Siemens SIMODRIVE POSMO A Function Manual

SIMOTION
Supplement to SIMODRIVE POSMO A Positioning Motor
Introduction
Fundamental safety
instructions
1
Function Manual
Description
Function blocks
Application example
Appendix
2
3
4
A
01/2015

Legal information
Warning notice system
This manual contains notices you have to observe in order to ensure your personal safety, as well as to prevent
damage to property. The notices referring to your personal safety are highlighted in the manual by a safety alert
symbol, notices referring only to property damage have no safety alert symbol. These notices shown below are
graded according to the degree of danger.
DANGER
indicates that death or severe personal injury will result if proper precautions are not taken.
WARNING
indicates that death or severe personal injury may result if proper precautions are not taken.
CAUTION
indicates that minor personal injury can result if proper precautions are not taken.
NOTICE
indicates that property damage can result if proper precautions are not taken.
If more than one degree of danger is present, the warning notice representing the highest degree of danger will be
used. A notice warning of injury to persons with a safety alert symbol may also include a warning relating to property
damage.
Qualified Personnel
The product/system described in this documentation may be operated only by personnel qualified for the specific
task in accordance with the relevant documentation, in particular its warning notices and safety instructions. Qualified
personnel are those who, based on their training and experience, are capable of identifying risks and avoiding
potential hazards when working with these products/systems.
Proper use of Siemens products
Note the following:
WARNING
Siemens products may only be used for the applications described in the catalog and in the relevant technical
documentation. If products and components from other manufacturers are used, these must be recommended or
approved by Siemens. Proper transport, storage, installation, assembly, commissioning, operation and
maintenance are required to ensure that the products operate safely and without any problems. The permissible
ambient conditions must be complied with. The information in the relevant documentation must be observed.
Trademarks
All names identified by ® are registered trademarks of Siemens AG. The remaining trademarks in this publication
may be trademarks whose use by third parties for their own purposes could violate the rights of the owner.
Disclaimer of Liability
We have reviewed the contents of this publication to ensure consistency with the hardware and software described.
Since variance cannot be precluded entirely, we cannot guarantee full consistency. However, the information in
this publication is reviewed regularly and any necessary corrections are included in subsequent editions.
Siemens AG
Division Digital Factory
Postfach 48 48
90026 NÜRNBERG
GERMANY
Ⓟ 02/2015 Subject to change
Copyright © Siemens AG 2015.
All rights reserved

Introduction
Contents of the function manual
This document is part of the SIMOTION Programming - References documentation package.
This documentation serves as a supplement to the documentation on SIMODRIVE POSMO
A in the
This documentation is included in the SIMOTION SCOUT scope of delivery as electronic
documentation!
This manual describes how you can use function blocks to control and assign parameters for
a POSMO A drive from a SIMOTION program.
This manual describes differences in handling that arise when controlling and assigning
parameters for a POSMO A drive from the SIMOTION system as compared to the SIMATIC
system.
Function block
The function blocks for communication between the SIMOTION system and the distributed
SIMODRIVE POSMO A positioning motor are part of the program library of the "SIMOTION
SCOUT" engineering system.
Distributed Positioning Motor on PROFIBUS DP
user manual.
SIMOTION Documentation
An overview of the SIMOTION documentation can be found in the SIMOTION Documentation
Overview document.
This documentation is included as electronic documentation in the scope of delivery of
SIMOTION SCOUT. It comprises ten documentation packages.
The following documentation packages are available for SIMOTION V4.4:
● SIMOTION Engineering System Handling
● SIMOTION System and Function Descriptions
● SIMOTION Service and Diagnostics
● SIMOTION IT
● SIMOTION Programming
● SIMOTION Programming - References
● SIMOTION C
● SIMOTION P
● SIMOTION D
● SIMOTION Supplementary Documentation
Supplement to SIMODRIVE POSMO A Positioning Motor
Function Manual, 01/2015 3

