Page 1

SCIENTIFIC
SCIENTIFIC
CALCULATOR
CALCULATOR
OPERATION GUIDE
OPERATION GUIDE
<W Series>
Page 2

C O N TENTS
HOW TO OPERATE
Read Before Using
Key layout/Reset switch 2
Display pattern
Display format 3
Exponent display 4
Angular unit 5
Function and Key Operation
O N /O FF, entry correction keys 6
Data entry keys 7
Random key
Modify key
Basic arithmetic keys, parentheses 10
Percent 11
Inverse, square, cube, xth power of y,
square root, cube root, xth root of y
10 to the power of x, common logarithm 13
e to the power of x, natural logarithm 14
Factorials 15
Permutations, combinations 16
3
8
9
12
Time calculation 17
Fractional calculations 18
Memor y calculations 19
Last answer memory 20
Trigonometric functions 21
Arc trigonometric functions 22
Hyperbolic functions 23
C oordinate conversion 24
Binary, pental, octal, decimal, and
hexadecimal operations (N-base)
STATISTICS FUNCTION
Data input and correction
“AN S” keys for 1-variable statistics
“AN S” keys for 2-variable statistics
1
~
25
26
27
31
Page 3
H ow to O pe ra te
≈Read B efore Using≈
This operation guide has been written based on the EL-531W , EL-509W , and EL-531W H
models. Some functions described here are not featured on other models. In addition,
key operations and symbols on the display may differ according to the model.
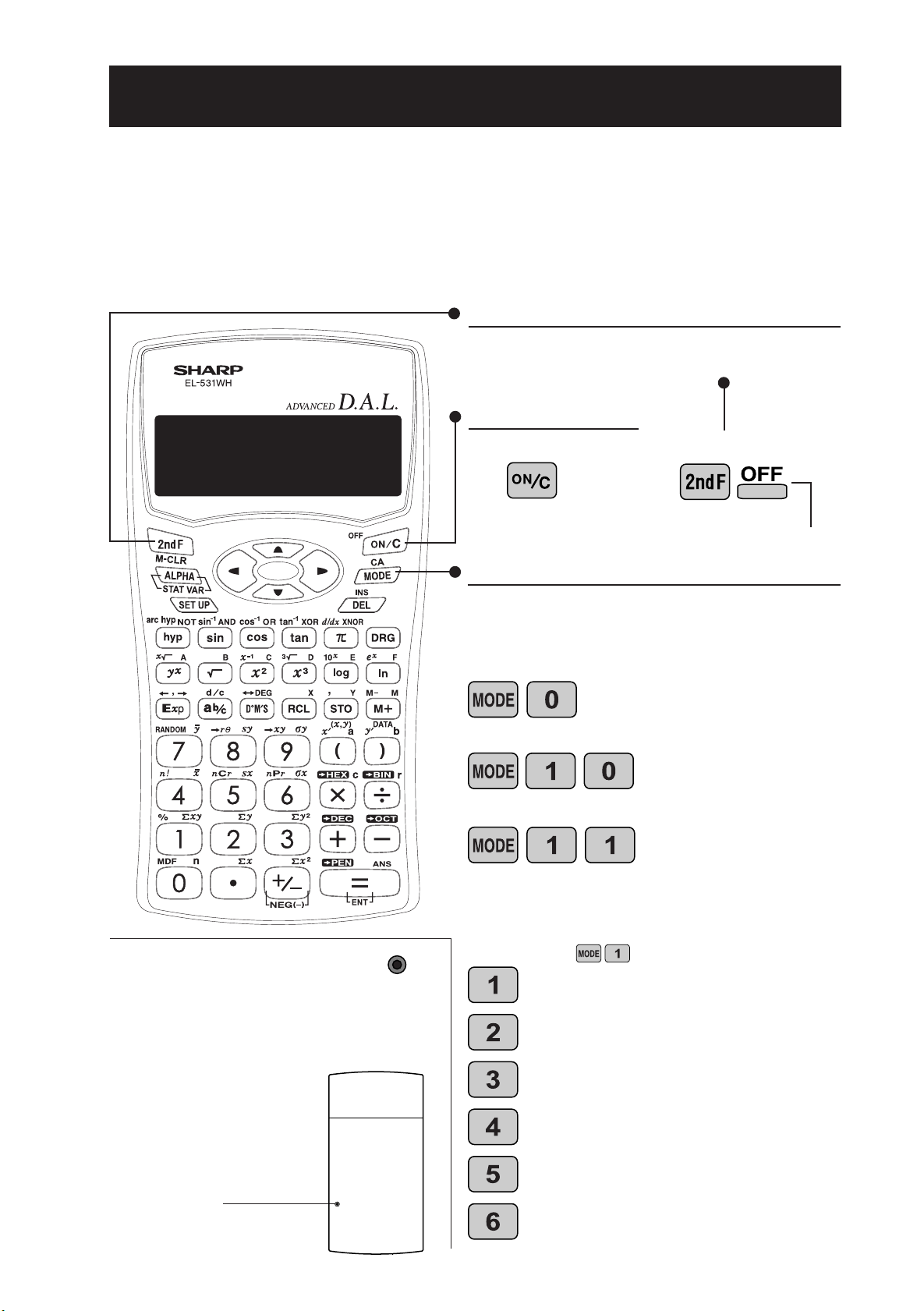
1 . K E Y L AY O U T
2nd function key
Pressing this key will enable the functions
written in orange above the calculator
buttons.
ON/C, OFF key
2 . R E S E T S W I T C H
If the calculator fails to operate normally,
press the reset switch on the back to
reinitialise the unit. The display format
and calculation mode will return to their
initial settings.
RESET
D irect function
<Power on>
Mode key
This calculator can operate in three different
modes as follows.
<Example>
[Normal mode]
[STAT-0 mode]
[STAT-1–6 mode]
W hen changing to the statistical sub-mode,
press the corresponding number key after
performing the operation to select the statistics
