Page 1
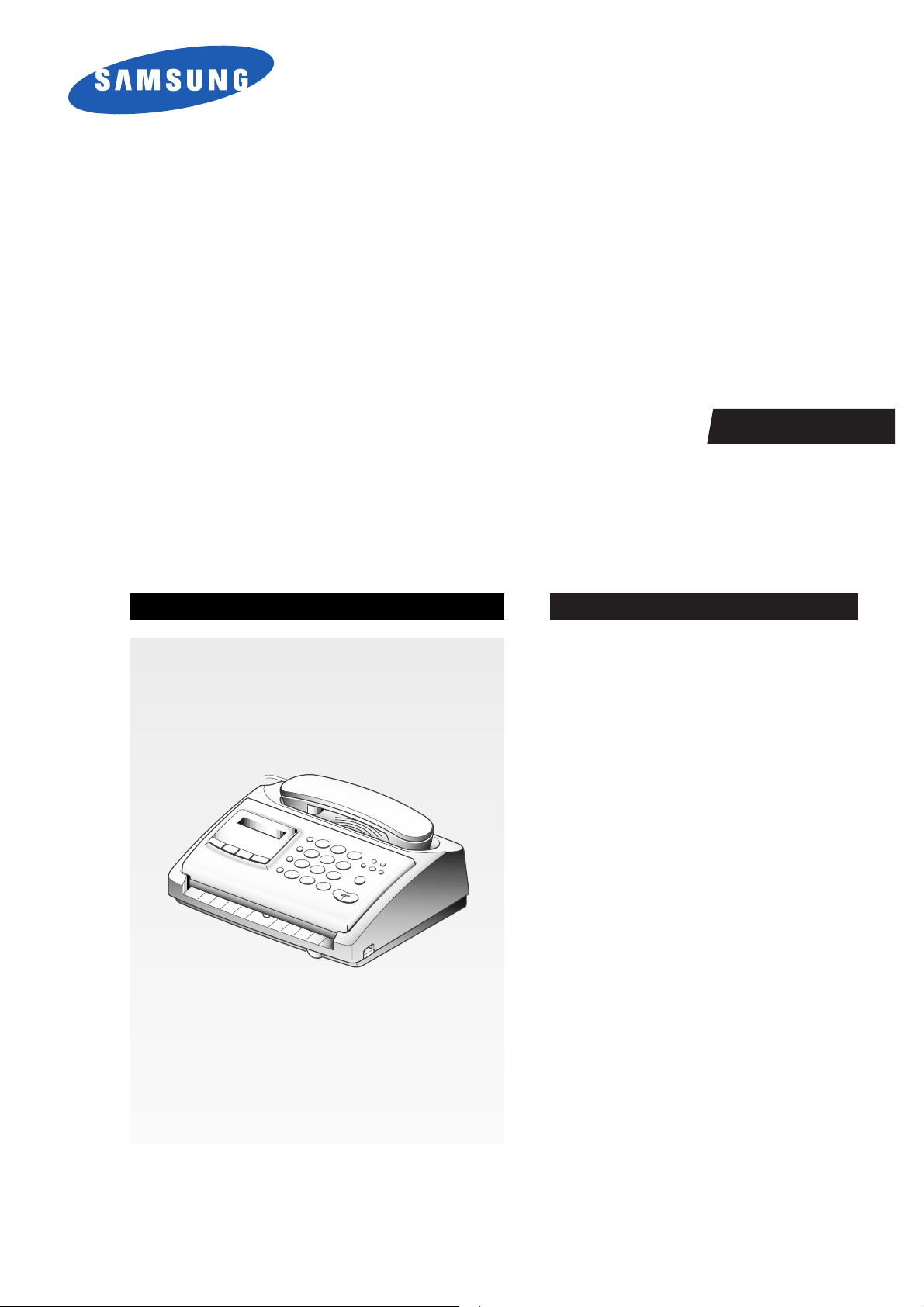
FACSIMILE
SF150T
CONTENTS
1. Precautions
2. Specification
3. Operating Instructions
4. Disassembly and Reassembly
5. Circuit Description
6. Troubleshooting
7. Electrical Parts List
8. Exploded Views and Parts List
9. PCB Diagrams
10. Block Diagram
11. Wiring Diagram
12. Schematic Diagrams
FACSIMILE
SERVICE
Manual
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
Page 2

Samsung Electronics Co.,Ltd. Mar. 1998.
Printed in Korea.
JF68-60936A
Page 3

SF150T 1-1
1. Be sure that all built-in protective devices are
in place. Restore any missing protective
shields.
2. Make sure there are no cabinet openings
through which people- particularly childrenmight insert fingers or objects and contact
moving parts or dangerous voltages.
3. When re-installing chassis and assemblies, be
sure to restore all protective devices, including
control knobs and compartment covers.
4. Design Alteration Warning:
Never alter or add to the mechanical or
electrical design of this equipment, such as
auxiliary connectors, etc. Such alterations and
modifications will void the manufacturer's
warranty.
5 Components, parts, and wiring that appear to
have overheated or are otherwise damaged
should be replaced with parts which meet the
original specifications. Always determine the
cause of damage or overheating, and correct
any potential hazards.
6. Observe the original lead dress, especially near
sharp edges, AC, and high voltage power
supplies. Always inspect for pinched, out-ofplace, or frayed wiring. Do not change the
spacing between components and the printed
circuit board.
7. Product Safety Notice:
Some electrical and mechanical parts have
special safety-related characteristics which
might not be obvious from visual inspection.
These safety features and the protection they
provide could be lost if a replacement
component differs from the original. This
holds true, even though the replacement may
be rated for higher voltage, wattage, etc.
8. Components critical for safety are indicated in
the parts list with symbols . Use only
replacement components that have the same
ratings, especially for flame resistance and
dielectric specifications. A replacement part
that does not have the same safety
characteristics as the original may create
shock, fire, or other safety hazards.
1 Precautions
Follow these safety, ESD, and servicing precautions to prevent personal injury and equipment damage.
1-1 Safety Precautions
Page 4

1. Immediately before handling a semiconductor
component or semiconductor-equipped
assembly, drain off any electrostatic charge on
your body by touching a known earth ground.
Alternatively, employ a commercially
available wrist strap device, which should be
removed for your personal safety reasons prior to
applying power to the unit under test.
2. After removing an electrical assembly
equipped with ESDs, place the assembly on a
conductive surface, such as aluminum or
copper foil, or conductive foam, to prevent
electrostatic charge buildup in the vicinity of
the assembly.
3. Use only a grounded-tip soldering iron to
solder or desolder ESDs.
4. Use only an "anti-static" solder removal device.
Some solder removal devices not classified as
"anti-static" can generate electrical charges
sufficient to damage ESDs.
5. Do not use Freon-propelled chemicals. When
sprayed, these can generate electrical charges
sufficient to damage ESDs.
6. Do not remove a replacement ESD from its
protective packaging until immediately before
installing it. Most replacement ESDs are
packaged with all leads shorted together by
conductive foam, aluminum foil, or a
comparable conductive material.
7. Immediately before removing the protective
shorting material from the leads of a
replacement ESD, touch the protective material
to the chassis or circuit assembly into which
the device will be installed.
8. Maintain continuous electrical contact between
the ESD and the assembly into which it will be
installed, until completely plugged or soldered
into the circuit.
9. Minimize bodily motions when handling
unpackaged replacement ESDs. Normal
motions, such as the brushing together of
clothing fabric and lifting one's foot from a
carpeted floor, can generate static electricity
sufficient to damage an ESD.
Precautions
1-2 SF150T
1. Exercise caution when replacing a Lithium
battery. There could be a danger of explosion
and subsequent operator injury and/or
equipment damage if incorrectly installed.
2. Be sure to replace the battery with the same or
equivalent type recommended by the
manufacturer.
3. Lithium batteries contain toxic substances and
should not be opened, crushed, or burned for
disposal.
1-3 Lithium Battery Precautions
1-2 ESD Precautions
Certain semiconductor devices can be easily damaged by static electricity. Such components are commonly
called "Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices", or ESDs. Examples of typical ESDs are: integrated circuits,
some field effect transistors, and semiconductor "chip" components.
The techniques outlined below should be followed to help reduce the incidence of component damage
caused by static electricity.
CAUTION: Be sure no power is applied to the chassis or circuit, and observe all other safety precautions.
Page 5
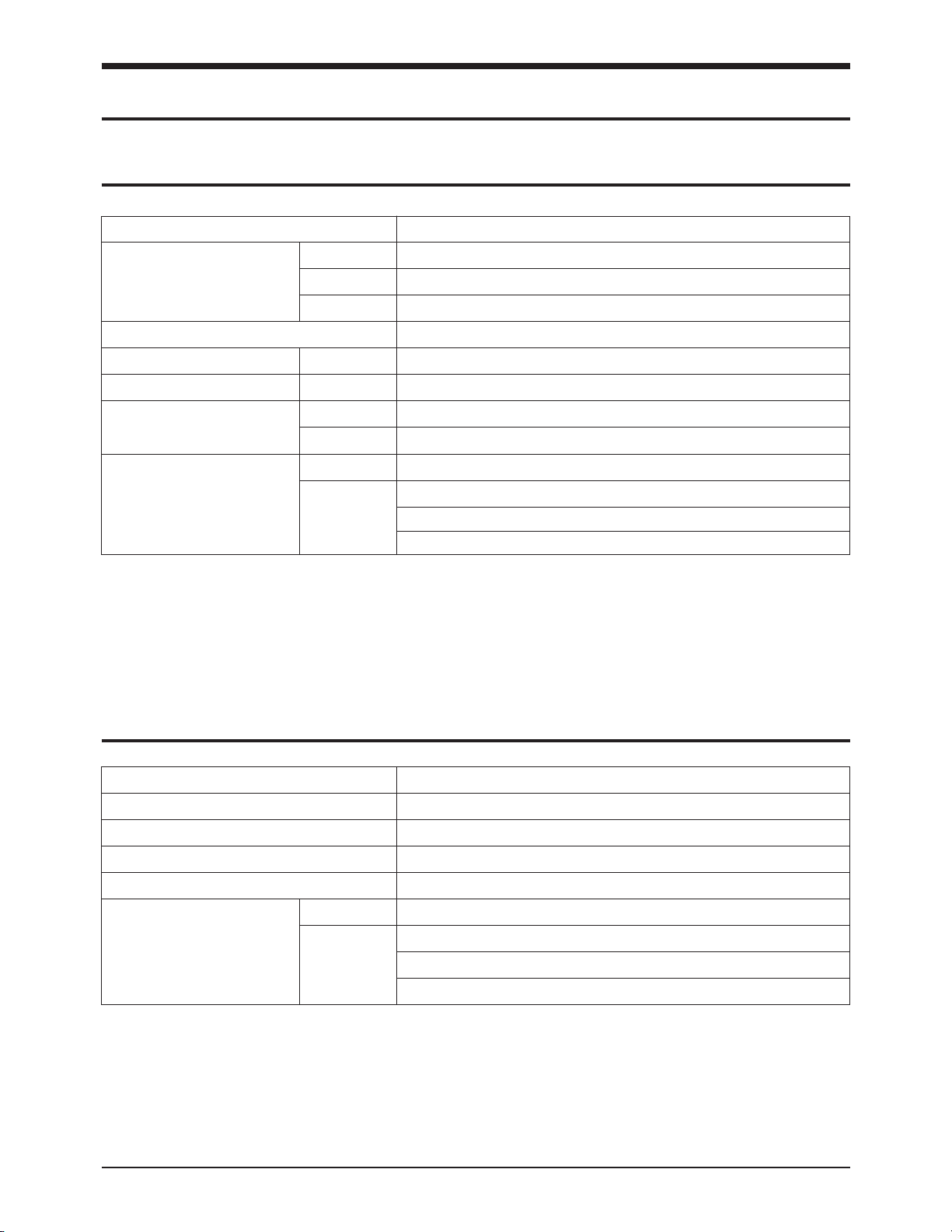
Parameter Specification
Coding Scheme MH (Modified Huffman)/MR (Modified READ)
Recording Paper Size 216 mm x 30 m; core diametre: 12.7 mm
Effective Recording Width 210 mm
Recording Method Solid state Thermal Printing Head
Horizontal 8 dots/mm
Resolution
Standard: 3.85 lines/mm
Vertical Fine: 7.7 lines/mm
Super Fine: 15.4 lines/mm
Parameter Specification
Normal 210 x 297 mm
Document Size Max. 216 x 1500 mm
Min. 152 x 76 mm
Document Thickness 0.085 x 0.115 mm
Scan Line Length Horizontal A4 paper,1728 scan elements along 216 line length
Effective Scanning Width Vertical 216 mm
Scanning Method Horizontal Flat-bed scanning using CIS
Vertical Stepping motor
Horizontal 8 dots/mm
Resolution
Standard: 3.85 lines/mm
Vertical Fine: 7.7 lines/mm
Super Fine: 15.4 lines/mm
SF150T 2-1
2 Specification
2-1 Transmitter
2-2 Receiver
Page 6
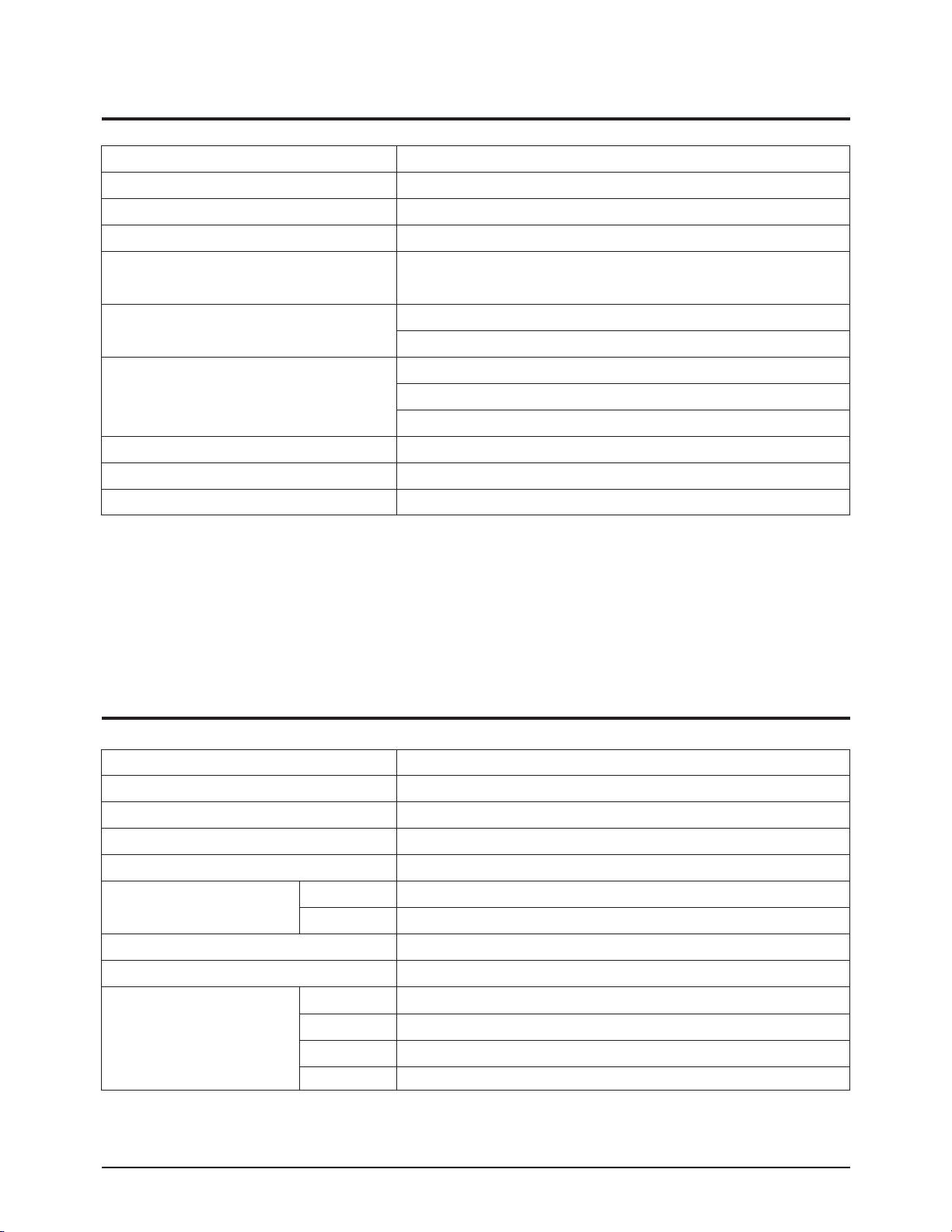
Specifications
2-2 SF150T
Parameter Specification
Dialling Signal DP/DTMF
Dialling Method Manual; Memory dialling; Last Number Redialling
Memory Capacity 34 memory dial (power on)
Power Requirement Check power label attached near the power cord connection.
Power Consumption
Stand-by 7 Watt
In use Max. 115 Watt
Temperature 5 °C to 45 °C
Relative Humidity 20 to 80 % RH (Non-Condensing)
Width 278 mm
Dimension
Depth 211 mm
Height 107 mm
Weight 2.5 kg
Parameter Specification
Communication Facility Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN)
Line Coupling Direct
Transmission Speed 9600, 7200, 4800, 2400 bps
Modem QAM, DPSK and FSK
(V.29, V.27ter with fall back function and V.21)
Carrier Frequency 1700 Hz (9600/7200 bps)
1800 Hz (4800/2400 bps)
Control Signal 1100 Hz (CNG)
2100 Hz (CED)
300 bps (FSK)
Output Level 0 dBm to - 15 dBm +0.0 / -3 dBm, adjustable in 1 dB steps
Input Sensitivity 0 dBm to - 48 dBm in two ranges
Input & Output Impedance 600 ohm
2-3 Line Control Blockk
2-4 Others
Page 7

