
Preface
Open Source Software
Table of Contents
SIPROTEC 4
Line Differential Protection
7SD80
V4.7
Manual
Introduction
Functions
Mounting and Commissioning
Technical Data
Ordering Information and Accessories
Terminal Assignments
Connection Examples
Current Transformer Requirements
Default Settings and Protocol-dependent
Functions
1
2
3
4
A
B
C
D
E
E50417-G1100-C474-A2
Functions, Settings, Information
Literature
Glossary
Index
F
i
i
NOTE
For your own safety, observe the warnings and safety instructions contained in this document, if available.
Disclaimer of Liability
This document has been subjected to rigorous technical
review before being published. It is revised at regular intervals, and any modifications and amendments are included
in the subsequent issues. The content of this document has
been compiled for information purposes only. Although
Siemens AG has made best efforts to keep the document as
precise and up-to-date as possible, Siemens AG shall not
assume any liability for defects and damage which result
through use of the information contained herein.
This content does not form part of a contract or of business
relations; nor does it change these. All obligations of
Siemens AG are stated in the relevant contractual agreements.
Siemens AG reserves the right to revise this document from
time to time.
Document version: E50417-G1100-C474-A2.01
Edition: 02.2018
Version of the product described: V4.7
Copyright
Copyright © Siemens AG 2018. All rights reserved.
The disclosure, duplication, distribution and editing of this
document, or utilization and communication of the content
are not permitted, unless authorized in writing. All rights,
including rights created by patent grant or registration of a
utility model or a design, are reserved.
Registered Trademarks
SIPROTEC®, DIGSI®, SIGUARD®, SIMEAS®, and SICAM® are
registered trademarks of Siemens AG. Any unauthorized
use is illegal. All other designations in this document can
be trademarks whose use by third parties for their own
purposes can infringe the rights of the owner.
Preface
Purpose of the Manual
This manual describes the functions, operation, installation, and commissioning of devices 7SD80. In particular, one will find:
Information regarding the configuration of the scope of the device and a description of the device func-
•
tions and settings → Chapter 2;
Instructions for Installation and Commissioning → Chapter 3;
•
Compilation of the Technical Data → Chapter 4;
•
As well as a compilation of the most significant data for advanced users → Appendix.
•
General information with regard to design, configuration, and operation of SIPROTEC 4 devices are set out in
the SIPROTEC 4 System Description /1/ SIPROTEC 4 System Description.
Target Audience
Protection-system engineers, commissioning engineers, persons entrusted with the setting, testing and maintenance of selective protection, automation and control equipment, and operating personnel in electrical
installations and power plants.
Scope
This manual applies to: SIPROTEC 4 Line Differential Protection 7SD80; Firmware-Version V4.7.
Indication of Conformity
Additional Standards IEEE Std C37.90 (see Chapter 4 "Technical Data")
This product is UL-certified according to the Technical Data. file E194016
[ul-schutz-7sx80-100310, 1, --_--]
This product complies with the directive of the Council of the European Communities on the
approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to electromagnetic compatibility
(EMC Council Directive 2004/108/EC) and concerning electrical equipment for use within
specified voltage limits (Low-voltage Directive 2006/95 EC).
This conformity is proved by tests conducted by Siemens AG in accordance with the Council
Directive in agreement with the generic standards EN 61000-6-2 and EN 61000-6-4 for EMC
directive, and with the standard EN 60255-27 for the low-voltage directive.
The device has been designed and produced for industrial use.
The product conforms with the international standards of the series IEC 60255 and the
German standard VDE 0435.
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018
3

!
!
!
Preface
Additional Support
For questions about the system, please contact your Siemens sales partner.
Support
Our Customer Support Center provides a 24-hour service.
Phone: +49 (180) 524-7000
Fax: +49 (180) 524-2471
E-Mail: support.energy@siemens.com
Training Courses
Inquiries regarding individual training courses should be addressed to our Training Center:
Siemens AG
Siemens Power Academy TD
Humboldtstraße 59
90459 Nürnberg
Germany
Phone: +49 (911) 433-7415
Fax: +49 (911) 433-7929
E-Mail: poweracademy@siemens.com
Internet: www.siemens.com/poweracademy
Notes on Safety
This document is not a complete index of all safety measures required for operation of the equipment (module
or device). However, it comprises important information that must be followed for personal safety, as well as
to avoid material damage. Information is highlighted and illustrated as follows according to the degree of
danger:
DANGER
DANGER means that death or severe injury will result if the measures specified are not taken.
²
WARNING
WARNING means that death or severe injury may result if the measures specified are not taken.
²
CAUTION
Comply with all instructions, in order to avoid death or severe injuries.
Comply with all instructions, in order to avoid death or severe injuries.
CAUTION means that medium-severe or slight injuries can occur if the specified measures are not taken.
Comply with all instructions, in order to avoid moderate or minor injuries.
²
4 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018
NOTICE
i
i
NOTICE means that property damage can result if the measures specified are not taken.
Comply with all instructions, in order to avoid property damage.
²
NOTE
Important information about the product, product handling or a certain section of the documentation
which must be given particular attention.
Qualified Electrical Engineering Personnel
Only qualified electrical engineering personnel may commission and operate the equipment (module, device)
described in this document. Qualified electrical engineering personnel in the sense of this manual are people
who can demonstrate technical qualifications as electrical technicians. These persons may commission,
isolate, ground and label devices, systems and circuits according to the standards of safety engineering.
Proper Use
The equipment (device, module) may be used only for such applications as set out in the catalogs and the
technical description, and only in combination with third-party equipment recommended and approved by
Siemens.
Problem-free and safe operation of the product depends on the following:
Proper transport
•
Proper storage, setup and installation
•
Proper operation and maintenance
•
When electrical equipment is operated, hazardous voltages are inevitably present in certain parts. If proper
action is not taken, death, severe injury or property damage can result:
The equipment must be grounded at the grounding terminal before any connections are made.
•
All circuit components connected to the power supply may be subject to dangerous voltage.
•
Hazardous voltages may be present in equipment even after the supply voltage has been disconnected
•
(capacitors can still be charged).
Preface
Operation of equipment with exposed current-transformer circuits is prohibited. Before disconnecting the
•
equipment, ensure that the current-transformer circuits are short-circuited.
The limiting values stated in the document must not be exceeded. This must also be considered during
•
testing and commissioning.
Typographic and Symbol Conventions
The following text formats are used when literal information from the device or to the device appear in the
text flow:
Parameter Names
Designators of configuration or function parameters which may appear word-for-word in the display of the
device or on the screen of a personal computer (with operation software DIGSI), are marked in bold letters in
monospace type style. The same applies to titles of menus.
1234A
Parameter addresses have the same character style as parameter names. Parameter addresses contain the
suffix A in the overview tables if the parameter can only be set in DIGSI via the option Display additional
settings.
Parameter Options
Possible settings of text parameters, which may appear word-for-word in the display of the device or on the
screen of a personal computer (with operation software DIGSI), are additionally written in italics. The same
applies to the options of the menus.
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 5
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018
Preface
Indications
Designators for information, which may be output by the relay or required from other devices or from the
switch gear, are marked in a monospace type style in quotation marks.
Deviations may be permitted in drawings and tables when the type of designator can be obviously derived
from the illustration.
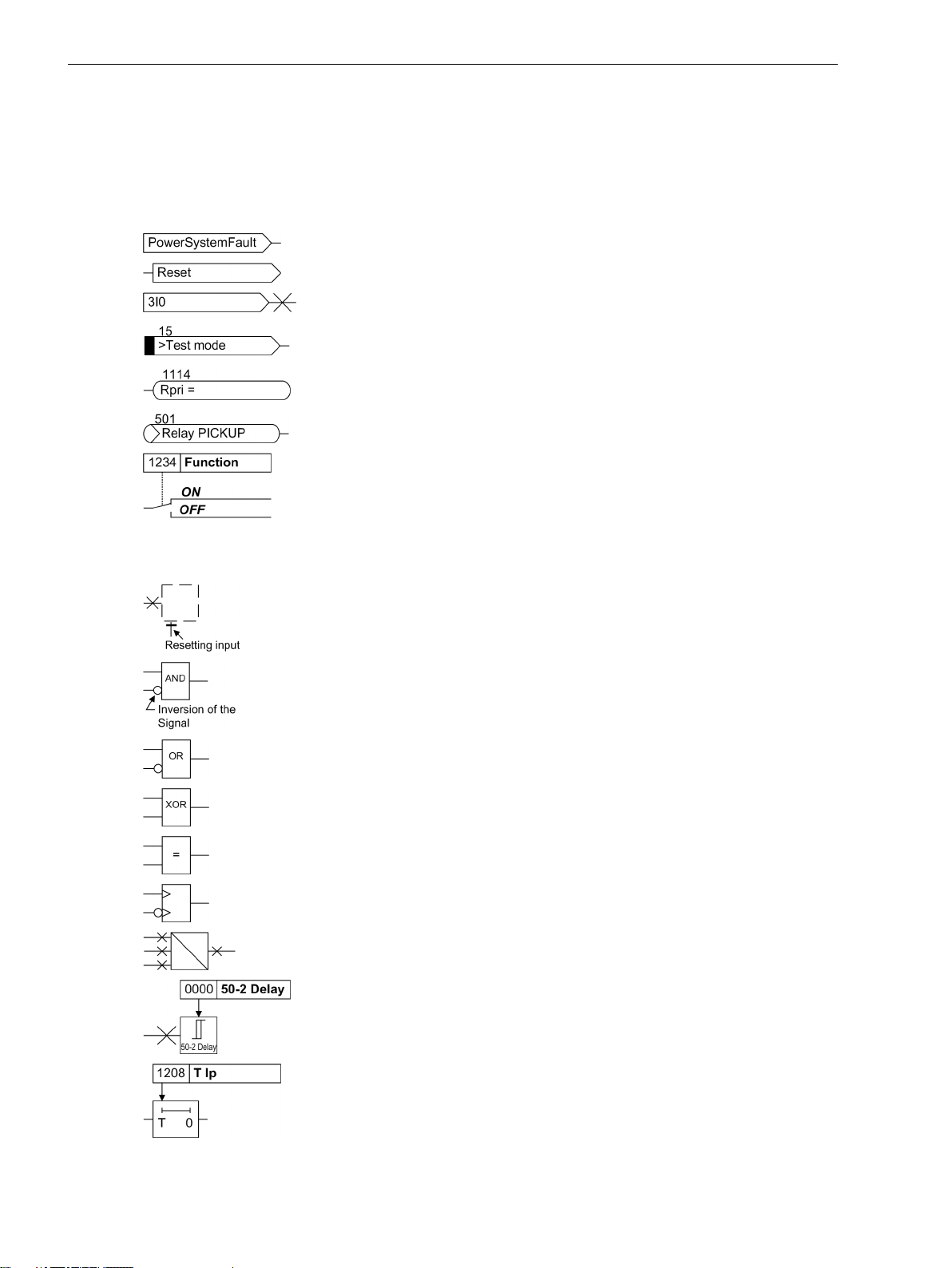
The following symbols are used in drawings:
Device-internal logical input signal
Device-internal logical output signal
Internal input signal of an analog quantity
External binary input signal with number (binary input,
input indication)
External binary output signal with number
(example of a value indication)
External binary output signal with number (device indication) used as
input signal
Example of a parameter switch designated FUNCTION with address
1234 and the possible settings ON and OFF
Besides these, graphical symbols are used in accordance with IEC 60617-12 and IEC 60617-13 or similar.
Some of the most frequently used are listed below:
Analog input variable
AND-gate operation of input values
OR-gate operation of input values
Exclusive OR gate (antivalence): output is active, if only one of the
inputs is active
Coincidence gate: output is active, if both inputs are active or inactive
at the same time
Dynamic inputs (edge-triggered) above with positive, below with
negative edge
Formation of one analog output signal from a number of analog input
signals
Limit stage with setting address and parameter designator (name)
Timer (pickup delay T, example adjustable) with setting address and
parameter designator (name)
6 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Timer (dropout delay T, example non-adjustable)
Dynamic triggered pulse timer T (monoflop)
Static memory (SR flipflop) with setting input (S), resetting input (R),
output (Q) and inverted output (Q), setting input dominant
Static memory (RS-flipflop) with setting input (S), resetting input (R),
output (Q) and inverted output (Q), resetting input dominant
Preface
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 7
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

8 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Open Source Software
The product contains, among other things, Open Source Software developed by third parties. The Open
Source Software used in the product and the license agreements concerning this software can be found in the
Readme_OSS. These Open Source Software files are protected by copyright. Your compliance with those
license conditions will entitle you to use the Open Source Software as foreseen in the relevant license. In the
event of conflicts between Siemens license conditions and the Open Source Software license conditions, the
Open Source Software conditions shall prevail with respect to the Open Source Software portions of the software. The Open Source Software is licensed royalty-free. Insofar as the applicable Open Source Software
License Conditions provide for it you can order the source code of the Open Source Software from your
Siemens sales contact - against payment of the shipping and handling charges - for a period of at least 3 years
since purchase of the Product. We are liable for the Product including the Open Source Software contained in
it pursuant to the license conditions applicable to the Product. Any liability for the Open Source Software
beyond the program flow intended for the Product is explicitly excluded. Furthermore any liability for defects
resulting from modifications to the Open Source Software by you or third parties is excluded. We do not
provide any technical support for the Product if it has been modified.
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018
9

10 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Table of Contents
Preface..........................................................................................................................................................3
Open Source Software..................................................................................................................................9
1 Introduction................................................................................................................................................19
1.1 Overall Operation..............................................................................................................20
1.2 Application Scope............................................................................................................. 23
1.3 Characteristics.................................................................................................................. 25
2 Functions.................................................................................................................................................... 29
2.1 General.............................................................................................................................30
2.1.1 Functional Scope......................................................................................................... 30
2.1.1.1 Functional Description........................................................................................... 30
2.1.1.2 Setting Notes......................................................................................................... 30
2.1.1.3 Settings................................................................................................................. 32
2.1.2 Device, General Settings.............................................................................................. 33
2.1.2.1 Functional Description........................................................................................... 33
2.1.2.2 Setting Notes......................................................................................................... 34
2.1.2.3 Settings................................................................................................................. 34
2.1.2.4 Information List..................................................................................................... 34
2.1.3 General Power System Data (Power System Data 1)......................................................36
2.1.3.1 Setting Notes......................................................................................................... 36
2.1.3.2 Settings................................................................................................................. 38
2.1.4 Oscillographic Fault Records........................................................................................ 39
2.1.4.1 Functional Description........................................................................................... 40
2.1.4.2 Setting Notes......................................................................................................... 40
2.1.4.3 Settings................................................................................................................. 40
2.1.4.4 Information List..................................................................................................... 40
2.1.5 Change Group............................................................................................................. 40
2.1.5.1 Functional Description........................................................................................... 41
2.1.5.2 Setting Notes......................................................................................................... 41
2.1.5.3 Settings................................................................................................................. 41
2.1.5.4 Information List..................................................................................................... 41
2.1.6 General Protection Data (Power System Data 2)........................................................... 42
2.1.6.1 Setting Notes......................................................................................................... 42
2.1.6.2 Settings................................................................................................................. 43
2.1.6.3 Information List..................................................................................................... 44
2.1.7 EN100-Modul 1........................................................................................................... 45
2.1.7.1 Functional Description........................................................................................... 45
2.1.7.2 Information List..................................................................................................... 45
2.1.8 Protection Interface..................................................................................................... 45
2.1.8.1 Functional Description........................................................................................... 45
2.1.8.2 Setting Notes......................................................................................................... 46
2.1.8.3 Settings................................................................................................................. 46
2.1.8.4 Information List..................................................................................................... 47
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 11
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Table of Contents
2.2 Phase Comparison Protection and Ground Differential Protection.......................................48
2.2.1 Differential Topology................................................................................................... 48
2.2.1.1 Setting Notes......................................................................................................... 48
2.2.1.2 Settings................................................................................................................. 48
2.2.1.3 Information List..................................................................................................... 48
2.2.2 Phase Comparison Protection.......................................................................................49
2.2.2.1 Functional Description........................................................................................... 49
2.2.2.2 Setting Notes......................................................................................................... 53
2.2.3 Ground Current Differential Protection in Grounded Systems........................................54
2.2.3.1 Funktionsbeschreibung..........................................................................................54
2.2.3.2 Setting Notes......................................................................................................... 57
2.2.4 Restricted Ground-Fault Protection in Resonant-grounded/Isolated Systems..................58
2.2.4.1 Funktionsbeschreibung..........................................................................................58
2.2.4.2 Setting Notes......................................................................................................... 61
2.2.5 Differential Protection Pickup Logic and Tripping Logic.................................................62
2.2.5.1 Functional Description........................................................................................... 62
2.2.6 87 Differential Protection.............................................................................................63
2.2.6.1 Settings................................................................................................................. 63
2.2.6.2 Information List..................................................................................................... 64
2.2.7 Differential Protection Test and Commissioning........................................................... 65
2.2.7.1 Differential Protection Test.....................................................................................65
2.2.7.2 Differential Protection Commissioning....................................................................66
2.3 Breaker Intertrip and Remote Tripping............................................................................... 69
2.3.1 Functional Description.................................................................................................69
2.3.2 Setting Notes...............................................................................................................70
2.3.3 Settings.......................................................................................................................71
2.3.4 Information List...........................................................................................................71
2.4 Backup overcurrent........................................................................................................... 72
2.4.1 Operating Modes.........................................................................................................72
2.4.2 Non-directional Overcurrent Protection........................................................................72
2.4.3 Directional Overcurrent Protection...............................................................................76
2.4.4 Setting Notes...............................................................................................................82
2.4.5 Settings.......................................................................................................................85
2.4.6 Information List...........................................................................................................88
2.5 InRush Restraint................................................................................................................ 91
2.5.1 Functional Description.................................................................................................91
2.5.2 Setting Notes...............................................................................................................92
2.5.3 Settings.......................................................................................................................92
2.5.4 Information List...........................................................................................................93
2.6 Circuit Breaker Failure Protection 50BF.............................................................................. 94
2.6.1 Functional Description.................................................................................................94
2.6.2 Setting Notes.............................................................................................................100
2.6.3 Settings.....................................................................................................................102
2.6.4 Information List.........................................................................................................103
2.7 Thermal Overload Protection 49...................................................................................... 104
2.7.1 Functional Description...............................................................................................104
2.7.2 Setting Notes.............................................................................................................105
2.7.3 Settings.....................................................................................................................107
2.7.4 Information List.........................................................................................................107
12 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Table of Contents
2.8 Undervoltage and Overvoltage Protection (optional) 27/59..............................................108
2.8.1 Overvoltage Protection (ANSI 59)...............................................................................108
2.8.2 Undervoltage Protection (ANSI 27)............................................................................ 112
2.8.3 Setting Notes.............................................................................................................115
2.8.4 Settings.....................................................................................................................117
2.8.5 Information List.........................................................................................................119
2.9 Frequency Protection (optional) 81................................................................................. 123
2.9.1 Functional Description...............................................................................................123
2.9.2 Setting Notes.............................................................................................................125
2.9.3 Settings.....................................................................................................................127
2.9.4 Information List.........................................................................................................127
2.10 Direct Local Trip.............................................................................................................. 129
2.10.1 Functional Description...............................................................................................129
2.10.2 Setting Notes.............................................................................................................129
2.10.3 Settings.....................................................................................................................130
2.10.4 Information List.........................................................................................................130
2.11 Automatic Reclosure Function (optional) 79.................................................................... 131
2.11.1 Functional Description...............................................................................................131
2.11.2 Setting Notes.............................................................................................................136
2.11.3 Settings.....................................................................................................................139
2.11.4 Information List.........................................................................................................140
2.12 Circuit Breaker Test......................................................................................................... 142
2.12.1 CB Close Detection.................................................................................................... 142
2.12.2 Circuit-Breaker Position Detection.............................................................................. 144
2.12.3 Circuit-Breaker Test....................................................................................................146
2.12.4 Information List.........................................................................................................146
2.13 Direct Remote Trip and Transmission of Binary Information..............................................147
2.13.1 Functional Description...............................................................................................147
2.13.2 Information List.........................................................................................................147
2.14 Monitoring Functions......................................................................................................149
2.14.1 Measurement Supervision......................................................................................... 149
2.14.1.1 Hardware Monitoring...........................................................................................149
2.14.1.2 Software Monitoring ........................................................................................... 150
2.14.1.3 External Transformer Circuits............................................................................... 150
2.14.1.4 Fault Responses................................................................................................... 158
2.14.1.5 Setting Notes....................................................................................................... 159
2.14.1.6 Settings............................................................................................................... 160
2.14.1.7 Information List................................................................................................... 161
2.14.2 74TC Trip Circuit Supervision..................................................................................... 162
2.14.2.1 Functional Description......................................................................................... 162
2.14.2.2 Setting Notes....................................................................................................... 165
2.14.2.3 Settings............................................................................................................... 165
2.14.2.4 Information List................................................................................................... 165
2.15 Flexible Protection Functions...........................................................................................167
2.15.1 Functional Description...............................................................................................167
2.15.2 Setting Notes.............................................................................................................170
2.15.3 Settings.....................................................................................................................174
2.15.4 Information List.........................................................................................................175
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 13
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Table of Contents
2.16 Function Logic................................................................................................................ 177
2.16.1 Pickup Logic for the Entire Device.............................................................................. 177
2.16.2 Tripping Logic for the Entire Device............................................................................177
2.17 Auxiliary Functions..........................................................................................................181
2.17.1 Message Processing...................................................................................................181
2.17.1.1 LEDs and Binary Outputs (Output Relays)..............................................................181
2.17.1.2 Information via Display Field or PC........................................................................181
2.17.1.3 Information to a Control Center............................................................................182
2.17.2 Statistics....................................................................................................................183
2.17.2.1 Functional Description......................................................................................... 183
2.17.2.2 Information List................................................................................................... 183
2.17.3 Measurement During Operation.................................................................................184
2.17.3.1 Functional Description......................................................................................... 184
2.17.3.2 Information List................................................................................................... 185
2.17.4 Differential Protection Values.....................................................................................186
2.17.4.1 Measured Values of the Differential Protection..................................................... 186
2.17.4.2 Information List................................................................................................... 186
2.17.5 Measured Values Constellation.................................................................................. 186
2.17.5.1 Functional Description......................................................................................... 186
2.17.6 Min/Max Measurement Setup.................................................................................... 187
2.17.6.1 Functional Description......................................................................................... 187
2.17.6.2 Setting Notes....................................................................................................... 187
2.17.6.3 Settings............................................................................................................... 187
2.17.6.4 Information List................................................................................................... 188
2.17.7 Demand Measurement Setup.....................................................................................189
2.17.7.1 Functional Description......................................................................................... 189
2.17.7.2 Setting Notes....................................................................................................... 190
2.17.7.3 Settings............................................................................................................... 190
2.17.7.4 Information List................................................................................................... 190
2.17.8 Set Points (Measured Values).....................................................................................190
2.17.8.1 Setting Notes....................................................................................................... 190
2.17.8.2 Information List................................................................................................... 191
2.17.9 Energy.......................................................................................................................191
2.17.9.1 Energy Metering.................................................................................................. 191
2.17.9.2 Setting Notes....................................................................................................... 192
2.17.9.3 Information List................................................................................................... 192
2.18 Breaker Control...............................................................................................................193
2.18.1 Control Device...........................................................................................................193
2.18.1.1 Functional Description......................................................................................... 193
2.18.1.2 Information List................................................................................................... 194
2.18.2 Types of Commands.................................................................................................. 194
2.18.2.1 Functional Description......................................................................................... 194
2.18.3 Command Sequence..................................................................................................195
2.18.3.1 Functional Description......................................................................................... 195
2.18.4 Switchgear Interlocking............................................................................................. 196
2.18.4.1 Functional Description......................................................................................... 196
2.18.5 Command Logging.................................................................................................... 202
2.18.5.1 Functional Description......................................................................................... 202
2.19 Notes on Device Operation..............................................................................................203
2.19.1 Different operation....................................................................................................203
14 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Table of Contents
3 Mounting and Commissioning................................................................................................................. 205
3.1 Mounting and Connections............................................................................................. 206
3.1.1 Configuration Information......................................................................................... 206
3.1.2 Hardware Modifications.............................................................................................209
3.1.2.1 Disassembly.........................................................................................................209
3.1.2.2 Connections of the Current Terminals...................................................................212
3.1.2.3 Connections of the Voltage Terminals...................................................................214
3.1.2.4 Interface Modules................................................................................................ 214
3.1.2.5 Reassembly..........................................................................................................217
3.1.3 Installation................................................................................................................ 218
3.1.3.1 General................................................................................................................218
3.1.3.2 Panel Flush Mounting...........................................................................................218
3.1.3.3 Cubicle Mounting.................................................................................................219
3.1.3.4 Panel Surface Mounting....................................................................................... 220
3.2 Checking Connections.....................................................................................................222
3.2.1 Checking the Data Connections of the Interfaces........................................................222
3.2.2 Checking the Protection Data Communication............................................................224
3.2.3 Checking the System Connections............................................................................. 225
3.3 Commissioning............................................................................................................... 227
3.3.1 Test Mode and Transmission Block.............................................................................228
3.3.2 Checking Time Synchronization................................................................................. 228
3.3.3 Testing the System Interface .....................................................................................228
3.3.4 Configuring Communication Modules........................................................................230
3.3.5 Checking the Status of Binary Inputs and Outputs...................................................... 233
3.3.6 Checking the Protection Data Communication............................................................236
3.3.7 Checking Circuit Breaker Failure Protection................................................................ 238
3.3.8 Checking the Instrument Transformer Connections of One Line End...........................239
3.3.9 Checking the Instrument Transformer Connections of Two Line Ends......................... 244
3.3.10 Checking the Pilot Protection for Internal and External Remote Tripping..................... 244
3.3.11 Checking User-defined Functions...............................................................................244
3.3.12 Trip and Close Test with the Circuit Breaker................................................................244
3.3.13 Switching Check for the Configured Equipment......................................................... 245
3.3.14 Triggering Oscillographic Recording for Test...............................................................245
3.4 Final Preparation of the Device........................................................................................247
4 Technical Data.......................................................................................................................................... 249
4.1 General Device Data........................................................................................................250
4.1.1 Analog Inputs............................................................................................................250
4.1.2 Auxiliary Voltage....................................................................................................... 250
4.1.3 Binary Inputs and Outputs......................................................................................... 251
4.1.4 Communication Interfaces.........................................................................................252
4.1.5 Electrical Tests...........................................................................................................254
4.1.6 Mechanical Stress Tests............................................................................................. 256
4.1.7 Climatic Stress Tests.................................................................................................. 256
4.1.8 Service Conditions..................................................................................................... 257
4.1.9 Design.......................................................................................................................257
4.1.10 UL Certification Conditions........................................................................................ 257
4.2 Protection Interfaces and Connections.............................................................................259
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 15
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Table of Contents
4.3 87 Differential Protection Phase Comparison Protection...................................................261
4.4 Ground Fault Differential Protection in Grounded Systems...............................................264
4.5 Ground Fault Differential Protection in Resonant-grounded / Isolated Systems..................265
4.6 Breaker Intertrip and Remote Tripping- Direct Local Trip...................................................266
4.7 Time Overcurrent Protection ...........................................................................................267
4.8 Inrush Current Restraint Breaker Intertrip and Remote Tripping........................................ 274
4.9 Circuit-Breaker Failure Protection (Optional).................................................................... 275
4.10 Thermal Overload Protection 49...................................................................................... 276
4.11 Voltage Protection (Optional)..........................................................................................278
4.12 Frequency Protection (Optional)......................................................................................281
4.13 Automatic Reclosing (Optional)....................................................................................... 282
4.14 Transmission of Binary Information and Commands.........................................................283
4.15 Monitoring Functions......................................................................................................284
4.16 Flexible Protection Functions ..........................................................................................286
4.17 User-defined Functions (CFC).......................................................................................... 289
4.18 Additional Functions....................................................................................................... 293
4.19 Dimensions.....................................................................................................................296
4.19.1 Panel Flush Mounting and Cabinet Flush Mounting (Housing Size 1/6) ...................... 296
4.19.2 Panel Surface Mounting (Housing Size 1/6) ............................................................... 297
4.19.3 Bottom View............................................................................................................. 297
A Ordering Information and Accessories.....................................................................................................299
A.1 Ordering Information 7SD80 V4.7 .................................................................................. 300
A.2 Accessories.....................................................................................................................303
B Terminal Assignments..............................................................................................................................305
B.1 7SD80 — Housing for Panel Flush Mounting, Cabinet Flush Mounting and Panel
Surface Mounting .......................................................................................................... 306
C Connection Examples............................................................................................................................... 313
C.1 Connection Examples for Current and Voltage Transformers............................................314
D Current Transformer Requirements......................................................................................................... 317
D.1 Current Transformer Ratio .............................................................................................. 318
D.2 Overcurrent Factors........................................................................................................ 319
D.3 Class Conversion............................................................................................................. 320
D.4 Core Balance Current Transformer...................................................................................321
E Default Settings and Protocol-dependent Functions............................................................................... 323
E.1 LEDs............................................................................................................................... 324
E.2 Binary Input.................................................................................................................... 325
E.3 Binary Output................................................................................................................. 326
E.4 Function Keys................................................................................................................. 327
E.5 Default Display................................................................................................................328
E.6 Pre-defined CFC Charts....................................................................................................331
E.7 Protocol-dependent Functions.........................................................................................332
16 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Table of Contents
F Functions, Settings, Information..............................................................................................................333
F.1 Functional Scope............................................................................................................ 334
F.2 Settings.......................................................................................................................... 336
F.3 Information List.............................................................................................................. 352
F.4 Group Indications............................................................................................................392
F.5 Measured Values.............................................................................................................393
Literature.................................................................................................................................................. 401
Glossary.................................................................................................................................................... 403
Index.........................................................................................................................................................413
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 17
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