mode (press ).
(LINE): Linear regression calculation
(Q UAD): Q uadratic regression calculation
(EX P): Exponential regression calculation
2nd function
<Power off>
W ritten in orange above
the O N/C key
•Mode = 0; normal mode for
performing nor mal arithmetic
and function calculations.
•Mode = 1; STAT- 0 mode for
performing 1-variable statistical calculations.
•Mode = 1; STAT -1–6 mode
for performing 2-variable
statistical calculations.
N O T E :
Pressing the reset switch
will erase any data stored
in memory.
Reset switch
(LOG): Logarithmic regression calculation
(PW R): Power regression calculation
RESET
(IN V): Inverse regression calculation
2
Page 4
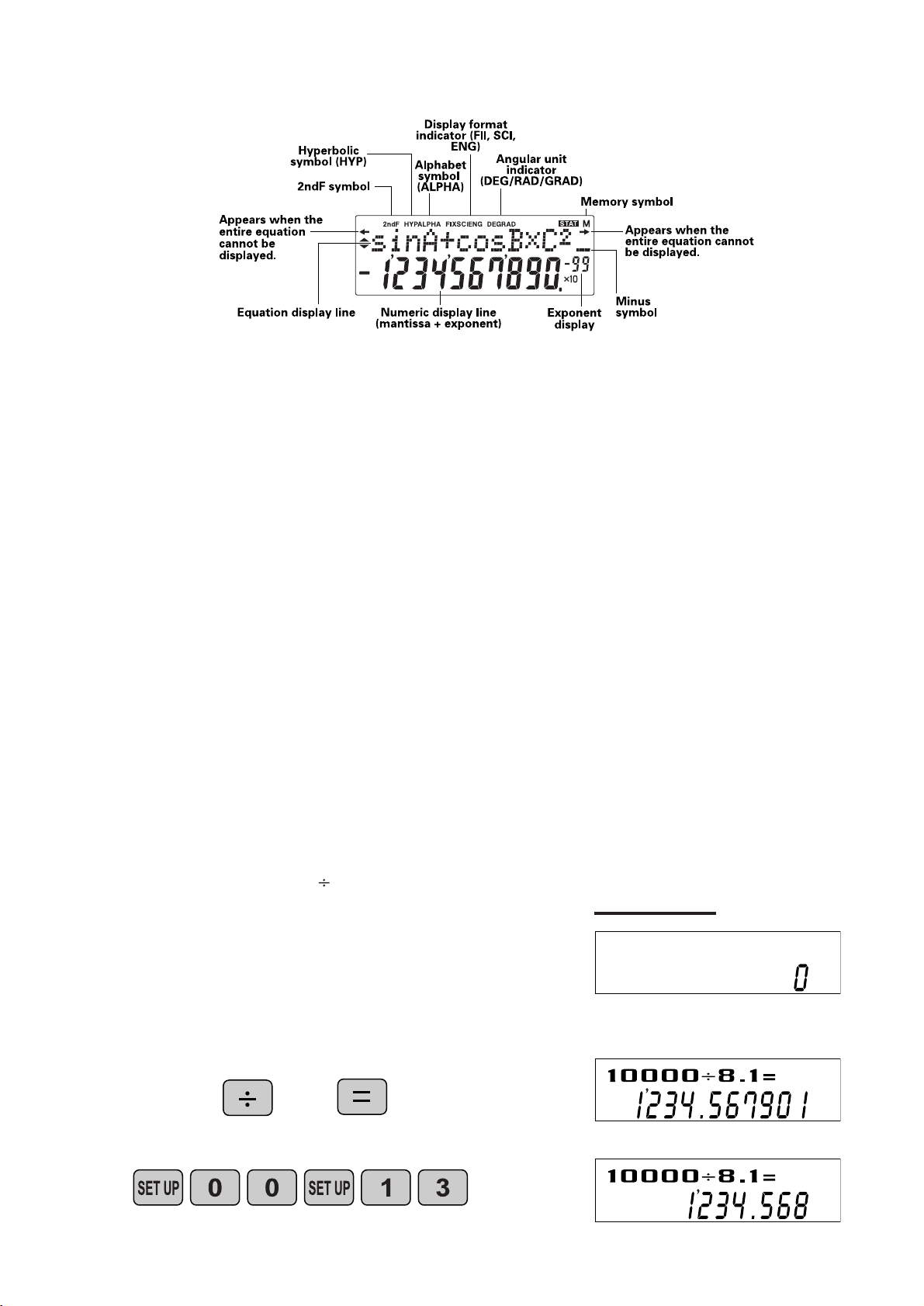
3 . DI S P L AY P AT T E R N
DEG
DEG
DEGFIX
The actual display does not appear like this.
This illustration is for explanatory purposes only.
4 . DI S P L AY F O R M AT A N D
D E C I M A L S E T T I N G F U N C T I O N
For convenient and easy operation, this model can be used in one of four display modes.
The selected display status is shown in the upper part of the display (Format Indicator).
N ote: If more 0’s (zeros) than needed are displayed when the O N /C key is pressed, check
whether or not the calculator is set to a Special D isplay Format.
• Floating decimal point format (no symbol is displayed)
Valid values beyond the maximum range are displayed in the form of a [10-digit
(mantissa) + 2-digit (exponent)]
• Fixed decimal point format (FIX is displayed)
Displays the fractional part of the calculation result according to the specified
number of decimal places.
• Scientific notation (SCI is displayed)
Frequently used in science to handle extremely small or large numbers.
• Engineering scientific notation (ENG is displayed)
C onvenient for converting between different units.
<Example>
Let’s compare the display result of
[10000 8. 1 =] in each display format.
(specifies normal mode)
Initial display
N ote: The calculator has two settings for displaying a
