Low Voltage Single Supply Flash Memory
■ SINGLE 2.7 to 3.6V SU PPL Y VO LT AG E fo r
PROGRAM, ERAS E and READ O PER AT IONS
■ ACCESS TIME: 55ns
■ PROGRAMMING TIME
– 10µs per Byte typical
■ PROGRAM/ERA SE CON T ROL LER
– Embedded Byte Program algorithm
– Embedded Chip Erase algorithm
– Status Register Polling and Toggle Bits
■ UNLOCK BYPASS PROGRAM COMMAND
– Faster Production/Batch Programming
■ LOW POWER CONSUMPTION
– Standby and Automatic Standby
■ 100,000 PROGRAM/ERASE CYCL ES
■ 20 YEARS DATA RETENTI ON
– Defectivity below 1 ppm/year
■ ELECTRONIC SIGNATURE
– Manufacturer Code: 20h
– Device Code: 27h
512 Kbi t (64K b x8, Bu l k)
TSOP32 (NZ)
8 x 14mm
Figure 1. Logic Diagram
V
CC
M29W512B
PLCC32 (K)
A0-A15
W
16
M29W512B
E
G
V
SS
8
DQ0-DQ7
AI02743
1/18March 2000
M29W512B
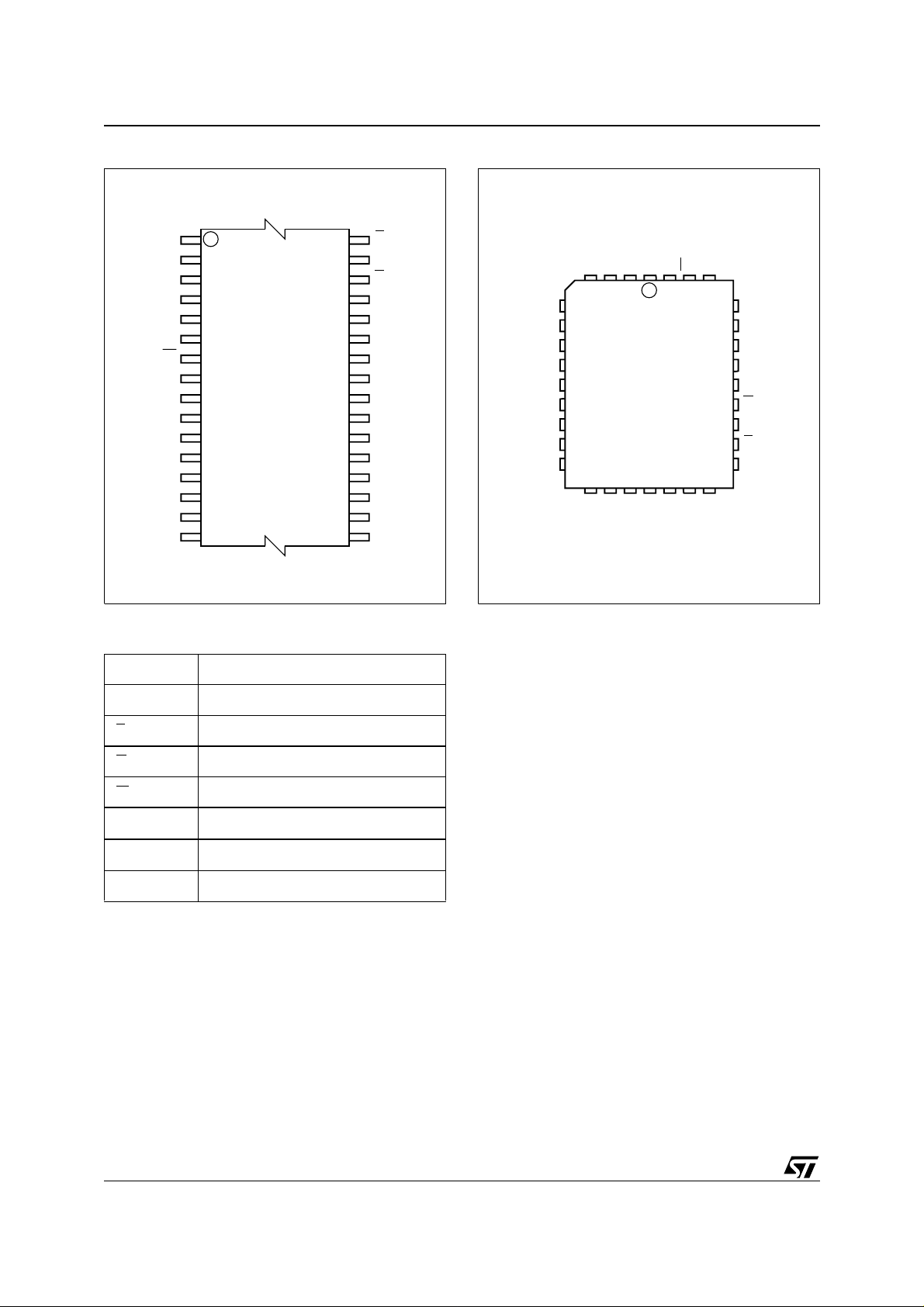
Figure 2. TSOP Connection s
A11 G
A9
A8
A13
A14
NC
V
CC
NC
NC
A15
A12
A7
A6
A5
A4 A3
1
W
8
M29W512B
9
16 17
32
25
24
AI02976
A10
E
DQ7
DQ6
DQ5
DQ4
DQ3
V
SS
DQ2
DQ1
DQ0
A0
A1
A2
Figure 3. PLCC Connections
NC
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
DQ0
A12
9
DQ1
NC
V
17
SS
1
32
DQ3
V
DQ4
A15
M29W512B
DQ2
CC
W
DQ5
NC
25
DQ6
A14
A13
A8
A9
A11
G
A10
E
DQ7
AI02755
Table 1. Signal Names
A0-A15 Address Inputs
DQ0-DQ7 Data Inputs/Outputs
E
G
W
V
CC
V
SS
NC Not Connected Internally
Chip Enable
Output Enable
Write Enable
Supply Voltage
Ground
SUMMARY DESCRIPTION
The M29W512B is a 512 Kbit (64Kb x8) non-volatile memory that can be read, erased and reprogrammed. These operations can be performed
using a single low voltage (2.7 to 3.6V) supply. On
power-up the memory defaults to its Read mode
where it can be read in the same way as a ROM or
EPROM.