SF150T 3-1
3. Operating Instructions
3-1 Service Mode
In Service Mode, the technician can check the machine and perform various tests to isolate a machine
malfunction.
To enter Service Mode, press ÔMENU, #, 1, 9, 3, 4Õ in sequence, and ' ' will be displayed in the LCD to
confirm that the machine has entered Service Mode. While in Service Mode, the machine still performs all
normal operations. To return to normal User Mode, press 'MENU, #, 1, 9, 3, 4' in sequence again, or turn
the power off, then on by unplugging and replugging the power cord.
3-2 Changing Options
3-2-1 Selectable Options
CONFIRMATION REPORT
Select whether a confirmation report prints each
time a user sends a fax.
YES: The machine prints a report automatically
after each fax sent.
ERROR : The machine prints a report only when
there is an error.
NO: The machine does not print a report
automatically. User can print the list on
demand.
DIAL TYPE
Select the type of dial system to which the machine
is connected.
Select MF if connected to a tone dial system.
Select DP if connected to a pulse dial system.
Use ^ or v buttons to select, then press Start.
RING COUNT
Select the number of rings the machine allows
before it answers a call in automatic receiving
mode.
CALLER ID
This is the number of the person faxing you.
Choose YES to turn on Caller ID display.
Choose NO to disable.
REMOTE RECEIVE CODE
This code can be used only with a phone extension
connected to the FAX machine. The user can
initiate FAX receive mode by entering a remote
receiving code on the extension phone. The code is
factory preset to 9 , and the middle character
may be changed to any digit between 0 and 9.
AUTO PRINT
The machine prints a TX/RX journal automatically
after every 20 fax sessions.
MODEM SPEED
Select baud rate of 9600, or 4800 bps. The lower the
baud rate, the larger the acceptable error rate. T30
protocol has a fixed speed of 300 bps in the
protocol mode. When the TX speed is set to 9600
bps, the RX speed will be V.29. When the TX
speed is set to 4800 bps, the RX speed will be V.27
ter.
T
Page 8
Operating Instructions
3-2 SF150T
CALL TRANSFERRING
This feature allows the fax machine to transfer
incoming caller's message to a specified remote
location.
Choose YES to turn on this feature. The LCD
display asks to enter the telephone number you
want to be transferred.
Choose NO to turn off the feature.
CALL MONITORING
This feature enables you to hear callers leaving
messages on the machine.
Choose YES to turn on this feature.
Choose NO to turn off this feature.
CHARGE SAVER
This feature lets the user dial into this machine
from a remote phone and check whether anyone
has left a message without being charged for a
charge call. When toll saver is on and there are
messages waiting to be heard, the machine
answers on the number of rings you specify in the
ring count option. If there are no messages, the
machine answers on the second ring after the
number specified. This gives the user time to hang
up the phone before the machine answers - and
saves the price of the call.
Choose YES to turn on charge saver.
Choose NO to turn off charge saver.
MESSAGE RECORDING TIME
You can select the maximum time allowed for
caller messages and memos.
If you choose YES, the LCD display shows you the
time limits available : 0 second, 30 seconds, 60
seconds or 90 seconds. Choose the proper time. If
you choose 0, it allows callers to hear the greeting
message but doesn't permit them to leave
messages.
REMOTE PASSWORD
You can change the three-character password used
to access your machine from a remote phone. The
password is preset to "#139#" (pound one three
nine pound) at the factory. The first and the last #'s
are fixed, but you can change the middle numbers
from 0 to 9.
Enter the characters you want to use, then press
Start.
BATTERY ALARM
You can turn on the battery alarm feature. With
this feature on, the machine displays the low
battery message in the LCD and sounds beeps to
alert you low battery condition.
Choose YES to turn on the battery alarm feature.
Choose NO to turn off the battery alarm feature.
TAD SILENCE CHECK
In TAD mode, The machine decides the next
action when detected a silence of 10 seconds.
The actions are:
RX : Swiches to receive mode.
REC : Keeps the recording the silence.
CUT : Disconnect the line and returns to standby
mode.
TX LEVEL
From -9 dBm to -15 dBm is acceptable. You can set
the transmission level to between 0 and -15 dBm
in 1dB steps using the control panel keypad.
Accuracy is + 0 / -3 dBm.
CABLE EQUALIZER
Copper telephone wire attenuates low frequencies
less than high frequencies. The longer a cable is,
the more pronounced the effect. To compensate for
this attenuation you may need to set the machine
to match the cable length currently used. Select
short or long.
Page 9

Operating Instructions
SF150T 3-3
LINE MONITOR
Allows you to monitor line signals through the
speaker.
RX LEVEL
Reception level may be too low due to cable losses.
If set to - 43 dBm, reception sensitivity will be
between 0 and - 43 dBm.
If set to - 48 dBm, reception sensitivity will be
between -5 and -48 dBm.
BUSY TONE DETECTION LEVEL
While checking tone in ANS/FAX mode, If any
signal which is great than set level is detected for a
few seconds the machine will disconnect the line.
BUSY ON DROP OUT TIME
While checking busy on time, if any signal noise is
detected, the machine will ignore the signal noise
unless it is greater than a specified time.
BUSY OFF DROP OUT TIME
While checking busy off time, if any signal noise is
detected, the machine will ignore the signal noise
unless it is greater than a specified time.
PAUSE TIME
Adjust the period of pause time to wait for a
second dial tone in a PABX or mobile paging
system. You can adjust the time from 0 sec to 9 sec
(0 to 9).
RECALL TIME
When a call comes in and you want to connect it to
another party, you can transfer the call by using a
timed-break recall funtion.
This funtion must make a properly timed break
authorized by the country. The machine can select
times of 100, 280, or 600 msat an accuracy of ± 10
ms of the setting.
MH/MR CODING
Selection the coding method used for picture
detail
MR = Use MR and MH coding.
MH = Use only MH coding.
RING ON CHECK TIME
The machine must receive a ring signal with a
specified active time from a telephone exchange in
automatic reception mode. The detection time that
the machine considers valid is adjustable via this
option. If the active time of the ring signal is less
than the set value of the Ring On Check Time, the
machine will not consider it a ring signal.
RING OFF CHECK TIME
The machine must receive a ring signal with a
specified inactive time, as well as an active time. If
the inactive time of the ring signal is longer than
the value of the Ring Off Check Time, the machine
will not consider it a valid ring signal.
3-2-2 Changing Options
Press ÔMENU, 3, Start/COPYÕ in sequence. Press
^ or v to select the desired option item.
When the desired item appears, press Start and
use ^ or v to change the status of the selected
option.
Page 10

3-4 SF150T
Operating Instructions
3-3 Test Mode
Test Mode is used to test machine functions. To enter Test Mode, press ÔMENU, 0, START/COPYÕ in
sequence.
TPH TEST
The TPH test pattern checks the heating element of the TPH. Figure 3-1 is a sample test pattern.
Figure 3-1: TPH Test Pattern
Page 11
Operating Instructions
SF150T 3-5
3-4 Report Printout
A number of useful reports can be printed in Service Mode. One of these lists is the protocol list, which
contains detailed information which may be required when contacting technical support. To print this list,
press MENU, 4, START/COPY in sequence.
When a report name appears in the display, scroll through the list of reports by pressing ^ or v. When a
desired report is selected, press START/COPY.
CONFIRMATION REPORT
Shows the last transmission result.
TX/RX JOURNAL
Shows information about faxes sent and received.
SYSTEM DATA LIST
Shows all option settings.
TEL. NUMBER LIST
Lists all numbers stored in the machine's OneTouch and Speed-Dialling memory.
PROTOCOL LIST
This list is available in Service Mode only, and
shows the sequence of the CCITT group 3 T.30
protocol during the most recent TX or RX
operation. You can check for send and receive
errors with this list.
If a communication error occurs while the machine
is in Service Mode, the protocol list will print
automatically.
HELP LIST
This report illustrates the machine's basic
functions and commands. Use as a quick reference
guide.
To print this list, press HELP (#).
MODEM TEST
The modem will transmit send various signals on
the telephone line to check the following:
¥ FSK Test
¥ Tone Test: 1100 Hz, 1650 Hz, 1850 Hz, 2100 Hz
¥ G3 training: 9600, 4800 bps
¥ RX Loop Test
¥ DTMF Test
ROM TEST
Tests machine ROM (Read Only Memory). The
result and the software version appear in the LCD
in the following format:
CHKSUM= VXX/XX, OK
ALL MEMORY CLEAR
Erases contents of RAM. When memory is cleared,
the machine returns to default settings.
Page 12

