Rockwell Automation 9VT201-011HTNNN, 9VT201-043HTANN, 9VT201-017HTANN, 9VT201-062HTANN, 9VT201-025HTANN User Manual
...
VTAC 9 AC Drive
Firmware Version 3.xx
User Manual
Important User Information
Solid state equipment has operational characteristics differing from those of
electromechanical equipment. Safety Guidelines for the Application, Installation
and Maintenance of Solid State Controls (Publication SGI-1.1 available from your
local Rockwell Automation sales office or online at http://
www.rockwellautomation.com/vtac/) describes some important differences between
solid state equipment and hard-wired electromechanical devices. Because of this
difference, and also because of the wide variety of uses for solid state equipment,
all persons responsible for applying this equipment must satisfy themselves that
each intended application of this equipment is acceptable.
In no event will Rockwell Automation, Inc. be responsible or liable for indirect or
consequential damages resulting from the use or application of this equipment.
The examples and diagrams in this manual are included solely for illustrative
purposes. Because of the many variables and requirements associated with any
particular installation, Rockwell Automation, Inc. cannot assume responsibility or
liability for actual use based on the examples and diagrams.
No patent liability is assumed by Rockwell Automation, Inc. with respect to use of
information, circuits, equipment, or software described in this manual.
Reproduction of the contents of this manual, in whole or in part, without written
permission of Rockwell Automation, Inc. is prohibited.
Throughout this manual, when necessary we use notes to make you aware of safety
considerations.
WARNING: Identifies information about practices or circumstances
that can cause an explosion in a hazardous environment, which may
lead to personal injury or death, property damage, or economic loss.
Important: Identifies information that is critical for successful application and
VTAC 9 and VS Utilities are registered trademarks of Rockwell Automation, Inc.
understanding of the product.
ATTENTION: Identifies information about practices or circumstances
that can lead to personal injury or death, property damage, or economic
loss. Attentions help you:
• identify a hazard
• avoid the hazard
• recognize the consequences
Shock Hazard labels may be located on or inside the equipment (e.g.,
drive or motor) to alert people that dangerous voltage may be present.
Burn Hazard labels may be located on or inside the equipment (e.g.,
drive or motor) to alert people that surfaces may be at dangerous
temperatures.

Summary of Changes
The information below summarizes the changes to the VTAC 9 User
Manual since the June 2007 release.
Manual Updates
Description of New or Updated Information Page
Additional documentation needed when installing Bypass Package
(Style B) Drives.
Suggested Analog Signal Wiring section added. 1-23, 1-30
Interlock Connection Considerations added. 1-24, 1-31
Important statement regarding the two types of I/O Terminal Blocks
added.
Parameter 178 [Sleep Wake Mode] description updated. 3-38
Sleep Wake Mode definitions updated. C-11
, 1-23, 1-30
1-1
1-25, 1-32

soc-2

Preface Overview
Who Should Use this Manual? . . . . . . . . . P-1
What Is Not in this Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . P-1
Getting Assistance from
Rockwell Automation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . P-1
Manual Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . P-2
General Precautions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . P-3
VTAC 9 Catalog Numbers . . . . . . . . . . . . P-4
System (VTAC Builder/Order)
Catalog Number Explanation . . . . . . . . P-4
Model Number Explanation . . . . . . . . . . . P-5
Chapter 1 Installation/Wiring
Bypass Package (Style B) Drives . . . . . . . 1-1
Opening the Cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Mounting Considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
AC Supply Source Considerations . . . . . . 1-5
General Grounding Requirements . . . . . . 1-6
Fuses and Circuit Breakers . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
Power Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
Using Input/Output Contactors. . . . . . . . 1-16
Disconnecting MOVs and
Common Mode Capacitors . . . . . . . . . 1-18
I/O Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-21
Speed Reference Control . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-35
Auto/Manual Examples. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-36
EMC Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-37
FCC Instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-40
Chapter 2 Start Up
Prepare For Drive Start-Up . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
Status Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
Running the Start-Up Routines. . . . . . . . . 2-4
Chapter 3 Programming and Parameters
About Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
How Parameters are Organized. . . . . . . . . 3-3
Accessing the Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
Ensuring Program Security. . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
Monitor File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-11
Motor Control File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-12
Speed Command File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-18
Dynamic Control File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-30
Utility File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-41
Communication File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-51
Inputs & Outputs File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-54
Parameter Cross Reference – by Name. . 3-66
Table of Contents
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

ii
Chapter 4 Troubleshooting
Drive Faults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
Manually Clearing Faults . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
Fault Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
Drive Alarms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8
Clearing Alarms. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
Alarm Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-10
Diagnostic Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-12
Common Symptoms and
Corrective Actions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-13
Troubleshooting Using the LCD OIM. . . 4-16
Appendix A Supplemental Drive Information
Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-1
Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-8
Drive, Fuse & Circuit Breaker Ratings . . A-21
Appendix B Using the LCD OIM
External and Internal Connections . . . . . . B-1
Install/Remove the Local LCD OIM. . . . . B-5
Display Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-6
LCD OIM Menu Structure . . . . . . . . . . . . B-8
Power Up and Adjust the LCD OIM . . . . . B-9
Select a Device in the System . . . . . . . . . . B-9
Program the Drive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-10
Monitor the Drive Using the
Process Display Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . B-12
Control the Drive From the LCD OIM . . B-18
Appendix C Application Notes
External Brake Resistor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-1
Motor Overload . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-2
Motor Overload Memory Retention
Per 2005 NEC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-3
Overspeed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-4
Power Loss Ride Through . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-5
Process PI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-6
Skip Frequency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-9
Sleep Wake Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-11
Start At PowerUp. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-13
Stop Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-14
Index
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

Preface
Overview
The purpose of this manual is to provide you with the basic information
needed to install, start-up and troubleshoot the VTAC 9 Adjustable
Frequency AC Drive Packages.
For information on… See page…
Who Should Use this Manual?
What Is Not in this Manual P-1
Manual Conventions P-2
General Precautions P-3
VTAC 9 Catalog Numbers P-4
Who Should Use this Manual?
This manual is intended for qualified personnel. You must be able to
program and operate Adjustable Frequency AC Drive devices. In
addition, you must have an understanding of the parameter settings and
functions.
What Is Not in this Manual
P-1
The VTAC 9 User Manual is designed to provide basic start-up and drive
operation information. For detailed installation information, please refer
to the VTAC 9 Installation Instructions, publication 9VT-IN001.
Manuals are available online at http://www.rockwellautomation.com/vtac/.
Getting Assistance from Rockwell Automation
If you have any questions or problems with the products described in this
instruction manual, contact your authorized Rockwell Automation
VTAC drive representative.
For technical assistance, call 1-440-646-7271.
Before calling, please review the troubleshooting section of this manual
and for additional information visit VTAC Drives online at
http://www.rockwellautomation.com/vtac/.
