Siemens TDA4605-2 Datasheet
Control IC for Switched-Mode Power Supplies
using MOS-Transistors
Features
● Fold-back characteristics provides overload protection for
external components
● Burst operation under secondary short-circuit condition
implemented
● Protection against open or a short of the control loop
● Switch-off if line voltage is too low (undervoltage switch-off)
● Line voltage depending compensation of fold-back point
● Soft-start for quiet start-up without noise generated by the
transformer
● Chip-over temperature protection implemented (thermal
shutdown)
● On-chip ringing suppression circuit against parasitic
oscillations of the transformer
TDA 4605-2
Bipolar IC
P-DIP-8-1
Type Ordering Code Package
TDA 4605-2 Q67000-A5020 P-DIP-8-1
The IC TDA 4605-2 controls the MOS-power transistor and performs all necessary regulation and
monitoring functions in free running flyback converters. Because of the fact that a wide load range
is achieved, this IC is applicable for consumer as well as industrial power supplies.
The serial circuit and primary winding of the flyback transformer are connected in series to the input
voltage. During the switch-on period of the transistor, energy is stored in the transformer. During the
switch-off period the energy is fed to the load via the secondary winding. By varying switch-on time
of the power transistor, the IC controls each portion of energy transferred to the secondary side
such that the output voltage remains nearly independent of load variations. The required control
information is taken from the input voltage during the switch-on period and from a regulation winding
during the switch-off period. A new cycle will start if the transformer has transferred the stored
energy completely into the load.
Semiconductor Group 54 06.94

TDA 4605-2
In the different load ranges the switched-mode power supply (SMPS) behaves as follow:
No load operation
The power supply is operating in the burst mode at typical 20 to 40 kHz. The output voltage can be
a little bit higher or lower than the nominal value depending of the design of the transformer and the
resistors of the control voltage divider.
Nominal operation
The switching frequency is reduced with increasing load and decreasing AC-voltage. The duty
factor primarily depends on the AC-voltage.
The output voltage is only dependent on the load.
Overload point
Maximal output power is available at this point of the output characteristic.
Overload
The energy transferred per operation cycle is limited at the top. Therefore the output voltages
declines by secondary overloading.
Semiconductor Group 55
TDA 4605-2
Pin Definitions and Functions
Pin No. Function
1 Information Input Concerning Secondary Voltage. By comparing the
regulating voltage - obtained from the regulating winding of the transformer - with
the internal reference voltage, the output impulse width on pin 5 is adjusted to the
load of the secondary side (normal load, overload, short-circuit, no load).
2 Information Input Regarding the Primary Current. The primary current rise in
the primary winding is simulated at pin 2 as a voltage rise by means of external
RC-circuit. If a voltage level is reached which is derived from the control voltage
at pin 1, the output impulse at pin 5 is terminated. The RC-circuit is used to set
the maximum power of the foldback point.
3 Input for Primary Voltage Monitoring: In the normal operation
between the thresholds V3Hand V
V
< V3L: SMPS is switched OFF (line voltage too low).
3
V
> V3H: Compensation of the overload point regulation (controlled by pin 2)
3
3L(V3H
> V3 > V3L).
V
is moving
3
starts at V3H: V3L = 1.7.
4 Ground
5 Output: Push-pull output for charging or discharging the gate capacity of the
power MOSFET-transistor.
6 Supply Voltage Input. From the voltage at pin 6 a stable internal reference
voltage
supply voltage detector are derived. If V6 > V6E then V
V
and the switching thresholds V6A, V6E, V
REF
and V
6 max
is switched on. The
REF
6 min
for the
reference voltage will be switched off if V6< V6A. In addition the logic is only
enable, for V
6 min
< V6< V
6 max
.
7 Input for Soft-Start and Integrator Circuit. The capacitor connected to ground
causes a slow increase of the duration of the output pulse during start-up and an
integrating response of the control amplifier.
8 Input for the Feedback of the Oscillator. After the oscillations of the SMPS
started, every transition of the feedback voltage through zero (falling edge)
triggers an output pulse at pin 5. The trigger threshold is at + 50 mV typical.
