Page 1
ToolStick-F330DC
TOOLSTICK C8051F330 DAUGHTER CARD USER’S GUIDE
1. Handling Recommendations
To enable development, the ToolStick Base Adapter and daughter cards are distributed without any protective
plastics. To prevent damage to the devices and/or the host PC, please take into consideration the following
recommendations when using the ToolStick:
Never connect or disconnect a daughter card to or from the ToolStick Base Adapter while the Base Adapter is
connected to a PC.
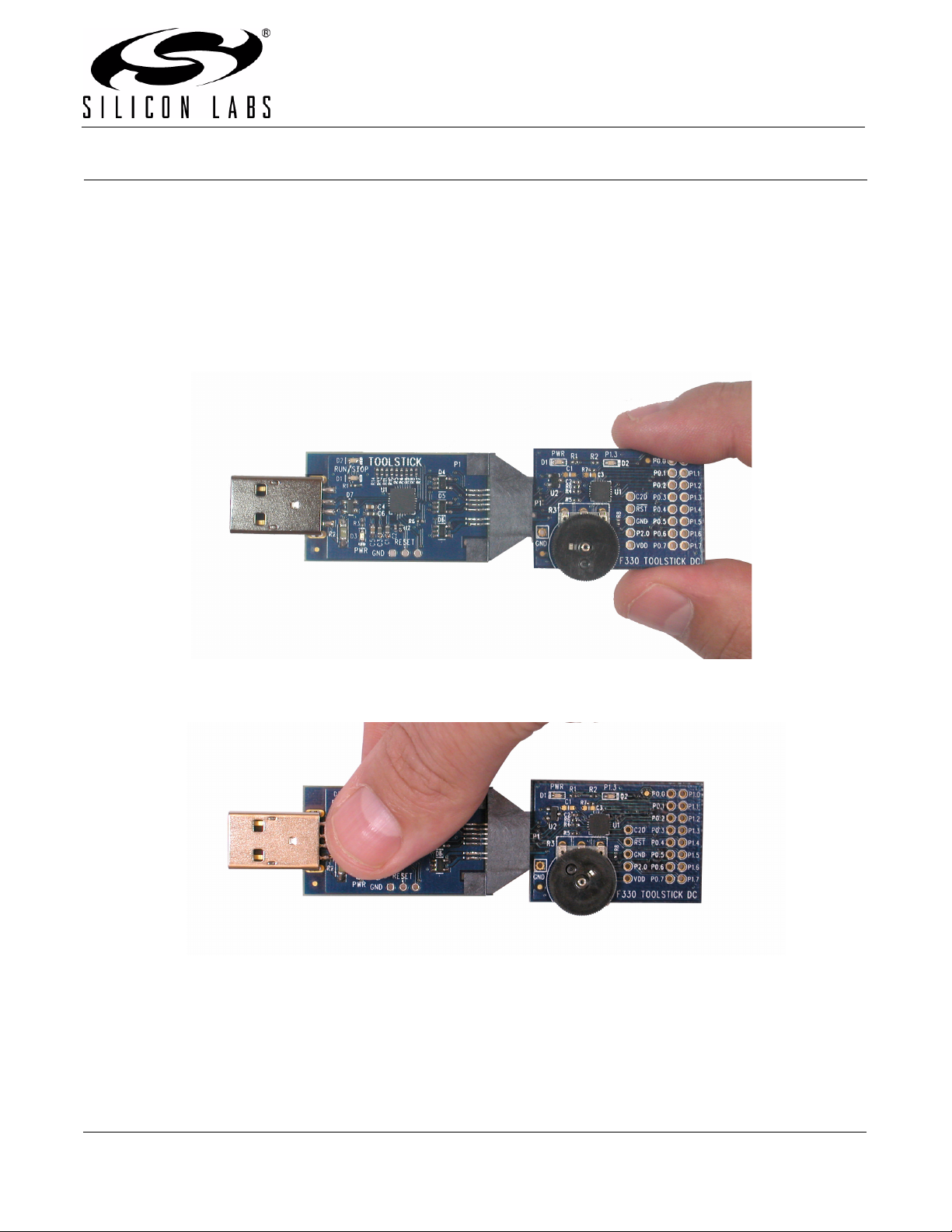
Always connect and disconnect the ToolStick Base Adapter from the PC by holding the edges of the boards.
Figure 1. Proper Method of Holding the ToolStick
Avoid directly touching any of the other components.
Figure 2. Improper Method of Holding the ToolStick
Manipulate mechanical devices on the daughter cards, such as potentiometers, with care to prevent the Base
Adapter or daughter card from accidentally dislodging from their sockets.
Rev. 0.3 1/07 Copyright © 2007 by Silicon Laboratories ToolStick-C8051F330DC
Page 2
ToolStick-F330DC
2. Contents
The ToolStick-F330DC kit contains the following items:
ToolStick C8051F330 Daughter Card
The ToolStick Starter Kit includes the following items:
ToolStick Base Adapter
ToolStick C8051F330 Daughter Card
3-foot USB extension cable
A ToolStick daughter card requires a ToolStick Base Adapter to communicate with the PC. If the daughter card was
not purchased as part of a Starter Kit, ToolStick Base Adapters can be purchased separately at
www.silabs.com/toolstick.
