Siemens SINAMICS G110M, SINAMICS G120, SINAMICS G120P, SINAMICS G120C, SINAMICS G120D Function Manual



___________________
___________________
___________________
___________________
___________________
___________________
___________________
___________________
___________________
SINAMICS
SINAMICS G120, G120P, G120C,
G120D, G110M
Fieldbuses
Function Manual
Edition 04/2018, firmware V4.7 SP10
04/2018, FW V4.7 SP10
A5E34229197B AE
Preface
Fundamental safety
instructions
1
General information
2
Communication via
PROFIBUS and PROFINET
3
Communication via
EtherNet/IP
4
Communication via RS485
5
Communication over
CANopen
6
Communication via AS-i only for G110M
7
Appendix
A

Siemens AG
Division Digital Factory
Postfach 48 48
90026 NÜRNBERG
GERMANY
A5E34229197B AE
Ⓟ
Copyright © Siemens AG 2014 - 2018.
All rights reserved
Legal information
Warning notice system
DANGER
indicates that death or severe personal injury will result if proper precautions are not taken.
WARNING
indicates that death or severe personal injury may result if proper precautions are not taken.
CAUTION
indicates that minor personal injury can result if proper precautions are not taken.
NOTICE
indicates that property damage can result if proper precautions are not taken.
Qualified Personnel
personnel qualified
Proper use of Siemens products
WARNING
Siemens products may only be used for the applications described in the catalog and in the relevant technical
maintenance are required to ensure that the products operate safely and without any problems. The permissible
ambient conditions must be complied with. The information in the relevant documentation must be observed.
Trademarks
Disclaimer of Liability
This manual contains notices you have to observe in order to ensure your personal safety, as well as to prevent
damage to property. The notices referring to your personal safety are highlighted in the manual by a safety alert
symbol, notices referring only to property damage have no safety alert symbol. These notices shown below are
graded according to the degree of danger.
If more than one degree of danger is present, the warning notice representing the highest degree of danger will
be used. A notice warning of injury to persons with a safety alert symbol may also include a warning relating to
property damage.
The product/system described in this documentation may be operated only by
task in accordance with the relevant documentation, in particular its warning notices and safety instructions.
Qualified personnel are those who, based on their training and experience, are capable of identifying risks and
avoiding potential hazards when working with these products/systems.
Note the following:
documentation. If products and components from other manufacturers are used, these must be recommended
or approved by Siemens. Proper transport, storage, installation, assembly, commissioning, operation and
All names identified by ® are registered trademarks of Siemens AG. The remaining trademarks in this publication
may be trademarks whose use by third parties for their own purposes could violate the rights of the owner.
We have reviewed the contents of this publication to ensure consistency with the hardware and software
described. Since variance cannot be precluded entirely, we cannot guarantee full consistency. However, the
information in this publication is reviewed regularly and any necessary corrections are included in subsequent
editions.
for the specific
04/2018 Subject to change

Preface
About this manual
Fieldbuses for SINAMICS G120
Additional fieldbuses for SINAMICS G120P
Additional fieldbuses for SINAMICS G110M
Changes in this edition
What is the meaning of the symbols in the manual?
This manual describes the settings and preconditions that are required to communicate with
a higher-level control system with the subsequently listed fieldbus systems.
● PROFIBUS DP
● PROFINET
● EtherNet/IP
● USS
● Modbus RTU
● CANopen
● BACnet MS/TP
● P1
● AS-Interface
Inverter settings are described in the context of the Startdrive PC commissioning tool. The
descriptions for settings using STARTER have been removed.
Reference to further information in the manual
Download from the Internet
DVD that can be ordered
End of a handling instruction.
❒
Fieldbuses
Function Manual, 04/2018, FW V4.7 SP10, A5E34229197B AE
3

Preface
Fieldbuses
4 Function Manual, 04/2018, FW V4.7 SP10, A5E34229197B AE

Table of contents
Preface ................................................................................................................................................... 3
1 Fundamental safety instructions .............................................................................................................. 9
2 General information .............................................................................................................................. 13
3 Communication via PROFIBUS and PROFINET ................................................................................... 17
1.1 General safety instructions ....................................................................................................... 9
1.2 Warranty and liability for application examples ........................................................................ 9
1.3 Industrial security .................................................................................................................... 10
2.1 Ethernet and PROFINET protocols that are used .................................................................. 14
3.1 PROFIDRIVE profile - Cyclic communication ......................................................................... 17
3.1.1 Assigning control and status words ........................................................................................ 21
3.1.1.1 Control and status word 1 ....................................................................................................... 21
3.1.1.2 Control and status word 2 ....................................................................................................... 25
3.1.1.3 Control and status word 3 ....................................................................................................... 26
3.1.2 NAMUR message word .......................................................................................................... 28
3.1.3 Control and status word, encoder ........................................................................................... 29
3.1.4 Position actual value of the encoder ....................................................................................... 31
3.1.5 Extend telegrams and change signal interconnection ............................................................ 33
3.1.6 Data structure of the parameter channel ................................................................................ 35
3.1.6.1 Application examples .............................................................................................................. 39
3.1.7 Slave-to-slave communication ................................................................................................ 41
3.2 PROFIDRIVE profile - Acyclic communication ....................................................................... 42
3.3 PROFIdrive profile - Diagnostic channels ............................................................................... 47
3.3.1 Diagnostics with PROFINET ................................................................................................... 48
3.3.2 Diagnostics with PROFIBUS .................................................................................................. 50
3.4 Identification & maintenance data (I&M) ................................................................................. 54
3.5 S7 communication .................................................................................................................. 55
3.5.1 Directly accessing a SINAMICS G120 converter from a SIMATIC panel ............................... 55
3.6 Communication via PROFINET .............................................................................................. 59
3.6.1 Converter with PROFINET interface ....................................................................................... 61
3.6.2 Integrating inverters into PROFINET ...................................................................................... 62
3.6.3 PROFINET IO operation ......................................................................................................... 63
3.6.3.1 What do you have to set for communication via PROFINET?................................................ 63
3.6.3.2 Configuring communication to the control .............................................................................. 63
3.6.3.3 Installing GSDML .................................................................................................................... 65
3.6.3.4 Activating diagnostics via the control ...................................................................................... 65
3.6.4 PROFIenergy .......................................................................................................................... 65
3.6.4.1 General inverter behavior when in the PROFIenergy energy-saving mode ........................... 66
3.6.4.2 Supported PROFIenergy energy-saving modes ..................................................................... 66
3.6.4.3 Settings and displays for PROFIenergy in the inverter ........................................................... 67
3.6.4.4 Control commands and status queries ................................................................................... 68
Fieldbuses
Function Manual, 04/2018, FW V4.7 SP10, A5E34229197B AE
5

Table of contents
4 Communication via EtherNet/IP ............................................................................................................ 81
5 Communication via RS485 ................................................................................................................... 107
3.6.5 The inverter with PROFINET interface as Ethernet node. ..................................................... 70
3.7 Communication via PROFIBUS ............................................................................................. 72
3.7.1 Inverters with PROFIBUS interface ....................................................................................... 73
3.7.2 What do you have to set for communication via PROFIBUS? .............................................. 75
3.7.3 Integrating inverters into PROFIBUS ..................................................................................... 76
3.7.4 Configuring communication to the control system ................................................................. 76
3.7.4.1 Configuring the communication using SIMATIC S7 control ................................................... 76
3.7.4.2 Configuring the communication with a third-party control system ......................................... 76
3.7.4.3 Installing the GSD .................................................................................................................. 77
3.7.5 Setting the address ................................................................................................................ 78
3.8 Select telegram ...................................................................................................................... 79
4.1 Inverters with Ethernet/IP interface ........................................................................................ 82
4.2 Connect converter to Ethernet/IP........................................................................................... 84
4.3 What do you need for communication via Ethernet/IP?......................................................... 85
4.4 Configuring communication via EtherNet/IP .......................................................................... 86
4.4.1 Communication settings ......................................................................................................... 86
4.4.2 Special issues if you wish to use the ODVA AC/DC Drive profile ......................................... 87
4.5 Supported objects .................................................................................................................. 88
4.5.1 Supported ODVA AC/DC assemblies .................................................................................. 102
4.6 Create generic I/O module ................................................................................................... 103
4.7 The inverter as an Ethernet station ...................................................................................... 104
5.1 Inverter with RS485 interface ............................................................................................... 108
5.2 Integrating inverters into a bus system via the RS485 interface ......................................... 110
5.3 Communication via USS ...................................................................................................... 111
5.3.1 Basic settings for communication ........................................................................................ 111
5.3.1.1 Setting the address .............................................................................................................. 112
5.3.1.2 Parameters to set communication via USS ......................................................................... 113
5.3.2 Telegram structure ............................................................................................................... 114
5.3.3 User data range of the USS telegram .................................................................................. 115
5.3.4 USS parameter channel ....................................................................................................... 116
5.3.4.1 Telegram examples, length of the parameter channel = 4 .................................................. 120
5.3.5 USS process data channel (PZD) ........................................................................................ 122
5.3.6 Time-out and other errors .................................................................................................... 123
5.4 Communication using Modbus RTU .................................................................................... 125
5.4.1 Basic settings for communication ........................................................................................ 126
5.4.1.1 Setting the address .............................................................................................................. 127
5.4.1.2 Parameters for Modbus communication settings ................................................................. 128
5.4.2 Modbus RTU telegram ......................................................................................................... 130
5.4.3 Baud rates and mapping tables ........................................................................................... 131
5.4.4 Mapping tables - inverter data ............................................................................................. 133
5.4.5 Acyclic communication via Modbus RTU ............................................................................. 136
5.4.6 Write and read access using function codes ....................................................................... 137
5.4.7 Acyclically read and write parameter via FC 16 ................................................................... 140
Fieldbuses
6 Function Manual, 04/2018, FW V4.7 SP10, A5E34229197B AE

