Page 1

Siemens Hearing Solutions
User guide
Behind-the-Ear-Instruments
PRISMA 2
PRISMA 2 D SPPRISMA 2
PRISMA 2 P
Page 2

A friendly guide to your
new Siemens hearing
instruments
Congratulations!
You have decided in favour of hearing instruments from
Siemens. You have taken an important step towards being
able to hear and understand better once again.
Your new hearing instruments will be your constant companions from now on. With these technically perfected
hearing instruments you profit from our many years research
and experience in microelectronics. Soon it will be easy for
you to hear again. Good hearing is an important requirement
for your physical well being. With your new hearing instruments, which will accompany you daily, you will again enjoy
taking an active part in the world of speech and music.
And as with any constant companion, you’ll need some time
at first to get used to handling your hearing instruments.
With a little patience, we trust that your new hearing
experience will be all the more pleasant for you.
For this purpose we are providing you with this brief user
guide for your hearing instruments it should contribute to
deepening your friendship with your new partners in the
matter of better hearing. We want to help you to handle
your hearing instruments correctly, so that they will become
an important part of your life.
Wishing you much success,
Your Siemens Team
2
Page 3

Applicable to all PRISMA 2 instruments
How to insert your ear mould Page24
Handling batteries Page26
Notes for cleaning and care Page27
The best way to handle your hearing instruments Page 29
How to solve some failures yourself Page30
Hearing training made easy Page 32
In this brief guide you will find instructions for inserting,
placing and adjusting your hearing instruments. There are
also tips and information on correct handling, cleaning, care
and battery changing. And naturally information about how
you can solve some failures yourself if you cannot visit a
hearing instrument specialist immediately.
One important note: Your hearing success depends
largely on how well your instruments fit in the ears and
how carefully you maintain and handle them.
The best way to use your
new hearing instruments
3
Contents:
This is your
Instrument
PRISMA 2/PRISMA 2 P Page 5
PRISMA 2 D SP Page 13
2/2 P
2 D SP
All
Page 4

