Samsung S6B0715A01-B0CY, S6B0715A01-B0CZ, S6B0715A01-xxX0, S6B0715A11-B0CY, S6B0715A11-B0CZ Datasheet
...
ed or
transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, for any purpose, without the express written
permission of LCD Driver IC Team.
S6B0715
33 COM / 100 SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD
January.2000
Ver. 4.0
Prepared by: Jae-Su, Ko
Ko1942@samsung.co.kr
Contents in this document are subject to change without notice. No part of this document may be reproduc
33 COM / 100 SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD S6B0715
S6B0715 Specification Revision History
Version Content Date
CAP3P → C3+, CAP2P → C2+, CAP1P → C1+
CAP3M → C3-, CAP2M → C2-, CAP1M → C1-
1.0
Oscillator frequency
FOSC (kHz) = → 19 (Min.): 22.5 (Typ.): 26 (Max.)
FCL (kHz) = → 2.37 (Min.): 2.81 (Typ.): 3.25 (Max.)
Temperature coefficient
TEMPS = L: -0.0%/°C → -0.05%/°C
Absolute maximum ratings
2.0
VLCD: +0.3 to +15.0 → -0.3 to +17.0
Dynamic current consumption
IDD1: 40µA (Max.)
IDD2: 75µA (Typ.), 100µA (Max.)
Oscillator frequency (internal)
3.0
19: 22.5: 26 → 17: 22.5: 27
Oscillator frequency (external)
2.13: 2.81: 3.25 → 2.13: 2.81: 3.37
3.1 Apr.1999
4.0
Change VDD Range : 2.4V to 5.5V → 2.4V to 3.6V
Jan.2000
2

S6B0715 33 COM / 100 SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD
CO
NTENTS
INTRODUCTION.................................................................................................................................................. 1
FEATURES ......................................................................................................................................................... 1
BLOCK DIAGRAM.............................................................................................................................................. 3
PAD CONFIGURATION....................................................................................................................................... 4
PAD CENTER COORDINATES........................................................................................................................... 5
PIN DESCRIPTION.............................................................................................................................................. 7
POWER SUPPLY......................................................................................................................................... 7
LCD DRIVER SUPPLY................................................................................................................................. 7
SYSTEM CONTROL .................................................................................................................................... 8
MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACE .............................................................................................................. 9
LCD DRIVER OUTPUTS.............................................................................................................................11
TEST PINS ..................................................................................................................................................11
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION............................................................................................................................12
MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACE .............................................................................................................12
DISPLAY DATA RAM (DDRAM)..................................................................................................................16
LCD DISPLAY CIRCUITS ............................................................................................................................19
LCD DRIVER CIRCUIT................................................................................................................................21
POWER SUPPLY CIRCUITS.......................................................................................................................22
REFERECE CIRCUIT EXAMPLES..............................................................................................................28
RESET CIRCUIT.........................................................................................................................................29
INSTRUCTION DESCRIPTION...........................................................................................................................30
SPECIFICATIONS..............................................................................................................................................43
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS...............................................................................................................43
DC CHARACTERISTICS.............................................................................................................................44
REFERENCE DATA....................................................................................................................................47
AC CHARACTERISTICS.............................................................................................................................49
REFERENCE APPLICATIONS...........................................................................................................................53
MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACE .............................................................................................................53
CONNECTIONS BETWEEN S6B0715 AND LCD PANEL............................................................................54
TCP PIN LAYOUT (SAMPLE)......................................................................................................................57
3

S6B0715 33 COM / 100 SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD
INTRODUCTION
The S6B0715 is a driver & controller LSI for graphic dot-matrix liquid crystal display systems. It contains 33 common
and 100 segment driver circuits. This chip is connected directly to a microprocessor, accepts serial or 8-bit parallel
display data and stores in an on-chip display data RAM of 65 x 132 bits. It provides a highly-flexible display section
due to 1-to-1 correspondence between on-chip display data RAM bits and LCD panel pixels. And it performs display
data RAM read/write operation with no external operating clock to minimize power consumption. In addition,
because it contains power supply circuits necessary to drive liquid crystal, it is possible to make a display system
with the fewest components.
FEATURES
Driver Output Circuits
− 33 common outputs / 100 segment outputs
On-chip Display Data RAM
− Capacity: 65 x 132 = 8,580 bits
− Bit data "1": a dot of display is illuminated.
− Bit data "0": a dot of display is not illuminated.
