Samsung S6B0723 Datasheet

S6B0723
permission of LCD Driver IC Team.
132 SEG / 65 COM DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD
Contents in this document are subject to change without notice. No part of this document may be reproduced or
transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, for any purpose, without the express written
June. 2000.
Ver. 0.9
Prepared by: Kyu-tae, Lim
Kyutae@samsung.co.kr

132 SEG / 65 COM DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD PRELIMINARY SPEC. VER. 0.9 S6B0723
S6B0723 Specification Revision History
Version Content Date
0.0 Initial version 1998
1. VDD level changed(1.8V ~ 3.6V → 2.4V ~ 5.5V)
2. Power save mode changed (compound instruction)
0.1
3. Oscillator ON command deleted
Mar.1999
4. Vref voltage changed (1.4V → 2.1 V)
5. Internal resistor (Ra / Rb) ratio changed
6. n-line inversion deleted
0.2
1. PAD name changed (VSS → TEST4)
Mar.1999
0.3 1. Eq2. changed (page 32) Mar.1999
0.4 1. figure 10. figure 11. changed Mar.1999
0.5 1. Set static indicator register changed (page 46) Apr.1999
1. Modify following sections
0.6
Introduction, Features, Pad Configuration, Pin Description,
Power Supply Circuits, Reference Circuit Examples,
Apr.1999
DC/AC Characteristics, Connection Between S6B0723 and LCD Panel
0.7
0.8
0.9
1. S6B0723 Application circuit is changed(page 65~67)
1. Operating VDD range is changed
1. READ timing is changed(Figure 5)
Aug.1999
Oct.1999
Jun.2000
2

S6B0723 PRELIMINARY SPEC. VER. 0.9 65 COM / 132 SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD
CO
NTENTS
INTRODUCTION ..................................................................................................................................................1
FEATURES..........................................................................................................................................................1
BLOCK DIAGRAM...............................................................................................................................................3
PAD CONFIGURATION .......................................................................................................................................4
PAD CENTER COORDINATES ............................................................................................................................5
PIN DESCRIPTION ..............................................................................................................................................8
POWER SUPPLY ..........................................................................................................................................8
LCD DRIVER SUPPLY..................................................................................................................................8
SYSTEM CONTROL .....................................................................................................................................9
MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACE.............................................................................................................11
LCD DRIVER OUTPUTS.............................................................................................................................13
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION............................................................................................................................ 14
MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACE.............................................................................................................14
DISPLAY DATA RAM (DDRAM)..................................................................................................................18
LCD DISPLAY CIRCUITS............................................................................................................................21
LCD DRIVER CIRCUITS.............................................................................................................................24
POWER SUPPLY CIRCUITS ......................................................................................................................25
REFERENCE CIRCUIT EXAMPLES ...........................................................................................................32
RESET CIRCUIT.........................................................................................................................................34
INSTRUCTION DESCRIPTION...........................................................................................................................35
SPECIFICATIONS..............................................................................................................................................50
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS...............................................................................................................50
DC CHARACTERISTICS .............................................................................................................................51
AC CHARACTERISTICS.............................................................................................................................54
REFERENCE APPLICATIONS........................................................................................................................... 58
MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACE.............................................................................................................58
CONNECTIONS BETWEEN S6B0723 AND LCD PANEL............................................................................59
S6B0723 APPLICATION CIRCUIT (6800 / 8080 / SERIAL) .........................................................................65
TCP PIN LAYOUT (SAMPLE)......................................................................................................................68
3

S6B0723 PRELIMINARY SPEC. VER. 0.9 65 COM / 132 SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD
INTRODUCTION
The S6B0723 is a single-chip driver & controller LSI for graphic dot-matrix liquid crystal display systems. This chip
can be connected directly to a microprocessor, accepts serial or 8-bit parallel display data from the microprocessor,
