Page 1
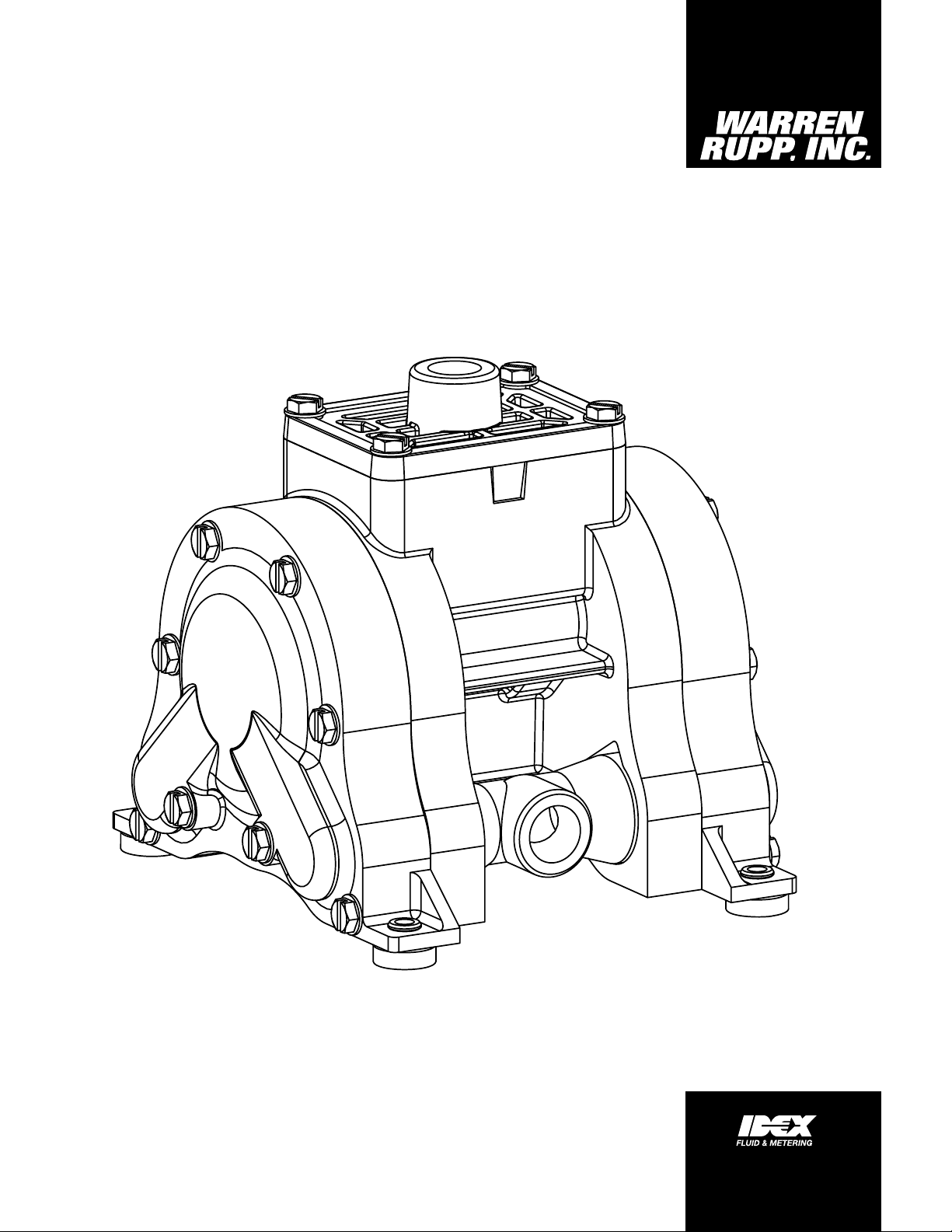
WR10 3/8"
Bolted Plastic Pumps
Operating Instructions
• Polypropylene
• Kynar
Warren Rupp, Inc. • A Unit of IDEX Corporation • 800 N. Main St., Manseld, Ohio 44902 USA
Telephone (419) 524-8388 • Fax (419) 522-7867 • warrenrupp.com
Page 2