3. ToolStick Overview
The purpose of the ToolStick is to provide a development and demonstration platform for Silicon Laboratories
microcontrollers and to demonstrate the Silicon Laboratories software tools, including the Integrated Development
Environment (IDE).
The ToolStick development platform consists of two components: the ToolStick Base Adapter and a daughter card.
The ToolStick Base Adapter provides a USB debug interface and data communications path between a Windows
PC and a target microcontroller.
The target microcontroller and application circuitry are located on the daughter card. Some daughter cards, such
as the C8051F330 Daughter Card, are used as general-purpose development platforms for the target
microcontrollers and some are used to demonstrate a specific feature or application.
The C8051F330 Daughter Card includes a pair of LEDs, a potentiometer, a resistor across the C8051F330’s
current DAC output pin, and a small prototyping area which provides access to all of the pins of the device. This
prototyping area can be used to connect additional hardware to the microcontroller and use the daughter card as a
development platform. See Section "10. Board Revision Information‚" on page 14 for information regarding the
prototyping area.
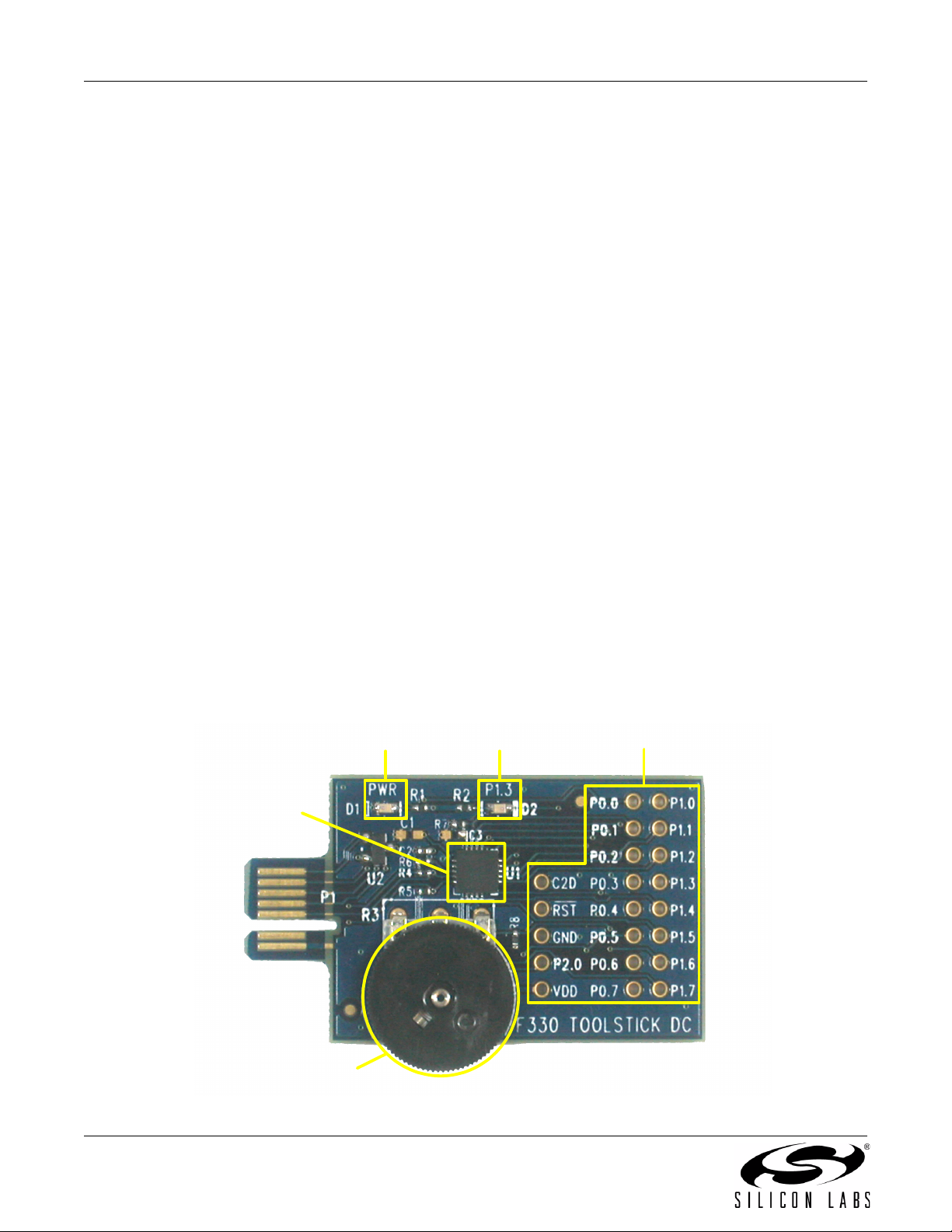
Figure 3 shows the ToolStick C8051F330 Daughter Card and identifies the various components.
