SAMSUNG DVD905 Service Manual
DIGITAL VIDEO DISC PLAYER
DVD905
SERVICE
1. Precautions
2. Reference Information
3. Product Specifications
4. Disassembly and Reassembly
5. Thoubleshooting
6. Exploded Views and Parts List
7. Electrical Parts List
8.
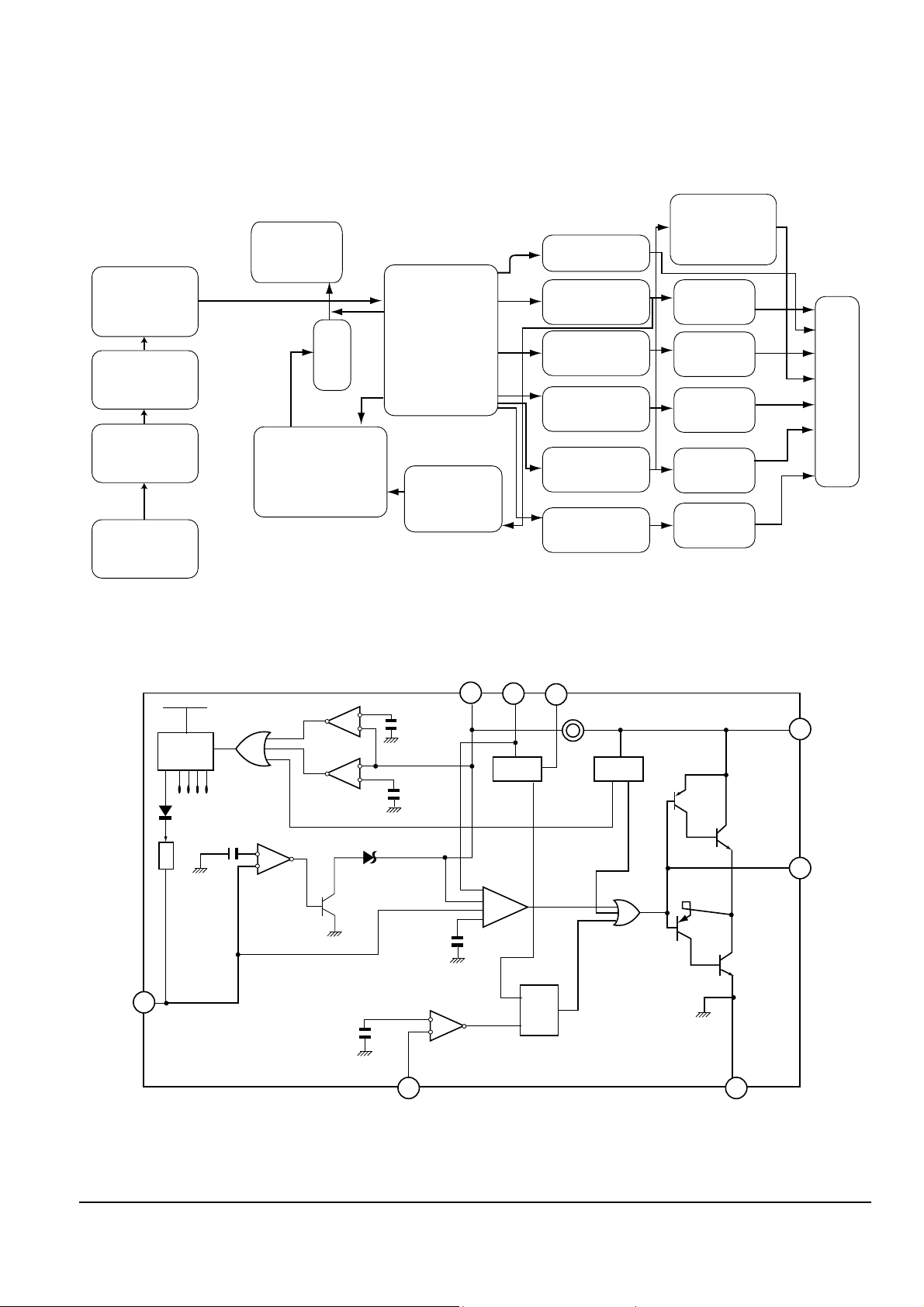
Block Diagram
9. PCB Diagrams
10. Wiring Diagram
11. Schematic Diagrams
Manual
DIGITAL VIDEO DISC PLAYER CONTENTS
© Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. MAY. 1997 AH68-20166A / AH68-20167A
Samsung Electronics 1-1
1. Precautions
1. Be sure that all of the built-in protective devices are
replaced. Restore any missing protective shields.
2. When reinstalling the chassis and its assemblies, be
sure to restore all pretective devices, including :
control knobs and compartment covers.
3. Make sure that there are no cabinet openings
through which people--particularly children
--might insert fingers and contact dangerous
voltages. Such openings include the spacing
between the picture tube and the cabinet mask,
excessively wide cabinet ventilation slots, and
improperly fitted back covers.
If the measured resistance is less than 1.0 megohm
or greater than 5.2 megohms, an abnormality exists
that must be corrected before the unit is returned
to the customer.
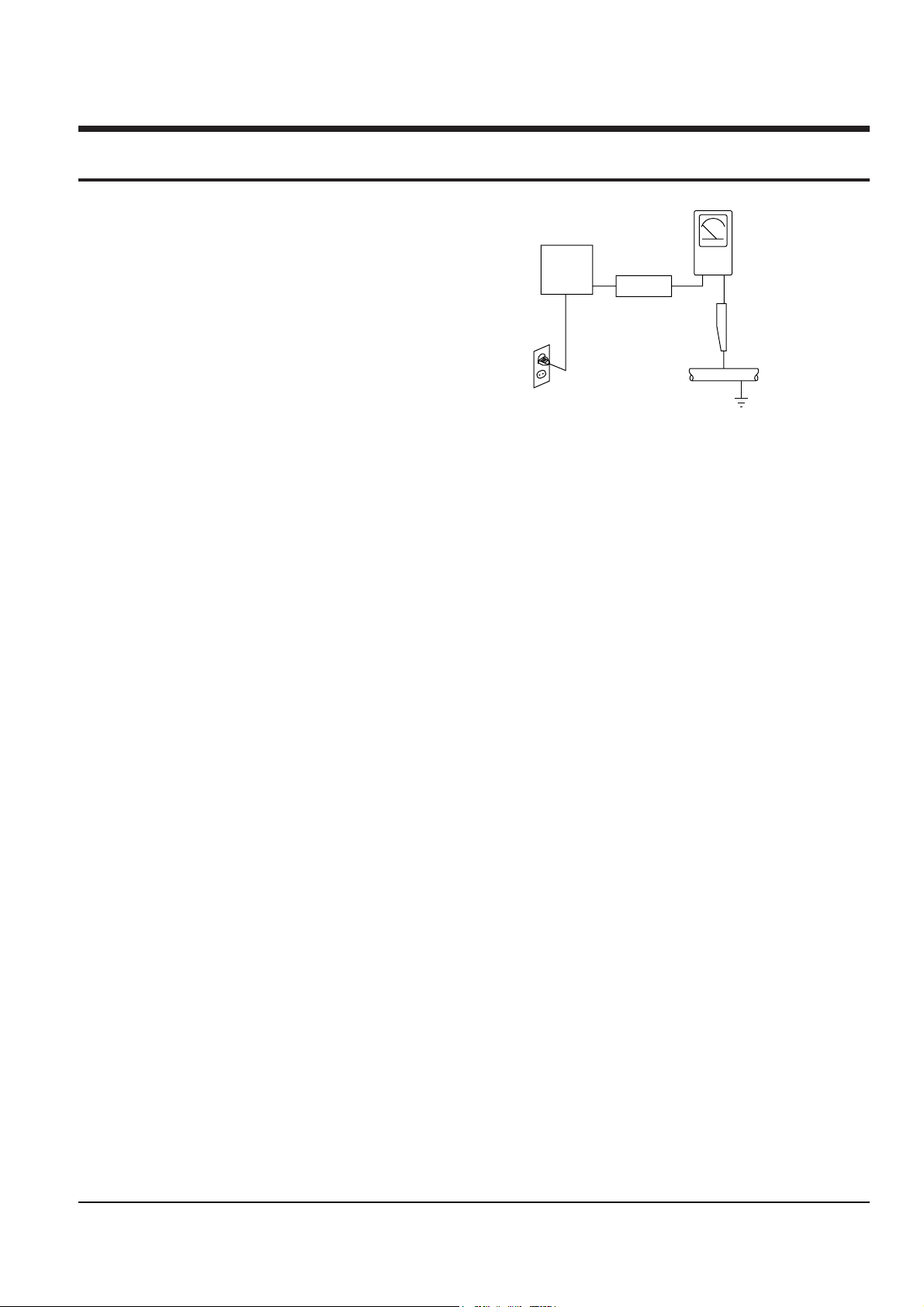
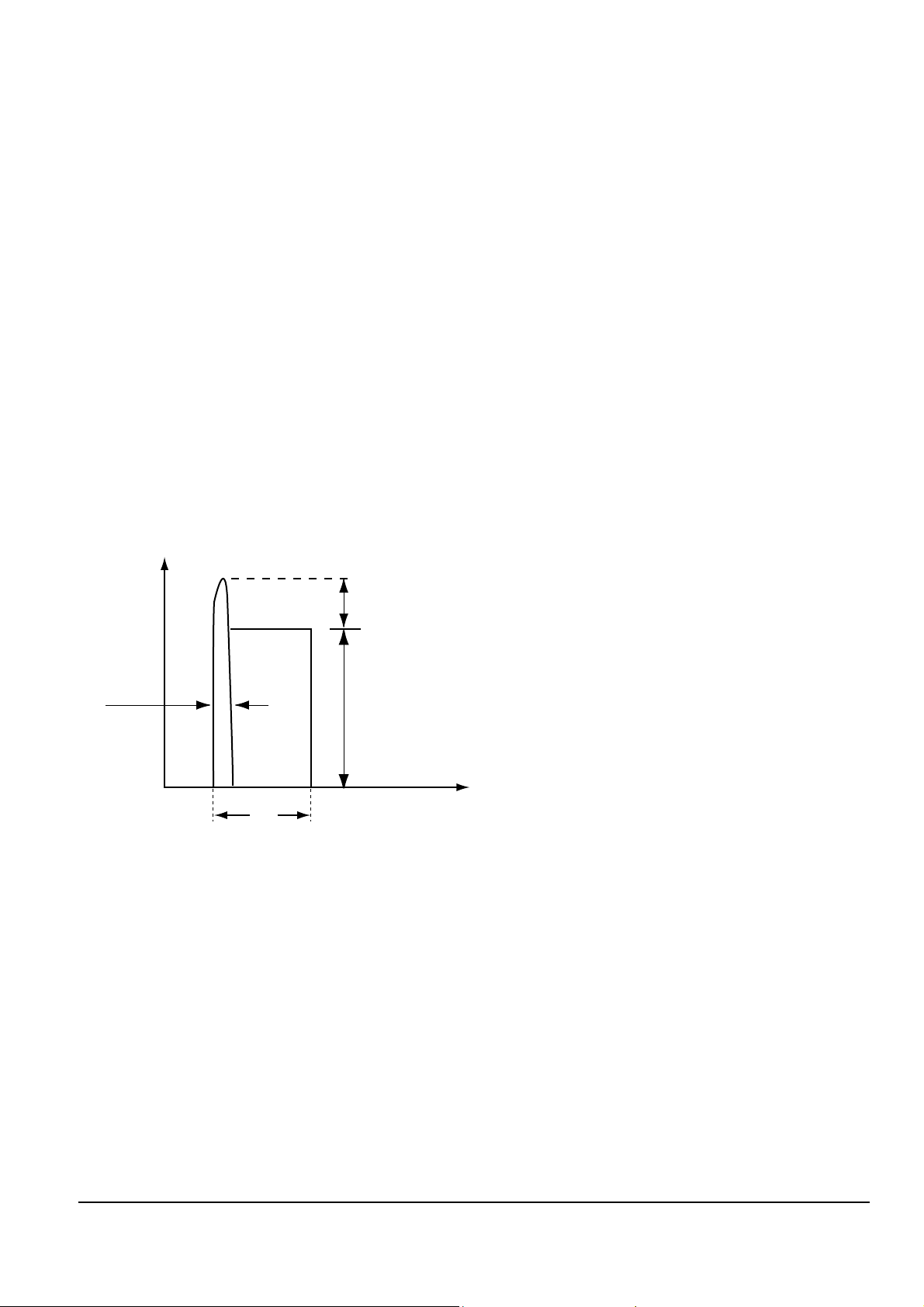
4. Leakage Current Hot Check (See Fig. 1) :
Warning : Do not use an isolation transformer
during this test. Use a leakage current tester or a
metering system that complies with American
National Standards Institute (ANSI C101.1,
Leakage Current for Appliances), and Underwriters
Laboratories (UL Publication UL1410, 59.7).
5. With the unit completely reassembled, plug the AC
line cord directly the power outlet. With the unitÕs
AC switch first in the ON position and then OFF,
measure the current between a known erath
ground (metal water pipe, conduit, etc.) and all
exposed metal parts, including : antennas, handle
brackets, metal cabinets, screwheads and control
shafts. The current measured should not exceed
0.5 milliamp. Reverse the power-plug prongs in the
AC outlet and repeat the test.
6. X-ray Limits :
The picture tube is designed to prohibit X-ray
emissions. To ensure continued X-ray protection,
replace the picture tube only with one that is the
same type as the original.
Fig. 1 AC Leakage Test
7. Antenna Cold Check :
With the unitÕs AC plug disconnected from the
AC source, connect an electrical jumper across the
two AC prongs. Connect one lead of the ohmmeter
to an AC prong.
Connect the other lead to the coaxial connector.
8. High Voltage Limit :
High voltage must be measured each time
servicing is done on the B+, horizontal deflection
or high voltage circuits.
Heed the high voltage limits. These include the
X-ray protection Specifications Label, and the
Product Safety and X-ray Warning Note on the
service data schematic.
9. Some semiconductor (Òsolid stateÓ) devices are
easily damaged by static electricity.
Such components are called Electrostatically
Sensitive Devices (ESDs); examples include
integrated circuits and some field-effect transistors.
The following techniques will reduce the
occurrence of component damage caused by static
electricity.
10. Immediately before handling sny semiconductor
components or assemblies, drain the electrostatic
charge from your body by touching a known
earth ground. Alternatively, wear a discharging
Wrist-strap device. (Be sure to remove it prior to
applying power--this is an electric shock
precaution.)
Device
Under
Test
(Reading should
not be above
0.5mA)
Leakage
Currant
Tester
Earth
Ground
Test all
exposed metal
surfaces
Also test with
plug reversed
(using AC adapter
plug as required)
2-Wire Cord
Precautions
1-2 Samsung Electronics
11. High voltage is maintained within specified limits
by close-tolerance, safety-related components and
adjustments. If the high voltage exceeds the
specified limits, check each of the special
components.
12. Design Alteration Warning :
Never alter or add to the mechanical or electrical
design of this unit. Example : Do not add
auxiliary audio or video connectors. Such
alterations might create a safety hazard. Also, any
design changes or additions will void the
manufacturerÕs warranty.
13. Hot Chassis Warning :
Some TV receiver chassis are electrically
connected directly to one conductor of the AC
power cord. If an isolation transformer is not
used, these units may be safely serviced only if
the AC power plug is inserted so that the chassis
is connected to the ground side of the AC source.
To confirm that the AC power plug is inserted
correctly, do the following : Using an AC
voltmeter, measure the voltage between the
chassis and a known earth ground. If the reading
is greater than 1.0V, remove the AC power plug,
reverse its polarity and reinsert. Re-measure the
voltage between the chassis and ground.
14. Some TV chassis are designed to operate with 85
volts AC between chassis and ground, regardless
of the AC plug polarity. These units can be safely
serviced only if an isolation transformer inserted
between the receiver and the power source.
15. Never defeat any of the B+ voltage interlocks.
Do not apply AC power to the unit (or any of its
assemblies) unless all solid-state heat sinks are
correctly installed.
16. Always connect a test instrumentÕs ground lead to
the instrument chassis ground before connecting
the positive lead; always remove the instrumentÕs
ground lead last.