Table of contents
6 Communication over CANopen ........................................................................................................... 169
7 Communication via AS-i - only for G110M ........................................................................................... 215
5.4.7.1 Read parameter .................................................................................................................... 141
5.4.7.2 Write parameter .................................................................................................................... 142
5.4.8 Communication procedure .................................................................................................... 144
5.4.9 Application example .............................................................................................................. 145
5.5 Communication via BACnet MS/TP - only CU230P-2 HVAC / BT ....................................... 146
5.5.1 Basic settings for communication ......................................................................................... 147
5.5.1.1 Setting the address ............................................................................................................... 148
5.5.1.2 Parameters for setting communication via BACnet .............................................................. 149
5.5.2 Supported services and objects ............................................................................................ 151
5.5.3 Acyclic communication (general parameter access) via BACnet ......................................... 160
5.6 Communication via P1 - only CU230P-2 HVAC, CU230P-2 BT........................................... 162
5.6.1 Basic settings for communication via P1 .............................................................................. 163
5.6.2 Setting the address ............................................................................................................... 164
5.6.3 Point numbers ....................................................................................................................... 165
6.1 Network management (NMT service) ................................................................................... 172
6.2 SDO services ........................................................................................................................ 175
6.2.1 Access to SINAMICS parameters via SDO .......................................................................... 175
6.2.2 Access PZD objects via SDO ............................................................................................... 177
6.3 PDO services ........................................................................................................................ 179
6.3.1 Predefined connection set .................................................................................................... 182
6.3.2 Free PDO mapping ............................................................................................................... 184
6.3.3 Interconnect objects from the receive and transmit buffers .................................................. 187
6.3.4 Free PDO mapping for example of the actual current value and torque limit....................... 189
6.4 CANopen operating modes .................................................................................................. 191
6.5 RAM to ROM via the CANopen object 1010 ........................................................................ 193
6.6 Object directories .................................................................................................................. 194
6.6.1 General objects from the CiA 301 communication profile .................................................... 194
6.6.2 Free objects .......................................................................................................................... 203
6.6.3 Objects from the CiA 402 drive profile .................................................................................. 204
6.7 Integrating the inverter into CANopen .................................................................................. 206
6.7.1 Connecting inverter to CAN bus ........................................................................................... 207
6.7.2 Setting the node ID and baud rate ........................................................................................ 207
6.7.3 Setting the monitoring of the communication ....................................................................... 208
6.8 Error diagnostics ................................................................................................................... 210
6.9 CAN bus sampling time ........................................................................................................ 214
7.1 Setting the address ............................................................................................................... 217
7.2 Single Slave mode ................................................................................................................ 219
7.3 Dual Slave mode ................................................................................................................... 221
7.4 Assignment tables ................................................................................................................. 224
7.5 Cyclic and acyclic communication via CTT2 ........................................................................ 226
7.5.1 Cyclic communication ........................................................................................................... 227
Fieldbuses
Function Manual, 04/2018, FW V4.7 SP10, A5E34229197B AE
7

Table of contents
A Appendix ............................................................................................................................................. 231
Index ................................................................................................................................................... 239
7.5.2 Acyclic communication - standard ....................................................................................... 228
7.5.3 Acyclic communication - manufacturer-specific ................................................................... 228
A.1 Application examples for communication with STEP7......................................................... 231
A.2 Manuals and technical support ............................................................................................ 232
A.2.1 Overview of the manuals ..................................................................................................... 232
A.2.2 Configuring support .............................................................................................................. 236
A.2.3 Product Support ................................................................................................................... 237
Fieldbuses
8 Function Manual, 04/2018, FW V4.7 SP10, A5E34229197B AE

1
1.1
General safety instructions
WARNING
Danger to life if the safety instructions and residual risks are not observed
WARNING
Malfunctions of the machine as a result of incorrect or changed parameter settings
1.2
Warranty and liability for application examples
If the safety instructions and residual risks in the associated hardware documentation are
not observed, accidents involving severe injuries or death can occur.
• Observe the safety instructions given in the hardware documentation.
• Consider the residual risks for the risk evaluation.
As a result of incorrect or changed parameterization, machines can malfunction, which in
turn can lead to injuries or death.
• Protect the parameterization (parameter assignments) against unauthorized access.
• Handle possible malfunctions by taking suitable measures, e.g. emergency stop or
emergency off.
Application examples are not binding and do not claim to be complete regarding
configuration, equipment or any eventuality which may arise. Application examples do not
represent specific customer solutions, but are only intended to provide support for typical
tasks.
As the user you yourself are responsible for ensuring that the products described are
operated correctly. Application examples do not relieve you of your responsibility for safe
handling when using, installing, operating and maintaining the equipment.
Fieldbuses
Function Manual, 04/2018, FW V4.7 SP10, A5E34229197B AE
9
Fundamental safety instructions
1.3
Industrial security
Note
Industrial security
Siemens provides products and solutions with industrial security functions that support the
secure operation of plants, systems, machines and networks.
In order to protect plants, systems, machines and networks against cyber threats, it is
necessary to implement
security concept. Siemens’ products and solutions constitute one element of
Customers are responsible for preventing unauthorized access to their plants, systems,
machines and networks. Such systems, machines and components should only be
connected to an enterprise network or the Internet if and to the extent such
necessary and only when appropriate security measures (e.g. firewalls and/or network
segmentation) are in place.
For additional information on industrial security measures that may be implemented, please
visit:
Industrial security (
Siemens’ products and solutions undergo continuous development to make them more
secure. Siemens strongly recommends that product updates are applied as soon as they are
available and that the latest product versions are used. Use of product versions that are no
longer supported, and failure to apply the latest updates may increase customer’s exposure
to cyber threats.
To stay informed about product updates, subs
Feed at:
Industrial security (
1.3 Industrial security
– and continuously maintain – a holistic, state-of-the-art industrial
such a concept.
a connection is
http://www.siemens.com/industrialsecurity)
cribe to the Siemens Industrial Security RSS
http://www.siemens.com/industrialsecurity)
Further information is provided on the Internet:
Industrial Security Configuration Manual
(https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/ww/en/view/108862708)
Fieldbuses
10 Function Manual, 04/2018, FW V4.7 SP10, A5E34229197B AE

Fundamental safety instructions
WARNING
Unsafe operating states resulting from software manipulation
1.3 Industrial security
Software manipulations (e.g. viruses, trojans, malware or worms) can cause unsafe
operating states in your system that may lead to death, serious injury, and property
damage.
• Keep the software up to date.
• Incorporate the automation and drive components into a holistic, state-of-the-art
industrial security concept for the installation or machine.
• Make sure that you include all installed products into the holistic industrial security
concept.
• Protect files stored on exchangeable storage media from malicious software by with
suitable protection measures, e.g. virus scanners.
• Protect the drive against unauthorized changes by activating the "know-how protection"
drive function.
Fieldbuses
Function Manual, 04/2018, FW V4.7 SP10, A5E34229197B AE
11

