
User and maintenance manual
for generating sets
R44
C
3
33504024301NE_0_1


1. Preface .................................................................................................................................................................................................. 3
1.1. General recommendations ....................................................................................................................................................... 3
1.2. Pictograms and their meanings ................................................................................................................................................ 4
1.3. Instructions and safety regulations ........................................................................................................................................... 6
1.3.1 General advice ......................................................................................................................................................................... 6
1.3.2 Risks related to exhaust gases and fuels ................................................................................................................................. 7
1.3.3 Risks related to toxic products .................................................................................................................................................. 7
1.3.4 Risk of fire, burns and explosion ............................................................................................................................................... 8
1.3.5 Risks related to electrical networks .......................................................................................................................................... 8
1.3.6 Dangers presented by electric currents (first aid) ..................................................................................................................... 9
1.3.7 Risks related to moving the set ................................................................................................................................................. 9
1.3.8 Risks related to noise .............................................................................................................................................................. 9
2. General description .............................................................................................................................................................................. 10
2.1. Technical specifications ......................................................................................................................................................... 13
2.2. Identifying sets ....................................................................................................................................................................... 15
2.3. Fluid retention ........................................................................................................................................................................ 16
2.4. Fuel and consumables ........................................................................................................................................................... 16
2.4.1 Specifications ......................................................................................................................................................................... 17
2.4.1.1. Oil grades ................................................................................................................................................................. 17
2.4.1.2. Specifications of coolants ......................................................................................................................................... 18
3. Installation-Connections ...................................................................................................................................................................... 19
3.1. Unloading ............................................................................................................................................................................... 19
3.1.1 Safety during unloading .......................................................................................................................................................... 19
3.1.2 Instructions for unloading ....................................................................................................................................................... 20
3.2. Choice of location .................................................................................................................................................................. 21
3.3. Moving the genset .................................................................................................................................................................. 21
3.4. Connections ........................................................................................................................................................................... 22
3.4.1 Connections - general information .......................................................................................................................................... 22
3.4.2 Power cables .......................................................................................................................................................................... 22
3.4.3 Power connections ................................................................................................................................................................. 23
3.4.4 Battery installation ................................................................................................................................................................. 24
3.5. Protection for individuals and equipment ............................................................................................................................... 24
3.5.1 Earth connection ..................................................................................................................................................................... 24
3.5.2 Earthing system principle ....................................................................................................................................................... 25
3.5.3 TT system ............................................................................................................................................................................... 26
3.5.4 Differential protection .............................................................................................................................................................. 26
3.5.5 Adjusting the genset differential protection ............................................................................................................................. 27
3.6. Connection summary ............................................................................................................................................................. 28
3.7. Special arrangements ............................................................................................................................................................ 29
4. Trailer .................................................................................................................................................................................................. 29
4.1. Trailer linkage ........................................................................................................................................................................ 29
4.2. Check before towing .............................................................................................................................................................. 29
4.3. Operation ............................................................................................................................................................................... 30
4.4. Unhitching the trailer .............................................................................................................................................................. 30
4.5. Implementation for installation ............................................................................................................................................... 31
4.6. Break transmission adjustment .............................................................................................................................................. 31
4.7. Faults and repairs .................................................................................................................................................................. 33
4.8. Electrical connection diagram ................................................................................................................................................ 34
4.9. Complete wheels technical information .................................................................................................................................. 34
5. Preparation before operating the set ................................................................................................................................................... 35
5.1. Installation checks .................................................................................................................................................................. 35
5.2. Checks after starting the generating set ................................................................................................................................ 35
1/202

6. Using the generator set ....................................................................................................................................................................... 36
6.1. Pre-Start Inspection ............................................................................................................................................................... 36
6.2. Generator set with NEXYS control panel ............................................................................................................................... 39
6.2.1 Control panel presentation ..................................................................................................................................................... 39
6.2.1.1. Introduction to pictograms ......................................................................................................................................... 40
6.2.2 Manual starting ....................................................................................................................................................................... 41
6.2.3 Switching off .......................................................................................................................................................................... 42
6.2.4 Alarms and faults ................................................................................................................................................................... 42
6.2.5 Faults and alarms - Details ..................................................................................................................................................... 42
6.3. Generator set with TELYS control panel ................................................................................................................................ 44
6.3.1 Control panel presentation ..................................................................................................................................................... 44
6.3.1.1. View of the front panel .............................................................................................................................................. 44
6.3.1.2. Description of the screen .......................................................................................................................................... 46
6.3.1.3. Description of the pictograms in zone 1 .................................................................................................................... 47
6.3.1.4. Description of the pictograms in zone 2 .................................................................................................................... 48
6.3.1.5. Description of the pictograms in zone 3 .................................................................................................................... 49
6.3.1.6. Display of messages in zone 4 ................................................................................................................................. 51
6.3.2 Starting ................................................................................................................................................................................... 55
6.3.3 Switching off .......................................................................................................................................................................... 56
6.3.4 Alarms and faults .................................................................................................................................................................... 56
6.3.4.1. Viewing alarms and faults ......................................................................................................................................... 56
6.3.4.2. Activation of an alarm or fault ................................................................................................................................... 57
6.3.4.3. Activation of an alarm and a fault .............................................................................................................................. 58
6.3.4.4. Engine fault codes display ........................................................................................................................................ 59
6.3.4.5. Horn reset ................................................................................................................................................................. 60
7. Maintenance schedule ......................................................................................................................................................................... 60
7.1. Reminder of use ..................................................................................................................................................................... 60
7.2. Maintenance safety instructions ............................................................................................................................................. 60
7.3. Table of maintenance operations ........................................................................................................................................... 61
7.4. Fault finding ........................................................................................................................................................................... 62
7.5. No load and under load tests ................................................................................................................................................. 62
8. Battery ................................................................................................................................................................................................. 63
8.1. Storage and transport ............................................................................................................................................................ 63
8.2. Battery setting into service ..................................................................................................................................................... 64
8.3. Check ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 64
8.4. Load preconization ................................................................................................................................................................. 65
8.5. Faults and remedies .............................................................................................................................................................. 66
9. Appendix .............................................................................................................................................................................................. 67
9.1. Appendix A – Engine user and maintenance manual ............................................................................................................ 67
9.2. Appendix B - Alternator user and maintenance manual .......................................................................................................165
2/202

1. Preface
1.1. General recommendations
Thank you for choosing an electrical generating set from our company.
This manual has been designed to help you operate and maintain your electrical generating set correctly.
The information contained in this manual is taken from technical data available at the time of print. In lin e with our policy of continually
improving the quality of our products, this information may be amended without warning.
Read the safety instructions attentively in order to prevent any accidents, faults or damage. These instructions must always be
followed.
You are likely to encounter several warning symbols in this manual.
This symbol indicates an immediate danger to human he alth and life in case of exposure. Fai lure to follow
the corresponding advice entails serious consequences for human health and life in case of exposure.
Danger
This symbol draws attention to the potential risks to human health and life in case of exposure. Failure to
follow the corresponding advice entails serious consequences for human health an d life in case of exposure.
Warning
This symbol indicates a dangerous situation if the warning is not heeded.
Failure to follow the corresponding advice risks resulting in minor injury of personnel or damage to any other
object in case of exposure.
Important
In order to obtain optimum efficiency and the longest poss ible life for the electrical generating sets, maintenance operations must be
carried out according to the periods indicated in the attached prevent ative maintenance tables. If the electrical generating set is us ed
under dusty or unfavourable conditions, some of these periods will be shorter.
Ensure that all repairs and adjustments are carried out by personnel who have received appropriate training. Dealers have this
qualification, and can answer all of your questions. They can also supply you with spare parts and other services.
The left and right sides can be seen from the back of the electrical generating set (the radiator is at the front).
Our electrical generating sets have been designed so that damaged or worn parts can be replaced by new or reconditioned parts
thereby reducing the out of action period to a minimum.
For any replacement of parts, contact your nearest dealer for our company who will have the necessary equipment and can offer
properly trained and informed staff to carry out maintenance, parts replacement and even total reconditioning of generating sets.
Contact your local dealer for the available repair manuals and to make the necessary arrangements for training personnel in
implementation and maintenance.
Some user and maintenance manuals for the engines fitted to generating sets cover control units and
include the start-up and shutdown procedures for the engines.
As the generating sets are fitted with control units that are specific to the generating sets, only the
information that appears in the documentation for the generating sets' control units should be taken into
consideration.
In addition, according to the manufacturing criteria of the generating sets , some engines may be fitted with
specific electrical wiring different to that described in the engine documentation.
Important
3/202

1.2. Pictograms and their meanings
Safety notices are clearly mounted on the equipment to draw the operator's or maintenance technician's attention to the potential
dangers and explain the action to be taken in the interest of safety. These notices are reproduced in this publication for ease of
identification by the operator.
Replace any notice that is missing or illegible.
Warning: danger
Publications delivered
with the generating set
must be referred to
Warning: risk of explosion
Warning: risk of
electric shock
Protective clothing
must be worn
Naked flames and
unprotected lights
prohibited.
No smoking
Warning: toxic
materials
Your eyes and ears
must be protected
Entry prohibited to nonauthorised persons
Warning:
pressurised fluids
Periodic maintenance
must be carried out
Jet washing prohibited
Warning: high
temperature, risk
of burns
Battery level must be
checked
Earth
Warning: rotating
or moving parts
(risk of getting
caught in the
machinery)
Lifting point required
Warning: corrosive product
Figure 1.1: Pictograms and their meanings
4/202

Battery isolating
switch
Fuel
External fuel connections
Inspection hatch
Retention container
drainage
Fuel drainage
Oil drainage
Oil filling
Coolant filling
Coolant drainage
Forklift required for
lifting
Bulk tank level high
Fuel supply selection valves
During any operation on the
batteries, wear protective
glasses and protective clothing
Rinse any splashes of acid on the
skin or in the eyes using clean water.
Consult a doctor immediately.
Contaminated clothes must be
washed with water
Important: refer to the docum entatio n accompanying the generating set.
Warning: emission of toxic exhaust gases. Do not use in a confined or badly
ventilated area.
Figure 1.1 ( continued ) : Pictograms and their meanings
5/202

1.3. Instructions and safety regulations
THESE SAFETY GUIDELINES ARE IMPORTANT
If you do not understand or have any questions about any point in this manua l, contact your de al er who will expla in it t o you o r give you
a demonstration. A list of risks and precautionary measures to take follows. You should also refer to any local and nationa l regulations
that apply in accordance with your own jurisdiction.
KEEP THIS MANUAL
This manual contains important instructions which must be followed when installing or carrying out maintenance on a generating set or
batteries.
1.3.1 General advice
Use
The operating and safety instructions must be made known to operating personnel. They will be regularly up dated.
Read and understand the manuals provided with the generating set, pump unit or li ghting column properly. The manufacturer's
instructions must remain at the disposal of technicians, if possible in situ.
The facility must be operated under the direct or indirect supervision of a person appoi nted by the operator, who is familiar wit h th e
operation of the facility, and the dangers and drawbacks of the products used or stored in the facility.
Do not wear loose clothing, or get close to machines in operation. Note that the fans are not clear ly visible when the engine is
running.
Warn personnel present to keep their distance during operation.
Do not run the generating set, pump unit or lighting column without refitting the protective covers and closing all the access doors.
Never let a child touch the generating set, pump unit or lighting column, even when shut down.
Avoid operating the generating set, pump unit or lighting tower in the presence of animals (disturbance, scares, etc.).
Enga ge the parking brake when the generating set or lighti ng tower on its trailer is installed on the operating site. When chocking
the trailer on a slope; ensure that there is nobody in the path of the trailer.
Never start the engine without an air filter or exhaust.
Engine with turbocharger: never start the engine without fitting the air filter. The compres sor wheel rotating inside the t urbocharger
may cause serious bodily injury. Foreign objects in the inlet pipe may cause mechanical damag e.
Engi ne with air preheating (starting components): never use a startin g spray or any other similar starter assistance product. Upon
contact with the starting component, an explosion may occur in the inlet tube, causing bodily injury.
Do not touch the lighting column lights when they are switched on.
Maintenance
Follow the maintenance table and its instructions.
Always use tools in goo d condition which are suited to the work to be done. Ensure you have understood the instr uctions before
beginning any operation.
Goggles should be worn when carrying out maintenance operations and watches, bracelets etc. should be removed.
Fit only original parts.
Disconnect the battery and the pneumatic starter (if fitted) before undertaking any repairs, to prevent the engine from starting
accidentally. Fit a panel over the controls to prevent any attempt to start.
Only use the correct crankshaft turning techniques for turning the crankshaft manually. Do not try to turn the crankshaft by pulling it
or levering the fan. This method may cause serious bodily or material damage, or damage the vanes of the fan, reducing the
service life of the fan.
Clean off any trace of oil, fuel or coolant using a clean cloth.
Do not use a soapy solution containing either chlorine or ammonia, as these two chemicals prevent bu bble formation.
Never use petrol or other inflammable substances to clean the parts. Use only approved cleaning solvents.
Do not use a high pressure cleaner for cleaning the engine and equipment. The radiator, hoses, electric al components, etc. may be
damaged.
Avoid accidental contact with parts at high temperatures (exhaust manifold, exhaust).
Before any maintenance operation on a lighting column light, cut the electrical power supply and wait for the bulbs to cool down.
Consumables
Observe regulations in force concerning use of fuel before using your generating set, pump unit or lighting tower.
Under no circumstances use seawater or any other corrosive or electrolytic product in the cooling circuit.
Environment
The operator must take the necessary measures to comply with the aesthetics of the site of use. The whole site must be maintained
in a good state of cleanliness.
The premises must be kept clean, and be regularly cleaned so as t o avoid accumulation of dangerous materials or pollutants and
dust, which could ignite or cause an explosion. The cleaning equipment must be suited to the risks posed b y the products and dust.
The presence of dangerous or combustible materials inside premises ho using combustion devices shall b e limited to the operating
requirements.
Facilities must be operated under the constant supervision of a qualified person, who must regularly check that th e safety devices
are operating correctly and ensure that the combustion devices have the correct fuel supply.
Apart from the combustion devices, it is prohibited to use fire in any form. This restriction must be clearly displayed.
6/202

Spreading of waste water, sludge and waste is prohibited.
The fuels to be used must correspond to those featured in the declaration file and the specifications recommended by the
combustion device manufacturer.
The fuel is considered to remain in the same physical state as when it is introduced into the combustion chamber.
Burning of waste in the open air is prohibited.
Always protect your hands when checking f or leaks. Pressurised liquids may penetrate body tissue and cause serious damage.
Risk of blood contamination.
Drain and dispose of engine oil in a specially provided container (fuel distributors can collect your used oil).
Exce pt by special agreement, once closed, the gas supply main un it must only be re-opened by the g as distributor. However, the
user may access it under certain conditions. Check these for each site.
1.3.2 Risks related to exhaust gases and fuels
The carbon monoxide present in exhaust gases may cause death if the concentration levels in the air
breathed are too high.
Always use generating sets, pump units or lighting towers in a well-ventilated place where gases cannot
accumulate.
In case of indoor use:
Be sure to evacuate exhaust gases outdoors.
Provide appropriate ventilation so that personnel present are not affected.
Danger
Observe the local regulations in force for generating sets, pump units or lighting towers, as well as local regulations for us e of fuel
(petrol, diesel fuel and gas) before using your generating set, pump unit or lighting tower.
Fuel filling should be carried out when the engine is off (except for generating sets with an automatic filling system).
Engine exhaust gases are toxic: do not run the generating set, pump unit or lighting column in unventi lated premises. If insta lled in
a ventilated room, additional requirements for fire and explosion protection must be observed.
A leaking burnt gas exhaust may increase the sound level of the generating set, pump unit or li ghting column. To check on its
efficiency, regularly examine the burnt gas exhaust.
Pipes must be replaced as soon as their condition demands it.
1.3.3 Risks related to toxic products
The corrosion inhibitor contains alkali.
Do not swallow it.
This substance should not come into contact with the
eyes. In the event of contact with the eyes, rinse
immediately with plenty of water for at least 15
minutes.
Avoid prolonged or repeated contact with the skin. In
the event of contact with the skin, wash thoroughly
with water and soap. CONSULT A DOCTOR
IMMEDIATELY. KEEP THE PRODUCT OUT OF
THE REACH OF CHILDREN.
The anti-rust product is toxic and dangerous if
absorbed. Avoid all contact with the skin and eyes.
Read the instructions on the packaging.
Glycol is a toxic product and dangerous if absorbed.
Avoid all contact with the skin and eyes. Read the
instructions on the packaging.
Warning
Caution: fuels and oils are dangerous to inhale. Ensure proper ventilation, and use a protective mask.
Never expose the equipment to liquid splashes or rainfall, and do not place it on wet ground.
The battery electrolyte is harmful to skin and especially eyes. If splashes get into eyes, rinse immed iately with running water and/or
a 10% diluted boric acid solution.
Wear protective eyewear and strong base resistant gloves for handling the electrolyte.
7/202

