Siemens Sinamics SM150 6SL3845-2NN41-8AD0 Operating And Installation Instructions
www.siemens.com/drives
This documentation pertains to
Operating Instructions
Installation Instructions
Medium-Voltage Drive
SINAMICS SM150
Type 6SL3845-2NN41-8AD0
EXAMPLE
Edition 08/2019

01.08.2019 09:08
V32.00

Medium-Voltage Drive
SINAMICS SM150
Type 6SL3845-2NN41-8AD0
This documentation pertains to
EXAMPLE
Introduction
1
Operating Instructions
Installation Instructions
Safety instructions
Description
Preparations for use
Installation
Electrical connection
Start-up
Operation
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Maintenance
Spare parts
Disposal
Service & Support
Technical data and drawings
Checklists and forms
9
10
11
A
B
C
Edition 08/2019

Legal information
Warning notice system
This manual contains notices you have to observe in order to ensure your personal safety, as well as to prevent
damage to property. The notices referring to your personal safety are highlighted in the manual by a safety alert
symbol, notices referring only to property damage have no safety alert symbol. These notices shown below are
graded according to the degree of danger.
DANGER
indicates that death or severe personal injury will result if proper precautions are not taken.
WARNING
indicates that death or severe personal injury may result if proper precautions are not taken.
CAUTION
indicates that minor personal injury can result if proper precautions are not taken.
NOTICE
indicates that property damage can result if proper precautions are not taken.
If more than one degree of danger is present, the warning notice representing the highest degree of danger will be
used. A notice warning of injury to persons with a safety alert symbol may also include a warning relating to property
damage.
Qualified Personnel
The product/system described in this documentation may be operated only by personnel qualified for the specific
task in accordance with the relevant documentation, in particular its warning notices and safety instructions. Qualified
personnel are those who, based on their training and experience, are capable of identifying risks and avoiding
potential hazards when working with these products/systems.
Proper use of Siemens products
Note the following:
WARNING
Siemens products may only be used for the applications described in the catalog and in the relevant technical
documentation. If products and components from other manufacturers are used, these must be recommended or
approved by Siemens. Proper transport, storage, installation, assembly, commissioning, operation and
maintenance are required to ensure that the products operate safely and without any problems. The permissible
ambient conditions must be complied with. The information in the relevant documentation must be observed.
Trademarks
All names identified by ® are registered trademarks of Siemens AG. The remaining trademarks in this publication
may be trademarks whose use by third parties for their own purposes could violate the rights of the owner.
Disclaimer of Liability
We have reviewed the contents of this publication to ensure consistency with the hardware and software described.
Since variance cannot be precluded entirely, we cannot guarantee full consistency. However, the information in this
publication is reviewed regularly and any necessary corrections are included in subsequent editions.
Siemens AG
Large Drives Applications
Vogelweiherstr. 1-15
90441 NÜRNBERG
GERMANY
Document order number: 0005000025-038452
Ⓟ 08/2019 Subject to change
Copyright © Siemens AG 2018 - 2019.
All rights reserved

Table of contents
1 Introduction.................................................................................................................................................13
1.1 About these instructions.........................................................................................................13
2 Safety instructions ......................................................................................................................................15
2.1 Warning symbol on the device ...............................................................................................15
2.2 Qualified personnel ................................................................................................................15
2.3 The 5 safety rules...................................................................................................................15
2.4 Safe handling .........................................................................................................................16
2.5 Electromagnetic fields in electrical power engineering installations ......................................19
2.6 Components that can be destroyed by electrostatic discharge (ESD)...................................19
2.7 Information for nominated persons in control of an electrical installation...............................20
2.7.1 Proper usage..........................................................................................................................20
2.7.2 Grounding concept.................................................................................................................22
2.7.3 Installation site safety.............................................................................................................22
2.7.4 Measures for operator protection in electromagnetic fields ...................................................23
2.8 Residual risks.........................................................................................................................23
2.9 Security information ...............................................................................................................25
3 Description..................................................................................................................................................27
3.1 Applications............................................................................................................................27
3.2 Safety concept .......................................................................................................................27
3.2.1 Safety components and functions..........................................................................................27
3.2.2 External safety components...................................................................................................28
3.2.3 Protection and monitoring functions of internal components .................................................28
3.2.4 Protection and monitoring functions for external components ...............................................29
3.3 Design ....................................................................................................................................29
3.3.1 Components...........................................................................................................................29
3.3.2 Design of the Basic Line Module............................................................................................30
3.3.3 Design of the Motor Module...................................................................................................31
3.3.4 Gating.....................................................................................................................................32
3.4 Operating principle .................................................................................................................32
3.5 Description of the components...............................................................................................33
3.5.1 SIMOTION Control Unit .........................................................................................................33
3.5.2 Power Stack Adapter .............................................................................................................34
3.5.3 Terminal Modules...................................................................................................................35
3.5.4 Voltage Sensing Module ........................................................................................................36
3.5.5 Precharging............................................................................................................................36
3.5.6 Electromechanical door interlock system...............................................................................36
3.5.7 Make-proof grounding switch.................................................................................................37
3.5.8 Circuit-breaker (provided by the customer)............................................................................37
SINAMICS SM150 6SL3845-2NN41-8AD0
Operating Instructions Rev.201908010908 EXAMPLE 5

Table of contents
3.5.9 Converter transformer............................................................................................................37
3.5.10 Actual value acquisition..........................................................................................................39
3.5.11 Common power supply ..........................................................................................................39
3.5.11.1 Field of application .................................................................................................................39
3.5.11.2 Design ....................................................................................................................................40
3.5.11.3 Connections ...........................................................................................................................40
3.5.12 DM10 diagnostics module......................................................................................................41
3.5.12.1 Functions................................................................................................................................41
3.5.12.2 Signal processing...................................................................................................................42
3.5.12.3 Voltage monitoring .................................................................................................................43
3.5.13 Re-cooling unit ......................................................................................................................44
3.5.13.1 Re-cooling unit requirements .................................................................................................44
3.5.13.2 Operating principle of the re-cooling unit ...............................................................................44
3.5.13.3 The internal deionized water circuit........................................................................................45
3.5.14 Customer terminal strips ........................................................................................................45
3.6 Description of options.............................................................................................................46
3.6.1 NAMUR terminal strip (option B00)........................................................................................46
3.6.2 Isolation amplifiers for optional analog inputs (option E86)....................................................46
3.6.3 Isolation amplifiers for optional analog outputs (option E87) .................................................46
3.6.4 Additional Terminal Module TM31 (option G61) ....................................................................47
3.6.5 Additional Terminal Module TM15 (option G63) ....................................................................47
3.6.6 PADU8 diagnosis module (option G66) .................................................................................48
3.6.7 Pulse distributor for splitting speed encoder signal (option G70)...........................................48
3.6.8 Optical bus terminal (OBT) for PROFIBUS (option G71).......................................................48
3.6.9 Indicator lamps in the cabinet door (option K20)....................................................................48
3.6.10 Display instruments in the cabinet door for voltage, current, speed, and output plus
indicator lamps (option K21) ..................................................................................................49
3.6.11 Safe Torque Off......................................................................................................................49
3.6.11.1 Safety information regarding the "Safe Torque Off / safe standstill" function ........................50
3.6.12 dv/dt filter (option L10) ...........................................................................................................52
3.6.13 Motor-side grounding switch (option L49) ..............................................................................53
3.6.14 Cabinet illumination and service socket in closed-loop control unit (option L50) ...................54
3.6.15 Disconnector at the drive output (option L51) ........................................................................54
3.6.16 Circuit breaker at the drive output (option L52)......................................................................54
3.6.17 EMERGENCY STOP Category 1 (option L60) ......................................................................54
3.6.18 Safety locking system (option M10) .......................................................................................55
3.6.19 Power cable connection at the drive input from above (option M13) .....................................55
3.6.20 Signal and control cable (max. 2.5 mm²) (option M32) ..........................................................55
3.6.21 IP54 degree of protection (option M54)..................................................................................56
3.6.22 Redundant fan in the power unit (option M61) .......................................................................56
3.6.23 Suitability for marine use (option M66)...................................................................................56
3.6.24 Capacitor Modules to increase the DC-link capacitance (option N08)...................................56
3.6.25 Controlled outgoing circuit for auxiliary equipment 400 V 3 AC (option N30) .......................57
3.6.26 Sine-wave filter (option Y15) ..................................................................................................57
4 Preparations for use ...................................................................................................................................59
4.1 Requirements for installation location ....................................................................................59
4.2 Inspections when receiving the delivery.................................................................................59
4.2.1 Scope of delivery....................................................................................................................59
4.2.2 Checking shock and tilt indicators..........................................................................................60
4.2.3 Checking the load handling attachments ...............................................................................61
SINAMICS SM150 6SL3845-2NN41-8AD0
6 Operating Instructions Rev.201908010908 EXAMPLE

