NMEA 2000 network
T
12/24V DC
MX61xJB
Junction Box
12/24V DC
Where:
N2K Backbone
Drop line
NMEA 0183 line
GN70/MX610/MX612
HS80/HS80A
GPS Compass
Ports 3&4
Port 2
Port 1
N2K Converter
T
Page 60

58 |
Wiring Diagrams | HS80/HS80A/MX575C/MX575D User Manual
Page 61

Page 62

*988-10221-003*
 Loading...
Loading...