1.3.4 Risk of fire, burns and explosion
The engine should not be operated in environments containing explosive products. As not all of the
electrical and mechanical components are shielded, there is a risk of sparks forming.
Danger
Make sure not to create sparks or flames, and not to smoke near the batteries, as the electrolyte gases are highly flammable
(especially if the battery is charging). Their acid also poses a risk to the skin, and in particular to the eyes.
Never cover the generating s et, pump unit or lighting tower with any material during operation or just after shutdown (wait for the
engine to cool).
Do not touch hot parts such as the exhaust pipe, or put combustible materials on it.
Keep all flammable or explosive materials (e.g. petrol, oil, cloth, etc.) out of the way when the set is running.
Proper ventilation is required for your generating set, pump unit or l ighting column to work properly. Without this ventilation, the
engine would very quickly rise to an excessively high temperature, causing accidents or damage to the equipment and to
surrounding property.
Do not remove the radiator cap if the engine is hot and the coolant is pressurised, due to risks of burns.
Depressurise the air, oil and cooling circuits before removing or disconnecting all the fittings, pipes or connected components.
Watch out for the possible presence of pressure when disconnecting a device from a pressurised system. Do not try to find
pressure leaks by hand. Oil at high pressure can cause bodily damage.
Some preservative oils are flammable. Also, some are dangerous to inhale. Ensure proper ventilation. Use a protective mask.
Hot oil causes burns. Avoid contact with hot oil. Check that the s ystem is no l onger pr ess urised before c arrying o ut an y proc edures.
Never start or run the engine with the oil filler cap off (oil may splash out).
Never coat the generating set, pump unit or lighting column with a thin layer of oil to protect it from rust.
Never top up the oil or coolant if the generating set, pump unit or lighting column is running, or if the engine is hot.
A generating set can only operate when stationary, and cannot be installed on a vehicle or other mobile equipment, without a prior
study taking into account the various specific features of using the generating set.
1.3.5 Risks related to electrical networks
The electrical equipment supplied with the generating set complies with standard NF C15.100 (Franc e), or with the standards of the
countries in question.
The earth connection must be installed in accordance with the standards in force in each country in qu estion, and with the neutral
system sold.
Read the manufacturer's identification plate carefully. The values for voltage, power, current and frequency are shown. Ch eck that
these values match the supply use.
Never accidentally touch stripped cables or loose connections.
Never handle a generating set with wet hands or feet.
Maintain electrical wires and connections in good condition. Using equipment in poor condition can lead to electrocution and
damage to equipment.
Al ways disconnect the power to the equipment or faci lity (generating set voltage, battery v oltage and network voltage) before any
operation.
The electrical connections must be made in accordance with current standards and regulations in the country of use.
Do not use faulty, poorly insulated or provisionally connected wires.
Never reverse the positive and negative terminals on batteries when connecting them. This could ca use severe damage to the
electrical equipment. Follow the wiring diagram supplied by the manufacturer.
The generating set should not be connected to any other power sources, such as the mains s upply network. In specific cases
where there is to be a connection to existing electrical networks, this must only be install ed by a qualified electrician, who should
take the operating differences of the equipment into account, according to whether the mains supply net work or generating set is
being used.
8/202

Protection against electric shocks is ensured by an assembly of specific equipment. If this needs to be replac ed, it should be by
components with identical nominal values and specifications.
If the protective plates (blanking covers) need to be removed to route cables, the protector (blanking cover) must be refitted when
the operations are finished.
Due to high mechanical stresses, use only strong flexible wiring with rubber sheathing, compliant with IEC 245-4, or equivalent
wiring.
1.3.6 Dangers presented by electric currents (first aid)
First aid
In the event of an electric shock, shut off the power immediately and activate the
emergency stop on the generating set or lighting colum n. If the voltage has not yet
been cut off, move the victim out of contact with the live conductor as quickly as
possible. Avoid direct contact both with the live conductor and the victim's body. Use
a dry plank of wood, dry clothes or other non-conductive materials to move the victim
away. The live wire may be cut with an axe. T ake great care to avoid the electric arc
that will be generated by this.
Begin emergency procedures
Resuscitation
If breathing has stopped, begin artificial respiration at once i n the same pla ce the acci dent took plac e u nless the victim or operator's lif e
could be endangered by this.
In the event of cardiac arrest, carry out cardiac massage.
1.3.7 Risks related to moving the set
To unload the generating sets, pump units or lighting columns from their transport support brackets under optimum safety and
efficiency conditions, you must ensure that the following points are observed:
The lifting machinery or equipment is suited to the work required, in good condition and with sufficient lifting capacity.
The slings are positioned in the rings provided for this operation, the forklift arms are resting fully underneath all of the base frame
cross-beams, or the lifting bars are inserted in the apertures provided for this purpose in the base to l ift the entire generating set
(according to models).
For completely safe working conditions and to prevent damage to the components fitted on the upper edge of the set, pump u nit or
lighting column, the generating set, pump unit or lighting column m ust be lifted up with an adjustable boom. All the chains and
cables must be parallel with each other, and as perpendicular as possible with the upper edge of the gen erating set, pump unit or
lighting column.
If other equipment fitted on the generating set, pump unit or lighting column alters its centre of gravity, special lifting devices may be
necessary to maintain correct balance and completely safe working conditions.
The ground must be able to withstand the load of the generating set, pump unit or lighting column and its lifting mac hinery without
stress (otherwise, put down beams of sufficient strength in a stable configuration).
Position the generating set, pump unit or lighting column as close as possible to its plac e of use or transport, in a clear space with
free access.
Never perform work on a generating set, pump unit or lighting tower just hanging from a lifting device.
1.3.8 Risks related to noise
Dangerous noise
Risk of hearing loss
Important
Prolonged exposure to a noise level above 80dB (A) can lead to permanent hearing damage.
Therefore, it is recommended that ear defenders are used when working in close proximity to a generating set which is in oper ation.
9/202

2. General description
Overview
Figure 2.1.1 : General description of the generating set
1 Acces to maintenance area 4 Acces to control unit
2 Lifting ring 5 Acces to power connections
3 Forklift grooves 6 Drawbar
6
2
4
1
3
5
10/202

Figure 2.1.2 : General description of the generating set
1 Protective grille 4 Alternator
2 Battery isolating switch 5
External fuel supply combined tap
(optional)
3 Starter battery 6 Charging alternator
3
1
2
4
6
5
11/202

Control
Figure 2.1.3 : General description of the generating set
Note : Photo presented with the Nexys control unit.
1 Control unit 4 Working hours counter
2 Emergency stop 5 Power circuit breaker
3 Socket control panel 6 Connection terminal block
6
5
2
3
1
4
12/202

2.1. Technical specifications
Range / Generating set type RENTAL POWER / R44C3
Weights and Dimensions
Dimensions with high autonomy tank
Dimensions l x w x h
2200 mm x 1000 mm x 1528 mm
Weight:
1150 kg dry weight / 1350 kg in operating configuration
Hood:
M3127
Sound pressure level:
at 1 m: 73 dB(A)
measurement uncertainty : 0.70
Output
Voltage Hz Phase Load factor
Max current (A)
Emergency
power
1
kW / kVA
Prime power
2
kW / kVA
400/230 50 3 0.8 58 32 / 40 29 / 36
(1) ESP: Stand-by output available for emergency use under variable charge up to 200hrs per year as per lSO 8528-1, no overload availabl
e
under these service conditions.
(2) PRP: Main output available continuously under variable load f or an unlimited time period p er year as per ISO 8528-1, an overload of 10
%
one hour every 12 hours is available, as per ISO 3046-1.
- Term of use :
Standard reference conditions ESP/PRP 40° / 40°, Air Intlet Temp, 1000m / 1000m mA.S.L. 60 % relative humidity.
Engine data
Manufacturer / model MITSUBISHI S4S-Z3DT61SD
Type 4 Cycles Naturally aspirated
Cylinder configuration 4 XL
Cubic capacity 3.33 L
Rotation speed 1500 Rpm
prime power at nominal speed 36 kW
Adjustment type Mechanical
Fuel consumption
100 % main power 10.4 L/h
Fuel
Fuel type Diesel
High autonomy fuel tank 220 L
Lubrication
Oil capacity 10 L
Min. Oil pressure 1 bar
Nominal oil pressure 3.9 bar
Oil consumption (100 % load) 0.11 L/h
Oil sump capacity 9 L
Type of lubricant Genlub
Cooling
Engine capacity with radiator 9.5 L
Max coolant temperature 102 °C
Fan power 0.8 kW
Refrigerant type Gencool
Thermostat 76.5 – 90 °C
13/202

Alternator data
● Compliant with NEMA MG21 standards, UTE NF C51 111,
VDE 0530, BS 4999, IEC 34.1, CSA
● The alternator is protected against short circuits
● Vacuum impregnation, epoxy winding, IP23 protection rating
Type LEROY SOMER LSA43.2S159
Number of phases 3
Power factor (cos Phi) 0.8
Number of poles 4
Excitation type AREP
Insulation classe H
Number of bearings 1
Coupling Direct
Control unit(s)
NEXYS
Standard specifications:
Frequency meter, Voltmeter, Ammeter
Alarms and faults
:
Oil pressure, Coolant temperature, Fail to start, Overspeed,
Alternator min/max, Fuel level low, Emergency shutdown
Engine parameters
:
Working hours counter, Engine speed, Battery voltage, Fuel
Level, Air Preheating
TELYS
Standard specifications:
Voltmeter, Ammeter, Frequency meter
Alarms and faults:
Oil pressure, Water temperature, Start failure, Overspeed,
Alternator min/max, Battery voltage min/max, Emergency stop
Engine parameters
:
Timer, Oil pressure, Water temperature, Fuel level, Engine
speed, Battery voltage
14/202

2.2. Identifying sets
Generating sets and their components are identified by means of identification plates.
The precise rules for identifying each major comp onent (engine, alternator etc.) are set out in each manufacturer's documentation
contained in the appendices of this manual.
1 - Generating set
2 - Manufacturer name
3 - Model
4 - Serial number
5 - Year of manufacture
6 - Rated output (kVA and kW) according to the ISO
8528-1 standard
PRP: main power
ESP: emergency power
7 - Rated power factor
8 - Maximum altitude of the site above sea level (m)
for the rated power
9 - Maximum ambient temperature for the rated power
(°C)
10 - Rated frequency (Hz)
11 - Generating set rotation speed (RPM)
12- Rated voltage (V)
13 - Rated current (A)
14 - Weight (kg)
15 - CE marking
16 - Non CE standard marking e.g.: GOSSTANDART)
17 - Sound pressure
18 - Sound power
Figure 2.2: Example of generating set identification plate
15/202

2.3. Fluid retention
Any outflow of the fluids contained in the generating sets (fuel , oil and coolant, or rainwater or condensation) will be collected in a
retention container.
The containers have a capacity which allows 110% of the fluids contained in the generating set fitted with this option to be collected.
Diagram 2.3: Fluid retention container
The generating sets are fitted with a visual alarm warning when the upper limit of the retention container has been reached.
In all cases, the retention containers must be regularly checked to ensure they contain no fluid (fuel, oil and coo lant, or rainwater or
condensation). If necessary, drain the containers via the drain port.
Note: Never allow these fluids to drain onto the ground; ensure they are collected in a designated container.
2.4. Fuel and consumables
All specifications (product features) are given in the engine maintenance manuals attached to this manual.
Fuels:
The specifications refer to European or international standards. Fuels complying with the standards indicated in the engine
maintenance manuals can be used without any contraindications. Only these fuels may be used.
Consumables:
In addition to the specifications indicated in the engine maintenance manuals, the consumables mentioned in the section entitled
"Specifications" are recommended.
16/202

2.4.1 Specifications
2.4.1.1. Oil grades
Engine Oil
Make Type Make Type
John Deere All
John Deere John Deere PLUS-50
GenPARTS GENLUB TDX 15W40
MITSUBISHI All GenPARTS GENLUB TDX 15W40
Volvo All GenPARTS GENLUB TDX 15W40
GENLUB TDX 15W-40
Top-of-the-range lubricant recommended for diesel engines: for generating sets used under severe conditions.
USES:
Particularly suited to more modern engines with or without turbochargers, intercoolers, or sophisticated injection systems (e.g.
HEUI, injector-pumps).
All types of use: can cope with the most demanding applications.
Depolluted engines: complies with EURO 2 and EURO 3 technology and can be used with all types of diesel fuel, especially
ecological diesel with low sulphur content.
PERFORMANCE:
ACEA E3
API CH-4
Meets level E3 of the specifications defined by European manufacturers in the ACEA standards 98 edition.
ADVANTAGES:
Less frequent oil services: this product has been put to the test during thousands of hours of use on worksites under varying
conditions, demonstrating its high quality.
Conformity with new environmental legislation: adherence to new anti-pollution standards required for new EURO 2 and
EURO 3 engines.
SPECIFICATIONS:
SAE Grade
15W-40
Density at 15°C 0.883
Cinematic viscosity at 40 °C
Cinematic viscosity at 100 °C
105
14.1
mm2/s (cSt)
mm2/s (cSt)
Viscosity index 140
Dynamic viscosity at -15 °C 3000 mPa.s(cP)
Pour point - 30 °C
Flash point 220 °C
Sulphated ash content 1.4 % weight
(Values given as examples only)
17/202

2.4.1.2. Specifications of coolants
Engine Coolants
Make Type Make Type
John Deere All GenPARTS GENCOOL PC -26°C
MITSUBISHI All
Mitsubishi LLC
GenPARTS GENCOOL PC -26°C
Volvo All GenPARTS GENCOOL PC -26°C
GenCOOL PC -26
High-protection coolant, approved by manufacturers.
GenCOOL PC -26 is a ready-to-use, highly protective coolant which is pr oduced from an antifreeze recommended by the majority of
European manufacturers.
It is made from antifreeze and G 48 inhibitors.
It protects up to -26°C.
It is free from nitrates, amines and phosphates.
It is a clear, fluorescent orange liquid.
REFERENCES/APPROVALS (for the antifreeze):
HEAVY GOODS VEHICLE LIGHTER VEHICLES
Approved by MTU, MERCEDES BENZ, MAN, KHD,
GENERAL MOTORS
Conforms with VOLVO, IVECO, VAN HOOL and STAYR
TRUCK specifications
Approved by BMW, VOLKSWAGEN, MERCEDES, PORSCHE
Conforms with VOLVO, OPEL, SEAT and SKODA
specifications
Conforms with the NF R 15.601 standard
REINFORCED ANTI-CORROSION FEATURES:
Protects against high-temperature corrosion by oxidisation of ethylene (cylinder head protection).
Protects against high-temperature cavitation (top of cylinder and coolant pump protection).
Non-corrosive for seals and hoses.
Improves the efficiency and longevity of the cooling system.
GenCOOL PC -26 is especially recommended for engines fitted with aluminium or light alloy radiators.
HIGH TEMPERATURE SUITABILITY:
Provides good conditions for thermal exchange.
Perfect stability at high temperatures.
GenCOOL PC -26 is specially adapted for engines with high power densities.
LONG LASTING PROTECTION:
High alkaline reserve/stability and longevity of corrosion inhibitors.
Maintains its technical properties during prolonged use at high temperatures (neutralisation of acids).
Ensures maximum heat transfer without the build up of deposits in the cooling system.
GenCOOL PC -26 ensures optimum protection against overheating and corrosion in extreme conditions of vehicle use.
18/202

PACKAGING/STORAGE:
GenCOOL PC -26 is supplied in 210 l metallic barrels with smooth interior linings.
It can be stored for 2 years in its original container and packaging.
Avoid zinc coated containers.
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR USE:
Compatible with the original fluid.
It is recommended that the cooling system is completely drained when replacing the fluid.
SPECIFICATIONS UNITS SPECIFIED VALUES
TRIAL
METHODS
Density at 20°C
kg/m3
1,059 +/- 3
R 15-602-1
pH
pH
7.5 to 8.5
NF T 78-103
Alkalinity reserve
ml
>=10
NF T 78-101
Boiling point
°C
105 +/- 2
R 15-602-4
Freezing point:
°C
-26 +/- 2
NF T 78-102
Glassware corrosion :
(test with antifreeze)
mg/test piece
R 15-602-7
- Copper
+/- 2.6
- Weld
+/- 0.5
- Brass
+/- 2.3
- Steel
+/- 1.6
- Cast iron
+/- 0.8
- Cast aluminium
+/- 1.0
Corrosion on warm plate
(test with antifreeze)
mg/(cm²week)
+/- 0.17
R 15-602-8
3. Installation-Connections
3.1. Unloading
3.1.1 Safety during unloading
To unload electrical generating sets from their transport supports with optimum safety and efficiency, you must ensure that the
following points are observed:
- The lifting machinery or equipment is suitable for the work required.
- The sling is correctly position ed in the central lifting eye or the lifting arms are correctly positioned in the fork-lift poc kets intended
for this purpose.
- The ground is able to bear the load of the generating set and its lifting machinery without stress (otherwise lay do wn stabilising
beams of sufficient strength).
- The generating set is put down as close as possible to its place of use or transport, in a clear space with free access.
Example of equipment to be used:
crane, slings, lifting beam, safety hook, shackles.
Forklift truck.
19/202

3.1.2 Instructions for unloading
Hoisting
Attach the sling on the lifting equipment to the ring on the generating set (no. 1) provided for this purpose. Tension the slings
slightly.
Check that the sling is correctly attached and the equipment is steady.
Lift the generating set carefully.
Direct the generating set towards the chosen location and stabilise it.
Carefully set down the equipment while continuing to position it.
Release the sling, then detach it.
Forklift truck:
Position the arms of the forklift truck in the forklift pockets (no. 2).
Lift the equipment, handling it gently.
Set down the generating set in its unloading position.
1
2
20/202

3.2. Choice of location
This shall be determined according to the application. There are no strict rules governing the choice of location, other than the proximity
of the electrical supply panel and the disturbance cause d by the no ise. Ho wever, it is important to take i nto account the f uel suppl y, the
evacuation of burnt gases, the direction of these gases and evacuation noises.
The choice of location will therefore be the result of a carefully considered compromise!
Examples of problems that may be encountered:
Incorrect ventilation and exhaust Building or terrain too rough.
Generating set incorrectly seated
Reduced access
Impossible to fill with fuel Impossible to open enclosure doors
Figure 3.1: Examples of problems that may be encountered
Ensure that the generating set is placed on a flat surface.
Warning
3.3. Moving the genset
Whenever the generating set is moved, the appropriate equipm ent must be used (sling, forklift, etc.) and you must know the parts of
the generating set which enable it to be moved ( see below).
Central lifting ring
Forklift pockets
Drawbars
21/202

