Shibaura cm284 Operator Manual

FRONT MOWER
CM284
CM364
WORKSHOP MANUAL

Introduction
Shibaura developed a front mower incorporating new technology for more
improved passenger mowing garden tractor.
This manual describes the structure, functions, maintenance and service of
models CM284 and CM364 so that their functions are fully exhibited in actual
operation.
Please read this carefully to promote sales and service, to improve the service
techniques and guide users for proper operation of Shibaura tractors.
Figures or other conditions in this manual may be changed without notice in
order to improve the performance or for other objects.
Ishikawajima-Shibaura Machinery Co., Ltd.
Tractor Division
Quality Assurance Department
1

INDEX
Chapter 1. GENERAL ············································ 3
1-1 Specifications & Performances ······························ 4
1-2 Precautions Before Ser v icing ································· 5
1-3 Basic Understanding on Servicing ························· 5
Chapter 2. ENGINE ················································ 7
2-1 Engine Removal ···················································· 8
2-2 Disassembly, Inspection and Reasse mbly ··············· 9
1. Disassembly ·························································· 9
2. Disassembly, Inspection and Reassembly
of Engine Main Parts ··········································· 13
3. Engine Reassembly ············································· 36
2-3 Electrical Units ···················································· 46
1. Alternator ···························································· 46
2. Starting Motor ····················································· 53
3. Glow Plug ··························································· 68
4. Thermometer and Thermosensor ·························· 69
5. Buzze r Alarm Warning Syste m ···························· 70
6. Oil P ressure Switch ············································· 71
7. Engine Stop Solenoid ·········································· 72
8. Fusible Link ························································ 72
9. Wiring Harness ···················································· 72
2-4 Trouble Shooting ················································· 73
2-5 Engine Maintenance Standard Table····················· 75
Chapter 3. TRANSMISSION AND BRAKE ······ 83
1. DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ···················· 84
2. TRANSMISSION UNIT ····································· 88
1) Removal ························································ 88
2) Front Transmission Uni t ································· 93
3) Rear Transmission Unit ································· 101
4) PTO Clutch Unit ··········································· 105
5) Front Wheel Shaft and Brake Unit ················· 108
6) Two W ay Clutch Unit ···································· 110
7) Differential Gear Unit ··································· 111
Chapter 4. HST SYSTEM ·································· 117
1. OIL FLOW ·································· ······················ 118
2. HST U N IT REMOVAL ······································ 121
3. PRECAUTIONS BEFORE DISASSEMBLY ······ 124
4. DISASSEMBLY ················································ 124
5. INSPECTION ···················································· 125
6. REASSEMBLY ·················································· 126
7. ASSEMBLY······················································· 126
8. ADJUSTMENT ················································· 128
9. TROUBLE SHOOTING AND
SPECIFICATIONS ············································· 132
Chapter 6. REAR AXLE ASSEMBLY ·············· 149
1. DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ·················· 150
2. REAR AXLE REMOVAL ································· 151
3. INSTALLATION ··············································· 151
4. DISASSEMBLY ··············································· 152
5. INSPECTION ··················································· 154
6. ASSEMBLY ······················································ 155
7. INSTALLATION ··············································· 156
Chapter 7. HYDRAULIC LIFT SYSTEM ······· 157
1. DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ·················· 158
2. OIL FLOW ································· ··· ···················· 159
3. OVERHAUL ····················································· 162
Chapter 8. IMPLEMEN T DRIVE ······ ··· ··· ··· ······ 167
1. DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION ·················· 168
2. POWER FLOW ················································ 169
3. AUTOMATICALLY PTO
DISENGAGE SYSTEM ···································· 171
4. ADJUSTMENT AND SPECIFICATION ··········· 172
Chapter 9. MAINTENANCE
STANDARDS TABLE ····················· 173
Maintenance Standards Table ·································· 174
Chapter 10. ELECTRICAL SYSTEM ·············· 177
1. DESCRIPTION ················································· 178
2. COMPONENT LOCATION AND FUNCTION · 178
3. FUNCTION INSPECTION
AND ADJUSTMENT ········································ 181
Chapter 11. MOWER ········································· · 207
11-1 Sectional Vier: FM60SD ······························· ····· 208
11-2 Specifications ·································· ·················· 209
11-3 Disassembly ······································· ··············· 210
11- 4 Reassembly and Adjustm ent ······························ 216
Chapter 5. POWER STEERING ······················· 135
1. OIL FLOW ·································· ······················ 136
2. CONTROL VALVE ASSEMBLY ······················· 141
3. POWER STEERING CYLINDER ······················ 145
4. PIPING ······························································ 146
5. TROUBLE SHOOTING ····································· 147
2

Chapter 1. GENERAL
3
×
1-1 Specifications & Performances
Model
Model J843 N843L
Type Water-Cooled 4-Cycle Vertical Diesel Engine
Number of Cylinders 3
T ota l Stroke Volume 1330 cc 1662 cc
Maximum Output 20.8 kW (28 HP)/2700 rpm 26 kW (35 PS)/2700 rpm
Engine
Compression Ratio 22.5 : 1
Fuel Diesel Fuel Oil
Starting Method By Starting Motor
Overall Length 2415 mm
Overall Height 1390 mm
Overall Width 1220 mm (narrow), 1370 mm (wide)
Weight 730 kg 750 kg
Tire
No. of Running Speeds 2 Forward Speeds, 2 Reverse Speeds (Continuously variable speed)
Transmission System L/H Switching, All Hydraulic Continuously Variable Speed (HST)
Brake Wet Disc Brake
Maine Body
Lift Control Valve Relief Set Pressure 9.8 MPa {100 kgf/cm2}
Relief Set Pressure/ Steering 5.88 – 6.56 MPa {60 – 67 kgf/cm2}/ Full Hydraulic Power Steering
Running Speed
Fuel T ank 50.5 ℓ
Engine Oil 4.6 ℓ (Including oil filter) 5.6 ℓ (Including oil filter)
Transmission Gear Oil Front 20 ℓ, Rear 2.3 ℓ
Capacity
Cooling Water 5.1 ℓ 5.3 ℓ
Battery 75 D 26 L
Starting Motor 12 V – 1.7 kW 12 V – 2.0 kW
Alternator 12 V – 40 A
Head Light 23 W
Monitor Lamp 3 W
Electric Units
Dash Panel Lamp 2 W
Light Switch Lamp 1.4 W
Front Wheel
Rear Wheel
Forward: L 0 – 10.0 km/h
Forward: H 0 – 17.2 km/h
Reverse: L 60 – 70 % of Forward Speed
Reverse: H 60 – 70 % of Forward Speed
CM284 CM364
10.5 – 12
23
20 × 8.00 – 10
4
1-2 Precautions Before Servicing
1. Have the tractor washed clean and have the oil, fuel, and cooling water drained out as would be required by
the work to be performed.
2. Service shop should always be kept clean to prevent dust from rising and should be well lighted.
3. The disassembled parts shall have the oil and grease washed off and arranged on a stand separated by groups.
4. Clothing, service tools and equipments shall be checked to ensure safety in performing the operations.
1-3 Basic Understanding on Servicing
1. Engine, transmission, and hydraulic apparatus have been specially manufactured to high accuracy so that
care shall be exercised to maintain them in clean state and not to do any unnecessary disassembly.
2. Defective parts due to wear and other causes shall be discarded and new parts ordered with the tractor model,
serial No., code No., and part name clearly defined. (Keep the defective parts on hand to enable showing it to
the customer.)
3. When assembling, it is essential to have oil applied to all moving parts so that they will be provided with
initial oil film until normal lubrication takes place.
4. Unless specially instructed, bolts and nuts shall be tightened by proper tools to the proper tightening torque.
5
N
N
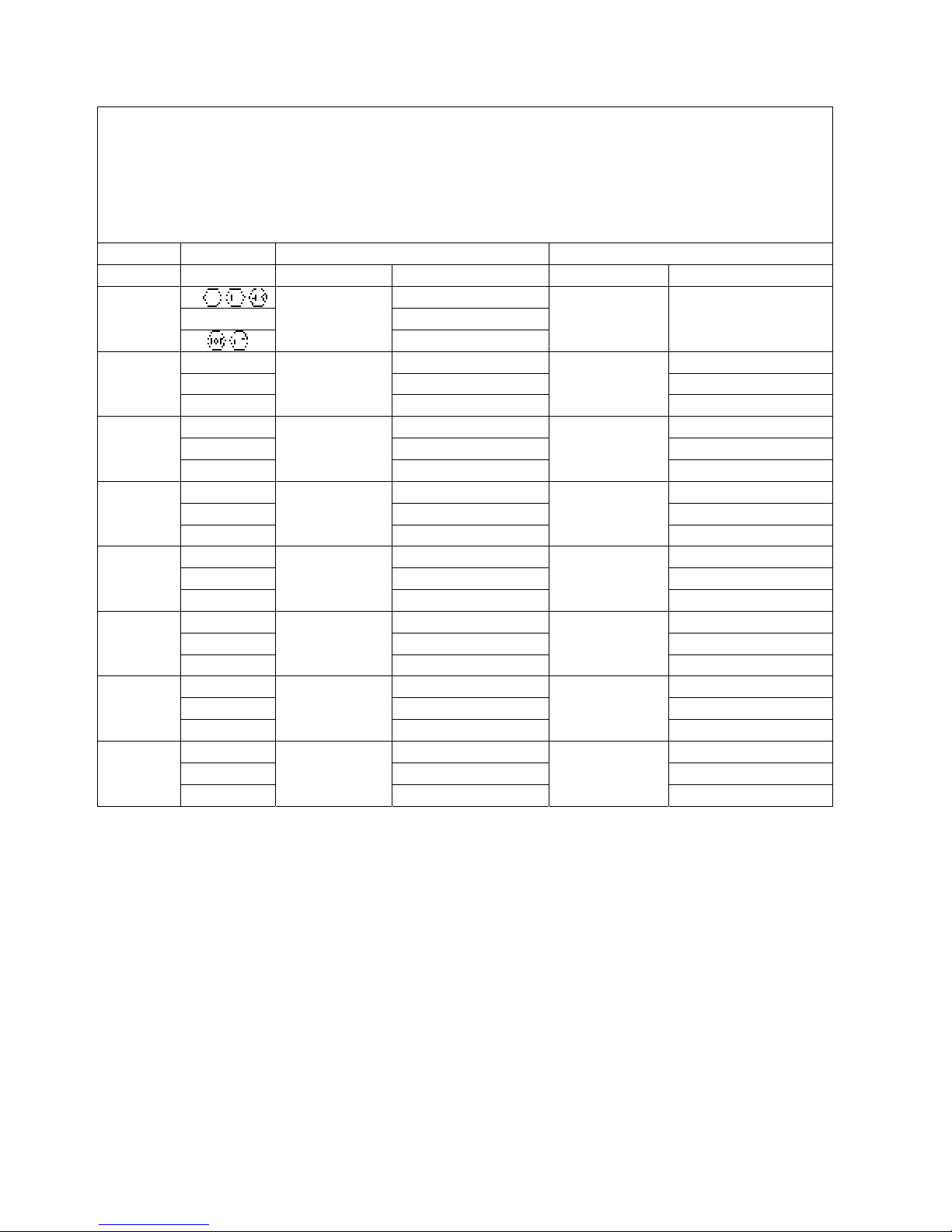
GENERAL METRIC BOLT TORQUE SPECIFICATION TABLE
USE THE FOLLOWING TORQUES WHEN SPECIAL TORQUES ARE NOT GIVEN
NOTE : These values apply to fasteners as received from supplier, dry, or when lubricated
with normal engine oil. They do not apply if special graphited or molly disulphide grasses
or other extreme pressure lubricants are used.
Coarse Thread Fine Thread
Bolt Size Grade No. Pitch (mm)
4T
M6
M8
M10
M12
M14
M16
M18
M20
10T 11.7 – 15.7
4T
7T 22.6 – 28.4 26.5 – 34.3
10T 28.5 – 36.3 30.4 – 40.2
4T
7T 44.1 – 55.9 49.0 – 62.8
10T 54.0 – 69.6 57.9 – 73.5
4T
7T 65.7 – 83.4 74.5 – 94.1
10T 92.2–116 99.0 – 127
4T
7T 104 – 131 117 – 148
11T 139 – 175 147 – 186
4T
7T 149–184 157 – 192
11T 206 – 255 221 – 270
4T
7T 196 – 235 230 – 279
11T 275 – 333 299 – 368
4T
7T 240 – 289 275 – 333
11T 363 – 441 397 – 485
1.0
1.25
1.5
1.75
2.0
2.0
2.0
2.5
ewton Meters Pitch (mm)
4.9 – 6.9
– – 7T 8.3 – 11.3
12.7 – 16.7
1.0
25.5 – 33.3
1.25
37.3 – 47.1
1.25
62.8 – 80.4
1.5
86.3 – 110
1.5
114 – 141
1.5
144 – 179
1.5
ewton-Meters
15.2 – 20.1
28.4 – 36.2
43.1 – 54.9
69.6 – 87.3
91.2 – 115
131 – 163
172 – 211
6
Chapter 2. ENGINE
NOTE:
Due to Pollutant Regulations, some of parts relating to Engine exhaust are not
available for spares as an individual part.
