Siemens SIMATIC CPU 410, SIMATIC 410 SMART, SIMATIC PCS 7 System Manual

___________________
___________
___________
___________________
___________
___________________
___________________
___________________
___________
___________________
___________________
___________________
___________________
___________________
___________________
___________________
___________________
___________________
___________________
___________________
___________________
SIMATIC
PCS 7 process control system
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU
410 SMART
System Manual
05/2017
A5E31622160
Preface
1
Introduction to the CPU 410
2
Configuration of the CPU
410
3
PROFIBUS DP
4
PROFINET IO
5
I/O configuration variants
6
System and operating states
of the CPU 410
7
Link-up and update
8
Special functions of the CPU
410
9
Time synchronization and
time stamping
10
Plant changes in RUN - CiR
11
Plant changes during
redundant operation - H-CiR
12
Replacement of failed
components during
redundant operation
13
Synchronization modules
14
System expansion card
15
Technical data
16
Properties and technical
specifications of CPU 410
SMART
17
Supplementary information
18
Characteristic values of
redundant automation
systems
A
Function and communication
modules that can be used in
a redundant configuration
B
Connection examples for
redundant I/Os
C
-AC

Siemens AG
Division Process Industries
Postfach 48 48
90026 NÜRNBERG
GERMANY
A5E31622160-AC
Ⓟ
Copyright © Siemens AG 2017.
All rights reserved
Legal information
Warning notice system
DANGER
indicates that death or severe personal injury will result if proper precautions are not taken.
WARNING
indicates that death or severe personal injury may result if proper precautions are not taken.
CAUTION
indicates that minor personal injury can result if proper precautions are not taken.
NOTICE
indicates that property damage can result if proper precautions are not taken.
Qualified Personnel
personnel qualified
Proper use of Siemens products
WARNING
Siemens products may only be used for the applications described in the catalog and in the relevant technical
maintenance are required to ensure that the products operate safely and without any problems. The permissible
ambient conditions must be complied with. The information in the relevant documentation must be observed.
Trademarks
Disclaimer of Liability
This manual contains notices you have to observe in order to ensure your personal safety, as well as to prevent
damage to property. The notices referring to your personal safety are highlighted in the manual by a safety alert
symbol, notices referring only to property damage have no safety alert symbol. These notices shown below are
graded according to the degree of danger.
If more than one degree of danger is present, the warning notice representing the highest degree of danger will
be used. A notice warning of injury to persons with a safety alert symbol may also include a warning relating to
property damage.
The product/system described in this documentation may be operated only by
task in accordance with the relevant documentation, in particular its warning notices and safety instructions.
Qualified personnel are those who, based on their training and experience, are capable of identifying risks and
avoiding potential hazards when working with these products/systems.
Note the following:
documentation. If products and components from other manufacturers are used, these must be recommended
or approved by Siemens. Proper transport, storage, installation, assembly, commissioning, operation and
All names identified by ® are registered trademarks of Siemens AG. The remaining trademarks in this publication
may be trademarks whose use by third parties for their own purposes could violate the rights of the owner.
We have reviewed the contents of this publication to ensure consistency with the hardware and software
described. Since variance cannot be precluded entirely, we cannot guarantee full consistency. However, the
information in this publication is reviewed regularly and any necessary corrections are included in subsequent
editions.
for the specific
and Drives
06/2017 Subject to change

Table of contents
1 Preface ................................................................................................................................................. 17
2 Introduction to the CPU 410 .................................................................................................................. 23
3 Configuration of the CPU 410 ................................................................................................................ 35
4 PROFIBUS DP ..................................................................................................................................... 49
5 PROFINET IO ....................................................................................................................................... 51
6 I/O configuration variants ...................................................................................................................... 55
1.1 Preface .................................................................................................................................... 17
1.2 Security information ................................................................................................................ 20
1.3 Documentation ........................................................................................................................ 21
2.1 Area of application of the CPU 410 in SIMATIC PCS 7 ......................................................... 23
2.2 Possible applications .............................................................................................................. 25
2.3 The CPU 410 basic system for stand-alone operation ........................................................... 27
2.4 The basic system for redundant operation ............................................................................. 28
2.5 Rules for H station assembly .................................................................................................. 30
2.6 I/O for the CPU 410 ................................................................................................................ 30
2.7 I/O configuration variants of the fault-tolerant system ............................................................ 31
2.8 Configuration tools (STEP 7 HW Config, SIMATIC PCS 7) ................................................... 31
2.9 The SIMATIC PCS 7 project ................................................................................................... 31
2.9.1 Scaling and licensing (scaling concept) .................................................................................. 32
3.1 Operator controls and indicators on the CPU 410 .................................................................. 35
3.2 CPU 410 monitoring functions ................................................................................................ 39
3.3 Status and error displays ........................................................................................................ 41
3.4 PROFIBUS DP interface (X1) ................................................................................................. 45
3.5 PROFINET IO interfaces (X5, X8) .......................................................................................... 45
3.6 Summary of parameters for CPU 410 .................................................................................... 48
4.1 CPU 410 as PROFIBUS DP master ....................................................................................... 49
4.2 Diagnostics of the CPU 410 as PROFIBUS DP master ......................................................... 49
5.1 Introduction ............................................................................................................................. 51
5.2 PROFINET IO systems ........................................................................................................... 52
5.3 Device replacement without exchangeable medium / ES ...................................................... 53
6.1 Stand-alone operation............................................................................................................. 55
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC
3

Table of contents
7 System and operating states of the CPU 410 ....................................................................................... 101
8 Link-up and update .............................................................................................................................. 119
6.2 Fail-safe operation ................................................................................................................. 58
6.3 Fault-tolerant automation systems (redundancy operation) .................................................. 61
6.3.1 Redundant SIMATIC automation systems ............................................................................. 61
6.3.2 Increase of plant availability, reaction to errors ..................................................................... 62
6.4 Introduction to the I/O link to fault-tolerant system ................................................................ 65
6.5 Using single-channel switched I/O ......................................................................................... 66
6.6 Versions of I/O connection to the PROFINET IO interface .................................................... 73
6.6.1 Use of I/O connected to the PROFINET IO interface, system redundancy ........................... 73
6.6.2 Redundant I/O in an ET 200SP HA ....................................................................................... 76
6.7 Connection of two-channel I/O to the PROFIBUS DP interface ............................................ 80
6.7.1 Connecting redundant I/O ...................................................................................................... 80
6.7.2 Signal modules for redundancy ............................................................................................. 83
6.7.3 Evaluating the passivation status ........................................................................................... 97
6.8 Media redundancy ................................................................................................................. 97
7.1 CPU 410 operating modes ................................................................................................... 101
7.1.1 RUN mode ........................................................................................................................... 101
7.1.2 STOP mode ......................................................................................................................... 102
7.1.3 STARTUP mode .................................................................................................................. 103
7.1.4 HOLD mode ......................................................................................................................... 104
7.1.5 LINK-UP and UPDATE modes ............................................................................................ 105
7.1.6 ERROR-SEARCH mode ...................................................................................................... 105
7.1.7 DEFECTIVE state ................................................................................................................ 106
7.2 System states of the redundant CPU 410 ........................................................................... 107
7.2.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................... 107
7.2.2 The system states of the fault-tolerant system .................................................................... 109
7.2.3 Displaying and changing the system state of a fault-tolerant system .................................. 110
7.2.4 System status change from the STOP system state ........................................................... 110
7.2.5 System status change from the standalone mode system status ....................................... 111
7.2.6 System status change from the redundant system state ..................................................... 111
7.2.7 System diagnostics of a fault-tolerant system ..................................................................... 112
7.3 Self-test ................................................................................................................................ 114
7.4 Performing a memory reset ................................................................................................. 117
8.1 Effects of link-up and updating ............................................................................................. 119
8.2 Link-up and update via an ES command ............................................................................. 120
8.3 Time monitoring ................................................................................................................... 120
8.3.1 Time response ..................................................................................................................... 123
8.3.2 Determining the monitoring times ........................................................................................ 123
8.3.3 Performance values for link-up and update ......................................................................... 130
8.3.4 Influences on time response ................................................................................................ 130
8.4 Special features in link-up and update operations ............................................................... 131
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
4 System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC

Table of contents
9 Special functions of the CPU 410 ........................................................................................................ 133
10 Time synchronization and time stamping ............................................................................................. 151
11 Plant changes in RUN - CiR ................................................................................................................ 155
9.1 Security functions of the CPU 410 ........................................................................................ 133
9.2 Security levels ....................................................................................................................... 134
9.3 Security event logging........................................................................................................... 136
9.4 Field Interface Security ......................................................................................................... 139
9.5 Access-protected blocks ....................................................................................................... 139
9.6 Retentive load memory ......................................................................................................... 140
9.7 Type update with interface change in RUN .......................................................................... 141
9.8 Resetting the CPU 410 to delivery condition (reset to factory setting) ................................. 142
9.9 Reset during operation.......................................................................................................... 143
9.10 Response to fault detection .................................................................................................. 144
9.11 Reading service data ............................................................................................................ 145
9.12 Updating firmware in stand-alone operation ......................................................................... 146
9.13 Updating firmware in redundant mode.................................................................................. 148
11.1 Motivation for CiR via PROFINET IO .................................................................................... 155
11.2 Permitted changes over PROFINET IO ................................................................................ 157
11.3 Procedure for PROFINET IO ................................................................................................ 158
11.3.1 Overview ............................................................................................................................... 158
11.3.2 Add IO devices or I/O modules ............................................................................................. 159
11.3.3 Rebuild hardware when adding an IO device ....................................................................... 160
11.3.4 Change process image partition assignment ....................................................................... 160
11.3.5 Re-configuring existing I/O modules in IO devices ............................................................... 161
11.3.6 Replacing IO devices or I/O modules ................................................................................... 161
11.4 Re-configuring I/O modules and ports in IO devices ............................................................ 161
11.4.1 Requirements for Reconfiguration ........................................................................................ 161
11.4.2 I/O module response to re-configuration .............................................................................. 162
11.4.3 CPU response during reconfiguration ................................................................................... 162
11.4.4 Reconfiguration Procedure ................................................................................................... 164
11.4.4.1 Using a Previously Unused Channel .................................................................................... 164
11.4.4.2 Reconfiguring an already used channel. .............................................................................. 164
11.4.4.3 Delete an already used channel. .......................................................................................... 166
11.4.4.4 Change the update time ....................................................................................................... 166
11.5 Motivation for CiR via PROFINET DP .................................................................................. 166
11.6 Permitted changes over PROFIBUS DP .............................................................................. 168
11.7 CiR objects and CiR modules for PROFINET DP ................................................................ 170
11.7.1 Basic Requirements .............................................................................................................. 170
11.7.2 Types of CiR Elements ......................................................................................................... 170
11.7.3 CiR Elements and I/O Address Areas .................................................................................. 171
11.8 Procedure for PROFIBUS DP ............................................................................................... 172
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC
5

Table of contents
12 Plant changes during redundant operation - H-CiR ............................................................................... 197
11.8.1 Basic Procedures in STOP Mode ........................................................................................ 172
11.8.1.1 Overview .............................................................................................................................. 172
11.8.1.2 Defining CiR Elements ......................................................................................................... 174
11.8.1.3 Deleting CiR Elements ......................................................................................................... 176
11.8.2 Basic Procedure in RUN Mode ............................................................................................ 177
11.8.2.1 Overview .............................................................................................................................. 177
11.8.2.2 add slaves or modules ......................................................................................................... 178
11.8.2.3 Reconfigure the hardware when adding a slave .................................................................. 179
11.8.2.4 change process image partition assignment ....................................................................... 179
11.8.2.5 reconfigure existing modules in ET200M / ET200iSP stations ............................................ 179
11.8.2.6 Undo previous changes (Undo function): ............................................................................ 180
11.8.2.7 Replacing Slaves or Modules .............................................................................................. 180
11.8.2.8 Using CiR Elements in RUN Mode ...................................................................................... 181
11.8.2.9 Undoing Previous Changes ................................................................................................. 184
11.9 Reconfigure existing modules in ET200M / ET200iSP stations .......................................... 185
11.9.1 Requirements for Reconfiguration ....................................................................................... 185
11.9.2 Module Response During a Reconfiguration ....................................................................... 186
11.9.3 CPU response during reconfiguration .................................................................................. 186
11.9.4 Reconfiguration Procedure .................................................................................................. 188
11.9.4.1 Using a Previously Unused Channel ................................................................................... 188
11.9.4.2 Reconfiguring an already used channel. ............................................................................. 188
11.9.4.3 Delete an already used channel. ......................................................................................... 189
11.10 Notes on Reconfiguration in RUN Mode Depending on the I/O .......................................... 190
11.10.1 Modules in IO devices of the type ET 200SP HA ................................................................ 190
11.10.2 DP and PA Slaves ............................................................................................................... 190
11.10.3 Modules in ET 200M Modular Slaves .................................................................................. 193
11.10.4 Modules in ET200iSP Modular Slaves ................................................................................ 194
11.11 Effects on the process when re-configuring in RUN ............................................................ 194
11.11.1 Effects on Operating System Functions During the CiR Synchronization Time .................. 194
11.11.2 Behavior of the CPU after download of the configuration in RUN ....................................... 195
11.11.2.1 Overview .............................................................................................................................. 195
11.11.2.2 Error displays ....................................................................................................................... 196
12.1 The H-CiR wizard ................................................................................................................. 197
12.2 Replacing central components ............................................................................................. 198
12.3 Addition of interface modules ............................................................................................... 199
12.4 Motivation for H-CiR via PROFINET IO ............................................................................... 201
12.5 Permitted changes over PROFINET IO ............................................................................... 202
12.6 Motivation for H-CiR via PROFIBUS DP ............................................................................. 204
12.7 Permitted changes over PROFIBUS DP ............................................................................. 205
12.8 Adding components ............................................................................................................. 207
12.8.1 Modify hardware................................................................................................................... 207
12.8.2 Change hardware configuration offline ................................................................................ 208
12.8.3 Opening the H-CiR wizard ................................................................................................... 209
12.8.4 Modify and download the user program .............................................................................. 210
12.8.5 Use of free channels on an existing module ........................................................................ 211
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
6 System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC

Table of contents
13 Replacement of failed components during redundant operation ........................................................... 223
14 Synchronization modules .................................................................................................................... 239
15 System expansion card ....................................................................................................................... 251
16 Technical data .................................................................................................................................... 253
17 Properties and technical specifications of CPU 410 SMART ................................................................ 283
12.9 Removal of components ....................................................................................................... 211
12.9.1 Change hardware configuration offline ................................................................................. 212
12.9.2 Modify and download the user program ............................................................................... 213
12.9.3 Opening the H-CiR wizard .................................................................................................... 214
12.9.4 Modify hardware ................................................................................................................... 215
12.9.5 Removal of interface modules .............................................................................................. 216
12.10 Editing CPU parameters ....................................................................................................... 217
12.10.1 Editing CPU parameters ....................................................................................................... 217
12.10.2 Changing CPU parameters offline ........................................................................................ 219
12.10.3 Opening the H-CiR wizard .................................................................................................... 219
12.11 Re-parameterization of a module ......................................................................................... 220
12.11.1 Re-configuring a module/PDEV submodule ......................................................................... 220
12.11.2 Editing parameters offline ..................................................................................................... 221
12.11.3 Opening the H-CiR wizard .................................................................................................... 221
13.1 Replacement of central components .................................................................................... 223
13.1.1 Replacement of a CPU during redundant operation ............................................................. 223
13.1.2 Replacement of a power supply module............................................................................... 225
13.1.3 Replacement of an input/output module or function module ................................................ 226
13.1.4 Replacement of a communication module............................................................................ 227
13.1.5 Replacement of synchronization module or fiber-optic cable ............................................... 228
13.1.6 Replacement of an IM 460 and IM 461 interface module ..................................................... 231
13.2 Replacement of components of the distributed I/O on PROFINET IO ................................. 231
13.2.1 Replacement of a PROFINET IO device .............................................................................. 231
13.2.2 Replacement of PROFINET IO cables ................................................................................. 232
13.3 Replacement of components of the distributed I/O on PROFIBUS DP ................................ 233
13.3.1 Replacement of a PROFIBUS DP master ............................................................................ 234
13.3.2 Replacement of a redundant PROFIBUS DP interface module ........................................... 236
13.3.3 Replacement of a PROFIBUS DP slave ............................................................................... 236
13.3.4 Replacement of PROFIBUS DP cables ................................................................................ 237
14.1 Synchronization modules for the CPU 410. .......................................................................... 239
14.2 Installation of fiber-optic cables ............................................................................................ 243
14.3 Selecting fiber-optic cables ................................................................................................... 245
15.1 Variants of the system expansion card ................................................................................. 251
16.1 Technical specifications of CPU 410-5H; (6ES7410-5HX08-0AB0) ..................................... 253
16.2 Technical specifications of CPU 410E (6ES7410-5HM08-0AB0) ........................................ 263
16.3 Technical specifications of the system expansion card ........................................................ 273
17.1 CPU 410 SMART .................................................................................................................. 283
17.2 Technical specifications of the CPU 410 SMART; (6ES7 410-5HN08-0AB0) ...................... 285
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC
7

Table of contents
18 Supplementary information .................................................................................................................. 297
17.3 Technical specifications of the SEC PO 800 ....................................................................... 295
18.1 Supplementary information on PROFIBUS DP ................................................................... 297
18.2 Supplementary information on diagnostics of the CPU 410 as PROFIBUS DP master ...... 298
18.3 System status lists for PROFINET IO .................................................................................. 301
18.4 Configuring with STEP 7 ...................................................................................................... 302
18.4.1 Rules for arranging fault-tolerant station components ......................................................... 302
18.4.2 Configuring hardware ........................................................................................................... 303
18.4.3 Assigning parameters to modules in a fault-tolerant station ................................................ 304
18.4.4 Recommendations for setting CPU parameters, fixed settings ........................................... 304
18.4.5 Networking configuration ..................................................................................................... 305
18.5 The STEP 7 user program ................................................................................................... 306
18.5.1 The user program................................................................................................................. 306
18.6 Programming device functions in STEP 7 ........................................................................... 308
18.7 Communication services ...................................................................................................... 308
18.7.1 Overview of communication services................................................................................... 308
18.7.2 PG communication ............................................................................................................... 310
18.7.3 OP communication ............................................................................................................... 310
18.7.4 S7 communication ............................................................................................................... 310
18.7.5 S7 routing ............................................................................................................................. 312
18.7.6 Data set routing .................................................................................................................... 316
18.7.7 SNMP network protocol ....................................................................................................... 317
18.7.8 Open Communication Via Industrial Ethernet ...................................................................... 318
18.8 Basics and terminology of fault-tolerant communication ..................................................... 321
18.9 Usable networks................................................................................................................... 325
18.10 Communication via S7 connections ..................................................................................... 325
18.10.1 Communication via S7 connections - one-sided mode........................................................ 326
18.10.2 Communication via redundant S7 connections ................................................................... 328
18.10.3 Communication via point-to-point CP on the ET 200M ....................................................... 329
18.10.4 Custom connection to single-channel systems .................................................................... 331
18.11 Communication via fault-tolerant S7 connections ................................................................ 332
18.11.1 Communication between fault-tolerant systems .................................................................. 334
18.11.2 Communication between fault-tolerant systems and a fault-tolerant CPU .......................... 337
18.11.3 Communication between fault-tolerant systems and PCs ................................................... 338
18.12 Consistent data .................................................................................................................... 340
18.12.1 Consistency of communication blocks and functions .......................................................... 340
18.12.2 Consistency rules for SFB 14 "GET" or read variable, and SFB 15 "PUT" or write
variable ................................................................................................................................. 340
18.12.3 Consistent reading and writing of data from and to DP standard slaves/IO devices ........... 341
18.13 Link-
up and update sequence .............................................................................................. 343
18.13.1 Link-up sequence ................................................................................................................. 346
18.13.2 Update sequence ................................................................................................................. 347
18.13.3 Switch to CPU with modified configuration .......................................................................... 351
18.13.4 Disabling of link-up and update ............................................................................................ 352
18.14 The user program................................................................................................................. 353
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
8 System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC

Table of contents
A Characteristic values of redundant automation systems ...................................................................... 379
B Function and communication modules that can be used in a redundant configuration .......................... 389
C Connection examples for redundant I/Os ............................................................................................. 391
18.15 Other options for connecting redundant I/Os ........................................................................ 354
18.16 CPU 410 cycle and reaction times ........................................................................................ 357
18.16.1 Cycle time ............................................................................................................................. 357
18.16.2 Calculating the cycle time ..................................................................................................... 359
18.16.3 Cycle load due to communication ......................................................................................... 362
18.16.4 Response time ...................................................................................................................... 364
18.16.5 Calculating cycle and response times .................................................................................. 369
18.16.6 Examples of calculating the cycle and response times ........................................................ 370
18.16.7 Interrupt response time ......................................................................................................... 373
18.16.8 Example of calculation of the interrupt response time .......................................................... 375
18.16.9 Reproducibility of delay and watchdog interrupts ................................................................. 376
18.17 Runtimes of the FCs and FBs for redundant I/Os ................................................................ 377
A.1 Basic concepts ...................................................................................................................... 379
A.2 Comparison of MTBF for selected configurations ................................................................ 383
A.2.1 System configurations with redundant CPU 410 .................................................................. 383
A.2.2 System configurations with distributed I/Os .......................................................................... 384
A.2.3 Comparison of system configurations with standard and fault-tolerant communication ...... 388
C.1 MTA terminal modules (Marshalled Termination Assemblies) ............................................. 391
C.2 Interconnection of output modules ........................................................................................ 391
C.3 8-channel HART analog input MTA ...................................................................................... 393
C.4 8-channel HART analog output MTA .................................................................................... 394
C.5 SM 321; DI 16 x DC 24 V, 6ES7 321–1BH02–0AA0 ............................................................ 395
C.6 SM 321; DI 32 x DC 24 V, 6ES7 321–1BL00–0AA0 ............................................................. 396
C.7 SM 321; DI 16 x AC 120/230V, 6ES7 321–1FH00–0AA0 .................................................... 397
C.8 SM 321; DI 8 x AC 120/230 V, 6ES7 321–1FF01–0AA0 ...................................................... 398
C.9 SM 321; DI 16 x DC 24V, 6ES7 321–7BH00–0AB0 ............................................................. 399
C.10 SM 321; DI 16 x DC 24V, 6ES7 321–7BH01–0AB0 ............................................................. 400
C.11 SM 326; DO 10 x DC 24V/2A, 6ES7 326–2BF01–0AB0 ...................................................... 401
C.12 SM 326; DI 8 x NAMUR, 6ES7 326–1RF00–0AB0 ............................................................... 402
C.13 SM 326; DI 24 x DC 24 V, 6ES7 326–1BK00–0AB0 ............................................................ 403
C.14 SM 421; DI 32 x UC 120 V, 6ES7 421–1EL00–0AA0 ........................................................... 404
C.15 SM 421; DI 16 x DC 24 V, 6ES7 421–7BH01–0AB0 ............................................................ 405
C.16 SM 421; DI 32 x DC 24 V, 6ES7 421–1BL00–0AB0 ............................................................. 406
C.17 SM 421; DI 32 x DC 24 V, 6ES7 421–1BL01–0AB0 ............................................................. 407
C.18 SM 322; DO 8 x DC 24 V/2 A, 6ES7 322–1BF01–0AA0 ...................................................... 408
C.19 SM 322; DO 32 x DC 24 V/0,5 A, 6ES7 322–1BL00–0AA0 ................................................. 409
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC
9

Table of contents
Index ................................................................................................................................................... 429
Tables
C.20 SM 322; DO 8 x AC 230 V/2 A, 6ES7 322–1FF01–0AA0 .................................................... 410
C.21 SM 322; DO 4 x DC 24 V/10 mA [EEx ib], 6ES7 322–5SD00–0AB0 .................................. 411
C.22 SM 322; DO 4 x DC 15 V/20 mA [EEx ib], 6ES7 322–5RD00–0AB0 .................................. 412
C.23 SM 322; DO 8 x DC 24 V/0.5 A, 6ES7 322–8BF00–0AB0 .................................................. 413
C.24 SM 322; DO 16 x DC 24 V/0.5 A, 6ES7 322–8BH01–0AB0 ................................................ 414
C.25 SM 332; AO 8 x 12 Bit, 6ES7 332–5HF00–0AB0 ................................................................ 415
C.26 SM 332; AO 4 x 0/4...20 mA [EEx ib], 6ES7 332–5RD00–0AB0 ......................................... 416
C.27 SM 422; DO 16 x AC 120/230 V/2 A, 6ES7 422–1FH00–0AA0 .......................................... 417
C.28 SM 422; DO 32 x DC 24 V/0.5 A, 6ES7 422–7BL00–0AB0 ................................................ 418
C.29 SM 331; AI 4 x 15 Bit [EEx ib]; 6ES7 331–7RD00–0AB0 .................................................... 419
C.30 SM 331; AI 8 x 12 Bit, 6ES7 331–7KF02–0AB0 .................................................................. 420
C.31 SM 331; AI 8 x 16 Bit; 6ES7 331–7NF00–0AB0 .................................................................. 421
C.32 SM 331; AI 8 x 16 Bit; 6ES7 331–7NF10–0AB0 .................................................................. 422
C.33 AI 6xTC 16Bit iso, 6ES7331-7PE10-0AB0 .......................................................................... 423
C.34 SM331; AI 8 x 0/4...20mA HART, 6ES7 331-7TF01-0AB0 ................................................. 424
C.35 SM 332; AO 4 x 12 Bit; 6ES7 332–5HD01–0AB0 ................................................................ 426
C.36 SM332; AO 8 x 0/4...20mA HART, 6ES7 332-8TF01-0AB0 ................................................ 427
Table 3- 1 LED displays on the CPUs ........................................................................................................... 36
Table 3- 2 Possible states of the RUN and STOP LEDs .............................................................................. 41
Table 3- 3 Possible states of the MSTR, RACK0 and RACK1 LEDs ............................................................ 42
Table 3- 4 Possible states of the INTF and EXTF LEDs ............................................................................... 42
Table 3- 5 Possible states of the BUS1F, BUS5F, and BUS8F LEDs .......................................................... 42
Table 3- 6 Possible states of the IFM1F and IFM2F LEDs ........................................................................... 43
Table 3- 7 Possible states of the LINK and RX/TX LEDs ............................................................................. 43
Table 3- 8 Possible states of the REDF LED ................................................................................................ 43
Table 3- 9 Possible states of the LINK1 OK and LINK2 OK LEDs ............................................................... 44
Table 4- 1 Meaning of the "BUSF" LED of the CPU 410 as DP master ....................................................... 49
Table 6- 1 System modifications during operation ........................................................................................ 56
Table 6- 2 Measures in PROFIsafe for error avoidance ............................................................................... 60
Table 6- 3 Interface modules for use of single-channel switched I/O configuration at the PROFIBUS
DP interface ................................................................................................................................. 67
Table 6- 4 Bus modules for hot swapping ..................................................................................................... 68
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
10 System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC

Table of contents
Table 6- 5 Interface module for use of single-channel switched I/O configuration at the PROFINET
IO interface ................................................................................................................................... 71
Table 6- 6 Signal modules for redundancy ................................................................................................... 84
Table 7- 1 Causes of error leading to redundancy loss .............................................................................. 102
Table 7- 2 Overview of system states of the fault-tolerant system ............................................................. 109
Table 7- 3 Response to errors during the self-test ...................................................................................... 114
Table 7- 4 Response to a recurring comparison error ................................................................................ 115
Table 7- 5 Reaction to checksum errors ..................................................................................................... 115
Table 7- 6 Hardware fault with one-sided OB 121 call, checksum error, 2nd occurrence .......................... 116
Table 8- 1 Properties of link-up and update functions ................................................................................ 119
Table 8- 2 PG commands for link-up and update ....................................................................................... 120
Table 8- 3 Typical values for the user program part ................................................................................... 130
Table 9- 1 Protection levels of a CPU ......................................................................................................... 134
Table 9- 2 CPU properties in the factory settings ....................................................................................... 142
Table 9- 3 LED patterns .............................................................................................................................. 142
Table 12- 1 Modifiable CPU parameters ....................................................................................................... 218
Table 14- 1 Accessory fiber-optic cable ........................................................................................................ 246
Table 14- 2 Specification of fiber-optic cables for indoor applications .......................................................... 247
Table 14- 3 Specification of fiber-optic cables for outdoor applications ........................................................ 248
Table 18- 1 Reading the diagnostics data with STEP 7 ................................................................................ 298
Table 18- 2 Event detection of the CPU 41xH as a DP master .................................................................... 300
Table 18- 3 Comparison of the system status lists of PROFINET IO and PROFIBUS DP........................... 301
Table 18- 4 Communication services of the CPUs ....................................................................................... 308
Table 18- 5 Availability of connection resources ........................................................................................... 309
Table 18- 6 SFBs for S7 Communication ...................................................................................................... 311
Table 18-
7 Job lengths and "local_device_id" parameter ............................................................................ 320
Table 18- 8 For the monitoring times with redundant I/O .............................................................................. 357
Table 18- 9 Cyclic program processing ......................................................................................................... 358
Table 18- 10 Factors influencing cycle time .................................................................................................... 359
Table 18- 11 Portion of the process image transfer time, CPU 410-5H.......................................................... 360
Table 18- 12 Extending the cycle time ............................................................................................................ 361
Table 18- 13 Operating system execution time at the cycle control point ...................................................... 361
Table 18- 14 Extended cycle time due to nested interrupts ............................................................................ 361
Table 18- 15 Direct access of the CPUs to I/O modules in the central controller ........................................... 368
Table 18- 16 Direct access of the CPUs to I/O modules in the expansion unit with local link ........................ 368
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC
11

Table of contents
Figures
Table 18- 17 Direct access of the CPUs to I/O modules in the expansion unit with remote link, setting
100 m ......................................................................................................................................... 369
Table 18- 18 Example of calculating the response time ................................................................................. 370
Table 18- 19 Hardware and interrupt response times; maximum interrupt response time without com-
munication .................................................................................................................................. 373
Table 18- 20 Reproducibility of time-delay and cyclic interrupts of the CPUs ................................................ 376
Table 18- 21 Runtimes of the blocks for redundant I/Os ................................................................................. 377
Table C- 1 Interconnecting digital output modules with/without diodes ....................................................... 391
Figure 2-1 Purpose of redundant automation systems ................................................................................. 23
Figure 2-2 Overview ...................................................................................................................................... 26
Figure 2-3 Hardware of the S7-400H basic system ...................................................................................... 27
Figure 2-4 Hardware of the S7-400H basic system ...................................................................................... 28
Figure 3-1 Arrangement of the operator controls and indicators on the CPU 410 ........................................ 35
Figure 6-1 Processing chain: acquire, process, output ................................................................................. 58
Figure 6-2 Safety-related communication ..................................................................................................... 59
Figure 6-3 Operating objectives of redundant automation systems .............................................................. 61
Figure 6-4 Example of redundancy in a network without error ...................................................................... 63
Figure 6-5 Example of redundancy in a 1-out-of-2 system with error ........................................................... 64
Figure 6-6 Example of redundancy in a 1-out-of-2 system with total failure ................................................. 65
Figure 6-7 Single-channel switched distributed I/O configuration at the PROFIBUS DP interface............... 67
Figure 6-8 Single-channel switched distributed I/O configuration at the PROFINET IO interface ................ 70
Figure 6-9 System redundancy ..................................................................................................................... 74
Figure 6-10 IO devices in multiple cabinets..................................................................................................... 76
Figure 6-11 S7-400 H-system with sensors and actuators on module pairs (redundant signal pro-
cessing) ........................................................................................................................................ 78
Figure 6-12 AS 410 with redundant module pairs ........................................................................................... 79
Figure 6-13 Redundant I/O in the switched DP slave ..................................................................................... 80
Figure 6-14 Fault-tolerant digital input module in 1-out-of-2 configuration with one encoder ......................... 89
Figure 6-15 Fault-tolerant digital input modules in 1-out-of-2 configuration with two encoders ...................... 90
Figure 6-16 Fault-tolerant digital output modules in 1-out-of-2 configuration.................................................. 90
Figure 6-17 Fault-tolerant analog input modules in 1-out-of-2 configuration with one encoder ...................... 92
Figure 6-18 Fault-tolerant analog input modules in 1-out-of-2 configuration with two encoders .................... 94
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
12 System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC

Table of contents
Figure 6-19 Fault-tolerant analog output modules in 1-out-of-2 configuration ................................................ 95
Figure 7-1 Synchronizing the subsystems .................................................................................................. 108
Figure 8-1 Meanings of the times relevant for updates ............................................................................... 122
Figure 8-2 Correlation between the minimum I/O retention time and the maximum inhibit time for
priority classes > 15 ................................................................................................................... 125
Figure 14-1 Synchronization modules 6ES7 960-1AA08-0XA0 and 6ES7 960-1Ax06-0xA0 ....................... 240
Figure 14-2 Fiber-optic cables, installation using distribution boxes ............................................................. 249
Figure 15-1 SEC ............................................................................................................................................ 252
Figure 18-1 Diagnostics with CPU 410 ......................................................................................................... 299
Figure 18-2 S7 routing ................................................................................................................................... 313
Figure 18-3 S7 routing gateways: PROFINET IO - DP - PROFINET IO ....................................................... 314
Figure 18-4 S7 routing: TeleService application example ............................................................................. 315
Figure 18-5 Data set routing .......................................................................................................................... 316
Figure 18-6 Example of an S7 connection .................................................................................................... 322
Figure 18-7 Example that shows that the number of resulting partial connections depends on the con-
figuration .................................................................................................................................... 324
Figure 18-8 Example of linking standard and fault-tolerant systems in a simple bus system ....................... 326
Figure 18-9 Example of linking standard and fault-tolerant systems in a redundant bus system ................. 327
Figure 18-10 Example of linking of standard and fault-tolerant systems in a redundant ring ......................... 327
Figure 18-11 Example of linking standard and fault-tolerant systems in a single bus system ........................ 328
Figure 18-12 Example of redundancy with fault-tolerant systems and a redundant bus system with re-
dundant standard connections ................................................................................................... 329
Figure 18-13 Example of connecting a fault-tolerant system to a single-channel third-party system via
switched PROFIBUS DP ............................................................................................................ 330
Figure 18-14 Example of connecting a fault-tolerant system to a single-channel third-party system via
PROFINET IO with system redundancy .................................................................................... 330
Figure 18-15 Example of linking a fault-tolerant system to a single-channel third-party system .................... 331
Figure 18-16 Example of redundancy with fault-tolerant system and redundant ring .....................................
335
Figure 18-17 Example of redundancy with fault-tolerant system and redundant bus system ........................ 335
Figure 18-18 Example of fault-tolerant system with additional CP redundancy .............................................. 336
Figure 18-19 Example of redundancy with fault-tolerant system and fault-tolerant CPU ............................... 337
Figure 18-20 Example of redundancy with fault-tolerant system and redundant bus system ........................ 339
Figure 18-21 Example of redundancy with a fault-tolerant system, redundant bus system and redun-
dant connection to the PC. ......................................................................................................... 339
Figure 18-22 Sequence of link-up and update ................................................................................................ 344
Figure 18-23 Update sequence ....................................................................................................................... 345
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC
13

Table of contents
Figure 18-24 Example of minimum signal duration of an input signal during the update ............................... 346
Figure 18-25 Redundant one-sided and switched I/O ..................................................................................... 354
Figure 18-26 Flow chart for OB 1 .................................................................................................................... 356
Figure 18-27 Elements and composition of the cycle time .............................................................................. 358
Figure 18-28 Formula: Influence of communication load ................................................................................ 362
Figure 18-29 Distribution of a time slice .......................................................................................................... 362
Figure 18-30 Dependency of the cycle time on communication load .............................................................. 363
Figure 18-31 DP cycle times on the PROFIBUS DP network ......................................................................... 365
Figure 18-32 Shortest response time .............................................................................................................. 366
Figure 18-33 Longest response time ............................................................................................................... 367
Figure A-1 MDT ............................................................................................................................................ 380
Figure A-2 MTBF .......................................................................................................................................... 381
Figure A-3 Common Cause Failure (CCF) .................................................................................................. 382
Figure A-4 Availability .................................................................................................................................. 383
Figure C-1 Interconnection example for SM 331, Al 8 x 0/4...20mA HART ................................................. 393
Figure C-2 Interconnection example for SM 322, Al 8 x 0/4...20mA HART ................................................. 394
Figure C-3 Example of an interconnection with SM 321; DI 16 x DC 24 V.................................................. 395
Figure C-4 Example of an interconnection with SM 321; DI 32 x DC 24 V.................................................. 396
Figure C-5 Example of an interconnection with SM 321; DI 16 x AC 120/230 V ......................................... 397
Figure C-6 Example of an interconnection with SM 321; DI 8 x AC 120/230 V ........................................... 398
Figure C-7 Example of an interconnection with SM 321; DI 16 x DC 24V................................................... 399
Figure C-8 Example of an interconnection with SM 321; DI 16 x DC 24V................................................... 400
Figure C-9 Example of an interconnection with SM 326; DO 10 x DC 24V/2A ........................................... 401
Figure C-10 Example of an interconnection with SM 326; DI 8 x NAMUR .................................................... 402
Figure C-11 Example of an interconnection with SM 326; DI 24 x DC 24 V.................................................. 403
Figure C-12 Example of an interconnection with SM 421; DI 32 x UC 120 V................................................ 404
Figure C-13 Example of an interconnection with SM 421; DI 16 x 24 V ........................................................ 405
Figure C-14 Example of an interconnection with SM 421; DI 32 x 24 V ........................................................
406
Figure C-15 Example of an interconnection with SM 421; DI 32 x 24 V ........................................................ 407
Figure C-16 Example of an interconnection with SM 322; DO 8 x DC 24 V/2 A ........................................... 408
Figure C-17 Example of an interconnection with SM 322; DO 32 x DC 24 V/0.5 A ...................................... 409
Figure C-18 Example of an interconnection with SM 322; DO 8 x AC 230 V/2 A.......................................... 410
Figure C-19 Example of an interconnection with SM 322; DO 16 x DC 24 V/10 mA [EEx ib] ....................... 411
Figure C-20 Example of an interconnection with SM 322; DO 16 x DC 15 V/20 mA [EEx ib] ....................... 412
Figure C-21 Example of an interconnection with SM 322; DO 8 x DC 24 V/0.5 A ........................................ 413
Figure C-22 Example of an interconnection with SM 322; DO 16 x DC 24 V/0.5 A ...................................... 414
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
14 System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC

Table of contents
Figure C-23 Example of an interconnection with SM 332, AO 8 x 12 Bit ...................................................... 415
Figure C-24 Example of an interconnection with SM 332; AO 4 x 0/4...20 mA [EEx ib] ............................... 416
Figure C-25 Example of an interconnection with SM 422; DO 16 x 120/230 V/2 A ...................................... 417
Figure C-26 Example of an interconnection with SM 422; DO 32 x DC 24 V/0.5 A ...................................... 418
Figure C-27 Example of an interconnection with SM 331, AI 4 x 15 Bit [EEx ib] ........................................... 419
Figure C-28 Example of an interconnection with SM 331; AI 8 x 12 Bit ........................................................ 420
Figure C-29 Example of an interconnection with SM 331; AI 8 x 16 Bit ........................................................ 421
Figure C-30 Example of an interconnection with SM 331; AI 8 x 16 Bit ........................................................ 422
Figure C-31 Example of an interconnection AI 6xTC 16Bit iso ...................................................................... 423
Figure C-32 Interconnection example 1 SM 331; AI 8 x 0/4...20mA HART ................................................... 424
Figure C-33 Interconnection example 2 SM 331; AI 8 x 0/4...20mA HART ................................................... 425
Figure C-34 Example of an interconnection with SM 332, AO 4 x 12 Bit ...................................................... 426
Figure C-35 Interconnection example 3 SM 332; AO 8 x 0/4...20mA HART ................................................. 427
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC
15

Table of contents
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
16 System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC

1
1.1
Preface
Purpose of this manual
Changes compared with the previous version
Scope of the manual
The information in this manual enables you to look up operator inputs, function descriptions
and technical specifications of the CPU 410-5H Process Automation, CPU 410E Process
Automation and CPU 410 SMART.
For information on installing and wiring this and other modules in order to set up an
automation system, refer to Manual
Changes compared with the previous version of the SIMATIC PCS 7 Process Control
System CPU 410-5H Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART, 09/2014 edition
(A5E32631620-AB):
Automation System S7-400, Hardware and Installation
.
● CPU 410E has been added.
● The connection of redundant I/O via the PROFINET interface is described.
● The "Configuration changes during operation" functionality via the PROFINET interface is
● The "Configuration changes during redundant operation" functionality via the PROFINET
● The retentive load memory is described.
● A two-step firmware update procedure is described.
● Time synchronization for purposes of time stamping via PROFINET is described.
● The signaling of security events via SysLog is described.
The manual is relevant to the following components:
● CPU 410-5H Process Automation; 6ES7 410-5HX08-0AB0 as of Firmware Version V8.2
● CPU 410E Process Automation; 6ES7410-5HM08-0AB0 as of Firmware Version V8.2
● CPU 410 SMART; 6ES7 410-5HN08-0AB0 as of firmware version V8.2
described.
interface is described.
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC
17

Preface
Note
CPU 410-5H and CPU 410E
Except for different technical specifications and quantity frameworks, the CPU 410E behaves
the same as a CPU 410
CPU 410 apply to both the CPU 410
Note
CPU 410 and CPU 410 SMART
Except for the special features described in the s
specifications of CPU 410 SMART
While taking this section into co
410 also apply to the CPU 410 SMART.
Basic knowledge required
Approvals
Online help
1.1 Preface
Use of the current version of PCS 7 or the engineering tools is only required if the current
CPU has new functions compared to the last firmware version and you want to use these
functions. The same applies when an old CPU is replaced by a CPU with current firmware: If
you do not want to use any properties beyond the scope of the replaced CPU, you can use
the CPU with the old article number and old firmware version when configuring in HW
Config.
-5H. For this reason, the statements made in this manual about a
-5H and the CPU 410E.
ection Properties and technical
(Page 283), CPU 410 SMART reacts like a CPU 410.
nsideration, the statements made in this manual about CPU
This manual requires general knowledge of automation engineering.
Knowledge of the use of computers or PC-like tools such as programming devices with a
Windows operating system is also required. The SIMATIC PCS 7 readme includes
information on which operating system is suitable for your SIMATIC PCS 7 configuration.
The CPU 410 is configured using the SIMATIC PCS 7 software, and you should therefore be
familiar with this software.
In particular when operating a CPU 410 in potentially explosive atmospheres, please always
observe the information on the safety of electronic control systems provided in the appendix
Automation System S7-400, Hardware and Installation
to the
For details on certifications and standards, refer to Manual
Module Data
specification for the entire S7-400.
You will need the SIMATIC PCS 7 Programming Package V9.0 or higher to work with CPU
410.
In addition to the manual, you will find detailed support on how to use the software in the
integrated online help system of the software.
manual.
S7-400 Automation System,
, section 1.1, Standards and Certifications. Here you will also find the technical
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
18 System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC

Preface
Help
Contents
Configuring fault-tolerant systems
Using Help
Recycling and disposal
Additional support
Functional Safety Services
1.1 Preface
The help system can be accessed using various interfaces:
● The
help on fault-tolerant systems in
●
● The context-sensitive help system provides information on the current context, for
example, on an open dialog or active window. You can call this help by clicking "Help" or
using the F1 key.
● The status bar provides a further form of context-sensitive help. It shows a short
description of each menu command when you position the mouse pointer over a
command.
● A short info text is also shown for the toolbar buttons when you hold the mouse pointer
briefly over a button.
If you prefer to read the information of the online help in printed form, you can print individual
topics, books or the entire help system.
Because it is constructed from environmentally compatible materials, the CPU 410 can be
recycled. For ecologically compatible recycling and disposal of your old device, contact a
certificated disposal service for electronic scrap.
menu contains several commands:
provides detailed instructions on using the online help system.
opens the Help index. You will find
.
If you have any questions relating to the products described in this manual, and do not find
the answers in this documentation, please contact your Siemens partner at our local offices.
You will find information on who to contact at:
Contact partners (http://www.siemens.com/automation/partner)
A guide to the technical documents for the various SIMATIC products and systems is
available at:
Documentation (http://www.automation.siemens.com/simatic/portal/html_76/techdoku.htm)
You can find the online catalog and order system under:
Catalog (http://mall.automation.siemens.com/)
Siemens Functional Safety Services is a comprehensive performance package that supports
you in risk assessment and verification all the way to plant commissioning and
modernization. We also offer consulting services for the application of fail-safe and faulttolerant SIMATIC S7 automation systems.
Additional information is available at:
Functional Safety Services (http://www.siemens.com/safety-services)
Submit your requests to:
Mail Functional Safety Services (mailto:safety-services.industry@siemens.com)
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC
19
Preface
Training center
Technical Support
Service & Support on the Internet
1.2
Security information
1.2 Security information
We offer a range of relevant courses to help you to get started with the SIMATIC S7
automation system. Please contact your local training center or the central training center.
Training (http://www.sitrain.com/index_en.html)
For technical support of all Industry Automation products, fill in and submit the online
Support Request:
Support Request (http://www.siemens.de/automation/support-request)
In addition to our documentation, we offer a comprehensive online knowledge base on the
Internet at:
Service & Support (http://www.siemens.com/automation/service&support)
There you will find:
● The newsletter containing the latest information on your products.
● The latest documents via our search function in Service & Support.
● A forum for global information exchange by users and specialists.
● Your local Automation representative.
● Information on field service, repairs and spare parts. Much more can be found under
"Services".
Siemens provides products and solutions with industrial security functions that support the
secure operation of plants, systems, machines, and networks.
In order to protect plants, systems, machines and networks against cyber threats, it is
necessary to implement – and continuously maintain – a holistic, state-of-the-art industrial
security concept. Siemens’ products and solutions only form one element of such a concept.
Customer is responsible to prevent unauthorized access to its plants, systems, machines
and networks. Systems, machines and components should only be connected to the
enterprise network or the internet if and to the extent necessary and with appropriate security
measures (e.g. use of firewalls and network segmentation) in place.
Additionally, Siemens’ guidance on appropriate security measures should be taken into
account. For more information about industrial security, please visit:
http:/www.siemens.com/industrialsecurity.
Siemens’ products and solutions undergo continuous development to make them more
secure. Siemens strongly recommends to apply product updates as soon as available and to
always use the latest product versions. Use of product versions that are no longer supported,
and failure to apply latest updates may increase customer’s exposure to cyber threats.
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
20 System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC
Preface
1.3
Documentation
User documentation
Topic
Documentation
See also
ns.com/WW/view/en/1117849)
ns.com/WW/view/en/1117740)
System
en)
ns.com/WW/view/en/22063748)
ns.com/WW/view/en/1142696)
en)
8/en)
1.3 Documentation
To stay informed about product updates, subscribe to the Siemens Industrial Security RSS
Feed under
http://www.siemens.com/industrialsecurity.
The table below provides an overview of the descriptions of the various components and
options in the S7-400 automation system.
Setting up an automation system
Data of the standard modules of
an automation system
IM 155-6 PN HA ET 200SP HA Distributed I/O
IM 152 ET 200iSP Distributed I/O Sys-
IM 153-2
IM 153-4 PN
IM 157
S7-400, Hardware and Installation
S7-400 Module Data SIMATIC S7-400 S7-400 Auto-
tem
ET 200M Distributed I/O Device SIMATIC ET 200M Distributed
DP/PA Link and Y Link Bus
Links
S7-400 Automation System
Hardware and Installation
(http://support.automation.sieme
mation System Module Data
(http://support.automation.sieme
SIMATIC Distributed I/O System
ET 200iSP
(https://support.industry.siemen
s.com/cs/ww/de/view/28930789/
I/O Device, HART Analog Modules
(http://support.automation.sieme
SIMATIC Bus Links DP/PA
Coupler, Active Field Distributors, DP/PA Link and Y Link
(http://support.automation.sieme
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC
IM 153-2 FF FF Link Bus Links SIMATIC Bus Links - FF Link
Bus Link
(https://support.industry.siemen
s.com/cs/ww/de/view/47357205/
Compact FF Link Compact FF Link Bus Links SIMATIC Bus Link Compact FF
Link
(https://support.industry.siemen
s.com/cs/ww/de/view/10973957
21
Preface
Topic
Documentation
See also
IO system
ns.com/WW/view/en/19292127)
0/en)
dok-pcs7/Seiten/Default.aspx)
ns.com/WW/view/en/18652631)
ns.com/WW/view/en/14044916)
1.3 Documentation
Configuring, commissioning,
and operation of a PROFINET
Fail-safe systems
Configuring and programming
fail-safe systems
Working with S7 F-Systems V
6.2
Solution concepts
Function mechanisms
Configurations of SIMATIC PCS
7
Configuring hardware Configuring Hardware and
System Modifications during
Stand-Alone Operation
PROFINET IO System Description
S7 F/FH Systems SIMATIC Industrial Software S7
SIMATIC PCS 7 Technical Documentation
Communication Connections
with STEP 7
Modifying the System during
Operation via CiR
PROFINET system description
(http://support.automation.sieme
F/FH Systems - Configuring and
Programming
(https://support.industry.siemen
s.com/cs/ww/de/view/10974210
SIMATIC PCS 7 Process Control System
(http://www.automation.siemenh
ttps://support.industry.siemens.c
om/cs/ww/en/view/59538371s.c
om/mcms/industrial-automationsystemssimatic/en/handbuchuebersicht/tech-
Configuring Hardware and
Communication Connections
with STEP 7
(http://support.automation.sieme
Modifying the System during
Operation via CiR
(http://support.automation.sieme
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
22 System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC
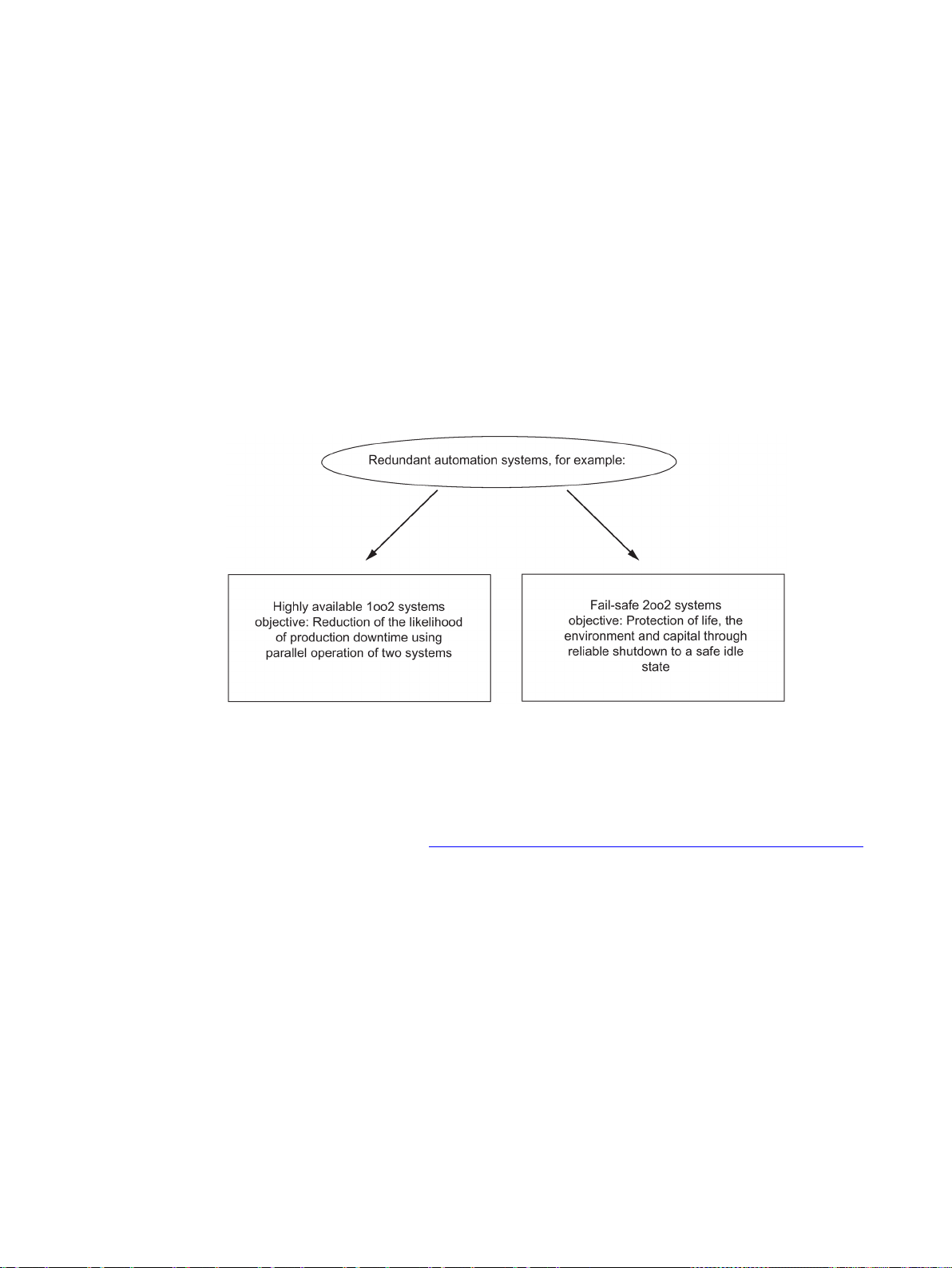
2
2.1
Area of application of the CPU 410 in SIMATIC PCS 7
Purpose of redundant automation systems
Why use fault-tolerant automation systems?
In practice, redundant automation systems are used to achieve fault-tolerant or fail-safe
systems.
Figure 2-1 Purpose of redundant automation systems
Please note the difference between fail-tolerant and fail-safe
systems. The AS 410 H is a fault-tolerance automation system. You may only use it for
controlling safety-related processes if you program and configure it in accordance with the
rules for F systems. You can find information on this in following manual: SIMATIC Industrial
Software S7 F/FH Systems (http://support.automation.siemens.com/WW/view/en/2201072)
The purpose of fault-tolerance automation systems is to reduce production downtime caused
by faults or by maintenance work.
The greater the costs of downtime, the more worthwhile a fault-tolerant system. The costs of
investing in a fault-tolerant system are generally higher, but are rapidly recovered by the
avoidance of production downtime.
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC
23