3.4. Connections
3.4.1 Connections - general information
As with low voltage electrical installations, use and maintenance is governed by standard NFC 15. 100 (France) or by the standards in
the relevant country, based on international standard IEC 60364-6-61.
They must also adhere to the regulations in the NFC 15.401 application guide (France) or to the regulations and standards in th e
relevant country.
3.4.2 Power cables
These can be unipolar or multipolar according to the power of the generating set.
Power cables should preferably be installed in ducts or on a cable tray for this purpose.
The cable cross-section and number of cables should be determined according to th e cable type and the current standards to be
observed in the country of installation. The choice of conductors must comply with international standard IEC 30364-5-52.
Three phase - Calculation hypothesis
Fitting method = wiring in cable runs or non perforated trays.
Permissible voltage drop = 5%
Multiconductors or single conductor joined when precision 4X…(1)
Cable type PVC 70°C (e.g. H07RNF).
Ambient temperature = 30°C.
Circuit breaker
calibre
(A)
Cable sizes
0 - 50m 51 - 100m 101 - 150m
mm²/AWG mm²/AWG mm²/AWG
10 1.5 / 14 2.5 / 12 4 / 10
16 2.5 / 12 4 / 10 6 / 9
20 2.5 / 12 4 / 10 6 / 9
25 4 / 10 6 / 9 10 / 7
32 6 / 9 6 / 9 10 / 7
40 10 / 7 10 / 7 16 / 5
50 10 / 7 10 / 7 16 / 5
63 16 / 5 16 / 5 25 / 3
80 25 / 3 25 / 3 35 / 2
100 35 / 2 35 / 2 4X(1X50) / 0
125 (1) 4X(1X50) / 0 4X(1X50) / 0 4X(1X70) / 2/0
160 (1) 4X(1X70) / 2/0 4X(1X70) / 2/0 4X(1X95) / 4/0
250 (1) 4X(1X95) / 4/0 4X(1X150) / 2350MCM 4X(1X150) / 2350MCM
400 (1) 4X(1X185) / 0400MCM 4X(1X185) / 0400MCM 4X(1X185) / 0400MCM
630 (1) 4X(2X1X150) / 2x 2350MCM 4X(2X1X150) / 2x 2350MCM 4X(2X1X150) / 2x 2350MCM
Single phase - Calculation hypothesis
Fitting method = wiring in cable runs or non perforated trays.
Permissible voltage drop = 5%
Multiconductors.
Cable type PVC 70°C (e.g. H07RNF).
Ambient temperature = 30°C.
Circuit breaker
rating (A)
Cable sizes
0 - 50m 51 - 100m 101 - 150m
mm²/AWG mm²/AWG mm²/AWG
10 4 / 10 10 / 7 10 / 7
16 6 / 9 10 / 7 16 / 5
20 10 / 7 16 / 5 25 / 3
25 10 / 7 16 / 5 25 / 3
32 10 / 7 25 / 3 35 / 2
40 16 / 5 35 / 2 50 / 0
50 16 / 5 35 / 2 50 / 0
63 25 / 3 50 / 0 70 / 2/0
80 35 / 2 50 / 0 95 / 4/0
100 35 / 2 70 / 2/0 95 / 4/0
125 50 / 0 95 / 4/0 120 / 2250MCM
22/202

3.4.3 Power connections
Disconnect the battery leads or use the battery isolating switch before carrying out any operations
on the generating set.
(To disconnect the battery, disconnect the negative lead (-) first).
Warning
1. Open the access hatch to the power section.
2. Feed the power cables through the access hatch on the genset control unit.
3. Connect the power cables to the bars. (N/L0-L1-L2-L3 or N2-R2-S2-T2).
4. Connect the power cables to the installation ensuring the live and neutral wires are correctly connected.
Ensure that the direction of rotation of the phases is identical on the genset and the installation.
(Our gensets are factory-set with a conventional direction of phase rotation)
Warning
N/L0
or
N2
L
3
or
T2
L2
or
S2
L
1
or
R2
USE
Acces hatch
23/202

3.4.4 Battery installation
Install the battery or batteries in the immediate vicinity of the electric starter motor. The cables will be connecte d directly from the
battery terminals to the starter motor terminals.
The primary instruction to follow is to ensure that the polarities between the battery and starter motor match. Never reverse the positiv e
and negative battery terminals when connecting them. This could cause severe damage to the electrical equipment.
The minimum cross-section of the cables will be 70 mm
2
. It varies according to the power of the starter motor but also the distance
between the batteries and the set (voltage drops on the line).
3.5. Protection for individuals and equipment
3.5.1 Earth connection
For effective protection against electric shocks, the generating set needs to be earthed. To do this, use a copper wire, with a minimum
cross-section of 25 mm2 for a stripped cable and 16 mm2 for an insulated cable, connected to the generating set earth socket and a
galvanised steel earthing rod embedded vertically into the ground.
The earthing rod resistance value should comply with the values shown in the table below.
Note: use the highest differential setting from the installation as a guideline.
The resistance value is calculated in the following way:
R = Ul
I Δn
Maximum resistance value of the earth socket R (Ω) according to the diff erential unit operational
current (operation time should not be longer than 1 second).
I Δn
differential
Earth R
(Ω)
Ul: 50 V
Earth R
(Ω)
Ul: 25 V
≤ 30 mA 500 > 500
100 mA 500 250
300 mA 167 83
500 mA 100 50
1A 50 25
3A 17 8
5A 10 5
10A 5 2.5
The Ul value: 25 V is required for work site installations, and livestock buildings, etc.
generating set earth socket
24/202

For a default voltage of 25 V and a default current of 30 mA, this rod must be of a minimum length of: see table below
Nature of ground
Length of
rod in
metres
Thick arable land,
moist compact ballast
1
Lean arable land,
Gravel, coarse ballast
1
Bare stony soils, dry sand,
impermeable rock
3.6
To obtain an equivalent length, you can use several earthing rods
connected in parallel and set apart by at least their length.
Example: 4 interconnected 1 metre rods separated by 1 metre.
Note: For the United States (National Electrical Code reference NFPA-70).
The generating set must be earthed. To do this, use a copper wire with a minimum cross-section of 13.3 mm² (or AWG 6, at most)
connected to the generating set earth socket and a galvanised steel earthing rod fully embedded into the ground vertically.
This earthing rod embedded fully in the ground must have a minimum length of 2.5 m.
3.5.2 Earthing system principle
The Earthing system, or SLT (formerly Neutral system) of the electrical facility defines the situation of the generating s et neutral in
relation to earth and the grounds of the electrical facility at the user end.
The purpose of the earthing systems is to protect personnel and equipment by managing risks posed by insulation defects. For safety
reasons, any live conducting part of a facility must be insulated from the earth. This insulation may be achieved by distance, or by using
insulating materials. But with time, insulation may deteriorate (due to vibrations, mechanical impacts, dust, etc.), and therefore generate
an earth with dangerous potential. This defect poses risks for personnel and property, but also continuity of service.
Earthing systems are codified by two letters that define the connections:
The first letter defines the neutral connection:
I Insulated or earthed via an impedance device
T Connected to earth
The second letter defines the grounding situation of the electrical facility:
T Connected to earth
N Connected to neutral
E.g.: IT = Isolated Neutral + Ground earthed
Speed
Number of
conductors
Detection Note
TT 4 poles Measurement of residual current Triggering of 1
s
t
fault by RCD
TN
C 3 poles
No measurement of residual current
Triggered by overcurrent protection
upon 1
st
fault
S 4 poles
IT SN 3 poles Insulation resistance measurement
Triggered upon 2
n
d
fault by
overcurrent protection
25/202

3.5.3 TT system
R
Ph 1
Ph 2
Ph 3
N
PE
R
R
Neutral connected
to earth T
Ground connected
to earth T
Neutral
earth
Ground
earth
R
Ph 1
Ph 2
Ph 3
N
PE
R
id
id
id
Figure 3.2: TT neutral system.
The alternator neutral is earthed, and the grounds of the user equipment have their own earth connection.
In the TT system, automatic power cut-off via a Residual Current Device (RCD) is obligatory at the upstream part of the facility, t o
ensure protection of personnel (with a maximum 30 mA device on outlet circuits).
3.5.4 Differential protection
In order to ensure that people are protected from electric shocks from the TT system, the generating set is equipped with a residual
current device: this can be fixed or adjustable depending on the option chosen.
• If the generating set's residual current device is not adjustable and the activation threshold has been set at 30 mA, all terminal
circuits in use are protected.
• If the generating set's residual current device is not adjustable and the activation threshold has been set at 300 mA, a 30mA
residual current device must be added to each of the circuit outlets in use.
• If the generating set's residual current device is adjustable, (located upstream) this must be above those devices located
downstream (terminal circuits); this means that continuity on clean circuits will be maintained in the event of a fault on one of
the terminal circuits.
Example:
Any change to the setting on the generating set's resid ual curren t device could pose a risk to personal safety.
The user will be held liable - any changes must only be made by trained, qualified engineers.
When the generating set is disconnected from an inst allation after use, the general residual current device
must be restored to factory settings by a qualified engineer who can then check this.
Important
Generating set's residual
current device
Residual current device
Terminal circuit 1
Residual current device
Terminal circuit 2
Residual current device
Terminal circuit 3
300mA
30mA
30mA
30mA
Generating set
26/202
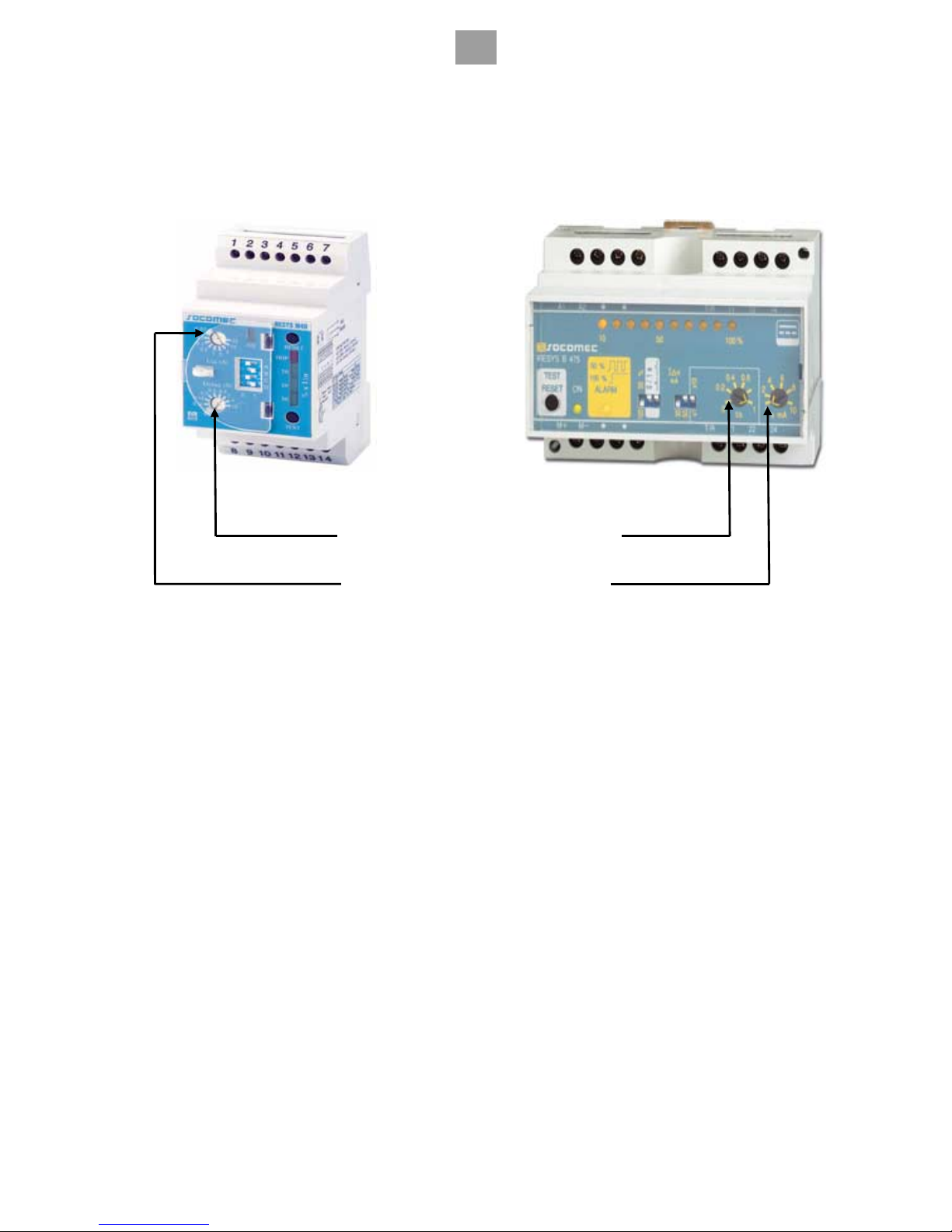
3.5.5 Adjusting the genset differential protection
Before adjusting the settings on the generating set's residual c urrent device, the f ollowing two parameters must be taken into account:
the sensitivity of the current threshold and the activation time.
The generating set's residual current device must have, in relation to the downstream device (terminal circuit):
- a sensitivity three times greater.
- a longer cut-off time.
Type A/AC
Type B
Two types of differential relay are fitted on the generating sets:
Type A:
Differential device for which operation is guaranteed:
for residual sinusoidal alternating currents,
for continuous pulsed residual currents,
for continuous pulsed residual currents with a continuous component of 0.006 A with or without phase check, independent of
the polarity.
Type B:
Device for which operation is guaranteed:
as in the case of type A,
for residual sinusoidal currents up to 1000 Hz,
for residual sinusoidal currents superimposed on a pure continuous current,
for continuous pulsed currents superimposed on a pure continuous current,
for residual currents which could come from rectifier circuits i.e.:- three phase half-wave rectifier or a three-phase full-wave
bridge rectifier, full-wave bridge rectifier between phases, with or without phase angle check, independen t of the polarity.
Our residual current devices are factory-set with an activation threshold of 30 mA and with automatic cut-off. Depending on the use, if
the residual current device is modified, it is recommended to fit a seal to prevent any tampering when the generating set is being use d.
Time setting potentiometer
Current threshold adjustment potentiomete
r
27/202

3.6. Connection summary
Identify its earthing system
TT
Option « Application EDF »
France uniquement
Mark the type of differential protection
Fixed genset differential protection
Adjustable genset differential protection
30 mA 30 mA 300 mA 300 mA
No operation required:
terminal circuits protected
No operation required:
terminal circuits protected
Add differential protection
set to 30 mA to the terminal
circuit output(s)
Add differential protection
set to
30 mA to the terminal circuit
output(s)
Earth the generating set
Connect to the power supply
28/202

3.7. Special arrangements
Generating sets are not fitted with protection against power surges caused by drops in atmospheric pressure or manoeuvring.
The company does not accept any responsibility regarding damage caused b y these occurrences.
However, lightning conductors can be installed, on the understanding that this does not give total protection.
4. Trailer
4.1. Trailer linkage
Before attaching the trailer, check the trailer hook on the tow vehicle; it should fit the trailer ring perfectly.
Trying to tow a trailer with a non-matching device (bar, wires, cords, etc.) could lead to serious
accidents.
Also check:
- no incipient fractures or excessive wear on the hitching system.
- locking system is operating properly.
Warning
To hitch the trailer, proceed as follows:
Lock the wheels to stop the trailer from moving
Lift up the rear trailer supports and lock them
Release the parking brake
Release the locking levers for the draw bar arms and adjust the ring to the same height as the vehicle hook
Hitch the trailer, remove the locks on each side of the wheels then lift up the front wheel fully using its handle
Connect the electrical circuit of the trailer to that of the tow vehicle
Hook the handbrake safety wire onto the hook on the tow vehicle.
Diagram 4.1 : Coupling a trailer
4.2. Check before towing
Before towing, check the following:
Tightness of the generating set enclosure bolts.
Wheel tightness.
Hitching hook locked.
Tyre pressure.
Signalling lights working, for "on-road" trailers.
Enclosure doors closed.
Parking brake released, for "on-road" trailers.
Guide wheels (jockey wheels) and stands lifted (if fitted).
Towbar arm locking levers tightened and pinned (if fitted with an adjustable towbar).
Brake test, for "on-road" trailers.
Safety cable fitted, for "on-road" trailers.
Tow vehicle
Trailer
CORRECT
Tow vehicle
Trailer
CORRECT
Tow vehicle
Trailer
INCORRECT
Tow vehicle
Trailer
INCORRECT
29/202

4.3. Operation
"On-site" trailer
These trailers are not fitted with a main brake, and so cannot be braked in motion; t he tyr es allo w for a maximum speed of 27 km/h. So
it is absolutely prohibited to exceed this speed.
Nor are these trailers fitted with signalling lights. On-road use is prohibited.
"On-road" trailer
The driving speed must be suited to the condition of the road and the handling of the trailer.
Driving at high speed causes heating of the tyres; so it is important to stop from time to time, and check them. Excessive heating may
cause a puncture, and therefore a serious accident. For reversing manoeuvres, remember to lock the inertia brake.
Particular attention must be paid to the tightness of the wheels on new vehicles.
In the first few miles' driving, heating of the brake hubs a nd drums will ac tually reduce the wheel tightne ss. It
is therefore essential to check the tightness every 6 miles (10 kilometres) until no further loosening is noted.
Nonetheless the tightness must be checked whenever you are about to tow the trailer.
Warning
Lights/signalling (only for "on-road" trailers)
Warning lights are obligatory for on-road driving. Signalling must comply with regulations in force in the country of use.
Figure 4.2: Example of French signalling
4.4. Unhitching the trailer
This operation should be carried out on horizontal, flat, stable ground.
Lock the wheels
Lower the front wheel
Disconnect the road signals wire
Refit the hitch using the wheel to release the hook ring from the tow vehicle,
Release the tow vehicle
Engage the handbrake.
Red rear lights + direction indicators+ stop lights
Front reflective devices (white)
Side reflective devices (orange)
Rear reflective devices (red triangle)
30/202