Program and Erase command s are written to the
Command Interface of the memory. An on-chip
Program/Erase Controller simplifies the process of
programming or erasing the memory by taking
care of all of the special operations that are required to update the memory contents. The end of
a program or erase operation can be detected and
any error conditions identified. The command set
required to control the memory is consistent with
JEDEC standards.
Chip Enable, Output Enable and Write Enable signals control the bus operation of the memory.
They allow simple conne ction to most m icroprocessors, often without additional logic.
The memory is offered in TSOP32 (8 x 14mm) and
PLCC32 packages and it is supplied with all the
bits erased (set to ’1’).
2/18
M29W512B
Table 2. Absolute Maximum Ratings
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
T
A
T
BIAS
T
STG
(2)
V
IO
V
CC
V
ID
Note: 1. Except for the ratin g " Operati ng Temperat ure Range" , stresses above th ose liste d i n t he Table " A bsolute M aximum Ratings" may
cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation of the device at these or any other conditions
above those indi cated in the Operating sections of this s pecification is not impli ed. Exposure to A bsolute M aximum Rating conditions for extended per iods may aff ect device reliabilit y. Refer also to the STMicroel ectronics SURE Program an d other relevan t qual ity docum en ts .
2. Mini m um Voltage ma y undershoot to –2V duri ng transit i on and for less t han 20ns duri ng transit io ns.
Ambient Operating Temperature 0 to 70 °C
Temperature Under Bias –50 to 125 °C
Storage Temperature –65 to 150 °C
Input or Output Voltage –0.6 to 4 V
Supply Voltage –0.6 to 4 V
Identification Voltage –0.6 to 13.5 V
SIGNAL DESCRIPTIONS
See Figure 1, Logic Diagram, and Table 1, Sign al
Names, for a brief overview of the signals connected to this device.
Address Inputs (A0-A15). The Address Inputs
select the cells i n the memory array to a ccess during Bus Read operations. During Bus Write operations they control the commands sent to the
Command Interface of the internal state machine.
Data Inputs/Outputs (DQ0-DQ7). The Data Inputs/Outputs output the data stored at the selected
address during a Bus Read operation. During Bus
Write operations they represent the commands
sent to the Command Interface of the internal state
machine.
Chip Enable (E
). The Chip Enable, E, activates
the memory, allowing Bus Read and Bus Write operations to be performed. When Chip Enable is
High, V
Output Enable (G
, all other pins are ignored.
IH
). The Output Enable, G, con-
trols the Bus Read operation of the memory.
(1)
Write Enable (W
). The Write Enable, W, controls
the Bus Write operation of the memory’s Command Interf a c e .
Supply Voltage. The VCC Supply Voltage
V
CC
supplies the power for all operations (Read, Program, Erase etc.).
The Command Interface is disabled when the V
CC
Supply Voltage is less than the L ockout Voltage,
V
. This prevents Bus Write operations from ac-
LKO
cidentally damaging the data during power-up,
power-down and power surges. If the Program/
Erase Controller is programming or erasing during
this time then the operation aborts and the memory contents being altered will be invalid.
A 0.1µF capacitor should be connected between
the V
Supply Voltage pin and the VSS Ground
CC
pin to decouple the current surges from the power
supply. The PCB track widths must be sufficient to
carry the currents required during program and
erase operations, I
Vss Ground. The V
.
CC3
Ground is the reference
SS
for all voltage measurements.
3/18
M29W512B
BUS OPERATIONS
There are five standard bus operations that control
the device. These are Bus Read, Bus Wri te, Output Disable, Standby and Automatic Standby. See
Table 3, Bus Operations, for a summary. Typically
glitches of less than 5ns are ig nored b y the mem ory and do not affect bus operations.
Bus Read. Bus Read operations read from the
memory cells, or specific registers in the Command Interface. A valid Bus Read operation involves setting the desired address on the Address
Inputs, applying a Low sig nal, V
, to Chip Enable
IL
and Output Enable and keeping Write Enable
High, V
. The Data Inputs/Outputs will output the
IH
value, see Figure 8, Rea d Mode AC Wav eforms,
and Table 10, Read AC Characteristics, for details
of when the output becomes valid.
