Page 1

Allen-Bradley
Ethernet
SLC 500t
Quick Start
Processors
(Catalog Numbers
1747-L551, -L552, and -L553)
for
Experienced
Users
Page 2
Important User Information
Because of the variety of uses for the products described in this
publication, those responsible for the application and use of this
control equipment must satisfy themselves that all necessary steps
have been taken to assure that each application and use meets all
performance and safety requirements, including any applicable laws,
regulations, codes and standards.
The illustrations, charts, sample programs and layout examples
shown in this guide are intended solely for purposes of example.
Since there are many variables and requirements associated with any
particular installation, Allen-Bradley does not assume responsibility
or liability (to include intellectual property liability) for actual use
based upon the examples shown in this publication.
Allen-Bradley publication SGI-1.1, Safety Guidelines for the
Application, Installation, and Maintenance of Solid-State Control
(available from your local Allen-Bradley office), describes some
important differences between solid-state equipment and
electromechanical devices that should be taken into consideration
when applying products such as those described in this publication.
Reproduction of the contents of this copyrighted publication, in
whole or in part, without written permission of Allen-Bradley
Company, Inc., is prohibited.
Throughout this manual we use notes to make you aware of safety
considerations:
ATTENTION: Identifies information about practices
or circumstances that can lead to personal injury or
!
Attention statements help you to:
death, property damage or economic loss.
• identify a hazard
• avoid the hazard
• recognize the consequences
Important: Identifies information that is critical for successful
application and understanding of the product.
SLC 5/05, SLC 500, and Data Highway Plus are trademarks of Rockwell Automation.
RSLogix 500 and RSLinx are trademarks of Rockwell Software., Inc.
Ethernet is a registered trademark of Digital Equipment Corporation, Intel, and Xerox Corporation.
Microsoft Windows is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
Page 3

Table of Contents
Preface
SLC 5/05 Ethernet Processor
Features
Who
Should Use this Manual
Purpose
Conventions
Allen-Bradley
of This Manual
Related
Local
Technical Product Assistance P–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Your Questions or Comments on this Manual P–4. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Documentation
Used in this Manual
Support
Product Support
Chapter 1
SLC
5/05 Processors and Ethernet Communication
Passthru
SLC 5/05
Hardware
Processor
Keyswitch
Feature
Performance Considerations
Features
Status LED Operation
Operation
RUN
Position
PROG
Position
REM
Position
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . .
P–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
P–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
P–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
P–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
P–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
P–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1–1
1–2
1–2
1–2
1–3
1–4
1–4
1–4
1–4
Setting Up the SLC and PC
Hardware
Configuring the Ethernet
Channel for Local
Chapter 2
Required Tools and Equipment
Install
the Power Supply
Install the Processor
Apply Power to the Processor
Connect
Load Y
the SLC 5/05 and the PC to the Ethernet Network
Ethernet Network Topology
Ethernet
Cables
Channel 1 8-Pin 10Base-T Connector
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
our Programming Software
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 3
Configuration Methods
Configuration
Define
Create Program and Configure Comms Drivers
Download
Switch
Using RSLogix500 Programming Software
SLC 5/05 Processor and I/O Modules
the Program
to the Ethernet Network and Go ONLINE
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . .
2–1
2–1
2–3
2–4
2–4
2–4
2–5
2–5
2–5
3–1
3–2
3–2
3–5
3–6
3–7
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 4

ii
Communicating on the
Ethernet Network
Configuration Via BOOTP
Using DOS/Windows BOOTP
Install the DOS/Windows BOOTP server
Edit
the DOS/Windows BOOTP Configuration File
Run
the Boot Server Utility
Running the DOS-Based Utility
Running
the Windows-Based Utility
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 4
Ethernet
MSG
Interpreting MSG Error Codes
Interpreting
Using Subnet Masks and Gateways
Connections
Instruction
Limitation
Control Block Layouts
MSG
Manually
Using
for Manipulating the Control Block Bits
Instruction Control Block
Ethernet Status Data
Configuring Channel 1 for Processors on Subnets
BOOTP to Configure Channel 1 for Processors on
Subnets
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3–7
3–8
3–9
3–9
3–1
3–1
3–12
4–1
4–2
4–2
4–3
4–4
4–6
4–8
4–10
4–1
4–12
1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1. .
Using RS232-to-Ethernet
Channel-to-Channel
Passthru
Specifications
(Optional) Return
Processor to Initial Factory
Conditions
Chapter 5
Passthru
Status
MSG
Passthru Examples
Feature
Address
File Bits
Error Code
Example
Example
Routing T
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
able
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1: DF1-to-Ethernet and Ethernet-to-DF1
2: DH485-to-Ethernet and Ethernet-to-DH485
. . . . . . . . .
5–1
5–1
5–2
5–2
5–3
5–3
5–1
1. . . . .
Appendix A
System Test General Specifications
Processor
General Specifications
A–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Appendix B
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 5

Preface
Read this preface to familiarize yourself with the rest of the manual.
This preface covers the following topics:
• who should use this manual
• how to use this manual
• related publications
• conventions used in this manual
• Allen-Bradley support
Who Should Use this Manual
Purpose of This Manual
Use this manual if you are responsible for designing, installing,
programming, or troubleshooting control systems that use
Allen-Bradley small logic controllers.
You should have a basic understanding of SLC 500t products. You
should understand programmable controllers and be able to interpret
the ladder logic instructions required to control your application. If
you do not, contact your local Allen-Bradley representative for
information on available training courses before using this product.
This manual is for users of the Ethernet SLC 5/05 processor. It:
• presents you with the basic information you need to get your
system up and running
• provides “memory jogger” information, such as specific bit and
switch settings for modules
• includes high-level procedures with cross-reference to other
manuals for more detail
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 6
PrefaceP–2
Related Documentation
The table below provides a listing of publications that contain
important information about Allen-Bradley Small Logic Controllers
and their installation and application. You may want to reference
them while you are installing the SLC 500 controller. (To obtain a
copy of one of these publications, contact your local Allen-Bradley
office or distributor.)
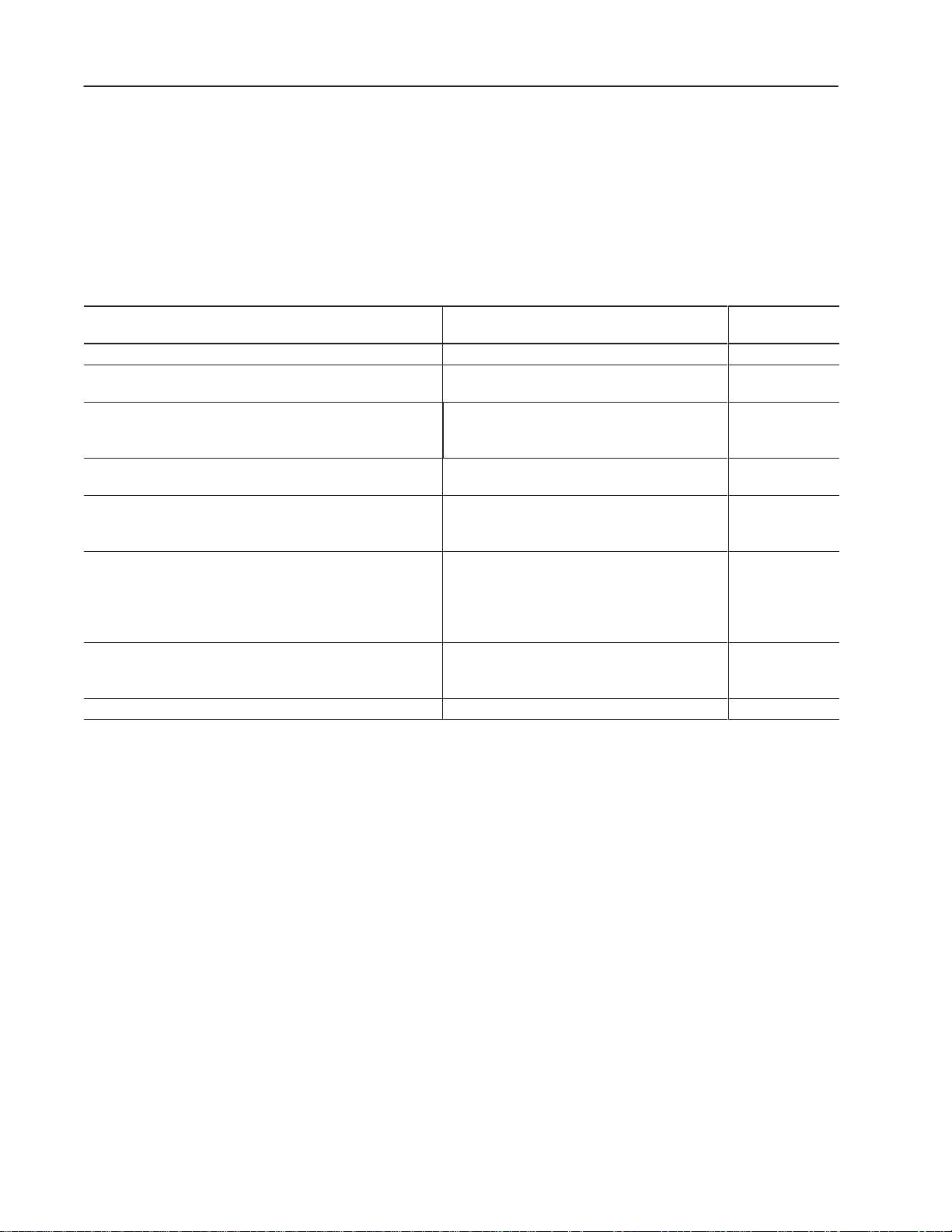
For Read This Document
An overview of the SLC 500 family of products SLC 500 System Overview 1747-2.30
A description on how to install and use your Modular SLC 500
programmable controller
A reference manual that contains status file data and instruction set
information for the SLC 500 processors and MicroLogix 1000
Controllers.
In-depth information on grounding and wiring Allen-Bradley
programmable controllers
A description of important differences between solid-state
programmable controller products and hard-wired
electromechanical devices
An article on wire sizes and types for grounding electrical
equipment
A complete listing of current Allen-Bradley documentation,
including ordering instructions. Also indicates whether the
documents are available on CD-ROM or in multiple languages.
A glossary of industrial automation terms and abbreviations Allen-Bradley Industrial Automation Glossary AG-7.1
Installation & Operation Manual for Modular
Hardware Style Programmable Controllers
SLC 500 and MicroLogix 1000 Instruction Set
Reference Manual
Allen-Bradley Programmable Controller Grounding
and Wiring Guidelines
Application Considerations for Solid-State Controls SGI-1.1
National Electrical Code
Allen-Bradley Publication Index SD499
Document
Number
1747-6.2
1747-6.15
1770-4.1
Published by the
National Fire
Protection
Association of
Boston, MA.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 7

Preface P–3
Conventions Used in this Manual
Allen-Bradley Support
The following conventions are used throughout this manual:
• Bulleted lists such as this one provide information, not procedural
steps.
• Numbered lists provide sequential steps
• Italic type is used for emphasis.
• Text in this
font
indicates words or phrases you should type.
• Text enclosed “in quotation marks” indicates selections you
should make.
Allen-Bradley offers support services worldwide, with over 75
Sales/Support Offices, 512 authorized Distributors and 260
authorized Systems Integrators located throughout the United States
alone, plus Allen-Bradley representatives in every major country in
the world.
Local Product Support
Contact your local Allen-Bradley representative for:
• sales and order support
• product technical training
• warranty support
• support service agreements
Technical Product Assistance
If you need to contact Allen-Bradley for technical assistance, please
record information about the problem situation, including any error
codes and state of LED indicators. If possible, please also have the
following information ready: hardware series, operating system
used, firmware level, and software release. Then call your local
Allen-Bradley representative.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 8

