
SIX CHANNEL MICROPHONE MIXER
Model M367 User Guide
DESCRIPTION
The Shure M367 is a portable, six–input, two-output (mono),
battery-powered microphone and line level mixer/preamplifier. Its
transformer–isolated design, low-noise performance, and compact
and rugged construction make the M367 an ideal choice for studio
and mobile broadcast, electronic news gathering (ENG), and
electronic field production (EFP) applications.
This versatile mixer can also be used for the following:
• Digital transmission links
• Digital video/audio recording media (ISDN, hard disk
recording, and DAT)
• Sound reinforcement
The M367 comes with rubber feet, detachable power cord, and spare power line fuse. It can be rack mounted using the optional Model A367R rack mount kit.
FEATURES
• Six selectable mic/line inputs
• Selectable mic/line output and dedicated line output
• Transformer-balanced inputs and outputs for sup erior
of RFI and electromagnetic hum
• Professional mechanical VU meter–LED backlighting for high
reliability, no lamp replacement
• Headphone monitoring 3.5 mm, (1/4 in.)
• Output peak limiter with switchable threshold and bi-colored
LED indicator
• Peak indicator LED, and switchable low-cut filters on each
1/4 in. return monitor input
• AC power or (2) 9V battery operation
rejection
input
ADDITIONAL FEATURES
• 48 Vdc or 12 V phantom power for condenser microphones
• 1 kHz tone oscillator
• Mutes all input channels when activated
• Tone level control is on the master
• Wide–range input gain controls handle ho t signal levels
attenuators
• Customized operation via internal DIP switches, trim pots, and
optional alternate wiring
• Battery check switch and low battery warning indication
• Power-on LED
• Input expansion via mix bus jack to link M367s or other mixers
• Rugged all metal chassis with protective end caps
• Detachable AC power cord
without
©2005 Shure Incorporated
27
C8511 (Rev. 4)
Printed in U.S.A.
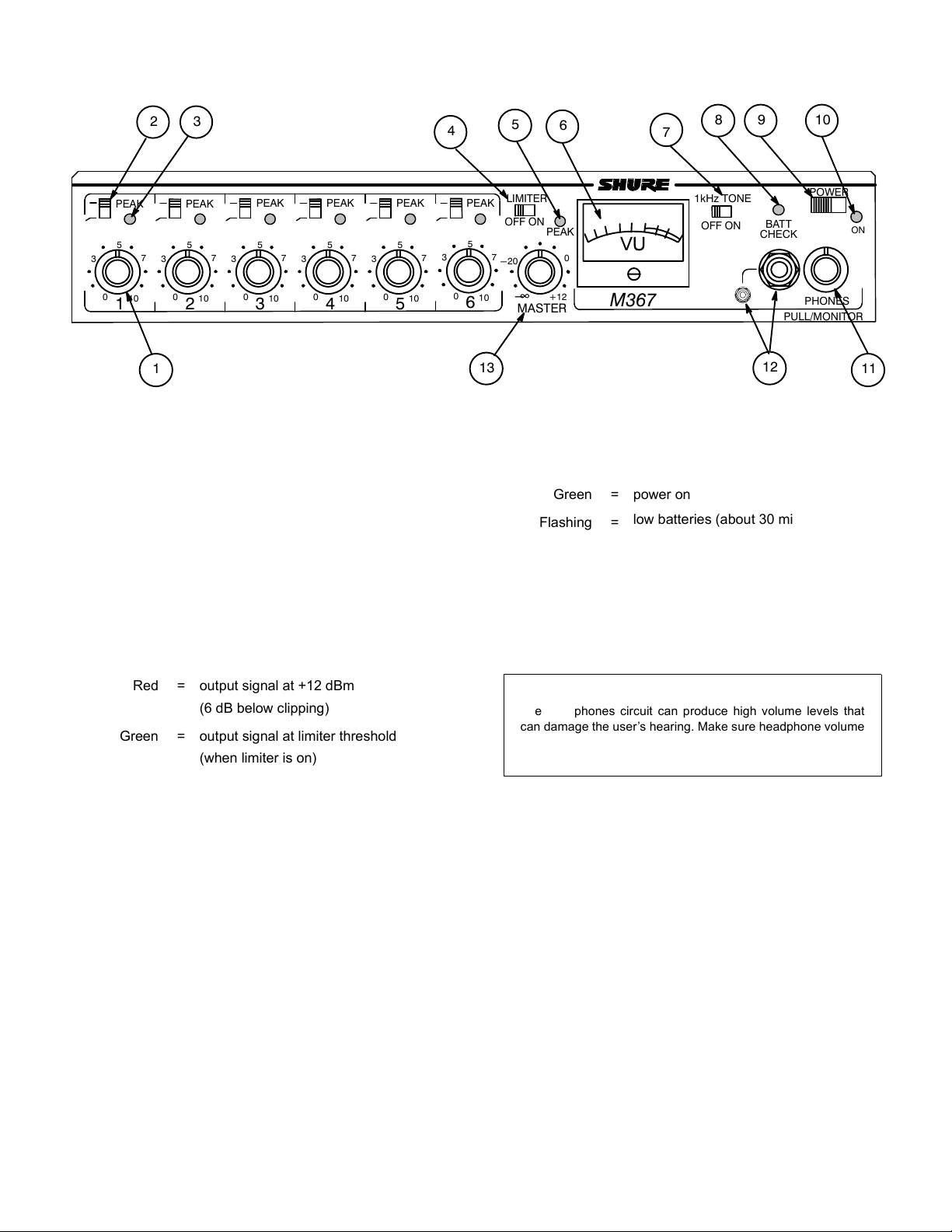
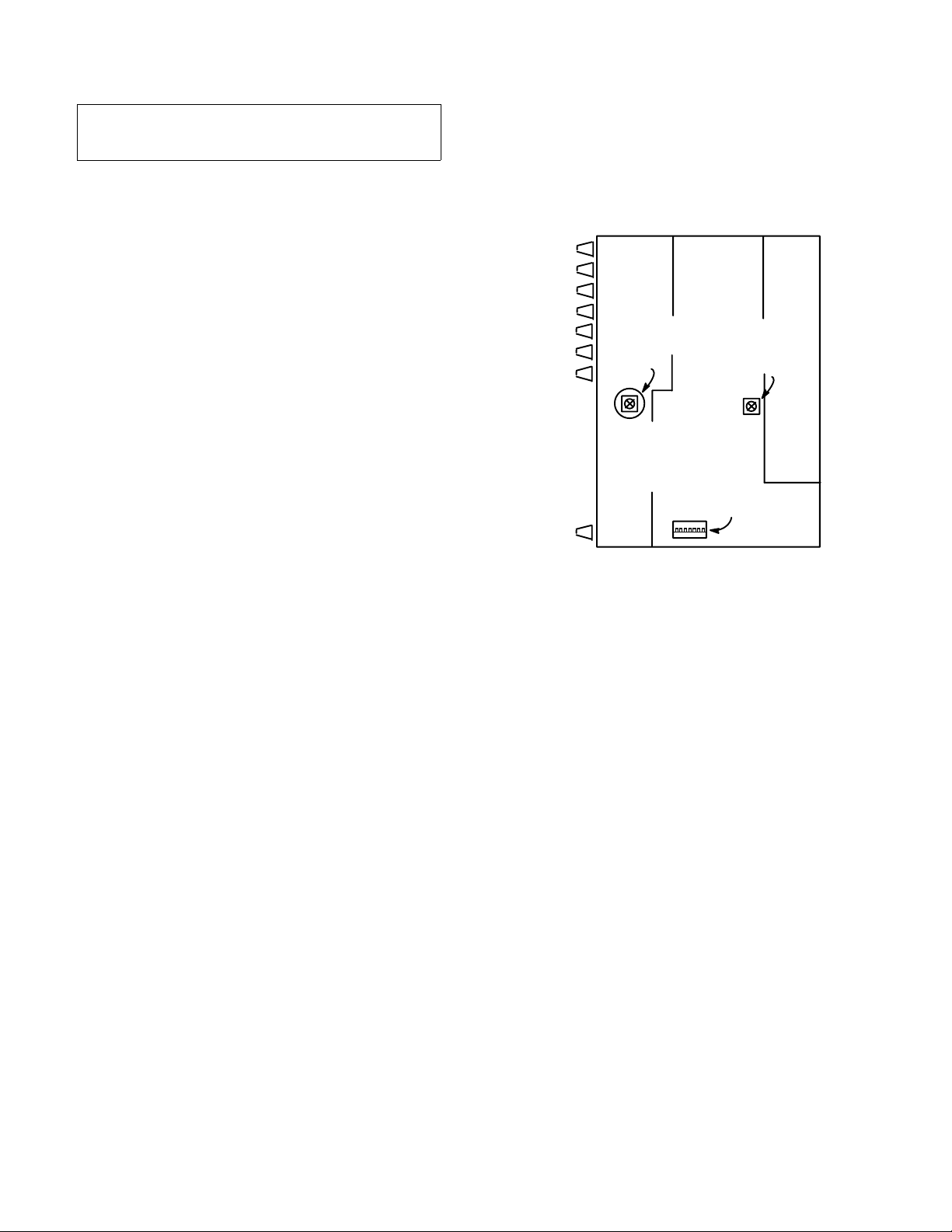
FRONT PANEL CONTROLS AND INDICATORS
Ñ
Ñ
2 3
PEAK
5
3
0
10
PEAK
5
7
3
0
10
21
PEAK
5
7
3
0
10
PEAK
5
7
3
0
10
PEAK
5
7
3
0
543
4
3
7
10
1
FRONT PANEL CONTROLS AND INDICATORS
FIGURE 1
1. Input Gain Control: For best performance, adjust each Input
Gain Control so the associated Input Peak LED illuminates red
only on the loudest signal peaks.
2. Input Low-Cut Filter Switch: Provides low-frequency roll–off
to reduce wind noise and rumble. When using the filter, the
frequency response is down 7 dB at 150 Hz. Roll-off slope is 6
dB per octave.
3. Input Peak LED: Illuminates at 6 dB below clipping.
4. Limiter Switch: Activates a fast-acting, peak-responding
limiter optimized for speech. An internal modification can
provide a slower release time for music signals (see DIP
Switches).
5. Output Peak/Limiter Bi-Color LED:
8 9
1kHz TONE
OFF ON
0
PEAK
5
10
6
OFF ON
7
-20
5
LIMITER
MASTER
6
PEAK
+12
7
0
VU
M367
13
9. Power-On/Off Switch: Turns the mixer on and off.
10. Power-On LED:
Green = power on
Flashing =
low batteries (about 30 minutes of
operation remaining)
11. Dual function control knob:
Headphones Gain Control: Rotate to adjust headphone
level.
Pull/Monitor Switch: When using headphones, pull out to
listen to audio from the MONITOR IN jack. Add attenuated
program signal using DIP switch 4 (see DIP Switches).
BATT
CHECK
PULL/MONITOR
12
10
POWER
ON
PHONES
11
Red = output signal at +12 dBm
(6 dB below clipping)
Green = output signal at limiter threshold
(when limiter is on)
6. Output Level (VU) Meter: Meter response approximates true
VU characteristics (about 300 ms rise and fall, 1% to 5% over
shoot). For a slower response, see Internal Modifiable Func-
tions. 0 VU is switchable between +4 and +8 dBm (see DIP
Switches). When using batteries, use the BATT CHECK
switch to illuminate the meter.
7. 1 kHz Tone Oscillator Switch: Sends a 1 kHz tone to all out-
puts and mutes all inputs. The MASTER control adjusts tone
level.
8. Battery Check Button: Press and hold to show battery level
on the VU meter. Press once to illuminate the VU meter for 10
seconds, or set DIP switch 6 to toggle the meter light (see DIP
Switches).
WARNING
The headphones circuit can produce high volume levels that
can damage the user’s hearing. Make sure headphone volume
setting (PHONES) is low (Full CCW before putting
headphones on.
12. Headphones Outputs: Stereo 1/4 in. and 3.5 mm phone
jacks.
13. Master Gain Control: Sets mixer output gain. Set to 0 dB
position for unity gain.
2
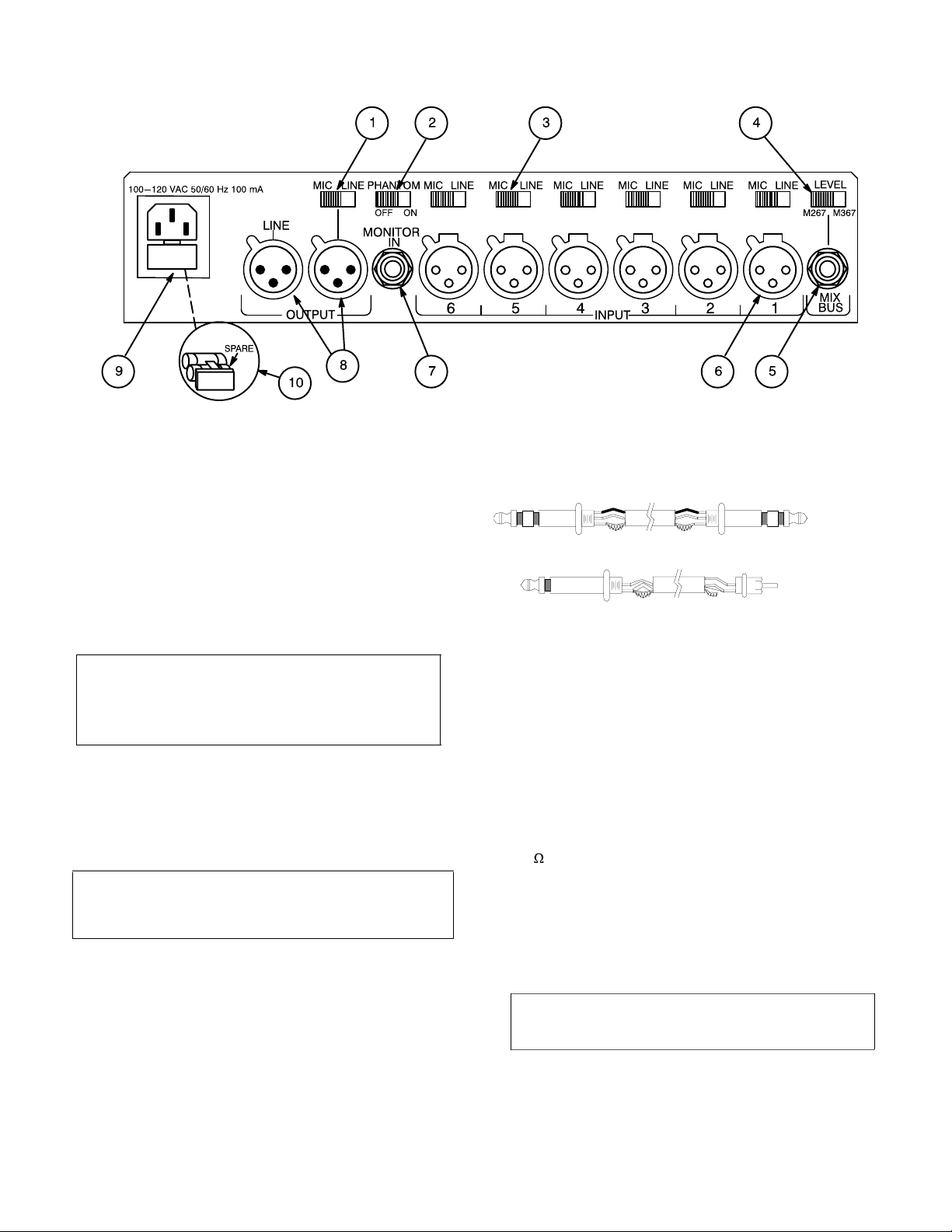
REAR PANEL CONNECTORS AND CONTROLS
REAR PANEL CONNECTORS AND CONTROLS
FIGURE
1. Mic/Line Level Output Switch: Sets output to microphone or line level.
2. Phantom Power Switch: Adds 12-volt phantom power to all inputs set to MIC. Use DIP switch 7 to increase voltage to 48 volts (see DIP Switches).
3. Mic/Line Level Input Switches 1-6: Sets input to microphone or line level. Phantom power is disabled for inputs set to LINE.
4. M267/M367 Mix Bus Level Switch: Set to M267 when connecting to a SHURE M267, FP42, FP51, M67, or SE30. Use
the M367 setting with another M367 or SHURE FP32A.
IMPORTANT
Unless required, leave the mix bus LEVEL switch in the
M367
position. The M267 setting may increase mixer out-
t noise up to 30 dB, depending on the MASTER output
pu
setting.
5. Mix Bus Jack: Allows you to connect the M367 to another
mixer. The mix bus connection is "two-way" and pre-master.
When two M367 mixers are connected, all 12 inputs appear at
both mixers' outputs. The MASTER gain control of either
M367 can be adjusted without affecting the other mixer’s
output.
The output level of each M367 mixer drops by 6 dB when connected through the MIX BUS, increase the Master Gain to compensate.
For a balanced mix bus connection between two M367s, use a
mix bus cable with two 1/4 in. stereo (tip, ring, sleeve) plugs.
When connecting other types of Shure mixers, construct a mix
bus cable with a 1/4 in. mono phone plug (tip = signal, sleeve =
ground) and the appropriate connector for the other mixer's mix
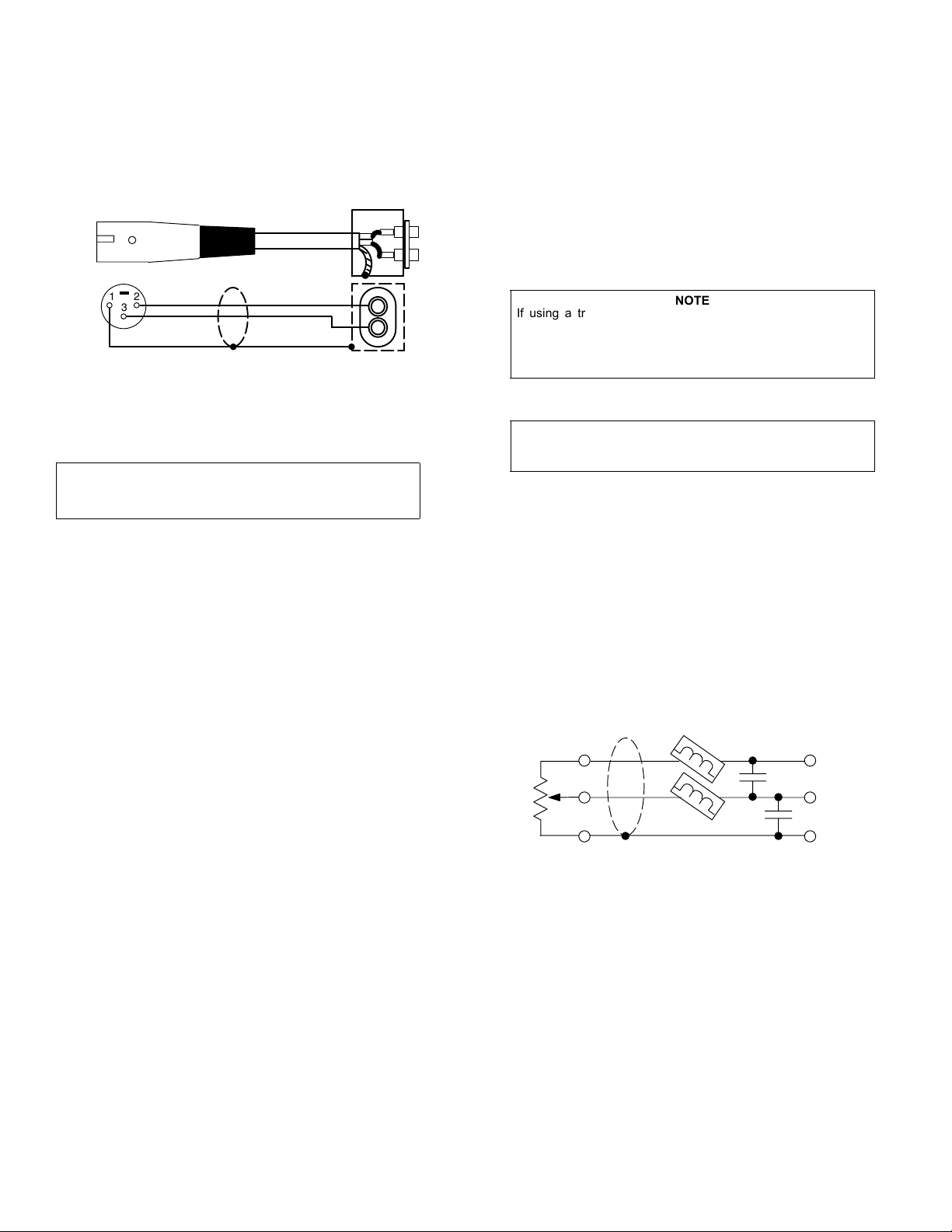
bus jack (see Figure 3).
NOTE
2
BALANCED
TO M367 #1 TO M367 #2
UNBALANCE
TO M367 TO M267
MIX BUS CONNECTIONS
FIGURE 3
6. Channel Inputs: These female XLR inputs are transformerbalanced to provide superior rejection of hum, RFI, and other
interference.
7. Monitor In Jack: Accepts mono line-level signals (tip = signal,
sleeve = ground) for "tape return" or a communications channel input. See Pull/Monitor switch description.
You can also modify the MONITOR IN jack to accept a stereo
input and provide a stereo sum monitor signal (see Internal
Modificable Functions ).
8.
Mixer Output:
The Line output is preset to line level, but can be modified to a true
output impedance or changed to microphone level (see Inter-
600
nal Modifiable Functions ).
9. Power Connector: See AC Operation .
10. Time Delay Fuses: The slide-out compartment contains two power line fuses. The outer (toward you) is a spare.
M367: 0.125A, 250V fuse
M367E: 0.063A, 250V fuse
For continued protection against fire, replace with the same
type and rating of fuse.
These male XLR outputs are transformer-balanced.
WARNING
D
N.C.
3
AC OPERATION
23
Limiter Threshold
= +16 dBm
= +8 dBm
= +4 dBm
= 0 dBm
Use the supplied power adapter to connect the M367 to a power
outlet.
M367: 100-120 VAC, 50/60 Hz
M367E: 220-240 VAC, 50/60 Hz
The operating voltage can be switched internally (see Internal
Modifiable Functions).
NOTE
Appliance inlet is the main disconnect device (to power off the
M367, you must unplug the power supply).
BATTERY OPERATION
Open the battery compartment by grasping the sides of the
compartment, squeezing to release the locks, and pulling the compartment outward. Insert two 9-volt batteries.
During battery operation, use the BATT CHECK button. Press
and hold to show battery level on the VU meter. Press once to illuminate the VU switch for 10 seconds, or set DIP switch 6 for continuous illumination (see DIP Switches).
BATTERY LIFE
With two fresh 9-volt alkaline batteries, the M367 operates for
about eight hours. Some mixer features decrease battery life, as illustrated in the following table.
SETTING LEVELS
1. Set the MASTER gain knob to the full off position.
2. Activate the 1 khz tone oscillator by setting the 1 KHZ TONE
switch to ON. Adjust the MASTER gain until the VU meter
needle indicates "0". Adjust the input levels on the equipment
connected to the M367 outputs accordingly. Deactivate the
tone by setting the 1 KHZ TONE switch to OFF.
3. Adjust the Input gain controls based on the incoming signal levels. The input PEAK LEDs should flicker red only on loud input peaks.
4. Observe the output on the VU meter and adjust the MASTER gain to obtain the desired levels. try to keep the average levels around "0 VU". The PEAK LED adjacent to the VU meter should illuminate only on loud output peaks.
DIP SWITCHES
1
234567
Access the DIP switches by removing the battery compartment
and top cover. Use the following table to set the switches
(Bold = factory setting.)
S701
Momentary use of headphones or meter illumination will not appreciably affect battery life.
Mixer Operation Battery
No Signal 40 9
With +4 dBm continuous output 45 8
With six mics at 12 V phantom power 55 6.5
With six mics at 48 V phantom power 70 5
With output to headphones 50 7
With meter illumination continuously on 75 4.5
*until Power LED begins to flash, allowing approximately 30 minutes
to replace batteries.
NOTE
Current
(mA)
Battery
Life
(hours)*
CONNECTING M367 OUTPUTS TO TELEPHONE LINES
Use the XLR outputs at line level to drive dc-biased, "dialed up"
telephone lines. A slight increase in distortion may occur. Use the
M367 limiter with the limiter threshold set to +4 dBm. Modify the
M367 output impedance to 600 W for proper fidelity (see Internal
Modifiable Functions). When connecting the M367 to a telephone
line, you must use an FCC-Registered interface adapter between
the mixer and telephone line.
Function Up
Switch
1 Meter 0 VU 0 VU = +4 dBm 0 VU = +8 dBm
2 Limiter
Threshold
3
4 Program to
Monitor
5 Monitor In
Gain
6 VU Lamp (Batt
Check button)
7 Phantom
Power
Normal High
Timed (Turns off
after 10 seconds)
12 Vdc 48 Vdc
See Figure 4
Off On (adds attenu-
Down
ated program signal
in headphones with
Pull/Monitor switch
on)
Toggled (press on,
press off)
LIMITER THRESHOLD SETTINGS
FIGURE 4
4
SPECIFICATIONS
Frequency Response
20 to 20,000 Hz ± 2.0 dB (channel controls centered)
Total Harmonic Distortion
0.25% THD at +4 dBm output, 55 to 20,000 Hz
Voltage Gain
Output
Actual
(Internal)
Actual
(Internal)
Mix Bus (M367)
Mix
Bus
(M267)
Clipping
Level
+23 dBV
Clipping
Level
+11 dBV
Input
Low-Z Mic
W
(150
Line
Monitor
Mix Bus
(M367)
MixBus (M267)
Line Mic Phones
87 dB 40 dB 103 dB 66 dB 27 dB
)
37 dB -11 dB 53 dB 15 dB -25 dB
--
10 dB -38 dB 26 dB -- --
50 dB 2 dB 66 dB -- --
--
12 dB -- --
Inputs
IMPEDANCE Input
Input
Mic 19 to 600 W 1 kW -10 dBV
Line £10 kW 50 kW +36 dBV
Monitor £1 kW 13 kW 0 dBV
Mix Bus
(M367)
Mix Bus
(M267)
Designed for
Use With
930 W bal.;
1860 W unbal.
3.5 kW 3.5 kW -17 dBV
930 W bal.;
1860 W unbal.
Outputs
IMPEDANCE Output
Output Designed for
Use With
Mic Low-Z inputs 1 W -31 dBV
Line 600 W 150 W +18 dBm
Phones 8 to 200 W 300 W +11 dBV
Mix Bus
(M367)
Mix Bus
(M267)
930 W bal.;
1860 W unbal.
3.5 kW 3.5 kW -28 dBV
930 W bal.;
1860 W unbal.
Equivalent Input Noise
£ –127 dBV with 150 W source, 400 to 20,000 Hz
Output Noise
Master level full CCW: –100 dBV, 400 to 20,000 Hz
Master level full CW: –80 dBV, 400 to 20,000 Hz
Hum and Noise
Equivalent Input:
£125 dBV, 20 to 20,000 Hz
Output: –95 dBV (Master CCW), –75 dBV; (Master CW), 20 to
20,000 Hz
Common Mode Rejection Ratio
65 dB at 100 Hz, –20 dBV input
Polarity
Mic/Line In to Mic/Line Out Non-Inverting
Mic/Line In to Phones Non-Inverting
Mic/Line In to Mix Bus (tip) Inverting
Monitor to Phones Non-Inverting
Mix Bus to Mic/Line Out Inverting
Overload and Shorting
Shorted outputs, even for prolonged periods, cause no damage.
Microphone inputs of up to 3 Vrms cause no damage. Line and
monitor can withstand signals of up to 30 Vrms.
Input Peak Indicators
6 dB below clipping level
Output Peak Indicator
Lights red at 6 dB below clipping level
Output Clipping Level
£ +18 dBm at line output into 600 W
Low-Cut Filters
7 dB down at 150 Hz; 6 dB/octave slope (3 dB down at 260 Hz)
Tone Oscillator
1 kHz ± 20%
Limiter
Threshold: Switchable: 0, +4, +8, +16 dBm
Attack Time: 1 ms ± 0.5 ms
Release Time Constant: 100 ms ± 30 ms
Indicator: Green when limiting by 1 dB or more
Phantom Power
12 V Phantom: 12 V through 340 W
48 V Phantom : 48 V through 3.4 kW
AC Power
M367: 100–120 Vac, 50/60 Hz, 100 mA
M367E: 220–240 Vac, 50/60 Hz, 50 mA; no-signal current drain
25 mA
DC Power
18 Vdc nominal at 40 mA typical no-signal, 45 mA typical at +4
dBm output; 13.5 Vdc minimum
Batteries
Two 9 V alkaline batteries
Battery Life
Up to 8 hours* at +4 dBm output in continuous use.
*(see Battery Operation)
Temperature Range
Operating: -18° to 57° C (0° to 135° F)
Storage: -29° to 74°C (-20° to 165° F)
Overall Dimensions (H x W x D)
71.9 mm x 308 mm x 233 mm (2 13/16 in. x 12
5/32 in. x 9 5/32 in.) including feet.
Weight (without batteries)
3 kg (6.6 lb)
Measurement conditions (unless otherwise specified): operating
voltage 120 Vac, 60 Hz (18 ±1 Vdc for dc test); operating temperature 22°C (72°F); input signal 1 kHz; internal DIP switches 1–7 open;
Power switch on; Mic/Line switches to Line; low-cut switches to flat;
Limiter out; Phantom power off; Mix Bus to M367; channel 1 gain full
CW; channel 2 through 6 full CCW; Master full CW; Phones level full
W
CCW; Line output terminations 600
(pins 2 and 3); Mic output ter-
minations 150 W (pins 2 and 3); Phones (1/4"–ring) 300 W to ground;
W
Phones (1/4"–tip) 300
W
Bus 930
(M367 position) or 3.5 kW (M267 position), not connected
to ground; Phones (3.5 mm) unloaded; Mix
unless specified; 1 kHz input signal.
5