4.5. Implementation for installation
Operations to be carried out:
Ensure that the ground is strong enough for the assembly not to sink into it.
Unhitch the trailer.
Immobilise the trailer by placing chocks under the wheels.
Fully engage the parking brake (if fitted).
Using the front wheel, position the generating set as close to horizontal as possible.
Lower the stands (if fitted), and lock them.
4.6. Break transmission adjustment
- The handbrake is used only as a parking brake.
- Setting is carried out starting with the brakes moving to the brake control.
Important
After fitting the wheels on the axle, turn the wheels in the FORWARD direction (on all R A 2 type brake s, check that the adjustm ent
screw 8 reaches the “FORWARD” stop on the brake backing plate).
Adjust the brake setting using screw 8, with the cables not connected to the cross bar(s). The shoes should rub the drum slightly.
Connect the brake cables to the cross bars(s) and tighten the nuts and lock nuts, leaving the end of the threaded en d protruding
by around 10 mm (Fig. 4.4).
IMPORTANT: Wherever possible, cables must cross over to achieve the highest possible gain curve (Fig. 4.5).
Check that the parking lever 1 is in the ‘REST” position and that the compensating spring 4 is completely free on its rod (unscrew
the nuts 5 fully).
Check that the hook slide 2 is not compressed and the yoke 3 is in the pulled out position.
Fit the transmission and adjust the assembly using the tensioner 6 until a gap (J1) of 1 mm max is obtained bet ween the linkage 9
and slide 2.
Adjust the compensating spring 4 at one end pressing it against the anchorage plate, and at the other end leaving a 2 mm gap (J2)
max between the spring and nuts 5.
Tighten all the lock nuts.
Checking the setting (trailer on axle stands):
Pull the parking lever 2 notches - the wheels cannot turn in a FORWARD direction.
The wheels can turn in REVERSE (adjustment screw 8 switches to the REAR position).
Pull the parking lever fully.
The wheels will not turn either in FORWARD or REVERSE and the cross bar(s) must remain parallel with the axle body.
Check the transmission setting after 180 miles (300 km) (running in period) and if necessary adjust the gap (J1) using the
tensioner.
Parking
The lever must be fully pulled up, so that the compensating spring is fully compressed.
Every 900 miles (1500 km), check the braking settings and distribution on all the wheels.
Important
The brake controls are designed to draw trailers behind flexible suspension touring vehicles. If used behin d an HGV, be sure
to provide the fitted ball joint with a shock absorber to prevent premature wear.
During any manoeuvres with the trailer coupled, do not turn more than 90° or force reverse.
The specifications of our brake controls are indicated on a manufacturer's plate, and the items on this should be su pplied to us
when requesting replacement parts, in particular for the shock absorber, of a special type, approved by the Service des Mines
to correspond to European standards (it is advisable to have a spare shock absorber to enable instant repairs).
31/202

Figure 4.3: Braking transmission
Figure 4.4: Cross bar fitting Figure 4.5: Tandem bearing fitting
32/202

4.7. Faults and repairs
Fault observed Origin Solutions
Erratic braking of trailer - Faulty shock absorber Replace the shock absorber
Braking too weak
- Jaws worn Replace the jaws
- Jaws not run in Fault will disappear only after running in
- Incorrect linkage setting Adjust the setting
- Significant friction on the slide Grease the sliding parts
- Slide corrosion Remove the corrosion and grease
- Coupling height does not match that of
the towing vehicle
Adjust the height so that the two parts
are in the same horizontal plane
Drum temperature abnormally high
- Incorrect linkage setting Adjust the settings
- Incorrect brake setting Adjust the settings
- High levels of dust in the drums Remove the dust
- Jaws, springs, drums damaged Replace the damaged parts
- Brake cables or link rod damaged Replace the damaged parts
Jerky braking
- Incorrect linkage setting Adjust the settings
- Interfering parts on the slide Remove, clean and grease
- Corroded slide Remove the corrosion and grease
- Damage to slide guide rings
Replace the rings (and possibly the
slide) and grease
- Faulty shock absorber Replace the shock absor ber
Trailer tending to swerve upon braking
- Cross-bar(s) not balanced Adjust the cross-bar(s)
- Different brake setting on the two sides Adjust the brake settings
- Cables damaged or incorrectly fitted
Replace the damaged parts
Refit the cables
- Poor load distribution Check the load distribution
When starting the trailer holds back the
towing vehicle
- Damage to slide or to guide rings Replace the faulty parts and grease
- Slide corrosion Remove the corrosion and grease
- Tie rod damaged
Replace the tie rod and adjust the
settings
- Linkage damaged or incorrectly set
Replace the damaged parts and adjust
the settings
- Brake on Loosen the brake
Play in the coupling head
- Head worn (see wear indicator) Replace the head
- Ball joint worn Replace the ball joint
Parking braking too weak
- Compensating spring incorrectly set Adjust the setting
- Braking system incorrectly set Adjust the setting
- Notched sector damaged
Replace the sector and adjust the
setting
- Lever ratchet worn Replace the lever and adjust the setting
- Cable ruptured Replace the cable and adjust the setting
33/202

4.8. Electrical connection diagram
Figure 4.6 : Electrical connection diagram
4.9. Complete wheels technical information
TYRES COMPLETE
WHEELS
Dimensions Indices Diameter (mm) Cross section
(mm)
Radius under
load
(mm)
Load
(Kg)
Pressure
(bar)
135 R 13 70 T 550 134 265 335 2.4
145 R 13 75 T 566 145 272 387 2.4
155 R 13 79 T 578 150 277 437 2.4
145/70 R 13 71 T 534 150 259 345 2.5
155/70 R 13 75 T 548 147 263 387 2.5
185/70 R 13 86 T 594 185 285 530 2.5
165 R 14 C 98 N 622 172 284 650 3.8
155/70 R12 100 N 525 155 244 650
(1)
800
(2)
6.25
185 R 14 C 102 P 650 188 316 675
(1)
850
(2)
4.5
195 R 14 C 106 P 666 198 32 950 4.5
195/50 x 10 98 N 450 190 - 750 6.0
(1)
Wheel with 4 holes
(2)
Wheel with 5 holes
34/202

5. Preparation before operating the set
The inspections referred to in this section enable the electrical generator set to operate.
Specific skills are required to carry out these operations.
They must only be entrusted to personnel with the necessary skills.
Failure to follow these instructions in any way could result in malfunction or very serious accidents.
Danger
5.1. Installation checks
• Check that the general recommendations from section "Installation" (ventilation, exhaust, connections, etc.) are followed.
• Carry out level checks (oil, coolant, diesel, battery).
• Ensure that the generating set is correctly earthed (earthing rod).
• Ensure that the electrical connections have been made properly.
• Ensure that the fuel connection has been made properly (valve position), if the generating set is equipped with the three-way valve
option enabling external supply.
5.2. Checks after starting the generating set
• Carry out the mechanical checks (oil pressure, water temperature, absence of noise, etc.).
• Carry out the electrical checks (voltage, current, frequency, rotary field, etc.).
• Carry out the safety checks (emergency shutdown, oil pressure, coolant temperature, etc.).
• Carry out the check on Normal/Emergency Inverter switching or coupling (if fitted).
35/202

6. Using the generator set
6.1. Pre-Start Inspection
• Inspecting the engine compartment
Make sure there is no combustible material near the engine or battery. Also, check to
make sure that the engine and battery are clean. If combustib le materials or dust are
found near the engine or battery, remove them.
Check the electrical wiring for such components as the starter and alternator for
looseness
Check the entire engine for fuel leakage, engine oil or coolant. If leaka ges are found,
repair.
Make sure the following valves, plugs and cocks are open or closed (tightened) properly:
Fuel feed valve: Open
Coolant drain cock (plug): Closed (Tightened)
Oil drain valve: Closed
• Checking the engine oil level
- Do not top up the oil if the oil level is not below the low level marker.
Important
Pull out the oil level gauge and wipe it clean using a waste cloth.
Insert the oil level gauge fully into the oil level gauge guide, then pull out the gauge again.
The proper oil level is between the high and low marks on the oil level gauge. If the oi l level is lo w, add engine oil of th e specified
type.4. Install the oil filler cap after refilling.
Check the oil pan and other area for oil leakage.
36/202

• Checking the coolant level
Remove the radiator filler cap only after the engine has cooled to room temperature. Place a waste cloth
over the cap, and loosen the cap about a half-turn or stand the lever to the upright position to release
internal pressure. Never open the radiator filler cap while the engine is hot, otherwise the steam or hot
coolant spurts out and you may be scald with it.
Warning
Open the radiator filler cap and check the coolant level.
If the coolant level is low, add coolant to the speci-fied level.
Check for leaks in the cooling circuit.
• Checking the air filter
A clogged filter element limits the engine's air intake and a reduced air supply to the engine.
Important
If the air filter is fitted with a dust control valve (A), press the tip
of the valve to evacuate any accumulated dust particles.
Check the air filter clogging indicator (B). If the indicator is red,
clean the air filter.
B
A
37/202

• Checking the fuel filters
When handling fuel, make sure there are no open flames or other fire hazards near the engine. Wipe
off any spilled fuel completely.Spilled fuel can ignite and cause a fire.
Danger
Drain water for the fuel filter if the warning of water draining for fuel filter is occurred.
Place a drip tray under the drain hose.
Loosen the drain plug and drain water from the fuel filter.
Feed fuel by pushing down on the priming pump (about seven strokes) to facilitate draining.
After draining, tighten the drain plug securely.
After drain the fuel filter, bleed the fuel system.For bleeding air from fuel system.
For bleeding air from fuel system:
Loosen the air vent plug on the fuel filter about 1.5 turns.
Apply a cloth to the air vent plug.
Repeat pumping until the fuel flow from air vent plug becomes free of bubbles.
Tighten the air vent plug and clean.
38/202

6.2. Generator set with NEXYS control panel
6.2.1 Control panel presentation
Fig. 6.1 – View of the front side
Emergency stop button for switching off the generating set in the event of a fault which could endanger personnel or damage
equipment
Key switch for starting up/shutting down the module and RESET function
Electronic card protection fuse
Screen-scroll button, press successively to access the various screens which are available
STOP button, press to switch off the generating set
START button, press to switch on the generating set
Normal operation LEDs and alarm and fault warning LEDs
Slot reserved for panel fascia options
Mounting bolt.
LCD for displaying alarms and faults, operating states, electrical and mechanical quantities
2
1
3
5
9
9
9
6
7
8
4
9
10
39/202

Fig. 6.2 – Description of the LEDs
A lit LED indicates:
Module being supplied (green, lights up and remains lit)
Emergency stop activated (control panel or external emergency stop) (red, lights up and remains lit)
Visualisation of starting phase and speed/voltage stabilisation (flashing) and generating set operating OK or set ready to
generate (green, lights up and remains lit)
General alarm (orange, flashing)
General fault (red, flashing).
6.2.1.1. Introduction to pictograms
The pictograms are as follows:
Operating temperature
Fuel
Overspeed
Non-starting fault
Starting on external command
Preheating
Air intake
Oil pressure
Battery
Delay
Fig. 6.3 – View of pictograms
The "fuel level" pictogram is used to display the fault, the alarm and the fuel level.
The "operating temperature" and "oil pressure" pictograms are used to display the fa ult and analog value
The "overspeed" and "non-starting fault" pictograms are used to display the fault.
The "battery" pictogram is used to display the "alternator charge" fault and to indicate the battery voltage.
1 2 3 4 5
Symbols for electric and
mechanical sizes
40/202

6.2.2 Manual starting
Check that the generating set circuit breaker has triggered.
Danger
connect the generating set battery.
turn the key switch to the ON position (without forcing it)
All of the LEDs light up for 2 seconds, to confirm that they are operating correctly.
If the LEDs do not light up, check the protection fuse and replace it if necessary.
All the items on the screen are displayed for 2 seconds.
Only the "ON" LED remains lit to indicate that the module is powered up.
The following screen appears.
The first line displays the motor speed in RPM.
The second line displays the battery voltage in
volts (V).
Check the battery voltage (min. 12 V)
Press (once briefly) the green "START" button.
If the motor is equipped with an air preheating system, there is a 10-second delay before the motor starts (preheating
activation period).
The following screen appears
The third line displays the air preheating time
remaining (with pictograms representing a
resistor and an hourglass).
If the motor is not fitted with an air preheating system or once the preheating delay has elapsed, the engine starts up
(start of a cycle comprising 3 attempts to start up the engine).
The following screen appears.
The number of successive and automatic starting attempts is limited to 3.
Warning
Note: the LED
flashes as soon as the START button is pressed and continues to flash until the frequen cy stabilises if
a "measurements" card has not been inserted and until the frequency and voltage stabilise if a "m easurements" card has been
inserted.
Following stabilisation, the LED light comes on
continuously.
41/202

6.2.3 Switching off
trigger the circuit breaker located at the base of the centre console
Let the motor run under no load for 1 to 2 minutes to allow it to cool.
press the "STOP" button to stop the generating set.
switch off the MICS Nexys module by switching the key to "OFF" (without forcing it).
6.2.4 Alarms and faults
The appearance of a fault or an alarm caus es the following
screen to be displayed (one or more pictograms or a fault
code along with the SOS message are displayed).
The user can access the following screens by pressing the key
The fault or alarm screen will disappear once the fault or alarm has been removed.
Only one fault is displayed on this screen (the fault which caused the generating set to stop).
If one or more faults have appeared after the first fault, they can only be displayed after the first fault has been reset
(press "Reset" as many times as the number of faults present).
Note: an alarm can appear at the same time as a fault.
6.2.5 Faults and alarms - Details
List of faults which will cause the generating set to stop and generate a pictogram
Oil pressure fault: Indicates that the oil pressure is incorrect
Associated pictogram
Engine temperature fault: Indicates that the engine
temperature is too high.
Associated pictogram
Non-starting fault: Indicates that there have been three
consecutive unsuccessful starting attempts.
Associated pictogram
Overspeed fault: Indicates an excessive generating set
running speed.
Associated pictogram
Low fuel level fault: Indicates the need to top up the fuel.
Associated pictogram
42/202

List of faults which will cause the generating set to stop and generate a fault code
Low coolant level fault: indicates that the level of coolant is
low in the radiator (linked to a two second time delay).
Or
Overload or short-circuit fault (optional): with the circuit
breaker SD contact closing (overload or short-circuit), the
generating set switches off immediately also causing the
main circuit breaker to be triggered.
Associated message
Additional fault linked to message opposite: is displaye d in
the following two cases:
Differential fault (1)
insulation fault (2)
(1) Differential fault (optional): with a differential fault
causing the activation of the differential relay, the
generating set stops immediately also causing the
main circuit breaker to be tripped.
(2) Insulation fault (optional): with an insulation fault
causing the activation of the control unit performing
insulation, the generating set stops immediately.
Associated message
Underspeed fault: indicates an incorrect rotation speed
(below 1000 rpm).
Associated message
Emergency stop or external emergency stop fault
Associated message
"STOP" fault activated if the "STOP" button is pressed
whilst the "AUT" LED is flashing to indicate that the
generating set is operating in automatic mode.
Associated message
List of alarms associated with a pictogram
Low fuel level alarm: Indicates the need to fill up with fuel.
Associated pictogram
"Alternator charging fault" alarm indicates a problem
affecting the alternator charging rate.
Associated pictogram
43/202

6.3. Generator set with TELYS control panel
6.3.1 Control panel presentation
6.3.1.1. View of the front panel
Fig. 6.4 - View of the front panel
1 Emergency stop button (AU) for switching off the generating set in the event of a fault which could endanger personnel or damage
equipment.
2 Key switch for switching the module on/off.
3 Electronic board protection fuse.
4 Scrolling and selection wheel for scrolling through the menus and screens and selecting items simply by pressing the wheel.
5 STOP button, press to switch off the generating set.
6 START button, press to switch on the generating set.
7 Power ON LEDs and alarm/fault warning LEDs.
8 Location of USB ports.
9 Mounting bolt.
10 LCD for displaying alarms and faults, operating statuses, electrical and mechanical quantities.
11 ESC button: for returning to the previous selection and for default RESET function.
12 MENU button for accessing the menus.
13 Lighting for the emergency stop button.
2
1
3
5
9
6
7
8
4
9
10
9
11
12
13
9
44/202

Fig. 6.5 – Description of the LEDs
A lit LED indicates:
1 Alarm activated (flashing yellow).
2 Fault found (flashing red).
3 Module on (green, on continuously).
Fig. 6.6 – Close-up of USB ports
1 USB key connection (HOST): file transfer between USB key and TELYS and vice versa.
2 Connection for microcomputer (DEVICE):
file transfer between PC and TELYS and vice versa,
main module power supply.
3 Protective cover.
1 2 3
2
3
1
45/202

6.3.1.2. Description of the screen
The screen is backlit and requires no contrast adjustments. This screen is divided into 4 zones.
SERIAL No.: 08030010000
SOFTWARE: 5.3.5
NOMINAL VOLTAGE: 400V
FREQUENCY: 50Hz
NOMINAL KW: 320kW
EARTH SYSTEM: TNS
Fig. 6.7 – description of the screen (example)
Zone 1: in this zone, the status of the generating set is displayed
Zone 2: in this zone, pictograms relating to dimensions measured are displayed, as well as Alarm and Fault pictograms
Zone 3: in this zone, the measured values corresponding to the measured dimensions are dis played with the corresponding units of
measurement
Zone 4: in this zone, messages relating to the control of the generating set and the menus are displayed.
Note: the information displayed on measurements, alarms and faults as well as messages and menus relating to control of the
generating set will depend on the equipment level of each generating set. Certai n screens may therefore not be present.
46/202

6.3.1.3. Description of the pictograms in zone 1
Pictograms in zone 1
Pictograms Display
A
ctivation conditions
"MANU" Mode
Fixed TELYS in manual mode (MANU)
Flashing
For 5 seconds when switching from
AUTO mode to MANU mode
"AUTO" Mode
Fixed TELYS in automatic mode (AUTO)
Flashing
For 5 seconds when switching from
MANU mode to AUTO mode
Flashing Generating set in start-up phase
Fixed Generating set started
Fixed
Generating set stabilised (voltage and
frequency)
Flashing (appearance of constant
movement from left to right)
The generating set is powering the
installation
Fixed The installation is supplied
Not used
Not used
47/202