Page 5
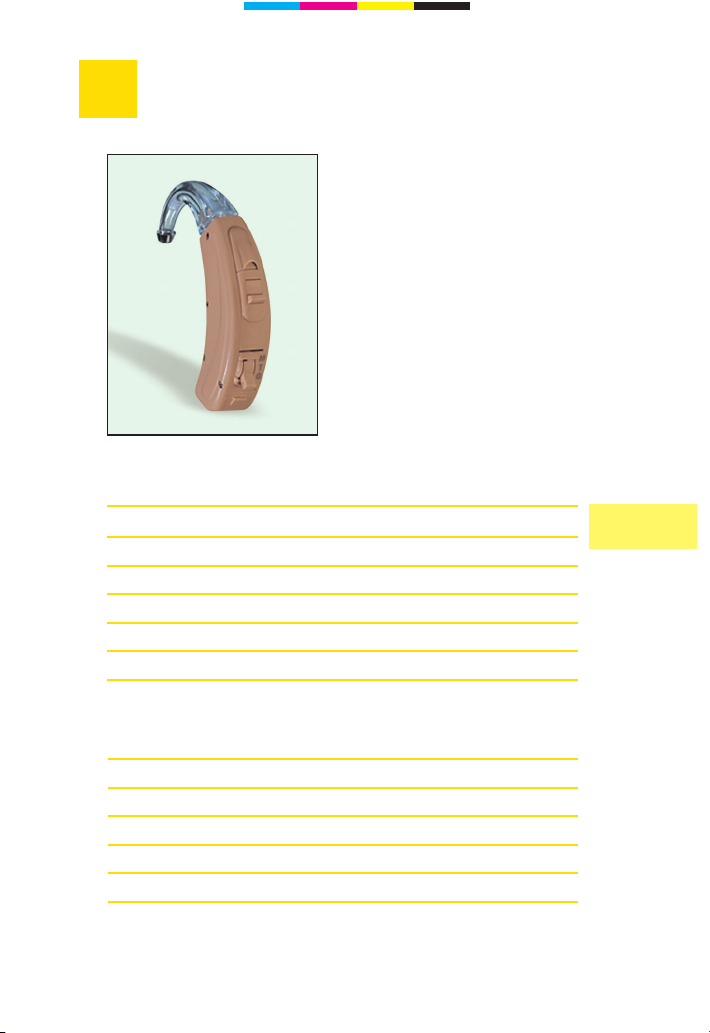
5
PRISMA 2/PRISMA 2 P
Description of the PRISMA 2/PRISMA 2 P
hearing instruments Page 6
Battery changing Page 7
Safety notes for batteries Page 8
How to switch your instrument on/off Page 8
Program button Page 9
Children’s safety device Page 10
Audio input Page 11
2/2 P
Applicable to all PRISMA 2 instruments
How to insert your ear mould Page24
Handling Batteries Page26
Notes for cleaning and care Page27
The best way to handle your hearing instruments Page 29
How to solve some failures yourself Page30
Hearing training made easy Page 32
Page 6
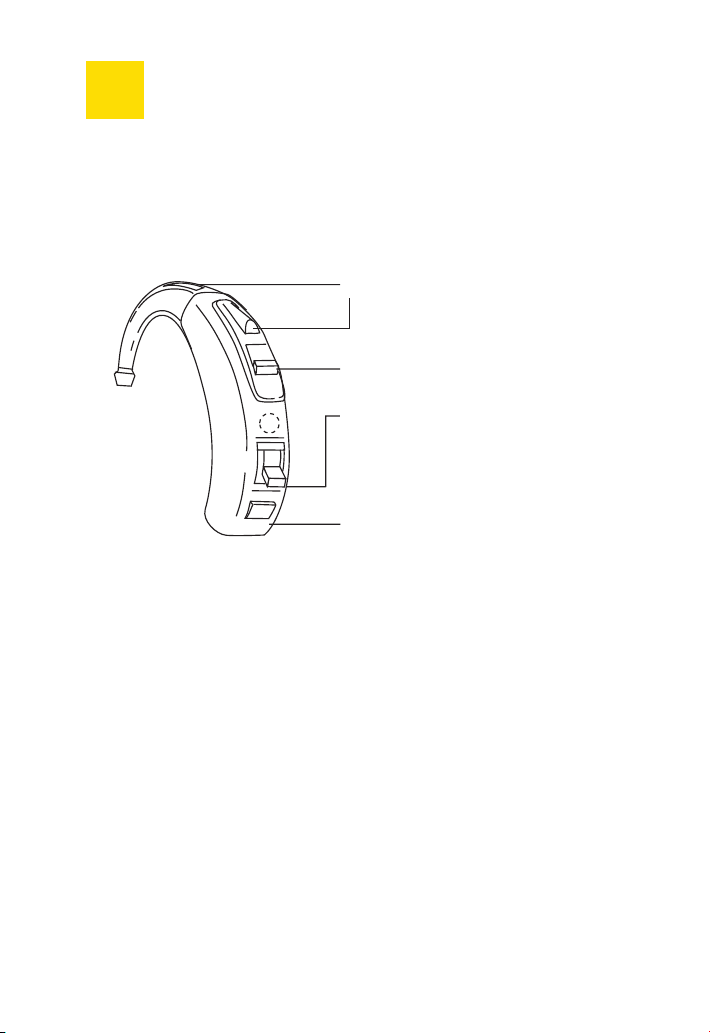
6
Description of the PRISMA 2,
PRISMA 2 P hearing instrument
Microphone opening
Program button
Selection of operating mode
M = hearing via microphone
T = induction coil switched on
O = Off
Battery compartment
with lock
For your instrument you will need Battery Type 13.
Page 7
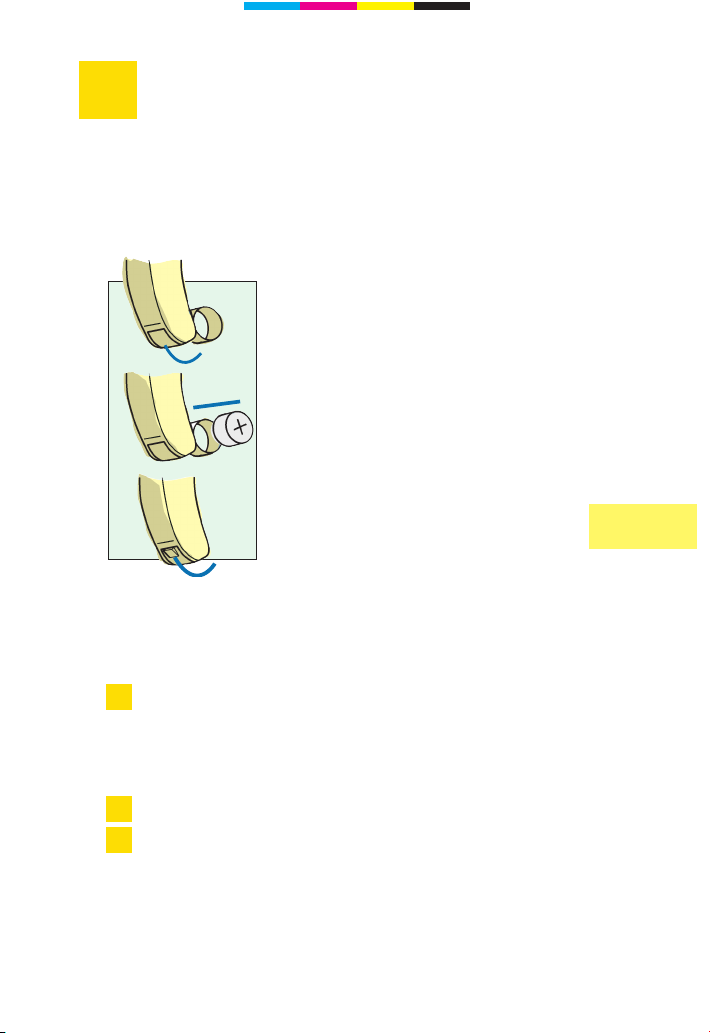
7
Battery changing
When inserting the battery please pay attention to the
plus side on the battery.