Table of contents
4.3 Transportation ........................................................................................................................62
4.3.1 Transport markings ................................................................................................................62
4.3.2 Transport requirements..........................................................................................................62
4.3.3 Observe center of gravity.......................................................................................................63
4.3.4 Transport with a fork-lift truck.................................................................................................63
4.3.5 Transport with a crane ...........................................................................................................64
4.3.6 Using lifting rods.....................................................................................................................64
4.3.7 Transporting transportation units packed in boxes ................................................................66
4.4 Unpacking ..............................................................................................................................67
4.4.1 Removing the packaging........................................................................................................67
4.4.2 Removing load securing devices ...........................................................................................68
4.4.3 Lifting the cabinet off the transport pallet ...............................................................................68
4.4.4 Opening doors in preparation for use.....................................................................................69
4.4.5 Checking the shock and tilt indicators inside the cabinet.......................................................70
4.5 Storage...................................................................................................................................70
4.5.1 Emptying the drive .................................................................................................................70
4.5.2 Storing a device .....................................................................................................................71
5 Installation ..................................................................................................................................................73
5.1 Safety instructions for assembly ............................................................................................73
5.2 Tools required ........................................................................................................................74
5.3 Preparations...........................................................................................................................74
5.3.1 Remove the rear panel...........................................................................................................74
5.3.2 Mounting the side panels .......................................................................................................74
5.4 Screwing the transport units together ....................................................................................76
5.5 Connect the capacitor cabinet with the power section ...........................................................77
5.6 Connecting to the foundation .................................................................................................78
5.7 Connecting the grounding bars ..............................................................................................79
5.8 Connecting the DC bus ..........................................................................................................80
5.9 Connecting the interface terminals.........................................................................................83
5.10 Connecting the water circuits .................................................................................................83
6 Electrical connection...................................................................................................................................85
6.1 Safety instructions for electrical connections .........................................................................85
6.2 Electromagnetic compatibility.................................................................................................87
6.3 Potential concept....................................................................................................................90
6.4 Electrical requirements...........................................................................................................90
6.5 Connection .............................................................................................................................91
6.5.1 Manually unlocking power-unit doors.....................................................................................91
6.5.2 Connecting ground.................................................................................................................91
6.5.3 Preparations for connecting the power cables.......................................................................92
6.5.4 Connecting power cables.......................................................................................................92
6.5.5 Connect the power cable to the motor and the supply system ..............................................93
6.5.6 Connect the auxiliary voltage.................................................................................................95
SINAMICS SM150 6SL3845-2NN41-8AD0
Operating Instructions Rev.201908010908 EXAMPLE 7

Table of contents
6.5.7 Interconnecting optional connections.....................................................................................95
6.5.8 Connecting the re-cooling unit to the drive.............................................................................95
6.5.9 Fastening the cable ducts with cable ties...............................................................................96
6.6 Mounting the rear panel .........................................................................................................96
7 Start-up ......................................................................................................................................................97
8 Operation....................................................................................................................................................99
8.1 Safety instructions for operation.............................................................................................99
8.2 Operating the drive...............................................................................................................100
8.3 Touch screen operator panel ...............................................................................................101
8.4 Parameter ............................................................................................................................102
8.4.1 Parameters...........................................................................................................................102
8.4.2 Parameter types...................................................................................................................102
8.5 Functions..............................................................................................................................103
8.5.1 Setpoint channel and closed-loop control ............................................................................103
8.5.1.1 Setpoint channel ..................................................................................................................103
8.5.1.2 Vector control .......................................................................................................................107
8.5.1.3 U/f control.............................................................................................................................110
8.5.2 Analog and digital inputs/outputs .........................................................................................111
8.5.2.1 Analog outputs .....................................................................................................................111
8.5.2.2 Additional settings for analog outputs ..................................................................................113
8.5.2.3 Scaling the input signal of the analog inputs........................................................................116
8.5.2.4 Digital inputs/outputs............................................................................................................117
8.5.2.5 Digital outputs ......................................................................................................................118
8.5.3 Monitoring functions and protective functions......................................................................119
8.5.3.1 Insulation monitoring ............................................................................................................120
8.5.3.2 Tripping of the circuit-breaker in case of undervoltage ........................................................121
8.5.3.3 DC-link short-circuiter...........................................................................................................121
8.5.3.4 Protection responses in an emergency................................................................................122
8.5.3.5 Vdc-max closed-loop control................................................................................................122
8.5.3.6 Speed monitoring with incremental encoder ........................................................................124
8.5.3.7 Controlled stop, EMERGENCY STOP category 1 ...............................................................125
8.6 Fault and system messages ................................................................................................125
8.6.1 External alarms and faults....................................................................................................125
8.6.2 Message from the grounding switch ....................................................................................126
8.6.3 Diagnosis .............................................................................................................................127
8.6.3.1 Indicating and rectifying faults..............................................................................................127
8.6.3.2 Diagnostics via LEDs ...........................................................................................................127
8.6.3.3 Diagnostics via parameters..................................................................................................129
9 Maintenance .............................................................................................................................................133
9.1 Safety instructions for maintenance .....................................................................................133
9.2 Grounding the system ..........................................................................................................135
9.2.1 Grounding with a grounding device......................................................................................135
9.2.2 Grounding using a make-proof grounding switch.................................................................137
9.3 Opening the doors................................................................................................................138
9.3.1 Opening the power unit doors for maintenance work...........................................................138
9.3.2 Manually unlocking power unit doors...................................................................................139
SINAMICS SM150 6SL3845-2NN41-8AD0
8 Operating Instructions Rev.201908010908 EXAMPLE