stores the display data in an on-chip display data RAM of 65 x 132 bits and generates a liquid crystal display drive
signal independent of the microprocessor. It provides a high-flexible display section due to 1-to-1 correspondence
between on-chip display data RAM bits and LCD panel pixels. It contains 65 common driver circuits and 132
segment driver circuits, so that a single chip can drive a 65 x 132 dot display. And the capacity of the display can be
increased through the use of master/slave multi-chip structures. This chip is able to minimize power consumption
because it performs display data RAM read/write operation with no external operation clock. In addition, because it
contains power supply circuits necessary to drive liquid crystal, which is a display clock oscillator circuit, high
performance voltage converter circuit, high-accuracy voltage regulator circuit, low power consumption voltage
divider resistors and OP-Amp for liquid crystal driver power voltage, it is possible to make the lowest power
consumption display system with the fewest components for high performance portable systems.
FEATURES
Display Driver Output Circuits
− 65 common outputs / 132 segment outputs
On-chip Display Data RAM
− Capacity: 65 x 132 = 8,580 bits
− RAM bit data “1”: a dot of display is illuminated.
− RAM bit data “0”: a dot of display is not illuminated.
Applicable Duty Ratios
Duty ratio Applicable LCD bias Maximum display area
1/65 1/7 or 1/9
1/55 1/6 or 1/8
1/49 1/6 or 1/8
1/33 1/5 or 1/6
Microprocessor Interface
− High-speed 8-bit parallel bi-directional interface with 6800-series or 8080-series
− Serial interface (only write operation) available
Various Function Set
− Display ON / OFF, set initial display line, set page address, set column address, read status, write / read display
data, select segment driver output, reverse display ON / OFF, entire display ON / OFF, select LCD bias,
set/reset modify-read, select common driver output, control display power circuit, select internal regulator
resistor ratio for V0 voltage regulation, electronic volume, set static indicator state.
− H/W and S/W reset available
− Static drive circuit equipped internally for indicators with 4 flashing modes
65 × 132
55 × 132
49 × 132
33 × 132
1

132 SEG / 65 COM DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD PRELIMINARY SPEC. VER. 0.9 S6B0723
Built-in Analog Circuit
− On-chip oscillator circuit for display clock (external clock can also be used)
− High performance voltage converter (with booster ratios of x2, x3, x4 and x5, where the step-up reference
voltage can be used externally)
− High accuracy voltage regulator (temperature coefficient: -0.05%/°C or external input)
− Electronic contrast control function (64 steps)
− Vref = 2.1V ± 3% (V0 voltage adjustment voltage)
− High performance voltage follower (V1 to V4 voltage divider resistors and OP-Amp for increasing drive
capacity)
Operating Voltage Range
− Supply voltage (VDD): 2.4 to 3.6V
− LCD driving voltage (VLCD = V0 - VSS): 4.5 to 15.0V
Low Power Consumption
− Operating power: 40µΑ typical (conditions: VDD = 3V, x 4 boosting (VCI = VDD), V0 = 11V, Internal power supply
ON, display OFF and normal mode is selected)
− Standby power: 10 µΑ maximum (during power save[standby] mode)
Operating Temperatures
− Wide range of operating temperatures : -40 to 85°C
CMOS Process
Package Type
− TCP
2
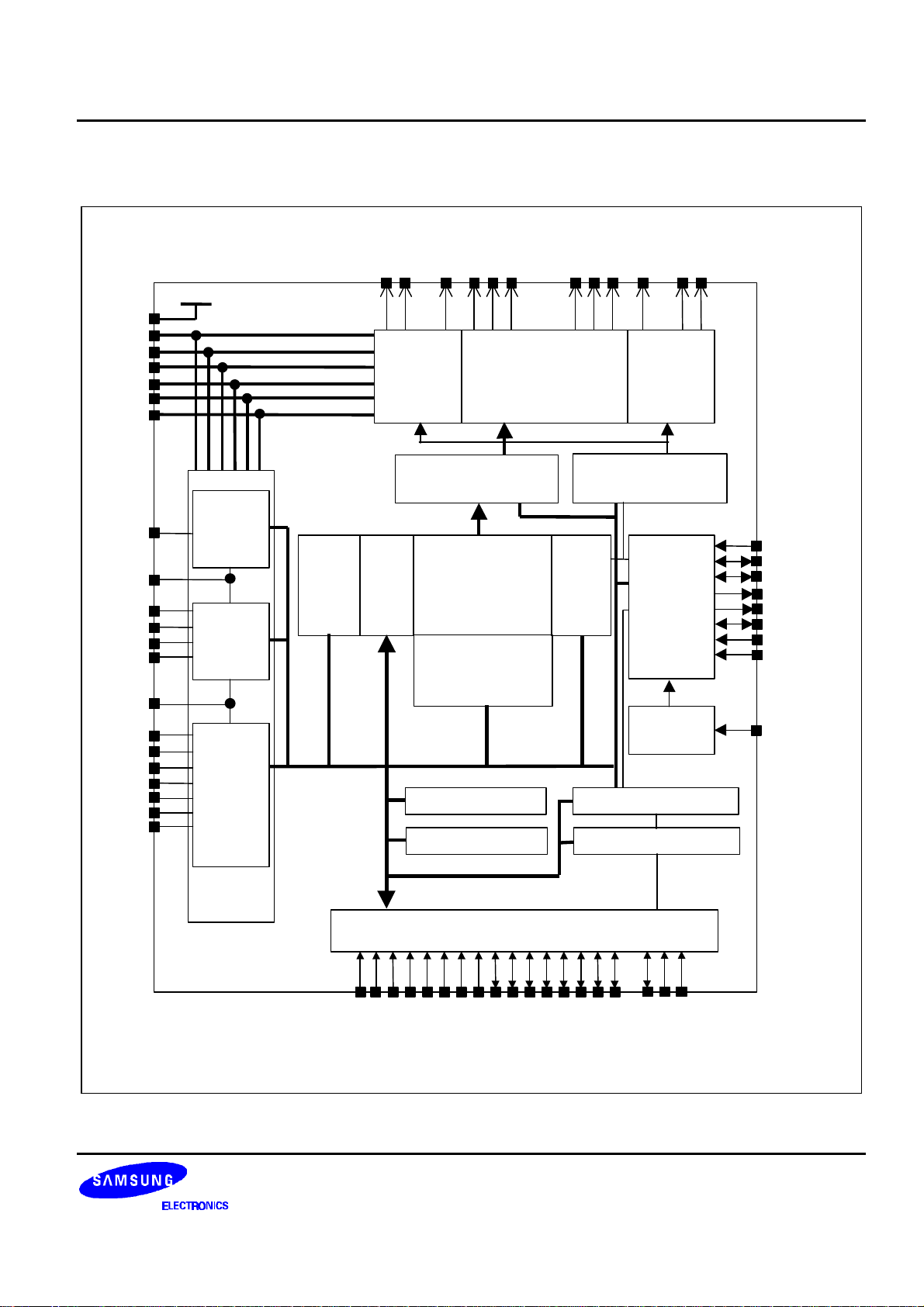
S6B0723 PRELIMINARY SPEC. VER. 0.9 65 COM / 132 SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD
V
TEST1
TEST2
TEST3
COMS
COM63
BLOCK DIAGRAM
SEG131
SEG130
VDD
V0
V1
V2
V3
V4
SS
COMS
COM0
:
33 COMMON
DRIVER
CIRCUITS
COM31
SEG0
SEG2
SEG1
132 SEGMENT
DRIVER CIRCUITS
SEG129
:
:
COM32
:
33 COMMON
DRIVER
CIRCUITS
HPMB
V0
VR
INTRS
REF
VEXT
VOUT
C1-
C1+
C2C2+
C3+
C4+
VCI
V / F
CIRCUIT
V / R
CIRCUIT
V / C
CIRCUIT
PAGE
ADDRESS
CIRCUIT
I/O
BUFFER
DISPLAY DATA
CONTROL CIRCUIT
DISPLAY DATA RAM
65 X 132 = 8,580 Bits
COLUMN ADDRESS
CIRCUIT
STATUS REGISTER INSTRUCTION REGISTER
COMMON OUTPUT
CONTROLLER CIRCUIT
LINE
ADDRESS
CIRCUIT
INSTRUCTION DECODERBUS HOLDER
DISPLAY
TIMING
GENERATOR
CIRCUIT
OSCILLATOR
MS
CL
M
FRS
FR
DISP
DUTY0
DUTY1
CLS
MPU INTERFACE (PARALLEL & SERIAL)
DB0
DB1
DB2
DB3
DB4
DB5
DB6(SCLK)
DB7(SID)
C68
RESETB
PS
RW_WRB
E_RD
RS
CS2
CS1B
Figure 1. Block Diagram
3

132 SEG / 65 COM DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD PRELIMINARY SPEC. VER. 0.9 S6B0723
137
296
136
297
126
307
125
1
ðððð
- - - -
ðððð
ðððð
- - - -
ðððð
(+4078.7, -397.2)
(+4078.25, +186.95)
30
µ
m
30
µ
m
30
µ
m
60
µ
m
30
µ
m
42
µ
m
108
µ
m
42
µ
m
108
µ
m
(-4134.2, +451.95)
(+4144.25, +436.95)
PAD CONFIGURATION
ррр ррррррррррррррррррр
- - - - - - - - - -
Y
ррррррррррррррррррр
S6B0723
(TOP VIEW)
рррррррррррррррррррррр
Figure 2. S6B0723 Chip Configuration
Table 1. S6B0723 Pad Dimensions
Item Pad No.
Chip size - 8850 1980
2 to 21, 105 to 124
138 to 150, 283 to 295
Pad pitch
Bumped pad size
(Bottom)
Bumped pad height All pad 14 (Typ.)
150 to 151, 282 to 283 75
1 to 2, 124 to 125
137 to 138, 295 to 296
126 to 136, 297 to 307 150
21 to 22, 104 to 105 226
1, 125, 137, 296 62 70
2 to 21, 105 to 124
138 to 150, 283 to 295
126 to 136, 297 to 307 38 70
(0,0)
- - - - - - - - - -
X
ррррррррррррррррррррррр
Size
X Y
151 to 282 52
55
22 to 104 70
80
34 70
151 to 282 34 70
22 to 104 52 70
ððð
Unit
µm
COG Align Key Coordinate ILB Align Key Coordinate
30µm 30µm 30µm
4
30µm 30µm 30µm
42µm 108µm
42µm108µm
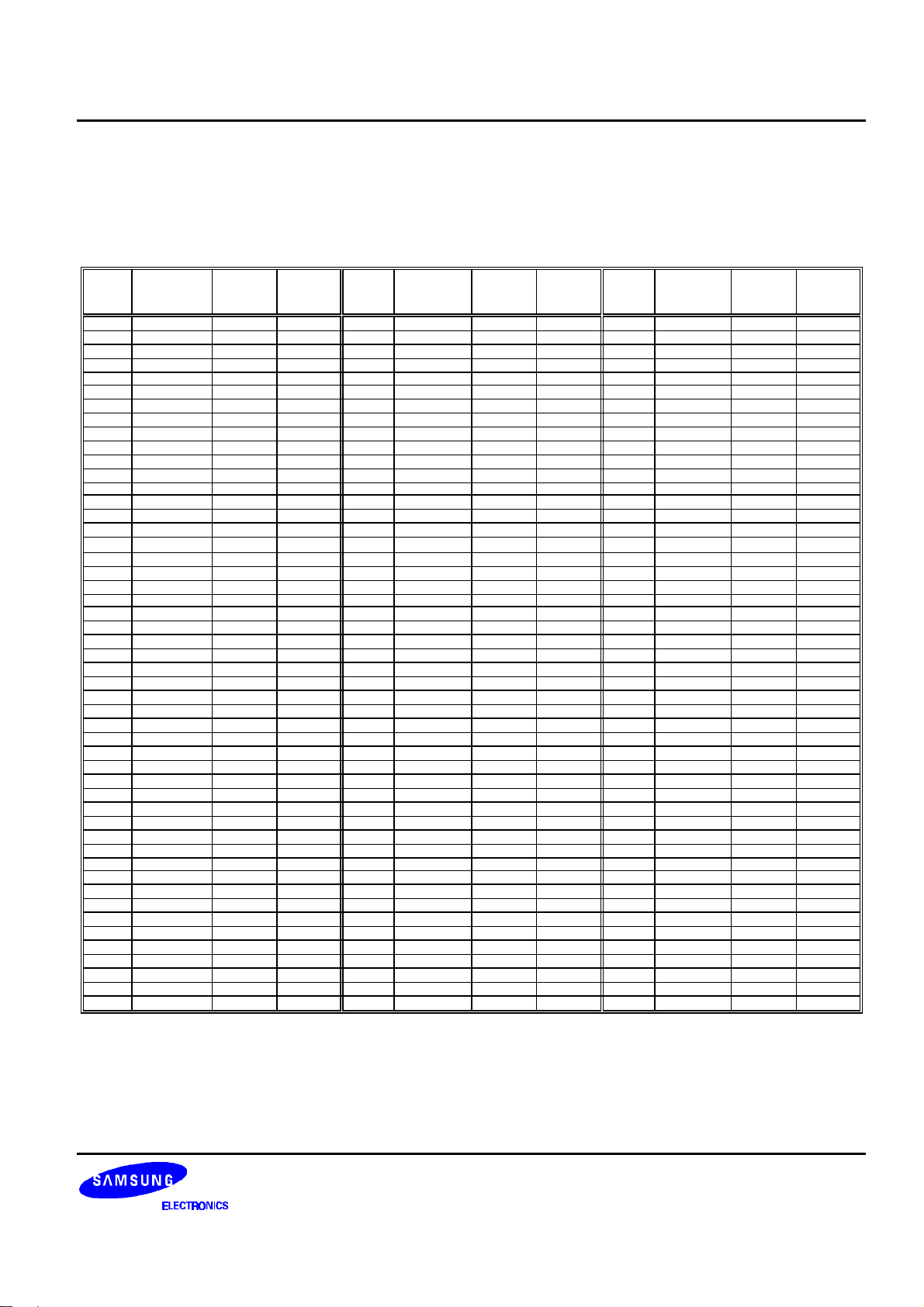
S6B0723 PRELIMINARY SPEC. VER. 0.9 65 COM / 132 SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD
PAD CENTER COORDINATES
Table 2. Pad Center Coordinates
[Unit: µm]
Pad
No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
Pad
name
DUMMY
COM45
COM46
COM47
COM48
COM49
COM50
COM51
COM52
COM53
COM54
COM55
COM56
COM57
COM58
COM59
COM60
COM61
COM62
COM63
COMS
FRS
FR
TEST1
TEST2
TEST3
M
CL
DISP
TEST4
VSS
CS1B
CS2
VDD
RESETB
RS
VSS
RW_WRB
E_RDB
VDD
DB0
DB1
DB2
DB3
DB4
DB5
DB6
DB7
VSS
VDD
X Y
-4221
-4141
-4086
-4031
-3976
-3921
-3866
-3811
-3756
-3701
-3646
-3591
-3536
-3481
-3426
-3371
-3316
-3261
-3206
-3151
-3096
-2870
-2800
-2730
-2660
-2590
-2520
-2450
-2380
-2310
-2240
-2170
-2100
-2030
-1960
-1890
-1820
-1750
-1680
-1610
-1540
-1470
-1400
-1330
-1260
-1190
-1120
-1050
-980
-910
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
Pad
No.