Fundamental safety instructions
1.3 Industrial security
Fieldbuses
12 Function Manual, 04/2018, FW V4.7 SP10, A5E34229197B AE

2
Communication with the control, even when the line voltage is switched off
If, in your plant or system, communication with the control system should continue to function
even when the line voltage is switched off, then you must externally supply the
inverter/Control Unit with 24 V DC. To do this, use terminals 31 and 32 – or connector X01.
You can find additional details in the operating instructions for the inverter or the Control
Unit.
Fieldbuses
Function Manual, 04/2018, FW V4.7 SP10, A5E34229197B AE
13
General information
2.1
Ethernet and PROFINET protocols that are used
Protocol
Port
number
Layer
(2) Link layer
(4) Transport layer
Function/description
Accessible stations, PROFINET Discovery and configuration
xx-xx-xx = Organizationally Unique Identifier
PROFINET Link Layer Discovery protocol
01-80-C2-00-00-0E
PROFINET medium redundancy
xx-xx-xx = Organizationally Unique Identifier
PROFINET send clock and time synchronization, based on IEEE
1588
xx-xx-xx = Organizationally Unique Identifier
(PROFINET)
PROFINET Cyclic IO data transfer
PROFINET connection less RPC
order to establish an application relationship (PROFINET AR).
2.1 Ethernet and PROFINET protocols that are used
The inverter supports the protocols listed in the following tables. The address parameters,
the relevant communication layer as well as the communication role and the communication
direction are specified for each protocol.
You require this information to set the appropriate safety measures to protect the automation
system, e.g. in the firewall.
As the security measures are limited to Ethernet and PROFINET networks, no PROFIBUS
protocols are listed in the table.
Table 2- 1 PROFINET protocols
DCP:
Discovery and
configuration
protocol
LLDP:
Link Layer
Discovery
Protocol
MRP:
Media Redun-
dancy Protocol
PTCP
Precision
Transparent
Clock Protocol
Not
relevant
Not
relevant
Not
relevant
Not
relevant
(2) Ethernet II and
IEEE 802.1Q and
Ethertype 0x8892
(PROFINET)
(2) Ethernet II and
IEEE 802.1Q and
Ethertype 0x88CC
(PROFINET)
(2) Ethernet II and
IEEE 802.1Q and
Ethertype 0x88E3
(PROFINET)
(2) Ethernet II and
IEEE 802.1Q and
Ethertype 0x8892
(PROFINET)
DCP is used by PROFINET to determine PROFINET devices and to
make basic settings.
DCP uses the special multicast MAC address:
xx-xx-xx-01-0E-CF,
LLDP is used by PROFINET to determine and manage neighborhood relationships between PROFINET devices.
LLDP uses the special multicast MAC address:
MRP enables the control of redundant routes through a ring topology.
MRP uses the special multicast MAC address:
xx-xx-xx-01-15-4E,
PTC is used to implement send clock synchronization and time synchronization between RJ45 ports, which are required for IRT operation.
PTCP uses the special multicast MAC address:
xx-xx-xx-01-0E-CF,
PROFINET IO
data
PROFINET
Context Manager
Fieldbuses
14 Function Manual, 04/2018, FW V4.7 SP10, A5E34229197B AE
Not
relevant
34964 (4) UDP
(2) Ethernet II and
IEEE 802.1Q and
Ethertype 0x8892
The PROFINET IO telegrams are used to transfer IO data cyclically
between the PROFINET IO controller and IO devices via Ethernet.
The PROFINET context manager provides an endpoint mapper in
General information
Protocol
Port
number
Layer
(2) Link layer
(4) Transport layer
Function/description
Net/IP.
Net/IP.
Protocol
Port
number
Layer
(2) Link layer
(4) Transport layer
Function/description
ISO-on-TCP protocol
oriented data exchange to a remote CPU, WinAC or devices of other
and is always required.
Simple network management protocol
It is activated in the factory setting, and is always required
(4) UDP
2.1 Ethernet and PROFINET protocols that are used
Table 2- 2 Ethernet/IP protocols
Implicit messaging
Explicit messaging
2222 (4) UDP Used for exchanging I/O data.
This is inactive when delivered. Is activated when selecting Ether-
44818 (4) TCP
(4) UDP
Used for parameter access (writing, reading).
This is inactive when delivered. Is activated when selecting Ether-
Table 2- 3 Connection-oriented communication protocols
ISO on TCP
(according to
RFC 1006)
102 (4) TCP
ISO on TCP (according to RFC 1006) is used for the message-
suppliers.
Communication with ES, HMI, etc. is activated in the factory setting,
SNMP
Simple Net-
work Manage-
161 (4) UDP
SNMP enables network management data to be read out and set
(SNMP managed objects) by the SNMP manager.
ment Protocol
Reserved 49152 ...
(4) TCP
65535
Fieldbuses
Function Manual, 04/2018, FW V4.7 SP10, A5E34229197B AE
Dynamic port area that is used for the active connection endpoint if
the application does not specify the local port.
15