Engine Model Tractor Model
J843 CM284
N843L CM364
7

2-1 Engine Removal
1) If necessary, rem ove bolts an d nut s and the bon net.
2) Remove the muffler and stay from the engine.
3) Disconnect the wiring from the air cleaner clogging
sensor.
4) Disconnect the wiring from the water temperature
sensor and water temperature switch.
5) Remove the radiator hoses from the engine.
6) Disconnect the wiring from the alternator.
7) Disconnect the wiring from the starting motor.
8) Remove the bolt and ground wire from the cylinder
head.
9) Disconnect the fuel return hose from the fuel return
pipe.
10) Disconnect the wiring from the engine oil pressure
switch.
11) Disconnect the wiring from the glow plug connector.
12) Disconnect the wiring from the engine stop solenoid.
13) Disconnect the fuel pipe from the injection pump.
14) Remove the accelerator wire from the engine.
15) Disconnect the drain hose from the drain cock.
16) Disconnect the oil hoses from the hydraulic oil pump.
17) Remove the engine attaching nuts and hoist the
engine from the flame.
3
1
2
4
① Water temperature switch ④ Alternator
② Water temperature sensor ⑤ Starting motor
③ Radiator hose
① Air cleaner clogging sensor ③ Glow plug connector
② Ground wire ④ Fuel return hose
3
1
6
① Engine stop solenoid ⑤ Hydraulic oil pump
② Accelerator wire ⑥ Engine attaching nut
③ Fuel hose
④ Drain cock
5
002X
003X
2
5
4
004X
8
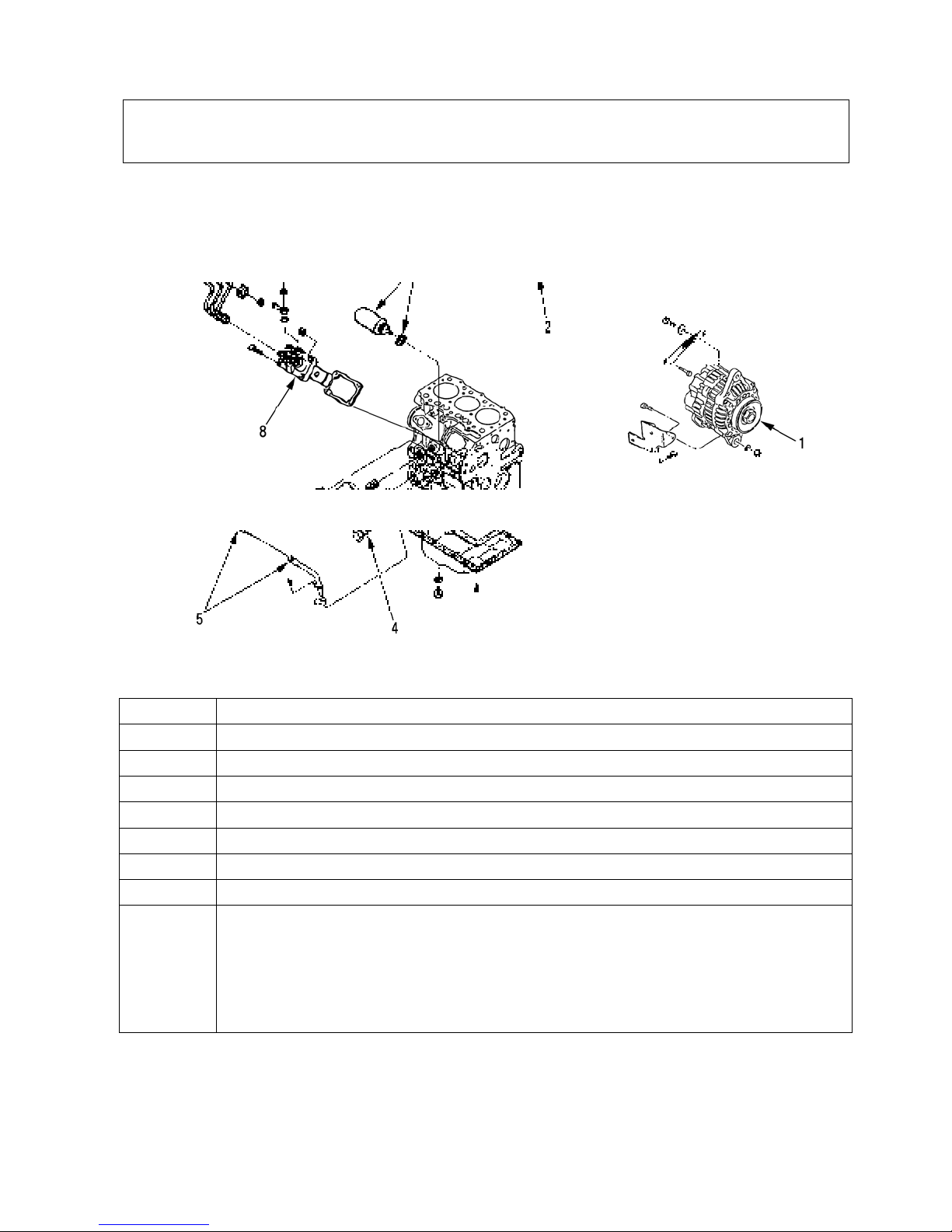
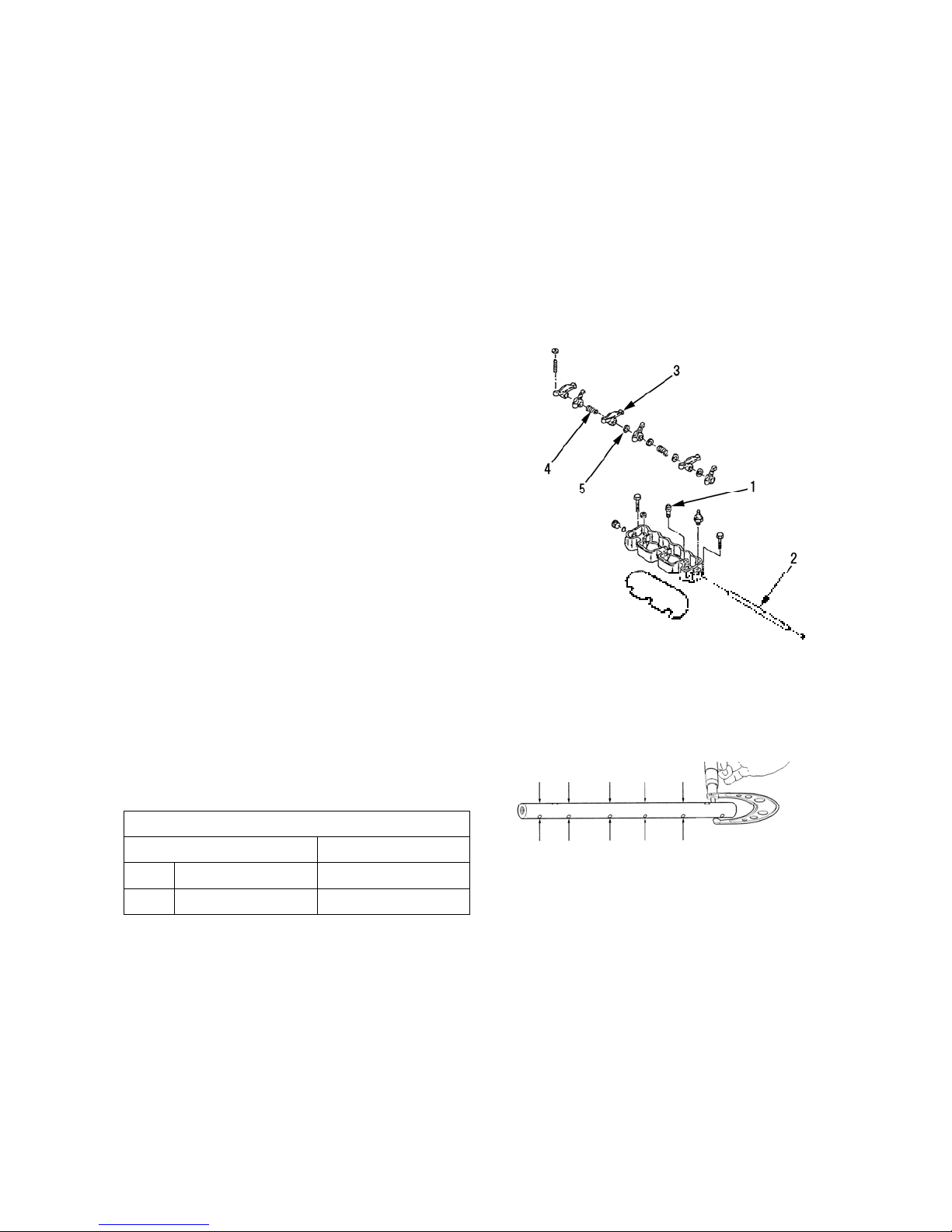
2-2 Disassembly , Inspection and Reassembly
1. Disassembly
Order Disassemble Parts Name
1 Alternator
2 Starting motor
3 Oil filter
4 Relief valve
5 Oil level gauge · Gauge guide
6 Engine stop solenoid · Seal washer
7 Injection pipe
8 Injection pump
NOTE:
1. Remove the injection pipes and engine stop solenoid before remove the injection pump.
2. Raise the injection pump and disconnect the governor link from the control rack by remove
the snap pin.
3. Injection timing has been adjusted by the shims between injection pump and cylinder block.
Take note of their thickness and number when removing the injection pump.
005X
9
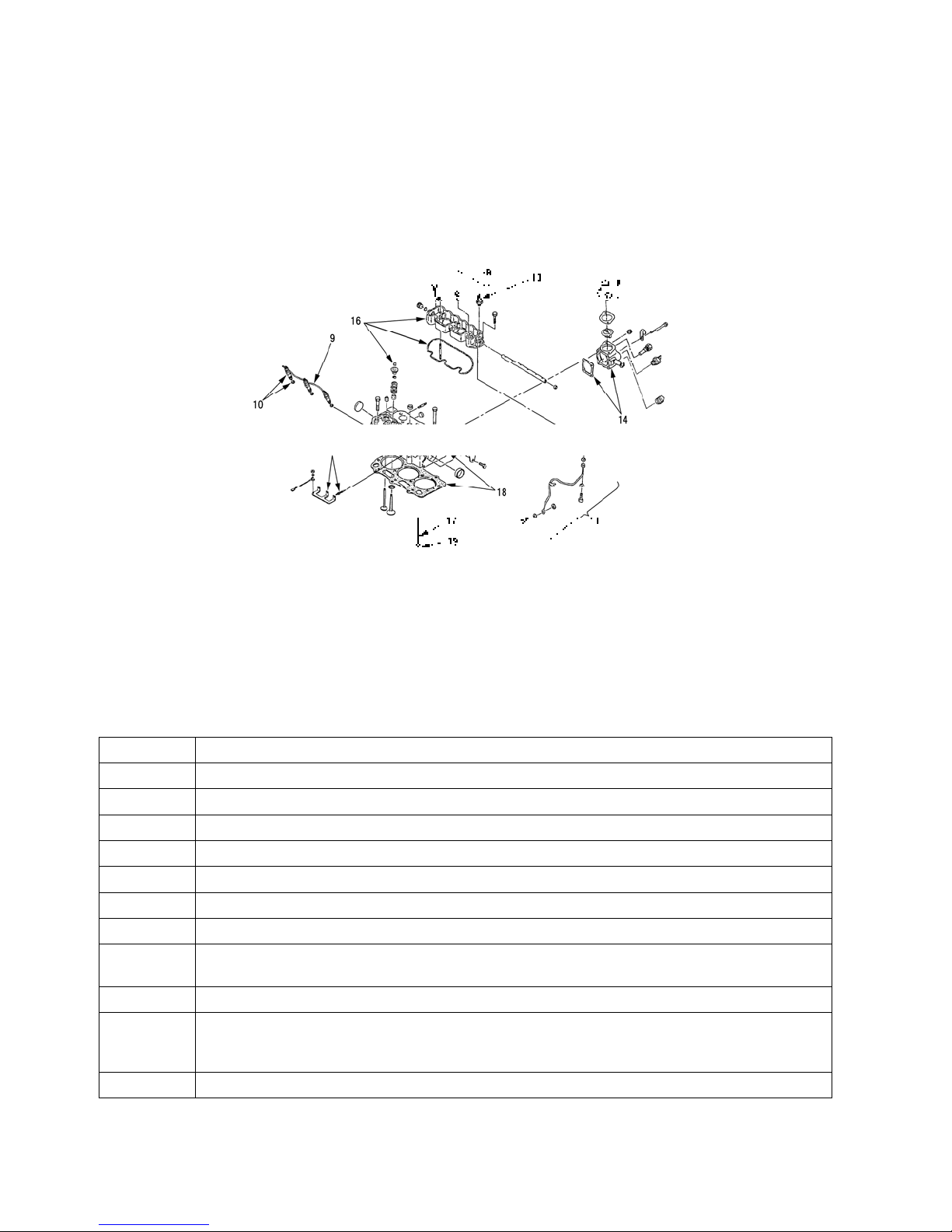
r
Order Disassemble Parts Name
9 Return pipe
10 Injection nozzle · Gasket
11 Oil transfer pipe · Eye bolt · Seal washe
12 Connector · Glow plug
13 Oil pressure switch
14 Thermostat case · Gasket
15 Head cover · O-Ring · Intake manifold · Spacer
16 Rocker arm assembly · O-Ring · Cap
NOTE: Remove the caps from intake valves and exhaust valves.