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
Pad
name
DUTY0
DUTY1
VSS
VDD
VDD
VDD
VCI
VCI
VSS
VSS
VSS
VOUT
VOUT
C4+
C4+
C3+
C3+
C1C1C1+
C1+
C2+
C2+
C2C2VDD
VEXT
REF
VSS
V1
V1
V2
V2
V3
V3
V4
V4
V0
V0
VR
VR
VSS
VSS
VDD
MS
CLS
VSS
C68
PS
VDD
X Y
-840
-770
-700
-630
-560
-490
-420
-350
-280
-210
-140
-70
0
70
140
210
280
350
420
490
560
630
700
770
840
910
980
1050
1120
1190
1260
1330
1400
1470
1540
1610
1680
1750
1820
1890
1960
2030
2100
2170
2240
2310
2380
2450
2520
2590
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
Pad
No.
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
Pad
name
HPMB
VSS
INTRS
VDD
COM31
COM30
COM29
COM28
COM27
COM26
COM25
COM24
COM23
COM22
COM21
COM20
COM19
COM18
COM17
COM16
COM15
COM14
COM13
COM12
DUMMY
DUMMY
DUMMY
DUMMY
DUMMY
DUMMY
DUMMY
DUMMY
DUMMY
DUMMY
DUMMY
DUMMY
DUMMY
COM11
COM10
COM9
COM8
COM7
COM6
COM5
COM4
COM3
COM2
COM1
COM0
COMS
X Y
2660
2730
2800
2870
3096
3151
3206
3261
3316
3371
3426
3481
3536
3591
3646
3701
3756
3811
3866
3921
3976
4031
4086
4141
4221
4345
4345
4345
4345
4345
4345
4345
4345
4345
4345
4345
4221
4141
4086
4031
3976
3921
3866
3811
3756
3701
3646
3591
3536
3481
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-865
-750
-600
-450
-300
-150
0
150
300
450
600
750
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
5
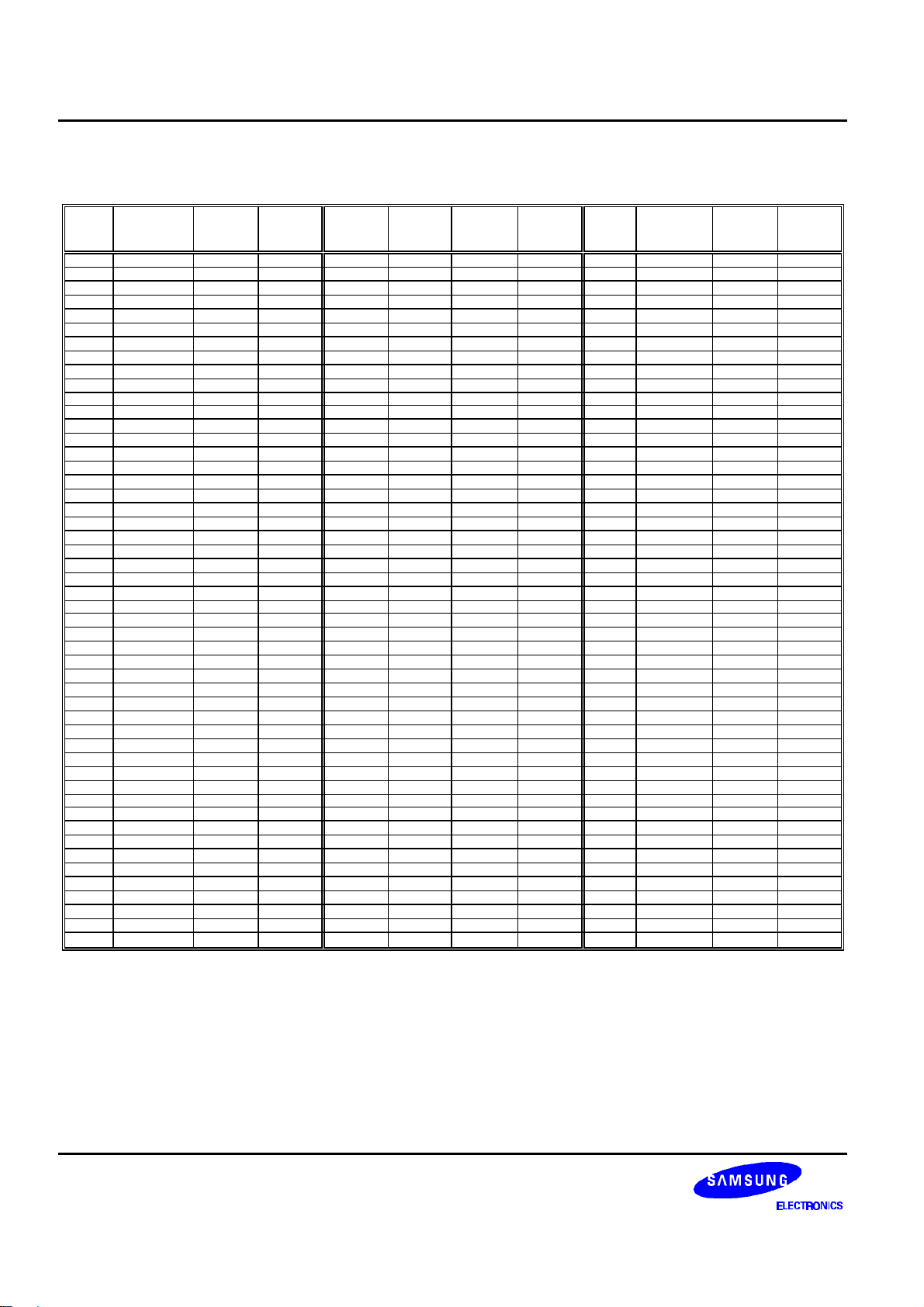
132 SEG / 65 COM DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD PRELIMINARY SPEC. VER. 0.9 S6B0723
Table 2. Pad Center Coordinates (Continued)
[Unit: µm]
Pad
No.
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
Pad
name
SEG0
SEG1
SEG2
SEG3
SEG4
SEG5
SEG6
SEG7
SEG8
SEG9
SEG10
SEG11
SEG12
SEG13
SEG14
SEG15
SEG16
SEG17
SEG18
SEG19
SEG20
SEG21
SEG22
SEG23
SEG24
SEG25
SEG26
SEG27
SEG28
SEG29
SEG30
SEG31
SEG32
SEG33
SEG34
SEG35
SEG36
SEG37
SEG38
SEG39
SEG40
SEG41
SEG42
SEG43
SEG44
SEG45
SEG46
SEG47
SEG48
SEG49
X Y
3406
3354
3302
3250
3198
3146
3094
3042
2990
2938
2886
2834
2782
2730
2678
2626
2574
2522
2470
2418
2366
2314
2262
2210
2158
2106
2054
2002
1950
1898
1846
1794
1742
1690
1638
1586
1534
1482
1430
1378
1326
1274
1222
1170
1118
1066
1014
962
910
858
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
Pad
No.
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
Pad
name
SEG50
SEG51
SEG52
SEG53
SEG54
SEG55
SEG56
SEG57
SEG58
SEG59
SEG60
SEG61
SEG62
SEG63
SEG64
SEG65
SEG66
SEG67
SEG68
SEG69
SEG70
SEG71
SEG72
SEG73
SEG74
SEG75
SEG76
SEG77
SEG78
SEG79
SEG80
SEG81
SEG82
SEG83
SEG84
SEG85
SEG86
SEG87
SEG88
SEG89
SEG90
SEG91
SEG92
SEG93
SEG94
SEG95
SEG96
SEG97
SEG98
SEG99
X Y
806
754
702
650
598
546
494
442
390
338
286
234
182
130
78
26
-26
-78
-130
-182
-234
-286
-338
-390
-442
-494
-546
-598
-650
-702
-754
-806
-858
-910
-962
-1014
-1066
-1118
-1170
-1222
-1274
-1326
-1378
-1430
-1482
-1534
–1586
-1638
-1690
-1742
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
Pad
No.
