Page 1
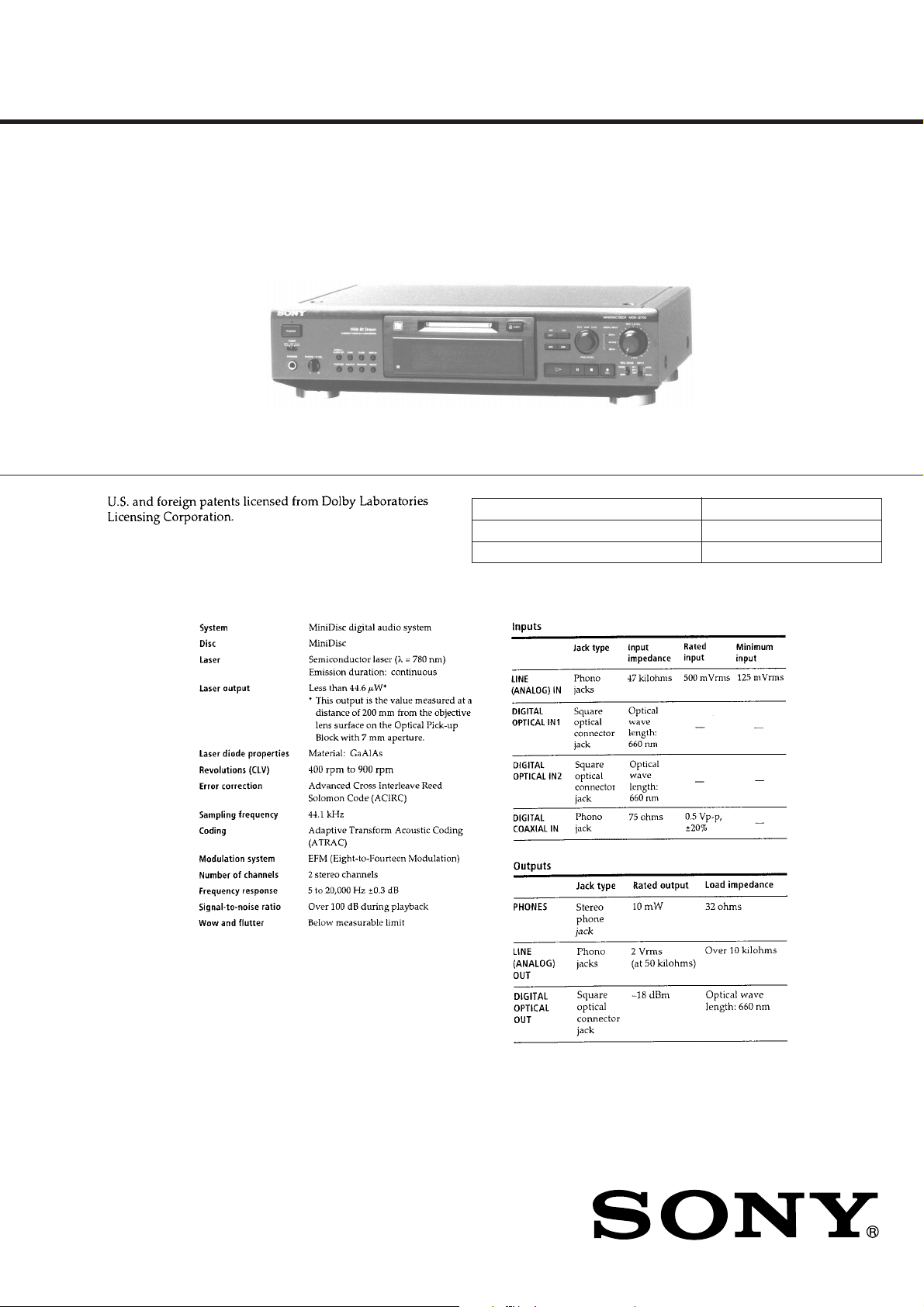
MDS-JE700
SERVICE MANUAL
Ver 1.1 2004. 09
Model Name Using Similar Mechanism MDS-JE500
MD Mechanism Type MDM-3A
Optical Pick-up Type KMS-260A/J1N
SPECIFICATIONS
US Model
Canadian Model
AEP Model
UK Model
9-960-804-12
2004I02-1
© 2004.09
— Continued on next page —
MiNi DiSC DECK
Sony Corporation
Audio Group
Published by Sony Engineering Corporaton
— 1 —
Page 2
CAUTION
Danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced.
Replace only with the same or equivalent type recommended by
the equipment manufacturer.
Discard used batteries according to manufacture’s instructions.
ADVARSEL!
Lithiumbatteri - Eksplosionsfare ved fejlagtig håndtering.
Udskiftning må kun ske med batteri af samme fabrikat og type.
Levér det brugte batteri tilbage til leverandøren.
ADVARSEL
Eksplosjonsfare ved feilakting skifte av batteri.
Benytt samme batteritype eller en tilsvarende type anbefalt av
apparatfabrikanten.
Brukte batterier katterier kasseres i henhold til fabrikantens
VARNIG
Explosionsfara vid felaktigt batteribyte.
Använd samma batterityp eller en likvärdig typ som rekommenderas
av apparattillverkaren.
Kassera använt batteri enligt gällande föreakrifter.
VAROITUS
Parist voi räjähtää, jos se on virheellisesti asennettu.
V aihda paristo ainoastaan laite valmistajan suosittelemaan tyyppiin.
Hävitä käytetty paristo valmistajan ohjeiden mukaisesti.
MODEL IDENTIFICATION
— BACK PANEL —
Parts No.
Parts No. MODEL
4-985-444-1
4-985-444-2
4-985-444-3
4-985-444-4
AEP model
UK model
US model
Canadian model
— 2 —
Page 3
The laser component in this product is
capable of emitting radiation exceeding
the limit for Class 1.
This appliance is classified as a CLASS 1
LASER product. The CLASS 1 LASER
PRODUCT MARKING is located on the
rear exterior.
The following caution label is located
inside the unit.
CAUTION
Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures
other than those specified herein may result in hazardous radiation exposure.
Notes on chip component replacement
• Never reuse a disconnected chip component.
• Notice that the minus side of a tantalum capacitor may be
damaged by heat.
Flexible Circuit Board Repairing
• Keep the temperature of soldering iron around 270˚C
during repairing.
• Do not touch the soldering iron on the same conductor of the
circuit board (within 3 times).
• Be careful not to apply force on the conductor when soldering
or unsoldering.
SAFETY CHECK-OUT
After correcting the original service problem, perform the following safety checks before releasing the set to the customer:
Check the antenna terminals, metal trim, “metallized” knobs, screws,
and all other exposed metal parts for A C leakage. Check leakage as
described below.
LEAKAGE
The AC leakage from any exposed metal part to earth Ground and
from all exposed metal parts to any exposed metal part having a
return to chassis, must not exceed 0.5 mA (500 microampers). Leakage current can be measured by any one of three methods.
1. A commercial leakag e tester, such as the Simpson 229 or RCA
WT-540A. Follow the manufacturers’ instructions to use these
instruments.
2. A ba ttery-operated AC milliammeter. The Data Precision 245
digital multimeter is suitable for this job.
3. Measuring the voltage drop across a resistor by means of a VOM
or battery-operated A C v oltmeter. The “limit” indication is 0.75
V, so analog meters must have an accurate low-voltage scale.
The Simpson 250 and Sanwa SH-63Trd are examples of a passive VOM that is suitable. Nearly all battery operated digital
multimeters that have a 2V AC range are suitable. (See Fig. A)
To Exposed Metal
Parts on Set
0.15µF
1.5k
Ω
Earth Ground
AC
voltmeter
(0.75V)
Fig. A. Using an AC voltmeter to check AC leakage.
SAFETY-RELATED COMPONENT WARNING !!
COMPONENTS IDENTIFIED BY MARK ! OR DO TTED LINE
WITH MARK ! ON THE SCHEMATIC DIAGRAMS AND IN
THE PARTS LIST ARE CRITICAL TO SAFE OPERATION.
REPLACE THESE COMPONENTS WITH SONY PARTS
WHOSE PART NUMBERS APPEAR AS SHOWN IN THIS
MANUAL OR IN SUPPLEMENTS PUBLISHED BY SONY.
ATTENTION AU COMPOSANT AYANT RAPPORT
À LA SÉCURITÉ!!
LES COMPOSANTS IDENTIFIÉS P AR UNE MARQUE ! SUR
LES DIAGRAMMES SCHÉMATIQUES ET LA LISTE DES
PIÈCES SONT CRITIQUES POUR LA SÉCURITÉ DE
FONCTIONNEMENT. NE REMPLA CER CES COMPOSANTS
QUE PAR DES PIÈCES SONY DONT LES NUMÉROS
SONT DONNÉS DANS CE MANUEL OU DANS LES
SUPPLÉMENTS PUBLIÉS PAR SONY.
— 3 —
Page 4

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. SERVICING NOTE
.......................................................... 5
2. GENERAL .......................................................................... 8
3. DISASSEMBLY
3-1. Case and Front Panel Assembly..........................................24
3-2. Bracket (T), (L) and (R)......................................................24
3-3. BD Board ...........................................................................25
3-4. SUB Chassis........................................................................ 25
3-5. Shutter Assembly ................................................................ 26
3-6. Over Write Head ................................................................. 26
3-7. Slider Complete Assembly..................................................27
4. TEST MODE ..................................................................... 28
5. ELECTRICAL ADJUSTMENTS ............................... 31
6. DIAGRAMS
6-1. Circuit Boards Location ...................................................... 36
6-2. Brock Diagrams
• BD Section....................................................................... 37
• Main Section .................................................................... 39
6-3. Waveforms .........................................................................41
6-4. Printed Wiring Board — BD Section —............................. 43
6-5. Schematic Diagram — BD Section — ............................... 45
6-6. Schematic Diagram — Main Section — ............................ 49
6-7. Printed Wiring Board — Main Section —.......................... 53
6-8. Printed Wiring Board — Panel Section — ......................... 55
6-9. Schematic Diagram — Panel Section — ............................ 57
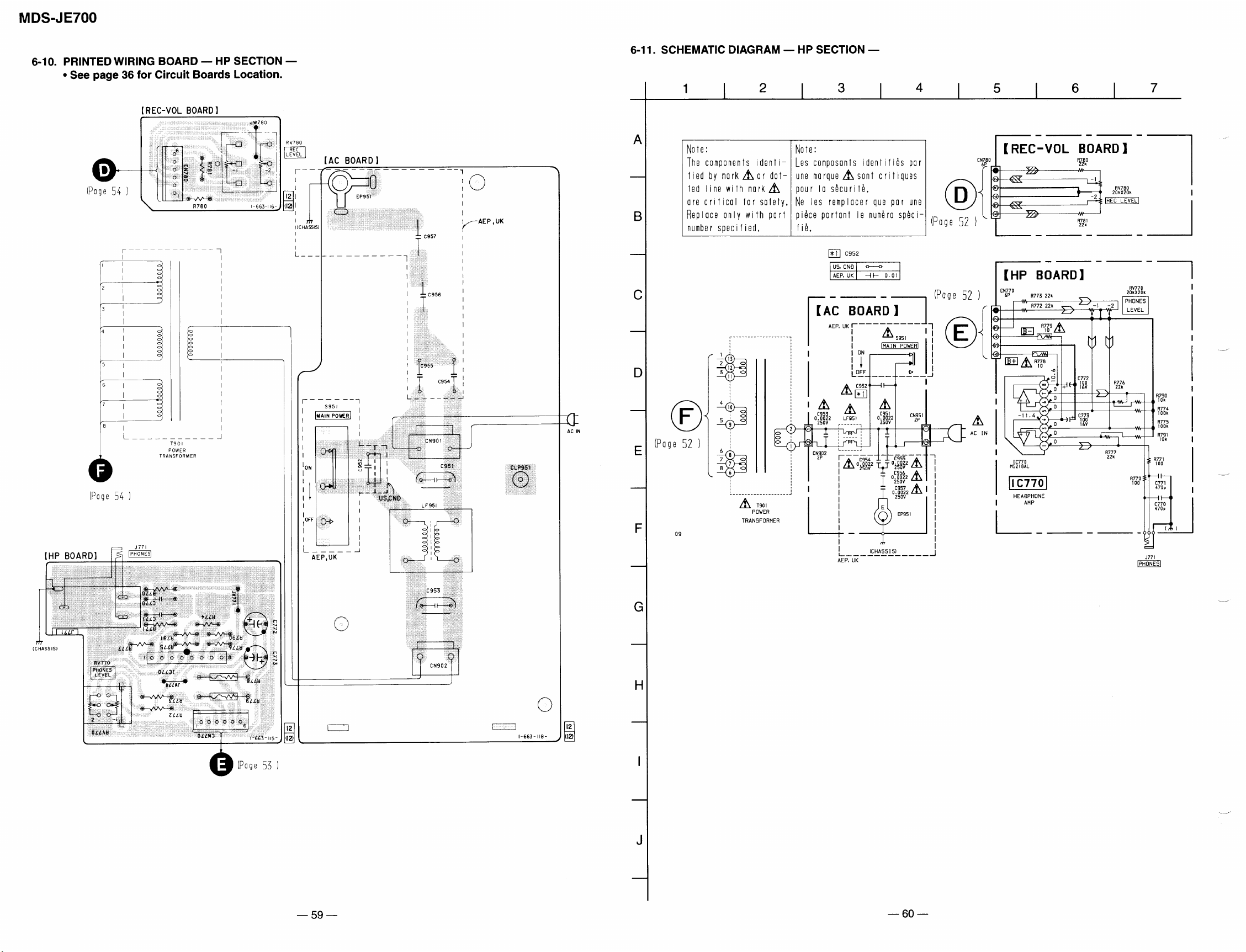
6-10. Printed Wiring Board — HP Section — .......................... 59
6-11. Schematic Diagram — HP Section — ............................. 60
6-12. IC Block Diagrams ........................................................... 61
6-13. IC Pin Functions ............................................................... 67
7. EXPLODED VIEWS
7-1. Case and Main Board Section............................................. 76
7-2. Front Panel Section ............................................................. 77
7-3. Mechanism Deck Section (1) (MDM-3A) .......................... 78
7-4. Mechanism Deck Section (2) (MDM-3A) .......................... 79
8. ELECTRICAL PARTS LIST ........................................ 80
— 4 —
Page 5
SECTION 1
SERVICING NOTE
JIG FOR CHECKING BD BOARD WAVEFORM
The special jig (J-2501-124-A) is useful for checking the waveform of the BD board. The names of terminals and the checking items to be
performed are shown as follows.
I+3V : For measuring IOP (Check the deterioration of the optical pick-up laser)
IOP : For measuring IOP (Check the deterioration of the optical pick-up laser)
TEO : TRK error signal (Traverse adjustment)
VC : Reference level for checking the signal
RF : RF signal (Check jitter)
RF
VC
TEO
IOP
I + 3V
Jig
(J-2501-124-A)
CN110
FORCED RESET
The system microprocessor can be reset in the following way.
Use these methods when the unit cannot be operated normally due to the overrunning of the microprocessor, etc.
Method :
Disconnect the power plug, short-circuit the land of RESET.
[MAIN BOARD] (Conductor Side)
Mechanism deck
IC401
CN303
Short land
TP (RESET)
— 5 —
Page 6