REPLACEMENT PARTS
Foot Kit (4 in kit)........................................................... 90S8100
M367 Fuse, 0.125 A, 250 V ........................................... 80E380
M367E Fuse, 0.063 A, 250 V .........................................80G380
Knob
Master .......................................................................... 95A8238
Channel Gain, Phones................................................. 95B8238
Line (Power) Cord
M367 ............................................................................ 95A8389
M367E.......................................................................... 95B8389
OPTIONAL ACCESSORIES
Rack Mount Kit.................................................................A367R
STATEMENT OF CONFORMITY
This certifies that the Shure M367E Microphone Mixer meets the
specifications and regulations embodied in Vfg 243/1991, amended 1992. The Bundesamt für Zulassungen in der Telekom munikation has been notified that this device has been marketed and has
been provided the right to verify the device or system for compliance with the specifications.
Conforms to European Union directives, eligible to bear CE mark
ing; VDE GS-Certified to EN 60 950; meets European Union EMC
Immunity Requirements (EN 50 082-1, 1992): RF radiated (IEC
801-3): meets Criterion A, ESD: meets Criterion B, EFT (IEC 801-
4): meets Criterion B.
GENERAL INFORMATION
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by Shure, Inc.
could void your authority to operate this equipment.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits
for a Class B digital device pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules
and as set out in the Radio Interference Regulations of the Canadian Department of Communications. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a
residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to
radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment
causes harmful interference to radio or television reception, determined by turning the equipment off and on, try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
1. Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
2. Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
3. Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from
that to which the receiver is connected.
4. Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for
help.
6
INTERNAL ADJUSTMENTS
NOTE
Only qualified service technicians should perform these
modifications.
These internal adjustments require only removal of the top
cover:
1. Remove battery compartment.
2. Remove four screws securing two plastic end caps and one
ground-bonding screw on the side opposite the battery compart ment.
3. Slowly slide cover up and off chassis.
VCA DISTORTION TRIMPOT (R607)
DO NOT ADJUST! This potentiometer is precisely calibrated on
each mixer for minimum distortion.
VU METER ADJUSTMENT (R684)
This trimpot adjusts the VU meter to indicate 0 VU at a preset output level. The factory setting is +4 dBm. The user adjustment range is -10 dBV to +4 dBm (-6 dBV to +8 dBm with DIP switch 1 down).
To set the VU meter to a value other than the factory setting
(0 VU = +4 dBm), proceed as follows:
1. Connect a 600 W load to an XLR output set for Line.
2. Connect an ac voltmeter with 1 MW or greater input
impedance (Fluke 77 or equivalent) in parallel with the load.
3. Set the 1 kHz tone oscillator switch to the ON position.
4. Adjust the 1 kHz tone oscillator level with the Master gain
con-
trol until the ac voltmeter reading is at the level desired
5. With the M367 top cover removed, adjust the VU Level Calibration trim pot R684 with a screwdriver until the VU Meter
reads 0.
6. For 0 VU settings between +4 and +8 dBm, set internal DIP switch S701 position 1 "down", and perform steps 1 through 5.
VU METER
CALIBRATION
TRIMPOT
R684
(ACCESSED
THROUGH
HOLE IN
UPPER FRONT
PC BOARD)
DIP SWITCH
INTERNAL ADJUSTMENTS
FIGURE 5
VCA
DISTORTION
TRIMPOT
R607
S701
7
INTERNAL MODIFIABLE FUNCTIONS
NOTE
Only qualified service technicians should perform these
modifications.
Perform all modifications through solder points accessible on
the main PC board.
DISASSEMBLING THE M367
1. Remove the mixer top cover as previously described.
2. Carefully remove three multi-pin cable assembly connectors from upper front PC board (nearest front panel). Remove the three Phillips head screws securing the PC board. Remove up per front PC board.
3. Carefully remove four multi-pin cable assembly connectors from upper rear PC board (nearest rear panel). Remove the three Phillips head screws securing the PC board. Remove upper rear PC board.
4. Perform modification (refer to appropriate following procedure). Note that all modifications can be performed without
removing the main PC board.
5. Reassemble M367 by performing above steps in reverse, assembling the Phillips screws in the order indicated on the upper front and upper rear PC boards.
CHANGING LINE LEVEL OUTPUT IMPEDANCE TO 600 W
Locate resistor R621 (near IC U602 pin 8) on the main PC board and remove it. Locate empty pads X621 (near resistor R621). Solder a 430 W, 1/2 W resistor through the holes at X621.
CHANGING UNSWITCHED LINE OUTPUT TO MIC LEVEL
Locate resistor R632 (near output transformer T601) and remove. Locate empty pads X632 (near transformer T601). Solder a jumper wire through the holes of X632.
CHANGING MIXER AUDIO LEVELS IN HEADPHONES
(Pull/Monitor Switch Activated, DIP Switch S701 Position
4 Closed)
Locate empty pads X649 (near Phones potentiometer R648).
Solder a 68 kW, 1/4 W resistor through the holes at X649 to hear
program audio 12 dB down from standard headphones level with
Pull/ Monitor switch on (pulled out). Solder a 24 kW, 1/4 W resistor
through the holes at X649 to hear program audio 6 dB from
standard headphones level with Pull/Monitor switch on (pulled out).
CHANGING LOW-CUT FILTER CORNER FREQUENCY
(3 DB DOWN POINT)
To decrease corner frequency:
1. Calculate new capacitor value for lower low-cut corner
frequency. Use the following formula:
C in mF= (85/frequency) - 0.33
Example: for 200 Hz corner frequency,
85/200 9 0.43
0.43 - 0.33 = 0.1
For 200 Hz corner frequency, use a 0.1 mF capacitor.
Pad Channel Pad Channel
X421 1 X451 4
X431 2 X521 5
X441 3 X531 6
2. Locate the following empty pads: Find all pads near ribbon cable assemblies W811, W812 and
W813.
3. Solder a new capacitor through the holes of the empty pads
for each channel to be modified.
To increase corner frequency:
Note: Low-cut corner frequencies much higher than the factory
preset of 260 Hz may excessively attenuate desired low- to
mid-frequency program material.
1. Locate the following capacitors near empty pads:
Capacitor
C425
C435
C445
X421 1 C455 X451 4
X431 2 C525 X521 5
X441 3 C535 X531 6
Pad
Channel
Capacitor Pad
Channel
2. Remove the indicated capacitor for each channel to be
modified.
3. Calculate new capacitor value for higher high-cut corner fre
quency. Use the following formula:
C in mF= (85/frequency)
Example: for 400 Hz corner frequency,
C = (85/400) = 0.21
For 400 Hz corner frequency, use a 0.22 mF capacitor.
4. Solder a new capacitor through the holes of the empty pads
for each channel to be modified.
SLOWING OUTPUT METER FROM "True VU" BALLISTICS
Locate empty pads X691 (at left of VU meter M1). Solder a 100
mF x 6.3 V electrolytic capacitor through the holes of X691. Observe capacitor polarity as marked on the PC board. The response
time is now 500 ms with no overshoot. To further slow the meter
response, use a larger capacitor value.
CHANGING MIC LEVEL OUTPUT IMPEDANCE
Locate resistor R631 (near output transformer T601) and
remove it. Locate empty pads X631 (near T601). Solder desired
value 1/4 W resistor through the holes of X631. For example, use
a 150 W, 1/4 W resistor for 150 W output impedance.
Capacitor must be non-polarized; ceramic or film type;
NOTE:
16V rating or higher.
8
ADAPTING LINE OUT TO DUAL BANANA JACK
CW
TIP
RING
SLEEVE
Add a dual banana jack, balanced, line-level output capability by
purchasing a commercial unit (Sescom XLR F-3BP or equivalent),
or obtaining a female XLR connector (Radio Shack 274-011 or
equivalent), a dual banana jack (ITT 2269 or equivalent), a small
utility box, and a short length of high-quality shielded output cable
and constructing the adapter shown in Figure 6.
CHANGING MONITOR IN HIGH GAIN (DIP Switch S701
Position 5 Down)
Locate resistor R647 (near Phones potentiometer R648) and remove it. Locate empty pads X647 (near R647). Solder a 330 W,1/4 W
resistor in the holes of X647 for 6 dB gain boost with DIP switch S701
W
position 5 down (input impedance equals 6.5 k
in this position).
CHANGING MONITOR IN JACK FROM MONO INPUT TO
STEREO SUM INPUT
Locate empty pads X645 (near Monitor In jack J863). Solder a 1 kW, 1%, 1/4 W resistor in the holes of X645. The Monitor In jack will now accept a stereo input signal (tip left, ring right, sleeve ground), and sum these signals to the monitor circuit.
231
DUAL BANANA JACK OUTPUT
FIGURE 6
Connect this adapter to the M367 Line output.
CHANGING MONITOR IN TO AUX IN
NOTE:
This modification disables the M367's monitor function.
Remove resistors R642 and R647 (near Phones potentiometer
R648).
Locate empty pads X601 (near output transformer T601) and
X643 (near Monitor In jack J683).
Solder a jumper wire from X643 to X601. The Monitor In jack is
now an unbalanced (tip positive, sleeve ground) Aux In jack, with
an input impedance of 11 kW and a maximum gain to Line Out
(loaded with 600 W) of 17 dB. The Aux In signal is only controlled
by the Master control.
To change Aux In gain, locate resistor R605 (near X601). Care
fully remove R605 and replace it with a surface-mount resistor
(0805 package) of the desired value. If replacing R605 with 15 kW,
maximum Aux In to Line Out gain equals 14 dB and input
impedance equals 16 kW; if replaced with 6.8 kW, maximum Aux In
to Line Out gain equals 20 dB and input impedance equals 7.8 kW.
If using a true stereo feed to drive the M367 Monitor In and
another stereo device, the source impedance must be 20 W or
less to maintain at least 40 dB separation in the stereo device.
Use a stereo distribution amplifier or buffer to maintain optimum
stereo separation.
NOTE
MASTER GAIN REMOTE CONTROL
This modification disables both the M367's monitor function and
its front-panel Master gain control.
NOTE
1. Remove resistor R641 (near Monitor In jack J863).
2. Remove resistor R746 (near Master potentiometer R706).
3. Locate empty pad X702 (near Master potentiometer R706).
Solder one end of a 100 W, 1/4 W resistor in the hole of X702.
Solder an insulated wire to the other end of the 100 W resistor.
Locate empty pad X644 (near jack J863). Solder the other end
of the insulated wire to X644.
4. Locate empty pad X701 (next to empty pad X702). Solder an insulated wire to X701. Locate empty pads X645 (near jack J863). Solder the other end of the insulated wire to the empty pad X645 nearest channel 6 input connector J856.
5. Construct a remote control potentiometer/cable assembly as shown in Figure 7.
MASTER GAIN REMOTE CONTROL
FIGURE 7
Recommended parts are:
Potentiometer, 10-25 kW, linear taper (Radio Shack
271-1715)
1/4 in. Stereo Phone Plug (Switchcraft 280)
Ferrite Bead Rings (Ferronics 21-031J)
Capacitors, ceramic, 0.001 mF, 50 V
Cable, 2-conductor, shielded, 50 ft maximum (15 m)
Ferrite bead rings and capacitors should be as close to the
phone plug as possible.
6. Insert the phone plug in the Monitor In jack. The remote control potentiometer now controls M367 gain with a control taper
similar to that of the Master gain control.
9
CHANGING LIMITER RELEASE TIME TO ONE SECOND
R6 =
1
R3
–
1
R1
1
1
11
= 49.4 k:
R
7=
1
150,000
1
52,30018,000
105,000
Remove resistor R741 (about 15 mm behind ribbon cable
assembly W813).
CHANGING LIMITER THRESHOLD PRESETS
1. Select the equivalent resistor values for the desired limiter thresholds from the following table. Then fill in the following work sheet with the resistor selections.
Limiter Threshold
(dBm into 600 W)
0181081
1211193
2 25 12 105
3 30 13 122
4 35 14 139
5 41 15 156
6 47 16 175
7 54 17 194
8 62 18 215
971
R
(kW)
equiv
Limiter Threshold (
dBm into 600 W)
R
(kW)
equiv
6. Calculate resistor R6 value as follows:
Select a 1/4 W, 1% resistor closest in value to R6 and solder it
to the holes of X734.
7. Calculate resistor R7 value as follows:
R7 =
1
R4
–
1
R1
1
1
–
R5
1
–
R6
Select a 1/4 W, 1% resistor closest in value to R7 and solder it
to the holes of X735. (See Changing Limiter Threshold Presets:
Samples Calculations later in the Appendix for an example of
limiter threshold preset component calculations.)
CHANGING LIMITER THRESHOLD PRESETS: SAMPLES
CALCULATIONS
For the following limiter thresholds:
DIP Switch S701 Limiter Threshold R
Position 2Position
–
dBm
equiv
–
3
(above)
DIP Switch S701 Limiter Threshold
Position 2 Position 3
up up high _____ kW = R1
down up med. high _____ kW = R2
up down med. low _____ kW = R3
down down low _____ kW = R4
–
dBm
R
equiv
–
2. Remove resistors R721, R731, R732, R733, R734 and R735 (surrounding IC U704).
3. Locate empty pads X732, X733, X734 and X735 (surrounding IC U704).
4. Select a 1/4 W, 1% resistor closest in value to R1 (from the work sheet), and solder it to the holes of X732.
Note: Use parallel or series combinations of resistors to match
the chosen values as closely as possible if 1% resistors are not
available.
5. Calculate resistor R5 value as follows:
R5 =
1
R2
1
1
–
R1
Select a 1/4 W, 1% resistor closest in value to R5 and solder it
to the holes of X733.
up up high 12 105
kW=R1
down up med. high 8
up down med. low 4
down down low 0
62 kW=R2
35 kW=R3
18 kW=R4
1. Obtain a 105 kW, 1/4 W, 1% resistor and solder it to the holes of X732.
2. Obtain a 150 kW, 1/4 W, 1% resistor and solder it to the holes of X733.
1
R
5=
1
62,000
1
105,000
= 151.4 k:
3. Obtain a 52.3 kW, 1/4 W, 1% resistor and solder it to the holes of X734.
1
R
6=
1
35,000
4. Obtain a 49.9 kW, 1/4 W, 1% resistor and solder it to the holes of X735.
1
105,000
= 52.5 k:
10