Introduction
Hotline and Internet addresses
Additional information
Click the following link to find information on the following topics:
● Ordering documentation / overview of documentation
● Additional links to download documents
● Using documentation online (find and search manuals/information)
http://www.siemens.com/motioncontrol/docu
My Documentation Manager
Click the following link for information on how to compile documentation individually on the
basis of Siemens content and how to adapt it for the purpose of your own machine
documentation:
http://www.siemens.com/mdm
Training
FAQs
Technical support
Click the following link for information on SITRAIN - Siemens training courses for automation
products, systems and solutions:
http://www.siemens.com/sitrain
Frequently Asked Questions can be found in SIMOTION Utilities & Applications, which are
included in the scope of delivery of SIMOTION SCOUT, and in the Service&Support pages
in Product Support:
http://support.automation.siemens.com
Country-specific telephone numbers for technical support are provided on the Internet under
Contact:
http://www.siemens.com/automation/service&support
Supplement to SIMODRIVE POSMO A Positioning Motor
4 Function Manual, 01/2015

Table of contents
Introduction...................................................................................................................................................3
1 Fundamental safety instructions...................................................................................................................7
1.1 General safety instructions.......................................................................................................7
1.2 Industrial security.....................................................................................................................7
2 Description....................................................................................................................................................9
2.1 General....................................................................................................................................9
2.2 Installation and startup...........................................................................................................11
2.3 Inserting a SIMODRIVE POSMO A positioning motor into a SIMOTION project...................12
2.4 Integrating the function blocks in the user project..................................................................13
2.5 Creating I/O Variables............................................................................................................14
3 Function blocks...........................................................................................................................................17
3.1 Overview of function blocks...................................................................................................17
3.2 Function block _POSMOA_control.........................................................................................17
3.3 Function block _POSMOA_nControl......................................................................................24
3.4 Function block _POSMOA_rwParameter...............................................................................29
3.5 Function block _POSMOA_rwAllParameter...........................................................................32
3.6 Calling function blocks...........................................................................................................38
4 Application example...................................................................................................................................41
4.1 General information on the application example....................................................................41
4.2 Operator control and monitoring of the application example in the detail view......................43
4.3 Variables used in application example...................................................................................47
A Appendix.....................................................................................................................................................51
A.1 SIMOTION and SIMATIC names...........................................................................................51
A.2 List of abbreviations...............................................................................................................55
Index...........................................................................................................................................................57
Supplement to SIMODRIVE POSMO A Positioning Motor
Function Manual, 01/2015 5

Table of contents
Supplement to SIMODRIVE POSMO A Positioning Motor
6 Function Manual, 01/2015
Fundamental safety instructions
1.1 General safety instructions
WARNING
Risk of death if the safety instructions and remaining risks are not carefully observed
If the safety instructions and residual risks are not observed in the associated hardware
documentation, accidents involving severe injuries or death can occur.
● Observe the safety instructions given in the hardware documentation.
● Consider the residual risks for the risk evaluation.
WARNING
Danger to life or malfunctions of the machine as a result of incorrect or changed
parameterization
As a result of incorrect or changed parameterization, machines can malfunction, which in turn
can lead to injuries or death.
● Protect the parameterization (parameter assignments) against unauthorized access.
● Respond to possible malfunctions by applying suitable measures (e.g. EMERGENCY
STOP or EMERGENCY OFF).
1
1.2 Industrial security
Note
Industrial security
Siemens provides products and solutions with industrial security functions that support the
secure operation of plants, solutions, machines, equipment and/or networks. They are
important components in a holistic industrial security concept. With this in mind, Siemens’
products and solutions undergo continuous development. Siemens recommends strongly that
you regularly check for product updates.
For the secure operation of Siemens products and solutions, it is necessary to take suitable
preventive action (e.g. cell protection concept) and integrate each component into a holistic,
state-of-the-art industrial security concept. Third-party products that may be in use should also
be considered. For more information about industrial security, visit http://www.siemens.com/
industrialsecurity.
To stay informed about product updates as they occur, sign up for a product-specific
newsletter. For more information, visit http://support.automation.siemens.com
Supplement to SIMODRIVE POSMO A Positioning Motor
Function Manual, 01/2015 7