Operating Instructions
3-6 SF150T
3-5 LCD Display
3-5-1 During communication
In User Mode, the LCD shows the remote
machine's TTI number, communication type, (send
or receive), and page number.
In Service Mode, the display shows the
communication type, abbreviations for the CCITT
Group 3 T.30 protocol as they occur, the protocol
type (G3), coding type (MH), baud rate in kbps,
and line time.
3-5-2 If a communication problem
occurs:
In User Mode, the display shows one of the
following reasons: CAM JAM, COMM. ERROR,
CHECK DOCUMENT.
In Service Mode, the display shows all error
messages available in User Mode, as well as
additional error messages not available in User
Mode.
Error messages shown only in Service Mode are:
PRE-MESSAGE ERROR:
problem occurred during phase B of session
MESSAGE ERROR:
problem occurred during phase C of session
POST-MESSAGE ERROR:
problem occurred during phase D of session
LINE ERROR:
machine cannot connect or has lost connection
with the remote machine
Additional messages, not shown above, will
appear in the TX/RX journals printed in Service
Mode.
Page 13
SF150T 4-1
4. Disassembly and Reassembly
Note: Make sure power is OFF by removing the power cord from the wall outlet.
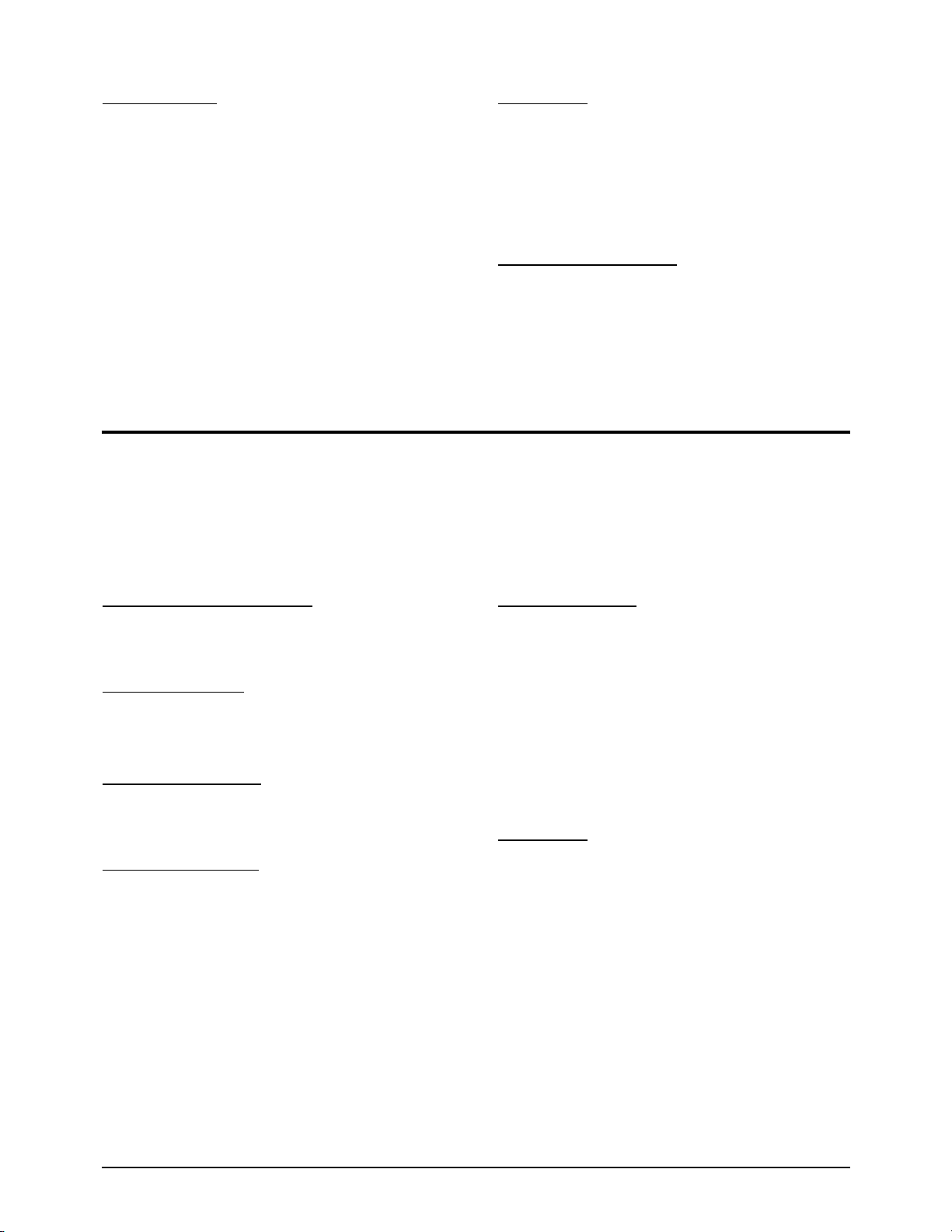
4-1 Tx Guide
¥ Open the operating panel assembly.
¥ Carefully lift the TX guide, as shown in the figure.
OPE Cover
TX Guide
Figure 4-1
Figure 4-2
4-2 Top Cover
¥ Loosen the 5 screws fastening the top cover.
¥ Carefully lift the top cover.
¥ Remove the wire harness from the base, as
shown in the figure.
2
1
1
3
3
3
3
3
Page 14
Disassembly Instruction
4-2 SF150T
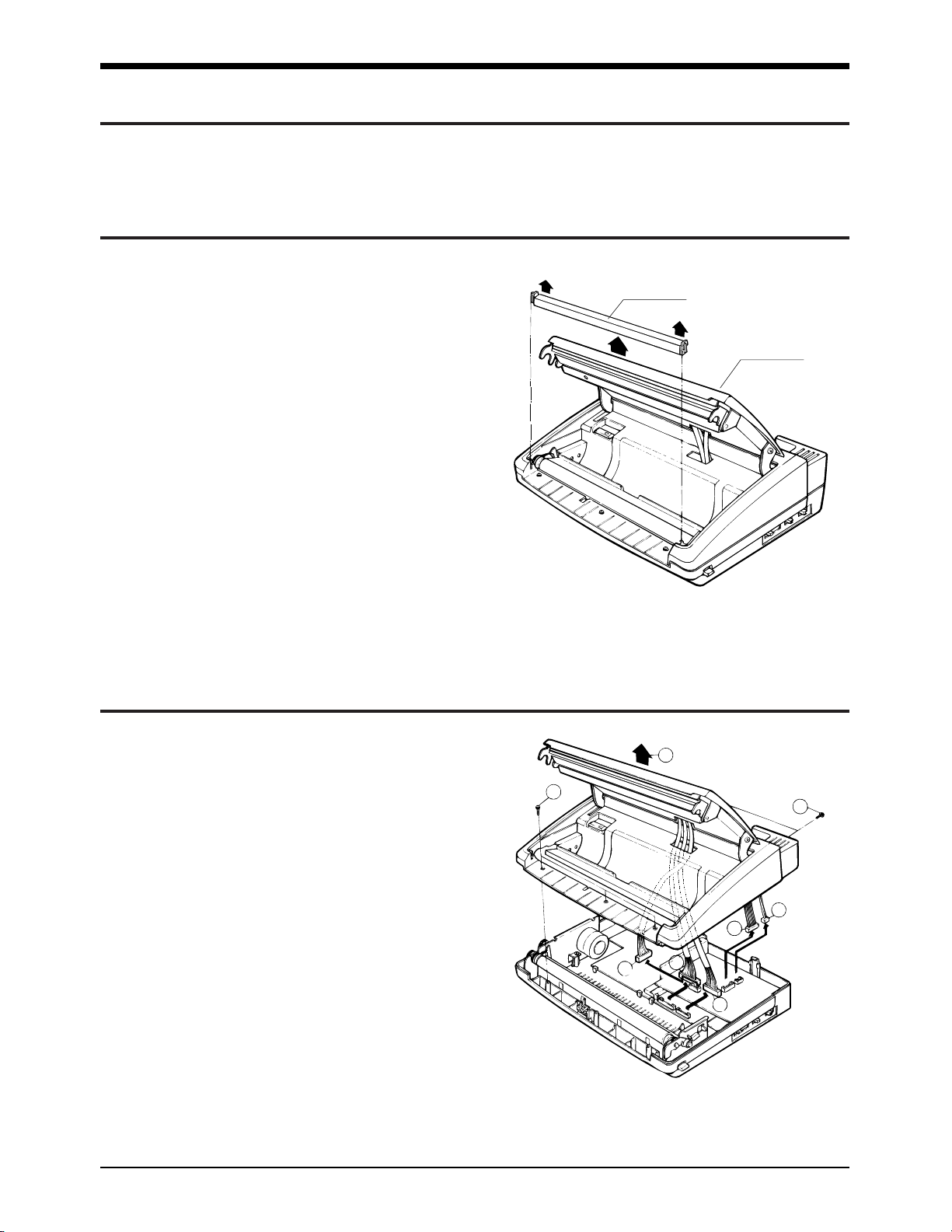
4-3. OPE Unit
4-4.
OPE Cover
¥ Loosen the 2 screws fastening the top cover.
¥ Carefully lift the OPE assembly, as shown by
the arrow.
¥ Loosen the 2 screws fastening the OPE chassis.
¥ Remove the Paper Empty sensor connector
from the OPE board.
¥ Remove the OPE unit from the OPE chassis, as
shown by the arrows.
Top Cover
OPE Unit
OPE Cover
OPE Chassis
Figure 4-3
Figure 4-4
Page 15
Disassembly Instruction
SF150T 4-3
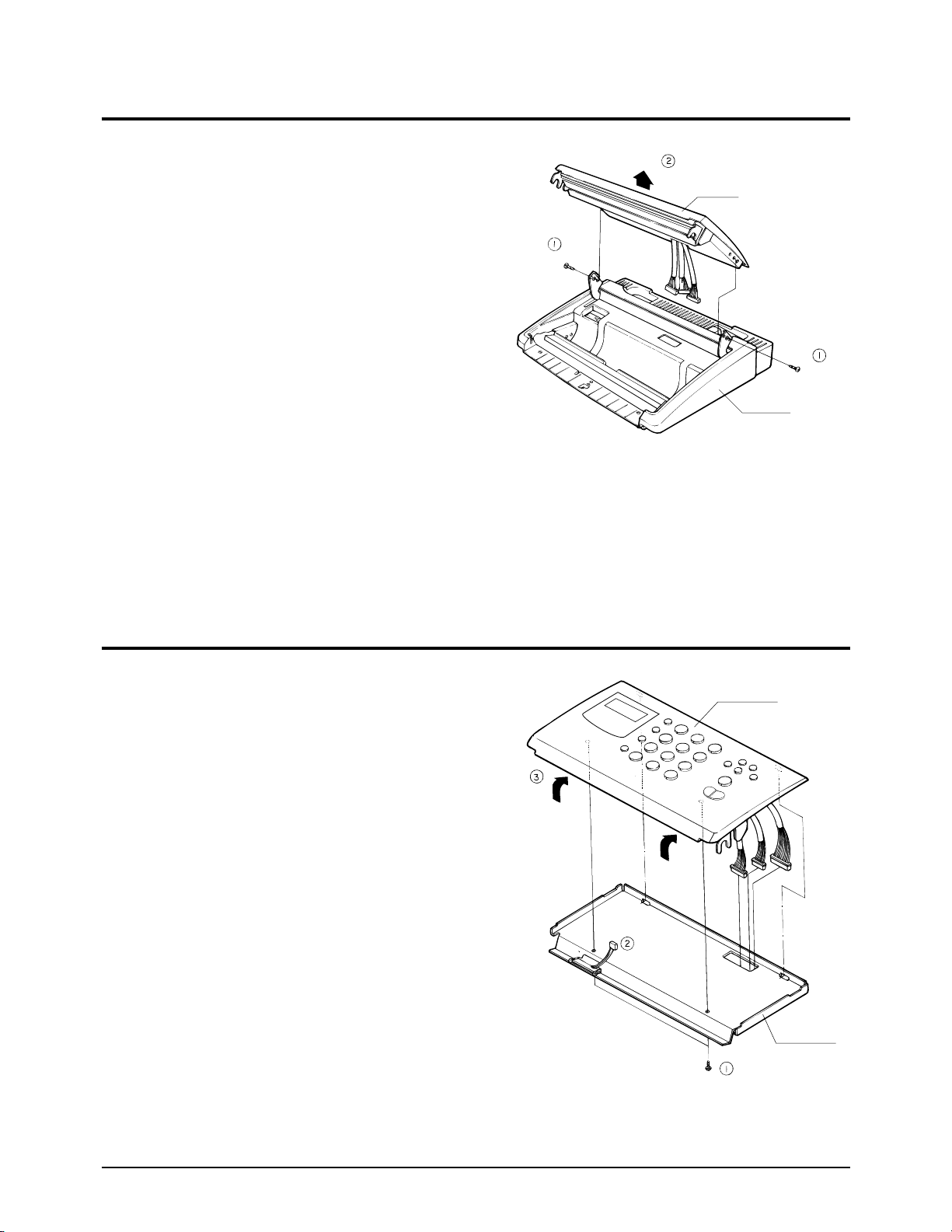
4-5. TPH
¥ Remove the TPH assembly from the OPE unit.
¥ Remove the TPH from the TPH assembly.
¥ Remove the TPH harness from the TPH
connector.
¥ Remove the TPH guide from the TPH.
¥ Lift the white roller assembly.
¥ Loosen the 2 E-rings fastening the main chassis
assembly.
¥ Remove the spring-lock.
¥ Loosen the 2 screws fastening the main chassis
assembly.
¥ Lift the CIS assembly.
¥ Remove the document guide from the CIS
assembly (2 screws).
¥ Remove the CIS guide from the CIS (2 screws).
OPE Cover
TPH Bracket
TPH Guide
TPH
Base Ass'y
Main chassis Ass'y
4-6. Main Frame
Figure 4-5
Figure 4-6
Page 16
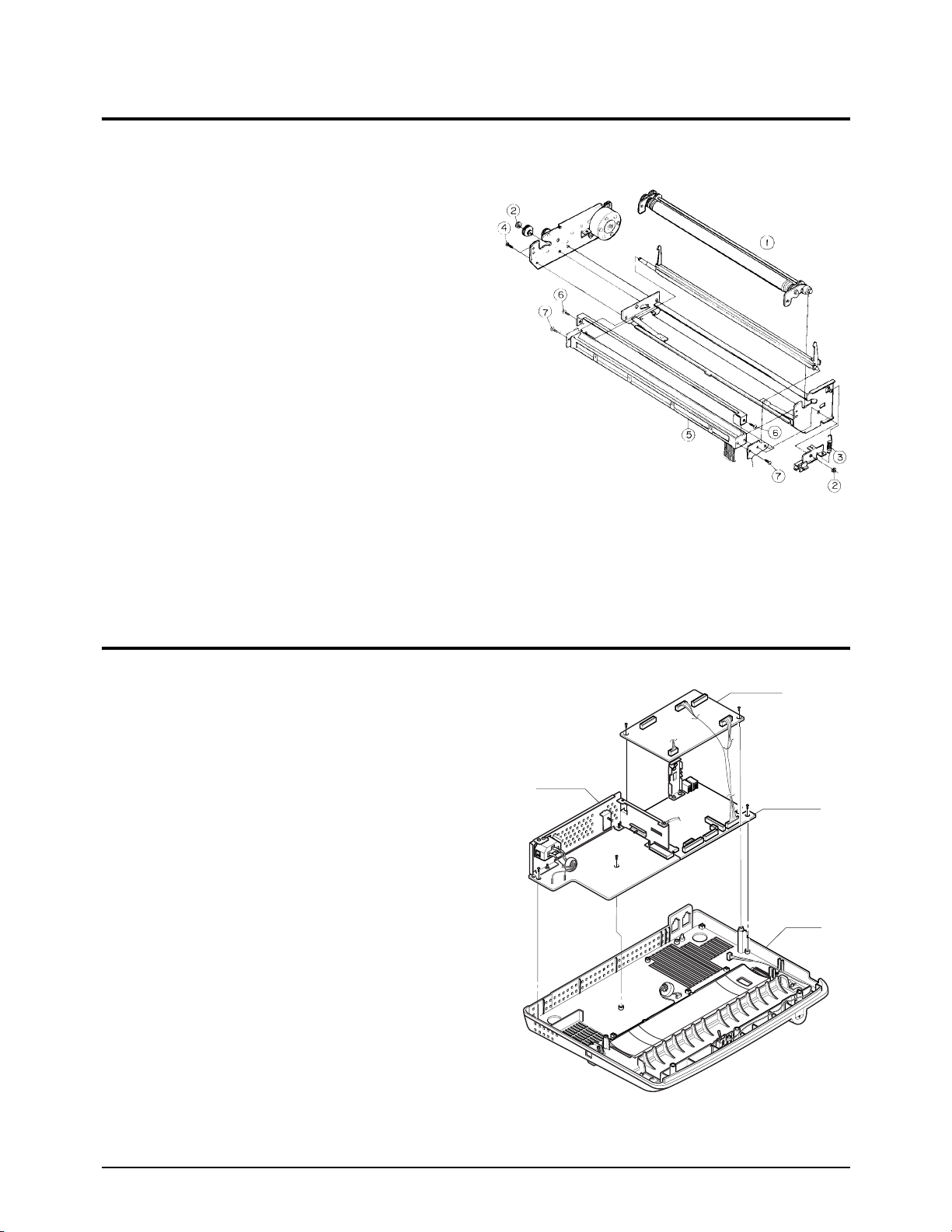
Disassembly Instruction
4-4 SF150T
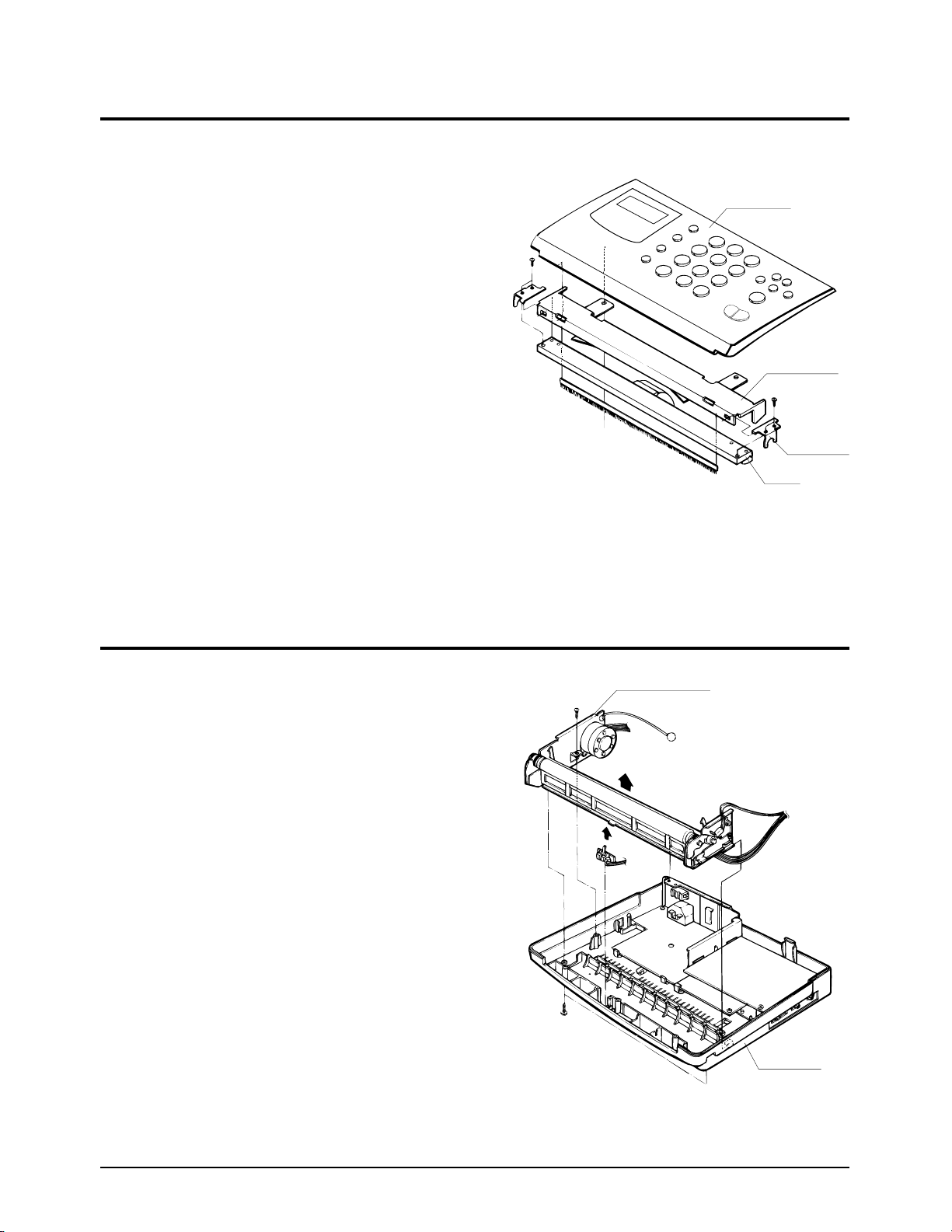
4-8. BOARDS & POWER SUPPLY
LIU PBA
MAIN PBA
BASE
POWER
¥ Remove the handset modular harness from the
LIU board.
¥ Loosen the screw fastening the LIU board and
carefully lift the LIU board as shown by the
arrow.
¥ Loosen the 3 screws connecting the main and
daughter boards. Lift the rear bracket.
¥ Loosen the screw fastening the daughter board
to the base. Lift the daughter board.
¥ Loosen the 2 screws fastening the power supply
to the base. Lift the power supply and the main
board to remove them.
¥ Lift the modular jack and the earth spring.
¥ Lift the white roller assembly.
¥ Loosen the 2 E-rings fastening the main chassis
assembly.
¥ Remove the spring-lock.
¥ Loosen the 3 screws fastening the main chassis
assembly.
¥ Lift the CIS assembly.
¥ Remove the document guide from the CIS
assembly (2 screws).
¥ Remove the CIS guide from the CIS (2 screws).
4-7. CIS
Figure 4-7
Figure 4-7
Page 17
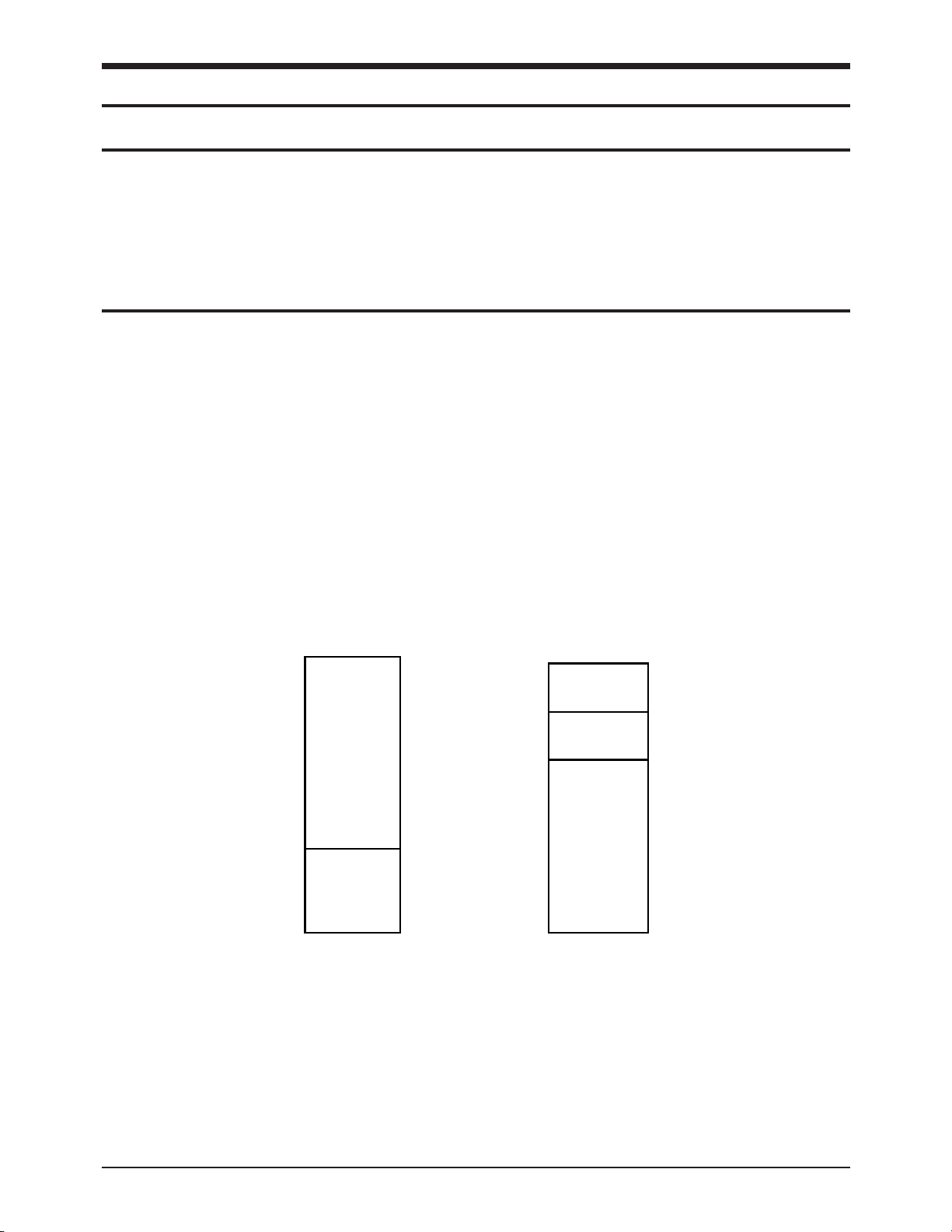
SF150T 5-1
5. Circuit Description
5-1 General
The main circuit board controls the machine, and consists of Super Fax Chip (KS16118), External memory,
CODEC circuit with modem-TX and RX signal path and some parts of the Line Interface Unit, Digital TAD
circuit with DSP amd DRAM, witch controls the system.
5-2 System Control Section
This circuit consists of the EP-ROM and SRAM, external Real Time Clock crystal, RTC and memory back-up
circuitry, and the Super Fax Chip (KS16118).
The KS16118 Super Fax Chip is an integrated 9600 bps modem, image processor, 8-bit MPU, peripheral
controller, and analog front end circuit on a single-chip.
Peripheral functions inculde 2-channel SI0, 3-channel DMA, 6-bit Half flash A/D converter, scanner and
video processor units, TPH interface, CODEC unit, and tone generator.
Modem is a 9600 bps, half duplex monolithic device incorporating digital filters, a Samsung SSP1600 digital
signal processor and CPU-Interface logic.
Figure 5-1: KS16118 External Memory Map
1FFFH
0100H
00FFH
0000H
0000H
FFFFH
FF80H
FF7FH
FF00H
FEFFH
/DMS
(SRAM)
Peripheral
PCS0
DSP /CS
PCS1
Interrupt
Vectors
/PMS
(EP-ROM)
[ Program Memory ]
[ Data Memory ]
5-2-1 Memory Map
The external memory of the CPU is devided into, 1 byte(FF00H) DSP chip select, 32kbyte SRAM (0000H
through 7FFFH) and 128kbyte EP-ROM (0100H through 1FFFH).
Page 18
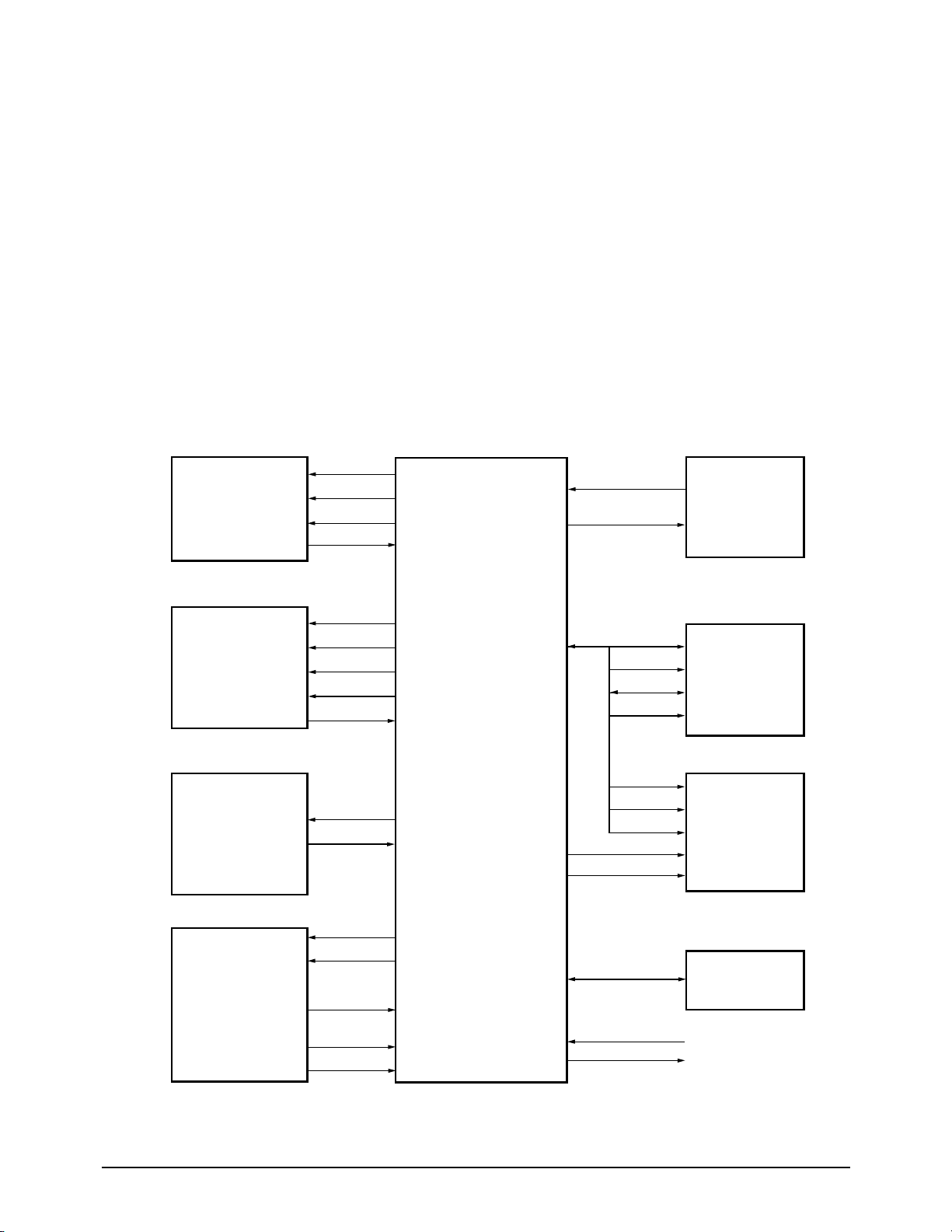
Circuit Description
5-2 SF150T
Figure 5-2: XFC Hardware Interface Signals
5-2-2 lExternal Chip Control
KS16118 internal logic generates chip select signals for both memory chips and peripherals.
To support external access, from one to three wait cycles can be inserted under program control during
external access.
A chip select signal line goes active (low) whenever its corresponding device is accessed over the external
interface. The peripheral addresses are located in data memory space.
/DMS : SRAM chip select active (low)
/PMS : EP-ROM chip select active (low)
/PCSn : Peripheral chip select active (low)
D0 - D7 : 8 bit data bus
A0 - A15 : address bus
5-2-3 System Clock
The 12 MHz internal system clock frequency is generated by dividing the 24 MHz clock.
OPERATING
PANEL
PRINTER DATA
CONTROL AND
SENSORS
MOTOR
DRIVER
(MOTOR)
SCANNER
CONTROL
AND
PROCESSING
RTC
CRYSTAL
DATA
MEMORY
PROGRAM
MEMORY
GENERAL
PURPOSE I/ 0
OP00-OP06
LED_CTL
LCD_EN
OPI0-OPI3
STB 0-3
PDAT
PCLK
PLAT
THADI
SM0-SM3
MODE
SI
CLK1
Vin
+Vref
-Vref
XIN
XOUT
/DMS
/RD /WR
D0~D7
A0~A14
/RD
D0~D7
A0~A15
A16
/PMS
RESTOUT
/RESET
KS16118
Page 19
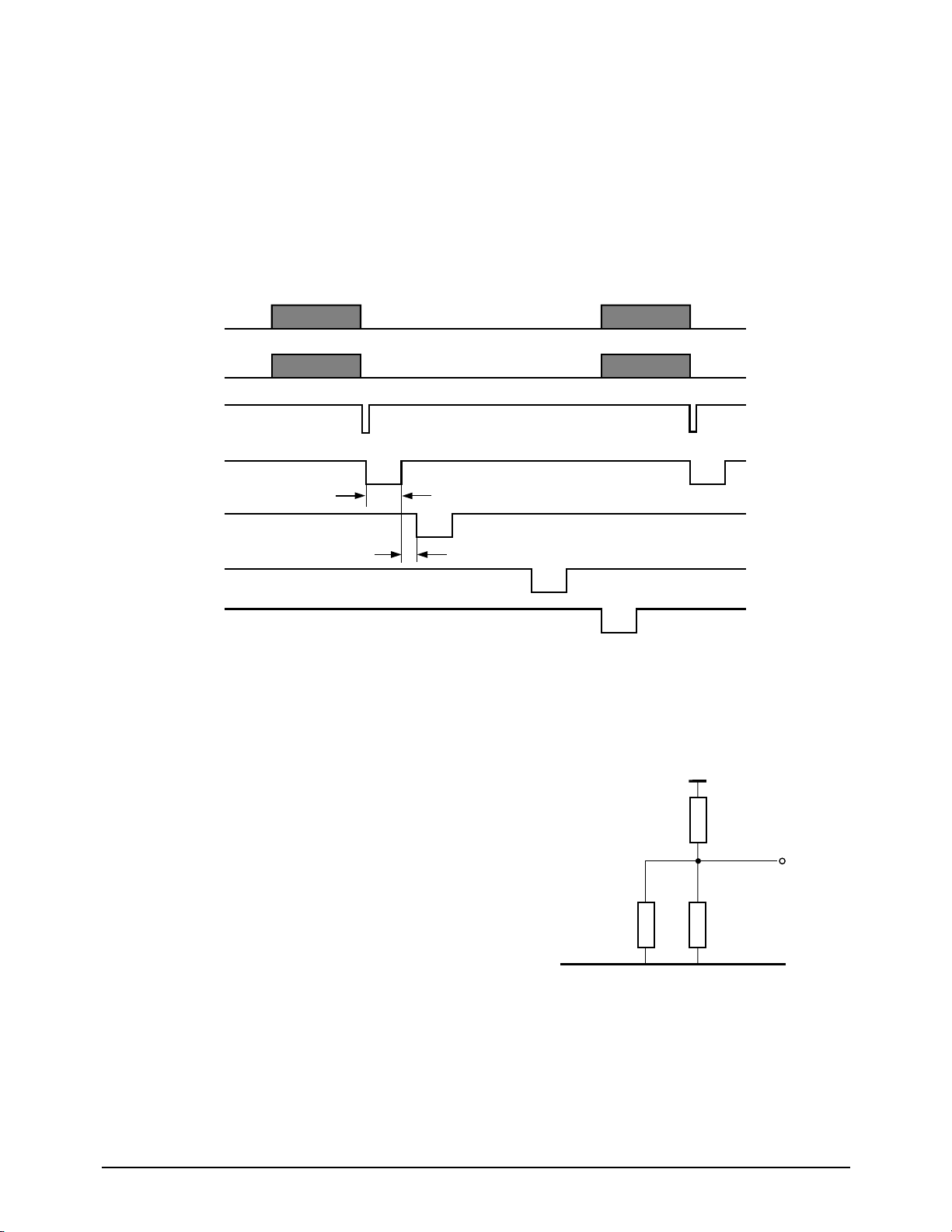
Circuit Description
SF150T 5-3
Figure 5-4: Printer Timing
5-2-4 Real Time Clock (RTC)
This circuit receives clock pulses from an external
32.768 kHz crystal, which it divides into hours,
minutes, seconds, year, month, and day.
A battery maintains operation when power is off.
KS16118 can up-track 100 years, begining with
1992.
5-2-5 Print Control
The PCLK and PDATA signals synchronize serial
print data to the TPH.
PLAT latches TPH serial print data to the TPH
from a shift register through PDATA.
STB0 - STB3 enable TPH printing in four steps.
This system has a 10ms/line printing format and
sets STB High/Low enable status
according to the STBPOL signal.
PDATA
PCLK
PLAT
STB0
STB1
STB2
STBWID
[0:11]
STB0FF
[0:11]
STB3
Figure 5-6: THD Connection Circuit
GND5
THD1
+5V
R5
R4
Rth
(T)
TPH
Thermistor
5-2-6. A/D Converter (Scanner & TPH
Temperature)
Using a half-flash conversion technique, the 6-bit
A/D converter supports a 0.8µs peak conversion
time and dissipates only 7mA, maximum.
The half-flash unit uses 16 comparators, a most
significant 3-bit ADC, and a least significant 3-bit
ADC.
If the analog input voltage is greater than +Vref,
the A/D conversion result is 3FH.
If the analog input voltage is less than -Vref, the
A/D conversion result is 00H.
A/D conversion register, ADCON (19H), is used
to select an internal or external source for the A/D
converter, to enable or disable the converter, and
to select the operating mode (H: ADin 1 (Scanner),
L: ADin 0 (TPH)).
Page 20