Bedienungsanleitung für Modell M367
6-KANAL-MIKROFONMISCHER
BESCHREIBUNG
Der Shure M367 ist ein tragbarer, batteriegespeister Mikrofon- und
Line-Pegelmischer/-Vorverstärker mit sechs Eingängen und zwei Ausgängen (Mono). Durch das vom Transformator isolierte Design, die
rauscharme Arbeitsweise sowie die kompakte und robuste Konstruktion eignet sich der M367 auf ideale Weise für Studio- und Mobilsendungen, elektronische Berichterstattung und Außenaufnahmen.
Dieser vielseitige Mischer kann auch folgendermaßen eingesetzt werden:
• Digitale Übertragungsstrecken
• Digitale Video-/Audioaufzeichnungsmedien (ISDN,
Festplattenaufzeichnungen und DAT)
• Beschallung
Das M367 wird mit Gummifüßchen, abziehbarem Netzkabel und einer Ersatz-Netzsicherung geliefert. Es kann mit Hilfe des optionalen Rackkits Modell A367R in ein Rack eingebaut werden.
TECHNISCHE EIGENSCHAFTEN
• Sechs wählbare Mikrofon-/Line-Eingänge
• Wählbarer Mikofon/Line-Ausgang und separater Line-Ausgang
• Transformator-symmetrische Eingänge und Ausgänge für über-
ragende Unterdrückung von HF-Störungen und elektromagnetischem Brumm
• Mechanisches
Profi-VU-Meter-LED-Hintergrundausleuchtung für hohe Zuverlässigkeit; kein Lampenersatz erforderlich
• Abhörung durch Kopfhörer (3,5 mm, 1/4 Zoll)
• Ausgangs-Spitzenwertbegrenzer mit schaltbarer Schwelle und
zweifarbiger LED-Anzeige
• LED zur Spitzenwertanzeige und schaltbare Hochpassfilter an je-
dem Eingang
• 1/4-Zoll-Return-Abhöreingang
• Betrieb mit Netzspannung oder 2 9-V-Batterien
WEITERE EIGENSCHAFTEN
• 48-V- oder 12-Volt-Phantomspeisung für
Kondensatormikrofone
• 1-kHz-Pegelton-Oszillator
• Stummschaltung aller Eingangskanäle bei Aktivierung
• Tonpegelsteller befindet sich am Master-Pegelsteller
• Breitspektrum-Eingangspegelsteller bewältigen hohe Signalpegel
ohne Dämpfungsglieder
• Benutzerdefinierter Betrieb über interne DIP-Schalter, Trimpotis
und optionale alternative Verdrahtung
• Batterieprüfschalter und Warnanzeige für geringe Batteriespannung
• An/Aus-LED
• Eingangserweiterung über Mix-Bus-Steckerbuchse zur Zusammenschaltung von M367s oder anderen Mischern
• Robustes Ganzmetallchassis mit Schutzendplatten
• Abziehbares Netzkabel
11

BEDIENELEMENTE UND ANZEIGEN AN DER FRONTSEITE
Ñ
Ñ
2 3
PEAK
5
3
0
10
PEAK
5
7
3
0
10
21
PEAK
5
7
3
0
10
PEAK
5
7
3
0
10
PEAK
5
7
3
0
3
7
10
543
1
BEDIENELEMENTE UND ANZEIGEN AN DER FRONTSEITE
ABBILDUNG 1
1. Eingangspegelsteller: Zur optimalen Leistung jeden Einga-
ngspegelsteller so einstellen, dass die zugehörige Eingangsspitzen-LED nur bei den lautesten Signalspitzen rot
aufleuchtet.
2. Eingangshochpassfilter-Schalter: Bietet Bassabsenkungs-
Rolloff zur Verringerung von Windgeräuschen und Rumpeln.
Bei Verwendung des Filters wird der Frequenzgang bei 150
Hz um 7 dB abgesenkt. Die Rolloff-Flanke beträgt 6dB je
Oktave.
3. Eingangsspitzen-LED: Leuchtet 6 dB unter dem Begren-
zungspegel auf.
4. Begrenzerschalter: Aktiviert einen schnell reagierenden
Spitzenwertbegrenzer, der für Sprachsignale optimiert ist.
Durch eine interne Modifizierung wird eine langsamere Auslösezeit für Musiksignale ermöglicht (siehe DIP-Schalter).
5. Zweifarbige Spitzen/Begrenzer-LED:
Rot = Ausgangssignal bei +12 dBm (6 dB unter
Begrenzungspegel)
Grün = Ausgangssignal bei Begrenzerschwelle
(wenn Begrenzer eingeschaltet ist)
6. Ausgangspegelanzeige (VU). Pegelanzeigeverhalten weist
näherungsweise echte VU-Eigenschaften auf (ungefähr 300
ms Anstieg und Abfall, 1 % bis 5 % Übersteuerung). Informationen zu langsamerem Ansprechen sind im Abschnitt Intern
veränderbare Funktionen zu finden. 0 VU ist zwischen +4 und
+8 dBm schaltbar (siehe DIP-Schalter). Bei Verwendung von
Batterien kann die Pegelanzeige mit dem Batterieprüfschalter
(BATT CHECK) beleuchtet werden.
7. 1-kHz-Pegeltonoszillator-Schalter: Sendet einen 1-kHz-
Pegelton an alle Ausgänge und schaltet alle Eingänge stumm.
Der Tonpegel wird über den MASTER-Pegelsteller eingestellt.
8 9
1kHz TONE
OFF ON
BATT
CHECK
PULL/MONITOR
12
PEAK
5
10
6
OFF ON
7
-20
5
LIMITER
4
0
PEAK
MASTER
+12
6
0
7
VU
M367
13
8. Batterieprüfknopf: Drücken und festhalten, um den Batterie-
stand am VU-Meter anzuzeigen. Einmal drücken, um das VUMeter 10 Sekunden lang zu beleuchten oder den DIP-Schalter
6 so einstellen, dass die Anzeigenbeleuchtung ein- und ausgeschaltet wird (siehe DIP-Schalter).
9. An/Aus-Schalter: Schaltet den Mischer an und aus.
10. An/Aus-LED:
Grün = Gerät eingeschaltet
Blinkend = Batterien schwach (ungefähr 30 Minuten
Betriebszeit verbleiben)
11. Reglerknopf mit Doppelfunktion:
Kopfhörer-Pegelsteller: Drehen, um den Kopfhörerpegel einzustellen.
Zug-/Abhörschalter: Bei Verwendung von
Kopfhörern herausziehen, um die Audiosignale vom
MONITOR IN (Abhöreingang) zu hören. Das
bedämpfte Programmsignal kann mit Hilfe des DIP
Schalters 4 hinzugefügt werden (siehe DIP Schalter).
ACHTUNG
Der Kopfhörerstromkreis kann hohe Lautstärkepegel erzeugen,
die das Gehör des Benutzers schädigen können. Sicherstellen,
dass die Kopfhörer-Lautstärkeeinstellung (
PHONES) auf den
Minimalwert (bis zum Anschlag nach links) gedreht wurde, bevor die Kopfhörer aufgesetzt werden.
12. Kopfhörerausgänge: 3,5-mm-Stereo- und 1/4-Zoll-Klinken-
buchsen.
13. Master-Pegelsteller: Stellt Ausgangsverstärkung des Mis-
chers ein. Auf 0-dB-Stellung für 1:1-Verstärkung einstellen.
10
POWER
ON
PHONES
11
12