Table of contents
9.3.3 Secure locking system (option M10)....................................................................................140
9.4 Inspection and maintenance ................................................................................................141
9.4.1 Inspection.............................................................................................................................141
9.4.2 Checklist...............................................................................................................................141
9.4.3 Cleaning...............................................................................................................................142
9.4.3.1 Cleaning aluminum parts .....................................................................................................143
9.4.4 Visual inspections ................................................................................................................143
9.4.4.1 Equipment for visual inspections..........................................................................................143
9.4.4.2 Checking hoisting solenoids and security bolts....................................................................143
9.4.4.3 Checking the isolating clearances........................................................................................143
9.4.4.4 Checking the capacitor release............................................................................................144
9.4.4.5 Checking the cable and screw terminals..............................................................................144
9.4.4.6 Checking the plug connections. ...........................................................................................144
9.4.5 Replacing filter mats.............................................................................................................145
9.4.6 Replacing the filter mats in the roof assembly .....................................................................145
9.4.7 Maintaining the fan...............................................................................................................146
9.5 Repair...................................................................................................................................147
9.5.1 Torques................................................................................................................................147
9.5.2 Replacing the AVT combination module..............................................................................149
9.5.3 Replacing the operator panel...............................................................................................149
9.5.3.1 Replacing the operator panel ...............................................................................................149
9.5.4 Replacing the CompactFlash card.......................................................................................151
9.5.5 Replacing the phase module or diode module.....................................................................152
9.5.5.1 Attaching the changing device to the stacker.......................................................................152
9.5.5.2 Replacing the phase module................................................................................................153
9.5.5.3 Replacing the diode module.................................................................................................161
9.5.6 Replacing the Power Stack Adapter ....................................................................................165
9.5.7 Replace the sponge for the leak detector ............................................................................166
9.5.8 Replacing fuses....................................................................................................................167
9.5.9 Replacing the current transformer........................................................................................168
9.5.10 Door interlock system...........................................................................................................168
9.5.11 Replacing the precharging transformer................................................................................168
9.5.12 Replacing the precharging rectifier ......................................................................................170
10 Spare parts ...............................................................................................................................................171
11 Disposal....................................................................................................................................................173
11.1 Disposing of packaging material ..........................................................................................173
11.2 Removing device components and old devices ...................................................................173
A Service & Support.....................................................................................................................................175
B Technical data and drawings....................................................................................................................177
B.1 Technical specifications .......................................................................................................177
B.1.1 Standards and regulations ...................................................................................................177
C Checklists and forms ................................................................................................................................179
C.1 Mechanical installation: Checklist ........................................................................................179
C.2 Checklist for electrical installation ........................................................................................180
Index.........................................................................................................................................................185
SINAMICS SM150 6SL3845-2NN41-8AD0
Operating Instructions Rev.201908010908 EXAMPLE 9

Table of contents
Tables
Table 3-1 Deionized water requirements.....................................................................................................45
Table 3-2 Max. permissible cable lengths ...................................................................................................57
Table 6-1 Dimensioning cables ...................................................................................................................90
Table 6-2 Cable cross-sections...................................................................................................................91
Table 6-3 Drive and motor connection terminals.........................................................................................94
Table 8-1 Parameter..................................................................................................................................104
Table 8-2 Parameter..................................................................................................................................105
Table 8-3 Parameter..................................................................................................................................105
Table 8-4 Parameter..................................................................................................................................106
Table 8-5 LEDs of the Power Stack Adapters ..........................................................................................127
Table 8-6 LEDs of the DM10 diagnostics module .....................................................................................128
Table 9-1 Tightening torque for screws.....................................................................................................147
Table 9-2 Tightening torques for screw terminals for copper cables without cable lug 1).........................148
Table B-1 Standards and conformity .........................................................................................................177
Figures
Figure 2-1 ESD information ..........................................................................................................................20
Figure 3-1 Design of the power unit..............................................................................................................30
Figure 3-2 Basic Line Module with diodes in 12-pulse configuration............................................................31
Figure 3-3 Phase module .............................................................................................................................32
Figure 3-4 Overview of PSA interfaces.........................................................................................................35
Figure 3-5 AVT combination module ............................................................................................................39
Figure 3-6 Design when using IGCTs...........................................................................................................40
Figure 3-7 Overview ....................................................................................................................................40
Figure 3-8 Schematic diagram: Printed circuit board of the diagnostics module..........................................41
Figure 3-9 Logical design of the DM10 diagnosis module............................................................................42
Figure 3-10 Circuit diagram option L10 ..........................................................................................................52
Figure 3-11 Connecting the motor to the dv/dt filter .......................................................................................53
Figure 3-12 Connecting the motor to the sine-wave filter...............................................................................58
Figure 4-1 Example of attaching and displaying the shock and tilt indicators ..............................................61
Figure 4-2 Example illustration of centers of gravity.....................................................................................63
Figure 4-3 Lifting bar label............................................................................................................................65
Figure 4-4 Securing the lifting rods...............................................................................................................65
Figure 4-5 Transporting a transportation unit (still in packaging) with a crane .............................................67
Figure 4-6 Example: Label with instructions for opening the doors..............................................................69
Figure 5-1 Connecting the transport units ....................................................................................................75
SINAMICS SM150 6SL3845-2NN41-8AD0
10 Operating Instructions Rev.201908010908 EXAMPLE

Table of contents
Figure 5-2 Connecting the capacitor cabinet and the power section............................................................77
Figure 5-3 Connecting cabinets....................................................................................................................79
Figure 5-4 Removing the device fuse...........................................................................................................80
Figure 5-5 Removing the dust protection......................................................................................................80
Figure 5-6 Connecting the DC bus ...............................................................................................................82
Figure 6-1 Shield connection using a clip.....................................................................................................89
Figure 6-2 Bridging shield gaps....................................................................................................................89
Figure 6-3 Potential concept.........................................................................................................................90
Figure 6-4 Grounding lug..............................................................................................................................92
Figure 6-5 Example: Connecting the power cables......................................................................................92
Figure 6-6 Connection of the supply-system power cable............................................................................94
Figure 6-7 Schematic diagram: Fastening the cable ties..............................................................................96
Figure 8-1 Operator panel .........................................................................................................................101
Figure 8-2 Parameter types........................................................................................................................102
Figure 8-3 Switchover conditions................................................................................................................109
Figure 8-4 Operating areas and characteristic curves for the induction motor with drive supply ...............110
Figure 8-5 Example: Setting analog output 0 .............................................................................................112
Figure 8-6 Potential supply of external signals...........................................................................................117
Figure 8-7 Digital signal output to the system I/O.......................................................................................118
Figure 8-8 Networked structures for safe shutdown in an emergency .......................................................122
Figure 9-1 Grounding points.......................................................................................................................135
Figure 9-2 Example: Attaching the grounding spider..................................................................................136
Figure 9-3 Attaching the grounding spider..................................................................................................137
Figure 9-4 Make-proof-grounding switch closed.........................................................................................138
Figure 9-5 Principle of the mechanical door interlock.................................................................................140
Figure 9-6 Components of the secure locking system................................................................................140
Figure 9-7 Example diagram: Replacing filter mats....................................................................................145
Figure 9-8 Changing the filter in the roof assembly....................................................................................146
Figure 9-9 Example of an AVT combination module ..................................................................................149
Figure 9-10 Remove the operator panel.......................................................................................................150
Figure 9-11 Card slots ..................................................................................................................................151
Figure 9-12 Attaching the changing device to the forklift truck.....................................................................153
Figure 9-13 Attaching the changing device to the forklift truck.....................................................................153
Figure 9-14 Lifting solenoid ..........................................................................................................................154
Figure 9-15 Water connection ......................................................................................................................155
Figure 9-16 Fiber-optic conductors and power supply cable........................................................................155
Figure 9-17 Busbar package ........................................................................................................................156
Figure 9-18 Motor current acquisition module ..............................................................................................156
Figure 9-19 Busbar.......................................................................................................................................157
SINAMICS SM150 6SL3845-2NN41-8AD0
Operating Instructions Rev.201908010908 EXAMPLE 11