RETRY CAUSE DISPLAY MODE
• In this test mode, the causes for retry of the unit during recording can be displayed on the fluorescent display tube.
This is useful for locating the faulty part of the unit.
• The data amount stored in D RAM, number of retries, and retry cause are displayed. Each is displayed in hexadecimal number.
• The display of the D RAM data amount enables data reading, accumulation, ejection, and writing to be performed smoothly. If writing is
not smooth, data may decrease considerably.
Method:
1. Load a recordable disc whose contents can be erased into the unit.
2. Press the EDIT/NO button several times to display “All Erase?” on the fluorescent display tube.
3. Press the YES button.
4. When “All Erase??” is displayed on the fluorescent display tube, the numbers on the music calendar will start blinking.
5. Press the YES button to display “Complete”, and press the p button immediately and continue pressing for about 10 seconds.
6. When the “TOC” displayed on the fluorescent display tube goes off, release the p button.
7. Press the r REC button to start recording.
8. Press the DISPLAY button to display the test mode (Fig. 1), and check the display.
9. The Rt value increases with each retry. If an error occurs after a retry , “Retry Error” will be displayed, and the number of retries counted
will be set back to 0.
10. To exit the test mode, press the POWER button. Turn OFF the power, and after “TOC” disappears, disconnect the power plug from the
outlet.
Fig. 1 Reading the Test Mode Display
SC @@ Rt # # ∗ ∗
Fluorescent Display Tube Signs
@@ : Displays the DRAM memory amount when at all times.
# # : Displays the number of retries. When a retry error occurs, the number will be set back to 0.
* * : Cause of retry
All three displays above are in hexadecimal numbers.
— 6 —
Page 7
Reading the Retry Cause Display
Higher Bits Lower Bits
Hexadecimal
Bit
Binary
*1 Some displays are not used depending on the microprocessor version.
Reading the Display:
Convert the hexadecimal display into binary display. If more than two causes, they will be added.
Example
When 42 is displayed:
Higher bit : 4 = 0100 n b6
Lower bit : 2 = 0010 n b1
In this case, the retry cause is combined of “CLV unlock” and “ader5”.
84218421
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
00000000
00000001
00000010
00000100
00001000
00010000
00100000
01000000
10000000
Hexa-
decimal
00
01
02
04
08
10
20
40
80
Cause of Retry Occurring conditions
Spindle is slow
shock *1
ader5
Discontinuous address
(Not used)
FCS incorrect
IVR rec error
CLV unlock
Access fault
When spindle rotation is detected as slow
When more than 3.5 shocks are detected
When ADER was counted more than
five times continuously
When ADIP address is not continuous
(Not used)
When not in focus
When ABCD signal level exceeds the specified range
When CLV is unlocked
When access operation is not performed normally
When A2 is displayed:
Higher bit : A = 1010 n b7+b5
Lower bit : 2 = 0010 n b1
The retry cause in this case is combined of “access fault”, “IVR rec error”, and “ader5”.
Hexadecimal n Binary Conversion Table
Hexadecimal Binary Hexadecimal Binary
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
0000
0001
0010
0011
0100
0101
0110
0111
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
1000
1001
1010
1011
1100
1101
1110
1111
— 7 —
Page 8
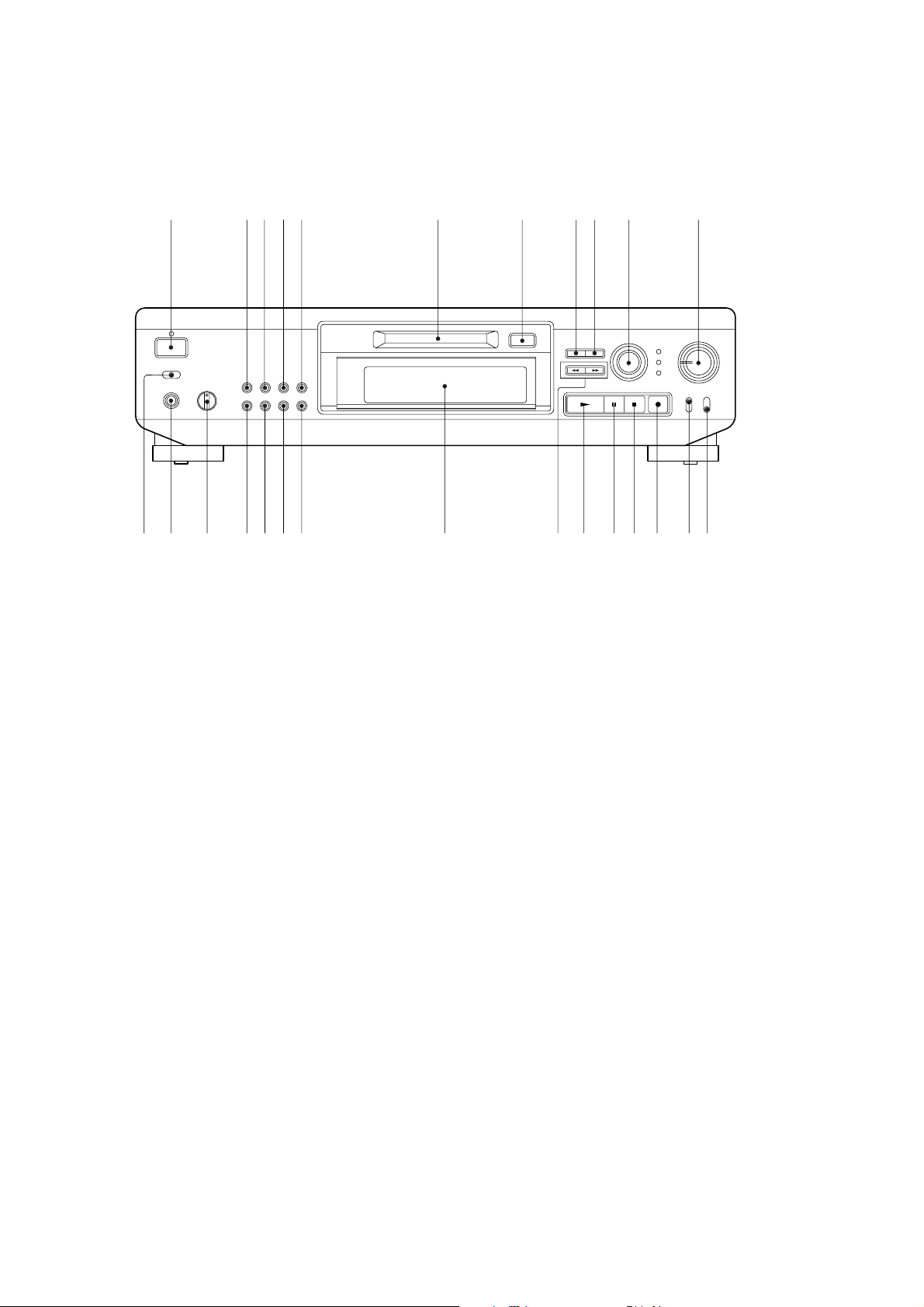
Location of Parts and Controls
SECTION 2
GENERAL
1
@¢
@∞@§
1 POWER switch
2 SCROLL/CLOCK SET button
3 CHAR button
4 CLEAR button
5 DISPLAY button
6 Disc compartment
7 § EJECT button
8 EDIT/NO button
9 YES button
!º AMS knob
!¡ REC LEVEL knob
!™ INPUT switch
!£ REC MODE swicth
234
5
@º@¡@™@£
6
!ª
!¢ r (recording) button
!∞ p (stop) button
!§ P (pause) button
!¶ ( (play) button
!• 0/) (fast backward/forward) buttons
!ª Display window
@º REPEAT button
@¡ PROGRAM button
@™ SHUFFLE button
@£ CONTINUE button
@¢ PHONE LEVEL knob
@∞ PHONES jack
@§ TIMER switch
7890 !¡
!•
!¶
!§
!∞
!¢
!™!£
— 8 —
Page 9
This section is extracted from
instruction manual.
— 9 —
Page 10
— 10 —
Page 11
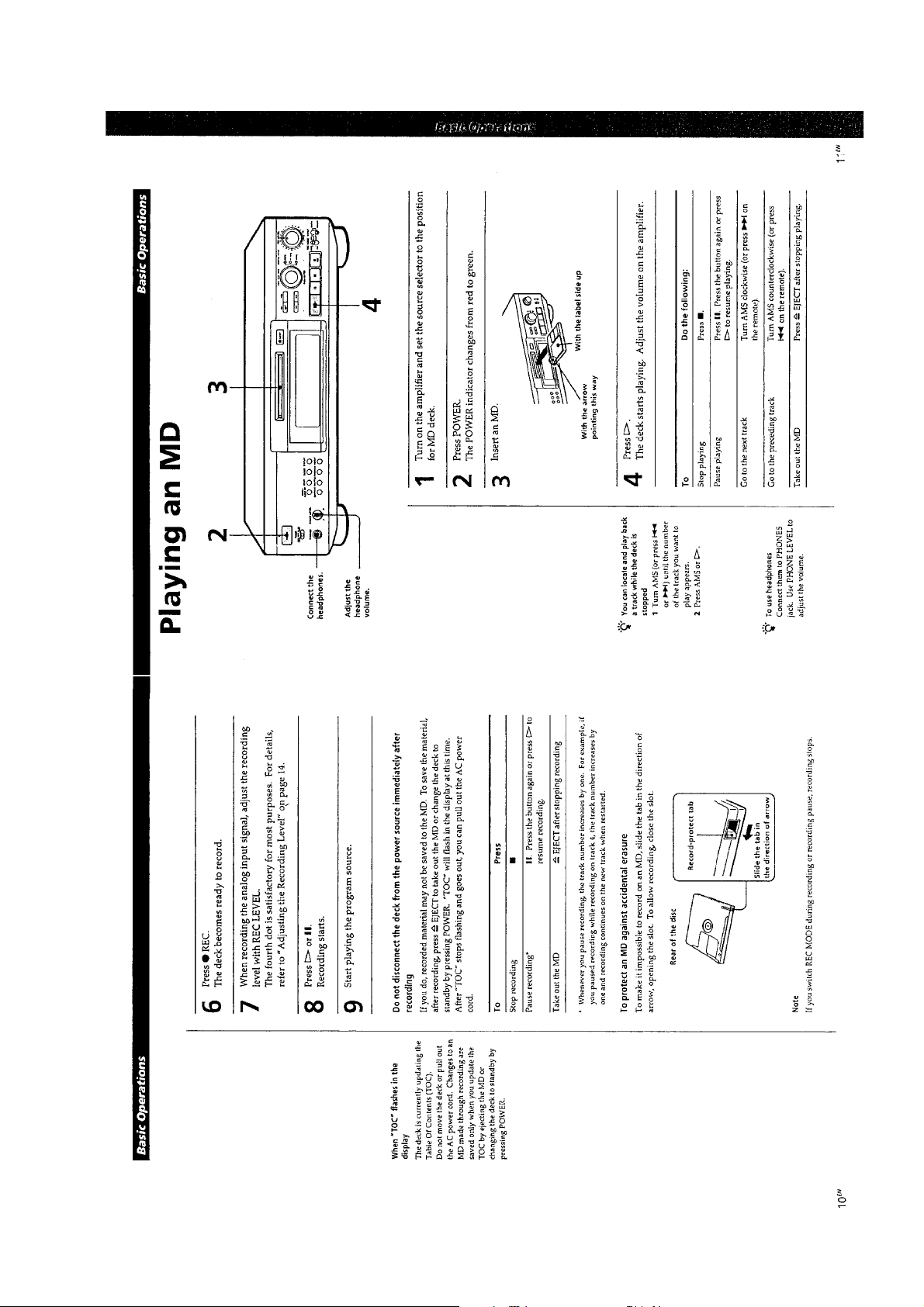
— 11 —
Page 12

— 12 —
Page 13
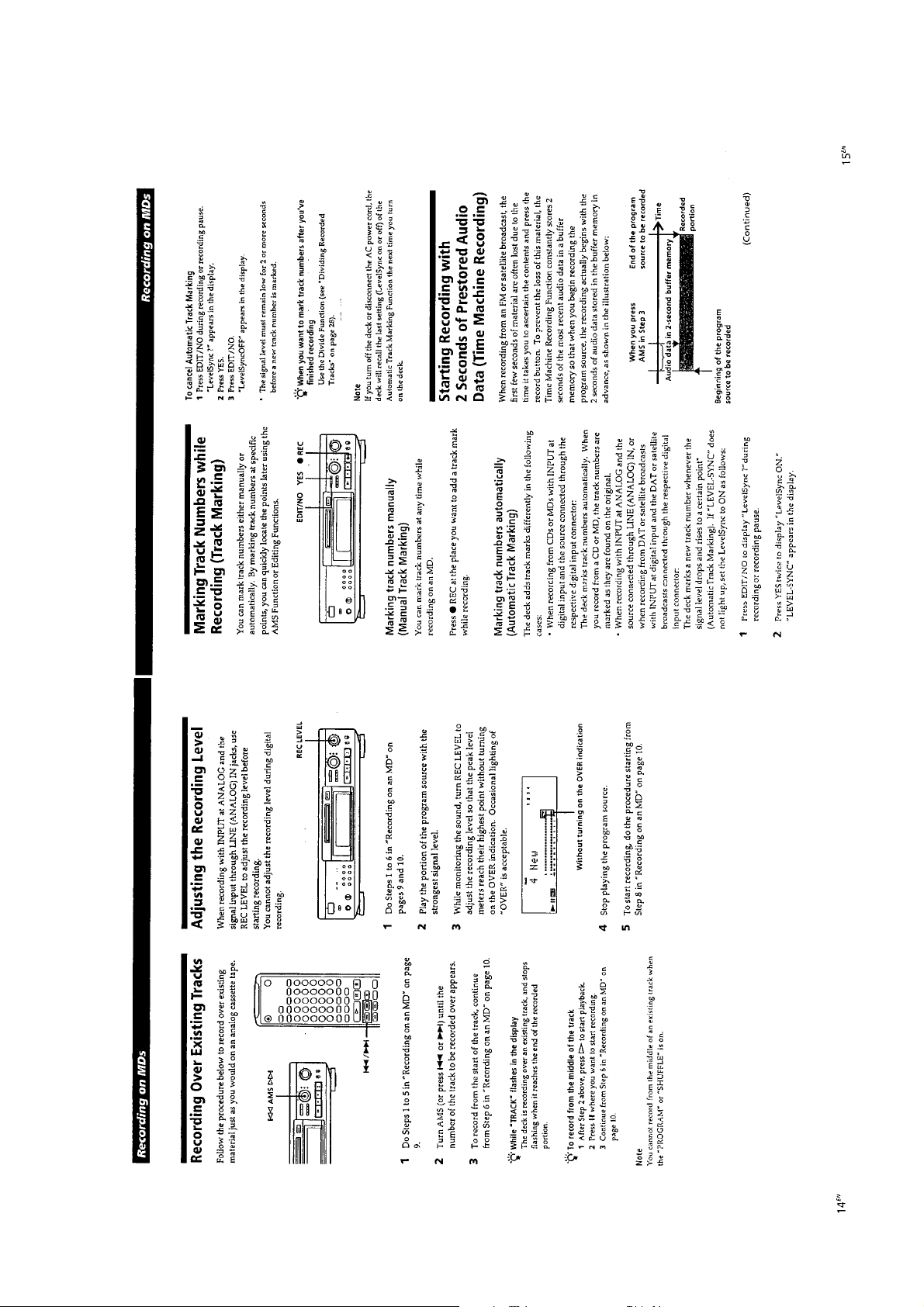
— 13 —
Page 14
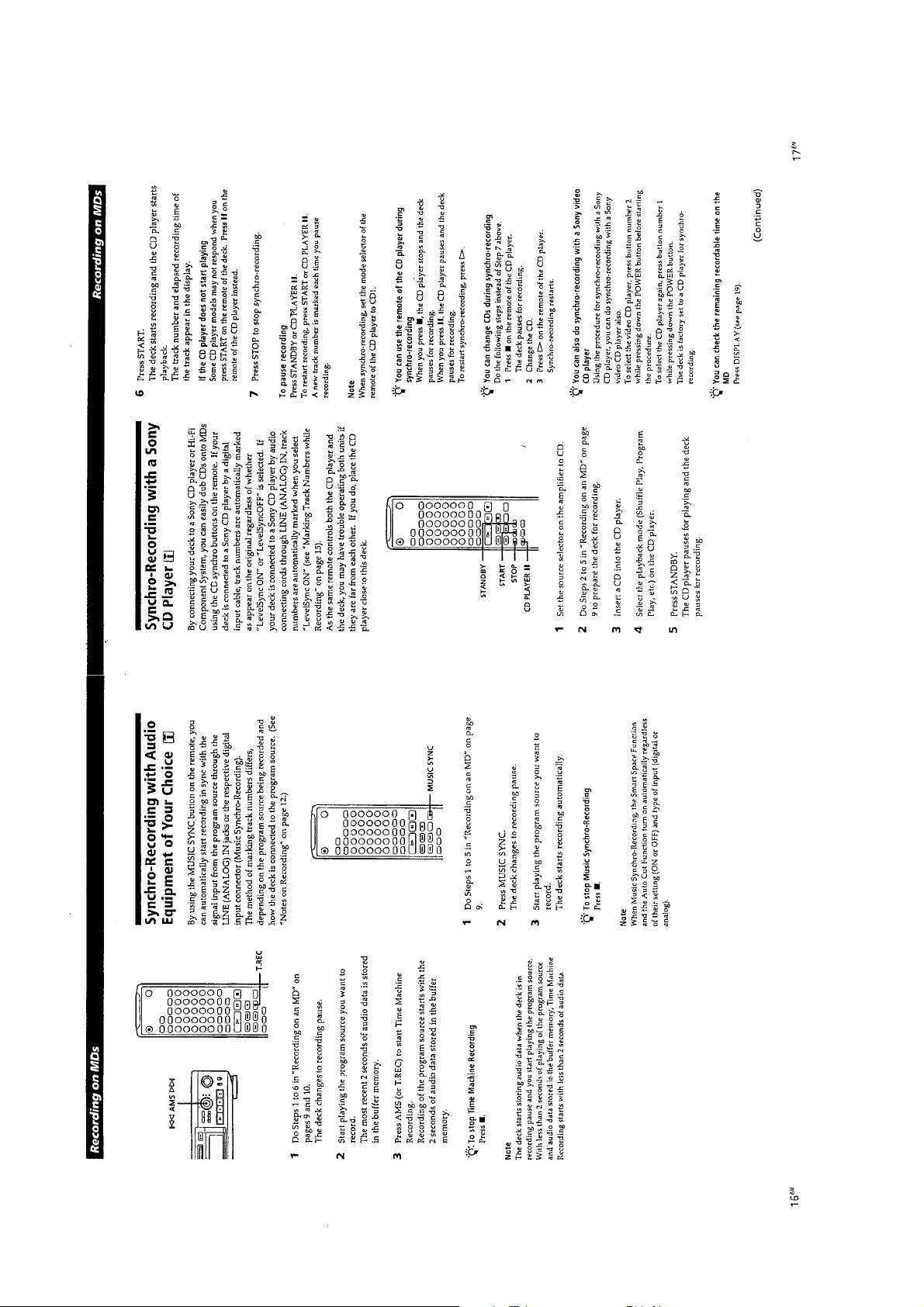
— 14 —
Page 15
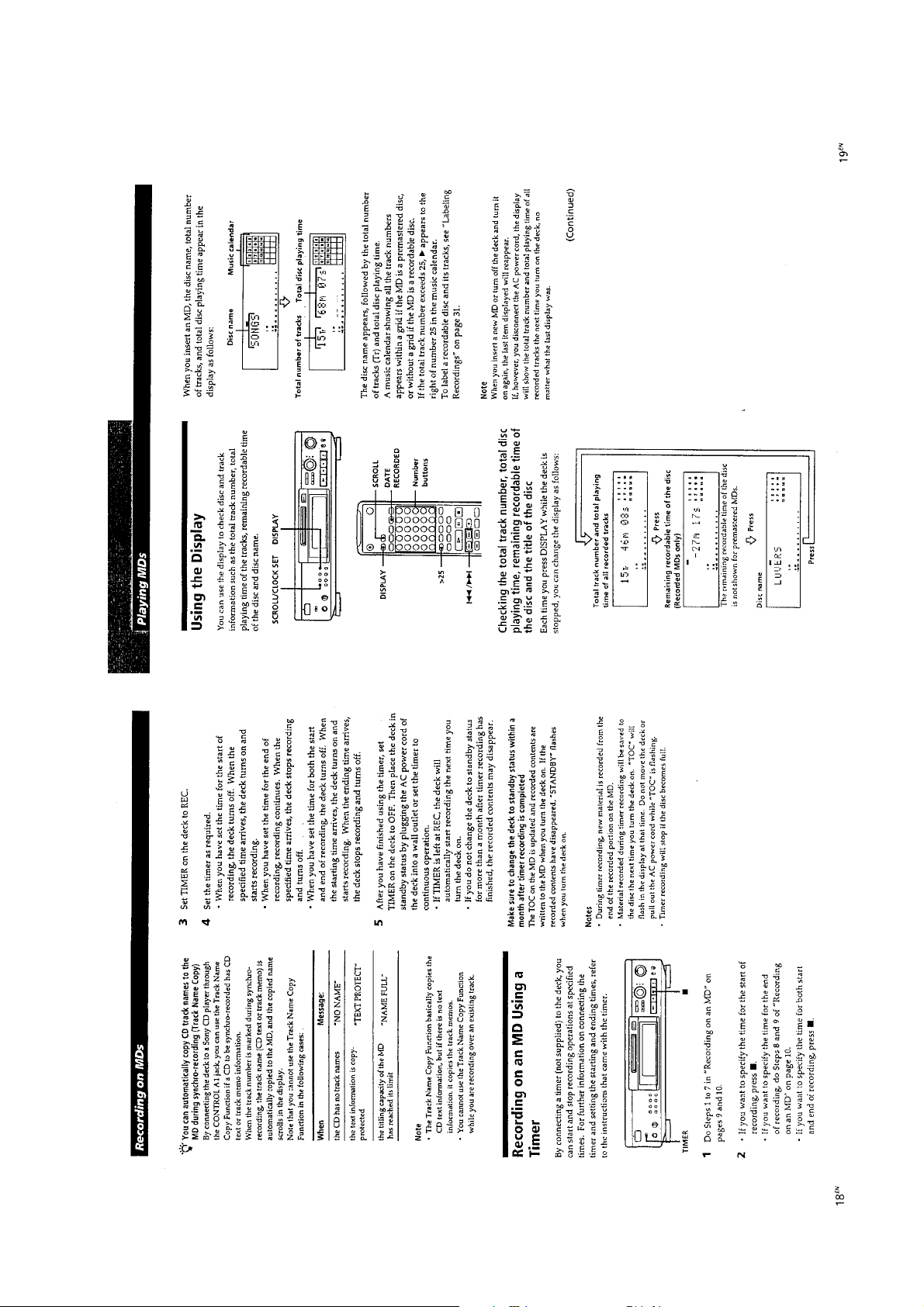
— 15 —
Page 16
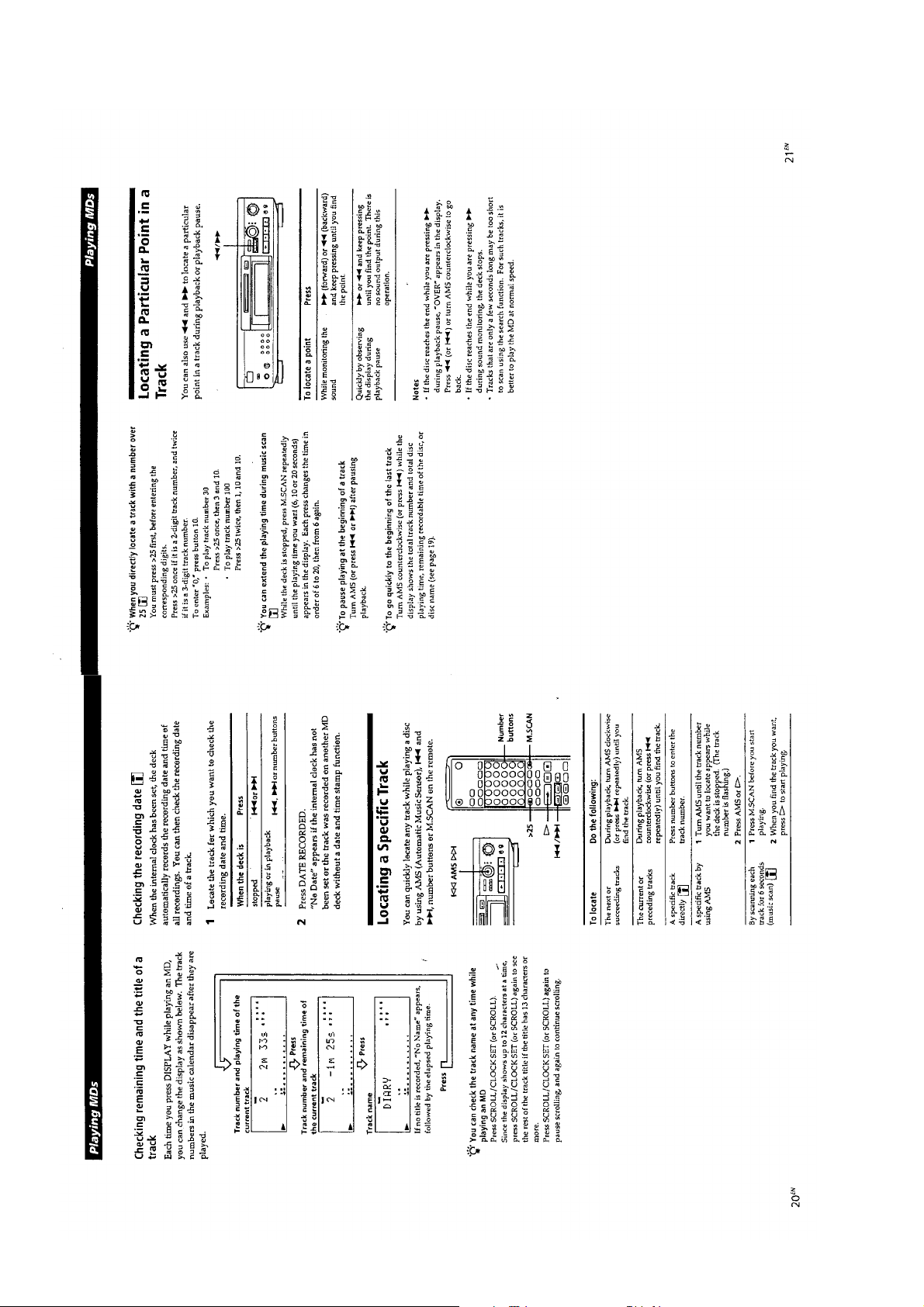
— 16 —
Page 17
— 17 —
Page 18
— 18 —
Page 19