ANSCHLÜSSE UND BEDIENELEMENTE AN DER RÜCKSEITE
Ñ
SYMMETRISCH
UNSYMMETRISCH
ZUM M367 NR. 1 ZUM M367 NR. 2
ZUM M367 ZUM M267
KEIN KONTAKT
1 2 3 4
100-120 VAC 50/60 Hz 100 mA
SPARE
9
LINE
MIC LINE PHANTOM
OFF ON
MONITOR
OUTPUT
8
10
MIC LINE MIC
IN
6
7 6 5
ANSCHLÜSSE UND BEDIENELEMENTE AN DER RÜCKSEITE
ABBILDUNG 2
1. Mikrofon/Line-Pegelausgangsschalter: Stellt Ausgang auf
Mikrofon oder Line-Pegel ein.
2. Phantomspeisungsschalter: Legt 12-Volt-Phantomspeisung
an alle Eingänge an, die auf MIC eingestellt sind. Die Spannung kann mit Hilfe des DIP-Schalters 7 auf 48 Volt erhöht
werden (siehe DIP-Schalter).
3. Mikrofon/Line-Pegeleingangsschalter 1-6: Stellt Eingang
auf Mikrofon oder Line-Pegel ein. Phantomspeisung wird für
Eingänge, die auf LINE eingestellt sind, deaktiviert.
4. M267/M367-Mix-Bus-Pegelschalter: Auf M267 einstellen,
wenn das Gerät an einen Shure M267, FP42, FP51, M67 oder
SE30 angeschlossen wird. Die Einstellung M367 für den
Anschluss an einen weiteren M367 oder einen Shure FP32A
verwenden.
WICHTIG
Falls nicht anderweitig erforderlich, den Mix-Bus-LEVEL-Schalter in
der Stellung
cherausgangsrauschen um bis zu 30 dB erhöhen, je nach Einstellung
MASTER-Ausgangs.
des
M367 belassen. Die Einstellung M267 kann das Mis-
5. Mix-Bus-Buchse: Ermöglicht es, den M367 an einen weit-
eren Mischer anzuschließen. Beim Mix-Bus-Anschluss handelt es sich um eine „Zwei-Wege-Verbindung“, die vor dem
Master-Pegelsteller liegt. Wenn zwei M367 Mischer verbunden sind, erscheinen alle 12 Eingänge an den Ausgängen
beider Mischer. Der MASTER-Pegelsteller jedes M367 kann
eingestellt werden, ohne sich auf den Ausgang des anderen
Mischers auszuwirken.
Der Ausgangspegel jedes M367 Mischers fällt um 6 dB ab, wenn
er durch den
MIX-BUS angeschlossen wird. Den Master-Pegel-
steller zur Kompensation höher einstellen.
HINWEIS
LEVEL
M267 M367
MIX
BUS
5
LINE
LINEMIC LINEMIC LINEMIC LINEMIC
4321
INPUT
MIX-BUS-ANSCHLÜSSE
ABBILDUNG 3
6. Kanaleingänge: Diese XLR-Eingangsbuchsen sind transfor-
mator-symmetrisch, um überragende Unterdrückung von elektromagnetischem Brumm, HF-Störungen und anderen
Störungen zu bewirken.
7. Abhöreingangsbuchse: Nimmt Mono-Line-Pegelsignale (Tip
= Signal, Hals = Masse) für „Band-Return“ oder einen Kommunikationskanaleingang an. Siehe die Beschreibung des
Zug-/Abhörschalters.
Der MONITOR IN (Abhöreingang) kann auch so modifiziert werden, dass er einen Stereoeingang annimmt
und ein Stereosummen-Abhörsignal liefert (siehe In-
tern veränderbare Funktionen).
8. Mischerausgang: Diese XLR-Ausgangsstecker sind transfor-
mator-symmetrisch. Der Line-Ausgang ist auf Line-Pegel voreingestellt, kann aber auf eine echte 600-W-
Ausgangsimpedanz modifiziert oder auf Mikrofonpegel
verändert werden (siehe Intern veränderbare Funktionen).
9. Netzanschluss: Siehe Wechselspannungsbetrieb.
10. Feinsicherungen mit Zeitverzögerung: Das Ausziehfach
enthält zwei Netzsicherungen. Die äußere (näher beim
Benutzer liegende) ist eine Ersatzsicherung.
M367: 0,125-A-/250-V-Sicherung
M367E: 0,063-A-/250-V-Sicherung
Für eine symmetrische Mix-Bus-Verbindung zwischen zwei
M367s ein Mix-Bus-Kabel mit zwei 1/4-Zoll-Stereosteckern (Tip,
Ring, Hals) verwenden. Wenn andere Shure Mischerausführungen verwendet werden, ein Mix-Bus-Kabel aus einem 1/4-ZollMonoklinkenstecker (Tip = Signal, Hals = Masse) und dem zweckmäßigen Stecker für die Mix-Bus-Buchse des anderen Mischers
erstellen (siehe Abbildung 3).
ACHTUNG
Zum Zwecke ständigen Brandschutzes durch eine Sicherung desselben Typs und Nennwerts ersetzen.
13

WECHSELSPANNUNGSBETRIEB
Den M367 mit dem mitgelieferten Netzadapter an eine Steckdose anschließen.
M367: 100-120 V AC, 50/60 Hz
M367E: 220-240 V AC, 50/60 Hz
Die Betriebsspannung kann intern umgeschaltet werden (siehe Intern veränderbare Funktionen).
HINWEIS
Der Geräteeingang ist die Haupttrennvorrichtung (zum Abschalten
des M367 muss das Netzteil ausgesteckt werden).
BATTERIEBETRIEB
Das Batteriefach öffnen, indem die Seiten des Fachs erfasst und zusammengedrückt werden, um die Verriegelungen zu lösen, und dann das Fach herausgezogen wird. Zwei 9-Volt-Batterien einlegen.
Während des Batteriebetriebs den BATT CHECK-Knopf (Bat-
terieprüfung) verwenden. Drücken und festhalten, um den Batteriestand am VU-Meter anzuzeigen. Einmal drücken, um das VUMeter 10 Sekunden lang zu beleuchten oder den DIP-Schalter 6
auf kontinuierliche Beleuchtung einstellen (siehe DIP-Schalter).
BATTERIELEBENSDAUER
Mit zwei frischen 9-Volt-Alkalibatterien kann der M367 ungefähr acht Stunden lang betrieben werden. Manche Mischerfunktionen verkürzen die Batterielebensdauer, wie in der folgenden Tabelle dargestellt ist.
HINWEIS: Die kurzzeitige Verwendung von Kopfhörern oder Pegelanzeigenbeleuchtung beeinträchtigt die Batterielebensdauer nicht merklich.
PEGELEINSTELLUNG
1. Den MASTER-Pegelsteller auf die völlig ausgeschaltete Stellung drehen.
2. Den 1-kHz-Pegelton-Oszillator aktivieren, indem der 1 KHZ
TONE-Schalter auf ON geschaltet wird. Die MASTER-Ver-
stärkung einstellen, bis die Nadel des VU-Meters „0“ anzeigt.
Die Eingangspegel an den mit den Ausgängen des M367 verbundenen Geräten entsprechend einstellen. Den Pegelton
deaktivieren, indem der 1 KHZ TONE-Schalter auf OFF
geschaltet wird.
3. Die Eingangspegelsteller entsprechend der Eingangssignalpegel einstellen. Die Eingangs-PEAK-LEDs sollten nur bei
lauten Eingangsspitzen rot flackern.
4. Den Ausgang am VU-Meter beobachten und den MASTER-
Pegelsteller so einstellen, dass die gewünschten Pegel erzielt
werden. Die Durchschnittspegel sollten ungefähr bei „0 VU“
gehalten werden. Die PEAK-LED neben dem VU-Meter sollte
nur bei lauten Ausgangsspitzen aufleuchten.
DIP-SCHALTER
1
2 34567
Auf die DIP-Schalter zugreifen, indem das Batteriefach und die
obere Abdeckung entfernt werden. Die Schalter anhand der folgenden Tabelle einstellen.
(Fettdruck = Werkseinstellung)
Funktion Oben Unten
S701
Mischerbetrieb Batteriestrom
Kein Signal 40 9
Bei kontinuierlichem +4-dBmAusgangspegel
Mit sechs Mikrofonen auf 12V-Phantomspeisung
Mit sechs Mikrofonen auf 48V-Phantomspeisung
Bei Ausgabe an Kopfhörer 50 7
Bei ständiger Pegelanzeigenbeleuchtung
*bis An/Aus-LED zu blinken beginnt, wonach ungefähr 30 Minuten zum Ersetzen der Batterien verbleiben.
(in mA)
45 8
55 6,5
70 5
75 4,5
Batterielebens-
dauer
(in Stunden)*
ANSCHLUSS DER M367-AUSGÄNGE AN
TELEFONLEITUNGEN
Die XLR-Ausgänge auf Line-Pegel können zur Ansteuerung ruhestromabgeglichener, „angewählter“ Telefonleitungen verwendet
werden. Die Verzerrung kann sich geringfügig steigern. Den
M367-Begrenzer verwenden, wobei die Begrenzerschwelle auf +4
dBm eingestellt ist. Die M367-Ausgangsimpedanz zur richtigen
Klangtreue auf 600 W ändern (siehe Intern veränderbare Funktion-
en). Wenn der M367 an eine Telefonleitung angeschlossen wird,
muss ein von der Telekom zugelassener Schnittstellenadapter
zwischen Mischer und Telefonleitung verwendet werden.
Schalter
1 Festlegung von
2 Begrenzer-
3
4 Programm zu
5 Abhöreingangs-
6 VU-Lampe
7 Phantom-
0 VU
schwelle
Abhörung
verstärkung
(Batterieprüf-
knopf)
speisung
0 VU = +4 dBm 0 VU = +8 dBm
Siehe Abbildung 4.
Aus An (fügt bedämpftes
Normal Hoch
Zeitschaltung
(schaltet sich nach 10
Sekunden aus)
12 V DC 48 V DC
Begrenzerschwelle
= +16 dBm
= +8 dBm
= +4 dBm
= 0 dBm
23
BEGRENZERSCHWELLENEINSTELLUNGEN
ABBILDUNG 4
Programmsignal in Ko-
pfhörern hinzu, wenn
Zug-/Abhörschalter
eingeschaltet ist)
Umschaltung (An-/Ab-
schaltung bei
Tastendruck)
14

TECHNISCHE DATEN
Frequenzgang
20 bis 20.000 Hz ± 2,0 dB (Kanalregler in Mittenstellung)
Gesamtklirrfaktor
0,25 % Gesamtklirrfaktor bei +4 dBm Ausgang, 55 bis 20.000
Hz
Spannungsverstärkung
Ausgang
Eingang Line Mikrofon Kopfhör-erMix-Bus
Niederohmig-
es Mikrofon
(150 W)
Line 37 dB -11 dB 53 dB 15 dB -25 dB
Abhörung --
Mix-Bus
(M367)
Mix-Bus
(M267)
87 dB 40 dB 103 dB 66 dB 27 dB
--
10 dB -38 dB 26 dB -- --
50 dB 2 dB 66 dB -- --
12 dB -- --
(M367)
Eingänge
IMPEDANZ Eingang
Eingang ausgelegt für Ist-Impedanz
Mikrofon 19 bis 600 W 1 kW -10 dBV
Line £ 10 kW 50 kW +36 dBV
Abhörung £ 1 kW 13 kW 0 dBV
Mix-Bus (M367) 930 W symm.;
1860 W
unsymm.
Mix-Bus (M267) 3,5 kW 3,5 kW -17 dBV
(intern)
930 W symm.;
1860 W
unsymm.
Ausgänge
IMPEDANZ Ausgang
Ausgang ausgelegt für Ist-Impedanz
Mikrofon Niederohmige
Line 600 W 150 W +18 dBm
Kopfhörer 8 bis 200 W 300 W +11 dBV
Mix-Bus (M367) 930 W symm.;
Mix-Bus (M267) 3,5 kW 3,5 kW -28 dBV
Eingänge
1860 W
unsymm.
(intern)
1 W -31 dBV
930 W symm.;
1860 W
unsymm.
Äquivalentes Eingangsrauschen
£ –127 dBV bei 150 W Quelle, 400 bis 20.000 Hz
Ausgangsrauschen
Masterpegel bis zum Anschlag nach links: –100 dBV, 400 bis
20.000 Hz
Masterpegel bis zum Anschlag nach rechts:–80 dBV, 400 bis
20.000 Hz
Brumm und Rauschen
Äquivalentes Eingangsrauschen: £125 dBV, 20 bis 20.000 Hz
Ausgang: –95 dBV (Master–Pegelsteller bis zum Anschlag
nach links); -75 dBV (Master–Pegelsteller bis zum Anschlag
nach rechts), 20 bis 20.000 Hz
Gleichtaktunterdrückungs-Verhältnis
65 dB bei 100 Hz,–-20 dBV Eingang
Mix-Bus
(M267)
Begren-
zungspegel
+23 dBV
Begren-
zungspegel
+11 dBV
Poarität
Mikrofon/Line-Eingang zu
Mikrofon/Line-Ausgang
Mikrofon/Line-Eingang zu Kopfhörern phasengleich
Mikrofon/Line-Eingang zu Mix-Bus (Tip) phasenumkehrend
Abhörung zu Kopfhörern phasengleich
Mix-Bus zu Mikrofon/Line-Ausgang phasenumkehrend
phasengleich
Übersteuerung und Kurzschluss
Kurzschluss der Ausgänge verursacht auch bei längerer Dauer
keinen Schaden. Mikrofoneingangsspannungen bis zu 3 V Effektivspannung verursachen keine Schäden. Line und Abhörung können Signale bis zu 30 V Effektivspannung
standhalten.
Eingangsspitzenanzeigen
6 dB unter Begrenzungspegel
Ausgangsspitzenanzeige
Leuchtet bei 6 dB unter Begrenzungspegel rot auf
Ausgangsbegrenzungspegel
³ +18 dBm am Line-Ausgang bei 600 W
Hochpassfilter
7 dB Abfall bei 150 Hz; 6 dB/Oktave Flanke (3 dB Abfall bei 260
Hz)
Pegelton-Oszillator
1 kHz ± 20 %
Begrenzer
Schwellwert: schaltbar: 0, +4, +8, +16 dBm
Ansprechzeit: 1 ms ± 0,5 ms
Auslösezeitkonstante: 100 ms ± 30 ms
Anzeige: Grün, wenn um 1 dB oder mehr begrenzt wird
Phantomspeisung
12–V-Phantomspannung: 12 V an 340 W
48–V-Phantomspannung: 48 V an 3,4 kW
Wechselspannungsversorgung
M367: 100-120 V AC, 50/60 Hz, 100 mA
M367E: 220-240 V AC, 50/60 Hz, 50 mA; Stromaufnahme ohne
Signal: 25 mA
Gleichspannungsversorgung
Nennwert 18 V DC bei 40 mA typisch ohne Signal, 45 mA
typisch bei +4 dBm Ausgangspegel; mindestens 13,5 V DC
Batterien
Zwei 9–V–Alkalibatterien
Batterielebensdauer
Bis zu 8 Stunden* bei +4 dBm Ausgangspegel im Dauerbetrieb.
*(siehe Batteriebetrieb)
Temperaturbereich
Betriebstemperatur: –18bis 57 °C
Lagerungstemperatur: –29bis 74 °C
Gesamtabmessungen (H x B x T)
71,9 mm x 308 mm x 233 mm
einschließlich Füßchen
Gewicht (ohne Batterien)
3 kg
Messbedingungen (soweit nicht anders angegeben): Betriebsspannung 120 V AC, 60 Hz (18 ±1 V DC für Gleichspannungsprüfung); Betriebstemperatur 22 °C; Eingangssignal 1 kHz; interne
DIP-Schalter 1–7 offen; Netzschalter an; Mikrofon/Line-Schalter
auf Line; Hochpassfilter auf ebenem Frequenzgang; Begrenzer
aus; Phantomspeisung aus; Mix-Bus auf M367; Verstärkung von
Kanal 1 bis zum Anschlag nach rechts; Kanal 2 bis 6 bis zum Anschlag nach links; Master–Pegelsteller bis zum Anschlag nach rechts; Kopfhörerpegel bis zum Anschlag nach links; LineAusgangs–Abschlussimpedanzen 600 W (Pins 2 und 3); Mikrofonausgangs–Abschlussimpedanzen 150 W (Pins 2 und 3); Kopf-
15