Bus Write. Bus Write operations write to the
Command Interface. A valid Bus Write operation
begins by setting the desire d address on t he Address Inputs. The Address Inputs are latched by
the Command Interface on the falling edge of Chip
Enable or Write Enable, whichever occurs last.
The Data Inputs/Outputs a re latched by the Command Interface on the rising edge of Chip Enable
or Write Enable, whichever occurs first. Output Enable must remain High, V
, during the whole Bus
IH
Write operation. See Figures 9 and 10, Write AC
Waveforms, and Tables 11 and 12, Write AC
Characteristics, for details of the timing requirements.
Output Disa bl e . The Data Inputs/Outputs are in
the high impedance s tate when Output Enable is
High, V
Standby. When Chip Enable is High, V
.
IH
, the
IH
memory enters Standby mode and the Data Inputs/Outputs pins are placed in the high-impedance state. To reduce the S upply Current to the
Standby Supply Current, I
be held within V
± 0.2V. For the Standby current
CC
, Chip Enable should
CC2
level see Table 9, DC Characteristics.
During program or erase operations the memory
will continue to use the Program/Erase Supply
Current, I
, for Program or Erase operations un-
CC3
til the operation completes.
Automatic Standby. If CMOS levels (V
± 0.2V)
CC
are used to drive the bus and the bus is inactive for
150ns or more the memory enters Automatic
Standby where the internal Supply Current is reduced to the Standby Supply Current, I
CC2
. The
Data Inputs/Outputs will still output data if a Bus
Read operation is in progress.
Special Bus Operations
Additional bus operations can be performed to
read the Electronic S ignature. These bus operations are intended for use by programming equipment and are not usually used in applications.
They require V
to be applied to some pins.
ID
Electronic Signature. The memory has two
codes, the manufacturer code and the device
code, that can be read to identify the memory.
These codes can be read by applying t he signals
listed in Table 3, Bus Operations.
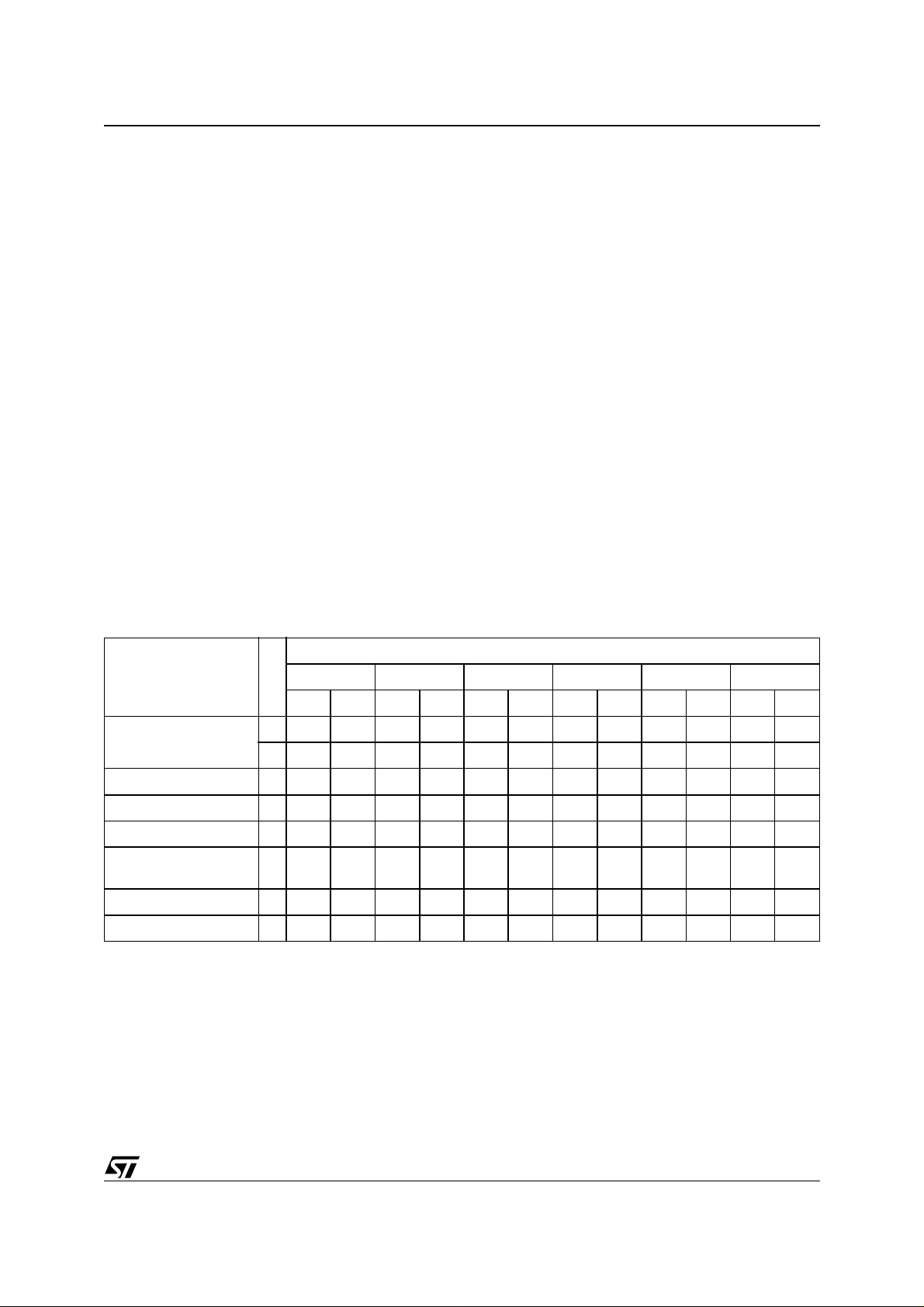
Table 3. Bus Operations
Operation E G W Address Inputs
Bus Read
Bus Write
Output Disable X
Standby
Read Manufacturer
Code
Read Device Code
Note: X = VIL or VIH.