General information
2.1 Ethernet and PROFINET protocols that are used
Fieldbuses
16 Function Manual, 04/2018, FW V4.7 SP10, A5E34229197B AE
3
3.1
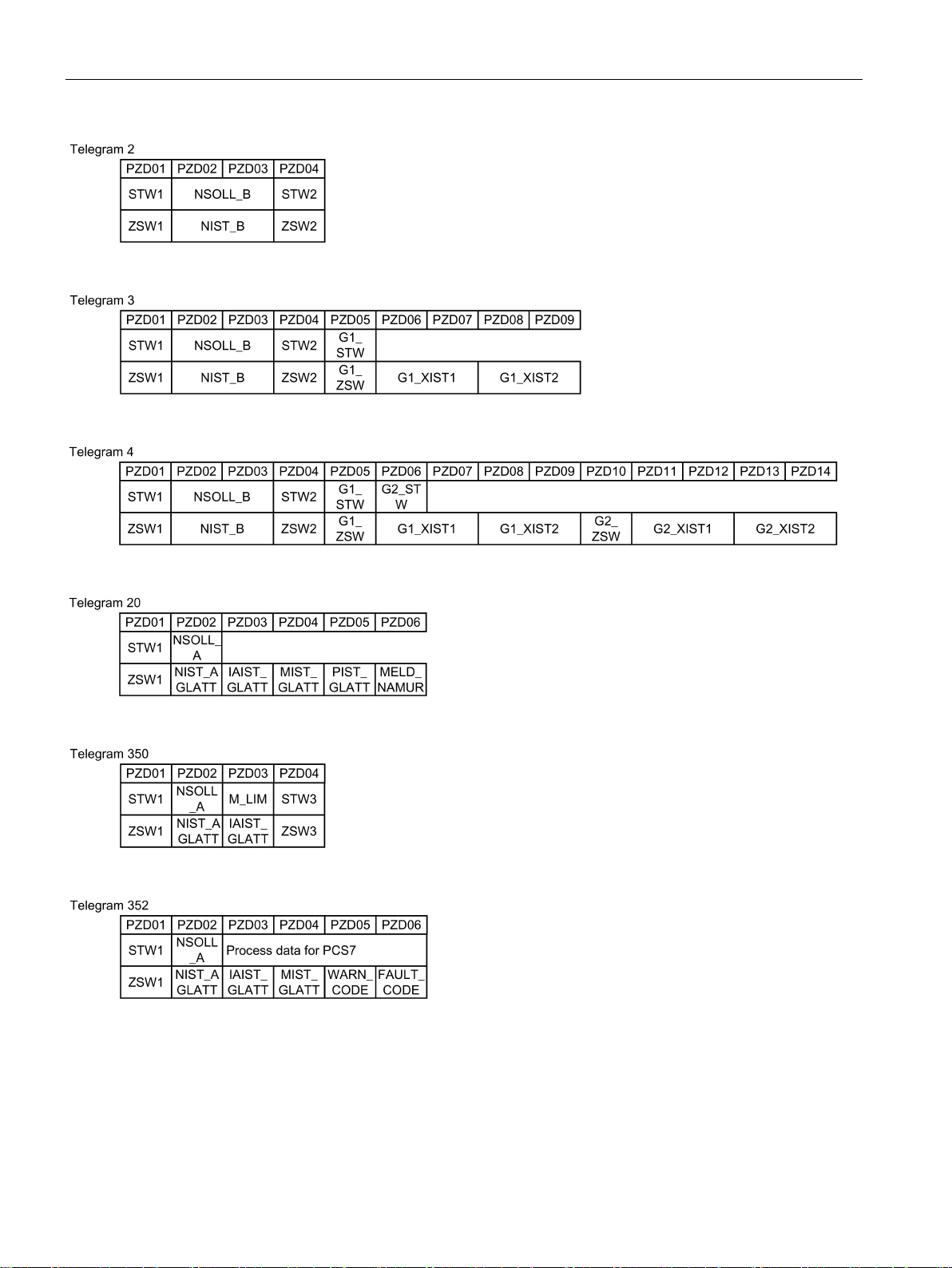
PROFIDRIVE profile - Cyclic communication
Communication telegrams if "basic positioner" has been configured
Communication telegrams for speed control
Depending on the Control Unit or inverter, there are different telegrams for communication
via PROFIBUS DP or PROFINET IO. The structure of the individual telegrams are listed
below.
The Startdrive commissioning tool or an operator panel only list the telegrams for selection
that are possible with your particular inverter.
How to commission the inverter and select a telegram are described in the operating
instructions.
Overview of the manuals (Page 232)
The inverter has the following telegrams if you have configured the "Basic positioner"
function:
● Standard telegram 7, PZD-2/2
● Standard telegram 9, PZD-10/5
● SIEMENS telegram 110, PZD-12/7
● SIEMENS telegram 111, PZD-12/12
● Telegram 999, free interconnection
Telegrams 7, 9, 110 and 111 are described in the "Basic positioner" Function Manual
Overview of the manuals (Page 232)
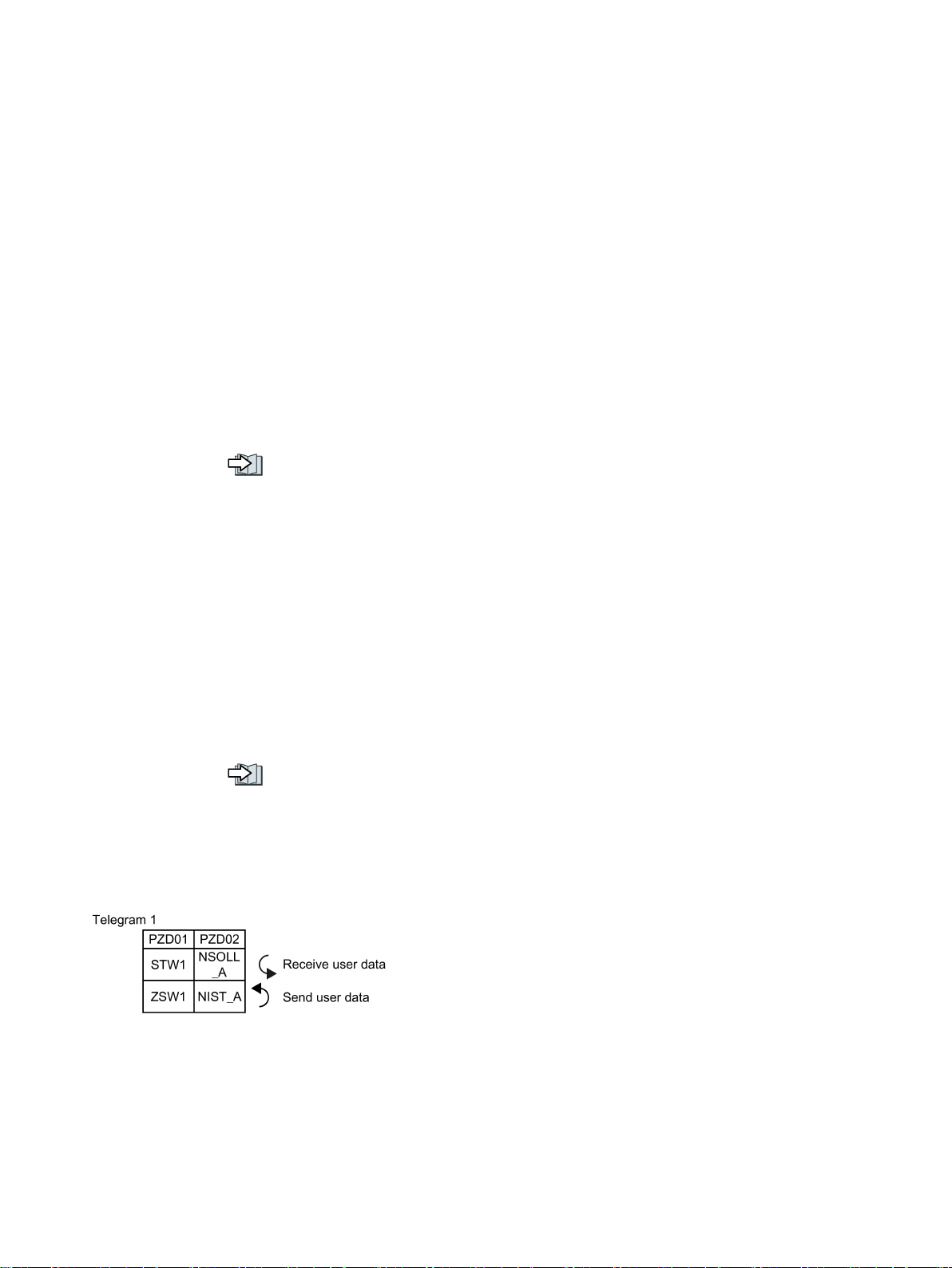
The send and receive telegrams of the inverter for closed-loop speed control are structured
as follows:
Figure 3-1 16-bit speed setpoint
Fieldbuses
Function Manual, 04/2018, FW V4.7 SP10, A5E34229197B AE
17
Communication via PROFIBUS and PROFINET
3.1 PROFIDRIVE profile - Cyclic communication
Figure 3-2 32-bit speed setpoint
Figure 3-3 32-bit speed setpoint with 1 position encoder
Figure 3-4 32-bit speed setpoint with 2 position encoders
Figure 3-5 16-bit speed setpoint for VIK-Namur
Figure 3-6 16-bit speed setpoint with torque limiting
Figure 3-7 16-bit speed setpoint for PCS7
Fieldbuses
18 Function Manual, 04/2018, FW V4.7 SP10, A5E34229197B AE

