Seagate ST100FM0052, ST100FM0012, ST100FM0002, ST200FM0002, ST200FM0012 User Manual
...
Product Manual
Pulsar®.2 SAS
Standard Models
ST800FM0002
ST800FM0032
ST400FM0002
ST400FM0042
ST200FM0002
ST200FM0042
ST100FM0002
ST100FM0052
Self-Encrypting Drive Models
ST800FM0012
ST800FM0042
SED FIPS140-2 Models
ST800FM0022
100666271
Rev. C
March 2013
Document Revision History
Revision Date Description of changes
Rev. A 08/11/2011 Initial release.
Rev. B 04/16/2012 fc, 1-2, 6-7, 11, 13-14, 17, 23, 39, 41-43, 54, 56-57 & 63.
Rev. C 03/08/2013 fc & 1-2.
© 2013 Seagate Technology LLC. All rights reserved.
Publication number: 100666271, Rev. C March 2013
Seagate, Seagate Technology and the Wave logo are registered trademarks of Seagate Technology LLC in the United States and/or
other countries. Pulsar and SeaTools are either trademarks or registered trademarks of Seagate Technology LLC or one of its affiliated
companies in the United States and/or other countries. The FIPS logo is a certification mark of NIST, which does not imply product
endorsement by NIST, the U.S., or Canadian governments.All other trademarks or registered trademarks are the property of their
respective owners.
No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form without written permission of Seagate Technology LLC.
Call 877-PUB-TEK1 (877-782-8351) to request permission.
When referring to drive capacity, one gigabyte, or GB, equals one billion bytes and one terabyte, or TB, equals one trillion bytes. Your
computer’s operating system may use a different standard of measurement and report a lower capacity. In addition, some of the listed
capacity is used for formatting and other functions, and thus will not be available for data storage. Actual quantities will vary based on
various factors, including file size, file format, features and application software. Actual data rates may vary depending on operating
environment and other factors. The export or re-export of hardware or software containing encryption may be regulated by the U.S.
Department of Commerce, Bureau of Industry and Security (for more information, visit www.bis.doc.gov), and controlled for import
and use outside of the U.S. Seagate reserves the right to change, without notice, product offerings or specifications.
CONTENTS
1.0 SCOPE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
2.0 APPLICABLE STANDARDS AND REFERENCE DOCUMENTATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2.1 STANDARDS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2.1.1 Electromagnetic compatibility. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2.1.2 Electromagnetic compliance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
2.1.3 European Union Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
2.1.4 China Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2.2 REFERENCE DOCUMENTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
3.0 GENERAL DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
3.1 STANDARD FEATURES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
3.2 MEDIA DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
3.3 PERFORMANCE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
3.4 RELIABILITY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
3.5 FORMATTED CAPACITIES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
3.6 PROGRAMMABLE DRIVE CAPACITY. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3.7 FACTORY-INSTALLED OPTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3.8 THIN PROVISIONING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3.8.1 Logical Block Provisioning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3.8.2 Thin Provisioning capabilities. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3.8.3 UNMAP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
3.8.4 FORMAT UNIT command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
3.8.5 Protection Information (PI) and Security (SED) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
4.0 PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
4.1 INTERNAL DRIVE CHARACTERISTICS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
4.2 PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
4.2.1 Access time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
4.2.2 FORMAT UNIT command execution time for 512-byte LBA’s (minutes) . . . . . . 10
4.2.3 Performance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
4.3 START/STOP TIME . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
4.4 CACHE CONTROL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
4.4.1 Caching write data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
5.0 RELIABILITY SPECIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
5.1 ERROR RATES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
5.1.1 Unrecoverable Errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
5.1.2 Interface errors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
5.2 ENDURANCE MANAGEMENT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
5.2.1 Wear Leveling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
5.2.2 Garbage Collection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
5.2.3 Write Amplification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
5.2.4 UNMAP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
5.2.5 Data Retention . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
5.2.6 Lifetime Endurance Management (Available on select models) . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
5.2.7 SSD Percentage Used Endurance Indicator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
5.3 RELIABILITY AND SERVICE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.3.1 Annualized Failure Rate (AFR) and Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF) . . . . 15
5.3.2 Preventive maintenance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.3.3 Hot plugging the drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.3.4 S.M.A.R.T. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.3.5 Thermal monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
5.3.6 Drive Self Test (DST) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
PULSAR.2 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C I

CONTENTS
5.3.7 Product warranty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
6.0 PHYSICAL/ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
6.1 POWER SPECIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
6.1.1 Power consumption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
6.2 AC POWER REQUIREMENTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
6.3 DC POWER REQUIREMENTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
6.3.1 Conducted noise immunity. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
6.3.2 Power sequencing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
6.3.3 Current profiles. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
6.4 POWER DISSIPATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
6.5 ENVIRONMENTAL LIMITS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
6.5.1 Temperature. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
6.5.2 Relative humidity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
6.5.3 Effective altitude (sea level) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
6.5.4 Shock and vibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
6.5.5 Air cleanliness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
6.5.6 Corrosive environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
6.5.7 Electromagnetic susceptibility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
6.6 MECHANICAL SPECIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
7.0 ABOUT FIPS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
8.0 ABOUT SELF-ENCRYPTING DRIVES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
8.1 DATA ENCRYPTION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
8.2 CONTROLLED ACCESS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
8.2.1 Admin SP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
8.2.2 Locking SP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
8.2.3 Default password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
8.3 RANDOM NUMBER GENERATOR (RNG) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
8.4 DRIVE LOCKING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
8.5 DATA BANDS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
8.6 CRYPTOGRAPHIC ERASE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
8.7 AUTHENTICATED FIRMWARE DOWNLOAD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
8.8 POWER REQUIREMENTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
8.9 SUPPORTED COMMANDS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
8.10 SANITIZE - CRYPTOGRAPHIC ERASE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
8.11 REVERTSP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
8.12 SANITIZE FEATURE SET ON SED DRIVES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
9.0 DEFECT AND ERROR MANAGEMENT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
9.1 DRIVE INTERNAL DEFECTS/ERRORS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
9.2 DRIVE ERROR RECOVERY PROCEDURES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
9.3 SAS SYSTEM ERRORS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
9.4 BACKGROUND MEDIA SCAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
9.5 AUTO-REALLOCATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
9.6 PROTECTION INFORMATION (PI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
9.6.1 Levels of PI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
9.6.2 Setting and determining the current Type Level. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
9.6.3 Identifying a Protection Information drive. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
10.0 INSTALLATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
10.1 DRIVE ORIENTATION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
10.2 COOLING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
PULSAR.2 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C II

CONTENTS
10.3 DRIVE MOUNTING. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
10.4 GROUNDING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
11.0 INTERFACE REQUIREMENTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
11.1 SAS FEATURES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
11.1.1 Task management functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
11.1.2 Task management responses. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
11.2 DUAL PORT SUPPORT. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
11.3 SCSI COMMANDS SUPPORTED . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
11.3.1 INQUIRY data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
11.3.2 MODE SENSE data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
11.4 MISCELLANEOUS OPERATING FEATURES AND CONDITIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
11.4.1 SAS physical interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
11.4.2 Physical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
11.4.3 Connector requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
11.4.4 Electrical description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
11.4.5 Pin descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
11.4.6 SAS transmitters and receivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
11.4.7 Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
11.5 SIGNAL CHARACTERISTICS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
11.5.1 Ready LED Out . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
11.5.2 Differential signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
11.6 SAS-2 SPECIFICATION COMPLIANCE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
11.7 ADDITIONAL INFORMATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
PULSAR.2 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C III

FIGURES
Figure 1. Current profiles for 800GB models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Figure 2. Current profiles for 400GB models. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Figure 3. Current profiles for 200GB models. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Figure 4. Current profiles for 100GB models. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Figure 5. 800GB (at 6Gb) DC current and power vs. input/output operations per second . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Figure 6. 400GB (at 6Gb) DC current and power vs. input/output operations per second . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Figure 7. 200GB (at 6Gb) DC current and power vs. input/output operations per second . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Figure 8. 100GB (at 6Gb) DC current and power vs. input/output operations per second . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Figure 9. Temperature check point location - 15mm drives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Figure 10. Temperature check point location - 7mm drives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Figure 11. Recommended mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Figure 12. Mounting configuration dimensions (800GB models) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Figure 13. Mounting configuration dimensions (400, 200 & 100GB models) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Figure 14. Example of FIPS tamper evidence labels. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Figure 15. Physical interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Figure 16. Air flow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Figure 17. Physical interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Figure 18. SAS device plug dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Figure 19. SAS device plug dimensions (detail) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Figure 20. SAS transmitters and receivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
PULSAR.2 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C IV

Seagate Technology Support Services
For information regarding online support and services, visit
Available services include:
• Presales & Technical support
• Global Support Services telephone numbers & business hours
• Authorized Service Centers
Warranty terms will vary based on type of warranty chosen: “Managed Life” or “Usage Based”. Consult your Seagate sales
representative for warranty terms and conditions.
