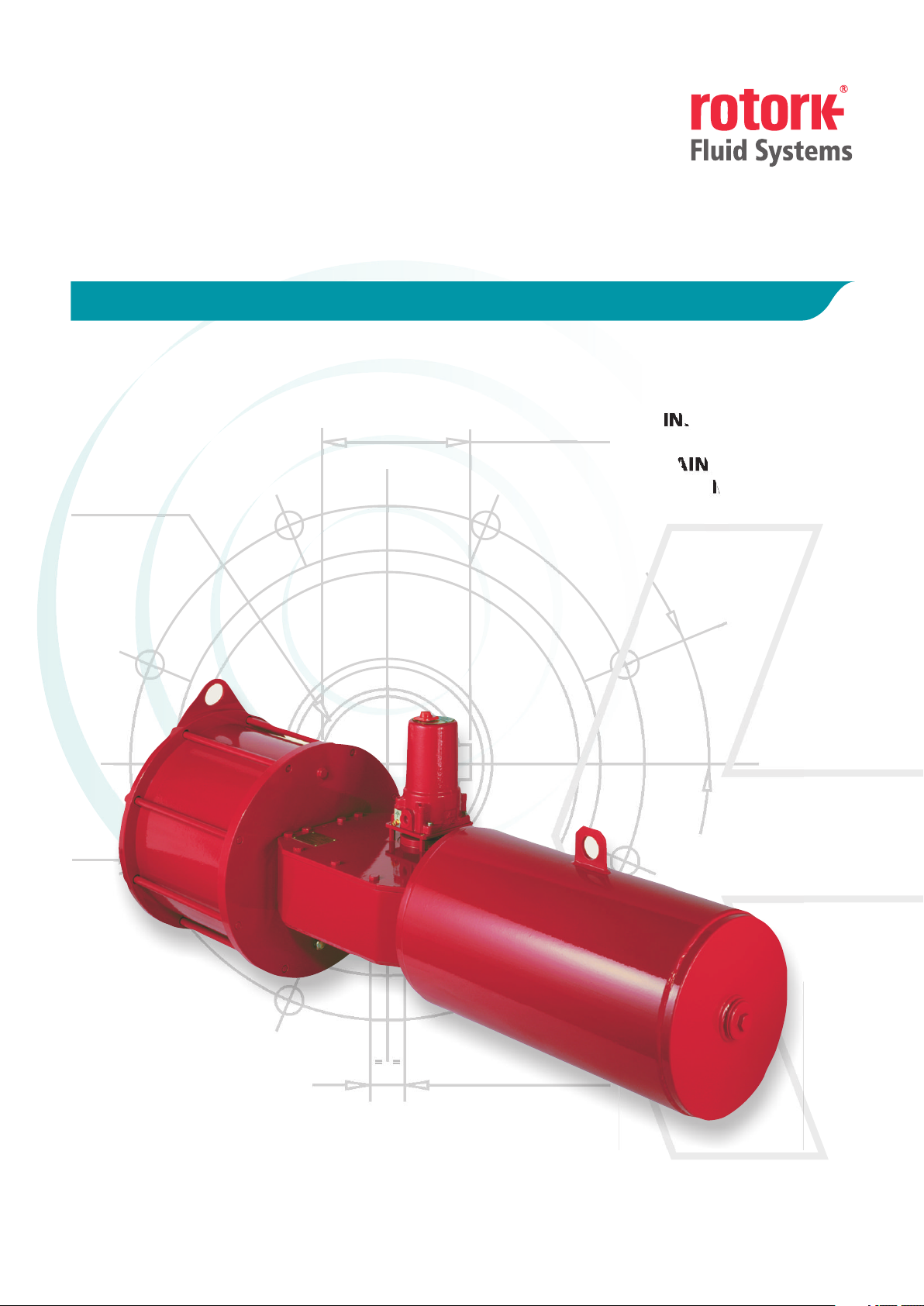
Established Leaders in Valve Actuation
GP RANGE
PNEUMATIC SCOTCH YOKE ACTUATORS
INSTALLATION
AND
MAINTENANCE
MANUAL
Publication F130E
Date of issue 04/08

CONTENTS
GP RANGE
INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE
SECTION
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Appendix
CONTENT PAGE
Introduction
Installation
Maintenance
Grease and Hydraulic Oil Specifications
Cylinder Seal Replacement
Fault Detection
Actuator Drawing / Parts List
3
3
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
Stop Bolt Adjustment
MB1 Switchbox Setting Procedure
Page 2 of 12 Publication F130E
10
11
Date of issue 04/08

INTRODUCTION
1.0 Introduction
This manual is produced to enable a competent user to install, operate, adjust, inspect, and maintain Rotork Fluid Systems GP
range actuators. Users are responsible to follow the instructions in this manual as well as any additional documentation that
has been supplied regarding the actuator or accessories supplied by Rotork Fluid Systems. Should further information or
guidance relating to the safe use of GP range actuators be required, it will be provided on request. Users are also responsible to
be familiar with and follow any relevant legislation or statutory provisions regarding health and safety.