The plus (+) side of the battery is always the smooth
side. You can recognise the minus (–) side by the
coloured ring.
You should always keep spare batteries at hand.
If you feel you cannot change the battery yourself, ask
someone to help you: a family member, friend or your
hearing instrument specialist.
▼
▼
▼
▼
Open the
battery
compartment
Insert the
battery
Close the
battery
compartment
2/2 P
Page 8
8
Safety notes for batteries
WARNING
Keep batteries away from children!
Batteries must not be swallowed.
Remove the batteries when the instrument is not in
use over a prolonged period. Replace leaking batteries
without delay.
Do
not throw away your dead batteries!
Return them to your hearing instrument specialist for
proper, environmentally conscious disposal.
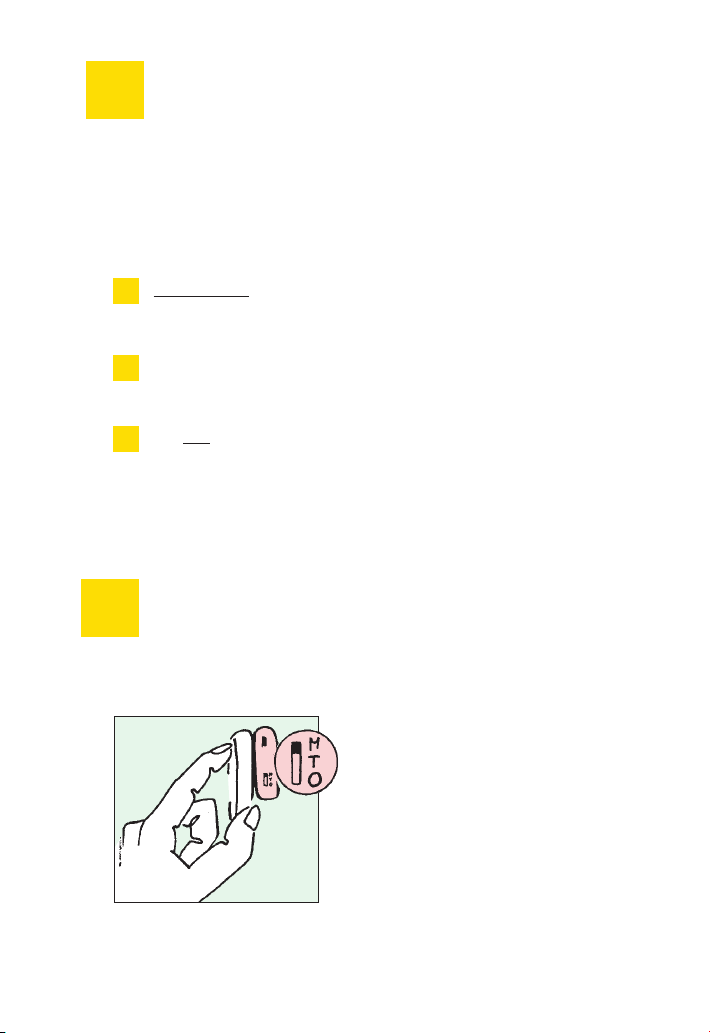
Set the switch to position M
The hearing instrument is ready
for use without any further
adjustment. Even if the sound
level changes, your instrument
is always adjusted correctly
according to your personal needs.
Thus soft sounds aren’t lost and
loud sounds aren’t amplified or
are amplified only insignificantly.