Page 3

Operating and Service Manual
Model WR10 3/8" Bolted Plastic Pumps
Table of Contents
Warnings, Cautions & Notices .........................................................................1
Specications & Performance ..........................................................................2
Installation, Operation & Maintenance .............................................................3
Troubleshooting ...............................................................................................4
Parts List .........................................................................................................5
Pump Drawing, Exploded View ........................................................................6
Materials, Temperature Limits & Compatibility ................................................7
Declaration of Conformity ................................................................................8
Notes ................................................................................................................9
Page 4
WARNINGS, CAUTIONS & NOTICES
Please read all cautions, warnings and notes
completely before installation and start-up.
It is the responsibility of the purchaser to retain this
WARNINGS
To prevent static sparking the pump, piping,
valves, and containers must be grounded.
CAUTIONS
You must check the tightness of all hardware
prior to installation.
Maximum temperature limits are based on
mechanical stress only. Certain chemicals
will signicantly reduce maximum safe operating
temperatures. For chemical compatibility and temperature limits
please refer to the Chemical Resistance Guide.
Check temperature limits for all wetted
components when choosing pump materials.
Temperature limits may vary depending on the material.
manual for reference. Failure to comply with the
recommendations stated in this manual may damage
the pump and void the factory warranty.
Pump exhaust may contain contaminants that
can cause serious injury. Take precautions
to pipe exhaust away from work area if pumping
chemicals, hazardous or ammable materials.
Do not exceed the maximum inlet air pressure
as stated on the pump model tag.
Disconnect the compressed air line to the
pump and allow all air pressure to bleed
from pump prior to performing any maintenance
on the pump. Disconnect all intake, discharge and
air lines. Drain the pump and dispose of uid into a
suitable container.
All operators of the equipment should
be properly trained to ensure safe working
practices.
The process uid and cleaning uids must be
chemically compatible with all wetted pump
components. Please refer to the Chemical Resistance Guide for
additional information.
Thoroughly ush pump before installing into
process lines. FDA and sanitary approved pumps should
be cleaned or sanitized before use.
NOTICES
Blow out air line for at least 15 seconds
before attaching to pump to make sure that all debris
is removed. Use an in-line air lter.
Clamp style pumps tted with PTFE or XLTPE
come standard from the factory with expanded PTFE liquid
chamber gaskets. PTFE gaskets cannot
be reused.
Tighten both outer pistons at the same
time to ensure a tight t when installing
PTFE diaphragms. See torque settings for additional details.
Never allow the piping system to be supported
by the pump manifolds or valve housing. These
components are not designed to support structural weight and pump
failure may result..
Noise levels can exceed 85 dBA.
Always wear ear and eye protection when
operating or repairing pumps.
Compressed air should not be applied to
the exhaust port. If this happens the pump will not
function.
Before disassembly of clamp band pumps,
mark a line from each liquid chamber to its
corresponding air chamber. This will ensure proper
alignment when reassembling.
The pump does not require continuous
lubrication.
Page 1 Rev 0614
Page 5

2.79
[71]
0.94
[24]
Opposite Side:
1/4" Female NPT Air Exhaust
Removable Foot Pad
5/16" Mounting Hole
3/8" Female NPT
Fluid Discharge Connection
3/8" Female NPT
Fluid Suction
Connection
1/4" Female NPT
Air Inlet Connection
5.32
[135]
0.20
[5]
15.71
[399]
2.07
[53]
4.09
[104]
POLY
5.13
[130]
KYNAR
5.08
[129]
POLY
5.72
[145]
KYNAR
5.67
[144]
2.07
[53]
WR10 SPECIFICATIONS & PERFORMANCE
Specifications
Flow Rate adjustable to . 0-6.8 gpm (261 lpm)
Port Size
Inlet and Discharge .... 3/8" Female NPT (BSP)
Air Inlet ............... 0.25" Female NPT
Air Exhaust ........... 0.25" Female NPT
Suction Lift ...............8' (2.44 m) Dry
Max. Particle Size (Diameter)
dB(A) Reading .................... 78 dB(A)
Shipping Weights
Polypropylene ............... 3 lbs (1.40 kg)
Kynar .....................4.5 lbs. (2.04 kg)
0.10"(2.25 mm)
Performance
Displacement Per Stroke, 0.009 Gal. (0.034 L)
AIR CONSUMPTION IN SCFM
AIR PRESSURE IN PSI
5
64 98720
Capacity in U.S. Gallons Per Minute
Capacity in Liters Per Minute
SCFM M3/HR
1 1.7
3 5.1
5 8.5
75
240
70
220
65
200
60
55
180
50
160
45
140
40
120
35
100
30
25
80
20
60
15
40
10
20
5
0
0
Meters Feet
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
BAR
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
Discharge Head in PSI
20
10
0
0
1
3
1 53
5 10 15 20 25 30 35
CAUTION: Do not exceed 100 psig (6.8 bars) air supply or liquid pressure.
Front
CAUTION: Nonmetallic pumps and plastic components are not UV stabilized. Ultraviolet
radiation can damage these parts and negatively affect material properties. Do not expose to
UV light for extended periods of time.
Dimensions
Side Bottom
Inches
[mm]
Consult factory for certied drawings.
Page 2 Rev 0614
Page 6