4/18
Data
Inputs/Outputs
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
V
IH
XXX Hi-Z
V
IL
V
IL
V
V
V
V
V
Cell Address Data Output
IH
Command Address Data Input
IL
XHi-Z
IH
A0 = VIL, A1 = VIL, A9 = VID,
IH
Others V
A0 = VIH, A1 = VIL, A9 = VID,
IH
Others V
IL
IL
or V
or V
IH
IH
20h
27h
M29W512B
COMMAND INTERFACE
All Bus Write operations t o the me mory are in terpreted by the Command Interface. Commands
consist of one or more sequential Bus Write operations. Failure to observe a valid sequence of Bus
Write operations will result in the memory returning to Read mode. The long command sequences
are imposed to maximize data security.
The commands are summarized in Table 4, Commands. Refer to Table 4 in conjunction with the
text descriptions below.
Read/Reset Command. The Read/Reset command returns the memory to its Read mode where
it behaves like a ROM or EPROM. It also resets
the errors in the Status Register. Either one or
three Bus Write operations can be u sed to issue
the Read/Reset command.
If the Read/Reset command is issued during a
Chip Erase operation the memory will take about
10µs to abort the Chip Erase. During the abort period no valid data can be read from the memory.
Issuing a Read/Reset command during a Chip
Erase operation will leave invalid data in the memory.
Auto Select Command. The Auto Select command is used to read the Man ufacturer Code and
the Device Code. Three consecutive Bus Write operations are required to issue the Auto Select command. Once the Auto Select command is issued
the memory remains in Auto Select mode until another command is issued.
From the Auto Select mode the Manufacturer
Code can be read using a Bus Read operation
with A0 = V
may be set to either V
and A1 = VIL. The other address bits
IL
or VIH. The Manufa cturer
IL
Code for STMicroelectronics is 20h.
The Device Code can be read using a B us Read
operation with A0 = V
address bits may be set to e ither V
and A1 = VIL. The other
IH
or VIH. The
IL
Device Code for the M29W512B is 27h.
Program Command. The Program command
can be used to program a value to one address in
the memory array at a time. The command requires four Bus Write operations, the final write operation latches the address and data in the internal
state machine and starts the Program/Erase Controller.
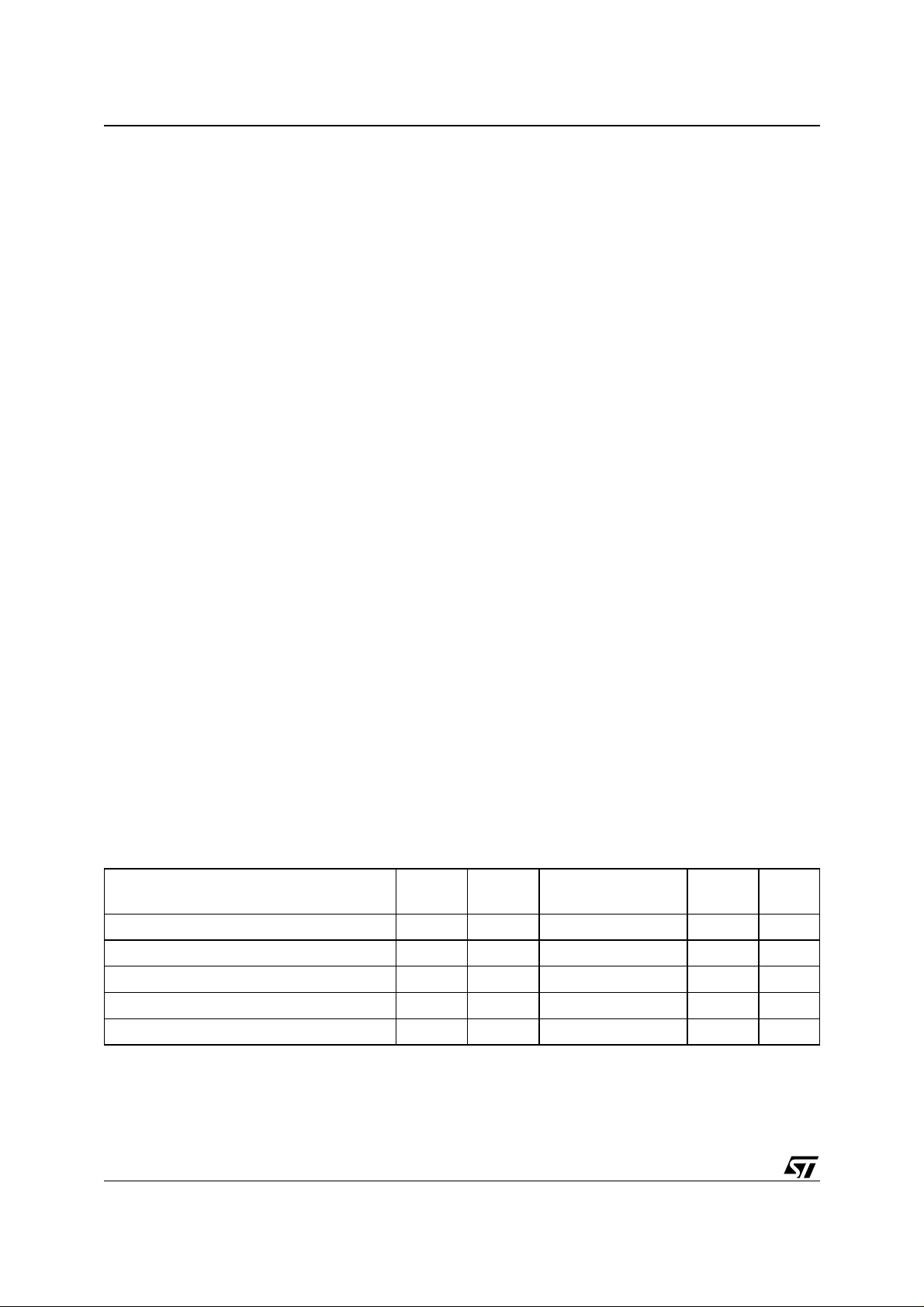
Table 4. Commands
Bus Write Operations
Command
Read/Reset
Auto Select 3 555 AA 2AA 55 555 90
Program 4 555 AA 2AA 55 555 A0 PA PD
Unlock Bypass 3 555 AA 2AA 55 555 20
Unlock Bypass
Program
Unlock Bypass Reset 2 X 90 X 00
Chip Erase 6 555 AA 2AA 55 555 80 555 AA 2AA 55 555 10
Note: X Don’t Care, PA Program Address, PD Program Data.
All values in the table are in hexadecimal.
The Comman d Interface only uses address bits A0-A10 to ver i fy the commands, the upper address bi ts are Don’t Care.
Read/Re set. After a Read/Reset command, read the memory as normal until another command is issued.
Auto Select. After an Auto Select command, read Manufacturer ID or Device ID.
Program, Un lock Bypa ss Program, Ch ip Erase. Aft er t hese commands read the S ta tus Register until the Program/Erase Cont roller com -