How to switch your
instrument on/off
Page 9
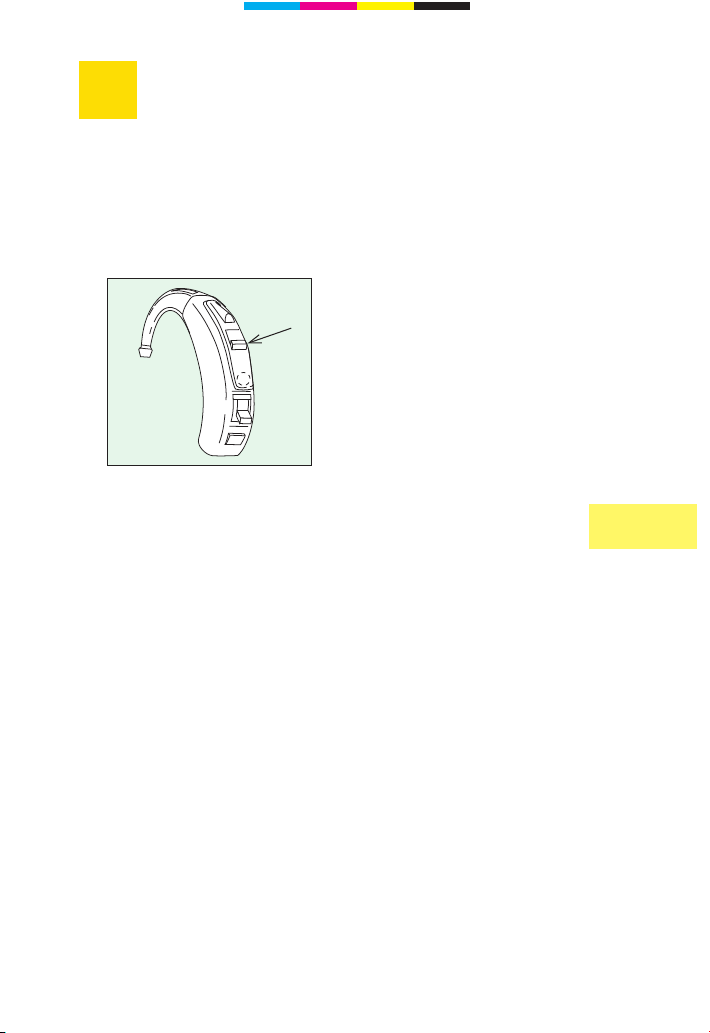
9
2/2 P
You can adapt to a changed
hearing situation by lightly
pressing the program button.
For instance, you are better able
to understand the person
you’re talking to even in
disturbing background noise.
You simply press the button
to choose between two
programs.
Program button
Your acoustician can adapt the two programs exactly to
your individual needs. In this way it is possible to take
account of different microphone characteristics.
A beep indicates which hearing program is selected.
One beep is when changing to microphone program “1” or
to “T” setting. Two beeps is when changing to microphone
program “2”.
If required, your hearing instrument specialist can switch the
beeps off.
Page 10
10
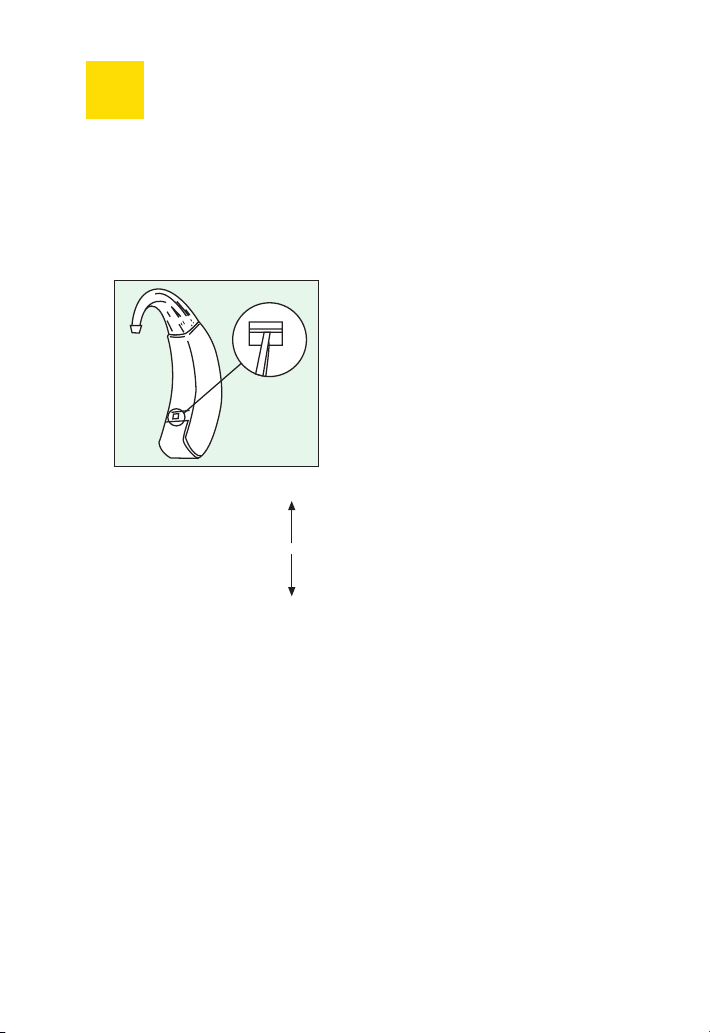
Children’s safety device
Your instrument is equipped
with a “children’s safety
device“. This is intended to
prevent the unintentional
removal of batteries from their
compartment, such as by small
children. This safety device is on