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
Pad
name
SEG100
SEG101
SEG102
SEG103
SEG104
SEG105
SEG106
SEG107
SEG108
SEG109
SEG110
SEG111
SEG112
SEG113
SEG114
SEG115
SEG116
SEG117
SEG118
SEG119
SEG120
SEG121
SEG122
SEG123
SEG124
SEG125
SEG126
SEG127
SEG128
SEG129
SEG130
SEG131
COM32
COM33
COM34
COM35
COM36
COM37
COM38
COM39
COM40
COM41
COM42
COM43
COM44
DUMMY
DUMMY
DUMMY
DUMMY
DUMMY
X Y
-1794
-1846
-1898
-1950
-2002
-2054
-2106
-2158
-2210
-2262
2314
-2366
-2418
-2470
-2522
-2574
-2626
-2678
-2730
-2782
-2834
-2886
-2938
-2990
-3042
-3094
-3146
-3198
-3250
-3302
-3354
-3406
-3481
-3536
-3591
-3646
-3701
-3756
-3811
-3866
-3921
-3976
-4031
-4086
-4141
-4221
-4345
-4345
-4345
-4345
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
865
750
600
450
300
6

S6B0723 PRELIMINARY SPEC. VER. 0.9 65 COM / 132 SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD
Table 2. Pad Center Coordinates (Continued)
[Unit: µm]
Pad
No.
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
Pad
name
DUMMY
DUMMY
DUMMY
DUMMY
DUMMY
DUMMY
DUMMY
X Y
-4345
-4345
-4345
-4345
-4345
-4345
-4345
150
-150
-300
-450
-600
-750
Pad
No.
0
Pad
name
X Y
Pad
No.
Pad
name
X Y
7
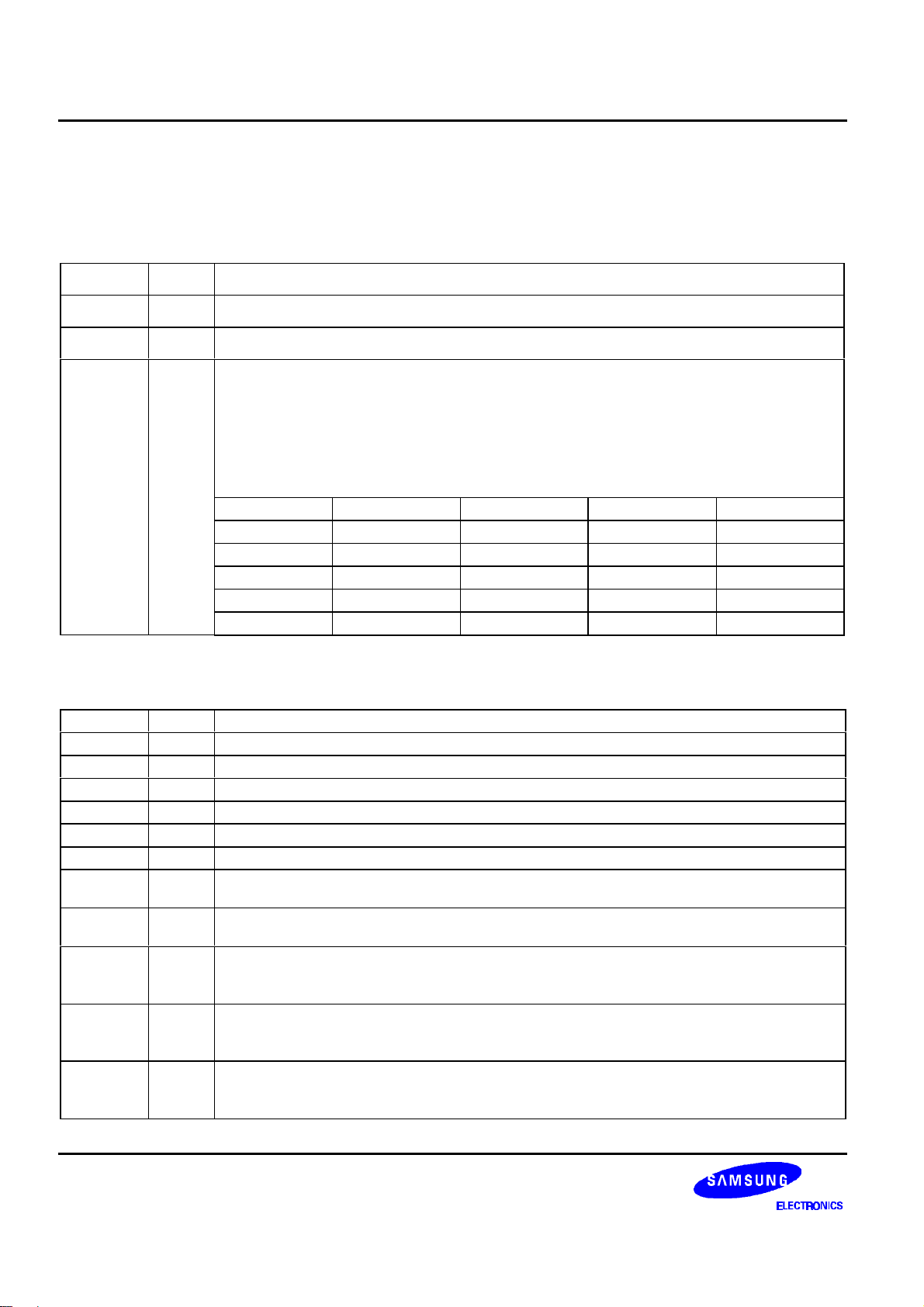
132 SEG / 65 COM DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD PRELIMINARY SPEC. VER. 0.9 S6B0723
PIN DESCRIPTION
POWER SUPPLY
Table 3. Power Supply Pins Description
Name I/O Description
VDD Supply Power supply
VSS Supply Ground
LCD driver supply voltages
The voltage determined by LCD pixel is impedance-converted by an operational amplifier
for application.
Voltages should have the following relationship;
V0
V1
V2
V3
V4
I/O
V0 ≥ V1 ≥ V2 ≥ V3 ≥ V4 ≥ VSS
When the internal power circuit is active, these voltages are generated as following table
according to the state of LCD bias.
LCD bias V1 V2 V3 V4
1/9 bias (8/9) x V0 (7/9) x V0 (2/9) x V0 (1/9) x V0
1/8 bias (7/8) x V0 (6/8) x V0 (2/8) x V0 (1/8) x V0
1/7 bias (6/7) x V0 (5/7) x V0 (2/7) x V0 (1/7) x V0
1/6 bias (5/6) x V0 (4/6) x V0 (2/6) x V0 (1/6) x V0
1/5 bias (4/5) x V0 (3/5) x V0 (2/5) x V0 (1/5) x V0
LCD DRIVER SUPPLY
Table 4. LCD Driver Supply Pins Description
Name I/O Description
C1- O
C1+ O
C2- O
C2+ O
C3+ O
C4+ O
VOUT I/O
VR I
VCI I
VEXT I
REF I
Capacitor 1 negative connection pin for voltage converter
Capacitor 1 positive connection pin for voltage converter
Capacitor 2 negative connection pin for voltage converter
Capacitor 2 positive connection pin for voltage converter
Capacitor 3 positive connection pin for voltage converter
Capacitor 4 positive connection pin for voltage converter
Voltage converter input/output pin
Connect this pin to VSS through capacitor.
V0 voltage adjustment pin
It is valid only when internal voltage regulator resistors are not used (INTRS = "L").
This is the reference voltage for the voltage converter circuit for the LCD driving.
Whether internal voltage converter use or not use, this pin should be fixed.
The voltage should have the following range: 2.4V ≤ VCI ≤ 3.6V
This is the external-input reference voltage (VREF) for the internal voltage regulator.
It is valid only when external VREF is used (REF = "L").
When using internal VREF, this pin is Open
Select the external VREF voltage via VEXT pin
− REF = "L": using the external VREF
− REF = "H": using the internal VREF
8

S6B0723 PRELIMINARY SPEC. VER. 0.9 65 COM / 132 SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD
SYSTEM CONTROL
Table 5. System Control Pins Description
Name I/O Description
Master / slave mode select input
Master makes some signals for display, and slave gets them. This is for display
synchronization.
− MS = "H": master mode
− MS = "L": slave mode
The following table depends on the MS status.