pletes and the memory returns to Read Mode.
Unlock Bypass. After the Unlock Bypass command issue Unlock Bypass Program or Unlock Bypass Reset commands.
Unlock Bypass Reset. After the Unlock Bypass Reset command read the memory as normal until another command is issued.
1X F0
3 555 AA 2AA 55 X F0
2X A0PAPD
1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th
Length
Addr Data Addr Data Addr Data Addr Data Addr Data Addr Data
5/18
M29W512B
During the program operat ion the memo ry will ignore all commands. I t is n ot poss ible t o iss ue any
command to abort or pause the operation. Typical
program times are given in Table 5. Bus Read operations during the program o peration will output
the Status Register on the Data Inputs/Outputs.
See the section on the S tatus Register for more
details.
After the program operation has completed the
memory will return to the Read mode, unle ss an
error has occurred. When an error occurs the
memory will continue to output the Status Register. A Read/Reset command must be issued to reset the error condition and return to Read mode.
Note that the Program command cannot change a
bit set at ’0’ back to ’1’. The Chip Erase command
must be used to set all the bits in the memory from
’0’ to ’1’.
Unlock Bypass Command. The Unlock Bypass
command is used in conjunction with the Unlock
Bypass Program command to program the memory. When the access time to the device is long (as
with some EPROM programmers) considerable
time saving can be made by using these commands. Three Bus Write operations are requ ired
to issue the Unlock Bypass command.
Once the Unlock Bypas s command has bee n issued the memory will only accept the Unloc k Bypass Program command and the Unlock Bypass
Reset command. The memory can be read as if in
Read mode.
Unlock Bypass Program Command. The Unlock Bypass Prog ram comma nd can be used to
program one address in memory at a time. The
command requires two B us Write operations, the
final write operation latches the address and data
in the internal stat e machine and starts th e Program/Erase Controller.
The Program operation using the Unlock Bypass
Program command behaves identically to the Program operation using the Program command. The
operation cannot be aborted and t he Status Register is read. Errors must be reset using the Read/
Reset command, which l eaves the device in Unlock Bypass Mode. See the Program command for
details on the behavior.
Unlock Bypass Reset Command. The Unlock
Bypass Reset command can be used to return t o
Read/Reset mode from Unlock Bypass Mode.
Two Bus Write operations are required to issue the
Unlock Bypass Reset command.
Chip Erase Command. The Chip Erase command can be used to erase the m emory. Six B us
Write operations are required to issue the Chip
Erase Command and start the Program/Erase
Controller.
All Bus Read operations during the Chip Erase operation will output the Status Register on the Data
Inputs/Outputs. See the section on the Status
Register for more details. Typical chip erase times
are given in Table 5.