PrefaceP–4
Your Questions or Comments on this Manual
If you find a problem with this manual, please notify us using the
enclosed Publication Problem Report.
If you have any suggestions for how this manual could be made
more useful to you, please contact us at the address below:
Allen-Bradley Company, Inc.
Control and Information Group
Technical Communication, Dept. A602V, T122
P.O. Box 2086
Milwaukee, WI 53201-2086
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 9
Chapter 1
essors and
SLC 5/05 Ethernet Processor
Features
This chapter:
• describes SLC 5/05 processors and Ethernet communication
• describes SLC 5/05 performance considerations
• illustrates SLC 5/05 hardware features
• explains processor status LED operation
• explains keyswitch operation
SLC 5/05 Proc
Ethernet Communication
Ethernet is a local area network that provides communication
between various devices at 10 Mbps. The physical communication
media options for the SLC 5/05 are:
• built-in
– twisted pair (10Base-T)
• with media converters or hubs
– fiber optic
– broadband
– thick-wire coaxial cable (10Base-5)
– thin-wire coaxial cable (10Base-2)
See page 2–4 for more information on Ethernet physical media.
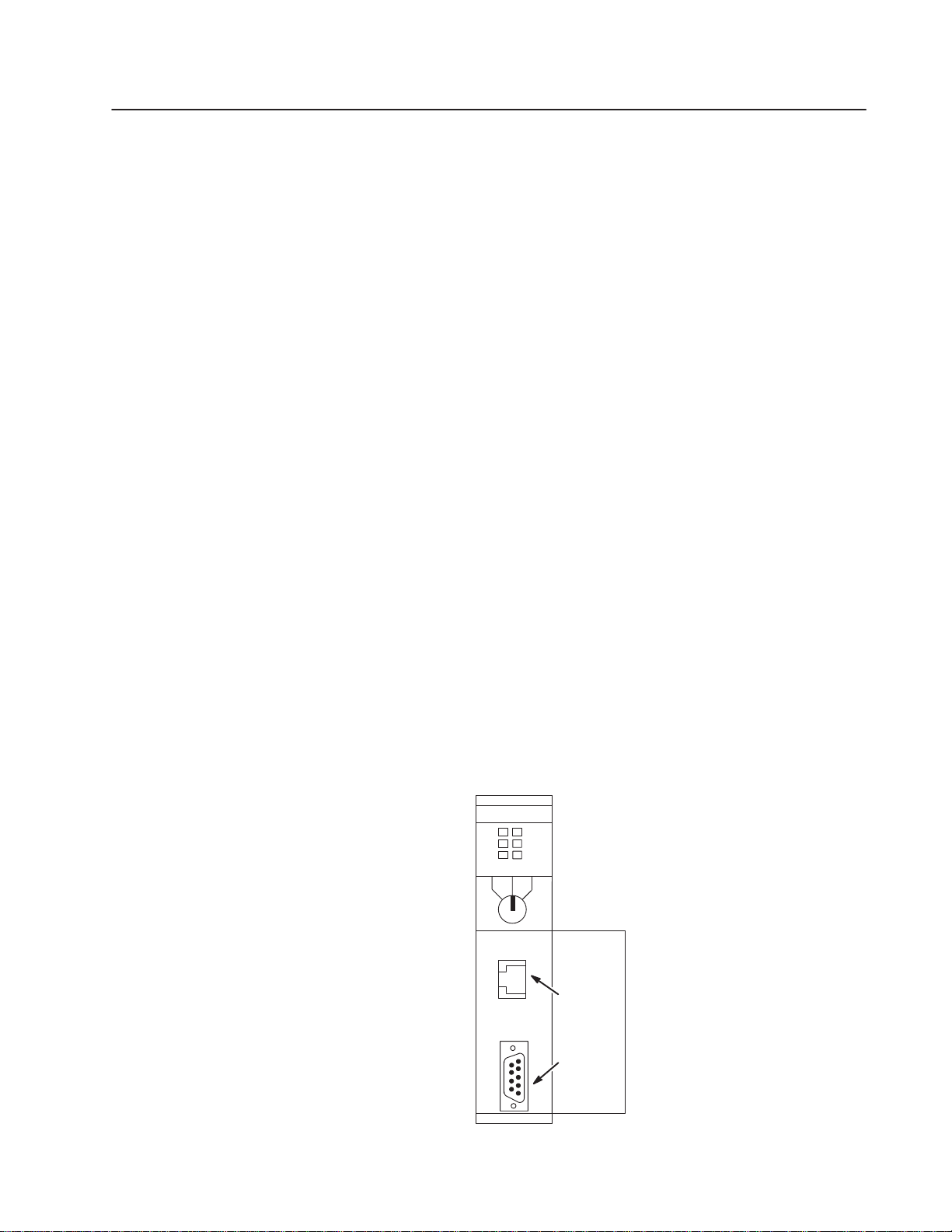
The SLC 5/05 supports Ethernet communication via the Ethernet
communication channel 1 shown in the drawing below.
SLC
5/05 CPU
FORCE
RUN
ENET
FLT
RS232BATT
RUN PROG
REM
Channel 1
Ethernet
(10Base-T)
Channel 0
RS232
(DH485,
DF1, or
ASCII)
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 10
1–2
SLC 5/05 Ethernet Processor Features
Passthru Feature
SLC 5/05 Performance Considerations
SLC 5/05 (1747-OS501, FRN 3) processors support
RS232-to-Ethernet channel-to-channel passthru. See Chapter 5 for
more information on using the new passthru feature.
Actual performance of an SLC 5/05 processor varies according to:
• size of Ethernet messages
• frequency of Ethernet messages
• network loading
• the implementation of and performance of your processor
application program
Optimal Performance: SLC 5/05 to SLC 5/05 Processor
(2-node Ethernet network)
Operation
Single
Typed reads
MSG per
Words
1 33 30.8 33
20 32 31.1 640
100 32 31.2 3200
second
ms per
MSG
Words per
second
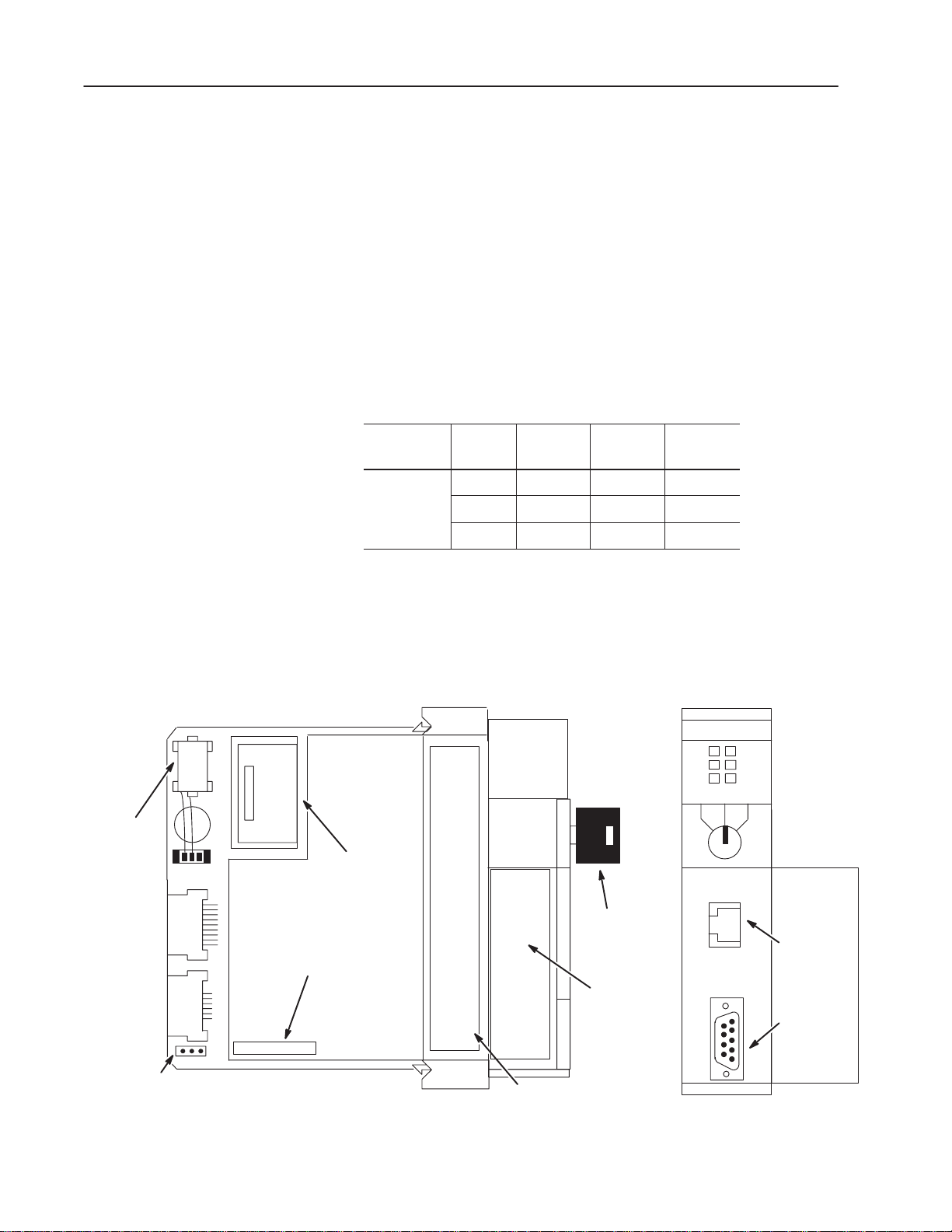
Hardware Features
Battery
(Battery Provides
Back-up Power for
the CMOS RAM)
xx:xx:xx
Hardware
Address
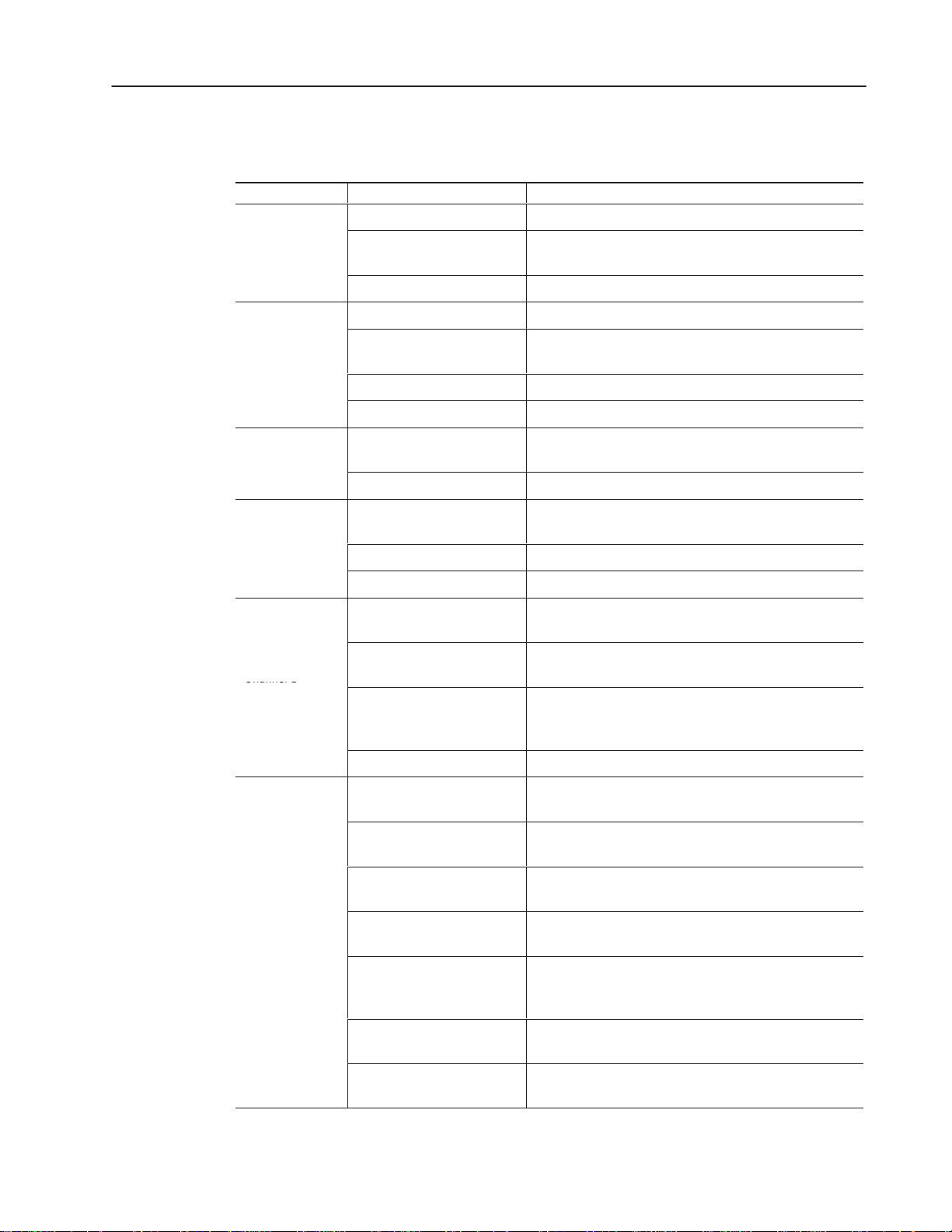
The figure below shows some of the hardware components of the
SLC 5/05 processors (1747-L551, 1747-L552, and 1747-L553).
SLC
5/05 CPU
Memory Module
_______ . _______ . _______ . _______
IP
ADDRESS
Keyswitch
Write-on
Area for
Address
IP
RUN
FLT
BATT
RUN PROG
FORCE
ENET
RS232
REM
Channel 1
Ethernet
(10Base-T)
Channel 0
RS232
(DH485,
DF1, or
ASCII)
Operating System
Memory Module
Download Protection
Jumper
Publication
1747-10.4
Location of Serial and
Left Side View Front View
Catalog Numbers
Page 11
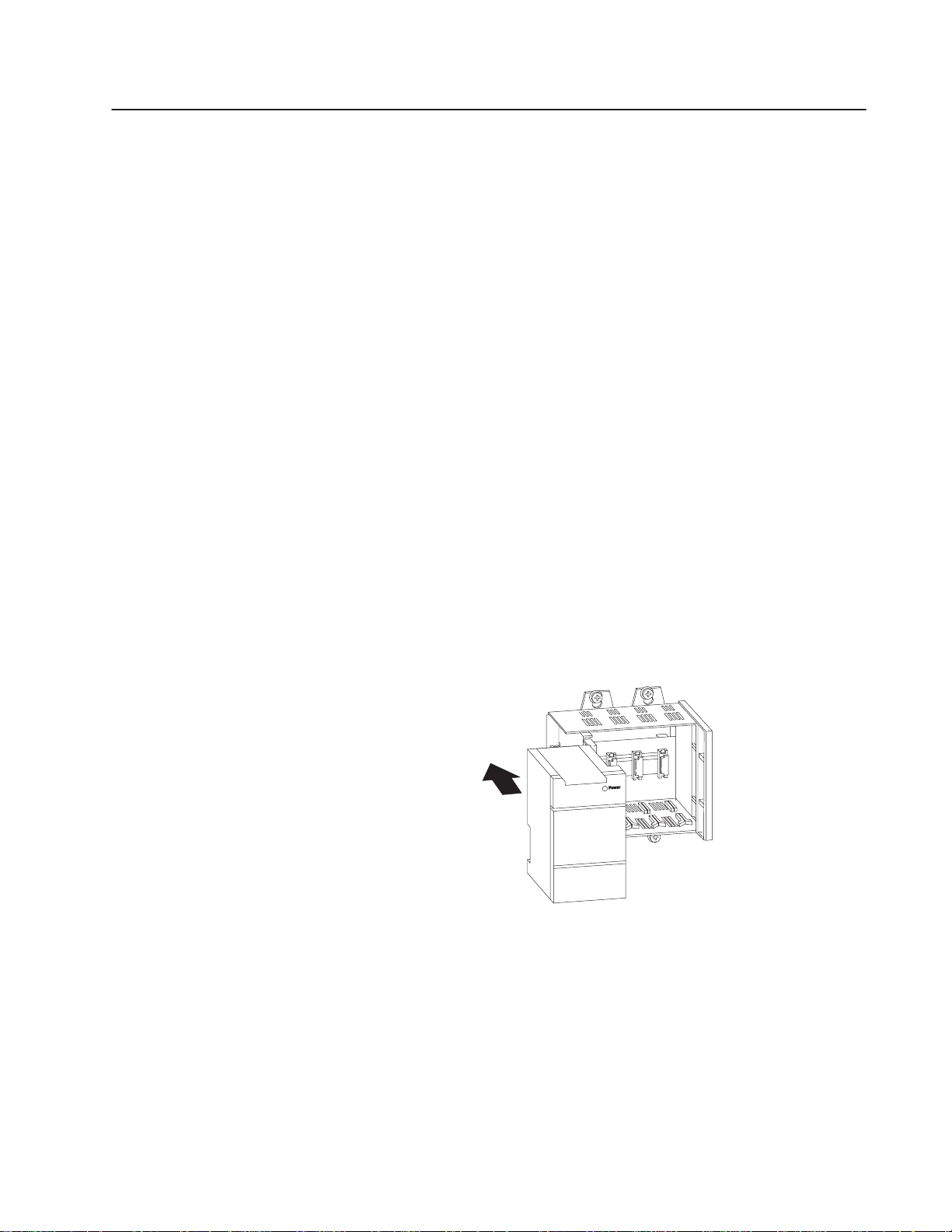
SLC 5/05 Ethernet Processor Features
(Color: red)
(Color: red)
FORCE
FORCE
Channel 1
(Color: green)
(Color: green)
1–3
Processor Status LED Operation
Processor LED When It Is Indicates that
RUN
(Color: green)
FLT
BATT
(Color: amber)
The table below provides a general explanation of the processor
status LEDs.
On (steadily) The processor is in Run mode.
Flashing (during operation)
Off The processor is in a mode other than Run.
Flashing (at power up) The processor has not been configured.
Flashing (during operation)
On (steadily) A fatal error is present (no communications).
Off There are no errors.
On (steadily)
Off The battery is functional, or the battery jumper is present.
Flashing
On (steadily)
The processor is transferring a program from RAM to the
memory module.
The processor detects a major error either in the processor,
expansion chassis, or memory.
The battery voltage has fallen below a threshold level, or the
battery or the battery jumper is missing or not connected.
One or more input or output addresses have been forced to an
On or Off state, but the forces have not been enabled.
The forces have been enabled.
ENET
Channel 1
(Color:
green or red)
RS232
Channel 0
Off No forces are present or enabled.
Solid Green
Flashing Green
Flashing Red
Off No Ethernet connection or port not configured.
On (steadily)
DF1 Protocol
Off
DF1 Protocol
On (steadily)
ASCII Mode
Off
ASCII Mode
On (steadily)
DH485 Protocol
Flashing
DH485 Protocol
The Ethernet port is functioning properly and is connected to
an active Ethernet network.
The Ethernet port is functioning properly, is connected to an
active Ethernet network, and is transmitting packets.
A hardware or software fault has occurred and is being
reported via a code. Contact Allen-Bradley Global Technical
Services for assistance.
The SLC 5/05 processor is transmitting.
The SLC 5/05 processor is not transmitting.
The SLC 5/05 processor is transmitting.
The SLC 5/05 processor is not transmitting.
The Channel 0 Communications Active Bit (S:33/4) is set in
the System Status file, and the processor is actively
communicating on the network.
The processor is trying to establish communications, but there
are no other active nodes on the network.
Off
DH485 Protocol
A fatal error is present.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 12