Table of contents
Figure 9-20 Installing the busbars ................................................................................................................157
Figure 9-21 Insulators of the phase module and lifting lugs .........................................................................158
Figure 9-22 Changing device: roller tracks...................................................................................................158
Figure 9-23 Changing device: joining the roller tracks..................................................................................159
Figure 9-24 Changing device: stop brackets ................................................................................................159
Figure 9-25 Diode module: water connection...............................................................................................162
Figure 9-26 Diode module: phase connections ............................................................................................162
Figure 9-27 Diode module: insulators...........................................................................................................163
Figure 9-28 Diode module: lugs....................................................................................................................163
Figure 9-29 Changing device: roller tracks...................................................................................................163
Figure 9-30 Changing device: joining the roller tracks..................................................................................164
Figure 9-31 Changing device: stop brackets ................................................................................................164
Figure 9-32 Sponge......................................................................................................................................166
Figure 9-33 Replacing the sponge................................................................................................................167
Figure 9-34 Example: Replacing the precharging transformer.....................................................................169
Figure 9-35 Replacing the precharging rectifier............................................................................................170
SINAMICS SM150 6SL3845-2NN41-8AD0
12 Operating Instructions Rev.201908010908 EXAMPLE

Introduction
1.1 About these instructions
These Operating Instructions describe the device and provide you with information about
handling it - from the initial shipment up to disposal. Keep these instructions for later use.
Read these Operating Instructions and comply with the information provided in them. In this
way you can ensure safe, problem-free operation and a long service life.
Safety information and handling-related warnings are provided in these Operating Instructions.
For your own safety, the safety of other persons and to avoid material damage, carefully follow
these instructions when carrying out any work.
If you have suggestions for improving the document, please contact our Service Center
(Page 175).
Text format features
You can find the following text format features in these instructions:
1. Handling instructions are always formatted as a numbered list. Always perform the steps in
the order given.
● Lists are formatted as bulleted lists.
1
– Lists on the second level are hyphenated.
Note
The note provides you with additional information about the product itself, handling the product
- and the relevant documentation.
SINAMICS SM150 6SL3845-2NN41-8AD0
Operating Instructions Rev.201908010908 EXAMPLE 13

Introduction
1.1 About these instructions
SINAMICS SM150 6SL3845-2NN41-8AD0
14 Operating Instructions Rev.201908010908 EXAMPLE
Safety instructions
In the individual chapters of this document, you will find safety instructions that must be obeyed
absolutely, for your own safety, to protect other people and to avoid damage to property.
Carefully comply with the following safety instructions when performing all of the activities.
See also
Safety information regarding the "Safe Torque Off / safe standstill" function (Page 50)
2.1 Warning symbol on the device
Please observe the warning symbols attached to the device. The warning symbols have the
following meaning:
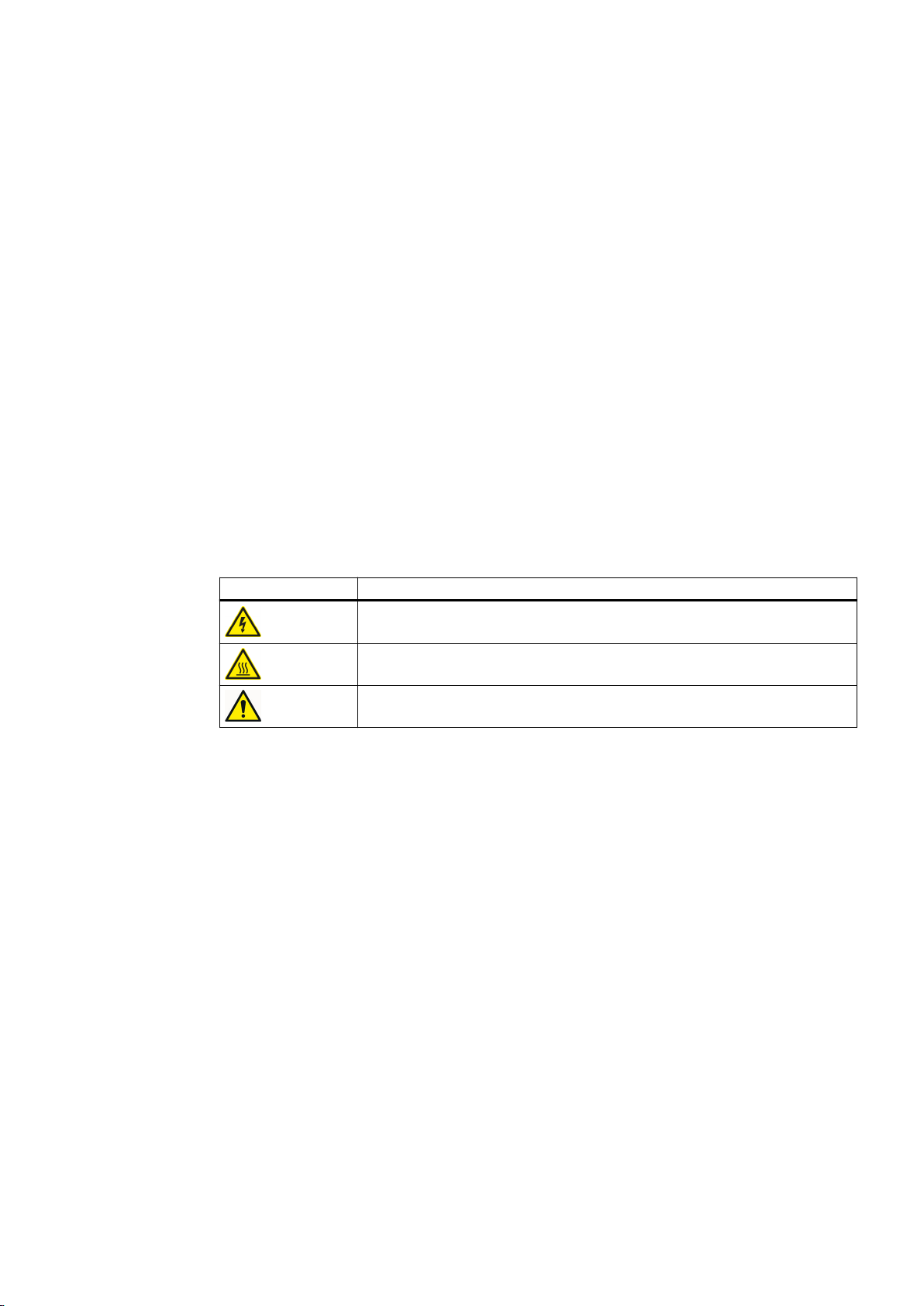
Warning symbol Meaning
Warning: Voltage
2
Warning: Hot surface
General warning symbol: Observe the explanations about the hazard on the
device labels.
For transportation, observe the "transportation markings (Page 62)" on the device packaging.
2.2 Qualified personnel
The product/system described in this documentation may only be operated by personnel
qualified for the specific task in accordance with the relevant documentation for the specific
task, in particular its warning notices and safety instructions. Because of their training and
experience, qualified personnel can recognize any risks involved with handling these products/
systems and avoid any possible dangers.
2.3 The 5 safety rules
To ensure your own personal safety as well as to avoid material damage, always comply with
the safety-relevant instructions when carrying out any work. Also carefully comply with the 5
safety rules according to EN 50110‑1 "Working in a no-voltage state" in the specified sequence.
SINAMICS SM150 6SL3845-2NN41-8AD0
Operating Instructions Rev.201908010908 EXAMPLE 15