Fundamental safety instructions
1.2 Industrial security
WARNING
Danger as a result of unsafe operating states resulting from software manipulation
Software manipulation (e.g. by viruses, Trojan horses, malware, worms) can cause unsafe
operating states to develop in your installation which can lead to death, severe injuries and/
or material damage.
● Keep the software up to date.
Information and newsletters can be found at:
http://support.automation.siemens.com
● Incorporate the automation and drive components into a state-of-the-art, integrated
industrial security concept for the installation or machine.
For more detailed information, go to:
http://www.siemens.com/industrialsecurity
● Make sure that you include all installed products into the integrated industrial security
concept.
Supplement to SIMODRIVE POSMO A Positioning Motor
8 Function Manual, 01/2015

Description
2.1 General
Overview
SIMODRIVE POSMO A is an intelligent distributed positioning drive on the PROFIBUS DP
field bus (DP standard slave).
The power unit and all of the motion control are located in the motor.
All of the signals and data for commissioning and operating the drive are transferred via the
PROFIBUS DP.
The operating energy is supplied by a 24 VDC connection (for a 75 W motor) or a 48 VDC
connection (for a 300 W motor).
The integrated positioning functionality is suitable for a variety of simple single-axis
applications, such as adjusting endstops and formats.
Note
Hardware and software requirements
The following requirements apply for the functionalities described in this manual:
● Hardware release POSMO A 75 W: As of O
● Software release POSMO A 75 W: As of V3.0
● Hardware release POSMO A 300 W: As of G
● Software release POSMO A 300 W: As of V3.0
2
POSMO A positioning motors with different hardware and software requirements can be
controlled with function blocks integrated in SIMOTION SCOUT V4.1. The functionality is
restricted by the hardware/software release of the POSMO A positioning motor used.
Requirement
The following software versions are required for the standard functions described in this
documentation:
● SIMOTION SCOUT V4.1 or higher
● SIMOTION Kernel V4.1 or higher
● SIMOTION technology packages V4.1 or higher
Communication
The PROFIBUS DP field bus allows rapid cyclical data exchange between the DP slave
(POSMO A) and the higher-level DP master (SIMOTION hardware platform, such as
SIMOTION C2xx).
Supplement to SIMODRIVE POSMO A Positioning Motor
Function Manual, 01/2015 9
Description
2.1 General
Further information
Note
For more information, refer to the "Product brief" section of the
on PROFIBUS DP
This documentation is included in the SIMOTION SCOUT scope of delivery as electronic
documentation!
Installation and connection
For a description of how to install and connect a SIMODRIVE POSMO A and points you must
be aware of when doing so, refer to the "Installation and connection" section of the
Positioning Motor on PROFIBUS DP
On the SIMOTION device (hardware platform), connect SIMODRIVE POSMO A to one of the
PROFIBUS DP interfaces.
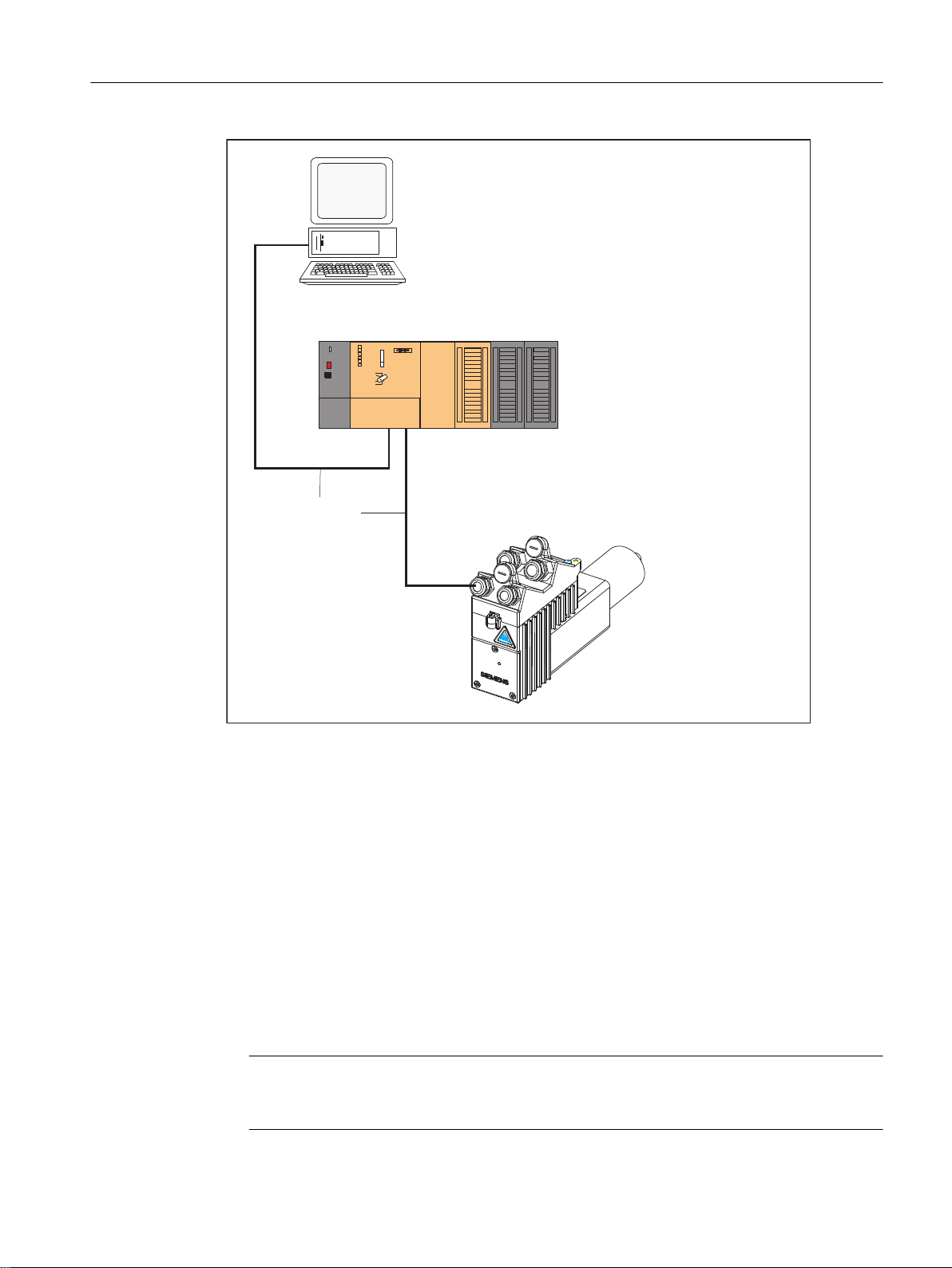
The following figure shows how to connect a SIMODRIVE POSMO A drive to a SIMOTION
hardware platform (such as SIMOTION C2xx).
Distributed Positioning Motor
user manual.
Distributed
user manual.
Supplement to SIMODRIVE POSMO A Positioning Motor
10 Function Manual, 01/2015
6,027,21
+DUGZDUHSODWIRUP
VXFKDV&[[
352),%86'3
&[[
60V36
3RVLWLRQLQJ0RWRU
:
3*3&
Description
2.2 Installation and startup
2.2 Installation and startup
Overview
Supplement to SIMODRIVE POSMO A Positioning Motor
Function Manual, 01/2015 11
Figure 2-1 Connection of SIMODRIVE POSMO A to the SIMOTION C2xx hardware platform
You must perform the following steps to commission the SIMODRIVE POSMO A and control
it from the SIMOTION system:
1. Mount and wire the SIMODRIVE POSMO A positioning motor.
2. Set the PROFIBUS DP node address on the connection cover of the SIMODRIVE
POSMO A.
3. Switch on the terminating resistor at the first and last bus node.
Note
For steps 1 to 3, refer to
Motor on PROFIBUS DP
Section "Installation and Connection"
user manual.
of the
Distributed Positioning