1–4
SLC 5/05 Ethernet Processor Features
Keyswitch Operation
The processors include a 3-position keyswitch on the front panel that
lets you choose from three modes of operation: Run, Program, and
Remote. You can remove the key in any of the three positions.
ATTENTION: Depending on the size of your user
program, the processor can take up to 2.5 seconds to
!
change modes when you change the position of the
keyswitch from RUN to PROG or to REM. Do not use
the keyswitch in place of a hardwired master control
relay or an emergency-stop switch.
RUN Position
This position places the processor in the Run mode. The processor
scans/executes the ladder program, monitors input devices, energizes
output devices, and acts on enabled I/O forces. You can only change
the processor mode by changing the key position. You cannot
perform online program editing.
To change the mode to Run, turn the key from PROG or REM to
RUN. When the key is in the RUN position, you cannot use a
programmer/operator interface device to change modes.
PROG Position
This position places the processor in the Program mode. The
processor does not scan/execute the ladder program, and the
controller outputs are de-energized. You can perform online
program editing. You can only change the mode by changing the
key position.
To change the processor mode to Program, turn the key from REM
or RUN to PROG. When the key is in the PROG position, you
cannot use a programmer/operator interface device to change
modes.
REM Position
This position places the processor in the Remote mode: either the
REMote Run, REMote Program, or REMote Test mode. You can
change the processor mode by changing the keyswitch position or by
changing the mode from a programmer/operator interface device.
You can perform online program editing in this position.
To change the mode to REM, turn the key from RUN or PROG to
REM. When the key is in the REM position, you can use a
programmer/operator interface device to change modes.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 13
Chapter 2
nd
Setting Up the SLC and PC
Hardware
This chapter tells you:
• what tools and equipment you need
• how to install and wire your power supply
• how to install and apply power to your processor
• how to configure the SLC 5/05 processor to communicate on the
Ethernet network
Required Tools a
Equipment
Install the Power Supply
Have the following tools and equipment ready:
• a medium blade screwdriver
• programming equipment
• a 1747-CP3 programmer cable, a 10Base-T Ethernet PC card and
a 10Base-T Ethernet hub
Follow the steps below:
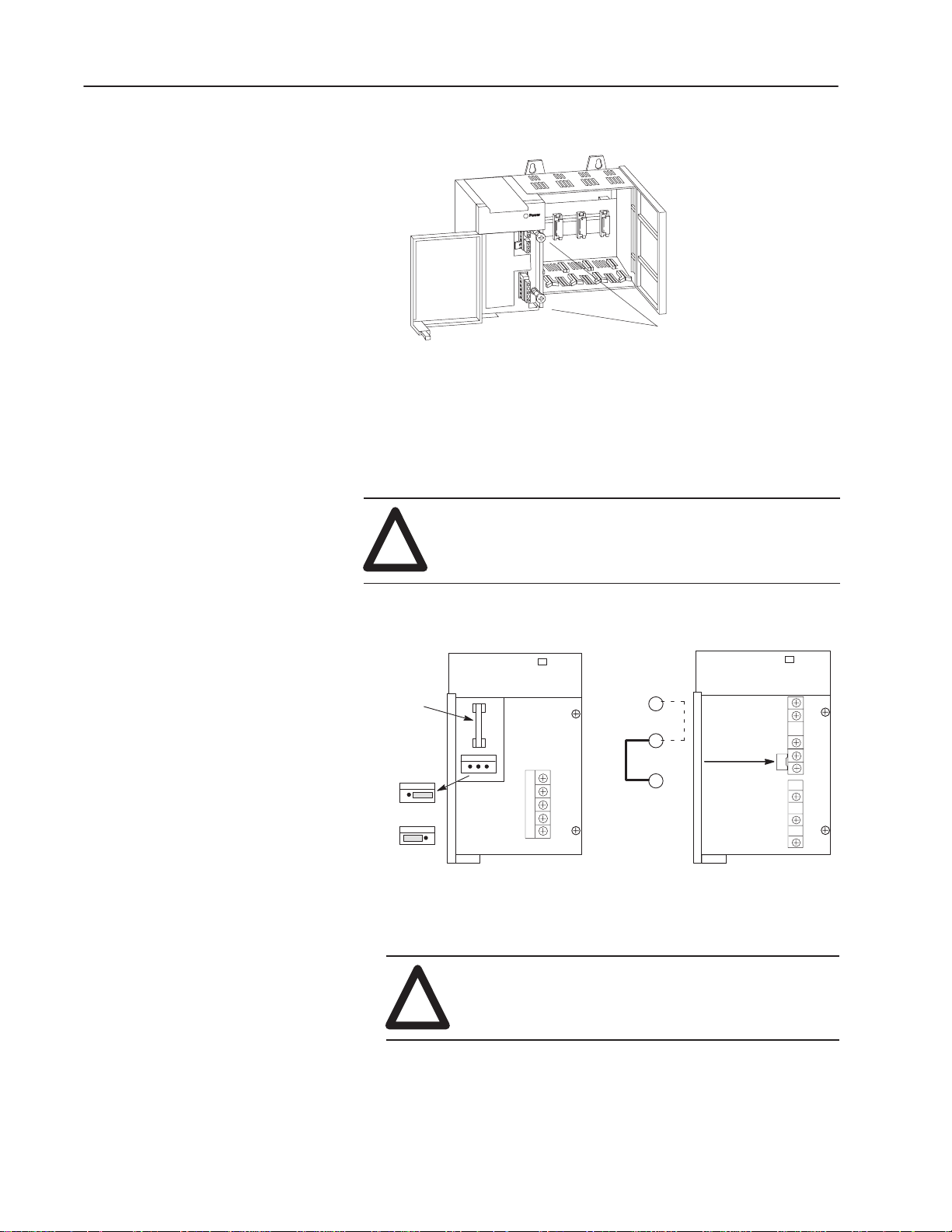
1. Align the circuit board of the power supply with the card guides
on the left side of the chassis, and slide the power supply in until
it is flush with the chassis.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 14
2–2
Setting Up the SLC and PC Hardware
2. Fasten the power supply to the chassis.
3. Make jumper selection for 120/240V ac on 1746-P1, 1746-P2,
and 1746-P4 Power Supplies.
Place the input voltage jumper to match the input voltage. This
does not apply to the 1746-P3 or 1746-P5, which do not have
jumpers.
!
Use these screws to fasten the
power supply to the chassis.
ATTENTION: Set the input jumper before applying
power. Hazardous voltage is present on exposed pins
when power is applied; contact with the pin may cause
injury to personnel.
Catalog Number
1746-P1 & P2
POWER
Fuse
Jumper Selection
100/120 Volts
200/240 V
olts
4. Wire power to power supply.
ATTENTION: Turn off incoming power before
connecting wires; failure to do so could cause injury
!
to personnel and/or equipment.
Jumper Selection
85–132 V
AC
170–265 V
AC
Catalog Number
1746-P4
POWER
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 15
Setting Up the SLC and PC Hardware
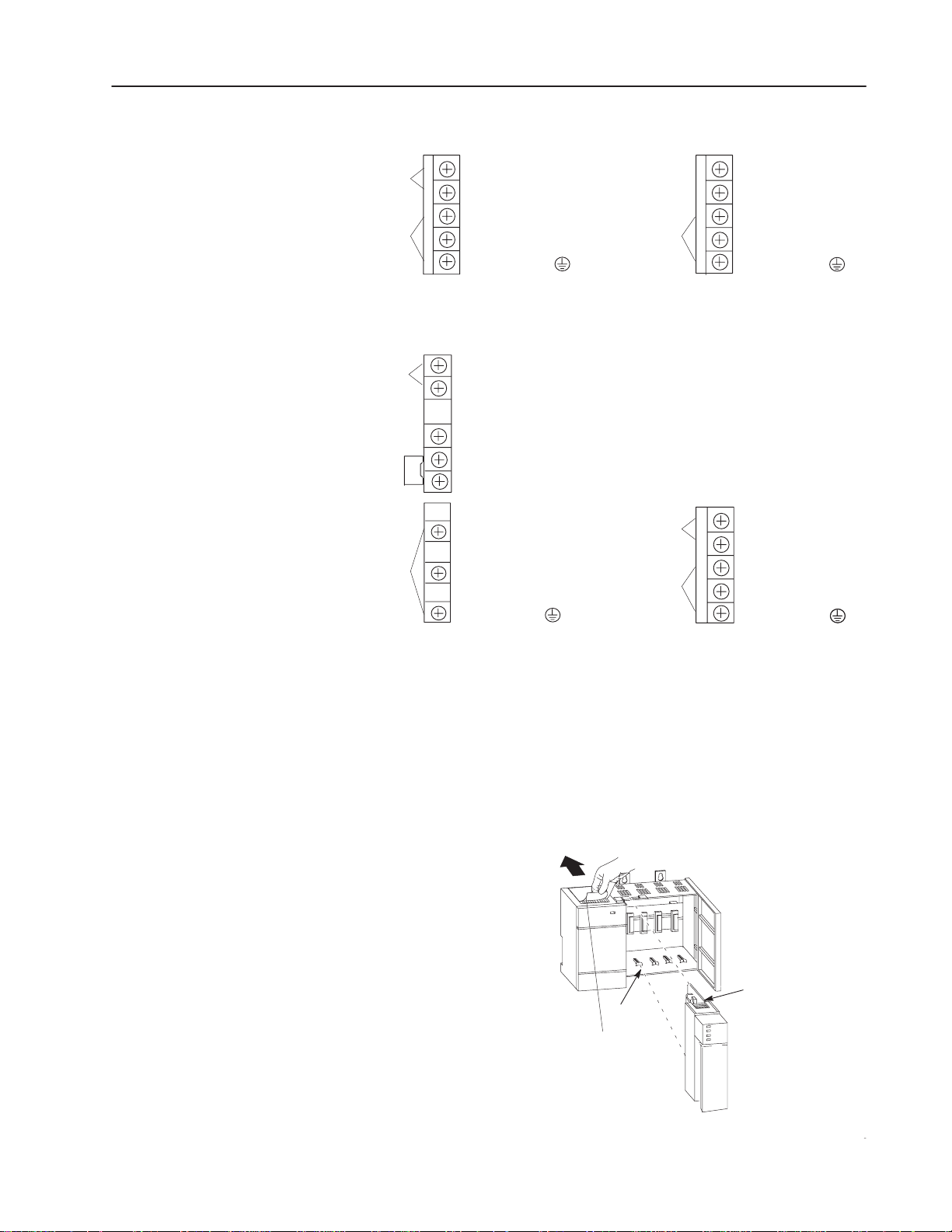
5. Connect incoming power, as shown in the following diagrams.
2–3
User
Power
Incoming
Power
User
Power
Incoming
Power
PWR OUT +24V dc
PWR OUT COM
120/240V
ac
V ac NEUT
CHASSIS GROUND
1746-P1 and -P2
PWR OUT +24V dc
PWR OUT COMMON
85–132V ac
JUMPER
170–265V ac
L185–132/170–265
L2
NEUTRAL
CHASSIS GROUND
Incoming
Power
User
Power
Incoming
Power
NOT USED
NOT USED
+ 24V dc
dc NEUT
CHASSIS GROUND
1746-P3
PWR OUT +24V dc
PWR OUT COM
+125V dc
dc NEUT
CHASSIS GROUNDCHASSIS GROUND
Install the Processor
1746-P4 1746-P5
Make sure system power is off; then insert the processor into the
1746 chassis.
Important: SLC 500 Modular Processors must be inserted into the
left slot (slot 0), as shown below. Remove the
protective label after installing the processor.
Module Release
Card Guide
Protective Label
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 16
2–4
Setting Up the SLC and PC Hardware
Apply Power to the Processor
Connect the SLC 5/05 and the PC to the Ethernet Network
Follow the steps below:
1. Energize the chassis power supply.
2. Check the chassis power supply and processor LEDs. The power
LED on the power supply should be on and the fault LED on the
processor should be flashing.
Power supply and LED Indicators
POWER
RUN
FLT
BATT
FORCE
ENET
RS232
Indicates the LED is OFF.
Indicates the LED is ON.
Indicates the LED is FLASHING.
Status of LED does not matter.
The SLC 5/05 Ethernet connector conforms to ISO/IEC 8802-3 STD
802.3 and utilizes 10Base-T media. Connections are made directly
from the SLC 5/05 to an Ethernet hub. Typical network topology is
pictured below.
Ethernet Network Topology
RJ45
Ethernet
Hub
to PC Ethernet Card
Important: The SLC 5/05 processor contains a 10Base-T, RJ45
Ethernet connector which connects to standard Ethernet
hubs via 8-wire phone jack cable. To access other
Ethernet mediums, use Ethernet hubs that can be
connected together via fiber, thin-wire, or thick-wire
coaxial cables, or any other physical media
commercially available with Ethernet hubs. In addition,
media converters are commercially available to convert
10Base-T to other Ethernet media.
connectors
on both ends of cable
(10Base-T)
to SLC 5/05
Channel 1
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 17