It is the users responsibility to ensure that the equipment is operated in a safe manner and that any personnel working with or
on the equipment are properly trained for the work they are performing and are also aware of their responsibilities relating to
health and safety in the workplace. It is extremely important that precautions are taken to avoid spark or static discharge in any
areas of potentially explosive atmosphere.
All Rotork Fluid Systems actuators are tested prior to despatch. Job specific documentation is shipped with the actuator. Test
certificates and replacement documentation are available upon request. The latest general information regarding any Rotork
product is available on our website www.rotork.com.
INSTALLATION
GP RANGE
INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE
2.0 Installation
2.1 Electrical Considerations
2.1.1 Any electrical connections required are the responsibility of the user. Connection documentation is supplied with the actuator.
Refer to the applicable wiring diagram to identify functions of terminals. Verify that the electrical supply characteristics are
compatible with the supplied actuator control components.
2.1.2 Only appropriate certified explosion-proof entry reducers, glands or conduit may be used if the unit is installed in a hazardous
area. Remove any plastic transit plugs. Make cable entries appropriate to the cable type and size. Ensure that threaded
adaptors, cable glands or conduit are tight and fully waterproof. Seal unused cable entries with a steel or brass plug. In
hazardous areas an appropriately certified threaded blanking plug must be used.
2.1.3 Access to live electrical conductors is forbidden in hazardous areas unless done under a special permit to work. Otherwise, all
power should be isolated and the unit moved to a non-hazardous area for repair or attention.
2.1.4 The actuator and control components must be protected from electrical spikes, surges, and lightning strikes as well as
magnetic or electro-magnetic fields. This is the responsibility of the user.
2.2 Motive Power Supply (pneumatic, hydraulic)
2.2.1 Ensure that the actuator will not be exposed to pressure in excess to the maximum rating as indicated on the nameplate.
2.2.2 Verify that medium composition (e.g., filtration, hydration) correspond to that for with the actuator was manufactured.
Rotork Fluid System must be contacted to verify compatibility of any proposed changes to supply medium.
2.2.3 Ensure that throughout the installation that there are no leaks of a potentially explosive supply medium (e.g., natural gas).
Note: Depending upon control circuit design, pneumatically powered actuators may exhaust the power supply gas to
atmosphere in the course of normal operation. This may present an unacceptable hazard in some applications. Consult Rotork
Fluid Systems if in doubt as to the suitability of the equipment supplied for your application.
Page 3 of 12
Publication F130E
Date of issue 04/08

INSTALLATION
GP RANGE
INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE
2.3 Maximum Allowable Temperature
2.3.1 The maximum temperature allowable for standard build actuators is 100°C (212°F).Other maximum temperature build
options are available. It is the responsibility of the user to ensure that the maximum allowable temperature as indicated on the
nameplate is not exceeded and also, in the case of sites where a potentially explosive atmosphere may exist, that the surface
temperature of the actuator does not exceed the ignition point of the potentially explosive atmosphere.