18 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

1
Introduction
This chapter introduces the SIPROTEC 4 7SD80 and gives an overview of the device's application, properties
and functions.
1.1 Overall Operation 20
1.2 Application Scope 23
1.3 Characteristics 25
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 19
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018
Introduction
1.1 Overall Operation
1.1
Analog Inputs
Overall Operation
The digital SIPROTEC 7SD80 overcurrent protection is equipped with a powerful microprocessor. It allows all
tasks to be processed digitally, from the acquisition of measured quantities to sending commands to circuit
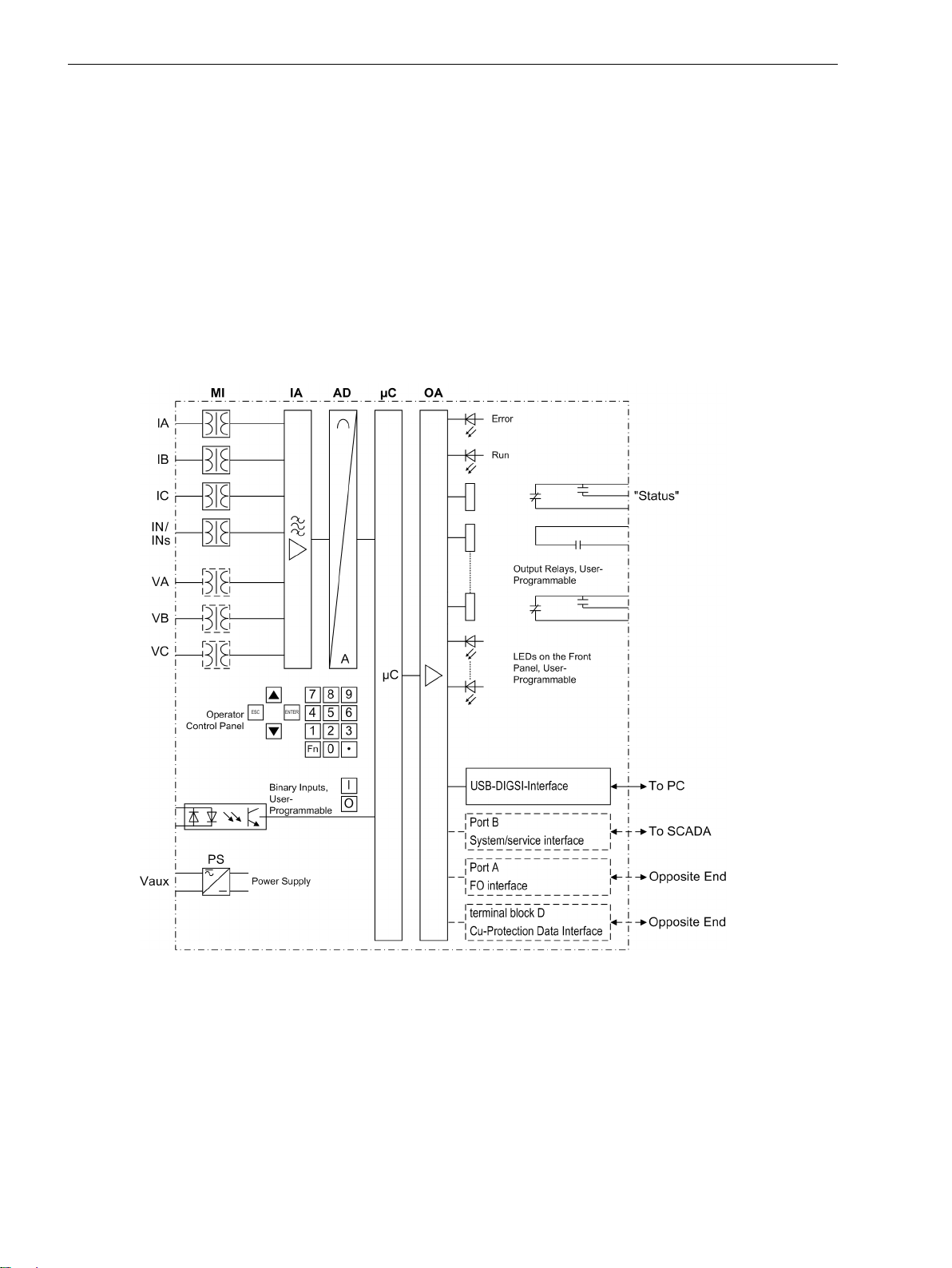
breakers. Figure 1-1 shows the basic structure of the 7SD80 device.
The measuring inputs (MI) convert the currents and voltages coming from the instrument transformers and
adapt them to the level appropriate for the internal processing of the device. The device provides 4 current
transformers and - depending on the model - additionally 3 voltage transformers. Three current inputs serve
for the input of the phase currents, another current input (ΙN) may be used for measuring the ground fault
current ΙN (current transformer starpoint) or for a separate ground current transformer (for sensitive ground
fault detection ΙNs and directional determination of ground faults) - depending on the model.
[hw-struktur-7sd80-100801, 1, en_US]
Figure 1-1
There is one voltage input available for each phase-to-ground voltage. The differential protection does not
need measuring voltages due to its functional principle. Directional overcurrent protection, however, requires
the phase-to-ground voltage VA, VB and VC to be connected. Additionally, voltages can be connected that allow
displaying voltages and power values and also measuring the line voltage for automatic reclosing. The analog
quantities are forwarded to the input amplifier group (IA).
The input amplifier group IA provides high-resistance termination for the analog input quantities. It consists of
filters that are optimized for measured value processing with regard to bandwidth and processing speed.
20 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
Hardware structure of the 7SD80 differential protection
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

The analog-to-digital (AD) element consists of an analog-to-digital (A/D) converter and memory components
for data transmission to the microcomputer system.
Microcomputer System
Apart from processing the measured values, the microcomputer system μC also executes the actual protection
and control functions. They especially consist of:
Filtering and preparation of the measured quantities
•
Continuous monitoring of the measured quantities
•
Monitoring of the pickup conditions for the individual protection functions
•
Interrogation of limit values and time sequences
•
Control of signals for the logic functions
•
Decision on trip and close commands
•
Recording of messages, fault data and fault values for analysis
•
Administration of the operating system and its functions, e.g. data storage, realtime clock, communica-
•
tion, interfaces, etc.
Formation of the local differential protection values (phase comparision for phase-to-phase faults and
•
phasor analysis for phase-to-ground faults) and creation of the transmission protocol
Decoding the received transmission protocol, synchronization of differential protection values and
•
totaling the differential currents and charge currents
Introduction
1.1 Overall Operation
Monitoring the communication with the device of the remote end
•
The information is provided via output amplifier OA.
Binary Inputs and Outputs
Binary inputs and outputs to and from the computer system are relayed via the input/output modules. The
computer system obtains information from the system (e.g. remote resetting) or from other devices (e.g.
blocking commands). Outputs are, in particular, commands to the switchgear units and annunciations for
remote signaling of important events and statuses.
Front Elements
Information such as messages related to events, states, measured values and the functional status of the
device are visualized by light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and a display screen (LCD) on the front panel.
Integrated control and numeric keys in conjunction with the LCD enable communication with the remote
device. These elements enable the user to retrieve all device information such as configuration and setting
parameters, operational indications and fault indications or measured values and to edit setting parameters.
In addition, control of circuit breakers and other equipment is possible from the front panel of the device.
Interfaces
Communication with a PC can be implemented via the USB DIGSI interface using the DIGSI software allowing
the user to conveniently handle all device functions.
Port A can be used as protection interface to communicate with another 7SD80 device via an optical fiber
cable.
If you are using a copper link to create a connection to the other 7SD80 device, use the voltage terminals D1
and D2 as protection interface.
The protection data interfaces are used to transfer the data of the measured quantities from each end of the
protected zone to the opposite end. Further information such as closing of the local circuit breaker or other
externally injected trip commands can be transmitted to the opposite end via the protection interface.
In addition to the device communication via DIGSI, Port B can also be used to transmit all device data to a
central evaluator or a control center. This interface may be provided with various protocols and physical transmission schemes to suit the particular application.
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 21
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Introduction
1.1 Overall Operation
Power Supply
The functional units described are supplied by a power supply (PS) with the adequate power in the different
voltage levels. Transient voltage dips may occur if the auxiliary voltage supply system becomes short-circuited.
Usually, they are bridged by a capacitor storage (see also the Section 4 Technical Data).
A buffer battery is located behind the lower front cover.
22 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Introduction
1.2 Application Scope
1.2
Protection Functions
Application Scope
The digital Line Differential Protection SIPROTEC 4 7SD80 is a selective short-circuit protection for overhead
lines and cables with single- and multi-ended infeeds in radial, ring or any type of meshed systems of any
transmission level. The measured data are compared separately for each phase.
A major advantage of the differential protection principle is the instantaneous tripping in the event of a short
circuit at any point within the entire protected zone. The current transformers limit the protected zone at the
ends towards the remaining system. This rigid delimitation is the reason why the differential protection
scheme shows such an ideal selectivity.
The differential protection system requires a 7SD80 device as well as a set of current transformers at either
end of the protected zone. Voltage transformers are not required for the differential protection functions in
the 7SD80; they are, however, available to record and display measured values (voltages, power, power
factor) or when using a directional overcurrent protection element.
The devices located at the ends of the protected zone exchange measuring information via protection interfaces using communication links (usually optical fiber or copper cables).
Since fault-free data transmission is the prerequisite for the proper operation of the protection, it is continuously monitored internally.
The device's basic function is to detect short-circuits or ground faults in the protected zone – even weakcurrent or high-resistance short-circuits. Even complex multiphase faults are detected correctly, as the measured values are evaluated separately for each phase. The protection is restraint against inrush currents of
power transformers. When switching a line onto a fault, it is possible to send an instantaneous trip signal. The
7SD80 line differential protection includes the differential protection functions of phase comparison protection and ground fault differential protection. Both differential protection functions operate independently of
each other.
In the event of a communication failure, the devices can automatically switch to emergency operation using
an integrated overcurrent protection until communication is restored. The overcurrent protection comprises
two definite time-overcurrent protection elements and one inverse time-overcurrent protection element. Both
elements operate directional or non-directional. Additionally, the device features a third definite time-overcurrent protection element that always operates non-directionally.
For inverse time overcurrent protection, several characteristic curves of different standards are available.
Alternatively, the time overcurrent protection can be used as a backup time overcurrent protection, i.e. it oper-
ates independent of and parallel to the differential protection at either end.
The communication link can be used for transmitting further information. Besides measured values, it is
possible to transmit binary information.
All protection functions in the 7SD80 always trip 3-pole. They can work together with an integrated automatic
reclose function (optional). The automatic reclose functions enables 3-pole automatic reclosing with two
reclose attempts.
The thermal overload protection protects cables and power transformers from inadmissible heating due to
overload.
Additionally, a two-element overvoltage and undervoltage protection and a four-element frequency protection can be used. A circuit-breaker failure protection monitors the response of the circuit breaker following a
trip command.
Control Functions
The device provides a control function which can be accomplished for activating and deactivating switchgear
via operator buttons, port B, binary inputs and - using a PC and the DIGSI software - via the front interface.
The switch positions are fed back to the device via auxiliary contacts of the circuit breakers and binary inputs.
The current switch positions can be read out at the device and used for plausibility monitoring and interlockings. The number of the devices to be switched is limited by the binary inputs and outputs available in the
device or the binary inputs and outputs allocated for the switch position feedbacks. Depending on the equipment, one binary input (single point indication) or two binary inputs (double point indication) can be used.
The release to switch can be restricted by appropriate settings for the switching authority (remote or local),
and by the operating mode (interlocked/non-interlocked, with or without password validation). Interlocking
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 23
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Introduction
1.2 Application Scope
conditions for switching (e.g. switchgear interlocking) can be defined with the help of integrated user-configurable logic functions.
Messages and Measured Values; Recording of Event and Fault Data
The operational indications provide information about conditions in the power system and the device. Measurement quantities and values that are calculated can be displayed locally and communicated via the serial
interfaces.
Device messages can be assigned to a number of LEDs on the front cover (allocatable), can be externally
processed via output contacts (allocatable), linked with user-definable logic functions and/or issued via serial
interfaces.
During a fault (system fault) important events and changes in conditions are saved in fault protocols (Event
Log or Trip Log). Instantaneous fault values are also saved in the device and may be analyzed subsequently.
Communication
The following interfaces are available for communication with external operating, control and memory
systems.
The USB DIGSI interface on the front cover serves for local communication with a PC. With the SIPROTEC 4
operating software DIGSI, all operation and evaluation tasks can be executed using this operator interface, for
instance specifying and editing configuration parameters and settings, configuring user-specific logic functions, retrieving operational messages and measured values, inquiring device conditions and measured values,
issuing control commands.
Port A is located on the bottom side of the device. This protection data interface connects the device to its
partner device at the remote end of the protected object.
Alternatively, you can implement the communication link using the voltage terminals D-1 and D-2.
Port B serves for central communication between the device and a control center. It can be operated via data
lines or optical fiber cables. For the data transfer, standardized protocols according IEC 60870-5-103 are available. The integration of the devices into the SINAUT LSA and SICAM automation systems can also be implemented with this profile.
Alternatively, there are additional connection options available in connection with PROFIBUS DP and the
DNP3.0 and MODBUS protocols. If an EN100 module is available, it is also possible to use the IEC61850
protocol.
You can also use Port B to connect a time synchronization device such as DCF77 or IRIG-B.
24 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Introduction
1.3 Characteristics
1.3
General Properties
Phase Comparison Protection
Characteristics
Powerful 32-bit microprocessor system
•
Complete digital processing of measured values and control, from the sampling of the analog input
•
values, the processing and organization of the communication between devices up to the closing and
tripping commands to the circuit breakers.
Total galvanic and fail-safe separation of the internal processing circuits from the measuring, control and
•
supply circuits of the system via measuring transformers, binary input and output modules and DC or AC
converters
Suited for lines with two ends
•
Easy device operation using the integrated operator panel or from a connected personal computer
•
running DIGSI
Storage of fault indications as well as instantaneous values for fault recording
•
Digital protection data transmission; communication of the device through optical fiber cables
•
Communication is possible via a single copper wire pair (typically 8 km (4.97 miles), max. 20 km (12.43
•
miles), depending on the used cable type, see Section 4 Technical Data).
Permanent supervision of the protection data transmission for disturbance, failure or transfer time varia-
•
tions
Differential protection for two ends with digital protection data transmission
•
Protection for all types of short-circuits in systems with any starpoint conditioning
•
Reliable distinction between load and short-circuit conditions using adaptive measurement methods, also
•
for high-resistance faults with small fault currents
High sensitivity in light load operation, highest stability against load steps and power fluctuations
•
Due to phase segregated measurement, the pickup sensitivity is independent of the fault type
•
Detection of high-resistance, weak-current faults due to high sensitivity of the protection functions
•
Fast tripping also on weak or zero infeed ends (breaker intertrip)
•
No frequency dependency
•
Ground Fault Differential Protection for Grounded Systems
Short command time
•
High sensitivity for short circuits to ground
•
High stability against external ground faults by stabilizing the through-flowing ground current
•
Ground Fault Differential Protection for Isolated / Grounded Systems
Short command time
•
High sensitivity for short circuits to ground
•
High stability against external short-circuits to ground using the magnitude and phase relationship of the
•
ground current flowing through for stabilization
External Direct and Remote Tripping
Tripping of the local end by an external device via binary input
•
Tripping of the opposite end by local protection functions or by an external device via binary input
•
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 25
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Introduction
1.3 Characteristics
Time Overcurrent Protection
Optionally selectable as emergency function during protection data communication failure or as backup
•
function or both
A maximum of 3 definite time elements and one inverse time element, each for phase currents and
•
ground current
A maximum of 2 directional definite time elements and one directional inverse time element, each for
•
phase currents and ground current
For inverse time overcurrent protection, selection from various characteristics of different standards
•
possible
Blocking options e.g. for reverse interlocking with any element
•
Instantaneous tripping when closing onto a short circuit possible with any element
•
Inrush Current Restraint
Insensitive to inrush currents and against higher-frequency transients
•
High stability also for different current transformer saturation
•
Circuit-Breaker Failure Protection
With independent current elements for the monitoring of the current flow through each pole of the
•
circuit breaker
Separate pickup thresholds for phase and ground currents
•
Monitoring time element for tripping
•
Initiation by the trip command of each integrated protection function
•
Initiation by external trip functions possible
•
Single-element or two-element
•
No dropout and seal-in times
•
Thermal Overload Protection
Thermal replica of the current heat losses of the protected object
•
RMS measurement for all three phase currents
•
Adjustable thermal and current-dependent warning elements
•
Voltage Protection
Overvoltage and undervoltage detection with different elements
•
2 overvoltage elements for the phase-to-ground voltages
•
2 overvoltage elements for the phase-to-phase voltages
•
2 overvoltage elements for the positive sequence voltage
•
2 overvoltage elements for the negative sequence system of the voltages
•
2 overvoltage elements for the zero system of the voltages or for any other single-phase voltage
•
Adjustable dropout conditions
•
2 undervoltage elements for the phase-to-ground voltages
•
2 undervoltage elements for the phase-to-phase voltages
•
2 undervoltage elements for the positive sequence system of the voltages
•
Adjustable current criterion for undervoltage protection functions
•
26 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Frequency Protection 81 (Optional)
Monitoring of falling below (f<) and/or exceeding (f>) with 4 frequency limits and time delays that are
•
independently adjustable
Particularly insensitive to harmonics and abrupt phase angle changesbesonders unempfindlich gegen
•
Oberschwingungen und Phasensprünge
Wide frequency range (approx. 25 Hz to 70 Hz)
•
Automatic Reclose Function (Optional)
For reclosing after 3-pole open condition
•
2 reclosing attempts
•
With separate action times for each reclosing attempt, optionally without action times
•
With separate dead times
•
Optionally controlled by protection element pickup with separate dead times after 1-pole, 2-pole or 3-
•
pole pickup
Monitoring Functions
Reliability of the device is greatly increased because of self-monitoring of the internal measurement
•
circuits, the auxiliary power supply as well as the hardware and software
Introduction
1.3 Characteristics
Monitoring of the current transformer and voltage transformer secondary circuits using summation and
•
symmetry check techniques
Monitoring of communication with statistics showing the availability of transmission telegrams
•
Check of the consistency of protection settings at both line ends: no processor system start-up with
•
inconsistent settings which could lead to a malfunction of the differential protection system
Trip circuit monitoring possible
•
Check of local and remote measured values and comparison of both
•
Broken wire supervision for the secondary CT circuits with fast phase segregated blocking of the differen-
•
tial protection system in order to avoid malfunction
Supervision of measuring voltage failure using "Fuse Failure Monitor"
•
Flexible Protection Functions
Up to 20 customizable protection functions with 3-phase or 1-phase operation
•
Any calculated or directly measured variable can theoretically be evaluated
•
Standard protection logic with a constant (i.e. definite time) characteristic curve
•
Internal and configurable pickup and dropout delay
•
Editable indication texts
•
User-defined Logic Functions (CFC)
Internal and external signals can be logically combined to realize user-defined logic functions
•
All common logic functions
•
Time delays and limit value interrogations
•
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 27
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Introduction
1.3 Characteristics
Command Processing
Switching devices can be opened and closed manually using control keys, programmable function keys,
•
via port B (e.g. of SICAM or SCADA), or via the user interface (using a personal computer and the DIGSI
operating software)
Feedback of the circuit-breaker states via the breaker auxiliary contacts (for commands with feedback)
•
Plausibility monitoring of the circuit-breaker positions and interlocking conditions.
•
Commissioning; Operation; Maintenance
Indication of the local and remote measured values according to magnitude and phase angle
•
Indication of the calculated differential and restraint currents
•
Indication of the measured values of the communication connection, as runtime and availability
•
Additional Functions
Battery-buffered clock which can be synchronized via a synchronization signal (DCF77, IRIGB via satellite
•
receiver), binary input or system interface
Continuous calculation and indication of operational measured values on the front display, indication of
•
measured values of the far end or all ends (for devices with active interfaces)
Fault event memory (trip log) for the last eight network faults (faults in the power system), with real time
•
stamps
Fault recording and data transfer for fault recording for a maximum time range of 15 seconds.
•
Switching statistics: Counting of the trip and close commands initiated by the device as well as recording
•
of the short-circuit data and accumulation of the disconnected fault currents
Communication with central control and memory components via serial interfaces possible (depending
•
on the ordered variant), optionally via RS232, RS485 connection, modem or fiber optic cable
Commissioning aids such as connection check, direction check and circuit-breaker check
•
28 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