Setting Up the SLC and PC Hardware
2–5
Ethernet Channel 1 8-Pin 10Base-T Connector
The Ethernet connector is an RJ45, 10Base-T connector. The pin-out
for the connector is shown below:
Pin Pin Name
1 TD+
2 TD–
3 RD+
4 not used by 10BASE-T
5 not used by 10BASE-T
6 RD–
7 not used by 10BASE-T
8 not used by 10BASE-T
When to use straight-through and cross-over pin-out:
• SLC 5/05 Ethernet port to 10Base-T Ethernet hub cables utilize a
straight-through pin-out (1-1, 2-2, 3-3, 6-6).
• Direct point-to-point 10Base-T cables, with cross-over pin-out
(1-3, 2-6, 3-1, 6-2), connect the SLC 5/05 Ethernet port directly
to another SLC 5/05 Ethernet port (or a computer 10Base-T port).
Load Your Programming Software
Cables
Shielded and non-shielded twisted-pair 10Base-T cables with RJ45
connectors are supported. The maximum cable length between an
SLC 5/05 Ethernet port and a 10Base-T port on an Ethernet hub
(without repeaters or fiber) is 100 meters (328 feet). However, in an
industrial application, the cable length should be kept to a minimum.
Install RSLogix500 programming software and RSLinx
communication software. Refer to your software package’s
documentation for installation instructions. Be sure to use the
version of the software listed below. Earlier versions of the software
do not support the SLC 5/05 processor.
• RSLogix500 – Rev. 2.10.12 or later (OS500)
– Rev. 2.51.0 or later (OS501)
• RSLinx – Rev. 1.70.62 or later
Contact Rockwell Software for information on upgrading your
software.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 18

2–6
Setting Up the SLC and PC Hardware
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 19
Chapter 3
Configuring the Ethernet
Channel for Local
Communication
This chapter:
• describes the configuration methods and configuration parameters
• explains how to configure the Ethernet channel using RSLogix
Programming Software
• explains how to configure the Ethernet channel via BOOTP
Configuration Methods
There are two ways to configure the SLC 5/05 Ethernet channel 1.
The configuration can be done via a BOOTP request at processor
powerup, or by manually setting the configuration parameters using
RSLogix 500 Programming Software. The configuration parameters
are shown below and the configuration procedures follow.
Parameter Description Default Status
Diagnostic File
Number
MSG
Connection
Timeout
MSG Reply
Timeout
Inactivity
Timeout
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Broadcast
Address
Gateway
Address
BOOTP Enable
Hardware
Address
The file number, which states the channel status diagnostic counters for this channel. A
Diagnostic File Number value of zero means that no diagnostics file was configured for this
channel. The Diagnostic File Number must be an integer within the limits of 7, 9–255.
The amount of time (in ms) allowed for a MSG instruction to establish a connection with the
destination node. The MSG Connection Timeout has 250 ms resolution and a range from 250 to
65,500.
The amount of time (in ms) that the SLC 5/05 waits for a reply to a command it initiated via a
MSG instruction. The MSG Reply Timeout has 250 ms resolution and a range from 250 to
65,500.
The amount of time (in minutes) that a MSG connection may remain inactive before it is
terminated. The Inactivity Timeout has a 1 minute resolution and a range from 1 to 65,500
minutes.
The SLC 5/05 internet address (in network byte order). The internet address must be specified
to connect to the TCP/IP network.
The SLC 5/05 subnet mask (in network byte order). The Subnet Mask is used to interpret IP
addresses when the internet is divided into subnets. A Subnet Mask of all zeros indicates that
no subnet mask has been configured.
NOT
SUPPORTED AT THIS TIME. The SLC 5/05 broadcast address (in network byte order). The
Broadcast Address is used in sending multicast messages. A Broadcast Address of all zeros
indicates that no broadcast address was configured. In this case, the network code chooses a
valid broadcast address when needed for that current subnet.
The address of a gateway (in network byte order) that provides connection to another IP
network. A Gateway Address of all zeros indicates that no gateway was configured.
The BOOTP enable switch. When BOOTP is enabled, the SLC 5/05 attempts to learn its
network related parameters at powerup via a BOOTP request. There must be a BOOTP server
on the network capable of responding to this BOOTP request. When BOOTP is disabled, the
SLC 5/05 uses the locally configured network related parameters (IP Address, Subnet Mask,
Broadcast Address, etc.).
The SLC 5/05 Ethernet hardware address.
0 read/write
15,000 ms read/write
3,000 ms read/write
30 minutes read/write
0 (undefined) read/write
0 read/write
0
0 read/write
1 (enabled) read/write
Ethernet
hardware
address
read only
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 20

3–2
Configuring the Ethernet Channel for Local Communication
Configuration Using RSLogix500 Programming Software
The following step-by-step procedure shows how to set up the
SLC 5/05 and establish local communication on an Ethernet
network. You need to assign a unique IP address for your processor.
This procedure also shows how to create a ladder program for an
SLC 5/05 processor and download it via the RS232 COM port on
your computer to channel 0 (RS232) on the SLC 5/05. You can use
the 1747-CP3 Programmer Cable to make the physical connection.
Important: For this configuration method, you must first download
a program to the SLC 5/05 (via RS232) before you can
establish Ethernet communications.
Finally, this procedure assumes that you have previous experience
with SLC 500 processors and RSLogix500 programming software.
If you do not, the following publications will help with the SLC 500
hardware and the instruction set. For the software (RSLogix500 and
RSLinx), use the online HELP screens to guide you through
developing a program and configuring channel 0 communication
parameters.
• SLC 500 and MicroLogix 1000 Instruction Set Reference Manual,
publication 1747-6.15.
• SLC 500 Modular Hardware Style Installation and Operation
Manual, publication 1747-6.2.
Define SLC 5/05 Processor and I/O Modules
1. Start RSLinx software.
2. When the RSLinx window appears, click on the
“Communications” pull-down menu and select “Configure
Drivers”.
3. In this step, you will configure RS232 driver.
In the “Configure Drivers” window, select “RS232 DF1 Devices”
and click on the “Add New” box. The “Configure Allen-Bradley
DF1 Communications Device” window appears.
Select the communications port you wish to use. This is the PC
serial port COM1 through COM9.
Under Device Type, select “SLC–CH0” and “CRC error
checking”.
If you have an RS232 cable connected between the selected COM
port on your PC and channel 0 on your SLC 5/05, you can click
on “Auto-configure” to define your interface parameters.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 21

Configuring the Ethernet Channel for Local Communication
3–3
If you do not use “Auto-Configure”, you must enter the channel 0
default parameters as follows:
• Device Type: SLC-CH0
• Baud Rate: 19200
• Parity: None
• Error Checking: CRC
• Stop Bits: 1
• Protocol: Full Duplex
When finished, click “OK”. “AB_DF1-1 DH485 Sta:0 COMn:
RUNNING” is added to the list of configured drivers (where n =
the number of the COM port you selected).
Minimize the RSLinx window.
4. Start RSLogix500 programming software and create a new file.
5. In the “Select Processor Type” window, choose the SLC 5/05
processor type:
• 1747-L551, 16K memory
• 1747-L552, 32K memory
• 1747-L553, 64K memory
Assign a name to the processor and click “OK”. A ladder
programming screen appears showing only an END rung.
6. Using the list on the left side of the screen, double-click on
“Controller Properties” under the “Controller” category (folder).
7. In the “Controller Properties” window, click on the “Controller
Communications” tab. In this window, select “AB_DF–1” as the
driver. Click “OK”.
8. Using the list on the left side of the screen, double-click on “I/O
Configuration” under the “Controller” category.
9. In the “I/O Configuration” window, you can identify your SLC
hardware (chassis and I/O modules) either manually or
automatically.
Note: For automatic configuration, you need to have
your SLC hardware installed and the
programming cable (1747-CP3 or equivalent)
connected between the SLC 5/05 channel 0 and
the PC COM port.
Manually –
In the “I/O Configuration” window, select the chassis and I/O
modules that you have. Close this screen (click the close button
[x] in the upper right corner of the window).
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 22

3–4
Configuring the Ethernet Channel for Local Communication
Automatically –
In the “I/O Configuration” window, click on “Read I/O Config”.
The “Read I/O Configuration from Online Processor” pop-up
appears. Select “AB_DF1–1” as the driver and click on the
“Read I/O Config” button. Your chassis and I/O configuration
updates automatically. Close this window.
10.Using the list on the left side of the screen, double-click on
“Channel Configuration” under the “Controller” category.
11. In the Channel 1 section of the General tab, enter an unused file
number, such as 9, in the “Diagnostic File” field. This allows the
programming software to display Channel 1 status, which are the
Ethernet communications diagnostic counters.
12.In the “Channel Configuration” window, click on the “Chan. 1 –
System” tab. Deselect the “BOOTP Enable” option by clicking
on the checked box. Enter your unique IP address in the space
provided.
A subnet mask is used to interpret IP addresses when the internet
is divided into subnets. If your network is not divided into
subnets, then leave the “Subnet Mask” at the default. If you
change the default and need to reset it, type 0.0.0.0.
Note: The “Hardware Address” is filled in by the
processor when you download this program to
the SLC 5/05 processor.
After you have entered your IP address and disabled the BOOTP
option, click “Apply” and then “OK”.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 23

Configuring the Ethernet Channel for Local Communication
Create Program and Configure Comms Drivers
1. You are now ready to create your ladder logic. An example is
shown below. In this example, there are two SLC 5/05
processors. The MSG instruction from the first processor reads
the seconds value of the Real Time Clock (S:42) from the second
processor and constantly places the value in the first processor’s
file at N7:60. Add the MSG rung to the ladder.
Note: The control block length for Ethernet MSGs is
51 words (when not using Logical ASCII
addressing).
3–5
2. In the “Message Setup” window, enter the MSG parameters and
click “OK”. Then click on the “verify file” button at the top of
the screen. Then save your program file.
3. With RSLogix500 still up and running, click on the RSLinx
program previously minimized at the bottom of the screen.
4. When the RSLinx window appears, click on the
“Communications” pull-down menu and select “Configure
Drivers”.
5. In this step, you will configure the Ethernet driver.
Note: If you have not configured the RS232 DF1
Device, refer to the procedure “Define SLC 5/05
Processor and I/O Modules” on page 3–2
before configuring the Ethernet driver.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 24