Communication via PROFIBUS and PROFINET
Abbreviation
Explanation
Abbreviation
Explanation
PZD
Process data
PKW
Parameter channel
STW
Control word
PIST_GLATT
Actual active power value, smoothed
ZSW
Status word
M_LIM
Torque limit
definition
G2_STW
G2_ZSW
G2_XIST1
encoder 2
G2_XIST2
encoder 2
3.1 PROFIDRIVE profile - Cyclic communication
Figure 3-8 16-bit speed setpoint with PKW range to read and write parameters
Figure 3-9 16-bit speed setpoint for PCS7 with PKW range to read and write parameters
Figure 3-10 Telegram with free interconnection and length
NSOLL_A Speed setpoint 16 bit FAULT_CODE Fault code
NSOLL_B Speed setpoint 32 bit WARN_CODE Alarm code
NIST_A Speed actual value 16 bit MELD_NAMUR Message according to the VIK-NAMUR
NIST_B Speed actual value 32 bit G1_STW /
IAIST Current actual value G1_ZSW /
IAIST_GLATT Current actual value, smoothed G1_XIST1 /
MIST_GLATT Torque actual value, smoothed G1_XIST2 /
Control word for encoder 1 or encoder 2
Status word for encoder 1 or encoder 2
Position actual value 1 from encoder 1 or
Position actual value 2 from encoder 1 or
Fieldbuses
Function Manual, 04/2018, FW V4.7 SP10, A5E34229197B AE
19
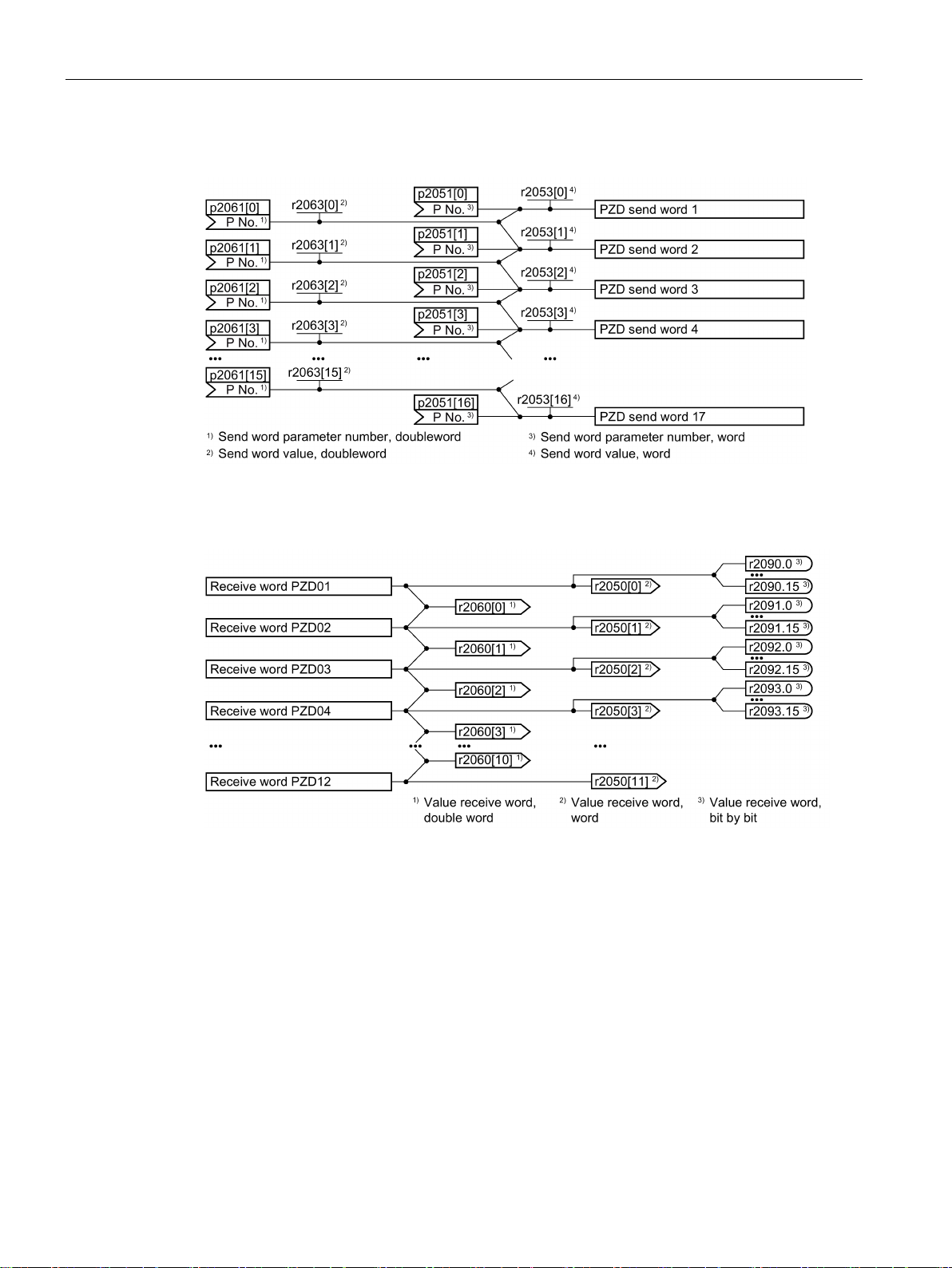
Communication via PROFIBUS and PROFINET
Interconnection of the process data
3.1 PROFIDRIVE profile - Cyclic communication
Figure 3-11 Interconnection of the send words
Figure 3-12 Interconnection of the receive words
The telegrams use - with the exception of telegram 999 (free interconnection) - the word-byword transfer of send and receive data (r2050/p2051).
If you require an individual telegram for your application (e.g. for transferring double words),
you can adapt one of the predefined telegrams using parameters p0922 and p2079. For
details, please refer to the List Manual, function diagrams 2420 and 2472.
Fieldbuses
20 Function Manual, 04/2018, FW V4.7 SP10, A5E34229197B AE