Circuit Description
5-4 SF150T
5-2-7 Operation Panel Control
Communication
The Operation Panel is controlled by the Port 1,
Port2, and Port 5 registers.
Port 1 (E2H) is a 4-bit general output port for LCD
display data.
This port can be configured for normal data (P1.4P1.7) or alternately as internal MODEM V.24
interface output signals (P1.0-P1.3).
Port 2 (E4H) is an 8-bit port with both input and
I/O pins.
P2.0-P2.3 are input ports for OPE key scan data,
and P2.6-P2.7 are not used for SF150T.
Port 5 (EAH) is an 8-bit port with both output and
I/O pins.
P5.0 and P5.4 are used for LED control and LCD
enable.
5-2-8 Image Sensor
The shading wave is formed by scanning the white
roller prior to a document.
The slice level is determined by the shading wave,
and compensates for shading distortion according
to the CIS characteristics.
The wave format from the CIS is converted into a 6
bit digital value in the KS16118 image processor,
and processed in B/W or intermediate mode.
5-2-9 CIS Input Processor
To process the B/W input signal, maximum (+Vref)
and minimum (-Vref) values of the CIS input signal
are adjusted by calibrating KS16118 in the high state
for maximum level, and setting them to earth for
minimum level.
Shading correction uses a multiplier composed of a
9-bit sequential adder for simple H/W Logic.
5-2-10 CIS Driver
The CIS driver clock (CLK1) frequency is 250 kHz.
A 75% low duty cycle lengthens the charging time.
A start signal (SI) is provided every 10 ms to
match the line scanning time.
Actual image signal (VIN) is provided in less than
6.8 ms, based on A4 paper size using the 250 kHz
clock.
Figure 5-10: CIS Driver Clock Timing
250 KHZ (L:DUTY 75%)
SI
CLOCK
SIG
1 LINE
Page 21
Circuit Description
SF150T 5-5
5-2-11 I/O Port Table
High Bank Memory
DSP Inactive
DATA = 1
DATA = 1
Active
Active
Active
Active
-
Active
Active
DSP Reset
DSP High Byte
Normal
Normal
CIS LED On
High
OPE LED On
Normal
Normal
-
Open
No Paper
No Document
Normal
Normal
CODEC Serial Clock
CODEC Serial Data
CODEC Enable
-
Closed
Paper Exist
Document Exist
Incomming Ring
Active DSP Data Transfer
Low Bank Memory
DSP Active
DATA = 0
DATA = 0
Inactive
Inactive
Inactive
Inactive
-
Inactive
Inactive
Normal
DSP Low Byte
Low Battery
DSP Response Mode
Off
Low
OPE LED Off
No Barttery
Circuit Symbol
I/O
Pin No.
Port Name
High Low
A16
/DSP_CS
IRXD
ITXD
MOTOR A
MOTOR /A
MOTOR B
MOTOR /B
/CML2
/CML1
/24VCTL
DSPRST
DSPHL
/LOWBAT
DSPACK
/GLED
-
LEDCTL
/NOBAT
SCLK
SDATS
/SDEN
/HOOK DET2
MODE
P_EMPTY
D_DET
RING_DET
/DSPFLAG
P0.0
P0.1
P2.4
P2.5
P3.0
P3.1
P3.2
P3.3
P3.4
P3.5
P3.6
P4.1
P4.2
P4.4
P4.5
P4.6
P4.7
P5.0
P5.3
P5.5
P5.6
P5.7
P6.1
P6.2
P6.3
P6.4
P6.5
P6.6
O
PCS
I
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
I
O
O
O
O
I
O
O
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
34
35
45
46
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
93
92
90
89
87
88
126
96
137
138
139
59
60
61
62
63
116
Page 22