17. Observe the original lead dress, especially near
the following areas : Antenna wiring, sharp
edges, and especially the AC and high voltage
power supplies. Always inspect for pinched, outof-place, or frayed wiring. Do not change the
spacing between components and the printed
circuit board. Check the AC power cord for
damage. Make sure that leads and components
do not touch thermally hot parts.
18. Picture Tube Implosion Warning :
The picture tube in this receiver employs
Òintegral implosionÓ protection. To ensure
continued implosion protection, make sure that
the replacement picture tube is the same as the
original.
19. Do not remove, install or handle the picture tube
without first putting on shatterproof goggles
equipped with side shields. Never handle the
picture tube by its neck. Some Òin-lineÓ picture
tubes are equipped with a permanently attached
deflection yoke; do not try to remove such
Òpermanently attachedÓ yokes from the picture
tube.
20. Product Safety Notice :
Some electrical and mechanical parts have special
safety-related characteristics which might not be
obvious from visual inspection. These safety
features and the protection they give might be
lost if the replacement component differs from the
original--even if the replacement is rated for
higher voltage, wattage, etc.
Components that are critical for safety are
indicated in the circuit diagram by shading,
( or ).
Use replacement components that have the same
ratings, especially for flame resistance and
dielectric strength specifications. A replacement
part that does not have the same safety
characteristics as the original might create shock,
fire or other hazards.
21. Cautions for handling Pick-up
Body grounding (hand) : Be sure to wear a wrist
strip with one side grounded. (Impedance :
Below 10
-8
½ )
Work table grounding : Put A grounded electric
conductor such as copper plate on tne work
table.
Caution: Do not let clothing touch the product
(to prevent possible damage from static electricty).
FPC operation : Handle the FPC carefully because
it is easily damaged.
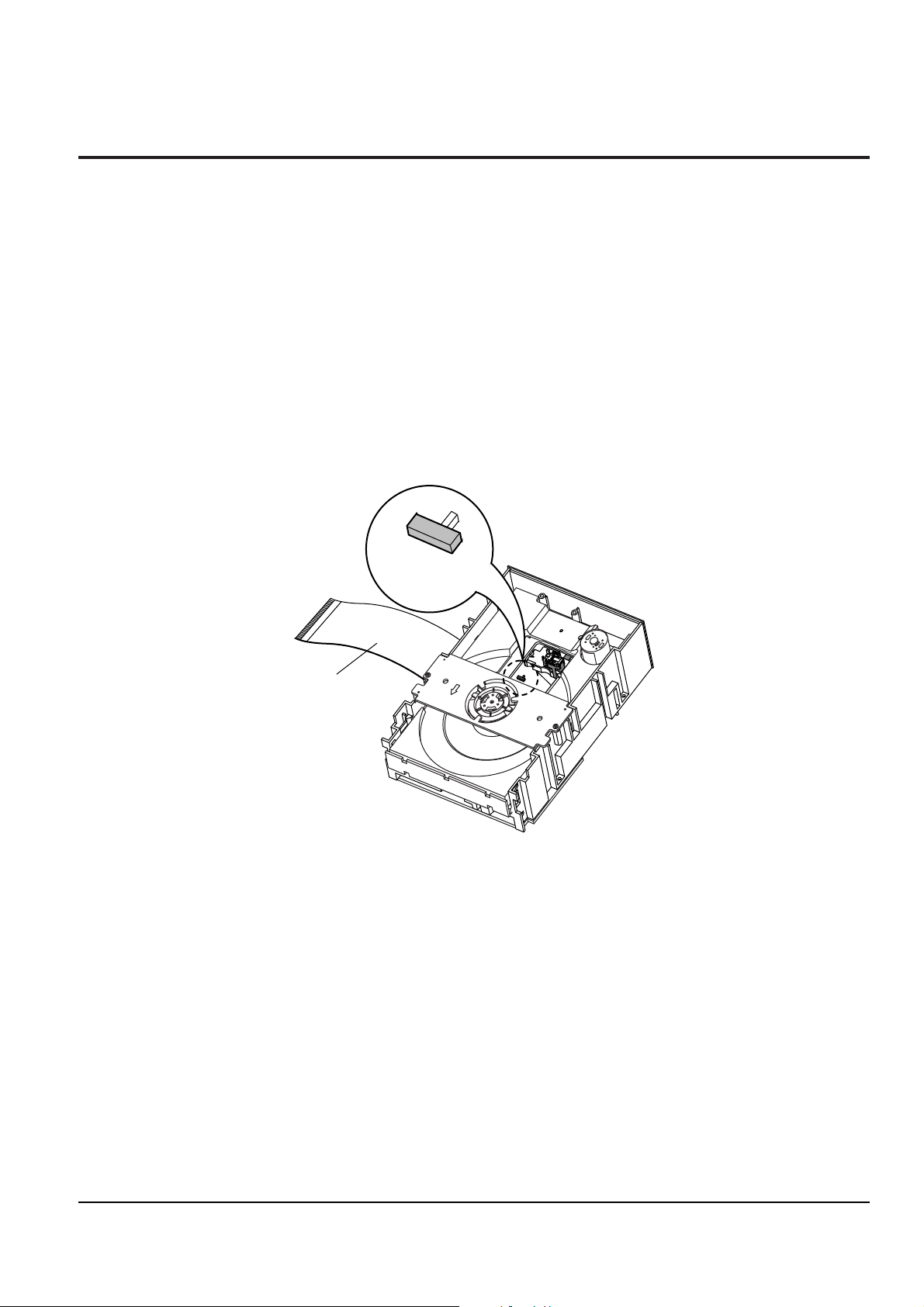
Precautions
Samsung Electronics 1-3
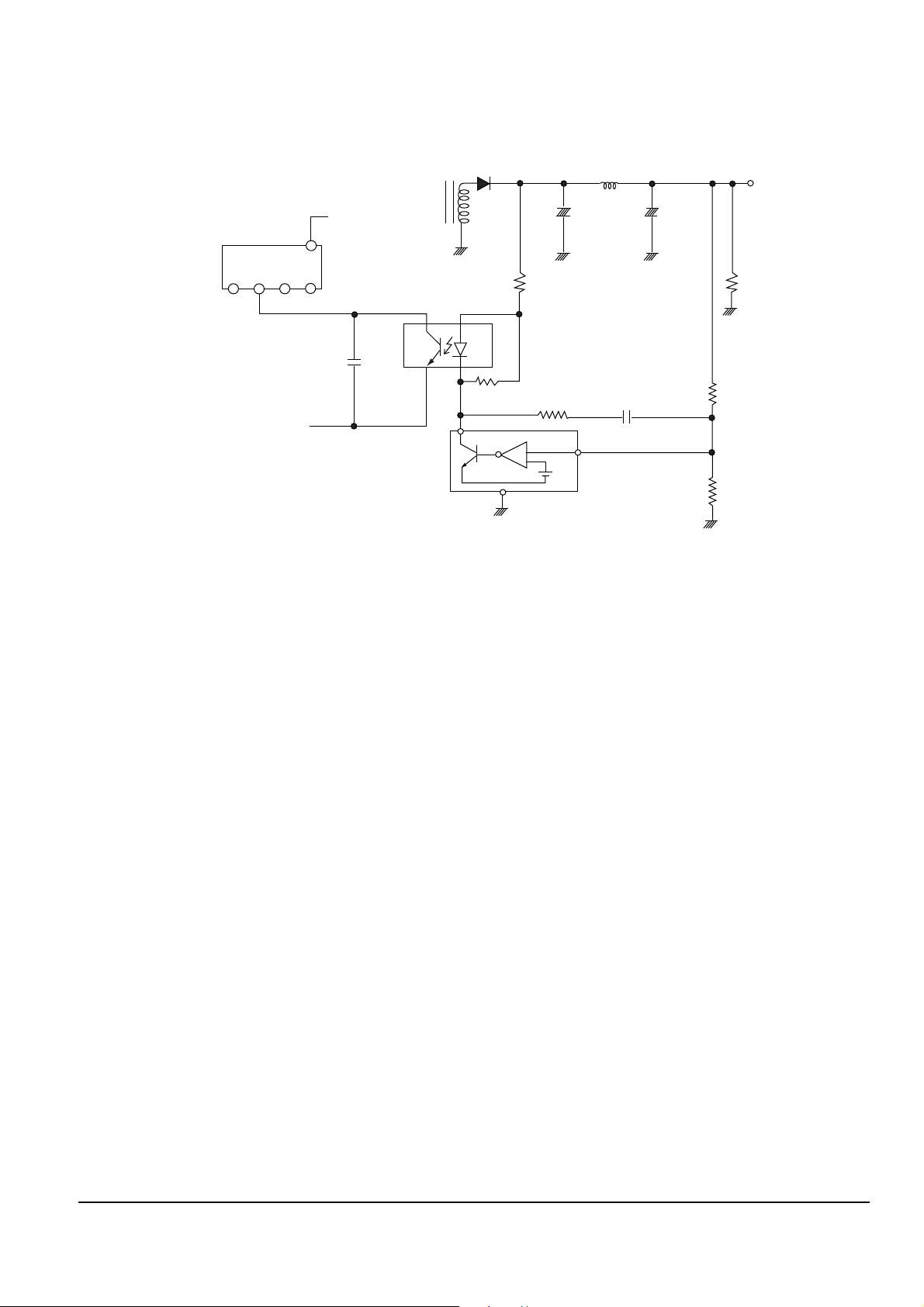
1) Remove the power cable.
2) Switch LD SW3 on deck PCB to ÔSÕ before removing the FPC ( inserted into Main PCB CN1.
See Fig 1-2.)
3) Disassemble the deck.
4) Disassemble the deck PCB.
5) Replace the Pick-up.
O
S
LD
SW3
FPC
1-2-1 Disassembly
1-2 Pick-up disassembly and ressembly
1-2-2 Assembly
Note : If the assembly and disassembly are not done in correct sequence, the Pick-up may be damaged.
Fig. 1-2
1) Replace the Pick-up.
2) Assemble the deck PCB.
3) Reassemble the deck.
4) Switch LD SW3 on deck PCB to ÔOÕ and insert
FPC into Main PCB CN1 (See Fig 1-2).

Precautions
1-4 Samsung Electronics
MEMO
Samsung Electronics 3-1
3. Product Specifications
The specifications and design may be changed without notice. The weight and dimensions are approximate.
MODEL DVD905
G
E
N
E
R
A
L
D
I
S
C
V O
I U
D T
E P
O U
T
A O
U U
D T
I P
O U
T
120 Voltage, 60Hz
23W
4.4Kg
(W)420mm x (D)339mm x (H)120mm
+ 5 °C ~ 35 °C
50% ~ 95%
Reading Speed ; 1.2 ~ 1.4mm/sec
Maximum Play Time ; 135 minutes
Reading Speed ; 1.2 ~ 1.4mm/sec
Maximum Play Time ; 74 minutes
Reading Speed ; 1.2 ~ 1.4mm/sec
Maximum Play Time ; 74 minutes
Reading Speed ; 1.2 ~ 1.4m/sec
Maximum Play Time ; 74 minutes(Video + Audio)
2 channel ; 1.0Vp-p
R(Red) ; 0.714Vp-p
G(Green) ; 0.714Vp-p
B(Blue) ; 0.714Vp-p
S(Sync) ; 4.0Vp-p
Luminance Signal ;1Vp-p (75Ω load)
Color Signal ; 0.286Vp-p (75Ω load)
L(1/L), R(2/R)
F/L, F/R, R/L, R/R, C/T, S/W
Analog ; 2Vrms(1KHz)
Digital ; 5Vp-p
* Frequency Response ; 4Hz ~20KHz, S/M Ratio : 105dB
* Dynamic Range ; 95dB
* Total Harmonic Distortion 0,005%
Power Requirements
Power Consumption
Weight
Set Size
Operating Temperature Range
Operating Humidity Range
DVD
(DIGITAL VERSATILE DISC
CD : 12cm
(COMPACT DISC)
CD : 8cm
(COMPACT DISC)
VIDEO - CD
12cm
RCA JACK
SUPER VIDEO
2 channel
5 channel
Output Level
Digital Frequency
Response

Product Specifications
3-2 Samsung Electronics
MEMO
Disassembly and Reassembly
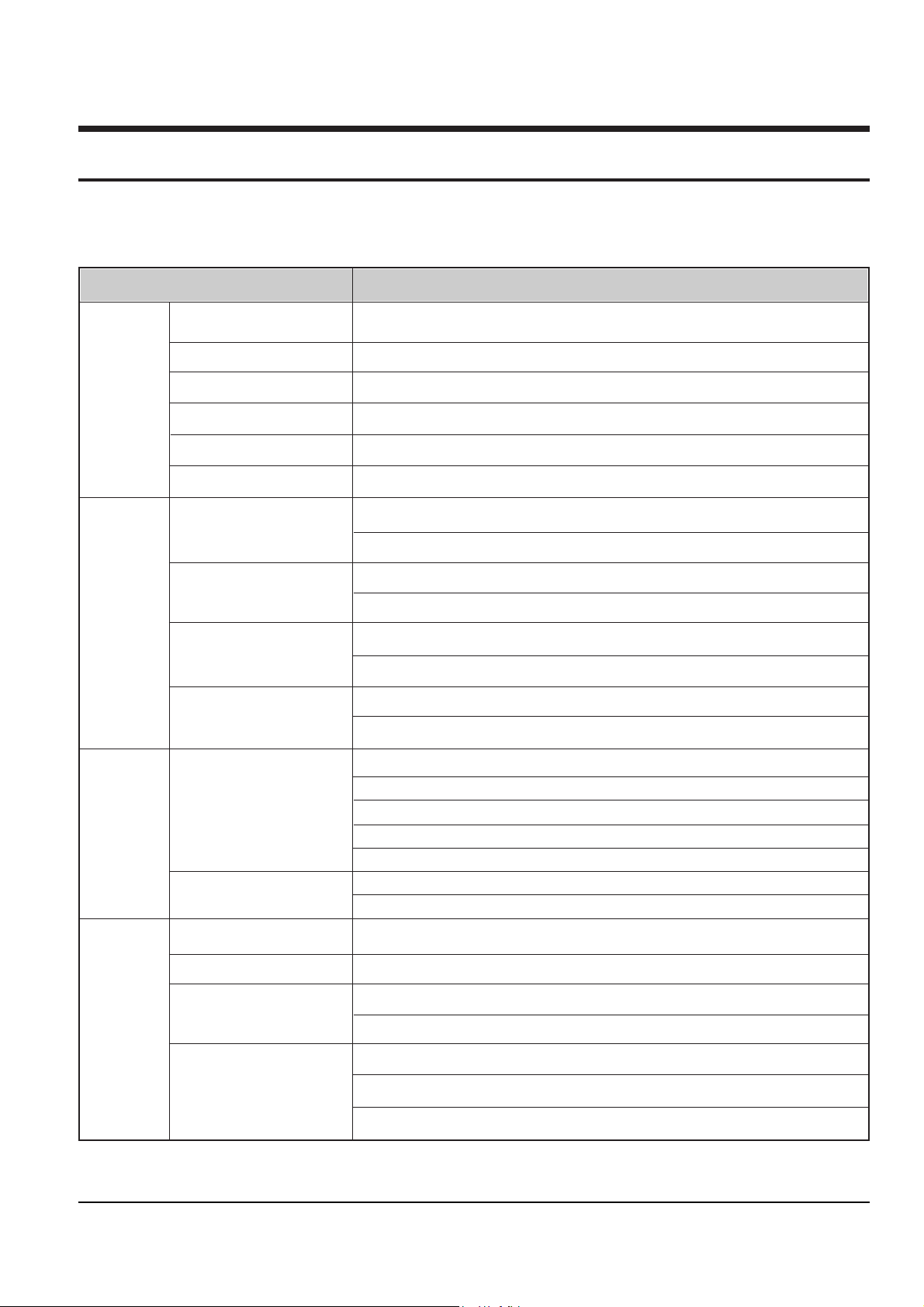
1) Supply power and open Tray Œ.
2) Disassemble the door-tray ´ in direction of arrow.
3) Close Tray Πand power off.