2
Functions
This chapter describes the numerous functions available on the SIPROTEC 4 device 7SD80. It shows the setting
possibilities for each function in maximum configuration. Information with regard to the determination of
setting values as well as formulas, if required, are also provided.
Based on the following information, it can also be determined which of the provided functions should be
used.
2.1 General 30
2.2 Phase Comparison Protection and Ground Differential Protection 48
2.3 Breaker Intertrip and Remote Tripping 69
2.4 Backup overcurrent 72
2.5 InRush Restraint 91
2.6 Circuit Breaker Failure Protection 50BF 94
2.7 Thermal Overload Protection 49 104
2.8 Undervoltage and Overvoltage Protection (optional) 27/59 108
2.9 Frequency Protection (optional) 81 123
2.10 Direct Local Trip 129
2.11 Automatic Reclosure Function (optional) 79 131
2.12 Circuit Breaker Test 142
2.13 Direct Remote Trip and Transmission of Binary Information 147
2.14 Monitoring Functions 149
2.15 Flexible Protection Functions 167
2.16 Function Logic 177
2.17 Auxiliary Functions 181
2.18 Breaker Control 193
2.19 Notes on Device Operation 203
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 29
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018
i
i
Functions
2.1 General
2.1
2.1.1
2.1.1.1
Setting the Scope of Functions
General
You can edit the function parameters via the user interface or service interface from a PC running the DIGSI
software; some parameters can also be changed using the controls at the front panel of the device. The procedure is set out in detail in the /1/ SIPROTEC 4 System Description.
Functional Scope
The 7SD80 device comprises protection functions and additional functions. The hardware and firmware are
designed for this scope of functions. Additionally, the control functions can be matched to the system requirements. Individual functions can be activated or deactivated during the configuration procedure or the interaction of functions be modified.
Functional Description
Example for the configuration of the scope of functions:
A system consists of overhead lines and underground cables. Since automatic reclosing is only needed for the
overhead lines, the automatic reclosing function is disabled for the relays protecting the underground cables.
The available protection functions and additional functions can be configured as Enabled or Disabled. For
some functions, there is a choice between several alternatives possible, as described below.
Functions configured as Disabled are not processed in the 7SD80. There are no messages issued and the
corresponding settings (functions, limit values) are not queried during configuration.
NOTE
Available functions and default settings depend on the ordered variant of the relay A Ordering Information
and Accessories).
2.1.1.2
Setting the Functional Scope
Special Settings
Setting Notes
Your protection device is configured using the DIGSI software. Connect your personal computer either to the
USB port on the device front or to port B on the bottom side of the device depending on the device version
(ordering code). The operation via DIGSI is explained in the SIPROTEC 4 System Description.
The Device Configuration dialog box allows you to adjust your device to the prevailing system conditions.
Password no. 7 is required (for parameter set) to change configuration parameters in the device. Without the
password you can only read the settings but not edit and transmit them to the device.
Most settings are self-explaining. The special cases are described in the following.
If you want to use the setting group change function, set address 103 Grp Chge OPTION to Enabled. In
this case, you can select up to four different groups of function parameters between which you can switch
quickly and conveniently during operation. Only one setting group can be used when selecting the option
Disabled.
The differential protection function 87 DIFF.PROTEC. (address 112) as a main function of the device should
always be Enabled. This also applies to the supplementary functions of the differential protection such as
breaker intertrip.
The external trip initiation (address 122 DTT Direct Trip) is a command that is initiated from an external
device for tripping the local circuit breaker.
At address 126 Back-Up O/C, you can set the characteristic group which the time overcurrent protection
uses for operation. In addition to the definite-time overcurrent protection an inverse-time overcurrent protection can be configured that either operates according to an IEC characteristic (50(N) 51(N) IEC) or to an
30 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.1 General
ANSI characteristic (50(N) 51(N)ANSI). This selection is independent of whether the time overcurrent
protection is intended to operate as emergency protection (only in case of protection communication failure)
or as independent backup protection. Device versions equipped with directional overcurrent protection (MLFB
position 14 = R or S) additionally provide a directional definite time overcurrent protection element and a
directional inverse time overcurrent protection element. The characteristic curves of the two inverse time
overcurrent protection elements are identical. The different characteristic curves are shown in the Technical
Data (Section 4.7 Time Overcurrent Protection ). You can also disable the time overcurrent protection (Disa-
bled).
Set to Disabled, the entire time overcurrent protection can be disabled.
For overload protection you can define in address 142 49 whether the function is to be Enabled or Disa-
bled.
In address 139 you can set the breaker failure protection to Enabled or Disabled. The setting option
enabled w/ 3I0> subjects the ground current and the negative sequence current to a plausibility check.
If the device features an automatic reclosing function, address 133 and 134 are of importance. Automatic
reclosure is only permitted for overhead lines. It must not be used in any other case. If the protected object
consists of a combination of overhead lines and other equipment (e.g. overhead line/cable), reclosing is only
permissible if it is ensured that reclosing will only be performed in the event of a fault on the overhead line. If
no automatic reclosing function is desired for the feeder at which 7SD80 operates, or if an external device is
used for reclosure, set address 133 79 Auto Recl. to Disabled. Or you can enter the number of desired
reclosing attempts there. You can select 1 AR-cycle or 2 AR-cycles.
The AR control mode at address 134 allows a maximum of four options. On the one hand, it can be determined whether the automatic reclosure cycles are carried out according to the fault type detected by the
pickup of the starting protective function(s) or according to the type of trip command. On the other hand,
the automatic reclosing function can be operated with or without action time.
The setting Trip ... (with trip command ..., default setting) allows you to specify different dead times for
each automatic reclose cycle.
The setting Pickup ... (with pickup ...) allows you to enter different dead times for the automatic reclose
cycles for 1-phase, 2-phase and 3-phase short circuits. The pickup status of the protection functions at the
instant the trip command disappears is decisive here. This operating mode enables making the dead times
dependent on the type of fault also for three-pole reclosure cycles. Tripping is always 3-pole.
The setting ... w/ Tact (with ... action time) provides an action time for each automatic reclose cycle. The
action time is started by a general pickup of all protection functions. If there is no trip command yet when the
action time has expired, the corresponding automatic reclosure cycle cannot be executed. Section 2.11
provides detailed information on this topic. For time graded protection this setting is recommended. If the
protection function which is to operate with automatic reclosure does not have a general pickup signal for
starting the action times, select ... w/o Tact (without action time).
Address 137 27/59 allows activating the voltage protection function with a variety of undervoltage and overvoltage protection elements.
For the trip circuit supervision enter the number of trip circuits to be monitored at address 140 74 Trip Ct
Supv 1 trip circuit, 2 trip circuits or 3 trip circuits, unless you omit it (Disabled).
If the device is connected to voltage transformers, specify this condition in address 144 V-TRANSFORMER. The
voltage-based functions, for instance the directional overcurrent protection elements, the ground fault differential protection in resonant-grounded/isolated systems or determination of the voltage-based measured
values, can only be activated if voltage transformers are connected.
The flexible protection functions can be configured via parameter FLEXIBLE FUNC.. You can create up to 20
flexible functions by setting a checkmark in front of the desired function. If the checkmark of a function is
removed, all settings and configurations made previously will be lost. After re-selecting the function, all
settings and configurations are in default setting. The flexible function can be configured in DIGSI at
“Settings”, “Additional Functions” and “Settings”. The routing is done, as usual, under “Settings” and “Masking
I/O”. If you want to use the flexible protection function, the device must be connected to voltage transformers.
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 31
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.1 General
2.1.1.3
Settings
Addr. Parameter Setting Options Default Setting Comments
103 Grp Chge OPTION Disabled
Disabled Setting Group Change Option
Enabled
112 87 DIFF.PROTEC. Enabled
Enabled 87 Differential protection
Disabled
122 DTT Direct Trip Disabled
Disabled DTT Direct Transfer Trip
Enabled
126 Back-Up O/C Disabled
50(N) 51(N) IEC Backup overcurrent
50(N) 51(N) IEC
50(N) 51(N)ANSI
50(N) 67(N) IEC
50(N) 67(N)ANSI
133 79 Auto Recl. Disabled
Disabled 79 Auto-Reclose Function
1 AR-cycle
2 AR-cycles
134 AR control mode PU w/ActionTime
Trip w/ActionT. Auto-Reclose control mode
PU w/o ActionT.
Trip w/ActionT.
Trip w/oActionT
136 81 O/U Disabled
Enabled
137 27/59 Disabled
Enabled
139 50BF Disabled
Disabled 81 Over/Underfrequency Protec-
tion
Disabled 27, 59 Under/Overvoltage Protec-
tion
Disabled 50BF Breaker Failure Protection
Enabled
enabled w/ 3I0>
140 74 Trip Ct Supv Disabled
Disabled 74TC Trip Circuit Supervision
1 trip circuit
142 49 Disabled
Disabled 49 Thermal Overload Protection
Enabled
144 V-TRANSFORMER Not connected
connected Voltage transformers
connected
ONLY VN
617 ServiProt (CM) Disabled
T103 Port B usage
T103
DIGSI
TIME SYNCH
32 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Addr. Parameter Setting Options Default Setting Comments
- FLEXIBLE FCT. 1...20 Flexible Function 01
Please select Flexible Functions 1...20
Flexible Function 02
Flexible Function 03
Flexible Function 04
Flexible Function 05
Flexible Function 06
Flexible Function 07
Flexible Function 08
Flexible Function 09
Flexible Function 10
Flexible Function 11
Flexible Function 12
Flexible Function 13
Flexible Function 14
Flexible Function 15
Flexible Function 16
Flexible Function 17
Flexible Function 18
Flexible Function 19
Flexible Function 20
Functions
2.1 General
2.1.2
Device, General Settings
The device requires some general information. This may be, for example, the type of annunciation to be
issued in the event of an occurrence of a power system fault.
2.1.2.1
Functional Description
Command-dependent Messages "No Trip – No Flag"
The indication of messages masked to local LEDs and the generation of additional messages can be made
dependent on whether the device has issued a trip signal. This information is then not output if during a
system disturbance one or more protection functions have picked up but no tripping by the 7SD80 resulted
because the fault was cleared by a different device (e.g. on another line). These messages are then limited to
faults in the line to be protected.
The following figure illustrates the creation of the reset command for stored messages. By the moment of the
device dropout, the presetting of the parameter 610 FltDisp.LED/LCD decides, whether the new fault will
be stored or reset.
[ruecksetzbefehl-fuer-n-speicher-led-lcd-meld-260602-kn, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-1 Creation of the reset command for the latched LED and LCD messages
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 33
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.1 General
Spontaneous Messages on the Display
You can determine whether or not the most important data of a fault event is displayed automatically after
the fault has occurred (see also Subsection "Fault Messages" in Section "Auxiliary Functions").
2.1.2.2
Setting Notes
Fault Display
A new pickup by a protection element generally turns off any previously lit LEDs so that only the latest fault is
displayed at any one time. It can be selected whether the stored LED displays and the spontaneous fault indications on the display appear upon the new pickup, or only after a new trip signal is issued. In order to select
the desired displaying mode, select the submenu Device in the SETTINGS menu. Under address 610
FltDisp.LED/LCD the two alternatives Target on PU and Target on TRIP ("No trip – no flag") can be
selected.
Use parameter 615 Spont. FltDisp. to specify whether or not a spontaneous fault message should appear
automatically on the display (YES) or not (NO).
Selection of Default Display
The start page of the default display appearing after startup of the device can be selected in the device data
via parameter640 Start image DD. The pages available for each device version are listed in the Appendix
E Default Settings and Protocol-dependent Functions.
Protection Interface Test Mode
To check the communication quality of the two 7SD80 devices during commissioning, set parameter 650 PDI
Test Mode to ON. The availability of the communication link via the protection interface is displayed as a stat-
istical value (see Section 2.17.2 Statistics).
2.1.2.3
Settings
Addresses which have an appended “A” can only be changed with DIGSI, under “Additional Settings”.
Addr.
610 FltDisp.LED/LCD Target on PU
Parameter Setting Options Default Setting Comments
Target on PU Fault Display on LED / LCD
Target on TRIP
615 Spont. FltDisp. NO
YES
NO Spontaneous display of flt.annun-
ciations
625A T MIN LED HOLD 0 .. 60 min 0 min Minimum hold time of latched
LEDs
640 Start image DD image 1
image 1 Start image Default Display
image 2
image 3
image 4
image 5
image 6
image 7
image 8
650 PDI Test Mode OFF
OFF PDI Test Mode
ON
2.1.2.4
No.
Information List
Information Type of
Comments
Information
- Test mode IntSP Test mode
34 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.1 General
No. Information Type of
Comments
Information
- DataStop IntSP Stop data transmission
- UnlockDT IntSP Unlock data transmission via BI
- Reset LED IntSP Reset LED
- SynchClock IntSP_Ev Clock Synchronization
- >Light on SP >Back Light on
- HWTestMod IntSP Hardware Test Mode
- Error FMS1 OUT Error FMS FO 1
- Error FMS2 OUT Error FMS FO 2
- Distur.CFC OUT Disturbance CFC
- Brk OPENED IntSP Breaker OPENED
- Feeder gnd IntSP Feeder GROUNDED
1 Not configured SP No Function configured
2 Non Existent OUT Function Not Available
3 >Time Synch SP >Synchronize Internal Real Time Clock
5 >Reset LED SP >Reset LED
11 >Annunc. 1 SP >User defined annunciation 1
12 >Annunc. 2 SP >User defined annunciation 2
13 >Annunc. 3 SP >User defined annunciation 3
14 >Annunc. 4 SP >User defined annunciation 4
15 >Test mode SP >Test mode
16 >DataStop SP >Stop data transmission
51 Device OK OUT Device is Operational and Protecting
52 ProtActive IntSP At Least 1 Protection Funct. is Active
55 Reset Device OUT Reset Device
56 Initial Start OUT Initial Start of Device
60 Reset LED OUT_Ev Reset LED
67 Resume OUT Resume
68 Clock SyncError OUT Clock Synchronization Error
69 DayLightSavTime OUT Daylight Saving Time
70 Settings Calc. OUT Setting calculation is running
71 Settings Check OUT Settings Check
72 Level-2 change OUT Level-2 change
73 Local change OUT Local setting change
110 Event Lost OUT_Ev Event lost
113 Flag Lost OUT Flag Lost
125 Chatter ON OUT Chatter ON
126 ProtON/OFF IntSP Protection ON/OFF (via system port)
140 Error Sum Alarm OUT Error with a summary alarm
160 Alarm Sum Event OUT Alarm Summary Event
177 Fail Battery OUT Failure: Battery empty
181 Error A/D-conv. OUT Error: A/D converter
182 Alarm Clock OUT Alarm: Real Time Clock
183 Error Board 1 OUT Error Board 1
184 Error Board 2 OUT Error Board 2
185 Error Board 3 OUT Error Board 3
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 35
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.1 General
No. Information Type of
Information
186 Error Board 4 OUT Error Board 4
187 Error Board 5 OUT Error Board 5
190 Error Board 0 OUT Error Board 0
191 Error Offset OUT Error: Offset
193 Alarm adjustm. OUT Alarm: Analog input adjustment invalid
194 Error neutralCT OUT Error: Neutral CT different from MLFB
320 Warn Mem. Data OUT Warn: Limit of Memory Data exceeded
321 Warn Mem. Para. OUT Warn: Limit of Memory Parameter exceeded
322 Warn Mem. Oper. OUT Warn: Limit of Memory Operation exceeded
323 Warn Mem. New OUT Warn: Limit of Memory New exceeded
2054 Emer. mode OUT Emergency mode
32200 PDITestFOon/OFF IntSP PDI Test Mode FO ON/OFF
32201 PDITestCuon/OFF IntSP PDI Test Mode Cu ON/OFF
32202 PDI Test Mode OUT PDI Test Mode
32203 PDI Test remote OUT PDI Test Mode remote
32224 PDI FO: AGING OUT PDI FO: aging (distance damping high)
32225 PDI Cu: AGING OUT PDI Cu: aging (distance damping high)
Comments
2.1.3
2.1.3.1
Polarity of Current Transformers
General Power System Data (Power System Data 1)
The device requires certain data regarding the network and substation so that it can adapt its functions to this
data depending on the application. The data required include for instance rated data of the substation and the
measuring transformers, polarity and connection of the measured quantities, if necessary features of the
circuit breakers, and others. Furthermore, there are several function parameters associated with several functions rather than one specific protection, control or monitoring function. The Power System Data 1 can generally only be changed from a PC running DIGSI and are discussed in this section.
Setting Notes
In address 201 CT Starpoint the polarity of the current transformers must be entered, in other words, the
location of the CT starpoint (Figure 2-2). The setting defines the measuring direction of the device (current in
line direction is defined as positive at both line ends). The reversal of this parameter also reverses the polarity
of the ground current input ΙN.
36 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