3–6
Configuring the Ethernet Channel for Local Communication
Ethernet –
In the “Configure Drivers” window, select “Ethernet to
PLC-5 or 5820-EI” and click on the “Add New” box. The
“Configure Ethernet-to-AB Communications” window appears.
Enter the IP address for your SLC 5/05 processor beginning with
node 1 under “Current Mappings”. Use the “IP Address or
hostname” box to enter the address and click “Accept”. After
entering the IP address, click “OK”. “AB_ETH-1 A-B Ethernet
RUNNING” is added to the list of Configured Drivers.
Close the “Configure Drivers” window and minimize RSLinx as
before.
Download the Program
1. In RSLogix, click on the “Comms” pull-down menu and select
“System Comms”.
2. Be sure that you have connected your PC COM1 port to
SLC 5/05 channel 0 (RS232 Programmer Cable 1747-CP3). In
the RSLogix “System Options” window, verify that “AB_DF1-1”
driver is selected and click on “Download”.
Enter a version number when asked, click “OK”, and answer
“yes” to any further pop-up windows that appear. Your program
will be downloaded to the processor. When asked if you wish to
go online, click “yes”.
3. Using the list on the left side of the screen, double-click on
“Channel Configuration” under the “Controller” category. Select
the “Chan.1 – System” tab to view the IP address you entered and
the hardware Ethernet address assigned by the SLC 5/05
processor. Verify that this information is correct. Click on
“Cancel”.
4. Go “OFFLINE”.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 25

Configuring the Ethernet Channel for Local Communication
3–7
Switch to the Ethernet Network and Go ONLINE
1. Connect your computer and your SLC 5/05 processor to any
standard Ethernet hub. You need an Ethernet communication
card to connect your PC to the Ethernet hub.
2. In RSLogix, click on the “Comms” pull-down menu and select
“System Comms”. In the “System Options” window, change the
“Driver” to “AB_ETH-1” and “Apply”. Click on “Who Active”.
3. The “Who Active” window appears, showing your Ethernet node.
Your computer will be “STA 63 AB_ETH-1” with its assigned
name. Your SLC 5/05 will be “STA 1” with its assigned name.
Double-click on the “STA 1” icon. Then go on-line with your
SLC 5/05 via Ethernet.
4. If you have a second SLC 5/05 processor, set it up following the
same procedure as for the first SLC 5/05, but using its own
unique IP address. Also assign this address to the next available
STA address in RSLinx.
Configuration Via BOOTP
5. If you have two SLC 5/05 processors, and you have entered the
one-rung MSG into both of them, you may put them both in the
“RUN” mode and monitor N7:60 in either processor. The value
of N7:60 should increment with each tick of the Real Time Clock
in the other SLC 5/05 processor.
If you only have one SLC 5/05, you cannot send MSGs, but you
are on-line with your processor via 10 Mbps Ethernet.
BOOTP is a standard protocol that TCP/IP nodes use to obtain
start-up information. By default, the SLC 5/05 broadcasts BOOTP
requests at powerup. The BOOTP valid parameter remains clear
until a BOOTP reply has been received. BOOTP lets you
dynamically assign IP Addresses to processors on the Ethernet link.
To use BOOTP, a BOOTP server must exist on the local Ethernet
subnet. The server is a computer that has BOOTP server software
installed and reads a text file containing network information for
individual nodes on the network.
The BOOTP request can be disabled by clearing the BOOTP Enable
parameter in the channel Configuration File. When BOOTP Enable
is cleared (disabled), the SLC 5/05 uses the existing channel
configuration data.
Important: If BOOTP is disabled, or no BOOTP server exists on
the network, you must use SLC 500 programming
software to enter/change the IP address for
each processor. See page 3–2 for that configuration
procedure.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 26

3–8
Configuring the Ethernet Channel for Local Communication
The host system’s BOOTP configuration file must be updated to
service requests from SLC 5/05 processors. The following
parameters must be configurable:
Parameter Description
IP Address A unique IP Address for the SLC 5/05 processor.
Subnet Mask
Gateway
Specifies the net and local subnet mask as per the standard on
subnetting RFC 950, Internet Standard Subnetting Procedure.
Specifies the IP address of a gateway on the same subnet as the
SLC 5/05 that provides connections to another IP network.
Note: If you do not have BOOTP server capabilities on your
network, and you want to dynamically configure
Channel 1, you can download the utility from
http://supportbbs.ra.rockwell.com or via modem at
440-646-5441.
When BOOTP is enabled, the following events occur at power-up:
• The processor broadcasts a BOOTP request message containing
its hardware address over the local network or subnet.
• The BOOTP server compares the hardware address with the
addresses in its look-up table in the BOOTPTAB file.
• The BOOTP server sends a message back to the processor with
the IP address and other network information that corresponds
to the hardware address it received.
With all hardware and IP addresses in one location, you can easily
change IP addresses in the BOOTP configuration file if your
network needs change.
Using DOS/Windows BOOTP
Both the DOS-based and Windows-based BOOTP server utilities
provide BOOTP services for SLC 5/05 processors. Regardless of the
platform you are using, you must:
• install the boot-server utility
• edit the boot-server configuration file
• run the boot-server utility
Important: Do not use the BOOTP utility if you already have
INTERCHANGE software installed. Instead, use the
boot-server capabilities that came with your
INTERCHANGE software.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 27

Configuring the Ethernet Channel for Local Communication
3–9
Install the DOS/Windows BOOTP server
To install the DOS BOOTP server:
1. Change the directory to the drive containing the BOOTP utility.
2. Type
3. The software is installed in
install, and press [Enter].
the path statement of your
C:\ABIC\BIN. Put this directory in
AUTOEXEC.BAT file.
Edit the DOS/Windows BOOTP Configuration File
The boot-server configuration file,
BOOTPTAB, is located in the
C:\ABIC\BIN directory. This file contains the information needed to
boot SLC 5/05 processors.
You must edit the
BOOTPTAB file, which is an ASCII text file, to
include the name, IP address, and hardware address for each
SLC 5/05 processor you want the server to boot. To edit this file:
1. Open the
BOOTPTAB file using a text editor.
The file contains lines that look like this:
#Default
defaults5E: ht=1:vm=rfc1048
string for each type of Ethernet client
These are the default parameters for SLC 5/05 processors and
must always precede the client lines in the
BOOTPTAB file.
The file also contains a line that looks like this:
plc5name:
tc=defaults5E:ip=aa.bb.cc.dd:ha=0000BC1Cxxyy
Important: Use this line as the configuration template for
SLC 5/05 processors.
2. Make one copy of the SLC 5/05 processor template for every
SLC 5/05 processor in your system.
3. Edit each copy of the template as follows:
A. Replace plc5name with the name of the SLC 5/05 processor.
Use only letters and numbers; do not use underscores.
B. Replace
aa.bb.cc.dd with the IP address to be assigned to
the processor.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 28

3–10
Configuring the Ethernet Channel for Local Communication
C. Replace xxyy with the last four digits of the hardware
address. Use only valid hexadecimal digits (0-9, A-F); do
not use the hyphens that separate the numbers. (You will
find the hardware address on a label affixed to the printed
circuit board of the SLC 5/05 processor. Note: See page
1–2 for an illustration showing the location of the hardware
address.)
4. Save, close, and make a backup copy of this file.
Example
In this example, there are three SLC 5/05 processors and an HP 9000
programming terminal. The names and hardware addresses are
device specific:
HP 9000
(HP-UNIX)
computer)
BOOTP
server
Device Name IP
SLC 5/05
SLC 5/05
SLC 5/05
802.3/Ethernet (TCP/IP)
SLC-5/05
processor
sigma1
sigma1 12.34.56.1 00–00–BC–1D–12–34
sigma2 12.34.56.2 00–00–BC–1D–56–78
sigma3 12.34.56.3 00–00–BC–1D–90–12
Address Hardware Address
SLC-5/05
processor
sigma2
SLC-5/05
processor
sigma3
Based on this configuration, the BOOTPTAB file looks like:
# Legend: gw –– gateways
#ha
#ht
#ip
#sm
#vm
#tc
#Default string for each type of Ethernet client
defaults5E: ht=1:vm=rfc1048
#Entries for SLC 5/05 processors:
sigma1: tc=defaults5E:ip=12.34.56.1:ha=0000BC1D1234
sigma2: tc=defaults5E:ip=12.34.56.2:ha=0000BC1D5678
sigma3: tc=defaults5E:ip=12.34.56.3:ha=0000BC1D9012
––
hardware address
––
hardware type
––
host IP address
––
subnet mask
––
BOOTP vendor extensions format
––
template host
➀
➁
Publication
1747-10.4
➀
1 = 10MB Ethernet
➁
Use rfc1048
Page 29

Run the Boot Server Utility
You can run either the DOS-based utility or the Windows-based
BOOTP utility, but not both.
3–1
1Configuring the Ethernet Channel for Local Communication
If you have BOOTP enabled and the message
BOOTP response
not received appears, check the cabling connections and the
BOOTP server system.
If you’re using
this platform
DOS-based
Windows DTLBOOTW.EXE Windows Program
then invoke this
executable from the See page
DTLBOOTD.EXE DOS command line
(specify optional
parameters if necessary)
Manager
3–11
3–12
Both utilities are located in the C:\ABIC\BIN directory and use the
information contained in the
Be sure to place the
BOOTPTAB file in the directory from which you
BOOTPTAB file.
are running the BOOTP utility. If this file is not found in that
directory, the utility will try to find the file in the directory specified
by the environment variable ABIC_CONFIG.
Running the DOS-Based Utility
To run the boot-server utility,
DTLBOOTD.EXE, follow these steps:
1. At the DOS prompt, type:
DTLBOOTD [–D
[
–F
<numfiles>
Parameter Description
–D
–T <timeout> exit after <timeout> seconds of inactivity.
–B <numboots> exit after answering <numboots> number of boot requests.
–F <numfiles> exit after answering <numfiles> number of file requests.
configfile name of the boot server configuration file to use. The default
logfile name of the log file to use. The default log file is
] [
–T
<timeout>
] [
configfile
provide additional information for debug purposes.
configuration file is
%ABIC_CONFIG%\DTLBOOTD.LOG.
] [
–B
<numboots>
] [
logfile
%ABIC_CONFIG%\BOOTPTAB.
]
]
Once you invoke the utility, it runs until the specified exit
parameter is satisfied. Exit any time by pressing
[Esc].
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 30

3–12
Configuring the Ethernet Channel for Local Communication
2. Apply power to all chassis containing SLC 5/05 processors.
At power-up, each SLC 5/05 processor broadcasts a
BOOTP
request if BOOTP was enabled at the channel 1 configuration
screen. The Ethernet boot server compares the hardware address
with those listed in
BOOTPTAB and responds by sending the
corresponding IP address and other configuration data to the
client via a
BOOTP reply.
Running the Windows-Based Utility
To run the boot-server utility,
DTLBOOTW.EXE, follow these steps:
1. Start Microsoft Windows, if it is not already running.
2. Open the Program Manager window, if it is not already open.
3. Choose File on the menu bar and select Run from the menu.
4. In the dialog box, type
“OK” or press
[Enter].
C:\ABIC\BIN\DTLBOOTW; then choose
Once you invoke the utility, it will run until you terminate it by
closing the
DTLBOOTW.EXE
window and exiting from Windows.
5. Apply power to all chassis containing and SLC 5/05 processors.
At power-up, each SLC 5/05 processor broadcasts a BOOTP
request. The Ethernet boot server compares the hardware address
with those listed in
the
BOOTPTAB
file and responds by sending
the corresponding IP address and other configuration data to the
client via a BOOTP reply.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 31

Chapter 4
Ethernet Conne
ons
Communicating on the
Ethernet Network
This chapter:
• describes how Ethernet connections are established
• provides information on MSG instruction parameters, interpreting
MSG error codes, and interpreting Ethernet status data
• explains how to use advanced Ethernet functions
cti
TCP/IP is the mechanism used to transport Ethernet messages. On
top of TCP, the Client/Server Protocol is required to establish
connections and to send the MSG commands. Connections can be
initiated by either a client program (INTERCHANGE or RSLinx
application) or a processor.
The client program or processor must first establish a connection to
the SLC 5/05 to enable the SLC 5/05 to receive messages from a
client program or another processor. In order to send an outgoing
message, the SLC 5/05 must first establish a connection with the
destination node at a specified IP address on the Ethernet network.
A connection is established when a MSG instruction executes and no
previous connection to that particular Ethernet device exists.
When a MSG instruction executes, the SLC 5/05 checks to see
whether a connection was established with the destination IP
address. If a connection was not established, the SLC 5/05 attempts
to establish a connection.
In order to receive messages from another device on Ethernet, an
“incoming” connection must be established. This incoming
connection is made by the sending processor and uses one incoming
connection in the receiving processor.
The SLC 5/05 supports a maximum of 16 connections, allowing
simultaneous communication with up to 16 other devices or
applications. The connections are dedicated as follows:
Number of Connections Dedicated to:
4 outgoing messages
4 incoming messages
8 either incoming or outgoing messages
Important: For outgoing connections, no more that one connection
per destination IP address is established. If multiple
MSG instructions use the same destination IP address,
they share the same connection.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 32