For information regarding data recovery services, visit
For Seagate OEM and Distribution partner portal, visit
For Seagate reseller portal, visit
http://www.seagate.com/support/downloads/seatools/
http://www.seagate.com/about/contact-us/technical-support/
http://www.seagate.com/services-software/data-recovery-services/
http://www.seagate.com/partners
Pulsar.2 SAS Product Manual, Rev. C 1
1.0 SCOPE
This manual describes Seagate Technology® LLC, Pulsar
Pulsar.2 drives support the SAS Protocol specifications to the extent described in this manual. The SAS Interface Manual (part number
100293071) describes the general SAS characteristics of this and other Seagate SAS drives. The Self-Encrypting Drive Reference
Manual, part number 100515636, describes the interface, general operation, and security features available on Self-Encrypting Drive
models.
Product data communicated in this manual is specific only to the model numbers listed in this manual. The data listed in this manual may
not be predictive of future generation specifications or requirements. If you are designing a system which will use one of the models listed
or future generation products and need further assistance, please contact your Field Applications Engineer (FAE) or our global support
services group as shown in See “Seagate Technology Support Services” on page 1.
Unless otherwise stated, the information in this manual applies to standard and Self-Encrypting Drive models.
Standard models Standard SED models FIPS 140-2 LEVEL 2
ST800FM0002 ST800FM0012 ST800FM0022
ST800FM0032 ST800FM0042
ST400FM0002
ST400FM0042
ST200FM0002
ST200FM0042
ST100FM0002
ST100FM0052
®
.2 SAS (Serial Attached SCSI) drives.
Note. Previous generations of Seagate Self-Encrypting Drive models were called Full Disk Encryption (FDE) models before a differ-
entiation between drive-based encryption and other forms of encryption was necessary.
Note. The Self-Encrypting Drive models indicated on the cover of this product manual have provisions for “Security of Data at Rest”
based on the standards defined by the Trusted Computing Group (see www.trustedcomputinggroup.org).
For more information on FIPS 140-2 Level 2 certification Section 7.0 on page 34.
For product certification status visit -
http://csrc.nist.gov/groups/STM/cmvp/documents/140-1/1401vend.htm.
PULSAR.2 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 2

2.0 APPLICABLE STANDARDS AND REFERENCE DOCUMENTATION
The drives documented in this manual have been developed as system peripherals to the highest standards of design and construction.
The drives depend on host equipment to provide adequate power and environment for optimum performance and compliance with
applicable industry and governmental regulations. Special attention must be given in the areas of safety, power distribution, shielding,
audible noise control, and temperature regulation. In particular, the drives must be securely mounted to guarantee the specified
performance characteristics. Mounting by bottom holes must meet the requirements of Section 10.3.
2.1 STANDARDS
The Pulsar.2 family complies with Seagate standards as noted in the appropriate sections of this manual and the Seagate SAS Interface
Manual, part number 100293071.
The drives are recognized in accordance with UL 60950 and CSA 60950 as tested by UL(CSA) and EN60950 as tested by TUV.
The security features of Self-Encrypting Drive models are based on the “TCG Storage Architecture Core Specification” and the “TCG
Storage Workgroup Security Subsystem Class: Enterprise_A” specification with additional vendor-unique features as noted in this product
manual.
2.1.1 Electromagnetic compatibility
The drive, as delivered, is designed for system integration and installation into a suitable enclosure prior to use. The drive is supplied as a
subassembly and is not subject to Subpart B of Part 15 of the FCC Rules and Regulations nor the Radio Interference Regulations of the
Canadian Department of Communications.
The design characteristics of the drive serve to minimize radiation when installed in an enclosure that provides reasonable shielding. The
drive is capable of meeting the Class B limits of the FCC Rules and Regulations of the Canadian Department of Communications when
properly packaged; however, it is the user’s responsibility to assure that the drive meets the appropriate EMI requirements in their system.
Shielded I/O cables may be required if the enclosure does not provide adequate shielding. If the I/O cables are external to the enclosure,
shielded cables should be used, with the shields grounded to the enclosure and to the host controller.
2.1.1.1 Electromagnetic susceptibility
As a component assembly, the drive is not required to meet any susceptibility performance requirements. It is the responsibility of those
integrating the drive within their systems to perform those tests required and design their system to ensure that equipment operating in the
same system as the drive or external to the system does not adversely affect the performance of the drive. See Tables 10 through 12, DC
power requirements.
PULSAR.2 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 3

2.1.2 Electromagnetic compliance
Seagate uses an independent laboratory to confirm compliance with the directives/standards for CE Marking and C-Tick Marking. The
drive was tested in a representative system for typical applications. The selected system represents the most popular characteristics for
test platforms. The system configurations include:
• Typical current use microprocessor
• Keyboard
• Monitor/display
• Printer
• Mouse
Although the test system with this Seagate model complies with the directives/standards, we cannot guarantee that all systems will comply.
The computer manufacturer or system integrator shall confirm EMC compliance and provide the appropriate marking for their product.
Electromagnetic compliance for the European Union
If this model has the CE Marking it complies with the European Union requirements of the Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive 2004/
108/EC as put into place on 20 July 2007.
Australian C-Tick
If this model has the C-Tick Marking it complies with the Australia/New Zealand Standard AS/NZ CISPR22 and meets the Electromagnetic
Compatibility (EMC) Framework requirements of Australia’s Spectrum Management Agency (SMA).
Korean KCC
If these drives have the Korean Communications Commission (KCC) logo, they comply with KN22 and KN61000.
Taiwanese BSMI
If this model has the Taiwanese certification mark then it complies with Chinese National Standard, CNS13438.
2.1.3 European Union Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS)
The European Union Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive restricts the presence of chemical substances, including Lead
(Pb), in electronic products effective July 2006.
A number of parts and materials in Seagate products are procured from external suppliers. We rely on the representations of our suppliers
regarding the presence of RoHS substances in these parts and materials. Our supplier contracts require compliance with our chemical
substance restrictions, and our suppliers document their compliance with our requirements by providing material content declarations for
all parts and materials for the drives documented in this publication. Current supplier declarations include disclosure of the inclusion of any
RoHS-regulated substance in such parts or materials.
Seagate also has internal systems in place to ensure ongoing compliance with the RoHS Directive and all laws and regulations which
restrict chemical content in electronic products. These systems include standard operating procedures that ensure that restricted
substances are not utilized in our manufacturing operations, laboratory analytical validation testing, and an internal auditing process to
ensure that all standard operating procedures are complied with.