MS I
CLS I
MS CLS
H
L - Disabled Disabled Input Input Output Input
Built-in oscillator circuit enable / disable select pin
− CLS = “H”: enable
− CLS = “L”: disable (external display clock input to CL pin)
H Enabled Enabled Output Output Output Output
L Disabled Enabled Input Output Output Output
OSC
circuit
Power
supply
circuit
CL M FR DISP
CL I/O
M I/O
FRS O
FR O
DISP I/O
INTRS I
Display clock input / output pin
When the S6B0723 is used in master/slave mode (multi-chip), the CL pins must be
connected each other.
LCD AC Signal input / output pin
When the S6B0723 is used in master/slave mode (multi-chip), the M pins must be
connected each other.
− MS = “H”: output
− MS = “L”: input
Static driver segment output pin
This pin is used together with the FR pin.
Static driver common output pin
This pin is used together with the FRS pin.
LCD display blanking control input / output
When S6B0723 is used in master/slave mode (multi-chip), the DISP pins must be
connected each other.
− MS = “H”: output
− MS = “L”: input
Internal resistor select pin
This pin selects the resistors for adjusting V0 voltage level and is valid only in master
operation.
− INTRS = "H": use the internal resistors.
− INTRS = "L": use the external resistors.
V0 voltage is controlled by VR pin and external resistive divider.
9

132 SEG / 65 COM DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD PRELIMINARY SPEC. VER. 0.9 S6B0723
Table 5. System Control Pins Description (Continued)
Name I/O Description
The LCD driver duty ratio depends on the following table.
DUTY1 DUTY0 Duty ratio
DUTY0
DUTY1
I
L L 1/33
L H 1/49
H L 1/55
H H 1/65
Power control pin of the power supply circuits for LCD driver.
HPMB I
− HPMB = "H": normal mode
− HPMB = "L": high power mode
This pin is valid only in master operation.
10
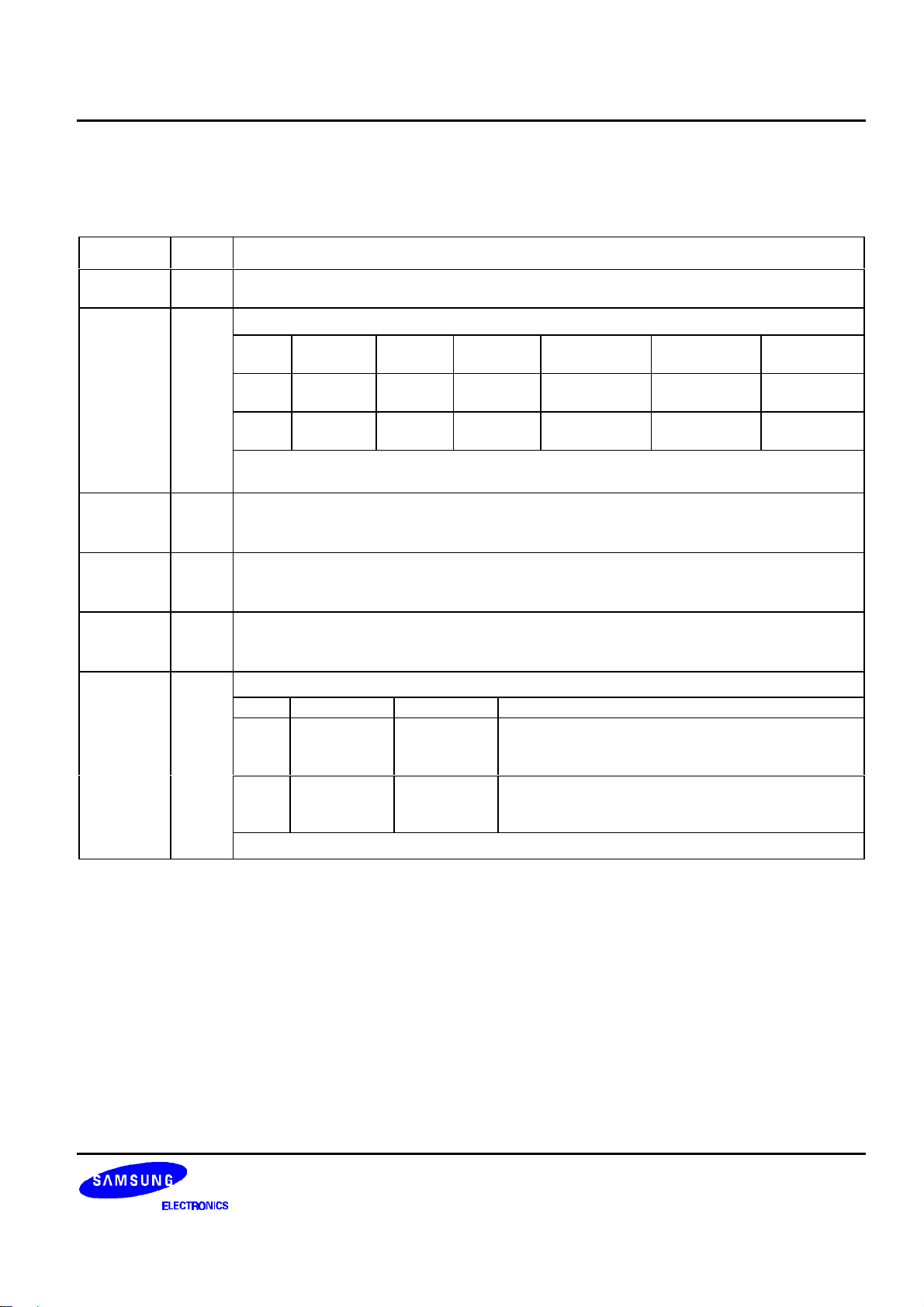
S6B0723 PRELIMINARY SPEC. VER. 0.9 65 COM / 132 SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD
MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACE
Table 6. Microprocessor Interface Pins Description
Name I/O Description
RESETB I
PS I
C68 I
CS1B
CS2
RS I
RW_WRB I
Reset input pin
When RESETB is "L", initialization is executed.
Parallel / Serial data input select input
PS
*NOTE: In serial mode, it is impossible to read data from the on-chip RAM. And DB0 to
DB5 are high impedance and E_RDB and RW_WRB must be fixed to either "H" or "L".
Microprocessor interface select input pin in parallel mode
− C68 = "H": 6800-series MPU interface
− C68 = "L": 8080-series MPU interface
Chip select input pins
I
Data/instruction I/O is enabled only when CS1B is "L" and CS2 is "H". When chip
select is non-active, DB0 to DB7 may be high impedance.
Register select input pin
− RS = "H": DB0 to DB7 are display data
− RS = "L": DB0 to DB7 are control data
Read / Write execution control pin
C68 MPU Type RW_WRB Description
H 6800-series RW
Interface
mode
H Parallel
L Serial
L 8080-series /WRB
Chip
select
CS1B,
CS2
CS1B,
CS2
Data /
instruction
RS DB0 to DB7
RS SID (DB7) Write only SCLK (DB6)
Read / Write control input pin
− RW = "H": read
− RW = "L": write
Write enable clock input pin
The data on DB0 to DB7 are latched at the rising
edge of the /WRB signal.