INSTALLATION, OPERATION & MAINTENANCE
Installation Pump Operation
The pump should be mounted in a vertical
position. In permanent installations, the pump should be
attached to plant piping using a exible coupling on both the
intake and discharge connections to reduce vibration
to the pump and piping. To
further reduce vibration, a
Air Connection
surge suppressor next to the
pump may
be used.
Suction pipe size should be
at least the same diameter
as the inlet connection size,
even larger if highly viscous
AODD PUMP
uid is to be pumped. If suction hose is used, it must be
of a non-collapsible
reinforced type.
Discharge piping should be
of at least the same diameter
as the discharge connection.
It is critical, especially on the
Fluid
Inlet
Manometer
Shut Off Valve
Flexible
Connection
Union or Pipe Flange
Connection
suction side of the pump, that
all ttings and connections are air tight or pumping efciency
will be reduced and priming will be difcult.
rated from the
uid by a membrane called a diaphragm.
The diaphragm in turn applies pressure on
the uid and forces it
Air Exhaust
Pulsation Dampener
out of the pump
discharge. While this is
occurring, the opposite air
Discharge Pressure
Flexible
Connection
Union or Pipe Flange
Gauge
Connection
Fluid
Discharge
Shut Off Valve
chamber is
depressurized and
exhausted to
atmosphere and uid is
drawn into the pump suction.
The cycle again repeats, thus
creating a constant reciprocating action which maintains
Flexible
Connection
Filter
Separator
ow through the pump.
The ow is always in through
the bottom
suction connection and out
through the top
discharge connection. Since
the air pressure acts directly
Pressure-reducing
Valve
Air Exhaust Muffler
Air Stop Valve/
Needle Valve
on the diaphragms, the pres-
sure applied to the uid
roughly approximates the air supply
pressure supplied to the main air valve.
Make certain the air supply line and connections
and compressor are capable of supplying the
required pressure and volume of air to operate
the pump at the desired ow rate. The quality of
the compressed air source should be considered.
Air that is contaminated with moisture and dirt
may result in erratic pump performance and
increased maintenance cost as well as frequent
process “down time” when the pump fails to
operate properly.
The pump is powered by compressed air.
Compressed air is directed to the pump air
chamber by the main air valve. The compressed air is sepa-
Recommended Piping Connections
Pump Size Minimum Air Line Size Minimum Suction Line
Size
1/4" 1/4" 1/4"
3/8" 1/4" 3/8"
1/2" 1/2" 1/2"
1" 1/2" 1"
1-1/2" 1/2" 1-1/2"
2" 1/2" 2"
3" 3/4" 3"
Page 3 Rev 0614
Page 7