Safety instructions
2.4 Safe handling
5 safety rules
1. Disconnect the system.
Also disconnect the auxiliary circuits, for example, anti-condensation heating.
2. Secure against reconnection.
3. Verify absence of operating voltage.
4. Ground and short-circuit.
5. Provide protection against adjacent live parts.
To energize the system, apply the measures in reverse order.
2.4 Safe handling
Electric shock from external supplies
Even if the circuit breaker is open, parts of the drive can be under voltage (live) as a result of
the auxiliary voltage at the premagnetization, precharging or demagnetization transformers.
This danger is not limited to the drive, but can also occur with components that are electrically
connected to the drive (e.g. circuit breakers or isolators). Touching live parts can result in death,
serious injury and material damage
● Isolate all components that can feed voltage to the drive before commencing work.
Electric shock due to high voltages in operation
When operating this equipment very high voltages develop. Even after switching off the mains
voltage, or while the connected machine is still turning, high voltages can remain for a
prolonged length of time. High voltages can cause death or serious injury if the safety rules are
not observed or if the equipment is handled incorrectly.
● Operate the device properly.
● Always follow the "The five safety rules (Page 15)" when performing any work.
● Service and maintain the device regularly and correctly.
Electric shock if the grounding switch is defective
A grounding switch is a component that has an associated certain probability of failure. This
means that it is possible that the feedback signal regarding the switching state no longer
matches the actual switching state of the grounding switch. This means that if the power unit
door is open, hazardous voltages could still be present at the active parts of the drive. Touching
the device can result in death or serious injury.
● Check the function of the grounding switch before carrying out any other work at the drive.
● Carefully comply with the 5 safety rules (Page 15).
SINAMICS SM150 6SL3845-2NN41-8AD0
16 Operating Instructions Rev.201908010908 EXAMPLE

Danger as a result of inactive safety functions
Inactive safety functions or ones that have not been adapted can result in machine
malfunctions. These malfunctions can result in death or severe injury.
● Before commissioning, carefully comply with the safety information and instructions
provided in Chapters "Safety notes" and "Safe Torque Off / Safe standstill (option K80)
(Page 50)".
● Carry out a safety inspection for functions relevant to safety on the entire system, including
all safety-related components.
● Ensure that the safety functions used in your drives and automation tasks are adjusted and
activated using the appropriate parameterizing.
● Carry out a function test.
● Only put your plant/system into live operation once you have ensured that the functions
relevant to safety are operating correctly.
Electric shock due to induced voltage
Rotating machinery can induce dangerous high voltages and synchronous motors that are not
de-excited immediately can also pose a hazard. If the connection to the motor is not isolated or
grounded, these voltages can also remain. Touching live parts can result in death or serious
injury.
Safety instructions
2.4 Safe handling
● Before opening the doors, wait until the connected machine has come to a standstill.
Electric shock at DC link capacitors
High voltages are still present at the DC link capacitors even after shutdown. Touching live
parts can result in death or serious injury.
● A label specifies the discharge times of the DC link capacitors. Only open the doors once
these discharge times have elapsed.
● Observe the five safety rules when performing any work.
Electric shock caused by high auxiliary voltages
High auxiliary voltages are still present even after shutdown. Touching live parts can result in
death or serious injury.
● Observe the five safety rules when performing any work.
Danger due to hazardous arcing
Hazards caused by arcing can occur as result of the following factors, for example:
● The input currents are exceeded.
● Incorrectly dimensioned circuit breaker or transformers.
● Incorrectly connected cables or cables that have not been connected.
SINAMICS SM150 6SL3845-2NN41-8AD0
Operating Instructions Rev.201908010908 EXAMPLE 17

Safety instructions
2.4 Safe handling
● Contamination and dirt.
● Tools that have been forgotten, e.g. when mounting and installing the equipment.
Arcing can result in death, serious injury or material damage.
● Make sure that the system is properly dimensioned and that the power cables are correctly
connected. The maximum permissible input currents are listed in the "Technical
specifications".
● Remove contamination and dirt.
● After installation and mounting, carefully check that no objects have been left in the device.
Danger due to live stationary parts, moving or rotating parts
Contact with the parts mentioned can result in death, serious physical injury or damage to
property.
● Observe the instructions regarding installation and operation.
● Always take protective measures before touching any components.
● Do not remove any covers.
Risk of burns due to hot component surfaces
Certain components (e.g. heat sinks and reactors) can become very hot during operation.
These components can remain hot for a long time after operation. Contact can result in serious
injury, such as skin burns.
● After the device has been shut down, do not touch any hot components.
Risk of injury at places that are difficult to access
If you do not use appropriate protective equipment when working in places that are difficult to
access you are at risk of injury. For example, sharp edges and splinters can cause injuries to
the head and skin. If you carry out work in the upper section using unsuitable ladders or similar,
you can fall and injure yourself.
● Use appropriate protective equipment, especially a hard hat and gloves.
● Use suitable steps or ladders when working in the upper area.
Eye and skin injuries caused by deionized water
Deionized water is harmful to eyes and skin and can damage surfaces.
● Therefore, use appropriate protective clothing when you carry out any work on the drive.
However, if your eyes or skin do come into contact with deionized water, rinse the affected
area thoroughly with tap water as soon as possible.
● If deionized water leaks out, eliminate the source of the problem and remove the liquid from
the surfaces affected.
SINAMICS SM150 6SL3845-2NN41-8AD0
18 Operating Instructions Rev.201908010908 EXAMPLE