[polung-stromwandler-020313-kn, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-2 Polarity of current transformers
Nominal Values of Transformers
In addresses 203 Vnom PRIMARY and 204 Vnom SECONDARY the device obtains information on the primary
and secondary rated voltage (phase-to-phase voltage) of the voltage transformers and in addresses 205 CT
PRIMARY and 206 CT SECONDARY the information on the primary and secondary rated current of the current
transformers (phases).
The voltage connection is required for all functions that work on the basis of power or voltage values, e.g.
ground fault differential protection in resonant-grounded/isolated systems, directional overcurrent protection,
voltage protection, frequency protection, and to display and record the voltages.
Please make sure that the rated secondary transformer current matches the rated current of the device.
Correct entry of the primary data is a prerequisite for the correct computation of operational measured values
with primary magnitude. If the settings of the device are performed with primary values using DIGSI, these
primary data are an indispensable requirement for the correct function of the device.
Functions
2.1 General
Current Connection
The device features four current measurement inputs, three of which are connected to the set of current
transformers. Various possibilities exist for the fourth current input Ι4:
Connection of the Ι4 input to the ground current in the neutral point of the set of current transformers on
•
the protected feeder (normal connection, see Appendix C Connection Examples):
Address 220 is then set to: I4 transformer = In prot. line and address 221 I4/Iph CT = 1.
Connection of the Ι4 input to a separate ground current transformer on the protected line (e.g. a summa-
•
tion CT or core balance CT, see Appendix C Connection Examples):
Address 220 is then set to: I4 transformer = In prot. line and Address 221 I4/Iph CT is set:
[uebersetzung-erd-phase-260702-wlk, 1, en_US]
Example:
Phase current transformers 500 A / 5 A
Core balance 60 A / 1 A
[formel-strmwdl-parallelschlt-270702-wlk, 1, en_US]
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 37
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.1 General
If the input Ι4 is not required, set:
•
Address 220 I4 transformer = Not connected,
Address 221 I4/Iph CT is then irrelevant.
In this case, the neutral current is calculated by summing the phase currents.
Rated Frequency
The rated frequency of the system is set at address 230 Rated Frequency. The factory setting of the model
variant must only be changed if the device is to be used for a purpose other than intended when ordering. You
can set 50 Hz or 60 Hz.
System Starpoint
The manner in which the system neutral point is grounded must be considered for the correct processing of
ground faults and double ground faults. Accordingly, set address 207 SystemStarpoint = Grounded,
Peterson-C.Gnd. or Isolated. For low-resistance or high-resistance (“impedance grounded”) systems, set
Grounded.
Depending on the setting of this parameter, the ground fault differential protection uses either the measured
ground current (Grounded) or the values calculated from the power values (Peterson-C.Gnd. or
Isolated).
Command Duration
In address 240 the minimum trip command duration TMin TRIP CMD is set. It applies to all protection and
control functions that can initiate a trip command. It also determines the duration of the trip pulse when a
circuitbreaker trip test is initiated via the device. This parameter can only be set in DIGSI under Display Addi-
tional Settings.
In address 241 the maximum close command duration TMax CLOSE CMD is set. This applies to all close
commands issued by the device. It also determines the length of the close command pulse when a circuitbreaker test cycle is issued via the device. It must be long enough to ensure that the circuit breaker has
securely closed. An excessive duration causes no problem since the closing command is interrupted in the
event that another trip is initiated by a protection function. This parameter can only be set in DIGSI under
Display Additional Settings.
Circuit-Breaker Test
7SD80 allows a circuit-breaker test during operation using a trip-and-close command entered on the front
panel or from DIGSI. The duration of the trip command is set as explained above. Address 242 T-CBtest-dead
determines the duration from the end of the trip command until the start of the close command for this test. It
should not be less than 0.1 s.
Pickup Thresholds of the Binary Inputs (BI Thresholds)
At addresses 260 Threshold BI 1 to 266 Threshold BI 7 you can set the pickup thresholds of the
binary inputs of the device. The settings Thresh. BI 176V, Thresh. BI 88V or Thresh. BI 19V are
possible here.
2.1.3.2
Settings
Addresses which have an appended “A” can only be changed with DIGSI, under “Additional Settings”.
Addr.
201 CT Starpoint towards Line
203 Vnom PRIMARY 0.4 .. 500.0 kV 10.0 kV Rated Primary Voltage
204 Vnom SECONDARY 80 .. 125 V 100 V Rated Secondary Voltage (Ph-Ph)
205 CT PRIMARY 10 .. 20000 A 400 A CT Rated Primary Current
38 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
Parameter Setting Options Default Setting Comments
towards Line CT Starpoint
towards Busbar
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.1 General
Addr. Parameter Setting Options Default Setting Comments
206 CT SECONDARY 1A
1A CT Rated Secondary Current
5A
207 SystemStarpoint Grounded
Grounded System Starpoint is
Peterson-C.Gnd.
Isolated
220 I4 transformer Not connected
In prot. line I4 current transformer is
In prot. line
221 I4/Iph CT 0.010 .. 5.000 1.000 Matching ratio I4/Iph for CT's
230 Rated Frequency 50 Hz
50 Hz Rated Frequency
60 Hz
240A TMin TRIP CMD 0.02 .. 30.00 sec 0.10 sec Minimum TRIP Command Duration
241A TMax CLOSE CMD 0.01 .. 30.00 sec 1.00 sec Maximum Close Command Dura-
tion
242 T-CBtest-dead 0.00 .. 30.00 sec 0.10 sec Dead Time for CB test-autoreclo-
sure
260 Threshold BI 1 Thresh. BI 176V
Thresh. BI 176V Threshold for Binary Input 1
Thresh. BI 88V
Thresh. BI 19V
261 Threshold BI 2 Thresh. BI 176V
Thresh. BI 176V Threshold for Binary Input 2
Thresh. BI 88V
Thresh. BI 19V
262 Threshold BI 3 Thresh. BI 176V
Thresh. BI 176V Threshold for Binary Input 3
Thresh. BI 88V
Thresh. BI 19V
263 Threshold BI 4 Thresh. BI 176V
Thresh. BI 176V Threshold for Binary Input 4
Thresh. BI 88V
Thresh. BI 19V
264 Threshold BI 5 Thresh. BI 176V
Thresh. BI 176V Threshold for Binary Input 5
Thresh. BI 88V
Thresh. BI 19V
265 Threshold BI 6 Thresh. BI 176V
Thresh. BI 176V Threshold for Binary Input 6
Thresh. BI 88V
Thresh. BI 19V
266 Threshold BI 7 Thresh. BI 176V
Thresh. BI 176V Threshold for Binary Input 7
Thresh. BI 88V
Thresh. BI 19V
2.1.4
Oscillographic Fault Records
The 7SD80 multifunctional protection with control is equipped with a fault record memory. The instantaneous
values of the measured values
iA, iB, iC, iE, iEE und vA, vB, vC, 3Ι0
diff
, 3Ι0
rest
(voltages in accordance with connection) are sampled at intervals of 1.0 ms (for 50 Hz) and stored in a
revolving buffer (20 samples per cycle). In the event of a fault, the data is stored for a set period of time, but
not for more than 5 seconds. Up to 8 fault events can be recorded in this buffer. The fault record memory is
automatically updated with every new fault so that there is no acknowledgment for previously recorded faults
required. In addition to protection pickup, the recording of the fault event data can also be started via a binary
input or via the serial interface.
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 39
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

i
i
Functions
2.1 General
2.1.4.1
2.1.4.2
Specifications
Functional Description
The data of a fault event can be read out via the device interface and evaluated with the help of the SIGRA 4
graphic analysis software. SIGRA 4 graphically represents the data recorded during the fault event and also
calculates additional information from the measured values. Currents and voltages can be presented either as
primary or as secondary values. Signals are additionally recorded as binary tracks (marks) e.g. "pickup", "trip".
If port B of the device has been configured correspondingly, the fault record data can be imported by a central
controller via this interface and evaluated. Currents and voltages are prepared for a graphic representation.
Signals are additionally recorded as binary tracks (marks) e.g. "pickup", "trip".
The retrieval of the fault data by the central controller takes place automatically either after each protection
pickup or after a tipping.
Setting Notes
The actual storage time encompasses the pre-fault time PRE. TRIG. TIME (address 411) ahead of the reference instant, the normal recording time and the post-fault time POST REC. TIME (address 412) after the
storage criterion has reset. The maximum storage time for each fault recording (MAX. LENGTH) is entered in
address 410. Recording per fault must not exceed 5 seconds. A total of 8 records can be saved. However, the
total length of time of all fault records in the buffer must not exceed 25 seconds.
NOTE
The signals used for the binary tracks can be allocated in DIGSI.
2.1.4.3
Addr.
402A WAVEFORMTRIGGER Save w. Pickup
403A WAVEFORM DATA Fault event
410 MAX. LENGTH 0.30 .. 5.00 sec 2.00 sec Max. length of a Waveform
411 PRE. TRIG. TIME 0.05 .. 0.50 sec 0.25 sec Captured Waveform Prior to
412 POST REC. TIME 0.05 .. 0.50 sec 0.10 sec Captured Waveform after Event
415 BinIn CAPT.TIME 0.10 .. 5.00 sec 0.50 sec Capture Time via Binary Input
2.1.4.4
No.
- FltRecSta IntSP Fault Recording Start
4 >Trig.Wave.Cap. SP >Trigger Waveform Capture
30053 Fault rec. run. OUT Fault recording is running
Settings
Addresses which have an appended “A” can only be changed with DIGSI, under “Additional Settings”.
Parameter Setting Options Default Setting Comments
Save w. Pickup Waveform Capture
Save w. TRIP
Start w. TRIP
Fault event Scope of Waveform Data
Pow.Sys.Flt.
Capture Record
Trigger
Information List
Information Type of
Information
Comments
2.1.5
40 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
Change Group
Up to four different setting groups can be created for establishing the device's function settings.
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.1 General
2.1.5.1
Functional Description
Changing Setting Groups
During operation the user can switch back and forth setting groups locally, via the operator panel, binary
inputs (if so configured), the service interface using a personal computer, or via the system interface. For
reasons of safety it is not possible to change between setting groups during a power system fault.
A setting group includes the setting values for all functions that have been selected as Enabled during
configuration (see Section 2.1.1.2 Setting Notes). In 7SD80 relays, four independent setting groups (A to D)
are available. While setting values may vary, the selected functions of each setting group remain the same.
2.1.5.2
Setting Notes
General
If setting group change option is not required, Group A is the default selection. Then, the rest of this section is
not applicable.
If the changeover option is desired, group changeover must be set to Grp Chge OPTION = Enabled
(address 103) when the function extent is configured. For the setting of the function parameters, each of the
required setting groups A to D (a maximum of 4) must be configured in sequence. The SIPROTEC 4 System
Description gives further information on how to copy setting groups or reset them to their status at delivery
and also how to change from one setting group to another.
Section 3.1 Mounting and Connections of this manual tells you how to change between several setting groups
externally via binary inputs.
2.1.5.3
Settings
Addr.
301 ACTIVE GROUP Group A
Parameter Setting Options Default Setting Comments
Group A Active Setting Group is
Group B
Group C
Group D
302 CHANGE Group A
Group A Change to Another Setting Group
Group B
Group C
Group D
Binary Input
Protocol
2.1.5.4
No.
Information List
Information Type of
Comments
Information
- P-GrpA act IntSP Setting Group A is active
- P-GrpB act IntSP Setting Group B is active
- P-GrpC act IntSP Setting Group C is active
- P-GrpD act IntSP Setting Group D is active
7 >Set Group Bit0 SP >Setting Group Select Bit 0
8 >Set Group Bit1 SP >Setting Group Select Bit 1
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 41
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.1 General
2.1.6
2.1.6.1
Rated Values of Protected Lines
General Line Data
General Protection Data (Power System Data 2)
The general protection data (P.System Data 2) include settings associated with all functions rather than a
specific protection, monitoring or control function. In contrast to the P.System Data 1 as discussed before,
they can be changed over with the setting groups and set on the operator panel of the device.
Setting Notes
With address 1103 FullScaleVolt. you inform the device of the primary nominal voltage (phase-to-phase)
of the equipment to be protected (if voltages are applied). This setting influences the displays of the operational measured values in %.
The primary nominal current (address 1104 FullScaleCurr.) is that of the protected object. For cables the
thermal continuous current-loading capacity can be selected. For overhead lines the rated current is usually
not defined. set the rated current of the current transformers (as set in address 205 CT PRIMARY, Section
2.1.3.1 Setting Notes). If the current transformers have different nominal currents at the ends of the protected
object, set the highest nominal current value for all ends.
This setting will not only have an impact on the indication of the operational measured values in per cent, but
must also be exactly the same for each end of the protected object, since it is the basis for the current
comparison at the ends.
The directional values (power, power factor, work and based on work: minimum, maximum, average and
threshold values), calculated in the operational measured values, are usually defined positive in direction to
the protected object. This requires that the connection polarity for the entire device is configured accordingly
in the P.System Data 1 (compare also “Polarity of the Current Transformers”, address 201). But it is also
possible to define the „forward“ direction for the protection functions and the positive direction for the power
etc. differently, e.g. so that the active power flow (from the line to the busbar) is indicated in the positive
sense. To do so, set address 1107 P,Q sign to reversed. If the setting is not reversed (default), the
positive direction for the power etc. corresponds to the “forward” direction for the protection functions.
Circuit-Breaker Status
Information regarding the circuit-breaker position is required by various protection and supplementary functions to ensure their optimal functionality. The device has a circuit-breaker status recognition which processes
the status of the circuit-breaker auxiliary contacts and contains also a detection based on the measured
currents and voltages (see also Section 2.16.2 Tripping Logic for the Entire Device).
In address 1130 the residual current PoleOpenCurrent is set, which will definitely not be exceeded when
the circuit-breaker pole is open. If parasitic currents (e.g. through induction) can be excluded when the circuit
breaker is open, this setting may be very sensitive. Otherwise this setting must be increased. Usually the
presetting is sufficient. This parameter can only be set in DIGSI at Display Additional Settings.
The seal-in time SI Time all Cl. (address 1132) determines the period of time during which the active
protection functions are enabled following each energization of the line. This time is started when the internal
switching detection function recognizes closing of the circuit breaker or if the circuit-breaker auxiliary contacts
or a binary device input signal that the circuit breaker was closed. The time must therefore be longer than the
command time of these protection functions plus a safety margin. This parameter can only be set in DIGSI at
Display Additional Settings.
In address 1134 Line Closure the criteria for the internal recognition of line energization are determined.
only with ManCl means that only the manual close signal via binary input or the integrated control is evaluated as closure. I OR V or ManCl means that additionally the measured currents or voltages are used to
determine closure of the circuit breaker, whereas 52a OR I or M/C implies that either the currents or the
states of the circuit-breaker auxiliary contacts are used to determine closure of the circuit breaker. If the
voltage transformers are not arranged on the line side, the setting 52a OR I or M/C must be used. In the
case of I or Man.Close only the currents or the manual close signals are used to recognize closing of the
circuit breaker.
42 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

i
i
Functions
2.1 General
Before each closing detection, the circuit breaker must be recognized as being open for the settable time 1133
T DELAY SOTF.
Address 1135 Reset Trip CMD determines under which conditions a trip command is reset. If CurrentO-
penPole is set, the trip command is reset as soon as the current disappears. It is important that the value set
in address 1130 PoleOpenCurrent (see above) is undershot. If Current AND 52a is set, the circuitbreaker auxiliary contact must send a message that the circuit breaker is open. It is a prerequisite for this
setting that the position of the auxiliary contacts is allocated via a binary input.
For special applications, in which the device trip command does not always lead to a complete cutoff of the
current, the setting Pickup Reset can be chosen. In this case, the trip command is reset as soon as the
pickup of the tripping protection function drops off and - just as with the other setting options- the minimum
trip command duration (address 240) has elapsed. The setting Pickup Reset makes sense, for instance,
during the test of the protection equipment, when the system-side load current cannot be cut off and the test
current is injected in parallel to the load current.
While the time SI Time all Cl. (address 1132, see above) is activated following each recognition of line
energization, SI Time Man.Cl (address 1150) defines the time following
special influence on the protection functions is activated. This parameter can only be set in DIGSI at Display
Additional Settings.
NOTE
For CB Test and automatic reclosure the CB auxiliary contact status derived with the binary inputs >CB1 ...
No. 371, 410 and 411) are relevant for the circuit-breaker test and for automatic reclosure to be able to
indicate the circuit-breaker position. The other binary inputs >CB ... (no. 379 and 380) are used to detect
the status of the line (address 1134) and to reset the trip command (address 1135). Address 1135 is also
used by other protection functions, e.g. switching on overcurrent. For applications with 2 circuit breakers
per feeder (1.5 circuitbreaker systems or ring bus), the binary inputs >CB1... must be connected to the
correct circuit breaker. The binary inputs >CB... then need the correct signals for detecting the circuitbreaker status. In certain cases, an additional CFC logic may be necessary.
manual closure during which
For commands via the integrated control (local control, DIGSI, serial interface) address 1152 Man.Clos.
Imp. determines whether a close command via the integrated control function should be treated by the
protection regarding the MANUAL CLOSE (like instantaneous re-opening when switching onto a fault). This
address also informs the device to which switchgear this applies. You can select from the switching devices
which are available to the integrated control. Select the circuit breaker which operates for manual closure and,
if required, for automatic reclosure (usually Q0). If none is set here, a CLOSE command via the control will not
generate a MANUAL CLOSE impulse for the protection function.
2.1.6.2
Addr.
1103 FullScaleVolt. 0.4 .. 500.0 kV 10.0 kV Measurem:FullScale-
1104 FullScaleCurr. 10 .. 20000 A 400 A Measurem:FullScaleCur-
1107 P,Q sign not reversed
1130A PoleOpenCurrent 1A 0.05 .. 1.00 A 0.10 A Pole Open Current
1131A PoleOpenVoltage 2 .. 70 V 30 V Pole Open Voltage
1132A SI Time all Cl. 0.01 .. 30.00 sec 0.10 sec Seal-in Time after ALL
Settings
Addresses which have an appended “A” can only be changed with DIGSI, under “Additional Settings”.
The table indicates region-specific default settings. Column C (configuration) indicates the corresponding
secondary nominal current of the current transformer.
Parameter C Setting Options Default Setting Comments
Voltage(Equipm.rating)
rent(Equipm.rating)
not reversed P,Q operational measured
reversed
5A 0.25 .. 5.00 A 0.50 A
values sign
Threshold
Threshold
closures
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 43
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.1 General
Addr. Parameter C Setting Options Default Setting Comments
1133A T DELAY SOTF 0.05 .. 30.00 sec 0.25 sec minimal time for line open
before SOTF
1134 Line Closure only with ManCl
I OR V or ManCl
only with ManCl Recognition of Line
Closures with
52a OR I or M/C
I or Man.Close
1135 Reset Trip CMD CurrentOpenPole
CurrentOpenPole RESET of Trip Command
Current AND 52a
Pickup Reset
1150A SI Time Man.Cl 0.01 .. 30.00 sec 0.30 sec Seal-in Time after MANUAL
closures
1152 Man.Clos. Imp. (Einstellmöglichkeiten
anwendungsabhängig)
none MANUAL Closure Impulse
after CONTROL
2.1.6.3
No. Information Type of
Information List
Comments
Information
301 Pow.Sys.Flt. OUT Power System fault
302 Fault Event OUT Fault Event
356 >Manual Close SP >Manual close signal
357 >Blk Man. Close SP >Block manual close cmd. from external
361 >FAIL:Feeder VT SP >Failure: Feeder VT (MCB tripped)
371 >Bkr1 Ready SP >Breaker 1 READY (for AR,CB-Test)
378 >52 faulty SP >52 Breaker faulty (for 50BF)
379 >52a 3p Closed SP >52a Bkr. aux. contact (3pole closed)
380 >52b 3p Open SP >52b Bkr. aux. contact (3pole open)
383 >Enable ARzones SP >Enable all AR Zones / Elements
385 >Lockout SET SP >Lockout SET
386 >Lockout RESET SP >Lockout RESET
410 >52a Bkr1 3p Cl SP >52a Bkr1 aux. 3pClosed (for AR,CB-Test)
411 >52b Bkr1 3p Op SP >52b Bkr1 aux. 3p Open (for AR,CB-Test)
501 Relay PICKUP OUT Relay PICKUP
502 Relay Drop Out OUT Relay Drop Out
503 Relay PICKUP ØA OUT Relay PICKUP Phase A
504 Relay PICKUP ØB OUT Relay PICKUP Phase B
505 Relay PICKUP ØC OUT Relay PICKUP Phase C
506 Relay PICKUP G OUT Relay PICKUP GROUND
510 Relay CLOSE OUT Relay GENERAL CLOSE command
511 Relay TRIP OUT Relay GENERAL TRIP command
530 LOCKOUT IntSP LOCKOUT is active
533 Ia = VI Primary fault current Ia
534 Ib = VI Primary fault current Ib
535 Ic = VI Primary fault current Ic
536 Definitive TRIP OUT Relay Definitive TRIP
545 PU Time VI Time from Pickup to drop out
546 TRIP Time VI Time from Pickup to TRIP
561 Man.Clos.Detect OUT Manual close signal detected
44 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.1 General
No. Information Type of
Information
563 CB Alarm Supp OUT CB alarm suppressed
590 Line closure OUT Line closure detected
2.1.7
2.1.7.1
2.1.7.2
No. Information Type of
009.0100 Failure Modul IntSP Failure EN100 Modul
009.0101 Fail Ch1 IntSP Failure EN100 Link Channel 1 (Ch1)
009.0102 Fail Ch2 IntSP Failure EN100 Link Channel 2 (Ch2)
EN100-Modul 1
Functional Description
The Ethernet EN100-Modul enables integration of the 7SD80 in 100-Mbit communication networks in control
and automation systems with the protocols according to IEC 61850 standard. This standard permits uniform
communication of the devices without gateways and protocol converters. Even when installed in heterogeneous environments, SIPROTEC 4 relays therefore provide for open and interoperable operation. Parallel to the
process control integration of the device, this interface can also be used for communication with DIGSI and for
inter-relay communication via GOOSE.
Information List
Information
Comments
Comments
2.1.8
2.1.8.1
General
Protection Interface
Functional Description
For a layout of lines with two ends, you need one protection interface for each device. Depending on the
ordering code, the device features a protection interface via optical fiber (Prot FO) and/or a protection interface via copper connection (Prot Cu). To connect Prot Cu, use the voltage terminals D1 and D2.
The input of the protection interface Prot Cu has an insulated design. The integrated overvoltage protection
reduces the insulation strength. Use an external isolating transformer to increase the insulation strength. The
ordering data can be found in Section A Ordering Information and Accessories under Accessories.
If the device has 2 protection interfaces, the data are preferably exchanged with the device at the other end of
the protected object via the FO protection interface. If the optical fiber link fails, the device automatically
switches to the Cu protection interface. When the optical fiber link is restored, the FO protection interface
automatically resumes communication.
If you want to have the communication link monitored, you have to define the minimum reception level, the
maximum permissible fault rate and monitoring times for each device during parameterization. The device's
role within the communication line, i.e. whether it operates as master or slave, is defined in the differential
protection topology. For further information, please refer to Section 2.2.1 Differential Topology.
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 45
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.1 General
[ws-master-slave-110104, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-3 Connecting 2 7SD80 devices via protection data interfaces
Communication Failure
The communication is continuously monitored by the devices. Single faulty data telegrams are not a direct risk
if they occur only occasionally. They are recognized and counted in the device which detects the disturbance
and can be read out as statistical information.
If several faulty or no telegrams are received, this is considered a communication disturbance. A corresponding indication is issued.
2.1.8.2
Setting Notes
General
The protection interfaces connect the devices via optical fiber or copper cables. The communication is permanently monitored by the devices. Address 4510 TD-DATA DISTURB defines after which time delay the user is
informed about a faulty or missing telegram.
Once a fault has been detected in the protection interface communication, the time at address 4512 Td
ResetRemote is started for resetting the remote signals. Please note that only the time of the device whose
remote end has failed is effective.
Protection Interface Optical Fiber
If you use an optical fiber connection, switch it ON or OFF at address 4501 PDI FO.
Address 4502 PDI FO TER allows you to enter the permissible maximum fault rate in percent.
Address 4503 PDI FO level you can define the minimum receiving level.
Notes on the settings are given in the Technical Data.
Protection Interface Copper Cable Cu
If you use a copper cable connected to the voltage terminals of the device, switch it ON or OFF at address 4601
PDI Cu.
Address 4602 PDI Cu TER allows you to enter the permissible maximum fault rate in percent.
At address 4604 PDI Cu MAX ATT you can set the maximum attenuation.
At address 4605 PDI Cu S/N you can define the minimum signal/noise ratio.
At address 4603 PDI Cu mode you can specify the transmission parameters.
Notes on the settings are given in the Technical Data.
2.1.8.3
Addr.
4501 PDI FO ON
Settings
Parameter Setting Options Default Setting Comments
ON Protection Data Interface fibre
OFF
optic
4502 PDI FO TER 0.5 .. 20.0 % 1.0 % PDI FO max. telegram error rate
4503 PDI FO level -30 .. -10 dBm -28 dBm PDI FO min. receive level
4510 TD-DATA DISTURB 0.05 .. 2.00 sec 0.10 sec Time delay for data disturbance
alarm
46 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.1 General
Addr. Parameter Setting Options Default Setting Comments
4512 Td ResetRemote 0.00 .. 300.00 sec 0.00 sec Remote signal RESET DELAY for
comm.fail
4601 PDI Cu ON
ON Protection Data Interface copper
OFF
4602 PDI Cu TER 0.5 .. 20.0 % 1.0 % PDI Cu max. telegram error rate
4603 PDI Cu mode 01
01 PDI Cu operation mode
02
03
04
05
06
4604 PDI Cu MAX ATT 0 .. 46 dB 46 dB PDI Cu maximum attenuation
4605 PDI Cu S/N 6 .. 30 dB 6 dB PDI Cu min signal to noise ratio
2.1.8.4
No. Information Type of
Information List
Comments
Information
3217 PDI FO mirror OUT PDI FO data mirror
3218 PDI Cu mirror OUT PDI Cu data mirror
3227 >PDI FO stop SP >PDI FO is stopped
3228 >PDI Cu stop SP >PDI Cu is stopped
3230 PDI FO faulty OUT PDI FO failure
3232 PDI Cu faulty OUT PDI Cu failure
3243 PDI FO con. to. VI PDI FO connected to relay ID
3244 PDI Cu con. to. VI PDI Cu connected to relay ID
3258 PDI FO TER OUT PDI FO telegram error rate exceeded
3259 PDI Cu TER OUT PDI Cu telegram error rate exceeded
32227 PDI-FO RQ LOW OUT PDI-FO receive level to low
32228 PDI-Cu ATT HIGH OUT PDI-FO attenuation to high
32229 PDI-Cu S/N LOW OUT PDI-FO signal to noise ratio to low
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 47
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.2 Phase Comparison Protection and Ground Differential Protection
2.2
2.2.1
2.2.1.1
Protection Data Topology
Phase Comparison Protection and Ground Differential Protection
The differential protection can be used in solid or resistive grounded, isolated and resonant-grounded
systems.
It comprises a phase comparison protection and a ground differential protection. The sensitive ground
element operates directionally or non-directionally.
The following chapter describes the functions
Differential protection topology
•
Phase comparison protection
•
Ground current differential protection in grounded systems
•
Ground fault differential protection in resonant-grounded/isolated systems
•
Differential protection test and commissioning
•
Differential Topology
The devices at both ends of the protected object communicate over their protection interfaces with one device
acting as master, the other as slave.
The device configured as master can perform the time synchronization for both devices.
Setting Notes
At address 4701 ID OF MASTER and 4702 ID OF SLAVE you can enter the device identification number of
the two protection devices at the line ends.
Use address 4710 LOCAL RELAY to define which of the two devices acts as master and which as slave.
If you want the master to perform the time synchronization for both devices, please observe for which of the
two device a stable time signal is available.
2.2.1.2
Addr.
4701 ID OF MASTER 1 .. 65534 1 Identification number of Master
4702 ID OF SLAVE 1 .. 65534 2 Identification number of Slave
4710 LOCAL RELAY Master
2.2.1.3
No.
3491 Master Login OUT Master in Login state
3492 Slave Login OUT Slave in Login state
Settings
Parameter Setting Options Default Setting Comments
Master Local relay is
Slave
Information List
Information Type of
Information
Comments
48 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.2 Phase Comparison Protection and Ground Differential Protection
2.2.2
2.2.2.1
General
Phase Comparison Protection
Functional Description
The phase comparison protection evaluates the phase currents at both ends of the protected object. The 2
7SD80 devices at the ends of the protected object communicate over their protection interfaces. The phasespecific comparison and the resulting decision to trip the circuit breaker is made separately for each end.
The digitalized currents are first filtered to suppress DC components and higher harmonics.
[lo-pvl-erf-20101117, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-4 Phase comparison protection, determination of the input variables
These filtered values are available to a sensitive dynamic element and a static element. By comparing the
polarity of the currents at the two ends of the protected object, they recognize whether the fault is external or
internal. An internal fault applies if the polarity of the fault currents is identical on both sides; an external fault
or a load step occurs with different polarities.
If the comparison shows without any doubt that a fault is present, the trip command is sent. It is maintained
over a set minimum command duration.
The phase comparison protection may trip only at one end in case of single-end infeed. The non-feeding end
can also be switched off by means of a transfer trip signal.
Element Ιdyn
The dynamic filter algorithm generates the value idyn(t). It represents the current change of the filtered value
(fundamental component) over two cycles. If the current change exceeds the set threshold 87L Idyn>, the
phase comparison protection is started.
The polarity of the current change is transmitted to the device at the remote end of the protected object.
The dynamic element operates very sensitively in case of internal faults. In case of external faults, the method
is very stable even during different primary rated currents or different saturation of the current transformers at
the two ends.
Element Ιstat
The static element Ιstat operates directly with the filtered fundamental value. If the amplitude of the fundamental component exceeds the set threshold 87L Isteady>, the phase comparison protection is started.
The polarity of the current is transmitted to the device at the remote end of the protected object.
The static element is insensitive towards low fault currents.
Pickup Logic
The dynamic and the static element pick up independently of each other selectively for each phase.
To prevent tripping during an energization, a separate dynamic switch-on threshold 87L Idyn close> is
used.
The pickup is maintained over 2 measuring cycles. After the 2 measuring cycles have expired, the dynamic
sign comparison is blocked.
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 49
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.2 Phase Comparison Protection and Ground Differential Protection
If the pickup is successful, an internal pickup signal is transmitted to the other device.
The element Ιdyn is blocked if the frequency deviates by more than 10 % from the rated frequency.
The function is blocked if the communication between the two devices at the ends of the protected object
fails for more than two measuring cycles.
This function can also be blocked via binary input
The following figure shows the formation of the phase-specific pickup of the elements 87L Isteady> and
87L Idyn>.
>87L block
.
[lo-pvl-anr-20101117, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-5
Logic diagram of the phase comparison protection, phase-selective generation of the Ιstat and
Ιdyn signal
The pickup signals created locally, signs of idyn and istat and the blocking information are sent to the device at
the opposite end.
50 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.2 Phase Comparison Protection and Ground Differential Protection
[lo-pvl-senden-20110530, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-6
Phase comparison protection, sending the differential protection information to the opposite
end
The received pickup and blocking information is compared with the own differential protection information
and element-specific pickup indications are created.
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 51
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.2 Phase Comparison Protection and Ground Differential Protection
[lo-pvl-empfangen-20110530, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-7
Phase comparison protection, receiving the differential protection information from the opposite end
The following figure shows the formation of the phase-specific pickup of the phase comparison protection.
Figure 2-
[lo-pvl-anr-gegenende-20110530, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-8 Logic diagram of phase comparison protection for pickup in a grounded system
The following figure shows the pickup behavior of the phase comparison protection in resonant-grounded or
isolated systems.
52 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