Description
2.3 Inserting a SIMODRIVE POSMO A positioning motor into a SIMOTION project
4. You can use any of the following to commission the SIMODRIVE POSMO A:
– C1 master "SIMODRIVE POSMO A PROFIBUS MASTER"
– Commissioning tool "SimoCom A"
Note
Refer to the
Distributed Positioning Motor on PROFIBUS DP
user manual,
Section
"Commissioning of DP Master".
– "Drive ES" tool. This tool includes "SimoCom A"
Note
Refer to the
5. Insert the SIMODRIVE POSMO A into the SIMOTION project (refer to Section Inserting a
SIMODRIVE POSMO A positioning motor into a SIMOTION project (Page 12)).
6. Control the SIMODRIVE POSMO A from the SIMOTION system using function blocks, see
Section Function blocks (Page 17).
Note
Refer to the
information on the following topics:
● Axis commissioning
● Communication via PROFIBUS DP
● Description of functions
● Error handling and diagnostics
● Assembly and service
Drive ES Basic
Distributed Positioning Motor on PROFIBUS DP
function description.
user manual for more
2.3 Inserting a SIMODRIVE POSMO A positioning motor into a
SIMOTION project
Requirement
The following requirements must be met:
1. You have created a project in SIMOTION SCOUT and have inserted a rack with a
SIMOTION hardware platform in the hardware configuration.
2. You have configured a PROFIBUS subnet.
Note
For information on creating a project and configuring a PROFIBUS subnet, refer to the
online help for SIMOTION SCOUT.
Supplement to SIMODRIVE POSMO A Positioning Motor
12 Function Manual, 01/2015