6.3.1.4. Description of the pictograms in zone 2
Alarm and fault pictograms in zone 2
All the pictograms in this zone are activated when TELYS is initialised.
Data displayed
Fuel level indicator
Alarm / Fault
low fuel level
Alarm / Fault
high fuel level
Coolant level / temperature indicator
Alarm
Low level
fault
High
level fault
alarm
Alarm
High
temperature
fault
No preheating
fault
alarm
Battery
Min battery
voltage
(flashing)
Max battery
voltage (flashing)
Battery charge
indicator
(flashing bars)
Oil pressure / temperature indicator
Oil pressure
Alarm / Fault
High or low oil
level
Alarm /
Fault
High or low oil
temperature
Alarm / Fault
Emergency stop
Emergency stop fault
Overload or short circuit
Tripping of circuit breaker following an overload
or short circuit
Engine speed
Underspeed fault
Overspeed fault
Non-starting fault
48/202

6.3.1.5. Description of the pictograms in zone 3
Pictograms in zone 3
All the pictograms in these zones are activated when TELYS is initialised. The pictograms below are given as exam ples.
Generating set stopped
Screen
no.
Pictograms Data displayed
P1
Fuel Level Indicator
Indication of Temperature of High Temperature
coolant (HT) (units according to settings menu)
Indication of Battery Voltage
Indication of Oil Temperature (units according to
settings menu)
Generating set start-up or generating set started or generating set switching off in progress
Screen
no.
Pictograms Data displayed
P2
Engine Speed Indication
Indication of Temperature of High Temperature
coolant (units according to settings menu)
Indication of Oil Pressure (units according to
settings)
Indication of Oil Temperature (units according to
settings menu)
Generating set started
Screen
no.
Pictograms Data displayed
P3
Default
screen in
operation
Fuel Level Indicator
Alternator composite Voltage Indicator
Total Active Power Indicator
Alternator Frequency Indicator
P4
U12 Alternator composite Voltage Indicator
U23 Alternator composite Voltage Indicator
U31 Alternator composite Voltage Indicator
Alternator Frequency Indicator
49/202

Screen
no.
Pictograms Data displayed
P5
V1 Alternator single Voltage Indicator
V2 Alternator single Voltage Indicator
V3 Alternator single Voltage Indicator
Alternator Frequency Indicator
P6
U12 Alternator composite Voltage Indicator
V2 Alternator single Voltage Indicator
V1 Alternator single Voltage Indicator
Alternator Frequency Indicator
P7
V1 Alternator single Voltage Indicator
Single phase Alternator current indicator
Alternator Frequency Indicator
P8
Single phase Alternator current indicator
Two phase Alternator current indicator
Three phase Alternator current indicator
Neutral Alternator current indicator
P9
Total Active Power Indicator
Total Reactive Power Indicator
Total Effective Power Indicator
Total Power Factor Indicator (lagging or leading)
50/202

Screen
no.
Pictograms Data displayed
P10
Fuel Level Indicator
Indication of Battery Voltage
Indication of Battery Amps
Screen order of appearance according to network type with the generating set on.
Type of network
Order of appearance 3P+N 3P 2P+ N 1P+N
1 P3 P3 P3 P3
2 P4 P4 P6 P7
3 P5 P8 P8 P9
4 P8 P9 P9 P2
5 P9 P2 P2 P10
6 P2 P10 P10
7 P10
Change screens by using the scrolling and selection wheel.
When the wheel is rotated clockwise, the screens scroll upwards and vice-versa.
The screens scroll in a loop.
E.g.: On three-phase + neutral network, then screen 7, then screen 1 and vice-versa.
6.3.1.6. Display of messages in zone 4
The display (zone 4), among other things, displays messages r elating to the operation of the generating set. The messages are as
follows:
Initialisation of TELYS
Screen no. Screen Data displayed
G 1
Initialisation of TELYS when the power is switched
on and/or when loading a configuration
G 2
SERIAL No.: 08030010000
SOFTWARE: 6.1.0
NOMINAL VOLTAGE: 400V
FREQUENCY: 50Hz
NOMINAL KW: 320kW
EARTH SYSTEM: TNS
Generating set serial no.
Software version of TELYS
Alternator Nominal Voltage
Alternator Nominal Frequency
Nominal Active Output
Neutral Point
Bar graph indicating the display delay of the screen
51/202

Generating set stopped
Screen
no.
Screen Data displayed
G 3
OPERATION
MANUAL
Press START
to start
24/08/2005 13:12
Operating mode - generating set in Manual Mode
ready to start
Date and time (depending on settings)
G 4
OPERATION
AUTO
WARNING
START-UP POSSIBLE
IMMEDIATELY
24/08/2005 13:12
Operating mode - generating set in Auto Mode
ready to start
Date and time (depending on settings)
G 5
WARNING
AUTOMATIC Start
19 min 30 sec
24/08/2005 13:12
Operating mode - generating set in Auto Mode with
programmed start
Countdown to micro disconnection delay or EJP
notice delay (for France only)
Date and time (depending on settings)
Generating set start-up
Screen
no.
Screen Data displayed
G 6
START-UP
IN PROGRESS
24/08/2005 13:12
Operating phase - generating set in starting phase
Date and time (depending on settings)
52/202

Screen
no.
Screen Data displayed
G 7
AIR PREHEATING
10 seconds
24/08/2005 13:12
Operating phase - air preheating prior to starting
generating set
Countdown for air preheating delay
Date and time (depending on settings)
Generating set started
Screen
no.
Screen Data displayed
G 8
Default
screen
AVAILABLE POWER
75%
24/08/2005 13:12
Operating phase – generating set in operation –
stable voltage and frequency
Available power
Date and time (depending on settings)
G 9
AUTOMATIC STOP
IN PROGRESS
LOAD SUPPRESSION
1 min 30 sec
24/08/2005 13:12
Operating mode - operation in Auto Mode
Opening of power supply device (motorised circuit
breaker or source changeover switch controlled by
TELYS)
Countdown for the mains return delay OR the load
test delay
Date and time (depending on settings)
G 10
AUTOMATIC STOP
IN PROGRESS
COOLING DOWN
1 min 30 sec
24/08/2005 13:14
Operating mode - operation in Auto Mode
Generation set cooling in progress
Countdown for Engine Stop delay (cooling) OR
Gradual Stop delay (Coolant temperature) OR
Overload Gradual Stop delay OR OFF load test
delay
Date and time (depending on settings)
53/202

Generating setstop
Screen
no.
Screen
Data displayed
G 11
OFF
IN PROGRESS
24/08/2005 13:16
Generating set stop in progress
Date and time (depending on settings)
Operating mode changeover (switching from Manual Mode to Auto Mode following auto start demand)
Screen
no.
Screen
Data displayed
G 12
Start Demand
AUTO
Do you wish to change
to Auto Mode?
WARNING
Immediate start
OK Esc
Operating mode - operation in Manual Mode
AUTOMATIC start demand
Generating set stop request due to fault or by pressing STOP in Auto Mode
Screen
no.
Screen
Data displayed
G 13
Manual Mode
activated
Do you wish to change
to AUTO mode?
OK Esc
Operating mode - operation in Auto Mode
(generating set in operation)
Warning message for switching to Manual Mode
after the STOP button has been pressed or a fault
has appeared
54/202

6.3.2 Starting
Check that the generating set circuit breaker has triggered.
Danger
Connect the generating set battery
Turn the key switch to the ON position (without forcing it to the ON position), the ON lamp will light up (if the lamp does not
light up, check and replace the fuse if necessary)
Test the Alarm and Fault LEDs (menu 15 – TEST LAMPS)
1 ACTIONS
1/5
11 MANUAL <> AUTO
12 CONTROL LOAD
13 TEST GENERATING SET
14 PROGRAMS
15 TEST LAMPS
12 OK Esc
Press "Esc" several times to return to the following home menu
OPERATION
MANUAL
Press START
to start
24/08/2005 13:12
Check the battery voltage
Press START:
AIR PREHEATING
10 seconds
24/08/2005 13:12
If the engine is equipp ed with an
air preheating system, there is a
delay (adjustable) before the
engine starts (preheating
activation period).
If the motor is not fitted with an
air preheating system or once the
preheating delay has elapsed,
the engine starts up (start of a
cycle comprising 3 attempts to
start up the engine).
START-UP
IN PROGRESS
24/08/2005 13:12
Warning: the number of successive
and automatic starting attempts is
limited to 3.
The following pictogram will flash
AVAILABLE POWER
100.0%
24/08/2005 13:12
The following pictogram is displayed
The following information is displayed
Speed of rotation
Coolant temperature
Options
Oil pressure
Oil Temperature
55/202

6.3.3 Switching off
Open the circuit breaker
manually OR by selecting menu 12 "CONTROL LOAD"
The following display will disappear (supply stopped)
Press the STOP button
The following screen is displayed and the generating set will stop
OFF
IN PROGRESS
24/08/2005 13:12
Switch TELYS off by turning the key to "OFF" (without forcing it to the "OFF" position).
6.3.4 Alarms and faults
6.3.4.1. Viewing alarms and faults
Alarms and faults are displayed as follows:
Alarms
All alarms will cause:
the yellow LED to flash "General alarm".
In conjunction with this LED:
a flashing pictogram appears on the LCD screen
representing the circuit affected by the alarm and the
associated indicator
, if present
(example)
message on graphic display (example)
FAULT
ALARM
Low Fuel Level
25/12/05 15:30
OK=HELP
56/202

Faults
All faults will cause:
the generating set to stop: immediate or gradual stop (coolant temperature and overload or short circuit)
the red LED to flash "General fault".
In conjunction with this LED:
a flashing pictogram
appears on the LCD screen
representing the circuit affected by the fault and the
associated indicator, if present
(example)
message on graphic display (example)
FAULT
FAULT
Oil Pressure
25/12/05 15:30
OK=HELP
Faults have priority over alarms. Faults are displayed in the descending order of their ap pearance (from the most recent to the oldest).
6.3.4.2. Activation of an alarm or fault
The appearance of an alarm o
r
a fault causes the corresponding screen to be displayed (examples below)
FAULT
ALARM
Low coolant Level
06/10/06 10:30
OK=HELP
FAULT
FAULT
Emergency Stop
06/10/06 15:30
Esc=RESET OK=HELP
Press OK (on the scrolling and selection wheel) to access the help message if it is available (example below)
HELP
Check the level
fuel
Esc=EXIT
If the alarm is no longer active, it is reset automatically (cause disappears).
Press Esc to reset a fault:
- reset acknowledged if the cause of the fault has been removed
- reset not performed if the cause of the fault is still present.
57/202

6.3.4.3. Activation of an alarm and a fault
The appearance of an alarm and a fault causes:
The yellow and red LEDs to flash
the related screen to be displayed (example below)
FAULTS 1/2
FAULT
Emergency Stop
25/12/05 15:30
Esc=RESET OK=LIST
If several faults are present, the number of faults is
displayed at the top of the screen.
The faults list can be accessed by pressing OK (of the scrolling and selection wheel) (examples below)
FAULTS
1/2
FAULT 25/12/05 15:30
Emergency Stop
ALARM 25/12/05 15:30
Low Fuel Level
12 OK=HELP Esc
Press Esc to return to the previous screen.
Press OK to go to the HELP screen (help on the
highlighted fault)
Use the scrolling and selection wheel to scroll through
the list of faults.
HELP
Check:
- Emerg. Stop Pos.
- Connector(s)
Esc
If the alarm is no longer active, it is reset automatically (cause disappears).
Press Esc to reset a fault:
- reset acknowledged if the cause of the fault has been removed
- reset not performed if the cause of the fault is still present.
58/202

6.3.4.4. Engine fault codes display
Certain alarms and engine faults generate specific fault codes. T hese codes are standardised according to the J1939 and/or J1587
standards.
Terminology used by the SAE CAN J1939 standard
SPN: Suspect Parameter
Number
This represents the system or component at fault, for example: SPN 100,
indicates an oil pressure problem or a problem with the oil pressure sensor.
FMI: Failure Mode identifier
This represents the type of fault that has occurred. This may be an electrical,
mechanical or equipment fault.
Terminology used by VOLVO
SID: System Identifier
This term, used in the J1587 standard, has an equivalent in the J193 9 standard
(SPN).
However, this term corresponds, more particularly, to an assembly of
components, for example, the injection system.
PID: Parameter Identifier
This term, used in the J1587 standard, has an equivalent in the J193 9 standard
(SPN).
However, this term corresponds, more particularly, to a specific component, for
example, a sensor.
PPID: Parameter Identifier
This term, used in the J1587 standard, has an equivalent in the J193 9 standard
(SPN).
PPID corresponds to PID, but is only used by VOLVO.
FMI: Failure Mode identifier
This represents the type of fault that has occurred. This may be an electrical,
mechanical or equipment fault. VOLVO uses a SID-FMI or PID-FMI or PPID-FMI
combination.
Terminology used by JOHN DEERE
SPN: Suspect Parameter
Number
This represents the system or component at fault, for example: SPN 100,
indicates an oil pressure problem or a problem with the oil pressure sensor.
FMI: Failure Mode identifier
This represents the type of fault that has occurred. This may be an electrical,
mechanical or equipment fault.
59/202

In the event of a fault, the screen will display the following message:
FAULT
ALARM
ENGINE GENERAL 110 18
25/12/2005 15:30
OK=HELP
Engine fault code
.
Pressing OK will display fault finding information.
In addition, appendix D indicate the meaning of the
code. The checking and maintenance operations to
carry out in order to solve the fault are included in the
user and maintenance manuals of the engines
supplied with the generating set documentation.
For JOHN DEERE (JD) and VOLVO (VO) engines, the codes displayed are SPN and FMI codes.
6.3.4.5. Horn reset
Depending on the settings made (menu 363 - HORN), the activation of an alarm and/or a fault leads to the hor n
sounding and the following screen appearing:
HORN STOP
PRESS OK
25/12/2005 15:30
This screen will display first any messages relating to
the alarms and faults that appear as soon as OK is
pressed.
7. Maintenance schedule
7.1. Reminder of use
The maintenance interval frequency and the operations to be carried out are outlined in the maintenance schedule, given as a guideline.
N.B. the environment in which the generating set is operating determines this schedule.
If the generating set is used in extreme conditions, shorter intervals between maintenance procedures should be observed
These maintenance intervals only apply to generating sets runni ng on fuel, oil and coolan t which conform to the specifications given in
this manual.
7.2. Maintenance safety instructions
Before each operation, please observe the following maintenance safety instructions:
read the safety instructions carefully (chapter 1),
refer systematically to the maintenance instructions,
the battery isolating switch must be in the open position,
no operations must be carried out while the motor is running,
wear protective equipment (gloves, goggles, safety shoes etc.),
before operating on a pressurised circuit, ensure that the circuit pressure has been reduced (atmosp heric pressure),
after the operations, ensure that the equipment is clean, or clean it if necessary.
60/202

7.3. Table of maintenance operations
OPERATIONS
10 h
Daily
250 h 500 h 1000 h 1500 h 3000 h 2 years
20 000 h
3 years
Generator set
• Check the general condition
●
• Check the tightening torques
●
• Check the absence of leaks
●
• Check the condition of battery charge
●
• Clean the battery terminals
●
• Check condition and connections of
electrical equipment
●
• Clean with compressed air the relays and
contactors
●
Engine
• Check engine oil and coolant level
●
• Check fuel filter / Water bowl
●
• Check air cleaner
●
• Replace engine oil and oil filtera
●
• Inspect belt and adjust and belt tension
●
• Check and Clean radiator fins
●
• Add grease to link joints, etc.
●
• Replace fuel filter (in-line type fuel injection
pump)
●
• Inspect valve clearance
●
• Check glow plug
●
• Inspect starter
●
• Inspect alternator
●
• Retighten bolts and nuts on the enginea
●
• Clean nozzle tip
●
• Check and Clean fuel injectio n nozzle
●
• Inspect turbocharger
●
• Change coolant
●
Alternator
• Check the tightening torques
After the first 20 hours
• Check the general condition
• Check the various electrical connections of
the installation
• Grease the bearings
●
a
After the first 50 service hours for a new or overhauled engine
61/202

7.4. Fault finding
Refer to the user manual and engine and alternator maintenance manuals appended.
Additionally, in the event of an abnormal rise in engine temperature, check that the radiator is clean.
7.5. No load and under load tests
Notes on operation at no load and under load:
When operating at no load or low load (< 30% of nominal power), the operating condition s do not allo w optimum running of the engine.
The main causes are as follows:
The low volume of fuel burned in the combustion chamber leads to incomplete combustion; the resultin g thermal en ergy means that
the optimum engine operating temperature cannot be reached.
Overheated engines h ave lower compression ratios (low compression ratio without turbochar ging), which are defined for full load
and not suitable for good combustion at low load.
All of these factors lead to choking of the engine, in particular the piston rings and valves, which leads to:
Accelerated wear and glazing of the cylinder liners
Loss of sealing of seats, and sometimes sticking of valve stems.
Consequently, operating any turbocharged engine at low load (< 30%) can only hav e adverse repercussions on an engine's op eration
and its service life. Maintenance intervals will have to be shortened to accompany ha rsh operating conditions. Shortening draining
intervals, among other things, will enable you to change the oil more fre quently, which will tend to be choked with unburnt par ticles and
contaminated with fuel. Adding a load bench is ge nerally used to limit low lo ad phases, and obtain the peri odic full loads necessar y to
unchoke the engine.
Finally, when operating under load, we advise vigilance towards th e oil breather circuit, and more particularly towards engines wh ich
have the crankcase vent connected to the turbocharger inlet (risk of oil or oil vapour absorption and accelerated engine speed).
On load tests:
It is recommended to conduct an on load test on the generating set mon thly, for a period of around 1 hour after stabilisation of the
parameters.
The load must be greater than 50% of nominal power (ideally 80%), to ensure unchoking of the engine and to obtain a decent picture of
the generating set operation.
Off load test (no load):
This test is not recommended; it must not exceed 10 minutes, and must not be repeated without a monthly on load test. This test onl y
allows you to check for correct engine start-up. It does not allow you to check that the generating set is working properly.
62/202