4–2
M
Ins
on
Communicating on the Ethernet Network
SG
tructi
The SLC 5/05 processors use the MSG instruction to communicate
over the Ethernet network. The table below describes MSG
instruction parameters for Ethernet.
Parameter Value
Supported MSG Commands
Message Sizes (Channel 1)
Modifying Connections
Limitation for Manipulating the Control Block Bits
485 CIF Read
485 CIF Write
PLC5 Typed Read
PLC5 Typed Write
SLC 500 CPU Read
SLC 500 CPU Write
256 elements maximum, with two exceptions:
•PLC5 Type MSG, Timer File – 201 elements maximum
•All MSG Types, String File – 23 elements maximum
The user may change a MSG instruction destination while the processor is in
the RUN mode. If a MSG instruction’s destination IP address changes, the
next time the MSG instruction executes, a new connection is established with
the new destination node. The old connection remains open as long as either
another MSG instruction was sharing it, or the connection inactive timer has
not expired.
Do not manipulate the MSG instruction control block values except
as noted below. For example, do not clear the first word of the
control block, do not unlatch the time-out control bit, and so on.
The only MSG instruction control bits that may be manipulated by
the ladder program without adversely affecting the operation of the
instruction are the CO, EN, and TO bits. The enable bit
(EN = bit 15) may be unlatched, but only when the done bit
(DN = bit 13) or error bit (ER = bit 12) has been set, indicating the
successful or unsuccessful completion of the previous message.
In addition, when a MSG is in progress and the ladder program
wishes to terminate it for any reason, this may be done by enabling
the time-out bit (TO = bit 8). The next time the processor scans the
MSG instruction with the TO bit set, it will error the MSG (ER = 1).
The MSG instruction may then be re-enabled with a false-to-true
transition on the next program scan.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 33

Communicating on the Ethernet Network
4–3
Control Block Layouts
The SLC 5/05 MSG control block length varies with the type of
communication and with the addressing you use. Control block
layouts are shown for:
• SLC 5/05 Channel 1 (Ethernet port)
MSG Control Block without Logical ASCII Addressing
• SLC 5/05 Channel 1 (Ethernet port)
MSG Control Block with Logical ASCII Addressing
valid for PLC-5 typed read or write only
The AO bit (word 12, bit 15) is used for PLC-5 type reads and
writes. If AO bit is reset to 0, then logical binary addressing is used
for PLC-5 type reads and writes. If AO is set to 1, then logical
ASCII addressing is selected; in this case the processor expects the
ASCII address string information to be stored in words 14 to 55 of
the MSG control block (see control block layout on page 4–5).
The AO bit has no meaning for 485CIF and 500CPU types of reads
and writes.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 34

4–4
Communicating on the Ethernet Network
MSG Instruction Control Block
The following are MSG control blocks, without and with logical
ASCII addressing. The length of the control block without logical
ASCII addressing is 51 words. With logical ASCII addressing, the
length of the control block is 93 words.
MSG Control Block without Logical ASCII Addressing
WORD 15 14 13 12 11 10 09 08 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00
0 EN ST DN ER CO EW NR TO Error Code
1 Reserved (Target Node Not Used)
2 Number of Elements
3 Not Used
4 File Type (based on local source or destination address)
5 Not Used
6 Not Used
7 Reserved (Internal Messaging Bits) WQ
8 Message Timer Preset
9 Message Timer Scaled Zero
10 Message Timer Accumulator
11 Data Length in Bytes
12 AO=0 Reserved (Internal Messaging Bits) Reserved
13 Reserved
14
First Byte of IP Address String
15 Third Byte of IP Address String …
… …
… …
34 Forty-First Byte of IP Address String NULL Byte of Longest IP Address String
35 Reserved Reserved (Ethernet Message Type); must be 0
36–50 Reserved for Future Use
➀
The
IP Address string format is up to 42 ASCII characters including a terminating NULL character
left-most character in the string as written. For example: If the IP Address is 423.156.78.012, the first byte is the ASCII character “4”. If
the MSG destination is an INTERCHANGE client on a host computer, the destination is specified as “client” and stored as a NULL
terminated string.
➀
SLC 5/05 Channel 1 (Ethernet port)
Second Byte of IP Address String
. The first byte in the array is the
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 35

Communicating on the Ethernet Network
4–5
SLC 5/05 Channel 1 (Ethernet port)
MSG Control Block with Logical ASCII Addressing
valid for PLC-5 typed r
ead or write only
WORD 15 14 13 12 11 10 09 08 07 06 05 04 03 02 01 00
0 EN ST DN ER CO EW NR TO Error Code
1 Reserved (Target Node Not Used)
2 Number of Elements
3 Not Used
4 File Type (based on local source or destination address)
5 Not Used
6 Not Used
7 Reserved (Internal Messaging Bits) WQ
8 Message Timer Preset
9 Message Timer Scaled Zero
10 Message Timer Accumulator
11 Data Length in Bytes
12 AO=1 Reserved (Internal Messaging Bits) Reserved
13 Reserved
14 Logical ASCII Address String Length including NULL Termination Character (bytes)
15 First Byte of ASCII Address String Second Byte of ASCII Address String
16 Third Byte of ASCII Address String …
… …
… …
55 Eighty-First Byte of ASCII Address String NULL Byte of Longest ASCII Address String
56
First Byte of IP Address String
➀
Second Byte of IP Address String
57 Third Byte of IP Address String …
… …
… …
76 Forty-First Byte of IP Address String NULL Byte of Longest IP Address String
77 Reserved Reserved (Ethernet Message Type); must be 0
78–92 Reserved for Future Use
➀
The
IP Address string format is up to 42 ASCII characters including a terminating NULL character
left-most character in the string as written. For example: If the IP Address is 423.156.78.012, the first byte is the ASCII character “4”. If
the MSG destination is an INTERCHANGE client on a host computer, the destination is specified as “client” and stored as a NULL
terminated string.
. The first byte in the array is the
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 36

4–6
Communicating on the Ethernet Network
Interpreting MSG Error Codes
Error Code Description of Error Condition
02H
03H Target node cannot respond because message is too large.
04H
05H Local processor is offline (possible duplicate node situation).
06H Target node cannot respond because requested function is not available.
07H Target node does not respond.
08H Target node cannot respond.
09H Local modem connection was lost.
0AH Buffer unavailable to receive SRD reply.
OBH Target node does not accept this type of MSG instruction.
0CH Received a master link reset (one possible source is from the DF1 master).
10H Target node cannot respond because of incorrect command parameters or unsupported command.
11H Local file has constant file protection.
12H Local channel configuration protocol error exists.
13H Local MSG configuration error in the Remote MSG parameters.
15H Local channel configuration parameter error exists.
16H Target or Local Bridge address is higher than the maximum node address.
17H Local service is not supported.
18H Broadcast (Node Address 255) is not supported.
19H Improperly formatted Logical ASCII Address string. String not properly terminated with a NULL character, or the string
20H PCCC Description: Host has a problem and will not communicate.
30H PCCC Description: Remote station host is not there, disconnected, or shutdown.
37H Message timed out in local processor.
38H Message disabled pending link response.
40H PCCC Description: Host could not complete function due to hardware fault.
50H Target node is out of memory.
60H Target node cannot respond because file is protected.
70H PCCC Description: Processor is in Program Mode.
80H PCCC Description: Compatibility mode file missing or communication zone problem.
90H PCCC Description: Remote station cannot buffer command.
B0H PCCC Description: Remote station problem due to download.
C0H PCCC Description: Cannot execute command due to active IPBs.
D0H No IP address configured for the network, –or–
D1H Maximum connections used – no connections available.
D2H Invalid internet address or host name.
D3H No such host / cannot communicate with the name server.
Target node is busy. The MSG instruction automatically reloads. If other messages are waiting, the message is
placed at the bottom of the stack.
Target node cannot respond because it does not understand the command parameters OR the control block was
inadvertently modified.
length does not match the value in the length parameter.
Bad command – unsolicited message error, –or–
Bad address – unsolicited message error, –or–
No privilege – unsolicited message error
When the processor detects an error during the transfer of message
data, the processor sets the .ER bit and enters an error code that you
can monitor from your programming software.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 37

Communicating on the Ethernet Network
Error Code Description of Error Condition
D4H Connection not completed before user-specified timeout
D5H Connection timed out by the network
D7H Connection refused by destination host
D8H Connection was broken
D9H Reply not received before user-specified timeout
DAH No network buffer space available
E1H PCCC Description: Illegal Address format, a field has an illegal value.
E2H PCCC Description: Illegal Address format, not enough fields specified.
E3H PCCC Description: Illegal Address format, too many fields specified.
E4H PCCC Description: Illegal Address, symbol not found.
E5H PCCC Description: Illegal Address format, symbol is 0 or greater than the maximum number of characters supported
by this device.
E6H PCCC Description: Illegal Address, address does not exist, or does not point to something usable by this command.
E7H Target node cannot respond because length requested is too large.
E8H PCCC Description: Cannot complete request, situation changed (file size, for example) during multi-packet operation.
E9H PCCC Description: Data or file is too large. Memory unavailable.
EAH PCCC Description: Request is too large; transaction size plus word address is too large.
EBH Target node cannot respond because target node denies access.
ECH Target node cannot respond because requested function is currently unavailable.
EDH PCCC Description: Resource is already available; condition already exists.
EEH PCCC Description: Command cannot be executed.
EFH PCCC Description: Overflow; histogram overflow.
F0H PCCC Description: No access
F1H Local processor detects illegal target file type.
F2H PCCC Description: Invalid parameter; invalid data in search or command block.
F3H PCCC Description: Address reference exists to deleted area.
F4H PCCC Description: Command execution failure for unknown reason; PLC-3 histogram overflow.
F5H PCCC Description: Data conversion error.
F6H PCCC Description: The scanner is not able to communicate with a 1771 rack adapter. This could be due to the
scanner not scanning, the selected adapter not being scanned, the adapter not responding, or an invalid request of a
“DCM BT (block transfer)”.
F7H PCCC Description: The adapter is not able to communicate with a module.
F8H PCCC Description: The 1771 module response was not valid – size, checksum, etc.
F9H PCCC Description: Duplicated Label.
FAH Target node cannot respond because another node is file owner (has sole file access).
FBH Target node cannot respond because another node is program owner (has sole access to all files).
FCH PCCC Description: Disk file is write-protected or otherwise inaccessible (off-line only).
FDH PCCC Description: Disk file is being used by another application; update not performed (off-line only).
FFH Local communication channel is shut down.
4–7
Note: For 1770–6.5.16 DF1 Protocol and Command Set Reference Manual Users:
The MSG error code reflects the STS field of the reply to your MSG instruction.
Codes E0–EF represent EXT STS codes 0–F.
Codes F0–FD represent EXT STS codes 10–1D.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 38

4–8
Communicating on the Ethernet Network
Interpreting Ethernet Status Data
Monitor the status of SLC 5/05 processors by accessing the Ethernet
channel 1 status screen of your programming software.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 39

Communicating on the Ethernet Network
The diagnostic counter data displayed is stored in the diagnostic file
defined on the Ethernet channel 1 configuration screen.
Status field: Bytes: Displays the number of:
Commands
Replies sent 8-11 Replies sent by the channel.
Ethernet In Octets 28-31 Octets received on the channel.
sent 0-3 Commands sent by the channel.
received 4-7 Commands received by the channel.
received 12-15 Replies received by the channel.
sent with error 16-19 Replies containing errors sent by the channel.
received with error 20-23 Replies containing errors received by the channel.
timed out 24-27 Replies not received within the specified timeout period.
Out Octets 32-35 Octets sent on the channel.
In Packets 36-39 Packets received on the channel, including broadcast packets.
Out Packets 40-43 Packets sent on the channel, including broadcast packets.
alignment errors 44-47 Frames received on the channel that are not an integral number of octets in length.
FCS errors 48-51 Frames received on the channel that do not pass the FCS check.
carrier sense errors 52-55 Times that the carrier sense condition was lost or never asserted while trying to transmit a
frame.
excessive collisions 56-59 Frames for which a transmission fails due to excessive collisions.
excessive deferrals 60-63 Frames for which transmission is deferred for an excessive period of time.
MAC receive errors 64-67 Frames for which reception on an interface fails due to internal MAC sublayer receive error.
MAC transmit errors 68-71 Frames for which reception on an interface fails due to internal MAC sublayer transmit error.
single collisions 72-75 Successfully transmitted frames for which transmission was delayed because of collision.
multiple collisions 76-79 Successfully transmitted frames for which transmission was delayed more than once
because of collision.
deferred transmission 80-83 Frames for which the first transmission attempt is delayed because the medium is busy.
late collisions 84-87 Times that a collision is detected later than 512 bit-times into the transmission of a packet.
4–9
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 40

4–10
Communicating on the Ethernet Network
Using Subnet Masks and Gateways
Configure subnet masks and gateways using the Ethernet channel 1
configuration screen:
Important: If BOOTP is enabled, you can’t change any of the
advanced Ethernet communications characteristics.
If your network is divided into subnetworks that use gateways or
routers, you must indicate the following information when
configuring channel 1:
• subnet mask
• gateway address
A subnet mask is a filter that a node applies to IP addresses to
determine if an address is on the local subnet or on another subnet.
If an address is located on another subnetwork, messages are routed
through a local gateway to be transferred to the destination
subnetwork.
If your network is not divided into subnets, then leave the subnet
mask field at the default.
If you are Then See page
manually configuring channel 1
and have a network with subnets
• be sure the BOOTP enable field is disabled
• use your programming software to enter the
subnet mask and gateway address.
4–11
using BOOTP to configure
channel 1 and have a network
with subnets
• be sure BOOTP is enabled
• configure the BOOTPTAB file to include the
subnet mask(s) and gateway address(es)
4–12
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 41