Note : If Tray Œ doesnÕt open, insert a clip ˇ into the hole (as shown in detailed drawing), and open Tray Œ
manually.
Fig. 4-1
Samsung Electronics 4-1
70mm
TRAY
DOOR-TRAY
CHIP
2
1
3
4. Disassembly and Reassembly
4-1 Exterior and PCB Disassembly
4-1-1 Door-tray
4-2 Samsung Electronics
Disassembly and Reassembly
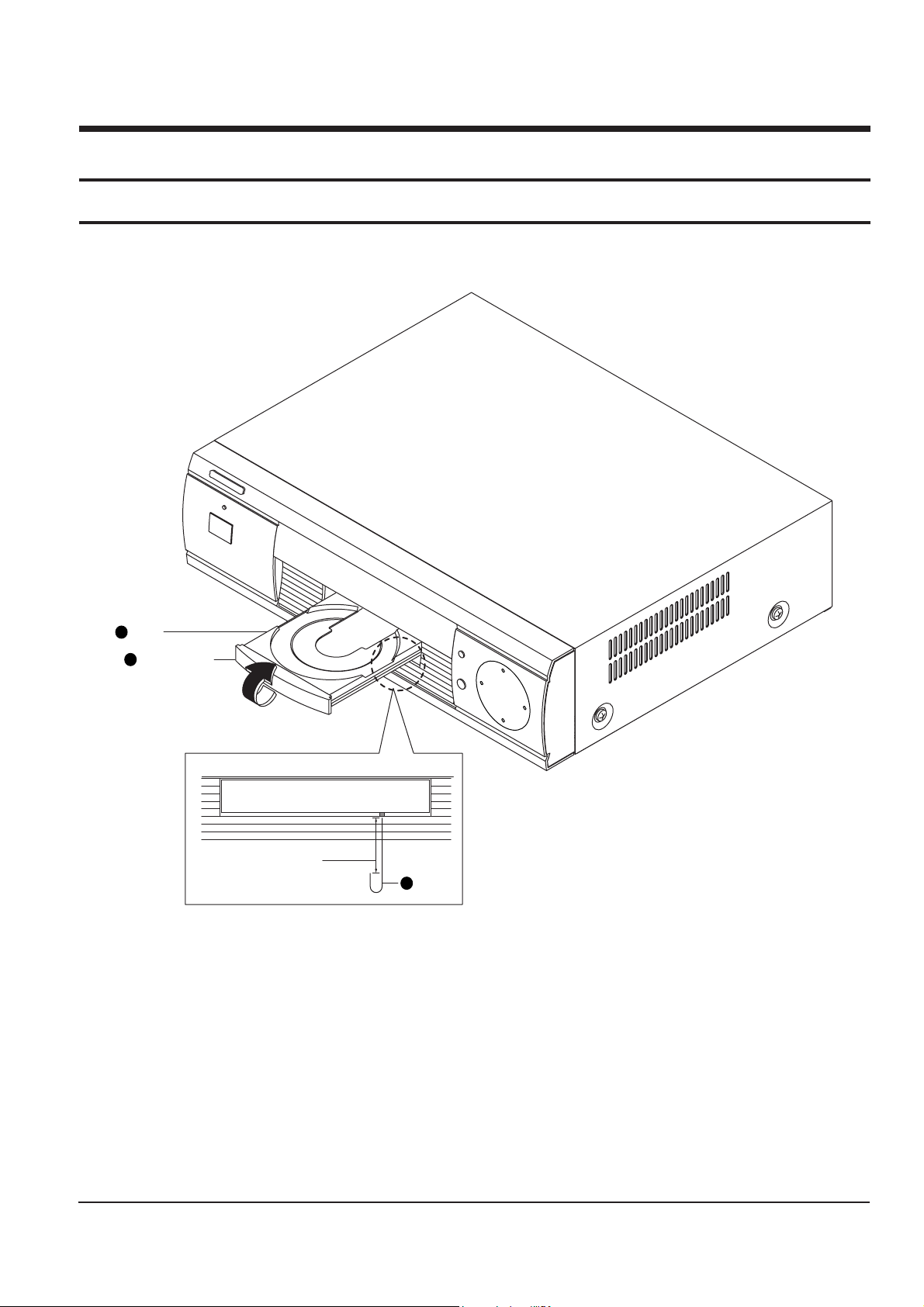
4-1-2 Top cabinet
1. Remove 3 screws Πon the back panel.
2. Remove 4 screws ´, ˇ on the left and right side.
3. Lift up the top cabinet in direction of arrow.
Fig. 4-2
CABINET-TOP
2SCREWS
3SCREWS
2SCREWS
22
33
11
Samsung Electronics 4-3
Disassembly and Reassembly
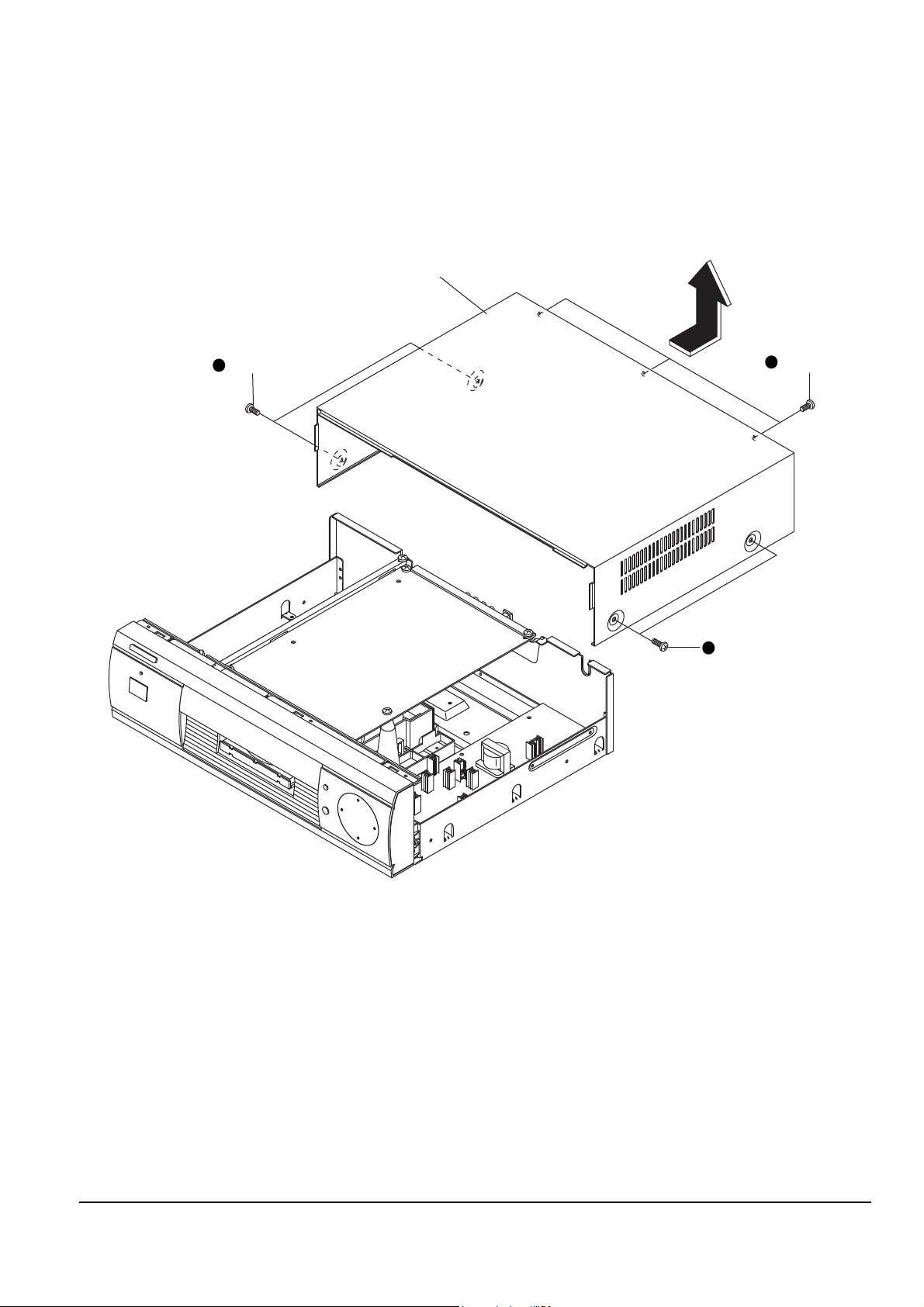
4-1-3 Front
1. Remove 2 screws Œ, ´ on the left and right side of panel-front assÕy
2. Remove 2 screws ˇ on the bottom of cover-panel assÕy and disassemble the front.
3. Remove 2 screws ¨ from PCB-front.
4. Remove 9 hooks to fix PCB-front and disassemble PCB-front.
5. Remove 2 screws ˆ on the top of cover-panel assÕy
6. Remove 4 top hooks Ø and 5 bottom hooks ∏ and disassemble the cover-panel assÕy.
Fig. 4-3
2 SCREWS
1 SCREW
4 HOOKS
2 SCREWS
COVER-PANEL ASS'Y
5 HOOKS
PANEL-FRONT ASS'Y
1 SCREW
2 SCREWS
PCB-FRONT
22
66
55
44
11
77
33
4-4 Samsung Electronics
Disassembly and Reassembly
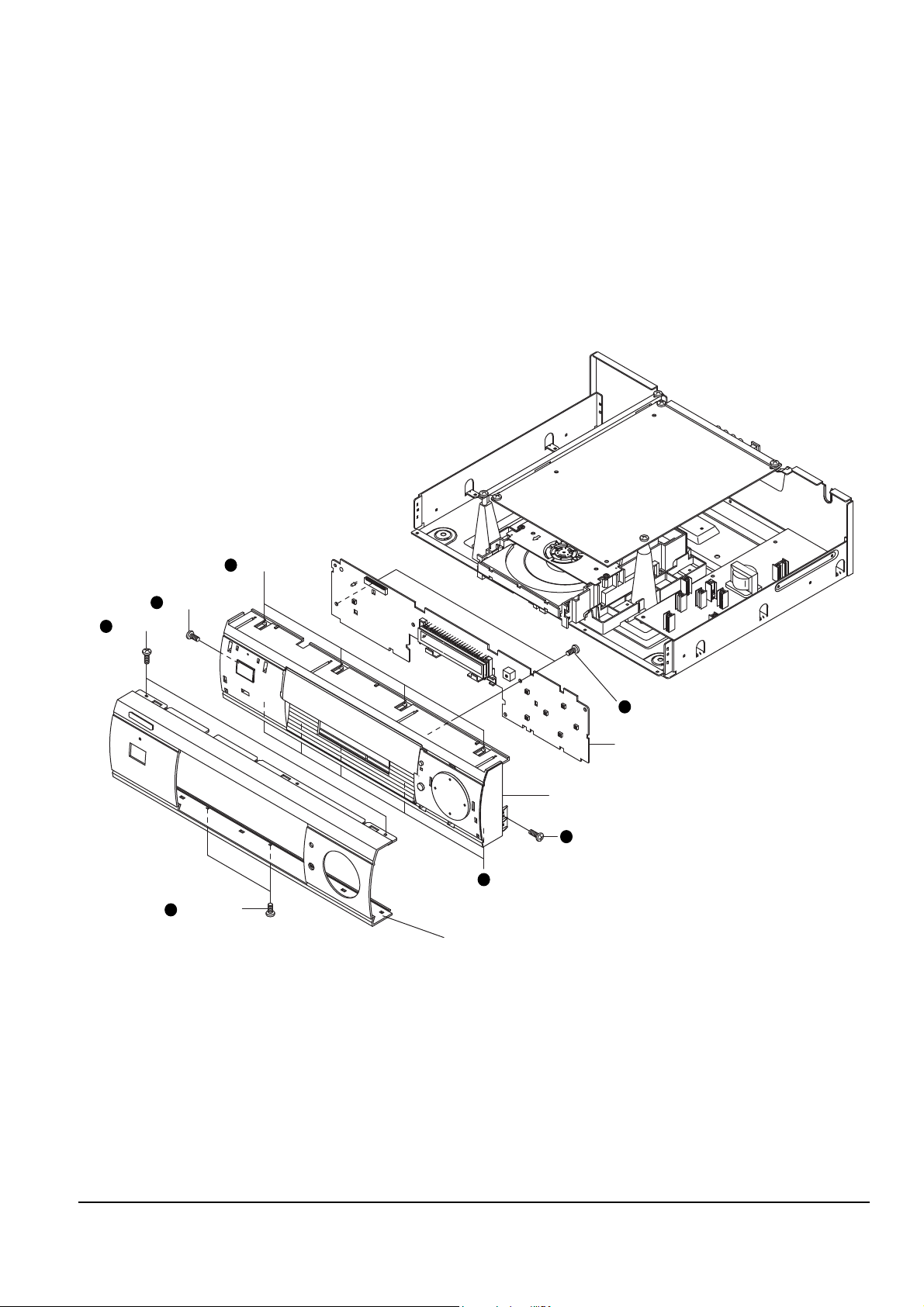
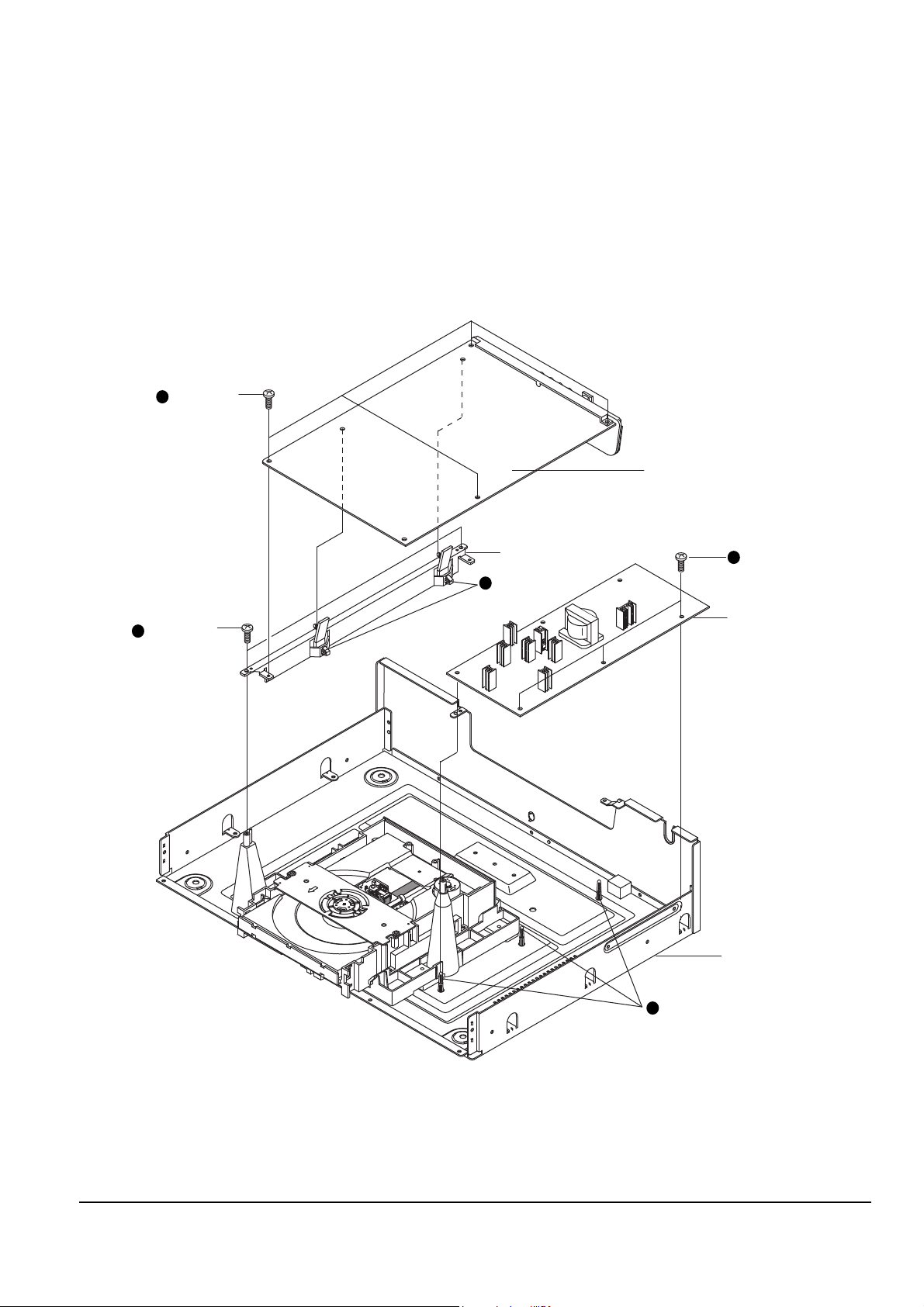
4-1-4 PCB-MAIN, PCB-SMPS
1. Remove 4 screws Πto fix PCB-MAIN.