floating point number: N O RM1 (default setting) and
N O RM2. In each display setting, a number is
automatically displayed in scientific notation outside a
preset range:
• N ORM1: 0.000000001 x 9999999999
• N ORM2: 0.01 x 9999999999
10000 8.1
(normal mode)
(FIX mode TAB = 3)
3
Page 5
SCI DEG
X10
(SC I mode)
ENG DEG
X10
(EN G mode)
DEG
(normal mode)
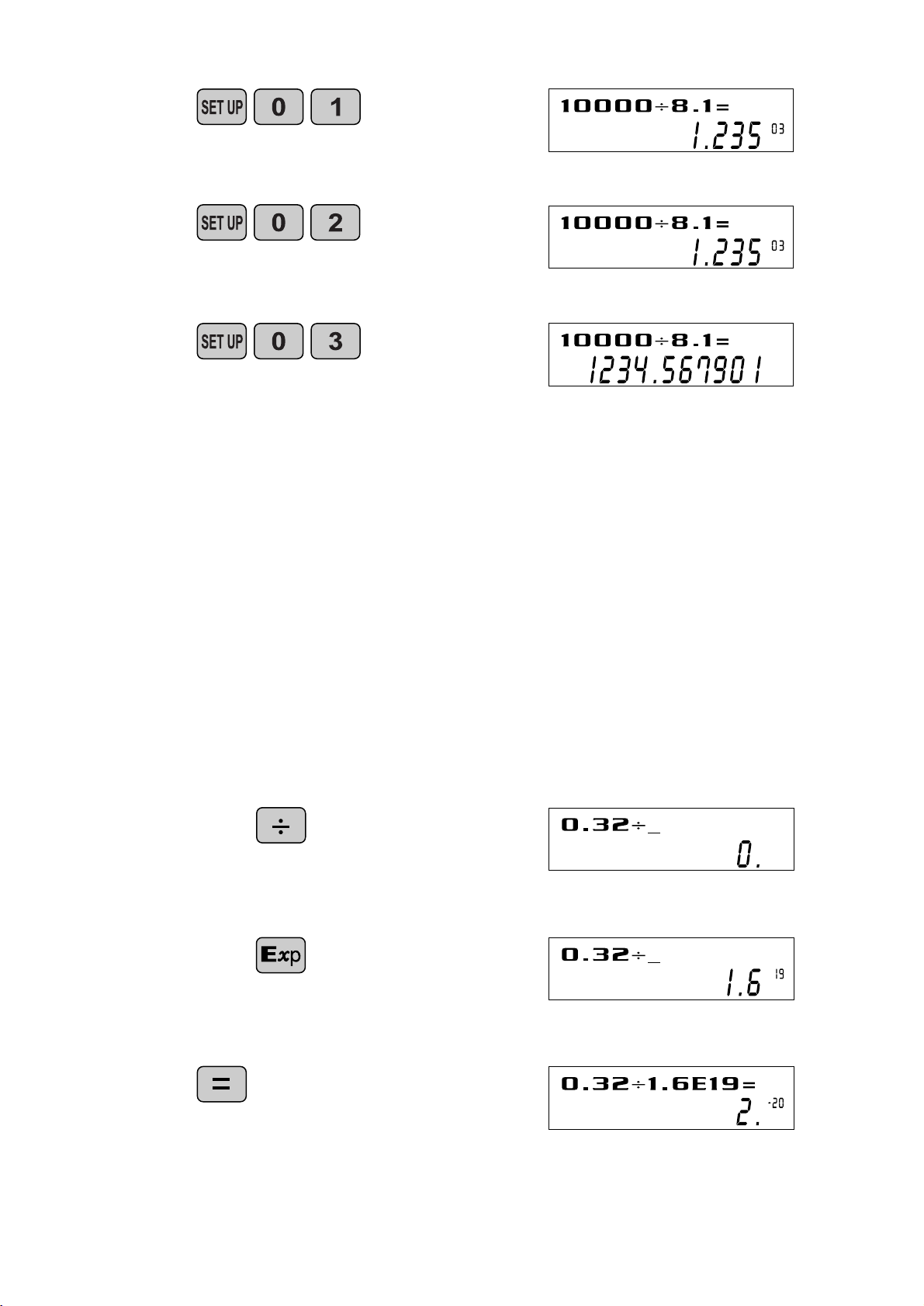
5 . E X P O N E N T D I S P L AY
The distance from the earth to the sun is approx. 150,000,000 (1.5 x 108) km. Values
such as this with many zeros are often used in scientific calculations, but entering the
zeros one by one is a great deal of work and it’s easy to make mistakes.
In such a case, the numerical values are divided into mantissa and exponent portions,
displayed and calculated.
<Example>
0.32
W hat is the number of electronics flowing in a conductor when
the electrical charge across a given cross-section is 0.32 cou-
DEG
DEG
-19
coulombs).
lombs. (T he charge on a single electron = 1.6 x 10
191.6
X10
DEG
X10
4
Page 6
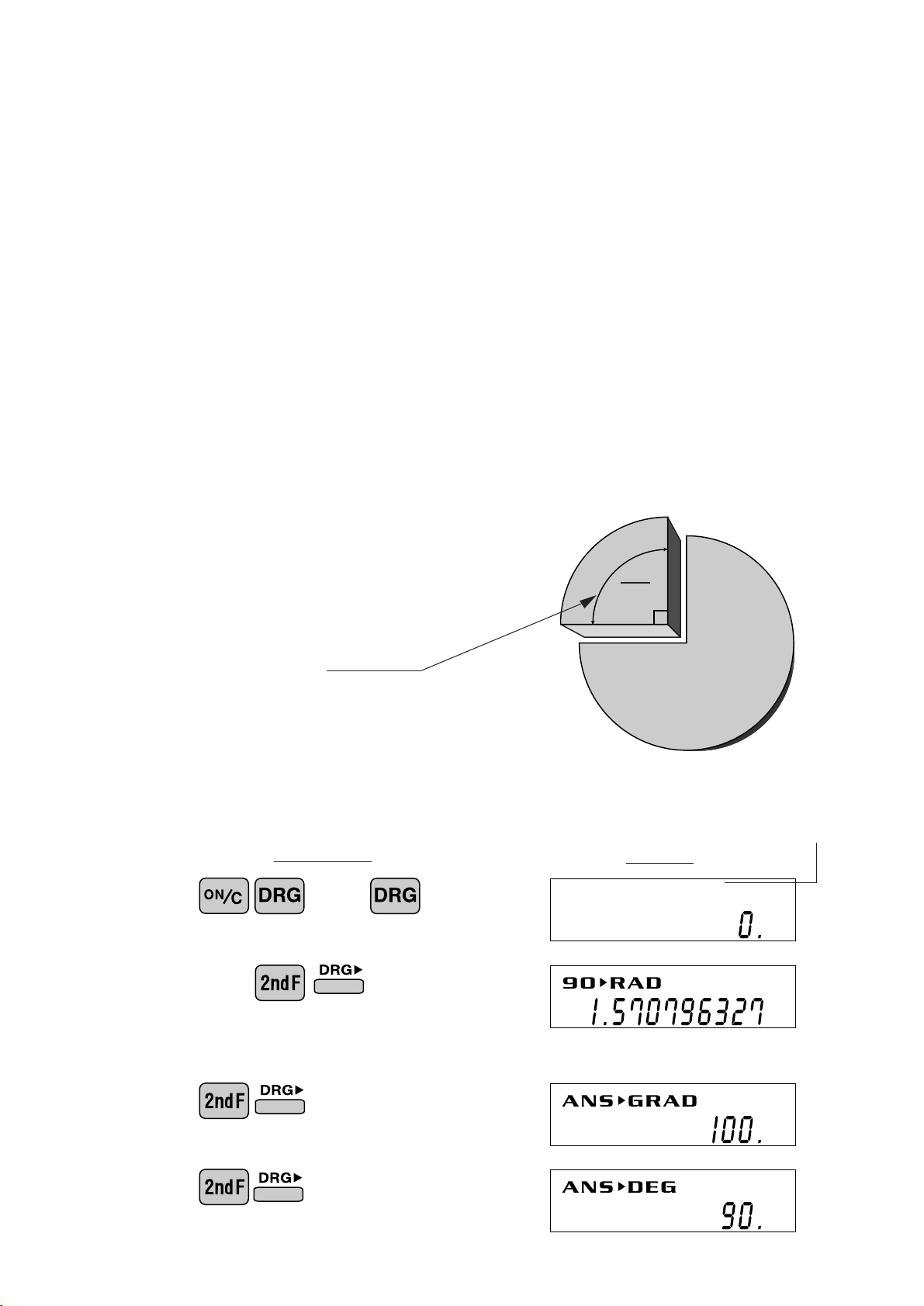
6 . A N G U L A R U N I T
Angular values are converted from D EG to RAD to G RAD with each push of the DRG
key. This function is used when doing calculations related to trigonometric functions or
coordinate geometry conversions.
D egrees ( D E G is shown at the top of the display)
A commonly used unit of measure for angles. The angular measure of a circle
is expressed as 360°.
R adians (R A D is shown at the top of the display)
Radians are different than degrees and express angles based on the circumference of a circle. 180° is equivalent to π radians. Therefore, the angular measure of a circle is 2π radians.
G r ads (G R A D is shown at the top of the display)
Grads are a unit of angular measure used in Europe, particularly in France. An
angle of 90 degrees is equivalent to 100 grads.
The relationships between the three types
of angular units can be expressed as right:
90° (DEG) =