5-2-12 Motor Controller
This facsimile machine perform sending, receving,
and printing functions utilising a single 24 volt
motor with a 120 ohm winding resistance.
Four drive strobe pulses operate the motor.
5-2-13 Serial communication Signals
The KS16118 have two full-duplex serial
communication port.
One port is used for I-LIU communication on LIU
PBA, and is a standart UART (Universal
Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter).
Another port, not used, may be configured for
UART or SRT (Synchronous
Receiver/Transmitter) operation.
5-2-14 Reset
To initialize the chipÕs internal logic, the reset
input (/RESET) must be held to 0 Volt for at least
22 CPU clocks. During this time, Vdd must be
greater than 3 Volt.
The watchdog timer can also invoke a system
reset.
When the reset input is released, the reset
condition continues for about 209.7 ms.
While the KS16118 is in this state, 0 Volt is applied
to the /RSTOUT pin.
[ +5V Power Monitoring ]
If 5 volt power to MX93000AFCÕs pin 6 (VPOW)
drops to between 4.6V and 4.4V (typically 4.5V),
power failure is indicated and the output of
MX93000AFCÕs pin 5 (/POWB) will go `lowÕ(GND5).
This causes the KS16118 to become active (low=reset).
The KS16118 reset causes the /REST0 terminal to be
reset.
Circuit Description
5-6 SF150T
Table 5-1: Motor Functions
Motor Function
Swing Gear Control
Document Out
100 pps
100pps
Drive Strobe Pulse
Phase
2
2
Other 100pps
2
Super Fine Mode 100pps
1-2
5-3 Memory
System memory consists of 128 kB EP-ROM and 32 kB SRAM. All of SRAM is backed up.
ROM and SRAM are selected by chip select lines, and data is accessed by the units position of the byte.
ROM has two banks. One Bank is as low bank that address range is 0100H-FFFFH.
Another bank is as high bank 10000H-1FFFFH. ROMÕs bank is selected port 0 (bit 0) of the KS16118.
5V power is applied to SRAM through VB. This model facsimile machine uses a Lithium battery.
A 1 kohm resistor in series with the positive battery terminal is for battery protection.
5-4 CODEC circuit with Modem-TX and RX signal path
This has PCB CODEC which has ablity that converts voice signal to A/D and is able to store is DRAM and convert
to voice signal passing through D/A transmission after scanning from voice digital stored in DRAM by DSP.
This has PRE-PGA(Programmable Gain Amplifier) that is able to amplift selectively among Mic input, remot
signal, rx signal.
This has ALC(Automatic Level Control) circuit has maximum 42dB gain to be convenient for recording using Mic.
This have two comparator having 1.25V reference voltage and two universal opamp.
This has 1 W speaker drive amplifir that is able to drive 8 ohm speaker.
Because MX93000AFCÕs control uses synchronous communication port, that is fast in action is convenient.
Page 23

Circuit Description
SF150T 5-7
5-5-1 DSP
This circuit consists of host interface, memory
interface, CODEC interface.
receives data to the compressed voice data to and
from KS16118.
Memory interface sends and receives data to the
compressed voice data to and from DRAM to play
back and record voice data.
DSP communicates with host KS16118 through host
interface.
5-5-2 Recording Path
The voltage is supplied with MIC as using the
MX93000AFC's Vref Voltage (2.25V), and the voltage
entering into MIC is trasmitted to electric signal and
enters into MX93000AFC's MIC terminal.
Input signal is amplified by MX93000AFC's ALC
until maximum 26dB (Max. 3VP-P) according to
signal size.
The signal enters into PCM CODEC that converts to
D/A and compresses in the DSP Chip and stores in
DRAM.
5-5-3 Play Path
The signal stored in DRAM is decomressed in DSP
and enters into MX93000AFC.
Input signal is converted to D/A again and is
amplified by LIU-DRV amplifier and comes into
LOUT terminal through or comes into terminal
after being attanuated by ATT (Electronic Volume)
or SPK-DRV.
5-5-4 Voice Backup
+5V is supplied for DSP or voice memory through
VBT when power is on.
When power is off, +5V is supplied from the 9V
backup battery.
When supply voltage is "ON", U9(5V Voltage
Regulator) makes 5V Supply Voltage.
The signal is supplied with DSP or DRAM and it
caused that the data is protected.
When supply voltage is "OFF", U9 makes 5V Voltage
as using the 9V Battery.
And then the voltage is used to "backup supply
voltage" in DSP or DRAM.
If the supply voltage were "OFF" as using the full
charged 9V Battery, voice data is usually protected
for twenty hours.
5-5 TAD
TAD circuit consists of a voice coprocessor to record and play voice messages and voice memory.
1) TX CIRCUIT
The output signal coming from internal modem
KS16118 enters MX93000AFC through AUX2
terminal after amplfied by OP AMP U1.
That signal passes through internal switch, is
amplified by LIN-DRV amplfier and is sent to LIU
board through LOUT terminal.
2) RX CIRCUIT
The signal goming into LIU terminal through LIU
board is amplified by MX93000AFC's PRE-PGA,
passes through internal switch and goes into FILT
terminal.
After the singal is diminished by OP AMP U1, it
enters internal modem of KS16118.
Page 24

Circuit Description
5-8 SF150T
5-6-1 FAX section
MODEM/LINE INTERFACE
This is the path for data and control signals.
¥ CML201 relay: switches telephone line between
FAX and telephone circuits.
¥ U201 pin 3 TIT: single-ended input for
transformer T202.
¨ TIT: Transmit Input from Transformer
¥ U201 pin 40 ROT : Output for driving a
transformer T203 with an AC impedance
exceeding 10Kohm.
¨ ROT: Receive Output Transformer
¥ C212: DTMF and CNG detect path to T201
20Kohm winding under idle conditons; and DC
blocking for 20Kohm winding.
¥ AC impedance: the AC impedance of U201 (I-
LIU) is set at 1000ohm by external capacitor
C228 at U201 pin 8 CI (Complex Impedance
input) port. With an external resistor (R244) at
U201 pin 34 ACI port it can be programmed to
600ohm. And U201 pin 35 CS (Current Shunt
control output) port is N-channel open drain
output to control the external high power shunt
transistor for synthesizing AC and DC
impedance.
¥ DC conditions : normal operating mode is from
15mA to 100mA. An operating mode with
reduced performance is from 5mA to 15mA. In
the line hold range from 0mA to 5mA the device
is in a power down mode and the voltage at
U201 pin 37 LI (Line Input) port is reduced to a
maximum of 3.5V. The DC characteristic is
determined by the voltage at U201 pin 37 LI port
and a R215 resistor between U201 pin 37 LI and
pin 39 LS port. It can be calculated by the
following equation : VLS = VLI + ILINE X R215.
RING DETECT
¥ U201 pin 28(MO) is ring melody output port and
this signal drive the Q207 which drive the
FET201 which drive Photo coupler U204 for
artificial ring.
MF DIAL (Same as telephone section)
¥ U201 pin 2 DMS(Dial Mode Selection) port is set
to VDD by R227 It is M/B ratio 33:66, and no
power operation mode conducts only DP.
¥ MF signal appears (tone level of low group :
typical -14dBm) at U201 pin 4 MFO(DTMF
Generator Output). This signal is leveled by
R226, R225 and C239, then to amplier U201 pin 9
MFI(DTMF Amplier Input).
¥ Line dial signals appear at U201 pin 39 LS(Line
Current Sense Input).
DP DIAL (Same as Telephone section)
¥ U201 pin 2(DMS) is set to Vdd(33/67) or
VSS(40/60) by R227 or R228 resistor.
¥ Dial pulses originate at U201 pin 27(DPn), which
toggles Q205, which drives Q201. The resulting
intermittent voltage interrupts the telephone
line.
¥ Pulse M/B ratio is set by U201 pin 2 MDS port.
Vdd = 33/66, and Vss = 40/60.
¥ U201 pin 35 CS port : Modulation of line voltage
and shorting the line during make period of
pulse dialling.
LLC (Line Loss Compensation) / LOOP
CURRENT DETECT
¥ When the LLC pin option. it is activated, the
transmit and receive gains for both I/O are
decreased 6dB at line currents above 20mA
when the U201 pin 31 LLC is connected to
AGND, and from 75mA when this pin is
connected to VDD. The LLC is deactivated
when LLC pin is connected to VSS.
¥ When CML201 or Hook Switch switches to
telephone line, U201 on the LIU board and CPU
(U1) on the Main board begin communication.
U201 sends an <Ack> message containing the
line current information to recognize a parallel
phone.
5-6 LIU PBA
The LIU (Line Interface Unit) interfaces the MODEM and telephone to the telephone line. The FAX and
telephone portions of the LIU are active with machine power on. When machine power is off, only the
telephone circuitry operates, powered by telephone line voltage. The FAX portion of LIU consists of the
interface between MODEM and telephone line; and the circuits for DC loop feeding, DP signal, loop current
and ring detect. The telephone portion is divided into ringer, dialling, and speech circuits. Refer to the
schematic and connection diagram sections of this manual.
Page 25

Circuit Description
SF150T 5-9
Serial interface
¥ U201 pin 11 RXD: Schmitt trigger input
(threshold = 2.5V) to serial interface.
¥ U201 pin 29 TXD: Open drain output from serial
interface.
¥ The communication is standard UART :
Baud Rate 9600
Start Bit 1
Stop Bit 1
Data Bits 8
Parity Bit None
LSB is transferred prior to MSB.
5-6-2 Telephone Section
RINGER CIRCUIT
¥ When a ringing signal is applied to the line, Vdd
of U201 (I-LIU) is charged via an external path.
After Vdd has reached the operating voltage the
oscillator starts and U201 detects the ring
frequency.
After a valid ring frequency is applied to the
U201 pin 25 RFD (Ring Frequency
Discrimination) port, the ring melody generator
of U201 sends out a 3-tone melody via U201 pin
28 MO (Ring Melody Output) port.
¥ U201: I-LIU and associated components.
¥ Ring frequency passes through DC blocking
capacitor C206 (C205 for Switzerland or Austria)
and Zener-diode ZD205 (ZD209 for Switzerland
or Austria) to U201 pin 25 RFD port.
¥ Line ring voltage passes through DC blocking
capacitor C201, current limit resistor R205,
bridge diode BD201, CML relay, and Hook
Switch to FET201 (BS170) pin 3, C214, ZD203
and R246.
¥ The ring frequency discriminator of U201
assures that only signals with a frequency
between 13Hz and 70Hz are regarded as valid
ring signals.
¥ When a valid ring signal is present for at least
73ms, the ring melody generator (pin 28, MO) is
activated and remains active as long as a valid
ring signal is present.
¥ U201 filters the ring signals and output is pin 28
(MO).
¥ The 3 basic melody frequencies are : F1 = 880 Hz,
F2 = 1067 Hz, and F3 = 1333 Hz. The repetition
rate is set to 4 which means that the sequence of
F!, F2, F3, F1, F2, F3 is repeated 4 times within a
second.
Speech Circuit
¥ U201 (STI9510) and associated components.
¥ Handset transmitting circuit: Handset
transmitter audio (Condensor MIC.) is filtered
by R240, C232, C224, C225, C226, C227, C229 and
C230, and then amplified by U201 pin 32 and 33
(M1, M2).
¥ Handset receiving circuit: Handset receiver
(Dynamic unit) is filtered by R229, C241, C209,
C203 and C231, and then applied to U201 pin 1
(ROH) and VSS.
¥ U201 pin 39 (LS) is audio output to telephone
line.
Sidetone Circuit
¥ Sidetone audio characteristics are controlled by
R238, R235, R237, R239, and C202 connected to
U201 pin 7 STB.
Page 26