PULSAR.2 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 4
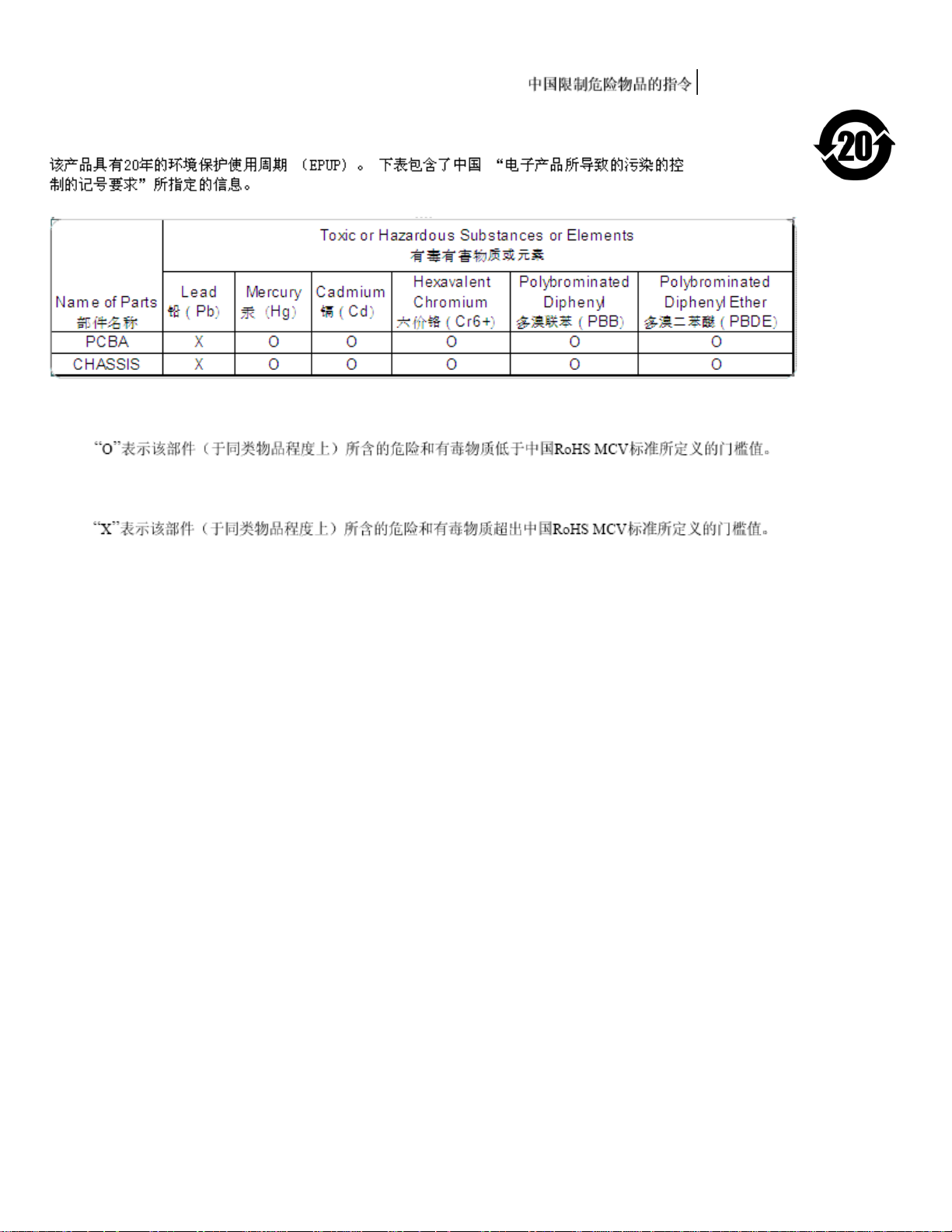
2.1.4 China Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive
This product has an Environmental Protection Use Period (EPUP) of 20 years. The following table contains information
mandated by China's "Marking Requirements for Control of Pollution Caused by Electronic Information Products" Standard.
"O" indicates the hazardous and toxic substance content of the part (at the homogenous material level) is lower than the threshold defined
by the China RoHS MCV Standard.
"X" indicates the hazardous and toxic substance content of the part (at the homogenous material level) is over the threshold defined by the
China RoHS MCV Standard.
2.2 REFERENCE DOCUMENTS
SCSI Commands Reference Manual Seagate part number: 100293068
SAS Interface Manual Seagate part number: 100293071
ANSI SAS Documents
SFF-82232.5” Drive Form Factor with Serial Connector
SFF-8460HSS Backplane Design Guidelines
SFF-8470Multi Lane Copper Connector
SFF-8482SAS Plug Connector
ANSI INCITS.xxx Serial Attached SCSI (SAS-2) Standard (T10/1760-D)
ISO/IEC 14776-xxxSCSI Architecture Model-3 (SAM-4) Standard (T10/1683-D)
ISO/IEC 14776-xxxSCSI Primary Commands-3 (SPC-4) Standard (T10/1731-D)
ISO/IEC 14776-xxxSCSI Block Commands-3 (SBC-3) Standard (T10/1799-D)
ANSI Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) Documents
X3.270-1996(SCSI-3) Architecture Model
Trusted Computing Group (TCG) Documents (apply to Self-Encrypting Drive models only)
TCG Storage Architecture Core Specification, Rev. 1.0
TCG Storage Security Subsystem Class Enterprise Specification, Rev. 1.0
Self-Encrypting Drives Reference Manual Seagate part number: 100515636
JEDEC Standards
JESD218 - Solid-State Drive (SSD) Requirements and Endurance Test Method
JESD219 - Solid-State Drive (SSD) Endurance Workloads
In case of conflict between this document and any referenced document, this document takes precedence.
PULSAR.2 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 5

3.0 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Pulsar.2 drives provide high performance, high capacity data storage for a variety of systems with a Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) interface.
The Serial Attached SCSI interface is designed to meet next-generation computing demands for performance, scalability, flexibility and
high-density storage requirements.
Pulsar.2 drives are random access storage devices designed to support the Serial Attached SCSI Protocol as described in the ANSI
specifications, this document, and the SAS Interface Manual (part number 100293071) which describes the general interface
characteristics of this drive. Pulsar.2 drives are classified as intelligent peripherals and provide level 2 conformance (highest level) with the
ANSI SCSI-1 standard. The SAS connectors, cables and electrical interface are compatible with Serial ATA (SATA), giving future users the
choice of populating their systems with either SAS or SATA drives. This allows users to continue to leverage existing investment in SCSI
while gaining a 6Gb/s serial data transfer rate.
The Self-Encrypting Drive models indicated on the cover of this product manual have provisions for “Security of Data at Rest” based on the
standards defined by the Trusted Computing Group (see www.trustedcomputinggroup.org).
Note. Never disassemble and do not attempt to service items in the enclosure. The drive does not contain user-replaceable parts.
Opening for any reason voids the drive warranty.
3.1 STANDARD FEATURES
Pulsar.2 SAS drives have the following standard features:
• 1.5 / 3.0 / 6.0 Gb Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) interface
• Integrated dual port SAS controller supporting the SCSI protocol
• Support for SAS expanders and fanout adapters
• Firmware downloadable using the SAS interface
• 128 - deep task set (queue)
• Supports up to 32 initiators
• Jumperless configuration
• User-selectable logical block size (512, 520, 524, 528, 4096, 4160, 4192, or 4224 bytes per logical block)
• Industry standard SFF 2.5-inch dimensions
• ECC maximum burst correction length of 96 bits
• No preventive maintenance or adjustments required
• Self diagnostics performed when power is applied to the drive
• Vertical, horizontal, or top down mounting
• Drive Self Test (DST)
• Background Media Scan (BMS)
• Parallel flash access channels
• Power loss data protection
• Thin Provisioning with Block Unmap Support
• Silent operation
• Lifetime Endurance Management (available on certain models)
Pulsar.2 SAS Self-Encrypting Drive models have the following additional features:
• Automatic data encryption/decryption
• Controlled access
• Random number generator
• Drive locking
• 16 independent data bands
• Cryptographic erase of user data for a drive that will be repurposed or scrapped
• Authenticated firmware download
PULSAR.2 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 6
3.2 MEDIA DESCRIPTION
The media used on the drive consists of Multi Layer Cell (MLC) NAND Flash for improved reliability and performance.
3.3 PERFORMANCE
• Programmable multi-segmentable cache buffer
• 600MB/s maximum instantaneous data transfers.
• Background processing of queue
• Non-Volatile Write Cache
Note. There is no significant performance difference between Self-Encrypting Drive and standard (non-Self-Encrypting Drive) mod-
els.
3.4 RELIABILITY
• Annualized Failure Rate (AFR) of 0.44%
• Mean time between failures (MTBF) of 2,000,000 hours
• Incorporates industry-standard Self-Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology (S.M.A.R.T.)
• "Managed Life" or "Usage Based" warranty options [1]
[1] Warranty terms will vary based on type of warranty chosen: “Managed Life” or “Usage Based” Consult your Seagate sales representative for war-
ranty terms and conditions.