Power LED P1.3 LED
C8051F330
P1.6 Potentiometer
Figure 3. ToolStick C8051F330 Daughter Card
2 Rev. 0.3
Full Pin Access
Page 3

ToolStick-F330DC
4. Getting Started
The necessary software to download, debug and communicate with the target microcontroller must be downloaded
from www.silabs.com/toolstick. The following software is necessary to build a project, download code to, and
communicate with the target microcontroller:
Silicon Laboratories Integrated Development Environment (IDE)
Keil Demonstration Tools
ToolStick Terminal application
The Keil Demo Tools include a compiler, assembler, and linker. The limits of the demo version are: 1) the resulting
object code is limited to 2 kBytes and 2) the floating point library is not included. ToolStick Terminal communicates
with the target microcontroller's UART through the ToolStick Base Adapter. It can also read/write the two GPIO pins
available on the ToolStick Base Adapter.
Other useful software that is provided on the Silicon Labs Downloads (www.silabs.com/mcudownloads) website
includes:
Configuration Wizard 2
Keil uVision2 and uVision3 Drivers
All of the above software is described in more detail in Section “5. Software Overview”.
To simplify the download process, the necessary software described above is provided in two download packages.
The ToolStick Download package includes the Keil Tools, example code, documentation including User’s Guides
and data sheets, and the ToolStick Terminal application. The IDE, Configuration Wizard 2, and the Keil uVision
Drivers are available as a separate download. After downloading and installing these two packages, see the
following sections for information regarding the software and running one of the demo applications.
5. Software Overview
5.1. Silicon Laboratories IDE
The Silicon Laboratories IDE integrates a source-code editor, source-level debugger, and an in-system Flash
programmer. See Section “6. ToolStick C8051F330 Daughter Card Features Demo” for detailed information on how
to use the IDE. The Keil Demonstration Toolset includes a compiler, linker, and assembler and easily integrates
into the IDE. The use of third-party compilers and assemblers is also supported.
5.1.1. IDE System Requirements
The Silicon Laboratories IDE requirements:
Pentium-class host PC running Microsoft Windows 2000 or Windows XP.
One available USB port.
64 MB RAM and 40 MB free HD space recommended.
5.1.2. 3rd Party Toolsets
The Silicon Laboratories IDE has native support for many 8051 compilers. The full list of natively supported tools is:
Keil
IAR
Raisonance
Tasking
Hi-Tech
SDCC
Dunfield
Please note that the demo applications for the C8051F330 Daughter Card are written for the Keil toolset.
Rev. 0.3 3
Page 4
ToolStick-F330DC
5.2. Keil Demonstration Toolset
5.2.1. Keil Assembler and Linker
The assembler and linker that are part of the Keil Demonstration Toolset are the same versions that are found in
the full Keil Toolset. The complete assembler and linker reference manual can be found on-line under the Help
menu in the IDE or in the “SiLabs\MCU\hlp” directory (A51.pdf).
5.2.2. Keil Demonstration C51 C Compiler
The demonstration version of the C51 compiler is the same as the full version except code size is limited to 2 kB