When you call this number, you will be asked for the drive model
number and this instruction manual number.
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

P-2 Overview
Manual Conventions
• In this manual we refer to the VTAC 9 Adjustable Frequency AC
Drive as; drive, VTAC 9 or VTAC 9 Drive.
• To help differentiate parameter names and LCD display text from
other text, the following conventions will be used:
– Parameter Names will appear in [brackets].
– Display Text will appear in “quotes.” For example: “Enabled.”
• The following words are used throughout the manual to describe an
action:
Word Meaning
Can Possible, able to do something
Cannot Not possible, not able to do something
May Permitted, allowed
Must Unavoidable, you must do this
Shall Required and necessary
Should Recommended
Should Not Not recommended
For example: [DC Bus Voltage].
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
Overview P-3
General Precautions
ATTENTION: This drive contains ESD (Electrostatic Discharge)
sensitive parts and assemblies. Static control precautions are required
!
when installing, testing, servicing or repairing this assembly.
Component damage may result if ESD control procedures are not
followed. If you are not familiar with static control procedures,
reference A-B publication 8000-4.5.2, “Guarding Against Electrostatic
Damage” or any other applicable ESD protection handbook.
ATTENTION: An incorrectly applied or installed drive can result in
component damage or a reduction in product life. Wiring or application
!
errors, such as, undersizing the motor, incorrect or inadequate AC
supply, or excessive ambient temperatures may result in malfunction of
the system.
ATTENTION: Only qualified personnel familiar with adjustable
frequency AC drives and associated machinery should plan or
!
implement the installation, start-up and subsequent maintenance of the
system. Failure to comply may result in personal injury and/or
equipment damage.
ATTENTION: To avoid an electric shock hazard, verify that the
voltage on the bus capacitors has discharged before performing any
!
work on the drive. Measure the DC bus voltage at the +DC terminal of
the Power Terminal Block and the -DC test point (refer to Chapter
locations). The voltage must be zero.
1 for
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
P-4 Overview
VTAC 9 Catalog Numbers
Each VTAC 9 drive can be identified by its catalog number. There are
two distinct catalog numbers associated with each rating: the System
(VTAC Builder/Order) Catalog Number and the Model Number.
System (VTAC Builder/Order) Catalog Number Explanation
The System (VTAC Builder/Order) Catalog Number is used for ordering
and may appear on shipping or order documentation.
9VT
a bcde fg hi j
Code Type
9VT VTAC 9
Code Hp Drive Frame
22B
33B
55C
7 7.5 D
10 10 D
15 15 D
20 20 E
25 25 E
30 30 4
40 40 5
50 50 5
60 60 6
75 75 6
100 100 6
Code Hp Drive Frame
33B
55B
7 7.5 C
10 10 C
15 15 D
20 20 D
25 25 D, 2
30 30 D, 3
40 40 E, 3
50 50 E, 3
60 60 4
75 75 5
100 100 5
125 125 6
150 150 6
200 200 6
5041H0N
–
a
Drive
b1
Horsepower Rating
208V, 60 Hz Input
Code Voltage Phase Precharge
b2
Horsepower Rating
480V, 60 Hz Input
Drive Frame B, C, D, E only.
Position
b3
Horsepower Rating
650V dc Input
Code Hp Drive Frame
75 75 5