Multi-chip Operation (Master, Slave) Available
Applicable Duty Ratios
Duty ratio Applicable LCD bias Maximum display area
1/33 1/5 or 1/6
Microprocessor Interface
− 8-bit parallel bi-directional interface with 6800-series or 8080-series
− Serial interface (only write operation) available
Various Instruction Setting
On-chip Low Power Analog Circuit
− On-chip oscillator circuit
− Voltage converter (x2, x3 and x4)
− Voltage regulator (temperature coefficient: -0.05%/°C, -0.2%/°C)
− On-chip electronic contrast control function (32 steps)
− Voltage follower (LCD bias: 1/5 or 1/6)
Operating Voltage Range
− Supply voltage (VDD): 2.4 to 3.6 V
− LCD driving voltage (VLCD = V0 - VSS): 4.0 to 15.0 V
Low Power Consumption
− 100 µΑ Typ. (VDD = 3V, x4 boosting, V0 = 8V, internal power supply ON and display OFF)
− 10 µΑ Max. (during power save [standby] mode)
Wide Operating Temperature Range
33 × 100
− Ta = -40°C to +85°C
Package Type
− Gold bumped chip or TCP
1

33 COM / 100 SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD S6B0715
Series Specifications
Product code TEMPS pin Temp. coefficient
S6B0715A01-B0CZ
S6B0715A01-B0CY
S6B0715A11-B0CZ
S6B0715A11-B0CY
S6B0715A01-xxX0 670 µm
S6B0715A01-xxX0
0
(VSS connected)
1
(VDD connected)
0
(VSS connected)
-0.05%/°C
-0.2%/°C
-0.05%/°C
Package Chip thickness
670 µm
470 µm
COG
670 µm
470 µm
470 µm
TCP
S6B0715A11-xxX0 670 µm
S6B0715A11-xxX0
(VDD connected)
1
-0.2%/°C
470 µm
* xx: TCP ordering number
2

S6B0715 33 COM / 100 SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD
V
DB0
DB1
COMS
COM31
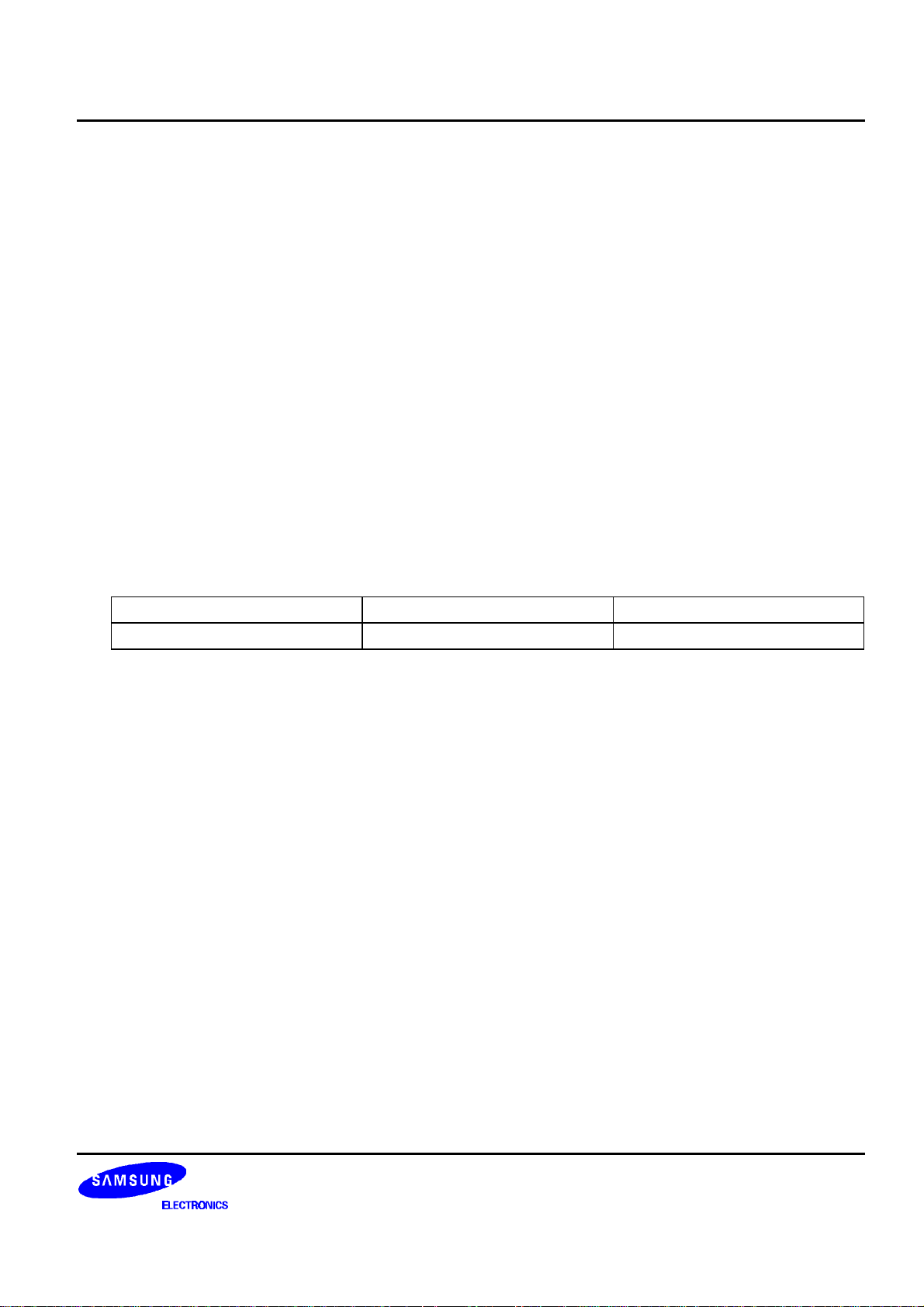
BLOCK DIAGRAM
SEG99
SEG98
SEG66
SEG65
VDD
V0
V1
V2
V3
V4
SS
SEG64
SEG1
SEG0
:
100 SEGMENT
DRIVER CIRCUITS
:
COMS
COM0
:
:
34 COMMON
DRIVER CIRCUITS
V0
VR
TEMPS
VOUT
C1-
C1+
C2-
C2+
C3-
C3+
V / F
CIRCUIT
V / R
CIRCUIT
V / C
CIRCUIT
PAGE
ADDRESS
CIRCUIT
SEGMENT CONTROLLER
I/O
BUFFER
DISPLAY DATA RAM
65 X 132 = 8,580 Bits
COLUMN ADDRESS
CIRCUIT
STATUS REGISTER INSTRUCTION REGISTER
COMMON CONTROLLER
LINE
ADDRESS
CIRCUIT
INSTRUCTION DECODERBUS HOLDER
DISPLAY
TIMING
GENERATOR
CIRCUIT
OSCILLATOR
MS
CL
M
FRS
DISP
TESTL2
TESTL1
MPU INTERFACE (PARALLEL & SERIAL)
DB2
DB3
DB4
DB5
DB6(SCLK)
DB7(SID)
MI
RESETB
PS
RW_WR
E_RD
RS
CS2
CS1B
Figure 1. Block Diagram
3
33 COM / 100 SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD S6B0715
108
209
107
2108323482 1
ðððð
- - - -
ðððð
ðððð
- - - -
ðððð
(-3832, -1055)
(+3832, -1070)
30
µ
m
30
µ
m
30
µ
m
60
µ
m
30
µ
m
42
µ
m
108
µ
m
42
µ
m
108
µ
m
(-3870, +1230)
(+3870, +1230)
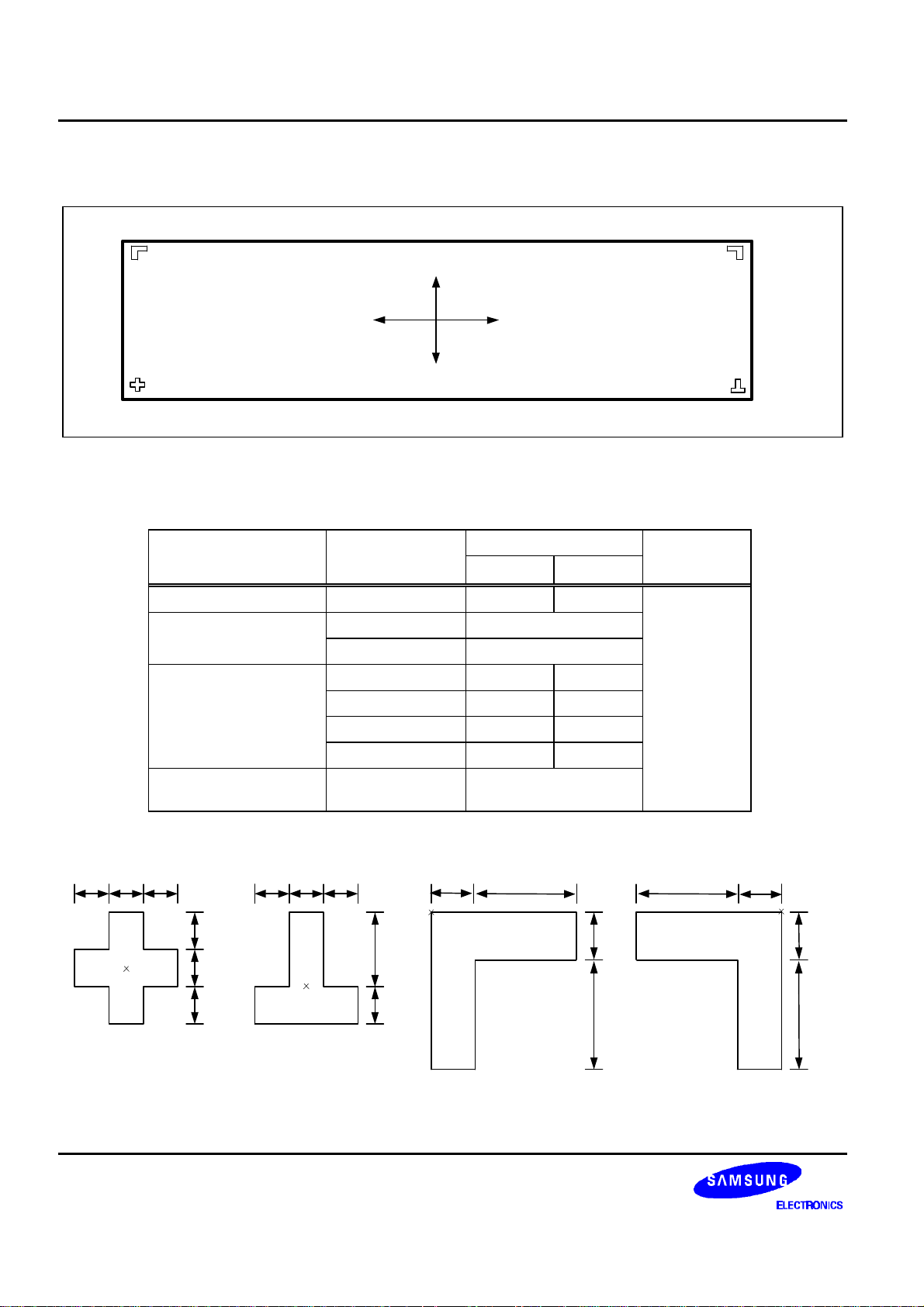
PAD CONFIGURATION
ррр ррррррррррррррррррр
- - - - - - - - - -
Y
S6B0715
(TOP VIEW)
рррррррррррррррррррррр
Figure 2. S6B0715 Chip Configuration
Table 1. S6B0715 Pad Dimensions
Item Pad No.
Chip size - 7980 2700
Pad pitch
Bumped pad size
(0,0)
- - - - - - - - - -
1 to 82 90
83 to 234 70
1 to 82 56 114
83 to 107 108 50
108 to 209 50 108
210 to 234 108 50
ррррррррррррррррррр
X
ððð
ррррррррррррррррррррррр
Size
X Y
Unit
µm
Bumped pad height All pad 17 (Typ.)