8. Battery
Fit the battery so that it is properly ventilated.
Maintenance should only be carried out by qualified personnel.
If replacing the batteries, use the same type of batteries. Do no t throw the old battery in the fire.
Only use insulated tools (the operator should not be wearing a watch, chain or any metal objec t).
Never use sulphuric acid or acid water to top up the electrolyte level . Use an a pproved batte ry fluid.
Batteries release oxygen and hydrogen gas, which are flammable.
Never bring flames or sparks near the battery (risk of explosion).
Discharge any static electricity before handling the batteries by first touching an earthed me tal surface .
Do not use the battery when the fluid level is below the minimum required level Using a battery with a low
electrolyte level could result in an explosion.
Do not short the battery terminals with a tool or other metal object.
When disconnecting battery cables, remove the cable from the negative (-) terminal first. When reconnecting the
battery, connect the positive lead (+) first.
Charge the battery in a well-ventilated place, with all the filler caps opened.
Ensure that the battery terminals are correctly tightened. A loose cable clamp can cause sparks that could result in
an explosion.
Before servicing electrical components or performing electric welding, set the battery switch to the [OFF] position
or disconnect the battery negative cable (-) to cut off the electrical current.
Electrolyte contains dilute sulphuric acid. Careless handling of the battery causing contact with sulphuric acid
could damage your eyesight or cause burns.
Wear safety goggles and rubber gloves when working with the battery (topping-up fluid, charg ing, etc.)
If electrolyte comes into contact with your skin or clothes, wash it off immediately with plenty of water, then
carefully wash the area with soap.
If electrolyte comes into contact with your eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical attention
as soon as possible.
If electrolyte is accidentally swallowed, gargle with plenty of water and drink large quantities of water. Consult a
doctor immediately.
Large quantities of electrolyte should be rinsed off using a neutralising agent. A common method is to use a
solution of 500g of bicarbonate of soda diluted in 4 litres of water. The bicarbonate of so da solution should
be added until the reaction has finished (lather). The remai ning liquid sh ould be r insed off with water and left
to dry.
Danger
Dry batteries do not require any servicing
Batteries ready for use must be recharged at the latest when the acid density drops below 1.20.
8.1. Storage and transport
Batteries ready for use must be stored in a cool and dry place (frost-free) protected from the sun (self-discharge).
Batteries must be transported and stored vertically (risk of acid spillage)
Leave the terminal cover on the positive terminal
63/202

8.2. Battery setting into service
- Batteries filled with acid have a density of 1.28 g/ml and are charg ed.
- In the case of dry batteries, fill each battery cell with acid up to the maximum level mark or to 15 mm above the plates. Let the
battery rest for 20 minutes.
- Before fitting the battery, stop the engine and any power consumer, clean the terminals a nd give them a light coating of grease.
When connecting, connect the positive terminal (+) first, and then the negative terminal (-).
8.3. Check
Acid density Charge status
V
oltage when idle
1.27 100% Above 12.60 V
1.25 80% 12.54 V
1.20 60% 12.36 V
From 50 % recharge
1.19 40% 12.18 V
Risk of sulphation
1.13 20% Under 11.88 V
Unusable
64/202

8.4. Load preconization
Highly discharged or sulphated batteries (formation of whitish lead sulphate deposit on the plates, which becomes hard and
insoluble to acid; this deposit reduce the active surface of the plates, and increases their internal resistance) can no longer
regenerate or be charged in a generating set.
A discharged battery should be recharged immediately, or else it will suffer irreparable damage.
Important
Battery charge
When several batteries are connected together, the following points should be checked:
Are the batteries connected in series?
Has the correct voltage been chosen? 1 battery x 12 V , 3 x 36V batteries.
Adjust the charge current to the lowest battery.
The power difference between the batteries must be as low as possible.
Example of charge:
12V 60 Ah battery = charging current 6 A.
Charge status: 50% (acid density 1.21/voltage when idle 12.30V).
The battery is short 30 Ah, and this must be recharged.
Charge factor: 1.2.
Ah x 1.2 = 36 Ah to be charged.
Charging current: 6A approximately 6 hours charging required.
Recharging is complete when the battery voltage and the acid density stop increasing.
→ The charging current must always be 1/10
th
of the nominal capacity of the battery.
The power of the charger must be suitable for the battery to be charged and the charging time available.
You need to use an automatic charger able to provide a sufficient voltage and charging current, as well as a compensation volta ge to
handle spontaneous battery discharge.
65/202

8.5. Faults and remedies
Fault observed Probable origin Measures or observations
The acid heats up when a new battery is
filled
- Incorrect composition
- Incorrect storage
- Prolonged storage in a damp place
- Cool
- Load
- Check the acid density
The acid escapes through the filler holes - Overfilled battery - Reduce the battery fluid level
Acid level too low
- Battery tray not leaktight
- Excessive charge voltage leading to
a significant accumulation of gas.
- Replace the battery
- Check the charger and repair if
necessary.
Acid level too low
Incorrect operation from start-up
- Insufficient charge
- Short circuit in the power circuit
- Consumption fault
- Recharge
- Check the electrical installation
Acid density too high
- The battery has been filled with acid
instead of battery fluid
- Reduce the acid level by filling with
distilled water. Repeat the operation if
necessary.
Starting problems
Starting test incorrect
- Battery empty
- Battery exhausted or faulty
- Capacity too low
- Battery sulphated
- Recharge the battery
- Fit a new battery
Battery terminals melted
- Incorrect electrical connection
- Battery cabling incorrect
- Tighten the ends of the battery
cables, or replace them if necessary
One or two cells release a lot of gas at
high charge
- Cell(s) faulty - Fit a new battery
The battery discharges very quickly
- Charge status too low
- Short circuit in the current circuit
- High self-discharge (through
electrolyte contamination etc.)
- Sulphation (storage of discharged
battery)
- Check the load
- Replace the battery
Short service life
- Incorrect battery part no.
- Repeated deep discharging
- Battery stored too long without
charge
- Define the correct battery part no. for
the recommended use
- It is recommended to charge the
battery using a regulator
High water consumption
- Overload
- Charging voltage too high
- Check the charger (voltage regulator)
The battery explodes
- Spark after battery charging
- Short circuit
- Connection or disconnection during
charging
- Internal fault and low electrolyte level
- Replace the battery
- Ventilate well
66/202

9. Appendix
9.1. Appendix A – Engine user and maintenance manual
67/202

68/202

User guide and maintenance manual
M
MII
T
T
S
S
U
U
B
BII
S
S
H
HII
E
Ennggiinnee
S
S
E
E
R
RII
E
E
S
S
S
S
99610-29120
01/07/2009
33522051001_3_1
69/202

70/202

July 2009
Pub. No. 99610-29120
The operator and supervisor are requested to read this Operation and Maintenance Manual carefully before operating the
engine or conducting inspection and maintenance.
Never operate the engine or conduct maintenance work without completely understanding this manual.
OPERATION &
MAINTENANCE MANUAL
199610-29120
71/202

i
INTRODUCTION
This operation and maintenance manual contains detailed operation, inspection
and maintenance information for engines from Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Please read this manual thoroughly before proceeding with operation, inspection,
and maintenance work for correct use and servicing.
Failure to follow directions in this manual may result in serious accidents.
72/202

ii
FOREWORD
Limited warranty
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. will repair or replace parts returned to us when we judges that the parts are defective in material and/or workmanship after conducting inspection.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.'s warranty is limited to the compensation work of repair or replacement of parts.
The warranty coverage is effective for the original purchaser only. Those to whom ownership is later transferred are
not provided with the warranty.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.'s makes no warranties, either expressed or implied,
except as provided in this manual, including, but not limited to, warranties as to marketability , merchantability, fitness for a p articular purpose or use, or against infringement of
any patent.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. will not be liable for any damages or consequential
damages, including, but not limited to, damages or other cost s resulting from any abuse,
misuse, misapplication of the engine and devices supplied from us.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. will not be liable for any damages or personal injuries
resulting from any modification, without our written permission, of the engine and
devices supplied from us.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. will not be li able for any damages or production losses
caused by the use of fuel, engine oil and/or long life coolant (LLC) that we are not recommended.
The owner of the engine is responsible for the p erf orm ance of th e r equir ed maint enan ce
listed in this operation manual.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. may deny the warranty coverage if the engine or part
has failed due to inadequate or improper maintenance.
73/202

iii
FOREWORD
Emission warranty
Warranty coverage
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. warrants to the first owner and each subsequent purchaser of a new non-road diesel engine that the emission control system of your engine:
is designed, built and equipped so as to conform at the time of sales with all applicable regulation of the U.S. Envi-
ronmental Protection Agency.If the vehicle in which the engine is installed is registered in the state of California, a
separate California emission regulation also applies.
is free from the defects in material and workmanship which will cause the engine to fail to meet these regulations
within the warranty period.
Then its warranty period is
The emission warranty period is shown below.
However, if your engine warranty period is longer than the emission warranty period, the emission warranty period
extends to same as the engine warranty period.
Below warranty period shall begin on the date the engine is delivered to the first owner.
Warranted parts
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. warrants the parts which will increase the emission of pollutants when they
become defective.
The followings are examples.
Inlet/Exhaust manifold
Crankcase ventilation system
Fuel system
Fuel injection nozzle
LIMITED WARRANTY
Refer to "LIMITED WARRANYT".
The following warranty applies to the engines that are approved of the emission regulation of the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
If your engine is certified as
And its maxi-
mum power is
And its rated speed is Then its warranty period is
Variable speed or constant
speed
kW < 19 Any speed
1,500 hours or 2 years, whichever
comes first.
Constant speed 19 ≤ kW < 37
3800 min
-1
or more
1,500 hours or 2 years, whichever
comes first.
Constant speed 19 ≤ kW < 37
Less than 3000 min
-1
3000 hours or 5 years, whichever
comes first.
Variable speed 19 ≤ kW < 37 Any speed
3000 hours or 5 years, whichever
comes first.
Variable speed or constant
speed
kW ≥ 37 Any speed
3000 hours or 5 years, whichever
comes first.
74/202

iv
FOREWORD
California emission control warranty statement
your warranty rights and obligations
The California Air Resources Board (CARB) is pleased to explain the emission control system warranty on
you 2008 or later engine.In California, new heavy-duty off-road engines must be designed, built, and equipped to
meet the State's stringent anti-smog standards.Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. must warrant the emission control
system on your engine for the periods of time listed below provided there has been no abuse, neglect or improper
maintenance of your engine.
Your emission control system may include parts such as the fuel-injection system and the air induction system. Also
included may be hoses, belts, connectors and other emission-related assemblies.
Where a warrantable condition exists, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. will repair your heavy-duty off-road engine
at no cost to you including diagnosis, parts, and labor.
MANUFACTURER'S WARRANTY COVERAGE:
The 2008 and later heavy-duty off-road engines are warranted for the Warranty Period. If any emission-related part
on your engine is defective, the part will be repaired or replaced by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
OWNER'S WARRANTY RESPONSIBILITIES:
As the heavy-duty off-road engine owner, you are responsible for the performance of the required maintenance
listed in your owner's manual.Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. recommends that you retain all receipts covering
maintenance on your heavy-duty off-road engine, but Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. cannot deny warranty
solely for the lack of receipts or for your failure to ensure the performance of all scheduled maintenance.
As the heavy-duty off-road engine owner, you should however be aware that Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. may
deny you warranty coverage if your heavy-duty off-road engine or a part has failed due to abuse, neglect, improper
maintenance or unapproved modifications.
Your engine is designed to operate on diesel fuel only. Use of any other fuel may result in your engine no longer
operating in compliance with California's emissions requirements.
You are responsible for initiating the warranty process. The Air Rexources Board suggests that you present your
heavy-duty off-road engine to a Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. dealer or distributor dealer as soon as problem
exists. The warranty repairs should be completed by the dealer or distributor as expeditiously as possible.
If you have any questions regarding your warranty rights and responsibilities, you should contact Mitsubishi
Engine North America at 1-630-268-0750.
The following warranty applies to the engines that are approved of the emission regulation of the California Air
Resources Board (CARB).
75/202

v
FOREWORD
Warranty coverage
(a) The warranty period shall begin on the date the engine or equipment is delivered to an ultimate purchaser.
(b) Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. warrants to the ultimate purchaser and each subsequent purchaser of the en-
gine registered in the state of California that the engine is:
(1) Designed, built and equipped so as to conform with all applicable regulations adopted by the Air Resources
Board.
(2) Free from defects in materials and workmanship which cause the failure of a warranted part to be identical
in all material respects to the parts as described in Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.'s application for certifi-
cation for a period of 5 years or 3,000 hours of operation, whichever occurs first. In the absence of a device
to measure hours of use, the engine shall be warranted for a period of 5 years. For all engines rated less
than 19kW, and for constant-speed engines rated under 37 kW with rated speeds higher than or equal to
3,000 min
-1
, the period of 2 years or 1,500 hours of operation, whichever occurs first, shall apply. In the ab-
sence of a device to measure hours of use, the engine shall be warranted for a period of 2 years.
(c) The warranty on emission-related parts shall be interpreted as follows:
(1) Any warranted part which is not scheduled for replacement as required maintenance in the written instruc-
tions required by Subsection (e) shall be warranted for the warranty period defined in Subsection (b) (2). If
any such part fails during the period of warranty cove rage, it shall be repaired or replaced by Mitsubishi
Heavy Industries, Ltd. according to Subsection (4) below. Any such part repaired or replaced under the war-
ranty shall be warranted for the remaining warranty period.
(2) Any warranted part which is scheduled only for regular inspection in the written instructions required by Sub-
section (e) shall be warranted for the warranty period defined in Subsection (b) (2). A statement in such writ-
ten instructions to the effect of "repair or repla ce as necessary" shall not reduce the period of warranty
coverage. Any such part repaired or replaced under the warranty shall be warranted for the remaining war-
ranty period.
(3) Any warranted part which is scheduled for replacement as required maintenance in the written instructions
required in Subsection (e) shall be warranted for the period of time prior to the first scheduled replacement
point for that part.If the part fails prior to the first scheduled replacement, the part shall be repaired or re-
placed by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. accordi ng to Subsection (4) below. Any s uch part repaired or
replaced under warranty shall be warranted for the remainder of the period prior to the first scheduled re-
placement point for the part.
(4) Repair or replacement of any warranted part under the warranty provisions shall be performed at no charge
to the owner at a warranty station.
(5) Notwithstanding the provisions of Subsection (4) above, warranty services or repairs shall be provided at all
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. distribution centers that are franchised to service the subject engines.
(6) The owner shall not be charged for diagnostic labor that leads to the determination that a warranted part is
in fact defective, provided that such diagnostic work is performed at a warranty station.
(7) Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. shall be liable for damages to other engine components proximately caused
by failure under warranty of any warranted part.
(8) Throughout the engine's warranty period defined in Subsection (b) (2), Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. shall
maintain a supply of warranted parts sufficient to meet the expected demand for such parts.
(9) Any replacement part may be used in the performance of any maintenance or repairs and must be provided
without charge to the owner. Such use shall not reduce the warranty obligations of Mitsubishi Heavy Indus-
tries, Ltd..
76/202

vi
FOREWORD
(10) Add-on or modified parts that are not exempted by the Air Resources Board may not be used. The use of
any non-exempted add-on or modified p arts shall be grounds for disallowing a warranty claim. Mitsubishi
Heavy Industries, Ltd. shall not be liable to warrant failures of warranted parts caused by the use of a non-
exempted add-on or modified part.
(11) The Air Resources Board may request and, in such case, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. shall provide,
any documents which describe that Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.'s warranty procedures or policies.
(d) Warranted parts list.
(1) Fuel metering system
(A) Fuel injection system.
(B) Air/fuel ratio feedback and control system.
(C) Cold start enrichment system.
(2) Air induction system
(A) Controlled hot air intake system.
(B) Intake manifold.
(C) Heat riser valve and assembly.
(D) Turbocharger/supercharger systems.
(E) Charged air cooling systems.
(3) Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system
(A) EGR valve body, and carburetor spacer if applicable.
(B) EGR rate feedback and control system.
(4) Air injection system
(A) Air pump or pulse valve.
(B) Valves affecting distribution of flow.
(C) Distribution manifold.
(5) Catalyst or thermal reactor system
(A) Catalytic converter.
(B) Thermal reactor.
(C) Exhaust manifold.
(6) Particulate controls
(A) Traps, filters, precipitators, and any other devices used to capture particulate emissions.
(B) Regenerators, oxidizers, fuel additive devices, and any other device used to regenerate or aid in the
regeneration of the particulate control device.
(C) Control device enclosures and manifolding.
(D) Smoke puff limiters.
(7) Advances oxides of nitrogen (NOx) controls
(A) NOx absorbers.
(B) Lean NOx catalysts.
(C) Selective catalyst reduction.
(D) Reductant (urea/fuel) containers/dispensing systems.
(8) Positive crankcase ventilation (PCV) system
(A) PCV valve.
(B) Oil filler cap.
77/202

vii
FOREWORD
(9) Miscellaneous items used in above systems
(A) Vacuum, temperature, and time sensitive valves and switches.
(B) Electronic control units, sensors, solenoids, and wiring harnesses.
(C) Hoses, belts, connectors, assemblies, clamps, fittings, tubing, sealing gaskets or devices, and mount-
ing hardware.
(D) Pulleys, belts and idlers.
(E) Emission control information labels.
(F) Any other part with the primary purpose of reducing emissions or that can increase emission during fail-
ure without significantly degrading engine performance.
(e) Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. shall furnish with each new engine written instructions for the maintenance and
use of the engine by the owner.
LIMITED WARRANTY:
Refer to "LIMITED WARRANTY".
78/202