— 19 —
Page 20
— 20 —
Page 21
— 21 —
Page 22
— 22 —
Page 23

— 23 —
Page 24

SECTION 3
DISASSEMBLY
Note : Follow the disassembly procedure in the numerical order given.
3-1. CASE AND FRONT PANEL ASSEMBLY
7
1
9
Connector (6P)
(CN770)
Two screws
(Case 3 TP2)
2
Screw (Case 3 TP2)
claw
Case
6
Screw (BVTP3x8)
3
Screw (Case 3 TP2)
5
Screw (BVTP3x8)
HP board
0
Eight screws
(BVTP3x8)
3-2. BRACKET (T), (L) AND (R)
2
Bracket (T)
6
Two screws
(BVTT2x3)
!¡
Front panel block assembly
1
Four screws
(BVTT2x3)
Main board
8
Flat type wire (23 core)
(CN303)
claw
4
5
Bracket (joint)
4
Two screws
(Case 3 TP2)
Screw (BVTT2x3)
3
Screw (BVTT2x3)
7
Bracket (L)
8
— 24 —
9
Bracket (R)
Two screws
(BVTT2x3)
Page 25

3-3. BD BOARD
4
OP relay flexible board
5
BD board
2
Flat type wire (15 core)
3
Screw (BVTT2x4)
1
Flexible board
(Over write head)
3-4. SUB CHASSIS
1
Two step screws
5
Sub chassis
3
Two insulators
Part
A
2
Two step screws
4
Two insulators
Part
Part
A
A
NG
OK
— 25 —
Take care so that the part A
may be right position when installing.
Page 26

3-5. SHUTTER ASSEMBLY
1
Stopper washer
2
Shaft (shutter)
3-6. OVER WRITE HEAD
3
Shutter assembly
Shaft (shutter)
1
Precision screw (P1.7x6)
Shutter assembly
Shaft (lid)
Hole B
Hole A
When installing, install the shaft
(shutter) into the hole as shown
in the figure before installing the
shaft (lid) into the hole B.
2
Over write head
— 26 —
Page 27

3-7. SLIDER COMPLETE ASSEMBLY
claw
4
Remove the slider complete assembly
in the direction of arrow with putting
out of two claws.
1
Screw
(M1.7x2)
claw
3
Set the shaft of Gear (LB) to be at the
position in the figure.
45°
2
Retainer (gear)
• Note for Installation of Slider Complete Assembly
OK
NG
Take care not to damage
the detective switch.
Slider assembly
Install the part A of lever (head up)
to pass over the slider complete assembly.
Part A
— 27 —
Page 28

SECTION 4
TEST MODE
4-1. PRECAUTIONS FOR USE OF TEST MODE
1 As loading related operations will be performed regardless of the test mode operations being performed, be sure to check that the disc is
stopped before setting and removing it.
Even if the §EJECT button is pressed while the disc is rotating during continuous playback, continuous recording, etc., the disc will not
stop rotating.
Therefore, it will be ejected while rotating.
Be sure to press the §EJECT button after pressing the NO button and the rotation of disc is stopped.
2 The erasing-protection tab is not detected in the test mode. Therefore, operating in the recording laser emission mode and pressing the
rREC button, the recorded contents will be erased regardless of the position of the tab. When using a disc that is not to be erased in the
test mode, be careful not to enter the continuous recording mode and traverse adjustment mode.
4-1-1. Recording laser emission mode and operating buttons
1. Continuous recording mode (CREC MODE)
2. Traverse adjustment mode (EFBAL ADJUST)
3. Laser power adjustment mode (LDPWR ADJUST)
4. Laser power check mode (LDPWR CHECK)
5. When pressing the rREC button.
4-2. SETTING THE TEST MODE
While pressing the AMS knob, insert the power plug into the power supply inlet, and release the AMS knob.
4-3. EXITING THE TEST MODE
When the REPEAT button is pressed, it becomes in the STANDBY mode. Or unplug the power plug from an outlet.
4-4. BASIC OPERATIONS OF THE TEST MODE
All operations are performed using the AMS knob, YES button, and NO button.
The functions of these buttons are as follows.
Function name
AMS knob
YES button
NO button
Changes parameters and modes
Proceeds onto the next step. Finalizes input.
Returns to previous step. Stops operations.
Function
4-5. SELECTING THE TEST MODE
Thirteen test modes are selected by turning the AMS knob.
Display
TEMP ADJUST
LDPWR ADJUST
LDPWR CHECK
EFBAL ADJUST
FBIAS ADJUST
FBIAS CHECK
CPLAY MODE
CREC MODE
DETRK CHECK
S curve CHECK
EEP MODE
MANUAL CMD
SVDATA READ
Temperature compensation offset adjustment
Laser power adjustment
Laser power check
Traverse adjustment
Focus bias adjustment
Focus bias check
Continuous playback mode
Continuous recording mode
Detrack check
S curve check ∗
Non-volatile memory mode ∗
Manual command transfer mode ∗
Data reading out mode ∗
Contents
For detailed description of each adjustment mode, refer to “5. Electrical Adjustments”.
If a different adjustment mode has been selected by mistake, press the NO button to exit from this mode.
* The EEP MODE, S curve CHECK, MANUAL CMD and SVDATA READ are not used in servicing. If set accidentally, press the NO button
immediately to exit this mode.
— 28 —
Page 29

4-5-1. Operating the Continuous Playback Mode
1. Entering the continuous playback mode
1 Set the disc in the unit. (Whichever recordable discs or discs for playback only are available.)
2 Rotate the AMS knob and display “CPLAY MODE”.
3 Press the YES button to change the display to “CPLAY IN”.
4 When access completes, the display changes to “C1 =
Note : The numbers “
” displayed show you error rates and ADER.
AD = ”.
2. Changing the parts to be played back
1 Press the YES button during continuous playback to change the display as below.
“CPLAY MID” n “CPLAY OUT”n “CPLAY IN”
4
When pressed another time, the parts to be played back can be moved.
2 When access completes, the display changes to “C1 =
Note : The numbers “
” displayed show you error rates and ADER.
AD = ”.
3. Ending the continuous playback mode
1 Press the NO button. The display will change to “CPLAY MODE”.
2 Press the §EJECT button to remove the disc.
Note : The playback start addresses for IN, MID, and OUT are as follows. In case you want to display the address of the playback position
on the display, press the DISPLAY button and display “CPLAY (
)”.
IN 40h cluster
MID 300h cluster
OUT 700h cluster
4-5-2. Operating the Continuous Recording Mode
1. Entering the continuous recording mode
1 Set a recordable disc in the unit. (Refer to Note 3)
2 Rotate the AMS knob and display “CREC MODE”.
3 Press the YES button to change the display to “CREC MID”.
4 When access completes, the display changes to “CREC (
Note : The numbers “
” displayed shows you the recording position addresses.
)” and REC lights up.
2. Changing the parts to be recorded
1 When the YES button is pressed during continuous recording, the display changes as below.
“CPLAY MID” n “CPLAY OUT”n “CPLAY IN”
4
When pressed another time, the parts to be recorded can be changed. REC goes off.
2 When access completes, the display changes to “CREC (
Note : The numbers “
” displayed shows you the recording position addresses.
)” and REC lights up.
3. Ending the continuous recording mode
1 Press the NO button. The display changes to “CREC MODE” and REC goes off.
2 Press the §EJECT button to remove the disc.
Note 1 : The recording start addresses for IN, MID, and OUT are as follows.
IN 40h cluster
MID 300h cluster
OUT 700h cluster
Note 2 :The NO button can be used to stop recording anytime.
Note 3 :During the test mode, the erasing-protection tab will not be detected. Therefore be careful not to set the continuous recording
mode when a disc not to be erased is set in the unit.
Note 4 :Do not perform continuous recording for long periods of time above 5 minutes.
Note 5 :During continuous recording, be careful not to apply vibration.
4-5-3. Non-Volatile Memory Mode
This mode reads and writes the contents of the non-volatile memory.
It is not used in servicing. If set accidentally, press the NO button immediately to exit it.
— 29 —
Page 30

4-6. FUNCTIONS OF OTHER BUTTONS
Function
¢
p
)
0
r REC
SCROLL
PLAY MODE
DISPLAY
Sets continuous playback when pressed in the STOP state. When pressed during continuous playback, the tracking servo turns ON/OFF.
Stops continuous playback and continuous recording.
The sled moves to the outer circumference only when this is pressed.
The sled moves to the inner circumference only when this is pressed.
Turns recording ON/OFF when pressed during continuous playback.
Switches between the pit and groove modes when pressed.
Switches the spindle servo mode (CLVS and A).
Switches the display when pressed.Returns to previous step. Stops operations.
Contents
Note : The erasing-protection tab is not detected during the test mode. Recording will start regardless of the position of the erasing-protec-
tion tab when the r REC button is pressed.
4-7. TEST MODE DISPLAYS
Each time the DISPLAY button is pressed, the display changes in the following order.
MODE displaynError rate displaynAddress displaynAuto gain displaynIVR display
The auto gain display and the IVR display are not used for servicing.
1. MODE display
Displays “TEMP ADJUST”, “CPLAY MODE”, etc.
2. Error rate display
Error rates are displayed as follows.
C1 =
C1 = : Indicates C1 error
AD= : Indicates ADER
3. Address display
Addresses are displayed as follows. (MO : Recordable disc, CD : Disc for playback only)
h=
h=
h= : Header address
s = : SUBQ address
a = : ADIP address
* “_” is displayed when the address cannot be read.
4. Auto gain display
Auto gains are displayed as follows.
AG F =
F= Focus auto gain collection value.
T= Tracking auto gain collection value.
AD =
s = (MO pit and CD)
a = (MO groove)
T =
4-8. MEANINGS OF OTHER DISPLAYS
Display
¢
P
REC
CLOCK
TRACK
DISC
DATE
A. SPACE
A – B
During continuous playback
Tracking servo OFF
Recording mode ON
CLV LOCK
Pit
High reflection
CLV-S
ABCD adjustment completed
Focus auto gain successful
Tracking auto gain successful
Light
Contents
Off
STOP
Tracking servo ON
Recording mode OFF
CLV UNLOCK
Groove
Low reflection
CLV-A
— 30 —
Blinking
Focus auto gain successful
Tracking auto gain failed
Page 31

SECTION 5
ELECTRICAL ADJUSTMENTS
5-1. PRECA UTIONS FOR CHECKING LASER DIODE
EMISSINON
T o check the emission of the laser diode during adjustments, never
view directly from the top as this may lose your eye-sight.
5-2. PRECAUTIONS FOR USE OF OPTICAL PICK-
UP (KMS-260A)
As the laser diode in the optical pick-up is easily damaged by static
electricity, solder the laser tap of the flexible board when using it.
Before disconnecting the connector, desolder first. Before connecting the connector, be careful not to remove the solder. Also take
adequate measures to prevent damage by static electricity. Handle
the flexible board with care as it breaks easily.
pick-up
laser tap
Optical pick-up flexible board
flexible board
5-3. PRECAUTIONS FOR ADJUSTMENTS
1) When replacing the following parts, perform the adjustments
and checks with ¬ in the order shown in the following table.
Optical
Pick-up
1. Temperature
compensation
offset adjustment
2. Laser power
adjustment
3. Traverse
adjustment
4. Focus bias
adjustment
5. Error rate check
IC171
G
¬
¬
¬
¬
¬
¬
¬
¬
¬
2) Set the test mode when performing adjustments.
After completing the adjustments, exit the test mode.
3) Perform the adjustments in the order shown.
4) Use the following tools and measuring devices.
• Check Disc (MD) TDYS-1
(Parts No. 4-963-646-01)
• Laser power meter LPM-8001 (Parts No. J-2501-046-A)
• Oscilloscope (Measure after performing CAL of prove.)
• Digital voltmeter
• Thermometer
• Jig for checking BD board waveform
(Parts No. : J2501-124-A)
5) When observing several signals on the oscilloscope, etc.,
make sure that VC and ground do not connect inside the oscilloscope.
(VC and ground will become short-circuited.)
6) Using the above jig enables the waveform to be checked without the need to solder.
(Refer to Servicing Note on page 5.)
BD Board
IC101, IC121, IC192
D101
¬
G
G
G
G
¬
¬
¬
¬
¬
5-4. CREATING CONTINUOUSLY RECORDED DISC
* This disc is used in focus bias adjustment and error rate check.
The following describes how to create a continuous recording
disc.
1. Insert a disc (blank disc) commercially available.
2. Rotate the AMS knob and display “CREC MODE”.
3. Press the YES button again to display “CREC MID”.
Display “CREC (0300)” and start to recording.
4. Complete recording within 5 minutes.
5. Press the NO button and stop recording .
6. Press the §EJECT button and remove the disc.
The above has been how to create a continuous recorded data for
the focus bias adjustment and error rate check.
Note :
• Be careful not to apply vibration during continuous recording.
— 31 —
Page 32

5-5. TEMPERATURE COMPENSATION OFFSET
ADJUTMENT
Save the temperature data at that time in the non-volatile memory
as 25 ˚C reference data.
Note :
1. Usually, do not perform this adjustment.
2. Perform this adjustment in an ambient temperature of 22 ˚C to
28 ˚C. Perform it immediately after the power is turned on when
the internal temperature of the unit is the same as the ambient
temperature of 22 ˚C to 28 ˚C.
3. When D101 has been replaced, perform this adjustment after
the temperature of this part has become the ambient temperature.
Adjusting Method :
1. Rotate the AMS knob and display “TEMP ADJUST”.
2. Press the YES button and select the “TEMP ADJUST” mode.
3. “TEMP =
4. To save the data, press the YES button.
When not saving the data, press the NO button.
5. When the YES button is pressed, “TEMP =
displayed and turned back to “TEMP ADJUST” display then.
When the NO button is pressed, “TEMP ADJUST” will be displayed immediatelly.
Specified Value :
The “TEMP =
0F”, “10 - 1F” and “20 - 2F”.
” and the current temperature data will be displayed.
SAVE” will be
” should be within “E0 - EF”, “F0 - FF”, “00 -
5-6. LASER PPOWER ADJUSTMENT
Connection :
Optical pick-up
objective lens
CN110 pin
CN110 pin
BD board
5
(I+3V)
4
(IOP)
Adjusting Method :
1. Set the laser power meter on the objective lens of the optical
pick-up. (When it cannot be set properly, press the 0 button
or ) button to move the optical pick-up.)
Connect the digital volt meter to CN110 pin 5 (I+3V) and
CN110 pin 4 (IOP).
2. Rotate the AMS knob and display “LDPWR ADJUST”.
(Laser power : For adjustment)
3. Press the YES button once and display “LD 0.9 mW $
4. Rotate the AMS knob so that the reading of the laser pow er meter
becomes 0.86 to 0.92 mW . Press the YES button after setting the
range knob of the laser power meter, and save the adjustment
results. (“LD SAVE $
5. Then “LD 7.0 mW $
” will be displayed for a moment.)
” will be displayed.
6. Rotate the AMS knob so that the reading of the laser pow er meter
becomes 6.9 to 7.1 mW, press the YES button and save it.
Note : Do not perform the emission with 7.0 mW more than 15
seconds continuously.
7. Then, rotate the AMS knob and display “LDPWR CHECK”.
8. Press the YES button once and display “LD 0.9 mW $
that the reading of the laser power meter become 0.85 to 0.91
mW.
9. Press the YES button once more and display “LD 7.0 mW $
”. Check that the reading the laser power meter and digital
volt meter satisfy the specified value.
Laser power
meter
Digital volt meter
”.
”. Check
Specified Value :
Laser power meter reading : 7.0 ± 0.1 mW
Digital voltmeter reading : Optical pick-up displayed value ± 10%
(Optical pick-up label)
KMS
260A
27X40
B0825
N
Iop = 82.5 mA in this case
Iop (mA) = Digital voltmeter reading (mV)/1 (
Ω
)
10. Press the NO button and display “LDPWR CHECK” and stop
the laser emission.
(The NO button is effective at all times to stop the laser emission.)
— 32 —
Page 33

5-7. TRA VERSE ADJUSTMENT
Connection :
Oscilloscope
CN110 pin
BD board
3
(TEO)
2
(VC)
V : 0.5 V/div
H : 10 ms/div
Input : DC mode
MO-R”.
of “EFB= ” changes
CN110 pin
Adjusting method :
1. Connect an oscilloscope to CN110 pin 3 (TEO) and CN110
pin 2 (VC) of the BD board.
2. Load a disc (any available on the market). (Refer to Note 1.)
3. Press the 0 button or ) button and move the optical pickup outside the pit.
4. Rotate the AMS knob and display “EFBAL ADJUST”.
5. Press the YES button and display “EFB =
(Laser power READ power/Focus servo ON/tracking servo OFF/
spindle (S) servo ON)
6. Rotate the AMS knob so that the waveform of the oscilloscope
becomes the specified value.
(When the AMS knob is rotated, the
and the waveform changes.) In this adjustment, waveform varies at intervals of approx. 2%. Adjust the waveform so that the
specified value is satisfied as much as possible.
(Read power traverse adjustment)
(Traverse Wav ef orm)
11. Rotate the AMS knob until the waveform of the oscilloscope
moves closer to the specified value.
In this adjustment, waveform varies at intervals of approx. 2%.
Adjust the waveform so that the specified value is satisfied as
much as possible.
(Traverse Waveform)
A
VC
B
Specification A = B
12. Press the YES button, and save the adjustment results in the
non-volatile memory . (“EFB =
SAVE” will be displayed for
a moment.)
Next “EFBAL CD” is displayed. The disc stops rotating automatically.
13. Press the §EJECT button and remove the disc.
14. Load the check disc (MD) TDYS-1.
15. Press the YES button and display “EFB =
CD”. Servo is
imposed automatically.
16. Rotate the AMS knob so that the wa v eform of the oscilloscope
moves closer to the specified value.
In this adjustment, waveform varies at intervals of approx. 2%.
Adjust the waveform so that the specified value is satisfied as
much as possible.
(Traverse Waveform)
A
VC
B
Specification A = B
7. Press the YES button and save the result of adjustment to the
non-volatile memory (“EFB =
moment. Then “EFB =
SAVE” will be displayed for a
MO-W” will be displayed).
8. Rotate the AMS knob so that the waveform of the oscilloscope
becomes the specified value.
(When the AMS knob is rotated, the
of “EFB- ” changes
and the waveform changes.) In this adjustment, waveform varies at intervals of approx. 2%. Adjust the waveform so that the
specified value is satisfied as much as possible.
(Write power traverse adjustment)
(Traverse Waveform)
A
VC
B
Specification A = B
A
VC
B
Specification A = B
17. Press the YES b utton, display “EFB = SA VE” for a moment
and save the adjustment results in the non-volatile memory.
Next “EFBAL ADJUST” will be displayed.
18. Press the §EJECT button and remove the check disc (MD)
TDYS-1.
Note 1 : MO reading data will be erased during if a recorded disc is
used in this adjustment.
Note 2 : If the traverse waveform is not clear, connect the oscillo-
scope as shown in the following figure so that it can be
seen more clearly.
Oscilloscope
Ω
330 k
10pF
CN110 pin
CN110 pin
BD board
3
(TEO)
2
(VC)
9. Press the YES button, and sa ve the adjustment results in the nonvolatile memory. (“EFB =
SAVE” will be displayed for a
moment.)
10. “EFB =
MO-P”. will be displayed.
The optical pick-up moves to the pit area automatically and servo
is imposed.
— 33 —
Page 34