the inner side of the hearing
instrument. Please use a tool
suited to the purpose to open
or close the safety device.
Pushing the slide towards the
battery compartment locks the
battery compartment; pushing
the slide towards the ear hook
unlocks the battery compartment so that it can be opened.
unlock
lock
Page 11
11
2/2 P
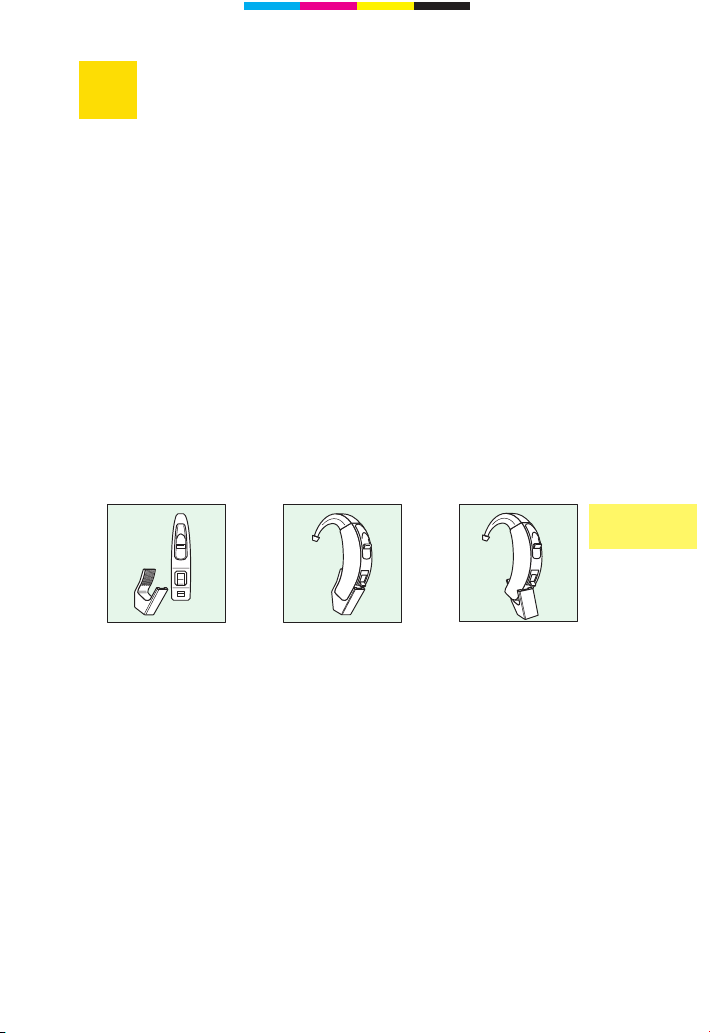
Safety note for instruments with audio input
The audio input can only be connected to power supplied
devices if they fulfil at least the safety provisions of
IEC 65 / DIN VDE 0860.
Your hearing instrument has an audio input. This enables the
connection between hearing instrument and accessories.
In this way you can understand better in certain hearing
situations. Take care that before you use the audio input you
pull off the protective foil.
The audio shoe connects the audio cable with your instrument.
Plug the audio shoe on to the hearing instrument (Fig. 1 and
Fig 2).
Remove the audio shoe from the hearing instrument
(Fig. 3).
Audio input
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Fig. 1
Page 12