COG Align Key Coordinate ILB Align Key Coordinate
30µm 30µm 30µm
30µm 30µm 30µm
42µm 108µm
42µm108µm
4
S6B0715 33 COM / 100 SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD
50
C3-
765
-1226
100
COM2
3830
350
150
SEG41
595
1190
PAD CENTER COORDINATES
Table 2. Pad Center Coordinates
[Unit: µm]
No. Name X Y No. Name X Y No. Name X Y
1 DUMMY -3645 -1226 51 C1+ 855 -1226 101 COM1 3830 420
2 TESTL1 -3555 -1226 52 C1+ 945 -1226 102 COM0 3830 490
3 VDD -3465 -1226 53 C1- 1035 -1226 103 COMS 3830 560
4 FRS -3375 -1226 54 C1- 1125 -1226 104 DUMMY 3830 630
5 M -3285 -1226 55 C2+ 1215 -1226 105 DUMMY 3830 700
6 CL -3195 -1226 56 C2+ 1305 -1226 106 DUMMY 3830 770
7 DISP -3105 -1226 57 C2- 1395 -1226 107 DUMMY 3830 840
8 VDD -3015 -1226 58 C2- 1485 -1226 108 DUMMY 3535 1190
9 MS -2925 -1226 59 VSS 1575 -1226 109 SEG0 3465 1190
10 VSS -2835 -1226 60 VSS 1665 -1226 110 SEG1 3395 1190
11 RESETB -2745 -1226 61 VR 1755 -1226 111 SEG2 3325 1190
12 VDD -2655 -1226 62 VR 1845 -1226 112 SEG3 3255 1190
13 PS -2565 -1226 63 V0 1935 -1226 113 SEG4 3185 1190
14 VSS -2475 -1226 64 V0 2025 -1226 114 SEG5 3115 1190
15 CS1B -2385 -1226 65 V0 2115 -1226 115 SEG6 3045 1190
16 CS2 -2295 -1226 66 V0 2205 -1226 116 SEG7 2975 1190
17 VDD -2205 -1226 67 V0 2295 -1226 117 SEG8 2905 1190
18 MI -2115 -1226 68 V0 2385 -1226 118 SEG9 2835 1190
19 VSS -2025 -1226 69 V1 2475 -1226 119 SEG10 2765 1190
20 VDD -1935 -1226 70 V1 2565 -1226 120 SEG11 2695 1190
21 RS -1845 -1226 71 V2 2655 -1226 121 SEG12 2625 1190
22 VSS -1755 -1226 72 V2 2745 -1226 122 SEG13 2555 1190
23 RW_WR -1665 -1226 73 V3 2835 -1226 123 SEG14 2485 1190
24 E_RD -1575 -1226 74 V3 2925 -1226 124 SEG15 2415 1190
25 VDD -1485 -1226 75 V4 3015 -1226 125 SEG16 2345 1190
26 VDD -1395 -1226 76 V4 3105 -1226 126 SEG17 2275 1190
27 VDD -1305 -1226 77 VSS 3195 -1226 127 SEG18 2205 1190
28 VDD -1215 -1226 78 VSS 3285 -1226 128 SEG19 2135 1190
29 VDD -1125 -1226 79 TEMPS 3375 -1226 129 SEG20 2065 1190
30 VDD -1035 -1226 80 VDD 3465 -1226 130 SEG21 1995 1190
31 DB0 -945 -1226 81 TESTL2 3555 -1226 131 SEG22 1925 1190
32 DB1 -855 -1226 82 DUMMY 3645 -1226 132 SEG23 1855 1190
33 DB2 -765 -1226 83 DUMMY 3830 -840 133 SEG24 1785 1190
34 DB3 -675 -1226 84 DUMMY 3830 -770 134 SEG25 1715 1190
35 DB4 -585 -1226 85 DUMMY 3830 -700 135 SEG26 1645 1190
36 DB5 -495 -1226 86 DUMMY 3830 -630 136 SEG27 1575 1190
37 DB6 -405 -1226 87 COM15 3830 -560 137 SEG28 1505 1190
38 DB7 -315 -1226 88 COM14 3830 -490 138 SEG29 1435 1190
39 VSS -225 -1226 89 COM13 3830 -420 139 SEG30 1365 1190
40 VSS -135 -1226 90 COM12 3830 -350 140 SEG31 1295 1190
41 VSS -45 -1226 91 COM11 3830 -280 141 SEG32 1225 1190
42 VSS 45 -1226 92 COM10 3830 -210 142 SEG33 1155 1190
43 VSS 135 -1226 93 COM9 3830 -140 143 SEG34 1085 1190
44 VSS 225 -1226 94 COM8 3830 -70 144 SEG35 1015 1190
45 VOUT 315 -1226 95 COM7 3830 0 145 SEG36 945 1190
46 VOUT 405 -1226 96 COM6 3830 70 146 SEG37 875 1190
47 C3+ 495 -1226 97 COM5 3830 140 147 SEG38 805 1190
48 C3+ 585 -1226 98 COM4 3830 210 148 SEG39 735 1190
49 C3- 675 -1226 99 COM3 3830 280 149 SEG40 665 1190
5
33 COM / 100 SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD S6B0715
200
SEG91
-2905
1190
Table 2. Pad Center Coordinates (Continued)
[Unit: µm]
No. Name X Y No. Name X Y No. Name X Y
151 SEG42 525 1190 201 SEG92 -2975 1190
152 SEG43 455 1190 202 SEG93 -3045 1190
153 SEG44 385 1190 203 SEG94 -3115 1190
154 SEG45 315 1190 204 SEG95 -3185 1190
155 SEG46 245 1190 205 SEG96 -3255 1190
156 SEG47 175 1190 206 SEG97 -3325 1190
157 SEG48 105 1190 207 SEG98 -3395 1190
158 SEG49 35 1190 208 SEG99 -3465 1190
159 SEG50 -35 1190 209 DUMMY -3535 1190
160 SEG51 -105 1190 210 DUMMY -3830 840
161 SEG52 -175 1190 211 DUMMY -3830 770
162 SEG53 -245 1190 212 DUMMY -3830 700
163 SEG54 -315 1190 213 DUMMY -3830 630
164 SEG55 -385 1190 214 COM16 -3830 560
165 SEG56 -455 1190 215 COM17 -3830 490
166 SEG57 -525 1190 216 COM18 -3830 420
167 SEG58 -595 1190 217 COM19 -3830 350
168 SEG59 -665 1190 218 COM20 -3830 280
169 SEG60 -735 1190 219 COM21 -3830 210
170 SEG61 -805 1190 220 COM22 -3830 140
171 SEG62 -875 1190 221 COM23 -3830 70
172 SEG63 -945 1190 222 COM24 -3830 0
173 SEG64 -1015 1190 223 COM25 -3830 -70
174 SEG65 -1085 1190 224 COM26 -3830 -140
175 SEG66 -1155 1190 225 COM27 -3830 -210
176 SEG67 -1225 1190 226 COM28 -3830 -280
177 SEG68 -1295 1190 227 COM29 -3830 -350
178 SEG69 -1365 1190 228 COM30 -3830 -420
179 SEG70 -1435 1190 229 COM31 -3830 -490
180 SEG71 -1505 1190 230 COMS -3830 -560
181 SEG72 -1575 1190 231 DUMMY -3830 -630