2.3.2 Be aware that the temperature of the contents of the valve/pipeline as well as that of the power supply gas will affect actuator
temperature. A build up of dust or dirt on the actuator can inhibit cooling and contribute to increased surface temperatures.
The user should plan and provide for a periodic cleaning/maintenance program that will maintain the installation environment
per the guidelines set forth in EN 1127-1 par 6.4.2.
2.4 Operating Environment
2.4.1 The user must ensure that the operating environment and any materials surrounding the unit cannot lead to a reduction in the
safe use of, or the protection afforded by the actuator. Where appropriate, the user must ensure the actuator is suitably
protected against its operating environment including, but not limited to, lightning strikes, vibration sources and vehicular
movement.
2.4.2 If the unit has a nameplate indicating that it is suitable for installation in potentially explosive atmosphere (hazardous area), it
must not be installed in a hazardous area that is not compatible with the gas groups and temperature class defined on the
nameplate.
2.5 Mechanical Considerations
2.5.1 It is recommended that before lifting an actuator onto a valve, great care is taken to ascertain the position of the valve and
orientate the actuator accordingly.
2.5.2 Rotork actuators can be mounted on valves in almost any desired position. It is usual however to align the centerline of the
cylinder to the centerline of the associated pipe work.
Note: Certain accessory and control components e.g., filter drains, hydraulic reservoirs; require proper orientation with
respect to gravity to function properly. Contact Rotork Fluid Systems if in doubt.
2.5.3 Ensure all fasteners are adequately tighten to avoid loosening during the course of operation, taking into account vibration
induced by the dynamics of the pipeline.
2.54 All tubing used to provide pneumatic/hydraulic power to the actuator must be free from contaminants and debris. Ensure
tubing runs are adequately fastened and supported to minimise repetitive stress induced by any vibration induced by the
dynamics of the pipeline.
2.5.5 When the actuator has been bolted to the flange or adapter, the position of the stop bolts should be checked to ensure full
opening and closing of the valve. If these end of travel positions are not correct, the stop bolts may be adjusted by first
loosening the fixing nut and then screwing the bolts in or out until desired end position is obtained. Stroke the yoke away from
the stop bolt when adjusting, then return it to check position. When the correct positioning is obtained, re-tighten the fixing
nut.
2.5.6 Certain valves incorporate their own stops. In these cases it is recommended that the actuator stop bolt positions coincide
with the valve stop positions.
2.5.7 Ensure there are no leaks from any pneumatic or hydraulic connections. Tighten as required.
2.5.8 Once in position, the actuator should operate the valve with a smooth continuous action. If uneven operation occurs, the
pneumatic/hydraulic power supply should be checked for correct pressure and volume flow. Flow may be restricted by
undersize pipe or fittings. These could throttle the flow thus reducing the pressure and volume at the actuator and causing
intermittent motion. Further fault detection procedures are outlined in Section 6.
Page 4 of 12
Publication F130E
Date of issue 04/08

MAINTENANCE
GP RANGE
INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE
3.0 Maintenance
3.1 Rotork actuators are designed to work for long periods of time in the most severe conditions. However, a preventative
approach to maintenance helps prevent costly down time and can actually reduce the cost of ownership. Rotork can provide
an actuator maintenance contract tailored to meet each customer’s individual requirements.
3.2 Any personnel working with or on the equipment must be properly trained for the work they are performing and be aware of
their responsibilities relating to health and safety in the workplace.
3.3 No inspection or repair should be undertaken unless it conforms to any applicable hazardous area certification requirements.
Under no circumstances should any modification or alteration be carried out on the unit as this could invalidate the
certification.
3.4 Before performing maintenance, the actuator should be isolated from remote control signals and the pneumatic/hydraulic
power supply. The system should be then be relieved of any internal pressure prior to disassembly.