3.5 FORMATTED CAPACITIES
Standard OEM models are formatted to 512 bytes per block. The block size is selectable at format time and must be a multiple of 4 bytes.
Users having the necessary equipment may modify the data block size before issuing a FORMAT UNIT command and obtain different
formatted capacities than those listed.
To provide a stable target capacity environment and at the same time provide users with flexibility if they choose, Seagate recommends
product planning in one of two modes:
Seagate designs specify capacity points at certain block sizes that Seagate guarantees current and future products will meet. We
recommend customers use this capacity in project planning, as it ensures a stable operating point with backward and forward compatibility
from generation to generation. The current guaranteed operating points for this product are shown below. The Capacity stated is identical
when the drive is formatted with or without PI enabled.
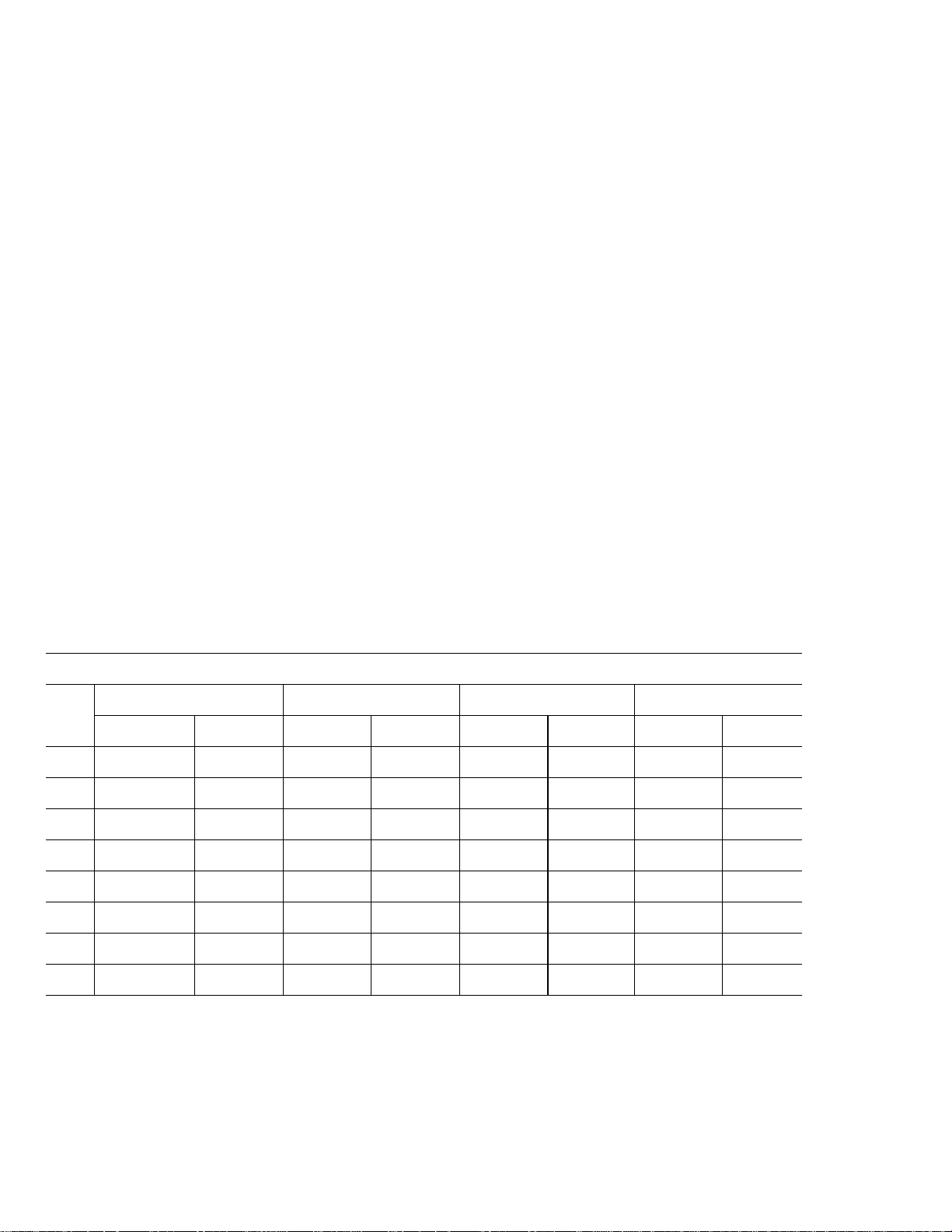
Table 1: Formatted Capacity LBA Count
CAPACITY (LBAS)
LBA
SIZE
512
520
524
528
4096
4160
4192
4224
DECIMAL HEX DECIMAL HEX DECIMAL HEX DECIMAL HEX
1,562,824,368 5D26CEB0h 781,422,768 2E9390B0h 390,721,968 1749F1B0h 195,371,568 BA52230h
1,529,743,600 5B2E08F0h 764,871,800 2D970478h 382,435,904 16CB8240h 191,217,952 B65C120h
1,509,354,136 59F6EA98h 754,677,072 2CFB7550h 377,338,536 167DBAA8h 188,669,272 B3EDD58h
1,487,666,080 58ABFBA0h 743,833,040 2C55FDD0h 371,916,520 162AFEE8h 185,958,264 B157F78h
195,353,046 BA4D9D6h 97,677,846 5D27216h 48,840,246 2E93E36h 24,421,446 174A446h
192,307,693 B7661EDh 96,153,847 5BB30F7h 48,076,924 2DD987Ch 24,038,462 16ECC3Eh
190,839,695 B5FFB8Fh 95,419,848 5AFFDC8h 47,709,924 2D7FEE4h 23,854,962 16BFF72h
189,393,940 B49EC14h 94,696,970 5A4F60Ah 47,348,485 2D27B05h 23,674,243 1693D83h
800GB 400GB 200GB 100GB
PULSAR.2 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 7

3.6 PROGRAMMABLE DRIVE CAPACITY
Using the MODE SELECT command, the drive can change its capacity to something less than maximum. See the MODE SELECT (6)
parameter list table in the SAS Interface Manual, part number 100293071. A value of zero in the Number of Blocks field indicates that the
drive will not change the capacity it is currently formatted to have. A number other than zero and less than the maximum number of LBAs
in the Number of Blocks field changes the total drive capacity to the value in the Number of Blocks field. A value greater than the maximum
number of LBAs is rounded down to the maximum capacity.
3.7 FACTORY-INSTALLED OPTIONS
OEMs may order the following items which are incorporated at the manufacturing facility during production or packaged before shipping.
Some of the options available are (not an exhaustive list of possible options):
• Other capacities can be ordered depending on sparing scheme and LBA size requested.
• Single-unit shipping pack. The drive is normally shipped in bulk packaging to provide maximum protection against transit damage. Units
shipped individually require additional protection as provided by the single unit shipping pack. Users planning single unit distribution
should specify this option.
• The Safety and Regulatory Agency Specifications, part number 75789512, is usually included with each standard OEM drive shipped,
but extra copies may be ordered.
3.8 THIN PROVISIONING
3.8.1 Logical Block Provisioning
The drive is designed with a feature called Thin Provisioning. Thin Provisioning is a technique which does not require Logical Blocks to be
associated to Physical Blocks on the storage medium until such a time as needed. The use of Thin Provisioning is a major factor in SSD
products because it reduces the amount of wear leveling and garbage collection that must be performed. The result is an increase in the
products endurance. For more details on Logical Block Provisioning and Thin Provisioning, Reference the SBC-3 document provided by
the T-10 committee.
3.8.2 Thin Provisioning capabilities
The level of Thin Provisioning support may vary by product model. Devices that support Thin Provisioning are allowed to return a default
data pattern for read requests made to Logical Blocks that have not been mapped to Physical Blocks by a previous WRITE command.
In order to determine if Thin Provisioning is supported and what features of it are implemented requires the system to send a READ
CAPACITY 16 (9Eh) command to the drive. Thin Provisioning and the READ CAPACITY 16 (9Eh) command is defined in the Seagate
SCSI Command Reference 100293068..