2. Remove 2 Holder-PCB ´ inserted in PCB-MAIN and lift up PCB-MAIN.
3. Remove 3 screws ˇ from PCB-SMPS.
4. Remove 3 Spacer-PCB ¨ inserted in PCB-SMPS and lift up PCB-SMPS.
5. Remove 2 screws ˆ to fix BRKT-PCB assÕy.
Fig. 4-4
4 SCREWS
2 SCREWS
PCB-MAIN
PCB-SMPS
3 SCREWS
BRKT-PCB ASS'Y
HOLDER-PCB
SPACER-PCB
ASS'Y BOTTOM
11
55
22
44
33
Samsung Electronics 4-5
Disassembly and Reassembly
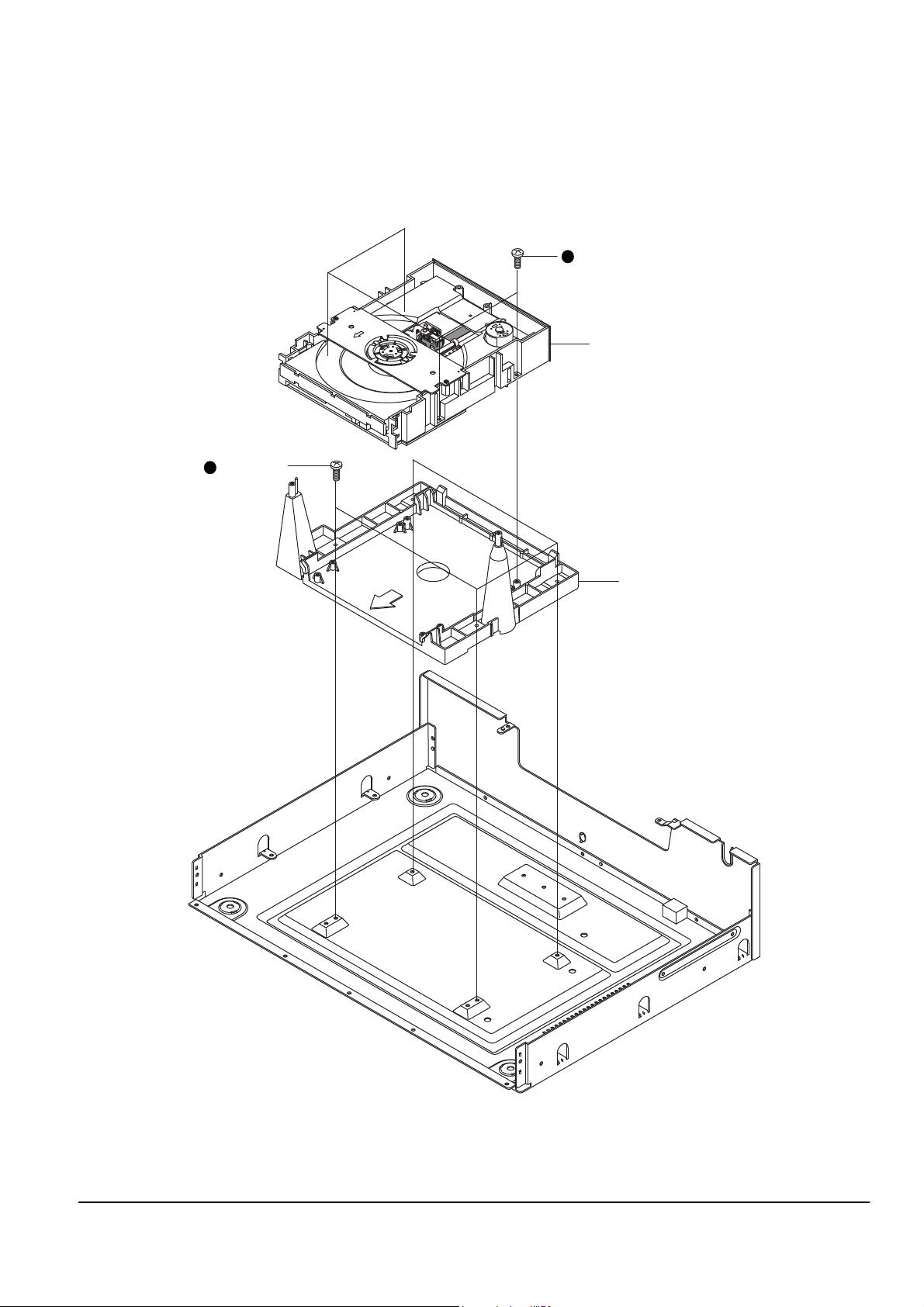
4-1-5 Deck, Frame-chassis
1. Remove 4 screws Πfrom the deck and lift it up.
2. Remove 4 screws ´ from the frame-chassis and lift it up.
Fig. 4-5
4 SCREWS
DECK
FRAME-CHASSIS
4 SCREWS
11
22
Disassembly and Reassembly
4-6 Samsung Electronics
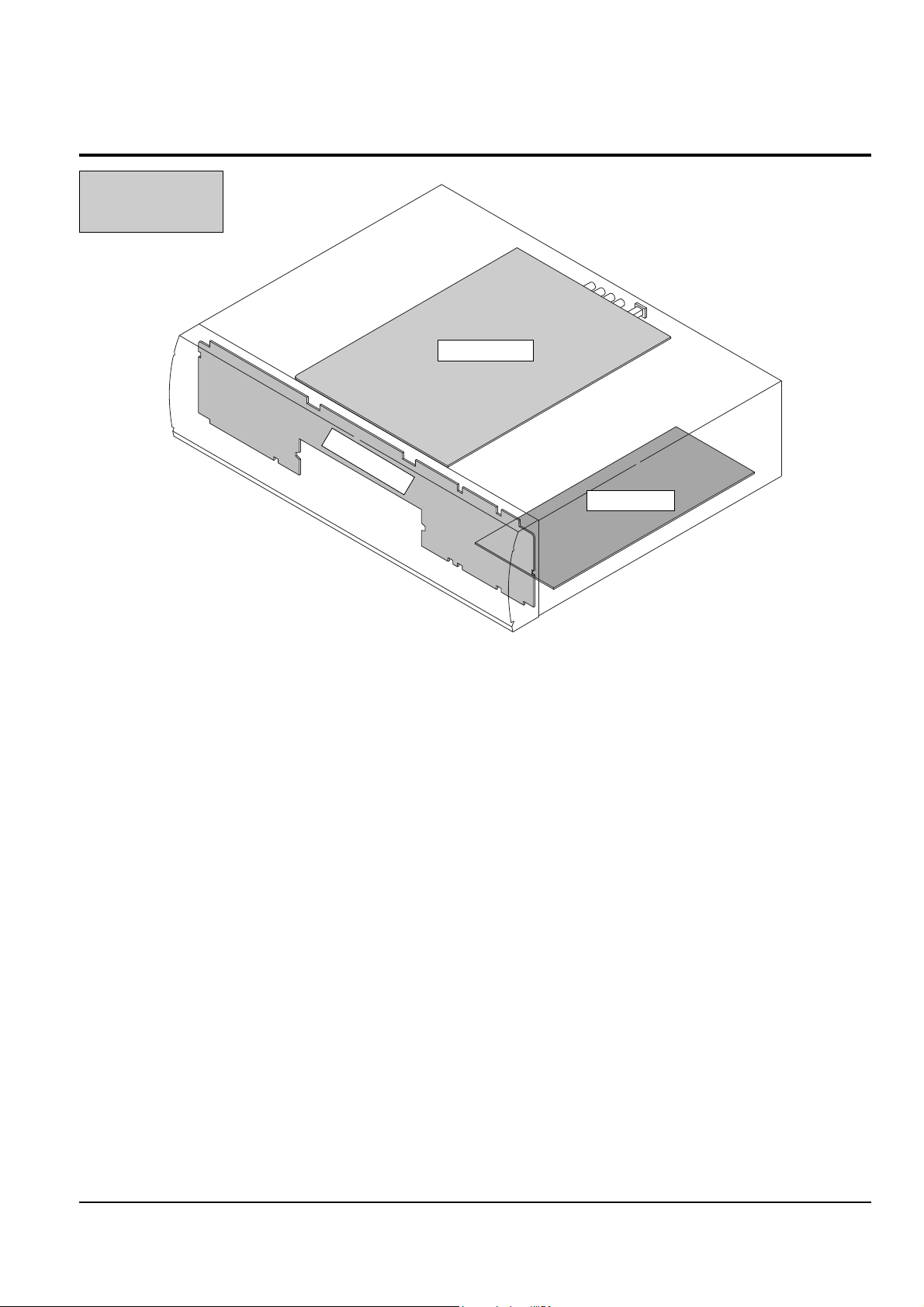
4-2 PCB Locations
PCB-MAIN
PCB-SMPS
PCB-FRONT
Fig. 4-6
DVD905
Disassembly and Reassembly
Samsung Electronics 4-7
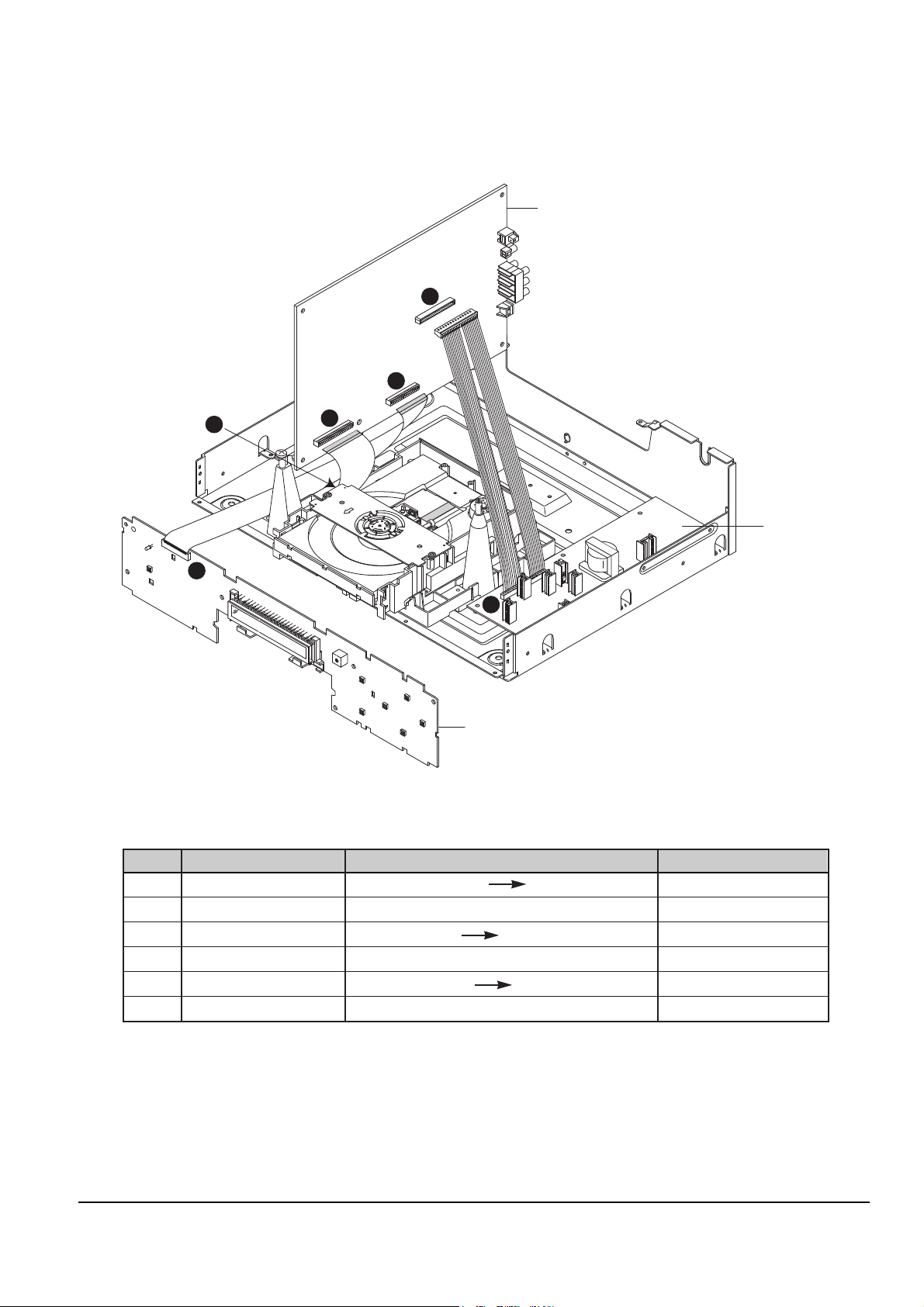
4-2-1 DVD905
Fig. 4-7
PCB-FRONT
1
PCB-SMPS
4
2
6
PCB-MAIN
3
5
No. Connector wafer No. Direction Connector wafer No.
ΠFCN1 PCB-FRONT PCB-MAIN VCN11
´ VCN11 PCB-FRONT FCN1
ˇ CN5 DECK PCB-MAIN CN1
¨ CN1 DECK CN5
ˆ PCN02 PCB-SMP PCB-MAIN VCN13
Ø VCN13 PCB-SMPS PCN02
Disassembly and Reassembly
4-8 Samsung Electronics
4-3 Deck Disassembly
4-3-1 Tray
1. Remove 2 screws Œ and lift up the assÕy-deck clamper ´.
2. Insert a clip into Emergency hole, and push Gear-Cam Center ˇ. When the tray ¨ comes out a little, pull it in
direction of arrow ÒCÓ.