π/2 (RAD) =
100 (GRAD) =
π
2
<Example>
O per ation
(in D EG mode)
90
C heck to confirm 90 degrees equaling π/2 radians
equaling 100 grads. (π=3.14159...)
Angular indicator
D isplay
DEG
••• •••••
RAD
( π /2)
GRAD
DEG
5
Page 7
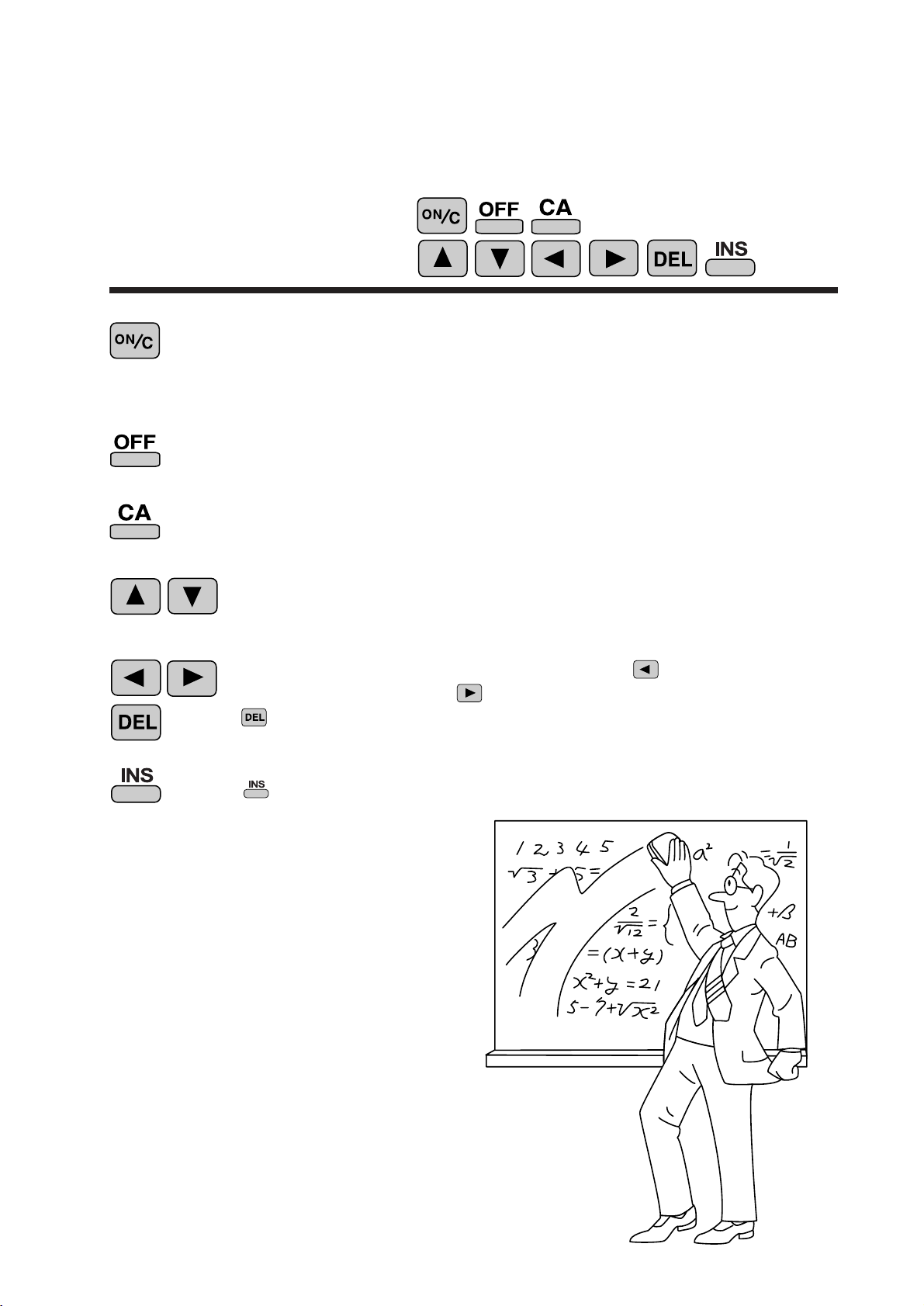
≈F unction and K ey Operation≈
ON/OFF, Entry
Correction Keys
Turns the calculator on or clears the data. It also clears the contents of the
calculator display and voids any calculator command; however, coefficients in 3-variable linear equations and statistics, as well as values stored
in the independent memory in normal mode, are not erased.
Turns the calculator off.
C lears all internal values, including coefficients in 3-variable linear equations and
statistics. Values stored in memory in normal mode are not erased.
These arrow keys are useful for Multi-Line playback, which lets you
scroll through calculation steps one by one. (refer to page 8)
These keys are useful for editing equations. The key moves the
cursor to the left, and the key moves the cursor to the right. T he
key deletes the symbol/number at the cursor.
key inserts the symbol/number at the cursor.
6
Page 8
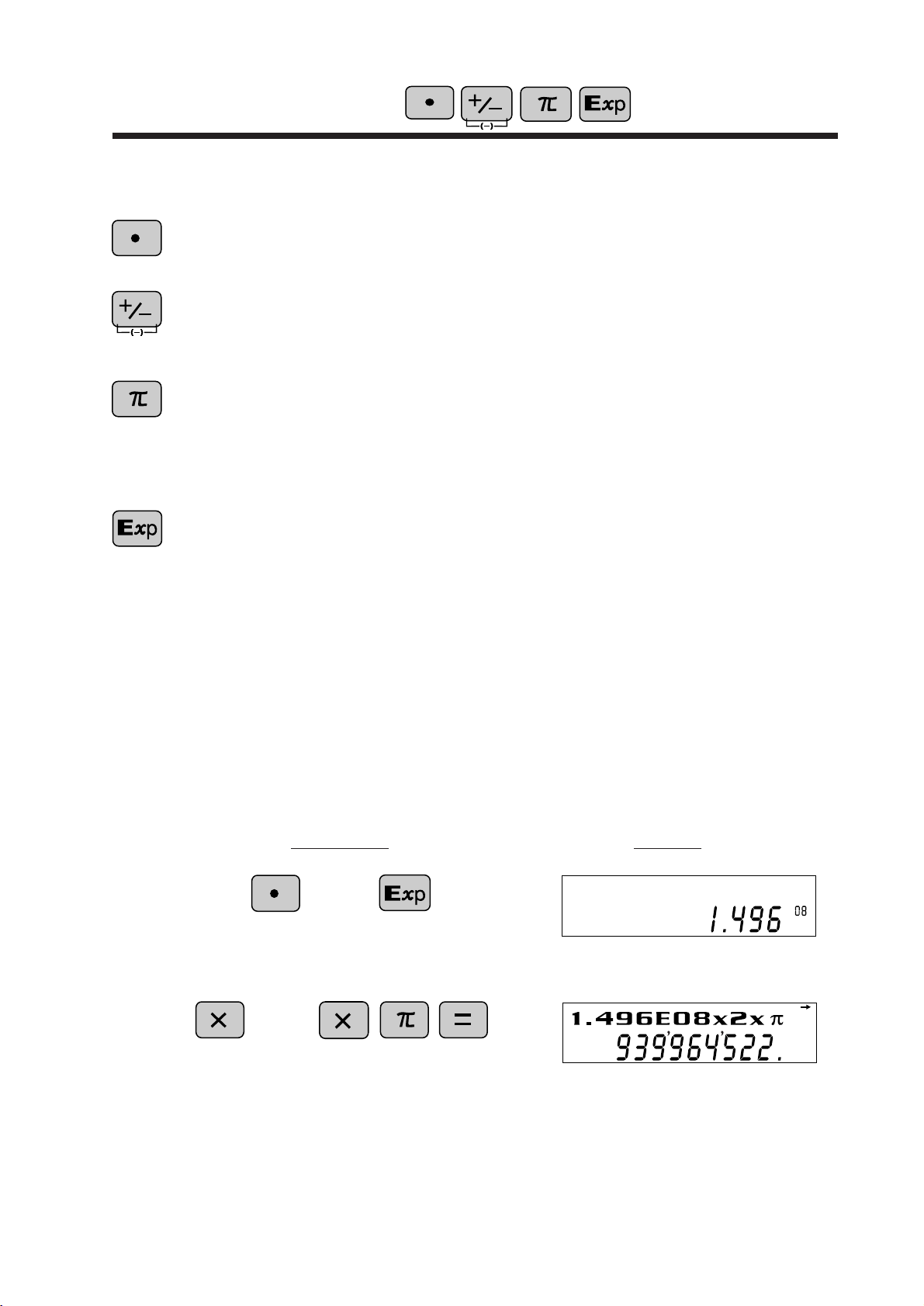
Data Entry Keys
0 to 9
N umeric keys for entering data values.
Decimal point key. Enters a decimal point.
Enters minus symbol or sign change key.
C hanges positive numbers to negative and negative numbers to positive.
Pressing π automatically enters the value for π (3.14159...).
The constant π, used frequently in function calculations, is the ratio of the
circumference of a circle to its diameter.
Pressing this key switches to scientific notation data entr y.
<Example>
Provided the earth is moving around the sun in a circular orbit,
how many kilometers will it travel in a year?
1
* The average distance between the earth and the sun being
1.496 x 10
C ircumference equals diameter x π; therefore,
1.496 x 10
O per ation D isplay
496
8
km.
8
x 2 x π
8
2
DEG
X10
DEG
7
Page 9