17 Push rod
18 Cylinder head assembly · Head gasket
NOTE:
1. Untighten the cylinder head bolts in several steps and remove the cylinder head assembly.
19 Tappet
006X
10
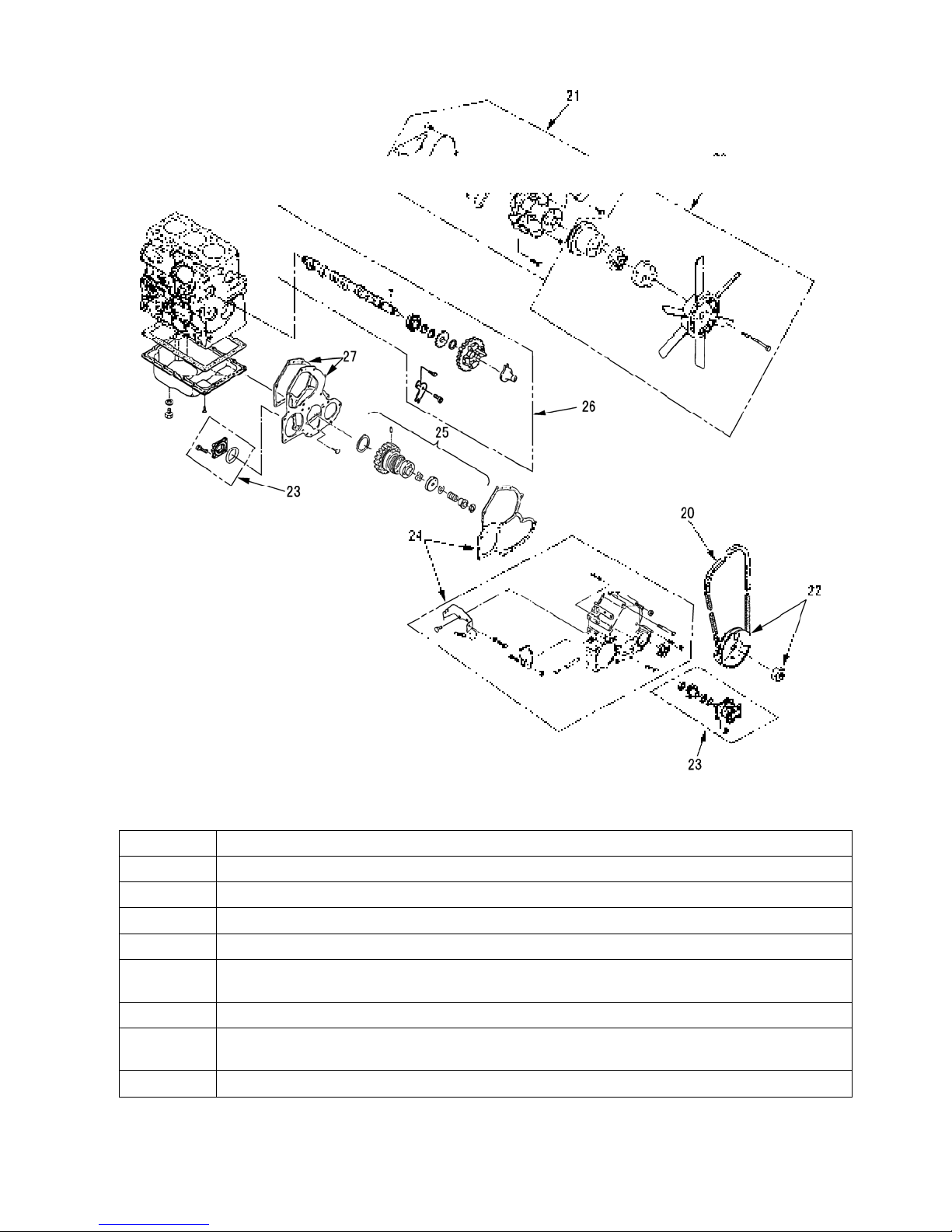
Order Disassemble Pats Name
20 V-belt · Cooling fan · Fan holder · Fan pulley
21 Water pump assembl y · Gasket
22 Crankshaft pulley
23 Hydraulic oil pump, Cover, Dr ain cock.
24 Timing gear case assembly · Gasket
NOTE: Remove the engine stop solenoid and injection pump assembly at first.
25 Idle gear · Oil pump assembly
26 Cam shaft assembly · Plate
NOTE: Remove the bolts and plate at first, and draw out the cam shaft assembly .
27 Front plate · Gasket
007X
11
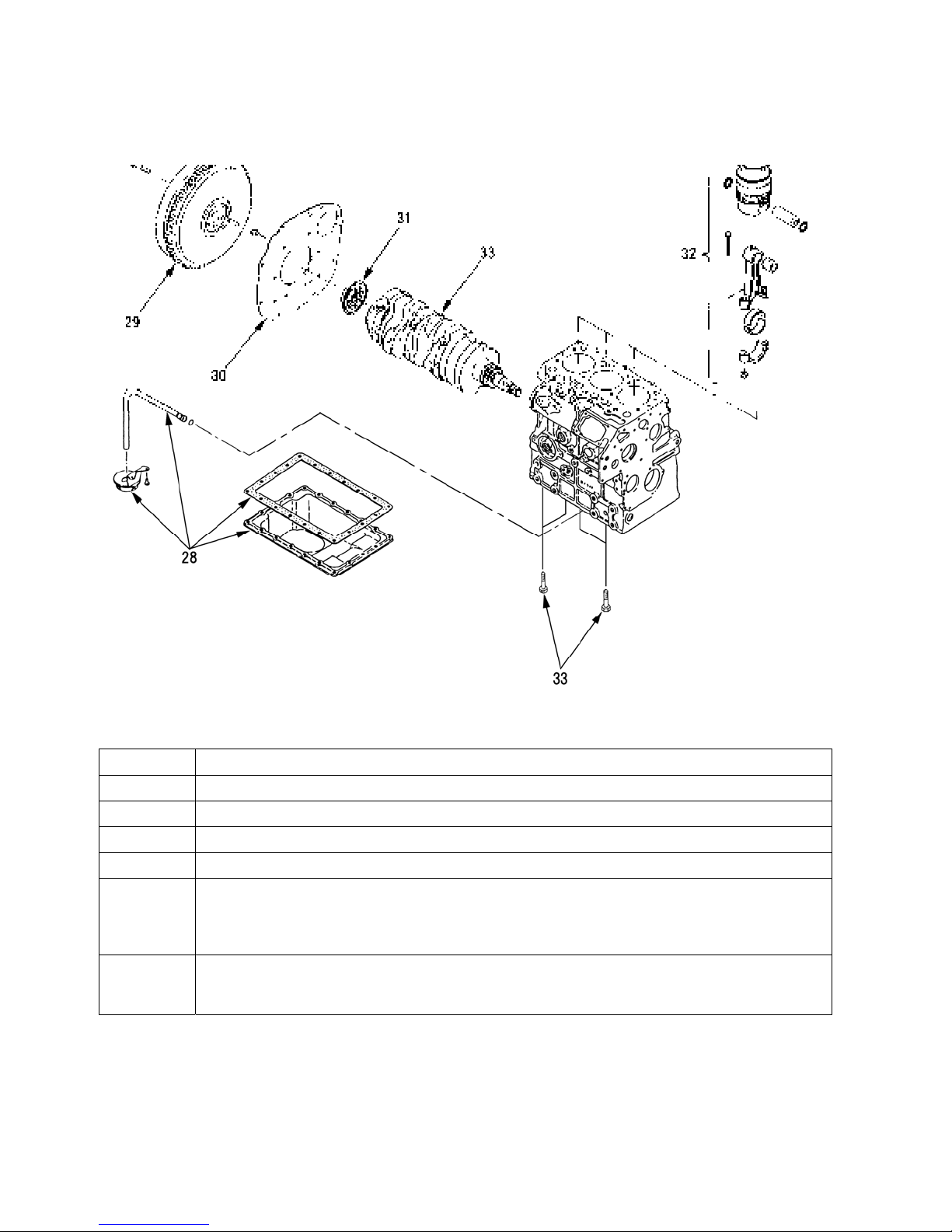
Order Disassemble Parts Name
28 Oil pan · Gasket · Suction filter · Suction pipe
29 Fly wheel
30 Rear plate
31 Oil seal
32 Piston and connecting rod assembly
NOTE:
1. Before extracting piston, remove the carbon deposit from the TDC in the cylinder.
2. Place the connecting rod, cap and bearing removed in order of the cylinders.
33 Crank shaft and bearing holder assembly
NOTE: Remove the four bolts, and draw out the crank shaft and bearing holder assembly as a
set.
008X
12
2. Disassembly, Inspection and Reassembly of Engine Main Parts
★ Cautions before start
1) Check the cylinder block and cylinder head for wear, leakage and damage.
2) Remove deposit in oil holes of each part with air and check for clogging.
3) Wash each part well to remove dust, contaminated oil, carbon , and other foreign matter.
4) Remove carbon deposite on the piston, cylinder head, valves, etc. carefully not to damage parts. (Great care is
necessary specifically for aluminum alloy parts.)
5) Valves, pistons, connecting rods, metals and other parts which are to be combined as specified should be
attached match marks beforehand to prevent confusion.
1) Rocker arm ass’y
Disassembly
(1) Extract the screw from the rocker arm bracket.
(2) Screw in a M8 bolt from the front side of the rocker
arm bracket and extract the rocker a rm shaft.
(3) Take out the spring and rocker arm from the rocker
arm bracket.
1. Screw
2. Rocker arm shaft
3. Rocker arm
4. Spring
5. Shim
Inspection and service
(1) Rocker arm shaft
Measure the outside diameter of the rocker arm shaft
with a micrometer and replace if the result is bellow
the service limit.
Rocker arm shaft diameter (ø)
Standard assembling value Service limit
J843 11.65 – 11.67 11.57
N843L 14.95 – 14.97 14.87
009X
010X
13

(2) Clearance between rocker arm and rocker arm
shaft
a. Measure the rocker arm bore.
b. Measure the clearance between the rocker arm
and rocker arm shaft, and replace if the service
limit is exceeded.
Clearance between rocker arm and rocker arm shaft
(mm)
Standard assembling value Service limit
0.032 – 0.068 0.2
(3) Inspection of rocker arm
Check the valve cap-contact surface for uneven wear
and streaks. Correct the curved surface with an oil
stone or grinder correctly if insignificant.
Reassembly
Reassembly parts reversely to disassembly.
2) Cylinder head ass’y
Disassembly
(1) Compress the valve spring with a valve spring
replacer and remove the valve cotter, retainer, spring
and valve.
(2) Remove the valve guide seal, if required.
Inspection and service
(1) Distortion of cylinder head bottom surface.
Apply a straight edge to the bottom surface of the
cylinder head, and insert a thickness gauge at 6 points
from A to F in the right figure and measure distortion.
If the distortion exceeds the repair value, correct with
surface grinder or the like.