hörer (1/4–Zoll–Ring) 300 W zu Masse; Kopfhörer (1/4Zoll-Tip) 300
W zu Masse; Kopfhörer (3,5 mm) unbelastet; Mix–Bus 930 W
(M367–Stellung) bzw. 3,5 kW (M267–Stellung), nicht angeschlossen, falls nicht anderweitig angegeben; 1–kHz-Eingangssignal.
ERSATZTEILE
Füßchensatz (4 im Satz) .............................................. 90S8100
M367-Sicherung, 0,125 A, 250 V ................................... 80E380
M367E-Sicherung, 0,063 A, 250 V.................................80G380
Knopf
Master .......................................................................... 95A8238
Kanalverstärkung, Kopfhörer ....................................... 95B8238
Netzkabel
M367 ............................................................................ 95A8389
M367E.......................................................................... 95B8389
SONDERZUBEHÖR
Rackkit .............................................................................A367R
ÜBEREINSTIMMUNGSERKLäRUNG
Hiermit wird bescheinigt, dass der Shure M367E Mikrofonmischer die technischen Daten und Verordnungen gemäß Vfg 243/
1991, Fassung 1992, erfüllt. Das Bundesamt für Zulassungen in
der Telekommunikation wurde benachrichtigt, dass dieses Gerät
vermarktet wird, und ist berechtigt, das Gerät oder System auf
Übereinstimmung mit den technischen Daten zu prüfen.
Entspricht den Richtlinien der Europäischen Union, zum Tragen
des CE-Zeichens berechtigt; VDE GS-Zulassung nach EN 60 950;
erfüllt die Anforderungen der Europäischen Union für elektromagnetische Verträglichkeit (EN 50 082-1, 1992): HF-Strahlung (IEC
801-3): erfüllt Kriterium A; EGB (ESD): erfüllt Kriterium B; EFT (IEC
801-4) erfüllt Kriterium B.
ALLGEMAINE INFORMATIONEN
Nicht ausdrücklich von Shure Inc. genehmigte Änderungen oder Modifikationen können den Entzug der Betriebsgenehmigung für das Gerät zur Folge haben.
Dieses Gerät wurde geprüft und entspricht demnach den Grenzwerten für ein digitales Gerät der Klasse B gemäß Teil 15 der
Richtlinien der US-Fernmeldebehörde (FCC Rules) sowie den Radiointerferenzvorschriften der kanadischen Fernmeldebehörde
(Radio Interference Regulations of the Canadian Department of
Communications). Diese Grenzwerte sollen einen angemessenen
Schutz gegen störende Interferenzen in Wohngebieten bieten.
Dieses Gerät erzeugt und verwendet HF-Energie und kann diese
ausstrahlen; wenn es nicht gemäß der Anweisungen installiert und
verwendet wird, kann es störende Interferenzen mit dem
Funkverkehr verursachen. Allerdings wird nicht gewährleistet,
dass es bei einer bestimmten Installation keine Interferenzen geben wird. Wenn dieses Gerät störende Interferenzen zum Radiound Fernsehempfang verursacht, (was durch Aus- und Anschalten
des Geräts festgestellt werden kann), sollte versucht werden, die
Interferenz durch eines oder mehrere der folgenden Verfahren zu
beheben:
1. Die Empfangsantenne anders ausrichten oder anderswo
platzieren.
2. Den Abstand zwischen dem Gerät und dem Empfänger ver-
größern.
3. Das Gerät in eine Steckdose eines Netzkreises einstecken,
der nicht mit dem des Empfängers identisch ist.
4. Den Händler oder einen erfahrenen Radio- und Fernsehtech-
niker zu Rate ziehen.
16

INTERNE EINSTELLUNGEN
ACHTUNG
Nur qualifizierte Wartungstechniker sollten diese
Veränderungen durchführen.
Diese Internen Einstellungen erfordern nur das Abnehmen
der oberen Abdeckung:
1. Das Batteriefach entfernen.
2. Die vier Schrauben, mit denen die beiden Plastikendplatten
befestigt sind, sowie eine Erdungsschraube an der dem Batteriefach gegenüberliegenden Seite entfernen.
3. Die Abdeckung langsam anheben und vom Chassis abnehmen.
VCA-VERZERRUNGSTRIMMPOTI (R607)
NICHT VERSTELLEN! Dieses Poti wurde bei jedem Mischer
präzise für minimale Verzerrung kalibriert.
VU-METER-EINSTELLUNG (R684)
Durch dieses Trimmpoti wird das VU-Meter so eingestellt, dass
es beim voreingestellten Ausgangspegel 0 VU anzeigt. Die Werkseinstellung beträgt +4 dBm. Der Benutzereinstellbereich liegt
zwischen -10 dBV und +4 dBm (-6 dBV und +8 dBm, wenn der
DIP-Schalter 1 unten ist).
Zur Einstellung des VU-Meters auf einen anderen Wert als die Werkseinstellung (0 VU = +4 dBm) folgendermaßen vorgehen:
1. Eine 600-W-Last an einen XLR-Ausgang, der auf Line
geschaltet ist, anschließen.
2. Ein Wechselspannungs-Voltmeter mit mindestens 1-MW-Ein-
gangsimpedanz (Fluke 77 oder gleichwertiges Gerät) parallel
zur Last anschließen.
INTERN VERÄNDERBARE FUNKTIONEN
ACHTUNG
Nur qualifizierte Wartungstechniker sollten diese
Veränderungen durchführen.
Alle Veränderungen durch Lötstellen, die an der
Hauptleiterplatte zugänglich sind, durchführen.
3. Den 1-kHz-Pegelton-Oszillator auf die Stellung AN schalten.
4. Den 1-kHz-Pegelton-Oszillatorpegel mit dem Master-Pegelsteller einstellen, bis das Wechselspannungs-Voltmeter den
gewünschten Pegel anzeigt.
5. Bei abgenommener oberer Abdeckung des M367 das VUPegelkalibrierungstrimmpoti R684 mit einem Schraubenzieher
verstellen, bis das VU-Meter 0 anzeigt.
6. Für 0-VU-Einstellungen zwischen +4 and +8 dBm den
internen DIP-Schalter S701 auf die Stellung 1 „unten“ einstellen und Schritte 1 bis 5 durchführen.
VU–METER–K
ALIBRIERUNG
STRIMMPOTI
R684
(ZUGRIFF
DURCH DIE
ÖFFNUNG IN
DER OBEREN
VORDEREN
LEITERPLATTE)
VCA–VERZER
RUNGSTRIMM
POTI R607
DIP–SCHALTER
S701
INTERNE EINSTELLUNGEN
ABBILDUNG 5
Veränderungen durchgeführt werden können, ohne die
Hauptleiterplatte zu entfernen.
5. Den M367 wieder zusammenbauen, indem die obigen Schritte in umgekehrter Reihenfolge durchgeführt werden, wobei die Kreuzkopfschrauben in der auf der oberen vorderen und oberen hinteren Leiterplatten angegebenen Reihenfolge eingeschraubt werden.
AUSEINANDERBAU DES M367
1. Die obere Abdeckung des Mischers wie zuvor beschrieben entfernen.
2. Die drei Mehrfach-Pin-Kabelstecker vorsichtig aus der oberen
vorderen Leiterplatte (der Frontseite am nächsten gelegen)
ausstecken. Die drei Kreuzkopfschrauben, mit denen die Leiterplatte befestigt ist, entfernen. Die obere vordere Leiterplatte
ausbauen.
3. Die vier Mehrfach-Pin-Kabelstecker vorsichtig aus der oberen
hinteren Leiterplatte (der Rückseite am nächsten gelegen)
ausstecken. Die drei Kreuzkopfschrauben, mit denen die Leiterplatte befestigt ist, entfernen. Die obere hintere Leiterplatte
ausbauen.
4. Die Veränderung durchführen (siehe das entsprechende
nachfolgende Verfahren). Es ist zu beachten, dass alle
ÄNDERUNG DER LINE-PEGELAUSGANGSIMPEDANZ
AUF 600 W
Den Widerstand R621 (in der Nähe des IC U602 Pin 8) auf der
Hauptleiterplatte ausfindig machen und entfernen. Die leeren Lötaugen X621 (in der Nähe des Widerstands R621) ausfindig machen. Einen 430–W-/1/2-W–Widerstand durch die Öffnungen bei
X621 anlöten.
ÄNDERUNG DES UNGESCHALTETEN
LINE-AUSGANGS ZU MIKROFONPEGEL
Den Widerstand R632 (in der Nähe des Ausgangstransformators T601) ausfindig machen und entfernen. Die leeren Lötaugen
X632 (in der Nähe des Transformators T601) ausfindig machen.
Eine Drahtbrücke durch die Öffnungen von X632 anlöten.
17

ÄNDERUNG DER MISCHERAUDIOPEGEL IN DEN
KOPFHÖRERN (Zug-/Abhörschalter aktiviert, DIPSchalter S701 Stellung 4 geschlossen)
Die leeren Lötaugen X649 (in der Nähe des Kopfhörerpotis
R648) ausfindig machen. Einen 68-kW-/1/4-W-Widerstand durch
die Öffnungen bei X649 anlöten, um die Programmaudiosignale
um 12 dB gegenüber dem standardmäßigen Ohrhörerpegel abzusenken, wenn der Zug-/Abhörschalter eingeschaltet (herausgezogen) ist. Einen 24-kW-/1/4-W-Widerstand durch die Öffnungen
bei X649 anlöten, um die Programmaudiosignale um 6 dB gegenüber dem standardmäßigen Ohrhörerpegel abzusenken, wenn
der Zug-/Abhörschalter eingeschaltet (herausgezogen) ist.
ÄNDERUNG DER HOCHPASSFILTER-ECKFREQUENZ
(3 DB ABSENKPUNKT)
Zur Senkung der Eckfrequenz:
1. Den neuen Kondensatorwert für die tiefere Hochpasseckfre-
quenz berechnen. Dabei folgende Formel verwenden:
C in mF= (85/Frequenz) - 0,33
Beispiel: für Eckfrequenz 200 Hz,
85/200 » 0,43
0,43 - 0,33 = 0,1
Für die Eckfrequenz 200 Hz einen 0,1-mF-Kondensa-
tor verwenden.
Bei dem Kondensator muss es sich um einen ungepolten
Baustein in keramischer oder Filmausführung mit mindestens 16
2. Folgende leere Lötaugen ausfindig machen:
Lötauge Kanal Lötauge Kanal
X421 1 X451 4
X431 2 X521 5
X441 3 X531 6
Alle Lötaugen in der Nähe der Bandkabel W811,
W812 und W813 ausfindig machen.
3. Einen neuen Kondensator durch die Öffnungen der leeren Lötaugen für jeden zu ändernden Kanal anlöten.
Zur Anhebung der Eckfrequenz:
HINWEIS
V Nennwert handeln.
2. Den angegebenen Kondensator für jeden zu ändernden Kanal entfernen.
3. Den neuen Kondensatorwert für die höhere Hochpasseckfrequenz berechnen. Dabei folgende Formel verwenden:
C in mF= (85/Frequenz)
Beispiel: für Eckfrequenz 400 Hz,
C = (85/400) = 0,21
Für die Eckfrequenz 400 Hz einen 0,22-mF-Kondensa-
tor verwenden.
4. Einen neuen Kondensator durch die Öffnungen der leeren Lötaugen für jeden zu ändernden Kanal anlöten.
VERLANGSAMUNG DER AUSGANGSPEGELANZEIGE
VON „Echter VU“-BALLISTIK
Die leeren Lötaugen X691 (links vom VU-Meter M1) ausfindig
machen. Einen 100-mF-/6,3-V-Elektrolytkondensator durch die
Öffnungen von X691 anlöten. Die Kondensatorpolung gemäß der
Markierung auf der Leiterplatte beachten. Die Ansprechzeit beträgt
jetzt 500 ms ohne Übersteuerung. Zur weiteren Verlangsamung
der Pegelanzeigenansprechzeit einen größeren Kondensatorwert
verwenden.
ÄNDERUNG DER
MIKROFONPEGEL-AUSGANGSIMPEDANZ
Den Widerstand R631 (in der Nähe des Ausgangstransformators T601) ausfindig machen und entfernen. Die leeren Lötaugen
X631 (in der Nähe von T601) ausfindig machen. Einen 1/4-W-Widerstand mit dem gewünschten Impedanzwert durch die Öffnungen
von X631 anlöten. Zum Beispiel einen 150-W-/1/4-W-Widerstand
für die Ausgangsimpedanz 150 W verwenden.
ANPASSUNG DES LINE-AUSGANGS AN EINE
DOPPELBUCHSE FÜR BANANENSTECKER
Einen symmetrischen Line-Pegelausgang mit Doppelbuchse für
Bananenstecker hinzufügen, indem eine handelsübliche Einheit
(Sescom XLR F-3BP oder gleichwertiges Produkt) oder eine XLRSteckbuchse (Radio Shack 274-011 oder gleichwertiges Produkt),
eine Doppelbuchse für Bananenstecker (ITT 2269 oder gleichwertiges Produkt), ein kleines Schaltungsgehäuse und etwas qualitativ hochwertiges abgeschirmtes Ausgangskabel gekauft werden
und der in Abbildung 6 dargestellte Adapter hergestellt wird.
Hochpasseckfrequenzen, die wesentlich höher als die Werksvoreinstellung 260 Hz sind, können gewünschte Programmsignale
im unteren bis mittleren Frequenzbereich übermäßig bedämpfen.
HINWEIS
1. Folgende Kondensatoren in der Nähe von leeren Lötaugen ausfindig machen:
Kondensa-
tor
C425 X421 1 C455 X451 4
C435 X431 2 C525 X521 5
C445 X441 3 C535 X531 6
Lö-
tauge
Kanal Kondensa-
tor
Lö-
tauge
Kanal
231
DOPPELBUCHSENAUSGANG FÜR BANANENSTECKER
ABBILDUNG 6
Diesen Adapter an den Line-Ausgang des M367 anschließen.
18