182 SEG73 -1645 1190 232 DUMMY -3830 -700
183 SEG74 -1715 1190 233 DUMMY -3830 -770
184 SEG75 -1785 1190 234 DUMMY -3830 -840
185 SEG76 -1855 1190
186 SEG77 -1925 1190
187 SEG78 -1995 1190
188 SEG79 -2065 1190
189 SEG80 -2135 1190
190 SEG81 -2205 1190
191 SEG82 -2275 1190
192 SEG83 -2345 1190
193 SEG84 -2415 1190
194 SEG85 -2485 1190
195 SEG86 -2555 1190
196 SEG87 -2625 1190
197 SEG88 -2695 1190
198 SEG89 -2765 1190
199 SEG90 -2835 1190
6

S6B0715 33 COM / 100 SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD
PIN DESCRIPTION
POWER SUPPLY
Table 3. Power Supply Pin Description
Name I/O Description
VDD Supply Power supply
VSS Supply Ground
LCD driver supply voltages
The voltage determined by LCD pixel is impedance-converted by an operational amplifier
for application.
V0
V1
V2
V3
V4
I/O
Voltages should have the following relationship;
V0 ≥ V1 ≥ V2 ≥ V3 ≥ V4 ≥ VSS
When the internal power circuit is active, these voltages are generated as following table
according to the state of LCD Bias.
LCD bias V1 V2 V3 V4
1/6 bias (5/6) x V0 (4/6) x V0 (2/6) x V0 (1/6) x V0
1/5 bias (4/5) x V0 (3/5) x V0 (2/5) x V0 (1/5) x V0
LCD DRIVER SUPPLY
Table 4. LCD Driver Supply Pin Description
Name I/O Description
C1- O Capacitor 1 negative connection pin for voltage converter
C1+ O Capacitor 1 positive connection pin for voltage converter
C2- O Capacitor 2 negative connection pin for voltage converter
C2+ O Capacitor 2 positive connection pin for voltage converter
C3- O Capacitor 3 negative connection pin for voltage converter
C3+ O Capacitor 3 positive connection pin for voltage converter
VOUT I/O Voltage converter input / output pin
VR I V0 voltage adjustment pin
7
33 COM / 100 SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD S6B0715
SYSTEM CONTROL
Table 5. System Control Pin Description
Name I/O Description
Master / Slave operation select pin
− MS = "H": master operation
− MS = "L": slave operation
The following table depends on the MS status.
MS I
CL I/O
M I/O
FRS O
DISP I/O
TEMPS I
MS
H Enabled Input Output Output Output Output
L Disabled Disabled Input Input Output Input
Display clock input / output pin
When the S6B0715 is used in master/slave mode (multi-chip), the CL pins must be
connected each other for sync.
LCD AC signal input / output pin
When the S6B0715 is used in master/slave mode (multi-chip), the M pins must be
connected each other.
− MS = “H” : output
− MS = “L” : input
Static driver segment output pin
This pin is used together with the M pin.
LCD display blanking control input/output.
When S6B0715 is used in master/slave mode
(multi-chip), the DISP pins must be connected each other.
− MS = “H” : output
− MS = “L” : input
Selects temperature coefficient of the reference voltage
− TEMPS = "L": -0.05%/°C
− TEMPS = "H": -0.2%/°C
OSC
circuit
Power
supply
circuit
CL M FRS DISP
8

S6B0715 33 COM / 100 SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD
MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACE
Table 6. Microprocessor Interface Pin Description
Name I/O Description
RESETB
PS I
MI I
CS1B
CS2
RS I
RW_WR
Reset input pin
I
When RESETB is “L”, initialization is executed.
Parallel / serial data input select input
PS
*NOTE: When PS is “L”, DB0 to DB5 a re high impedance and E_RD and RW_WR
should be fixed to either “H” or “L”.
Microprocessor interface select input pin
− MI = "H": 6800-series MPU interface
− MI = "L": 8080-series MPU interface
Chip select input pins
I
Data / instruction I/O is enabled only when CS1B is “L” and CS2 is “H”.
When chip select is non-active, DB0 to DB7 may be high impedance.
Register select input pin
− RS = "H": DB0 to DB7 are display data.
− RS = "L": DB0 to DB7 are control data.
Read / Write execution control pin
MI MPU type RW_WR Description
H 6800-series
I
Interface
mode
H Parallel
L Serial
L 8080-series
Chip
select
CS1B,
CS2
CS1B,
CS2
RW
/WR
Data /
instruction
RS DB0 to DB7
RS SID (DB7) Write only SCLK (DB6)
Read/Write control input pin
− RW = “H”: read
− RW = “L”: write
Write enable clock input pin
The data on DB0 to DB7 are latched at the rising
edge of the /WR signal.
Data Read / write Serial clock
E_RD
RW_WR
-
9

33 COM / 100 SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD S6B0715
Table 6. Microprocessor Interface Pin Description (Continued)
Name I/O Description
Read / Write execution control pin
MI MPU Type E_RD Description
Read / Write control input pin
− RW = “H”: When E is “ H”, DB0 to DB7 are in an
E_RD I
H 6800-series
E
output status.