Inserting SIMODRIVE POSMO A
To integrate the SIMODRIVE POSMO A into the PROFIBUS subnet of your project, proceed
as follows:
1. In SIMOTION SCOUT, open the User Projects dialog box with the Project > Open menu
command. In this dialog box, select your project and confirm your choice with OK.
2. Open HW Config (by double-clicking the SIMOTION device in the project navigator of
SIMOTION SCOUT).
3. In the HW Config window, open the hardware catalog with the View > Catalog menu
command.
4. In the hardware catalog, open the PROFIBUS DP folder and the SIMODRIVE subfolder
and select SIMODRIVE POSMO A.
5. Use a drag-and-drop operation to move the SIMODRIVE POSMO A onto the PROFIBUS
subnet of your project.
The Properties - PROFIBUS Interface SIMODRIVE POSMO A dialog box is displayed. In
this dialog box, you select the address you set in the connection cover of POSMO A (see
Section "Installation and Connection" of the Distributed Positioning Motor on PROFIBUS
DP
user manual) and confirm with OK.
The SIMODRIVE POSMO A positioning motor you have selected is inserted into the project.
Description
2.4 Integrating the function blocks in the user project
6. Input and output addresses of the POSMO A.
When you insert the POSMO A into your SIMOTION project, the input and output addresses
are assigned default values. You can see these values when you select the inserted
POSMO A. You can read the input and output addresses in the lower part of the HW
Config window.
You must create these addresses as I/O variables in the symbol browser before calling the
function blocks; see Section Creating I/O Variables (Page 14).
2.4 Integrating the function blocks in the user project
Creating the instance of the FBs in the user project
The function blocks are part of the program library of the SIMOTION SCOUT engineering
system. For working with the blocks, an instance has to be created in the user project for each
function block used and if using the _POSMOA_rwAllParameter function block, a variable of
type Struct_POSMOA_params.
Example:
VAR_GLOBAL
...
myPosmoAControl : _POSMOA_control; // FB for controlling of POSMO A
myPosmoArwParameter : _POSMOA_rwParameter; // FB for handling single parameter
myPosmoArwAllParameter : _POSMOA_rwAllParameter; // FB for handling parameterset
myAllParaPosmoA : Struct_POSMOA_params; // Variable for structure of all
// parameters POSMO A
Supplement to SIMODRIVE POSMO A Positioning Motor
Function Manual, 01/2015 13