3. Pull the tray ¨ to disassemble, while simultaneously pushing the hook ˆ, Ø in direction of arrow ÒAÓ, ÒBÓ.
Fig. 4-8
"A"
"C"
" B "
HOOK
EMERGENCY
HOLE
CLIP
33
GEAR-CAM CENTER
TRAY
HOOK
11
2 SCREWS
ASS'Y-DECK CLAMPER
22
55
66
33
44
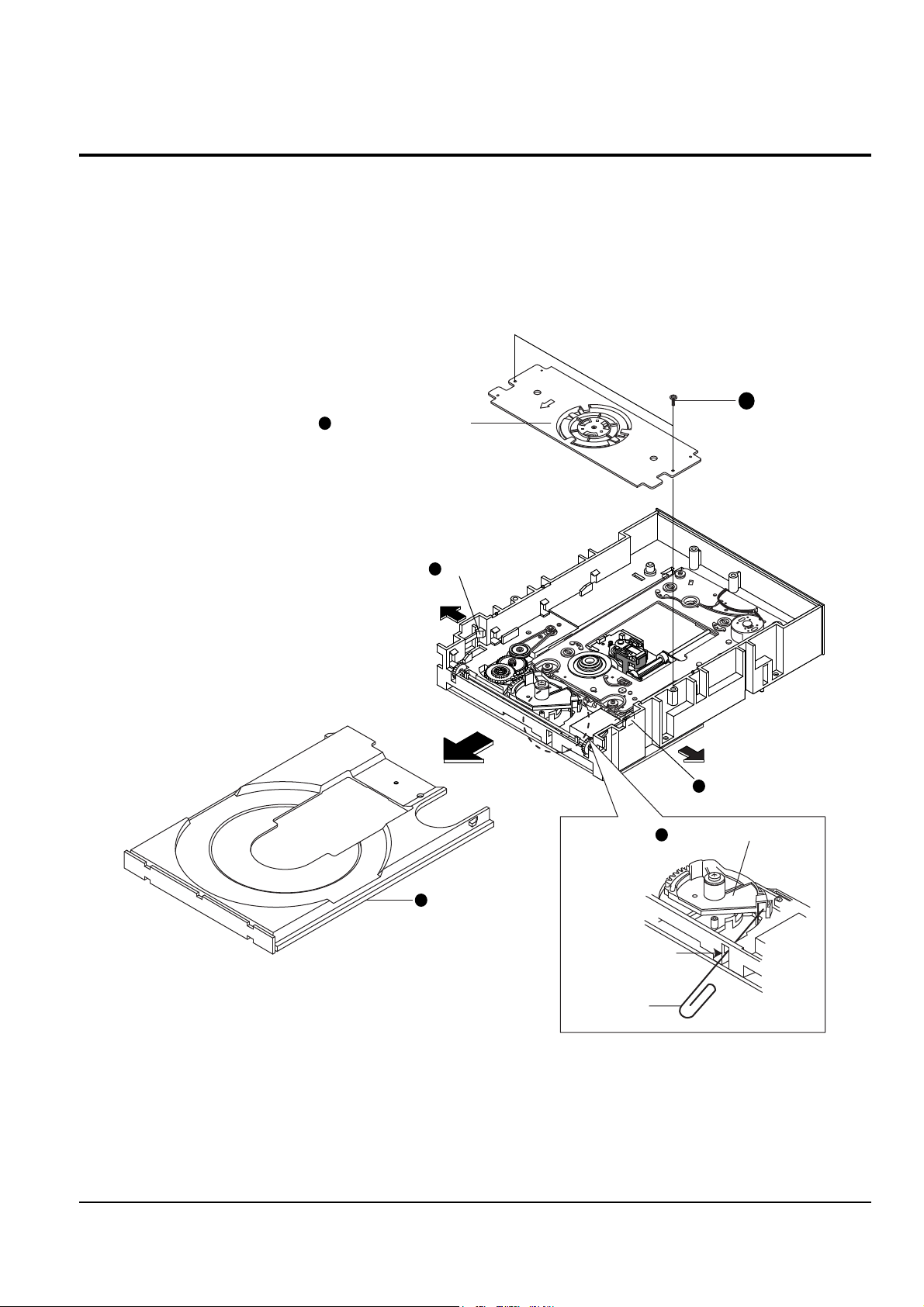
Disassembly and Reassembly
Samsung Electronics 4-9
4-3-2 Ass’y-Deck DVD
1. Remove 2 screws Œ and disassemble the assÕy-PCB deck ´.
2. Disassemble the assÕy-deck DVD ¨ in direction of arrow ÒBÓ, while simultaneously pushing the hook ˇ in
direction of arrow ÒAÓ.
Fig. 4-9
"B"
"A"
ASS'Y-DECK DVD
33
HOOK
ASS'Y-PCB DECK
2 SCREWS
11
22
33
44
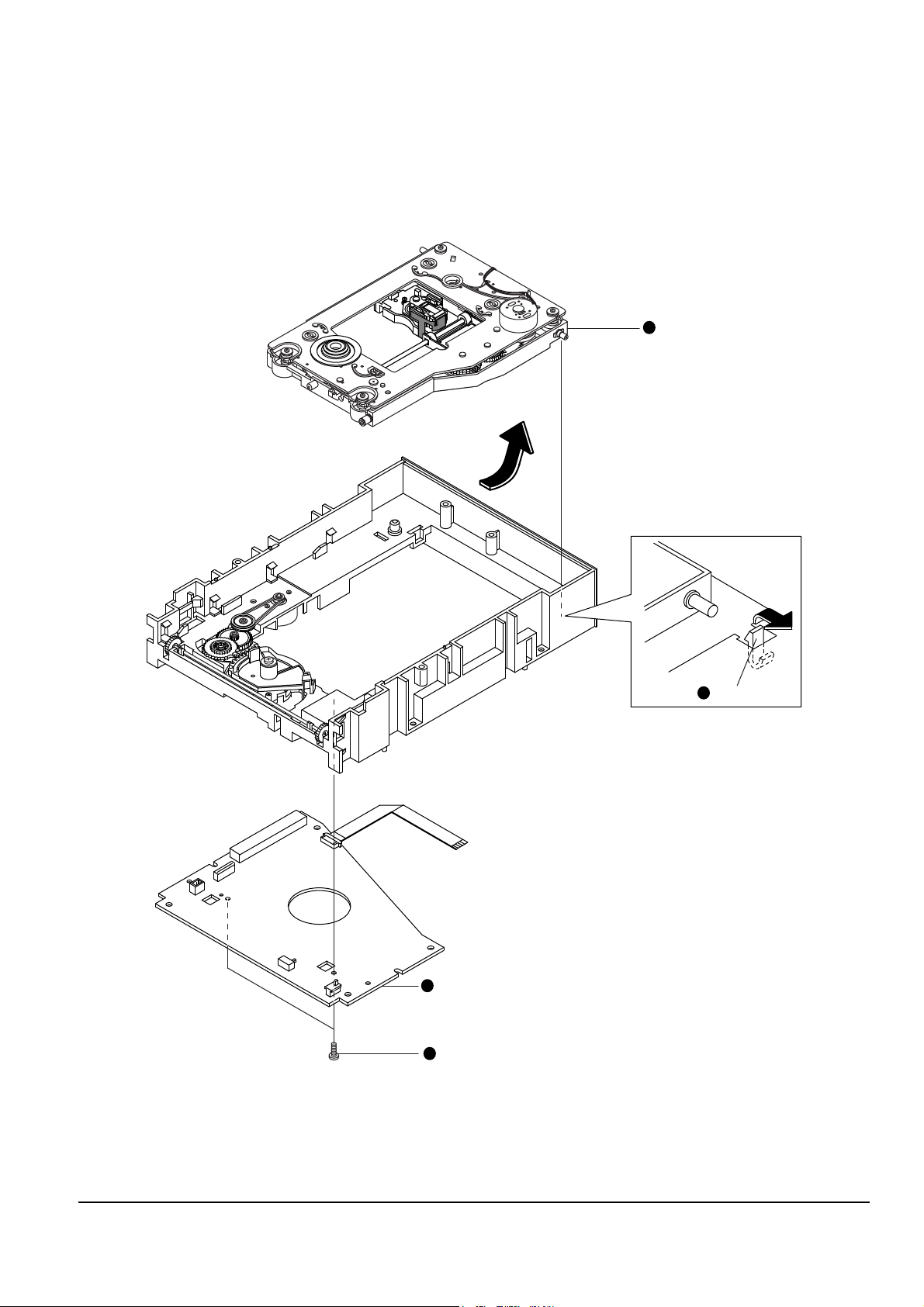
Disassembly and Reassembly
4-10 Samsung Electronics
4-3-3 Chassis-Main parts
1. Lift up the gear-tray Œ, remove 1 screw ´ and lift up the gear-cam center ˇ.
2. Lift up the belt-pulley ¨, remove 1 screwˆ and lift up the pulley-gear Ø.
3. Remove 1 screw ∏ and lift up the gear-tray A ” and gear-cam sub ’.
4. Remove 2 screws ˝ and disassemble the assÕy-motor load Ô.
5. Remove 1 screw and disassemble the lever-open S/W Ò.
6. Lift up the shaft-syncro Ú and remove the 2 gear-syncro Æ in both directions.
Assembling : Adjust the shaft end of motor-feed so that it is exactly equal to the height of the hump in gear pole
of assÕy-gear magnet.
Fig. 4-10
GEAR-CAM CENTER
1 SCREW
GEAR-CAM SUB
11
GEAR-TRY
GEAR-TRY A
BELT-PULLEY
1 SCREW
PULLEY-GEAR
2 SCREWS
LEVER-OPEN S/W
1 SCREW
MOTOR,PULLEY ASSEMBLING : ADJUST THE END OF MOTOR
SHAFT SAMELY AS HEIGHT OF PULLEY AT ASSEMBLY.