− RW = “L”: The data on DB0 to DB7 are latched at
the falling edge of the E signal.
DB0
to
DB7
I/O
L 8080-series
/RD
Read enable clock input pin
When /RD is “L”, DB0 to DB7 are in an output status.
8-bit bi-directional data bus that is connected to the standard 8-bit microprocessor data
bus. When the serial interface selected (PS = "L");
− DB0 to DB5: high impedance
− DB6: serial input clock (SCLK)
− DB7: serial input data (SID)
When chip select is not active, DB0 to DB7 may be high impedance.
10
S6B0715 33 COM / 100 SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD
LCD DRIVER OUTPUTS
Table 8. LCD Driver Outputs Pin Description
Name I/O Description
LCD segment driver outputs
The display data and the M signal control the output voltage of segment driver.
SEG0
to
SEG99
COM0
to
COM31
COMS O
O
O
Display data M
Segment driver output voltage
Normal display Reverse display
H H V0 V2
H L VSS V3
L H V2 V0
L L V3 VSS
Power save mode VSS VSS
LCD common driver outputs
The internal scanning data and M signal control the output voltage of common driver.
Scan data M Common driver output voltage
H H VSS
H L V0
L H V1
L L V4
Power save mode VSS
Common output for the icons
The output signals of two pins are same. When not used, these pins should be left open. In
multi-chip (master/slave) mode, all COMS pins on both master and slave units are the
same signal.
TEST PINS
Table 8. Test Pin Description
Name I/O Description
TESTL1
TESTL2
NOTE: DUMMY – These pins should be opened (floated).
IC test pins with pull-up
I
These pins must be open.
11
33 COM / 100 SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD S6B0715
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
MICROPROCESSOR INTERFACE
Chip Select Input
There are CS1B and CS2 pins for Chip Selection. The S6B0715 can interface with an MPU only when CS1B is “L”
and CS2 is “H”. When these pins are set to any other combination, RS, E_RD, and RW_WR inputs are disabled and
DB0 to DB7 are to be high impedance. And, in case of serial interface, the internal shift register and the counter are
reset.
Parallel / Serial Interface
S6B0715 has three types of interface with an MPU, which are one serial and two parallel interface. This parallel or
serial interface is determined by PS pin as shown in table 9.
Table 9. Parallel / Serial Interface Mode
PS Type CS1B CS2 MI Interface mode
H Parallel CS1B CS2
L Serial CS1B CS2
Parallel Interface (PS = "H")