4–1
Manually Configuring Channel 1 for Processors on Subnets
If you are manually configuring channel 1 for a processor located on
a subnet, deselect the “BOOTP Enable” option by clicking on the
checked box.
1Communicating on the Ethernet Network
See the table below to configure the subnet mask and gateway
address fields for each processor via your programming software.
Ethernet Channel 1 Configuration Screen Advanced Functions
This field: Specifies: Configure by doing the following:
Subnet Mask
Gateway Address The IP address of the gateway that
The processor’s subnet mask.
The subnet mask is used to interpret IP
addresses when the internet is divided
into subnets.
provides a connection to another
IP network.
This field is required when you
communicate with other devices not on a
local subnet.
Enter an address of the following form:
a.b.c.d Where: a, b, c, d are numbers between 0-255 (decimal)
If your network is not divided into subnets, then leave the subnet mask field
at the default. If you change the default and need to reset it, type 0.0.0.0.
Enter an address of the following form:
a.b.c.d Where: a, b, c, d are numbers between 0-255 (decimal)
The default address is No Gateway.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 42

4–12
Communicating on the Ethernet Network
Using BOOTP to Configure Channel 1 for Processors on Subnets
Configure the BOOTPTAB file according to the subnet mask and
gateway address for each SLC 5/05 processor on the link. See the
example below and the corresponding
next page.
Important: Because BOOTP requests are seen only on the local
BOOTPTAB file on the
subnet, each subnet needs its own BOOTP server and
BOOTPTAB file.
personal computer WINDOWS
or HP 9000 or VAX computer
BOOTP
server
Ethernet TCP/IP network
Ethernet gateway
or “router”
BOOTP
server
130.151.132.1 130.151.138.1
130.151.132.xxx
SLC 5/05
processor
Subnet A
130.151.194.xxx
Hostname: Iota1
IP address: 130.151.194.19
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Gateway Address: 130.151.194.1
130.151.194.1
BOOTP
server
130.151.138.xxx
Publication
Subnet B Subnet C
Hostname: Iota2
IP address: 130.151.132.110
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Gateway
Address: 130.151.132.1
1747-10.4
SLC 5/05
processor
SLC 5/05
processor
Hostname: Iota3
IP address: 130.151.138.123
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Gateway
Address: 130.151.138.1
Page 43

Communicating on the Ethernet Network
The BOOTPTAB files that correspond to this example look like:
# Legend: gw –– gateways
––
#ha
#ht
#ip
#sm
#vm
#tc
#Default string for each type of Ethernet client
defaults5E: ht=1:vm=rfc1048:sm=255.255.255.0
#Entries for SLC 5/05 processors:
iota1:\
tc=defaults5E:\
gw=130.151.194.1:\
ha=0000BC1D1234:/
ip=130.151.194.19
# Legend: gw –– gateways
#ha
#ht
#ip
#sm
#vm
#tc
#Default string for each type of Ethernet client
defaults5E: ht=1:vm=rfc1048:sm=255.255.255.0
#Entries for SLC 5/05 processors:
iota2:\
tc=defaults5E:\
gw=130.151.132.1:\
ha=0000BC1D5678:/
ip=130.151.132.110
hardware address
––
hardware type
––
host IP address
––
subnet mask
––
BOOTP vendor extensions format
––
template host
––
hardware address
––
hardware type
––
host IP address
––
subnet mask
––
BOOTP vendor extensions format
––
template host
4–13
# Legend: gw –– gateways
––
#ha
#ht
#ip
#sm
#vm
#tc
#Default string for each type of Ethernet client
defaults5E: ht=1:vm=rfc1048:sm=255.255.255.0
#Entries for SLC 5/05 processors:
iota3:\
tc=defaults5E:\
gw=130.151.138.1:\
ha=0000BC1D9012:/
ip=130.151.138.123
hardware address
––
hardware type
––
host IP address
––
subnet mask
––
BOOTP vendor extensions format
––
template host
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 44

4–14
Communicating on the Ethernet Network
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 45

Chapter 5
Passthru Feature
Using RS232toEthernet
ChanneltoChannel Passthru
This chapter contains information about the new passthru feature on
SLC 5/05 (1747-OS501, FRN 3) processors, including:
• Updated status file information
• Error code information
• An example of DF1-to-Ethernet and Ethernet-to-DF1 routing
• An example of DH485-to-Ethernet and Ethernet-to-DH485
routing
This feature permits an SLC 5/05 processor to act as a bridge,
allowing communication data packets to be passed between the
RS232 serial port (Channel 0) and the Ethernet port (Channel 1).
This RS232-to-Ethernet bridge operates only when the RS232 serial
port is configured for DF1 full-duplex communication or DH485
communication.
A maximum of 128 Ethernet devices may be accessed using the
passthru feature.
Important: For 1747-OS501 support, use RSLogix Rev. 2.51.0 or
higher, and RSLinx Rev. 1.70.62 or higher.
Address Routing Table
To enable passthru of data packets between the RS232 port and the
Ethernet port, the SLC 5/05 processor uses a routing table to
cross-reference the one-byte addressing used by DF1 and DH485
protocols with the four-byte IP address needed to support Ethernet
communication. The routing table is stored in a user-selectable
integer file and uses two word elements of the integer file to store
one IP address. The routing table file number must be between 9 and
255. The routing table must be at least two words in length.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 46

5–2
Using RS232-to-Ethernet Channel-to-Channel Passthru
Status File Bits
Two status file bits control whether or not the passthru function is
enabled. Their SLC 5/05 functions are described in the table below.
Address Classification Description
S:34/0 Dynamic
Configuration
S:34/5 Dynamic
Configuration
DH485 to Ethernet Passthru Disable Bit
(SLC 5/05, OS501 or later)
When this bit is set, passthru is disabled. When it is reset,
the processor allows packets to be passed from one
channel to the other. Channel 0 must be configured for
DH485 protocol. Only packets that contain the internet
network layer remote MSG packets are passed.
The default is reset.
DF1 to Ethernet Passthru Enable Bit
(SLC 5/05, OS501 or later)
When this bit is set, passthru is enabled. Channel 0 must
be configured for DF1 full-duplex protocol. Only Ethernet
packets that contain the internet network layer remote
MSG packets are passed from channel 1 to channel 0.
Only DF1 packets whose destination address (DST) is a
valid number (1-128) corresponding to a valid IP address
in the routing table are passed from channel 0 to channel
1. DF1 packets with a destination address equal to 0 are
processed locally.
MSG Error Code
The default is reset.
When the processor detects an error during the passage of message
data, it generates the error code 20H “Host has a problem and cannot
communicate”. The cause of the problem could be any of the
following:
• The routing table integer file number is out of range (9 to 255).
• The routing table file does not exist in the user program directory
or is less than 2 word elements in length.
• The IP Address entry in the routing table does not exist or is all
zeros.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 47

Using RS232-to-Ethernet Channel-to-Channel Passthru
5–3
Passthru Examples
The IP Addresses used in the following illustrations are for example
purposes only. Contact your system administrator for IP addresses
unique to your network.
Example 1: DF1-to-Ethernet and Ethernet-to-DF1
In the following diagram, the SLC 5/03 sends a local message via
DF1 to the SLC 5/05 #1. The SLC 5/05 #1 acts as a bridge, sending
the message out via Ethernet to the SLC 5/05 #2, whose address is
stored in the routing table. SLC 5/05 #2 can also initiate a message
via Ethernet to the SLC5/03 processor through SLC 5/05 #1. The
SLC 5/05 #1 routes the message to SLC 5/03 via DF1.
Important: In the SLC 5/05 #1 bridge, Status File Bit S:34/5 must
be set to 1 to enable DF1-to-Ethernet passthru. Set
Status File Bit S:34/0 to 1 to disable DH485-to-Ethernet
passthru.
DH485 Node 1
1747-PIC
Interface
Converter
RS232 Port
Ethernet Port
Personal Computer
with
RSLinx and RSLogix 500
SLC 5/03
DF1 Source ID = 1
Ethernet Hub
DF1
SLC 5/05 #1 Bridge
IP Address 130.151.81.104
DF1 Source ID = 0
Ethernet
SLC 5/05 #2
IP Address 130.151.81.139
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 48

5–4
SLC 5/03 Message Ladder Logic
Using RS232-to-Ethernet Channel-to-Channel Passthru
SLC
5/03 Using DF1
The message ladder logic, message setup, and channel configurations
for the SLC 5/03 using DF1 are shown below.
SLC 5/03 Message Setup
• Channel is set to zero for DF1 full-duplex protocol.
• Target Node is the station address in the SLC 5/05 #1 routing
table where the IP address for SLC 5/05 #2 is stored.
• The Message Timeout must be at least as long as the SLC 5/05
timeout for Ethernet connection. The SLC 5/05 default timeout is
23 seconds.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 49

SLC 5/03 Channel Configurations
Using RS232-to-Ethernet Channel-to-Channel Passthru
5–5
• Channel 0 Driver is set to DF1 Full Duplex.
• Source ID is the address of the sender of the message. It can be
any number from 0 to 254.
SLC 5/05 #1 Bridge Channel Configuration
5/05 #1 Bridge
SLC
Ladder logic is not required for the SLC 5/05 which acts as the
bridge from DF1-to-Ethernet. However, you must set up a passthru
routing table when configuring the bridge. The channel configuration
is shown below, followed by the routing table on
page 5–7.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 50

5–6
Using RS232-to-Ethernet Channel-to-Channel Passthru
Publication
Important: Channel 0 Source ID must be set to 0 when SLC 5/05
#1 is used as the bridge between DF1 full-duplex and
Ethernet.
1747-10.4
Page 51

Using RS232-to-Ethernet Channel-to-Channel Passthru
5–7
Passthru Routing Table
The passthru routing table is located under the channel configuration
selection in RSLogix 500 Programming Software. If a Passthru
Routing Table File number was entered in the General Tab in the
Channel Configuration dialog box, click on the + in front of
“Channel Configuration” to reveal the routing table selection.
Double-click on “Routing Table” to view and modify the passthru
routing table.
Important: The routing table must contain the IP address of SLC
5/05 #2 at station target node three, as shown in the
routing table above. Target node three was identified as
the target node in the SLC5/03 Message Setup dialog
box.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 52

5–8
SLC 5/05 #2 Ladder Logic
Using RS232-to-Ethernet Channel-to-Channel Passthru
SLC
5/05 #2 Using Ethernet
For DF1-to-Ethernet passthru, SLC 5/05 #2 is the receiver and does
not require message ladder logic, only a correct IP address and
proper channel configuration.
For Ethernet-to-DF1 passthru, SLC 5/05 #2 is the initiator and must
have ladder logic. The program below shows how the SLC 5/05 #2
processor can initiate a message to the SLC 5/03 via the SLC 5/05 #1
bridge.
The SLC 5/05 message ladder logic, remote message setup, and
channel configurations are shown below.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 53

SLC 5/05 #2 Message Setup
Using RS232-to-Ethernet Channel-to-Channel Passthru
5–9
• Channel is set to 1 for Ethernet.
• Message Timeout for any Ethernet MSG cannot be modified in
the Ethernet Message Setup dialog box. It is assigned by the
processor, and is determined by adding the Channel 1 MSG
Connection Timeout to the MSG Reply Timeout, then adding 5
seconds. This value can be modified by changing one or both of
the timeout values in the channel 1 channel configuration screen.
The modified message timeout applies to all MSG instructions.
• The Remote Bridge Link ID is the Link ID of Channel 0 of the
SLC 5/05 #1 bridge.
• The Remote Bridge Address is zero, since the SLC 5/05 #1, as
the bridge, is always node or Source ID 0 for its DF1 channel.
• The Local Bridge Address is the IP address of the SLC 5/05 #1
bridge.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 54

5–10
SLC 5/05 #2 Channel Configuration
Using RS232-to-Ethernet Channel-to-Channel Passthru
Note: A zero in the Passthru Routing Table File indicates that
this processor is not being used as a bridge. A passthru
routing table will not be created.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 55

5–1
Example 2: DH485-to-Ethernet and Ethernet-to-DH485
In the following diagram, the SLC 5/03 uses DH485 protocol to send
a remote message to SLC 5/05 #1. The SLC 5/05 #1 passes the
message through to SLC 5/05 #2 via Ethernet. The SLC 5/05 #2 can
also send a message to the SLC 5/03 via the SLC5/05 #1 bridge.
The SLC 5/05 #1 processor routes the message to the SLC 5/03 via
DH485.
Important: In the SLC 5/05 #1 bridge, Status File Bit S:34/0 must
be set to 0 to enable DH485-to-Ethernet passthru. Set
Status File Bit S:34/5 to 0 to disable DF1-to-Ethernet
passthru.
1Using RS232-to-Ethernet Channel-to-Channel Passthru
1747-PIC
Interface
Converter
RS232 Port
1747-AIC
DH485
1747-C11 Cable
Personal Computer
with
RSLinx and RSLogix 500
DH485
SLC 5/03
Channel 1
DH485 Node 1
Ethernet Port
SLC
5/03 Using DH485
Ethernet Hub
1761-NET-AIC
DH485
Ethernet
SLC 5/05 #1 Bridge
Channel 0
DH485 Node 2
IP Address 130.151.81.104
SLC 5/05 #2
IP Address 130.151.81.139
The remote message ladder logic, setup, and channel configuration
are shown on page 5–12.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 56

5–12
SLC 5/03 Ladder Logic
SLC 5/03 Message Setup
Using RS232-to-Ethernet Channel-to-Channel Passthru
Publication
• Channel is set to one, the DH485 default.
• Target Node is the address in the SLC 5/05 #1 routing table
where the IP address for SLC 5/05 #2 is stored.
• The Message Timeout must be at least as long as the SLC
5/05 timeout for Ethernet connection. The SLC 5/05 default
timeout is 23 seconds.
• The Remote Bridge Link ID is the Link ID of Channel 1 of
the SLC 5/05 #1 bridge.
• The Remote Bridge Address is always zero to point to the IP
address for the bridge’s (SLC 5/05 #1) Ethernet channel.
• The Local Bridge Address is the Channel 0 DH485 node
address of the SLC 5/05 #1 bridge.
1747-10.4
Page 57