Communication via PROFIBUS and PROFINET
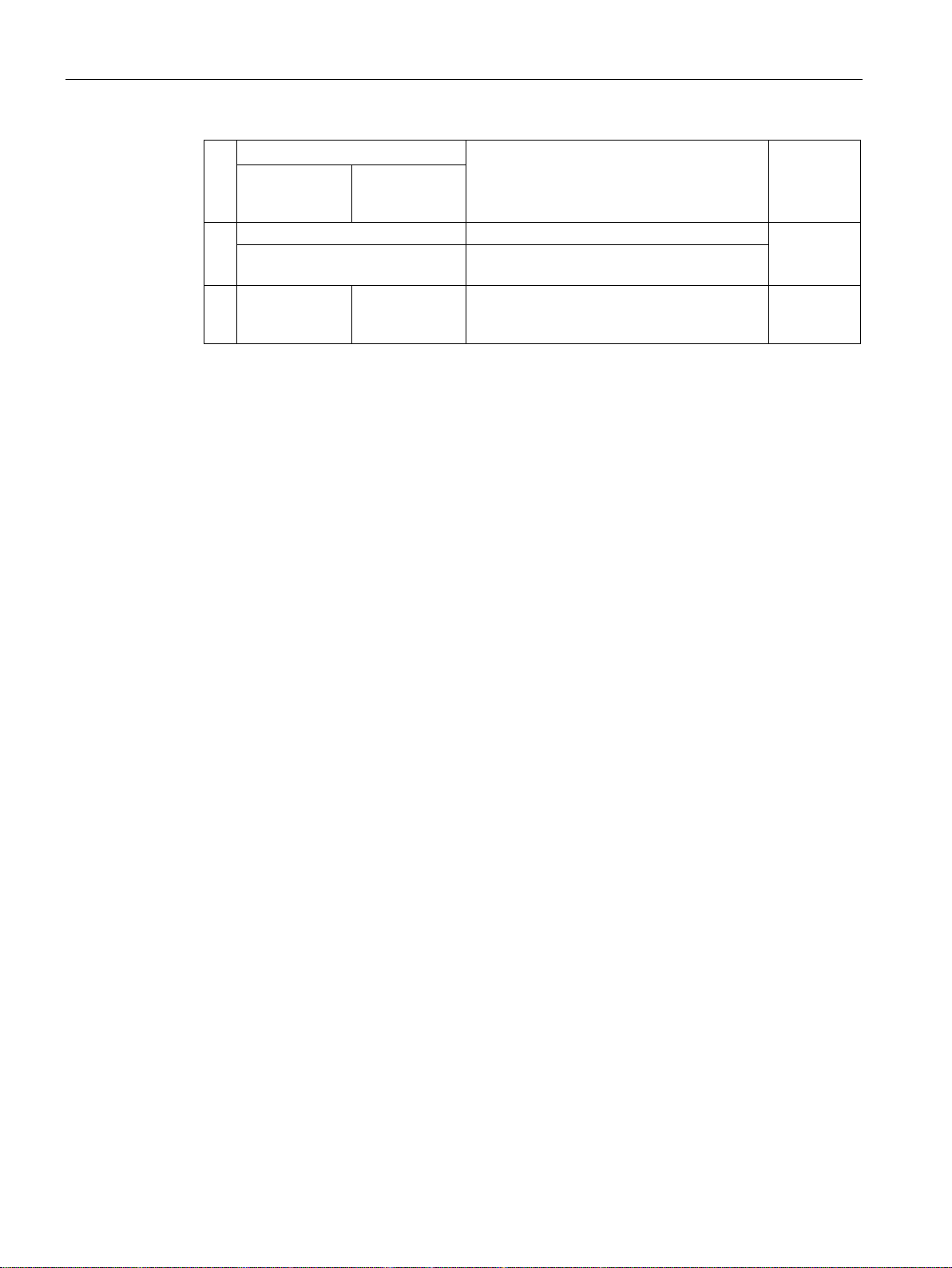
3.1.1
Assigning control and status words
3.1.1.1
Control and status word 1
3.1 PROFIDRIVE profile - Cyclic communication
Assigning control and status of words is specified in part by the definitions in the PROFIdrive
profile, Version 4.2 for the "Closed-loop speed control" operating mode; the other part is
assigned depending on the particular manufacturer.
A more detailed description of the individual control and status words is provided in the
following sections.
If you require an individual assignment for your application, you can adapt one of the existing
control and status words using p0922 and p2079.
Extend telegrams and change signal interconnection (Page 33)
Control word 1 is preassigned as follows:
● Telegrams 1, 2, 3 and 4:
– Bits 0 … 10 corresponding to the PROFIdrive profile,
– Bits 11… 15 manufacturer-specific
● Telegrams 7 and 9:
– Bits 0 … 11 corresponding to the PROFIdrive profile,
– Bits 12 … 15 manufacturer-specific
● Telegram 20 (VIK/NAMUR):
– Bits 0 … 11 corresponding to the PROFIdrive profile
– Bits 12 … 14 reserved
– Bit 15 corresponding to the PROFIdrive profile
Status word 1 is preassigned as follows:
● Telegrams 1, 2, 3 and 4:
– Bits 0 … 10 corresponding to the PROFIdrive profile,
– Bits 11… 15 manufacturer-specific
● Telegrams 7 and 9:
– Bits 0 … 13 corresponding to the PROFIdrive profile,
– Bits 14 … 15 manufacturer-specific
● Telegram 20 (VIK/NAMUR):
– Bits 0 … 11 corresponding to the PROFIdrive profile
– Bit 12 reserved
– Bits 13 … 15 corresponding to the PROFIdrive profile
Fieldbuses
Function Manual, 04/2018, FW V4.7 SP10, A5E34229197B AE
21
Communication via PROFIBUS and PROFINET
Control word 1 (STW1)
Bit
Significance
Explanation
Signal interconnection
in the inverter
Telegram 20
All other telegrams
inverter switches off the motor at standstill.
1, then the inverter switches on
the motor.
then coasts down to a standstill.
mand).
ramp-down time p1135 down to standstill.
mand).
0 = Inhibit operation
Immediately switch-off motor (cancel pulses).
1 = Enable operation
Switch-on motor (pulses can be enabled).
function generator output to 0.
1 = Do not disable RFG
The ramp-function generator can be enabled.
stops at the actual value.
follows the setpoint.
p1120 to the setpoint.
on inhibited" state.
8, 9
Reserved
fieldbus.
cess data from the fieldbus.
r2090.11
12
Not used
potentiometer.
r2090.13
3.1 PROFIDRIVE profile - Cyclic communication
0 0 = OFF1 The motor brakes with the ramp-down time
p1121 of the ramp-function generator. The
0 → 1 = ON The inverter goes into the "ready" state. If, in
addition bit 3 =
1 0 = OFF2 Switch off the motor immediately, the motor
1 = No OFF2 The motor can be switched on (ON com-
2 0 = Quick stop (OFF3) Quick stop: The motor brakes with the OFF3
1 = No quick stop (OFF3) The motor can be switched on (ON com-
3
4 0 = Disable RFG The inverter immediately sets its ramp-
5 0 = Stop RFG The output of the ramp-function generator
1 = Enable RFG The output of the ramp-function generator
p0840[0] =
r2090.0
p0844[0] =
r2090.1
p0848[0] =
r2090.2
p0852[0] =
r2090.3
p1140[0] =
r2090.4
p1141[0] =
r2090.5
6 0 = Inhibit setpoint The inverter brakes the motor with the ramp-
1 = Enable setpoint Motor accelerates with the ramp-up time
7 0 → 1 = Acknowledge faults Acknowledge fault. If the ON command is still
10 0 = No control via PLC Inverter ignores the process data from the
1 = Control via PLC Control via fieldbus, inverter accepts the pro-
11 1 = Direction reversal Invert setpoint in the inverter. p1113[0] =
13 ---1) 1 = MOP up Increase the setpoint saved in the motorized
Fieldbuses
22 Function Manual, 04/2018, FW V4.7 SP10, A5E34229197B AE
down time p1121 of the ramp-function generator.
active, the inverter switches to the "switching
p1142[0] =
r2090.6
p2103[0] =
r2090.7
p0854[0] =
r2090.10
p1035[0] =
Communication via PROFIBUS and PROFINET
Bit
Significance
Explanation
Signal interconnection
in the inverter
Telegram 20
All other telegrams
potentiometer.
r2090.14
1)
telegram is kept.
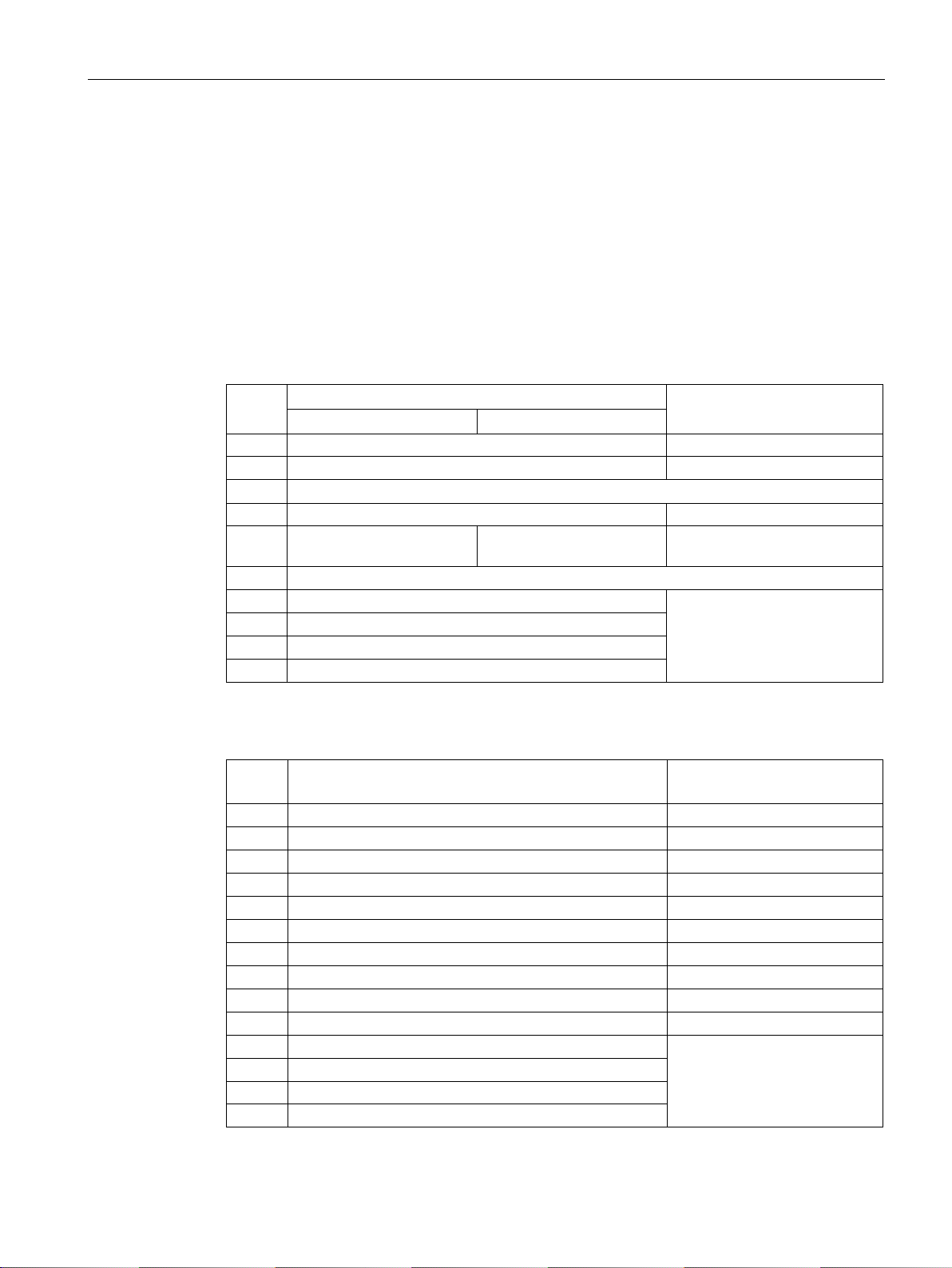
Status word 1 (ZSW1)
Bit
Significance
Remarks
Signal interconnection
in the inverter
Telegram 20
All other telegrams
ized; pulses locked.
r0899.0
motor.
bit 3.
r0899.2
using STW1.7.
r2139.3
r0899.4
r0899.5
an OFF1 followed by ON.
r0899.6
edgement is necessary.
r2139.7
tolerance range
tolerance range.
r2197.7
cept the inverter control.
r0899.9
1 = Comparison speed reached or
exceeded
sponding maximum speed.
r2199.1
reached
r1407.7
brake open
brake.
r0899.12
r2135.14
3.1 PROFIDRIVE profile - Cyclic communication
14 ---1) 1 = MOP down Reduce the setpoint saved in the motorized
15 CDS bit 0 Reserved Changes over between settings for different
If you change over from another telegram to telegram 20, then the assignment of the previous
0 1 = Ready for switching on Power supply switched on; electronics initial-
1 1 = Ready Motor is switched on (ON/OFF1 = 1), no fault