Page 13

13
2 D SP
PRISMA 2 D SP
Applicable to all PRISMA 2 instruments
How to insert your ear mould Page24
Handling batteries Page26
Notes for cleaning and care Page27
The best way to handle your hearing instruments Page 29
How to solve some failures yourself Page30
Some useful tips Page 31
Hearing training made easy Page 32
Description of the PRISMA 2 D SP
hearing instruments Page 14
Handling batteries Page 15
Battery changing Page 16
Setting the loudness Page18
Program switch Page 18
Children’s safety device Page20
Audio input Page21
Page 14

14
Volume control
Program switch
Description of the
PRISMA 2 D SP
hearing instrument
Programming socket
Audio input
Sound inlet openings
Battery compartment
with lock and
on/off switch
Ear hook
Page 15

15
2 D SP
Handling batteries
So-called zinc-air batteries are
used today almost exclusively
in hearing instruments to
minimize environmental
damage. These batteries
require oxygen for operation,
which they absorb from the
air. The battery is activated as
soon as the protective foil is pulled off and is used up even
if you do not use your hearing instrument.
You should always pull off the protective foil only if you
actually use the battery. Also, do not leave the batteries
in your hearing instruments if you do not use them over
a longer period. The batteries can leak and damage the
instruments. The batteries keep for from a few days up to
several weeks according to the way they are used. You can
recognize when a change of batteries becomes necessary,
because your hearing instruments become noticeably quieter
towards the end of the battery’s life. Then it is time for new
batteries. Two warning tones sound once per minute, indicating
that you must insert a new battery.
Your hearing instrument specialist can switch off the warning
tones if required.
Zinc-air batteries which are almost completely used up show
the following behaviour: After switching on the instruments
they function completely normally, but then rapidly become
quieter. The more the battery is used up, the faster the gain
falls off. You must then replace such batteries by new ones.
…
Page 16

16
Battery changing
Inserting the battery
Important! Make sure to note the
polarity of the battery!
If the battery is inserted incorrectly,
the battery compartment can be
closed only with considerable
force. This will damage the
instrument.
Closing the battery
compartment
Close the battery compartment by
pressing from below with your
finger tip.
The instrument is switched on.
Up to the first stop = the
instrument is then switched off
Completely open = to change
the battery open the battery
compartment completely by
applying more force
Removing the battery
Open the battery compartment
as shown in the figure.
Normally the battery drops out
when the battery compartment is
completely open.
Should this not be the case, you
can lightly tap the instrument or
push the battery out with a pencil
as shown in the picture.
Page 17

17
2 D SP
Three useful tips:
The plus (+) side of the battery is always the smooth
side. You can recognize the minus (–) side by the
coloured ring.
You should always keep spare batteries
at hand.
If you feel you cannot change the battery yourself,
ask someone to help you: a family member, friend
or your hearing instrument specialist.
Please do not throw used batteries into household refuse.
Return them to your hearing instrument specialist for
environmentally correct disposal.
Caution!
Please keep batteries out of the reach of children. They
are damaging to health when swallowed.
Page 18

18
Setting the loudness
2
Your hearing instrument specialist can program the possible
adjustment range for you. If you do not want to use the
volume control, then your hearing instrument specialist can
also switch it off. Turning the volume control then does not
change the adjustment of your PRISMA 2 D SP hearing
instrument.
PRISMA 2 D SP hearing
instruments are fully automatic. It is therefore not
necessary for you to change
the loudness manually.
However, if you still wish
to do so, PRISMA 2 D SP
offers you a volume control.
louder
quieter
turn
PRISMA 2 D SP hearing instruments have 4 hearing
programs. Three are selected
with a program switch. The
fourth program is activated
as soon as the audio shoe
is plugged to the audio input.
Your hearing specialist will program them
according to your individual needs.
Program switch
1
2
T
Program“1“
Program“2“
Program“3“
(telecoil)
Page 19

19
2 D SP
Function of the program switch without audio shoe
(recommended setting)
Switch position 1 - Program "1"
For the most frequently required hearing situation e.g. at
home or work place
Switch position 2 - Program "2"
For special situations according to your individual needs, e.g.
music.
Switch position T - Program "3"
For telephoning and for using induction loops e.g. in churches,
theatres or lecture rooms.
Using the "T" position for telephoning requires that the telephone is suitable for hearing instruments and emits a corresponding magnetic field. Not all modern phones, especially
cordless telephones and mobile phones produce a magnet
field. In such cases we recommend that you phone, if possible,
with program "1" or "2".
Switching between the positions 1-T-2 is indicated by beep
tones. One beep tone to position "1", two beep tones to
position "2" and three beep tones to position "T".
Function of the program switch with audio shoe
plugged on
The audioprogram is activated as soon as the audio
shoe is plugged on.
Switch position 1 - Program "1"
As without audio shoe
Switch position 2 - audio input mode
The heard signal comes via audio shoe only
Switch position T - Mixed mode
Microphone signal and signal via audio shoe are heard together
Switching between the positions 1-T-2 with audio shoe plugged
on is indicated by beep tones. One beep tone to position "1",
four beep tones to position "2" and "T".
Your hearing instrument specialist can switch off the beeps
if required.
Page 20

20
Children’s safety device
Your instruments are
equipped with a “children’s
safety device“. This is
intended to prevent the
unintentional removal of
batteries from their compartment, such as by small
children.
To lock the children’s safety
device open the battery
compartment up to the first
stop. Push the slide in the battery compartment to the right
with a suitable tool.
To unlock the battery compartment again, open the battery
compartment up to the first stop. Push the slide in the battery
compartment to the left with a suitable tool.
If you feel you cannot do this yourself, your hearing instrument
specialist will be pleased to help you.
locked
unlocked
Page 21