Distortion at cylinder head bottom surface (mm)
Standard assembling value Repair value
Less than 0.05 0.12
011X
013X
1. Valve 4. Valve cotter
2. Spring 5. Valve guide seal
3. Retainer
014X
015X
14
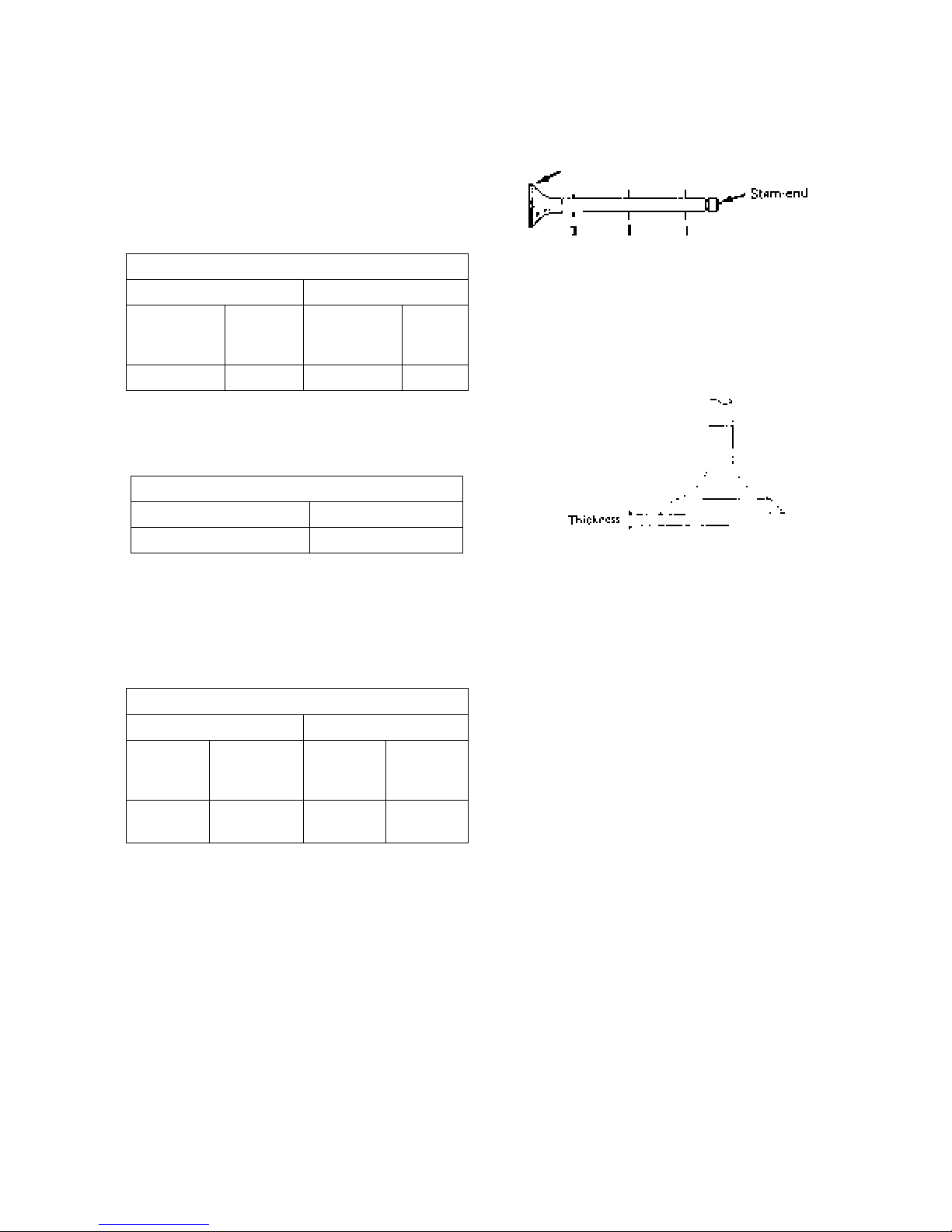
(2) Intake and exhaust valves and valve guide
a. Check the head and stem of each valve and
replace if burnout, wear or deformation is
remarkable.
b. Measure the outside diameter at the position I, II,
and III on the valve stem with a micrometer and
replace if the result is less than the service limit.
Valve stem diameter (mm)
Intake valve Exhaust valve
Standard
assembling
value
Service
limit
Standard
assembling
value
Service
limit
6.955 – 6.97 6.89 6.94 – 6.95 6.84
c. Replace a valve if its head thickness is less than
service limit.
Valve head thickness (mm)
Standard assembling value Service limit
0.775 – 1.075 0.5
d. Replace the valve if the clearance between the
stem and guide exceeds the service limit.
Clearance between valve stem and valve guide (mm)
Intake valve Exhaust valve
Standard
assembling
Service limit
value
0.03 – 0.06 0.2
Standard
assembling
value
0.045 –
0.075
Service
limit
0.25
016X
017X
018X
15
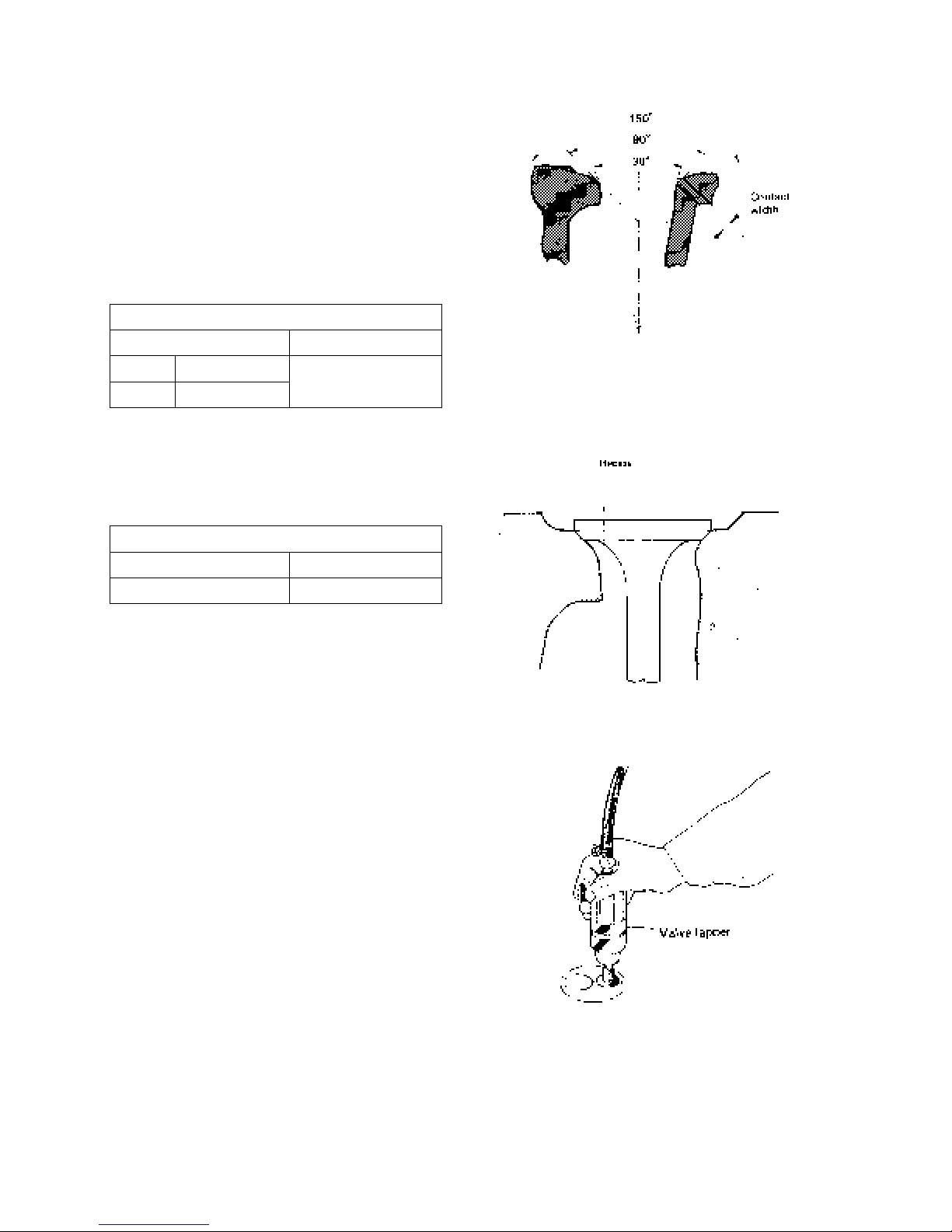
(3) Valve seat
a. Since the valve seat is corrected according to the
valve guide, be sure to check the valve guide for
wear condition first before corr ecting the seat.
b. Correct the seat using a seat cutter of 15°, 45°
and 75° so that the contact width is the standard
assembling value.
Valve seat contact width (mm)
Standard assembling value Repair value
Intake 1.66 – 1.87
2.5
Exhaust 1.66 – 1.73
c. When the seat recess exceeds the service limit,
replace the valve seat or valve.
Valve seat recess (mm)
Standard assembling value Service limit
0.85 – 1.15 1.8
d. Coat the valve seat surface with compound and
lap the contact surface turning the valve.
e. Check that the valve conta ct surf ac e is within the
standard value and the contact position is even.
019X
020X
021X
16
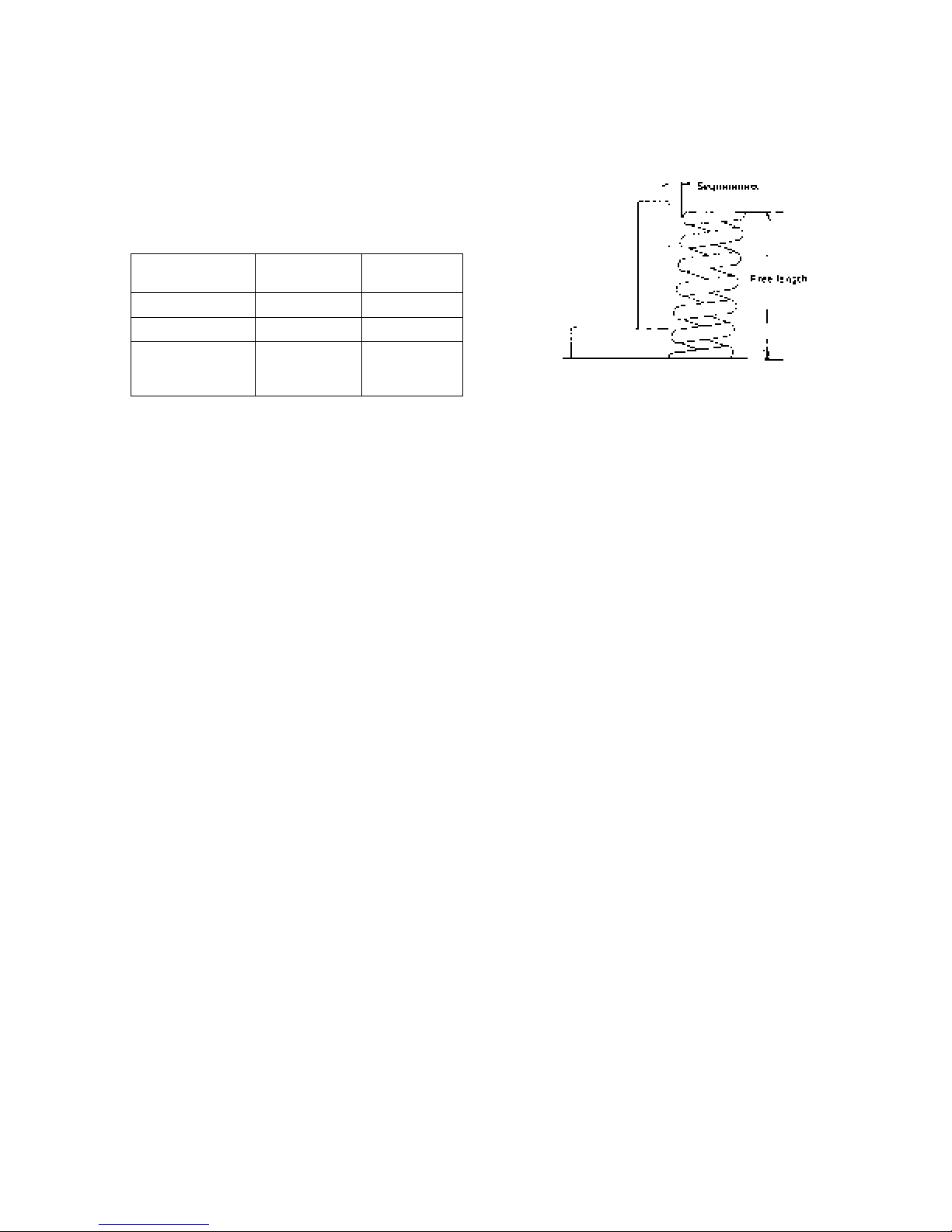
(4) Valve spring
a. Check the valve spring visually for damage.
b. Measure the squareness of the spring using a
square on a surface plate and replace if the
service limit is exceeded.
c. Check the free length and spring force with a
spring tester and replace if the service limit is
exceeded.