2 1 = Operation enabled Motor follows setpoint. See control word 1,
3 1 = Fault active The inverter has a fault. Acknowledge fault
operation interfaces (command data sets).
is active. With the command "Enable operation" (STW1.3), the inverter switches on the
p1036[0] =
p0810 =
r2090.15
p2080[0] =
p2080[1] =
r0899.1
p2080[2] =
p2080[3] =
4 1 = OFF2 inactive Coast down to standstill is not active. p2080[4] =
5 1 = OFF3 inactive Quick stop is not active. p2080[5] =
6 1 = Switching on inhibited active It is only possible to switch on the motor after
7 1 = Alarm active Motor remains switched on; no acknowl-
8 1 = Speed deviation within the
9 1 = Master control requested The automation system is requested to ac-
10
11 1 = current or
torque limit
12 ---1) 1 = Holding
13 0 = Alarm, motor overtemperature -- p2080[13] =
1 = torque limit
reached
Setpoint / actual value deviation within the
Speed is greater than or equal to the corre-
Comparison value for current or torque has
been reached or exceeded.
Signal to open and close a motor holding
p2080[6] =
p2080[7] =
p2080[8] =
p2080[9] =
p2080[10] =
p2080[11] =
r0056.13 /
p2080[12] =
Fieldbuses
Function Manual, 04/2018, FW V4.7 SP10, A5E34229197B AE
23
Communication via PROFIBUS and PROFINET
Bit
Significance
Remarks
Signal interconnection
in the inverter
Telegram 20
All other telegrams
1 = Motor rotates clockwise
Internal inverter actual value > 0
overload
r2135.15
1)
telegram is kept.
3.1 PROFIDRIVE profile - Cyclic communication
14
0 = Motor rotates counter-
Internal inverter actual value < 0
p2080[14] =
r2197.3
clockwise
15 1 = CDS display 0 = Alarm, in-
verter thermal
p2080[15] =
r0836.0 /
If you change over from another telegram to telegram 20, then the assignment of the previous
Fieldbuses
24 Function Manual, 04/2018, FW V4.7 SP10, A5E34229197B AE
Communication via PROFIBUS and PROFINET
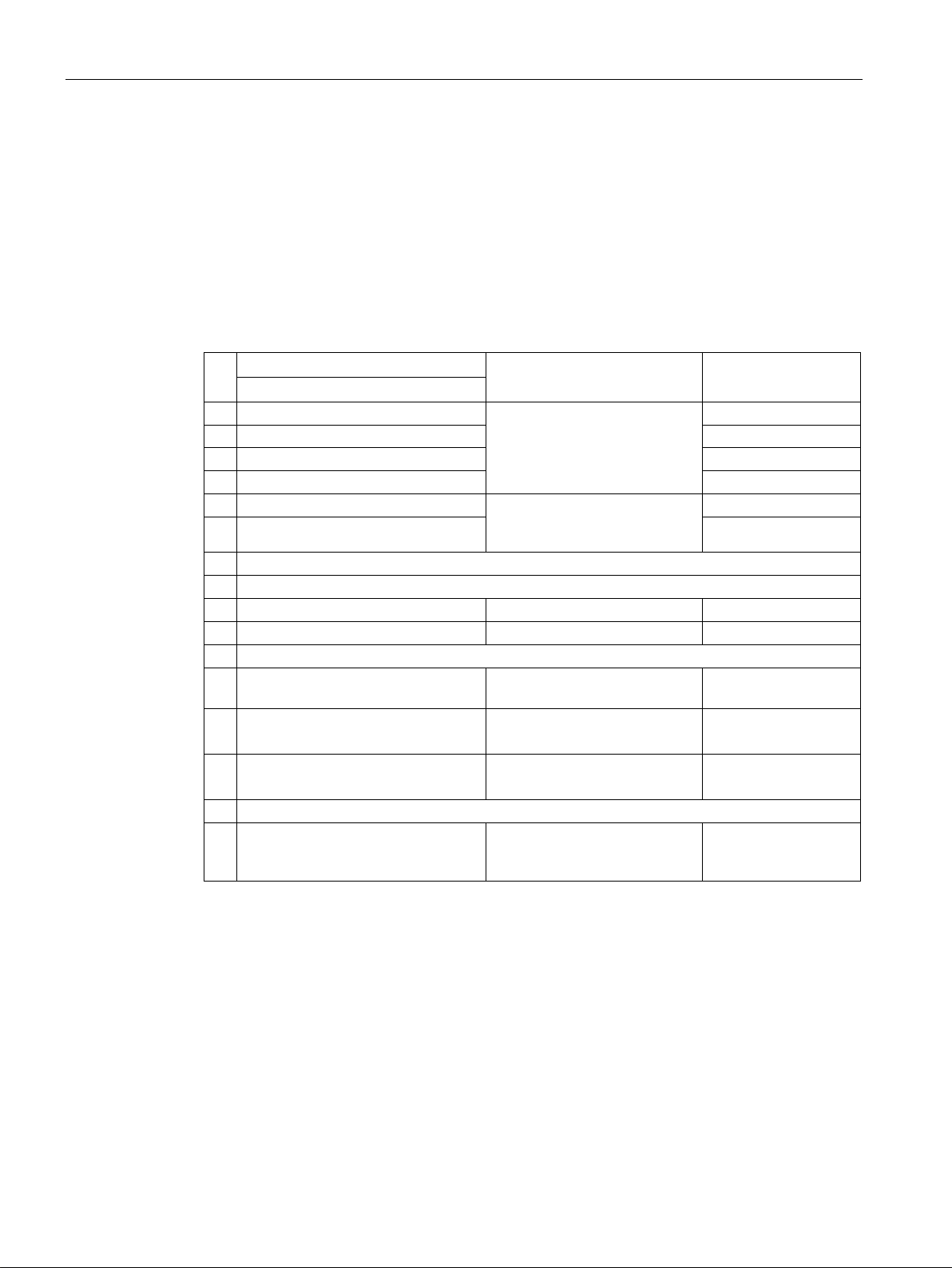
3.1.1.2
Control and status word 2
Control word 2 (STW2)
Bit
Meaning
Signal interconnection in the
inverter
Telegrams 2, 3 and 4
Telegrams 9, 110 and 111
0
1 = drive data set selection DDS bit 0
p0820[0] = r2093.0
1
1 = drive data set selection DDS bit 1
p0821[0] = r2093.1
7
1 = parking axis is selected
p0897 = r2093.7
active
9…11
Reserved
12
1 = master sign-of-life bit 0
13
1 = master sign-of-life bit 1
14
1 = master sign-of-life bit 3
15
1 = master sign-of-life bit 4
Status word 2 (ZSW2)
Bit
Meaning
Signal interconnection in the
inverter
0
1 = Drive data set DDS effective, bit 0
p2081[0] = r0051.0
1
1 = Drive data set DDS effective, bit 1
p2081[1] = r0051.1
2…4
Reserved
5
1 = Alarm class bit 0
p2081[5] = r2139.11
6
1 = alarm class bit 1
p2081[6] = r2139.12
7
Reserved
8
1 = travel to fixed stop active
p2081[8] = r1406.8
9
Reserved
10
1 = pulses enabled
p2081[10] = r0899.11
11
Reserved
12
Slave sign-of-life bit 0
14
Slave sign of life bit 2
3.1 PROFIDRIVE profile - Cyclic communication
Control word 2 is preassigned as follows:
● Bits 0 … 11 manufacturer-specific
● Bits 12 … 15 corresponding to the PROFIdrive profile
Status word 2 is preassigned as follows:
● Bits 0 … 11 manufacturer-specific
● Bits 12 … 15 corresponding to the PROFIdrive profile
2…6 Reserved
8 1 = travel to fixed stop
Reserved p1545[0] = r2093.8
p2045 = r2050[3]
13 Slave sign of life bit 1
15 Slave sign of life bit 3
Fieldbuses
Function Manual, 04/2018, FW V4.7 SP10, A5E34229197B AE
Internally interconnected
25
Communication via PROFIBUS and PROFINET
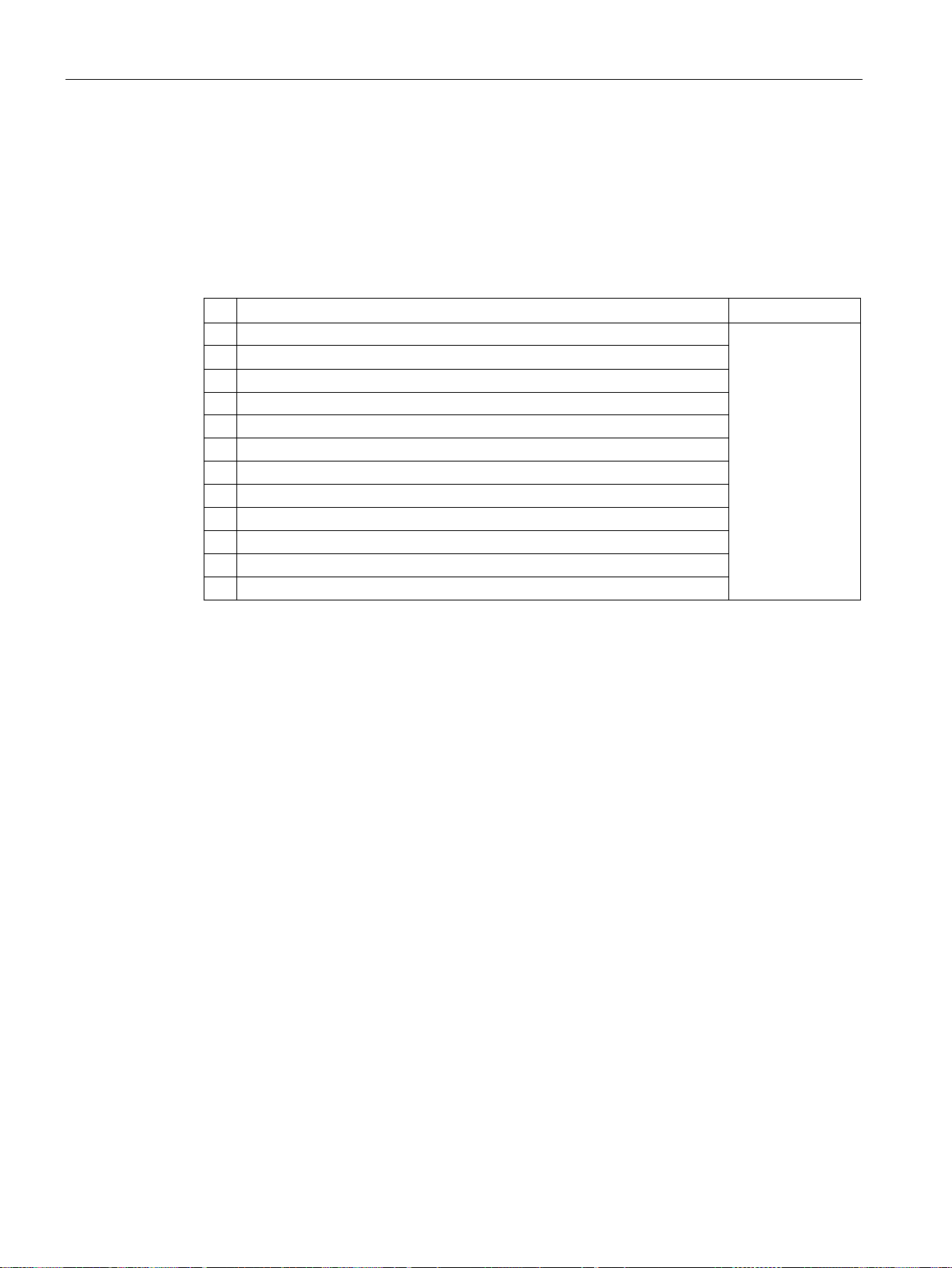
3.1.1.3
Control and status word 3
Control word 3 (STW3)
Bit
Meaning
Explanation
Signal interconnection
in the inverter 1)
Telegram 350
1
1 = fixed setpoint bit 1
p1021[0] = r2093.1
2
1 = fixed setpoint bit 2
p1022[0] = r2093.2
3
1 = fixed setpoint bit 3
p1023[0] = r2093.3
4
1 = DDS selection bit 0
sets).
p0820 = r2093.4
6
Not used
7
Not used
8
1 = technology controller enable
--
p2200[0] = r2093.8
9
1 = enable DC braking
--
p1230[0] = r2093.9
10
Not used
ler droop.
0 = speed control active
0 = external fault is active (F07860)
14
Not used
(command data sets).
1)
p1020, … to "0". Exception: p2106 = 1.
3.1 PROFIDRIVE profile - Cyclic communication
Control word 3 is preassigned as follows:
● Bits 0 … 15 manufacturer-specific
Status word 3 is preassigned as follows:
● Bits 0 … 15 manufacturer-specific
0 1 = fixed setpoint bit 0 Selects up to 16 different fixed
5 1 = DDS selection bit 1 p0821 = r2093.5
p1020[0] = r2093.0
setpoints.
Changes over between settings
for different motors (drive data
11 1 = Enable droop Enable or inhibit speed control-
12 1 = torque control active
13 1 = no external fault
15 1 = CDS bit 1 Changes over between settings
If you switch from telegram 350 to a different one, then the inverter sets all interconnections
Changes over the control mode
for vector control.
-- p2106[0] = r2093.13
for different operation interfaces
p1492[0] = r2093.11
p1501[0] = r2093.12
p0811[0] = r2093.15
Fieldbuses
26 Function Manual, 04/2018, FW V4.7 SP10, A5E34229197B AE