Data Read / Write Serial clock
E_RDB
RW_WRB
-
11
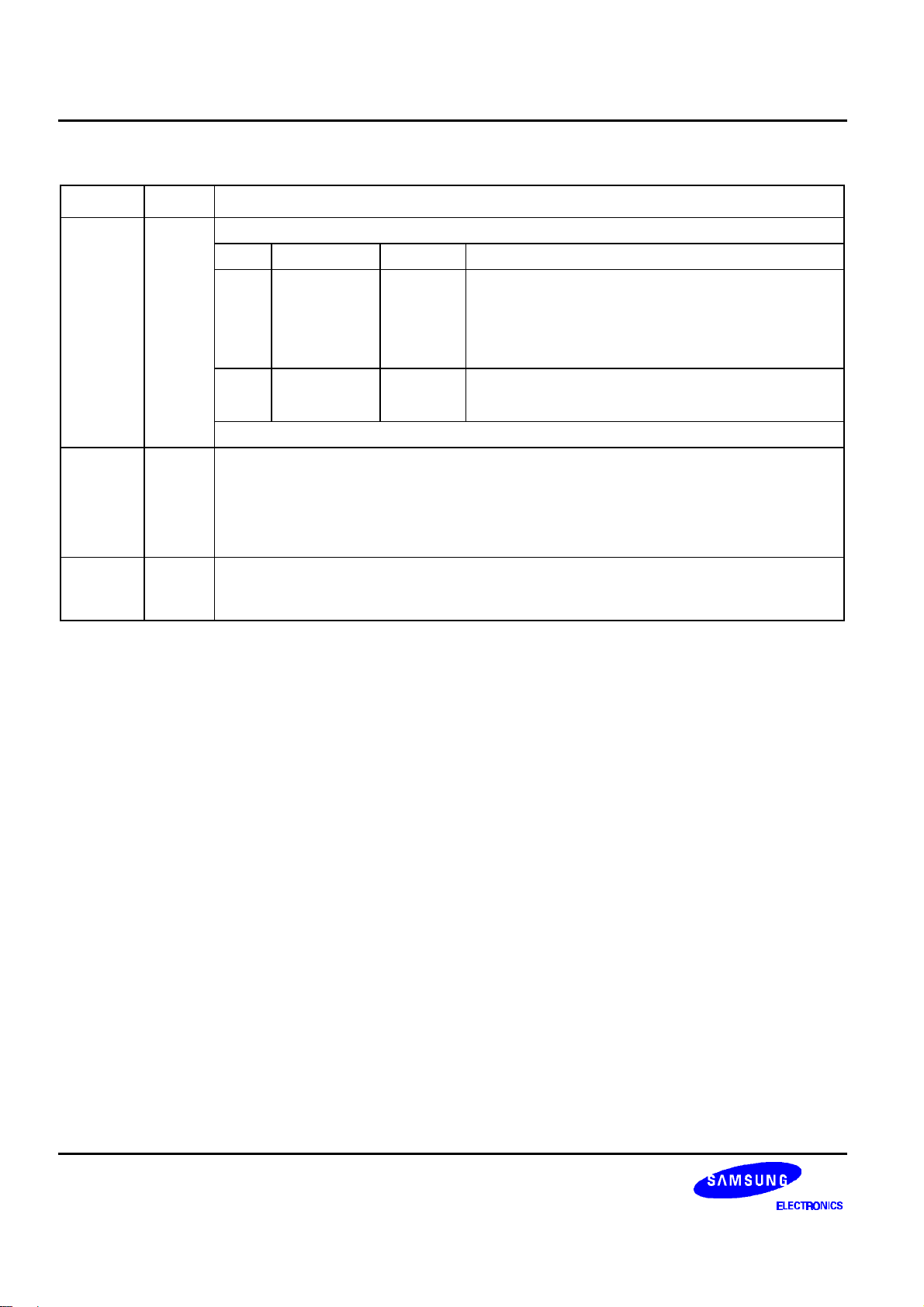
132 SEG / 65 COM DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD PRELIMINARY SPEC. VER. 0.9 S6B0723
Table 6. Microprocessor Interface Pins Description (Continued)
Name I/O Description
Read / Write execution control pin
C68 MPU Type E_RDB Description
Read/Write control input pin
− RW = "H": When E is "H", DB0 to DB7 are in an
E_RDB I
H 6800-series E
output status.
− RW = "L": The data on DB0 to DB7 are latched at
the falling edge of the E signal.
Read enable clock input pin
L 8080-series /RDB
When /RDB is "L", DB0 to DB7 are in an output
status.
8-bit bi-directional data bus that is connected to the standard 8-bit microprocessor data
DB0
to
DB7
I/O
bus. When the serial interface selected (PS = "L");
− DB0 to DB5: high impedance
− DB6: serial input clock (SCLK)
− DB7: serial input data (SID)
When chip select is not active, DB0 to DB7 may be high impedance.
TEST1
to
TEST4
I/O
These are pins for IC chip testing
They are set to Open.
NOTE: DUMMY – These pins should be opened (floated).
12
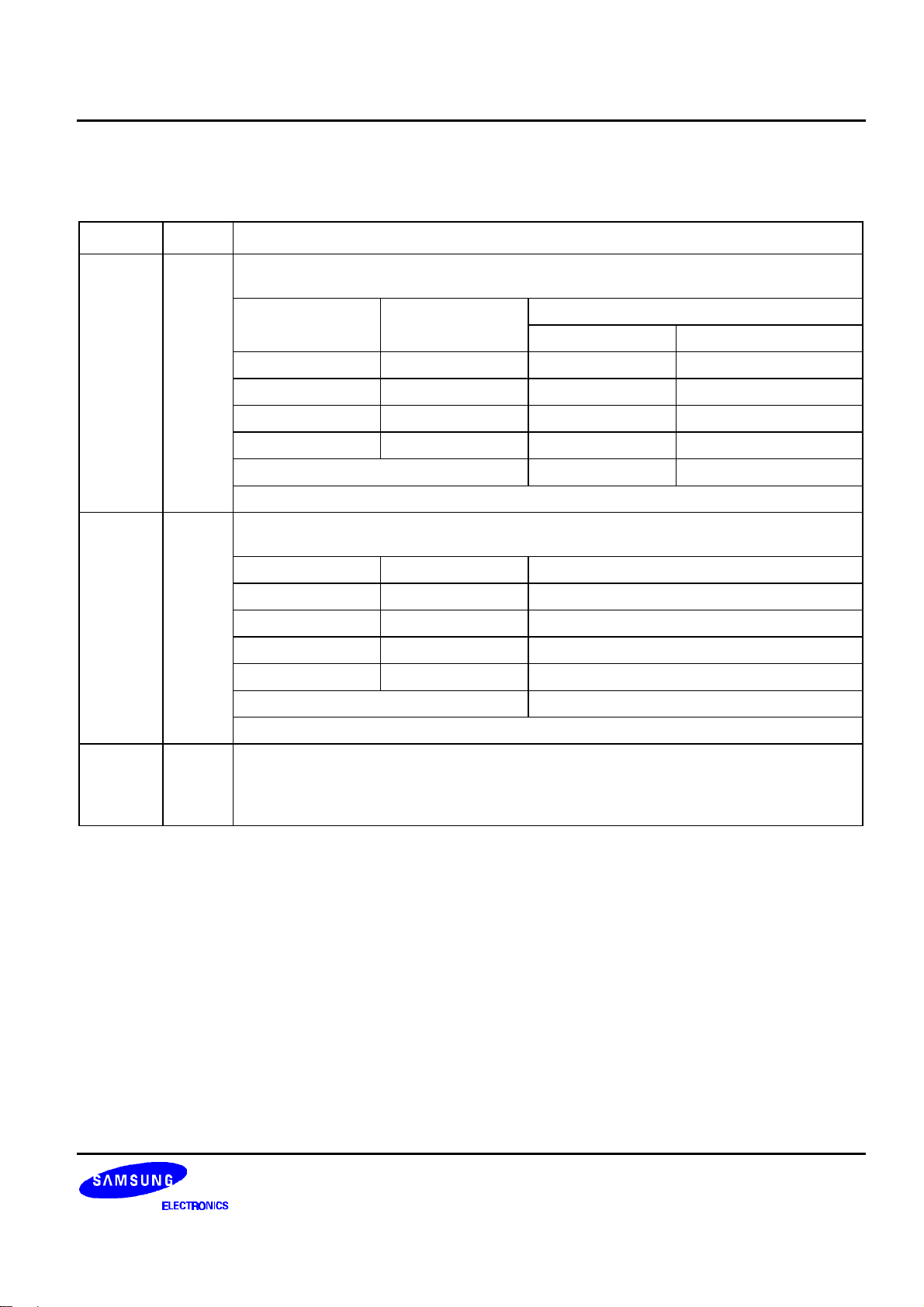
S6B0723 PRELIMINARY SPEC. VER. 0.9 65 COM / 132 SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD
LCD DRIVER OUTPUTS
Table 7. LCD Driver Output Pins Description
Name I/O Description
LCD segment driver outputs
The display data and the M signal control the output voltage of segment driver.
SEG0
to
SEG131
COM0
to
COM63
COMS O
Display data FR
H H V0 V2
O
LCD common driver outputs
The internal scanning data and M signal control the output voltage of common driver.
O
Common output for the icons
The output signals of two pins are same. When not used, these pins should be left Open. In
multi-chip (master / slave) mode, all COMS pins on both master and slave units are the
same signal.
H L VSS V3
L H V2 V0
L L V3 VSS
Power save mode VSS VSS
Scan data FR Common driver output voltage
H H VSS
H L V0
L H V1
L L V4
Power save mode VSS
Segment driver output voltage
Normal display Reverse display
13
132 SEG / 65 COM DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD PRELIMINARY SPEC. VER. 0.9 S6B0723
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACE
Chip Select Input
There are CS1B and CS2 pins for chip selection. The S6B0723 can interface with an MPU only when CS1B is "L"
and CS2 is "H". When these pins are set to any other combination, RS, E_RDB, and RW_WRB inputs are disabled
and DB0 to DB7 are to be high impedance. And, in case of serial interface, the internal shift register and the counter
are reset.
Parallel / Serial Interface
S6B0723 has three types of interface with an MPU, which are one serial and two parallel interfaces. This parallel or
serial interface is determined by PS pin as shown in table 8.
Table 8. Parallel / Serial Interface Mode
PS Type CS1B CS2 C68 Interface mode
H Parallel CS1B CS2
L Serial CS1B CS2
Parallel Interface (PS = "H")
The 8-bit bi-directional data bus is used in parallel interface and the type of MPU is selected by C68 as shown in
table 9. The type of data transfer is determined by signals at RS, E_RDB and RW_WRB as shown in table 10.