100 100 5
125 125 6
150 150 6
200 200 6
c
Voltage Rating
2 208V ac 3 –
4 480V ac 3 –
R 650V dc – Yes
d
Enclosure
Code Enclosure
1 Panel Mount - NEMA Type 1
Flange Mount - Front Chassis
NEMA Type 1, Rear Heatsink
F
Code OIM
H LCD OIM
Code Communications
0 None
UL Type 4X/12 for
Indoor/Outdoor Use
e
OIM
f
Communications
D00
–
g
Control and I/O
Code Control I/O
N Standard 24V B, C, D, E
A Standard 24V 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
h
Option Enclosure
Code Option
D Drive Only
i
Input Power
Code Option
0 None
j
Reactor
Code Type
0 None
Drive
Frame
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
Overview P-5
Model Number Explanation
The Model Number is located on the actual drive nameplate.
9VT 2 01
–
Position
017 H T A N N
abc defg hi
a
Code Type
Code Voltage Phase Precharge
2 208V ac 3 –
4 480V ac 3 –
R 650V dc – Yes
Code Enclosure
1F
Drive Frame B, C, D, E only.
Code Hp Drive Frame
Drive
9VT VTAC 9
b
Voltage Rating
c
Enclosure
01 NEMA Type 1
Flange Mount - Front Chassis
NEMA Type 1, Rear Heatsink
UL Type 4X/12 for
Indoor/Outdoor Use
d1
Horsepower Rating
208V, 60 Hz Input
007 2 B
011 3 B
017 5 C
025 7.5 D
032 10 D
043 15 D
062 20 E
078 25 E
092 30 4
120 40 5
130 50 5
177 60 6
221 75 6
260 100 6
Code Hp Drive Frame
005 3 B
008 5 B
011 7.5 C
014 10 C
022 15 D
027 20 D
034 25 D
034 25 2
040 30 D
040 30 3
052 40 E
052 40 3
065 50 E
065 50 3
077 60 4
096 75 5
125 100 5
156 125 6
180 150 6
248 200 6
Code Hp Drive Frame
096 75 5
125 100 5
156 125 6
180 150 6
248 200 6
d2
Horsepower Rating
480V, 60 Hz Input
d3
Horsepower Rating
650V dc Input
e
Code OIM
Code Brake
Code DC Bus Inductor
Code Communications
Code Control I/O
N Standard 24V B, C, D, E
A Standard 24V 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
OIM
B None
H LCD OIM
f
Braking Transistor
N None
T Braking Transistor
g
DC Bus
N None
Communications
N None
Control and I/O
seYA
h
i
Drive
Frame
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
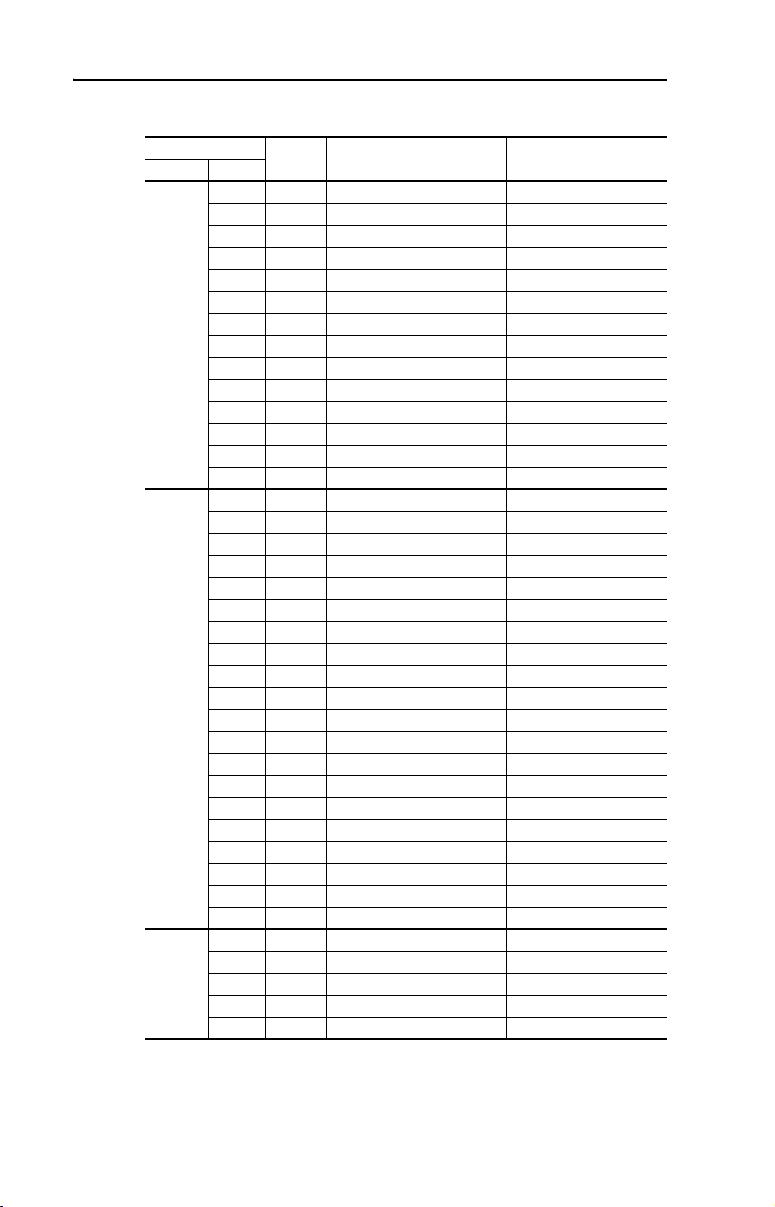
P-6 Overview
VTAC 9 NEMA 1 Catalog Number Explanation
Drive Ratings
208V AC 2 B 9VT201-007HTNNN 9VT-221H0N-D00
480V AC 3 B 9VT401-005HTNNN 9VT-341H0N-D00
650V DC 75 5 9VTR01-096HNANA 9VT-75R1H0A-D00
Frame Model Number
3 B 9VT201-011HTNNN 9VT-321H0N-D00
5 C 9VT201-017HTANN 9VT-521H0N-D00
7.5 D 9VT201-025HTANN 9VT-721H0N-D00
10 D 9VT201-032HTANN 9VT-1021H0N-D00
15 D 9VT201-043HTANN 9VT-1521H0N-D00
20 E 9VT201-062HTANN 9VT-2021H0N-D00
25 E 9VT201-078HTANN 9VT-2521H0N-D00
30 4 9VT201-092HNANA 9VT-3021H0A-D00
40 5 9VT201-120HNANA 9VT-4021H0A-D00
50 5 9VT201-130HNANA 9VT-5021H0A-D00
60 6 9VT201-177HNANA 9VT-6021H0A-D00
75 6 9VT201-221HNANA 9VT-7521H0A-D00
100 6 9VT201-260HNANA 9VT-10021H0A-D00
5 B 9VT401-008HTNNN 9VT-541H0N-D00
7.5 C 9VT401-011HTANN 9VT-741H0N-D00
10 C 9VT401-014HTANN 9VT-1041H0N-D00
15 D 9VT401-022HTANN 9VT-1541H0N-D00
20 D 9VT401-027HTANN 9VT-2041H0N-D00
25 D 9VT401-034HTANN 9VT-2541H0N-D00
25 2 9VT401-034HTANA 9VT-2541H0A-D00
30 D 9VT401-040HTANN 9VT-3041H0N-D00
30 3 9VT401-040HTANA 9VT-3041H0A-D00
40 E 9VT401-052HTANN 9VT-4041H0N-D00
40 3 9VT401-052HTANA 9VT-4041H0A-D00
50 E 9VT401-065HTANN 9VT-5041H0N-D00
50 3 9VT401-065HTANA 9VT-5041H0A-D00
60 4 9VT401-077HNANA 9VT-6041H0A-D00
75 5 9VT401-096HNANA 9VT-7541H0A-D00
100 5 9VT401-125HNANA 9VT-10041H0A-D00