Communication via PROFIBUS and PROFINET
Status word 3 (ZSW3)
Bit
Meaning
Description
Signal interconnection in the
inverter
0
1 = DC braking active
--
state detection
speed
threshold value 2
threshold value 2
6
1 = |n_act | ≧ r1119
Speed setpoint reached
value
value
ed
active.
the lower limit
p2292
the upper limit
put > p2291
13
Not used
15
Not used
3.1 PROFIDRIVE profile - Cyclic communication
p2051[3] = r0053
1 1 = |n_act | > p1226 Absolute current speed > stationary
2 1 = |n_act | > p1080 Absolute actual speed > minimum
3 1 = i_act ≧ p2170 Actual current ≥ current threshold
value
4 1 = |n_act | > p2155 Absolute actual speed > speed
5 1 = |n_act | ≦ p2155 Absolute actual speed < speed
7 1 = DC link voltage ≦ p2172 Actual DC link voltage ≦ threshold
8 1 = DC link voltage > p2172 Actual DC link voltage > threshold
9 1 = ramp-up or ramp-down complet-
10 1 = technology controller output at
11 1 = technology controller output at
12 Not used
14 Not used
Ramp-function generator is not
Technology controller output ≦
Technology controller out-
Fieldbuses
Function Manual, 04/2018, FW V4.7 SP10, A5E34229197B AE
27
Communication via PROFIBUS and PROFINET
3.1.2
NAMUR message word
Fault word according to the VIK-NAMUR definition (MELD_NAMUR)
Bit
Significance
P no.
0
1 = Control Unit signals a fault
2
1 = DC link overvoltage
4
1 = inverter overtemperature
5
1 = ground fault/phase fault in the motor cable or in the motor
6
1 = motor overload
7
1 = communication error to the higher-level control system
8
1 = fault in a safety-relevant monitoring channel
10
1 = fault in the internal inverter communication
11
1 = line fault
15
1 = other fault
3.1 PROFIDRIVE profile - Cyclic communication
Table 3- 1 Fault word according to the VIK-NAMUR definition and interconnection with parameters
in the inverter
p2051[5] = r3113
1 1 = line fault: Phase failure or inadmissible voltage
3 1 = Power Module fault, e.g. overcurrent or overtemperature
Fieldbuses
28 Function Manual, 04/2018, FW V4.7 SP10, A5E34229197B AE
 Loading...
Loading...