Description
2.5 Creating I/O Variables
...
END_VAR
Call (LAD representation)
The LAD representation of the individual function blocks can be found in the respective function
block descriptions.
Example of an application
The application example is contained on the "SIMOTION Utilities & Applications" CD-ROM
and is available for various SIMOTION hardware platforms.
The "SIMOTION Utilities & Applications" CD-ROM is provided free of charge and part of the
SIMOTION SCOUT scope of delivery.
2.5 Creating I/O Variables
Overview
Communication between the SIMOTION hardware platform and the SIMODRIVE POSMO A
takes place through direct access to the I/O. I/O variables are used to address the direct read/
write access to the I/O.
You can freely assign the names of I/O variables in SIMOTION SCOUT. You must define the
I/O variables as ARRAY [0..7] and [0..3] of BYTE. You assign the address settings in the
hardware configuration to these I/O variables.
The names of the I/O inputs must be transferred to the function blocks as call parameters. The
prepared data for the I/O outputs are provided by the function block as in/out parameters. The
in/out parameters must be be supplied with variables of type ARRAY [0..7] of BYTE and [0..3]
of BYTE. Once the block has been called, these variables must be assigned to the I/O variables
for the I/O outputs; see call example in Section Calling function blocks (Page 38).
Note
The variable for supplying the in/out parameters must not be created as a temporary variable
(VAR_TEMP or local variable of a function).
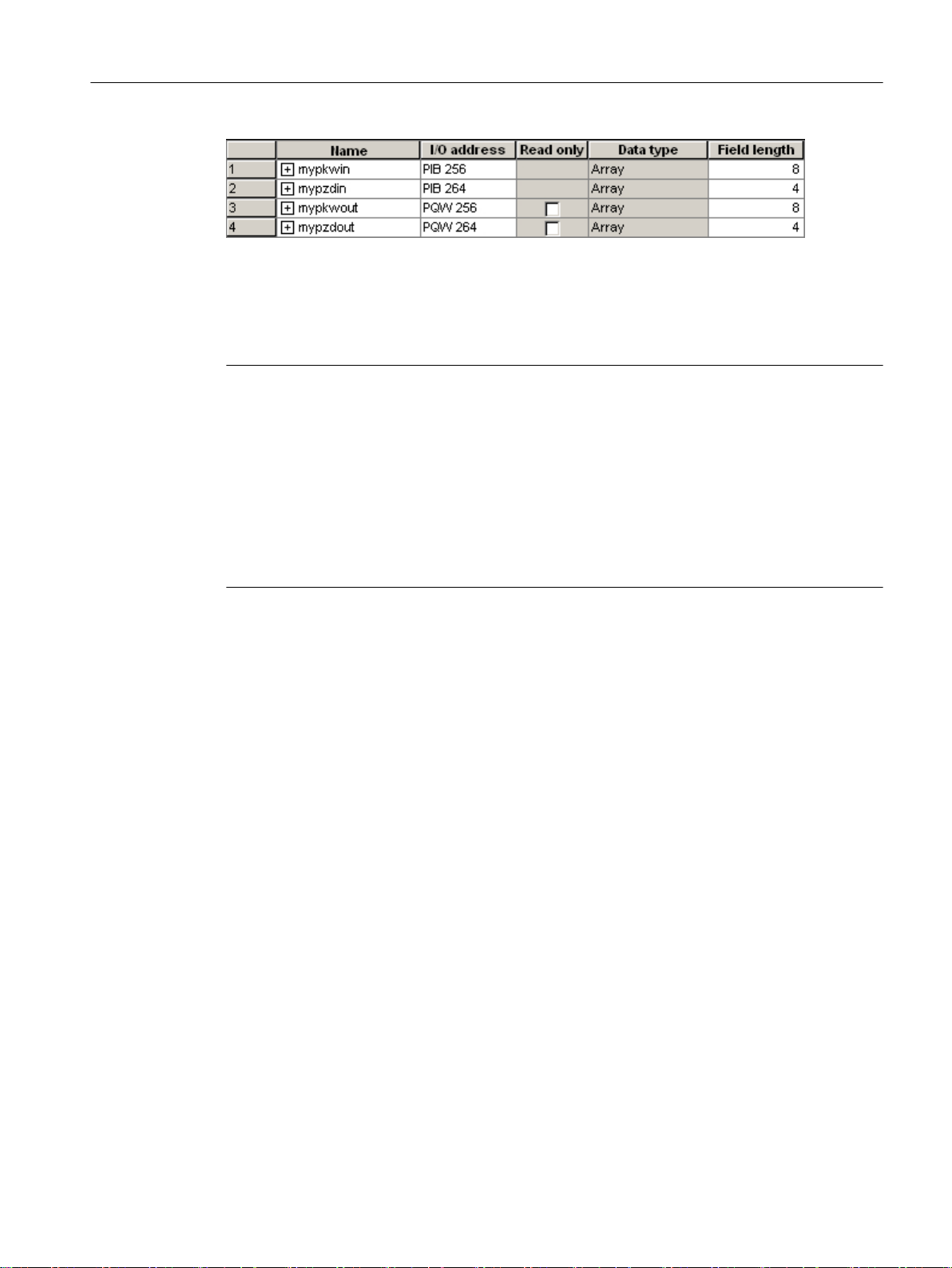
The following example shows how to assign the module addresses to the I/O variables in
SIMOTION SCOUT.
Supplement to SIMODRIVE POSMO A Positioning Motor
14 Function Manual, 01/2015
Description
2.5 Creating I/O Variables
Figure 2-2 Address assignment in SIMOTION SCOUT
Each input and output address has a range of 8 bytes (which corresponds to the parameter
identifier value (PKW) range of POSMO A) and a range of 4 bytes (which corresponds to the
process data (PZD) range of POSMO A).
Note
For additional information, refer to:
●
SIMOTION SCOUT
online help
● Programming Manual of the corresponding programming language, e.g.:
–
SIMOTION ST, Structured Text
–
SIMOTION MCC, Motion Control Chart Programming Manual
–
SIMOTION LAD/FBD, Ladder Diagram and Function Block Diagram Programming
Programming Manual
Manual
These documents are shipped with SIMOTION SCOUT in electronic form!
Supplement to SIMODRIVE POSMO A Positioning Motor
Function Manual, 01/2015 15