125 6 9VT401-156HNANA 9VT-12541H0A-D00
150 6 9VT401-180HNANA 9VT-15041H0A-D00
200 6 9VT401-248HNANA 9VT-20041H0A-D00
100 5 9VTR01-125HNANA 9VT-100R1H0A-D00
125 6 9VTR01-156HNANA 9VT-125R1H0A-D00
150 6 9VTR01-180HNANA 9VT-150R1H0A-D00
200 6 9VTR01-248HNANA 9VT-200R1H0A-D00
System Number
(Order Number)Vol ta ge H P
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
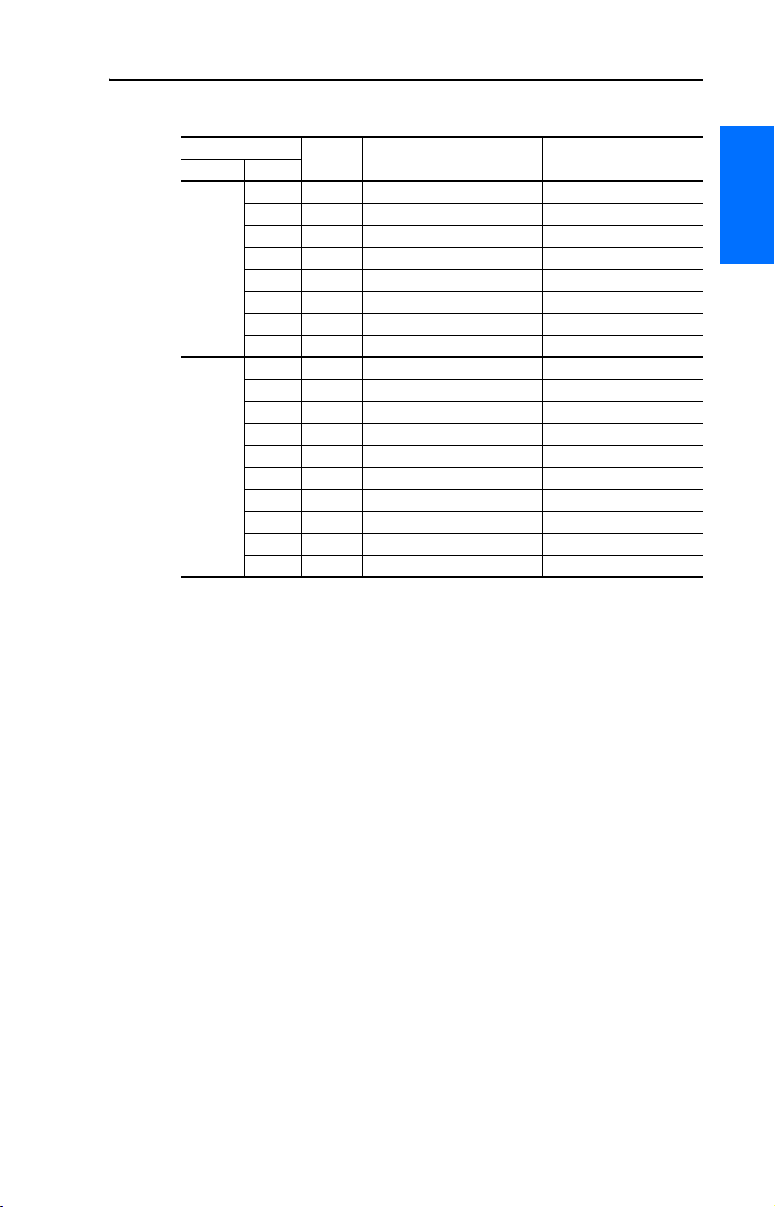
Overview P-7
VTAC 9 Flange Mount Catalog Number Explanation
Drive Ratings
Frame Model Number
208V AC 2 B 9VT21F-007HTNNN 9VT-22FH0N-D00
3 B 9VT21F-011HTNNN 9VT-32FH0N-D00
5 C 9VT21F-017HTANN 9VT-52FH0N-D00
7.5 D 9VT21F-025HTANN 9VT-72FH0N-D00
10 D 9VT21F-032HTANN 9VT-102FH0N-D00
15 D 9VT21F-043HTANN 9VT-152FH0N-D00
20 E 9VT21F-062HTANN 9VT-202FH0N-D00
25 E 9VT21F-078HTANN 9VT-252FH0N-D00
480V AC 3 B 9VT41F-005HTNNN 9VT-34FH0N-D00
5 B 9VT41F-008HTNNN 9VT-54FH0N-D00
7.5 C 9VT41F-011HTANN 9VT-74FH0N-D00
10 C 9VT41F-014HTANN 9VT-104FH0N-D00
15 D 9VT41F-022HTANN 9VT-154FH0N-D00
20 D 9VT41F-027HTANN 9VT-204FH0N-D00
25 D 9VT41F-034HTANN 9VT-254FH0N-D00
30 D 9VT41F-040HTANN 9VT-304FH0N-D00
40 E 9VT41F-052HTANN 9VT-404FH0N-D00
50 E 9VT41F-065HTANN 9VT-504FH0N-D00
System Number
(Order Number)Vol ta ge H P
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

P-8 Overview
Notes:
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
Chapter 1
Installation/Wiring
This chapter provides information on mounting and wiring the VTAC 9
Drive.
For information on… See page For information on… See page
Opening the Cover
Mounting Considerations 1-4
AC Supply Source Considerations 1-5 I/O Wiring 1-21
General Grounding Requirements 1-6 Speed Reference Control 1-35
Fuses and Circuit Breakers 1-7 Auto/Manual Examples 1-36
Power Wiring 1-7 EMC Instructions 1-37
Using Input/Output Contactors 1-16 FCC Instructions 1-40
Most start-up difficulties are the result of incorrect wiring. Every
precaution must be taken to assure that the wiring is done as instructed.
All items must be read and understood before the actual installation
begins.
ATTENTION: The following information is merely a guide for proper
installation. Rockwell Automation, Inc. cannot assume responsibility
!
for the compliance or the noncompliance to any code, national, local or
otherwise for the proper installation of this drive or associated
equipment. A hazard of personal injury and/or equipment damage
exists if codes are ignored during installation.
1-2 Disconnecting MOVs and
Common Mode Capacitors
1-18
Bypass Package (Style B) Drives
Important: If you are intalling a Bypass Package (Style B) Drive, also
refer to VTAC 9 AC Drive Installation Instructions,
publication 9VT-IN001 in addition to this publication.
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
1-2 Installation/Wiring
Opening the Cover
ATTENTION: DC bus capacitors retain hazardous voltages after
input power has been removed. After disconnecting input power, wait
!
five minutes for the DC bus capacitors to discharge and then check the
voltage with a voltmeter to ensure the DC bus capacitors are discharged
before touching any internal components. Failure to observe this
precaution could result in severe bodily injury or loss of life.
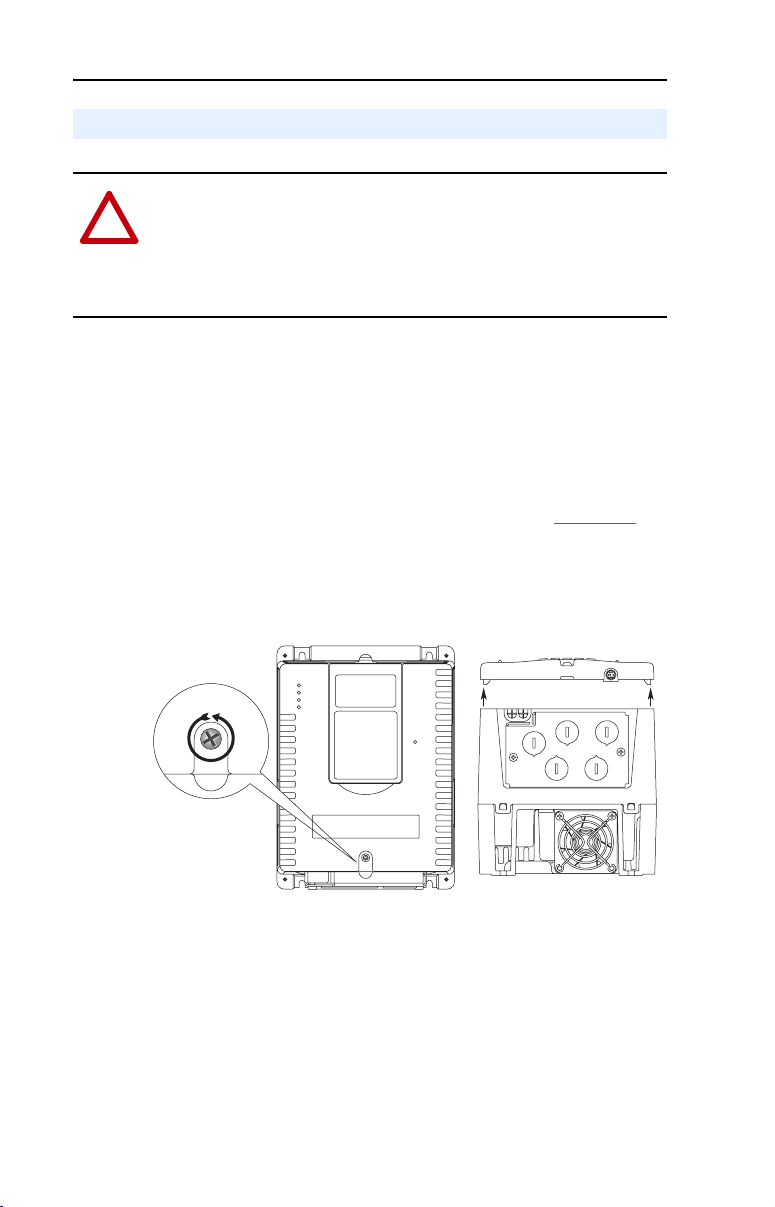
Drive Frames B, C, D, and E have removable covers.