ASS'Y-MOTOR LOAD
GEAR-SYNCHRO
SHAFT-SYNCHRO
GEAR-SYNCHRO
GEAR-CAM SUB
1 SCREW
33
GEAR-CAM-CENTER
POINT
1212
1313
1010
66
55
44
77
88
11
33
22
99
33
99
1515
1414
1515
1111
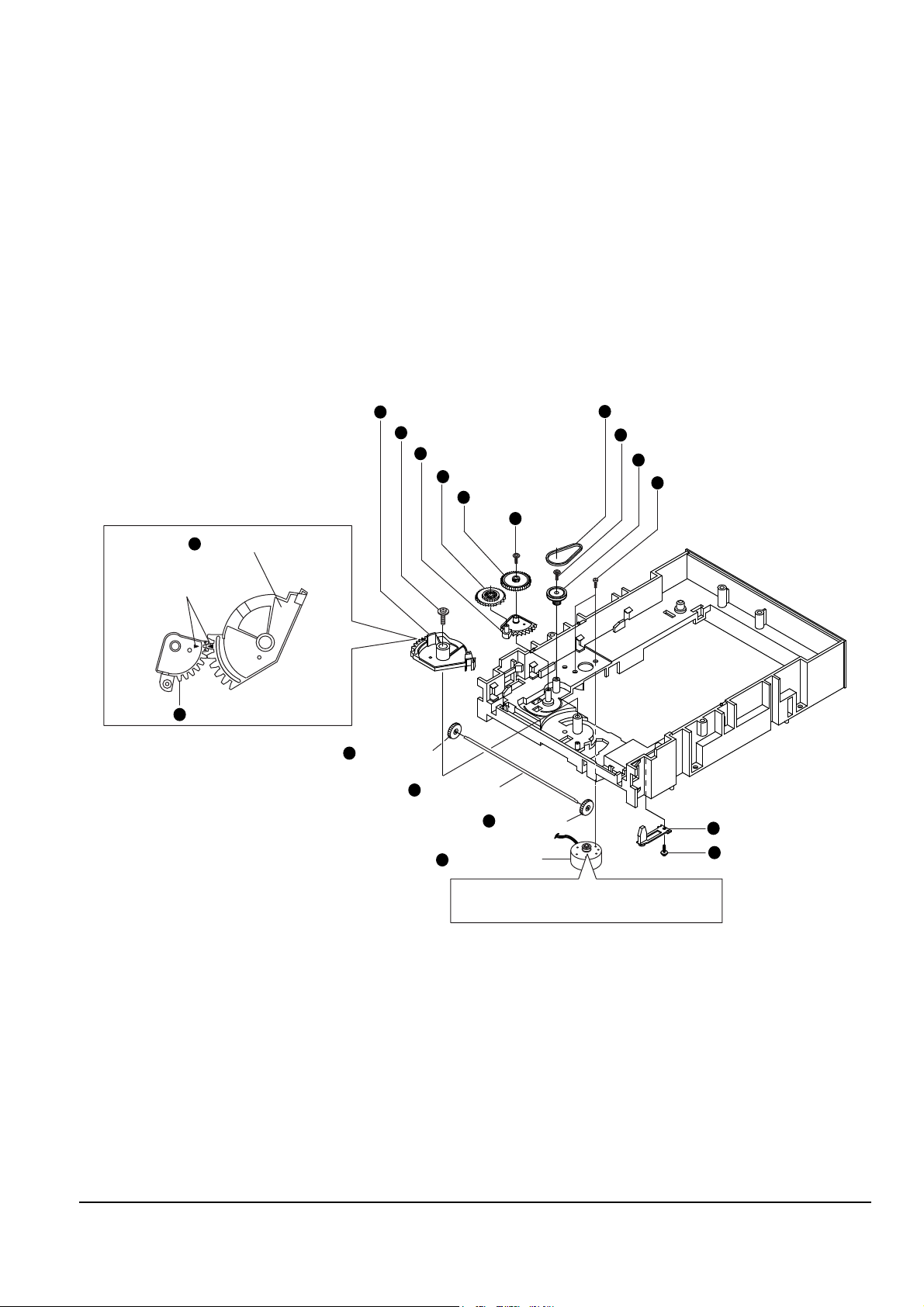
Disassembly and Reassembly
Samsung Electronics 4-11
4-3-4 Ass’y deck
1. Remove 4 screws Œ.
2. Lift up the assÕy-deck ´.
Fig. 4-11
4 SCREWS
ASS'Y-DECK
11
22
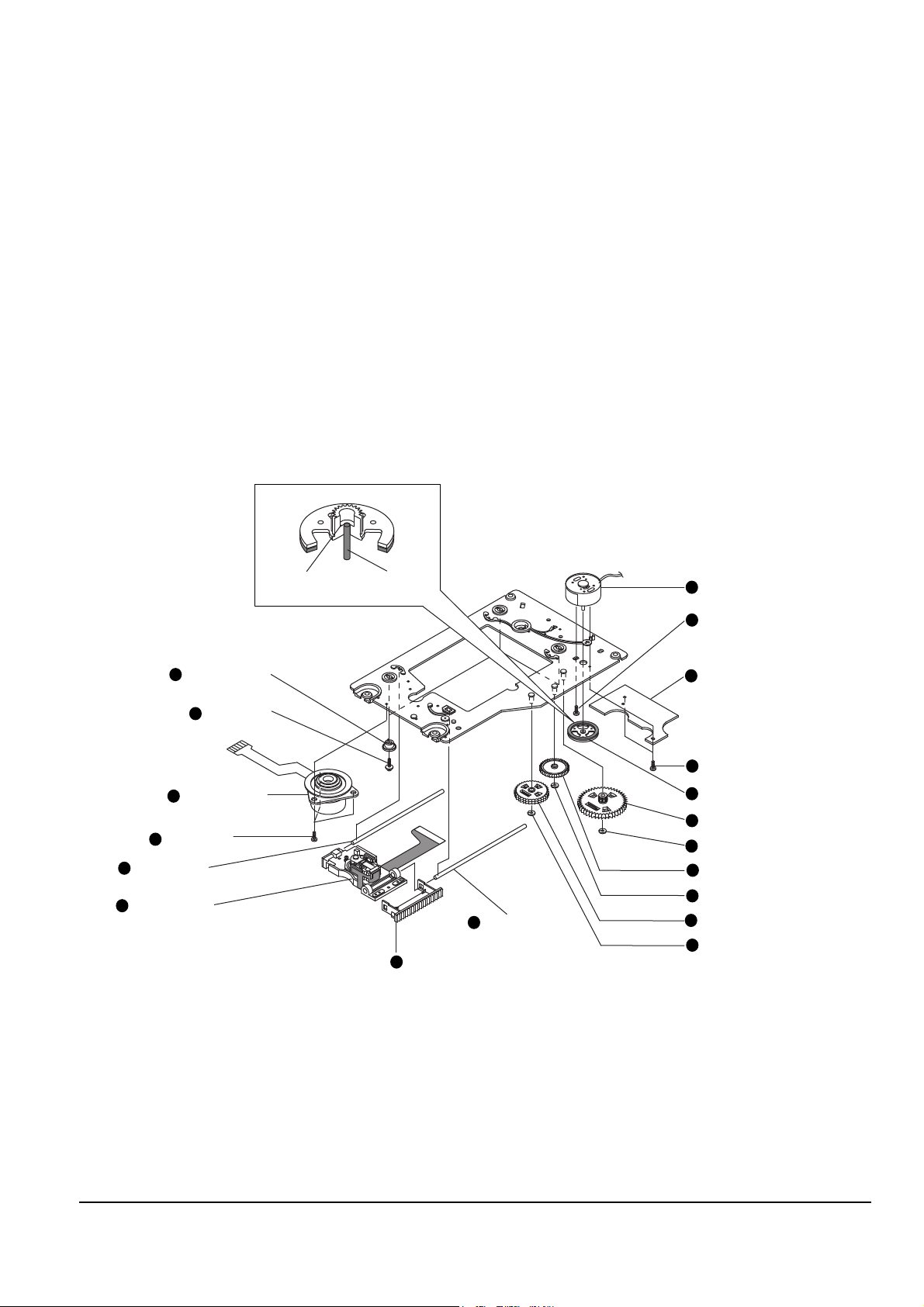
Disassembly and Reassembly
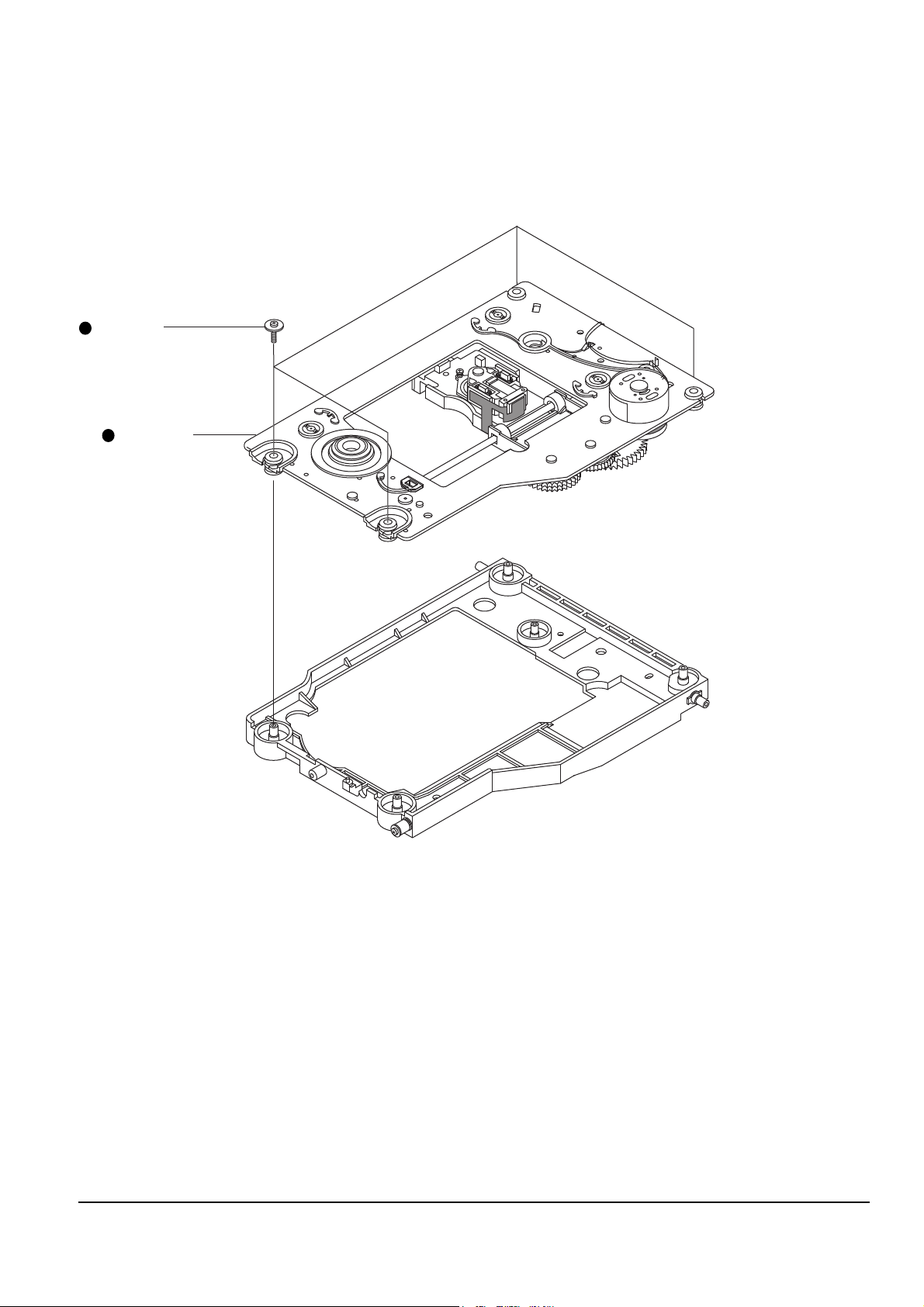
4-12 Samsung Electronics
4-3-5 Ass’y-Deck parts
1. Remove 3 screws Œ and disassemble 3 holder-cams ´.
2. Disassemble the rack-slide ˆ and assÕy-pickup Ø, while simultaneously removing the shaft-P/U-L ¨,
shaft-P/U-R ¨.
3. Remove 3 screws ∏ and disassemble the assÕy-motor spindle ”.
4. Remove the washer-plain ’ and disassemble the assÕy-gear feed AU/AL ˝.
5. Remove the washer-plain Ô and disassemble the gear-feed B .
6. Remove the washer-plain Ò and disassemble the assÕy-gear feed CU/CL Ú.
7. Disassemble the assÕy-gear magnet Æ.
8. Remove 2 screws ı and disassemble the assÕy-PCB hall sensor ˜.
9. Remove 1 screw ¯ and disassemble the motor-feed ˘.
Assembling : Adjsut the shaft end of motor-feed ˘ so that it is exactly equal to the height of the hump in gear
pole of assÕy-gear magnet.
Fig. 4-12
HUMP
MOTOR SHAFT
<DETAILED DRAWING : UPPER SIDE>
HOLDER-CAM
3 SCREWS
ASS'Y-MOTOR
SPINDLE
3 SCREWS
SHAFT-P/U-L
ASS'Y-PICKUP
MOTOR-FEED
1 SCREWS
ASS'Y-PCB HALL SENSOR
2 SCREWS
ASS'Y-GEAR MAGNET
ASS'Y-GEAR FEED AU/AL
WASHER-PLANE
GEAR FEED B
WASHER-PLANE
ASS'Y-GEAR FEED CU/CL
WASHER-PLANE
SHAFT-P/U-R
RACK-SLIDE
1818
1919
1717
1616
1515
1414
9 9
1212
1111
1414
1313
5 5
44
66
33
77
88
11
22
Samsung Electronics 2-1
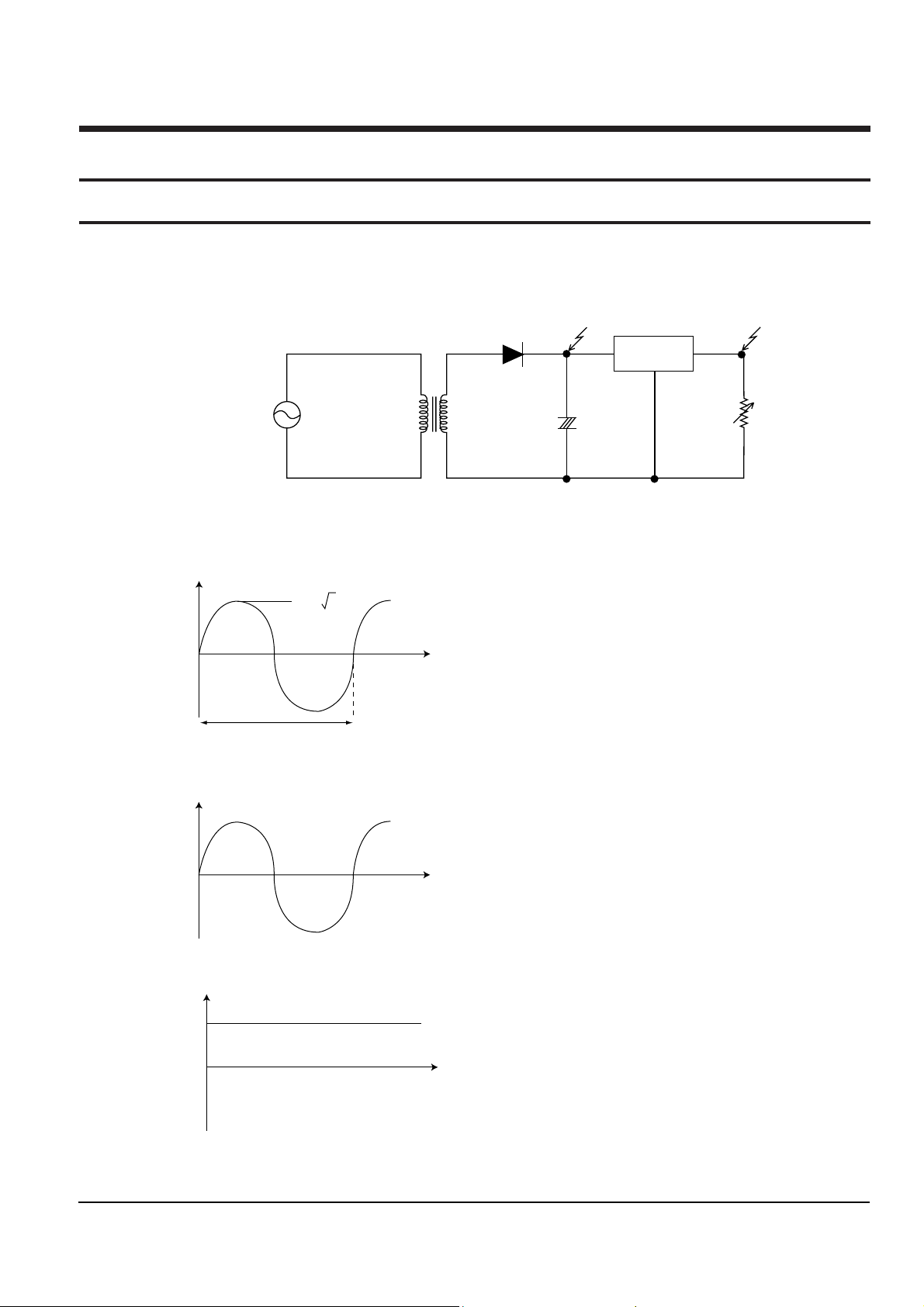
2-1-1 Comparison between linear power supply and SMPS
2-1-1(a) LINEAR
Fig. 2-1
Input : Common power to transformer(Vp)
Fig. 2-2
The output Vs of transformer is determined by the ratio of
1st Np and 2st Ns.
Vs = (Ns/Np) x Vp
Fig. 2-3
Vout is output (DC) by diode and
condensor.
Fig. 2-4
2. Circuit Operating Description
2-1 SMPS circuit description
Vreg
Vout
+
–
+
+
–
Vs
(Ns)
Vp
(Np)
Regulator
Common power
(Ex.220V60Hz)
Vs
t
0
220 2 V
20us
Vs
t
0
Vout
t
0
3 Waveform/Description
Reference Information
2-2 Samsung Electronics
3 Advantages and disadvantages of linear power supply
a. Advantages :
Little noise because the output waveform of transformer is
sine wave.
b. Disadvantages :
È Additional margin is required because Vs is changed
(depending on power source). (The regulator loss is
caused by margin design).
È Greater core size and condensor capacity are needed,
because the transformer works on a single power
frequency.
Fig. 2-5
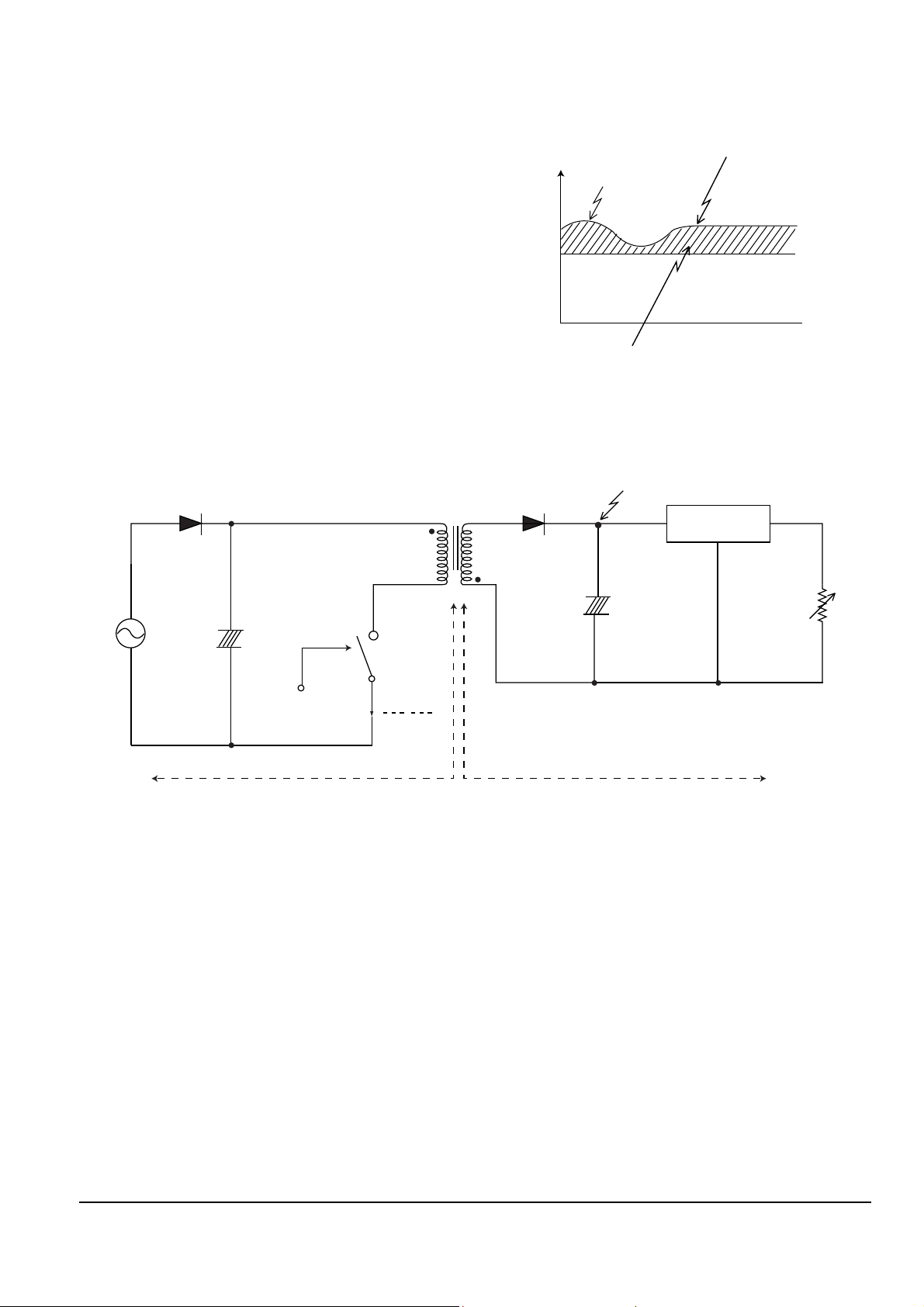
2-1-1 (B) SMPS(PULSE WIDTH MODULATION METHOD)
Fig. 2-6
3 Terms
- 1st : Common power input to 1st winding.
- 2d : Circuit followings output winding of transformer.