Introduction to the CPU 410
SIMATIC PCS 7 and CPU 410-5H Process Automation
The SIMATIC PCS 7 project
SIMATIC PCS 7 applications
2.1 Area of application of the CPU 410 in SIMATIC PCS 7
SIMATIC PCS 7 uses selected standard hardware and software components from the TIA
building block system for the process control system in the company-wide automation
network called Totally Integrated Automation. It offers an open basis for automation solutions
with its consistent data management, communication and configuration.
You can use SIMATIC PCS 7 to create customized and project-specific solutions tailored to
specific requirements. Further information about these customized solutions can be found in
the configuration manuals.
The CPU 410-5H Process Automation is a controller of the latest generation. This controller
is specifically designed for the SIMATIC PCS 7 control system. As with previous controllers
of the SIMATIC PCS 7 system, the CPU 410-5H Process Automation can be used in all
Process Automation industries. Highly flexible scalability based on SIMATIC PCS 7 process
objects makes it possible to cover the entire performance range from the smallest to the
largest controller in standard, fault-tolerant and fail-safe applications with just one hardware.
You must create a new configuration for use of a CPU 410-5H. The parameters of a CPU
410-5H are set to SIMATIC PCS 7 default values when a new configuration is created. Some
parameters that were previously freely assignable cannot be changed in the CPU 410-5H.
You can apply charts from existing SIMATIC PCS 7 projects.
A SIMATIC PCS 7 project includes the following objects:
● Hardware configuration
● Blocks
● CFCs and SFCs
These objects are always present - regardless of the number of operator stations and
modules and their networking.
You create a SIMATIC PCS 7 project on an engineering station (ES for short). A variety of
applications are available on the ES:
● SIMATIC Manager - the central application of SIMATIC PCS 7. From here, you can open
all other applications in which you need to make settings for the SIMATIC PCS 7 project.
You will set up your entire project from SIMATIC Manager.
● HW Config – configuration of all hardware of a system, e.g., CPUs, power supply,
communications processors.
● CFC editor and SFC editor - creation of continuous function charts (CFC) and sequential
control systems.
● SIMATIC PCS 7 OS in conjunction with various editors - Implementation of OS
configuration
Every application has a graphic user interface for easy operation and clear representation of
your configuration data.
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
24 System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC
Introduction to the CPU 410
Important information on configuration
WARNING
Open equipment
Additional information
See also
2.2
Possible applications
Important information on configuration
WARNING
Open equipment
2.2 Possible applications
Risk of death or serious injury.
S7–400 modules are classified as open equipment, meaning you must install the S7–400 in
an enclosure, cabinet, or switch room that can only be accessed by means of a key or tool.
Only instructed or authorized personnel are permitted to access these enclosures, cabinets,
or switch rooms.
The components of the standard S7-400 system, e.g., power supplies, I/O modules, CPs,
and FMs, are also used in the high availability S7-400H automation system. For a detailed
description of all hardware components for S7-400, refer to Reference Manual
Automation System, Module Data
.
S7-400
For the S7-400H high availability automation system, the same rules apply for planning the
user program and for using blocks as for a standard S7-400 system. Please observe the
descriptions in the
Programming with STEP 7
300/400 System and Standard Functions
Summary of parameters for CPU 410 (Page 48)
S7–400 modules are classified as open equipment, meaning you must install the S7–400 in
an enclosure, cabinet, or switch room that can only be accessed by means of a key or tool.
Only instructed or authorized personnel are permitted to access these enclosures, cabinets,
or switch rooms.
manual and the
reference manual.
System Software for S7-
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC
The following figure shows an example of an S7–400H configuration with shared distributed
I/O and connection to a redundant plant bus. The next pages deal with the hardware and
software components required for the installation and operation of the S7–400H.
25
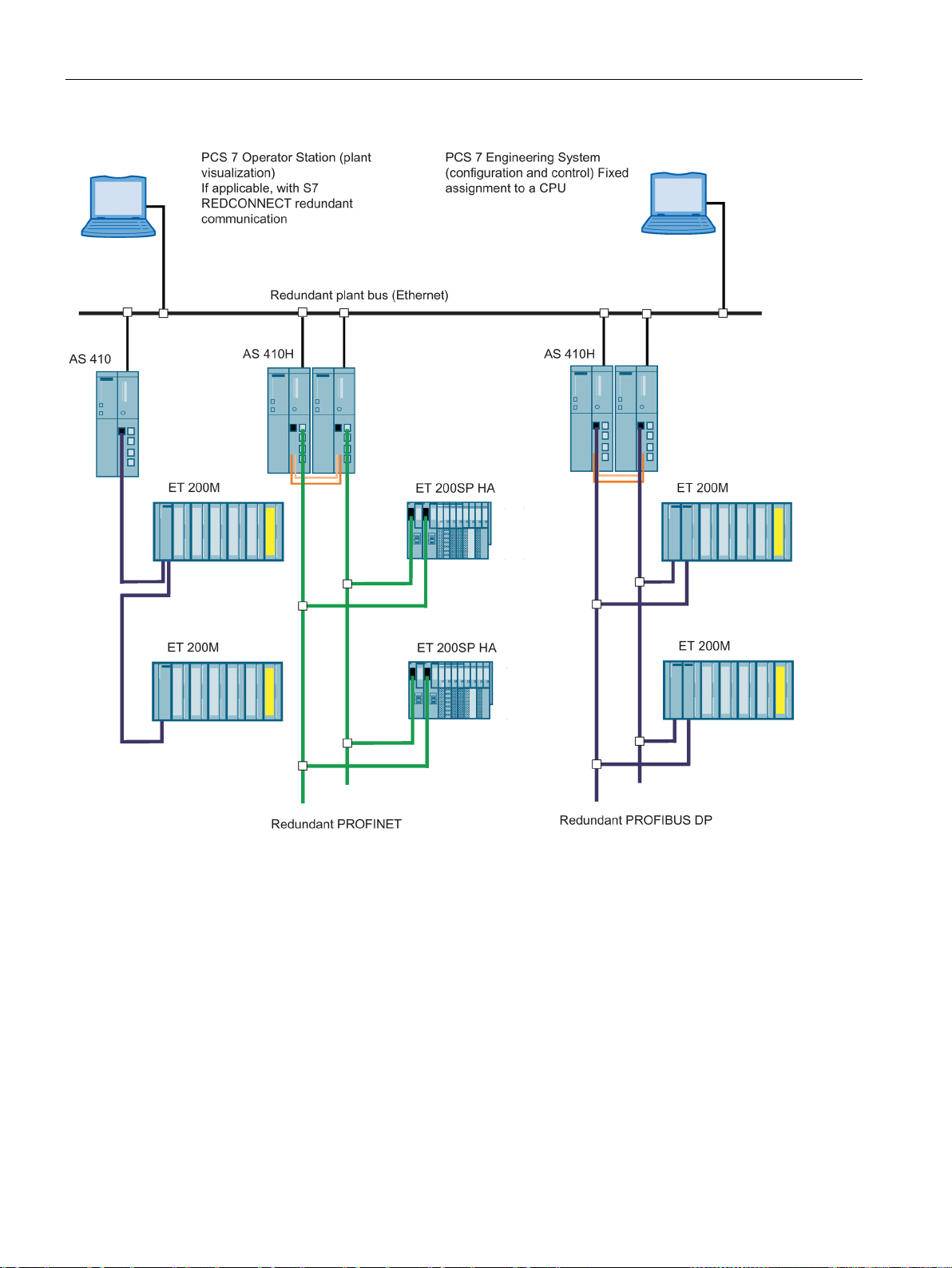
Introduction to the CPU 410
Additional information
2.2 Possible applications
Figure 2-2 Overview
The components of the S7–400 standard system are also used in connection with the CPU
410-5H Process Automation. For a detailed description of all hardware components for S7400, refer to Reference Manual
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
S7-400 Automation System; Module Specifications
26 System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC
.
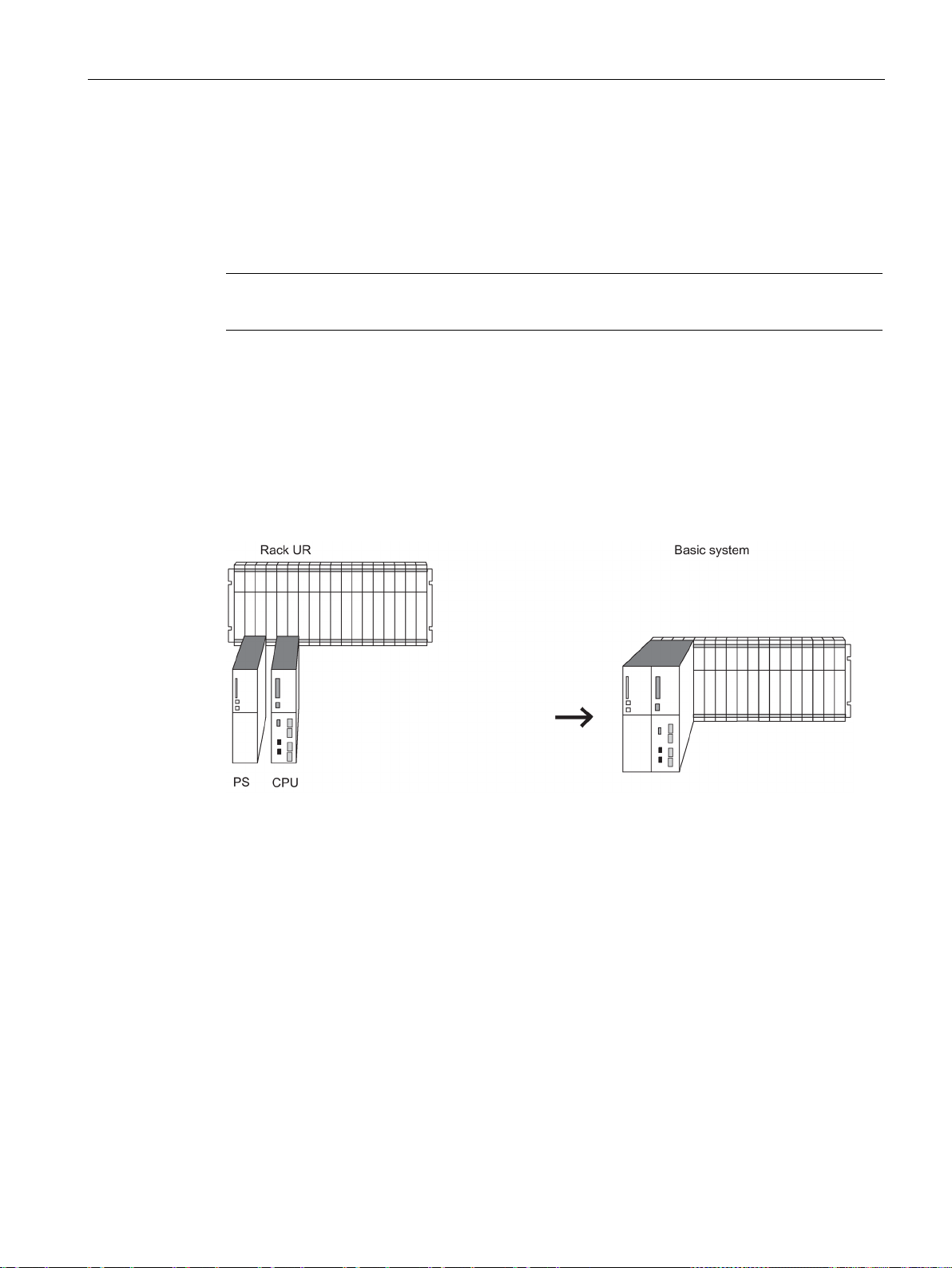
Introduction to the CPU 410
2.3
The CPU 410 basic system for stand-alone operation
Definition
Note
Rack number "0" must be set on the CPU.
Hardware of the basic system
Central controller and expansion units
Power supply
2.3 The CPU 410 basic system for stand-alone operation
Stand-alone operation refers to the use of a CPU 410 in a standard SIMATIC-400 station.
The basic system consists of the required hardware components of a controller. The
following figure shows the components in the configuration.
You can expand the basic system with standard S7-400 modules. There are limitations in the
case of function and communication modules. See Appendix Function and communication
modules that can be used in a redundant configuration (Page 389).
Figure 2-3 Hardware of the S7-400H basic system
The rack containing the CPU is called the central controller (CC). The racks in the system
that are equipped with modules and connected to the CC are the expansion units (EU).
For the power supply you need a power supply module from the standard S7-400 system
spectrum.
To increase availability of the power supply, you can also use two redundant power supplies.
In this case, you use the power supply modules PS 405 R / PS 407 R.
A combination of these can also be used in redundant configurations (PS 405 R with PS 407
R).
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC
27
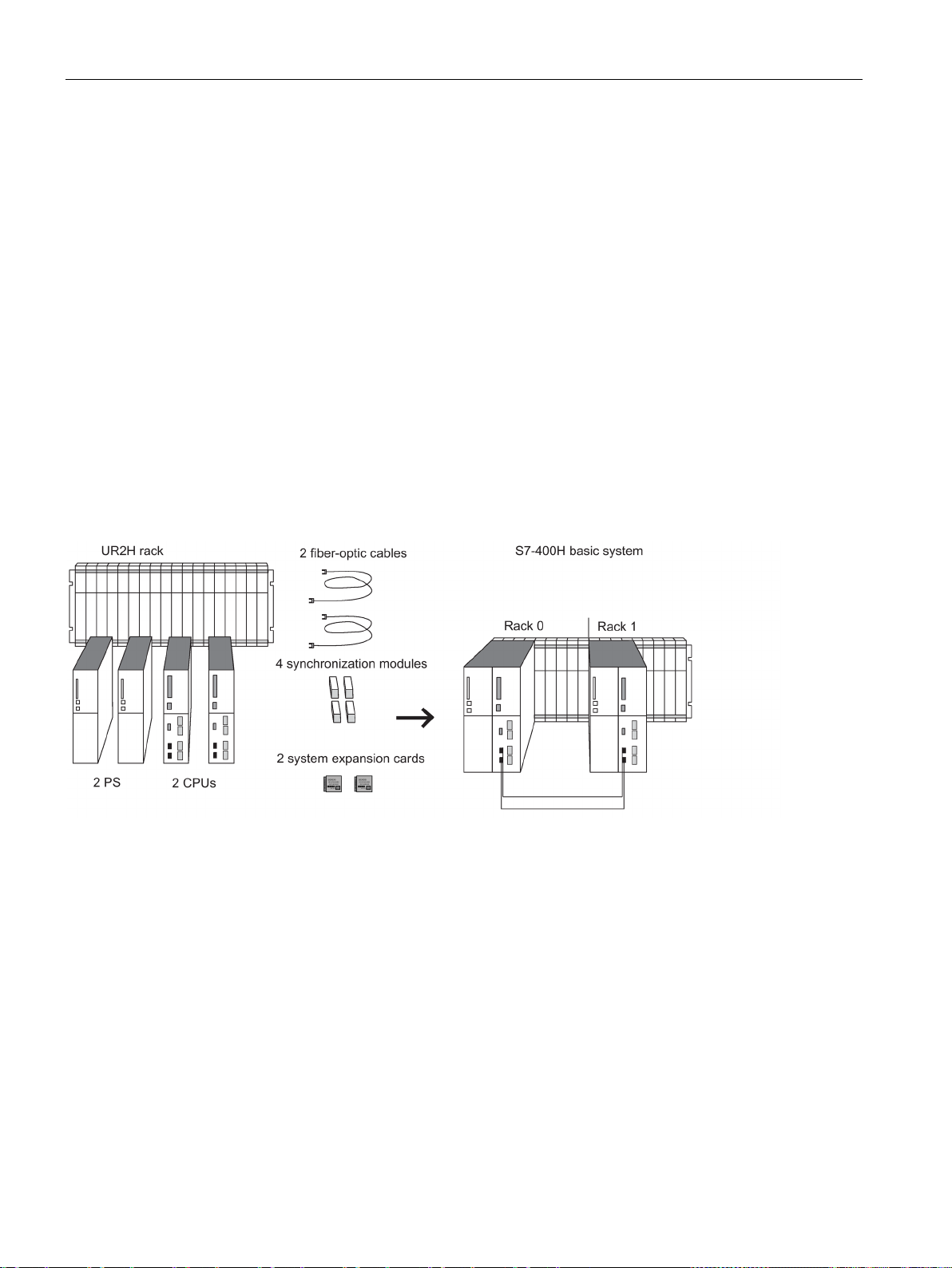
Introduction to the CPU 410
Operation
2.4
The basic system for redundant operation
Hardware of the basic system
Central processing units
on the rear
Rack for S7-400H
2.4 The basic system for redundant operation
You need a system expansion card for operation of a CPU 410. The system expansion card
specifies the maximum number of process objects that can be loaded to the CPU and saves
the license information in case of a system expansion. The system expansion card forms a
hardware unit with the CPU 410.
The basic system consists of the hardware components required for a fault-tolerant
controller. The following figure shows the components in the configuration.
The basic system can be expanded with standard modules of the S7-400. There are
restrictions for the function modules and communication processors. See Appendix Function
and communication modules that can be used in a redundant configuration (Page 389).
Figure 2-4 Hardware of the S7-400H basic system
The two CPUs are the heart of the S7-400H. Use the switch
the rack numbers. In the following sections, we will refer to the CPU in rack 0 as CPU 0, and
to the CPU in rack 1 as CPU 1.
of the CPU to set
The UR2-H rack supports the installation of two separate subsystems with nine slots each,
and is suitable for installation in 19" cabinets.
You can also set up the S7-400H in two separate racks. The racks UR1, UR2, and CR3 are
available for this purpose.
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
28 System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC

Introduction to the CPU 410
Power supply
Synchronization modules
Fiber-optic cable
Operation
2.4 The basic system for redundant operation
You require a power supply module from the standard system range of the S7-400 for each
of the two subsystems of the S7-400H.
To increase availability of the power supply, you can also use two redundant power supplies
in each subsystem. In this case, you use the power supply modules PS 405 R / PS 407 R.
A combination (PS 405 R with PS 407 R) can also be used.
The synchronization modules are used to link the two CPUs. They are installed in the CPUs
and interconnected by means of fiber-optic cables.
Two types of synchronization modules are available:
● Synchronization modules for synchronization cables up to 10 meters long
● Synchronization modules for synchronization cables up to 10 kilometers long
You must use 4 synchronization modules of the same type in a fault-tolerant system. For a
description of the synchronization modules, refer to the section Synchronization modules for
the CPU 410. (Page 239).
The fiber-optic cables are used to interconnect the synchronization modules for the
redundant link between the two CPUs. They interconnect the upper and lower
synchronization modules in pairs.
You will find the specification of the fiber-optic cables you can use in an S7-400H in the
section Selecting fiber-optic cables (Page 245).
You need a system expansion card for operation of a CPU 410. The system expansion card
specifies the maximum number of process objects that can be loaded to the CPU and saves
the license information in case of a system expansion. The system expansion card forms a
hardware unit with the CPU 410. In redundant operation, each CPU 410 must have a system
expansion card with identical quantity framework and scope of functions.
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC
29

Introduction to the CPU 410
2.5
Rules for H station assembly
2.6
I/O for the CPU 410
2.5 Rules for H station assembly
The following rules have to be complied with for a fault-tolerant station, in addition to the
rules that generally apply to the arrangement of modules in the S7-400:
● The CPUs have to be inserted in the same slots.
● Redundantly used external CP443-5DX DP master interfaces or communication modules
must be inserted in the same slots in each case.
● External DP master interface modules for redundant DP master systems may only be
inserted in central controllers and not in expansion units.
● Redundantly used CPUs must be identical, which means they must have the same article
number, product version and firmware version. It is not the marking on the front side that
is decisive for the product version, but the revision of the "Hardware" component
("Module status" dialog mask) to be read using STEP 7.
● Redundantly used other modules must be identical, i.e. they must have the same article
number, product version and - if available - firmware version.
● Two CPU 410-5H must have system expansion cards with the same configuration size
and the same functional scope.
You can use SIMATIC S7 input/output modules with the CPU 410. The I/O modules can be
used in the following devices:
● Central controllers
● Expansion units
● Distributed via PROFIBUS DP
● Distributed via PROFINET IO
The function modules (FM) and communication modules (CP) that can be used with CPU
410 are listed in the appendix Function and communication modules that can be used in a
redundant configuration (Page 389).
CPU 410 Process Automation/CPU 410 SMART
30 System Manual, 05/2017, A5E31622160-AC
 Loading...
Loading...