Standard
Squareness (mm)
Free length (mm)
Spring force (when
compressed to 30.4
mm)
assembling value
1.2 2
35 33.5
8.1 7
Service limit
(5) Inspection of combustion chamber
Check and clean the inside of the combustion
chamber.
Reassembly
Reassemble parts in the order reverse to disassembly taking care for the following points.
(1) When assembling the valve, spring, retainer and cotter, be careful not to damage the valve guide seal.
(2) Tighten the glow plug with the tightening torque of 14.7 – 19.6 N·m {1.5 – 2.0 kgf·m}.
022X
17
3) Cylinder block
Inspection and service
(1) Check for crack, damage and distortion on the top of
the block in the same way as in the cylinder head.
(2) Measurement of cylinder bore
a. There should be apparent scratches, rust,
corrosion, etc. on the cylinder bore.
b. Measure the cylinder bore at the top, center and
bottom respectively in the crankshaft direction
(A) and the direction at right angle to it (B). If
the repair value i s exceed ed, replac e engine l ong
block assembly.
Distortion on cylinder block top surface (mm)
Standard assembling value Repair value
Less than 0.05 More than 0.12
Model
J843
·
N843L
Standard assembling
value
φ84 – φ84.019
122V
Repair value
Replace engine long block assembly.
More than
φ84.2
18
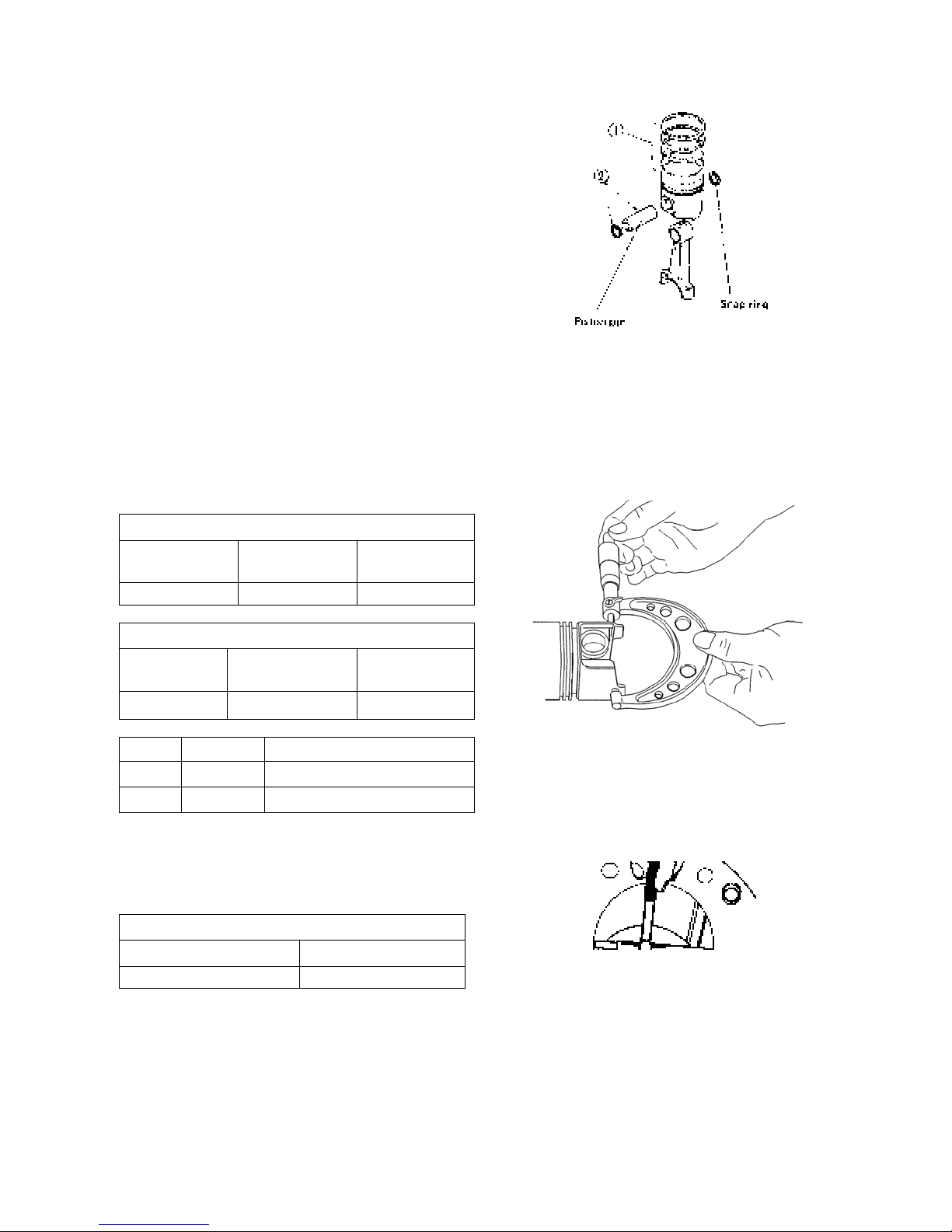
4) Piston and piston ring
Disassembly
(1) Remove the piston ring using a piston ring tool.
(2) Remove the snap ring and extract the piston pin.
Inspection
(1) Pisto n
a. Check the piston for crack, streak and burnout
on the outside surface and replace if remarkable.
b. Measure the longer diameter at 10 mm above the
lower end of the piston skirt and bore of the
cylinder in the thrust direction, calculate the
clearance, and replace if the repair value is
exceeded.
Clearance between cylinder and piston (mm)
Model
J843·N843L 0.0375 – 0.0715 0.25
Piston skirt bottom longer dia. (mm)
Model
Standard
assembling value
Standard
assembling value
Service limit
Service limit
024X
J843·N843L φ83.9475 – 83.96 φ83.7
Model Piston size Skirt bottom longer dia.
J843
N843L
S.T.D
S.T.D
83.9475
83.9475
– 83.9625
– 83.9625
d. Measure the piston pin hole diameter and piston
pin outside diameter and replace if the clearance
exceeds the service limit.
Clearance between piston pin hole and piston pin (mm)
Standard assembling value Service limit
-0.001 – +0.007 0.02
025X
026X
19
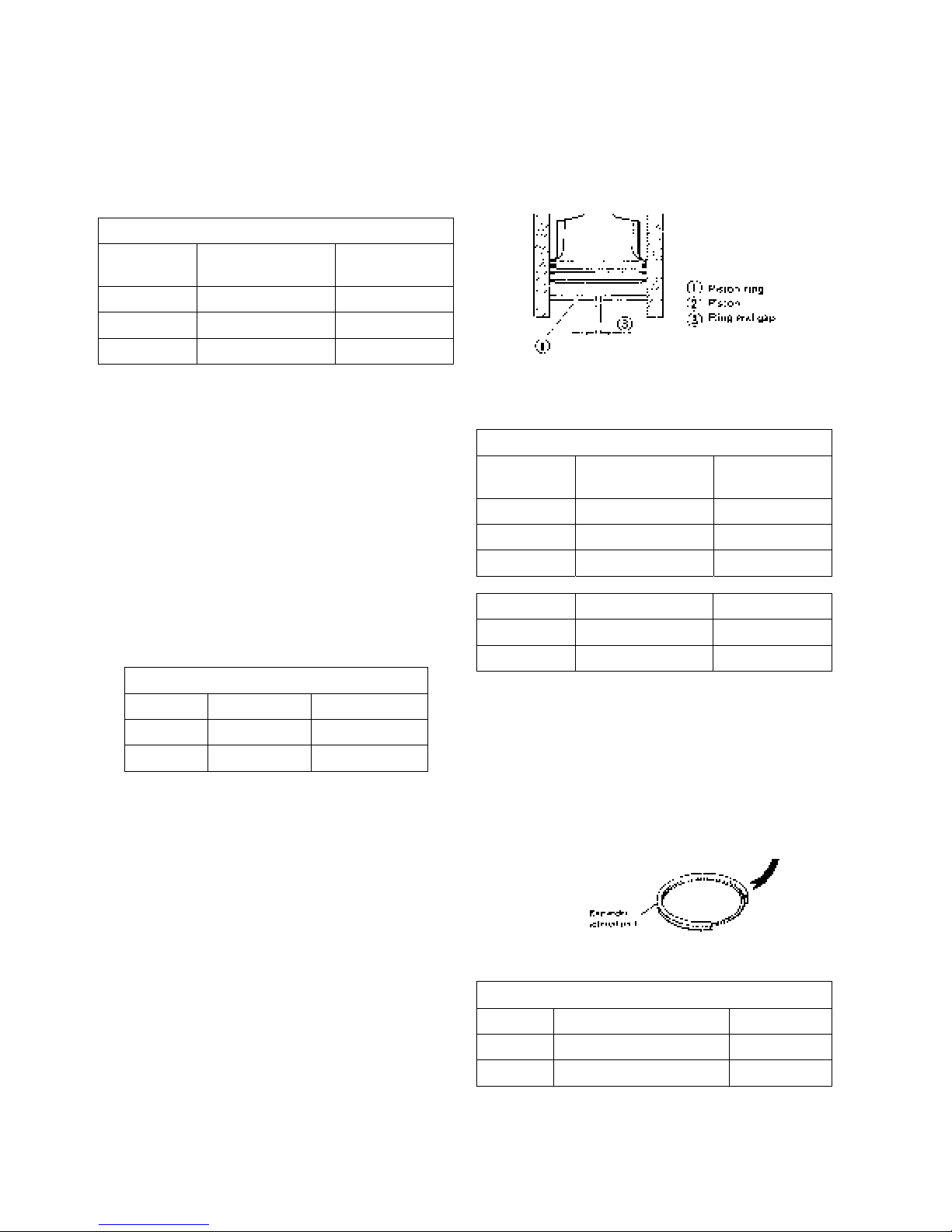
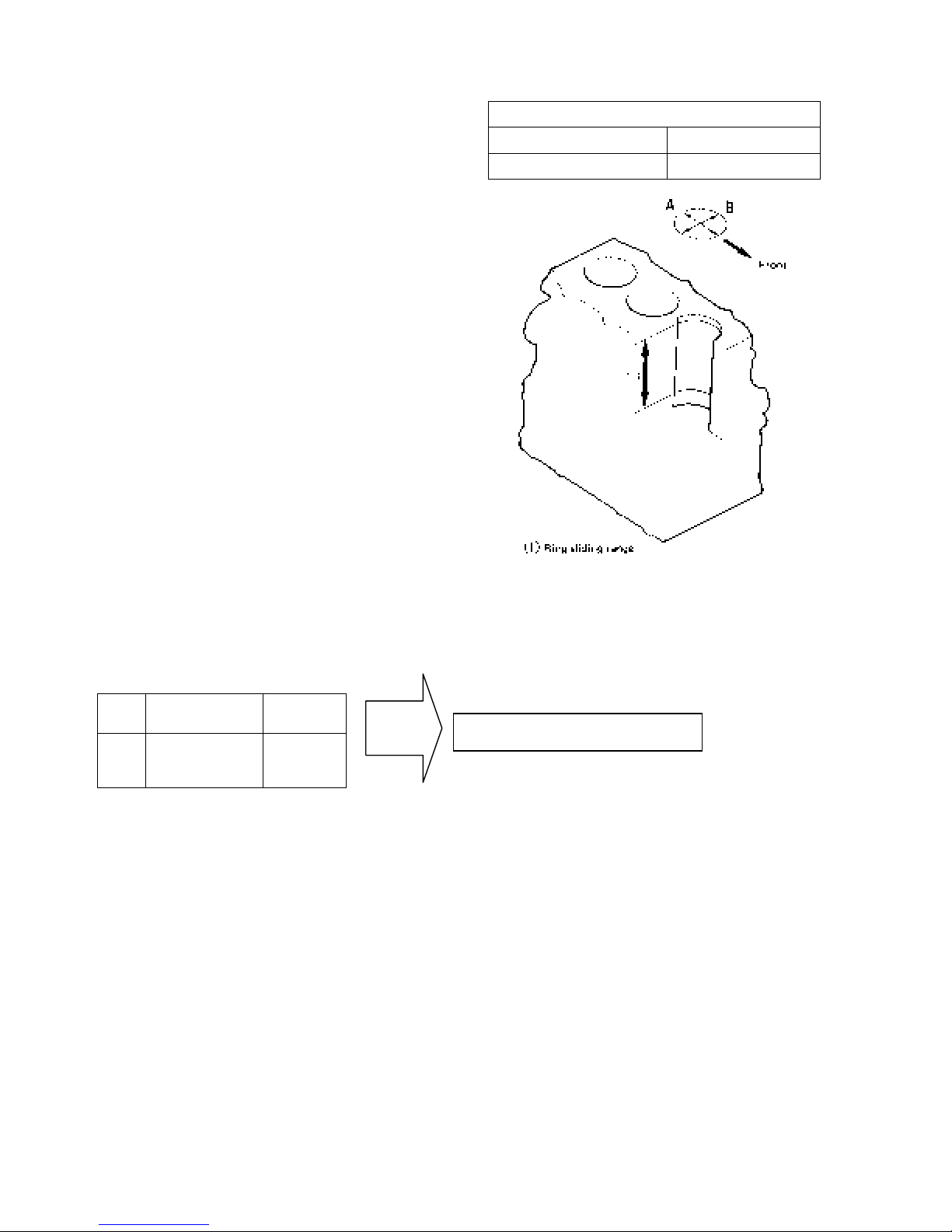
(2) Piston ring
a. Replace worn out or damaged piston ring, if any.
b. Insert a ring at a right angle to the least worn out
skirt of a cylinder, measure the clearance of ring
end gap with a thickness gaug e and replace if the
end gap exceeds the service limit.