2.2 Phase Comparison Protection and Ground Differential Protection
[lo-pvl-anr-iso-gel-netz-20110608, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-9 Phase comparison protection in resonant-grounded/isolated systems
Functions
You will find the logic diagram for the general pickup of the differential protection and the differential protection tripping in Section 2.2.5 Differential Protection Pickup Logic and Tripping Logic.
2.2.2.2
Setting Notes
General
The phase comparison protection can be switched ON or OFF at address 1201 87L PCC-Prot.. This requires
the differential protection to be set to Enabled at address 112 87 DIFF.PROTEC..
For cables and long lines, the capacitive charging current is decisive for determining the pickup values. The
charging current is calculated as follows:
ΙC = 2π · f
· CB' · s · V
Nom
Nom
/√3
where
Ι
f
C
Nom
Charging current in A
Rated power system frequency in Hz
CB' Referred rated capacitance of the line in F/km
V
Nom
Rated system voltage in V
s Line length in km
Pickup Values for Resistive or Solid Grounded, Resonant-grounded and Isolated Systems
At address 1202 87L Idyn> you can set the dynamic tripping threshold. The value for 87L Idyn> should be
set to at least 0.2 of the largest primary transformer rated current and larger than 2.5 to 3 times the capacitive
charging current of the line. If inductances can be connected in the protected zone (common-mode reactor)
for energized lines, 87L Idyn> should be greater than the maximum expected inrush current.
The dynamic tripping threshold for closing is set in address 1203 87L Idyn close>. The value for 87L
Idyn close> should be ≥ 87L Idyn>, but it should equal at least 3 times the value of the capacitive
charging current of the protected line. If inductances are present in the protected zone (common-mode
reactor), 87L Idyn close> should be set greater than the maximum expected inrush current.
The static tripping threshold is set in address 1204 87L Isteady>. The static tripping threshold should be set
to a value that is larger than at least 3 times the capacitive charging current of the line. If inductances are
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 53
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

i
i
Functions
2.2 Phase Comparison Protection and Ground Differential Protection
present in the protected zone (common-mode reactor), 87L Isteady> must be set greater than the
maximum expected inrush current.
At address 1205 87L I min you can enter the threshold for releasing the pickup signal. The value should at
least correspond to the setting of 87L Idyn>, but not exceed the largest transformer rated current of the
constellation.
NOTE
When using different transformers in the constellation, set identical primary setting values. The secondary
setting values can be different.
Time Delays
The trip time delay for 87L Isteady> is set in address 1206 87L Trip Delay.
With the inrush current detection activated, the time delay 87L Trip Delay must be at least 20 ms for the
blocking by the inrush current detection to be effective. In resonant-grounded or isolated systems, transients
must have subsided before tripping takes place. The delay should be at least 3 cycles (60 ms at 50 Hz and 54
Ms at 60 Hz). For large systems, the time delay must be increased accordingly (see Figure 2-16).
At address 1208 87L: T EFdetect you set the time after which an evolving fault is detected. The parameter is enabled in resonant-grounded or isolated power systems. In the specified time, the 1-phase trip
command of the dynamic element 87L: T EFdetect is not forwarded to the tripping logic.
Address 1207 87L Man. Close allows you to set the behavior of the phase comparison protection for
manual closing for 87L Isteady>. In this case, tripping can be DELAYED or UNDELAYED (see Figure 2-16).
At parameter 1214 87L:Inrush blk. you can enable or disable the blocking function for the phase
comparison in case of inrush. If the parameter is enabled, tripping of the element 87L Idyn> is generally
delayed by one cycle. Inrush blocking can thus become effective.
2.2.3
2.2.3.1
Basic Principle / Influencing Variables
Ground Current Differential Protection in Grounded Systems
The ground current differential protection of the 7SD80 operates as a stabilized (restrained) differential
protection in grounded systems. The 2 7SD80 devices exchange the phasors of the ground currents and the
associated restraining quantities over their protection interfaces. The restraining currents and the current
phasors are summed up in each device and compared to a pickup characteristic. In the event of an internal
short-circuit, the associated circuit breaker is tripped.
Funktionsbeschreibung
In healthy operation, both ends of a line carry the same current. This current flows into one side of the considered zone and leaves it again on the other side. A difference in current is a clear indication of a fault within
this line section.
If the actual current transformation ratios are the same, the secondary windings of the current transformers
CT1 and CT2 at the line ends can be connected to form a closed electric circuit with a secondary current Ι; a
measuring element M which is connected to the electrical balance point remains at zero current in healthy
operation.
When a fault occurs in the zone limited by the transformers, a current i1 + i2 which is proportional to the fault
currents
ensures reliable tripping of the protection if the fault current flowing into the protected zone during a fault is
high enough for the measuring element M to respond.
Ι1 + Ι2 flowing in from both sides is fed to the measuring element. As a result, the simple circuit
54 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.2 Phase Comparison Protection and Ground Differential Protection
[7sd80-diff-grundprinzip-20110530, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-10 Basic principle of the differential protection for a line with two ends
This principle only applies to the primary system as long as quadrature-axis components of current are negligible. Quadrature-axis components of current can be caused by line capacitances or excitation currents of
transformers and parallel reactors.
The secondary currents which are applied to the devices via the current transformers, are subject to measuring
errors caused by the response characteristic of the current transformers and the input circuits of the devices.
Transmission errors such as signal jitters can also cause deviations of the measured quantities. As a result of all
these influences, the total sum of all currents processed in the devices in healthy operation is not exactly zero.
The ground current differential protection is stabilized against these influences.
Additional measuring errors which may arise in the device itself by hardware tolerances, calculation tolerances, deviations in time or due to the “qualität” of the measured quantities such as harmonics and deviations
in frequency, are also estimated by the device and increase the local self-restraining quantity automatically.
Here, the permissible variations in the protection data transmission and processing periods are also considered.
For transient inrush currents the devices have a separate inrush current restraint feature.
Evaluation of Measured Values
The ground current differential protection in grounded systems evaluates the sum of the ground current
phasors.
Each device calculates a ground current at each end of the protected object (fundamental component of the
ground current) and transmits it to the partner device. The received and the locally measured ground current
phasor is added to the ground differential current. The ground differential current value equals the fault
current that the differential protection system “sees”. In the ideal case, it equals the short-circuit current. In
healthy operation, the differential current value is low and for lines about similar to the capacitive charging
current.
The restraining quantity counteracts the ground differential current. It is the total of the maximum measured
errors at the ends of the protected object and is calculated from the current measured quantities and power
system parameters that were set. Therefore, the highest possible error value of the current transformers
within the nominal range and/or the short-circuit current range is multiplied with the current flowing through
each end of the protected object. The total value, including the measured internal errors, is then transmitted
to the other end. This is the reason why the restraint current is a replica of the greatest possible measurement
error of the entire differential protection system.
The pickup characteristic of the differential protection is derived from the restraining characteristic Ι
(45° curve) which is cut off below the setting value 87N L: I-DIFF>. It complies with the equation
Ι
= 87N L: I-DIFF> + Σ (current transformer errors and other measuring errors).
rest
If the calculated differential current exceeds the pickup threshold and the greatest possible measurement
error, the fault must be internal (grayed area in the illustration).
diff
= Ι
rest
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 55
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.2 Phase Comparison Protection and Ground Differential Protection
[ansprechkennl-diffschutz-20110526, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-11 Pickup characteristic of the ground differential protection
If it is desired that an internal fault should initiate a TRIP command and additionally a local current of a specific
quantity should exist, the value of this current can be set at address 1225 87N L: I>RELEAS. The default
setting for this parameter is zero so that this additional criterion does not become effective.
The differential current and the restraint current 3I0diff and 3I0restr are included in the fault record.
Blocking / Interblocking
The ground current differential protection can be blocked via a binary input. The blocking at one end of a
protected object affects all ends via the communications link (interblocking). If the overcurrent protection is
configured as an emergency function, all devices will automatically switch to this emergency operation mode.
Pickup Logic
The following figure illustrates the pickup logic of the ground current differential protection for grounded
systems.
56 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.2 Phase Comparison Protection and Ground Differential Protection
[lo-esd-erd-anr-20101117, 2, en_US]
Figure 2-12
Ground current differential protection pickup, grounded system
You will find the logic diagram for the general pickup of the differential protection and the differential protection tripping in Section 2.2.5 Differential Protection Pickup Logic and Tripping Logic.
2.2.3.2
Setting Notes
General
The operating mode of the ground differential protection depends on the neutral point treatment in the
protected zone. In grounded systems, address 207 SystemStarpoint must be set to Grounded.
The ground differential protection can be switched ON or OFF at address 1221 87N L: Protect.. This
requires the ground differential protection to be set to Enabled at address 112 87 DIFF.PROTEC.. The
setting Alarm only is only relevant for ground fault detection in resonant-grounded or isolated systems.
If a device is switched off or if the ground differential protection is disabled or blocked in a device, calculation
of measured values becomes impossible. The entire ground differential protection system of both ends is
blocked in this case.
Pickup Value Ground Current Differential Protection
The current sensitivity is set at address 1222 87N L: I-DIFF>. It is determined by the entire current flowing
into a protected zone in case of a fault. This is the total fault current regardless of how it is distributed
between the ends of the protected object.
This pickup value must be set to a value that is higher than the total steady-state quadrature-axis component
of current of the protected object. For cables and long overhead lines, the charging current has to be considered in particular. It is calculated from the operational capacitance (see Section 2.2.2.2 Setting Notes).
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 57
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.2 Phase Comparison Protection and Ground Differential Protection
Considering the variations of voltage and frequency, the value set should be at least 2.5 to 3 times higher than
the calculated charging current. Moreover, the pickup value should not be smaller than 15 % of the primary
rated current of the largest transformer in the protection configuration.
If setting is performed from a personal computer using DIGSI, the parameters can be set either as primary or as
secondary quantities. If secondary quantities are set, all currents must be converted to the secondary side of
the current transformers.
Time Delays
In special application cases, it may be advantageous to delay the tripping of the differential protection using
an additional timer, e.g. in case of reverse interlocking. The time delay 87N L: T-DELAY (address 1224) is
only started upon detection of an internal fault. This parameter can only be set in DIGSI at Display Additional
Settings.
With the inrush current restraint activated, the time delay 87N L: T-DELAY must be at least 20 ms for the
blocking by the inrush current restraint to be effective.
If it is desired that a TRIP command is generated in the event of an internal fault only if simultaneously the
current of the local line end has exceeded a specific quantity, then this current threshold can be set for
enabling the differential protection TRIP at address 1225 87N L: I>RELEAS. This parameter can only be set
in DIGSI at Display Additional Settings.
2.2.4
2.2.4.1
General
Restricted Ground-Fault Protection in Resonant-grounded/Isolated Systems
The ground fault differential protection can be applied in power systems whose starpoint is not grounded or
grounded through an arc suppression coil (Petersen coil). It is based on the power values. This requires the
phase voltages or the 3V0 voltage (Appendix C Connection Examples, Figure C-5) to be connected to the
devices at both ends of the protected object.
Funktionsbeschreibung
Single-phase ground faults are not detected by the short-circuit protection since no short circuit current flows.
The power system operation is not immediately affected by a ground fault (the voltage triangle is maintained,
Figure 2-13). Therefore, fast tripping is usually not required or desired. The ground fault is to be detected,
indicated and the affected piece of equipment is to be localized, if possible, eliminating the ground fault by
initiating appropriate switching operations.
The 7SD80 enables the precise localization of the piece of equipment (line) affected by the ground fault.
In resonant-grounded systems, a core balance current transformer must be used to detect the ground current.
[erdschluss-im-nicht-geerdeten-netz-260702-wlk, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-13 Ground fault in non-grounded neutral system
Pickup
Pickup occurs when the settable threshold for the displacement voltage 3·V0 is exceeded. To obtain steadystate measured quantities, the ground fault detection can be delayed by a configurable time after the displace-
ment voltage has occurred.
58 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Determination of the Phase Affected by the Ground Fault
Following pickup caused by the displacement voltage, the phase affected by the ground fault is determined
first. To do this, the individual phase-to-ground voltages are measured. If the voltage magnitude for any given
phase is below the setting value V
, that phase is detected as the ground faulted phase as long as the
min
remaining phase-to-ground voltages are simultaneously above the setting value V
Sensitive Ground Fault Direction Determination
The direction of the ground fault can be determined from the direction of the ground fault current in relation
to the displacement voltage. The only restriction is that the active or reactive current components must be
available with sufficient magnitude at the point of measurement.
In networks with isolated starpoint, the ground fault current flows as capacitive current from the healthy lines
via the measuring point to the point of ground fault. For the determination of the direction the capacitive
reactive power is most relevant.
In networks with arc suppression coils, the Petersen coil superimposes a corresponding inductive current on
the capacitive ground fault current when a ground fault occurs, so that the capacitive current at the point of
fault is compensated. Depending on the measuring point in the system the resultant measured current may be
inductive or capacitive. Therefore, the reactive current is not suited for direction determination of the ground
current. In this case, only the ohmic (active) residual current which results from the losses of the Petersen coil
can be used for direction determination. This residual ground fault residual current is only about some per
cent of the capacitive ground fault current.
The active and reactive component of the power is decisive for the ground fault protection pickup.
A fault in forward direction must be detected at both ends of the protected object for the ground fault differ-
ential protection to pick up.
In case of a single feeder, the residual current per watt at the opposite end of the infeed can be so weak that it
is impossible to determine the direction at that end. In this case, the amplitudes of the active currents of the
two ends are additionally compared to initiate pickup and localize the ground fault.
The amplitude of the active current (resonant-grounded system) and the reactive current (for isolated starpoint) are included in the fault record. The local wattmetric ground current or reactive current is recorded as
Ιee1, the wattmetric ground current or the reactive current of the opposite end as Ιee2.
Functions
2.2 Phase Comparison Protection and Ground Differential Protection
.
max
Pickup Logic
The following figure shows the pickup logic of the ground fault differential protection resonant-grounded or
isolated systems.
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 59
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.2 Phase Comparison Protection and Ground Differential Protection
[lo-esd-anr-20101116, 2, en_US]
Figure 2-14
Ground fault differential protection pickup, isolated/resonant-grounded system
If only the V0 voltage is connected, only parameter 1226 87N L: 3V0> is effective. The threshold checks
87N L:Vph-g min and 87N L:Vph-g max (parameter 1227 and 1228) are not relevant.
You will find the logic diagram for the differential protection trip in Section 2.2.5 Differential Protection Pickup
Logic and Tripping Logic.
60 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.2 Phase Comparison Protection and Ground Differential Protection
2.2.4.2
Setting Notes
General
The operating mode of the ground differential protection depends on the neutral point treatment in the
protected zone. In resonant-grounded or isolated system, you have to set Peterson-C.Gnd. or Isolated
at address 207 SystemStarpoint.
The ground differential protection can be switched ON or OFF at address 1221 87N L: Protect.. If set to
Alarm only, an indication will be output when a fault is detected. Tripping is not initiated. This requires the
ground differential protection to be set to Enabled at address 112 87 DIFF.PROTEC..
If a device is switched off at any end of the protected object or if the protection interface communication is
interrupted, a calculation of measured values becomes impossible. The function then operates locally and only
issues directional indications and pickup indications but no pickup and tripping indications of the ground fault
differential protection.
Pickup Values
The pickup threshold of the displacement voltage is set in address 1226 87N L: 3V0>.
At address 1229 87N L: IN(s)> you can enter the minimum current for direction determination. The
pickup current is to be set as high as possible to avoid false pickup of the device provoked by unbalanced
currents in the system and by current transformers. Dependent on the grounding of the network starpoint, the
magnitude of the capacitive ground fault current (for isolated networks) or the wattmetric residual current
(for compensated networks) is decisive.
In isolated systems, a ground fault in a cable will allow the total capacitive ground fault currents of the entire
electrically connected system, with the exception of the faulted cable itself, to flow through the measuring
point as the latter flows directly to the fault location (i.e. not back via the measuring point). Enter about half
of this ground fault current as pickup value.
In resonant-grounded systems directional determination is made more difficult since a much larger reactive
current (capacitive or inductive) is superimposed on the critical wattmetric (active) current. Therefore,
depending on the system configuration and the position of the arc-compensating coil, the total ground
current supplied to the device may vary considerably in its values with regard to magnitude and phase angle.
The device, however, must evaluate only the active component of the ground fault current, the ground fault
residual current, that is ΙN·cosφ. This requires extremely high accuracy, particularly with regard to phase angle
measurement of all the instrument transformers. Furthermore, the device must not be set to operate too
sensitive. When applying this function in resonant-grounded systems, a reliable direction determination can
only be achieved when toroidal current transformers are connected. Here the following rule of thumb applies:
set the value to half the expected measured current, whereby only the residual wattmetric current is used.
Residual wattmetric current predominantly derives from losses of the Petersen coil.
For phase determination 87N L:Vph-g min (address 1227) is the criterion that applies to the groundfaulted phase if simultaneously the other two phase voltages 87N L:Vph-g max (address 1228) have been
exceeded. Accordingly, the setting 87N L:Vph-g min must be set smaller than the minimum phase-toground voltage that occurs during operation. This setting, too, is uncritical. 40 V (default setting) should
always be correct. 87N L:Vph-g max must be greater than the maximum phase-to-ground voltage occurring during operation, but less than the minimum phase-to-phase voltage occurring during operation. For
V
by the ground fault is a further prerequisite for alarming a ground fault. When connecting the voltage V
(Appendix C Connection Examples, Figure C-5), the check of the phase voltages does not take place.
= 100 V, the value must therefore be 75 V (default setting). The definite detection of the phase affected
Nom
0
Time Delays
The ground fault is detected and reported only when the displacement voltage has applied for at least the
time 87N L:TD-F.det. (address 1230). This stabilizing time also takes effect when ground fault conditions
change (e.g. change of direction).
The tripping can be delayed via the time delay 87N L:TripDelay (address 1231).
With the inrush current restraint activated, the time delay 87N L:TripDelay must be at least 20 ms for the
blocking by the inrush current restraint to be effective.
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 61
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.2 Phase Comparison Protection and Ground Differential Protection
2.2.5
2.2.5.1
Differential Protection Pickup Logic and Tripping Logic
Functional Description
Pickup Logic
Once the differential protection function has reliably registered a fault within its tripping zone, the signal
87(N)L Gen.Flt.
function itself, this pickup signal is of no concern since the tripping conditions are available at the same time.
This signal, however, is required to initiate the internal or external supplementary functions, e.g. fault
recording, automatic reclosing.
[lo-diff-g-anr-20110304, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-15 General pickup
Tripping Logic
The following figure shows the tripping logic of the differential protection.
(general pickup of the differential protection) is generated. For the differential protection
[lo-esd-erd-aus-20101117, 2, en_US]
Figure 2-16
Differential protection trip
If the pickup signals apply for longer than the configurable trip time delay, the differential protection trips.
62 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.2 Phase Comparison Protection and Ground Differential Protection
2.2.6
2.2.6.1
Addr. Parameter C Setting Options Default Setting Comments
1201 87L PCC-Prot. OFF
1202 87L Idyn> 1A 0.20 .. 20.00 A; ∞ 0.33 A Dynamic trip threshold
1203 87L Idyn close> 1A 0.20 .. 20.00 A; ∞ 0.33 A Dynamic trip threshold line
1204 87L Isteady> 1A 0.50 .. 20.00 A; ∞ 1.33 A Steady pick up threshold
1205 87L I min 1A 0.10 .. 20.00 A; ∞ 1.00 A Minimal phase current
1206 87L Trip Delay 0.00 .. 0.10 sec 0.00 sec Trip Delay
1207 87L Man. Close DELAYED
1208 87L: T EFdetect 0.00 .. 32.00 sec 0.00 sec Evolving fault detect.time
1214 87L:Inrush blk. NO
1221 87N L: Protect. OFF
1222 87N L: I-DIFF> 1A 0.10 .. 20.00 A 0.30 A 3I0-DIFF> Pickup value
1223 87NL:I-DIF>S.ON 1A 0.10 .. 20.00 A 0.30 A 3I0-DIFF> Value under
1224A 87N L: T-DELAY 0.00 .. 300.00 sec; ∞ 0.00 sec 3I0-DIFF Trip time delay
1225A 87N L: I>RELEAS 1A 0.00 .. 20.00 A 0.00 A Min.current to release 3I0-
1226 87N L: 3V0> 5 .. 150 V 50 V 3V0> pickup
1227 87N L:Vph-g min 10 .. 100 V 40 V Vph-g min of faulted phase
1228 87N L:Vph-g max 10 .. 100 V 75 V Vph-g max of healthy
1229 87N L: 3I0> 0.003 .. 1.000 A 0.050 A 3I0> to release directional
1230 87N L:TD-F.det. 0.00 .. 320.00 sec 1.00 sec Time delay for fault detec-
1231 87N L:TripDelay 0.00 .. 320.00 sec 0.00 sec Trip Delay
87 Differential Protection
The following tables provide an overview of the parameters and information of the functions:
- Phase comparison protection
- Ground current differential protection in grounded systems
- ground fault differential protection in resonant-grounded/isolated systems
Settings
Addresses which have an appended “A” can only be changed with DIGSI, under “Additional Settings”.
The table indicates region-specific default settings. Column C (configuration) indicates the corresponding
secondary nominal current of the current transformer.
ON Phase current comparison
ON
5A 1.00 .. 100.00 A; ∞ 1.65 A
5A 1.00 .. 100.00 A; ∞ 1.65 A
5A 2.50 .. 100.00 A; ∞ 6.65 A
5A 0.50 .. 100.00 A; ∞ 5.00 A
DELAYED Trip response after manual
UNDELAYED
NO Inrush blocking
YES
ON 87N L protection
ON
Alarm Only
5A 0.50 .. 100.00 A 1.50 A
5A 0.50 .. 100.00 A 1.50 A
5A 0.00 .. 100.00 A 0.00 A
protection
closure
close
1ph faults
switch on condit.
DIFF-Trip
phases
element
tion
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 63
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.2 Phase Comparison Protection and Ground Differential Protection
Addr. Parameter C Setting Options Default Setting Comments
1233 CT Err. I1 0.003 .. 1.600 A 0.050 A Current I1 for CT Angle
Error
1234 CT Err. F1 0.0 .. 5.0 ° 0.0 ° CT Angle Error at I1
1235 CT Err. I2 0.003 .. 1.600 A 1.000 A Current I2 for CT Angle
Error
1236 CT Err. F2 0.0 .. 5.0 ° 0.0 ° CT Angle Error at I2
1237 87NL:Inrush blk NO
NO Inrush blocking
YES
2.2.6.2
No. Information Type of
Information List
Comments
Information
3190 Test 87 IntSP 87 Set test state of 87
3191 Commiss.87 IntSP 87 Set Commissioning state of 87
3192 Test 87 remote OUT 87 Remote relay in test state
3193 Comm. 87 active OUT 87 Commissioning state is active
3197 >Test 87 ON SP 87 >Set test state of 87
3198 >Test 87 OFF SP 87 >Reset test state of 87
3199 Test 87 ON/off IntSP 87 Test state of 87 ON/OFF
3200 Test 87 ONoffBI IntSP 87 Test state ON/OFF via BI
3260 >Comm. 87 ON SP 87 >Commissioning state ON
3261 >Comm. 87 OFF SP 87 >Commissioning state OFF
3262 Comm 87 ON/OFF IntSP 87 Commissioning state ON/OFF
3263 Comm 87 ONoffBI IntSP 87 Commissioning state ON/OFF via BI
32100 >87L block SP >87L Protection blocking signal
32102 87L active OUT 87L Protection is active
32103 87L Fault A OUT 87L Fault detection A
32104 87L Fault B OUT 87L Fault detection B
32105 87L Fault C OUT 87L Fault detection C
32107 87L is blocked OUT 87L Protection is blocked
32108 87L is OFF OUT 87L Protection is switched off
32109 87L allow A OUT 87L A released
32110 87L allow B OUT 87L B released
32111 87L allow C OUT 87L C released
32112 87 CTRatioAlarm OUT 87 CT primary ratio is too high
32113 87L receive blk OUT 87L receive blocking
32114 87L send blk OUT 87L send blocking
32115 87L IDYN> A OUT 87L IDYN> A
32116 87L IDYN> B OUT 87L IDYN> B
32117 87L IDYN> C OUT 87L IDYN> C
32118 87L ISTAT> A OUT 87L ISTAT> A
32119 87L ISTAT> B OUT 87L ISTAT> B
32120 >87N L block SP >87N L Protection blocking signal
32121 >87N L active OUT >87N L: Protection is active
32122 87(N)L Gen.Flt. OUT 87(N)L Fault detection
32124 >87N L I> Flt. OUT >87N L: Fault detection of I-Diff>
64 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.2 Phase Comparison Protection and Ground Differential Protection
No. Information Type of
Information
32125 87(N)L Gen.TRIP OUT 87(N)L General TRIP
32126 87N L block OUT 87N L: Protection is blocked
32127 87N L OFF OUT 87N L: Protection is switched off
32128 87N L 3V0> OUT 87N L: detection 3V0> pickup
32129 87N L Forward OUT 87N L: detection Forward
32130 87N L Reverse OUT 87N L: detection Reverse
32131 87N L UndefDir OUT 87N L: detection Undef. Direction
32132 87N L rec. blk OUT 87N L: receive blocking
32133 87N L send blk OUT 87N L: send blocking
32134 87N L PU OUT 87N L: pickup
32150 87L ISTAT> C OUT 87L ISTAT> C
2.2.7
2.2.7.1
General
Differential Protection Test and Commissioning
Differential Protection Test
If differential protection test mode (test mode in the following) is activated, the differential protection is
blocked in the entire system. Depending on the configuration, the overcurrent protection acts as emergency
function.
In the local device all currents from the other devices are set to zero. The local device only evaluates the locally
measured currents, interprets them as differential current but does not send them to the other devices. This
enables measuring the thresholds of the differential protection. Moreover, the test mode prevents in the local
device that tripping of the differential protection generates a transfer trip signal.
The test mode can be activated/deactivated as follows:
Operation panel: Menu Control/Taggings/Set: “Test mode”
•
Via binary inputs (no. 3197
•
In DIGSI with Control / Taggings: “Diff: Test mode”
•
The test mode status of the other device of the line protection system is indicated on the local device by the
indication
Test 87 remote
>Test 87 ON
(No. 3192).
Comments
, no. 3198
>Test 87 OFF
) if this was routed
Functional Description
Below, the logic is shown in a simplified way:
[logik-testmodus, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-17 Logic diagram of the test mode
Depending on the way used for controlling the test mode, either the indication
Test 87 ONoffBI
or
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 65
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018
(no. 3200) is generated. The way used for deactivating the test mode always has to be
Test 87 ON/off
(no. 3199)