5-7 OPE PBA
OPE PBA serves as the Machine-User interface.
The OPE operates on a time-sharing basis. As shown below, OPE keys and LED control are divided into
key scanning, LED displaytime and display time. On each 2ms interrupt rising edge, OPE line turns off
after 125µsec initial delay, and after 1 CPUCLK cycle, LEDCTL-LOW makes LED turn off. During the next
128 CPUCLK cycles, OPE KEY STROBE is maintained and during the next 1 CPUCLK KEY, INPUT is
scanned and stored in KEY buffer.
After key scanning, through the OPO0-3 port the upper and lower nibble data are transferred to the LCD
module as LCDCTL goes high.
After key displaying DATA on LCD, LED lamps turn on with LEDCTL-ON.
OPO0-4 : Used as key board strobe or LCD, LED driver
OPO5-7 : Used as key board strobe.
OPI0-3 : Key scanning ports from key matrix.
7
01
2345
67
0
LED0
LED0
LED0 LED0 LED0
LED0 LED0 LED0 LED0
LED0
LED1
LED1
LED1 LED1 LED1
LED1 LED1 LED1 LED1
LED1
LED2
LED2
LED2 LED2 LED2
LED2 LED2 LED2 LED2
LED2
LED7
LED7
LED7 LED7 LED7
LED7 LED7 LED7 LED7
LED7
C2MS
125µsec
LEDCTL
LEDCTL
LED
OFF
LED
ON
LCDCS
LCDCS
LCD HI
LCD H
LCD LO
LCD L
KB STROBE
[X] = Time Interval of TSTCLK's
IRQ2MS
IRQ2MS
OPO0
OPO1
OPO2
OPI0
OPI1
OPI2
OPI7
OPI[3:0]
OPO7
(7)
(7)
(128)
(12)
(16)
(1) (1)
(3)
(1) (7) (1)
LED0
LED1
LED2
LED7
LCD DB0H LCD DB0L
LCD DB1L
LCD DB2L
LCD DB1H
LCD DB2H
5-10 SF150T
Page 27

Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
YY
Y
N
N
NN
YY Y
NN N N
N
N
6. Troubleshooting
6-1. Initial Checkout and Overall Troubleshooting Flow
SF150T 6-1
Plug in the power
cord
Load document in
feeder
Copy OK ?
OGM play back ?
Call machine from
another phone
Auto Answer
OK ?
ICM Recording ?
Manual
operation OK ?
OGM Recording
RX OK ?
Document feed ? Push 'START' Key CIS ON ?
System
initialized ?
See Section 6-3 See Section 6-2
See Section 6-5See Section 6-4
See Section 6-5
See Section 6-8
See Section 6-7
See Section 6-6
See Section 6-9 See Section 6-10
A
Power Supply
OK ?
Start
Page 28

Troubleshooting
6-2 SF150T
YY
N N
Lift Handset
off hook
Dial tone OK ? TX OK ?
See Section 6-11
End
See Section 6-12
A
Page 29

Troubleshooting
SF150T 6-3
6-2. Check Power Supply
N
N
Check AC socket
voltage
Power cord
connected ?
Start
220 - 240 VAC?
Y
Y
END
Connect as required Notify customer
N N
N
Check
Power Cord
Continuity
Replace Cord Replace Fuse Replace Q1
YY
Fuse OK ?
Q1 OK ?
Y
N
R5 changed
value ?
Remove short
End
Page 30

Troubleshooting
6-4 SF150T
6-2-1 No + 5 V
Y
NN
output shorted ?Start
N
Y Y
N
Remove short
Y
Replace D4
Check PCB Pattern Replace U2
Check CON 1
Check
U2 Input voltage
D4 Open or
Shorted ?
DC 6 V Check U2 ?
End
6-2-2 No -12 V
YY
N N
output shorted ?
Start
N
Y Y
N
Remove short Replace D5
Check PCB Pattern Replace U1
Check CON1
Check
U1 Input voltage
D5 Open or
Shorted ?
-15 VDC U1 Output ?
End
Page 31

Troubleshooting
SF150T 6-5
Y
Y
N
N
output shorted ?
Start
N
Y Y
N
Remove short
Replace D3
OVP operation
Restart Replace Q3
Check CON1
D3 Open or
Shorted ?
Check
OVP operation
Q3 OK ?
End
6-2-3 No + 24 V
6-2-4 + 24 V TPH Doesn't output
YN
Check
C/S port short ?
Start
N
Y
Remove short Replace Q5
Check CON1
Q5 OK ?
End
Page 32

Troubleshooting
6-6 SF150T
6-3. System Not Initialized
N
NG
N
N
NG
OK
N
N
N
Step motor driving
Start
Y
Y
Y
Y
OK
NG
Y
Y
See Section 6-2-2
Replace P5 Harness
or OPE PBA
Replace U3
Replace U7
Fax Engine IC
Replace U7
Fax Engine IC
Replace Main PBA
Replace U14
Motor Driver
Replace
X2 XTAL
Check
U3 Pin 5
= "High"
Check U3 Pin 6
(above +2.25 V)
Check
P5 Harness or OPE
PBA
Check 12 MHz
Clock U7-37
Check 24 MHz
Clock U7-129
O.K ?
O.K ?
Check
Vcc ³ 4.75 V
P1-4 (+5V)
P1-3 (GND5)
End
End
Page 33

Troubleshooting
SF150T 6-7
6-4 Document Not Loading
Start
P7-1 "L" ?
Check 24 V
P6-5, 6 ?
Insert Document
Replace Motor
END
Replace U14
Replace U7
Replace D-DET PBA
or P7 Harness
See Section 6-2
P6-1, 2, 3, 4
Motor Strobe
U7-49, 50, 51, 52
Motor Strobe
Y Y
OK
OK
NG
NG
N
N
Page 34

Troubleshooting
6-8 SF150T
6-5 No Copy Mode Operation
Start
TPH Test O.K ? CIS Test O.K ? Is Memory Clear ? Reload Document
Check U7-55
"H"
Check P1-10
"L"
Check +24 V
P1-8, 9 ?
Replace Main PBA
P2-4, 6, 8, 10
TPH strobe
Replace U7 Replace U5 See Section 6-2 Replace U7
P2-7, 11, 12 Replace TPH
Restart
Restart
Replace U5
Replace U7
Replace Main PBA
O.K ?
O.K ?
B
Y
Y
Y
Y Y Y Y
Y
N
N N N N
N
N
N
N N
Y Y
Page 35

Troubleshooting
SF150T 6-9
6-5 Continued
B
CIS LED on ?
Check P3-9
CLED ² 1 V
U7-87
"H"
Check P3-8
CLK1: 300 kHz
Check P3-6
START Signal
P3-4
- 12 V ?
Replace U7 Replace U7
Replace CIS Replace CIS
Replace U7
Replace Q2
See Section 6-2
Y
Y
H
Y
N
L
N
NG NG
OKOK
Page 36

Troubleshooting
6-10 SF150T
6-6. OGM Not Playing Back
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
Y
N
N
NN
N
N
Start End
End
OGM Play Back ?
Speaker On
Check
Mic signal from
P7-4, 5
Check
signal from
U3-16 ?
Replace main
board
End
Replace U3
Check
signal from
U3-29, 31 ?
Replace speaker
Replace Mic.
End
Check
P7 Harness ?
Page 37

Troubleshooting
SF150T 6-11
6-7. ICM Not Recording
Y
Y
Y
N
N
N
Start
End
Call machine
from other phone
ICM
Recording
mode ?
Check LIU board
OK ?
Replace LIU
board
Replace main
board
ICM Playback ?
Page 38

Troubleshooting
6-12 SF150T
6-8. Malfunction in Auto Answer
Y
N
Y
N
Start
Call machine from
another phone
Auto answer ?
Check signal
P4-16
Replace LIU board
END
Replace U7
+5V
0V
?
Page 39

Troubleshooting
SF150T 6-13
6-9. Malfunction in Manual Receiving
N
Y
Y
Y
N
N
Start
Lift handset
Press START
Machine goes
on-line ?
Check U7-45
(Hook Event)
OK ?
Replace U7
Replace main
board
End
Check LIU board
OK ? Replace LIU board
Page 40

Troubleshooting
6-14 SF150T
6-10. Automatic Receive Malfunction
Y
Y
Y
Y
N
N
N
N
Start
Call fax machine
Rings exceed
ÒRings To AnswerÓ
Setting ?
Auto Answer ?
Replace:
Main Board
Replace LIU Board
Go To 6-9
ÒManual Receive
MalfunctionÓ
Main Board
P4-18, 19
TX/RX
Receiving Data ?
Return
Machine to
Customer
Page 41

Troubleshooting
SF150T 6-15
6-11. No Dial Tone
NG
OK
OK
Y
H
OK
NG
NG
OK
N
L
NG
Start
Request
Telephone
Service
Check/Replace:
Speaker
Main Board U14
P4, 205, 206
Replace U3
Lift Handset
Dial tone ?
Service OK ?
Main PCB
U7-54
CML1
Main PCB
U3-29, 31
SPK_OUT
Dial tone ?
Return
machine to
Customer
Press
OHD/V.REQ.
Replace
Telephone Cord
Use a phone to check
service at wall jack
Test
Telephone
Cord
Check / Replace:
Handset cord
Handset
Hook Switch
LIU U201
LIU Board
Page 42

Troubleshooting
6-16 SF150T
6-12. Transmit Failure
Y
Y
N
N
Start
Load document
Feed OK ?
Dial Receiving
Machine
Transmit
Begin ?
Replace:
LIU board
Main Board
Return
Machine to
Customer
Chart 6-4
Document
Not Loading
Page 43

8-1SF150T
1
2
S4
4
8
10
11
S2
S2
S3
5
S1
S1
6
7
12
9
3
8. Exploded Views and Parts Lists
8-1. Total Assembly
Page 44

8-2 SF150T
Exploded Views and Parts Lists
Total Assembly Parts Lists
Location No. Description SEC. Code Q'ty Remark
1 ASS'Y-OPE UNIT JF96-01296A 1
2 ASS’Y-TOP COVER JF96-01297A 1
3 SPACER JF72-40611A 1
4 GUIDE-TX JF72-41122Z 1
5 PBA-LIU JF92-00843Q 1
6 REAR-BRKT JF70-10681A 1
7 PBA-MAIN JF92-00842E 1
8 SMPS-V2, AC/DC JF44-10059A 1
9 ASS’Y-BASE UNIT JF96-01298A 1
10 ASS’Y-MAIN CHASSIS UNIT JF96-01253A 1
11 ASS’Y-HANDSET JF96-01262A 1
12 CURL-CORD JF39-60075A 1
S1 SCREW, TAPTITE, BH, +, M3, L8 6003-000015 11
S2 SCREW, TAPTITE, BH, +, M3, L6 6003-000261 2
S3 SCREW, TAPTITE, BH, +, M3, L6 6003-000115 2
Page 45

Exploded Views and Parts Lists
8-2. Ass'y OPE Unit
SF150T 8-3
2
1
3
4
5
6
7
10
11
9
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
S1
S2
S3
26
8
12
27
Page 46

Ass'y OPE Unit Parts Lists
Exploded Views and Parts Lists
8-4 SF150T
Location No. Description SEC. Code Q'ty Remark
ASS'Y-OPE UNIT JF96-01296A 1
1 OPE COVER JF72-42016Z 1
2 LCD-WINDOW JF75-11004F 1
3 KEY-ONETOUCH JF72-42021A 1
4 KEY-OHD JF72-42022A 1
5 KEY-STOP JF72-42029A 1
6 KEY-START JF72-42028A 1
7 KEY-TEL JF72-42026A 1
8 KEY-TAD(A) JF72-42056A 1
9 KEY-TAD(B) JF72-42057A 1
10 KEY-MENU JF72-42020A 1
11 KEY-RESOLUTION JF72-42018B 1
12 KEY-RECEIVE JF72-42017B 1
13 KEY-ANSWER JF72-42019M 1
14 RUBBER-CONTACT JF73-40521A 1
15 DISPLAY-LCD JF07-20061A 1
16 CBF-WIRE, MAIN-OPE, 18 P JF39-41081A 1
17 CBF-WIRE, LIU-OPE, 7 P JF39-40957A 1
18 PBA-OPE JF92-00844B 1
19 CHASSIS OPE UNIT JF70-10863A 1
20 BRKT-TPH UNIT JF70-10861B 1
21 GUIDE-TPH(R) JF70-10679A 1
22 PRINT HEAD-THERMAL JF47-30069B 1
23 PBA-P.EMPTY JF92-00704B 1
24 GUIDE-TPH(L) JF70-10679B 1
25 CBF-WIRE, MAIN-TPH, 14P JF39-40955A 1
26 BRUSH-ANTISTATIC JF75-10650A 1
27 FLAT CABLE, OPE-LCD JF39-41018A 1
S1 SCREW, TAPTITE, PWH, +, B, M2. 6003-000193 11
S2 SCREW-MACHINE, BH, +, M3, L4 6001-000125 4
S3 SCREW, TAPTITE, BH, +, B, M3, L 6003-000015 2
Page 47

Exploded Views and Parts Lists
SF150T 8-5
8-3. Ass'y COVER TOP
1
2
3
4
6
7
8
S1
9
10
S2
S3
S3
11
12
5
Page 48

Exploded Views and Parts Lists
8-6 SF150T
Location No. Description SEC. Code Q'ty Remark
ASSEMBLY-COVER TOP JF96-01297A 1
1 TOP COVER JF72-42015A 1
2 HINGE-OPE(R) JF70-10676A 1
3 COVER-SPRING(R) JF70-40562A 1
4 HINGE-BRKT(R) JF70-10677A 1
5 BATTERY-COVER JF72-42027A 1
6 HINGE-BRKT(L) JF70-10677B 1
7 COVER-SPRING(L) JF70-40562B 1
8 HINGE-OPE(L) JF70-10676B 1
9 SWITCH-HOOK, 48 V, 200 mA 3409-000117 1
10 PBA-HOOK JF92-00845C 1
11 SPEAKER, 1 W, 8 OHM, 83dB 3001-001044 1
12 UNIT-FIXING BRKT GB70-10500A 1
S1 SCREW, TAPTITE, BH, +, M3, L6 6003-000261 3
S2 SCREW, TAPTITE, BH, +, M3, L8 6003-000015 2
S3 SCREW, TAPTITE, PWH, +, B, M2.5, L6 6003-000193 2
Ass'y COVER TOP Parts Lists
Page 49

Exploded Views and Parts Lists
SF150T 8-7
8-4. Ass’y Handset
3
2
S1
1
4
5
6
7
8
9
Page 50

Exploded Views and Parts Lists
8-8 SF150T
Ass’y Handset Parts Lists
Location No. Description SEC. Code Q'ty Remark
ASS'Y-HANDSET JF96-01262A 1
1 HANDSET-LOWER JF72-42014A 1
2 AUDIO-RECEIVER, 160 OHM 3009-001001 1
3 HOLD-DUMMY GB72-40792A 1
4 RUBBER-MIC JF73-40501A 1
5 PBA-H/S MIC JF92-00625A 1
6 CBF-HARNESS JF39-40834A 1
7 WEIGHT-BALANCE JF70-10864A 1
8 HANDSET-UPPER JF72-42013A 1
9 RING-OP, ID17, OD35 6044-000138 1
S1 SCREW, TAPTITE, PH, +, B, M3, 6003-000168 1
Page 51