Table 9. Microprocessor Selection for Parallel Interface
C68 CS1B CS2 RS E_RDB RW_WRB DB0 to DB7 MPU bus
H CS1B CS2 RS E RW DB0 to DB7 6800-series
L CS1B CS2 RS /RDB /WRB DB0 to DB7 8080-series
Table 10. Parallel Data Transfer
Common 6800-series 8080-series
RS
E_RDB
(E)
RW_WRB
(RW)
E_RDB
(/RDB)
RW_WRB
(/WRB)
H 6800-series MPU mode
L 8080-series MPU mode
*×
Description
Serial-mode
*×: Don't care
H H H L H Display data read out
H H L H L Display data write
L H H L H Register status read
L H L H L Writes to internal register (instruction)
14

S6B0723 PRELIMINARY SPEC. VER. 0.9 65 COM / 132 SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD
Serial Interface (PS = "L")
When the S6B0723 is active, serial data (DB7) and serial clock (DB6) inputs are enabled. And not active, the internal
8-bit shift register and the 3-bit counter are reset. Serial data can be read on the rising edge of serial clock going into
DB6 and processed as 8-bit parallel data on the eighth serial clock. Serial data input is display data when RS is high
and control data when RS is low. Since the clock signal (DB6) is easy to be affected by the external noise caused by
the line length, the operation check on the actual machine is recommended.
CS1B
CS2
SID
SCLK
RS
DB6DB7DB0DB1DB2DB3DB4DB5DB6DB7
Figure 3. Serial Interface Timing
Busy Flag
The Busy Flag indicates whether the S6B0723 is operating or not. When DB7 is "H" in read status operation, this
device is in busy status and will accept only read status instruction. If the cycle time is correct, the microprocessor
needs not to check this flag before each instruction, which improves the MPU performance.
15

132 SEG / 65 COM DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD PRELIMINARY SPEC. VER. 0.9 S6B0723
Data Transfer
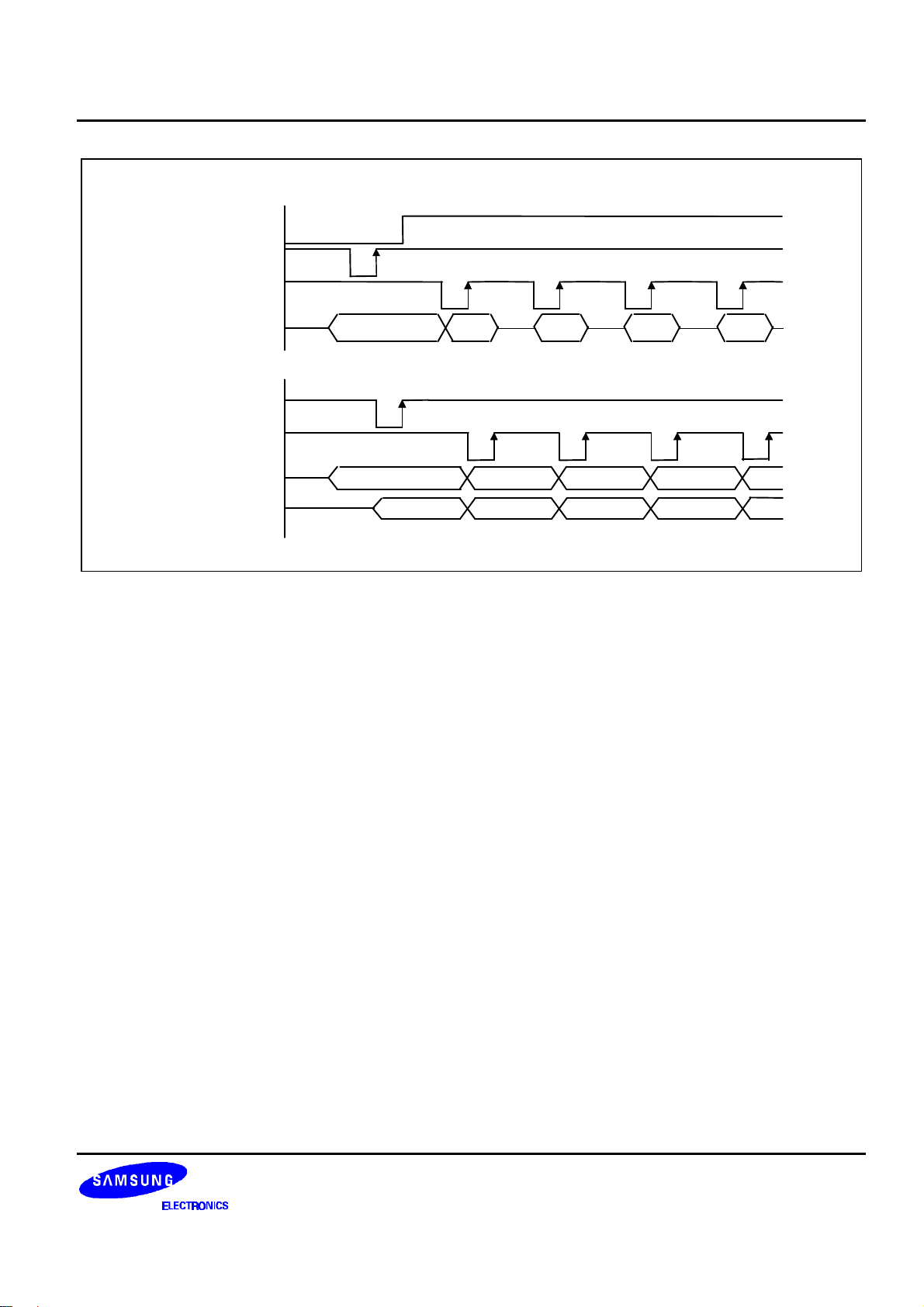
The S6B0723 uses bus holder and internal data bus for data transfer with the MPU. When writing data from the MPU
to on-chip RAM, data is automatically transferred from the bus holder to the RAM as shown in figure 4. And when
reading data from on-chip RAM to the MPU, the data for the initial read cycle is stored in the bus holder (dummy
read) and the MPU reads this stored data from bus holder for the next data read cycle as shown in figure5. This
means that a dummy read cycle must be inserted between each pair of address sets when a sequence of address
sets is executed. Therefore, the data of the specified address cannot be output with the read display data instruction
right after the address sets, but can be output at the second read of data.
MPU signals
RS
/WRB
DB0 to DB7
Internal signals
/WRB
BUS HOLDER
COLUMN ADDRESS
N D(N) D(N+1) D(N+2) D(N+3)
N D(N) D(N+1) D(N+2) D(N+3)
N N+1 N+2 N+3
Figure 4. Write Timing
16
S6B0723 PRELIMINARY SPEC. VER. 0.9 65 COM / 132 SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD
N
D(N)
D(N+1)
D(N+2)
N
N+1
N+2
N+3
MPU signals
RS
/WRB
/RDB
DB0 to DB7
Internal signals
/WRB
/RDB
BUS HOLDER
COLUMN ADDRESS
N
Dummy D(N) D(N+1)
Figure 5. Read Timing
D(N+2)
17
132 SEG / 65 COM DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD PRELIMINARY SPEC. VER. 0.9 S6B0723
DISPLAY DATA RAM (DDRAM)
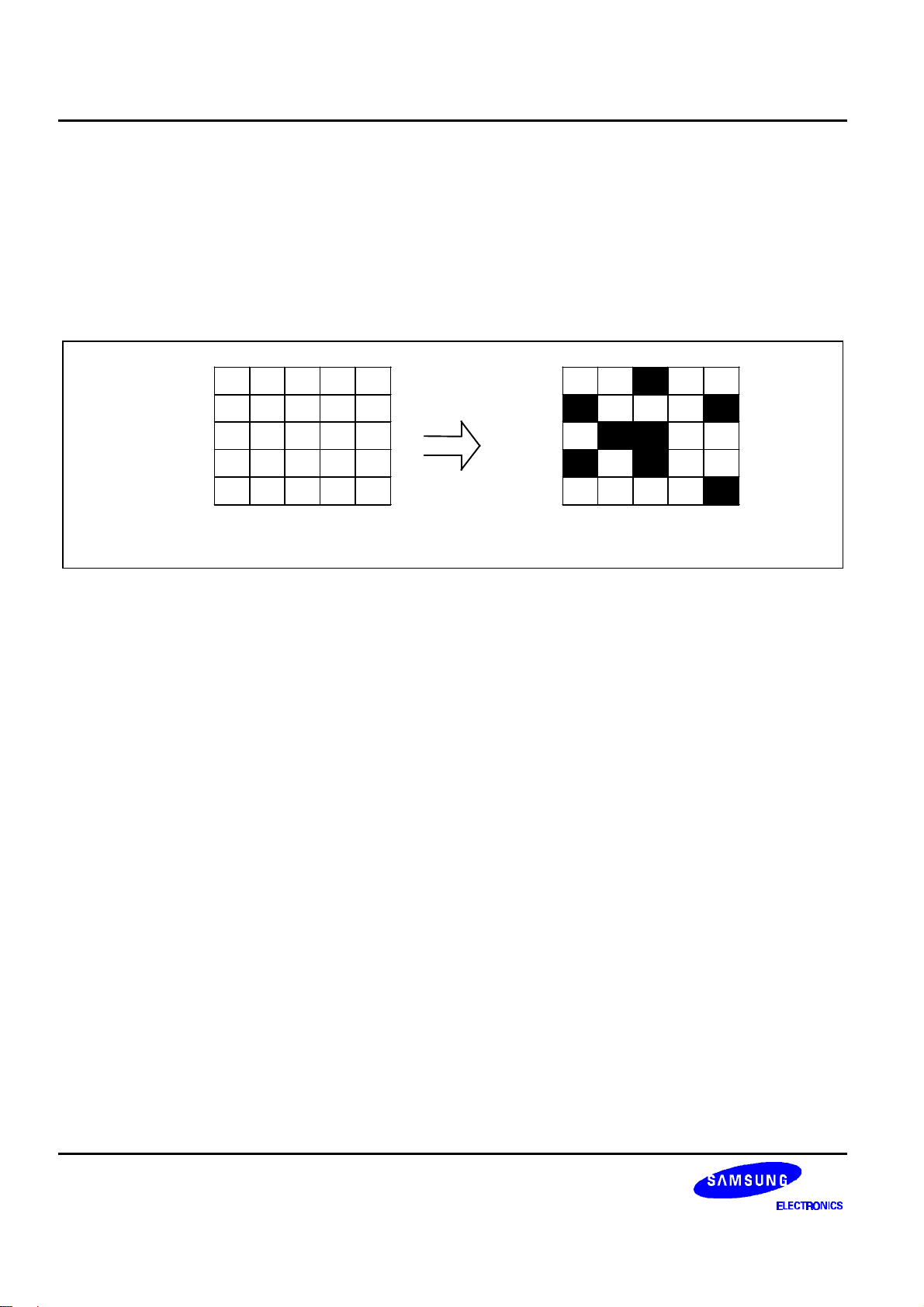
The Display Data RAM stores pixel data for the LCD. It is 65-row by 132-column addressable array. Each pixel can
be selected when the page and column addresses are specified. The 65 rows are divided into 8 pages of 8 lines and
the 9th page with a single line (DB0 only). Data is read from or written to the 8 lines of each page directly through
DB0 to DB7. The display data of DB0 to DB7 from the microprocessor correspond to the LCD common lines as
shown in figure 6. The microprocessor can read from and write to RAM through the I/O buffer. Since the LCD
controller operates independently, data can be written into RAM at the same time as data is being displayed without
causing the LCD flicker.