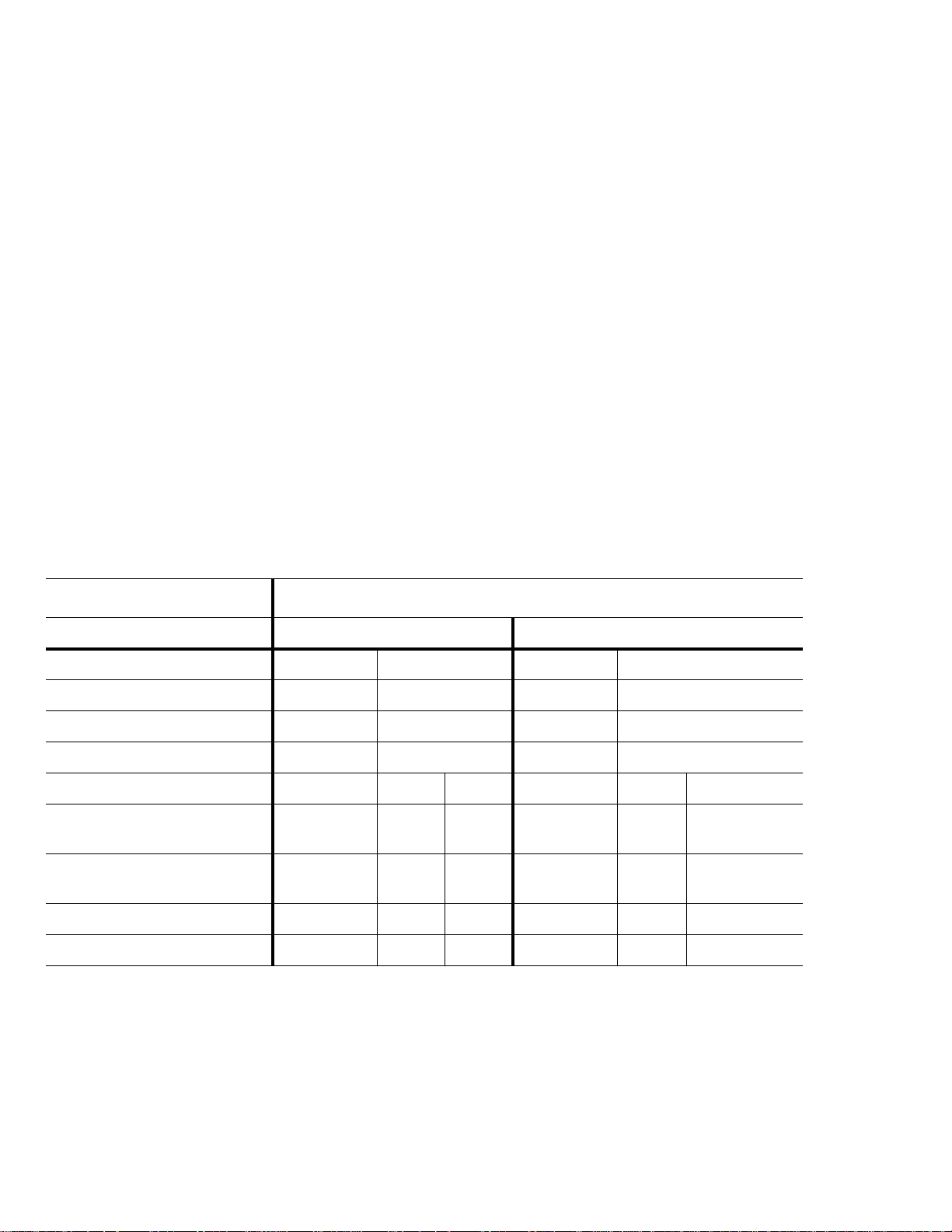
Table 2 Thin Provisioning Product Configuration
Product Configuration LBPME LBPRZ
Non-SED Supported Supported
SED Supported Not Supported
A logical block provisioning management enabled (LBPME) bit set to one indicates that the logical unit implements logical block
provisioning management. An LBPME bit set to zero indicates that the logical unit is fully provisioned and does not implement logical block
provisioning management.
A logical block provisioning read zeros (LBPRZ) bit set to one indicates that, for an unmapped LBA specified by a read operation, the
device server sends user data with all bits set to zero to the data-in buffer. An LBPRZ bit set to zero indicates that, for an unmapped LBA
specified by a read operation, the device server may send user data with all bits set to any value to the data-in buffer.
PULSAR.2 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 8
3.8.3 UNMAP
The UNMAP command requests that the device server break the association of a specific Logical Block address from a Physical Block,
thereby freeing up the Physical Block from use and no longer requiring it to contain user data. An unmapped block will respond to a READ
command with data that is determined by the setting of the LBPRZ bit in the READ CAPACITY parameter data.
3.8.4 FORMAT UNIT command
A device which supports Thin Provisioning will be capable of performing a SCSI FORMAT UNIT command which allocates Logical Blocks
Addresses that are not linked to Physical Block Locations. A FORMAT command will cause all LBAs to become unmapped.
3.8.5 Protection Information (PI) and Security (SED)
The requirements in this section apply to any device which supports LBA unmapping.
In SCSI devices, umapped LBAs are defined as part of the Thin Provisioning model. Support of the Thin Provisioning model is indicated by
the LBPME bit having a value of '1' in the READ CAPACITY (16) parameter data.
When a region of LBA's are erased via cryptographic erase, as part of the erase, the drive shall unmap those LBAs.
If the host attempts to access an unmapped or trimmed LBA, the drive shall return scrambled data. For a given LBA, the data shall be
identical from access to access, until that LBA is either updated with actual data from the host or that LBA is cryptographically erased. The
drive shall report a value of '0' in the LBPRZ field returned in the READ CAPACITY (16) parameter data.
If the host attempts to access an unmapped LBA on a drive that has been formatted with Protection Information (PI), the drive shall return
scrambled PI data for that LBA. Depending on the value of the RDPROTECT field in the data-access command CDB, this may result in the
drive returning a standard PI error to the host.
If the host reduces the addressable capacity of the drive via a MODE SELECT command, the drive shall unmap or trim any LBA within the
inaccessible region of the device.
Additionally, an UNMAP command is not permitted on a locked band.
Table 3 PI and SED Drive Configuration
DRIVE CONFIGURATION
Standard SED
PI Setting Disabled Enabled Disabled Enabled
PROT_EN bit 010 1
LBPME bit 111 1
LBPRZ bit 110 0
PI Check Requested N/A Yes No N/A Yes No
DATA Returned for
Thin Provisioned LBA
PI Returned for
Thin Provisioned LBA
PI Check Performed N/A No No N/A Yes No
0x00 0x00 0x00 Random None Random
None 0xFF 0xFF None None
Scrambled
PI data
Error reported to Host No No No No Yes No
PULSAR.2 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 9
4.0 PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
This section provides detailed information concerning performance-related characteristics and features of Pulsar.2 drives.
Note. Data provided is based on format at 512-bytes.
4.1 INTERNAL DRIVE CHARACTERISTICS
Drive capacity 800400 200100 GB
Flash Memory Type NAND MLC
Emulated LBA Size 512, 520, 524, 528, 4096, 4160, 4192, or 4224
Native Programmable
Page Size 8192 User Bytes
Default Transfer
Alignment Offset 0
4.2 PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
See Section 11.4.1, "SAS physical interface" and the SAS Interface Manual (part number 100293071) for additional timing details.
4.2.1 Access time
Access measurements are taken with nominal power at 25°C ambient temperature. All times are measured using drive diagnostics. The
specifications in the table below are defined as follows:
Page-to-page access time is an average of all possible page-to-page accesses in both directions for a sequentially preconditioned
•
drive.
• Average access time is a true statistical random average of at least 5000 measurements of accesses between programmable
pages on a randomly preconditioned drive.