Piston ring end gap (mm)
T op ring
Second ring
Oil ring
Standard assembling
value
0.2 – 0.35 1.0
0.2 – 0.4 1.0
0.2 – 0.8 1.2
Service limit
c. Measure the clearance between the piston ring
groove and ring and replace if the service limit is
exceeded.
d. Piston and piston ring kits of the following part
No. is available.
Piston/piston ring kit
Model Size Part code No.
J843 S.T.D.
N843L S.T.D.
115017390
115017310
e. Piston ring installing procedure
Install the piston ring to the piston as shown in
the right figure.
(3) Pisto n pin
Measure the outside diameter of the piston pin and
replace if the service limit is exceeded.
027X
Clearance between piston ring groove and ring (mm)
T op ring
Second ring
Oil ring
Standard assembling
value
Service limit
0.07 – 0.11 More than 0.25
0.04 – 0.08 More than 0.25
0.03 – 0.13 More than 0.25
Model Piston ring size Part code No.
J843 S.T.D.
N843L S.T.D.
115107840
115107290
028X
Piston pin outside dia.
(φ)
Model Standard assembling val ue Service limit
J843
N843L
24.996 – 25.0 24.98
27.996 – 28.0 27.98
20
5) Connecting rod
Inspection
(1) Check for torsion, parallelism and damage.
Measure the torsion and parallelism using a
connecting rod aligner and correct or replace if the
repair value is exceeded.
1. Gauge
2. Piston pin
3. Torsion
4. Flat part of aligner
5. Pin
(2) Measure the bore of the connecting rod small end
bush and replace if the clearance to the piston pin
exceeds the service limit.
(3) Install the connecting rod to the crankshaft, measure
the axial play and replace the connecting rod if the
service limit is exceeded.
6) Connecting rod metal
Inspection
(1) Check the metal and if peeling, melting, uneven wear,
improper contact or other damage is noticed, replace
the metal.
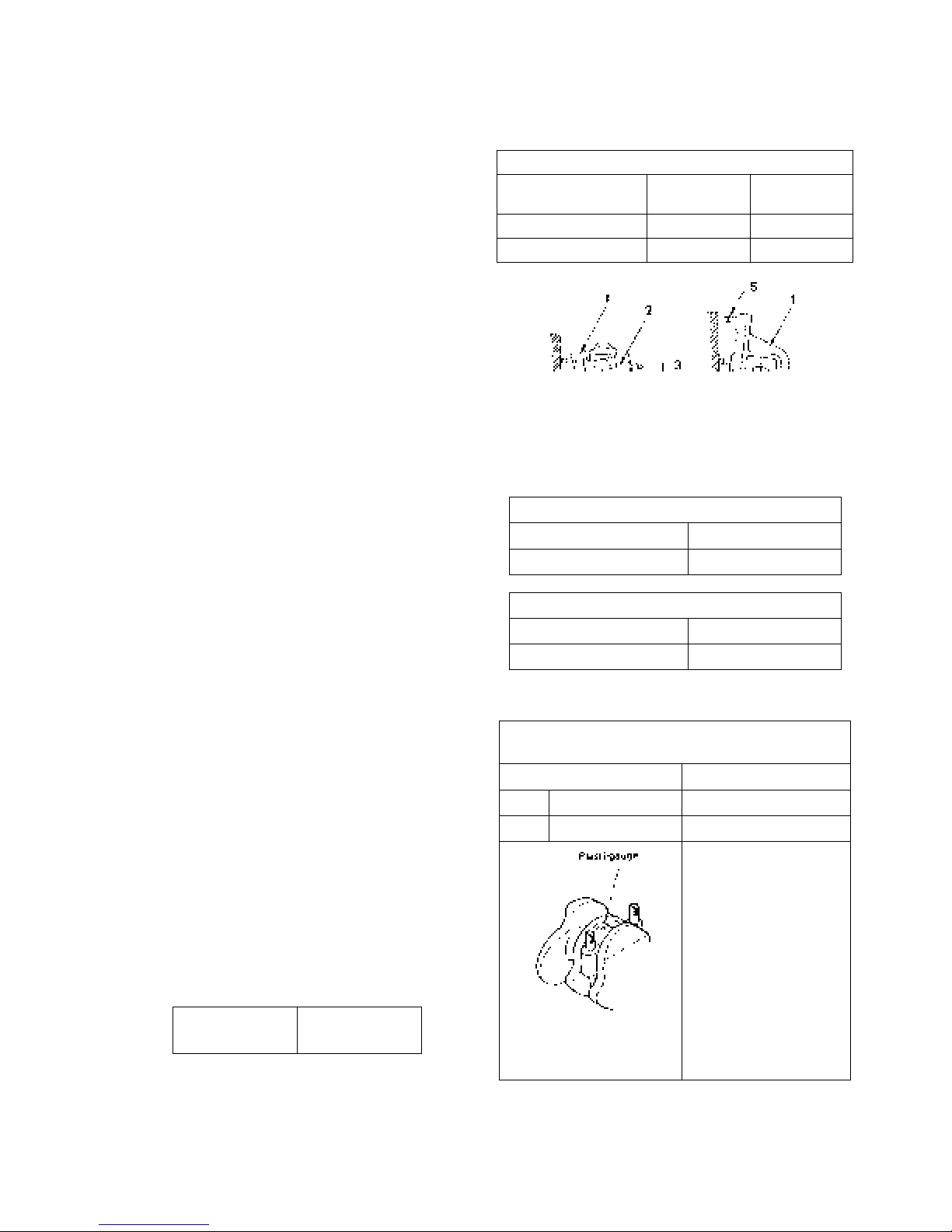
(2) Measure the oil clearance of the crank pin and metal
using plasti-gauge.
a. Remove oil dust or other foreign matter stuck to
the metal and crank pin.
b. Cut plasti-gauge to the length same as the metal
width and place it on the crank pin in parallel
with the crankshaft avoiding the oil hole.
c. Install the connecting rod metal and connecting
rod cap and tighten with the specified tightening
torque.
Tightening torque
NOTE: Never turn the connecting rod at this time.
49 – 53.9 N·m
{5.0 – 5.5 kgf·m}
Torsion and parallelism of connecting rod (mm)
Torsion (per 100 mm)
Parallelism (per 100 mm)
Standard
assembling value
Less than 0.08 More th an 0.2
Less than 0.05 More than 0 . 15
Repair value
029X
Clearance between bush and piston pin (mm)
Standard assembling value Service limit
0.010 – 0.025 More than 0.08
Axial play of connecting rod and crank pin (mm)
Standard assembling value Service limit
0.1 – 0.3 More than 0.7
Clearance between crank pin and connecting rod metal
(oil clearance) (mm)
Standard assembling value Service limit
J843
N843L
0.035 – 0.083 0.2
0.035 – 0.085 0.2
Set a plasti-gauge.
Measure the oil clearance
030X
031X
21
d. Remove the connecting rod cap and measure the
plasti-gauge width with the scale printed on the
gauge envelope.
NOTE: Measure the widest part of the
plasti-gauge.
(3) If the oil clearance exceeds the service limit
according to the result of the measurement, replace
the metal.
Reassembly (piston and connecting rod)
(1) Heat the piston to about 100°C with a piston heater or
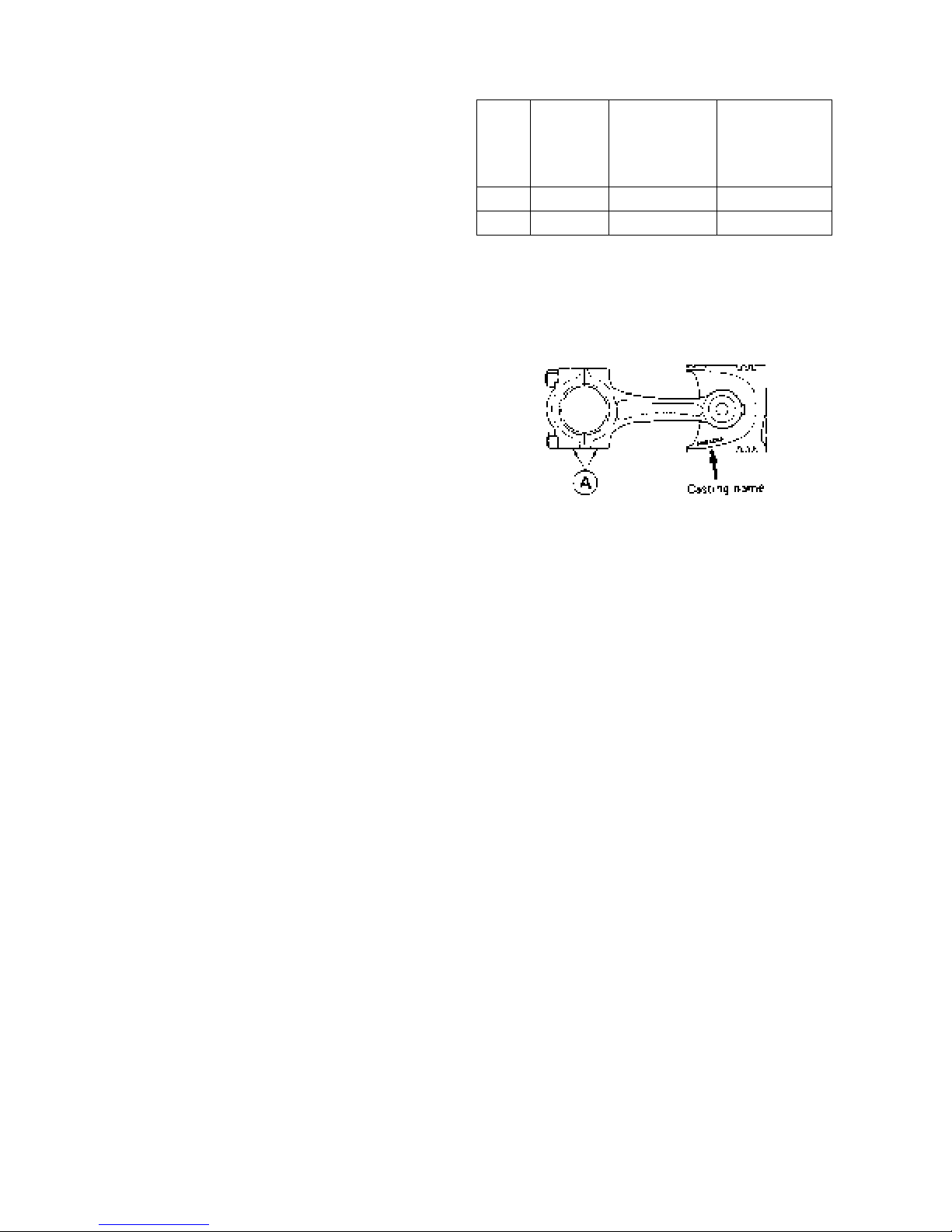
the like and install it aligning the SHIBAURA mark
in the piston and match mark at Ⓐ of the connecting
rod.
(2) Care should be taken to the figure match mark at Ⓐ
of the connecting rod.
(3) Install the piston ring to the piston facing the stamp at
the end surface of the ring end gap upward.
(4) When the connecting rod or piston and piston pin are
replaced, weight variation among cylinders with the
rod, piston and pist on ring installed shou ld be within
10 g.
Models Metal size Metal code No.
J843 S.T.D.
N843L S.T.D.
198517180 43.964 – 43.975
198517250 51.964 – 51.975
Crankshaft pin
outside dia.