After the Chip Erase operation has completed t he
memory will return to the Read Mode, unle ss an
error has occurred. When an error occurs the
memory will continue to output the Status Register. A Read/Reset command must be issued to reset the error condition and return to Read Mode.
The Chip Erase command sets all of the bits in the
memory to ’1’. All previous data is lost.
Table 5. Program, Erase Times and Progra m , Erase Endurance Cycles
= 0 to 70°C)
(T
A
Parameter Min
Chip Erase (All bits in the memory set to ‘0’) 0.5 0.5 sec
Chip Erase 1 1 6 sec
Program 10 10 200 µs
Chip Program 0.7 0.7 4 sec
Program/Erase Cycles 100,000 cycles
Note: 1. TA = 25°C, VCC = 3.3V.
6/18
Typ
(1)
Typical after
100k W/E Cycles
(1)
Max Unit

M29W512B
STATUS REGISTER
Bus Read operations from any address always
read the Status Register during Program and
Erase operations.
The bits in the Status Register are summarized in
Table 6, Status Register Bits.
Data Polling Bit (DQ7). The Data Polling Bit can
be used to identify whether the Program/Erase
Controller has successfully completed its operation. The Data Polling Bit is output on DQ7 when
the Status Register is read.
During Program operations the Data Polling Bit
outputs the complement of the bit being programmed to DQ7. After successful completion of
the Program operation the memory returns to
Read mode and Bus Read operations from the address just programmed o utput DQ7, not its complement.
During Er ase ope rations the Data Polling Bit ou t-
puts ’0’, the complement of the erased state of
DQ7. After successful completion of the Erase operation the memory returns to Read Mode.
Figure 4, Data Polling Flowchart, gives an example of how to use the Data Polling Bit. A Valid Address is the address being programmed or any
address while erasing the chip.
Toggle Bit (DQ6). The Toggle Bit can be used to
identify whether the Program/Erase Controller has
successfully completed its operation. The Toggle
Bit is output on DQ6 wh en the Status Register is
read.
During Program and Erase operations the Toggle
Bit changes from ’0’ to ’ 1’ to ’ 0’, et c., with su ccessive Bus Read operations at any address. After
successful completion of the operation the memory returns to Read mode.
Figure 5, Data Toggle Flowchart, g ives an example of how to use the Data Toggle Bit.
Error Bit (DQ5). The Error Bit can be used to
identify errors detected by the Program/Erase
Controller. The Error B it is set to ’1’ when a Program or Chip Erase operation fails to write the correct d ata to the mem ory. If the Er ror Bit is set a
Read/Reset command must be issued before other commands are issued. The Error bit is output on
DQ5 when the Status Register is read.
Note that the Program command cannot change a
bit set at ’0’ back to ’1’ and attempting to do so may
or may not set DQ5 at ’1’. In both cases, a successive Bus Read operation will show the bit is still ’0’.
The Chip Erase command must be us ed to set a ll
the bits the memory from ’0’ to ’1’.
Table 6. Status Register Bits
Operation Address DQ7 DQ6 DQ5
Program Any Address DQ7
Program Error Any Address DQ7
Chip Erase Any Address 0 Toggle 0
Erase Error Any Address 0 Toggle 1
Note: Unspecified data bi ts should be i gnored.
Toggle 0
Toggle 1
7/18

M29W512B
Figure 4. Dat a Po ll i ng Fl o wc h a rt
START
READ DQ5 & DQ7
at VALID ADDRESS
DQ7
DATA
NO
DQ5
READ DQ7
at VALID ADDRESS
DQ7
DATA
FAIL PASS
= 1
YES
=
NO
YES
YES
=
NO
AI03598
Figure 5. Dat a Toggle Flow c hart
START
READ
DQ5 & DQ6
READ DQ6
DQ6
=
TOGGLE
NO
DQ5
= 1
READ DQ6
TWICE
DQ6
=
TOGGLE
FAIL PASS
NO
YES
YES
NO
YES
AI01370B
8/18

Table 7. AC Measurement Conditions
Parameter
Supply Voltage
V
CC
M29W512B
M29W512B
55 70 / 90 / 120
3.0 to 3.6V 2.7 to 3.6V
Load Capacitance (C
Input Rise and Fall Times
)
L
30pF 30pF
10ns
≤
≤
Input Pulse Voltages 0 to 3V 0 to 3V
Input and Output Timing Ref. Voltages 1.5V 1.5V
Figure 6. AC Testing Input Output Waveform
3V
1.5V
0V
AI01417
Figure 7. AC Testing Load Cir c uit
0.8V
1N914
3.3kΩ
DEVICE
UNDER
TEST
CL = 30pF
10ns
OUT
CL includes JIG capacitance
Table 8. Capacitance
(T
= 25 °C, f = 1 MHz)
A
Symbol Parameter Test Condition Min Max Unit
V
V
IN
OUT
= 0V
= 0V
6pF
12 pF
C
IN
C
OUT
Note: Sampled only, not 100% tested.
Input Capacitance
Output Capacitance
AI02978
9/18

M29W512B
Table 9. DC Characteristics
(T
= 0 to 70°C)
A
Symbol Parameter Test Condition Min Max Unit
I
I
LO
I
CC1
I
CC2
I
CC3
V
V
V
OL
V
OH
V
I
ID
V
LKO
Note: 1. Sampled only, not 100% tested.