Functions
2.2 Phase Comparison Protection and Ground Differential Protection
identical to the way used for activating. The indication
chosen way. When deactivating the test mode via the binary inputs, a time delay of 500 ms becomes effective.
The following figures show possible variants for controlling the binary inputs. If a switch is used for the control
(Figure 2-19), it has to be observed that binary input
contact and that binary input
[logik-testmodus-ext-taster, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-18 External push-button wiring for controlling the differential protection test mode
Bu1 Push-button “Switching off the differential protection test mode”
BU2 Push-button “Switching on the differential protection test mode”
>Test 87 OFF
(no. 3198) is parameterized as NC contact.
Test 87
(no. 3190) is generated independently of the
>Test 87 ON
(no. 3197) is parameterized as NO
2.2.7.2
General
[logik-testmodus-ext-schalter, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-19 External switch wiring for controlling the differential protection test mode
S Switch“Switching the differential protection test mode on/off”
1) Binary input as make contact
2) Binary input as break contact
If a test switch is to be used for changing to test mode, we recommend the following procedure:
Block the differential protection via a binary input.
•
Use the test switch to activate/deactivate the test mode.
•
Reset the blocking of the differential protection via the binary input.
•
Differential Protection Commissioning
In differential protection commissioning mode (commissioning mode in the following) the differential protection does not generate TRIP commands. The commissioning mode is intended to support the commissioning
of the differential protection.
You can check:
Transformer polarity, using the constellation measured values
•
Differential currents
•
Restraint currents
•
By editing parameters, the operating point of the differential protection can be changed without any risk up to
the generation of a pickup.
66 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

[lo-dif-20101116, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-20 Commissioning mode - overview
The commissioning mode is activated on a device of the protective device constellation and also affects the
device at the other end of the protected object (indication no. 3193
mode has to be deactivated on the device on which it was activated.
The commissioning mode can be activated/deactivated as follows:
Operation panel: Menu Control/Taggings/Set: “Commissioning mode”
•
Via binary inputs (no. 3260
•
In DIGSI with Control / Taggings: “Diff: Commissioning mode”
•
Functional Descriptin
Below, the logic is shown in a simplified way:
>Comm. 87 ON
Functions
2.2 Phase Comparison Protection and Ground Differential Protection
, no. 3261
Comm. 87 active
>Comm. 87 OFF
) if this was routed
). The commissioning
[logik-ibs-modus, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-21 Logic diagram of the commissioning mode
There are two ways to set the commissioning mode. The first way is to use a command (commissioning mode
on / commissioning mode off) which is generated either when operating the integrated keypad or when operating with DIGSI. The second way is to use the binary inputs (no. 3260
).
OFF
Depending on the way used for controlling the commissioning mode, either the indication
(no. 3262) or
mode always has to be identical to the way used for activating. The indication
generated independently of the chosen way.
The following figures show possible variants for controlling the binary inputs. If a switch is used for control
(Figure 2-23), it has to be observed that binary input
contact and that binary input
[logik-ibs-modus-ext-taster, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-22 External push-button wiring for controlling the differential protection commissioning mode
Comm 87 ONoffBI
>Comm. 87 OFF
(no. 3263) is generated. The way used for deactivating the commissioning
>Comm. 87 ON
(no. 3261) is parameterized as NC contact.
>Comm. 87 ON
, no. 3261
>Comm. 87
Comm 87 ON/OFF
Commiss.87
(no. 3260) is parameterized as NO
(no. 3191) is
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 67
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.2 Phase Comparison Protection and Ground Differential Protection
Bu1 Push-button “Switching off the differential protection commissioning mode”
BU2 Push-button “Switching on the differential protection commissioning mode”
[logik-ibs-modus-ext-schalter, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-23 External switch wiring for controlling the differential protection commissioning mode
S Switch “Switching the differential protection commissioning mode on/off”
1) Binary input as make contact
2) Binary input as break contact
68 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.3 Breaker Intertrip and Remote Tripping
2.3
2.3.1
Transmit Circuit
Breaker Intertrip and Remote Tripping
The 7SD80 device allows transmitting a trip command created by the local differential protection to the other
end of the protected object (intertripping). Likewise, any desired command of another internal protection
function or of an external protection, monitoring or control equipment can be transmitted for remote tripping.
Functional Description
The transmission signal can originate from two different sources (Figure 2-24). If the parameter 85 DT:
SEND is set to YES, each tripping command of the differential protection is routed immediately to the trans-
mission function „ITrp.sen. A“ to "...C“ (intertrip) and transmitted via the protection data interfaces and
communication links.
The send function can be triggered via binary input
can be delayed with 85 DT: TD-BI and prolonged with 85 DT: TD-BI.
>85 DT 3pol
(remote tripping). The transmission signal
[lo-mitnahme-sendekreis-20101108, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-24 Logic diagram of the intertrip — Transmission circuit
Receive Circuit
On the receiving end the signal can lead to a trip. Alternatively, it can also cause an alarm only. In this way it is
possible to determine for each end of the protected object whether the received signal is to trip at this particular end or not.
If the received signal is to cause the trip, it will be forwarded to the tripping logic of the device.
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 69
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.3 Breaker Intertrip and Remote Tripping
[lo-mitnahme-empfangskreis-20101108, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-25 Logic diagram of the intertrip — receiving circuit
Additional Options
Since the signals for remote tripping can be set to just generate an indication, any other desired signals can be
transmitted as well. After the binary input(s) have been activated, the signals which are set to cause an alarm
at the receiving end are transmitted. These alarms can in turn execute any desired actions at the receiving
end.
2.3.2
Setting Notes
General
The intertrip function for tripping caused by the differential protection can be activated (YES) or deactivated
(NO) at address 1301 85 DT: SEND.
To ensure that the faulted line is cleared, the intertrip function must be activated. In some applications, e.g. a
single feed, it may be desirable to switch off the feeding end only. In such exceptional cases, the intertrip
function is not needed.
Breaker Intertrip / Remote Tripping
The activated intertrip function starts automatically when the differential protection trips at only one end.
If the relevant binary inputs are allocated and activated by an external source, the intertrip signal is trans-
mitted as well. In this case, the signal to be transmitted can be delayed with address 1303 85 DT: TD-BI.
This delay stabilizes the originating signal against dynamic interferences which may possibly occur on the
control cabling. Address 1304 85 DT:T-PROL BI is used to extend a signal after it has been effectively
injected from an external source.
The reaction of a device when receiving an intertrip/remote tripping signal is set in address 1302 85 DT:
RECEIVE. If it is desired to cause tripping, set the value Trip. If the received signal, however, is supposed to
cause an alarm only, Alarm only must be set if this indication is to be further processed externally.
The setting times depend on the individual case of application. A delay is necessary if the external control
signal originates from a disturbed source and a restraint seems appropriate. Of course, the control signal has
to be longer than the delay for the signal to be effective. If the signal is processed externally at the receiving
end, a prolongation time might become necessary for the transmitting end so that the reaction desired at the
receiving end can be executed reliably.
70 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Release Thresholds
Before the release for tripping is given, the phase and ground currents must exceed settable thresholds. You
can set these thresholds at the following addresses:
1305 85 DT Iph rel. for the minimum phase current
•
1306 85 DT 3I0 rel. for the minimum ground current 3I0
•
Functions
2.3 Breaker Intertrip and Remote Tripping
2.3.3
Addr. Parameter C Setting Options Default Setting Comments
1301 85 DT: SEND YES
1302 85 DT: RECEIVE Alarm only
1303 85 DT: TD-BI 0.00 .. 30.00 sec 0.00 sec 85 DT: Delay for intertrip
1304 85 DT:T-PROL BI 0.00 .. 30.00 sec 0.00 sec 85 DT: Prol. for intertrip via
1305 85 DT Iph rel. 1A 0.0 .. 25.0 A 0.0 A 85 DT minimal Phase
1306 85 DT 3I0 rel. 1A 0.0 .. 25.0 A 0.0 A 85 DT minimal 3I0 Current
2.3.4
No.
3504 >85 DT 3pol SP >86 DT: >Intertrip 3 pole signal input
3517 85 DT Gen. TRIP OUT 85 DT: General TRIP
17525 85 DT rec.3pole OUT 85 DT: Received 3pole
17526 85 DT sen.3pole OUT 85 DT: Sending 3pole
Settings
The table indicates region-specific presettings. Column C (configuration) indicates the corresponding secondary nominal current of the current transformer.
YES 85 DT: State of transm.the
NO
Trip 85 DT: React.if intertrip
Trip
5A 0.0 .. 125.0 A 0.0 A
5A 0.0 .. 125.0 A 0.0 A
intertrip cmd
cmd is receiv.
via bin.input
bin.input
Current to rel. trip
to rel. trip
Information List
Information Type of
Information
Comments
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 71
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.4 Backup overcurrent
2.4
2.4.1
Emergency Overcurrent Protection
Backup Time Overcurrent Protection
Backup overcurrent
The 7SD80 features an overcurrent protection function which can be used as either backup or emergency
overcurrent protection. All elements are independent of each other and can be combined as desired.
The overcurrent protection has two overcurrent elements with definite trip time and one overcurrent protection element with inverse time delay for the phase currents and for the ground current. These elements
operate directionally or non-directionally.
One additional definite-time overcurrent protection element always operates non-directionally. It features an
additional release input and can act as emergency element if the other elements are used for backup
purposes.
The elements are independent of each other and can be combined in any way. Blocking by external criteria via
binary inputs is possible.
Operating Modes
The differential protection as a whole can only operate correctly if both devices receive the data of the respective other device properly. The emergency overcurrent protection in contrast requires only the local currents.
Acting as emergency overcurrent protection, it automatically replaces the differential protection as shortcircuit protection if data communication of the differential protection is faulty (emergency operation). The
differential protection is blocked in this case.
If the overcurrent protection is set as backup time overcurrent protection, it will work independently of the
other protection and monitoring functions, i.e. also independently of the differential protection. The backup
overcurrent protection can also act as the only short-circuit protection if no suitable channels for the communication between the protection devices are available yet during the initial commissioning. It can be used as
busbar protection via reverse interlocking in combination with other protection devices or as backup protection function for protection device failure at continuing lines.
2.4.2
Measured Quantities
Definite Time High-set Element 50-1
Non-directional Overcurrent Protection
The phase currents are fed to the device via the input transformers of the measuring input. The ground
current Ι0 is calculated from the phase currents.
Each phase current is compared with the setting value 50-B2 PICKUP after numerical filtering; the ground
current is compared with 50N-B2 PICKUP. A trip command is issued after pickup of an element and expiration of the associated time delays 50-B2 DELAY or 50N-B2 DELAY. The dropout value is about 7 % below
the pickup value, but at least 5 % of the rated current.
Figure 2-26 shows the logic diagram of the 50-1 elements. They can be blocked via binary input
. Additionally, the ground current element can be blocked separately via the binary input
B2
The binary input
all elements. They may, however, separately affect the phase and/or ground current elements.
Parameter 50-B1 DELAY (address 2618) determines whether a non-delayed trip of this element via binary
input
>5X-B InstTRIP
before reclosing.
If parameter 50-B2 Inrush (address 2625) is set to YES, the element is blocked.
>5X-B InstTRIP
>BLOCK 50-
>BLOCK 50N-B2
and the evaluation of the indication “switch” (onto fault) are common to
is possible (YES) or impossible (NO). This parameter is also used for fast tripping
.
72 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.4 Backup overcurrent
[lo-i-vg-stufe-20101108, 2, en_US]
Figure 2-26
Logic diagram of the 50-1 element
Definite Time Overcurrent Element 50-2
The logic of the overcurrent elements 50-2 is the same as the logic of the 50-1 elements described above. In
all names, -1 has to be replaced by -2. The parameter names of the 50-2 elements are listed in Section
2.4.4 Setting Notes.
Definite Time Overcurrent Element 50-3
The 50-3 element operates independently of the other elements. Its logic corresponds to the 50-1 and 50-2
elements described above, but operates non-directional only.
If parameter 50-3 Inrush (address 2653) is set to YES, the element is blocked.
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 73
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.4 Backup overcurrent
[lo-i-3gr-stufe-20101115, 2, en_US]
Figure 2-27
Logic diagram of the 50-3 element
Inverse Time Overcurrent Element 51
The logic of the inverse overcurrent element basically operates in the same way as the other elements. The
time delay, however, is calculated based on the type of the set characteristic, the intensity of the current and a
time multiplier (following figure). A pre-selection of the available characteristics was already carried out
during the configuration of the protection functions. Furthermore, an additional constant time delay 51-B
AddT-DELAY or 51N-B AddTdelay may be selected which is added to the inverse time. The possible characteristics are shown in the Technical Data.
The non-directional and the directional inverse time overcurrent element 51 always uses the same characteristic curve that is parameterized via 2642 (IEC) or 2643 (ANSI). Different inverse times and additional times
can be parameterized here.
The following figure shows the logic diagram. The setting addresses of the IEC characteristic curves are shown
by way of example. In the setting notes (Section 2.4.4 Setting Notes), the different setting addresses are
described in detail.
If parameter 51-B Inrush (address 2637) is set to YES, the element is blocked.
74 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.4 Backup overcurrent
[lo-ip-stufe-amz-iec-20101108, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-28
Logic diagram of the 51 element (inverse time overcurrent protection) - Example for IEC characteristic
Pickup Logic and Tripping Logic
The pickup signals of the individual phases (or ground) and of the individual elements are interlinked in such a
way that both the phase information and the element which has picked up are indicated (Table 2-1).
Table 2-1
Pickup signals of the single phases
Internal indication Display Output indication No.
50-2 PU A
50-1 PU A
50-3 PU A
Figure 2-26
5X-B Pickup ØA
7162
51 PU A
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 75
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

i
i
Functions
2.4 Backup overcurrent
Internal indication Display Output indication No.
50-2 PU B
50-1 PU B
50-3 PU B
51 PU B
50-2 PU C
50-1 PU C
50-3 PU C
51 PU C
50-2 PU N
50-1 PU N
50-3 PU N
51 PU N
50-1 PU A
50-1 PU B
50-1 PU C
50-1 PU N
50-2 PU A
50-2 PU B
50-2 PU C
50-2 PU N
50-3 PU A
50-3 PU B
50-3 PU C
50-3 PU N
51 PU A
51 PU B
51 PU C
51 PU N
(All pickups)
Figure 2-26
Figure 2-26
Figure 2-26
Figure 2-26
Figure 2-26
Figure 2-26
Figure 2-26
Figure 2-26
Figure 2-26
Figure 2-26
Figure 2-26
5X-B Pickup ØB
5X-B Pickup ØC
5X-B Pickup Gnd
50(N)-B2 PICKUP
50(N)-B1 PICKUP
50-3 PICKUP
51(N)-B PICKUP
5X-B PICKUP
7163
7164
7165
7192
7191
7201
7193
7161
The trip is signaled specifically for each phase-element, e.g.
NOTE
There is no indication for tripping of the grounding stages. If you need information link the internal pickup
signal with the OFF command of the stage, e.g, 50-1 PU N and
2.4.3
Measured Quantities
76 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
Directional Overcurrent Protection
The phase currents are fed to the device via the input transformers of the measuring input. The ground
current 3I0 is calculated from the phase currents.
For the directional 67-1 elements, the used measuring voltage is determined by the fault type.
The current phase-to-ground voltage is used
for 1-phase or 3-phase faults
•
if the phase-to-ground voltage is > 4 V
•
not within the first 50 ms after short-circuit inception as the present voltage is disturbed by transients
•
during this time.
50(N)-B2 TRIP
50(N)-B2 TRIP
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018
.