3.5 Improper operation, adjustment or maintenance of the actuator and controls may, depending on the application, release
potentially explosive gas and or dangerous liquids.
3.6 After maintenance has been performed and re-assembly completed, follow the inspection guidelines as outlined section 3.6.
3.7 Periodic Inspection
3.7.1 Ensure that the actuator correctly operates the valve within the required cycle time. The actuator should be cycled several
times with all the existing controls e.g., remote control, local control and manual override; particularly if the actuator is not
frequently operated.
3.6.2 Verify that the power gas supply pressure value is within the required range.
3.7.3 Visually inspect external components of the actuator for physical damage.
3.7.4 Check pneumatic/hydraulic connections for leakage. Tighten pipe fittings as required.
3.7.5 Remove dust and dirt build-up from all actuator surfaces. They can inhibit cooling thus raising the temperature of the
actuator above the maximum allowable limit.
3.7.6 Inspect actuator paint work for damaged to ensure continued corrosion protection. Touch-up as required to applicable paint
specification.
Page 5 of 12
Publication F130E
Date of issue 04/08

GREASE AND HYDRAULIC OIL
4.0 Grease and Hydraulic Oil Specifications
4.1 Grease Specification
Manufacturer: Mobil
Trade name: Mobiltemp 78
Colour: Gray/black
Soap type: Inorganic
Oil type: Mineral
Consistency (NLGI GRADE)-ASTM D217: 1
Worked penetration at 25°C-ASTM D217: 295/325 dmm
Dropping point - ASTM D2265 260°C
Viscosity of base oil at 40°C-ASTM D445: 485 cSt
Viscosity of base oil at 100°C-ASTM D445: 32 cSt
GP RANGE
INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE
QUANTITY OF GREASE IN HOUSING
CENTRE BODY SIZE
065, 085, 100
130
160, 161, 200, 201
270, 271
350
QTY (kg/lb)
0.3/0.66
0.4/0.88
0.5/1.10
0.8/1.76
1.2/2.64
Note:
This is the standard grease specification for Rotork Fluid Systems actuators. If an alternative was specified and/or
supplied, it is noted in job specific documentation, which is available upon request.
4.2 Hydraulic Oil Specification
Manufacturer: Mobil
Trade name: DTE 11
Viscosity at 40°C: 16.5 cSt
Viscosity at 100°C: 4.2 cSt
Viscosity index ASTM: 168
ISO Grade: 16
Pour point: -42°C
Specific weight at 15°C: 0.85 kg/dm
Equivalent to: Statoil - Hydraway HVX-A15
Note:
This is the standard hydraulic oil specification for Rotork Fluid Systems actuators. If an alternative was specified
and/or supplied, it is noted in job specific documentation, which is available upon request.
3
Page 6 of 12
Publication F130E
Date of issue 04/08

CYLINDER SEAL REPLACEMENT
GP RANGE
INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE
5.0 Cylinder Seal Replacement
5.1 Disassembly
5.1.1 Disconnect pneumatic and electrical supply connections. For spring return actuators, ensure that the actuator is in the failed
position (i.e., at end of the spring stroke).
5.1.2 Remove stop bolt nut (33).
5.1.3 Loosen stop nut (31) and remove stop bolt (32).
5.1.4 Remove tie rod nuts (34) from the tie rods (22).
5.1.5 Remove bottom flange (21).
5.1.6 Remove cylinder tube (19).
5.1.7 Remove housing cover bolts (16), center body cover (15) and cover gasket (14).
5.1.8 Remove piston retaining nut (35) and separate piston (23), shoulder washer (30), and o-ring (36) from piston rod (20).