21
2 D SP
Audio input
Safety instructions for hearing instruments with audio
input
The audio input may be connected to line-operated
equipment only if this fulfils at least the safety
requirements of IEC 65 / DIN VDE 0860.
Fitting an audio shoe
Open the battery compartment
up to the first stop, open the
flap under the 1-T-2 switch, hook
the audio shoe in from the front
and press it to the rear into the
detent on the inner curved
piece.
Switching off instrument with
audio shoe
Press the audio shoe to the rear,
up to the first stop.
Removing the audio shoe
Press the audio shoe to the
front, unhook the audio shoe
and close the flap again.
Your hearing instruments are equipped with an audio input.
This enables the connection between hearing instrument
and accessories. It helps you to understand better in
certain hearing situations.
Page 22

Page 23

23
Applicable to all
PRISMA 2 instruments
PRISMA 2 D SPPRISMA 2
PRISMA 2 P
All
How to insert your ear mould Page24
Handling batteries Page26
Notes for cleaning and care Page27
The best way to handle your hearing instruments Page 29
How to solve some failures yourself Page30
Hearing training made easy Page 32
Page 24

Make sure that your hearing
instrument is turned off. The
battery compartment must be
opened up to the stop. Grip the
ear mould between your thumb
and index finger and place the
tip carefully into your auditory
canal.
You may find it helpful to pull
your ear slightly upwards or to
the rear. You may want to push
the ear mould very gently
with your index finger.
Once inserted, you should
feel that the ear mould is
correctly placed.
Now place your hearing
instrument behind your ear
and switch it on. Close the
battery compartment fully.
How to insert your
ear mould
24
Page 25

25
Tip:
Practice inserting and removing your hearing
instruments correctly.
One easy way to practice is to sit down at a table.
Place a mirror in front of you and prop your elbows
on the table so you can guide your hands easily and
safely. This will help you stay relaxed and comfortable
while you practice.
All
Page 26

26
So-called zinc-air batteries are
used today almost exclusively
in hearing instruments to
minimize environmental
damage. These batteries
require oxygen for operation,
which they absorb from the
air. The battery is activated as
soon as the protective foil is pulled off and is used up even
if you do not use your hearing instrument.
You should always pull off the protective foil only if you
actually use the battery. Also, do not leave the batteries in
your hearing instruments if you do not use them over a
longer period. The batteries can leak and damage the
instruments. The batteries last from a few days up to
several weeks according to the way they are used. You can
recognise when a change of batteries becomes necessary,
because your hearing instruments become noticeably quieter
towards the end of the battery’s life. Then it is time for new
batteries. Four warning tones sound once per minute,
indicating that you must insert a new battery.
Your hearing instrument specialist can switch off the warning
tones if required.
Zinc-air batteries which are almost completely used up show
the following behaviour: After switching on the instruments
they function completely normally, but then rapidly become
quieter. The more the battery is used up, the faster the gain
falls off. You must then replace such batteries by new ones.
Handling batteries
Page 27

All
27
Notes for cleaning
and care
It is essential to detach the ear mould from your behindthe-ear instrument and place it in a cleaning bath for
at least 15 minutes.
Caution: The hearing
instrument itself cannot
tolerate any moisture.
1.
Bring your hearing instruments regularly to your
hearing instrument
specialist, on the schedule
that he or she recommends,
to have the hearing tube
changed and the instrument checked.
2.
Ear wax accumulates on your ear mould. This can lead to
inflammation in your auditory canal if the instruments are
not cleaned regularly. Therefore:
Page 28

28
Two more tips:
You should place your hearing instruments in a
“dry bag“ with a special moisture-attracting capsule
overnight. The drying capsule draws damaging
moisture out of the instruments.
Your hearing instrument specialist stocks the special
care sets and dry bags you need to maintain your
hearing instruments and keep them in good
condition.
Page 29

29
The best way to handle your
hearing instruments
Your new hearing instruments are highly sensitive
instruments.
This naturally requires some care in their handling.
They should then always give you good service.
Caution!
As with all electrical, non gas-encapsulated instruments,
the hearing instruments must not be operated in
explosion-endangered rooms.
All
Page 30

30
Important tips:
How to solve failures
yourself
In selecting your PRISMA 2 hearing instruments you have
chosen extremely dependable devices. However, should a
fault occur, it can usually be corrected quickly.
If the instrument whistles
Test the instrument yourself by closing the sound
outlet opening with your fingertip.
If the whistling disappears, the instrument is in
order.
Check that the ear mould sits properly in your ear.
Also test the hearing tube for leaks.
If the whistling noise is still audible, only your hearing
instrument specialist can provide assistance.
Sound
outlet opening
Page 31