Random
Generates random numbers.
Random numbers are three-decimal-place values between 0.000 and 0.999. Using this
function enables the user to obtain unbiased sampling data derived from random
values generated by the calculator.
<Example>
[ R andom D ice]
To simulate a die-rolling, a random integer between 1 and 6 can be generated by
pressing . T o generate the next random dice number, press .
[ R andom C oin]
To simulate a coin flip, 0 (heads) or 1 (tails) can be randomly generated by pressing
[ R andom Integer]
An integer between 0 and 99 can be generated randomly by pressing .
To generate the next random integer, press .
0. * * * (A random number has been generated. )
. To generate the next random coin number, press .
A PP L IC AT I O N S:
Building sample sets for statistics or research.
8
Page 10
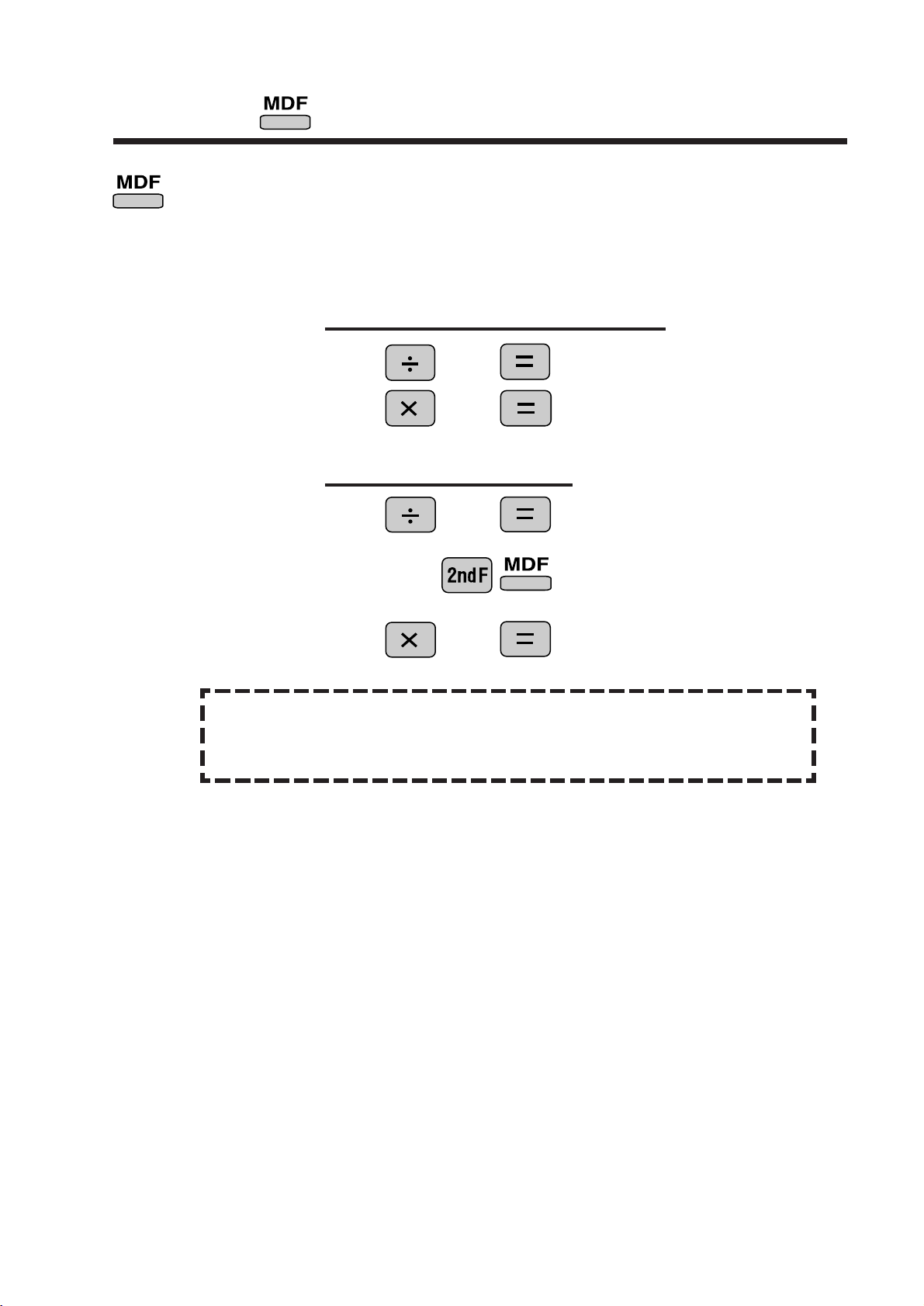
Modify
Function to round calculation results.
Even after setting the number of decimal places on the display, the calculator performs calculations using a larger number of decimal places than that which appears
on the display. By using this function, internal calculations will be performed using
only the displayed value.
<Example>
A PPL IC AT IO N S:
Frequently used in scientific and technical fields, as well as business,
when performing chained calculations.
FIX mode TAB = 1 (normal calculation)
0.6
5
9
9
Rounded calculation (MDF)
5 9
9
(internally, 0 . 6 )
(internally, 0. 5 55 5 ... )
5.0
0.6
(internally, 0 . 5 55 5 ... )
5.4
9
Page 11