Semiconductor Group 56
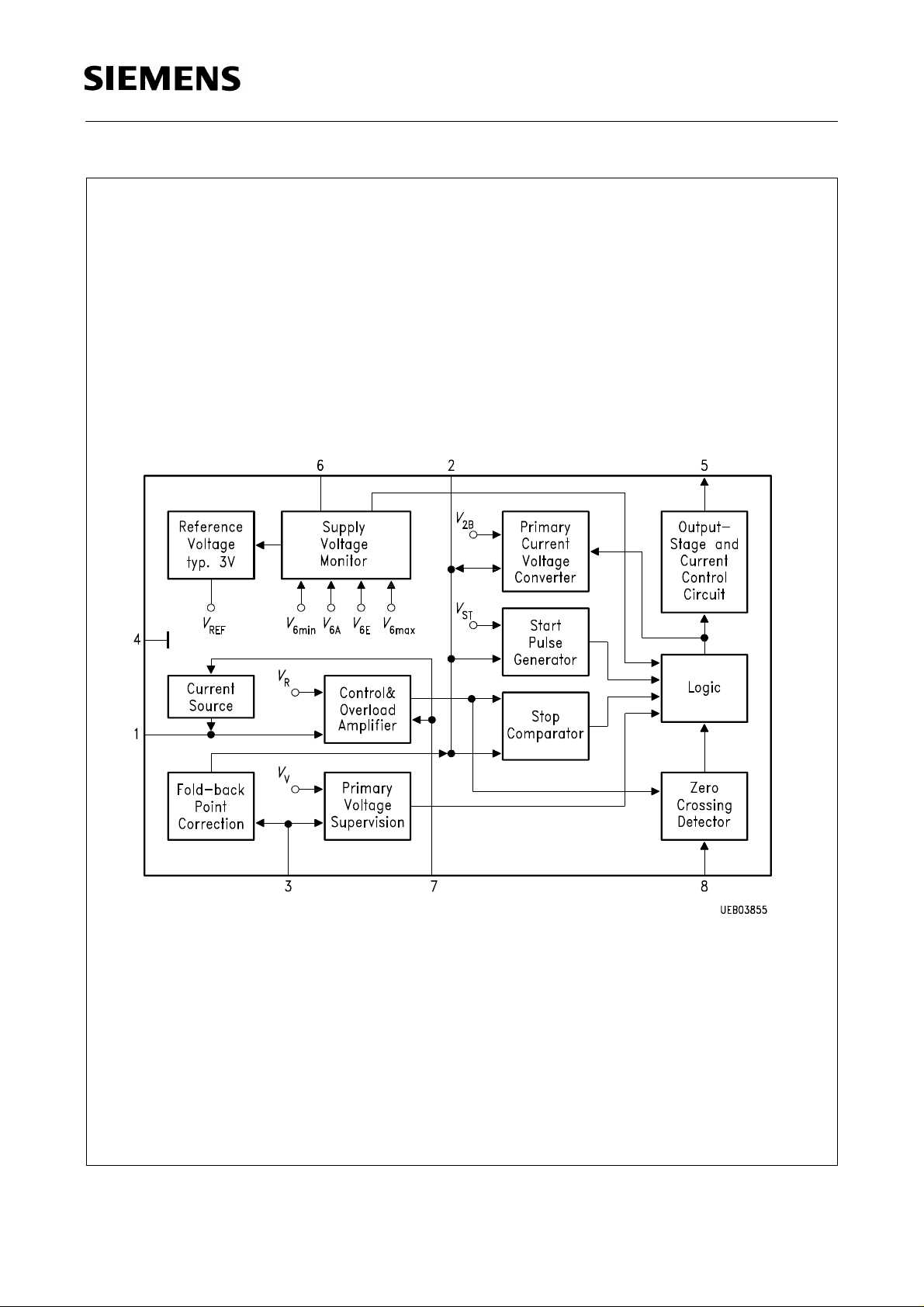
TDA 4605-2
Block Diagram
Semiconductor Group 57

TDA 4605-2
Circuit Description
Application Circuit
The application circuit shows a flyback converter for video recorders with an output power rating of
70 W. The circuit is designed as a wide-range power supply for AC-line voltages of 180 to 264 V.
The AC-input voltage is rectified by the bridge rectifier GR1 and smoothed by C1. The NTC limits
the rush-in current.