Drive Frames 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 have hinged covers.
Drive Frames B Through E
Follow these steps for Drive Frames B…E.
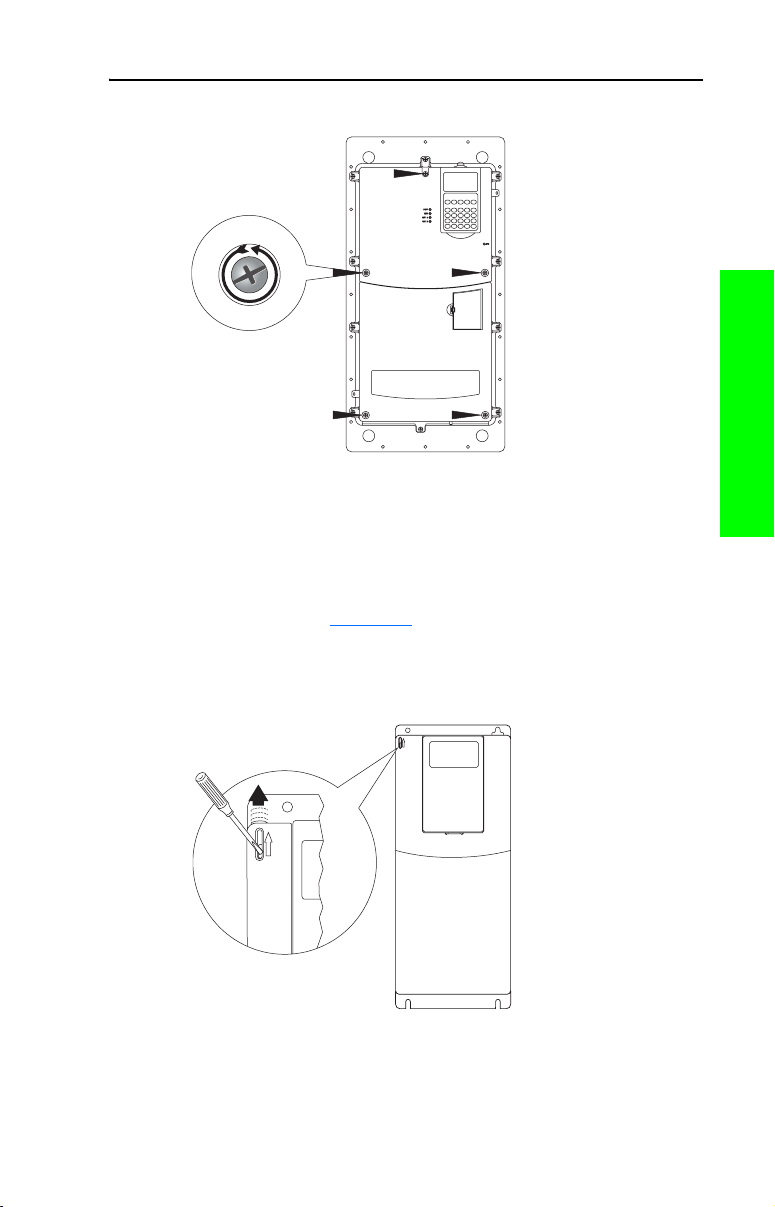
❏ Step 1. Loosen the drive cover screw(s) (refer to Figure 1.1).
❏ Step 2. Lift the cover straight off the drive to avoid damaging
the connector pins.
Figure 1.1 Removing the Drive Cover (Frames B…D)
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
Front View
Bottom View
Installation/Wiring 1-3
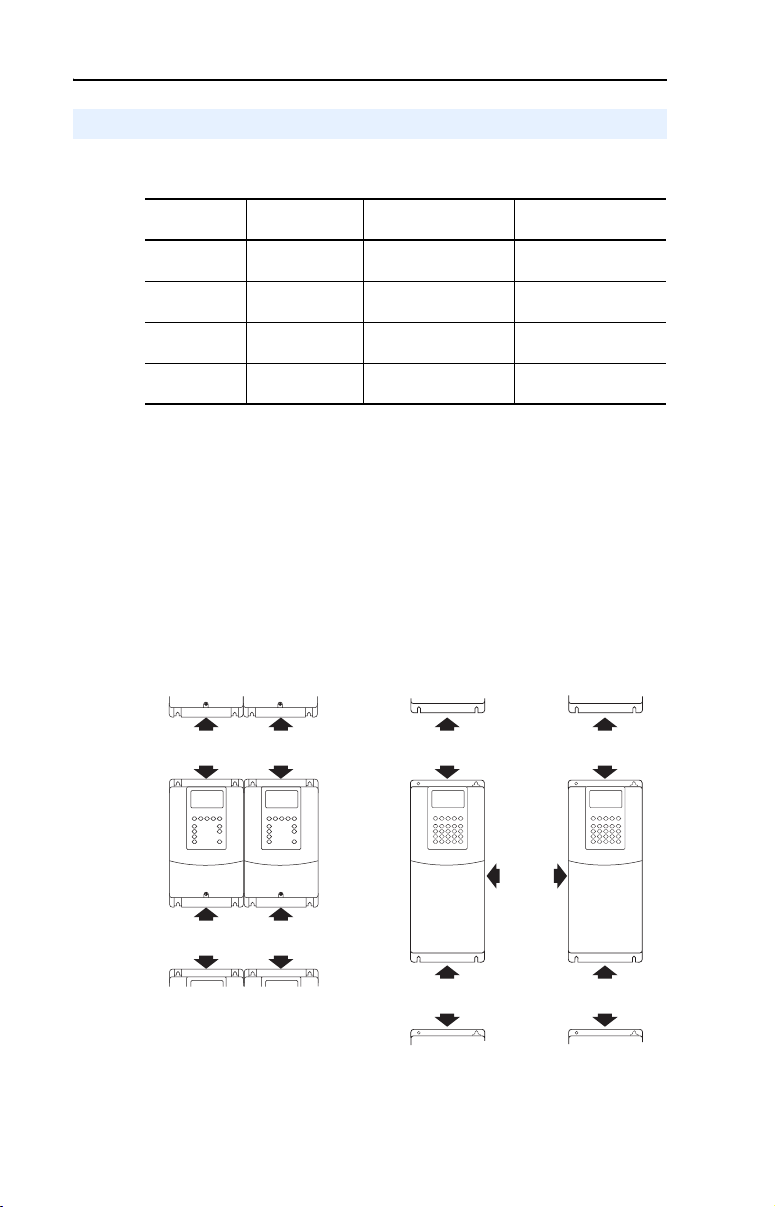
Figure 1.2 Removing the Drive Cover (Frame E)
Drive Frames 2 Through 6
Follow these steps for Drive Frames 2…6.