Description
2.5 Creating I/O Variables
Supplement to SIMODRIVE POSMO A Positioning Motor
16 Function Manual, 01/2015

Function blocks
3.1 Overview of function blocks
This section contains a description of all of the function blocks (FBs) and the data structure
you need for communication between a SIMOTION hardware platform and the SIMODRIVE
POSMO A.
The function blocks form the software interface between the SIMOTION system and the
SIMODRIVE POSMO A positioning motor.
These function blocks make it easier to control and assign parameters for a SIMODRIVE
POSMO A positioning motor from the SIMOTION program.
For example, you can assign parameters for a POSMO A without being familiar with
PROFIBUS parameter formats and request specifiers.
The function blocks must be called repeatedly (in cycles) from the user program.
The following function blocks are available:
● Function block _POSMOA_control (Page 17)
● Function block _POSMOA_nControl (Page 24) (V4.1 and higher):
● Function block _POSMOA_rwParameter (Page 29)
3
● Function block _POSMOA_rwAllParameter (Page 32)
Note
For the complete control and communication of the SIMODRIVE POSMO A from the
SIMOTION program, an instance must be created for each _POSMOA_rwParameter and
_POSMOA_rwAllParameter function block and, depending on the parameterized operating
mode (speed or position control mode), an instance of the _POSMOA_control or
_POSMOA_nControl function block.
Note
If the SIMODRIVE POSMO A is disconnected and then reconnected to the power system, any
MDI traversing block data (see the table titled "Parameters of the _POSMOA_control function
block") that had been transferred previously must be transferred to the POSMO A again.
3.2 Function block _POSMOA_control
Task
You can control the connected SIMODRIVE POSMO A with the _POSMOA_control function
block.
Supplement to SIMODRIVE POSMO A Positioning Motor
Function Manual, 01/2015 17

Function blocks
3.2 Function block _POSMOA_control
The functions are as follows:
● Initialize
Sets the drive in "ready to operate" mode.
Requirements:
– A drive fault has not been signaled (driveError = FALSE)
– Fault acknowledgement is not active (resetError = FALSE)
● Referencing
Sets the home position for the drive.
● Tippen
The drive travels at a controlled speed in a plus or minus direction.
● Program execution
Starts, stops, or aborts a single block addressed by blockNumber or a block within the
program.
● MDI
The drive travels at the assigned speed and acceleration to an assigned position.
The MDI parameters are transferred in block 3.
The MDI block can be started with blockNumber = 3 and start = TRUE.
● Fault acknowledgement
Acknowledges a fault in the drive.
Note
A fault must be acknowledged before the drive can move. This requires that parameter
enable = TRUE.
● Automatic single-block operation/automatic control
Checkback signals are as follows:
● Current traversing block
● Data Set Ready
● Warning and fault information
● Complete status (status word and checkback signal byte)
● Data transfer status
Supplement to SIMODRIVE POSMO A Positioning Motor
18 Function Manual, 01/2015
 Loading...
Loading...