Functions
2.4 Backup overcurrent
The saved phase-to-ground voltage is used
for 1-phase or 3-phase faults
•
up to max. 2 sec. after saving the phasors
•
if there was not pickup before short-circuit occurrence.
•
The unfaulted phase-to-phase voltage is used
for 1-phase faults
•
for unfaulted phase-to-ground voltages
•
if the voltage value is > 70% of the rated voltage.
•
The negative-sequence system quantities
for 1-phase or 2-phase faults
•
if Ι2 > 50 mA and U2 > 5 V.
•
When using the negative-sequence system quantities, it is the short circuit with the higher current which
determines the direction in case of two 1-phase short circuits.
If none of the above measured quantities is available, an already existing result of the direction determination
is used or the directional element is blocked for the corresponding phase.
The behavior in the even to a measuring voltage failure can be set. The elements operate directionally or
nondirectionally.
The time overcurrent protection only operates directionally if all 3 phase-to-ground voltages are connected.
Address 144 must be set to connected here.
V2 and Ι2 are used
Directional Characteristic
The directional characteristic of the directional overcurrent elements is fixed. The angle difference φ(
is calculated from the voltage phasors and current phasors using the impedance Z = V/I and the direction is
determined using the depicted directional characteristic.
V) - φ(I)
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 77
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.4 Backup overcurrent
[richtl-ueberstrom-060724, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-29
Directional characteristic of the time overcurrent protection
Definite Time Overcurrent Element 67-1
The directional overcurrent elements basically work in the same way as the non-directional elements. Pickup,
however, depends on the result of the direction determination. The direction determination is accomplished
using the measured quantities and the corresponding directional characteristics.
67-B2 PICKUP is used as setting values for the phase current; 67N-B2 PICKUP is used for the ground
current. A trip command is issued after pickup of an element and expiration of the associated time delays 67-
B2 DELAY or 67N-B2 DELAY. The dropout value is approximately 7% below the pickup value, but at least
1.8% of the nominal current, below the pickup value.
Figure 2-30 shows the logic diagram of the 67-1 elements. They can be blocked via the binary input
51N
. Additionally, the ground current element can be blocked separately via the binary input
TOC
.
The binary input
>5X-B InstTRIP
rately on the directional phase and/or ground element.
Parameter 67(N)-B2 Pil/BI (address 2628) determines whether a non-delayed trip of this element via
binary input
>5X-B InstTRIP
neous tripping before automatic reclosing.
The indications
67(N) forward
(7257 to 7264) determined specifically for the phase or current if a valid direction was determined for a phase
or ground current (forward or reverse). These indications can then be transmitted to another device where
they can cause instantaneous tripping there if an overcurrent element of the receiving device has picked up,
too. The indications must be linked via CFC to this end.
>BLOCK
>BLOCK 67N-
and the evaluation of the indication “switch” (onto fault) can act sepa-
is possible (YES) or impossible (NO). This parameter is also used for instanta-
or
67(N) reverse
are created from the individual directional indications
78 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.4 Backup overcurrent
[lo-i-gr-stufe-gerichtet-20101108, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-30
Logic diagram of the 67-1 element
Definite Time High-set Element 67-2
The directional overcurrent element basically works in the same way as the non-directional element. Pickup,
however, depends on the result of the direction determination. The direction determination is accomplished
using the measured quantities and the corresponding directional characteristics.
67-B1 PICKUP is used as setting values for the phase current; 67N-B1 PICKUP is used for the ground
current. A trip command is issued after pickup of an element and expiration of the associated time delays 67-
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 79
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.4 Backup overcurrent
B1 DELAY or 50N-B1 DELAY. The dropout value is approximately 7% below the pickup value, but at least
1.8% of the nominal current.
Figure 2-30 shows the logic diagram of the 67-1 elements. The same applies analogously to the high-set
current element 67-2
Inverse Time Overcurrent Element 67-TOC
The logic of the inverse overcurrent element basically operates in the same way as that of the non-directional
element. Pickup, however, depends on the result of the direction determination. The direction determination
is accomplished using the measured quantities and the corresponding directional characteristics.
The time delay, however, is calculated based on the type of the set characteristic, the intensity of the current
and the time factor 67-TOC TD ANSI or 67N-TOC TD ANSI. Furthermore, an additional constant time
delay 67-TOC AddTDel. or 67N-TOC AddTDel may be selected which is added to the inverse time. The
possible characteristics are shown in the Technical Data.
The indications
67(N) forward
(7257 to 7264) determined for the phase and ground current provided that a valid directional result (forward
or reverse) was determined for the phase or ground current. These indications can then be transmitted to
another device where they can cause instantaneous tripping if an overcurrent element of the received device
has picked up, too. The indications must be linked via CFC to this end.
The following figure shows the logic diagram of the directional 67-TOC element. The setting addresses for the
IEC characteristics are shown by way of example. In the setting notes (Section 2.4.4 Setting Notes), the
different setting addresses are described in detail.
The non-directional and the directional inverse time overcurrent element 51 always uses the same characteristic curve that is parameterized via 2642 (IEC) or 2643 (ANSI). Different inverse times and additional times
can be parameterized here.
or
67(N) reverse
are created from the individual directional indications
80 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.4 Backup overcurrent
[lo-ip-stufe-gerichtet-20101108, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-31
Logic diagram of the 67 TOC element (directional, inverse time overcurrent protection) example for IEC characteristic
Pickup Logic and Tripping Logic
The pickup signals of the individual phases (or ground) and of the individual elements are interlinked in such a
way that both the phase information and the element which has picked up are indicated (Table 2-2).
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 81
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