The 8-bit bi-directional data bus is used in parallel interface and the type of MPU is selected by MI as shown in table
10. The type of data transfer is determined by signals at RS, E_RD and RW_WR as shown in table 11.
Table 10. Microprocessor Selection for Parallel Interface
MI CS1B CS2 RS E_RD RW_WR
H CS1B CS2 RS E RW DB0 to DB7 6800-series
L CS1B CS2 RS /RD /WR DB0 to DB7 8080-series
Table 11. Parallel Data Transfer
Common
RS
H H H L H Display data read out
H H L H L Display data write
L H H L H Register status read
L H L H L Writes to internal register (instruction)
6800-series 8080-series
E_RD
(E)
RW_WR
(RW)
E_RD
(/RD)
RW_WR
(/WR)
H 6800-series MPU mode
L 8080-series MPU mode
*×
DB0 to DB7 MPU bus
Description
Serial-mode
*×: Don't care
12
S6B0715 33 COM / 100 SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD
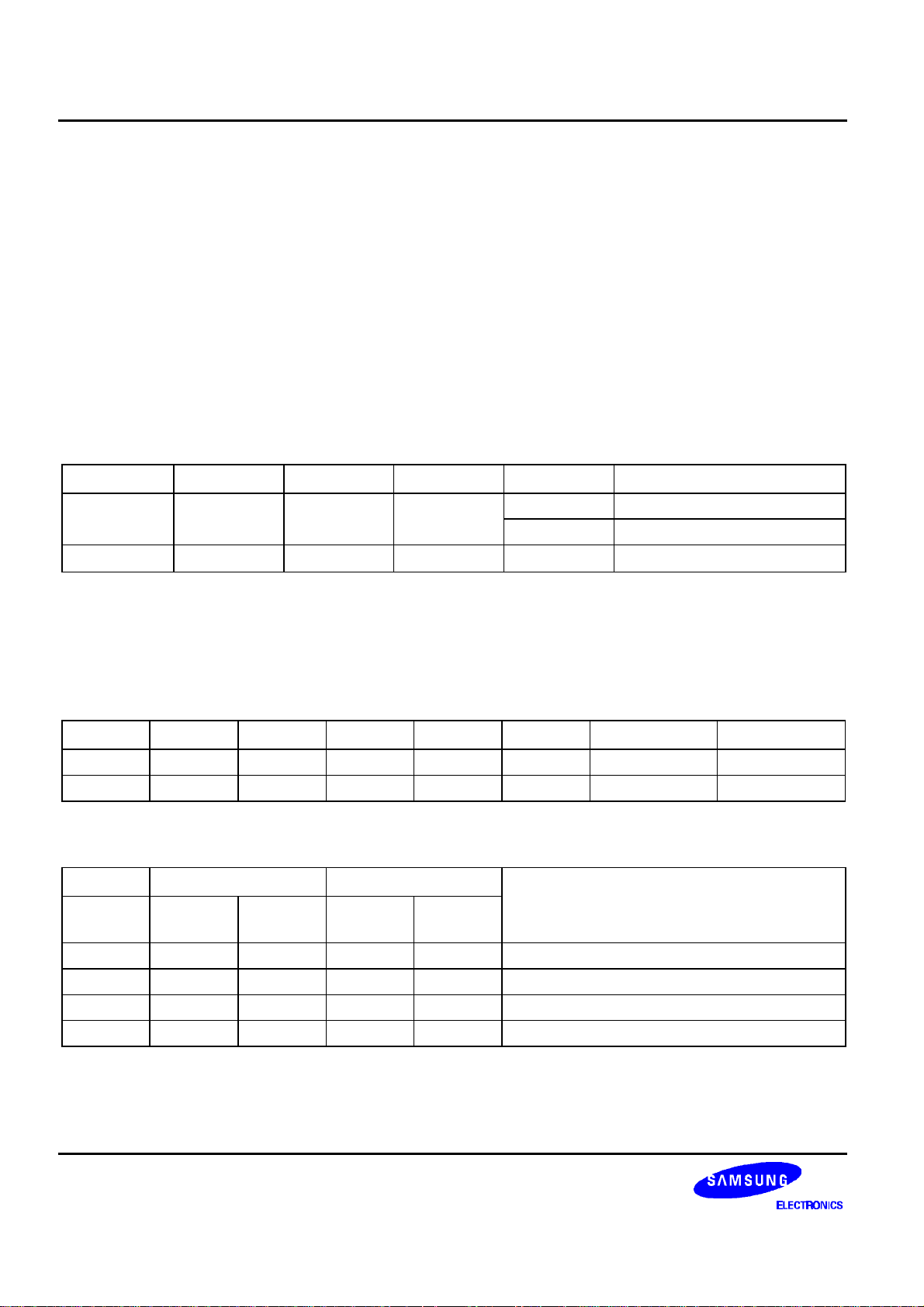
Serial interface (PS = "L")
When the S6B0715 is active, serial data (DB7) and serial clock (DB6) inputs are enabled. And not active, the internal
8-bit shift register and the 3-bit counter are reset. Serial data can be read on the rising edge of serial clock going into
DB6 and processed as 8-bit parallel data on the eighth serial clock. Serial data input is display data when RS is high
and control data when RS is low. Since the clock signal (DB6) is easy to be affected by the external noise caused by
the line length, the operation check on the actual machine is recommended.
CS1B
CS2
SID
SCLK
RS
DB6DB7DB0DB1DB2DB3DB4DB5DB6DB7
Figure 3. Serial Interface Timing
Busy Flag
The Busy Flag indicates whether the S6B0715 is operating or not. When DB7 is “H” in read status operation, this
device is in busy status and will accept only read status instruction. If the cycle time is correct, the microprocessor
needs not to check this flag before each instruction, which improves the MPU performance.
13

33 COM / 100 SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD S6B0715
Data Transfer
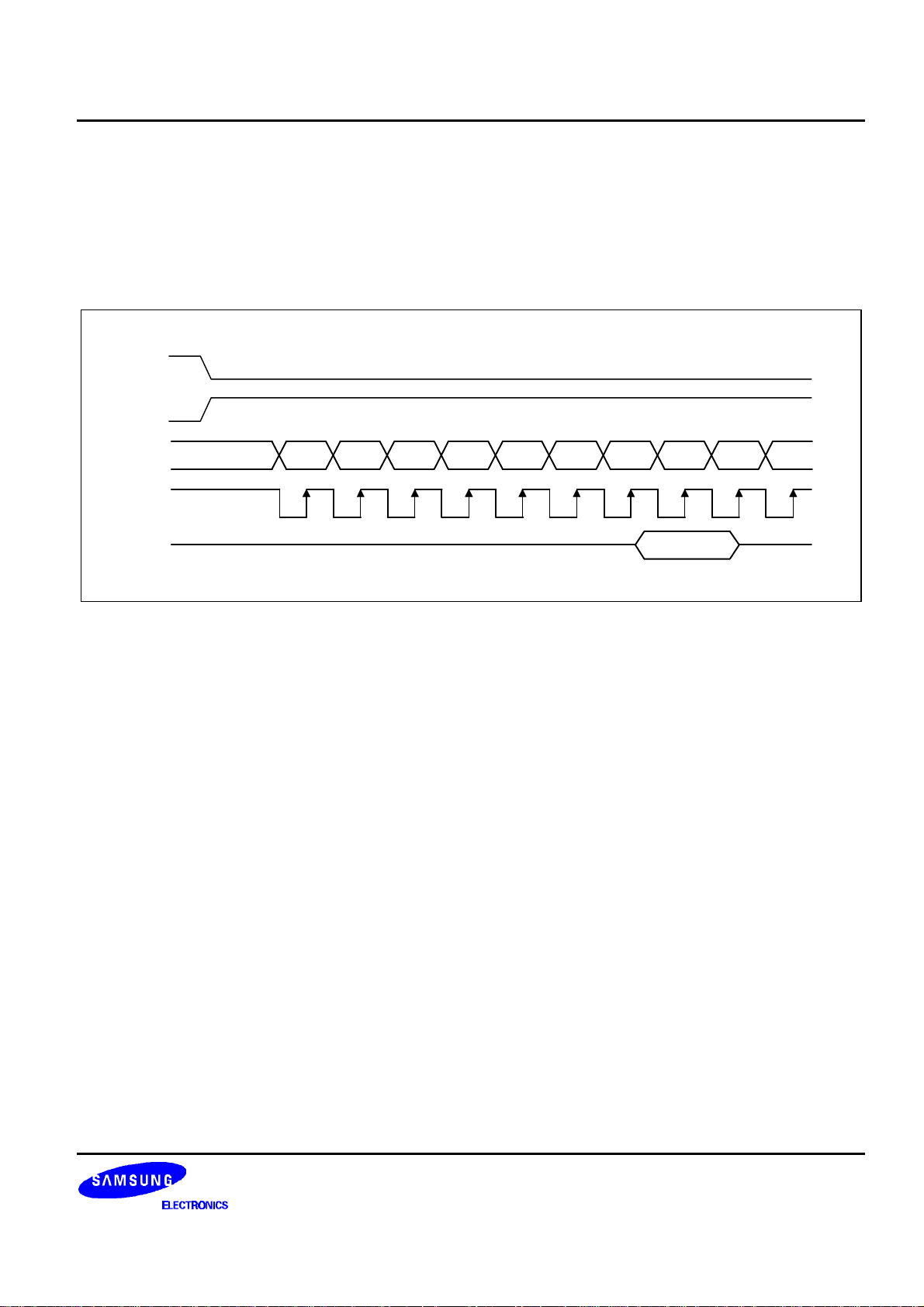
The S6B0715 uses bus holder and internal data bus for Data Transfer with the MPU. When writing data from the
MPU to on-chip RAM, data is automatically transferred from the bus holder to the RAM as shown in figure 4. And
when reading data from on-chip RAM to the MPU, the data for the initial read cycle is stored in the bus holder
(dummy read) and the MPU reads this stored data from bus holder for the next data read cycle as shown in figure 5.