Basic Arithmetic
Keys, Parentheses
The four basic operators. Each is used in the same way as a standard
calculator:
+ (addition), – (subtraction), x (multiplication), and ÷ (division).
Finds the result in the same way as a standard calculator.
Used to specify calculations in which certain operations have precedence.
You can make addition and subtraction operations have precedence over
multiplication and division by enclosing them in parentheses.
10
Page 12

Percent
For calculating percentages. Four methods of calculating percentages
are presented as follows.
1) $125 increased by 10%…137.5
125
2) $125 r educed by 20%…100
125
3) 15% of $125…18.75
125
4) W he n $ 125 equals 5% of X , X equals…2500
10
20
15
125 5
DEG
DEG
DEG
DEG
11
Page 13

Inverse, Square, Cube,
xth Power of y,Square Root,
Cube Root, xth Root of y
C alculates the inverse of the value on the display.
Squares the value on the display.
C ubes the value on the display.
C alculates exponential values.
C alculates the square root of the value on the display.
C alculates the cube root of the value on the display.
C alculates the xth root of y.
<Example>
O per ation D isplay
2 2 2 2
24
DEG
DEG
4
DEG
16
12
Page 14

10 to the Power of x,
Common Logarithm
C alculates the value of 10 raised to the xth power.
C alculates logarithm, the exponent of the power to which 10 must be
raised to equal the given value.
<Example>
O per ation
3
1000
D isplay
DEG
DEG
13
Page 15

e to the Power of x,
Natural Logarithm
C alculates powers based on the constant e (2.718281828).
C omputes the value of the natural logarithm, the exponent of the power
to which e must be raised to equal the given value.
<Example>
O per ation D isplay
5
10
DEG
DEG
14
Page 16