❏ Step 1. Locate the slot in the upper left hand corner of the drive
(refer to Figure 1.3
).
❏ Step 2. Slide the locking tab up and swing the door open.
Figure 1.3 Opening the Drive Cover (Frames 2…6)
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
1-4 Installation/Wiring
Mounting Considerations
Maximum Surrounding Air Temperature
Drive Frames HP IP20, NEMA Type 1
B, C, D, & E 3…25 @ 208V
2, 3, & 4 30 @ 208V
5 & 6 40…75 @ 208V
6 100 @ 208V
(1)
IP20, NEMA Type 1 general purpose enclosures are intended for indoor use primarily
to provide a degree of protection against contact with equipment. These enclosures
offer no protection against airborne contaminants such as dust or water.
(2)
Removing the adhesive top label from the drive changes the NEMA enclosure rating
from Type 1 to Open Type.
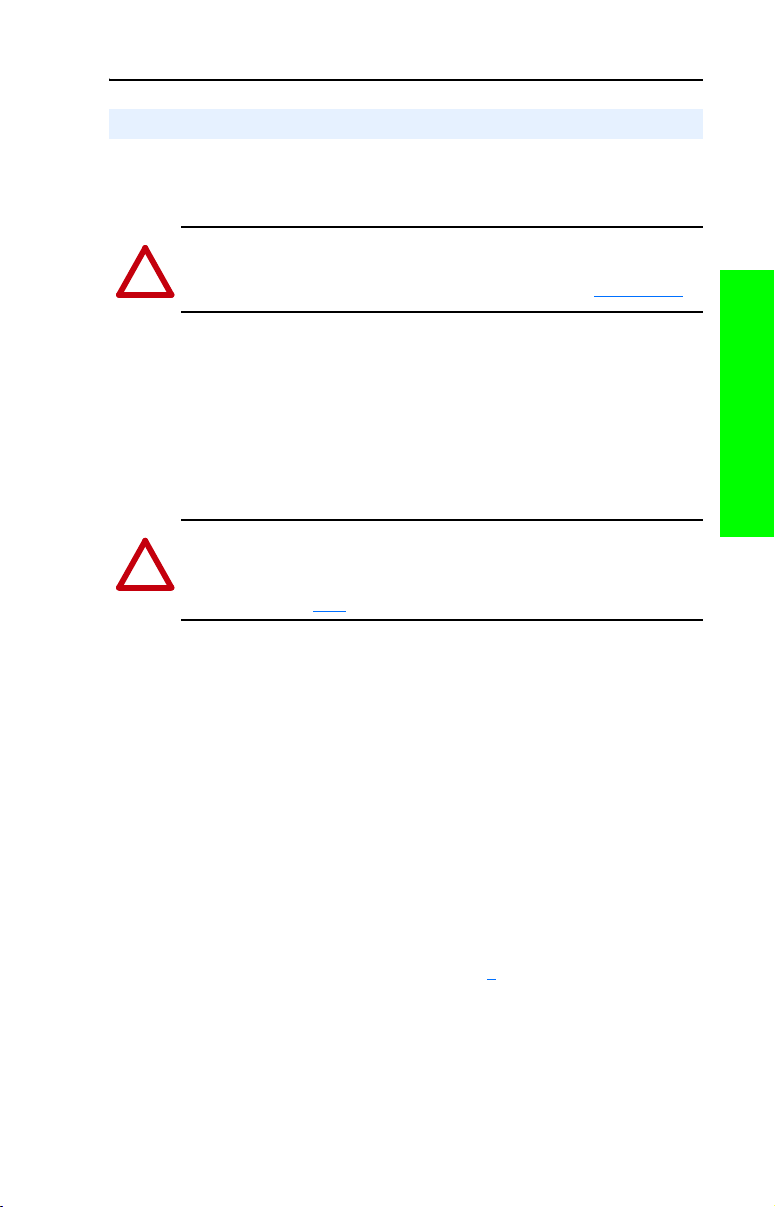
Minimum Mounting Clearances
Specified vertical clearance requirements are intended to be from drive
to drive. Other objects can occupy this space; however, reduced airflow
may cause protection circuits to fault the drive. In addition, inlet air
temperature must not exceed the product specification.
Frames B…E
2…50 @ 460V
25…60 @ 460V
75…150 @ 480V
200 @ 480V
50 degrees C
(122 degrees F)
40 degrees C
(104 degrees F)
50 degrees C
(122 degrees F)
45 degrees C
(113 degrees F)
(1)
IP20, NEMA Type Open
Top Label Removed
NA
50 degrees C
(122 degrees F)
NA
NA
Frames 2…6
(2)
76.2 mm
(3.0 in.)
76.2 mm
(3.0 in.)
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
76.2 mm
(3.0 in.)
76.2 mm
(3.0 in.)
101.6 mm
(4.0 in.)
101.6 mm
(4.0 in.)
101.6 mm
(4.0 in.)
PWR
STS
PORT
50.8 mm
MOD
NET A
NET B
(2.0 in.)
PWR
STS
PORT
MOD
NET A
NET B
101.6 mm
(4.0 in.)
Installation/Wiring 1-5
AC Supply Source Considerations
VTAC 9 drives are suitable for use on a circuit capable of delivering up
to a maximum of 200,000 rms symmetrical amperes, and a maximum of
480 volts.
ATTENTION: To guard against personal injury and/or equipment
damage caused by improper fusing or circuit breaker selection, use only
!
the recommended line fuses/circuit breakers specified in Appendix A
If a system ground fault monitor (RCD) is to be used, only Type B
(adjustable) devices should be used to avoid nuisance tripping.
Unbalanced or Ungrounded Distribution Systems
If phase to ground voltage will exceed 125% of normal line to line
voltage or the supply system is ungrounded, refer to the Wiring and
Grounding Guidelines for PWM AC Drives, publication
DRIVES-IN001.
ATTENTION: VTAC 9 drives contain protective MOVs and common
mode capacitors that are referenced to ground. These devices should be
!
disconnected if the drive is installed on an ungrounded distribution
system. See page 1-18
for jumper locations.
.
Input Power Conditioning
Certain events on the power system supplying a drive can cause
component damage or shortened product life. These conditions are
divided into 2 basic categories:
1. All drives
– The power system has power factor correction capacitors
switched in and out of the system, either by the user or by the
power company.