Input Leakage Current
LI
Output Leakage Current
Supply Current (Read)
Supply Current (Standby)
(1)
Supply Current (Program/Erase)
Input Low Voltage –0.5 0.8 V
IL
Input High Voltage 2
IH
Output Low Voltage
Output High Voltage
Identification Voltage 11.5 12.5 V
ID
Identification Current
Program/Erase Lockout Supply
(1)
Voltage
0V ≤ V
0V ≤ V
E
= VIL, G = VIH, f = 6MHz
E
≤ V
IN
CC
≤ V
OUT
= VCC ± 0.2V
CC
Program/Erase
Controller active
I
= 1.8mA
OL
I
= –100µA VCC – 0.4
OH
A9 = V
ID
±1 µA
±1 µA
10 mA
100 µA
20 mA
V
+ 0.5
CC
0.45 V
100 µA
1.8 2.3 V
V
V
10/18

Table 10. Read AC Characteristics
(TA = 0 to 70°C)
Symbol Alt Parameter Test Condition
= VIL,
Address Valid to Next Address
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
t
RC
Valid
t
Address Valid to Output Valid
ACC
Chip Enable Low to Output
t
LZ
Transition
t
Chip Enable Low to Output Valid
CE
Output Enable Low to Output
t
OLZ
Transition
t
Output Enable Low to Output Valid
OE
t
Chip Enable High to Output Hi-Z
HZ
t
Output Enable High to Output Hi-Z
DF
Chip Enable, Output Enable or
t
Address Transition to Output
OH
Transition
t
AVAV
t
AVQV
t
ELQX
t
ELQV
t
GLQX
t
GLQV
t
EHQZ
t
GHQZ
t
EHQX
t
GHQX
t
AXQX
Note: 1. Sampled only, not 100% tested.
E
G
= V
E
= VIL,
G
= V
= V
G
G
= V
= V
E
E
= V
G
= V
E
= V
IL
IL
IL
IL
IL
IL
IL
IL
M29W512B
M29W512B
Unit
55 70 90 / 120
Min 55 70 90 ns
Max 55 70 90 ns
Min000ns
Max 55 70 90 ns
Min000ns
Max 30 30 35 ns
Max 20 25 30 ns
Max 20 25 30 ns
Min000ns
Figure 8. Read Mode AC Waveforms
A0-A15
tAVQV tAXQX
E
G
DQ0-DQ7
tAVAV
VALID
tELQV
tELQX tEHQZ
tGLQX tGHQX
tGLQV
tGHQZ
VALID
tEHQX
AI02977
11/18

M29W512B
Table 11. Write AC Characteristics, Write Enable Controlled
(T
= 0 to 70 °C)
A
Symbol Alt Parameter
t
AVAV
t
ELWL
t
WLWH
t
DVWH
t
WHDX
t
WHEH
t
WHWL
t
AVWL
t
WLAX
t
GHWL
t
WHGL
t
VCHEL
t
Address Valid to Next Address Valid Min 55 70 90 ns
WC
t
Chip Enable Low to Write Enable Low Min 0 0 0 ns
CS
t
Write Enable Low to Write Enable High Min 40 45 45 ns
WP
t
Input Valid to Write Enable High Min 25 30 45 ns
DS
t
Write Enable High to Input Transition Min 0 0 0 ns
DH
t
Write Enable High to Chip Enable High Min 0 0 0 ns
CH
t
Write Enable High to Write Enable Low Min 30 30 30 ns
WPH
t
Address Valid to Write Enable Low Min 0 0 0 ns
AS
t
Write Enable Low to Address Transition Min 40 45 45 ns
AH
Output Enable High to Write Enable Low Min 0 0 0 ns
t
Write Enable High to Output Enable Low Min 0 0 0 ns
OEH
t
VCSVCC
High to Chip Enable Low
Min 50 50 50 µs
M29W512B
Unit
55 70 90 / 120
Figure 9. Write AC Waveforms, Write Enable Control led
tAVAV
A0-A15
E
G
W
DQ0-DQ7
V
CC
tAVWL
tELWL
tVCHEL
VALID
tWLWHtGHWL
tDVWH
tWLAX
tWHEH
tWHGL
tWHWL
tWHDX
VALID
AI02757
12/18

Table 12. Write AC Characteristics, Chip Enable Controlled
(T
= 0 to 70 °C)
A
Symbol Alt Parameter
t
AVAV
t
WLEL
t
ELEH
t
DVEH
t
EHDX
t
EHWH
t
EHEL
t
AVEL
t
ELAX
t
GHEL
t
EHGL
t
VCHWL
t
Address Valid to Next Address Valid Min 55 70 90 ns
WC
t
Write Enable Low to Chip Enable Low Min 0 0 0 ns
WS
t
Chip Enable Low to Chip Enable High Min 40 45 45 ns
CP
t
Input Valid to Chip Enable High Min 25 30 45 ns
DS
t
Chip Enable High to Input Transition Min 0 0 0 ns
DH
t
Chip Enable High to Write Enable High Min 0 0 0 ns
WH
t
Chip Enable High to Chip Enable Low Min 30 30 30 ns
CPH
t
Address Valid to Chip Enable Low Min 0 0 0 ns
AS
t
Chip Enable Low to Address Transition Min 40 45 45 ns
AH
Output Enable High Chip Enable Low Min 0 0 0 ns
t
Chip Enable High to Output Enable Low Min 0 0 0 ns
OEH
t
VCSVCC
High to Write Enable Low
Min 50 50 50 µs
M29W512B
M29W512B Unit
55 70 90 / 120
Figure 10. Write AC Waveforms, Chip Enable Controlled
tAVAV
A0-A15
W
G
E
DQ0-DQ7
V
CC
tAVEL
tWLEL
tVCHWL
VALID
tELEHtGHEL
tDVEH
tELAX
tEHWH
tEHGL
tEHEL
tEHDX
VALID
AI02758
13/18

M29W512B
Table 13. Ordering Information Scheme
Example: M29W512B 70 NZ 1 T
Device Type
M29
Operating Voltage
W = V
Device Function
512B = 512 Kbit (64Kb x8), Bulk
Speed
55 = 55 ns
70 = 70 ns
90 = 90 ns
120 = 120 ns
Package
NZ = TSOP32: 8 x 14 mm
K = PLCC32
= 2.7 to 3.6V
CC
Temperature Range
1 = 0 to 70 °C
Option
T = Tape & Reel Packing
Note: The last two characters o f the ordering code m ay be replaced by a letter code f or preprogram m ed
parts, otherwise devices are shipped from the factory with the memory content bits erased to ’1’.