5.1.9 Remove o-ring (25) and sliding ring (24) from piston (23).
5.1.10 Remove piston rod (20) by unscrewing it from the guide block (4).
5.1.11 Remove flange retaining bolts (13) and remove head flange (18).
5.1.12 Remove head flange and bottom flange o-rings (26).
5.1.13 Remove bolts (38) and shaft seal retaining flange (37) from the head flange (18).
5.1.14 Remove o-ring (28) and shaft seal (29).
5.1.15 Clean all sealing surfaces.
5.1.16 Coat new o-rings, seals and gaskets with grease.
5.2 Assembly
5.2.1 To reassemble the actuator, follow the disassembly procedure in reverse order.
5.2.2 Reconnect power gas supply lines to the actuator.
5.2.3 Cycle the actuator several times. Movement should be smooth and continuous. If not, refer to Section 6, Fault Detection.
RECOMMENDED TIGHTENING TORQUE
FT. LBSNMBOLT SIZE
M6
M8
M10
M12
M14
M16
M20
M22
M24
M27
M30
M33
M36
8.5
20
40
55
110
220
430
425
585
785
1,250
1,400
1,750
6
15
30
40
81
162
317
313
431
579
921
1,030
1,290
Page 7 of 12
Publication F130E
Date of issue 04/08

FAULT DETECTION
6.0 Fault Detection
In the unlikely event of a fault developing, the following Fault Location Table is provided to assist the maintenance technician.
This table is designed to cover as wide a range of Rotork Fluid Systems actuators as possible. Reference to equipment not
supplied should be ignored.
GP RANGE
INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE
SYMPTOM
6.1 Erratic movement
6.2 Short stroke
6.3 Apparent lack of power
CAUSE
6.1.1 Irregular supply of operating
medium.
6.1.2 Inadequate lubrication.
6.1.3 Worn parts.
6.1.4 Defective valve.
6.2.1 Incorrectly set stops
(valve and /or actuator).
6.2.2 Hardened grease.
6.2.3 Debris left in the cylinder or
housing during maintenance.
6.2.4 Defective valve.
6.3.1 Inadequate supply pressure.
REMEDY
6.1.1.1 Check operating medium for consistent
supply pressure and correct as necessary.
6.1.2.1 Dismantle, re-lubricate and reassemble.
6.1.3.1 Dismantle. Visually inspect for significant
wear. Actuator replacement may be required.
6.1.4.1 Consult the valve manufacturer's
documentation.
6.2.1.1 Check the position of the travel stops and
readjust as necessary.
6.2.2.1 Dismantle, remove any hard grease,
re-lubricate and reassemble.
6.2.3.1 Disassemble cylinder assembly to remove
debris. Reassemble cylinder assemble as
necessary.
6.2.4.1 Consult the valve manufacturer's
documentation.
6.3.1.1 Ensure supply pressure is above the minimum
operating pressure of the actuator and that
output torque produced at supply pressure
exceeds valve torque demand.
6.3.2 Incorrect speed control settings.
6.3.3 Exhaust port blocked.
6.3.4 Pipe work blocked, crushed
or leaking.
6.3.5 Defective controls.
6.3.6 Defective piston seal.
6.3.7 Defective rod seal.
6.3.8 High valve torque or valve seized.
Page 8 of 12
6.3.2.1 Adjust speed controls to increase flow.
6.3.3.1 Remove and clean the exhaust port
silencers and replace.
6.3.4.1 Examine the pipe work for blockages,
crushed pipe or leakage. Clear or replace
as necessary.
6.3.5.1 Examine the controls, refurbish or renew
as necessary. Refer to component
manufacturer's documentation.
6.3.6.1 Dismantle the cylinder assembly, remove
the defective piston seal. Fit new seal and
reassemble.
6.3.7.1 Dismantle the cylinder assembly, remove
the defective rod seal. Fit new seal and
reassemble.
6.3.8.1 Consult the valve manufacturers
documentation.