and the floating point library is not included. The C51 compiler reference manual can be found under the Help
menu in the IDE or in the “SiLabs\MCU\hlp” directory (C51.pdf).
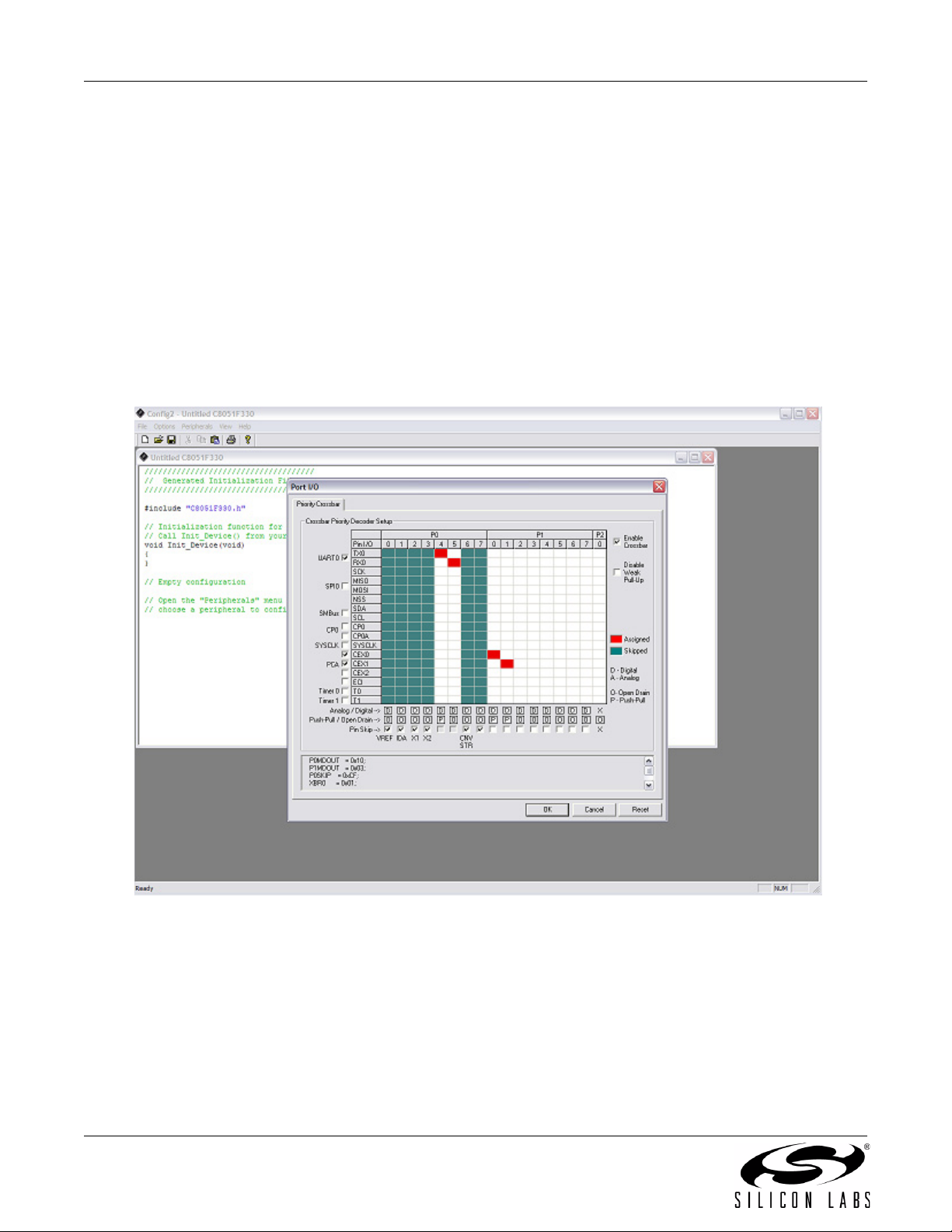
5.3. Configuration Wizard 2
The Configuration Wizard 2 is a code generation tool for all of the Silicon Laboratories devices. Code is generated
through the use of dialog boxes for each of the device's peripherals.
Figure 4. Configuration Wizard 2 Utility
The Configuration Wizard 2 utility helps accelerate development by automatically generating initialization source
code to configure and enable the on-chip resources needed by most design projects. In just a few steps, the wizard
creates complete startup code for a specific Silicon Laboratories MCU. The program is configurable to provide the
output in C or assembly.
For more information, please refer to the Configuration Wizard 2 documentation. The documentation and software
available from the Downloads webpage (www.silabs.com/mcudownloads).
4 Rev. 0.3
Page 5

ToolStick-F330DC
5.4. Keil uVision2 and uVision3 Silicon Laboratories Drivers
As an alternative to the Silicon Laboratories IDE, the uVision debug driver allows the Keil uVision2 and uVision3
IDEs to communicate with Silicon Laboratories on-chip debug logic. In-system Flash memory programming
integrated into the driver allows for rapidly updating target code. The uVision2 and uVision3 IDEs can be used to
start and stop program execution, set breakpoints, check variables, inspect and modify memory contents, and
single-step through programs running on the actual target hardware.
For more information, please refer to the uVision driver documentation. The documentation and software are
available from the Downloads webpage (www.silabs.com/mcudownloads).
5.5. ToolStick Terminal
The ToolStick Terminal program provides the standard terminal interface to the target microcontroller's UART.
However, instead of requiring the usual RS-232 and COM port connection, ToolStick Terminal uses the USB
interface of the ToolStick Base Adapter to provide the same functionality.
In addition to the standard terminal functions (send file, receive file, change baud rate), two GPIO pins on the target
microcontroller can be controlled using the Terminal for either RTS/CTS handshaking or software-configurable
purposes (see the demo software for an example).
See Section 6.8 for more information on using ToolStick Terminal. The software is available on the ToolStick
webpage (www.silabs.com/toolstick).
Rev. 0.3 5
Page 6
ToolStick-F330DC
6. ToolStick C8051F330 Daughter Card Features Demo
The ToolStick kit includes a few simple code examples. The example described in this section is titled
F330DC_FeaturesDemo. The purpose of this example is to guide a new user through the features and capabilities
of the IDE and demonstrate the microcontroller’s on-chip debug capabilities. The F330DC_FeaturesDemo
example code uses the potentiometer on the daughter card to vary the blinking rate of the LED. The first part of this
demo shows how to use the IDE to connect and download the firmware, view and modify registers, use watch
windows, use breakpoints, and single step through code. The second part of the demo shows how to use ToolStick
Terminal to receive UART data from the daughter card and how to use the GPIO pins.