i
i
Functions
2.4 Backup overcurrent
Table 2-2 Pickup signals of the single phases
Internal indication Display Output indication No.
67-1 PU A
67-2 PU A
67-TOC PU A
67-1 PU B
67-2 PU B
67-TOC PU B
67-1 PU C
67-2 PU C
67-TOC PU C
67-1 PU N
67-2 PU N
67-TOC PU N
67-1 PU A
67-1 PU B
67-1 PU C
67-1 PU N
67-2 PU A
67-2 PU B
67-2 PU C
67-2 PU N
67-TOC PU A
67-TOC PU B
67-TOC PU C
67-TOC PU N
(All pickups)
67 Pickup ØA
67 Pickup ØB
67 Pickup ØC
67N Pickup Gnd
67(N)-B2 PICKUP
67(N)-B1 PICKUP
67(N)-TOC PICK.
67(N) PICKUP
17536
17537
17538
17539
7251
7250
7252
17535
The trip is signaled specifically for each element, e.g.
NOTE
There is no indication for tripping of the grounding stages. If you need information link the internal pickup
signal with the OFF command of the stage, e.g, 67-1 PU N and
Behavior during Measuring Voltage Failure
An element-specific parameter, e.g. 67(N)-B1 on FFM allows you to define how the directional overcurrent
protection acts when the measuring voltage fails. The overcurrent protection then works either Non-Direc-
tional or it is BLOCKED.
2.4.4
General
Operating Modes
Setting Notes
The setting notes described in the following apply to non-directional and directional overcurrent protection.
You set the operating mode of the overcurrent protection elements specifically for each element. The setting
applies collectively to the corresponding phase and ground element.
50-1, 3I0>
address 2620
67(N)-B2 TRIP
67(N)-B2 TRIP
.
82 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Direction
Functions
2.4 Backup overcurrent
50-2, 3I0>> address 2610
50N, 3I0p address 2630
50-3, 3I0>>> address 2650
The following settings are possible:
If set to ON, the time overcurrent protection operates independently of the other protection functions as
•
backup overcurrent protection.
If set to Only Emer. prot, the overcurrent protection operates as emergency function.
•
If set to OFF, the element is disabled.
•
The elements 50-1, 50-2 and 50N operate directionally and non-directionally.
The direction is set specifically for each element. The setting applies collectively to the corresponding phase
and ground element.
50-1, 3I0> address 2621
50-2, 3I0>> address 2611
50N, 3I0p address 2631
The following settings are possible:
Non-Directional
•
Forward
•
Reverse
•
The operating mode of the directional element in the event of measuring voltage failure is set specifically for
each element. The setting applies collectively to the corresponding phase and ground element.
50-1, 3I0>
50-2, 3I0>> address 2612
50N, 3I0p address 2632
address 2622
The following settings are possible:
•
•
The 50-3 element always operates non-directionally.
Inrush Blocking
You can specify for each element of the overcurrent protection whether the element will be blocked when
inrush is detected. The setting applies collectively to the corresponding phase and ground element.
50-1, 3I0>
50-2, 3I0>> address 2615
50N, 3I0p address 2637
50-3, 3I0>>> address 2653
Pickup Values
The elements can be combined. The pickup values are determined by the type of protected object.
The pickup values are set specifically for each element:
50-B2 PICKUP
50N-B2 PICKUP, 67N-B2 PICKUP address 2626
50-B1 PICKUP, 67-B1 PICKUP address 2613
50N-B1 PICKUP, 67N-B1 PICKUP address 2616
Non-Directional
BLOCKED
address 2625
, 67-B2 PICKUP address 2623
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 83
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.4 Backup overcurrent
51-B PICKUP, 67-TOC PICKUP address 2633
51N-B PICKUP, 67N-TOC PICKUP address 2638
The setting of the current pickup value is basically determined by the maximum operational current. Pickup
due to overload must be excluded as the device operates as short-circuit protection in this mode with correspondingly short command times and not as overload protection. A pickup value setting of about 10% is
recommended for line protection, and a setting of about 20% of the expected peak load is recommended for
transformers and motors.
The ground current elements detect the smallest anticipated ground fault current.
For very long lines with small source impedance or on applications with large reactances (e.g. series reactors),
the 50-2 elements can also be used for current grading. In this case, they must be set such that they do not
pickup reliably on a short circuit at the line end.
For the inverse time elements a safety margin between pickup value and setting value has already been implemented. Pick up only occurs at a current which is approximately 10% above the set value. Please bear this in
mind when specifying the setting values of the inverse time elements.
If an element is not required, set the pickup value to ∞.
Time Delays
The time delays are set specifically for each element:
50-B2 DELAY, 67-B2 DELAY address 2624
50N-B2 DELAY, 67N-B2 DELAY address 2627
50-B1 DELAY, 67-B1 DELAY address 2614
50N-B1 DELAY, 67N-B1 DELAY address 2617
51-B TD IEC, 67-TOC TD IEC address 2634 (IEC characteristic)
51N-B TD IEC, 67N-TOC TD IEC address 2639 (IEC characteristic)
51-B TD ANSI, 67-TOC TD ANSI address 2635 (ANSI characteristic)
51N-B TD ANSI, 67N-TOC TD ANSI address 2640 (ANSI characteristic)
They are determined by the time grading chart created for the power system. If used as emergency overcurrent protection, shorter tripping times are advisable as this function is only activated in the case of the loss of
the local measuring voltage.
The times for the ground current elements can be set shorter, according to a separate time grading chart for
ground currents.
You can set additional time delays for definite-time elements with IEC characteristic.
51-B AddT-DELAY
51N-B AddTdelay, 67N-TOC AddTDel address 2641
Instantaneous Tripping via Binary Input
Binary input
collectively.
You can specify for each element whether instantaneous tripping takes effect. The setting applies collectively
to the corresponding phase and ground element.
50-1, 3I0>
50-2, 3I0>> address 2618
50N, 3I0p address 2644
The following settings are possible:
If set to YES, the element trips instantaneously when the binary input is activated.
•
If set to NO, the set time delays take effect.
•
>5X-B InstTRIP
, 67-TOC AddTDel. address2636
address 2628
allows you to bypass the time delays. The binary input applies to all elements
84 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Characteristic Curves for the 50N Element
During configuration of the scope of functions at address 126, the available characteristics were determined.
Depending on the selection made there, only the parameters associated with this characteristic curve are
accessible.
The inverse time elements enable the user to select different characteristic curves. Address 126 allows you to
specify whether you work with IEC characteristics 50(N) 51(N) IEC or ANSI characteristics 50(N)
51(N)ANSI).
Bei den stromabhängigen Stufen können verschiedene Kennlinien gewählt werden. Unter Adresse 126 stellen
Sie ein, ob Sie mit IEC-Kennlinien (50(N) 51(N) IEC) oder ANSI-Kennlinien arbeiten (50(N) 51(N)ANSI).
If you work with IEC characteristics, you can select the following setting options at address 2642:
Normal Inverse
•
Very Inverse
•
Extremely Inv.
•
LongTimeInverse
•
If you work with ANSI characteristics, you can select the following setting options at address 2643:
Inverse
•
Short Inverse
•
Long Inverse
•
Moderately Inv.
•
Very Inverse
•
Extremely Inv.
•
Definite Inv.
•
The characteristics and equations they are based on are listed in the “Technical Data”. They apply for directional and non-directional elements alike.
Functions
2.4 Backup overcurrent
2.4.5
Addr.
2603A 67N dir. meas. V0/I0 or V2/I2
2610 Op.Mode50(N)-B1 ON
2610 Op.Mode67(N)-B1 ON
2611 67(N)-B1 Dir. Non-Directional
2612 67(N)-B1 on FFM Non-Directional
2613 50-B1 PICKUP 1A 0.10 .. 25.00 A; ∞ 2.00 A 50-B1 Pickup
Settings
Addresses which have an appended “A” can only be changed with DIGSI, under “Additional Settings”.
The table indicates region-specific default settings. Column C (configuration) indicates the corresponding
secondary nominal current of the current transformer.
Parameter C Setting Options Default Setting Comments
V0/I0 or V2/I2 67N, Measurement of
with V0/I0
with V2/I2
OFF Operating Mode 50(N)-B1
Only Emer. prot
OFF
OFF Operating Mode 67(N)-B1
Only Emer. prot
OFF
Non-Directional 67(N)-B1 Direction
Forward
Reverse
BLOCKED 67(N)-B1 Direct. stage on
BLOCKED
5A 0.50 .. 125.00 A; ∞ 10.00 A
direction
Fuse Failure
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 85
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.4 Backup overcurrent
Addr. Parameter C Setting Options Default Setting Comments
2613 67-B1 PICKUP 1A 0.10 .. 25.00 A; ∞ 2.00 A 67-B1 Pickup threshold
5A 0.50 .. 125.00 A; ∞ 10.00 A
2614 50-B1 DELAY 0.00 .. 30.00 sec; ∞ 0.30 sec 50-B1 Delay
2614 67-B1 DELAY 0.00 .. 30.00 sec; ∞ 0.30 sec 67-B1 set time delay
2615 50-B1 Inrush NO
NO 50-B1 Inrush blocking
YES
2615 67-B1 Inrush NO
NO 67-B1 Inrush blocking
YES
2616 50N-B1 PICKUP 1A 0.05 .. 25.00 A; ∞ 0.50 A 50N-B1 Pickup
5A 0.25 .. 125.00 A; ∞ 2.50 A
2616 67N-B1 PICKUP 1A 0.05 .. 25.00 A; ∞ 0.50 A 67N-B1 Pickup threshold
5A 0.25 .. 125.00 A; ∞ 2.50 A
2617 50N-B1 DELAY 0.00 .. 30.00 sec; ∞ 2.00 sec 50N-B1 Delay
2617 67N-B1 DELAY 0.00 .. 30.00 sec; ∞ 2.00 sec 67N-B1 set time delay
2618 50(N)-B1 Pil/BI NO
YES
2618 67(N)-B1 Pil/BI NO
YES
2620 Op.Mode50(N)-B2 ON
YES Instantaneous trip via Pilot
Prot./BI
NO Instantaneous trip via Pilot
Prot./BI
Only Emer. prot Operating Mode 50(N)-B2
Only Emer. prot
OFF
2620 Op.Mode67(N)-B2 ON
Only Emer. prot Operating Mode 67(N)-B2
Only Emer. prot
OFF
2621 67(N)-B2 Dir. Non-Directional
Non-Directional 67(N)-B2 Direction
Forward
Reverse
2622 67(N)-B2 on FFM Non-Directional
BLOCKED
BLOCKED 67(N)-B2 Direct. stage on
Fuse Failure
2623 50-B2 PICKUP 1A 0.10 .. 25.00 A; ∞ 1.50 A 50-B2 Pickup
5A 0.50 .. 125.00 A; ∞ 7.50 A
2623 67-B2 PICKUP 1A 0.10 .. 25.00 A; ∞ 1.50 A 67-B2 Pickup threshold
5A 0.50 .. 125.00 A; ∞ 7.50 A
2624 50-B2 DELAY 0.00 .. 30.00 sec; ∞ 0.50 sec 50-B2 Delay
2624 67-B2 DELAY 0.00 .. 30.00 sec; ∞ 0.50 sec 67-B2 set time delay
2625 50-B2 Inrush NO
NO 50-B2 Inrush blocking
YES
2625 67-B2 Inrush NO
NO 67-B2 Inrush blocking
YES
2626 50N-B2 PICKUP 1A 0.05 .. 25.00 A; ∞ 0.20 A 50N-B2 Pickup
5A 0.25 .. 125.00 A; ∞ 1.00 A
2626 67N-B2 PICKUP 1A 0.05 .. 25.00 A; ∞ 0.20 A 67N-B2 Pickup threshold
5A 0.25 .. 125.00 A; ∞ 1.00 A
2627 50N-B2 DELAY 0.00 .. 30.00 sec; ∞ 2.00 sec 50N-B2 Delay
2627 67N-B2 DELAY 0.00 .. 30.00 sec; ∞ 2.00 sec 67N-B2 set time delay
2628 50(N)-B2 Pil/BI NO
YES
NO Instantaneous trip via Pilot
Prot./BI
86 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.4 Backup overcurrent
Addr. Parameter C Setting Options Default Setting Comments
2628 67(N)-B2 Pil/BI NO
YES
2630 Op.Mode 51(N)-B ON
NO Instantaneous trip via Pilot
Prot./BI
OFF Operating Mode 51(N)-B
Only Emer. prot
OFF
2630 Op.Mode67(N)TOC ON
Only Emer. prot
OFF Operating Mode 67(N)-
TOC
OFF
2631 67(N)-TOC Dir. Non-Directional
Non-Directional 67(N)-TOC Direction
Forward
Reverse
2632 67(N)-TOCon FFM Non-Directional
BLOCKED
BLOCKED 67(N)-TOC Direct. stage on
Fuse Failure
2633 51-B PICKUP 1A 0.10 .. 4.00 A; ∞ ∞ A 51-B Pickup
5A 0.50 .. 20.00 A; ∞ ∞ A
2633 67-TOC PICKUP 1A 0.10 .. 4.00 A; ∞ ∞ A 67-TOC Pickup threshold
5A 0.50 .. 20.00 A; ∞ ∞ A
2634 51-B TD IEC 0.05 .. 3.00 sec; ∞ 0.50 sec 51-B Time Dial for IEC char-
acteristic
2634 67-TOC TD IEC 0.05 .. 3.00 sec; ∞ 0.50 sec 67-TOC Time Dial for IEC
characteristic
2635 51-B TD ANSI 0.50 .. 15.00 ; ∞ 5.00 51-B Time Dial for ANSI
characteristic
2635 67-TOC TD ANSI 0.50 .. 15.00 ; ∞ 5.00 67-TOC Time Dial for ANSI
characteristic
2636 51-B AddT-DELAY 0.00 .. 30.00 sec 5.00 sec 51-B Additional Time Delay
2636 67-TOC AddTDel. 0.00 .. 30.00 sec 5.00 sec 67-TOC Additional Time
Delay
2637 51-B Inrush NO
NO 51-B Inrush blocking
YES
2637 67-TOC Inrush NO
NO 67-TOC Inrush blocking
YES
2638 51N-B PICKUP 1A 0.05 .. 4.00 A; ∞ ∞ A 51N-B Pickup
5A 0.25 .. 20.00 A; ∞ ∞ A
2638 67N-TOC PICKUP 1A 0.05 .. 4.00 A; ∞ ∞ A 67N-TOC Pickup threshold
5A 0.25 .. 20.00 A; ∞ ∞ A
2639 51N-B TD IEC 0.05 .. 3.00 sec; ∞ 0.50 sec 51N-B Time Dial for IEC
characteristic
2639 67N-TOC TD IEC 0.05 .. 3.00 sec; ∞ 0.50 sec 67N-TOC Time Dial for IEC
characteristic
2640 51N-B TD ANSI 0.50 .. 15.00 ; ∞ 5.00 51N-B Time Dial for ANSI
characteristic
2640 67N-TOC TD ANSI 0.50 .. 15.00 ; ∞ 5.00 67N-TOC Time Dial for
ANSI char.
2641 51N-B AddTdelay 0.00 .. 30.00 sec 0.00 sec 51N-B Additional Time
Delay
2641 67N-TOC AddTDel 0.00 .. 30.00 sec 0.00 sec 67N-TOC Additional Time
Delay
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 87
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.4 Backup overcurrent
Addr. Parameter C Setting Options Default Setting Comments
2642 IEC Curve Normal Inverse
Very Inverse
Extremely Inv.
LongTimeInverse
2642 IEC Curve Normal Inverse
Very Inverse
Extremely Inv.
LongTimeInverse
2643 ANSI Curve Inverse
Short Inverse
Long Inverse
Moderately Inv.
Very Inverse
Extremely Inv.
Definite Inv.
2643 ANSI Curve Inverse
Short Inverse
Long Inverse
Moderately Inv.
Very Inverse
Extremely Inv.
Definite Inv.
2644 51(N)-B PilotBI NO
YES
2644 67(N)TOC Pil/BI NO
YES
2650 50-3 OpMo ON
Only Emer. prot
OFF
2651 50-3 PICKUP 1A 0.10 .. 25.00 A; ∞ 1.50 A 50-3 Pickup
5A 0.50 .. 125.00 A; ∞ 7.50 A
2652 50-3 DELAY 0.00 .. 30.00 sec; ∞ 0.30 sec 50-3 Delay
2653 50-3 Inrush NO
YES
2654 50N-3 PICKUP 1A 0.05 .. 25.00 A; ∞ 0.20 A 50N-3 Pickup
5A 0.25 .. 125.00 A; ∞ 1.00 A
2655 50N-3 DELAY 0.00 .. 30.00 sec; ∞ 2.00 sec 50N-3 Delay
2656 50-3 Pilot/BI NO
YES
Normal Inverse IEC Curve
Normal Inverse IEC Curve
Inverse ANSI Curve
Inverse ANSI Curve
NO Instantaneous trip via Pilot
Prot./BI
NO Instantaneous trip via Pilot
Prot./BI
OFF 50(N)-3 Operating Mode
NO 50-3 Inrush blocking
NO Instantaneous trip via Pilot
Prot./BI
2.4.6
No.
7104 >BLOCK 50-B1 SP >BLOCK 50-B1 Backup OverCurrent
7105 >BLOCK 50-B2 SP >BLOCK 50-B2 Backup OverCurrent
7106 >BLOCK 51-B SP >BLOCK 51-B Backup OverCurrent
88 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
Information List
Information Type of
Information
Comments
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.4 Backup overcurrent
No. Information Type of
Comments
Information
7107 >BLOCK 50N-B1 SP >BLOCK 50N-B1 Backup OverCurrent
7108 >BLOCK 50N-B2 SP >BLOCK 50N-B2 Backup OverCurrent
7109 >BLOCK 51N SP >BLOCK 51N Backup OverCurrent
7110 >5X-B InstTRIP SP >50(N)/51(N) BackupO/C InstantaneousTrip
7112 >BLOCK 67-TOC SP >BLOCK Backup OverCurrent 67-TOC
7114 >BLOCK 67N-TOC SP >BLOCK Backup OverCurrent 67N-TOC
7115 >BLOCK 67-B1 SP >BLOCK Backup OverCurrent 67-B1
7116 >BLOCK 67N-B1 SP >BLOCK Backup OverCurrent 67N-B1
7117 >BLOCK 67-B2 SP >BLOCK Backup OverCurrent 67-B2
7118 >BLOCK 67N-B2 SP >BLOCK Backup OverCurrent 67N-B2
7130 >BLOCK 50-3 SP >BLOCK 50-3
7132 >BLOCK 50N-3 SP >BLOCK 50N-3
7152 5X-B BLOCK OUT 50(N)/51(N) Backup O/C is BLOCKED
7153 5X-B ACTIVE OUT 50(N)/51(N) Backup O/C is ACTIVE
7154 50(N)-B2 OFF OUT Backup O/C stage 50(N)-B2 is sw. OFF
7155 50(N)-B1 OFF OUT Backup O/C stage 50(N)-B1 is sw. OFF
7156 50(N)-3 OFF OUT Backup O/C stage 50(N)-3 is sw. OFF
7157 51(N)-B OFF OUT Backup O/C stage 51(N)-B is sw. OFF
7161 5X-B PICKUP OUT 50(N)/51(N) Backup O/C PICKED UP
7162 5X-B Pickup ØA OUT 50(N)/51(N) Backup O/C PICKUP Phase A
7163 5X-B Pickup ØB OUT 50(N)/51(N) Backup O/C PICKUP Phase B
7164 5X-B Pickup ØC OUT 50(N)/51(N) Backup O/C PICKUP Phase C
7165 5X-B Pickup Gnd OUT 50(N)/51(N) Backup O/C PICKUP GROUND
7191 50(N)-B1 PICKUP OUT 50(N)-B1 Pickup
7192 50(N)-B2 PICKUP OUT 50(N)-B2 Pickup
7193 51(N)-B PICKUP OUT 51(N)-B Pickup
7201 50-3 PICKUP OUT 50-3 Pickup
7211 5X-B TRIP OUT 50(N)/51(N)-B General TRIP command
7221 50(N)-B1 TRIP OUT 50(N)-B1 TRIP
7222 50(N)-B2 TRIP OUT 50(N)-B2 TRIP
7223 51(N)-B TRIP OUT 51(N)-B TRIP
7235 50-3 TRIP OUT 50-3 TRIP
7250 67(N)-B1 PICKUP OUT 67(N)-B1 Pickup
7251 67(N)-B2 PICKUP OUT 67(N)-B2 Pickup
7252 67(N)-TOC PICK. OUT 67(N)-TOC Pickup
7253 67(N) TRIP OUT 67(N) General TRIP command
7254 67(N)-B1 TRIP OUT 67(N)-B1 TRIP
7255 67(N)-B2 TRIP OUT 67(N)-B2 TRIP
7256 67(N)-TOC TRIP OUT 67(N)-TOC TRIP
7257 67 forward ØA OUT 67 Phase A forward
7258 67 forward ØB OUT 67 Phase B forward
7259 67 forward ØC OUT 67 Phase C forward
7260 67N forward GND OUT 67N Gnd forward
7261 67 reverse ØA OUT 67 Phase A reverse
7262 67 reverse ØB OUT 67 Phase B reverse
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 89
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.4 Backup overcurrent
No. Information Type of
Comments
Information
7263 67 reverse ØC OUT 67 Phase C reverse
7264 67N reverse GND OUT 67N Gnd forward
7265 67(N) forward OUT 67(N) forward
7266 67(N) reverse OUT 67(N) reverse
7267 >67(N) InstTRIP SP >67(N) BackupO/C InstantaneousTrip
17530 67(N) BLOCK OUT 67(N) Backup O/C is BLOCKED
17531 67(N) ACTIVE OUT 67(N) Backup O/C is ACTIVE
17532 67(N)-B2 OFF OUT Backup O/C stage 67(N)-B2 is sw. OFF
17533 67(N)-B1 OFF OUT Backup O/C stage 67(N)-B1 is sw. OFF
17534 67(N)-TOC OFF OUT Backup O/C stage 67(N)-TOC is sw. OFF
17535 67(N) PICKUP OUT 67(N) Backup O/C PICKED UP
17536 67 Pickup ØA OUT 67 Backup O/C PICKUP Phase A
17537 67 Pickup ØB OUT 67 Backup O/C PICKUP Phase B
17538 67 Pickup ØC OUT 67 Backup O/C PICKUP Phase C
17539 67N Pickup Gnd OUT 67N Backup O/C PICKUP GROUND
90 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.5 InRush Restraint
2.5
2.5.1
InRush Restraint
Functional Description
If the protected zone of the device reaches close to a transformer, a high inrush current must be anticipated
when switching on the transformer.
The inrush current can amount to a multiple of the rated current and is characterized by a considerable 2nd
harmonic content (double rated frequency) which is practically absent during a short circuit. If the second
harmonic content in the differential current exceeds a selectable threshold, tripping is blocked.
The inrush restraint has an upper limit: It no longer takes effect when a (configurable) current value is
surpassed since, in this case, it can only be an internal high-current fault.
Figure 2-32 shows a simplified logic diagram. The condition for the inrush current detection is examined in
each device in which this function has been activated. The blocking condition is transmitted to the other
device so that it is effective at both ends of the protected object.
[logikdia-einschaltstabilisierung-290803st, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-32 Logic diagram of the inrush restraint for one phase
Since the inrush restraint operates individually for each phase, the protection is fully operative when the transformer is switched onto a single-phase fault, in which case it is possible for an inrush current to flow through
one of the undisturbed phases. It is, however, also possible to set the protection in such a way that when the
permissible harmonic content in the current of only one single phase is exceeded, not only the phase with the
inrush current but also the remaining phases of the differential stage are blocked. This cross-block function
can be limited to a selectable duration. Figure 2-33 shows the logic diagram.
The cross-block function also affects both devices since it not only extends the inrush current detection to all
three phases but also sends it to the other device via the communication link.
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 91
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.5 InRush Restraint
[lo-crossblk-fkt-1ende-110428, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-33 Logic diagram of the cross-block function for one end
2.5.2
2.5.3
Addr.
2301 INRUSH REST. OFF
2302 2nd HARMONIC 10 .. 45 % 15 % 2nd. harmonic in % of funda-
2303 CROSS BLOCK NO
2305 MAX INRUSH PEAK 5.5 .. 125.0 A 75.0 A Maximum inrush-peak value
2310 CROSSB 2HM 0.00 .. 60.00 sec 0.00 sec Time for Crossblock with 2nd
Setting Notes
The inrush current detection is required for the following applications:
For the differential protection if an inductance is located in the protected zone.
•
For the time overcurrent protection if the protected line ends on a transformer.
•
Inrush current detection can be turned ON or OFF at address 2301 INRUSH REST..
It is based on the evaluation of the second harmonic which exists in the inrush current. Ex-works a ratio of
15 % of the 2nd HARMONIC Ι
the component required for restraint can be parameterized. In order to be able to achieve a higher degree of
restraint in case of exceptionally unfavorable inrush conditions, you may also set a smaller value.
However, if the local measured current exceeds a value set in address 2305 MAX INRUSH PEAK, there will be
no inrush restraint. The peak value is decisive. The set value should be higher than the maximum inrush
current peak value that can be expected. For transformers set the value above √2·Ι
on a transformer, a smaller value may be selected, considering the damping of the current by the line impedance.
The crossblock function can be activated (YES or deactivated (NO) in address 2303 CROSS BLOCK. The time
after exceeding of the current threshold for which this crossblock is to be activated is set under address 2310
CROSSB 2HM. With the setting ∞ the crossblock function is always active until the second harmonic content in
all phases has dropped below the set value.
is set under address 2302, which can normally be taken over. However,
2fN/ΙfN
NTransf/ukTransf
. If a line ends
Settings
Parameter Setting Options Default Setting Comments
OFF Inrush Restraint
ON
mental
NO Cross Block
YES
harmonic
92 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.5 InRush Restraint
2.5.4
No. Information Type of
3102 2nd Harmonic A OUT Tolerance invalid in phase A
3103 2nd Harmonic B OUT Tolerance invalid in phase B
3104 2nd Harmonic C OUT Tolerance invalid in phase C
Information List
Comments
Information
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 93
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.6 Circuit Breaker Failure Protection 50BF
2.6
2.6.1
General
Circuit Breaker Failure Protection 50BF
The circuit-breaker failure protection provides rapid backup fault clearance in the event that the circuit breaker
fails to respond to a trip command from a protection function of the local circuit breaker.
Functional Description
Each time a fault protection relay of a feeder issues a trip command to the circuit breaker, it is repeated to the
breaker failure protection (Figure 2-34). A timer T–BF in the breaker failure protection is started. The timer
runs as long as a trip command is present and current continues to flow through the breaker poles.
[funktionsschema-lvs-ueberwach-wlk-010802, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-34 Simplified function diagram of circuit-breaker failure protection with current flow monitoring
Normally, the breaker will open and interrupt the fault current. The current monitoring element quickly resets
(typical 10 ms) and stops the timer T–BF.
If the trip command is not carried out (breaker failure case), current continues to flow and the timer runs to its
set limit. The breaker failure protection then issues a command to trip the backup breakers and interrupt the
fault current.
The reset time of the feeder protection is not relevant because the breaker failure protection itself recognizes
the interruption of the current.
For protection functions where the tripping criterion is not dependent on current (e.g. Buchholz protection),
current flow is not a reliable criterion for proper operation of the breaker. In such cases, the circuit-breaker
position can be derived from the auxiliary contacts of the breaker. Therefore, instead of monitoring the
current, the condition of the auxiliary contacts is monitored (see Figure 2-35). For this purpose, the outputs
from the auxiliary contacts must be fed to binary inputs on the relay (refer also to Section 2.16.2 Tripping
Logic for the Entire Device).
[funktionsschema-lvs-lshiko-wlk-010802, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-35 Simplified function diagram of circuit-breaker failure protection controlled by circuit-breaker
auxiliary contact
94 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Monitoring the Current Flow
Each of the phase currents and an additional plausibility current (see below) are filtered by numerical filter
algorithms so that only the fundamental component is used for further evaluation.
Special measures are taken in order to detect a current interruption. In case of sinusoidal currents the current
interruption is detected after approximately 10 ms. With aperiodic DC current components in the fault current
and/or in the current transformer secondary circuit after interruption (e.g. current transformers with linearized
core), or saturation of the current transformers caused by the DC component in the fault current, it can take
one AC cycle before the interruption of the primary current is reliably detected.
The currents are monitored and compared with the set limit value. Besides the three phase currents, two additional current thresholds are provided in order to allow a plausibility check. For this plausibility check, a separate threshold value can be used if the configuration is made accordingly (see Figure 2-36).
As plausibility current, the ground current (residual current ΙE (3·Ι0) is preferably used. If the residual current
from the neutral of the current transformer set is connected to the device it is used. If the residual current is
not available, the device calculates it with the formula:
Ι0 = ΙA + ΙB + Ι
3·
C
Additionally, the value calculated by 7SD80 of three times the negative sequence current 3·Ι2 is used for plausibility check. This is calculated according to the equation:
3·Ι2 = ΙA + a2·ΙB + a·Ι
where
j120°.
a = e
These plausibility currents do not have any direct influence on the basic function of the breaker failure protection but they allow a plausibility check that at least two current thresholds must be exceeded before any of the
time delays are started.
In case of high-resistance ground faults, it can happen that the ground current exceeds the sensitive threshold
value 50NBF PICKUP (address 3912) whereas the phase current involved in the short circuit does not exceed
the threshold value 50BF PICKUP (address 3902). The plausibility check would prevent the start of the
breaker failure protection. In this case, the pickup threshold of the phase current monitoring 50BF PICKUP
can be switched to the threshold value 50NBF PICKUP. Use the binary input 1404 >50BF 3I0> for this
purpose. This binary input is linked to an external signal that is suggestive of a high-resistance fault, e.g.
ground fault or displacement voltage detected. The ground current threshold that is set more sensitive is thus
also used for monitoring the phase currents (Figure 2-36).
Functions
2.6 Circuit Breaker Failure Protection 50BF
C
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 95
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.6 Circuit Breaker Failure Protection 50BF
[logik-strmflsueberw-plausibilitaet-wlk-010802, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-36
Current flow monitoring with plausibility currents 3·Ι0 and 3·Ι
2
1) only usable/visible if address 139 is set to vorh. mit 3I0>
In-Phase Start
Common phase initiation is used for transformer feeders or if the busbar protection trips.
If the breaker failure protection is intended to be initiated by further external protection devices, it is recom-
mended, for security reasons, to connect two starting criteria to the device. Besides the trip command of the
external relay to the binary input
>50BF Start 3p
general device pickup to binary input
>50BF release
(FNo. 1415) it is recommended to connect also the
(FNo. 1432). For Buchholz protection it is recom-
mended that the trip command is connected to the device by two separate wire pairs.
Nevertheless, it is possible to initiate the breaker failure protection in single-channel mode should a separate
release criterion not be available. The binary input
>50BF release
(FNo. 1432) must then not be assigned
to any physical input of the device during configuration.
Figure 2-38 shows the operating principle. When the trip signal appears from any internal or external feeder
protection and at least one current flow criterion (according to Figure 2-36) is present, the breaker failure
protection is initiated and the corresponding time delay(s) is (are) started.
If the current criterion is not satisfied for any of the phases, the circuit-breaker auxiliary contact can be interrogated according to Figure 2-37. After a 3-pole trip command, the circuit breaker has only operated correctly
when no current flows over any of the poles.
96 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.6 Circuit Breaker Failure Protection 50BF
Figure 2-37 shows the generation of the internal signal “52 closed” (see Figure 2-38 left) if at least one breaker
pole is closed.
Using binary input 1424
has elapsed, the breaker failure protection TRIP command 1494
[lo-svs-signal-hiko-20101108, 1, en_US]
>50BFSTRTonlyT2
, the trip time delay 3906 50BF-2 Delay can be started. After it
50BF BusTrip
is generated.
Figure 2-37 Generation of the signal "CB aux closed"
If an internal protection function or an external protection device trips without current flow, the breaker
failure protection is initiated by the internal input “Start internal w/o I”, if the trip signal comes from the
internal voltage protection or frequency protection, or by the external input
>50BF STARTw/oI
. In this case
the start signal is maintained until the circuit breaker is signaled to be open by the auxiliary contact criterion.
Initiation can be blocked via the binary input
>BLOCK 50BF
(e.g. during test of the feeder protection relay).
[lo-svs-phasengem-anwurf-20101108, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-38 Circuit-breaker failure protection with common phase initiation
Time Delays
When the initiate conditions are fulfilled, the associated timers are started. The circuit-breaker pole(s) must
open before the associated time has elapsed.
Time delays can be set for 3-pole initiation and for two-element protection.
single-element breaker failure protection, the trip command is relayed to the adjacent circuit breakers
With
which interrupt the fault current if the local feeder breaker fails (see Figure 2-34 and Figure 2-35). The adjacent circuit breakers are those located at the busbar or busbar section to which the feeder under consideration
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 97
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

Functions
2.6 Circuit Breaker Failure Protection 50BF
is connected. The possible initiation conditions for the breaker failure protection are those discussed above.
Depending on the application of the feeder protection, common phase or phase-segregated initiation conditions may occur. Tripping by the breaker failure protection is always 3-pole.
T2 is used as time delay.
With two-element breaker failure protection, the trip command of the feeder protection is usually repeated,
after a first time element, to the feeder circuit breaker, often via a second trip coil or set of trip coils, if the
breaker has not responded to the original trip command. A second time element monitors the response to this
repeated trip command and trips the breakers of the relevant bus-bar section, if the fault has not yet been
cleared after this second time.
The time delay T2 is started after the T1 timer has expired if address 3913 T2StartCriteria = With exp.
of T1.
If address 3913 T2StartCriteria = Parallel withT1, T1 and T2 are started simultaneously. The T2
timer can be started by a separate binary input 1424
>50BFSTRTonlyT2
.
[lo-svs-2stufig-20101112, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-39 Logic diagram of the two-element circuit-breaker failure protection
Circuit-Breaker Malfunction
There may be cases when it is already obvious that the circuit breaker associated with a feeder protection relay
cannot clear a fault, e.g. when the tripping voltage or the tripping energy is not available.
In such a case it is not necessary to wait for the response of the feeder circuit breaker. If provision has been
made for the detection of such a condition (e.g. control voltage monitor or air pressure monitor), the monitor
alarm signal can be fed to the binary input
command by the feeder protection, a separate timer T3-BkrDefective, which is normally set to 0, is started
(Figure 2-40). Thus, the adjacent circuit breakers (bus-bar) are tripped immediately in case the feeder circuit
breaker is not operational.
[logik-ls-gestoert-wlk-010802, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-40 Circuit-breaker faulty
>52 faulty
of the 7SD80. On occurrence of this alarm and a trip
Transfer Trip to the Remote End Circuit Breaker
The device has the facility to provide an additional intertrip signal to the circuit breaker at the remote line end
in the event that the local feeder circuit breaker fails. For this, a suitable protection signal transmission link is
required (e.g. via communication cable, power line carrier transmission, radio transmission, or optical fiber
98 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

transmission). With devices using digital transmission via protection interface, the remote commands can be
applied (see also Section 2.13 Direct Remote Trip and Transmission of Binary Information).
To realize this intertrip, the desired command – usually the trip command which is intended to trip the adjacent breakers — is assigned to a binary output of the device. The contact of this output triggers the transmission device. When using digital signal transmission the command is connected to a remote command via the
userdefined logic (CFC).
End Fault Protection
An end fault is defined here as a fault which has occurred at the end of a line or protected object, between the
circuit breaker and the current transformer set.
This situation is shown in Figure 2-41. The fault is located — as seen from the current transformer (= measurement location) — on the busbar side, it will thus not be regarded as a feeder fault by the feeder protection
device. It can only be detected by either a reverse element of the feeder protection or by the busbar protection. However, a trip command given to the feeder circuit breaker does not clear the fault since the opposite
end continues to feed the fault. Thus, the fault current does not stop flowing even though the feeder circuit
breaker has properly responded to the trip command.
Functions
2.6 Circuit Breaker Failure Protection 50BF
[endfehler-ls-strwdlr-wlk-010802, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-41 End fault between circuit breaker and current transformers
The end fault protection has the task to recognize this situation and to transmit a trip signal to the remote
end(s) of the protected object to clear the fault. For this purpose, the output command
50BF EndFltTrip
is
available to trigger a signal transmission device (e.g. power line carrier, radio wave, or optical fiber) – if applicable, together with other commands that need to be transferred or (when using digital signal transmission)
as command via the protection data interface.
The end fault protection detects an end fault because it registers that current is flowing even though the
circuitbreaker auxiliary contacts signal that the circuit breaker is open. An additional criterion is the presence
of any breaker failure protection initiate signal. Figure 2-42 shows the functional principle. If the breaker
failure protection is initiated and current flow is detected (current criteria “L*> current criterion” according to
Figure 2-36), but no circuit-breaker pole is closed (auxiliary contact criterion “52 closed”), the timer EndFault
Delay is started. At the end of this time, a trip command is sent to the opposite end.
[lo-svs-endfehler-20101112, 1, en_US]
Figure 2-42 Functional diagram of the end fault protection
SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual 99
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018

i
i
Functions
2.6 Circuit Breaker Failure Protection 50BF
2.6.2
General
Breaker Failure Protection (50BF)
Two-Element Breaker Failure Protection
Setting Notes
The circuit-breaker failure protection and its ancillary functions (end fault protection, pole discrepancy supervision) can only operate if they were set during configuration of the scope of functions (address 139 50BF,
setting Enabled or enabled w/ 3I0>).
The breaker failure protection is switched ON or OFF at address 3901 FCT 50BF Break..
The current threshold 50BF PICKUP (address 3902) should be selected such that the protection will operate
with the smallest expected fault current. A setting of 10 % below the minimum fault current for which breaker
failure protection must operate is recommended. On the other hand, the value should not be set lower than
necessary
If the breaker failure protection is configured with zero sequence current threshold (address 139 = enabled
w/ 3I0>), the pickup threshold for the zero sequence current 50NBF PICKUP (address 3912) can be set
independently of 50BF PICKUP.
Normally, the breaker failure protection evaluates the current flow criterion as well as the position of the
breaker auxiliary contact(s). If the auxiliary contact(s) status is not available in the device, this criterion cannot
be processed. In this case, set address 3909 Chk BRK CONTACT to NO.
With two-element operation, the trip command is repeated after a time delay T1 to the local feeder breaker,
normally to a different set of trip coils of this breaker.
If the circuit breaker does not respond to this trip repetition, the adjacent circuit breakers are tripped after T2,
i.e. the circuit breakers of the busbar or of the concerned busbar section and, if necessary, also the circuit
breaker at the remote end unless the fault has been cleared.
The time delays can be set separately
for trip repetition to the local feeder circuit breaker after a trip of the feeder protection 50BF-1 Delay
•
3p (address 3905),
for trip of the adjacent circuit breakers (busbar zone and remote end if applicable) 50BF-2 Delay at
•
address 3906.
The time delays to be set should be based on the maximum circuit-breaker operating time plus the dropout
time of the current flow monitoring element plus a safety margin which takes into consideration the tolerance
of the time delay. Figure 2-43 illustrates the time sequences in an example. The dropout time for sinusoidal
currents is ≤ 15 ms. If current transformer saturation is anticipated, the time should be set to 25 ms.
NOTE
To prevent automatic reclosing after
that it elapses together with 50BF-2 Delayy.
50BF BusTrip
, you can set the time 3408 T-Start MONITOR so
100 SIPROTEC 4, 7SD80, Manual
E50417-G1100-C474-A2, Edition 02.2018
 Loading...
Loading...