DB0 0 0 1 - - 0
DB1 1 0 0 - - 1
DB2 0 1 1 - - 0
DB3 1 0 1 - - 0
DB4 0 0 0 - - 1
COM0 - -
COM1 - COM2 - COM3 - COM4 - -
Display Data RAM LCD Display
Figure 6. RAM-to-LCD Data Transfer
Page Address Circuit
This circuit is for providing a Page Address to Display Data RAM shown in figure 8. It incorporates 4-bit Page
Address register changed by only the "Set Page" instruction. Page Address 8 (DB3 is "H", but DB2, DB1 and DB0
are "L") is a special RAM area for the icons and display data DB0 is only valid. When Page Address is above 8, it is
impossible to access to on-chip RAM.
Line Address Circuit
This circuit assigns DDRAM a Line Address corresponding to the first line (COM0) of the display. Therefore, by
setting Line Address repeatedly, it is possible to realize the screen scrolling and page switching without changing
the contents of on-chip RAM as shown in figure 8. It incorporates 6-bit line address register changed by only the
initial display line instruction and 6-bit counter circuit. At the beginning of each LCD frame, the contents of register
are copied to the line counter which is increased by CL signal and generates the Line Address for transferring the
132-bit RAM data to the display data latch circuit. However, display data of icons are not scrolled because the MPU
can not access Line Address of icons.
18
S6B0723 PRELIMINARY SPEC. VER. 0.9 65 COM / 132 SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD
Column Address Circuit
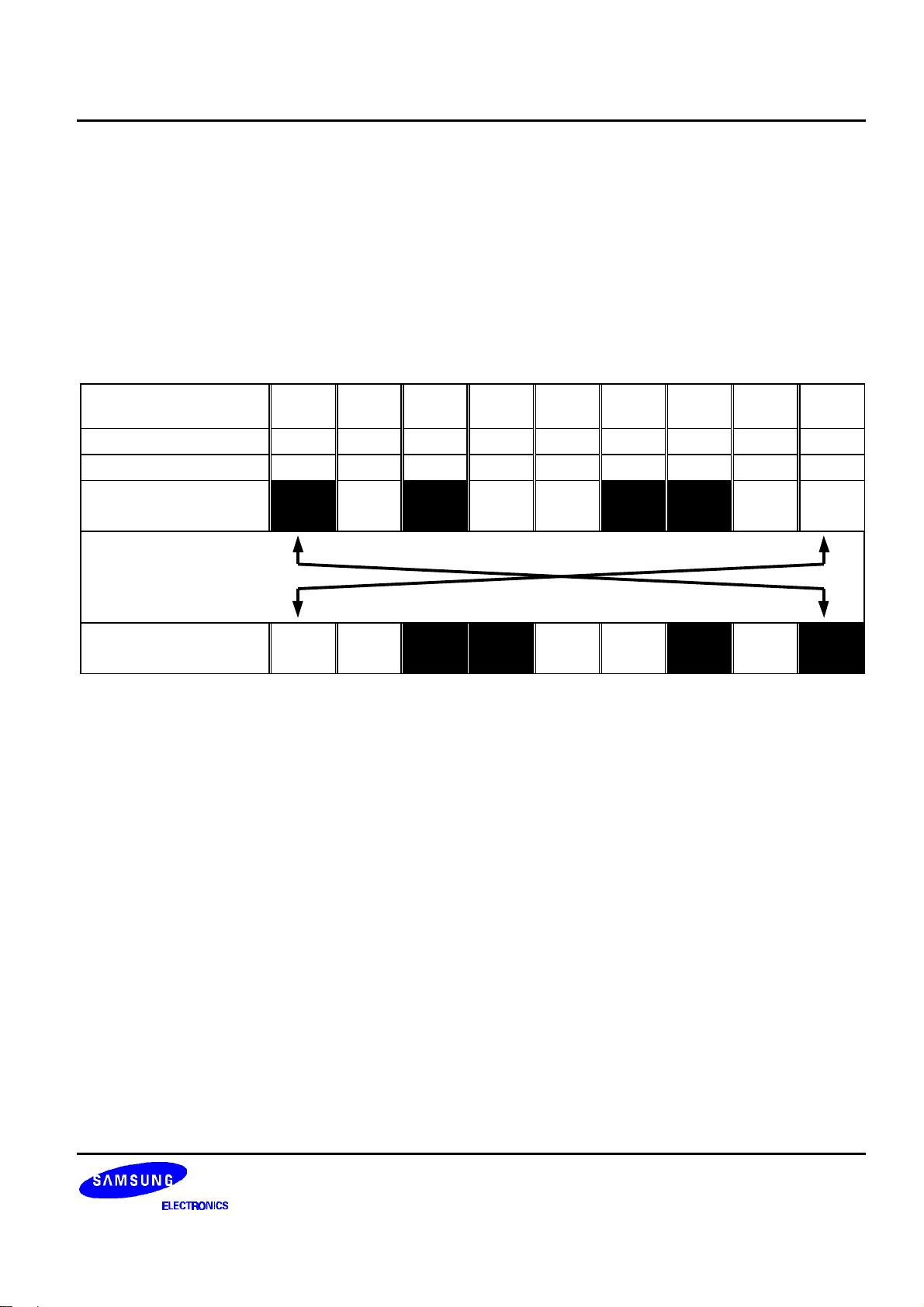
Column Address circuit has an 8-bit preset counter that provides column address to the Display Data RAM as shown
in figure 8. When Set Column Address MSB / LSB instruction is issued, 8-bit [Y7:Y0] is updated. And, since this
address is increased by 1 each a read or write data instruction, microprocessor can access the display data
continuously. However, the counter is not increased and locked if a non-existing address above 84H. It is unlocked
if a column address is set again by set Column Address MSB / LSB instruction. And the Column Address counter is
independent of page address register.
ADC Select instruction makes it possible to invert the relationship between the Column Address and the segment
outputs. It is necessary to rewrite the display data on built-in RAM after issuing ADC select instruction. Refer to the
following figure 7.
SEG output
SEG
0
SEG
1
SEG
2
SEG
3
... ...
SEG
128
SEG
129
SEG
130
SEG
131
Column address [Y7:Y0] 00H 01H 02H 03H ... ... 80H 81H 82H 83H
Display data 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0
LCD panel display
... ...
( ADC = 0 )
LCD panel display
( ADC = 1 )
... ...
Figure 7. The Relationship between the Column Address and the Segment Outputs
Segment Control Circuit
This circuit controls the display data by the display ON / OFF, reverse display ON / OFF and entire display ON / OFF
instructions without changing the data in the display data RAM.
19
 Loading...
Loading...