5-8. FOCUS BIAS ADJUSTMENT
Adjusting Method :
1. Load a continuously recorded disc (Refer to “5-4. Creating Continuously Recorded Disc”.).
2. Rotate the AMS knob and display “CPLAY MODE”.
3. Press the YES button and display “CPLAY MID”.
4. Press the NO button when “C1 =
5. Rotate the AMS knob and display “FBIAS ADJUST”.
6. Press the YES button and display “
The first four digits indicate the C1 error rate, the two digits
after [/] indicate ADER, and the 2 digits after [a =] indicate the
focus bias value.
7. Rotate the AMS knob in the clockwise direction and find the
focus bias value at which the C1 error rate becomes 220 (Refer
to Note 2).
8. Press the YES button and display “
9. Rotate the AMS knob in the counterclockwise direction and find
the focus bias value at which the C1 error rate becomes 220.
10. Press the YES button and display “
11. Check that the C1 error rate is below 50 and ADER is 00. Then
press the YES button.
12. If the “(
)” in “ - - ( )” is above 20, press the YES
button.
If below 20, press the NO button and repeat the adjustment from
step 2.
13. Press the §EJECT button to remove the continuously recorded
disc.
Note 1 : The relation between the C1 error and focus bias is as
shown in the following figure. Find points a and b in the
following figure using the above adjustment. The focal
point position C is automatically calculated from points a
and b.
Note 2 : As the C1 error rate changes, perform the adjustment us-
ing the average vale.
C1 error
220
b
c
AD = ” is displayed.
/ a = ”.
/ b = ”.
/ c = ”.
Focus bias value
(F. BIAS)
a
5-9. ERROR RATE CHECK
5-9-1. CD Error Rate Check
Checking Method :
1. Load a check disc (MD) TDYS-1.
2. Rotate the AMS knob and display “CPLAY MODE”.
3. Press the YES button twice and display “CPLAY MID”.
4. The display changes to “C1 =
AD = ”.
5. Check that the C1 error rate is below 20.
6. Press the NO button, stop playback, press the §EJECT button,
and remove the test disc.
5-9-2. MO Error Rate Check
Checking Method :
1. Load a continuously recorded disc (Refer to “5-4. Creating Continuously Recorded Disc”.).
2. Rotate the AMS knob and display “CPLAY MODE”.
3. Press the YES button and display “CPLAY MID”.
4. The display changes to “C1 =
AD = ”.
5. If the C1 error rate is below 50, check that ADER is 00.
6. Press the NO button, stop playback, press the §EJECT button,
and remove the continuously recorded disc.
5-10. FOCUS BIAS CHECK
Change the focus bias and check the focus tolerance amount.
Checking Method :
1. Load a continuously recorded disc (Refer to “5-4. Creating Continuously Recorded Disc”.).
2. Rotate the AMS knob and display “CPLAY MODE”.
3. Press the YES button twice and display “CPLAY MID”.
4. Press the NO button when “C1 =
5. Rotate the AMS knob and display “FBIAS CHECK”.
6. Press the YES button and display “
The first four digits indicate the C1 error rate, the two digits
after [/] indicate ADER, and the 2 digits after [c =] indicate the
focus bias value.
Check that the C1 error is below 50 and ADER is 00.
7. Press the YES button and display “
Check that the C1 error is not below 220 and ADER is not
above 00 every time.
8. Press the YES button and display “
Check that the C1 error is not below 220 and ADER is not above
00 every time.
9. Press the NO button, next press the §EJECT button, and remove the continuously recorded disc.
AD = ” is displayed.
/ c = ”.
/ b = ”.
/ a = ”.
Note 1 : If the C1 error and ADER are abov e 00 at points a (step 8.
in the above) or b (step 7. in the above), the focus bias
adjustment may not have been carried out properly. Adjust perform the beginning again.
— 34 —
Page 35

5-11. ADJUSTING POINTS AND CONNETING POINTS
[BD BOARD] (SIDE A)
CN101
15
RF
VC
TEO
D101
CN110
NOTE
1 + 3V
IOP
IC192
[BD BOARD] (SIDE B)
IC171
IC101
IC121
NOTE : It is useful to use the jig. for checking the waveform.
(Refer to Servicing Note on page 5.)
— 35 —
Page 36
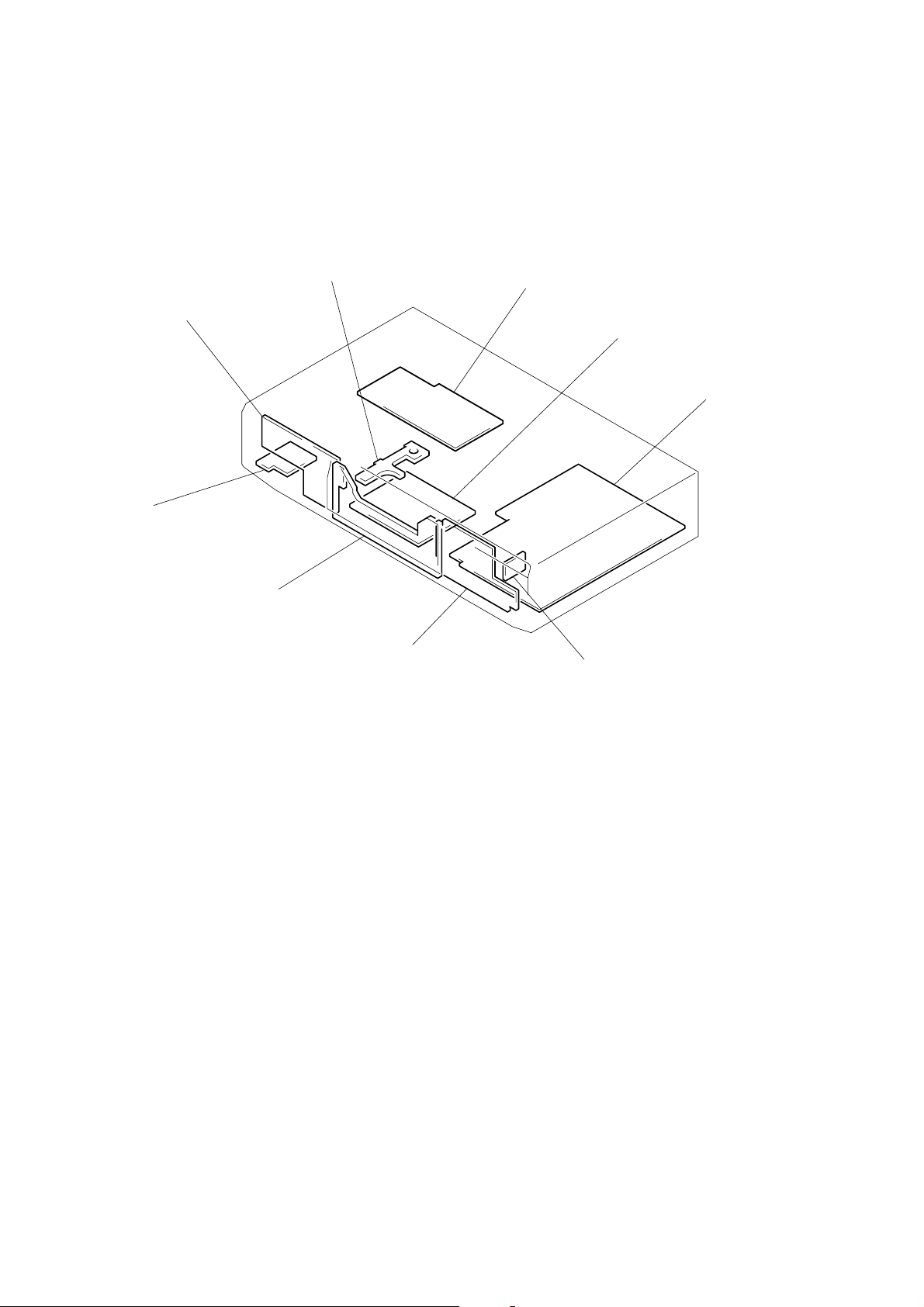
6-1. CIRCUIT BOARDS LOCATION
SECTION 6
DIAGRAMS
PANEL (L) board
HP board
DISPLAY board
SW board
AC board
BD board
MAIN board
PANEL (R) board
REC-VOL board
— 36 —
Page 37

6-2. BLOCK DIAGRAMS
— BD SECTION —
• Signal path
: PB
: REC
: PB (Digital out)
: REC (Digital in)
OPTICAL PICK-UP BLOCK
(KMS-260A/J1N)
DETECTOR
F
IJ
C
B
D
A
E
VC
PD
M902
SLED MOTOR
M901
SPINDLE MOTOR
ILCC
LD
HF
MODULE
TRAKING
COIL
FOCUS
COIL
09
M
M
HR901
OVER WRITE
HEAD
TRK–
TRK+
FSC+
FSC–
SLED+
SLED–
SPDL+
SPDL–
VC
D101
LASER ON
SW
Q101
Q162,163
HF MODULE
IC103,Q102-104
SLED/SPINDLE MOTOR DRIVE
FOCUS/TRACKING COIL DRIVE
10
12
21
23
27
25
6
8
APC
SW
Q181,182
1
2
4
5
6
7
8
9
3
15
14
10
DRIVER
DRIVER
DRIVER
DRIVER
HEAD
DRIVE
I
J
A
B
C
D
E
F
VC
TEMPR
TEMPI
PD
IC152
48 47 46 40
RFO
MORFI
MORFO
RF AMP
IV AMP
IV AMP
CVB
TEMP
AMP
APC
11
PSB
11
14
15
17
AGCI
APCREF
12
E-F
BALANCE
VCC
IC122
4
85
86
89
88
92
91
94
93
16
OVER WRITE HEAD DRIVE
RF AMP
IC101
RF AGC & EQ
BPF
VICONV
EQADJ
3TADJ
2522 23
1
2
TFDR
TRDR
FRDR
FFDR
SFDR
SRDR
SPFD
SPRD
XRST
IC181
P-P
WBLADJ
3
18 2
9
PEAK
&
BOTTOM
ABCD
AMP
FOCUS
ERROR
AMP
AT
AMP
TRACKING
ERROR
AMP
SERIAL
PARALLEL
DECODER
1
18
RF
38
AUX
33 66
BOTM
36
PEAK
37
ABCD
35
FE
34 65
VC
31
VC
29
BPF
ADFM
ADIN
30
ADFG
32
TE
26
SE
28
CSLED
27
SWDT
SCLK
FOCNT
XLAT
VC
16
17
18
20
Q180
FILTER
VC
DIGITAL SERVO SIGNAL PROCESSOR, DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSOR
EFM/ACIRC ENCODER/DECODER, SHOCK-PROOF MEMORY CONTROLLER,
ATRAC ENCODER/DECODER, 2M-BIT DRAM
EFMO
100
PCO
58
FILI
59
PLL
FILO
60
CLTV
61
RFI
55
AUX1
BOTM
63
PEAK
62
ANALOG
ABCD
EE
VC
TE
SE
ADFG
DTRF
CKRF
XLRF
FOCNT
MUX
ADIP
DEMODULATOR/
DECODER
SPINDLE
SERVO
SPRD
93
64
67
74
73
78
82
81
80
79
ENCODER/
DECODER
SPFD
94
EFM,
ACIRC,
IC121
RECP
APC
APCREF
15 14
TX
SHOCK
RESISTANT
MEMORY
CONTROLLER
A/D
CONVERTER
PWM
GENERATOR
FFDR
FRDR
TFDR
TRDR
XINIT
SERVO
DSP
SFDR
9192858689888313
SRDR
10
ENCODER/
DECODER
SAMPLING
CONVERTER
XRST
ATRAC
RATE
MDS-JE700
SCTX
XINT
DIN
21
ADDT
23
DIGITAL
AUDIO
I/F
DADT
24
DOUT
22
SQSY
IC171
M903
DQSY
MNT3
MNT2
MNT1
MNT0
SENS
SRDT
SCLK
SWDT
XLAT
XBCK
LRCK
OSCI
11
12
4
3
2
1
9
8
6
5
7
26
25
16
SDA
DETECT SW
S681 - 683,
S685 - 688
M
1 5
BUFFER
IC123
5
6
SUBCODE
PROCESSOR
MONITOR
CONTROL
CPU
I/F
3
AUTO
SEQUENCER
CLOCK
GENERATOR
EEP ROM
LOADING MOTOR
DIN
ADDT
DADT
DOUT
SQSY
DQSY
MNT3
MNT2
MNT1
MNT0
SENS
SRDT
SCLK
SWDT
XLAT
BCK
LRCK
512FS
LDON
WRPWR
MOD
SDA
SCLSCL
LIMIT
REFLECT
PROTECT
CHUCK IN
PACK OUT
PB P
REC P
LOAD-IN
LOAD-OUT
XRST
MAIN
SECTION
— 37 —
— 38 —
Page 38

MDS-JE700
— MAIN SECTION —
DIN
DOUT
ADDT
DADT
SCTX
XINT
BCK
LRCK
512FS
SQSY
DQSY
MNT3
MNT2
MNT1
MNT0
SENS
SRDT
SCLK
SWDT
XLAT
BD
SECTION
LIMIT
REFLECT
PROTECT
CHUCK IN
PACK-OUT
PB-P
REC-P
LDON
WRPWR
MOD
LOAD-IN
LOAD-OUT
XRST
SDA
SCL
BCK
LRCK
512FS
SCLK
SWDT
XLAT
2
10
LOADING MOTOR
DRIVE
IC351
DIGITAL
OPTICAL OUT
IC352
1
DRIVE
DRIVE
LOADING
Q351,352
DIGITAL
DATA SELECTOR
IC356
IC0
1Y
7
15
16
SLOCK
42
XBUSY
41
33
77
32
69
67
68
90
96
98
97
6
8
38
37
75
80
86
5
95
6
94
4
SW
39
52
53
81
A A B B
14
SQSY
DQSY
MNT3
MNT2
SHOCK
FOK
SENS
SRDT
SCLK
SWDT
XLATCH
LIMITIN
REFLECT
PROTECT
CHUCK IN
PACK OUT
PLAY P
REC P
LDON
WRPWR
MOD
LOAD IN
LOAD OUT
LOAD V
SDA
SCL
DIG-RST
IC1
IC2
2
12
84 85
89
XINT
SCTX
SYSTEM CONTROL
DSEL A
DSEL B
IC401
POWER DOWN
6
4
5
CNTRL A1 OUT
CNTRL A1 IN
AMUTE
TIMER SW
SOURCE SW
REMOCOM
FLCLK
FLDATA
VBAT
SYSTEM-RST
12
10
FLCS
8
KEY0
KEY1
KEY2
JOG1
JOG0
FS32
FS44
FS48
BUFFER
IC355
3
3
IC353
IC354
DIGITAL
COAXIAL IN
AMP
Q353
MATRIX
SW
IC730
OPTICAL IN1
OPTICAL IN2
SIRCS
RECEIVER
IC731
S1
S36
D1
D16
DIGITAL
DIGITAL
4
39
40
55
LRCK
512FS
SCLK
XLAT
D701 - 703
D750
POWER
BCK
27
18
16 DPD
SWDT
12
DADT
INIT
ADDT
J350
CONTROL A1
FL730
FLUORESCENT
INDICATOR
TUBE
10 11
25 28 26
AC
A/D, D/A CONVERTER
I/O
MCK1
15
22
35 36
XOUT
256CK
I/O
CPU INTERFACE
19 20 21
+3V
(BD)
X301
22MHz
IC304
XIN
5
+3V REG
IC192
SYS +3.3V
PH +5V
ANA +5V
A/D
CONVERTER
D/A
CONVERTER
1
INLM
INLP
INRP
INRM
+ L1
– L2
+ R1
– R2
LINE AMP
IC301
55
56
1
R-ch
2
41
39
30
R-ch
32
BUFFER
IC101
1
13
12 3
9
11
26 25
17
16
MUTE
2
22
4
23
8
26
610 5
25
15
4
CURRENT PULSE
IC303
ECL
SWITCHING
CIRCUIT
2324
FRONT-END
IC302
LPF 1
14
IC102
36
LPF
35
MUTE
SW
Q301
RV780
REC LEVEL
57
MUTE
Q101
R-ch
RV770
PHONES LEVEL
• R CH is omitted.
R-ch
R-ch
HEADPHONE
AMP
IC770
5 7
L
R
R
L
R-ch
IN
J301
LINE
(ANALOG)
OUT
J771
PHONES
• Signal path
: PB
: REC
: PB (Digital out)
: REC (Digital in)
+B
+6V REG
SWITCHING REG
IC901
S. RESET
P. DOWN
+5V REG
+3.3V REG
+5V REG
BACK UP
ON/OFF SW
8212 9
POWER
Q350, 402
1
5
4
6
+6V
3
7
–6V
–32V
IC903
–6V REG
–32V REG
31
+B
–B
IC904
IC902
RECT
D905,
906
RECT
D903,
904
RECT
D901,
902
RECT
D907,
908
23
13
AC
FL730
AC
T901
POWER
TRANSFORMAER
AEP, UK
MAIN POWER
S951
AC
IN
13
11
J352
9
83DA-RST
46
17
D351
93
3
4
5
9
10
50
51
54
LED DRIVE
55
Q701 - 703
56
LED DRIVE
43LED0
Q750,751
14
3 RM
DISPLAY DRIVER
71
62
72
73
13
23
20
36
STB
SCK
63
SDATA
61
CS
RST
60
XOUT
XIN
27 28
09
X402
12MHz
XIN-T
25 24
X401
32.768KHz
XOUT-T
— 39 — — 40 —
Page 39

Page 40

Page 41

Page 42

Page 43

Page 44

Page 45

Page 46
Page 47

6-12. IC BLOCK DIAGRAMS
IC101 CXA2523R
MORFO47MORFI46RFO45OPN
48
–
+
RFA1
+
–
1I
2J
CVB
3VC
4A
IVR
5B
IVR
6C
IVR
7D
IVR
8E
IVR
9F
IVR
GSW IV
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
RFA2
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
AA
BB
CC
DD
EE
FF
1
2
1
2
GRVA
HLPT
CFST
GRV
+
–
+
–
FBAL
OPO43ADDC42COMPP41COMPO40AGCI39RF AGC38RF37PEAK
44
USROP
EE'
–1
–2
–2
–1
+
+
+
+
+
+
–
–
–
–
+
+
FF'
+
–
BPF3T
PTGR
ABCDA
FEA
BPF22
WBL
ATA
WBL
–
+
–
+
EFB TESW
RF AGC EQ
USRC
PEAK
BOTTOM
WBL
PTGR
ADIP
AGC
PEAK3T
P-P
WBL
3T
EQ
3T
3T WBL
PBH
DET
–1
–2
–1
–2
DET
TEMP
EQ
BPFC
SEA
TEA
VI CONV
TG
TG
36
BOTM
35
ABCD
34
FE
33
AUX
32 ADFG
31 ADAGC
30 ADIN
29 ADFM
28 SE
27 CSLED
26 TE
25 WBLADJ
15
AUXSW
TEMPR
COMMAND
SCRI - PARA
DECODE
17
16
SWDT
SCLK
BGR
VREF
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
XLAT
XSTBY
F0CNT
VREF
EQADJ
3TADJ
VCC
10PD
11APC
12APCREF
+
–
+
–
14
13
GND
TEMPI
— 61 —
Page 48

IC121 CXD2650R
100
1
MNT0
2
MNT1
MNT2
MNT3
SWDT
SCLK
XLAT
SRDT
SENS
XRST
SQSY
DQSY
RECP
XINT
TX
OSCI
OSCO
XTSL
RVDD
RVSS
DIN
DOUT
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
MONITOR
CONTROL
CPU I/F
PROCESSOR
GENERATOR
EFMO
DVSS
TEST3
TEST2
TEST1
99 98 97 96 95 94 93
SUBCODE
CLOCK
TEST0
EACH
BLOCK
DEMODULATOR/
DECODER
EACH
BLOCK
EACH
BLOCK
SPFD
SPINDLE
SERVO
ADIP
SPRD
DIGITAL
AUDIO
SFDR91SRDR90FS489KRDR88FFDR87DVDD86TFDR85TRDR84LDDR83APCREF82DTRF81CKRF80XLRF79F0CNT78ADFG77APC76DCHG
92
PWM
SHOCK RESISTANT
MEMORY CONTROLLER
SAMPLING
I/F
RATE
CONVERTER
GENERATOR
SERVO
DSP
APC
CONVERTER
AUTO
A/D
SEQUENCER
ANALOG
DECODER
ENCODER/
EFM/ACIRC
COMP
MUX
PLL
75
AUX2
74
TE
73
SE
72
AVSS
71
ADRB
70
ADRT
69
AVDD
68
ADIO
67
VC
66
AUX1
65
FE
64
ABCD
63
BOTM
62
PEAK
61
CLTV
60
FILO
59
FILI
58
PCO
57
PDO
56
AVSS
55
RFI
54
BIAS
53
AVDD
52
ASYI
51
ASYO
ADDT
DADT
LRCK
23
24
25
28
26
27
XBCK
DVDD
FS256
ATRAC
ENCODER/DECODER
ADDRESS/DATA BUS A00 - A11, D0 - D3
40
39
A1138A0837A0736A0635A0534A0433A1032A0031A0130A0229A03
DVSS
DRAM
50
44
43
42
41
A09
XOE
XCAS
XRAS
XWE
49D348D247D046D145
MVCI
— 62 —
Page 49