TROUBLESHOOTING
Symptom
Pump cycles once
Pump will not operate
Pump cycles and will not
prime or ow
Potential Cause(s)
1 Incorrect pilot o-ring placement
2 Inner diaphragm plate installed backwards
3 Deadhead (system pressure meets or exceeds
air supply pressure)
4 Air valve or center block gaskets installed incorrectly
1 Pump is over lubricated
2 Lack of air (line size, PSI, CFM)
3 Worn o-rings
4 Wrong type of lubrication (attack on o-rings)
5 Debris in air valve
6 Clogged manifolds
7 Incorrect o-ring placement
8 Deadhead (system pressure meets or exceeds
air supply pressure)
1 Cavitation on suction side
2 Valve ball(s) not seating properly or sticking
3 Valve ball(s) missing (pushed into chamber)
4 Valve ball(s)/seat(s) damaged or attacked by product
5 Clogged suction line
Recommendation(s)
1 Reinstall pilot o-rings in correct positions
2 Reinstall inner diaphragm plate correctly
3 Check system for pressure ratio to pump
4 Install gaskets with holes properly aligned
1 Set lubricator on lowest possible setting or remove
• Elima-Matic is designed for lube free operation
2 Check the air line size and length, compressor
capacity (HP vs. cfm required)
3 Replace o-rings
4 Check compatibility of o-rings with lubrication
5 Clean air valve/lter
6 Clean suction or discharge manifolds/piping
7 Reinstall o-rings in correct position
8 Increase air supply pressure
1 Check suction condition (move pump closer to product)
2 Clean out around valve ball cage and valve seat area
• Replace valve ball or valve seat if damaged
• Use heavier valve ball material
3 Worn valve ball or valve seat
• Worn ngers in valve ball cage (replace part)
4 Check Chemical Resistance Guide for compatibility
5 Clean suction manifold and/or piping
Pump running
sluggish/stalling
Product leaking through
exhaust
Premature diaphragm
failure
1 Over lubrication
2 Icing
3 Clogged manifolds
4 Deadhead (system pressure meets or exceeds
air supply pressure)
5 Cavitation on suction side
6 Lack of air (line size, PSI, CFM)
1 Diaphragm failure, or diaphragm plates loose
2 Diaphragm stretched around center hole or bolt holes
3 Excessive air supply pressure
1 Cavitation
2 Excessive ooded suction pressure
3 Misapplication (chemical/physical incompatibility)
4 Wrong type of lubrication (attack on air side)
5 Incorrect diaphragm plates or plates on backwards
6 Incorrect shaft with corresponding elastomer
7 Start up at full air pressure
1 Set lubricator on lowest possible setting or remove
• Elima-Matic is designed for lube free operation
2 Clean or replace exhaust mufer
3 Clean manifolds to allow proper air ow
4 Check system to locate deadhead (equilibrium)
• Increase air supply pressure
5 Check suction (move pump closer to product)
6 Check the air line size, length, compressor capacity
1 Replace diaphragms, check for damage and ensure
diaphragm plates are tight
2 Check for excessive inlet pressure or air pressure
• Tighten bolts to recommended torque
3 Check Operating Manual for recommendations
1 Enlarge pipe diameter on suction side of pump
1,2 Move pump closer to product
• Raise pump/place pump on top of tank to reduce
inlet pressure
2 Add accumulation tank or pulsation dampener
as close to the pump as possible
3,4 Consult Chemical Resistance Chart for compatibility
with products, cleaners, temperature limitations
and lubrication
5,6 Check Operating Manual to check for correct part
and installation
7 Start up pump slowly (manually or with Smart Start)
Breaking and bending
shafts
1 Build up of solids in water chamber
2 Loose diaphragm plates
1 Flush pump, start pump slow
2 Tighten diaphragm plates when replacing diaphragms
Page 4 Rev 0614
Page 8

WR10 PARTS LIST
Item Description Qty. Standard: Polypropylene
Air Valve Assembly (Includes items 1-10) 1 E800
1 Valve Body 1 10-048
2 Valve Spool 1 E500B ASY (Includes (2) P98-104A)
3 Valve Spool U-Cup 2 P98-104A
4 End Cap 2 E800D (Includes (1) E800D ASY)
5 End Cap O-Ring 2 E500E
8 Air Diverter 1 10-075
9 Valve Insert 1 E500H
10 Valve Gasket 1 E800J
11 Valve Screw 4 10-050
Item Description Qty. Standard: Polypropylene
12 Center Section 1 E801A
18 Pilot Shaft 1 E803A
19 Pilot Shaft Spacer 5 E503C
20 Pilot Shaft O-Ring 6 E503B
21 Pilot Shaft Snap Ring 2 E503D
22 Shaft Retainer 2 E801B
25 Shaft Retainer Screw 4 E501C
33 Mufer 1 06-034
Item Description Qty. TPE PTFE
34 Main Shaft O-Ring 2 E503B E503B
35 Main Shaft 1 10-028 10-028
37 Inner Diaphragm Plate 2 C126 C126
38 Outer Diaphragm Plate 2 10-023 (Poly), 10-040 (Kynar) 10-023 (Poly), 10-040 (Kynar)
40 Diaphragm 2 10-032 (XL), 10-033 (Geolast) 10-044 (PTFE)
Item Description Qty. Standard: Polypropylene Option 1: Kynar
44 Water Chamber 2 10-002 10-036
45 Water Chamber Bolt (Long) 4 10-052 10-052
46 Water Chamber Bolt (Short) 12 10-051 10-051
50 Valve Seat 4 10-022 (Poly) 10-039 (Kynar)
51 Valve Seat Seal 8 10-073 (XL), 10-045 (PTFE) 10-073 (XL), 10-045 (PTFE)
52 Valve Stem 4 10-005 10-038
53 Spring 4 10-030 10-030
60 Manifold 2 10-003 10-037
62 Foot Pad 4 10-035 10-035
AIR VALVE ASSEMBLY
AIR END ASSEMBLY
DIAPHRAGM ASSEMBLY
WET END ASSEMBLY
Page 5 Rev 0614
Page 9