The IC includes an internal circuit to avoid the turn-on of the power transistor T1 because of static
charges applied to the transistors gate, during the turn-off state of the IC. The resistor R13 helps to
limit the spectrum of the radiated noise.
During the conductive phase of the power transistor T1 the current rise in the primary winding
depends on the winding inductance and the mains voltage.
The network consisting of R4-C5 is used to create a model of the sawtooth shaped rise of the
collector current. The resulting control voltage is fed into pin 2 of the IC. The RC-time constant given
by R4-C5 must be designed that way that driving the transistor core into saturation is avoided.
The ratio of the voltage divider R10/R11 is fixing a voltage level threshold. Below this threshold the
switching power supply shall stop operation because of the low mains voltage. The control voltage
present at pin 3 also determines the correction current for the foldback point.
This current added to the current flowing through R4 and represents an additional charge to C5 in
order to reduce the turn-on phase of T1. This is done to stabilize the fold-back point even under
higher mains voltages.
The control of the switched-mode power supply is done by means of a control voltage applied to
pin 1. The control voltage of winding n1 during the off-period of T1 is rectified by D3 smoothed byC
and stepped down at an adjustable ratio by R5, R6 and R7. The primary peak current, is adjusted
by the IC so that the voltage applied across the control winding, and hence the output voltages, are
at the desired level.
When the energy stored in the transformer is transferred into the load the control voltage passes
through zero. The IC detects the zero crossing via the series R9 connected to pin 8. But zero
crossings of the control voltage can also be produced by ringing of the transformer after the turn-off
of the power transistor for T1 or when a short-circuit is applied to the output of the SMPS.
The capacitor C8 is connected to pin 7. During the start-up phase this capacitor assures pulses with
a shorter duty cycle in order to keep the operating frequency outside the audible frequency range.
On the secondary side of the transformer 3 output voltages are produced using the windings n2 to
n
, rectified by D4 to D6 and smoothed byC9 to C11. The resistor R12 is used as a bleeder resistor,
5
the resistors with implemented fuse R15 and R16 protect the rectifies against short circuits in the
output circuits, which are designed to supply only small loads.
6
Semiconductor Group 58

TDA 4605-2
Block Diagram
Pin 1
In the control and overload amplifier the control voltage applied to this pin is compared with a stable
internal reference voltage V. The output signal of this stage is fed to the "stop" comparator. If the
control voltage is rather small at pin 1 an additional current is added by means of current source
which is controlled according the level at pin 7. This additional current is virtually reducing the
control voltage present at pin 1.
Pin 2
A voltage proportional to the drain current of the switching transistor is generated by means of an
external RC-combination in conjunction with the internal functional block primary current / voltage
converter. The output of this converter is controlled by the internal functional block "logic" and is
also connected to the internal reference voltage V2B. If the voltage V2 exceeds the output voltage
of the "control and overload amplifier" the stop comparator will reset the control logic. Consequently
the output of pin 5 is switched to low potential. Further inputs for the logic stage are the outputs of
the start impulse generator with the stable reference potential VST, the supply voltage monitoring
circuit as well as the primary voltage supervision circuit.
Pin 3
The primary voltage applied here via a voltage divider is used to stabilize the fold-back point. In
addition the logic is disable if - in comparison with the internal reference voltage VV - a mains
undervoltage condition is detected.
Pin 4
Ground
Pin 5
In the output stage the output signals from the "logic" block are converted into driving signals
suitable for power MOS-transistors.
Pin 6
From the supply voltage V6 applied to this pin internally a stable reference voltage V
the switching thresholdV6A,V6E,V
All other inter reference value (VR, V2B, VST and Vv) are derived for V
6 max
andV
, for the supply voltage monitor section of the IC.
6 min
. If V6> V6E the V
REF
as well as
REF
REF
voltage source is switched on and the source is switched off if V6< V6A. In addition the logic is
enable only if V
6 min
< V6 < V
6 max
.
Semiconductor Group 59
 Loading...
Loading...