Safety instructions
2.6 Components that can be destroyed by electrostatic discharge (ESD)
Shutdown as a result of an incorrect residual current monitoring device
If you use a residual current monitoring device (RCD), it is possible that the residual current
monitoring device will trip in error (nuisance trip). The converter may be switched off as a result
of the protection device tripping in error.
● To minimize the risk of faulty trips, use a type-B RCD.
2.5 Electromagnetic fields in electrical power engineering installations
Electromagnetic fields are generated during operation of electrical power engineering
installations. Electromagnetic fields can interfere with electronic devices, These devices can
malfunction if electromagnetic fields are present.
Interference with pacemakers
The functioning of cardiac pacemakers could be impaired by electromagnetic fields. Death or
serious physical injury can result.
● It is therefore not permissible for people with pacemakers to stand close to the device.
Data loss
Electromagnetic fields can cause data loss to magnetic or electronic data storage media.
● Therefore, do not carry magnetic or electronic data storage media with you.
Persons responsible for plants and systems can find additional information on electromagnetic
fields under "Information for persons responsible for plants and systems (Page 20)."
2.6 Components that can be destroyed by electrostatic discharge (ESD)
ESD guidelines
Material damage caused by electrostatic discharge.
Electronic components can be destroyed in the event of improper handling, transport, storage,
and shipping.
Pack the electronic components in appropriate ESD packaging; e.g. ESD foam, ESD
packaging bags and ESD transport containers.
To protect your equipment against damage, follow the instructions given below.
● Avoid physical contact with electronic components. If it is essential that you perform work on
these components, you must wear one of the following pieces of protective gear:
– Grounded ESD wrist strap
– ESD shoes or ESD shoe grounding strips if there is also an ESD floor.
● Do not place electronic components close to data terminals, monitors or televisions.
Maintain a minimum clearance to the screen (> 10 cm).
SINAMICS SM150 6SL3845-2NN41-8AD0
Operating Instructions Rev.201908010908 EXAMPLE 19
6HDWLQJSRVLWLRQ
6WDQGLQJSRVLWLRQ
6WDQGLQJVHDWLQJSRVLWLRQ
EE
D
F
D
IIIII
D
FF
H
GG
H
G
Safety instructions
2.7 Information for nominated persons in control of an electrical installation
● Electronic components should not be brought into contact with electrically insulating
materials such as plastic foil, plastic parts, insulating table supports or clothing made of
synthetic fibers.
● Bring components into contact only with ESD-compliant materials, e.g. ESD tables, ESD
surfaces, ESD packaging.
● Only carry out measurements on the components if one of the following conditions is met:
– The measuring device is grounded with a protective conductor, for example.
– The measuring head of a floating measuring device has been discharged directly before
the measurement.
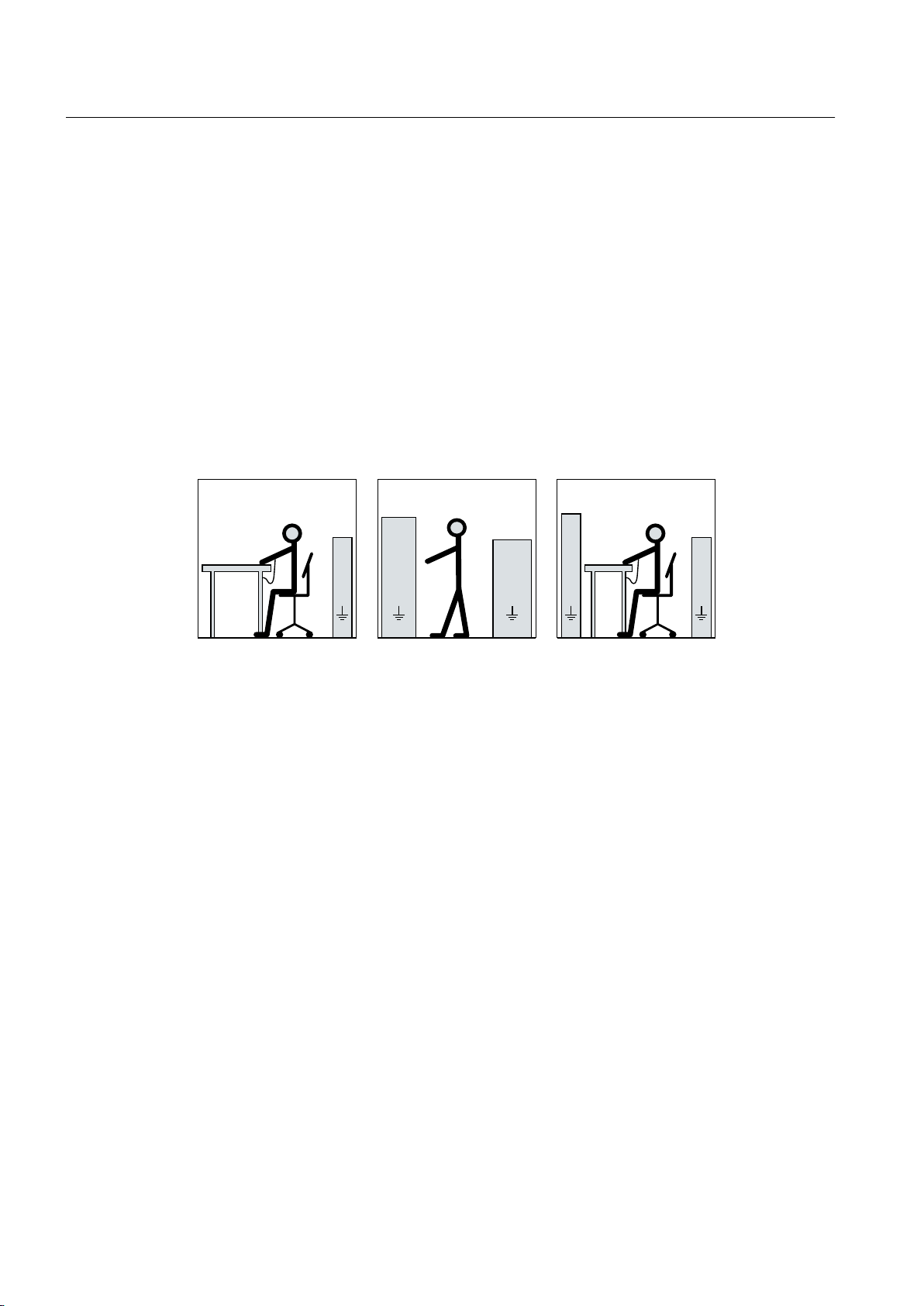
The necessary ESD protective measures for the entire working range for electrostatically
sensitive devices are illustrated once again in the following drawings.
Precise instructions for ESD protective measures are specified in the standard
DIN EN 61340‑5‑1.
a = Conductive floor covering
c = ESD shoes or ESD shoe grounding strips
e = ESD wrist strap f = Cabinet ground connection
1)
Only effective in conjunction with ESD shoes or ESD shoe grounding strips
2)
Only effective in conjunction with conductive floor covering
Figure 2-1 ESD information
1)
2)
b = ESD furniture
d = ESD clothing
2.7 Information for nominated persons in control of an electrical
installation
2.7.1 Proper usage
These devices are intended to be permanently installed in closed and dry rooms with a clean
atmosphere. You can find the ambient and operating temperatures to be adhered to in the
technical data. If the described environmental conditions are not observed, warranty claims
and other claims may be rejected.
Danger to life as a result of an explosion
If you operate the device in a hazardous zone, explosions can occur which can cause death,
serious injuries or material damage.
● Never operate the device in an explosive atmosphere (hazardous zone).
20 Operating Instructions Rev.201908010908 EXAMPLE
SINAMICS SM150 6SL3845-2NN41-8AD0

Safety instructions
2.7 Information for nominated persons in control of an electrical installation
Danger to life when not complying with proper use of the devices
Improper use of the devices described can result in death, severe injury or material damage.
● Please observe all instructions for proper use.
The nominated person in control of an electrical installation must ensure that the following
points are observed:
● Follow the local and industry-specific safety and setup regulations. Observe the
requirements in the guidelines specified in the "Standards and regulations" section of the
"Technical data and drawings." Ensure that the specific safety and construction regulations
and the regulations for using personal protective equipment are observed during all work.
● The operating instructions and the complete product documentation are always available
when carrying out any work.
● The technical data as well as the specifications relating to the permissible installation,
connection, ambient and operating conditions are taken into account at all times.
● Only qualified personnel or personnel supervised by responsible, skilled specialists are
allowed to carry out basic planning and all work on the device.
● During shipping, specific transport conditions are adhered to.
● Assembly is performed according to assembly instructions. Separate cabinet units are
connected properly (cables and busbars).
● All instructions for EMC-compatible installation, cabling, shielding, grounding, and for
adequate auxiliary power supply are to be observed.
● Commissioning is only to be performed by qualified personnel trained for that purpose in
accordance with the commissioning instructions.
● System configuration is carried out by an experienced system integrator. Additional system
components - such as circuit-breaker, transformer, cables and motor - are coordinated and
harmonized with one another for drive operation.
● The device is only operated in conjunction with the engineered components.
● Different operating modes, overloads, load cycles, and differing environmental conditions
are permitted only after special arrangement with the manufacturer.
Make use of the support and services offered by the relevant service center for planning,
installation, commissioning, and servicing work. You can find the relevant contact person under
"Service & Support (Page 175)".
SINAMICS SM150 6SL3845-2NN41-8AD0
Operating Instructions Rev.201908010908 EXAMPLE 21