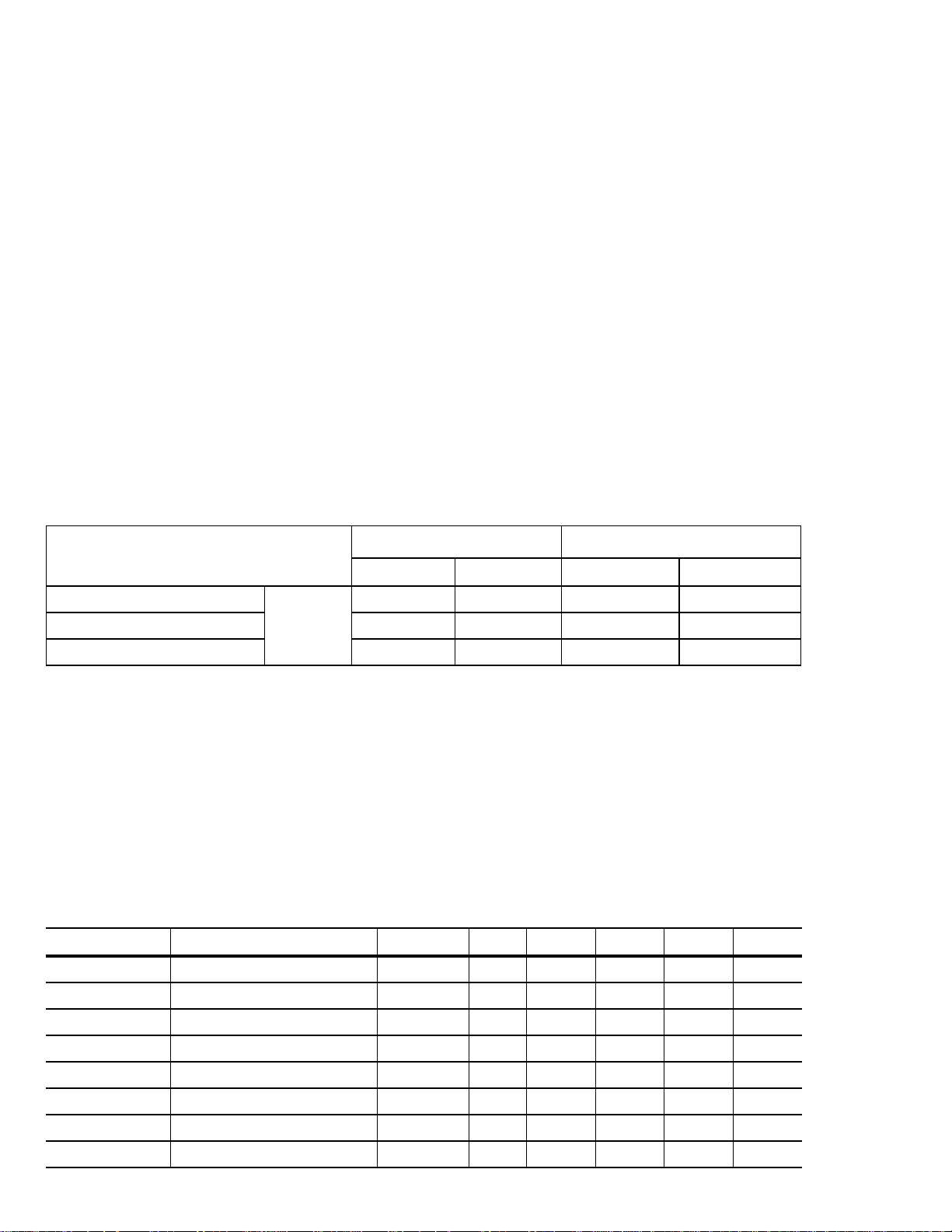
Table 4 Typical Access Time (μsec)
(formatted, rounded off value)
800GB
1,2
400, 200, 100 GB
1,2
READ WRITE READ WRITE
Average
Page to Page 62 136 60 120
Typical
3
Average Latency 273 206
1. Execution time measured from receipt of the Command to the Response.
2. Assumes no errors.
3. Typical access times are measured under nominal conditions of temperature, voltage, and horizontal orientation as measured on a
representative sample of drives.
293 137 227 120
Note. These drives are designed to provide the highest possible performance under typical conditions.
However, due to the nature of Flash memory technologies there are many factors that can result in
2.
4.2.2 FORMAT UNIT command execution time for 512-byte LBA’s (minutes)
The device may be formatted as either a Thin Provisioned device or a Fully Provisioned device. The default format is Thin Provisioned and
is
maximize endurance.
Table 5
CONFIGURATION
Non-SED (Default) Thin Provisioned DCRT = 0 IP = 0 5 5 5 5
Non-SED (Default) Thin Provisioned DCRT = 1 IP = 0 5 5 5 5
values different than those stated in this specification
recommended for most applications. Thin Provisioning provides the most flexibility for the device to manage the flash medium to
Maximum FORMAT UNIT Times (minutes)
Format Mode DCRT Bit IP Bit 800GB 400GB 200GB 100GB
Non-SED Fully Provisioned DCRT = 0 IP = 1 430 130 70 60
Non-SED Fully Provisioned DCRT = 1 IP = 1 280 100 50 30
SED (Default) Thin Provisioned DCRT = 0 IP = 0 5 N/A N/A N/A
SED (Default) Thin Provisioned DCRT = 1 IP = 0 5 N/A N/A N/A
SED Fully Provisioned DCRT = 0 IP = 1 430 N/A N/A N/A
SED Fully Provisioned DCRT = 1 IP = 1 280 N/A N/A N/A
PULSAR.2 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 10
4.2.3 Performance
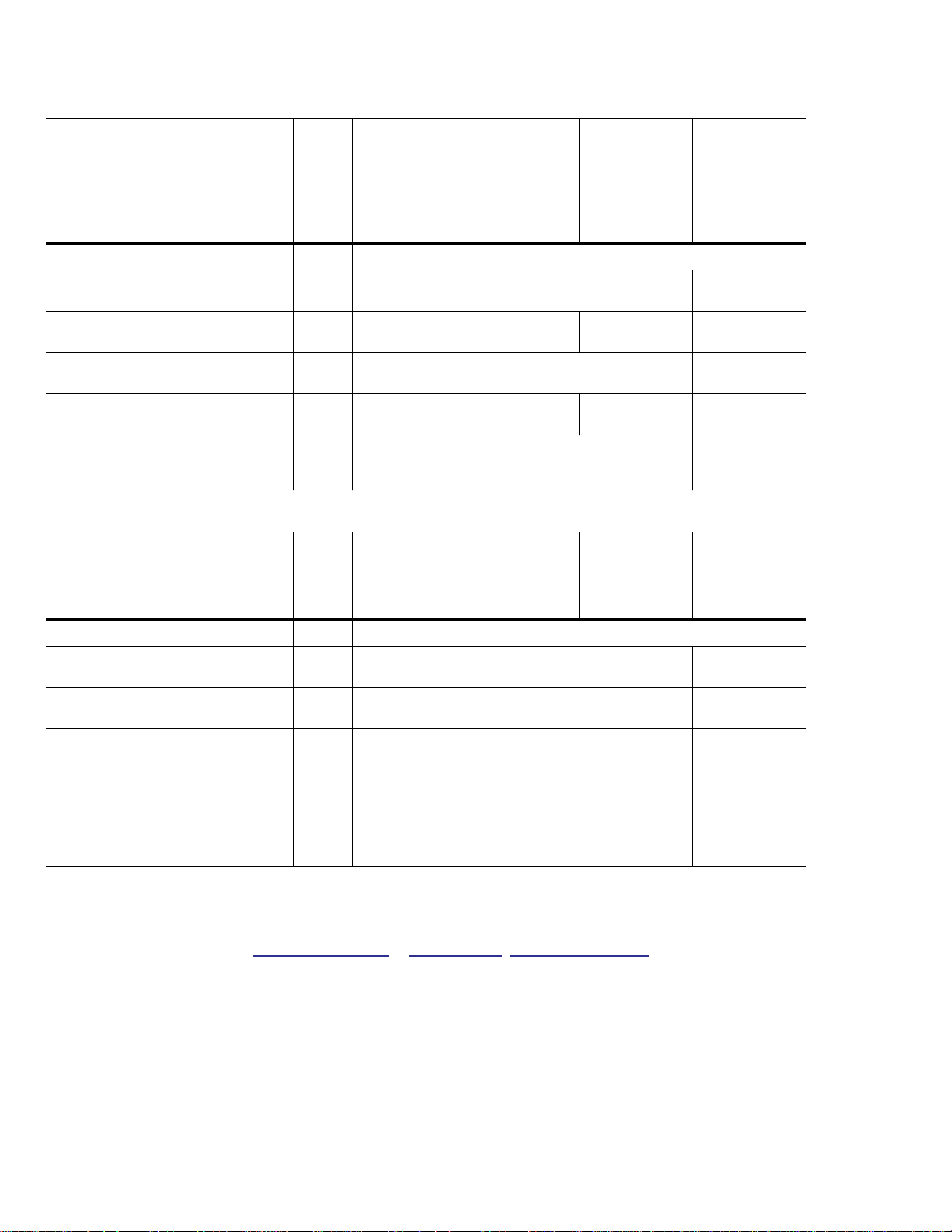
Table 6 Performance (Managed Life Warranty)
NOTE
S
ST800FM00
02
ST800FM00
12
ST800FM00
22
ST400FM0002ST200FM0002ST100FM00
02
Maximum Burst Transfer Rate
Peak sequential 128KB read/write
data transfer rate (MB/s max)
Sustained sequential 128KB read/
write data transfer rate (MB/s)
Peak 4KB random read/write
command rate (IOPs)
Sustained 4KB random read/write
command rate (IOPs)
Sustainable 4KB Random combined
IOPS for 5 year Endurance
(65%/35% R/W, 70% Duty Cycle)
Table 7 Performance (Usage Based Warranty)
[1] 370/200 370/190
[1] 370/200 370/140 370/70 370/35
[2] 48,000/15,000 48,000/12,000
[2] 48,000/15,000 48,000/11,000 48,000/5500 48,000/2800
[3] 23,000 22,000
NOTE
S
Maximum Burst Transfer Rate
Peak sequential 128KB read/write
data transfer rate (MB/s max)
Sustained sequential 128KB read/
write data transfer rate (MB/s)
[1] 370/200 370/190
[1] 370/200 370/190
ST800FM00
32
ST800FM00
42
600MB/s
ST400FM0042ST200FM0042ST100FM00
52
600MB/s
Peak 4KB random read/write
command rate (IOPs)
Sustained 4KB random read/write
command rate (IOPs)
Sustainable 4KB Random combined
IOPS for 5 year Endurance
(65%/35% R/W, 70% Duty Cycle)
[1] Testing performed at Queue Depth = 32, Sequentially Preconditioned drive, using IOMeter 2006.7.27.
[2] Testing performed at Queue Depth = 32, Randomly Preconditioned drive, using IOMeter 2006.7.27.
[3] Testing performed at Queue Depth = 32, Non-Preconditioned drive, using IOMeter 2006.7.27.
[2] 48,000/15,000 48,000/12,000
[2] 48,000/15,000 48,000/12,000
[3] 23,000 22,000
Note. IOMeter is available at http://www.iometer.org/ or http://sourceforge.net/projects/iometer/.
IOMeter is licensed under the Intel Open Source License and the GNU General Public License. Intel does not endorse any IOMeter results.
Peak performance is defined as the typical best case performance that the product will be able to achieve when the product is
preconditioned as mentioned and host commands are aligned on 4KB boundaries.
PULSAR.2 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 11

Sustained performance is defined as the worst case performance that the product will be able to achieve when the product is
preconditioned as mentioned and host commands are aligned on 4KB boundaries. For models that support Lifetime Endurance
Management, write values also take into account the worst case performance throttling that may occur to ensure the product meets
specified reliability specifications.
Due to the nature of Flash memory technologies there are many factors that can result in values different than those stated in this
specification. Some discrepancies can be caused by bandwidth limitations in the host adapter, operating system, or driver limitations. It is
not the intent of this manual to cover all possible causes of performance discrepancies.
When evaluating performance of SSD devices, it is recommended to measure performance of the device in a method that resembles the
targeted application using real world data and workloads. Test time should also be adequately large to ensure that sustainable metrics and
measures are obtained.
4.3 START/STOP TIME
The drive accepts the commands listed in the SAS Interface Manual less than 3 seconds after DC power has been applied.