IC152 BH6511FS-E2
CAPA–
CAPA+
IN2R
IN2F
VM2
OUT2F
PGND2
OUT2R
VM12
OUT1R
PGND1
OUT1F
VM1
IN1F
IN1R
32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17
AMP
PGND4
IN4F
AMP
AMP
VM4
OUT4F
INTERFACE
CHARGE
PUMP.
OSC
INTERFACE
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
VG
GND
IN4R
OUT4R
VM34
AMP
OUT3R
PGND3
AMP
AMPAMPAMP
OUT3F
PREDRIVEPREDRIVE
PREDRIVEPREDRIVE
VM3
INTERFACE
INTERFACE
IN3F
IN3R
IC171 XL24C01AF-E2
V
PSB
DD
V
DD
PSB
1
A0
7BIT
A1
A2
GND
ADDRESS
2
DECODER
3
HIGH VOLTAGE
4
GENERATION CIRCUIT
7BIT
CONTROL CIRCUIT
IC192 L88MS33T-TL
START UP
CIRCUIT
1024 BIT EEPROM ARRAY
SLAVE WORD
ADDRESS RESISTOR
START STOP
VOLTAGE
DET
REFERENCE
VOLTAGE
ACK
8BIT
DATA
RESISTOR
ERROR
AMP
8
CC
V
TEST
7
6
SCL
5
SDA
ON/OFF
CONTROL
1 2 3 4 5
VIN STB GND CN VOUT
PROTECTOR
CURRENT
LIMITER
— 63 —
Page 50

IC302 CXA8065S
IC303 CXA8055M
LINE02
PMUTE
LINE01
MUTE
LINE/MIC
V
+D/A1
+D/A1
+D/AO1
LP1N1
LPOUT1
GND1
LPOUT2
LPIN2
D/AO2
–D/A2
+D/A2
V
V
2.35k
2.35k
36
LINE1
EE
V
EE
35
MIC1
34
33
SW01
SWI1
32
–A/D1
31
30
INV1
+A/D1
29
A/DREF
28
27
VREF
+A/D2
26
INV2
25
24
–A/D2
23
SWI2
SWO2
22
MIC2
21
GND2
20
19
LINE2
CIREF
AGND
IOR–
IOR+
C7R
AVEES
AVEES
C4R
DVEE
C1R
DGND
1N1–R
1N1+R
1N2+R
1N2–R
1
NC
2
3
NC
4
5
6
7
C5
8
C6
9
10
11
12
C3
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
NC
20
21
SWITCHING
CONSTANT
CONTROL
CIRCUIT
ECL
CIRCUIT
ANALOG
VOLUME
CONTROL
CIRCUIT
LOGIC
REFERENCE
VOLTAGE
CIRCUIT
CONSTANT
CONTROL
CIRCUIT
ECL
SWITCHING
CIRCUIT
RIREF
42
VREF
41
VCNT
40
AGND
39
38
AV
CC
37
NC
IOL–
36
IOL+
35
C7L
34
AVEES
33
AVEES
32
C4L
31
EE
DV
30
29
DV
CC
28
C1L
27
DGND
26
1N1–L
1N1+L
25
NC
24
1N2+L
23
1N2–L
22
1
2
3
4
5
DD
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
CC
+
–
+
–
13.2k
13.2k
13.2k
–
+
–
+
CC
V
+
–
–
+
–
+
+
–
+
–
+
–
–
+
IC304 CXD8607N
INRP
1
INRM
2
REFI
3
AVDD
4
AVSS
5
APD
6
NU
7
NU
8
TEST1
9
LRCK1
10
BCK1
11
ADDT
12
V35A
13
VSS1 (LF)
14
MCKI
15
DPD
16
VSS2(LF)
17
INIT
18
MODE
19
SHIFT
20
LATCH
21
256CK
22
V35D
23
VSS2
24
512CK
25
BCK2
26
DADT
27
LRCK2
28
+
–
INTERFACE
MODULATOR MODULATOR
DECIMATION
FILTER
LOW CUT
FILTER
ATT PLM
CPU
I/O
ATT PLM
I/O
OVER
SAMP
FILTER
OVER
SAMP
FILTER
DECIMATION
FILTER
LOW CUT
FILTER
SHAPER
SHAPER
MOIZE
NOIZE
VOLTAGE
REFERENCE
+
–
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
INLP
INLM
REFO
LVSS
LVDD
AVSS(LF)
NU
NU
VSS1(LF)
TEST3
TEST2
VSS1
VDD1
VDD1
VDD2
L1
AVDDL
L2
AVSSL
XVSS
XIN
XOUT
XVDD
AVSSR
R2
AVDDR
R1
VDD2
— 64 —
Page 51
IC351 LB1641
PRE
DRIVER
INPUT LOGIC BLOCK
21
GND OUT1 P1 VZ IN1 IN2 V
IC356 SN74HC153AN
DATA INPUTS
STROBE
CC
V
16
12345678
STROBE1GB
A
2G
15 14 13 12
SELECT
2C3 2C2 2C1 2C0
SELECT
2C3 2C2
2G
1G
1C3 1C2 1C1 1C0 1Y
1C3 1C2 1C1 1C0 OUTPUT1YGND
DATA INPUTS
11 10
2C1 2C0 2Y
BABA
BABA
OUTPUT
2Y
9
CC
1VCC2 P2 OUT2
109876543
— 65 —
Page 52
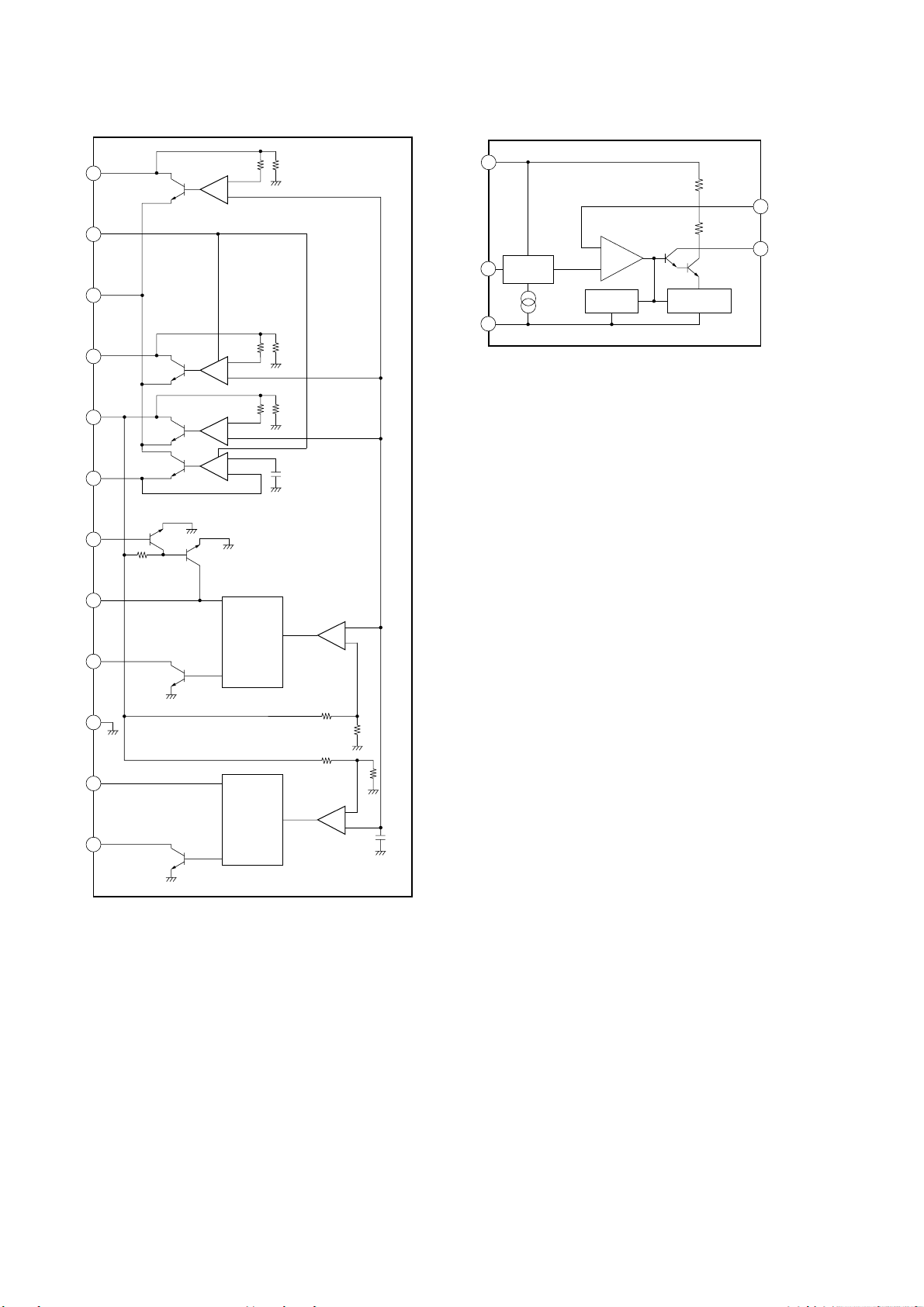
IC901 LA5620
PH5
1
2
STBY
3
CC
V
ANA5
4
5
SYS3.3
6
BACK
AC
7
IC902 M5293L
GND
2
–
+
+
ON/OFF
–
+
–
+
–
+
3.3V
VOLTAGE
1
IN
REFERENCE
4
–
OVERHEAT
PROTECTION
5k
27k
OVERCURRENT
LIMITTER
REFERENCE
5
VOLTAGE
3
OUT
CD1
P. DOWN
GND
CD2
S. RESET
8
DELAY
CIRCUIT
9
10
11
DELAY
CIRCUIT
12
–
+
–
+
VREF
— 66 —
Page 53

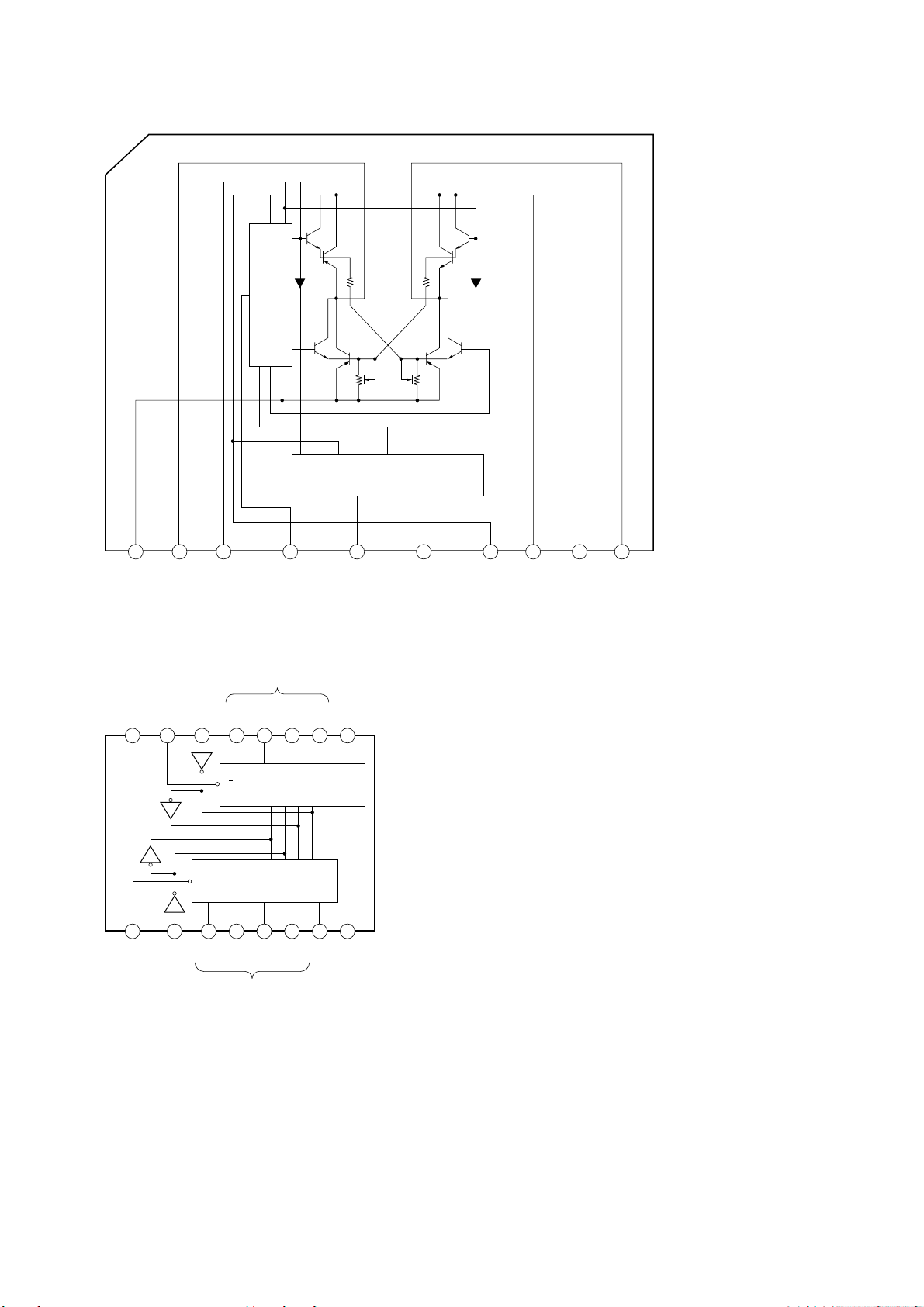
6-13. IC PIN FUNCTIONS
• IC101 RF Amplifier (CXA2523R)
Pin No.
1
2
3
4 to 9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
Pin Name I/O Function
I
J
VC
A to F
PD
APC
APCREF
GND
TEMPI
TEMPR
SWDT
SCLK
XLAT
XSTBY
F0CNT
VREF
EQADJ
3TADJ
Vcc
WBLADJ
TE
CSLED
SE
ADFM
ADIN
ADAGC
ADFG
AUX
FE
ABCD
BOTM
PEAK
RF
RFAGC
AGCI
COMPO
COMPP
ADDC
OPO
OPN
RFO
MORFI
MORFO
I
I-V converted RF signal I input
I
I-V converted RF signal J input
O
Middle point voltage (+1.5V) generation output
I
Signal input from the optical pick-up detector
I
Light amount monitor input
O
Laser APC output
I
Reference voltage input for setting laser power
—
Ground
I
Temperature sensor connection
O
Reference voltage output for the temperature sensor
I
Serial data input from the CXD2650R
I
Serial clock input from the CXD2650R
I
Latch signal input from the CXD2650R “L”: Latch
I
Stand by signal input “L”: Stand by
I
Center frequency control voltage input of BPF22, BPF3T, EQ from the CXD2650R
O
Reference voltage output (Not used)
I/O
Center frequency setting pin for the internal circuit EQ
I/O
Center frequency setting pin for the internal circuit BPF3T
—
+3V power supply
I/O
Center frequency setting pin for the internal circuit BPF22
O
Tracking error signal output to the CXD2650R
—
External capacitor connection pin for the sled error signal LPF
O
Sled error signal output to the CXD2650R
O
FM signal output of ADIP
I
ADIP signal comparator input ADFM is connected with AC coupling
—
External capacitor connection pin for AGC of ADIP
O
ADIP duplex signal output to the CXD2650R
O
3 signal/temperature signal output to the CXD2650R (Switching with a serial command)
I
O
Focus error signal output to the CXD2650R
O
Light amount signal output to the CXD2650R
O
RF/ABCD bottom hold signal output to the CXD2650R
O
RF/ABCD peak hold signal output to the CXD2650R
O
RF equalizer output to the CXD2650R
—
External capacitor connection pin for the RF AGC circuit
I
Input to the RF AGC circuit The RF amplifier output is input with AC coupling
O
User comparator output (Not used)
I
User comparator input (Fixed at “L”)
I/O
External capacitor pin for cutting the low band of the ADIP amplifier
O
User operation amplifier output (Not used)
I
User operation amplifier inversion input (Fixed at “L”)
O
RF amplifier output
I
Groove RF signal is input with AC coupling
O
Groove RF signal output
• Abbreviation
APC: Auto Power Control
AGC: Auto Gain Contr ol
— 67 —
Page 54

• IC121 Digital Signal Processor, Digital Servo Signal Processor, EFM/ACIRC Encoder/Decoder,
Shock-proof Memory Controller, ATRAC Encoder/Decoder, 2M Bit DRAM (CXD2650R)
FunctionPin No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29 to 32
33
34 to 38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
Pin Name I/O
MNT0 (FOK)
MNT1 (SHCK)
MNT2 (XBUSY)
MNT3 (SLOC)
SWDT
SCLK
XLAT
SRDT
SENS
XRST
SQSY
DQSY
RECP
XINT
TX
OSCI
OSCO
XTSL
DVDD
DVSS
DIN
DOUT
ADDT
DADT
LRCK
XBCK
FS256
DVDD
A03 to A00
A10
A04 to A08
A11
DVSS
XOE
XCAS
A09
XRAS
XWE
FOK signal output to the system control
O
“H” is output when focus is on
Track jump detection signal output to the system control
O
Monitor 2 output to the system control
O
Monitor 3 output to the system control
O
Writing data signal input from the system control
I
Serial clock signal input from the system control
I (S)
Serial latch signal input from the system control
I (S)
Reading data signal output to the system control
O (3)
Internal status (SENSE) output to the system control
O (3)
Reset signal input from the system control “L”: Reset
I (S)
Subcode Q sync (SCOR) output to the system control
O
“L” is output every 13.3 msec. Almost all, “H” is output
Digital In U-bit CD format subcode Q sync (SCOR) output to the system control
O
“L” is output every 13.3 msec Almost all, “H” is output
Laser power switching input from the system control “H”: Recording, “L”: Playback
I
Interrupt status output to the system control
O
Recording data output enable input from the system control
I
System clock input (512Fs=22.5792 MHz)
I
System clock output (512Fs=22.5792 MHz) (Not used)
O
System clock frequency setting “L”: 45.1584 MHz, “H”: 22.5792 MHz (Fixed at “H”)
I
+3V power supply (Digital)
—
Ground (Digital)
—
Digital audio input (Optical input)
I
Digital audio output (Optical output)
O
Data input from the A/D converter
I
Data output to the D/A converter
O
LR clock output for the A/D and D/A converter (44.1 kHz)
O
Bit clock output to the A/D and D/A converter (2.8224 MHz)
O
11.2896 MHz clock output (Not used)
O
+3V power supply (Digital)
—
O
O
DRAM address output (Not used)
O
O
Ground (Digital)
—
Output enable output for DRAM (Not used)
O
CAS signal output for DRAM (Not used)
O
Address output for DRAM (Not used)
O
RAS signal output for DRAM (Not used)
O
Write enable signal output for DRAM (Not used)
O
* I (S) stands for Schmidt input, I (A) for analog input, O (3) for 3-state output, and O (A) for analog output in the column I/O
— 68 —
Page 55