– The power source has intermittent voltage spikes in excess of
6000 volts. These spikes could be caused by other equipment on
the line or by events such as lightning strikes.
– The power source has frequent interruptions.
2. 5 HP or Less Drives (in addition to “1
– The nearest supply transformer is larger than 100kVA or the
available short circuit (fault) current is greater than 100,000A.
– The impedance in front of the drive is less than 0.5%.
If any or all of these conditions exist, it is recommended that the user
install a minimum amount of impedance between the drive and the
source. This impedance could come from the supply transformer itself,
” above)
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

1-6 Installation/Wiring
the cable between the transformer and drive or an additional transformer
or reactor. The impedance can be calculated using the information
supplied in Wiring and Grounding Guidelines for PWM AC Drives,
publication DRIVES-IN001.
General Grounding Requirements
The drive Safety Ground - PE must be connected to system ground.
Ground impedance must conform to the requirements of national and
local industrial safety regulations and/or electrical codes. The integrity
of all ground connections should be periodically checked.
For installations within a cabinet, a single safety ground point or ground
bus bar connected directly to building steel should be used. All circuits
including the AC input ground conductor should be grounded
independently and directly to this point/bar.
Figure 1.4 Typical Grounding
PE
SHLD
U (T1)
V (T2)
W (T3)
R (L1)
S (L2)
T (L3)
Safety Ground - PE
This is the safety ground for the drive that is required by code. This point
must be connected to adjacent building steel (girder, joist), a floor
ground rod or bus bar (see above). Grounding points must comply with
national and local industrial safety regulations and/or electrical codes.
Shield Termination - SHLD
The Shield terminal (see Figure 1.6 on page 1-11) provides a grounding
point for the motor cable shield. The motor cable shield should be
connected to this terminal on the drive (drive end) and the motor frame
(motor end). A shield terminating cable gland may also be used.
When shielded cable is used for control and signal wiring, the shield
should be grounded at the source end only, not at the drive end.
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
Installation/Wiring 1-7
RFI Filter Grounding
Using an optional RFI filter may result in relatively high ground leakage
currents. Therefore, the filter must only be used in installations with
grounded AC supply systems and be permanently installed and
solidly grounded (bonded) to the building power distribution ground.
Ensure that the incoming supply neutral is solidly connected (bonded) to
the same building power distribution ground. Grounding must not rely
on flexible cables and should not include any form of plug or socket that
would permit inadvertent disconnection. Some local codes may require
redundant ground connections. The integrity of all connections should be
periodically checked. Refer to the instructions supplied with the filter
Fuses and Circuit Breakers
The VTAC 9 can be installed with either input fuses or an input circuit
breaker. National and local industrial safety regulations and/or electrical
codes may determine additional requirements for these installations.
Refer to Appendix A
ATTENTION: The VTAC 9 does not provide branch short circuit
protection. Specifications for the recommended fuse or circuit breaker
!
to provide protection against short circuits are provided in Appendix A
for recommended fuses/circuit breakers.
.
.
Power Wiring
ATTENTION: National Codes and standards (NEC, VDE, BSI etc.)
and local codes outline provisions for safely installing electrical
!
equipment. Installation must comply with specifications regarding wire
types, conductor sizes, branch circuit protection and disconnect
devices. Failure to do so may result in personal injury and/or equipment
damage.
Cable Types Acceptable for 200-600 Volt Installations
A variety of cable types are acceptable for drive installations. For many
installations, unshielded cable is adequate, provided it can be separated
from sensitive circuits. As an approximate guide, allow a spacing of 0.3
meters (1 foot) for every 10 meters (32.8 feet) of length. In all cases,
long parallel runs must be avoided. Do not use cable with an insulation
thickness less than 15 mils (0.4 mm/0.015 in.). Use copper wire only.
Wire gauge requirements and recommendations are based on 75 degree
C. Do not reduce wire gauge when using higher temperature wire.
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

1-8 Installation/Wiring
Unshielded
THHN, THWN or similar wire is acceptable for drive installation in dry
environments provided adequate free air space and/or conduit fill rates
limits are provided. Do not use THHN or similarly coated wire in wet
areas. Any wire chosen must have a minimum insulation thickness of 15
mils and should not have large variations in insulation concentricity.
Shielded/Armored Cable
Shielded cable contains all of the general benefits of multi-conductor
cable with the added benefit of a copper braided shield that can contain
much of the noise generated by a typical AC Drive. Strong consideration
for shielded cable should be given in installations with sensitive
equipment such as weigh scales, capacitive proximity switches and other
devices that may be affected by electrical noise in the distribution
system. Applications with large numbers of drives in a similar location,
imposed EMC regulations or a high degree of communications /
networking are also good candidates for shielded cable.
Shielded cable may also help reduce shaft voltage and induced bearing
currents for some applications. In addition, the increased impedance of
shielded cable may help extend the distance that the motor can be
located from the drive without the addition of motor protective devices
such as terminator networks. Refer to Reflected Wave in “Wiring and
Grounding Guidelines for PWM AC Drives,” publication
DRIVES-IN001A-EN-P.
Consideration should be given to all of the general specifications
dictated by the environment of the installation, including temperature,
flexibility, moisture characteristics and chemical resistance. In addition,
a braided shield should be included and be specified by the cable
manufacturer as having coverage of at least 75%. An additional foil
shield can greatly improve noise containment.
A good example of recommended cable is Belden® 295xx (xx
determines gauge). This cable has four (4) XLPE insulated conductors
with a 100% coverage foil and an 85% coverage copper braided shield
(with drain wire) surrounded by a PVC jacket.
Other types of shielded cable are available, but the selection of these
types may limit the allowable cable length. Particularly, some of the
newer cables twist 4 conductors of THHN wire and wrap them tightly
with a foil shield. This construction can greatly increase the cable
charging current required and reduce the overall drive performance.
Unless specified in the individual distance tables as tested with the drive,
these cables are not recommended and their performance against the lead
length limits supplied is not known.
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
Table 1.A Recommended Shielded Wire
Location Rating/Type Description
Standard
(Option 1)
Standard
(Option 2)
Class I & II;
Division I & II
600V, 90°C (194°F)
XHHW2/RHW-2
Anixter
B209500-B209507,
Belden 29501-29507,
or equivalent
Tray rated 600V, 90°C
(194°F) RHH/RHW-2
Anixter OLF-7xxxxx or
equivalent
Tray rated 600V, 90°C
(194°F) RHH/RHW-2
Anixter 7V-7xxxx-3G
or equivalent
• Four tinned copper conductors with XLPE insulation.
• Copper braid/aluminum foil combination shield and tinned
copper drain wire.
• PVC jacket.
• Three tinned copper conductors with XLPE insulation.
• 5 mil single helical copper tape (25% overlap min.) with three
bare copper grounds in contact with shield.
• PVC jacket.