If the drive receives a NOTIFY (ENABLE SPINUP) primitive through either port and has not received a START STOP UNIT command with
the START bit equal to 0, the drive becomes ready for normal operations within 15 seconds (excluding the error recovery procedure).
If the drive receives a START STOP UNIT command with the START bit equal to 0 before receiving a NOTIFY (ENABLE SPINUP)
primitive, the drive waits for a START STOP UNIT command with the START bit equal to 1. After receiving a START STOP UNIT command
with the START bit equal to 1, the drive waits for a NOTIFY (ENABLE SPINUP) primitive. After receiving a NOTIFY (ENABLE SPINUP)
primitive through either port, the drive becomes ready for normal operations within 15 seconds (excluding the error recovery procedure).
If the drive receives a START STOP UNIT command with the START bit and IMMED bit equal to 1 and does not receive a NOTIFY
(ENABLE SPINUP) primitive within 5 seconds, the drive fails the START STOP UNIT command.
The START STOP UNIT command may be used to command the drive to stop. Stop time is 3 seconds (maximum) from removal of DC
power. SCSI stop time is 3 seconds. There is no power control switch on the drive.
4.4 CACHE CONTROL
All default cache mode parameter values (Mode Page 08h) for standard OEM versions of this drive family are given in Table 20 and 21.
4.4.1 Caching write data
Write caching is a write operation by the drive that makes use of a drive buffer storage area where the data to be written to the medium is
stored while the drive performs the WRITE command.
If the number of write data logical blocks exceed the size of the segment being written into, when the end of the segment is reached, the
data is written into the beginning of the same cache segment, overwriting the data that was written there at the beginning of the operation;
however, the drive does not overwrite data that has not yet been written to the medium.
If write caching is enabled (WCE=1), then the drive may return Good status on a WRITE command after the data has been transferred into
the cache, but before the data has been written to the medium. If an error occurs while writing the data to the medium, and Good status
has already been returned, a deferred error will be generated.
Data that has not been written to the medium is protected by a back up power source which provides the ability of the data to be written to
non-volatile medium in the event of an unexpected power loss.
The SYNCHRONIZE CACHE command may be used to force the drive to write all cached write data to the medium. Upon completion of a
SYNCHRONIZE CACHE command, all data received from previous WRITE commands will have been written to the medium. Tables 19,
20 and 21 show the mode default settings for the drive.
PULSAR.2 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 12

5.0 RELIABILITY SPECIFICATIONS
The following reliability specifications assume correct host and drive operational interface, including all interface timings, power supply
voltages, environmental requirements and drive mounting constraints.
Read Error Rates
Unrecovered Data Less than 1 LBA in 1016 bits transferred
Miscorrected Data Less than 1 LBA in 10
Interface error rate: Less than 1 error in 1012 bits transferred
Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF): 2,000,000 hours
Annualized Failure Rate (AFR): 0.44%
Preventive maintenance: None required
Typical Data Retention with
Power removed (at 40C)
Endurance Rating:
1. Error rate specified with automatic retries and data correction with ECC enabled and all flaws reallocated.
2. As NAND Flash devices age with use, the capability of the media to retain a programmed value begins to deteriorate.
This deterioration is affected by the number of times a particular memory cell is programmed and subsequently erased.
When a device is new, it has a powered off data retention capability of up to several years. With use the retention capability of the device is reduced. Temperature also has an effect on how long a Flash component can retain its programmed value with power removed. At high temperature the retention capabilities of the device are reduced. Data
retention is not an issue with power applied to the SSD. The SSD drive contains firmware and hardware features that
can monitor and refresh memory cells when power is applied.
3. Endurance rating is the expected amount of host data that can be written by product when subjected to a specified workload at a specified operating and storage temperature. For the specific workload to achieve this level of endurance,
please reference JEDEC Specification JESD218. TBW is defined as 1x10^12 Bytes.
1
21
bits transferred
3 months
2
3
Method 1: Full drive writes per day 10
Method 2: TBW (per JEDEC JESD218 800GB = 17,800 TB
400GB = 8800 TB
200GB = 4400 TB
100GB = 2200 TB
5.1 ERROR RATES
The error rates stated in this manual assume the following:
• The drive is operated in accordance with this manual using DC power as defined in paragraph 6.3, "DC power requirements."