- f(Frequency) : Switching frequency(T : Switching cycle)
- Duty : (Ton/T) x 100
V
Vreg
Vout
0 t
Change by common power
Regulator loss
Transformer Vout
(Np)
(Vp)
Switch
Vs switch
I switch
Vin
ON/OFF Control
+
–
+
–
+
+
+
–
(Vs)
(Ns)
Regulator
Reference Information
Samsung Electronics 2-3
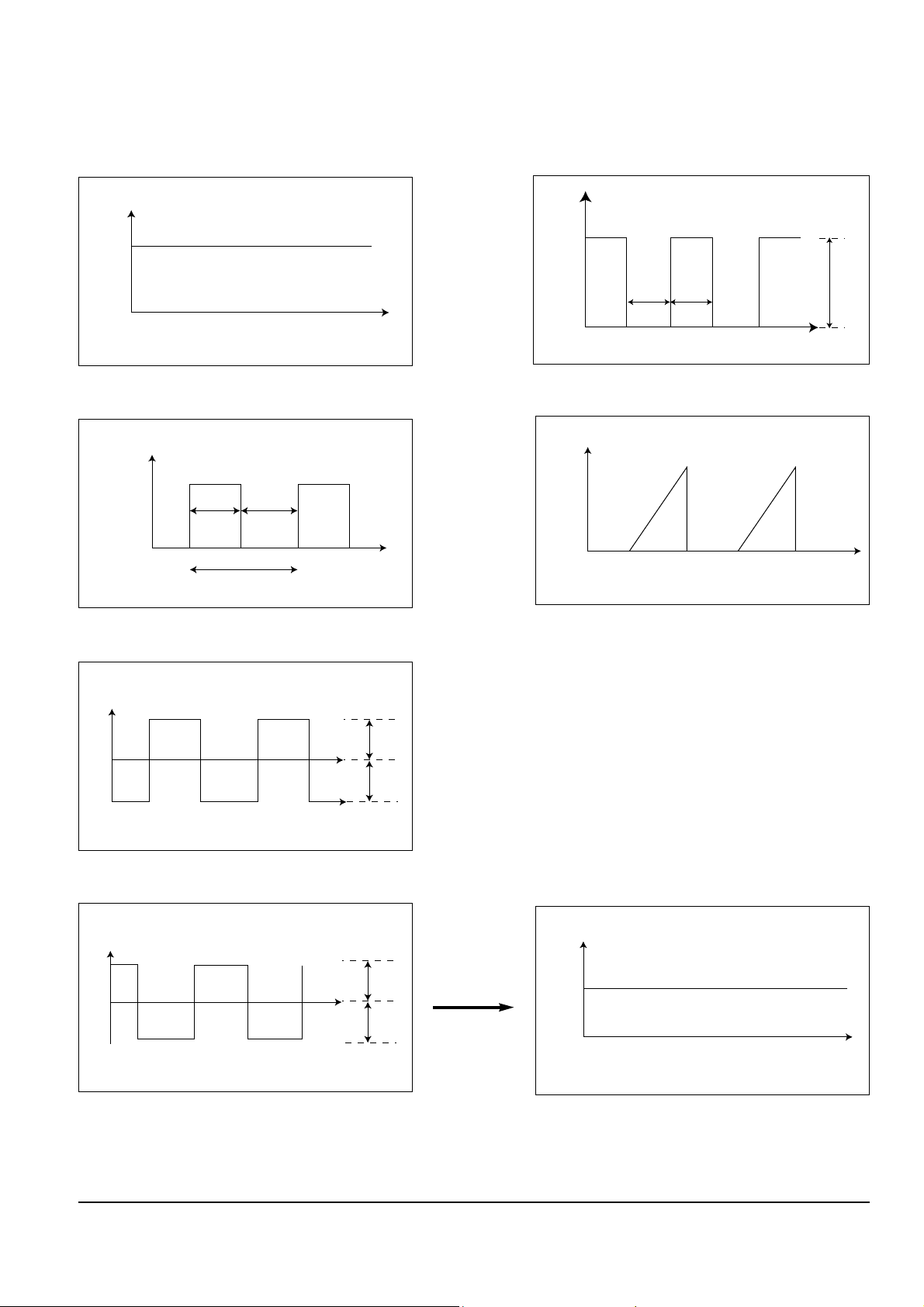
3 Waveform
Fig. 2-7 Fig.2-11
Fig. 2-8 Fig. 2-12
Fig. 2-9
Fig. 2-10 Fig. 2-13
Vin
0
t
Vswitch
ON/OFF
Control
Vp
0
Ton
Toff
0
Vin–Vp
t
Iswitch
Ton Toff
0
f t
0
t
Vin
t
Vps
Vs
0
Vs1
t
Vs2
Vout
0
t
Reference Information
2-4 Samsung Electronics
2-1-1(c) INTERNAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
1. Internal block diagram of SMPS circuit
Fig. 2-14
2. PIC1(KA7552) internal block diagram
Fig. 2-15
BIAS
OFF
2.8V
7.0V
CS
8 7
1
CT RT
10UA
OSC UVLD
VCC
OUT
GNDIS(+)
PB
4.3k
3.6V
ZD
G
D MAX
(46%, 70%)
R
S
Q
PWM
OCP
+
Ð
Ð
+
Ð
+
Ð
+
0.24V
6
5
4
3
2
Noise removing circuit at
power
input/output
Noise
removal
(SNUBBER)
Smoothing
circuit
Rectified circuit
Line filter
Power IN
(85-265V)
F
E
T
FLT driving
circuit
5V rectified
smoothing circuit
3.3V rectified
smoothing circuit
Convertor
PWM control circuit
(KA7552)
Voltage
detection
circuit
9V rectified
smoothing circuit
8V rectified
smoothing circuit
-8V rectified
smoothing circuit
5V rectified
voltage
circuit(x2)
3.3V rectified
voltage
circuit
9V rectified
voltage
circuit
8V rectified
voltage
circuit
-8V rectified
voltage
circuit
O
u
t
p
u
t
Reference Information
Samsung Electronics 2-5
2-1-2 SMPS circuit description
2-1-2(a) CIRCUIT METHOD
FLY-BACK PWM(Pulse width modulation) control
2-1-2(b) CIRCUIT DESCRIPTIONS
1. AC power rectification/smoothing terminal
- PD01 : Convert AC power to DC(Wave rectification)
- PO10 : Smooth the voltage converted to DC(Refer to Vin of Fig. 2-7)
- PC01, PC02, PC03, PC04, PC05, PC06, PL01, PL02, PL03 : Noise removal at power input/output
- PVA1 : SMPS protection at power surge input
- PVA2 : SMPS protection at 2st ground surge input(PVA1 pattern open : to remove noise)
- PR10 : Rush current limit resistance during power cord insertion.
È Rush current = (AC input voltage x 1.414 - Diode drop voltage) / Pattern resistance + PL02.01
resistance + PC10 resistance + PR10) (AC230V based : approx. 26A)
È Without PR10, the bridge diode might be damaged as the rush current increases.
2. SNUBBER circuit : PR17, PR18, PC11, PD10
- Prevent residual high voltage at the terminals of
switch during switch off/Suppress noise.
High inverted power occurs at switch off,
because of the 1st winding of transformer:
(V=L1xdi/dt. LI : Leakage Induction)
A very high residual voltage exists on both
terminals of PQ1 because dt is a very short.
- SNUBBER circuit protects PQ1 from damage
through leakage voltage suppression by RC,
(Charges the leakage voltage to PD10 and PC11,
and discharges to PR17 and PR18).
- PC12, PL11 : For noise removal
Fig. 2-16
3. PIC1 Vcc circuit
- PR11, PR12, PR13, PR14 : PIC1 driving resistance (PIC1 works through driving resistance at power cord in)
- PIC1 Vcc : PR20, PD12, PC17
1) Use the output of transformer as Vcc, because the current starts to flow into transformer while PIC1 is active.
2) Rectify to PD12 and smooth to PC17.
3) Use the output of transformer as PIC1 Vcc : The loads are different before and after PIC1 driving.
(Vcc of PIC1 decreases below OFF voltage, using only the resistance due to load increase after PIC1 driving.)
- PR20 : For noise removal
0
Vin–Vp
Vswitch
dt
Toff
t
Inverted power
by leakage
inductance
Reference Information
2-6 Samsung Electronics
4. PIC1 function : PWM control (Refer to Switch ON/OFF Control of Fig. 2-6)
- 0.56V
- -
OFF voltage 0.75V
SHUT OFF voltage 2.8V
DUTY MAX voltage 2.3V
LIMIT voltage 0.24V
- -
- -
Maximum DUTY 70%
ON voltage 16V
OFF voltage 8.7V
- -
OFF voltage 0.42V
ON voltage 0.56V
3.6V
SHUT OFF voltage 7V
MAX DUTY voltage 2.3V
1 RT
2 F/B
3 IS
4 GND
5 OUT
6 VCC
7 CT
8 CS
PIN NAME CLASS SPEC. FEATURES
* Resistance to determine OUT terminal(pin5) ON/OFF control frequency
- Determined with CT terminal(pin7) and for DVDP, 50KHz
RT : PR24, CT : PC13
* OUT terminal duty is determined by F/B potential
(Duty control : 2st output constant-voltage control)
* The voltage of PIC2(Output voltage freedback) is input to F/B terminal.
* If F/B terminal potential decreases below 0.75V, OUT duty is zero.
- SMPS 2st output voltage is zero.
* If F/B potential is above 2.8V, CS terminal(8pin) potential ascends in IC.
If CS potential rises above 7V, SHUT OFF mode is maintained.
* SHUT OFF mode : IC internal bias OFF state.(Operation stop)
* If IS terminal potential is above 0.24V, maintain on time only when IS
terminal potential is 0.24V without holding OUT duty determined in F/B
terminal(Duty limit).
* PQ1(F,E,T) current is distributed to PR22, PR21 in voltage, and input to IS
terminal.
* Purpose : Limit the overcurrent of PQ1(Current waveform : See Fig. 2-10)
* Ground(SMPS 1st ground)
* ON/OFF control pulse output terminal(f : fixed, ON TIME : variable)
* Maximum duty is 70% (Maximum).
* IC power supply terminal. IC function starts at exceeding 16V. Vcc less than
8.7V will be OFF after IC working.(See Clause 3. Vcc circuit)
- Vcc voltage is 10-12V at normal operation.
* ON/OFF frequency determining terminal(Refer to 1 pin RT terminal)
* OS potential setting : Connect the condenser to OS terminal(PC14)
* ON/OFF control : If CS potential is above 0.56V, IC function starts and if
below 0.42V, IC function stops.
* At normal operation : Maintain 3.6V in IC
* SHUT OFF mode : If CS potential is above 7V, shut off.(Overload
prevention)
- SHUT OFF function : When IS, F/B, CS terminal are all operated normally.
(Refer to Clause 6. MAX. POWER limiting circuit)
* SOFT START : Switch protection at initial starting
- F/B potential is 3.6V internally at initial starting.(Duty max.)
- PQ1 damage occurs due to overcurrent on switch at duty max.
- CS terminal sets the duty with F/B terminal
- Connect PC14 to CS terminal and set the voltage charging time at initial
starting.
- Increase the duty by raising the voltage gradually via PC14 at initial starting
for normal operation.
(Duty max. is limited by F/B potential at initial starting)
Normal operation
voltage
Reference Information
Samsung Electronics 2-7
5. Feedback control circuit
Fig. 2-17
- F/B terminal of PIC1 determines output duty cycle.
- Duty definition : Refer to Vs1 in Fig4-10.(Duty up: Vs1 up, Duty down: Vs2 down)
- C-E(Collector-Emitter) of PIC2 and F/B potential of PIC1 are same.
- At F/B terminal open : SHUT OFF mode
È F/B potential is set to 3.6V internally.
F/B potential decreases to 1-2V by C-E voltage of PIC2 ( controlled by normal
operation. )
È When F/B terminal is open, shut off occurs because 2.8V is exceeded.
(Refer to clause 4.)
3 Operation descriptions
a. Internal OP-Amp Ô+Õ base potential of PIC3 is 2.5V and external Ò-Ó input potential is connected with PR38
and PR39 to maintain Vout of 5.8V. (Vout = ((PR36 x PR39) / PR39) x 2.5V)
b. If load of 5.8 V terminal increases(or AC input voltage decreases) and Vout decreases below 5.8V, then :
PIC3 ÔPÕ potential down below 2.5V --> PIC3 A-K of base current down --> PIC3 of A-K current down -->
PIC2 Diode current down --> PIC2 C-E current down --> PIC2 C-E voltage up --> PIC1 F/B voltage up -->
OUT Duty up --> Transformer 1st current up --> Transformer 1st power up --> Vout up --> Maintain
Vout 5.8V
c. If load of 5.8 V terminal decreases(or AC input voltage rises) and Vout rises above 5.8V, then :
Reverse sequence of the above description ® Duty down ® Vout down ® Maintain 5.8V
(i.e., the feedback to maintains 5.8V).
- PR35, PR36 : Reduce 5.8V overshoot
- PR37, PC43 : Prevent IC3 oscillation(for phase correction)
- PC18 : Adjust feedback response rate
PIC1
OUT
ON/OFF Control
Trans
PC18
PIC2
C
E
A
P
K
2.5V
K
PR36
PR37
A
PR35
PC38 PC39
PR40
100/2W
PL37
5 .8V
PD35
PC43
PR38
PR39
GND
++ ++
GND
F/B
1
2
3
4
5
PIC3
-
+
Reference Information
2-8 Samsung Electronics
6. Maximum power limit circuit
* Circuit configuration : PIC1 F/B, CS, IS terminal PR23, PR21,
PR22, PC13A
* Role : Switch overcurrent protection
* The current on switch inputs to IS and outputs as voltage via
PR23, PR21, PR22.
* If the current on switch increases and IS terminal input
voltage exceeds 0.24V, duty is determined by F/B terminal.
Accordingly, the current on switch is limited less than specific
current.(If 2d load rises, the switch current increases. Refer to
clause 5. in circuit description).
* If I/S terminal is open : Switch and other parts are damaged
because the switch is not limited during abnormal status (for
example, 2d ouput terminal short).
Fig. 2-18
1) Intermittent operation mode
- Definition : PIC1 canÕt deliver normal output, and repeats Vcc ON/OFF operation(Vcc voltage is swing
between 16V(ON) and 8.7V(OFF).
- Operation description : for example. 2d output terminals shorted, then :
Specific 2d terminal short --> 2d power is concentrated on short terminal --> 5.8V(PC39)
voltage down --> F/B voltage up (Refer to clause 5.) --> Duty up --> Switch current up --> Limit switch
current to IS terminal(Duty limit) --> Apply 1st supply power in comparison with 2d power -->
Concentrate on 2d power short terminal --> PIC1 Vcc terminal TRANS. output voltage down below
8.7V --> PIC1 OFF --> PIC1 ON via driving resistance --> Above operations repeated ® Maintain
intermittent operation mode (See Fig. 2-19 Waveform).
At short release : normal operation
2) Short OFF mode
- Main examples : Feedback circuit Open, Max, Power
excess(Design spec.), 5.8V Terminal short
- Operation description :
Ex - 2d load is high abnormally;
1st supply power is low in comparison with 2d output power.
5.8V down --> Duty up --> Switch current up -->
IS terminal duty limit --> 1st supply power limit --> 5.8V
voltage down --> F/B potential above 2.8V(Shut OFF voltage)
--> OS terminal potential up (Refer to Clause 4.)F/B -->
OS potential above 7V --> Shut OFF mode
- The output voltage of SMPS is zero because PIC1 doesnÕt work
during Shut OFF mode.