Pin No.
46
47
48, 49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
Pin Name I/O
D1
D0
D2, D3
MVCI
ASYO
ASYI
AVDD
BIAS
RFI
AVSS
PDO
PCO
FILI
FILO
CLTV
PEAK
BOTM
ABCD
FE
AUX1
VC
ADIO
AVDD
ADRT
ADRB
AVSS
SE
TE
AUX2
DCHG
APC
ADFG
F0CNT
XLRF
CKRF
DTRF
APCREF
LDDR
TRDR
I/O
I/O
I/O
I (S)
O
I (A)
—
I (A)
I (A)
—
O (3)
O (3)
I (A)
O (A)
I (A)
I (A)
I (A)
I (A)
I (A)
I (A)
I (A)
O (A)
—
I (A)
I (A)
—
I (A)
I (A)
I (A)
I (A)
I (A)
I (S)
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
Function
Data input/output for DRAM (Not used)
Clock input from an external VCO (Fixed at “L”)
Playback EFM duplex signal output
Playback EFM comparator slice level input
+3V power supply (Analog)
Playback EFM comparator bias current input
Playback EFM RF signal input
Ground (Analog)
Phase comparison output for the clock playback analog PLL of the playback EFM
(Not used)
Phase comparison output for the recording/playback EFM master PLL
Filter input for the recording/playback EFM master PLL
Filter output for the recording/playback EFM master PLL
Internal VCO control voltage input for the recording/playback EFM master PLL
Light amount signal peak hold input from the CXA2523R
Light amount signal bottom hold input from the CXA2523R
Light amount signal input from the CXA2523R
Focus error signal input from the CXA2523R
Auxiliary A/D input
Middle point voltage (+1.5V) input from the CXA2523R
Monitor output of the A/D converter input signal (Not used)
+3V power supply (Analog)
A/D converter operational range upper limit voltage input (Fixed at “H”)
A/D converter operational range lower limit voltage input (Fixed at “L”)
Ground (Analog)
Sled error signal input from the CXA2523R
Tracking error signal input from the CXA2523R
Auxiliary A/D input (Fixed at “L”)
Connected to +3V power supply
Error signal input for the laser digital APC (Fixed at “L”)
ADIP duplex FM signal input from the CXA2523R (22.05 ± 1 kHz)
0 control output to the CXA2523R
Filter f
Control latch output to the CXA2523R
Control clock output to the CXA2523R
Control data output to the CXA2523R
Reference PWM output for the laser APC
PWM output for the laser digital APC (Not used)
Tracking servo drive PWM output (–)
• Abbreviation
EFM: Eight to Fourteen Modulation
PLL : Phase Locked Loop
VCO: Voltage Controlled Oscillator
— 69 —
Page 56

Pin No.
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96 to 98
99
100
• Abbreviation
EFM: Eight to Fourteen Modulation
Pin Name I/O
TFDR
DVDD
FFDR
FRDR
FS4
SRDR
SFDR
SPRD
SPFD
TEST0
TEST1 to TEST3
DVSS
EFMO
Tracking servo drive PWM output (+)
O
+3V power supply (Digital)
—
Focus servo drive PWM output (+)
O
Focus servo drive PWM output (–)
O
176.4 kHz clock signal output (X’tal) (Not used)
O
Sled servo drive PWM output (–)
O
Sled servo drive PWM output (+)
O
Spindle servo drive PWM output (–)
O
Spindle servo drive PWM output (+)
O
I (S)
Test input (Fixed at “L”)
I
Ground (Digital)
—
EFM output when recording
O
Function
— 70 —
Page 57

• IC307 A/D, D/A converter (CXD8607N)
Pin No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
Pin Name I/O Function
INRP
INRM
REFI
DD
AV
AVss
APD
NU
NU
TEST1
LRCK1
BCK1
ADDT
35A
V
VSS1 (LF)
MCKI
DPD
SS2 (LF)
V
INIT
MODE
SHIFT
LATCH
256CK
35D
V
VSS2
512CK
BCK2
DADT
LRCK2
DD2
V
R1
VDDR
A
R2
SSR
AV
XVDD
XOUT
XIN
SS
XV
AVSSL
L2
DDL
AV
I
I
I
—
—
I
—
—
I
I
I
O
—
—
I
I
—
I
I
I
I
O
—
—
O
I
I
I
—
O
—
O
—
—
O
I
—
—
O
—
Rch analog (+) input
Rch analog (–) input
A/D reference voltage input (+3.2V)
+5V power supply (A/D, analog)
Ground (A/D, analog)
A/D analog block power down “L”: Power down
Not used
Test pin (Fixed at “L”)
A/D LRCK input
A/D BCK input
A/D data output
+3.3V power supply
Ground (A/D, digital)
A/D master clock input (256 fs)
A/D digital block power down “L”: Power down/reset
Ground (D/A, digital)
D/A initialize “L”: Initialize
Mode flag input
Shift clock input
Latch clock input
256 fs clock output
+3.3V power supply
Ground (D/A, digital)
512 fs clock output
D/A BCK input
D/A data input
D/A LRCK input
+5V power supply (D/A, digital)
Rch PLM output 1
+5V power supply (D/A, Rch, analog)
Rch PLM output 2
Ground (D/A, Rch, analog)
+5V power supply (X’tal)
X’tal oscillation output (22 MHz)
X’tal oscillation input (512 fs ) (22 MHz)
Ground (X’tal)
Ground (D/A, Lch, analog)
Lch PLM output 2
+5V power supply (D/A, Lch, analog)
— 71 —
Page 58

Pin No.
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
Pin Name I/O
L1
DD2
V
VDD1
VDD1
VSS1
TEST2
TEST3
SS1 (LF)
V
NU
NU
SS (LF)
AV
LVDD
LVSS
REFO
INLM
INLP
O
Lch PLM output 1
—
+5V power supply (D/A, digital)
—
+5V power supply (A/D, digital)
—
—
Ground (A/D, digital)
I
Test pin (Fixed at “L”)
I
—
Ground (A/D, digital)
—
Not used
—
—
Ground (A/D, analog)
—
+5V power supply (A/D, buffer)
—
Ground (A/D, buffer)
O
A/D reference voltage output (+3.2V)
I
Lch analog (–) input
I
Lch analog (+) input
Function
— 72 —
Page 59

• IC401 System Control (RU8X11AMF-0113)
Pin No.
1
2
3 to 5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
Pin Name I/O Function
DAOUT 0
DAOUT 1
KEY 0 to KEY 2
CHUCK IN
PACK IN
PACK OUT
TIMER SW
SOURCE SW
(AVSS)
XINT
POWER DOWN
REMOCON
SQSY
DQSY
CNTRL A1 IN
—
—
SYSTEM-RST
(TEST)
3.3V
VBAT
XOUT -T
XIN-T
GND
XOUT
XIN
GND
(S1)
—
SENS
SHOCK
REC/OTHER
—
STB
REC P
PLAY
LOAD V
—
O
O
I
I
I
I
I
I
—
I
I
I
I
I
I
O
O
I
I
—
—
O
I
—
O
I
—
O
O
I
I
I
I
O
I
I
O
O
Test pin. C1 is output when test mode (Not used)
Test pin. ADER is output when test mode (Not used)
Key input pin (D/A input)
Detection input from the chucking-in switch “L”: Chucking
Detection input from the disc detection switch
Detection input from the loading out switch. Loaded out position: “L”, Others: “H”
Key input pin (D/A input)
Ground (Analog)
Interrupt status input from the CXD2650R
POWER DOWN signal input “L”: Down
Remote control signal interrupt input
ATP address sync or subcode Q sync (SCOR) input from the CXD2650R
“L” is input every 13.3 msec Almost all, “H”
Digital-In U-bit CD format subcode Q sync (SCOR) input from the CXD2650R
“L” is input every 13.3 msec Almost all, “H”
CONTROL A1 signal input
Not used
System reset signal input
For several hundreds msec after the power supply rises, “L” is input, then it changes to “H”
Test pin (Fixed at “L”)
+3.3V power supply
Power supply pin to RTC (clock) and RAM
Clock output (32.768 kHz) (For clock)
Clock input (32.768 kHz) (For clock)
Ground
Main clock output (12 MHz)
Main clock input (12 MHz)
Ground
Not used
Internal status (SENSE) input from the CXD2650R
Track jump signal input from the CXD2650R
BEEP sound output switching signal input (Not used)
Not used
Strobe signal output to the power supply circuit Power supply ON: “H”, stand by: “L”
Detection signal input from the recording position detection switch
Detection signal input from the playback position detection switch
Loading motor voltage control output
Not used
— 73 —
Page 60

Pin No.
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50, 51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
Pin Name I/O Function
MNT2
MNT3
LED0
—
—
CNTL A1 OUT
GND
+3.3V
—
JOG 1, JOG 0
SDA
SCL
FS32
FS44
FS48
—
—
—
SA/SW
—
—
CLKSET0
CLKSET1
GND
3.3V
SCLK
SWDT
SRDT
—
FLCLK
FLDATA
FLCS
—
LDON
PIT/GROOVE
FOK
—
LOCK
WRPWR
I
Monitor 2 input from the CXD2650R
I
Monitor 3 input from the CXD2650R
O
Drive output to the POWER ON/STANDBY display LED
I
Power supply ON: “H”, stand by: “L”
I
Not used
O
CONTROL A1 signal output
—
Ground
—
+3.3V power supply
I
Input from the BEEP sound output ON/OFF switch (Not used)
I
JOG dial pulse input from the rotary encoder
I/O
Data signal input/output pin with the backup memory
O
Clock signal output to the backup memory
O
O
Drive output to the DIGITAL INPUT LED “L”: Light
O
I
Terminal for switching the used model
I
I
Not used
O
Audio bus/remote control switching signal output (Not used)
I
Not used
O
I
Clock destination select pin (Fixed at “L”)
I
—
Ground
—
+3.3V power supply
O
Clock signal output to the serial bus
O
Writing data signal output to the serial bus
I
Reading data signal input from the serial bus
I
Not used
O
Serial clock signal output to the display driver
O
Serial data signal output to the display driver
O
Chip select signal output to the display driver
I
Not used
O
Laser ON/OFF control output “H”: Laser ON
I
Pit/groove detection input “H” is input for the playback only disc or T OC area (Not used)
FOK signal input from the CXD2650R
I
“H” is input when focus is on
I
Not used
O
Not used
O
Laser power switching signal output to the optical pick-up and CXD2650R
— 74 —
Page 61

Pin No.
81
82
83
84, 85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
Pin Name I/O Function
DIG-RST
BEEP
DA-RST
DSEL A, DSEL B
MOD
REC/PB
—
SCTX
XLATCH
—
—
AMUTE
LOAD OUT
LOAD IN
LIMITIN
PROTECT
REFLECT
GND
+3.3V
Reset signal output to the CXD2650R and motor driver Reset: “L”
O
BEEP PWM output (Not used)
O
Reset signal output to the D/A, A/D converter Reset: “L”
O
Digital input selection signal output
O
Laser modulation switching signal output
Playback power: “L”, stop: “H”
Recording power:
O
O
Not used
O
Writing data transmission timing output to the CXD2650R
O
Shared with the magnetic head ON/OFF output
Latch signal output to the serial bus
O
Not used
O
Not used
I
Line out muting output
O
O
Loading motor control output *1
O
Detection input from the limit switch
I
Sled limit-In: “L”
Recording-protection claw detection input from the protection detection switch
I
Protect: “H”
Disk reflection rate detection input from the reflect detection switch
I
Disk with low reflection rate: “H”
Ground
—
+3.3V power supply
—
0.5S
2S
*1 Loading motor control
Operation
Pin
LOAD IN 95 pin
LOAD OUT 94 pin
IN
“H”
“L”
OUT
“L”
“H”
Brake
“H”
“H”
— 75 —
Page 62

NOTE:
• Items marked “*” are not stocked since they are
seldom required for routine service. Some delay
should be anticipated when ordering these items.
• The mechanical parts with no reference number in
the exploded views are not supplied.
7-1. CASE AND MAIN BOARD SECTION
6
6
6
SECTION 7
EXPLODED VIEWS
• Hardware (# mark) list and accessories and packing materials are given in the last of this parts list.
• Abbreviation
CND : Canadian model
#4
7
9
#4
10
The components identified by mark !
or dotted line with mark ! are critical
for safety.
Replace only with part number
specified.
Les composants identifiés par une
marque ! sont critiques pour la sécurité.
Ne les remplacer que par une
piéce portant le numéro spécifié.
AEP model
12
#4
US, CND model
12
UK model
11
12
MDM-3A
#1
not supplied
#4
#5
#4
#4
#4
#4
#5
#4
5
not supplied
6
#3
#4
8
T901
8
#4
#4
4
#4
13
3
not supplied
not supplied
2
1
#4
Front panel
#4
#4
not supplied
#4
2
1
not supplied
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
1 X-4947-389-1 FOOT ASSY (F50150S)(AEP,UK)
1 X-4947-390-1 FOOT ASSY (F50150S)(US,CND)
2 4-983-762-02 CUSHION
3 1-777-278-11 WIRE (FLAT TYPE)(19 CORE)
4 1-777-275-11 WIRE (FLAT TYPE)(29 CORE)
* 5 1-663-118-11 AC BOARD
6 3-363-099-01 SCREW (CASE 3 TP2)
7 4-980-420-21 CASE (409526)
8 4-886-821-11 SCREW, S TIGHT, +PTTWH 3X6
* 9 4-985-444-11 PANEL, BACK (AEP)
* 9 4-985-444-21 PANEL, BACK (UK)
— 76 —
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
* 9 4-985-444-31 PANEL, BACK (US)
* 9 4-985-444-41 PANEL, BACK (CND)
* 10 4-923-873-01 BRACKET, CORD STOPPER
* 11 3-703-244-00 BUSHING (2104), CORD
! 12 1-558-568-21 CORD, POWER (AEP)
! 12 1-559-583-21 CORD, POWER (US,CND)
! 12 1-696-586-11 CORD, POWER (UK)
* 13 A-4699-578-A MAIN BOARD, COMPLETE (US,CND)
* 13 A-4699-585-A MAIN BOARD, COMPLETE (AEP,UK)
! T901 1-431-239-11 TRANSFORMER, POWER (US,CND)
! T901 1-431-240-11 TRANSFORMER, POWER (AEP,UK)
Page 63

7-2. FRONT PANEL SECTION
52
not supplied
Supplied
with J771
Supplied
with RV770
53
51
65
55
54
J771
RV770
56
65
70
63
72
69
71
65
59
65
65
#2
68
not supplied
60
57
62
73
FL730
66
61
75
74
67
RV780
Supplied
with RV780
58
73
not
supplied
63
65
65
65
76
65
65
64
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
51 4-985-442-11 PANEL, FRONT
52 4-979-587-01 EMBLEM (NO.5), SONY
53 4-985-454-01 INDICATOR (B)
54 4-950-189-01 KNOB (A)(VOL)
55 X-4947-592-1 BASE ASSY, PANEL
56 4-985-451-01 PLATE, INDICATION
57 3-356-957-01 SPRING
58 3-382-627-01 SPRING, RING
59 4-983-657-01 KNOB (AMS)
60 4-985-453-01 INDICATOR (A)
61 3-382-634-01 KNOB (REC-L)
62 3-382-635-01 KNOB (REC-R)
63 3-917-216-11 KNOB (TIMER)
* 64 A-4699-575-A PANEL (R) BOARD, COMPLETE (US,CND)
* 64 A-4699-582-A PANEL (R) BOARD, COMPLETE (AEP,UK)
— 77 —
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
65 4-951-620-01 SCREW (2.6X8), +BVTP
* 66 1-663-116-11 REC-VOL BOARD
67 4-985-449-11 BUTTON (EDIT)
68 4-985-447-11 BUTTON (MODE)
69 4-985-446-11 BUTTON (POWER)
* 70 1-663-115-11 HP BOARD
* 71 4-972-608-01 HOLDER (DIA. 5), LED
* 72 A-4699-573-A PANEL (L) BOARD, COMPLETE (US,CND)
* 72 A-4699-580-A PANEL (L) BOARD, COMPLETE (AEP,UK)
73 2-389-320-01 CUSHION
* 74 4-971-854-01 HOLDER (FL)
* 75 A-4699-574-A DISPLAY BOARD, COMPLETE (US,CND)
* 75 A-4699-581-A DISPLAY BOARD, COMPLETE (AEP,UK)
76 1-777-846-11 WIRE (FLAT TYPE)(23 CORE)
FL730 1-517-587-11 INDICATOR TUBE, FLUORESCENT
Page 64

7-3. MECHANISM DECK SECTION (1) (MDM-3A)
not supplied
#1
not supplied
#1
#1
204
not supplied
#1
205
201
202
203
201
202
not supplied
209
#1
206
207
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
201 4-628-167-01 SCREW, STEP
202 4-987-327-01 INSULATOR
203 4-986-959-01 WASHER, STOPPER
204 4-987-736-01 SHAFT (SHUTTER)
205 X-4947-825-1 SHUTTER ASSY
— 78 —
208
not supplied
#6
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
206 1-660-966-11 OP RELAY FLEXIBLE BOARD
* 207 A-4699-092-A BD BOARD, COMPLETE
208 1-777-517-11 WIRE (FLAT TYPE)(15 CORE)
209 4-987-910-01 SPRING, TORSION (O/C)
Page 65

Ver 1.1
7-4. MECHANISM DECK SECTION (2) (MDM-3A)
252
#1
#7
not supplied
253
not supplied
#1
254
271
#8
#7
272
251
261
255
273
259
260
#9
274
256
257
258
#8
262
M901
263
M903
269
HR901
#9
M902
264
266
265
267
Le
The components identified by
mark 0 or dotted line with
268
270
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
251 A-4672-138-E SLIDER ASSY, COMPLETE
* 252 4-983-439-01 BRACKET (DAMPER)
253 3-953-235-01 DAMPER, OIL
254 4-979-901-21 LEVER (LIMITTER)
255 3-342-375-11 SCREW (M1.7X1.4), SPECIAL
256 4-979-890-11 RETAINER (GEAR)
257 4-979-898-01 GEAR (LB)
258 4-979-899-01 GEAR (LC)
259 4-979-897-01 GEAR (LA)
260 4-979-885-01 LEVER (HEAD UP)
261 4-979-906-11 SPRING (LEAD SCREW)
262 4-984-556-01 SHAFT (MAIN SHAFT)
* 263 1-661-774-11 SW BOARD
264 A-3304-200-A SCREW ASSY, LEAD
0 are critical for safety.
Replace only with part number
specified.
265 4-963-914-02 RACK (INSERTER)
266 3-366-890-11 SCREW (M1.4)
0267 8-583-028-01 OPTICAL PICK-UP (KMS-260A/J1N)
268 4-987-061-01 SPACER (RACK)
269 4-988-560-01 SCREW (P1.7X6)
270 4-955-841-21 SCREW
* 271 4-983-437-01 SLIDER (CAM)
* 272 4-983-511-02 PIN (OUTSERT)
273 4-983-435-04 CHASSIS (OUTSERT), MECHANISM
274 X-4949-113-1 GEAR (LA) ASSY
HR901 1-500-396-11 HEAD, OVER WRITE
M901 A-4672-135-A MOTOR ASSY, SPINDLE
M902 A-4672-133-A MOTOR ASSY, SLED
M903 A-4672-134-A MOTOR ASSY, LOADING
mark
s composants identifiés par
une marque 0 sont critiq
la sécurité.
Ne les remplac
piéce portant
le numéro spécifié.
ues pour
er que par une
— 79 —
Page 66