• Errors caused by host system failures are excluded from error rate computations.
• Assume random data.
• Default OEM error recovery settings are applied. This includes AWRE, ARRE, full read retries, full write retries and full retry time.
5.1.1 Unrecoverable Errors
An unrecoverable data error is defined as a failure of the drive to recover data from the media. These errors occur due to read or write
problems. Unrecoverable data errors are only detected during read operations, but not caused by the read. If an unrecoverable data error
is detected, a MEDIUM ERROR (03h) in the Sense Key will be reported. Multiple unrecoverable data errors resulting from the same cause
are treated as 1 error.
5.1.2 Interface errors
An interface error is defined as a failure of the receiver on a port to recover the data as transmitted by the device port connected to the
receiver. The error may be detected as a running disparity error, illegal code, loss of word sync, or CRC error.
PULSAR.2 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 13

5.2 ENDURANCE MANAGEMENT
Customer satisfaction with Solid State Drives can be directly related to the internal algorithms which an SSD uses to manage the limited
number of Program-Erase (PE) cycles that NAND Flash can withstand. These algorithms consist of Wearleveling, Garbage Collection,
Write Amplification, Unmap, Data Retention, Lifetime Endurance Management.
5.2.1 Wear Leveling
Wear Leveling is a technique used by the drive to ensure that all Flash cells are written to or exercised as evenly as possible to avoid any
hot spots where some cells are used up faster than other locations. Wear Leveling is automatically managed by the drive and requires no
user interaction. The Seagate algorithm is tuned to operate only when needed to ensure reliable product operation.
5.2.2 Garbage Collection
Garbage Collection is a technique used by the drive to consolidate valid user data into a common cell range freeing up unused or obsolete
locations to be erased and used for future storage needs. Garbage Collection is automatically managed by the drive and requires no user
interaction. The Seagate algorithm is tuned to operate only when needed to ensure reliable product operation.
5.2.3 Write Amplification
While Write Amplification is not an algorithm, it is a major characteristic of SSD's that must be accounted for by all the algorithms that the
SSD implements. The Write Amplification Factor of an SSD is defined as the ratio of Host/User data requested to be written to the actual
amount of data written by the SSD internal to account for the user data and the housekeeping activities such as Wear Leveling and
Garbage Collection. The Write Amplification Factor of an SSD can also be directly affected by the characteristics of the host data being
sent to the SSD to write. The best Write Amplification Factor is achieved for data that is written in sequential LBA's that are aligned on 4KB
boundaries. The worst case Write Amplification Factor typically occurs for randomly written LBA's of transfer sizes that are less than 4KB
and that originate on LBA's that are not on 4KB boundaries.
5.2.4 UNMAP
A new SCSI command has been added to the SSD as part of the Thin Provisioning feature set. Use of the UNMAP command reduces the
Write Amplification Factor of the drive during housekeeping tasks such as Wear Leveling and Garbage Collection. This is accomplished
because the drive does not need to retain data which has been classified by the host as obsolete.
5.2.5 Data Retention
Data Retention is another major characteristic of SSD's that must be accounted for by all the algorithms that the SSD implements. While
powered up, the Data Retention of SSD cells are monitored and rewritten if the cell levels decay to an unexpected level. Data Retention
when the drive is powered off is affected by Program and Erase (PE) cycles and the temperature of the drive when stored.
5.2.6 Lifetime Endurance Management (Available on select models)
As stated in Section 5.2, an SSD has a limited number of Program and Erase (PE) cycles that are capable. In worse case applications, the
write workload could be such that the drive experiences a high Write Amplification Factor that could lead to potential wear out prior to the
drive achieving it's expected field life. Additionally, the Data Retention spec of the SSD needs to be considered to ensure the spec is met
once the drive is worn out. Seagate has implemented a Lifetime Endurance Management technique which helps OEMS and user to avoid
early wear out. By monitoring the write workload being sent to the drive, the drive can add additional response time to WRITE commands
to provide a sustainable level of performance that is capable of being sustained for the life of the drive. Most users may never see this
added response time in their applications.
5.2.7 SSD Percentage Used Endurance Indicator
An application can interrogate the drive through the host to determine an estimate of the percentage of device life that has been used. To
accomplish this, issue a LOG SENSE command to log page 0x11. This allows applications to read the contents of the Percentage Used
Endurance Indicator parameter code. The Percentage Used Endurance Indicator is defined in the T10 document SBC-3 available from the
T10 committee.
PULSAR.2 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 14

5.3 RELIABILITY AND SERVICE
Integrators can enhance the reliability of Pulsar.2 drives by ensuring that the drive receives adequate cooling. Section 6.0 provides
temperature measurements and other information that may be used to enhance the service life of the drive. Section 10.2 provides
recommended air-flow information.
5.3.1 Annualized Failure Rate (AFR) and Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF)
The production drive shall achieve an AFR of 0.44% (MTBF of 2,000,000 hours) when operated in an environment that ensures the case
temperatures do not exceed the values specified in Section 6.5. Operation at case temperatures outside the specifications in Section 6.5
may increase the product AFR (decrease the MTBF). The AFR (MTBF) is a population statistic not relevant to individual units.
The AFR (MTBF) specification is based on the following assumptions for Enterprise Storage System environments:
• 8760 power-on hours per year.
• 250 average on/off cycles per year.
• Operations at nominal voltages.
• Systems will provide adequate cooling to ensure the case temperatures specified in Section 6.5 are not exceeded. Temperatures outside
the specifications in Section 6.5 will increase the product AFR and decrease the MTBF.
5.3.2 Preventive maintenance
No routine scheduled preventive maintenance is required.
5.3.3 Hot plugging the drive
When a drive is powered on by switching the power or hot plugged, the drive runs a self test before attempting to communicate on its’
interfaces. When the self test completes successfully, the drive initiates a Link Reset starting with OOB. An attached device should
respond to the link reset. If the link reset attempt fails, or any time the drive looses sync, the drive initiated link reset. The drive will initiate
link reset once per second but alternates between port A and B. Therefore each port will attempt a link reset once per 2 seconds assuming
both ports are out of sync.
If the self-test fails, the drive does not respond to link reset on the failing port.
Note. It is the responsibility of the systems integrator to assure that no temperature, energy, voltage hazard, or ESD potential hazard
is presented during the hot connect/disconnect operation. Discharge the static electricity from the drive carrier prior to insert
ing it into the system.
5.3.4 S.M.A.R.T.
S.M.A.R.T. is an acronym for Self-Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology. This technology is intended to recognize conditions that
indicate imminent drive failure and is designed to provide sufficient warning of a failure to allow administrators to back up the data before
an actual failure occurs.
-
Note. The drive’s firmware monitors specific attributes for degradation over time but can’t predict instantaneous drive failures.
Each monitored attribute has been selected to monitor a specific set of failure conditions in the operating performance of the drive and the
thresholds are optimized to minimize “false” and “failed” predictions.
Controlling S.M.A.R.T.
The operating mode of S.M.A.R.T. is controlled by the DEXCPT and PERF bits on the Informational Exceptions Control mode page (1Ch).
Use the DEXCPT bit to enable or disable the S.M.A.R.T. feature. Setting the DEXCPT bit disables all S.M.A.R.T. functions. When enabled,
S.M.A.R.T. collects on-line data as the drive performs normal read and write operations. When the PERF bit is set, the drive is considered
to be in “On-line Mode Only” and will not perform off-line functions.
An application can measure off-line attributes and force the drive to save the data by using the REZERO UNIT command. Forcing
S.M.A.R.T. resets the timer so that the next scheduled interrupt is in one hour.
An application can interrogate the drive through the host to determine the time remaining before the next scheduled measurement and
data logging process occurs. To accomplish this, issue a LOG SENSE command to log page 0x3E. This allows applications to control
when S.M.A.R.T. interruptions occur. Forcing S.M.A.R.T. with the REZERO UNIT command resets the timer.
PULSAR.2 SAS PRODUCT MANUAL, REV. C 15
 Loading...
Loading...