Exploded Views and Parts Lists
SF150T 8-9
8-5. Ass'y Base
5
6
7
8
S1
2
1
3
4
10
9
Page 52

Exploded Views and Parts Lists
8-10 SF150T
Ass'y Base Parts Lists
Location No. Description SEC. Code Q'ty Remark
ASS'Y-BASE JF96-01298A 1
1 CBF-WIRE, MAIN-CIS/MODE JF39-41062A 1
2 MICRO-SWITCH 3405-000166 1
3 STEP-MOTER, 7.5 DEG, 24 V 3101-000171 1
4 ASS’Y-MAIN CHASSIS UNIT JF96-01253A 1
5 BASE JF72-42025A 1
6 PBA-D’DET JF92-00888A 1
7 CBF-WIRE, HANDSET-LIU JF39-41066A 1
8 RUBBER-FOOT JF73-10002A 2
9 MIC-CONDENSOR 3003-000120 1
10 MIC-ADAPTER GB72-40770A 1
S1 SCREW, TAPTITE, BH, +, M3, L6 6003-000261 2
Page 53

Exploded Views and Parts Lists
SF150T 8-11
8-6. Harness
1
2
3
11
3'
5
9
4
4'
6
8'
8
1'
2'
15
6'
4''
10'
11'
10
12
5'
7'
13
14
7
14'
Page 54

Exploded Views and Parts Lists
8-12 SF150T
Harness Parts Lists
Location No. Description SEC. Code Q'ty Remark
1 CBF-WIRE, MAIN-TPH, 14 P JF39-40955A
2 CBF-WIRE, MAIN-OPE, 18 P JF39-41081A
3 CBF-WIRE, LIU-OPE, 7 P JF39-40957A
4 CBF-WIRE, MAIN-LIU, 22 P JF39-41063A
5 CBF-WIRE, LIU-HANDSET JF39-41066A
6 CBF-WIRE, MAIN-CIS/MODE JF39-41062A
7 CBF-WIRE, MAIN-D.DET, MIC, 5 P JF39-41078A
8 STEP-MOTER, 7.5 DEG, 24 V 3101-000171
9 CBF-WIRE, LIU-HOOK JF39-41080A
10 CBF-WIRE, POWER-MOTOR JF39-40963B
11 CBF-WIRE, POWER-TOP COVER JF39-40962B
12 CURL CORD JF39-60075A
13 CABLE CLAMP 6502-001026
14 CBF-WIRE, MAIN-BATTERY, 2 P JF39-41082A
15 CBF-WIRE, MAIN-SPEAKER, 2 P JF39-41079A
Page 55

SF150T 7-1
Ref. No. Description SEC Code Remark
PBA, PCB Assembly, MAIN JF92-00842E
- Capacitors -
C1 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, J, 50 V, 2012 2203-000239
C2 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C3 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, J, 50 V, 2012 2203-000239
C4 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, J, 50 V, 2012 2203-000239
C5 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C7 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C8 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C9 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C10 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C11 Ceramic, Chip, 33 nF, K, 50 V, 2012 2203-000802
C12 Ceramic, Chip, 33 nF, K, 50 V, 2012 2203-000802
C13 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C14 TA, Chip, 1 µF, M, 10 V, 3216 2404-000291
C15 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C16 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C17 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C18 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C19 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C20 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C21 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C22 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, J, 50 V, 2012 2203-000239
C23 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C24 Ceramic, Chip, 10 pF, 0.05 pF, 50 V 2203-000281
C25 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C26 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C27 Ceramic, Chip, 18 pF, J, 50 V, 2012 2203-000429
C28 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, K, 50 V, 2012 2203-000444
C29 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, K, 50 V, 2012 2203-000444
C30 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C31 Ceramic, Chip, 39 pF, J, 50 V, 2012 2203-000858
C32 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C33 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C34 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
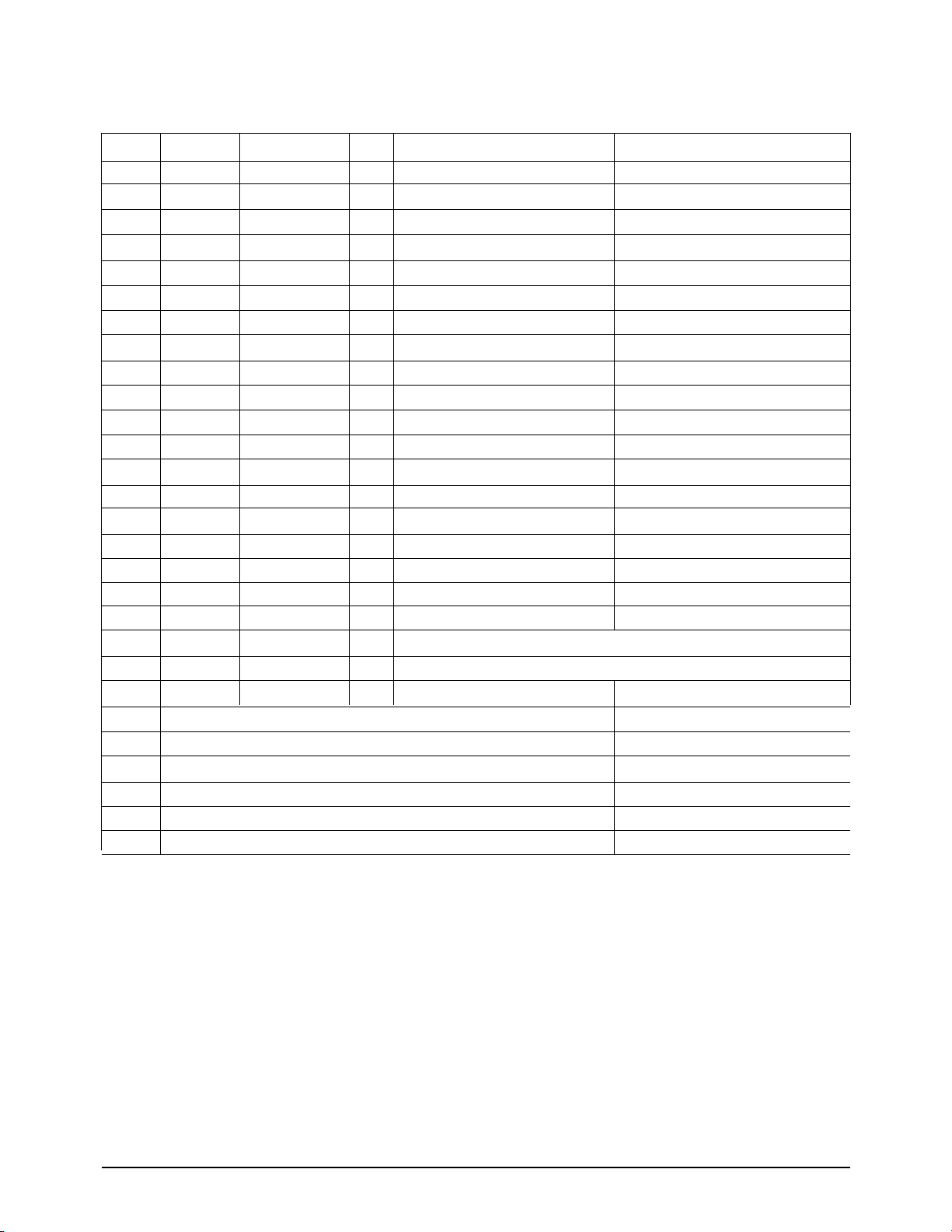
7 Electrical Parts List
7-1 MAIN PBA
Capacitor / Resistor tolerance:
D: 0.5 %, F: 1 %, G: 2 %, J: 5 %, K: 10 %, M: 20 %, Z: +80 %, -20 %
Page 56

Electrical Parts List
SF150T7-2
Ref. No. Description SEC Code Remark
C35 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, K, 50 V, 2012 2203-000444
C36 Ceramic, Chip, 18 pF, J, 50 V, 2012 2203-000429
C37 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C38 TA, Chip, 1 µF, M, 10 V, 3216 2404-000291
C39 TA, Chip, 1 µF, M, 10 V, 3216 2404-000291
C40 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C43 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, K, 50 V, 2012 2203-000444
C44 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, K, 50 V, 2012 2203-000444
C45 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, K, 50 V, 2012 2203-000444
C46 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, K, 50 V, 2012 2203-000444
C47 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C48 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, J, 50 V, 2012 2203-000239
C49 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C50 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C51 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, K, 50 V, 2012 2203-000444
C52 Ceramic, Chip, 10 pF, 0.5 pF, 50 V, 2012 2203-000281
C53 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C54 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C55 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C56 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C57 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C58 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C59 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C60 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C62 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C63 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C64 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C65 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C66 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, K, 50 V, 2012 2203-000444
C67 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, K, 50 V, 2012 2203-000444
C68 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, K, 50 V, 2012 2203-000444
C69 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, K, 50 V, 2012 2203-000444
C70 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C71 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, K, 50 V, 2012 2203-000444
C72 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, K, 50 V, 2012 2203-000444
C73 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, J, 50 V, 2012 2203-000239
C74 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C75 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, J, 50 V, 2012 2203-000239
C76 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C77 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C78 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C79 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, J, 50 V, 2012 2203-000239
Page 57

Electrical Parts List
SF150T 7-3
Ref. No. Description SEC Code Remark
C80 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, J, 50 V, 2012 2203-000239
C81 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, J, 50 V, 2012 2203-000239
C82 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, J, 50 V, 2012 2203-000239
C83 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, J, 50 V, 2012 2203-000239
C84 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, J, 50 V, 2012 2203-000239
C85 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, Z, 50 V, 2012 2203-000192
C87 Electrolytic, 10 µF, M, 25 V 2401-000448
C88 Electrolytic, 10 µF, M, 25 V 2401-000448
C89 Electrolytic, 22 µF, M, 25 V 2401-000943
C90 Electrolytic, 10 µF, M, 25 V 2401-000448
C91 Electrolytic, 10 µF, M, 25 V 2401-000448
C93 Electrolytic, 3.3 µF, M, 50 V, BP 2401-001014
C94 Electrolytic, 10 µF, M, 25 V 2401-000448
C95 Electrolytic, 10 µF, M, 25 V 2401-000448
C97 Ceramic, Chip, 220 nF, K, 50 V, 2012 2203-000609
- Connectors -
P1 Header, 1 Wall, 10 P, 1R, 2.5 mm, STR 3711-002034
P2 Header, Box, 14 P, 1R, 2 mm, STR 3711-002815
P3 Header, Box, 12 P, 1R, 2 mm, STR 3711-002813
P4 Header, 22 P, 2R, 2 mm, STR 3711-002002
P5 Header, 18 P, 2R, 2 mm, STR 3711-002000
P6 Header, 3 Wall, 6 P, 1R, 2 mm, STR 3711-000496
P7 Header, 3 Wall, 5 P, 1R, 2 mm, STR 3711-000484
P8 Header, 3 Wall, 2 P, 1R, 2 mm, STR 3711-000444
P9 Header, 3 Wall, 2 P, 1R, 2 mm, STR 3711-000443
SOK1 Socket-IC, 32 P, DIP, 2.54 mm 3704-000255
- Diodes -
D3 Switching, 100 V, 200 mA, 225 mW, 4 ns 0401-000116
D4 Switching, 100 V, 200 mA, 225 mW, 4 ns 0401-000116
D5 Switching, 100 V, 200 mA, 225 mW, 4 ns 0401-000116
D6 Switching, 100 V, 200 mA, 225 mW, 4 ns 0401-000116
D7 Switching, 100 V, 200 mA, 225 mW, 4 ns 0401-000116
D8 Switching, 100 V, 200 mA, 225 mW, 4 ns 0401-000116
ZD1 Zener, PTZ5.1B, 5.1V-5.7V, 1W 0403-000464
ZD2 Zener, PTZ12B, 5.1 V, 12.0V-13.5V, 1W 0403-001142
ZD3 Zener, 3.9 V, 5 %, 1 W, 1N4730 0403-000521
ZD4 Zener, 3.9 V, 5 %, 1 W, 1N4730 0403-000521
- ICs -
U1 4558, SOP, 8P 1201-000189
U2 74HC32, OR Gate, SOP, 14 P 0801-000410
U3 MX93000A, QFP, 44 P 1205-001333
U4 SRAM, 62256, 32k x 8 bit, DIP, 28 P 1106-001037
Page 58

Electrical Parts List
SF150T7-4
Ref. No. Description SEC Code Remark
U5 EPROM, 27010, 128k x 8 bit, DIP, 32 P 1102-000191
U6 44C1000, 1M x 4 bit, SOJ, 20 P 1105-000133
U7 Micro Computer JF09-10053A
U8 6305, 16 bit, QFP, 80 P 0904-001068
U9 Reset, 78L05, SOT-89, 3 P 1203-001037
U10 74HC245, Transceiver, SOP, 20 P 0801-000696
U11 Photo-Coupler, PC817, 200 mW, DIP-4 0604-000119
U12 Photo-Coupler, PC817, 200 mW, DIP-4 0604-000119
U14 TR-Array, UL2003L, NPN, SOP-16, ST 0506-000182
- Resistors -
R1 Chip, 20 kohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000546
R2 Chip, 205 kohm, F, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-007434
R3 Chip, 15 kohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000409
R4 Chip, 75 kohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000002
R5 Chip, 46.4 kohm, F, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000917
R6 Chip, 18 kohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000457
R8 Chip, 390 kohm, F, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-001663
R9 Chip, 150 kohm, F, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000392
R10 Chip, 2.2 kohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000493
R11 Chip, 330 kohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000757
R12 Chip, 4.7 kohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000872
R13 Chip, 470 ohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000931
R14 Chip, 330 kohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000757
R15 Chip, 470 ohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000931
R16 Chip, 470 ohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000931
R17 Chip, 10 kohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000300
R18 Chip, 100 ohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000290
R19 Chip, 100 ohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000290
R20 Chip, 10 kohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000300
R21 Chip, 100 ohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000290
R22 Chip, 51 ohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-007162
R23 Chip, 10 kohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000300
R24 Chip, 1 kohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000468
R25 Chip, 118 kohm, F, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000325
R26 Chip, 86.6 kohm, F, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-001220
R27 Chip, 86.6 kohm, F, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-001220
R28 Chip, 34.8 kohm, G, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000784
R29 Chip, 34.8 kohm, G, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000784
R30 Chip, 86.6 kohm, F, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-001220
R31 Chip, 300 ohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000728
R32 Chip, 787 kohm, F, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-002888
R33 Chip, 300 ohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000728
Page 59