ÄNDERUNG DES ABHÖREINGANGS ZU EINEM
CW
TIP
RING
SLEEVE
AUX-EINGANG
Hinweis: Diese Änderung deaktiviert die Abhörfunktion des M367.
Die Widerstände R642 und R647 (in der Nähe des Kopfhörer-
potis R648) entfernen.
Die leeren Lötaugen X601 (in der Nähe des Ausgangstransformators T601) und X643 (in der Nähe der Abhöreingangsbuchse
J683) ausfindig machen.
Eine Drahtbrücke zwischen X643 und X601 anlöten. Die Abhöreingangsbuchse ist jetzt ein unsymmetrischer (Tip positiv, Hals
geerdet) Aux-Eingang mit einer Eingangsimpedanz von 11 kW und
einer maximalen Verstärkung zum Line-Ausgang (bei Belastung
mit 600 W) von 17 dB. Das Aux-Eingangssignal wird nur mit dem
Master-Pegelsteller geregelt.
Zur Änderung der Aux-Eingangsverstärkung den Widerstand
R605 (in der Nähe von X601) ausfindig machen. R605 vorsichtig
entfernen und durch einen oberflächenmontierten Widerstand
(0805-Paket) mit dem gewünschten Wert ersetzen. Wenn R605
durch 15 kW ersetzt wird, beträgt die maximale Verstärkung zwischen Aux-Eingang und Line-Ausgang 14 dB und die Eingangsimpedanz 16 kW; wenn er durch 6,8 kW ersetzt wird, beträgt die
maximale Verstärkung zwischen Aux-Eingang und Line-Ausgang
20 dB und die Eingangsimpedanz 7,8 kW.
HINWEIS
FERNSTEUERUNG DES MASTER-PEGELSTELLERS
Diese Veränderung deaktiviert sowohl die Abhörfunktion des M367 als auch seinen Master-Pegelsteller an der Frontseite.
1. Den Widerstand R641 (in der Nähe des Abhöreingangs J863) entfernen.
2. Den Widerstand R746 (in der Nähe des Masterpotis R706) entfernen.
3. Das leere Lötauge X702 (in der Nähe des Masterpotis R706)
ausfindig machen. Ein Ende eines 100-W-/1/4-W-Widerstands
in der Öffnung von X702 anlöten. Einen isolierten Draht am
anderen Ende des 100-W-Widerstands anlöten. Das leere
Lötauge X644 (in der Nähe der Buchse J863) ausfindig
machen. Das andere Ende des isolierten Drahts an X644
anlöten.
4. Das leere Lötauge X701 (neben dem leeren Lötauge X702)
ausfindig machen. Einen isolierten Draht an X701 anlöten. Die
leeren Lötaugen X645 (in der Nähe der Buchse J863) ausfindig machen. Das andere Ende des isolierten Drahts an das
leere Lötauge X645, das am nähesten beim Eingangsstecker
J856 von Kanal 6 liegt, anlöten.
5. Eine Fernsteuer-Poti/Kabel-Baugruppe anfertigen, wie in Abbildung 7 dargestellt ist.
HINWEIS
ÄNDERUNG DER HOHEN VERSTÄRKUNG DES
ABHÖREINGANGS
(DIP-Schalter S701 Stellung 5 unten)
Den Widerstand R647 (in der Nähe des Kopfhörerpotis R648)
ausfindig machen und entfernen. Die leeren Lötaugen X647 (in der
Nähe von R647) ausfindig machen. Einen 330-W-/
1
/4-W-Wider-
stand in den Öffnungen von X647 anlöten, um einen 6-dB-Verstärkungszuwachs zu erzielen, wenn DIP-Schalter S701 Stellung
5 unten ist (Eingangsimpedanz beträgt in dieser Stellung 6,5 kW).
ÄNDERUNG DER ABHÖREINGANGSBUCHSE VON
MONOEINGANG ZU STEREOSUMMENEINGANG
Die leeren Lötaugen X645 (in der Nähe des Abhöreingangs
J863) ausfindig machen. Einen 1-W-/1-%-/
Öffnungen von X645 anlöten. Die Abhöreingangsbuchse nimmt
jetzt ein Stereoeingangssignal (Tip links, Ring rechts, Hals geerdet) an und summiert diese Signale zum Abhörkreis.
Wenn echte Stereosignale zur Ansteuerung des Abhöreingangs
des M367 und eines weiteren Stereogeräts verwendet werden,
darf die Quellimpedanz höchstens 20 W betragen, um mindestens 40 dB Kanaltrennung im Stereogerät aufrecht zu erhalten.
Einen Stereoverteilverstärker oder -puffer verwenden, um optimale Kanaltrennung aufrecht zu erhalten.
HINWEIS
1
/4-W-Widerstand in den
FERNSTEUERUNG DES MASTER-PEGELSTELLERS
ABBILDUNG 7
Empfohlene Teile:
Potentiometer, 10-25 kW, lineare Abschwächung
(Radio Shack 271-1715)
1/4-Zoll-Stereoklinkenstecker (Switchcraft 280)
Ferritperlenringe (Ferronics 21-031J)
Kondensatoren, keramisch, 0,001 mF, 50 V
Kabel, zweiadrig, abgeschirmt, maximal 15 m
Die Ferritperlenringe und Kondensatoren sollten sich möglichst
nahe am Klinkenstecker befinden.
6. Den Klinkenstecker in die Abhöreingangsbuchse einstecken.
Das Fernsteuerpoti regelt jetzt die Verstärkung des M367 mit
einer Regelungsabschwächung, die der des Master-Pegelstellers ähnelt.
ÄNDERUNG DER BEGRENZERAUSLÖSEZEIT AUF 1
SEKUNDE
Den Widerstand R741 (ungefähr 15 mm hinter dem Bandkabel
W813) entfernen.
19

ÄNDERUNG DER BEGRENZERSCHWELLEN-
R6 =
1
R3
–
1
R1
1
VOREINSTELLUNGEN
1. Die effektiven Widerstandswerte für die gewünschten Begrenzerschwellen aus der folgenden Tabelle auswählen. Dann die
ausgewählten Widerstandswerte in das folgende Arbeitsblatt
eintragen.
Begrenzerschwelle
(dBm in 600 W)
0 18 10 81
1 21 11 93
2 25 12 105
3 30 13 122
4 35 14 139
5 41 15 156
6 47 16 175
7 54 17 194
8 62 18 215
9 71
DIP-Schalter S701 Begrenzerschwelle R
Stellung 2 Stellung 3 - dBm -
oben oben hoch ____ ____kW = R1
unten oben mittelhoch ____ ____kW = R2
oben unten mittelniedrig ____ ____kW = R3
unten unten niedrig ____ ____kW = R4
2. Die Widerstände R721, R731, R732, R733, R734 und R735 (um IC U704 herum) entfernen.
3. Die leeren Lötaugen X732, X733, X734 und X735 (um IC U704 herum) ausfindig machen.
4. Einen 1/4-W-/1-%-Widerstand auswählen, dessen Wert am nähesten bei R1 (aus dem Arbeitsblatt) liegt, und diesen an die Öffnungen von X732 anlöten.
R
(kW) Begrenzerschwelle
eff
(dBm in 600 W)
eff
R
eff
(oben)
(kW)
6. Den Wert des Widerstands R6 wie folgt berechnen:
Einen 1/4-W-/1-%-Widerstand auswählen, dessen
Wert am nähesten bei R6 liegt, und diesen an die Öffnungen von X734 anlöten.
7. Den Wert des Widerstands R7 wie folgt berechnen:
R7 =
1
R4
–
1
R1
1
1
–
R5
1
–
R6
Einen 1/4-W-/1-%-Widerstand auswählen, dessen
Wert am nähesten bei R7 liegt, und diesen an die Öffnungen von X735 anlöten. (Ein Beispiel für die Komponentenberechnungen der BegrenzerschwellenVoreinstellungen ist im Abschnitt Änderung der Be-
grenzerschwellen-Voreinstellungen: Musterberechnungen weiter unten im Anhang zu finden.)
ÄNDERUNG DER BEGRENZERSCHWELLENVOREINSTELLUNGEN: MUSTERBERECHNUNGEN
Für die folgenden Begrenzerschwellen:
DIP-Schalter S701 Begrenzerschwelle R
Stellung 2 Stellung 3 - dBm -
oben oben hoch 12 105 kW=R1
unten oben mittelhoch 8 62 kW=R2
oben unten mittelnied-
4 35 kW=R3
rig
unten unten niedrig 0 18 kW=R4
1. Einen 105-kW-/1/-W-/1-%-Widerstand besorgen und ihn an die Öffnungen von X732 anlöten.
2. Einen 150-kW-/1/-W-/1-%-Widerstand besorgen und ihn an die Öffnungen von X733 anlöten.
eff
Parallel- oder Reihenschaltungen von Widerständen verwenden, um den ermittelten Werten möglichst genau zu entsprechen, wenn keine 1-%-Widerstände verfügbar sind.
HINWEIS
5. Den Wert des Widerstands R5 wie folgt berechnen:
R5 =
1
R2
1
1
–
R1
Einen 1/4-W-/1-%-Widerstand auswählen, dessen
Wert am nähesten bei R5 liegt, und diesen an die Öffnungen von X733 anlöten.
1
R
5=
1
62,000
1
105,000
= 151.4 k:
3. Einen 52,3-kW-/1/-W-/1-%-Widerstand besorgen und ihn an die Öffnungen von X734 anlöten.
1
R
6=
1
35,000
4. Einen 49,9-kW-/1/-W-/1-%-Widerstand besorgen und ihn an die Öffnungen von X735 anlöten.
R
7=
11
105,000
1
105,000
1
1
150,000
= 52.5 k:
1
52,30018,000
= 49.4 k:
20

Guía del usuario del modelo M367
MEZCLADOR PARA MICROFONOS DE SEIS CANALES
DESCRIPCION
El M367 de Shure es un mezclador/preamplificador portátil para
micrófonos y fuentes de nivel de línea con seis entradas y dos
salidas (monofónicas), alimentado por pilas. El diseño aislado por
transformadores, bajo nivel de ruido y fabricación compacta y
resistente hacen del M367 una elección ideal para tareas de
estudio o difusión móvil, captación electrónica de noticias (ENG) y
producciones electrónicas en campo (EFP).
Este mezclador versátil también puede usarse para lo siguiente:
• Enlaces de transmisión digital
• Medios de grabación digital de video/audio (ISDN, grabación en disco duro y DAT)
• Refuerzo de sonido
El M367 viene equipado con patas de caucho, cordón eléctrico desconectable y fusible de repuesto en la línea de alimentación. Puede montarse en rack usando el juego de montaje opcional modelo A367R.
CARACTERISTICAS
• Seis entradas seleccionables para micrófono/línea
• Salida seleccionable para micrófono/línea y salida dedica-
da para línea
• Entradas y salidas balanceadas por transformador para rechazo
superior de las interferencias de radiofrecuencias y electromagnéticas
• Medidor de VU mecánico de calidad profesional-Iluminación de
fondo con LED para mayor confiabilidad, no se requiere sustituir
bombillas
• Conector para auriculares de monitoreo (3,5 mm, 1/4 pulg)
• Limitador de picos de salida con umbral seleccionable y
LED indicador de dos colores
• LED indicador de picos y filtros seleccionables de corte de
frecuencias bajas en cada entrada
• Entrada de monitor de retorno de 1/4 pulg
• Alimentación por CA o por (2) pilas de 9 V
CARACTERISTICAS ADICIONALES
• Alimentación Phantom de 48 V ó 12 V para micrófonos de
condensador
• Oscilador de tono de 1 kHz
• Silencia todos los canales de entrada al activarse
• Control de tonos en maestro
• Los controles de ganancia de entrada de gama amplia
manejan señales intensas sin necesidad de atenuadores
• El funcionamiento puede ajustarse según preferencias con
los interruptores DIP, potenciómetros de ajuste y conexiones alternativas del alambrado
• Interruptor de revisión de pilas e indicador de descarga de
pilas
• LED de encendido
• Expansión de entradas por medio de jack de bus de mezcla
para conectar a otros M367 u otros mezcladores
• Chasis metálico resistente con protectores en sus esquinas
• Cordón de CA desconectable
21

CONTROLES E INDICADORES DEL PANEL DELANTERO
Ñ
Ñ
2 3
PEAK
5
3
0
10
PEAK
5
7
3
0
10
21
PEAK
5
7
3
0
10
PEAK
5
7
3
0
10
PEAK
5
7
3
0
543
4
3
7
10
1
CONTROLES E INDICADORES DEL PANEL DELANTERO
FIGURA 1
1. Control de ganancia de entrada: Para el mejor rendimiento,
ajuste cada control de ganancia de entrada de modo que su
LED de picos de entrada correspondiente se ilumine en rojo
únicamente en los picos más intensos de la señal.
2. Interruptor de filtro atenuador de frecuencias bajas:
Atenúa las frecuencias bajas para reducir los ruidos producidos por el viento y vibraciones. Cuando se usa el filtro, la
respuesta de frecuencia introduce una atenuación de 7 dB a
150 Hz. La pendiente de atenuación progresiva es de 6dB/
octava.
3. LED de picos de entrada: Se ilumina cuando la señal está 6
dB por debajo del nivel de limitación.
4. Interruptor del limitador: Activa un limitador de picos de
respuesta rápida cuyo diseño es óptimo para la voz hablada.
Una modificación interna permite prolongar el tiempo de liberación para señales de música (vea Interruptores DIP).
5. LED de dos colores de pico/limitador de salida:
Rojo = señal de salida a +12 dBm (6 dB por de-
bajo del nivel de limitación)
Verde = señal de salida a nivel umbral del limita-
dor (cuando el limitador está encendido)
8 9
1kHz TONE
OFF ON
BATT
CHECK
PULL/MONITOR
12
0
PEAK
5
10
6
13
OFF ON
7
-20
5
LIMITER
MASTER
6
PEAK
+12
7
0
VU
M367
8. Botón de revisión de pilas: Manténgalo pulsado para mos-
trar el nivel de carga de las pilas en el medidor de VU. Púlselo
una vez para iluminar el medidor de VU por 10 segundos, o
ajuste el interruptor DIP #6 para configurar este botón para
encender y apagar la luz del medidor (vea Interruptores DIP).
9. Interruptor de alimentación: Enciende y apaga el
mezclador.
10. LED de encendido:
Verde = alimentación conectada
Destellando = pilas descargadas (restan aproximada-
mente 30 minutos de funcionamiento)
11. Perilla de control de función doble:
Control de ganancia de auriculares: Gírelo para
ajustar el nivel sonoro en los auriculares.
Tirar para monitor: Cuando se usan auriculares,
tire de este control para escuchar la señal de audio
recibida en el jack MONITOR IN. Se puede añadir la
señal del mezclador atenuada usando el interruptor
DIP #4 (vea Interruptores DIP).
10
POWER
ON
PHONES
11
6. Medidor de nivel de salida (VU): El medidor ofrece una
aproximación de las características de un medidor de VU
(aprox. 300 ms de elevación y bajada, 1% a 5% de
sobreamplitud). Para una respuesta más lenta, vea Funciones
internas modificables. El nivel de 0 VU puede seleccionarse
entre + 4 dBm y +8 dBm (vea Interruptores DIP). Cuando se
usan las pilas, utilice el interruptor BATT CHECK para iluminar
el medidor.
7. Interruptor de oscilador de tono de 1 kHz: Envía un tono de
1 kHz a todas las salidas y silencia todas las entradas. El control maestro (MASTER) regula la intensidad del tono.
ADVERTENCIA
El circuito de los auriculares puede producir niveles intensos de
volumen capaces de dañar el o
el volumen de los auriculares (PHONES) esté a un nivel bajo
(completamente en sentido contrahorario) antes de colocarse
los auriculares en los o
ído del usuario. Compruebe que
ídos.
12. Salidas para auriculares: Jacks estereofónicos de 3,5 mm y
1/4 pulg.
13. Control maestro de ganancia: Fija la ganancia de salida del
mezclador. Colóquelo en la posición de 0 dB para obtener
ganancia unitaria.
22

CONECTORES Y CONTROLES DEL PANEL TRASERO
Ñ
1 2 3 4
100-120 VAC 50/60 Hz 100 mA
SPARE
9
LINE
MIC LINE PHANTOM
OFF ON
MONITOR
OUTPUT
8
10
MIC LINE MIC
IN
6
7 6 5
CONECTORES Y CONTROLES DEL PANEL TRASERO
FIGURA 2
1. Interruptor nivel de salida de micrófono/línea: Fija la señal
de salida a nivel de micrófono o de línea.
2. Interruptor de alimentación Phantom:Envía 12 V de ali-
mentación Phantom a todos los canales de entrada cuyo
interruptor selector está en la posición MIC. Utilice el interruptor DIP #7 para aumentar el voltaje a 48 voltios (vea Interrup-
tores DIP).
3. Interruptores de nivel de entrada de micrófono/línea 1-6:
Fija la señal de entrada a nivel de micrófono o de línea. La alimentación Phantom se desconecta de las entradas cuyo
interruptor está en la posición LINE.
4. Interruptor de nivel de bus de mezcla de M267/M367:
Colóquelo en la posición M267 cuando se conecta esta unidad
a un modelo M267, FP42, FP51, M67 ó SE30 de Shure.
Utilice la posición M367 cuando se conecta esta unidad a otro
M367 ó a un modelo FP32A de Shure.
5. Jack de bus de mezcla: Le permite conectar el M367 a otro
mezclador. La conexión del bus de mezcla es de "dos vías" y
anterior al control maestro. Cuando se conectan dos mezcladores M367 entre sí, las 12 entradas aparecen en las salidas
de ambos mezcladores. El control de ganancia MASTER de
cualquiera de los M367 puede ajustarse sin afectar la señal
de salida del otro mezclador.
El nivel de salida de cada mezclador M367 conectado por el jack
NOTA
MIX BUS disminuye 6 dB. Aumente el ajuste del control maestro
de ganancia para compensar este efecto.
Para una conexión balanceada del bus de mezcla entre dos
M367, utilice un cable de bus de mezcla con dos enchufes estereofónicos de 1/4 pulg (punta, anillo, manguito). Cuando se
conectan otros tipos de mezcladores Shure, fabrique un cable
para el cable del bus de mezcla con un enchufe monofónico de
1/4 pulg (punta = señal, manguito = tierra) y el conector apropiado para el jack del bus de mezcla del otro mezclador (vea la
Figura 3).
LEVEL
M267 M367
MIX
BUS
5
LINE
LINEMIC LINEMIC LINEMIC LINEMIC
4321
INPUT
BALANCEADA
AL M367 N_ 1 AL M367 N_ 2
AL M367
DESBALANCEADA
AL M267SIN CONEX.
CONEXIONES PARA BUS DE MEZCLA
FIGURA 3
6. Entradas de canal: Estas entradas con conector XLR
hembra están balanceadas por transformador para ofrecer un
rechazo superior de los zumbidos e interferencias de radiofrecuencias o de otros tipos.
7. Jack de entrada de monitor: Acepta señales monofónicas
de nivel de línea (punta = señal, manguito = tierra) para una
señal de "retorno de grabadora" o entrada de canal de
comunicaciones. Vea la descripción del interruptor Tirar para
monitor.
También es posible modificar el jack MONITOR IN para que
acepte una entrada estereofónica y ofrezca una señal de
suma de monitor (vea Funciones internas modificables).
8. Salida de mezcla: Estos conectores XLR macho están
balanceados por transformador. La salida de línea se
configura para entregar una señal a nivel de línea, pero puede
modificarse para presentar una impedancia de salida de 600
W o modificarse a nivel de micrófono (vea Funciones internas
modificables).
9. Enchufe de alimentación: Vea Funcionamiento con CA.
10. Fusibles con retardo: El compartimiento deslizante contiene
dos fusibles para la línea de alimentación. El que está en la
posición exterior (más cercano a usted) es de reserva.
M367: Fusible de 0,125 A, 250 V
M367E: Fusible de 0,063 A, 250 V
ADVERTENCIA
Para mantener la protección contra incendios, cambie el fusible
por otro de igual tipo y capacidad.
23