SLC 5/03 Channel Configuration
Using RS232-to-Ethernet Channel-to-Channel Passthru
5–13
• Channel 1 Driver is set to DH485.
• Node Address is the address of the SLC 5/03 processor.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 58

5–14
SLC 5/05 #1 Bridge Channel Configuration
Using RS232-to-Ethernet Channel-to-Channel Passthru
SLC
5/05 #1 Bridge
Ladder logic is not required for the SLC 5/05 which acts as a bridge
from DH485-to-Ethernet. However, you must set up a passthru
routing table file when configuring the bridge. The channel
configuration is shown below, along with the routing table.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 59

Using RS232-to-Ethernet Channel-to-Channel Passthru
5–15
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 60
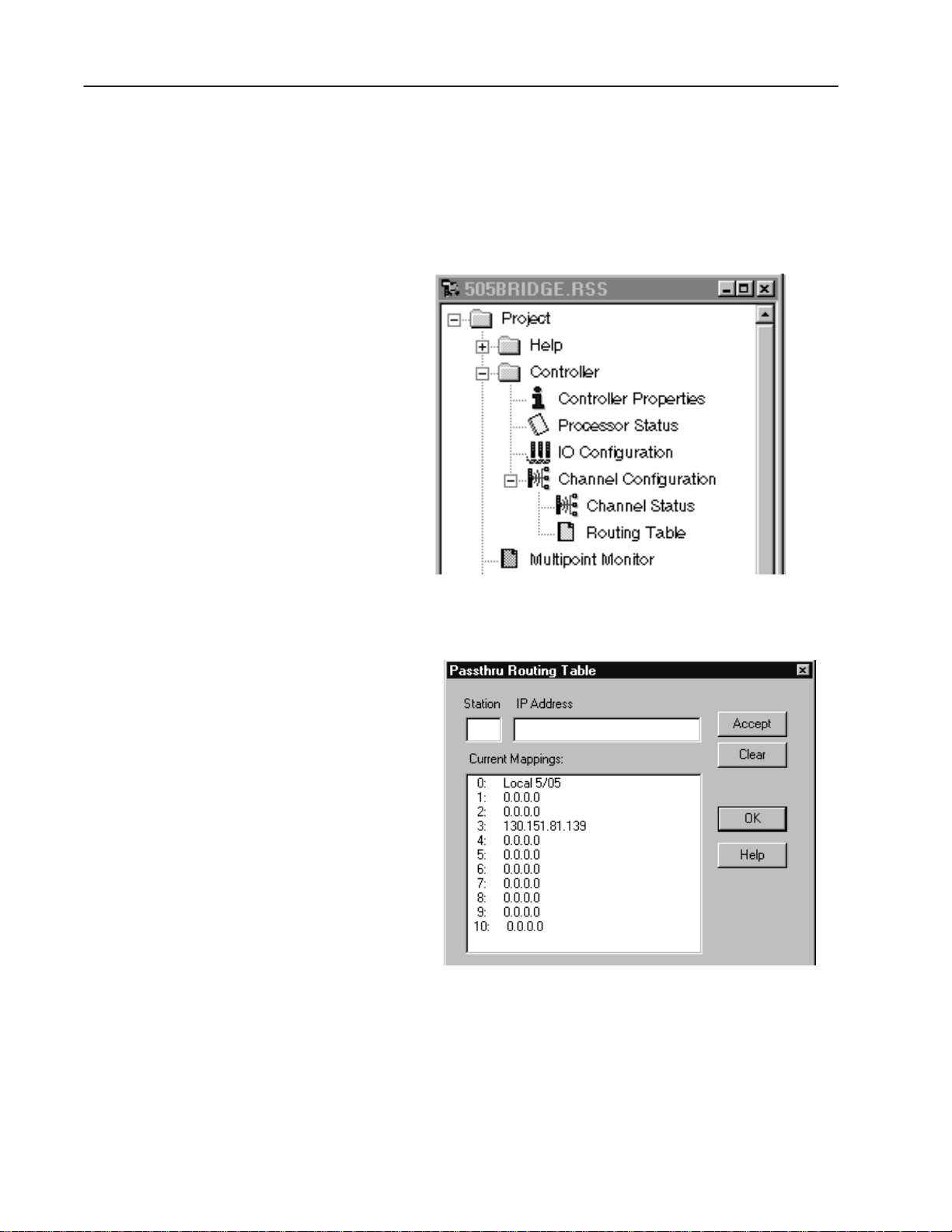
5–16
Using RS232-to-Ethernet Channel-to-Channel Passthru
Passthru Routing Table
The passthru routing table is located under the channel configuration
selection in RSLogix500 Programming Software. If a Passthru
Routing Table File number was entered in the General Tab in the
Channel Configuration dialog box, click on the + in front of
“Channel Configuration” to reveal the routing table selection.
Double-click on “Routing Table” to view and modify the routing
table.
Important: The routing table must contain the IP address of the
SLC 5/05 #2 at station target node three, as shown in
the routing table above. Target node three was
identified as the target node in the SLC 5/03 Message
Setup dialog box.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 61

SLC 5/05 #2 Ladder Logic
Using RS232-to-Ethernet Channel-to-Channel Passthru
SLC
5/05 # 2 Using Ethernet
5–17
For DH485-to-Ethernet passthru, SLC 5/05 #2 is the receiver and
does not require message ladder logic, only a correct IP address and
proper channel configuration.
For Ethernet-to-DH485 passthru, SLC 5/05 #2 is the initiator and
must have ladder logic to send a message to SLC 5/03 via the SLC
5/05 #1 bridge.
The SLC 5/05 remote message ladder logic, message setup, and
channel configurations are shown below.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 62

5–18
SLC 5/05 #2 Message Setup
Using RS232-to-Ethernet Channel-to-Channel Passthru
• Channel is set to one for Ethernet.
• Target Node is the DH485 node address of the SLC 5/03
destination processor.
• Message Timeout for any Ethernet MSG cannot be modified in
the Ethernet Message Setup dialog box. It is assigned by the
processor, and is determined by adding the Channel 1 MSG
Connection Timeout to the MSG Reply Timeout, then adding 5
seconds. This value can be modified by changing one or both of
the timeout values in the Channel 1 channel configuration screen.
The modified message timeout applies to all MSG instructions.
• The Remote Bridge Link ID is the Link ID of Channel 0 of the
SLC 5/05 #1 bridge.
• The Remote Bridge Address is the DH485 address for Channel
0 of SLC 5/05 #1.
• The Local Bridge Address is the IP address of the SLC 5/05 #1
bridge.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 63

SLC 5/05 #2 Channel Configuration
Using RS232-to-Ethernet Channel-to-Channel Passthru
5–19
Note: A zero in the Passthru Routing Table File indicates that
this processor is not being used as a bridge. A passthru
routing table will not be created.
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 64

5–20
Using RS232-to-Ethernet Channel-to-Channel Passthru
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 65

Specifications
Temperature
ibration
Free Fall (drop test)
Safety
Appendix
A
System Test General
The table below lists SLC 500 system test specifications.
Specifications
Description Specification Industry Standard
Operating: 0°C to +60°C (32°F to 140°F) Not Applicable
Storage: –40°C to +85°C (–40°F to 185°F) Not Applicable
Humidity 5 to 95% without condensation Not Applicable
V
Shock
Operating: 1.0G at 5 to 2000 Hz Not Applicable
Non-operating: 2.5Gs at 5 to 2000 Hz Not Applicable
Operating: 30.0Gs (3 pulses, 11 ms) Not Applicable
Operating: 10.0Gs (3 pulses, 11 ms)
Non-operating: 50.0Gs (3 pulses, 11 ms) Not Applicable
Portable, 2.268 kg (5 lbs) or less at 0.762m
(30 in.) (six drops)
Portable, 2.268 kg (5 lbs) or more at 0.1016m
(4 in.) (three flat drops)
Showering Arc: 1.5 kV NEMA ICS 2-230/NEMA ICS 3-304
Surge Withstand Capability: 3 kV IEEE Std. 472-1974/ANSI C37.90/90A-1974
Not Applicable
Not Applicable
Not Applicable
Fast Transient Burst (impulse): 2 kV for 1746
power supplies, 1kV for 1746 I/O and
Electromagnetic Compatibility
Certification
➀
Internal Rockwell Automation standards are based on Rockwell Automation’s extensive experience in industrial controls.
It is also based partly on industry and/or military specifications.
communication lines over 10m (32.84 ft), 5 ns
rise time
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD): 15 kV,
100 pF/1.5k ohm model
Radiated Electromagnetic Susceptibility: 5W
walkie-talkie at 464.5 MHz and 153.05 MHz
Dielectric Withstand: 1500V ac UL 508, CSA C22.2 No. 142
Isolation between Communication Circuits:
500V dc
Isolation between Backplane and I/Os: 1500V
ac
Flammability and Electrical Ignition: UL94V-0 Not Applicable
UL listed/CSA approved
Class 1, Groups A, B, C or D, Division 2
CE compliant for all applicable directives
Internal Rockwell Automation standard
Internal Rockwell Automation standard
Internal Rockwell Automation standard
Not Applicable
Not Applicable
Not Applicable
➀
➀
➀
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 66

A–2 Variable Content
ibration
TTL:Chap
Is Linked To HD:Running
Processor General Specifications
Specification 1747-L551 1747-L552 1747-L553
Memory Size 16K Words 32K Words 64K Words
I/O Capacity up to 4096 inputs and 4096 outputs
Maximum Chassis/Slots 3/30
Standard RAM Lithium Battery (2 years)
Memory Back-up Options Flash EPROM
LED Indicators Run, CPU Fault, Battery Low, Forced I/O, Ethernet, RS-232
Typical Scan Time
Bit Execution (XIC) .37 µs
Communication
Power Supply Loading at 5V dc 1A
Power Supply Loading at 24V
dc
Clock/Calendar Accuracy
➀
0.9 ms/K
Ch 1: Ethernet (10Base-T)
Ch 0: RS-232
(DF1, ASCII, or DH485 Protocols)
200 mA
±54 sec/month at 25°C (77°F)
±81 sec/month at 60°C (140°F)
The table below describes the general specifications for the SLC 5/05
processors.
Program Scan Hold-up Time
after Loss of Power
Noise Immunity NEMA Standard ICS 2-230
Ambient Temperature Rating
Humidity 5 to 95% without condensation
Shock (operating) 30Gs
V
Certification
➀
The
scan times are typical for a 1K ladder logic program consisting of simple ladder logic and communication servicing.
Actual scan times depend on your program size, instructions used, and communication protocol.
20 milliseconds to 3 seconds (dependent on power supply loading)
Operating: 0°C to +60°C (32°F to 140°F)
Storage: 40°C to +85°C (–40°F to 185°F)
Displacement: .015 in., peak-to-peak at 5 to 57 Hz
Acceleration: 2.5Gs at 57 to 2000 Hz
UL listed/CSA approved
Class I, Division 2, Groups A, B, C or D
CE compliant for all applicable directives
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 67

Appendix
B
(Optional) Return Processor to
Initial Factory Conditions
Use this procedure if the communication channels are shut down
because they were configured to be shut down, or if you absolutely
cannot establish communications with the processor.
ATTENTION: If you return the processor to the
initial factory conditions, the user program and
!
1. Remove power from the SLC 500 power supply.
2. Remove the processor from the chassis.
3. Disconnect the battery by removing the battery connector from its
socket.
communication configurations are returned to their
default settings.
Keyswitch
4. Locate the VBB and GND connections on the right side of the
motherboard.
5. Place a small bladed screwdriver across the VBB and GND
connections and hold for 60 seconds. This returns the processor
to the initial factory conditions.
GND
GND VBB
Mother Board
Mother Board
VBB
Right Side View
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 68

B–2 Variable Content
TTL:Chap
Is Linked To HD:Running
Publication
1747-10.4
Page 69

Publication 1747-10.4 – July 1998
Page 70

Worldwide representation.
Allen-Bradley, a Rockwell Automation Business, has been helping its customers improve
productivity and quality for more than 90 years. We design, manufacture and support a broad
range of automation products worldwide. They include logic processors, power and motion
control devices, operator interfaces, sensors and a variety of software. Rockwell is one of the
world’s leading technology companies.
Argentina •
Denmark • Ecuador • Egypt • El Salvador
Ireland
Philippines •
Sweden
Australia • Austria • Bahrain • Belgium
• Israel • Italy • Jamaica •
Poland • Portugal • Puerto Rico • Qatar • Romania • Russia–CIS • Saudi Arabia • Singapore
• Switzerland • T
Japan • Jordan • Korea • Kuwait • Lebanon
aiwan
• Thailand • T
• Brazil •
• Finland •
urkey • United Arab Emirates • United Kingdom • United States • Uruguay • V
Bulgaria • Canada • Chile • China, PRC • Colombia • Costa Rica • Croatia • Cyprus • Czech Republic
France • Germany • Greece • Guatemala • Honduras • Hong Kong • Hungary • Iceland • India • Indonesia •
• Malaysia • Mexico •
Netherlands
• New
• Slovakia • Slovenia •
Zealand • Norway
South Africa, Republic • Spain
enezuela • Y
ugoslavia
Allen-Bradley Headquarters, 1201 South Second Street, Milwaukee, WI 53204 USA, Tel: (1) 414 382-2000 Fax: (1) 414 382-4444
Publication 1747-10.4 – July 1998
Supercedes
Publication 1747-10.4 – Preliminary – August 5, 1997
Publication
1747-10.4 – July 1998
Copyright 1998 Rockwell International Corporation All rights reserved Printed in USA
• Pakistan •
Peru
•
•
•
 Loading...
Loading...