Publication F130E
Date of issue 04/08

DRAWING / PARTS LIST
GP RANGE
INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE
ITEM
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
CENTRE BODY ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION
Centre body
Guide Bar
Safety Valve
Guide Block
Yoke
Guide Block Shaft Bushing
O-ring
Upper Bushing
Lower Bushing
Sliding Block
Bar Pin
Retaining Ring
Flange Retaining Bolt
Cover Gasket
Cover
Cover Mounting Bolt
Flange Gasket
46
494847 45
50
MATERIAL
Carbon Steel or Ductile Iron
Alloy Steel - Chrome Plated
Brass/Stainless Steel
Carbon Steel
Carbon Steel or Ductile Iron
Steel/Bronze/PTFE
NBR
Bronze
Bronze
Bronze
Alloy Steel
Spring Steel
Carbon Steel
Vaporflex/SA
Carbon Steel
Carbon Steel
Vaporflex/SA
QTY
1
1
1
1
1
2
2
1
1
2
1
2
-
1
1
2
44
42
43
41 1
51
17
51 15
13
53
55
52
54
57
56
Typical fabricated carbon steel centre body and yoke illustrated.
Some models have a cast, ductile iron centre body and yoke.
2
5
13
16
14
7
3 18 33
6
26
4
27
4
7
8 29
10
12
11
9
17
3
39
222019
21
23
36
25 26 35 28
38
Centre body cross-section
37
31
32
40342430
PNEUMATIC CYLINDER ASSEMBLY
QTYMATERIALITEM DESCRIPTION
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
Head Flange
Cylinder Tube
Piston Rod
Bottom Flange
Tie Rod
Piston
Sliding Ring
O-ring
O-ring
Shaft Bushing
Seal Washer
Seal Washer
Shoulder Washer
Stop Bolt Fixing Nut
Stop Bolt
Stop Bolt Cap Nut
Tie Rod Nut
Piston Retaining Nut
O-ring
Seal Retaining Flange
Seal Retaining Flange Bolt
Bushing
O-ring
Carbon Steel
Carbon Steel - Nickel Plated
Carbon Steel - Chrome Plated
Carbon Steel
Alloy Steel
Carbon Steel
PTFE/Graphite
NBR
NBR
Steel/Bronze/PTFE
Carbon Steel/NBR
NBR/PTFE/Graphite
Alloy Steel
Carbon Steel
Alloy Steel
Carbon Steel
Carbon Steel
Carbon Steel
NBR
Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel
Carbon Steel
NBR
1
1
1
1
-
1
-
-
2
1
2
1
1
1
1
1
-
1
1
1
2
1
1
ITEM
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
ITEM
52
53
54
55
56
57
Quantity varies with size of the actuator.
Included in centre body seal kit.
Included in pneumatic cylinder seal kit.
SPRING CARTRIDGE ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION
Head Flange
Driving Flange
Connecting Rod
Bushing
Spring Canister
Spring
Stop Bolt
Bottom Flange
Protection Plug
O-ring
Shaft Bushing
CLOSURE ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION
Flange
Flange Nut
Seal Washer
Stop Bolt
Stop Bolt Cap Nut
Stop Bolt Fixing Nut
MATERIAL
Carbon Steel
Carbon Steel
Carbon Steel - Chrome Plated
Steel/Bronze/PTFE
Carbon Steel
Spring Steel
Carbon Steel
Carbon Steel
Carbon Steel
NBR
Steel/Bronze/PTFE
MATERIAL
Carbon Steel
Carbon Steel
Carbon Steel/NBR
Alloy Steel
Carbon Steel
Carbon Steel
QTY
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
1
1
1
1
QTY
1
4
2
1
1
1
Page 9 of 12
Publication F130E
Date of issue 04/08

APPENDIX A - Stop Bolt Adjustment
STOP SCREW
STOP NUT
SEALING WASHER
SEALING WASHER
STOP BOLT COVER
STOP SCREW
STOP NUT
SEALING WASHER
SEALING WASHER
STOP BOLT COVER
SPRING STOP
SPRING STOP CAP
INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE
GP RANGE
1.0 Overview
All RFS G Range actuators (ie., GP, GH, GO and HPG) incorporate adjustable stops
to limit the degree of travel in both directions. Steps are outlined below for
adjustment of the three stop configurations: pneumatic/hydraulic cylinder, spring
cartridge and, jackscrew.