- Shut OFF mode release : OS potential decreases below
7V.(Charge OS terminal forcely)
- Feedback terminal open : Shut OFF (Refer to clause 5.);
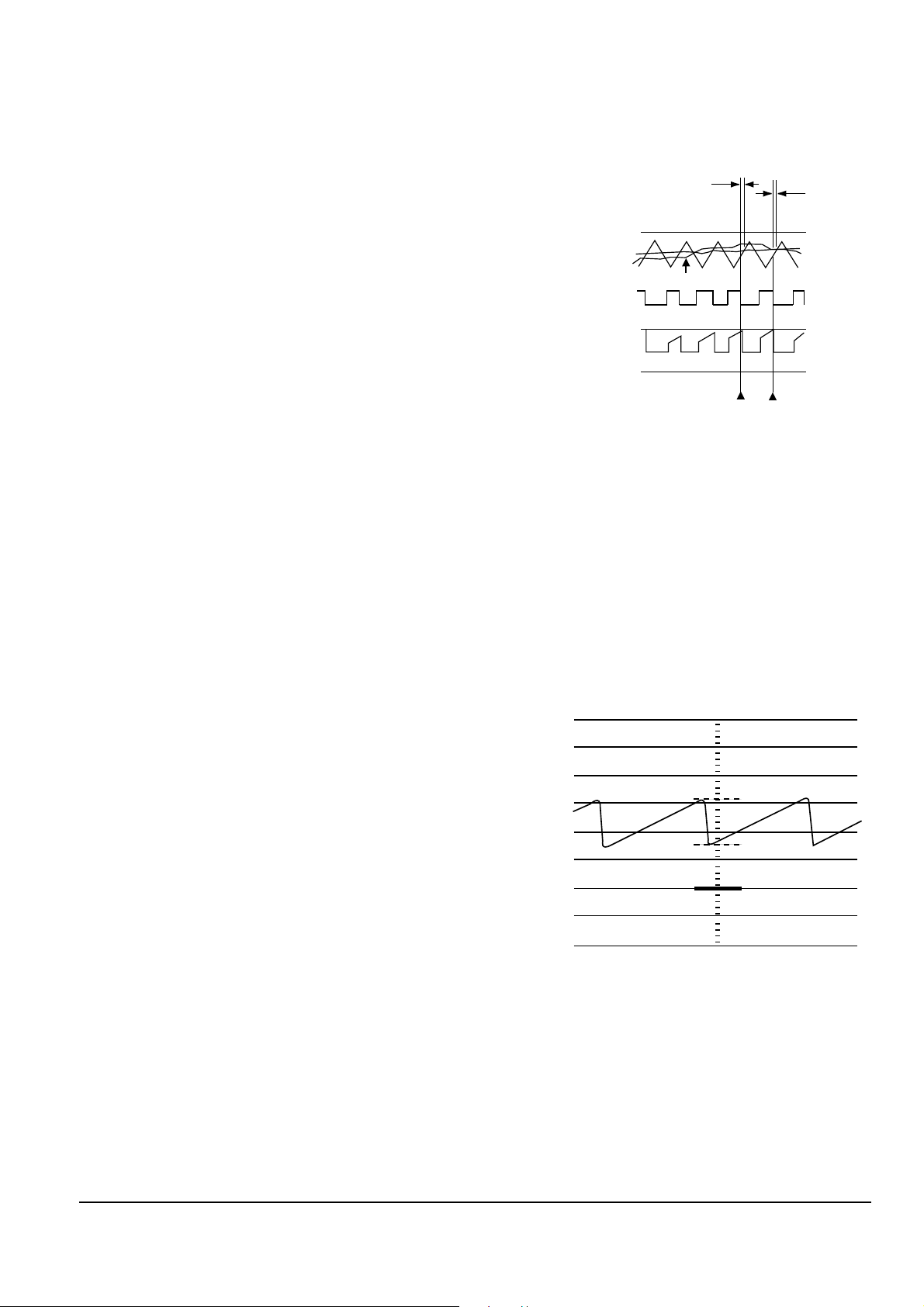
PC13A : For IS terminal input noise removal Fig. 2-19
CS Voltage(3.6V)
Duty Limit sector
FB Voltage
DT Voltage
OSC OUT
OUT Voltage
COM.C4(0.24V)
Over current protection
Over current protection
Blas voltage
IS(+) Voltage
Time : 100ms / div
Volt : 5V / div
16V
8V
GND

Reference Information
Samsung Electronics 2-9
7. Shut Off mode prevention circuit at instant load increase : PC15, PZD13
- During a sudden load increase;
By means of current concentration on specific output terminal, 5.8V voltage down --> F/B potential up -->
Maintain Shut Off mode.
Stablize F/B potential (Loading completion) below 7V by lengthening CS potential rise time to 7V
(in order to prevent Shut Off mode).
- Normal operation : CS potential is 3.6V and PZD13(4.7V ZENER) is open.
- OD potential above 4.7V at instant load increase --> PZD13, PC15 work --> OS terminal condenser capacity
increases in parallel with PC14 and PC15 --> CS potential rising rate down --> Instant operation completed
--> F/B potential stable --> Normal operation
8. Maximum power limiting circuit addition : PZD11, PR19
- SMPS efficiency : Below 25W : High efficiency at AC110V input
Above 25W : High efficiency at AC230V input
- The peak value of current on switch at overload is lower than that at 110V input because SMPS is highly
efficient above 25W at 230V input. Therefore, maximum power increases at 230V as compared to
110V at overload. Add PZD11, PR19 and set to the same level as 110V.
- Higher at 230V input than at PZD11 input, limit maximum power because IS terminal potential goes up.
9. PQ1(F,E,T) Gate Drive Circuit : PR15, PR16, PD11
- PIC1 OUT is square wave but charging and discharing by PR15, PR16 occurs due to internal condenser
between gate-sources of PQ1.
- PR15, PR16 : Switch ON Time setting - PD11 is reverse : PIC1 OUT --> PR15 --> PR16 --> Charge to gate
- PR16, PD11 : Switch OFF Time setting - PD11 is proper : GATE - PR16 --> PD11 --> Discharge to PIC1
OUT(GND)
- Switch ON/OFF time : Releated to switch loss and noise
10. PIC1 overcurrent protection : PZD12
- Operate PZD12 and protect PIC1 from damage from residual overcurrent (PIC1 Vcc, due to external surge
inflow and feedback line open).
2-10 Samsung Electronics
2-2-1 RIC1(TA1236F)
TA1236F is combined with TA1253FN, TC9240F and TC90A19F as bipolar IC developed for DVD SERVO system.
Main features include DVD waveform equalizing, CD waveform equalizing, focus error signal generation, 3-beam
tracking error signal generation, laser power control, etc. after receiving the pick-up output converted into I/V.
1. Basic potentiometer
TA1236F uses a single power method and each circuit is based on VREF of 2.1V. Note :
symmetrical about GND for VREF because VREF(pin20) terminal is needed for IC, which uses the peripheral VREF
and 2VREF output(pin18).
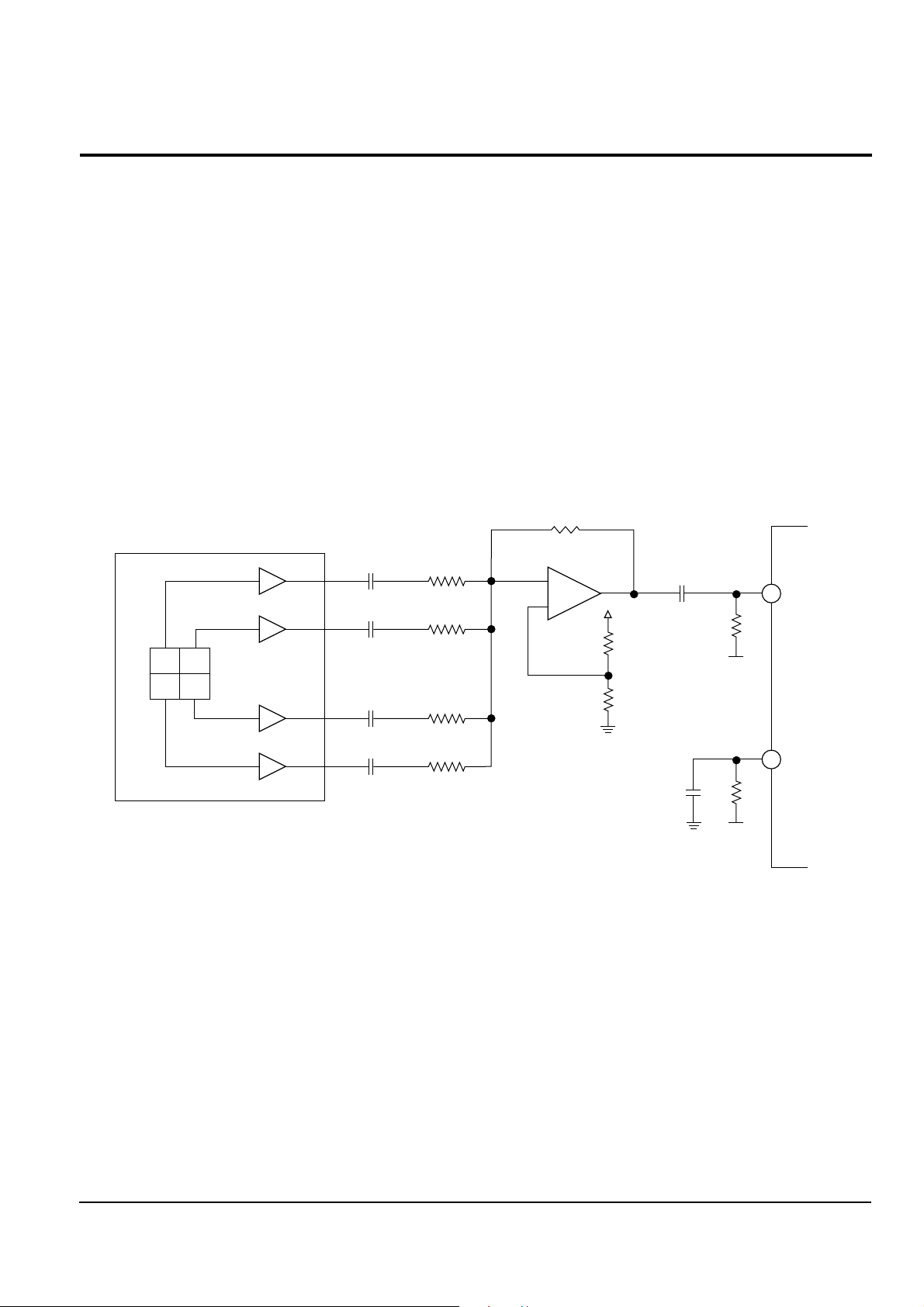
2. RF signal
Fig. 2-20 shows the flow of signal generated by the pick-up.
A, B, C, D signals detected from pick-up are converted in to RF signal(A+B+C+D) via RF summing AMP.
RF signal is inputted to RFN(pin55) among input terminals and RFP(pin54) is used for AC ground.
Fig. 2-20
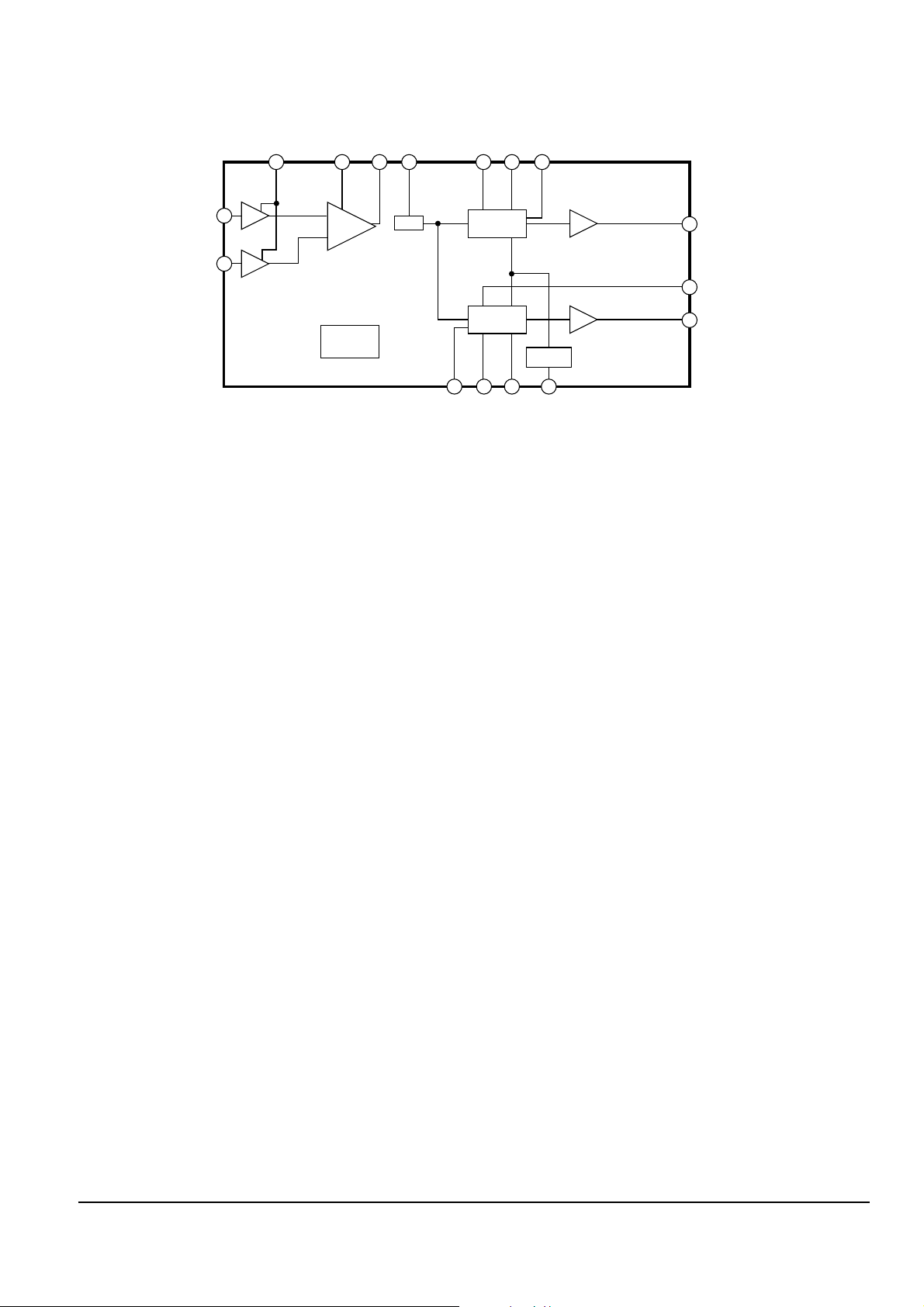
Fig. 2-21 shows the waveform-equalizing block diagram for the RF signal.
It outputs to EQout(pin 46) terminal by initially changing switching AMP gain of DVD and CD, and then
adjusting the level in VCA. It controls VCA gain by means of RF gain(pin 48) and interfaces with PWM signal,
(output from RFGC terminal of TC9420F, via low-pass filter to constitute a loop for adjustment of constant
amplitude). The gain in EQout is 1.0 for DVD and 1.67 for CD.
EQout terminal is connected with EQin(pin 45) externally, and inputs into DVD EQ and CD EQ(Waveform
equalizing circuit).
55
54
PICK-UP
PD
D A
C B
I-V AMP
RC12
104
RR20
1K
RC10
104
RR19
1K
+
–
RC15
104
RR24
1K
RC14
104
RR22
1K
RR18
1.2K
RIC3 OPA 650
SUMMING AMP
2
3
6
RC11
104
RR23
10K
RR50
5.6K
RR51
5.6K
RC22
104
RR33
10K
Vref
RIC1
TA1236
RFN
Vref
RFP
+5A
2-2 RF circuit description
Reference Information
Reference Information
Samsung Electronics 2-11
Fig. 2-21
The control parameters of DVD EQ and CD EQ are as follows.
1) DVD EQ control parameter
- DVDEQ(pin 43) : Changes the gain of peak frequency with EQ frequency characteristic. Convert PWM
signal, output from TC90A19F, into DC via low-pass filter.
- DVDTIME(pin 41) : Changes the peak frequency with EQ frequency characteristic. Convert PWM signal,
output from TC90A19F, into DC via low-pass filter.
- S/Dse1(pin 64) : Changes the peak frequency (like DVD TIME) as 2d control. ( Switched according to
regeneration speed ratio of single/double layer).
- MCK(pin 15) : Input the base clock and link the peak frequency with it. The amplitude of MCK might be
small (500mVp-p).
- DVDGD(pin 25) : Changes the group delay characteristics with EQ frequency characteristic.
2) CD EQ control parameter
- CD EQ(pin 40) : Changes the gain of peak frequency with EQ frequency characteristic. The constant DC is
supplied to a resistive voltage divider.
- CD TIME(pin 42) : Changes the peak frequency with EQ frequency characteristic. The constant DC is
supplied to a resistive voltage divider.
- S/Qse1(pin 44) : Changes the peak frequency (such as CD TIME) as 2d control. (Switched according to play
linear velocity ratio of quadruple/single rate. Set to Ô0Õ because only one rate is vaild in
this system).
Note : CD and DVD signals are equalized according to the above control parameters ,and then output to CD
EQ OUT (pin39) and DVD EQ OUT (pin34). Then, CD signal is transferred to TC9420F, DVD signal is
sent to TC90A19F and detected.
DVDsel RFgain EQout EQin
CDEQCD
TIME SQsel
RFN
RFP
47 48 46 45 40 42 44
55
54
64 41 43 15
34
25
39
VCA
ATT
CD EQ
DVD EQ
RIC1
TA1236F
GEN.
T/CON
SDsel DVD
TIME
DVDEQMCK
DVD G/D
DVD EQ OUT
CD EQ OUT
2-2-2 Description of data processor for DVD
(Including DIC1 and DIC5 protection IC)
1. Outline
The data processor IC for DVD does the following :
1) Converts RF signal to digital, demodulates original signal and corrects errors,
2) PLL circuit to generate the clock for data detection in accordance with play velocity,
3) CLV control circuit to control the rotation rate of disc,
4) DIC5 Protection IC, connected with input/output of data processor, which releases the protection for the
protected data (which is then transmitted to video decoder and Micom).
 Loading...
Loading...