For a list of available options (Speed, Pac kage, etc...) or for furthe r information on any aspect of this device, please contact the ST Sales Office nearest to you.
14/18

Table 14. Revision History
Date Revision Details
July 1999 First Issue
Document type: from Preliminary Data to Data Sheet
03/09/00
Status Register bit DQ5 clarification
Data Polling Flowchart diagram change (Figure 4)
Data Toggle Flowchart diagram change (Figure 5)
M29W512B
15/18

M29W512B
Table 15. TSOP32 - 32 lead Plastic Thin Small Outline, 8 x 14mm, Package Mechanical Data
Symbol
Typ Min Max Typ Min Max
A 1.20 0.0472
A1 0.05 0.15 0.0020 0.0059
A2 0.95 1.05 0.0374 0.0413
B 0.17 0.27 0.0067 0.0106
C 0.10 0.21 0.0039 0.0083
D 13.80 14.20 0.5433 0.5591
D1 12.30 12.50 0.4843 0.4921
E 7.90 8.10 0.3110 0.3189
e 0.50 – – 0.0197 – –
L 0.50 0.70 0.0197 0.0276
mm inches
α
N 32 32
CP 0.10 0.0039
0° 5° 0° 5°
Figure 11. TSOP32 - 32 lead Plastic Thin Small Outline, 8 x 14mm, Package Outline
A2
1 N
e
E
B
N/2
D1
D
A
CP
TSOP-a
Drawing is not to scale.
16/18
DIE
C
LA1 α

M29W512B
Table 16. PLCC32 - 32 lead Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier, rectangular, Packag e Mec han ical Data
Symbol
A 2.54 3.56 0.1000 0.1402
A1 1.52 2.41 0.0598 0 .0949
A2 0.38 0.0150
B 0.33 0.53 0.0130 0.0209
B1 0.66 0.81 0.0260 0 .0319
D 12.32 12.57 0.4850 0 .4949
D1 11.35 11.56 0.4469 0.4551
D2 9.91 10.92 0.3902 0 .4299
E 14.86 15.11 0.5850 0.5949
E1 13.89 14.1 0 0.5469 0.5551
E2 12.45 13.4 6 0.4902 0.5299
e 1.27 – – 0.0500 – –
F 0.00 0.25 0.0000 0.0098
R 0.89 – – 0.0350 – –
N32 32
Nd 7 7
Ne 9 9
CP 0.10 0.0039
Typ Min Max Typ Min Max
mm in ches
Figure 12. PLCC32 - 32 lead Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier, rectangular, Pac kage Ou tline
D
D1
1 N
Ne E1 E
F
D2/E2
A2
B
0.51 (.020)
1.14 (.045)
PLCC
Drawing is not to scale.
Nd
R
CP
A
A1
B1
e
17/18

M29W512B
Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, STMicroelectronics assumes no responsibility for the consequences
of use of such information nor for any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted
by implic ation or o therwise under any patent or patent rights of STMicroelectronics. Specifications menti oned in th i s publicati on ar e subject
to change without notice. This publication supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied. STMicroelectronics products are not
authorized for use as c ri t i cal components in life support dev i ces or systems without express writ t en approval of STMicro el ectronics.
The ST log o i s registered tradem ark of STMicroelectronics
2000 STMi croelectronics - All Ri ghts Rese rved
All other names are the property of their resp ective owners.
Australi a - Brazil - C hi na - Finland - F rance - Ger m any - Hong K ong - India - It al y - Japan - Ma la ysia - Malta - Morocco -
Singapor e - Spain - Sweden - Switz erl and - Unit ed Kingdom - U.S.A.
STMicroelect ro n ics GRO UP OF COMPANI ES
http://www.st.com
18/18
 Loading...
Loading...