AC
Note:
The components identified by mark !
or dotted line with mark ! are critical
for safety.
Replace only with part number specified.
Les composants identifiés par une
marque ! sont critiques pour la sécurité.
Ne les remplacer que par une
piéce portant le numéro spécifié.
When indicating parts by reference
number, please include the board
name.
BD
SECTION 8
ELECTRICAL PARTS LIST
• Due to standardization, replacements in the parts list
may be different from the parts specified in the
diagrams or the components used on the set.
• Items marked “*” are not stocked since they are
seldom required for routine service. Some delay
should be anticipated when ordering these items.
• RESISTORS
All resistors are in ohms
METAL: Metal-film resistor
METAL OXIDE: Metal Oxide-film resistor
F : nonflammable
• SEMICONDUCTORS
In each case, u: µ , for example:
uA...: µ A..., uPA...: µPA..., uPB...: µ PB...,
uPC...: µ PC..., uPD...: µ PD...
• CAPACITORS
uF : µ F
• COILS
uH : µ H
• Abbreviation
CND : Canadian model
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
* 1-663-118-11 AC BOARD
*********
< CAPACITOR >
! C951 1-113-920-11 CERAMIC 0.0022uF 20% 250V
! C952 1-113-925-11 CERAMIC 0.01uF 20% 250V
(AEP,UK)
! C953 1-113-920-11 CERAMIC 0.0022uF 20% 250V
! C954 1-113-920-11 CERAMIC 0.0022uF 20% 250V
(AEP,UK)
! C955 1-113-920-11 CERAMIC 0.0022uF 20% 250V
(AEP,UK)
! C956 1-113-920-11 CERAMIC 0.0022uF 20% 250V
(AEP,UK)
! C957 1-113-920-11 CERAMIC 0.0022uF 20% 250V
(AEP,UK)
< CONNECTOR >
* CN951 1-580-230-21 PIN, CONNECTOR (PC BOARD) 2P
CN952 1-564-321-00 PIN, CONNECTOR 2P
< GROUND PLATE >
* EP951 4-942-204-01 PLATE, GROUND (AEP,UK)
< LINE FILTER >
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
C111 1-164-344-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.068uF 10% 25V
C112 1-163-017-00 CERAMIC CHIP 0.0047uF 5% 50V
C113 1-107-682-11 CERAMIC CHIP 1uF 10% 16V
C115 1-164-489-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.22uF 10% 16V
C116 1-163-037-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.022uF 10% 25V
C117 1-164-004-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 25V
C119 1-104-851-11 TANTAL. CHIP 10uF 20% 10V
C121 1-126-206-11 ELECT CHIP 100uF 20% 6.3V
C122 1-164-232-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 50V
C123 1-163-038-91 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C124 1-163-038-91 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C127 1-163-038-91 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C128 1-164-232-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 50V
C129 1-107-823-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.47uF 10% 16V
C130 1-163-251-11 CERAMIC CHIP 100PF 5% 50V
C131 1-163-023-00 CERAMIC CHIP 0.015uF 5% 50V
C132 1-107-823-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.47uF 10% 16V
C133 1-163-017-00 CERAMIC CHIP 0.0047uF 5% 50V
C134 1-163-038-91 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C135 1-163-038-91 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C136 1-126-206-11 ELECT CHIP 100uF 20% 6.3V
C141 1-163-038-91 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C142 1-163-251-11 CERAMIC CHIP 100PF 5% 50V
C143 1-163-251-11 CERAMIC CHIP 100PF 5% 50V
C144 1-163-251-11 CERAMIC CHIP 100PF 5% 50V
! LF951 1-424-485-11 FILTER, LINE
< SWITCH >
! S951 1-762-764-11 SWITCH, POWER (MAIN POWER)(AEP,UK)
**************************************************************
* A-4699-092-A BD BOARD, COMPLETE
*******************
< CAPACITOR >
C101 1-104-851-11 TANTAL. CHIP 10uF 20% 10V
C102 1-163-038-91 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C103 1-104-851-11 TANTAL. CHIP 10uF 20% 10V
C104 1-104-851-11 TANTAL. CHIP 10uF 20% 10V
C105 1-164-232-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 50V
C106 1-163-275-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.001uF 5% 50V
C107 1-163-038-91 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C108 1-163-038-91 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C109 1-163-037-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.022uF 10% 25V
C110 1-163-038-91 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
— 80 —
C146 1-163-038-91 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C151 1-126-206-11 ELECT CHIP 100uF 20% 6.3V
C152 1-163-038-91 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C153 1-164-232-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 50V
C156 1-163-038-91 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C158 1-163-019-00 CERAMIC CHIP 0.0068uF 10% 50V
C160 1-104-601-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 10V
C161 1-104-601-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 10V
C163 1-164-232-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 50V
C164 1-164-232-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 50V
C167 1-163-038-91 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C168 1-163-038-91 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C169 1-104-851-11 TANTAL. CHIP 10uF 20% 10V
C171 1-163-038-91 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C181 1-126-206-11 ELECT CHIP 100uF 20% 6.3V
C182 1-163-038-91 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C183 1-163-038-91 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C184 1-107-836-11 ELECT CHIP 22uF 20% 8V
C185 1-164-611-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.001uF 10% 500V
C187 1-126-206-11 ELECT CHIP 100uF 20% 6.3V
Page 67

BD
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
C188 1-164-232-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 50V
C189 1-163-989-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.033uF 10% 25V
C190 1-126-206-11 ELECT CHIP 100uF 20% 6.3V
C191 1-163-038-91 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C195 1-164-346-11 CERAMIC CHIP 1uF 16V
C196 1-163-038-91 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C197 1-163-038-91 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
< CONNECTOR >
CN101 1-766-508-11 CONNECTOR, FFC/FPC (ZIF) 22P
CN102 1-778-461-11 CONNECTOR, FFC/FPC 29P
CN103 1-778-460-11 CONNECTOR, FFC/FPC 19P
CN104 1-766-898-21 HOUSING, CONNECTOR (PC BOARD) 4P
CN106 1-770-698-11 CONNECTOR, FFC/FPC 15P
CN110 1-774-731-21 PIN, CONNECTOR (PC BOARD) 5P
< DIODE >
D101 8-719-988-62 DIODE 1SS355
D181 8-719-046-86 DIODE F1J6TP
D183 8-719-046-86 DIODE F1J6TP
< IC >
IC101 8-752-074-77 IC CXA2523R
IC103 8-729-903-10 IC TRANSISTOR FMW1
IC121 8-752-378-54 IC CXD2650R
IC122 8-759-234-20 IC TC7S08F
IC123 8-759-242-70 IC TC7WU04F
IC152 8-759-430-25 IC BH6511FS-E2
IC171 8-759-428-58 IC XL24C01AF-E2
IC181 8-759-095-65 IC TC74ACT540FS
IC192 8-759-426-95 IC L88MS33T-TL
< COIL >
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
Q182 8-729-017-65 TRANSISTOR 2SK1764KY
< RESISTOR >
R101 1-216-295-91 CONDUCTOR, CHIP (2012)
R103 1-216-049-91 METAL GLAZE 1K 5% 1/10W
R104 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R105 1-216-065-00 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/10W
R106 1-216-133-00 METAL CHIP 3.3M 5% 1/10W
R107 1-216-113-00 METAL CHIP 470K 5% 1/10W
R109 1-216-295-91 CONDUCTOR, CHIP (2012)
R110 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R111 1-216-295-91 CONDUCTOR, CHIP (2012)
R112 1-216-089-91 METAL GLAZE 47K 5% 1/10W
R113 1-216-049-91 METAL GLAZE 1K 5% 1/10W
R115 1-216-049-91 METAL GLAZE 1K 5% 1/10W
R117 1-216-113-00 METAL CHIP 470K 5% 1/10W
R120 1-216-025-91 METAL GLAZE 100 5% 1/10W
R121 1-216-097-91 METAL GLAZE 100K 5% 1/10W
R123 1-216-033-00 METAL CHIP 220 5% 1/10W
R124 1-216-025-91 METAL GLAZE 100 5% 1/10W
R125 1-216-025-91 METAL GLAZE 100 5% 1/10W
R127 1-216-025-91 METAL GLAZE 100 5% 1/10W
R131 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R132 1-216-097-91 METAL GLAZE 100K 5% 1/10W
R133 1-216-117-00 METAL CHIP 680K 5% 1/10W
R134 1-216-049-91 METAL GLAZE 1K 5% 1/10W
R135 1-216-061-00 METAL CHIP 3.3K 5% 1/10W
R136 1-216-049-91 METAL GLAZE 1K 5% 1/10W
R137 1-216-025-91 METAL GLAZE 100 5% 1/10W
R140 1-216-029-00 METAL CHIP 150 5% 1/10W
R141 1-216-295-91 CONDUCTOR, CHIP (2012)
R142 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R143 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
L101 1-414-235-11 INDUCTOR, FERRITE BEAD
L102 1-414-235-11 INDUCTOR, FERRITE BEAD
L103 1-414-235-11 INDUCTOR, FERRITE BEAD
L105 1-414-235-11 INDUCTOR, FERRITE BEAD
L106 1-414-235-11 INDUCTOR, FERRITE BEAD
L121 1-414-235-11 INDUCTOR, FERRITE BEAD
L122 1-414-235-11 INDUCTOR, FERRITE BEAD
L151 1-412-622-51 INDUCTOR 10uH
L152 1-412-622-51 INDUCTOR 10uH
L153 1-412-039-51 INDUCTOR CHIP 100uH
L154 1-412-039-51 INDUCTOR CHIP 100uH
L161 1-414-235-11 INDUCTOR, FERRITE BEAD
L162 1-414-235-11 INDUCTOR, FERRITE BEAD
< TRANSISTOR >
Q101 8-729-403-35 TRANSISTOR UN5113
Q102 8-729-026-53 TRANSISTOR 2SA1576A-T106-QR
Q103 8-729-014-04 TRANSISTOR RN1307-TE85L
Q104 8-729-014-04 TRANSISTOR RN1307-TE85L
Q162 8-729-101-07 TRANSISTOR 2SB798-DL
Q163 8-729-403-35 TRANSISTOR UN5113
Q180 8-729-907-00 TRANSISTOR DTC114EU
Q181 8-729-018-75 TRANSISTOR 2SJ278MY
R144 1-216-025-91 METAL GLAZE 100 5% 1/10W
R146 1-216-037-00 METAL CHIP 330 5% 1/10W
R147 1-216-025-91 METAL GLAZE 100 5% 1/10W
R148 1-216-045-00 METAL CHIP 680 5% 1/10W
R150 1-216-295-91 CONDUCTOR, CHIP (2012)
R158 1-216-097-91 METAL GLAZE 100K 5% 1/10W
R159 1-216-097-91 METAL GLAZE 100K 5% 1/10W
R161 1-216-057-00 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/10W
R162 1-216-057-00 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/10W
R163 1-216-057-00 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/10W
R164 1-216-045-00 METAL CHIP 680 5% 1/10W
R165 1-216-097-91 METAL GLAZE 100K 5% 1/10W
R166 1-220-149-11 METAL GLAZE 2.2 10% 1/2W
R167 1-216-065-00 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/10W
R169 1-219-724-11 METAL CHIP 1 1% 1/4W
R170 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R171 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R172 1-216-295-91 CONDUCTOR, CHIP (2012)
R173 1-216-121-91 METAL GLAZE 1M 5% 1/10W
R175 1-216-061-00 METAL CHIP 3.3K 5% 1/10W
R176 1-216-295-91 CONDUCTOR, CHIP (2012)
R177 1-216-061-00 METAL CHIP 3.3K 5% 1/10W
R178 1-216-295-91 CONDUCTOR, CHIP (2012)
— 81 —
Page 68

BD DISPLAY HP
MAIN
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
R179 1-216-089-91 METAL GLAZE 47K 5% 1/10W
R180 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R181 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R182 1-216-089-91 METAL GLAZE 47K 5% 1/10W
R183 1-216-089-91 METAL GLAZE 47K 5% 1/10W
R184 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R185 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R186 1-216-296-91 CONDUCTOR, CHIP (3216)
R187 1-216-296-91 CONDUCTOR, CHIP (3216)
R188 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R189 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R190 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R195 1-216-295-91 CONDUCTOR, CHIP (2012)
R196 1-216-295-91 CONDUCTOR, CHIP (2012)
R198 1-216-295-91 CONDUCTOR, CHIP (2012)
R199 1-216-295-91 CONDUCTOR, CHIP (2012)
R200 1-216-295-91 CONDUCTOR, CHIP (2012)
R201 1-216-295-91 CONDUCTOR, CHIP (2012)
R202 1-216-295-91 CONDUCTOR, CHIP (2012)
R502 1-216-295-91 CONDUCTOR, CHIP (2012)
R504 1-216-295-91 CONDUCTOR, CHIP (2012)
**************************************************************
* A-4699-574-A DISPLAY BOARD, COMPLETE (US,CND)
*********************************
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
R734 1-247-807-31 CARBON 100 5% 1/4W
R741 1-249-401-11 CARBON 47 5% 1/4W F
R742 1-247-807-31 CARBON 100 5% 1/4W
< SWITCH >
S730 1-554-303-21 SWITCH, TACTILE (§ EJECT)
**************************************************************
* 1-663-115-11 HP BOARD
*********
< CAPACITOR >
C770 1-162-290-31 CERAMIC 470PF 10% 50V
C771 1-162-290-31 CERAMIC 470PF 10% 50V
C772 1-126-933-11 ELECT 100uF 20% 16V
C773 1-126-933-11 ELECT 100uF 20% 16V
< CONNECTOR >
* CN770 1-564-708-11 PIN, CONNECTOR (SMALL TYPE) 6P
< IC >
IC770 8-759-634-50 IC M5218AL
< JACK >
* A-4699-581-A DISPLAY BOARD, COMPLETE (AEP,UK)
*********************************
2-389-320-01 CUSHION
* 4-971-854-01 HOLDER (FL)
< CAPACITOR >
C732 1-162-306-11 CERAMIC 0.01uF 20% 16V
C738 1-162-215-31 CERAMIC 47PF 5% 50V
C739 1-162-306-11 CERAMIC 0.01uF 20% 16V
C740 1-162-294-31 CERAMIC 0.001uF 10% 50V
C741 1-162-294-31 CERAMIC 0.001uF 10% 50V
C742 1-162-294-31 CERAMIC 0.001uF 10% 50V
C743 1-128-057-11 ELECT 330uF 20% 6.3V
C744 1-162-306-11 CERAMIC 0.01uF 20% 16V
< CONNECTOR >
CN730 1-778-714-11 HOUSING, CONNECTOR 18P
CN731 1-778-716-11 HOUSING, CONNECTOR 9P
< FLUORESCENT INDICATOR >
FL730 1-517-587-11 INDICATOR TUBE, FLUORESCENT
< IC >
IC730 8-759-426-98 IC MSM9202-02GS-K
IC731 8-749-013-22 IC GP1UC8XB
< RESISTOR >
R730 1-247-842-11 CARBON 3K 5% 1/4W
R731 1-247-807-31 CARBON 100 5% 1/4W
R732 1-247-807-31 CARBON 100 5% 1/4W
R733 1-247-807-31 CARBON 100 5% 1/4W
J771 1-770-307-11 JACK (LARGE TYPE)(PHONES)
< RESISTOR >
R770 1-247-807-31 CARBON 100 5% 1/4W
R771 1-247-807-31 CARBON 100 5% 1/4W
R772 1-249-433-11 CARBON 22K 5% 1/4W
R773 1-249-433-11 CARBON 22K 5% 1/4W
R774 1-249-441-11 CARBON 100K 5% 1/4W
R775 1-249-441-11 CARBON 100K 5% 1/4W
R776 1-249-433-11 CARBON 22K 5% 1/4W
R777 1-249-433-11 CARBON 22K 5% 1/4W
! R778 1-212-857-00 FUSIBLE 10 5% 1/4W F
! R779 1-212-857-00 FUSIBLE 10 5% 1/4W F
R790 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R791 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
< VARIABLE RESISTOR >
RV770 1-225-405-11 RES, VAR 20K/20K (PHONES LEVEL)
**************************************************************
* A-4699-578-A MAIN BOARD, COMPLETE (US,CND)
******************************
* A-4699-585-A MAIN BOARD, COMPLETE (AEP,UK)
7-685-646-79 SCREW +BVTP 3X8 TYPE2 N-S
BT901 1-528-739-11 BATTERY, LITHIUM (VL2020 3V)
The components identified by
mark ! or dotted line with mark
! are critical for safety.
Replace only with part number
— 82 —
specified.
******************************
< BATTERY >
Les composants identifiés par
une marque ! sont critiques pour
la sécurité.
Ne les remplacer que par une
piéce portant le numéro spécifié.
Page 69

MAIN
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
< CAPACITOR >
C101 1-130-467-00 MYLAR 470PF 5% 50V
C102 1-124-673-11 ELECT 100uF 20% 10V
C103 1-124-721-11 ELECT 10uF 20% 50V
C104 1-137-368-11 FILM 0.0047uF 5% 50V
C105 1-137-368-11 FILM 0.0047uF 5% 50V
C106 1-136-157-00 FILM 0.022uF 5% 50V
C107 1-130-481-00 MYLAR 0.0068uF 5% 50V
C108 1-130-481-00 MYLAR 0.0068uF 5% 50V
C109 1-137-363-91 FILM 680PF 5% 50V
C110 1-137-363-91 FILM 680PF 5% 50V
C111 1-124-673-11 ELECT 100uF 20% 10V
C112 1-137-368-11 FILM 0.0047uF 5% 50V
C113 1-137-364-11 FILM 0.001uF 5% 50V
C114 1-126-233-11 ELECT 22uF 20% 50V
C115 1-130-467-00 MYLAR 470PF 5% 50V
C121 1-136-165-00 FILM 0.1uF 5% 50V
C122 1-136-165-00 FILM 0.1uF 5% 50V
C201 1-130-467-00 MYLAR 470PF 5% 50V
C202 1-124-673-11 ELECT 100uF 20% 10V
C203 1-124-721-11 ELECT 10uF 20% 50V
C204 1-137-368-11 FILM 0.0047uF 5% 50V
C205 1-137-368-11 FILM 0.0047uF 5% 50V
C206 1-136-157-00 FILM 0.022uF 5% 50V
C207 1-130-481-00 MYLAR 0.0068uF 5% 50V
C208 1-130-481-00 MYLAR 0.0068uF 5% 50V
C209 1-137-363-91 FILM 680PF 5% 50V
C210 1-137-363-91 FILM 680PF 5% 50V
C211 1-124-673-11 ELECT 100uF 20% 10V
C212 1-137-368-11 FILM 0.0047uF 5% 50V
C213 1-137-364-11 FILM 0.001uF 5% 50V
C214 1-126-233-11 ELECT 22uF 20% 50V
C215 1-130-467-00 MYLAR 470PF 5% 50V
C221 1-136-165-00 FILM 0.1uF 5% 50V
C222 1-136-165-00 FILM 0.1uF 5% 50V
C300 1-124-721-11 ELECT 10uF 20% 50V
C301 1-124-910-11 ELECT 47uF 20% 50V
C302 1-124-673-11 ELECT 100uF 20% 10V
C303 1-162-306-11 CERAMIC 0.01uF 20% 16V
C304 1-136-165-00 FILM 0.1uF 5% 50V
C305 1-124-721-11 ELECT 10uF 20% 50V
C306 1-136-153-00 FILM 0.01uF 5% 50V
C307 1-136-153-00 FILM 0.01uF 5% 50V
C308 1-124-721-11 ELECT 10uF 20% 50V
C309 1-126-233-11 ELECT 22uF 20% 50V
C310 1-136-153-00 FILM 0.01uF 5% 50V
C311 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C312 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C313 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C314 1-124-673-11 ELECT 100uF 20% 10V
C315 1-126-335-11 ELECT 220uF 20% 10V
C316 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C317 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C318 1-126-335-11 ELECT 220uF 20% 10V
C319 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C320 1-126-335-11 ELECT 220uF 20% 10V
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
C322 1-126-335-11 ELECT 220uF 20% 10V
C323 1-162-205-31 CERAMIC 18PF 5% 50V
C324 1-162-205-31 CERAMIC 18PF 5% 50V
C325 1-126-335-11 ELECT 220uF 20% 10V
C326 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C327 1-126-947-11 ELECT 47uF 20% 10V
C329 1-126-947-11 ELECT 47uF 20% 10V
C330 1-126-947-11 ELECT 47uF 20% 10V
C332 1-124-910-11 ELECT 47uF 20% 50V
C333 1-136-165-00 FILM 0.1uF 5% 50V
C334 1-136-165-00 FILM 0.1uF 5% 50V
C335 1-124-910-11 ELECT 47uF 20% 50V
C336 1-124-910-11 ELECT 47uF 20% 50V
C340 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C350 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C351 1-162-306-11 CERAMIC 0.01uF 20% 16V
C352 1-162-306-11 CERAMIC 0.01uF 20% 16V
C354 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C355 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C356 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C357 1-162-306-11 CERAMIC 0.01uF 20% 16V
C358 1-162-306-11 CERAMIC 0.01uF 20% 16V
C359 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 20% 50V
C360 1-162-306-11 CERAMIC 0.01uF 20% 16V
C361 1-162-306-11 CERAMIC 0.01uF 20% 16V
C373 1-162-306-11 CERAMIC 0.01uF 20% 16V
C380 1-162-306-11 CERAMIC 0.01uF 20% 16V
C401 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C402 1-162-294-31 CERAMIC 0.001uF 10% 50V
C403 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C404 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C405 1-162-203-31 CERAMIC 15PF 5% 50V
C406 1-162-203-31 CERAMIC 15PF 5% 50V
C407 1-162-282-31 CERAMIC 100PF 10% 50V
C408 1-162-282-31 CERAMIC 100PF 10% 50V
C409 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C410 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C411 1-162-282-31 CERAMIC 100PF 10% 50V
C412 1-162-282-31 CERAMIC 100PF 10% 50V
C414 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C415 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C901 1-117-150-21 ELECT 5600uF 20% 25V
C902 1-117-150-21 ELECT 5600uF 20% 25V
C903 1-117-401-11 ELECT 22000uF 20% 16V
C906 1-128-576-11 ELECT 100uF 20% 63V
C907 1-126-950-11 ELECT 330uF 20% 35V
C908 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C910 1-126-964-11 ELECT 10uF 20% 50V
C911 1-126-962-11 ELECT 3.3uF 20% 50V
C912 1-126-963-11 ELECT 4.7uF 20% 50V
C914 1-126-916-11 ELECT 1000uF 20% 6.3V
C915 1-126-767-11 ELECT 1000uF 20% 16V
C917 1-126-103-11 ELECT 470uF 20% 16V
C918 1-126-103-11 ELECT 470uF 20% 16V
C919 1-126-797-11 ELECT 1000uF 20% 10V
C321 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
— 83 —
Page 70