FUNCIONAMIENTO CON CA
23
Umbral del Limitador
= +16 dBm
= +8 dBm
= +4 dBm
= 0 dBm
Utilice el adaptador de alimentación provisto para conectar el M367 a un tomacorriente.
M367: 100-120 VCA, 50/60 Hz
M367E: 220-240 VCA, 50/60 Hz
El voltaje de funcionamiento puede seleccionarse con un interruptor interno (vea Funciones internas modificables).
NOTA
La conexión de entrada es el dispositivo de desconexión
principal (para apagar el M367, hay que desenchufar la
fuente de alimentación).
FUNCIONAMIENTO CON PILAS
Abra el compartimiento de las pilas sujetando sus costados,
comprimiéndolos para soltar las trabas y tirando del compartimiento hacia afuera. Inserte dos pilas de 9 voltios.
Cuando se trabaja con pilas, utilice el botón BATT CHECK.
Manténgalo pulsado para mostrar el nivel de carga de las pilas en
el medidor de VU. Púlselo una vez para iluminar el medidor de VU
por 10 segundos, o ajuste el interruptor DIP #6 para configurar
este botón para iluminación continua (vea Interruptores DIP).
VIDA UTIL DE LA PILA
Con dos pilas alcalinas frescas de 9 voltios, el M367 funciona
por aproximadamente ocho horas. Algunas funciones del mezclador acortan la vida útil de las pilas, como se ilustra en la tabla siguiente.
AJUSTE DE NIVELES
1. Fije la perilla de ganancia MASTER en la posición de completamente apagado.
2. Active el oscilador de 1 kHz poniendo el interruptor 1 KHZ
TONE en la posición de encendido. Ajuste el control de
ganancia MASTER hasta que la aguja del medidor de VU
indique "0". Ajuste los niveles de entrada del equipo
conectado a las salidas del M367 de modo correspondiente.
Desactive el oscilador poniendo el interruptor 1 KHZ TONE en
la posición de apagado (OFF).
3. Ajuste los controles de ganancia de entrada según las señales recibidas. Los LED PEAK de cada entrada deberán destellar en rojo únicamente durante los picos más altos de la señal de entrada.
4. Observe el nivel de la señal de salida en el medidor de VU y
ajuste el control de ganancia MASTER para obtener los niveles deseados. Procure mantener los niveles promedio alrededor de "0 VU". El LED PEAK que está junto al medidor de VU
deberá iluminarse solamente en los picos más altos de la
señal de salida.
INTERRUPTORES DIP
1
234567
Para acceder a los interruptores DIP, quite el compartimiento de las pilas y la cubierta superior. Utilice la tabla siguiente para fijar los interruptores. (Letra negrita = ajuste en fábrica.)
S701
El uso de los auriculares o la iluminación del medidor por períodos
cortos no afecta la duración de las pilas de modo significativo.
Función del mezclador Consumo de
Sin señal 40 9
Con salida continua de +4 dBm 45 8
Con seis micrófonos que usan 12 V de
alimentación Phantom
Con seis micrófonos que usan 48 V de
alimentación Phantom
Enviando señal a auriculares 50 7
Con la iluminación del medidor
continuamente encendida
* hasta el momento en que el LED de alimentación empieza a
destellar, dando aproximadamente 30 minutos para cambiar las pilas.
NOTA:
corriente de
pila (mA)
55 6,5
70 5
75 4,5
Duración
de la pila
(horas)**
CONEXION DE SALIDAS DEL M367 A LINEAS
TELEFONICAS
Utilice las salidas XLR a nivel de línea para conectarse a líneas
telefónicas comunes con polarización de CC. Se puede percibir un
aumento leve en la distorsión. Utilice el limitador del M367 con su
umbral fijado en +4 dBm. Modifique la impedancia de salida del
M367 a 600 W para obtener una fidelidad adecuada (vea Funciones internas modificables). Cuando se conecta el M367 a una
línea telefónica, es necesario utilizar un adaptador de conexión reconocido por FCC entre el mezclador y la línea telefónica.
DIP
1 Nivel de 0 VU en
2 Umbral del
3
4 Programa que
5 Ganancia de en-
trada de monitor
6 Lámpara de VU
7 Alimentación
24
Función Hacia arriba Hacia abajo
medidor
limitador
se desea
monitorear
(botón de re-
visión de
baterías)
Phantom
0 VU = +4 dBm 0 VU = +8 dBm
Vea la Figura 4.
Desactivada Activada (añade la
Normal Alta
Por tiempo (se apaga
luego de 10 segundos)
12 VCC 48 VCC
señal atenuada del
programa a los auriculares cuando se tira del
interruptor del monitor)
Conmutada (pulse
para encender, pulse
para apagar)
AJUSTES DE UMBRAL DEL LIMITADOR
FIGURA 4

ESPECIFICACIONES
Respuesta de frecuencia
20 hasta 20.000 Hz ± 2,0 dB (controles de canal en posición
central)
Distorsión armónica total
0,25% de distorsión armónica total (THD) con salida de +4
dBm, 55 hasta 20.000 Hz
Ganancia de voltaje
Salida
Entrada Línea Micró-
Micrófono de
baja impedancia (150 W)
Línea 37 dB -11 dB 53 dB 15 dB -25 dB
Monitor --
Bus de mezcla (M367)
Bus de mezcla (M267)
87 dB 40 dB 103 dB 66 dB 27 dB
10 dB -38 dB 26 dB -- --
50 dB 2 dB 66 dB -- --
fono
--
Entradas
IMPEDANCIA Entrada
Entrada Diseñado para
Micrófono 19 a 600 W 1 kW -10 dBV
Línea £10 kW 50 kW +36 dBV
Monitor £1 kW 13 kW 0 dBV
Bus de mezcla
(M367)
Bus de mezcla
(M267)
uso con
930 W bal.; 1860
W desbal.
3,5 kW 3,5 kW -17 dBV
Salidas
IMPEDANCIA Salida
Salida Diseñado para
Micrófono Entradas de baja Z 1 W -31 dBV
Línea 600 W 150 W +18 dBm
Auriculares 8 a 200 W 300 W +11 dBV
Bus de mezcla
(M367)
Bus de mezcla
(M267)
uso con
930 W bal.;
1860 W desbal.
3,5 kW 3,5 kW -28 dBV
Ruido equivalente de entrada
£ –127 dBV con fuente de 150 W, 400 a 20.000 Hz
Nivel de señal de salida
Control de nivel maestro completamente en sentido contrahorario: –100 dBV, 400 a 20.000 Hz
Control de nivel maestro completamente en sentido
horario: –80 dBV, 400 a 20.000 Hz
Zumbidos y ruido
Entrada equivalente: £125 dBV, 20 a 20.000 Hz
Salida: –95 dBV (control maestro completamente en sentido
contrahorario); –75 dBV (control maestro completamente en
sentido horario), 20 a 20.000 Hz
Relación de rechazo en modo común
65 dB con entrada de 100 Hz,–20 dBV
Auricu-
lares
12 dB -- --
Real (interna) Nivel de
930 W bal.; 1860
W desbal.
Real (interna) Nivel de
930 W bal.; 1860
W desbal.
Bus de
mezcla
(M367)
Bus de mezcla (M267)
limitación
+23 dBV
limitación
+11 dBV
Polaridad
Entrada de micrófono/línea a salida de
Entrada de micrófono/línea a auriculares Sin inversión
Entrada de micrófono/línea a bus de mezcla (punta) Con inversión
Bus de mezcla a salida de micrófono/línea Con inversión
micrófono/línea
Monitor a auriculares Sin inversión
Sin inversión
Protección contra sobrecargas y cortocircuitos
El poner las salidas en cortocircuito, aun por lapsos prolongados, no causa daño alguno. Las señales de hasta 3 Vrms en las
entradas de micrófono no causan daños. Los conectores de
línea y monitor soportan señales de hasta 30 Vrms.
Indicadores de picos de entrada
6 dB por debajo del nivel de limitación
Indicador de picos de salida
Se ilumina en rojo cuando la señal está a 6 dB por debajo del
nivel de limitación
Nivel de limitación de salida
³ +18 dBm con señal de salida de línea conectada a 600 W
Filtros de atenuación de bajos
7 dB de atenuación a 150 Hz, pendiente de 6 dB/octava (atenuación de 3 dB a 260 Hz)
Oscilador generador de tono
1 kHz ± 20%
Limitador
Umbral: Seleccionable: 0, +4, +8, +16 dBm
Tiempo de acometida: 1 ms ± 0,5 ms
Constante de tiempo de liberación: 100 ms ± 30 ms
Indicador: Verde cuando limita en 1 dB o más
Alimentación Phantom
Alimentación Phantom de 12 V: 12 V a través de 340 W
Alimentación Phantom de 48 V: 48 V a través de 3,4 kW
Alimentación de CA
M367: 100-120 VCA, 50/60 Hz, 100 mA
M367E: 220–240 VCA, 50/60 Hz, 50 mA; consumo de corriente
sin señal: 25 mA
Alimentación de CC
18 VCC nominales con consumo típico de 40 mA sin señal, 45
mA típico con salida de +4 dBm; 13,5 VCC mínimo
Pilas
Dos pilas alcalinas de 9 V
Duración de la pila
Hasta 8 horas* con salida de +4 dBm en uso continuo.
*(vea Funcionamiento con pilas)
Gama de temperatura
Funcionamiento: –18° a 57°C (0° a 135°F)
Almacenamiento: –29° a 74°C (–20° a 165°F)
Dimensiones generales (altura x ancho x profundidad)
71,9 x 308 x 233 mm (2
13
/16 x 125/32 x 95/32 pulg) incluyendo
las patas
Peso (sin pilas)
3 kg (6,6 lb)
Condiciones de medición (salvo indicación contraria): voltaje de
funcionamiento 120 VCA, 60 Hz (18 ±1 VCC para prueba de CC);
temperatura de funcionamiento 22°C (72°F); señal de entrada de
1 kHz; interruptores DIP internos 1–7 abiertos; interruptor de alimentación conectado; interruptores de micrófono/línea en
posición de línea; interruptores de atenuación de frecuencias bajas en posición de filtros desactivados; limitador apagado; alimentación Phantom desconectada; bus de mezcla a M367; ganancia
de canal 1 completamente en sentido horario; ganancia de
canales 2 al 6 completamente en sentido contrahorario; ganancia
maestra completamente en sentido horario; nivel de auriculares
25

completamente en sentido contrahorario; terminaciones de salida
de línea en 600 W (clavijas 2 y 3); terminaciones de salida de mi-
crófono en 150 W (clavijas 2 y 3); enchufe tipo auriculares (1/4
pulg-anillo) 300 W a tierra; enchufe tipo auriculares (1/4pulg
300 W a tierra; enchufe de auriculares (3,5 mm) sin carga; bus de
mezcla de 930 W (posición de M367) ó 3,5 kW (posición de M267),
no conectado salvo indicación contraria; señal de entrada de 1
kHz.
punta)
-
REPUESTOS
Juego de patas (4 por juego) ....................................... 90S8100
Fusible para M367, 0,125 A, 250 V................................ 80E380
Fusible para M367E, 0,063 A, 250 V ............................. 80G380
Perilla
Maestra ........................................................................ 95A8238
Ganancia del canal, auriculares................................... 95B8238
Cordón de alimentación
M367 ............................................................................ 95A8389
M367E.......................................................................... 95B8389
ACCESORIOS OPCIONALES
Juego de montaje en rack................................................A367R
DECLARACION DE HOMOLOGACION
Por este medio se certifica que el mezclador para micrófonos
M367E de Shure satisface las especificaciones y regulaciones
contenidas en la norma Vfg 243/1991, enmendada en 1992. La
Bundesamt für Zulassungen in der Telekommunikation ha sido notificada que este dispositivo ha sido puesto a la venta y se le ha
otorgado el derecho de verificar el dispositivo o sistema para asegurar su cumplimiento con las especificaciones.
Cumple con las directrices de la European Union, califica para
llevar las marcas CE; certificación de VDE GS según la norma EN
60 950; cumple con los requisitos de inmunidad y compatibilidad
electromagnética de la European Union (EN 50 082-1, 1992):
Radiación de radiofrecuencias (IEC 801-3): cumple con el Criterio
A, ESD: cumple con el Criterio B (IEC 801-4): cumple con el
Criterio B.
INFORMACION GENERAL
Las modificaciones o los cambios efectuados sin la aprobación expresa de Shure, Inc. podrían anular la autorización concedida para usar este equipo.
Este equipo ha sido probado y hallado en cumplimiento con los
límites correspondientes a un dispositivo digital de categoría B
definidos en la Parte 15 de las normas de la FCC y establecidos
en los Reglamentos de Interferencias de Radio del Departamento
Canadiense de Comunicaciones. Estos límites están diseñados
para brindar una protección razonable contra interferencias perjudiciales en instalaciones residenciales. Este equipo genera, emplea y puede emitir energía de radiofrecuencia y, si no se instala y
utiliza de acuerdo con las instrucciones, es posible que cause interferencias perjudiciales a las comunicaciones por radio. Sin embargo, no se garantiza que no se produzcan interferencias en una
instalación concreta. Si se determina que el presente equipo ocasiona interferencias dañinas a la recepción de señales de radio o
televisión, lo que puede verificarse al encender y apagar el equipo,
intente corregir la interferencia tomando una o más de las siguientes medidas:
1. Cambie la orientación o la posición de la antena del receptor.
2. Aumente la distancia entre el equipo y el receptor.
3. Conecte el equipo a un tomacorriente de un circuito diferente
al cual se ha conectado el receptor.
4. Consulte al concesionario o a un técnico de radio/TV con
experiencia para recibir ayuda.
26