Factorials
The product of a given positive integer n multiplied by all the lesser positive
integers from 1 to n-1 is indicated by n! and called the factorial of n.
<Example>
A PPL IC AT I O N S :
Used in statistics and mathematics. In statistics, this function is used
in calculations involving combinations and permutations.
O per ation D isplay
DEG
7
c.f
n! = 1 x 2 x 3 x …xn
15
Page 17

Permutations, Combinations
This function finds the number of different possible orderings in selecting
r objects from a set of n objects. For example, there ar e six different
ways of ordering the letters ABC in groups of three letters—ABC , AC B,
BAC, BC A, C AB, and CBA.
The calculation equation is
This function finds the number of ways of selecting r objects from a set of
n objects. For example, from the three letters ABC, there are three ways
we can extract groups of two different letters—AB, AC, and CB.
The calculation equation is
<Example>
O per ation D isplay
64
64
= 3 x 2 x 1 = 6 (ways).
3P3
.
3C2
DEG
DEG
A PP L IC AT I O N S:
Used in statistics (probability calculations) and in simulation hypotheses in fields such as medicine, pharmaceutics, and physics. Also,
can be used to determine the chances of winning in lotteries.
16
Page 18

Time Calculation
C onverts a sexagesimal value displayed in degrees, minutes, seconds to
decimal notation. Also, converts a decimal value to sexagesimal
notataion (degrees, minutes, seconds).
Inputs values in sexagesimal notation (degrees, minutes, seconds).
<Example>
C onvert 24° 28’ 35” (24 degrees, 28 minutes, 35 seconds) to decimal notation. Then conver t 24.476° to
sexagesimal notation.
O per ation D isplay
24 28 35
C onvert to decimal notation
DEG
DEG
DEG
Repeat last key operation to return to the previous display.
A P P L IC AT IO N S :
Used in calculations of angles and angular velocity in physics, and
latitude and longitude in geography.
17
Page 19

Fractional Calculations
Inputs fractions and converts mutually between fractions and decimals.
C onverts between mixed numbers and improper fractions.
<Example>
Add 3 and , and convert to decimal notation.
2
1
5
7
O per ation D isplay
31 2
57
C onvert to decimal notation
Press once to return to the previous display
DEG
DEG
DEG
C onvert to an improper fraction
Press once to return to the previous display
DEG
A PPL IC AT IO N S:
There is a wide variety of applications for this function because
fractions are such a basic part of mathematics. This function is useful
for calculations involving electrical circuit resistance.
18
Page 20

Memory Calculations
Stores displayed values in memories A~F, X, Y, M.
Recalls values stored in A~F, X, Y, M.
Adds the displayed value to the value in the independent memory M.
Subtracts the displayed value from the value in the independent memory M.
Temporar y memories
~
Independent memory
~
<Example 1>
O per ation D ispla
0
(Enter 0 for M)
25 27
73
<Example 2>
Calculates $/¥ at the designated exchange rate.
$1 = ¥110
¥26,510 = $?
$2,750 = ¥?
110
O per ation D ispla
110 Y
y
DEG
MDEG
MDEG
MDEG
y
DEG
26510
2750
DEG
26510 ÖY=
DEG
2750 xY=
19
Page 21

Last Answer Memory
Automatically recalls the last answer calculated by pressing
<Example>
23
4
Solve for x first and then solve for y using x.
y = 4 ÷ xandx = 2 + 3
O per ation D isplay
DEG
DEG
20
Page 22

Trigonometric Functions
Trigonometric functions determine the ratio of three sides
of a right triangle. The combinations of the three sides are
sin, cos, and tan. Their relations are:
a
b
θ
C alculates the sine of an angle.
C alculates the cosine of an angle.
C alculates the tangent of an angle.
<Example>
The angle from a point 15 meters from
a building to the highest floor of the
building is 45°. How tall is the building?
[DEG mode]
sinθ =
cosθ =
tanθ =
b
a
c
a
b
c
c
O per ation D isplay
45 15
1
V
iew point
A PPL IC AT I O N S :
Trigonometric functions are useful in mathematics and various engineering
calculations. They are often used in astronomical observations, civil engineering and in calculations involving electrical circuits, as well as in calculations for physics such as parabolic motion and wave motion.
5
DEG
21
Page 23

Arc Trigonometric Functions
Arc trigonometric functions, the inverse of trigonometric functions, are used to determine an angle from ratios
of a right triangle. The combinations of the three sides
are sin
-1
, cos-1, and tan-1. Their relations are;
(arc sine) D etermines an angle based on the ratio
b/a of two sides of a right triangle.
(arc cosine) Determines an angle based on the ratio
c/a for two sides of a right triangle.
(arc tangent) Determines an angle based on the
ratio a/b for two sides of a right triangle.
<Example>
At what angle should an airplane climb in order
to climb 80 meters in 100 meters?
a
b
θ
c
b
θ
= sin
θ
= cos
θ
= tan
-1
a
c
-1
a
b
-1
c
[DEG mode]
O per ation D isplay
DEG
80
100
22
Page 24

Hyperbolic Functions
The hyperbolic function is defined by using natural exponents in trigonometric functions.
Arc hyperbolic functions are defined by using natural logarithms in trigonometric functions.
A PPL IC AT I O N S :
Hyperbolic and arc hyperbolic functions are very useful in electrical
engineering and physics.
23
Page 25

Coordinate Conversion
C onverts rectangular coordinates to polar coordinates (x, y r, θ)
C onverts polar coordinates to rectangular coordinates (r,
θ
x, y)
←
←
Splits data used for dual-variable data input.
←
Displays r, θ and x, y. (Cx y or r
y
Rectangular coordinates
←
←
←
θ
)
y
Polar coordinates
P (r,θ)
y
o
P (x,y)
x
r
x
θ
o
x
<Example> Determine the polar coordinates (r, θ) when the rectangu-
lar coordinates of Point P are (x = 7, y = 3).
[ D E G m ode]
O per ation D isplay
DEG
73
DEG
DEG
7.6
A PPL IC AT I O N S :
C oordinate conversion is often used in mathematics and engineering, especially for impedance calculations in electronics and electrical engineering.
23.2
DEG
24
Page 26