MAIN
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
< CONNECTOR >
* CN301 1-564-708-11 PIN, CONNECTOR (SMALL TYPE) 6P
* CN302 1-564-708-11 PIN, CONNECTOR (SMALL TYPE) 6P
CN303 1-770-651-11 CONNECTOR, FFC/FPC 23P
CN304 1-770-657-11 CONNECTOR, FFC/FPC 29P
CN305 1-770-167-11 CONNECTOR, FFC/FPC 19P
CN903 1-691-770-11 PLUG (MICRO CONNECTOR) 8P
< DIODE >
D308 8-719-109-98 DIODE RD6.8ES-B3
D350 8-719-987-63 DIODE 1N4148M
D351 8-719-987-63 DIODE 1N4148M
D901 8-719-987-63 DIODE 1N4148M
D902 8-719-987-63 DIODE 1N4148M
D903 8-719-200-82 DIODE 11ES2
D904 8-719-200-82 DIODE 11ES2
D905 8-719-200-82 DIODE 11ES2
D906 8-719-200-82 DIODE 11ES2
D907 8-719-200-82 DIODE 11ES2
D908 8-719-200-82 DIODE 11ES2
D909 8-719-200-82 DIODE 11ES2
< GROUND PLATE >
* EP901 4-942-204-01 PLATE, GROUND
< IC >
IC101 8-759-916-14 IC SN74HC04AN
IC102 8-759-602-83 IC M5238P
IC201 8-759-916-14 IC SN74HC04AN
IC202 8-759-602-83 IC M5238P
IC301 8-759-602-83 IC M5238P
IC302 8-759-434-43 IC CXA8065S
IC303 8-759-361-58 IC CXA8055M
IC304 8-759-426-99 IC CXD8607N
IC351 8-759-822-09 IC LB1641
IC352 8-749-012-69 IC GP1F38T (DIGITAL OPTICAL OUT)
IC353 8-749-012-70 IC GP1F38R (DIGITAL OPTICAL IN1)
IC354 8-749-012-70 IC GP1F38R
IC355 8-759-917-18 IC SN74HCU04AN
IC356 8-759-921-17 IC SN74HC153AN
IC401 8-759-462-16 IC RU8X11AMF-0113
IC901 8-759-426-96 IC LA5620
IC902 8-759-633-42 IC M5293L
IC903 8-759-604-99 IC M5F78M06L
IC904 8-759-604-94 IC M5F79M06
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
< TRANSISTOR >
Q101 8-729-141-30 TRANSISTOR 2SC3623A-LK
Q201 8-729-141-30 TRANSISTOR 2SC3623A-LK
Q301 8-729-422-61 TRANSISTOR UN4115
Q350 8-729-422-61 TRANSISTOR UN4115
Q351 8-729-119-76 TRANSISTOR 2SA1175-HFE
Q352 8-729-900-80 TRANSISTOR DTC114ES
Q353 8-729-620-05 TRANSISTOR 2SC2603-EF
Q402 8-729-900-80 TRANSISTOR DTC114ES
< RESISTOR >
R101 1-249-421-11 CARBON 2.2K 5% 1/4W F
R102 1-249-441-11 CARBON 100K 5% 1/4W
R103 1-249-425-11 CARBON 4.7K 5% 1/4W F
R104 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R105 1-249-433-11 CARBON 22K 5% 1/4W
R106 1-247-868-11 CARBON 36K 5% 1/4W
R107 1-249-425-11 CARBON 4.7K 5% 1/4W F
R108 1-249-425-11 CARBON 4.7K 5% 1/4W F
R109 1-249-401-11 CARBON 47 5% 1/4W F
R110 1-249-401-11 CARBON 47 5% 1/4W F
R111 1-249-407-11 CARBON 150 5% 1/4W F
R112 1-249-407-11 CARBON 150 5% 1/4W F
R113 1-249-408-11 CARBON 180 5% 1/4W F
R114 1-249-408-11 CARBON 180 5% 1/4W F
R115 1-249-411-11 CARBON 330 5% 1/4W
R116 1-249-411-11 CARBON 330 5% 1/4W
R117 1-249-411-11 CARBON 330 5% 1/4W
R118 1-249-411-11 CARBON 330 5% 1/4W
R119 1-249-393-11 CARBON 10 5% 1/4W F
R120 1-249-393-11 CARBON 10 5% 1/4W F
R121 1-249-393-11 CARBON 10 5% 1/4W F
R122 1-249-393-11 CARBON 10 5% 1/4W F
R123 1-249-411-11 CARBON 330 5% 1/4W
R124 1-249-411-11 CARBON 330 5% 1/4W
R125 1-249-421-11 CARBON 2.2K 5% 1/4W F
R126 1-249-421-11 CARBON 2.2K 5% 1/4W F
R127 1-247-843-11 CARBON 3.3K 5% 1/4W
R128 1-247-843-11 CARBON 3.3K 5% 1/4W
R129 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R130 1-249-421-11 CARBON 2.2K 5% 1/4W F
R131 1-249-417-11 CARBON 1K 5% 1/4W F
R132 1-249-441-11 CARBON 100K 5% 1/4W
R133 1-247-807-31 CARBON 100 5% 1/4W
R134 1-247-807-31 CARBON 100 5% 1/4W
R201 1-249-421-11 CARBON 2.2K 5% 1/4W F
< JACK >
J301 1-778-064-11 JACK, PIN 4P (LINE (ANALOG))
J350 1-779-655-21 JACK, SMALL TYPE (2 GANG)(CONTROL A1)
J352 1-770-905-21 JACK, PIN 1P (DIGITAL COAXIAL IN)
< COIL >
L351 1-410-509-11 INDUCTOR 10uH
L352 1-410-509-11 INDUCTOR 10uH
R202 1-249-441-11 CARBON 100K 5% 1/4W
R203 1-249-425-11 CARBON 4.7K 5% 1/4W F
R204 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R205 1-249-433-11 CARBON 22K 5% 1/4W
R206 1-247-868-11 CARBON 36K 5% 1/4W
R207 1-249-425-11 CARBON 4.7K 5% 1/4W F
R208 1-249-425-11 CARBON 4.7K 5% 1/4W F
R209 1-249-401-11 CARBON 47 5% 1/4W F
R210 1-249-401-11 CARBON 47 5% 1/4W F
R211 1-249-407-11 CARBON 150 5% 1/4W F
R212 1-249-407-11 CARBON 150 5% 1/4W F
— 84 —
Page 71

PANEL (L)MAIN
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
R213 1-249-408-11 CARBON 180 5% 1/4W F
R214 1-249-408-11 CARBON 180 5% 1/4W F
R215 1-249-411-11 CARBON 330 5% 1/4W
R216 1-249-411-11 CARBON 330 5% 1/4W
R217 1-249-411-11 CARBON 330 5% 1/4W
R218 1-249-411-11 CARBON 330 5% 1/4W
R219 1-249-393-11 CARBON 10 5% 1/4W F
R220 1-249-393-11 CARBON 10 5% 1/4W F
R221 1-249-393-11 CARBON 10 5% 1/4W F
R222 1-249-393-11 CARBON 10 5% 1/4W F
R223 1-249-411-11 CARBON 330 5% 1/4W
R224 1-249-411-11 CARBON 330 5% 1/4W
R225 1-249-421-11 CARBON 2.2K 5% 1/4W F
R226 1-249-421-11 CARBON 2.2K 5% 1/4W F
R227 1-247-843-11 CARBON 3.3K 5% 1/4W
R228 1-247-843-11 CARBON 3.3K 5% 1/4W
R229 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R230 1-249-421-11 CARBON 2.2K 5% 1/4W F
R231 1-249-417-11 CARBON 1K 5% 1/4W F
R232 1-249-441-11 CARBON 100K 5% 1/4W
R233 1-247-807-31 CARBON 100 5% 1/4W
R234 1-247-807-31 CARBON 100 5% 1/4W
R301 1-249-401-11 CARBON 47 5% 1/4W F
R302 1-249-401-11 CARBON 47 5% 1/4W F
R303 1-249-411-11 CARBON 330 5% 1/4W
R304 1-247-903-00 CARBON 1M 5% 1/4W
R305 1-249-411-11 CARBON 330 5% 1/4W
R306 1-249-401-11 CARBON 47 5% 1/4W F
R307 1-249-401-11 CARBON 47 5% 1/4W F
R308 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R309 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R311 1-249-413-11 CARBON 470 5% 1/4W F
R314 1-249-441-11 CARBON 100K 5% 1/4W
R350 1-249-441-11 CARBON 100K 5% 1/4W
R351 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R352 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R353 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R354 1-249-426-11 CARBON 5.6K 5% 1/4W
R356 1-249-425-11 CARBON 4.7K 5% 1/4W F
R357 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R358 1-249-393-11 CARBON 10 5% 1/4W F
R359 1-247-895-00 CARBON 470K 5% 1/4W
R360 1-249-437-11 CARBON 47K 5% 1/4W
R361 1-247-804-11 CARBON 75 5% 1/4W
R363 1-247-895-00 CARBON 470K 5% 1/4W
R364 1-247-895-00 CARBON 470K 5% 1/4W
R365 1-249-437-11 CARBON 47K 5% 1/4W
R381 1-249-417-11 CARBON 1K 5% 1/4W F
R401 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R402 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R403 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R404 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R405 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R406 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
R412 1-249-441-11 CARBON 100K 5% 1/4W
R413 1-249-441-11 CARBON 100K 5% 1/4W
R414 1-249-441-11 CARBON 100K 5% 1/4W
(AEP,UK)
R415 1-249-441-11 CARBON 100K 5% 1/4W
(US,CND)
R416 1-249-441-11 CARBON 100K 5% 1/4W
(US,CND)
R417 1-249-441-11 CARBON 100K 5% 1/4W
(AEP,UK)
R418 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R419 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R420 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R422 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R424 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R425 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R426 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R427 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R428 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R430 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R431 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R442 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R901 1-247-807-31 CARBON 100 5% 1/4W
R902 1-249-417-11 CARBON 1K 5% 1/4W F
R903 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R904 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R905 1-249-409-11 CARBON 220 5% 1/4W F
R906 1-249-437-11 CARBON 47K 5% 1/4W
< VIBRATOR >
X301 1-579-314-11 VIBRATOR, CRYSTAL (22MHz)
X401 1-567-098-61 VIBRATOR, CRYSTAL (32.768kHz)
X402 1-767-157-21 VIBRATOR, CERAMIC (12MHz)
**************************************************************
* A-4699-573-A PANEL (L) BOARD, COMPLETE (US,CND)
**********************************
* A-4699-580-A PANEL (L) BOARD, COMPLETE (AEP,UK)
**********************************
* 4-972-608-01 HOLDER (DIA. 5), LED
< CONNECTOR >
CN750 1-778-715-11 CONNECTOR, BOARD TO BOARD 9P
< DIODE >
D750 8-719-313-40 DIODE SEL1516W (POWER)
< TRANSISTOR >
Q750 8-729-422-57 TRANSISTOR UN4111
Q751 8-729-900-74 TRANSISTOR DTC143TS
< RESISTOR >
R408 1-247-903-00 CARBON 1M 5% 1/4W
R409 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R410 1-249-441-11 CARBON 100K 5% 1/4W
R411 1-249-441-11 CARBON 100K 5% 1/4W
R752 1-249-399-11 CARBON 33 5% 1/4W F
R753 1-249-409-11 CARBON 220 5% 1/4W F
R754 1-247-843-11 CARBON 3.3K 5% 1/4W
R755 1-249-425-11 CARBON 4.7K 5% 1/4W F
— 85 —
Page 72

PANEL (L) PANEL (R) REC-VOL SW
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
R756 1-249-421-11 CARBON 2.2K 5% 1/4W F
R757 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R758 1-249-421-11 CARBON 2.2K 5% 1/4W F
R759 1-247-843-11 CARBON 3.3K 5% 1/4W
R760 1-249-425-11 CARBON 4.7K 5% 1/4W F
R761 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
< SWITCH >
S750 1-554-303-21 SWITCH, TACTILE (REPEAT)
S751 1-554-303-21 SWITCH, TACTILE (SCROLL/CLOCK SET)
S752 1-554-303-21 SWITCH, TACTILE (POWER)
S753 1-554-303-21 SWITCH, TACTILE (DISPLAY)
S754 1-554-303-21 SWITCH, TACTILE (CHAR)
S755 1-554-303-21 SWITCH, TACTILE (CLEAR)
S756 1-554-303-21 SWITCH, TACTILE (CONTINUE)
S757 1-554-303-21 SWITCH, TACTILE (SHUFFLE)
S758 1-554-303-21 SWITCH, TACTILE (PROGRAM)
S759 1-572-625-11 SWITCH, SLIDE (TIMER)
**************************************************************
* A-4699-575-A PANEL (R) BOARD, COMPLETE (US,CND)
**********************************
* A-4699-582-A PANEL (R) BOARD, COMPLETE (AEP,UK)
**********************************
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
R713 1-249-435-11 CARBON 33K 5% 1/4W
R714 1-249-421-11 CARBON 2.2K 5% 1/4W F
R715 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R716 1-249-421-11 CARBON 2.2K 5% 1/4W F
R717 1-247-843-11 CARBON 3.3K 5% 1/4W
R718 1-249-425-11 CARBON 4.7K 5% 1/4W F
R719 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R720 1-249-435-11 CARBON 33K 5% 1/4W
R721 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R722 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
< SWITCH >
S701 1-571-429-11 SWITCH, SLIDE (INPUT)
S702 1-473-779-11 ENCODER, ROTARY
(≠ AMS ±, PUSH ENTER)
S703 1-554-303-21 SWITCH, TACTILE (EDIT/NO)
S704 1-554-303-21 SWITCH, TACTILE (YES)
S705 1-554-303-21 SWITCH, TACTILE (P)
S706 1-554-303-21 SWITCH, TACTILE (·)
S707 1-572-624-11 SWITCH, SLIDE (REC MODE)
S708 1-554-303-21 SWITCH, TACTILE (r REC)
S709 1-554-303-21 SWITCH, TACTILE (p)
S710 1-554-303-21 SWITCH, TACTILE ())
S711 1-554-303-21 SWITCH, TACTILE (0)
< CAPACITOR >
C701 1-126-153-11 ELECT 22uF 20% 6.3V
C702 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
< CONNECTOR >
CN701 1-778-688-11 CONNECTOR, FFC/FPC 23P
CN702 1-778-713-11 CONNECTOR, BOARD TO BOARD 18P
< DIODE >
D701 8-719-313-50 DIODE SEL6810A-TH12 (DIGITAL INPUT 32kHz)
D702 8-719-313-50 DIODE SEL6810A-TH12
(DIGITAL INPUT 44.1kHz)
D703 8-719-313-50 DIODE SEL6810A-TH12 (DIGITAL INPUT 48kHz)
< TRANSISTOR >
Q701 8-729-422-57 TRANSISTOR UN4111
Q702 8-729-422-57 TRANSISTOR UN4111
Q703 8-729-422-57 TRANSISTOR UN4111
< RESISTOR >
R701 1-249-409-11 CARBON 220 5% 1/4W F
R702 1-249-409-11 CARBON 220 5% 1/4W F
R703 1-249-409-11 CARBON 220 5% 1/4W F
R704 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R705 1-247-843-11 CARBON 3.3K 5% 1/4W
**************************************************************
* 1-663-116-11 REC-VOL BOARD
*************
< CONNECTOR >
* CN780 1-564-708-11 PIN, CONNECTOR (SMALL TYPE) 6P
< RESISTOR >
R780 1-249-433-11 CARBON 22K 5% 1/4W
R781 1-249-433-11 CARBON 22K 5% 1/4W
< VARIABLE RESISTOR >
RV780 1-241-937-11 RES, VAR, CARBON 20K/20K (REC LEVEL)
**************************************************************
* 1-661-774-11 SW BOARD
*********
< CONNECTOR >
CN601 1-770-698-11 CONNECTOR, FFC/FPC 15P
CN602 1-778-638-21 PIN, CONNECTOR (PC BOARD) 2P
CN603 1-778-638-21 PIN, CONNECTOR (PC BOARD) 2P
< SWITCH >
R706 1-249-425-11 CARBON 4.7K 5% 1/4W F
R707 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R708 1-249-435-11 CARBON 33K 5% 1/4W
R709 1-249-421-11 CARBON 2.2K 5% 1/4W F
R710 1-247-843-11 CARBON 3.3K 5% 1/4W
R711 1-249-425-11 CARBON 4.7K 5% 1/4W F
R712 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
— 86 —
S681 1-572-467-61 SWITCH, PUSH (1 KEY)(LIMIT)
S682 1-692-377-31 SWITCH, PUSH (1 KEY)(REFLECT)
S683 1-692-847-21 SWITCH, PUSH (1 KEY)(PROTECT)
S685 1-572-467-61 SWITCH, PUSH (1 KEY)(CHUCKING IN)
S686 1-762-621-21 SWITCH, PUSH (1 KEY)(PACK OUT)
S687 1-572-688-11 SWITCH, PUSH (1 KEY)(PB POSITION)
S688 1-762-621-21 SWITCH, PUSH (1 KEY)(REC POSITION)
**************************************************************
Page 73

Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
MISCELLANEOUS
**************
3 1-777-278-11 WIRE (FLAT TYPE)(19 CORE)
4 1-777-275-11 WIRE (FLAT TYPE)(29 CORE)
! 12 1-558-568-21 CORD, POWER (AEP)
! 12 1-559-583-21 CORD, POWER (US,CND)
! 12 1-696-586-11 CORD, POWER (UK)
76 1-777-846-11 WIRE (FLAT TYPE)(23 CORE)
206 1-660-966-11 OP RELAY FLEXIBLE BOARD
208 1-777-517-11 WIRE (FLAT TYPE)(15 CORE)
! 267 8-583-028-01 OPTICAL PICK-UP KMS-260A/J1N
FL730 1-517-587-11 INDICATOR TUBE, FLUORESCENT
HR901 1-500-396-11 HEAD, OVER WRITE
M901 A-4672-135-A MOTOR ASSY, SPINDLE
M902 A-4672-133-A MOTOR ASSY, SLED
M903 A-4672-134-A MOTOR ASSY, LOADING
! T901 1-431-239-11 TRANSFORMER, POWER (US,CND)
! T901 1-431-240-11 TRANSFORMER, POWER (AEP,UK)
**************************************************************
ACCESSORIES & PACKING MATERIALS
*******************************
1-473-886-11 REMOTE COMMANDER (RM-D9M)
1-574-264-11 CORD, OPTICAL PLUG (CND,AEP,UK)
1-590-925-31 CORD, CONNECTION (AUDIO, 100cm)
3-858-098-11 MANUAL, INSTRUCTION
3-858-098-21 MANUAL, INSTRUCTION
3-858-098-31 MANUAL, INSTRUCTION (ENGLISH)(US)
4-983-537-01 COVER, BATTERY (for RM-D9M)
**************************************************************
#1 7-685-850-04 SCREW +BVTT 2X3 (S)
#2 7-685-102-19 SCREW (+BTP)(2X4)
#3 7-685-133-19 SCREW +BTP 2.6X6 TYPE2 N-S
#4 7-685-646-79 SCREW +BVTP 3X8 TYPE2 IT-3
#5 7-685-871-01 SCREW +BVTT 3X6 (S)
#6 7-685-851-04 SCREW +BVTT 2X4 (S)
#7 7-627-852-28 +P 1.7X3
#8 7-627-553-17 PRECISION SCREW +P 2X2 TYPE 3
#9 7-627-552-27 SCREW,PRECISION +P 1.7X2
(ENGLISH,FRENCH,SPANISH,PORTUGUESE)
(CND,AEP,UK)
(GERMAN,DUTCH,SWEDISH,ITALIAN)(AEP)
**************
HARDWARE LIST
**************
— 87 —
The components identified by
mark ! or dotted line with mark
! are critical for safety.
Replace only with part number
specified.
Les composants identifiés par
une marque ! sont critiques pour
la sécurité.
Ne les remplacer que par une
piéce portant le numéro spécifié.
Page 74

MDS-JE700
REVISION HISTORY
Clicking the version allows you to jump to the revised page.
Also, clicking the version at the upper right on the revised page allows you to jump to the next revised
page.
Ver. Date Description of Revision
1.0 1997.02 New
1.1 2004.09 Correction of exploded views parts list (Ref. No. 254, 271, 272, 273 and
274). (SPM-03039)
 Loading...
Loading...