WR10 EXPLODED VIEW
Torque Settings
Water Chamber Bolts 40 in-lbs (4.5 N-m)
Diaphragm Plates — Rubber 60 in-lbs (6.8 N-m)
Diaphragm Plates — PTFE 60 in-lbs (6.8 N-m)
Air Valve Cap Screws 25 in-lbs (2.8 N-m)
DETAIL A
45
40 in-lbs
(4.5 N-m)
46
60 in-lbs
(6.8 N-m)
44
38
40
37
DETAIL B
34
35
33
12
25 in-lbs
(2.8 N-m)
1
10
11
5
2
4
3
8
9
Torque
Settings
62
Detail A
25
18
22
19
20
21
WR10 Repair and Maintenance Kits
Air End Kit- Part #: WR10 AIR KIT
Description Qty Part Number
Valve Spool U-Cup 2 P98-104A
End Cap O-Ring 2 E500E
Air Diverter 1 10-075
Valve Insert 1 E500H
Valve Gasket 1 E800J
Pilot Shaft O-Ring 6 E503B
Main Shaft O-Ring 2 E503B
DETAIL B
Detail B
60
505253 5151
Wetted End Kits
Part Number Description
WR10 XL KIT XL Elastomer Kit
WR10 G KIT Geolast Elastomer Kit
WR10 TX KIT PTFE Elastomer Kit
Page 6 Rev 0614
Page 10

MATERIALS, TEMPERATURE LIMITS & COMPATIBILITY
Materials of Construction — Pumps
MODEL Acetal
WR10 (3/8") ● ●
®
Aluminum Cast Iron Hastelloy C Polypropylene PVDF
Diaphragms, Valve Seats & Valve Seals
Stainless Steel
PTFE
Thermoplastics
ELASTOMERS
Aluminum
PVDF
Buna-N
Neoprene
EPDM
Polypropylene
Polyurethane
316 Stainless
Steel
Versa-
Tef-Matic™
Tuff ™
FUSION™
Encapsulated
Silicone
Santoprene
(TPE XL)
FDA Hytrel®(FKM)
Fluorocarbon
DIAPHRAGMS ● ●
VALVE SEATS ● ●
VALVE SEALS ● ●
Temperature Limits
BUNA-N +10°F (-12°C) to +180°F (82°C)
PTFE +40°F (+4°C) to +220°F (105°C)
SANTOPRENE (TPE XL) -20°F (-29°C) to +300°F (149°C)
PLASTIC PUMPS can operate to the following temperature limits:
• POLYPROPYLENE 32°F (0°C) to 175°F (79°C)
• PVDF 10°F (-12°C) to 225°F (107°C)
NOTE: These are average temperatures. Chemicals and solvents can have
an effect on temperature limit
Page 7 Rev 0614
Page 11

Declaration of Conformity
Manufacturer:
®
Warren Rupp, Inc.
Mansfield, Ohio, 44902 USA
certifies that Air-Operated Double Diaphragm Pump Series: HDB, HDF,
M Non-Metallic, S Non-Metallic, M Metallic, S Metallic, T Series, G Series, RS Series
U Series, EH and SH High Pressure, W Series, SMA and SPA Submersibles,
and Tranquilizer Surge Suppressors comply with the European Community
Directive 2006/42/EC on Machinery, according to Annex VIII. This product
has used Harmonized Standard EN809:1998+A1:2009, Pumps and Pump Units
for Liquids - Common Safety Requirements, to verify conformance.
Signature of authorized person
, 800 N. Main Street
October 20, 2005
Date of issue
David Roseberry
Printed name of authorized person
Revision Level: F
Engineering Manager
Title
April 19, 2012
Date of revision
Page 12

Kynar is a registered tradename of Penwalt Corp. Warren Rupp is a registered tradename of Warren Rupp, Inc.
WARREN RUPP, INC.
A Unit of IDEX Corporation
800 North Main Street
Mansfield, OH 44902 USA
(419) 524-8388
Fax: (419) 522-7867
wr10om-0614
www.warrenrupp.com
 Loading...
Loading...