Safety instructions
2.7 Information for nominated persons in control of an electrical installation
2.7.2 Grounding concept
Draw-up a grounding concept and integrate the device into this concept. The grounding
concept must take into consideration national provisions and system specifics. Ensure that the
following criteria are fulfilled:
● At the installation site, the various subunits must be screwed together to establish a good
electrical connection between them.
● If shield busbars are provided, these must be connected together.
● The protective grounding conductor must be connected to the system the grounding point.
Select the highest cross-section of the protective grounding conductor from one of the
following variants:
– According to local wiring regulations
– Calculated according to IEC 60364-5-54, 543.1
– Half a phase conductor cross-section
2.7.3 Installation site safety
Danger due to an unsecured installation location
This device is used in industrial power installations. Improper use, incorrect operation,
insufficient maintenance, and access by unauthorized persons can lead to accidents. The
results can be death, serious bodily injury or damage to property.
● Install the device in electrical rooms where only qualified personnel have access. If this is
not possible, then ensure that a barrier prevents uncontrolled access. Use safety fences and
appropriate signs, for example, to prevent unauthorized entry to the zone that has been
fenced off.
● Place notices that indicate that only trained personnel are allowed to operate and carry out
maintenance and repair work.
● To comply with safety regulations, equip plants and systems with additional monitoring and
protective devices. Follow technical equipment legislation and accident prevention
regulations.
Note
The converter will be supplied on request without an electromechanical door interlocking
system if space is restricted. In this instance, the customer must provide an access interlock
system compliant with IEC 61800-5 /-1.
Note
The drive does not have a grounding breaker at the input/output. The system operator must,
therefore, ensure that there is sufficient grounding.
SINAMICS SM150 6SL3845-2NN41-8AD0
22 Operating Instructions Rev.201908010908 EXAMPLE

2.7.4 Measures for operator protection in electromagnetic fields
The plant operator is responsible for taking the following appropriate measures (labels and
hazard warnings) to adequately protect operating personnel against any possible risk.
● Observe the relevant nationally applicable health and safety regulations or the applicable
national regulations in the country of installation. In Germany, "electromagnetic fields" are
subject to regulations BGV B11 and BGR B11 stipulated by the German statutory industrial
accident insurance institution.
● Display adequate hazard warning notices on the installation.
● Place barriers around hazardous areas.
● Take measures, e.g. using shields, to reduce electromagnetic fields at their source.
● Make sure that personnel are wearing the appropriate protective gear.
Safety instructions
2.8 Residual risks
2.8 Residual risks
According to the EU machinery directive, machine manufacturers / plant operators must
conduct a risk assessment of their machine. Plant operators must conduct a risk assessment
of their plant. In particular, pay attention to Annex 1 "General Principles" of the EU machinery
directive.
SINAMICS SM150 6SL3845-2NN41-8AD0
Operating Instructions Rev.201908010908 EXAMPLE 23

Safety instructions
2.8 Residual risks
Pay attention to the following residual risks:
● Unintentional movements of driven machine parts
Unintentional movements of driven machine parts can occur during commissioning,
operation, maintenance, and repair, e.g. from the following causes:
– Hardware defects and/or software errors in the sensors, controllers, actuators, and
connection technology
– Response times of the controller and drive
– Operating and/or environmental conditions outside of the specification
– Condensation/conductive contamination
– Parameterization, programming, cabling, and installation errors
– Use of radio devices/cell phones in the immediate vicinity of the controller
– External influences/damage
● High temperatures and emissions
A fault can occur as a result of the following, for example:
– Component malfunctions
– Software errors
– Operating and/or environmental conditions outside of the specification
– External influences/damage
For instance, a fault can have the following effects:
– Extraordinarily high temperatures, including open fires as a result of the fault
– Emissions of light, noise, particles or gases
Devices with "Open Type/IP20 degree of protection" must be installed in an electrical room
or a comparable environment.
● Hazardous shock voltages
Hazardous shock voltages can result from the following causes, for example:
– Component malfunctions
– Induction of voltages in moving motors
– Operating and/or environmental conditions outside of the specification
– Condensation/conductive contamination
– External influences/damage
● The release of substances and emissions that are harmful to the environment
Improper operation or the improper disposal of components can harm the environment.
SINAMICS SM150 6SL3845-2NN41-8AD0
24 Operating Instructions Rev.201908010908 EXAMPLE

Safety instructions
2.9 Security information
● Damage from pressure build-up during electric arcs in the event of a fault
If the building has not been designed correctly in terms of how it has been dimensioned,
damage can result from the pressure that can possibly build up inside.
● Dangerous electric arcs during internal faults
The devices have been designed according to the relevant IEC standards, and tested in line
with strict type-testing procedures. They were developed and manufactured so that there is
a very low probability of internal faults occurring. However, internal faults cannot be
completely ruled out.
WARNING
Dangerous electric arcs during internal faults
Defects such as damage to components, overvoltages, or loose parts, as well as exceptional
operating statuses, can cause a failure within the enclosure. This can result in an internal
electric arc. If an electric arc occurs and people are nearby, this could lead to death, serious
physical injury, and damage to property.
● Ensure that only qualified personnel perform any work that is required.
● Observe the safety and operating instructions in this documentation and labels attached to
the device for any work that is performed.
2.9 Security information
Siemens provides products and solutions with industrial security functions that support the
secure operation of plants, systems, machines and networks.
In order to protect plants, systems, machines and networks against cyber threats, it is
necessary to implement – and continuously maintain – a holistic, state-of-the-art industrial
security concept. Siemens’ products and solutions constitute one element of such a concept.
Customers are responsible for preventing unauthorized access to their plants, systems,
machines and networks. Such systems, machines and components should only be connected
to an enterprise network or the internet if and to the extent such a connection is necessary and
only when appropriate security measures (e.g. firewalls and/or network segmentation) are in
place.
For additional information on industrial security measures that may be implemented, please
visit
https://www.siemens.com/industrialsecurity (
Siemens’ products and solutions undergo continuous development to make them more secure.
Siemens strongly recommends that product updates are applied as soon as they are available
and that the latest product versions are used. Use of product versions that are no longer
supported, and failure to apply the latest updates may increase customer’s exposure to cyber
threats.
To stay informed about product updates, subscribe to the Siemens Industrial Security RSS
Feed under
https://www.siemens.com/industrialsecurity (https://www.siemens.com/industrialsecurity).
https://www.siemens.com/industrialsecurity).
Additional notes for this product are provided in the Internet.
SINAMICS SM150 6SL3845-2NN41-8AD0
Operating Instructions Rev.201908010908 EXAMPLE 25
Safety instructions
2.9 Security information
"SINAMICS Industrial Security" Manual
Notes relating to Industrial Security are provided here (
support.industry.siemens.com/cs/ww/de/view/109751848/en).
"Security Guidelines for SIMATIC HMI devices" Manual
Notes relating to Industrial Security for HMI devices are available here. (https://
support.industry.siemens.com/cs/de/en/view/109481300)
https://
SINAMICS SM150 6SL3845-2NN41-8AD0
26 Operating Instructions Rev.201908010908 EXAMPLE