All
31
Some useful tips:
Never expose your hearing instruments to
extreme temperatures or high humidity.
Never let them lie in the blazing sun. Do not
wear them when taking a shower or when using
hairspray.
In short-wave therapy or if you work or are
medically treated with strong magnetic or
high-frequency fields or X-rays, under no
circumstances may you wear the instruments
during the therapy.
Make sure to switch off the instruments when
not in use. This saves the batteries.
If you don’t wear your instruments for a longer
time, remove the batteries. Batteries can leak
out. Replace batteries that have leaked out
without delay.
If the hearing instrument is too quiet
Most likely, you need to insert a new battery. If it
is still too quiet, clean the instrument or the ear
mould and hearing tube, following the directions
in the chapter
“Notes for cleaning and care“.
If neither a new battery nor cleaning helps,
as a precaution you should ask your hearing
instrument specialist to test your hearing again.
If the hearing instrument does not work at all
Is the instrument turned on? Is the battery
compartment completely closed? Is the battery
inserted correctly? Is it possible that the battery is
dead?
If none of these hints help, you should visit your
hearing instrument specialist.
Page 32

32
2nd step
1st step
Hearing training made easy
Hearing instruments reproduce an abundance of sounds
which frequently haven’t been experienced for many years.
Every person reacts differently the first time he or she wears
a hearing instrument. The familiarisation phase therefore
differs from person to person. There are people who are
quite happy to wear their hearing instruments the whole day
long right from the start. Others will regard it as a foreign
body at first. You’ll notice that even after a relatively short
time the positive new hearing experience prevails and you’ll
find your hearing instruments to be something quite normal.
Hearing training helps you here. You’ll become more and
more perfect, and naturally securer, step by step.
Experience sounds outdoors
First choose quiet surroundings for this. For instance, while
taking a stroll you’ll discover all sorts of sounds in the ”silence”
of the forest.
Discover simple sounds in your direct surroundings
Wear your instruments in different situations in different
rooms. Repeat this exercise and you’ll become more
and more familiar with the sounds.
Page 33

All
33
3rd step
Get used to conversations in a group
Conversation in a group of people speaking among
themselves is one of the most difficult hearing
situations. Try to distinguish between the voices by
noting their specific tonal colour and their characteristic
rhythm, and fit them to the individual persons.
Don’t be discouraged and repeat the exercise – think
about your goal: to be able to take part in conversations
again.
Become familiar with your own voice
You’ve already made remarkable progress! You’ve become
much more familiar with the sounds in your daily environment.
As an exercise read out aloud and concentrate on your own
voice.
4th step
Learn to understand the voices of others
Wear the instrument when you speak with someone in your
family. Make a date with a friend. Explain your new situation
and ask the person you’re talking to to speak at a normal
conversational level.
Exercise: Have sentences read out to you and repeat these
sentences.
5th step
6th step
Visit public events
At lectures or in church find a place as close as possible to
the speaker. Also choose a place at the front in theaters and
concert halls. Avoid niches, boxes and places behind pillars.
Page 34

34
8th step
Go on further voyages of discovery – undertake everything that gives you pleasure and experience the whole
wide world of hearing.
7th step
Telephoning with your hearing instrument
You can telephone in the “normal“ M position. Set the switch on the
hearing instrument to T if you have difficulties in understanding. Place
the telephone receiver behind your external ear against the hearing
instrument and find the most favorable and loudest transmission. You
can activate the telephone coil and the microphone by pressing the
program button so that you can hear the normal surroundings.
Your hearing instrument fulfils the IEC 118-13 standard
with regard to electromagnetic compatibility (concerning
for example interference by external radiotelephones).
If you use a radiotelephone (GSM) yourself, unfortunately
unavoidable disturbances can occur in your hearing
instrument under certain circumstances because of the
high field strengths.
This is certainly unpleasant but no reason for concern.
Your hearing instrument isn’t defective.
Page 35

All
35
We’re happy that you
can hear well again!
Once good hearing returns to
your everyday life – and you can
enjoy both speech and music
again – then we at Siemens are
also satisfied.
Because we’ve put all our
knowledge and skill into developing
your hearing instruments!
Page 36

Order No. A91100-M5100-1033-01-7600
Printed in Germany
35018 12.03.JK
78 19 191
Siemens
Audiologische Technik GmbH
Gebbertstrasse 125
91058 Erlangen
Germany
www.hearing-siemens.com
Subject to change without prior notice
 Loading...
Loading...