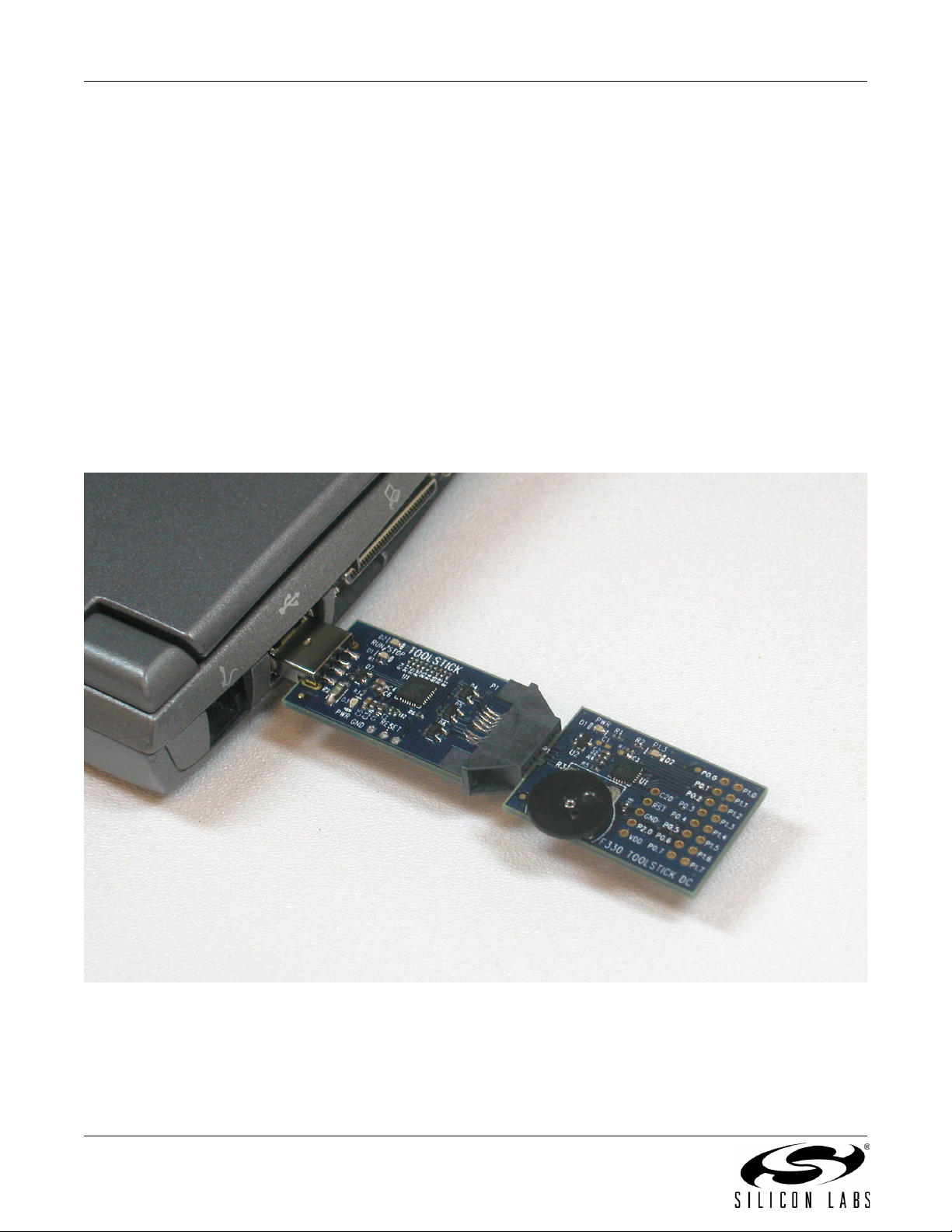
6.1. Hardware Setup
Connect the ToolStick hardware to the PC using the steps below while taking note of the recommendations in
Section 1:
1. Connect the ToolStick Base Adapter to the ToolStick C8051F330 Daughter Card.
2. If available, connect the USB extension cable to the ToolStick Base Adapter.
3. Connect the ToolStick to a USB port on a PC.
See Figure 5 below for an example hardware setup.
Figure 5. Hardware Setup Example
6 Rev. 0.3
Page 7

ToolStick-F330DC
6.2. Connecting to the Device and Downloading Firmware
This section describes how to open the IDE, open and build a project, connect to a device and download the
firmware.
1. Open the Silicon Laboratories IDE from the Start → Programs → Silicon Laboratories menu.
2. In the IDE, go to Project → Open Project.
3. Browse to C:\SiLabs\MCU\ToolStick\F330DC\Firmware\.
4. Select F330DC_FeaturesDemo.wsp and click OK.
5. In the IDE, select Project → Rebuild Project.
6. Go to Options → Connection Options.
7. Select “USB Debug Adapter” for the Serial Adapter and “C2” for the Debug Interface, and then click “OK”.
8. Go to Debug → Connect.
9. Download the code using the download button on the menu bar or use alt-D.
Once these steps are completed, the firmware is built into an object file (step 5) and downloaded to the device
(step 9). The device is now ready to begin executing code. If all of these steps were followed successfully, the “Go”
option is enabled in the Debug menu. A green circle icon in the IDE toolbar also indicates that the device is ready
to run. If one of the steps leads to an error, make sure that the ToolStick is properly inserted in a USB port and start
again with step 6.