Electrical Parts List
SF150T 7-5
Ref. No. Description SEC Code Remark
R34 Chip, 46.4 kohm, F, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000917
R35 Chip, 1 kohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000468
R36 Chip, 150 ohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000401
R38 Chip, 1 Mohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000477
R39 Chip, 3 kohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000844
R40 Chip, 10 kohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000300
R41 Chip, 10 kohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000300
R42 Chip, 100 kohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000282
R43 Chip, 20 ohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-001289
R44 Chip, 10 kohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000300
R45 Chip, 4.7 kohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000872
R46 Chip, 470 ohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000931
R47 Chip, 470 ohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000931
R48 Chip, 470 ohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000931
R49 Chip, 4.7 kohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000872
R50 Chip, 34.8 kohm, G, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000784
R51 Chip, 0 ohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000029
R52 Chip, 34.8 kohm, G, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000784
R53 Chip, 0 ohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000029
R54 Chip, 10 kohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000300
R55 Chip, 470 ohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000931
R56 Chip, 470 ohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000931
R57 Chip, 470 ohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000931
R58 Chip, 470 ohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000931
R59 Chip, 470 ohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000931
R60 Chip, 470 ohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000931
R61 Chip, 470 ohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000931
R62 Chip, 470 ohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000931
R63 Chip, 470 ohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000931
R64 Chip, 470 ohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000931
R65 Chip, 470 ohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000931
R68 220 ohm, J, 1/4 W 2001-000034
R69 Chip, 15 kohm, J, 1/10 W, 2012 2007-000409
- Miscellaneous -
Q1 Small Signal, KSA1182, PNP, 150mW 0501-000279
Q2 Small Signal, KSC5019, NPN, 750mW 0501-000385
Q3 Small Signal, KSC1623, NPN, 200mW 0501-000342
ARR2 Varistor, 600 V, 500 A, 7.0 x 3.3 mm, TP 1405-001009
ARR3 Varistor, 600 V, 500 A, 7.0 x 3.3 mm, TP 1405-001009
L1 Inductor, Chip, 3.3 µH, 5 % 2703-000185
L2 Inductor, Chip, 3.3 µH, 5 % 2703-000185
L3 Coil-Filter, 60 µH, 50 Mohm, 18 T JF27-60051A
Page 60

Electrical Parts List
SF150T7-6
Ref. No. Description SEC Code Remark
L4 Coil-Filter, 60 µH, 50 Mohm, 18 T JF27-60051A
L7 Coil-Filter, 60 µH, 50 mohm, 18 T JF27-60051A
L8 Coil-Filter, 60 µH, 50 mohm, 18 T JF27-60051A
L9 Coil-Filter, 60 µH, 50 mohm, 18 T JF27-60051A
MJ1 Modular-Jack, 6P/6C, Ivory 3722-000255
X1 Crystal, 32.768 kHz, 5 ppm 2801-001498
X2 Crystal, 24.00014 MHz, 50 ppm 2801-001528
X3 Crystal, 29.4912 MHz, 50 ppm 2801-001530
BAT Battery-LI, 3V, 210mAH, Button 4301-000108
BUZ1 Buzzer, 81 dB, 1.5 V, 70 mA, 2.731kHz 3002-000126
JP1 Wire, Jumper, 52 mm, AWG22
JP6 Wire, Jumper, 52 mm, AWG22
PCB PCB, MAIN, Blank
Page 61

Electrical Parts List
SF150T 7-7
Ref. No. Description SEC Code Remark
PBA, PCB Assembly, LIU JF92-00843A
- Capacitors -
C201 Electrolytic, 1 µF, M, 50 V, GP 2401-000597
C202 Electrolytic, 100 µF, M, 25 V, GP 2401-000310
C203 Electrolytic, 330 nF, M, 50 V, GP 2401-001087
C206 Film, MPEF, 1 µF, K, 250 V 2305-000505
C207 Electrolytic, 100 µF, M, 25 V, GP 2401-000310
C208 Electrolytic, 470 µF, M, 16 V, GP 2401-001368
C209 Electrolytic, 22 µF, M, 50 V, GP 2401-000966
C210 Electrolytic, 10 µF, M, 50 V, GP 2401-000486
C212 Film, MPEF, 15 nF, M, 630 V 2305-000199
C214 Electrolytic, 10 µF, M, 50 V, GP 2401-000486
C216 Film, PEF, 47 nF, K, 50 V 2301-000278
C217 Electrolytic, 1 µF, M, 50 V, GP 2401-000597
C218 Electrolytic, 100 nF, M, 50 V, GP 2401-000217
C220 Ceramic, Chip, 2.2 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000499
C221 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, J, 50 V 2203-000242
C222 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, J, 50 V 2203-000242
C223 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, J, 50 V 2203-000457
C225 Ceramic, Chip, 33 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000805
C226 Ceramic, Chip, 10 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000262
C227 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, J, 50 V 2203-000457
C228 Ceramic, Chip, 15 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000376
C229 Ceramic, Chip, 33 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000805
C230 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, J, 50 V 2203-000457
C231 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, K, 50 V 2203-001450
C232 Ceramic, Chip, 10 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000262
C233 Ceramic, Chip, 10 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000262
C234 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, J, 50 V 2203-000457
C235 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, J, 50 V 2203-000457
C236 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, J, 50 V 2203-000242
C239 Ceramic, Chip, 3.3 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000717
C240 TA, Chip, 1 µF, M, 10 V 2404-000291
C241 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, J, 50 V 2203-000457
C242 Ceramic, Chip, 10 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000262
C243 Ceramic, Chip, 15 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000376
C244 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, K, 50 V 2203-000242
C247 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, K, 50 V 2203-000242
C248 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, K, 50 V 2203-000242
C249 Ceramic, Chip, 68 nF, K, 50 V 2203-001145
7-2. LIU PBA
Page 62

Electrical Parts List
SF150T7-8
Ref. No. Description SEC Code Remark
PBA, PCB Assembly, LIU JF92-00843A
- Capacitors -
C201 Electrolytic, 1 µF, M, 50 V, GP 2401-000597
C202 Electrolytic, 100 µF, M, 25 V, GP 2401-000310
C203 Electrolytic, 330 nF, M, 50 V, GP 2401-001087
C206 Film, MPEF, 1 µF, K, 250 V 2305-000505
C207 Electrolytic, 100 µF, M, 25 V, GP 2401-000310
C208 Electrolytic, 470 µF, M, 16 V, GP 2401-001368
C209 Electrolytic, 22 µF, M, 50 V, GP 2401-000966
C210 Electrolytic, 10 µF, M, 50 V, GP 2401-000486
C212 Film, MPEF, 15 nF, M, 630 V 2305-000199
C214 Electrolytic, 10 µF, M, 50 V, GP 2401-000486
C216 Film, PEF, 47 nF, K, 50 V 2301-000278
C217 Electrolytic, 1 µF, M, 50 V, GP 2401-000597
C218 Electrolytic, 100 nF, M, 50 V, GP 2401-000217
C220 Ceramic, Chip, 2.2 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000499
C221 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, J, 50 V 2203-000242
C222 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, J, 50 V 2203-000242
C223 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, J, 50 V 2203-000457
C225 Ceramic, Chip, 33 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000805
C226 Ceramic, Chip, 10 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000262
C227 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, J, 50 V 2203-000457
C228 Ceramic, Chip, 15 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000376
C229 Ceramic, Chip, 33 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000805
C230 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, J, 50 V 2203-000457
C231 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, K, 50 V 2203-001450
C232 Ceramic, Chip, 10 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000262
C233 Ceramic, Chip, 10 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000262
C234 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, J, 50 V 2203-000457
C235 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, J, 50 V 2203-000457
C236 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, J, 50 V 2203-000242
C239 Ceramic, Chip, 3.3 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000717
C240 TA, Chip, 1 µF, M, 10 V 2404-000291
C241 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, J, 50 V 2203-000457
C242 Ceramic, Chip, 10 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000262
C243 Ceramic, Chip, 15 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000376
C244 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, K, 50 V 2203-000242
C247 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, K, 50 V 2203-000242
C248 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, K, 50 V 2203-000242
C249 Ceramic, Chip, 68 nF, K, 50 V 2203-001145
Ref. No. Description SEC Code Remark
C250 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, K, 50 V 2203-000242
Page 63

Electrical Parts List
SF150T 7-9
Ref. No. Description SEC Code Remark
PBA, PCB Assembly, LIU JF92-00843A
- Capacitors -
C201 Electrolytic, 1 µF, M, 50 V, GP 2401-000597
C202 Electrolytic, 100 µF, M, 25 V, GP 2401-000310
C203 Electrolytic, 330 nF, M, 50 V, GP 2401-001087
C206 Film, MPEF, 1 µF, K, 250 V 2305-000505
C207 Electrolytic, 100 µF, M, 25 V, GP 2401-000310
C208 Electrolytic, 470 µF, M, 16 V, GP 2401-001368
C209 Electrolytic, 22 µF, M, 50 V, GP 2401-000966
C210 Electrolytic, 10 µF, M, 50 V, GP 2401-000486
C212 Film, MPEF, 15 nF, M, 630 V 2305-000199
C214 Electrolytic, 10 µF, M, 50 V, GP 2401-000486
C216 Film, PEF, 47 nF, K, 50 V 2301-000278
C217 Electrolytic, 1 µF, M, 50 V, GP 2401-000597
C218 Electrolytic, 100 nF, M, 50 V, GP 2401-000217
C220 Ceramic, Chip, 2.2 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000499
C221 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, J, 50 V 2203-000242
C222 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, J, 50 V 2203-000242
C223 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, J, 50 V 2203-000457
C225 Ceramic, Chip, 33 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000805
C226 Ceramic, Chip, 10 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000262
C227 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, J, 50 V 2203-000457
C228 Ceramic, Chip, 15 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000376
C229 Ceramic, Chip, 33 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000805
C230 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, J, 50 V 2203-000457
C231 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, K, 50 V 2203-001450
C232 Ceramic, Chip, 10 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000262
C233 Ceramic, Chip, 10 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000262
C234 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, J, 50 V 2203-000457
C235 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, J, 50 V 2203-000457
C236 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, J, 50 V 2203-000242
C239 Ceramic, Chip, 3.3 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000717
C240 TA, Chip, 1 µF, M, 10 V 2404-000291
C241 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, J, 50 V 2203-000457
C242 Ceramic, Chip, 10 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000262
C243 Ceramic, Chip, 15 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000376
C244 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, K, 50 V 2203-000242
C247 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, K, 50 V 2203-000242
C248 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, K, 50 V 2203-000242
C249 Ceramic, Chip, 68 nF, K, 50 V 2203-001145
Ref. No. Description SEC Code Remark
C250 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, K, 50 V 2203-000242
Page 64

Electrical Parts List
SF150T7-10
Ref. No. Description SEC Code Remark
PBA, PCB Assembly, LIU JF92-00843A
- Capacitors -
C201 Electrolytic, 1 µF, M, 50 V, GP 2401-000597
C202 Electrolytic, 100 µF, M, 25 V, GP 2401-000310
C203 Electrolytic, 330 nF, M, 50 V, GP 2401-001087
C206 Film, MPEF, 1 µF, K, 250 V 2305-000505
C207 Electrolytic, 100 µF, M, 25 V, GP 2401-000310
C208 Electrolytic, 470 µF, M, 16 V, GP 2401-001368
C209 Electrolytic, 22 µF, M, 50 V, GP 2401-000966
C210 Electrolytic, 10 µF, M, 50 V, GP 2401-000486
C212 Film, MPEF, 15 nF, M, 630 V 2305-000199
C214 Electrolytic, 10 µF, M, 50 V, GP 2401-000486
C216 Film, PEF, 47 nF, K, 50 V 2301-000278
C217 Electrolytic, 1 µF, M, 50 V, GP 2401-000597
C218 Electrolytic, 100 nF, M, 50 V, GP 2401-000217
C220 Ceramic, Chip, 2.2 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000499
C221 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, J, 50 V 2203-000242
C222 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, J, 50 V 2203-000242
C223 Ceramic, Chip, 1 nF, J, 50 V 2203-000457
C225 Ceramic, Chip, 33 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000805
C226 Ceramic, Chip, 10 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000262
Page 65

Electrical Parts List
SF150T 7-11
Ref. No. Description SEC Code Remark
ASSEMBLY, OPE JF92-00844A
- Capacitors -
C301 Ceramic, Chip, 100 pF, J, 50 V 2203-000242
C302 Ceramic, Chip, 100 nF, K, 50 V 2203-000208
- Diodes -
D301 Switching, MMSD914T1 0401-000116
D302 Switching, MMSD914T1 0401-000116
D303 Switching, MMSD914T1 0401-000116
D304 Switching, MMSD914T1 0401-000116
D305 Switching, MMSD914T1 0401-000116
D306 Switching, MMSD914T1 0401-000116
LED301 LED, Chip, Red, 60 mW, 2 V 0601-000208
LED302 LED, Chip, Red, 60 mW, 2 V 0601-000208
LED303 LED, Chip, Red, 60 mW, 2 V 0601-000208
- Resistors -
R301 Chip, 300 ohm, J, 1/8 W 2007-000730
R302 Chip, 10 kohm, J, 1/8 W 2007-000303
R303 Chip, 300 ohm, J, 1/8 W 2007-000730
R306 Chip, 10 kohm, J, 1/8 W 2007-000303
R307 Chip, 10 kohm, J, 1/8 W 2007-000303
R308 Chip, 10 kohm, J, 1/8 W 2007-000303
R309 Chip, 10 kohm, J, 1/8 W 2007-000303
R310 Chip, 200 ohm, J, 1/8 W 2007-000542
R311 Chip, 300 ohm, J, 1/8 W 2007-000730
R312 Chip, 10 kohm, J, 1/8 W 2007-000303
- Miscellanceous -
J301 Resister, Chip, 0 ohm, J, 1/8 W 2007-000033
J302 Resister, Chip, 0 ohm, J, 1/8 W 2007-000033
J303 Resister, Chip, 0 ohm, J, 1/8 W 2007-000033
J304 Resister, Chip, 0 ohm, J, 1/8 W 2007-000033
P301 CBF, LIU-OPE Harness JF39-40957A
P302 CBF, MAIN-OPE Harness JF39-41081A
P303 CBF, MAIN-OPE Harness JF39-41081A
P304 Connector, Header, Box, 3 P 3711-000906
P305 CBF, OPE-LCD Harness, FFC JF39-41018A
Q301 Small Signal, NPN, KSC1623-Y 0501-000342
LCD Display-LCD JF07-20061A
7-3. OPE PBA
Page 66

Electrical Parts List
SF150T7-12
7-4. HOOK PBA
Ref. No. Description SEC Code Remark
Assembly, HOOK JF92-00845C
PCB PCB, Blank, HOOK
SW1 Switch, Hook, SPPY43-B-S-01 3409-000117
P1 CBF, LIU-HOOK Harness JF39-41080A
7-5. D.DET PBA
Ref. No. Description SEC Code Remark
Assembly, D.DET JF39-40956A
PCB PCB, Blank, D.DET
SEN1 Photo-Interrupter 0604-000230
P1 Harness, Main-D.DET JF39-40956A
7-6. P.EMPTY PBA
Ref. No. Description SEC Code Remark
Assembly, P.EMPTY JF92-00704B
PCB PCB, Blank
Photo-Reflect Sensor, TLP908(LB) 0604-000246
Harness, P,EMPRY-Main JF39-40960A
7-7. HANDSET PBA
Ref. No. Description SEC Code Remark
ASSEMBLY, HANDSET PCB JF92-00625A
PCB PCB, Blank, Handset
ZD1 Diode, Zener, 1N4736A 0403-000142
MIC Mic, Condensor 3003-000103
Page 67

Electrical Parts List
SF150T 7-13
7-8. OTHERS
Ref. No. Description SEC Code Remark
Display-LCD JF07-20061A
LCD Harness JF39-41018A
Harness, Main-OPE, RED JF39-41064A
Harness, Main-OPE, BK/RD JF39-40957A
Harness, Main-TPH JF39-40955A
Thermal Print Head (TPH) JF47-30069A
Earth Wire, Motor-Power, GRN JF39-40963B
Harness, Main-CIS JF39-4106A
Contact Image Sensor (CIS) 0609-001059
Motor-Step, 24V, 200 pps 3101-000143
Switch-Micro, 16V, 1A, SPST 3405-000166
Cord-Power GA39-10100A
Cord-Curl JF39-50054B
Cord-Tel Line JF39-50079A
Power Supply, AC220 V JF44-10059A
 Loading...
Loading...