AJUSTES INTERNOS
ADVERTENCIA
Solo técnicos calificados deben efectuar estas modificaciones.
Para hacer estos ajustes internos sólo hay que quitar la
cubierta superior:
1. Quite el compartimiento de las pilas.
2. Saque los cuatro tornillos que fijan las dos tapas de plástico y
un tornillo de puesta a tierra del lado opuesto al del compartimiento de las pilas.
3. Deslice la cubierta lentamente hacia arriba y quítela del chasis.
POTENCIOMETRO DE AJUSTE DE DISTORSION DE
VCA (R607)
¡NO LO AJUSTE! Este potenciómetro se calibra a precisión en
cada mezclador para reducir la distorsión al mínimo.
AJUSTE DE MEDIDOR DE VU (R684)
Este potenciómetro ajusta el medidor de VU para que indique 0 VU a un nivel determinado. El valor de ajuste en fábrica es de +4 dBm. El intervalo de ajuste oscila entre -10 dBV y +4 dBm (-6 dBV a +8 dBm, con el interruptor DIP #1 hacia abajo).
Para fijar el medidor de VU a un valor diferente del de fábrica (0 VU = +4 dBm), continúe de la manera siguiente:
1. Conecte una carga de 600 W a una salida XLR ajustada para
nivel de línea.
2. Conecte un voltímetro de CA con una impedancia de entrada
de 1 MW o mayor (Fluke 77 ó uno equivalente) en paralelo
con la carga.
3. Ponga el interruptor del oscilador de 1 kHz en la posición de
encendido.
4. Ajuste el nivel del oscilador de 1 kHz con el control maestro de ganancia hasta que el voltímetro de CA indique el nivel deseado.
5. Con la cubierta superior del M367 retirada, ajuste el potenciómetro de calibración de nivel de VU, R684, con un destornillador hasta que el medidor de VU indique 0.
6. Para ajustar el nivel de 0 VU entre +4 y +8 dBm, ajuste la posición del interruptor DIP (S701) 1 hacia abajo, y efectúe los pasos 1 al 5.
POTENCIOME
TRO DE
CALIBRACION
DE MEDIDOR
DE VU R684
(SE ACCEDE A
TRAVES DE UN
AGUJERO EN
LA TARJETA DE
CIRCUITOS
SUPERIOR
DELANTERA)
POTENCIOME
TRO DE
AJUSTE DE
DISTORSION
DE VCA R607
INTERRUPTOR
DIP S701
AJUSTES INTERNOS
FIGURA 5
FUNCIONES INTERNAS MODIFICABLES
Efectúe todas las modificaciones a través de los puntos de sol-
dadura accesibles de la tarjeta de circuitos principal.
DESARMADO DEL M367
1. Retire la cubierta superior del mezclador de la forma descrita anteriormente.
2. Quite cuidadosamente los tres conectores de clavijas múltiples de la tarjeta de circuitos delantera superior (más cercana
al panel delantero). Saque los tres tornillos Phillips que fijan la
tarjeta de circuitos. Quite la tarjeta de circuitos delantera
superior.
3. Quite cuidadosamente los cuatro conectores de clavijas múltiples de la tarjeta de circuitos trasera superior (más cercana al
panel trasero). Saque los tres tornillos Phillips que fijan la tarjeta de circuitos. Quite la tarjeta de circuitos trasera superior.
4. Efectúe la modificación del caso (consulte el procedimiento apropiado dado a continuación). Obsérvese que todas las modificaciones pueden efectuarse sin necesidad de quitar la tarjeta de circuitos principal.
5. Vuelva a armar el M367 invirtiendo el orden de los pasos anteriores, colocando los tornillos Phillips en el orden indicado en las tarjetas de circuitos superiores delantera y trasera.
CAMBIO DE LA IMPEDANCIA DE SALIDA DE NIVEL DE
LINEA A 600 W
Ubique la resistencia R621 (cerca de la clavija 8 del circuito integrado U602) en la tarjeta de circuitos principal y retírela. Ubique
las zonas terminales desocupadas X621 (cerca de la resistencia
R621). Suelde una resistencia de 430 W, 1/2 W a través de los
agujeros en X621.
CAMBIO DE SALIDA DE LINEA SIN CONMUTAR A
NIVEL DE MICROFONO
Localice la resistencia R632 (cerca del transformador de salida T601) y retírela. Localice las zonas terminales desocupadas X632 (cerca del transformador T601). Suelde un alambre de puente a través de los agujeros de X632.
CAMBIO DE NIVELES DE AUDIO DE MEZCLADORA EN
AURICULARES (Interruptor "Pull/monitor" Activado,
Interruptor Dip #4 S701 Cerrado)
Ubique las zonas terminales desocupadas X649 (cerca del potenciómetro de auriculares R648). Suelde una resistencia de 68
kW, 1/4 W a través de los agujeros en X649 para escuchar la señal
de programa atenuada 12 dB respecto al nivel normal de auriculares cuando se activa el interruptor "Pull/Monitor" (tirado hacia
afuera). Suelde una resistencia de 24 kW, 1/4 W a través de los
agujeros en X649 para escuchar la señal de programa atenuada 6
dB respecto al nivel normal de auriculares cuando se activa el interruptor "Pull/Monitor" (tirado hacia afuera).
27

CAMBIO DE FRECUENCIA DE CORTE (punto de
atenuación de 3 db) DE FILTRO ATENUADOR DE
BAJOS
Para reducir la frecuencia de corte:
1. Calcule el valor del condensador necesario para la frecuencia de corte deseada. Utilice la fórmula siguiente:
C en mF = (85/frecuencia) - 0,33
Ejemplo: para una frecuencia de corte de 200 Hz,
85/200 = 0,43
0,43 - 0,33 = 0,1
Para una frecuencia de corte de 200 Hz, utilice un condensador de
0,1 mF.
Nota: El condensador deberá ser no polarizado, de cerámica o
película; con capacidad de 16 V o superior.
2. Localice las zonas terminales desocupadas siguientes:
Zona terminal Canal Zona terminal Canal
X421 1 X451 4
X431 2 X521 5
X441 3 X531 6
Ubique todas las zonas terminales cerca de los conjuntos de
cables planos W811, W812 y W813.
3. Suelde un condensador nuevo a través de los agujeros de las
zonas terminales desocupadas correspondientes a cada
canal que se desea modificar.
Para aumentar la frecuencia de corte:
Nota: Si se aumenta la frecuencia de corte a un valor mucho
mayor que el valor fijado en fábrica de 260 Hz, se puede
causar la atenuación excesiva de las frecuencias bajas a
intermedias.
1. Localice los condensadores siguientes cerca de las zonas ter-
minales desocupadas:
REDUCCION DE VELOCIDAD DE RESPUESTA DEL
MEDIDOR DE SALIDA RESPECTO A LA
CARACTERISTICA "VU verdadera"
Localice las zonas terminales desocupadas X691 (a la izquierda del medidor de VU M1). Suelde un condensador electrolítico de
100 mF x 6,3 V a través de los agujeros en X691. Respete la polaridad que se indica en la tarjeta de circuitos para el condensador.
El tiempo de respuesta ahora es de 500 ms, sin sobreamplitud.
Para reducir aun más el tiempo de respuesta del medidor, utilice
un condensador de valor más grande.
CAMBIO DE IMPEDANCIA DE SALIDA DE NIVEL DE
MICROFONO
Localice la resistencia R631 (cerca del transformador de salida
T601) y retírela. Localice las zonas terminales desocupadas X631
(cerca del T601). Suelde una resistencia de 1/4 W y del valor
deseado a través de los agujeros de X631. Por ejemplo, utilice una
resistencia de 150 W, 1/4 W para fijar la impedancia de salida en
150 W .
ADAPTACION DE SALIDA DE LINEA PARA UTILIZAR
DOS JACKS TIPO BANANA
Añada la capacidad de usar dos jacks tipo banana para salidas
de nivel de línea, balanceadas, adquiriendo una unidad comercial
(Sescom XLR F-3BP o una equivalente), o adquiriendo un conector XLR hembra (Radio Shack 274-011 ó uno equivalente), un
conector con dos jacks tipo banana (ITT 2269 ó uno equivalente),
una cajilla auxiliar pequeña, y un tramo corto de cable blindado de
alta calidad para construir el adaptador ilustrado en la Figura 6.
Condensa-
dor
C425 X421 1 C455 X451 4
C435 X431 2 C525 X521 5
C445 X441 3 C535 X531 6
Zona
termi-
nal
Canal Condensa-
dor
Zona
termi-
nal
Canal
2. Retire el condensador indicado correspondiente a cada uno de los canales que se desea modificar.
3. Calcule el valor del condensador necesario para la frecuencia de corte deseada. Utilice la fórmula siguiente:
C en mF = (85/frecuencia)
Ejemplo: para una frecuencia de corte de 400 Hz,
C = (85/400) = 0,21
Para una frecuencia de corte de 400 Hz, utilice un condensador
de 0,22 mF.
4. Suelde un condensador nuevo a través de los agujeros de las zonas terminales desocupadas correspondientes a cada canal que se desea modificar.
231
SALIDA CON DOS JACKS TIPO BANANA
FIGURA 6
Conecte este adaptador a la salida de línea del M367.
28

CAMBIO DE ENTRADA DE MONITOR A ENTRADA
CW
TIP
RING
SLEEVE
AUXILIAR
NOTA
Esta modificación desactiva la función de monitor del M367.
Retire las resistencias R642 y R647 (cerca del potenciómetro
de auriculares R648).
Localice las zonas terminales desocupadas X601 (cerca del transformador de salida T601) y X643 (cerca del jack de entrada de monitor J683).
Suelde un alambre de puente de X643 a X601. El jack de entrada de monitor ahora es un jack de entrada auxiliar desbalanceada
(la punta es positivo, el manguito es tierra), con una impedancia
de entrada de 11 kW y una ganancia máxima hasta la salida de
línea (con una carga de 600 W) de 17 dB. La señal de esta entrada
auxiliar es controlada únicamente por el control maestro.
Para cambiar la ganancia de la entrada auxiliar, localice la resistencia R605 (cerca de X601). Retire cuidadosamente la resistencia R605 y reemplácela por una resistencia de montaje
superficial (paquete tipo 0805) del valor deseado. Si se sustituye
la resistencia R605 por una de 15 kW, la ganancia máxima de la
entrada auxiliar a la salida de línea será de 14 dB, y la impedancia
de entrada será de 16 kW; si se la sustituye por una resistencia de
6,8 kW, la ganancia máxima de la entrada auxiliar a la salida de
línea será de 20 dB y la impedancia de entrada será de 7,8 kW.
CAMBIO DE GANANCIA ALTA DE ENTRADA DE
MONITOR (Interruptor DIP S701 5 hacia abajo)
Localice la resistencia R647 (cerca del potenciómetro de auriculares R648) y retírela. Localice las zonas terminales desocupadas X647 (cerca de R647). Suelde una resistencia de 330 W, 1/4
W en los agujeros de X647 para un aumento de 6 dB en la ganancia con el interruptor S701 #5 hacia abajo (la impedancia de entrada será de 6,5 kW en esta posición).
CAMBIO DE ENTRADA DE MONITOR DE ENTRADA
MONOFONICA A ENTRADA DE SUMA DE PAR
ESTEREOFONICO
Localice las zonas terminales desocupadas X645 (cerca del
jack de entrada de monitor J863). Suelde una resistencia de 1 kW,
1%, 1/4 W en los agujeros de X645. El jack de entrada de monitor
ahora acepta una señal estereofónica de entrada (punta = canal
izq., anillo = canal der., manguito = tierra) y suma estas señales
para enviarlas al circuito de monitor.
CONTROL REMOTO DE GANANCIA MAESTRA
.
Esta modificación desactiva la función de monitor del M367 y su control de ganancia maestra en el panel delantero.
1. Retire la resistencia R641 (cerca del jack de entrada de monitor J863).
2. Retire la resistencia R746 (cerca del potenciómetro del control maestro R706).
3. Ubique las zonas terminales desocupadas X702 (cerca del
potenciómetro del control maestro R706). Suelde un extremo
de una resistencia de 100 W,
Suelde un alambre aislado al otro extremo de la resistencia de
100 W. Localice la zona terminal desocupada X644 (cerca de
J863). Suelde el otro extremo del alambre aislado a X644.
4. Localice la zona terminal desocupada X701 (junto a la zona
terminal desocupada X702). Suelde un alambre aislado a
X701. Localice las zonas terminales desocupadas X645
(cerca del jack J863). Suelde el otro extremo del alambre aislado a la zona terminal desocupada X645 más cercana al
conector de entrada del canal 6, J856.
5. Fabrique un conjunto de potenciómetro de control remoto y cable, como se muestra en la Figura 7.
CONTROL REMOTO DE GANANCIA MAESTRA
Las piezas que se recomiendan son:
Potenciómetro, 10-25 kW, variación lineal (Radio Shack
271-1715)
Enchufe tipo auriculares estereofónico de 1/4 pulg
(Switchcraft 280)
Anillos de ferrita (Ferronics 21-031J)
Condensadores de cerámica, 0,001 mF, 50 V
Cable de 2 conductores, blindado, 50 pies máx.
Los anillos de ferrita y los condensadores deben colocarse lo
más cerca posible del enchufe tipo auriculares.
6. Inserte el enchufe tipo auriculares en el jack de entrada de monitor. El potenciómetro de control remoto ahora regula la ganancia del M367, con una variación similar a aquélla del control maestro de ganancia.
NOTA
1
/4 W al agujero de X702.
FIGURA 7
Si se usa una señal estereofónica para alimentar la entrada de
monitor del M367 y otro dispositivo estereofónico, la impedancia de la
fuente deberá ser de 20 W o menos para mantener una separación de
al menos 40 dB en el dispositivo estereofónico. Utilice un amplificador
estereofónico de distribución o intermedio para mantener la
separación óptima entre los canales estereofónicos.
NOTA
CAMBIO DEL TIEMPO DE LIBERACION DEL
LIMITADOR A UN SEGUNDO
Retire la resistencia R741 (aproximadamente 15 mm detrás del
cable plano W813).
29

CAMBIO DE UMBRALES PREFIJADOS DEL LIMITADOR
R6 =
1
R3
–
1
R1
1
1. Seleccione los valores equivalentes de resistencia para los umbrales deseados del limitador, usando la tabla siguiente. Después llene la hoja de trabajo siguiente con las resistencias seleccionadas.
6. Calcule el valor de la resistencia R6 de la manera siguiente:
Umbral de limita-
dor (dBm hacia 600
Interruptor DIP S701 Umbral del limitador R
Posición 2 Posición 3 - dBm -
hacia arri-bahacia arri-baalta _____ kW = R1
hacia arri-bahacia
W)
0 18 10 81
1 21 11 93
2 25 12 105
3 30 13 122
4 35 14 139
5 41 15 156
6 47 16 175
7 54 17 194
8 62 18 215
9 71
hacia
abajo
hacia
abajo
hacia arri-bamed. alta _____ kW = R2
abajo
abajo
hacia
R
(kW) Umbral de limita-
equiv
med. baja _____ kW = R3
baja _____ kW = R4
dor (dBm hacia 600
W)
equiv
(de arriba)
R
equiv
(kW)
2. Retire las resistencias R721, R731, R732, R733, R734 y R735 (rodean al circuito integrado U704).
3. Localice las zonas terminales desocupadas X732, X733, X734 y X735 (rodean al circuito integrado U704).
4. Seleccione una resistencia de 1/4 W, 1% que sea el más próximo al valor de R1 (obtenido de la hoja de trabajo) y suéldela en los agujeros de X732.
Utilice combinaciones de resistencias en serie o en paralelo
para obtener un valor más cerca posible al valor seleccionado si
no se tienen resistencias de 1% disponibles.
NOTA
Seleccione una resistencia de 1/4 W, 1% que sea el más
próximo al valor de R6 y suéldela en los agujeros de X734.
7. Calcule el valor de la resistencia R7 de la manera siguiente:
R7 =
1
R4
–
1
R1
1
1
–
R5
1
–
R6
Seleccione una resistencia de 1/4 W, 1% que sea el más próximo al valor de R7 y suéldela en los agujeros de X735. (Vea Cam-
bio de umbrales prefijados del limitador: Cálculos de muestra, más
adelante en el Apéndice para un ejemplo del cálculo de compo-
nentes para fijar el umbral del limitador.)
CAMBIO DE UMBRALES PREFIJADOS DEL
LIMITADOR: CALCULOS DE MUESTRA
Para obtener los umbrales siguientes en el limitador:
Interruptor DIP S701 Umbral del limita-
dor
Posición 2 Posición 3 - dBm -
hacia arriba hacia arriba alta 12 105 kW=R1 hacia abajo hacia arriba med. alta 8 62 kW=R2
hacia arriba hacia abajo med. baja 4 35 kW=R3 hacia abajo hacia abajo baja 0 18 kW=R4
1. Obtenga una resistencia de 105 kW, 1/4 W, 1% y suéldela a
los agujeros de X732.
2. Obtenga una resistencia de 150 kW, 1/4 W, 1% y suéldela a
los agujeros de X733.
1
R
5=
1
62,000
1
105,000
= 151.4 k:
3. Obtenga una resistencia de 52,3 kW, 1/4 W, 1% y suéldela a
los agujeros de X734.
R
equiv
5. Calcule el valor de la resistencia R5 de la manera siguiente:
R5 =
1
R2
1
1
–
R1
Seleccione una resistencia de 1/4 W, 1% que sea el más próx-
imo al valor de R5 y suéldela en los agujeros de X733.
1
R
6=
1
35,000
4. Obtenga una resistencia de 49,9 kW, 1/4 W, 1% y suéldela a
los agujeros de X735.
R
7=
11
105,000
1
105,000
1
1
150,000
= 52.5 k:
1
52,30018,000
= 49.4 k:
30

SHURE Incorporated Web Address: http://www.shure.com
5800 W. Touhy Avenue, Niles, IL 60714-4608, U.S.A.
In U.S.A., Phone: 1-847-600-2000 Fax: 1-847-600-1212
In Europe, Phone: 49-7131-72140 Fax: 49-7131-721414
In Asia, Phone: 1-852-2893-4290 Fax: 1-852-2893-4055
International, Phone: 1-847-600-2000 Fax: 1-847-600-6446
 Loading...
Loading...