Finishing
dimension
(φ)
032X
22
(
)
7) Bearing holder
Disassembly and inspection
Center bearing (metal)
(1) Remove the bearing holder, and replace the metal if
peeling, melting, uneven wear, or improper contact is
noticed.
(2) Measure the oil clearance of the crankshaft center
journal and metal using a plasti-gauge.
(3) If the oil clearance exceeds the service limit
according to the result of the measurement, replace
the metal or/and crank shaft.
Metal
size
S.T .D.
Journal
size
S.T .D.
Thrust washer
Check the thrust washer and replace if wear, improper
contact, seizure, or other damage is noticed, or thickness
exceeds the service limit.
198517210 (Upper) 198517230 (Upper)
198517200 (Lower) 198517240 (Lower)
Finished dimensions of crankshaft journal
57.957 – 57.970 67.957 – 67.970
Metal code No.
J843 N843L
(
φ)
J843 N843L
Clearance between crankshaft center journal and m eta l
Models Standard assembling value Service limit
J843
N843L
No2, 3
·
and 4
Thrust washer thickness (mm)
Standard assembling value Service limit
2.95 – 3.0 Less than 2.8
oil clearance) (mm
0.044 – 0.116 0.2
033X
034X
23
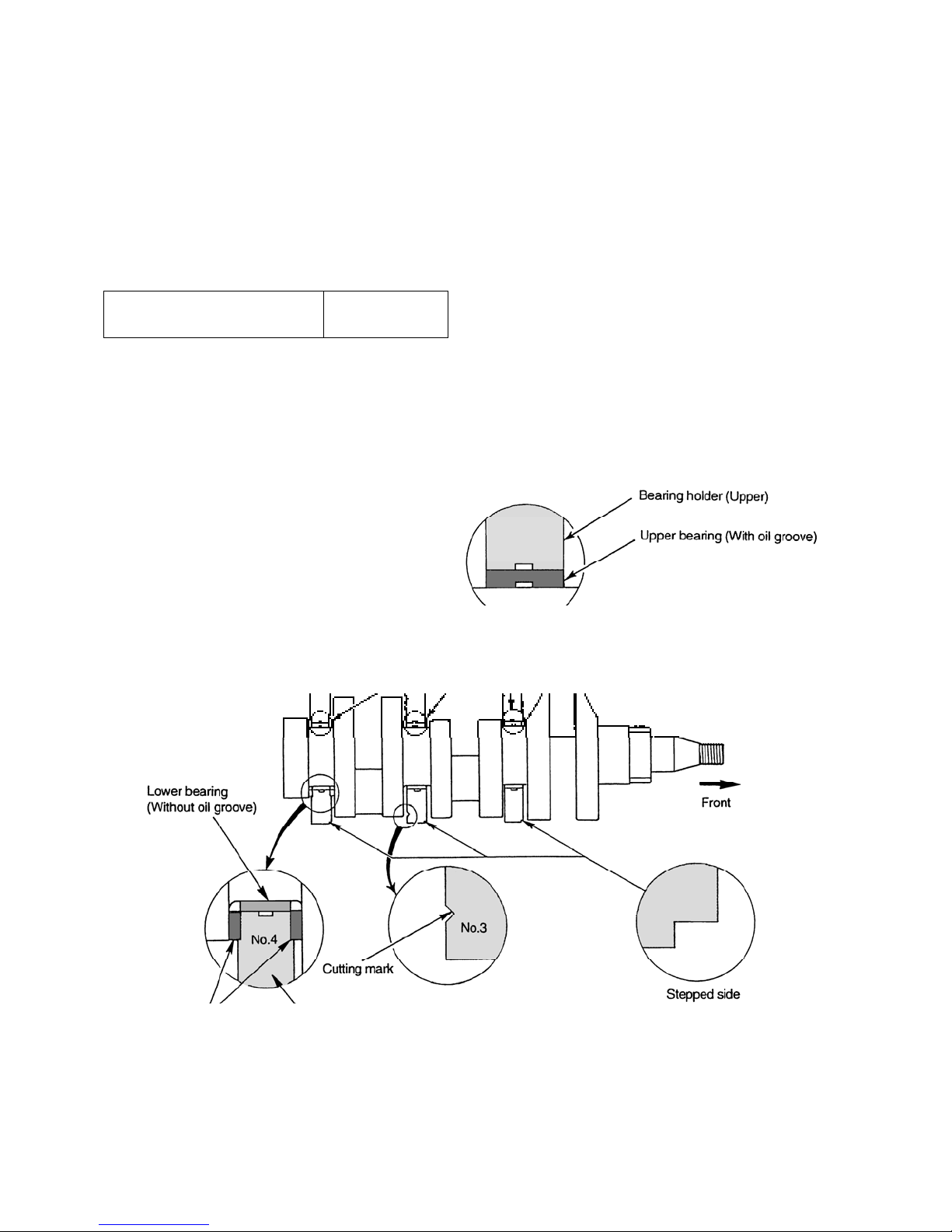
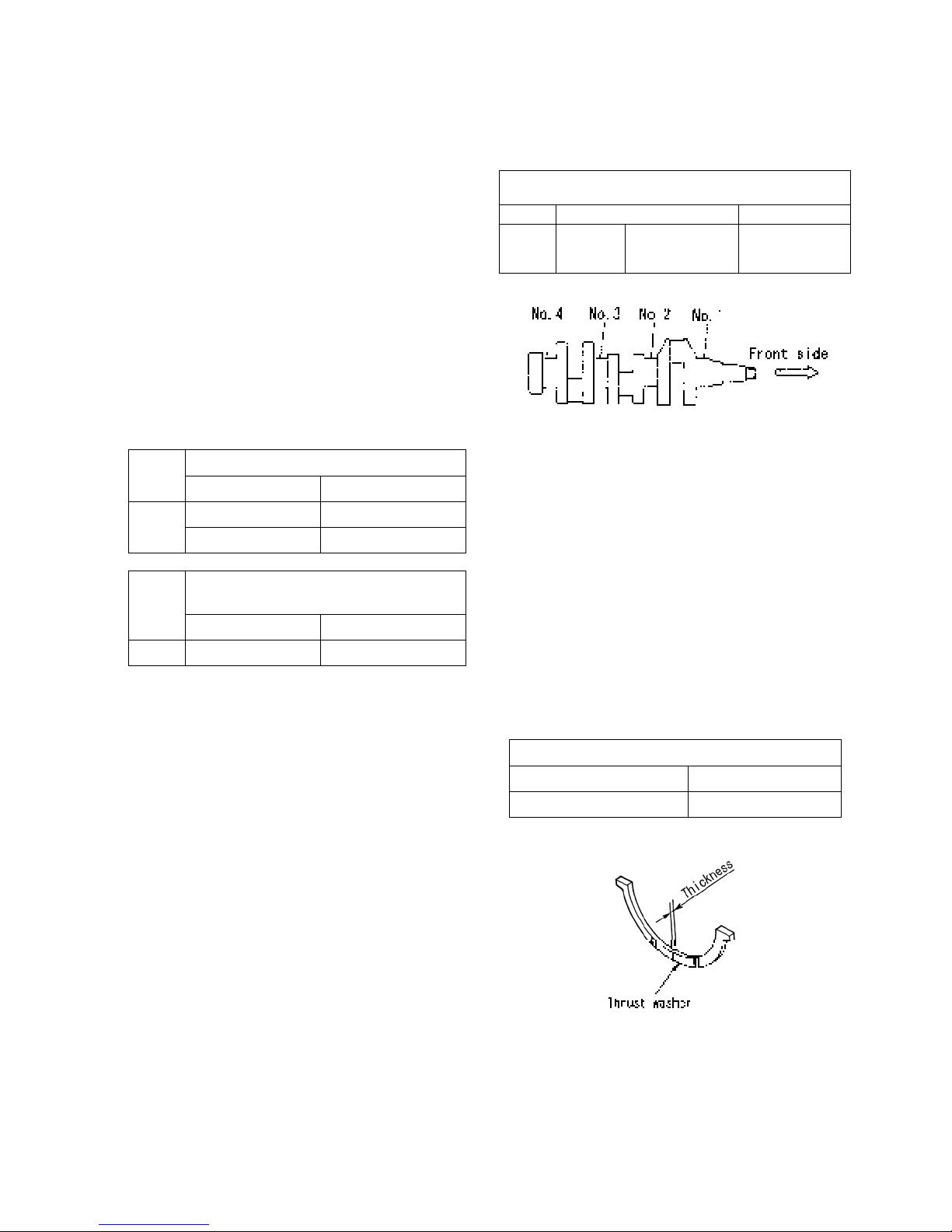
Reassembly
(1) Install the metal with oil groove to the upper bearing
holder and the metal without oil groove to the lower
bearing holder
(2) With the stepped area of the bearing holder facing the
front side, install the bearing holder to be fitted with
thrust washer on the flywheel side and the bearing
holder with identification cutting mark at the center.
Bearing holder tightening torque
(3) Install the thrust washer facing the oil groove towards
the crankshaft thrust surface.
NOTE: Be sure to confirm that the oil hole of the
bearing holder and that of the cylinder
block are in the same direction.
49 – 53.9 N·m
{5 – 5.5 kgf·m}
035X
24
8) Crankshaft bearing (bush)
0.044
116
0.2
Inspection
(1) Check the bearing (bush) and replace if peeling,
melting, uneven wear, improper contact, or other
damage is notice.
(2) Measure the oil clearance of the bearing (bush) and
crankshaft journal using a cylinder gauge and
micrometer.
(3) If the oil clearance exceeds the service limit
according to the result of measurement, replace the
bearing (bush) or/and crank shaft.
Clearance between cranksha ft journal and bearing (bush)
(oil clearance) (mm)
Standard assembling value Service limit
– 0.
Bush size Bush code No.
S.T.D.
Bush size
J843 N843L
198517190 198517220
Crankshaft journal outside dia. Finishing
dimension (φ)
036X
037X
S.T.D.
J843 N843L
57.957 – 57.970 67.957 – 67.970
NOTE:
1. Measure the dimensions in the A and B directions
at the position 1 and 2 in the right figure avoiding
the oil hole of the bearing (bush) and calculate
difference from the maximum value of the
crankshaft journal (oil clearance).
2. When replacing the bush, push it up using a
press or the like. At this time, align the oil holes
and push it up until the bush end surface
becomes level with the outside machined surface
of the cylinder block (see the arrow mark in the
right figure).
038X
25
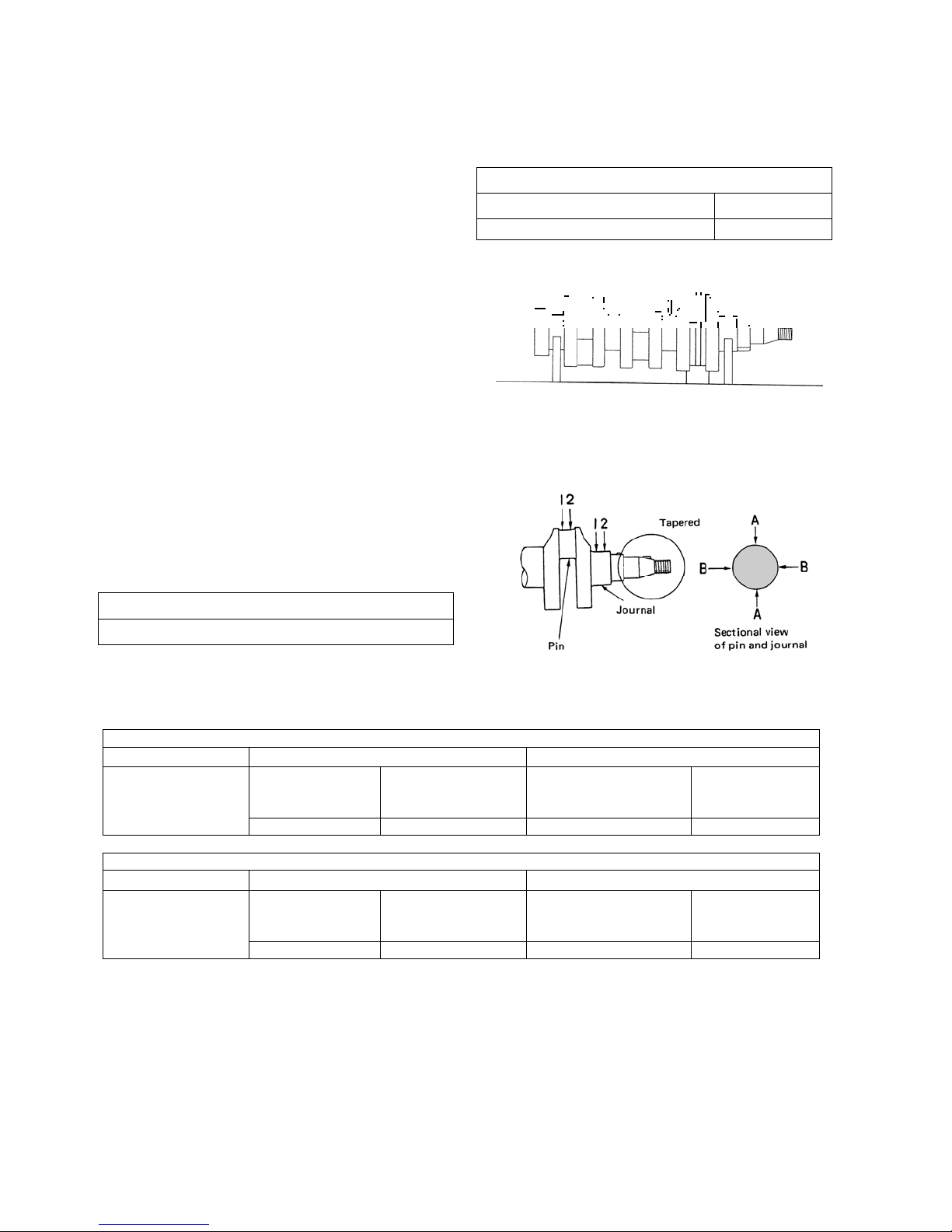
9) Crankshaft
L
03
0.06
Inspection
(1) To measure run-out of the crankshaft, support the
crankshaft using a V block as shown in the right
figure, apply a dial gauge to the crankshaft center
journal, read the indication on the dial gauge rotating
the shaft one turn gently. If the service value is
exceeded, correct or replace.