Binary, Pental, Octal,
Decimal, and Hexadecimal
Operations (N-Base)
This calculator can perform conversions between numbers expressed in binary, pental,
octal, decimal, and hexadecimal systems. It can also perform the four basic arithmetic
operations, calculations with parentheses and memory calculations using binary, pental,
octal, decimal, and hexadecimal numbers. In addition, the calculator can carry out the
logical operations AND, O R, NO T, N EG , X O R, and X N O R on binary, pental, octal, and
hexadecimal numbers.
C onverts to the binary system. "b" appears.
C onverts to the pental system. "P" appears.
C onverts to the octal system. "o" appears.
C onverts to the hexadecimal system. "H" appears.
C onverts to the decimal system. "b", "P", "o", and "H" disappear from the display.
C onversion is performed on the displayed value when these keys are pressed.
<Example 1>
HEX(1AC) ➞BIN ➞PEN ➞OCT ➞DEC
O per ation D isplay
DEG
1AC
DEG
1AC➞BIN
DEG
110101100➞PE
DEG
3203➞OCT
DEG
654➞DEC
<Example 2>
1011 AND 101 = (BIN) ➞DEC
O per ation D isplay
DEG
1011AND_
1011
101
DEG
1011AND101=
DEG
1➞DEC
25
Page 27

Statistics Function
The statistics function is excellent for analyzing qualities of an event. Though primarily
used for engineering and mathematics, the function is also applied to nearly all other
fields including economics and medicine.
DAT A I N P U T A N D C O R R E C T I ON
Enters data for statistical calculations.
C lears data input.
Splits data used for dual-variable data input.
(Used for dual-variable statistical calculations.)
<Example 1>
Here is a table of examination r esults. Input this data
for analysis.
D ata table 1
N o.
1 234567 8
Score 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
N o. of pupils 2 45712 108 2
O per ation D isplay
Stat 0
Select single-variable statistics mode
30
2
100 2
.
.
.
DATA SET=
DATA SET=
DEG
DEG
DEG
STAT
STAT
STAT
Score N umber of pupils
26
Page 28

“ A N S ” K E Y S F O R 1 -V A R I A B L E S T AT I S T I C S
C alculates the average value of the data (sample data x).
C alculates the standard deviation for the data (sample data x).
C alculates the standard deviation of a data population (sample data x).
Displays the number of input data (sample data x).
C alculates the sum of the data (sample data x).
C alculates the sum of the data (sample data x) raised to the second power.
N OT E :
1. Sample data refers to data selected r andomly from the population.
2. Standard deviation of samples is determined by the sample data
shift from an average value.
3. Standard deviation for the population is standard deviation when
the sample data is deemed a population (full data).
Let’s check the results based on the previous data.
69 (average value)
17.75686128 (standard deviation)
17.57839583 (standard deviation of the population)
50 (total count of data)
3450 (total)
27
Page 29

DA T A C O R R E C T I ON
C orrection prior to pr essing immediately after a data entry: Delete incorrect
data with , then enter the correct data.
C orrection after pressing :
Use to display the data previously entered.
Press to display data items in ascending (oldest first) order. To
reverse the display order to descending (latest first), press the key.
Each item is displayed with 'X n=', 'Yn=', or 'N n=' (n is the sequential
number of the data set).
Display the data item to modify, input the correct value, then press .
Using , you can correct the values of the data set all at once.
•W hen ▲ or ▼ appears, more data items can be browsed by pressing
or .
•T o delete a data set, display an item of the data set to delete, then
press . The data set will be deleted.
•T o add a new data set, press and input the values, then press .
<Example 2>
D ata table 2
X: 30, 40, 40, 50
X: 30, 45, 45, 45, 60
O per ation D isplay
Select single-variable statistics mode
30
40
2
Stat 0
DATA SET=
DATA SET=
DEG
DEG
DEG
STAT
STAT
STAT
50
28
DATA SET=
DEG
STAT
Page 30

O per ation D isplay
DEG
X2=
DEG
45
3
X2=
DEG
N2=
DEG
60
A PPL IC A T IO N S:
Single-variable statistical calculations are used in a broad range of fields,
including engineering, business, and economics. They ar e most often applied to
analysis in atmospheric observations and physics experiments, as well as for
quality contr ol in factories.
X3=
STAT
STAT
STAT
STAT
29
Page 31

<Example 3>
The table below summarizes the dates in April when cherry
blossoms bloom, and the average temperature for March in
that same area. D etermine basic statistical quantities for
data X and data Y based on the data table.
D ata table 3
Year 1983 1984 1985 1986 1987 1988 1989 1990
A ver age tem per ature
x
D ate blossom s bloom
y
6.2 7.0 6.8 8.7 7.9 6.5 6.1 8.2
13911 5712 157
O per ation D isplay
DEG
STAT
Stat 1
Select dual-variable statistics mode and linear regression calculation in sub-mode.
DEG
STAT
6 2 13
.
.
.
.
.
.
6 15
1
DATA SET=
DATA SET=
DEG
STAT
8 2 7
DateTemperature
30
DATA SET=
DEG
STAT
Page 32

“ A N S ” K E Y S F O R 2 -V A R I A B L E S T AT I S T I C S
In addition to the 1-variable statistic keys, the following keys have been added for calculating 2-variable statistics.
C alculates the sum of the product for sample data x and sample data y.
C alculates the sum of the data (sample data y).
C alculates the sum of the data (sample data y) raised to the second power.
C alculates the average value of the data (sample data y).
C alculates the standard deviation for the data (sample data y).
C alculates the standard deviation of a data population (sample data y).
N OT E :
The codes for basic statistical quantities of sample data x and their meanings
are the same as those for single-variable statistical calculations.
Let’ s check the results based on the previous data.
7.175 (Average for data x)
0.973579551 (Standard deviation for data x)
0.91070028 (Standard deviation of the population for data x)
9.875 (Average for data y)
3.440826313 (Standard deviation for data y)
3.218598297 (Standard deviation of the population for data y)
8 (Total count of data)
57.4 (Sum of data x)
418.48 (Sum of data x raised to the second power)
544.1 (Sum of the product of data x and data y)
79 (Sum of data y)
863 (Sum of data y raised to the second power)
31
Page 33

©SHARP CORP. (MAR. '05)
 Loading...
Loading...