6.3. Running and Stopping Code Execution
Once the IDE is connected to the device and the firmware is loaded, the IDE can start and stop the code execution.
The following steps can be performed using the buttons on the toolbar or using the options in the Debug menu.
1. To start code execution, click the green “Go” button on the toolbar or use the Debug → Go menu option. The
green LED on the daughter card will start to flash. The debug commands in the IDE (single-step, multiple-step,
set breakpoint, and others) are disabled when the device is running.
potentiometer on the daughter card can be turned to alter the blinking speed of the LED.
While the firmware is running, the
2. To stop code execution, click the red “Stop” button on the toolbar or use the Debug → Stop menu option. The
device will halt code execution and all of the registers and pins on the device will hold their state.
All debug windows and watch windows are refreshed when the device is stopped. If any of the values in these
windows have changed since the last time the device was halted, the new value is shown in red text instead of
black text.
Rev. 0.3 7
Page 8

ToolStick-F330DC
6.4. Viewing and Modifying Registers
All registers on the device can be viewed and modified when the device is in a halted state. The registers are
grouped together according to which peripheral or part of hardware they belong. As an example, this guide shows
how to open the ADC0 Debug Window and disable the ADC0 directly from the IDE.
1. Open the ADC0 Debug Window from the View → Debug Windows → SFR’s → ADC0 menu option. The
ADC0 Debug Window appears on the right-hand side of the IDE. In this window, the ADC0CN register is shown.
This register is used to enable and configure the on-chip ADC. When the firmware is running, the ADC0CN
register reads as 0x82 indicating that the ADC is running.
2. In the debug window, change the value of ADC0CN from 0x82 to 0x02. This value turns off the ADC on the
target microcontroller.
3. To write this new value to the device, select Refresh from the Debug Menu or click the Refresh button in the
toolbar.
4. Click “Go” to resume running the device with the new ADC0CN value.
5. Turn the potentiometer on the daughter card and notice that it has no effect on the blinking rate of the LED.
6. Re-enable the ADC by writing 0x82 to the ADC0CN and clicking the Refresh button.
Changing the values of registers does not require recompiling the code and redownloading the firmware. At any
time, the device can be halted and the values of the registers can be changed. After selecting “Go”, the firmware
will continue execution using the new values. This capability greatly speeds up the debugging process. See the
data sheet for the C8051F330 device for the definitions and usage for all registers.
The debug windows for other sets of registers are found in the View → Debug Windows → SFR’s menu.
8 Rev. 0.3
Page 9

ToolStick-F330DC
6.5. Enabling and Using Watch Windows
The Debug Windows in the View menu are used to view and modify hardware registers. To view and modify
variables in code, the IDE provides Watch Windows. Just as with register debug windows, variables in the watch
windows are updated each time the device is halted. This section of the User’s Guide explains how to add a
variable to the watch window and modify the variable. In the F330_FeatureDemo example code, the variable
Num_LED_Flashes is a counter that stores the number of times the LED blinks.
1. If the device is running, stop execution using the “Stop” button or use the Debug → Stop menu option.
2. In the File View on the left-hand side of the IDE, double-click on F330DC_FeaturesDemo.c to open the source
file.
3. Scroll to the Timer3_ISR function (line 334) and right-click on the variable “Num_LED_Flashes”. In the context
menu that appears, select “Add Num_LED_Flashes to Watch” and then choose “Default.” On the right-hand
portion of the IDE, the watch window appears and the variable is added. The current value of the variable is
shown to the right of the name.
4. Start and stop the device a few times. See that the value of the Num_LED_Flashes is incremented each time
the LED blinks.
5. When the device is halted, click on the value field in the watch window and change the value to 0. Then click the
Refresh button or select Debug → Refresh to write the new value to the device.
6. Start and stop the device a few times to watch the variable increment starting at 0.
Changing the values of variables does not require recompiling the code and redownloading the firmware. At any
time, the device can be halted and the values of the variables can be changed. The firmware will continue
execution using the new values.
Rev. 0.3 9
Page 10

ToolStick-F330DC
6.6. Setting and Running to Breakpoints
The Silicon Laboratories microcontroller devices support up to four hardware breakpoints. A breakpoint is
associated with a specific line of code. When the processor reaches a hardware breakpoint, the code execution
stops, and the IDE refreshes all debug and watch windows. The on-chip debug hardware allows for breakpoints to
be placed on any line of executable code, including code in Interrupt Service Routines. This section provides steps
to set a breakpoint on the line of source code that increments the Num_LED_Flashes variable.
1. If the device is running, stop execution using the “Stop” button or use the Debug → Stop menu option.
2. Scroll to the Timer3_ISR function (line 334) and right-click on the variable “Num_LED_Flashes”. In the context
menu that appears, select “Insert/Remove Breakpoint.” On the left side of the line in the editor window, a red
circle is added to indicate a breakpoint is placed on the source line.