Description
3.1 Applications
The drive is a medium-voltage drive for phase-rotation-controlled machines. The drive is a
single drive designed for applications with a quadratic, constant load characteristic and no
regenerative feedback. Typical applications include pumps, fans, compressors, extruders,
mixers, and mills.
3.2 Safety concept
The device and its associated components are subject to an extensive safety concept. When
used properly, the security concept guarantees safe installation, safe operation as well as safe
service and maintenance.
The safety concept encompasses safety components and functions to protect the device and
operators. The device is also equipped with monitoring functions to protect external
components.
3
The device operates safely when the interlock and protection systems are functioning properly.
Nevertheless, there are areas that are hazardous for personnel and that cause material
damage if the safety information of all the instructions and the labels on the device are not
strictly complied with.
3.2.1 Safety components and functions
The following safety components and functions are installed to protect personnel:
● The make-proof grounding switch for grounding the voltage DC link.
● The electromechanical door interlocking system prevents access to the power unit while
operational. The doors cannot be opened until the grounding switch has been closed. The
door for the control section, however, can be opened for monitoring purposes even during
operation.
● The electromechanical interlock system for the make-proof grounding switch prevents the
make-proof grounding switch from closing for the voltage DC link. The make-proof
grounding switch can only be closed if the circuit-breaker is open and the DC link has been
completely discharged.
● The EMERGENCY OFF mushroom pushbutton in the cabinet door is a pushbutton with
mechanical interlock system for EMERGENCY OFF, Stop Category 0 (standard).
SINAMICS SM150 6SL3845-2NN41-8AD0
Operating Instructions Rev.201908010908 EXAMPLE 27

Description
3.2 Safety concept
Note
As option, the make-proof grounding switch also serves to ground the input side (option L48)
and the output side (option L49).
3.2.2 External safety components
The following external components for the safety concept are provided:
● Circuit breaker
More detailed information is provided in Chapter Circuit-breaker (provided by the customer)
(Page 37).
● Input-side transformer
The transformer on the input side must be configured in such a way that the maximum shortcircuit current is not exceeded. Information on this is provided in the technical data sheet of
the transformer.
3.2.3 Protection and monitoring functions of internal components
The internal components of the drive have the following protection and monitoring functions:
● Crowbar
● Device protection using monitoring systems:
– Current monitoring
– DC-link monitoring
– Output voltage monitoring
– Thermal monitoring of the power unit
– Precharge monitoring
– Insulation monitoring
– Supply voltage monitoring
– GSV monitoring
– Circuit-breaker monitoring
– Re-cooling unit monitoring
● Shutdown in the event of semiconductor failure
● Shutdown in the event of control component failure
SINAMICS SM150 6SL3845-2NN41-8AD0
28 Operating Instructions Rev.201908010908 EXAMPLE

● Internal protection functions for the control hardware
● Protection against communication failure between the closed-loop control and the power
unit
3.2.4 Protection and monitoring functions for external components
Transformer and motor can be monitored in the device. A fast protective shutdown that you can
activate for external problems, e.g. short-circuits, is present.
3.3 Design
3.3.1 Components
Description
3.3 Design
The basis configuration is equipped with the following components:
● 12-pulse Basic Line Module
● DC link
● Motor Module
An optional 24-pulse Basic Line Module is also available for other configurations.
SINAMICS SM150 6SL3845-2NN41-8AD0
Operating Instructions Rev.201908010908 EXAMPLE 29
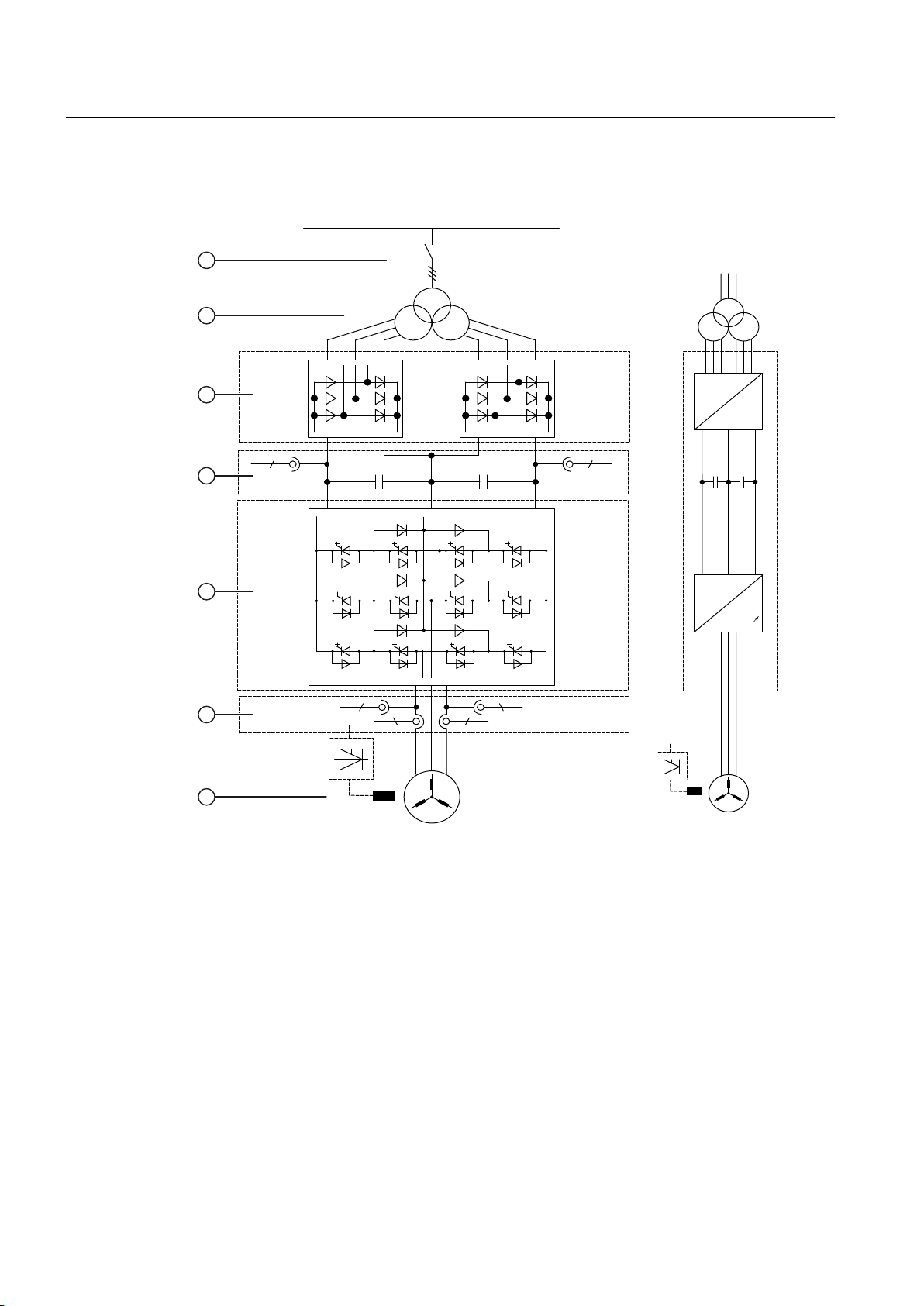
N9a+]
a
a
Description
3.3 Design
The drive is a three-level voltage DC-link drive.
1 Circuit-breaker 5 Motor Module (3-level inverter) with IGCT
3 Basic Line Module
(diode rectifier)
2 Drive transformer 6 Motor-side voltage/current transformers
7 High-voltage motor
4 DC link with dry-type capacitors
Figure 3-1 Design of the power unit
3.3.2 Design of the Basic Line Module
In a 12-pulse configuration, the Basic Line Module consists of a rectifier module. In a 24-pulse
configuration, the Basic Line Module comprises two rectifier modules.
SINAMICS SM150 6SL3845-2NN41-8AD0
30 Operating Instructions Rev.201908010908 EXAMPLE
 Loading...
Loading...