viii
FOREWORD
Important information
To avoid the potential hazard, accident prevention
activities must be planned methodically and con-
ducted continually by considering all aspect of
engine operation, maintenance and inspection.All
related personnel, including managers and supervi-
sors, should actively participate, recognize their roles
and organize themselves and their work to ensure a
safe environment.
The foremost safety objective is to prevent accidents
which may result in injury or death, or equipment
damage.
Always observe laws or regulations of the local or
federal/national government.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. cannot foresee all
potential dangers of the engine, potential danger
resulting from human error and other causes, or dan-
ger caused by a specific environment in which the
engine is used. Since there are many actions that
cannot be performed or must not be performed, it is
impossible to indicate every caution in this manual or
on warning labels. As such, it is extremely important
to follow directions in this manual and also to take
general safety measures when operating, maintain-
ing and inspecting the engine.
When the engine is used by individuals whose native
language is not English, the customer is requested to
provide thorough safety guidance to the opera-
tors.Also add safety, caution and operating signs that
describe the original warning label statements in the
native language of the operators.
The engine must be operated, maintained and
inspected only by qualified persons who have thor-
ough knowledge of engines and their dangers and
who also have received risk avoidance training.
To prevent an accident, do not attempt to carry out
any operation other than those described in this man-
ual, and do not use the engine for any unapproved
purpose.
When the ownership of the engine is transferred, be
sure to provide this manual with the engine to the
new owner. Also inform Mitsubishi Heavy Industries,
Ltd. of the name and address of the new owner of the
engine.
This manual is copyrighted and all rights are
reserved.No part of this manual, including illustra-
tions and technical references, may be photocopied,
translated, or reproduced in any electronic medium
or machine readable form without prior written con-
sent from Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
The contents in this manual are subject to change at
any time without notice for improvement of the
engine.
Pictures or illustrations of the product in this manual
may differ from those of product you have. Please
note that, depending on specifications, items
described in this manual may differ from those on
your engine in shape, or may not be installed on your
engine.
Please contact a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Indus-
tries, Ltd. if you need more information or if you have
any questions.
If you lost or damaged this manual, obtain a new
copy at a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
as soon as possible.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. recommends the
engine owner to install an hour meter on the engine
due to monitor correct running intervals and to per-
form the maintenance at the appropriate timing.
79/202

ix
FOREWORD
Wa rning indication
The following means are used to call the attention of the operators and maintenance personnel to potential dangers
of the engine.
Warning statements in the manual
Warning labels affixed on the engine
Warning statements
The warning statements in this manual describe potential danger in operating, inspecting or maintaining the engine,
using the following 5 classifications to indicate the degree of potential hazard.
Failure to follow these directions could lead to serious accidents which could result in personal injury, or death in
the worst case.
Understand the directions well, and handle engines with following directions.
Indicates an immediately hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death or
serious injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or
serious injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result in minor or
moderate injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result in property
damage.
Note : Indicates important information or information which is useful for engine operation.
80/202

x
FOREWORD
Units of measurement
Measurements are based on the International System of Units (SI), and they are converted to the metric system
units in this manual using the following conversion rates.
Pressure :1 MPa = 10.197 kgf/cm
2
Torque :1 N·m = 0.10197 kgf·m
Force :1 N = 0.10197 kgf
Horsepower :1 kW = 1.341 HP = 1.3596 PS
Meter of mercury :1 kPa = 0.75 cmHg
Meter of water :1 kPa = 10.197 cmH
2O(cmAq)
Engine speed :1 min
-1
= 1 rpm
Kinetic viscosity:1 mm
2
/s = 1 cSt
Abbreviations, standards and others
API = American Petroleum Institute
ASTM = American Society for Testing and Materials
ISO = International Organization for Standardization
JIS = Japanese Industrial Standards
LLC = Long Life Coolant
MIL = Military Specifications and Standards
MSDS = Material Safety Data Sheet
SAE = Society of Automotive Engineers
81/202

CONTENTS-1
CONTENTS
Chapter 1
BASIC SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Fire and explosions .............................1-1
Keep flames away............................................ 1-1
Keep engine surrounding area tidy and clean.. 1-1
Care for fuel, oil and exhaust gas leakage....... 1-1
Use explosion-proof lighting apparatus............ 1-1
Prevent electrical wires from short-circuiting.... 1-1
Keep fire extinguishers and a first-aid kit
handy ............................................................... 1-1
Stay clear of all rotating and moving
parts ....................................................1-2
Install protective covers around rotating
parts ................................................................. 1-2
Check work area for safety .............................. 1-2
Stay clear of moving parts while engine is
running ............................................................. 1-2
Lockout and tagout .......................................... 1-2
Keep engine stopped during servicing............. 1-2
Always restore engine turning tools after use .. 1-2
Changing the engine speed setting is
prohibited ......................................................... 1-2
Be careful of exhaust fume
poisoning .............................................1-3
Operate engine in a well-ventilated area.......... 1-3
Be careful of falling down ....................1-3
Lift engine carefully .......................................... 1-3
Do not climb onto the engine ........................... 1-3
Always prepare stable scaffold ........................ 1-3
Protect ears from noise .......................1-4
Wear ear plugs................................................. 1-4
Be careful of burns ..............................1-4
Do not touch the engine during or immediately
after operation .................................................. 1-4
Do not open the radiator filler cap when the
engine is hot..................................................... 1-4
Do not touch high pressure injection fuel ......... 1-4
Refill coolant only after the coolant
temperature dropped........................................ 1-4
Be careful when handling fuel, engine
oil or LLC .............................................1-5
Use only specified fuel, engine oil and LLC ..... 1-5
Handle LLC carefully........................................ 1-5
Proper disposal of waste oil, LLC and
coolant ............................................................. 1-5
When abnormality occurs....................1-5
Do not add coolant immediately after a sudden
stop due to overheating.................................... 1-5
Avoid immediate restart after abnormal stop.... 1-5
Avoid continuous engine operation at low oil
pressure ........................................................... 1-5
If belt breaks, stop engine immediately ............ 1-5
Service battery .................................... 1-6
Handle the battery correctly ............................. 1-6
Other cautions..................................... 1-7
Never modify engine ........................................ 1-7
Observe safety rules at work site ..................... 1-7
Work clothing and protective gear.................... 1-7
Never break seals ............................................ 1-7
Perform all specified pre-operation inspections
and periodic inspections................................... 1-7
Break-in the engine .......................................... 1-7
Warm up the engine before use....................... 1-7
Never operate the engine in an overloaded
condition........................................................... 1-7
Conduct cooling operation before stopping the
engine .............................................................. 1-8
Protection of the engine against water entry.... 1-8
Properly maintain the air cleaner and
pre-cleaner ....................................................... 1-8
Use of tools optimum for each work................. 1-8
Avoidance of prolonged time of starter
operation .......................................................... 1-8
Do not turn off the battery switch during
operation .......................................................... 1-8
Cautionary instructions for transporting the
engine .............................................................. 1-8
Chapter 2
NAME OF PARTS
Engine external diagrams ................... 2-1
Equipment and instrument .................. 2-8
Starter switch ................................................... 2-8
Preheat indicator .............................................. 2-8
Water temperature meter and thermo unit ....... 2-9
Ammeter........................................................... 2-9
Hour meter ....................................................... 2-9
Stop solenoid ................................................. 2-10
Engine protection devices................. 2-11
Oil pressure switch ......................................... 2-11
Thermo switch ................................................ 2-11
Air cleaner indicator ....................................... 2-11
82/202

CONTENTS-2
CONTENTS
Chapter 3
OPERATION
Preparations for operation...................3-1
Engine external - Inspect ................................. 3-1
Battery electrolyte level - Inspect..................... 3-1
Fuel tank oil level - Check................................ 3-2
Engine oil level - Check.................................... 3-2
Coolant level - Check....................................... 3-3
Starting................................................3-4
Warm up operation..............................3-4
Checking engine oil pressure........................... 3-4
External inspection during warm up................. 3-4
Operation.............................................3-5
Cautions when operating ................................. 3-5
Inspection during operation.............................. 3-5
Stopping ..............................................3-6
Inspection after stopping.................................. 3-6
Chapter 4
FUEL
Recommended fuel .............................4-1
Handling fuel........................................4-1
Chapter 5
ENGINE OIL
Recommended engine oil....................5-1
Selection of oil viscosity.......................5-1
Handling engine oil..............................5-1
Engine oil performance requirements..5-2
Engine oil deterioration mechanisms...5-2
Definition of properties of engine oil....5-3
Viscosity........................................................... 5-3
Total base number........................................... 5-3
Total acid number ............................................ 5-3
Water content................................................... 5-3
Flash point........................................................ 5-3
Insoluble........................................................... 5-3
Service Limits of engine oil..................5-4
Chapter 6
COOLANT
Recommended water for coolant........6-1
Long life coolant (LLC)........................6-1
Genuine LLC.......................................6-1
Other brand LLCs ...............................6-2
Standard for other brand LLC.............6-2
General demands of LLC................................. 6-2
LLC specification.................. ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... .. 6-3
Maintenance of LLC............................6-5
Replacement intervals of LLC..........................6-5
LLC concentration............................................ 6-5
Importance of LLC ..............................6-6
Characteristics of LLC additive and
important notes................................... 6-6
Examples of abnormalities caused by
LLC (amine type) ................................6-6
Pitting of iron parts ........................................... 6-6
Corrosion of aluminum parts............................ 6-6
Pitting and clogging of the radiator...................6-6
Chapter 7
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE
How to use the maintenance
schedule..............................................7-1
Maintenance schedule........................7-2
83/202

CONTENTS-3
CONTENTS
Chapter 8
PERIODIC INSPECTION AND
MAINTENANCE PROCEDURES
Basic engine........................................8-1
Belt and belt tension - Inspect and Adjust........ 8-1
Fuel system.........................................8-2
Fuel tank - Drain water..................................... 8-2
Fuel filter - Drain water..................................... 8-3
Fuel system (in-line type fuel injection pump)
- Bleed air......................................................... 8-4
Fuel system (distributor type fuel injection
pump) - Bleed air.............................................. 8-5
Fuel filter (in-line type fuel injection pump) -
Replace............................................................ 8-6
Fuel filter (distributor type fuel injection pump)
- Replace.......................................................... 8-7
Lubricating system...............................8-8
Engine oil and Oil filter - Replace.... ... .... ... ... ... . 8-8
Cooling system..................................8-11
Coolant - Change........................................... 8-11
Radiator fins - Check and Clean.................... 8-13
Inlet and exhaust systems.................8-14
Air cleaner - Check......................................... 8-14
Turbocharger - Inspect................................... 8-14
Pre-cleaner - Clean, Inspect and Replace..... 8-15
Air cleaner element - Clean, Check and
Replace.......................................................... 8-16
Electrical system................................8-17
Starter - Inspect.............................................. 8-18
Alternator - Inspect......................................... 8-18
Chapter 9
LONG-TERM STORAGE
Long-term storage...............................9-1
Storing the engine in a non-operable
condition for 3 months or more............9-1
Preparation for storage .................................... 9-1
Maintenance during storage............................. 9-1
Using the engine after storage......................... 9-2
Storing the engine in an operable
condition for 3 months or more............9-2
Operating the engine for maintenance............. 9-2
Chapter 10
TRANSPORTATION
Lifting the engine...............................10-1
Chapter 11
TROUBLESHOOTING
General precautions..........................11-1
Contact a dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy
Industries, Ltd. for repair service.......... ... ... .... 11-1
Considerations before work ...........................11-1
Cautions against contamination.....................11-1
Cautions regarding parts handling .................11-1
Work safety .......... ... ... .................................... 11-1
Troubleshooting................................ 11-2
The starter does not crank or cranks slowly,
resulting in start failure................................... 11-2
The starter cranks, but the engine does not
start ................................................................11-2
Output decrease............................................. 11-2
Exhaust smoke is white or blue......................11-4
Exhaust smoke is black or charcoal............... 11-5
Fuel consumption is high ...............................11-6
Engine oil consumption is high.......... ... ... ....... 11-7
Overheating....................................................11-8
Low engine oil pressure ................................. 11-8
When fuel has run out.......................11-9
Chapter 12
MAIN SPECIFICATIONS
Main specifications............................12-1
84/202

CONTENTS-4
CONTENTS
List of illustrations
Fig. 2-1 Engine left view....................................2-1
Fig. 2-2 Engine right view.................................. 2-1
Fig. 2-3 Engine left view....................................2-2
Fig. 2-4 Engine right view.................................. 2-2
Fig. 2-5 Engine left view....................................2-3
Fig. 2-6 Engine right view.................................. 2-3
Fig. 2-7 Engine left view....................................2-4
Fig. 2-8 Engine right view.................................. 2-4
Fig. 2-9 Engine left view....................................2-5
Fig. 2-10 Engine right view.................................. 2-5
Fig. 2-11 Engine left view.................................... 2-6
Fig. 2-12 Engine right view.................................. 2-6
Fig. 2-13 Engine left view.................................... 2-7
Fig. 2-14 Engine right view.................................. 2-7
Fig. 2-15 Starter switch........................................ 2-8
Fig. 2-16 Preheat indicator.................................. 2-8
Fig. 2-17 Water temperature meter and thermo
unit........................................................ 2-9
Fig. 2-18 Ammeter............................................... 2-9
Fig. 2-19 Hour meter ........................................... 2-9
Fig. 2-20 Stop solenoid......................................2-10
Fig. 2-21 Oil pressure switch............................. 2-11
Fig. 2-22 Thermo switch.................................... 2-11
Fig. 2-23 Air cleaner indicator............................ 2-11
Fig. 3-1 Battery electrolyte level - Inspect ......... 3-1
Fig. 3-2 Fuel tank oil level - Check.................... 3-2
Fig. 3-3 Oil filler and Oil level gauge.................. 3-2
Fig. 3-4 Radiator filler cap ................................. 3-3
Fig. 3-5 Radiator coolant level........................... 3-3
Fig. 3-6 Reserve tank coolant level................... 3-3
Fig. 4-1 Recommended fuel .............................. 4-1
Fig. 5-1 Recommended engine oil..................... 5-1
Fig. 5-2 Selection of oil viscosity ....................... 5-1
Fig. 6-1 GLASSY - LLC..................................... 6-1
Fig. 8-1 Belt and belt tension - Inspect and
Adjust ................................................... 8-1
Fig. 8-2 Fuel tank - Drain water......................... 8-2
Fig. 8-3 Fuel filter - Drain water (1).................... 8-3
Fig. 8-4 Fuel filter - Drain water (2).................... 8-3
Fig. 8-5 Priming pump - Handle......................... 8-4
Fig. 8-6 Fuel filter - Bleed air ..............................8-4
Fig. 8-7 Fuel injection pump - Bleed air..............8-4
Fig. 8-8 Fuel filter - Bleed air (1).........................8-5
Fig. 8-9 Fuel filter - Bleed air (2).........................8-5
Fig. 8-10 Fuel filter - Replace...............................8-6
Fig. 8-11 Fuel filter ............................... ... ... ..........8-6
Fig. 8-12 Fuel filter - Replace...............................8-7
Fig. 8-13 Engine oil drain plug..............................8-8
Fig. 8-14 Engine oil - Refill...................................8-9
Fig. 8-15 Oil filter - Change ................................8-10
Fig. 8-16 Oil filter............................ ... .................8-10
Fig. 8-17 Radiator filler cap ................................8-11
Fig. 8-18 Coolant drain cock (radiator)...............8-11
Fig. 8-19 Coolant drain plug (engine).................8-12
Fig. 8-20 Radiator coolant level..........................8-12
Fig. 8-21 Reserve tank.......................................8-12
Fig. 8-22 Radiator fins - Clean ...........................8-13
Fig. 8-23 Air cleaner - Check..............................8-14
Fig. 8-24 Turbocharger - Inspect........................8-14
Fig. 8-25 Pre-cleaner - Clean.............................8-15
Fig. 8-26 Air cleaner element - Remove.............8-16
Fig. 8-27 Air cleaner element - Clean and
Check..................................................8-16
Fig. 8-28 Air cleaner - Check..............................8-16
Fig. 8-29 Battery electrolyte level - Inspect ........8-17
Fig. 8-30 Specific gravity of battery electrolyte -
Check..................................................8-17
Fig. 8-31 Starter - Inspect...................................8-18
Fig. 8-32 Alternator - Inspect..............................8-18
Fig. 10-1 Hangers...............................................10-1
Fig. 10-2 Engine's center of gravity
(standard specification).......................10-1
85/202

CONTENTS-5
CONTENTS
List of tables
Table 3-1 Standard values at rated speed.............. 3-5
Table 4-1 Recommended limit and use limit of
fuel property............................................ 4-2
Table 5-1 Engine oil properties............................... 5-4
Table 6-1 Water quality standards.......................... 6-1
Table 6-2 LLC specification.................................... 6-3
Table 6-3 Recommended LLC concentration......... 6-5
Table 7-1 MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE................. 7-2
Table 8-1 Specific gravity of electrolyte................ 8-17
Table 9-1 Recommended rust-preventive oil
and corrosion inhibitor ............................ 9-1
Table 11-1 The starter does not crank or cranks
slowly, resulting in start failure.............. 11-2
Table 11-2 The starter cranks, but the engine
does not start ........................................ 11-2
Table 11-3 Output decrease................................... 11-3
Table 11-4 Exhaust smoke is white or blue............ 11-4
Table 11-5 Exhaust smoke is black or charcoal ..... 11-5
Table 11-6 Fuel consumption is high...................... 11-6
Table 11-7 Engine oil consumption is high............. 11-7
Table 11-8 Overheating .......................................... 11-8
Table 11-9 Low engine oil pressure........................ 11-8
Table 12-1 Main specifications ...............................12-1
Table 12-2 Main specifications ...............................12-2
86/202