3. Click the “Go” button or select the Debug → Go menu option.
4. After a short time, the IDE will show that the device is halted. A blue line will be placed in the editor window to
indicate where the code execution has stopped.
5. Start and stop the processor a few more times. Notice that the LED blinks once for every time the processor is
started and the Num_LED_Flashes variable also increments by one.
10 Rev. 0.3
Page 11

ToolStick-F330DC
6.7. Single-Stepping Through Firmware
The IDE supports the ability to single-step through firmware one assembly instruction at a time. The IDE reads the
Flash from the device, converts the instructions to assembly and displays them in a disassembly window. The
following steps show how to open the disassembly window and single step through firmware.
1. If there is already not a breakpoint set on line of code that increments the Num_LED_Flashes variable, set the
breakpoint using the steps described in Section 6.6.
2. Start the processor using the “Go” button and wait till it stops on the breakpoint.
3. Select View → Debug Windows → Disassembly. The disassembly window will appear on the right-hand side
of the IDE, if it is not already open.
4. To execute one assembly instruction at a time, click the “Step” button on the toolbar or select the Debug →
Step menu option. The highlighted line in the disassembly window indicates the next instruction to be executed.
The blue line marker in the editor window will stay on the same .C source line until all of the assembly
instructions are completed.
The disassembly window has three columns. The left column is the address of the instruction in Flash. The middle
column is the instruction in hex. The right column is the disassembled instruction. The Disassembly debug window
and the capability to single-step through firmware allows a developer to see exactly what instructions are executed
and their output.
Rev. 0.3 11
Page 12

ToolStick-F330DC
6.8. Using ToolStick Terminal
This section describes how to use ToolStick Terminal to communicate with UART from the PC to the daughter card
through the ToolStick Base Adapter.
1. If the Silicon Laboratories IDE is open, close the IDE. The IDE and the ToolStick Terminal cannot communicate
with the daughter card simultaneously.
2.
Open ToolStick Terminal from the
Start → Programs → Silicon Laboratories
menu.
3. Go to the ToolStick →
4. Under “Pin Settings”, change GPIO0 / RTS to “GPIO Output - Push Pull” and click “OK.” The rest of the default
settings are correct for the C8051F330 Features Demo.
5. In the top, left-hand corner of the Terminal application, available devices are shown in the drop-down
Connection menu. Click “Connect” to connect to the device. In the “Receive Data” window, text indicating the
blink rate of the LED will appear.
6. Turn the potentiometer on the daughter card and see that the blink rate is updated on the daughter card and the
new blink rate is printed to the Terminal.
In addition to the standard two UART pins (TX and RX), there are two GPIO/UART handshaking pins on the
ToolStick Base Adapter that are connected to two port pins on the target microcontroller. ToolStick Terminal is used
to configure and read/write these pins. For the F330DC_FeaturesDemo, one of these GPIO pins is connected to
an external interrupt pin on the C8051F330. The following steps describe how to change the level of one of the
GPIO pins and trigger an interrupt on the target microcontroller. The interrupt forces the firmware to switch modes
and send a pulse-width modulated (PWM) signal to the LED instead of blinking the LED using an on-chip Timer.
1. In ToolStick Terminal, under Pin State Configuration, select “Set GPIO0 Logic Low” and click on “Set Selected
Pin States.” This changes the level of the GPIO0 pin from Logic High to Logic Low and triggers a level-
sensitive interrupt on the microcontroller.
2. In the Receive window, see that the printed text has changed to indicate the LED PWM duty cycle.
3. Turn the potentiometer on the daughter card to change the brightness of the LED on the daughter card.
4. Change the GPIO0 pin state back to Logic High and notice that the firmware switches back to blinking the
LED.
The firmware on the C8051F330 target microcontroller does not need to be customized to use the UART and
communicate with ToolStick Terminal. The firmware on the microcontroller should write to the UART as it would in
any standard application and all of the translation is handled by the ToolStick Base Adapter.
Settings
menu.
12 Rev. 0.3
Page 13

ToolStick-F330DC
7. Additional Demo Examples
In addition to the F330DC_FeaturesDemo example firmware, the ToolStick download package also includes demo
projects named F330DC_ADC0_TemperatureSensor and F330DC_IDA0_SineWave. The instructions for
running these demos can be found at the top of the source file.
The project and source files for these demos can be found in the C:\SiLabs\MCU\ToolStick\F330DC\Firmware\
folder.
8. Using the C8051F330 Daughter Card as a Development Platform
The prototyping area on the ToolStick C8051F330 daughter card makes it easy to interface to external hardware.
All of the digital I/O pins are available so it possible to create a complete system.
8.1. C8051F330 Pin Connections
It is important to note that if external hardware is being added, some of the existing components on the board can
interfere with the signaling. The following is a list of port pins on the C8051F330 that are connected to other
components:
P0.1—This pin has a pull-down resistor (R7) to ground so that the IDAC output can be converted to a voltage.