Actuators may be damaged by improper adjustment procedure. Strictly follow
the instructions as outlined below with particular attention to the warnings is
steps 1.1.3, 1.2.2, 1.3 and 1.3.3.
1.1 Pneumatic/Hydraulic
Cylinder (See figure 1)
1.1.1 Remove stop bolt cover.
1.1.2 Loosen stop nut.
1.2 Spring Canister
(See figure 2)
1.2.1 Remove the spring stop cap.
1.2.2 Depressurize the cylinder to
allow the spring to relax.
1.1.3 Apply pressure to outboard
side of cylinder to remove load
Failure to do so may result in
damage to the actuator!
from stop bolt. Failure to do so
may result in damage to the
actuator!
1.1.4 Adjust stop bolt in/out as
desired.
1.2.3 Adjust the spring stop in/out as
desired.
1.2.4 Pressurize to outboard side of
power cylinder sufficiently to
induce a complete stroke of
1.1.5 Remove pressure from cylinder
to verify stop position.
1.1.6 Repeat steps 1.1.3 - 1.1.5 as
necessary to achieve desired
degree of travel.
1.1.7 Once desired po sition is
achieved, tighten stop nut,
ensuring sealing washer is
the actuator and then check
the stop position.
1.2.5 Repeat steps 1.2.2 - 1.2.4 as
necessary to achieve desired
degree of travel.
1.2.6 Once the desired position is
achieved, replace spring stop
cap.
properly centered on the shaft
and fitted in the machined
recess in the flange.
1.1.7 Re-install stop cover, ensuring
sealing washer is properly
centered on the shaft and
fitted in the machined recess in
the stop cover.
1.3 Jackscrew
(See figure 3)
Note: The jackscrew is not designed
to function as a travel stop.
Stroking the actuator against
the jackscrew may damage it.
1.3.1 Remove stop bolt cover.
1.3.2 Loosen stop nut.
1.3.3 Turn jackscrew fully in to
compress spring and remove
any load from the stop. Failure
to do so may result in damage
to the actuator!
On fail close actuators, this is
d o n e b y t u rn in g t h e
handwheel anti-clockwise.
On fail open actuators, this is
d o n e b y t u rn in g t h e
handwheel clockwise.
1.3.4 Adjust stop bolt in/out as
desired.
1.3.5 Back jackscrew out (opposite
direction of as determined in
1.3.3) until seated against stop
screw to verify stop position.
1.3.6 Repeat steps 1.3.3 - 1.3.5 as
necessary to achieve desired
degree of travel.
1.3.7 Once desired po sition is
achieved, tighten stop nut,
ensuring sealing washer is
properly centered on the shaft
and fitted in the machined
recess.
1.3.8 Re-install stop cover, ensuring
sealing washer is properly
centered on the shaft and
fitted in the machined recess in
the stop cover.
figure 1
Page 10 of 12
figure 2
figure 3
Publication F130E
Date of issue 04/08

APPENDIX B - MB1 Switch Adjustment
1.0 MB1 Limit Switch Adjustment
The MB1 is a Rotork Fluid Systems designed and manufactured switch enclosure suitable for use in harsh and/or hazardous
environments. It is available with either dry contact or proximity type switches. Consult the applicable job specific wiring
diagram for termination details. Contact Rotork Fluid Systems switch options and certification details.
GP RANGE
INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE
1.1 Setting Dry Contact Switches
1.1.1 Loosen the four screws (1) and remove the cover (2).
1.1.2 Setting the CLOSE limit switch.
1.1.2.1 Place the actuator/valve in the fully CLOSED position.
1.1.2.2 Locate the proper switch cam.
1.1.2.3 Loosen the setscrew (5) and rotate the cam (4) until
the switch operates. Tighten the setscrew. The
switch is now set.