This means that a dummy read cycle must be inserted between each pair of address sets when a sequence of
address sets is executed. Therefore, the data of the specified address cannot be output with the read display data
instruction right after the address sets, but can be output at the second read of data.
MPU signals
RS
/WR
DB0 to DB7
Internal signals
/WR
BUS HOLDER
COLUMN ADDRESS
N D(N) D(N+1) D(N+2) D(N+3)
N D(N) D(N+1) D(N+2) D(N+3)
N N+1 N+2 N+3
Figure 4. Write Timing
14
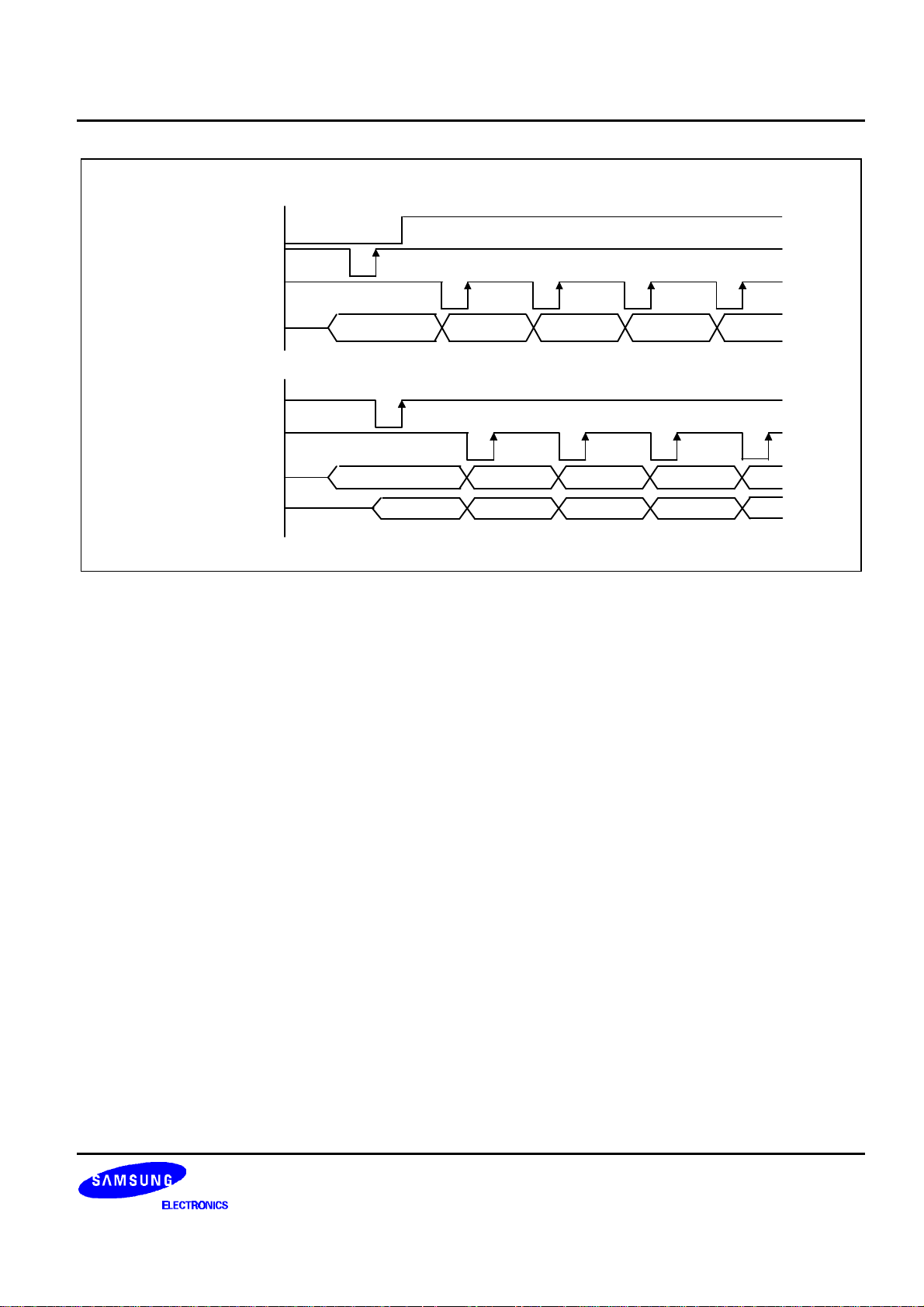
S6B0715 33 COM / 100 SEG DRIVER & CONTROLLER FOR STN LCD
N
D(N)
D(N+1)
D(N+2)
N
N+1
N+2
N+3
MPU signals
RS
/WR
/RD
DB0 to DB7
Internal signals
/WR
/RD
BUS HOLDER
COLUMN ADDRESS
N
Dummy D(N) D(N+1)
Figure 5. Read Timing
15
 Loading...
Loading...