R7 can be safely removed from the daughter card if it is not needed.
P0.4, P0.5—These pins are connected directly to the ToolStick Base Adapter for UART communication.
P0.6, P0.7—These pins are connected directly to the ToolStick Base Adapter’s GPIO pins. By default, these
GPIO pins on the Base Adapter are high-impedance pins so they will not affect any signaling. Configuring these
pins on the Base Adapter to output pin or handshaking pins could affect signaling.
P1.3—This pin is connected to the cathode of the green LED on the daughter card. The LED or the R2 resistor
can be removed to disconnect the LED from the pin.
P1.6—This pin is connected to the output of the potentiometer. The 0 ohm resistor can be removed to
disconnect the potentiometer from the pin.
See the daughter card schematic in Section 11 for more information.
8.2. VREF Capacitor
On the C8051F330 devices, if VREF is generated internally, it is output to port pin P0.0. For VREF stability, it is
highly recommended to place a capacitor on the VREF output pin. On the ToolStick C8051F330 Daughter Card,
there are pads on the board (C3) to populate a 0603 surface mount capacitor. The firmware examples for the
daughter card use VDD as VREF, so no external capacitor on P0.0 is necessary for proper operation.
8.3. C2 Pin Sharing
On the C8051F330, the debug pins, C2CK, and C2D, are shared with the pins /RST and P2.0 respectively. The
daughter card includes the resistors necessary to enable pin sharing which allow the /RST and P2.0 pins to be
used normally while simultaneously debugging the device. See Application Note “AN124: Pin Sharing Techniques
for the C2 Interface” at www.silabs.com for more information regarding pin sharing.
Rev. 0.3 13
Page 14

ToolStick-F330DC
9. Information Locations
Example source code is installed by default in the “C:\SiLabs\MCU\ToolStick\F330DC\Firmware” directory during
the ToolStick installation.
Documentation for the ToolStick kit, including this User’s Guide, can be found in the
C:\SiLabs\MCU\ToolStick\Documentation and the C:\SiLabs\MCU\ToolStick\F330DC\Documentation directories.
The installer for the ToolStick software is available at www.silabs.com/toolstick.
10. Board Revision Information
Revision SA-TS002-001 of the F330 Daughter Card has two test points swapped in the prototyping area. The test
point labeled P0.3 is connected to pin P1.3, and the test point labeled P1.3 is connected to pin P0.3 on the
microcontroller. This error is fixed on revision SA-TS002-002 and later boards. The revision number is located on
the back side of the daughter card.
14 Rev. 0.3
Page 15

11. C8051F330 Daughter Card Schematic
ToolStick-F330DC
Rev. 0.3 15
Page 16

ToolStick-F330DC
DOCUMENT CHANGE LIST
Revision 0.1 to Revision 0.2
Added Section "10. Board Revision Information‚" on
page 14.
Revision 0.2 to Revision 0.3
Added ToolStick Terminal, Configuration Wizard 2,
and Keil uVision drivers to Section “5. Software
Overview”.
Added images to Sections “6.3. Running and
Stopping Code Execution”, “6.4. Viewing and
Modifying Registers”, “6.5. Enabling and Using
Watch Windows”, “6.6. Setting and Running to
Breakpoints”, “6.7. Single-Stepping Through
Firmware”, and “6.8. Using ToolStick Terminal”.
Various small text edits.
16 Rev. 0.3
Page 17

NOTES:
ToolStick-F330DC
Rev. 0.3 17
Page 18

ToolStick-F330DC
CONTACT INFORMATION
Silicon Laboratories Inc.
400 West Cesar Chavez
Austin, TX 78701
Tel: 1+(512) 416-8500
Fax: 1+(512) 416-9669
Toll Free: 1+(877) 444-3032
Email: MCUinfo@silabs.com
Internet:
www.silabs.com
The information in this document is believed to be accurate in all respects at the time of publication but is subject to change without notice.
Silicon Laboratories assumes no responsibility for errors and omissions, and disclaims responsibility for any consequences resulting from
the use of information included herein. Additionally, Silicon Laboratories assumes no responsibility for the functioning of undescribed features
or parameters. Silicon Laboratories reserves the right to make changes without further notice. Silicon Laboratories makes no warranty, representation or guarantee regarding the suitability of its products for any particular purpose, nor does Silicon Laboratories assume any liability
arising out of the application or use of any product or circuit, and specifically disclaims any and all liability, including without limitation consequential or incidental damages. Silicon Laboratories products are not designed, intended, or authorized for use in applications intended to
support or sustain life, or for any other application in which the failure of the Silicon Laboratories product could create a situation where personal injury or death may occur. Should Buyer purchase or use Silicon Laboratories products for any such unintended or unauthorized application, Buyer shall indemnify and hold Silicon Laboratories harmless against all claims and damages.
Silicon Laboratories and Silicon Labs are trademarks of Silicon Laboratories Inc.
Other products or brandnames mentioned herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders.
18 Rev. 0.3
 Loading...
Loading...