1.1.3 Setting the OPEN limit switch.
1.1.3.1 Place the actuator/valve in the fully OPEN position.
1.1.3.2 Locate the proper switch cam.
Loosen the setscrew (5) and rotate the cam (4) until
the switch operates. Tighten the setscrew. The
switch is now set.
1.1.4 Replace the cover (2) and tighten the four screws (1).
1.2 Setting Proximity Type Contact Switches
1.2.1 Loosen the four screws (1) and remove the cover (2).
1.2.2 Setting the CLOSE limit switch.
1.2.2.1 Place the actuator/valve in the fully CLOSED position.
1.2.2.2 Locate the proper switch cam.
1.2.2.3 Loosen the setscrew (5) and rotate the cam (4) until
it is on the same axis as the switch and re-tighten the
setscrews.
1.2.2.4 Loosen the fixing nuts on the switch. Position the
switch the proper distance from the cam to activate
the switch. Re-tighten the fixing and lock nuts. The
switch is now set.
1.2.3 Setting the OPEN limit switch.
1.2.3.1 Place the actuator/valve in the fully OPEN position.
1.2.3.2 Locate the proper switch cam.
1.2.3.3 Loosen the setscrew (5) and rotate the cam (4) until
it is on the same axis as the switch and re-tighten the
setscrew.
1.2.3.4 Loosen fixing nuts on the switch. Position the switch
the proper distance from the cam to activate the
switch. Re-tighten the fixing and lock nuts.The
switch is now set.
ITEM
1
2
3
4
5
Page 11 of 12
1.2.4 Replace the cover (2) and tighten the four screws (1).
DESCRIPTION
Screw
Cover
Microswitch
Cam
Dowel
Publication F130E
Date of issue 04/08

Manufacturing Centres
Germany
Melle
Tel: +49 (0)5422 9414-0
Fax: +49 (0)5422 9414-10
sales@rfs-pci.de
Italy
Tassignano - Lucca
Tel: +39 0583 93061
Fax: +39 0583 934612
fluid@fluidsystem.com
Centres of Excellence
Australia
Bayswater, Victoria
Tel: +61 (0) 3 9729 8882
Fax: +61 (0) 3 9729 8884
sales@rfsaustralia.com
United Kingdom
Bramley, Leeds
Tel: +44 (0)113 236 3312
Fax: +44 (0)113 205 7266
sales@rotorkfluidsystem.co.uk
Canada
Calgary, Alberta
Tel: +1 403 569 9455
Fax: +1 403 569 9414
info@rotork.ca
United States
Houston, Texas
Tel: +1 713 856 5640
Fax: +1 713 856 8127
rfsinfo@rotork.com
Sweden
Falun
Tel: +46 (0)23-587 00
Fax: +46 (0)23-587 45
Email:
info@remotecontrol.se
Singapore
Tel: + 65 6457 1233
Fax: + 65 6457 6011
mail@rotork.com.sg
United States
Petaluma, California
Tel: +1 707 769 4880
Fax: +1 707 769 4888
rfsinfo@rotork.com
United States
Rochester, New York
Tel: +1 585 247 2304
Fax: +1 585 247 2308
rfsinfo@rotork.com
Spain
Bilbao
Tel: + 34 94 676 6011
Fax: + 34 94 676 6018
rotork@rotork.es
United States
North Kingstown, Rhode Island
Tel: +1 401 294 1400
Fax: +1 401 294 3388
Email: sales@remotecontrol.us
All Rotork Fluid Systems actuators
are manufactured under a third
party accredited ISO 9001:2000
quality assurance programme.
Published and produced by Rotork
Fluid Systems. Rotork recognises
all registered trademarks.
As we are continually developing our
products, their design is subject to
change without notice. RFSMH0408
Latest information is available on
www.rotork.com
 Loading...
Loading...