(2) Check the crankshaft oil seal for damage or wear on
the contact surface and oil hole clogging.
(3) Check the crankshaft journal and pin for damage,
irregular wear (ellipticity, conicalness) and shaft
diameter. If the service limit is exceeded, replace the
bearing (bush) and/or crankshaft. Measure the
dimensions of the journal and pin in the AA and BB
directions at the position 1 and 2 avoiding the oil
holes.
Irregular wear limit of crankshaft journal and pin
0.05 mm
Model J843
Journal and pin size
S.T.D.
Journal and pin size
S.T.D.
* Replace the crankshaft if diameter is below the repair value.
Shaft dia. at crankshaft journal (φ) Shaft dia. at crankshaft pin (φ)
Outside dia.
finishing
dimension
57.957 – 67.970 Less than 57.90 43.964 – 43.975 43.90
Shaft dia. at crankshaft journal (φ) Shaft dia. at crankshaft pin (φ)
Outside dia.
finishing
dimension
67.957 – 67.970 Less than 67.90 51.964 – 51.975 Less than 51.90
Repair value
Model N843L
Repair value Outside dia. finishing
Crankshaft run-out (mm)
Standard assembling value Service limit
ess than 0.
039X
040X
Outside dia. finishing
dimension Repair value
dimension Repair value
26
10) Flywheel and ring gear
Inspection
Check the ring gear and replace if damage or remarkable
wear is noticed.
When the wear is limited to a small area, remove the, ring
gear, turn it about 90 degrees and shrinkage-fit to reuse it.
To shrinkage-fit the ring gear, heat it to 120 – 150°C to
allow it to expand.
11) Cam shaft ass’y
Inspection
(1) Check the journal and cam for wear and damage and
replace if the service limit is exceeded.
(2) Correct insignificant uneven wear or scars on the cam
surface using oil stone or the like.
A. Height of intake/exhaust valve cams (mm)
Standard assembling value Service limi t
34.441 – 34.5076 34.1
B. Height of injection pump cams (mm)
Standard assembling value Service limit
42.99 – 43.01 42.8
12) Timing gear
Inspection
(1) If pitting or remarkable wear is observed on the tooth
face of gears, replace the gear.
(2) Measure the backlash of gears and replace if the
service limit is exceeded.
Timing gear backlash (mm)
Standard assembling value Service limi t
0.08 More than 0.25
042X
043X
044X
27
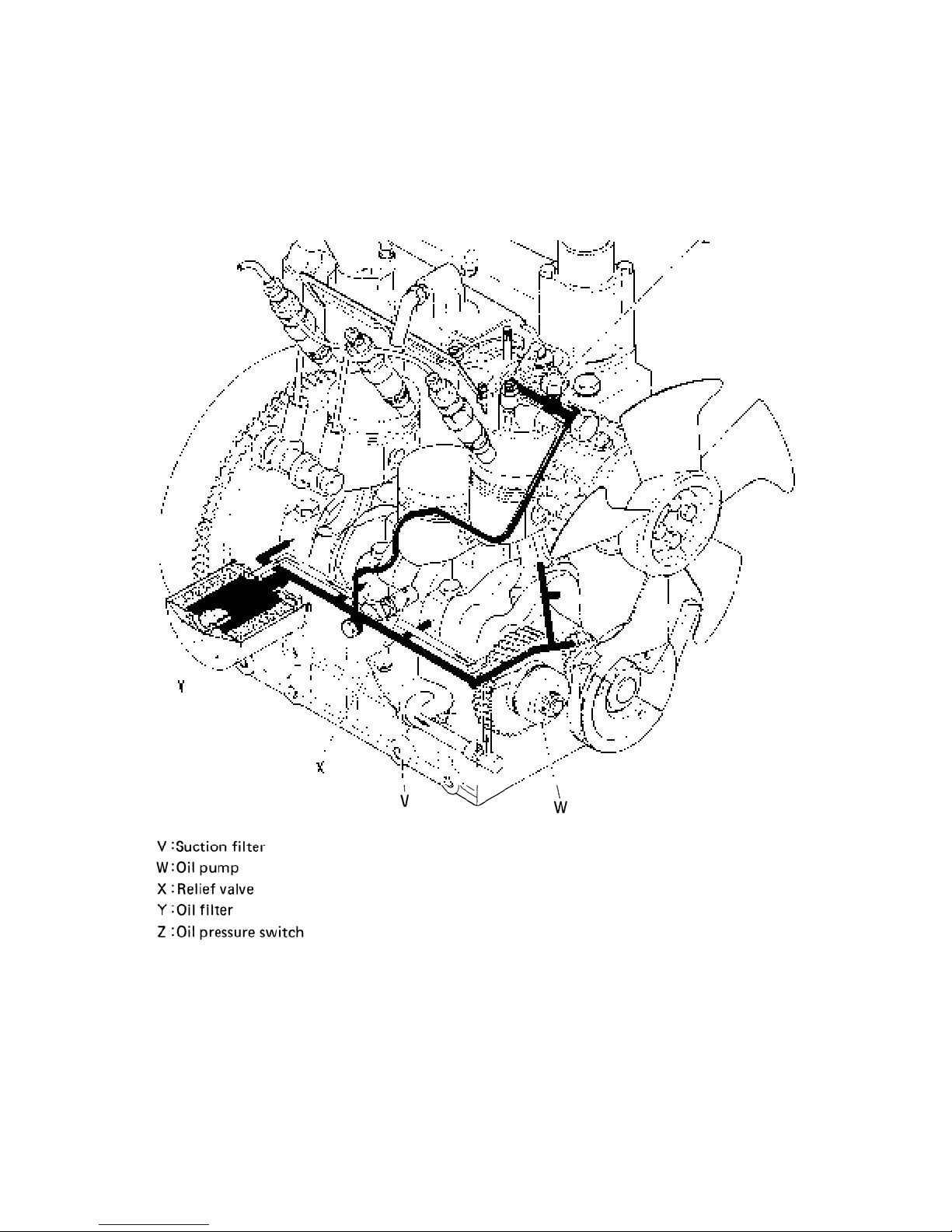
13) Oil flow
045X
28
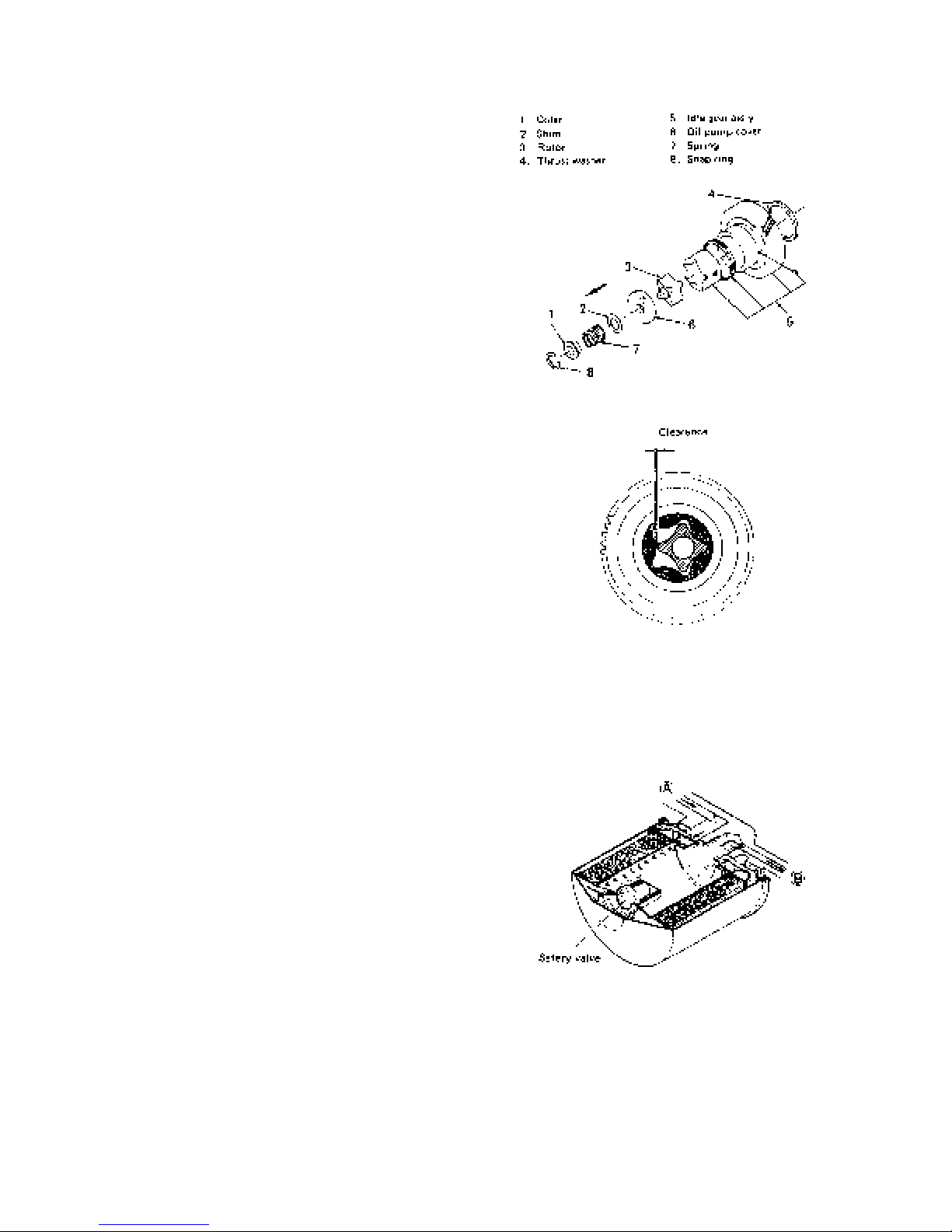
14) Oil pump
Disassembly
Removal from engine
(1) Remove the snap ring.
(2) Take out the collar, spring and shim.
(3) Take out the idle gear, vane, and oil pump cover
together.
(4) Extract the rotor and thrust washer.
(5) Extract the oil pump cover from the idle gear.
Inspection and reassembly
(1) Check the oil pump cover, rotor and vane and replace
if worn out or damaged remarkably.
(2) Check the clearance between the rotor and vane and
replace if the service limit (0.25 mm) is exceeded.
(3) Reassemble in the order reverse to disassembly.
a. Install the crankshaft gear and idle gear aligning
the match mark.
b. Adjust the side clearance of the rotor and vane to
0.1 – 0.15 mm. (Refer to Fig. 071X.)
15) Oil filter
Structure and Functions
(1) The cartridge type oil filter is excellent in filtering
performance.
(2) Since it is of the full-flow type, when the filter is
clogged, the safety valve is opened to allow the oil to
flow, preventing seizure or other troubles.
(3) The oil fed under pressure with the oil pump enters
Ⓐ, is filtered by t he element, and supplied t o each
part from Ⓑ.
When the element is clogged, the oil is supplied to
each part without passing through the element.
Replacement
(1) Replace the oil filter every 200 hours of operation.
(2) Coat the filter mounting surface with oil and tighten
the filter by hand.
(3) Do not reuse the filter if it is removed once.
046X
047X
048X
29
 Loading...
Loading...