87/202

1-1
Chapter 1 BASIC SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Fire and explosions
Keep flames away
Do not use flames near the engine (in
the engine room). Fuel vapor or other
gas can catch fire and produce dan-
gerous situations.
Wipe off spilled fuel, oil and LLC
immediately and thoroughly. Spilled fuel, oil and LLC
may ignite and cause a fire.
Store fuel and engine oil in a well-ventilated area.
Make sure that the caps of fuel and engine oil contain-
ers are tightly closed.
Keep engine surrounding area
tidy and clean
Do not leave combustible or explosive materials, such
as fuel, engine oil and LLC, near the engine. Such
substances can cause fire or explosion.
Remove dust, dirt and other foreign materials accu-
mulated on the engine and surrounding parts thor-
oughly. Such materials can cause fire or the engine to
overheat. In particular, clean the top surface of the
battery thoroughly. Dust can cause a short-circuit.
Care for fuel, oil and exhaust
gas leakage
If any fuel, oil or exhaust gas leakage is found, imme-
diately take corrective measures to stop it.
Such leakages, if left uncorrected, can cause fuel or
engine oil to reach hot engine surfaces or hot exhaust
gas to contact flammable materials, possibly leading
to personal injury and/or damage to equipment.
Use explosion-proof lighting
apparatus
When inspecting fuel, engine oil, coolant, battery elec-
trolyte, etc., use a flameproof light. An ordinary light-
ing apparatus may ignite gas and cause it to explode.
Prevent electrical wires from
short-circuiting
Avoid inspecting or servicing the electrical system with
the ground cable connected to the battery. Otherwise,
a fire could result from short-circuiting. Be sure to dis-
connect the battery cable from the negative (-) termi-
nal before beginning with the work procedure.
Short-circuits, possibly resulting in fire, may be
caused by a loose terminal or damaged cable/wire.
Inspect the terminals, cables and wires, and repair or
replace the faulty parts before beginning with the ser-
vice procedure.
Keep fire extinguishers and a
first-aid kit handy
Keep fire extinguishers handy, and
become familiar with their usage.
Keep a first-aid kit at the designated
place where it is easily accessible by
anyone at any time.
Establish response procedures to follow in the event
of fire or accident. Provide an emergency evacuation
route and contact points and means of communication
in case of emergency.
88/202

1-2
Chapter 1 BASIC SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Stay clear of all rotating and moving parts
Install protective covers around
rotating parts
Make sure the protective covers of
the engine are correctly installed.
Repair any damaged or loose covers.
Never remove the covers such as
damper cover, camshaft cover, or
rocker cover that enclose the revolving parts during
operation.
When the engine is coupled to driven equipment, be
sure to provide protective covers over the parts such
as the connecting belts and couplings that are
exposed.
Never remove protective covers.
Check work area for safety
Before starting the engine, make sure no one is near
the engine and tools are not left on or near the engine.
Verbally notify persons within the immediate area
when starting the engine.
When the starter device is posted with a sign that prohibits startup operation, do not operate the engine.
St ay clear of moving parts while
engine is running
Do not approach rotating or sliding
parts of the engine while the engine is
running. Keep objects likely to be
caught by rotating parts away from
such parts.
If any part of the clothing or outfitting is caught by a
rotating part, serious bodily injuries could result.
Lockout and tagout
Be sure to lockout and tagout before starting inspection and maintenance.
Lockout and tagout are effective methods of cutting off
machines and equipment from energy sources.
To accomplish the lockout/tagout, remove the starter
switch key, set the battery switch to "OFF" position
and attach a "Do Not Run" or similar caution tag to the
starter switch.
The starter switch key must be kept by the person
who performs inspection and maintenance during the
work.
Keep engine stopped during
servicing
Be sure to stop the engine before proceeding to
inspection and service procedure. Never attempt to
make adjustments on the engine parts while the
engine is running.
Rotating parts such as belt can entangle your body
and cause serious injuries.
Always restore engine turning
tools after use
Be sure to remove all turning tools used during maintenance and inspection work. Remember also that the
turning gear must be returned to the operating condition before starting the engine.
Starting the engine with the turning tools inserted or
with the turning gear in engagement can lead to not
only engine damage but also personal injuries.
Changing the engine speed setting is prohibited
Never change engine speed setting. Tampering with
the setting can cause the engine and its coupled
machine to operate at excessive speeds and result in
accidents.
89/202

1-3
Chapter 1 BASIC SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Be careful of exhaust
fume poisoning
Operate engine in a well-ventilated area
If the engine is installed in an
enclosed area, and the exhaust gas
is ducted outside, ensure that there is
no exhaust gas leakage from duct
joints.
When using the engine as portable generator set, do
not run it in doors such as a warehouse or tunnel, or in
an poorly-ventilated area near the shielding. When
running it indoors by necessity, discharge the exhaust
gas to outside and thoroughly ventilate the room.
Make sure the exhaust gas is not discharged directly
to surrounding buildings, plants or living passersby.
Exhaust gas from the engine contains carbon monoxide and other harmful substances. Operating the
engine in an poorly-ventilated area can produce gas
poisoning.
Be careful of falling down
Lift engine carefully
To lift the engine, use slings capable
of supporting the weight of the
engine.
Attach the wire rope to the hangers
provided on the engine using a correct sling.
During lifting process, keep the engine in a well-balanced position by taking the center of gravity of the
engine into consideration.
Keep the angle formed by slings attached to hangers
within 60°. If the angle exceeds this limit, excessive
load could be imposed on the hangers and this could
damage the hangers and result in a serious accident.
If the wire rope contacts the engine directly, place a
cloth or other soft padding to avoid damage to the
engine and wire rope.
Do not climb onto the engine
Do not climb onto the engine, nor step on any engine
parts located on the lateral sides.
To work on parts located on the upper section of
engine, use a ladder, stool, etc., that was firmly
secured.
Climbing on the engine may not only damage engine
parts but also cause falling down from the engine and
result in personal injuries.
Always prepare stable scaffold
When working on the upper part of
the engine and other hard-to-reach
places, use a stable work platform.
Standing on a decrepit stool or parts
box may result in personal injury.
Do not place any unnecessary objects on a work platform.
90/202

1-4
Chapter 1 BASIC SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Protect ears from noise
Wear ear plugs
Always wear ear plugs when entering
the machine room (engine room).
Combustion sound and mechanical
noise generated by the engine can
cause hearing problems.
Be careful of burns
Do not touch the engine during
or immediately after operation
To avoid burns, do not touch the
engine during or immediately after
operation.
A hot engine can cause burns.
To conduct maintenance and inspection work, wait until the engine has cooled sufficiently
by checking the temperature gauge.
Do not open the radiator filler
cap when the engine is hot
Never open the radiator filler cap while the engine is
running or immediately after the engine is stopped.
When opening the cap, stop the engine and allow the
coolant temperature to lower sufficiently.
When opening the radiator filler cap, open slowly to
discharge the pressure inside the tank. Also to avoid a
risk of getting scalded by steam, wear thick rubber
gloves or wrap a cloth around the cap.
When closing the cap, be sure to tighten securely.
The coolant is hot while engine is running and immediately after the engine stops. If the cap is opened when
the coolant is at operating temperature, steam and hot
coolant may blow out and result in burns.
Do not touch high pressure
injection fuel
If fuel leaks or sprays out from the high pressure injection pipe, do not touch the fuel.
Fuel in the fuel injection pipes is under high pressure
and if the fuel contact your skin, it goes into deep tissues and may result gangrene.
Refill coolant only after the
coolant temperature dropped
When refilling of coolant, perform it after coolant temperature drops, not immediately after the engine is
stopped. Otherwise you are scalded with hot coolant.
91/202

1-5
Chapter 1 BASIC SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Be careful when handling
fuel, engine oil or LLC
Use only specified fuel, engine
oil and LLC
Use fuel, oil and LLC specified in this manual, and
handle them carefully.
Use of any other fuel, oil or LLC, or improper handling
may cause various engine problems and malfunctions.
Obtain the MSDS issued by the fuel, oil and LLC suppliers, and follow the directions in the MSDSs for
proper handling.
Handle LLC carefully
When handling LLC, always wear rubber gloves and a
protective face mask. If LLC or cooling water containing LLC comes into contact with your skin or eyes, or if
it is swallowed, you would suffer from inflammation,
irritation or poisoning.
Should LLC be accidentally swallowed, induce vomiting immediately and seek medical attention. Should
LLC enter your eyes, flush them immediately with
plenty of water and seek medical attention. If LLC
splashes onto your skin or clothing, wash it away
immediately with plenty of water.
Keep flames away from LLC. The LLC can catch
flames, causing a fire. Coolant (containing LLC)
drained from the engine is toxic. Never dispose of
coolant into regular sewage. Abide by the applicable
law and regulations when discarding drained coolant.
Proper disposal of waste oil,
LLC and coolant
Do not discharge waste engine oil, LLC and coolant
into sewerage, river, lake or other similar places. Such
a way of disposal is strictly prohibited by laws and regulations.
Dispose of waste oil, LLC and coolant and other environmentally hazardous waste in accordance with the
applicable law and regulations.
When abnormality occurs
Do not add coolant immediately
after a sudden stop due to overheating
If the engine stops suddenly or if you have no choice
but stop the engine suddenly due to overheating, do
not add coolant immediately.
Adding water while the engine is hot can damage
parts such as cylinder heads due to a sudden drop of
temperature. Add coolant gradually after the engine
has completely cooled.
Avoid immediate restart after
abnormal stop
If the engine stops abnormally, do not restart the
engine immediately. If the engine stops with an alarm,
check and remedy the cause of the problem before
restarting. Sustained use of the engine without any
remedy could result in serious engine problems.
Avoid continuous engine operation at low oil pressure
If an abnormal engine oil pressure drop is indicated,
stop the engine immediately, and inspect the lubrication system to locate the cause. Continuous engine
operation with low oil pressure could cause bearings
and other parts to seize.
If belt breaks, stop engine
immediately
If the belt breaks, stop the engine immediately. Continuous engine operation with the broken belt could
cause the engine to overheat and thereby the coolant
to boil into steam, which may gush out from the
reserve tank or radiator, and you may be scalded with
it.
92/202

1-6
Chapter 1 BASIC SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Service battery
Handle the battery correctly
Never use flames or allow sparks to
generate near the battery. The battery releases flammable hydrogen
gas and oxygen gas. Any flames or
sparks in the vicinity could cause an
explosion.
Do not use the battery when the battery electrolyte
level of which is below "LOWER LEVEL" line. Sustained use of the battery could result in an explosion.
Do not short the battery terminals with a tool or other
metal object.
When removing battery, always remove the plug from
the negative (-) terminal first. When connecting battery, always connect the plug to the positive (+) terminal first.
Remove all plugs, then charge the battery in a well-
ventilated area.
Make sure the cable clamps are securely installed on
the battery terminals. A loose cable clamp can cause
sparks that may result in an explosion.
Before servicing electrical components or conducting
electric welding, set the battery switch to the "Open/
OFF" position or remove the plug from the negative () terminal to cut off the electrical current.
Battery electrolyte contains dilute sulfuric acid. Care-
less handling of the battery can cause the loss of sight
and/or skin burns. Also, do not consume the battery
electrolyte.
Wear protective goggles and rubber gloves when
working with the battery (when adding water, charging, etc.)
If battery electrolyte is spilled onto the skin or clothing,
immediately wash it away with lots of water. Use soap
to thoroughly clean.
The battery electrolyte can cause the loss of sight if
splashing into the eyes. If it gets into the eyes, immediately flush it away with plenty of clean water, and
seek immediate medical attention.
If the battery electrolyte is accidentally consumed,
gargle with plenty of water, then drink lots of water,
and seek immediate medical attention.
93/202

1-7
Chapter 1 BASIC SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Other cautions
Never modify engine
Unauthorized modification of the engine will void our
warranty.
Modification of the engine may not only cause engine
damage but also produce personal injuries.
If there is a need to modify the engine, contact a
dealer of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Observe safety rules at work
site
Observe the safety rules established at your workplace when operating and maintaining the engine.
Do not operate the engine if you are feeling ill, inform
your supervisor of your condition. Operation of the
engine with reduced awareness may cause improper
operation that could result in accidents.
When working in a team for two or more people, use
specified hand signals to communicate among workers.
Work clothing and protective
gear
Wear a hardhat, face shield, safety shoes, dust mask,
gloves and other protective gear as needed. When
handling compressed air, wear safety goggles, a hardhat, gloves and other necessary protective gear.
Works without wearing proper protective gear could
result in serious injuries.
Never break seals
To ensure proper engine operation, the fuel control
linkage is sealed to prevent accidental change of the
injection volume and rotation speed settings. Operating the engine without these seals in place can cause
problems described below, and also invalidates the
warranty.
Rapid wear of sliding and rotating parts
Engine damage such as seizing of engine parts
Considerably increased consumption of fuel and lu-
bricating oil
Degradation of engine performance due to improper
balance between fuel injection volume and governor
operation or overrunning of the engine which could
result in a serious accident
Perform all specified pre-operation inspections and periodic
inspections
Conduct the pre-operation inspections and periodic
inspections as described in this manual.
Failure to conduct the specified inspections may
cause various engine problems, damage to parts, and
serious accidents.
Break-in the engine
To break-in new engines or overhauled engines, operate the engine at a speed lower than the rated speed
in a light load condition during the first 50 hours of
operation.
Operating new engines or overhauled engines in a
severe condition during the break-in period shortens
the service life of the engine.
Warm up the engine before use
After starting the engine, run the engine at low idling
speeds for 5 to 10 minutes for warm up. Start the work
after this operation is completed. Warm up operation
circulates the lubricant through the engine. Therefore,
individual engine parts are well lubricated before they
are subjected to heavy loads.
Warm up operation circulates lubricants in the engine
and contributes to a longer service life and economical operation.
Do not conduct warm up operation for prolonged
period of time. Prolonged warm up operation causes
carbon build-up in the cylinders that leads to incomplete combustion.
Never operate the engine in an
overloaded condition
If the engine shows an overloaded condition such as
black exhaust smoke, reduce the load immediately to
operate the engine at an appropriate output and load.
Overloading causes not only high fuel consumption
but also excessive carbon deposits inside the engine.
Carbon deposits cause various problems and will
shorten the service life of the engine.
94/202

1-8
Chapter 1 BASIC SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Conduct cooling operation
before stopping the engine
Before stopping the engine, let it idle in low gear for 5
to 6 minutes to cool down.
Stopping the engine immediately after high-load operation will cause engine parts to heat up and shorten
the service life of the engine.
During cooling operation, check the engine for abnormalities.
Protection of the engine against
water entry
Do not allow rainwater, etc. to enter the engine
through the air inlet or exhaust openings.
Do not wash the engine while it is operating. Cleaning
fluid (water) can be sucked into the engine.
Starting the engine with water inside the combustion
chambers can cause the water hammer action which
may result in internal engine damage and serious
accidents.
Properly maintain the air
cleaner and pre-cleaner
Maintain the engine with air cleaner or pre-cleaner
according to the following instructions.
Do not maintain the air cleaner or pre-cleaner while
the engine is running. The turbocharger may suck
particles of foreign materials into the engine and could
result in serious accidents.
Remove the air cleaner or pre-cleaner slowly to pre-
vent foreign materials accumulated on the element
from falling off. After removing the air cleaner or precleaner, immediately cover the opening (inlet port of
air cleaner; port in body for pre-cleaner) with plastic
sheet or similar means to prevent foreign materials
from entering the engine.
Clean the pre-cleaner periodically. The pre-cleaner
clogging can cause insufficient intake air or increasing
in the exhaust temperature.
If the engine is equipped with a dust indicator, con-
duct maintenance when the clog warning sign appears.
Use of tools optimum for each
work
Always keep in mind to select most appropriate tools
for the work to be performed and use them correctly. If
tools are damaged, replace them with new tools.
Avoidance of prolonged time of
starter operation
Do not use the starter for more than 10 seconds at a
time. If the engine does not start, wait for at least 1
minute before cranking again.
Continuous operation of the starter will drain the battery power and cause the starter to seize.
Do not turn off the battery
switch during operation
Do not turn off the battery switch during operation.
If the battery switch is turned OFF when the engine is
running, not only various meters will stop working but
also the alternator may have its diode and transistor
deteriorated.
Cautionary instructions for
transporting the engine
When transporting the engine on a truck, consider the
engine weight, width and height to ensure safety.
Abide by road traffic law, road vehicles act, vehicle
restriction ordinance and other pertinent laws.
95/202

2-1
Chapter 2 NAME OF PARTS
Engine external diagrams
The external diagram is for the standard type of the engine. The installed equipment and shapes differ according to
the engine type.
S4S in-line type fuel injection pump left view
Fig. 2-1 Engine left view
S4S in-line type fuel injection pump right view
Fig. 2-2 Engine right view
Air inlet
Stop solenoid
Fuel injection nozzle
Rear
Flywheel
Oil filter
Oil level gauge
Coolant drain plug
Oil drain plug
Fuel filter
Governor
Fan
Water pump
(coolant inlet)
Fuel injection pump
Fuel feed pump
Crankshaft pulley
Fuel inlet
Front
Front hanger
Oil pan
Belt
Alternator
Thermostat case
Coolant outlet
Front
Rear hanger
Oil filler
Exhaust outlet
Flywheel housing
Starter
Rear
96/202

2-2
Chapter 2 NAME OF PARTS
S4S-DT in-line type fuel injection pump left view
Fig. 2-3 Engine left view
S4S-DT in-line type fuel injection pump right view
Fig. 2-4 Engine right view
Oil drain plug
Flywheel
Oil filter
Oil level gauge
Coolant drain plug
Stop solenoid
Rear
Fuel injection nozzle
Glow plug
Fuel filter
Governor
Water pump
(coolant inlet)
Fuel injection pump
Fuel feed pump
Crankshaft pulley
Fuel inlet
Fuel return port
Front
Oil cooler
Rear hanger
Air inlet
Front hanger
Oil filler
Flywheel housing
Starter
Oil pan
Belt
Alternator
Thermostat case
Coolant outlet
Rear
Front
Turbocharger (exhaust outlet)
97/202

2-3
Chapter 2 NAME OF PARTS
S4S distoributor type fuel injection pump left view
Fig. 2-5 Engine left view
S4S distoributor type fuel injection pump right view
Fig. 2-6 Engine right view
Fuel return port
Magnetic valve
(stop solenoid)
Oil drain plug
Flywheel
Oil filter
Oil level gauge
Coolant drain plug
Air inlet
Rear
Fuel injection nozzle
Fan
Water pump
(coolant inlet)
Fuel injection pump
Crankshaft pulley
Fuel inlet
Front
Fuel filter
Front hanger
Oil pan
Belt
Alternator
Thermostat case
Coolant outlet
Front
Rear hanger
Oil filler
Exhaust outlet
Flywheel housing
Starter
Rear
98/202
 Loading...
Loading...