• Three bare copper conductors with XLPE insulation and
impervious corrugated continuously welded aluminum armor.
• Black sunlight resistant PVC jacket overall.
• Three copper grounds on #10 AWG and smaller.
EMC Compliance
Refer to EMC Instructions
on page 1-37 for details.
Cable Trays and Conduit
If cable trays or large conduits are to be used, refer to guidelines
presented in Wiring and Grounding Guidelines for Pulse Width
Modulated (PWM) AC Drives.
Installation/Wiring 1-9
ATTENTION: To avoid a possible shock hazard caused by induced
voltages, unused wires in the conduit must be grounded at both ends.
!
For the same reason, if a drive sharing a conduit is being serviced or
installed, all drives using this conduit should be disabled. This will help
minimize the possible shock hazard from “cross coupled” motor leads.
Motor Cable Lengths
Typically, for 480V AC systems, motor lead lengths less than 150 meters
(approximately 500 feet) are acceptable if using an inverter rated motor
with 1600 volt insulation. However, if your application dictates longer
lengths, or if you are using a different motor, refer to Wiring and
Grounding Guidelines for Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) AC Drives
(publication VTAC-IN002) for details.
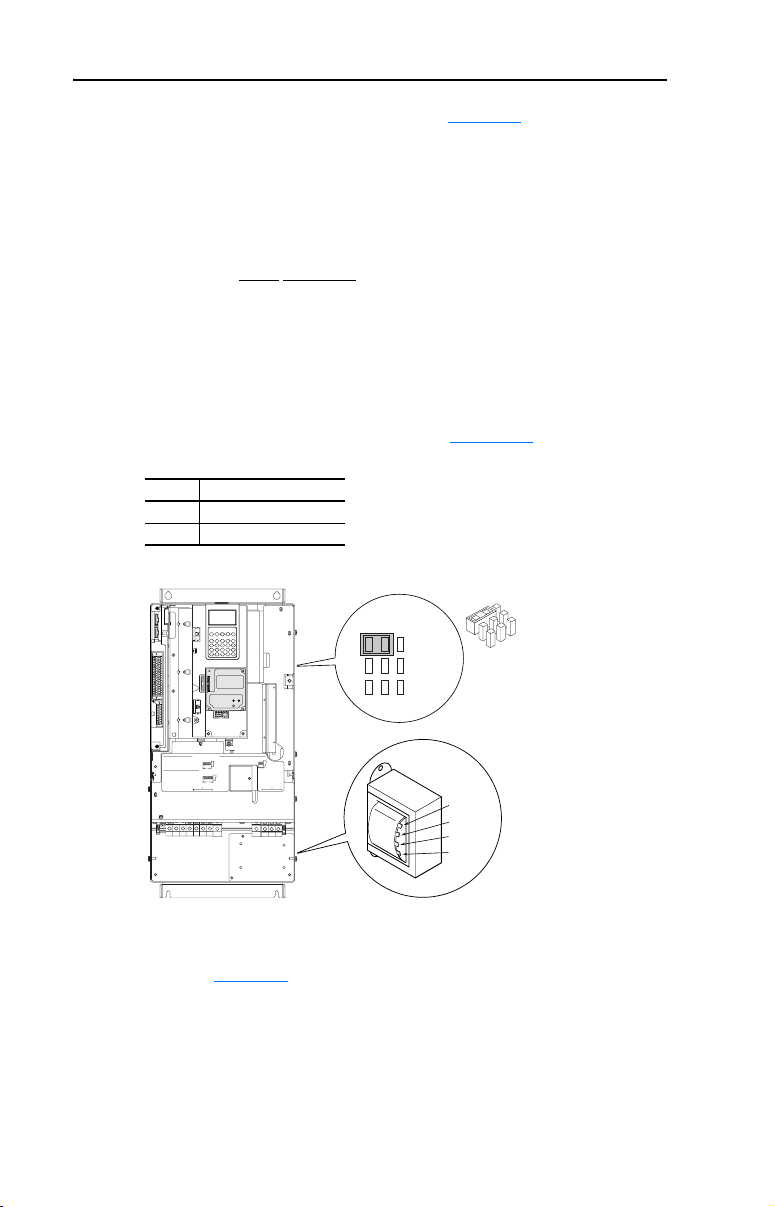
AC Input Phase Selection (Frames 5 & 6 Only)
ATTENTION: To avoid a shock hazard, ensure that all power to the
drive has been removed before performing the following.
!
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
1-10 Installation/Wiring
Moving the “Line Type” jumper shown in Figure 1.5 will allow single or
three-phase operation.
Important: When selecting single-phase operation, input power must
be applied to the R (L1) and S (L2) terminals only.
Selecting/Verifying Fan Voltage (Frames 5 & 6 Only)
Important: Read Attention statement above!
Frames 5 & 6 utilize a transformer to match the input line voltage to the
internal fan voltage. If your line voltage is different than the voltage class
specified on the drive nameplate, it may be necessary to change
transformer taps as shown below. Common Bus (DC input) drives
require user supplied 120 or 240V AC to power the cooling fans. The
power source is connected between “0 VAC” and the terminal
corresponding to your source voltage (see Figure 1.11
Table A Fan VA ratings (DC Input Only)
Frame Rating (120V or 240V)
5 100 VA
6 138 VA
Figure 1.5 Typical Locations - Phase Select Jumper & Transformer (Frame 5 shown)
Optional
Communications
Module
3-PH 1-PH
LINE
TYPE
SPARE 1
SPARE 2
).
Phase Selection
Jumper
POWER TERMINAL RATINGS
WIRE RANGE: 14-1/0 AWG (2.5-35 MM2)
TORQUE: 32 IN-LB (3.6 N-M)
STRIP LENGTH: 0.67 IN (17 MM)
USE 75° C CU WIRE ONLY
17
GROUND TERMINAL RATINGS (PE)
2
)
WIRE RANGE: 6-1/0 AWG (16-35 MM
TORQUE: 44 IN-LB (5 N-M)
STRIP LENGTH: 0.83 IN (21 MM)
21
Frame 6 Transformer Tap Access
The transformer is located behind the Power Terminal Block in the area
shown in Figure 1.5
from the rail. To release terminal block and change tap:
1. Locate the small metal tab at the bottom of the end block.
2. Press the tab in and pull the top of the block out. Repeat for next
block if desired.
3. Select appropriate transformer tap.
4. Replace block(s) in reverse order.
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
300 VDC EXT PWR SPLY TERM (PS+, PS-)
WIRE RANGE: 22-10 AWG (0.5-4 MM
TORQUE: 5.3 IN-LB (0.6 N-M)
STRIP LENGTH: 0.35 IN (9 MM)
2
)
9
INPUT ACOUTPUT
690 Volt Tap
600 Volt Tap
480 Volt Tap
400 Volt Tap
Fan Voltage
. Access is gained by releasing the terminal block
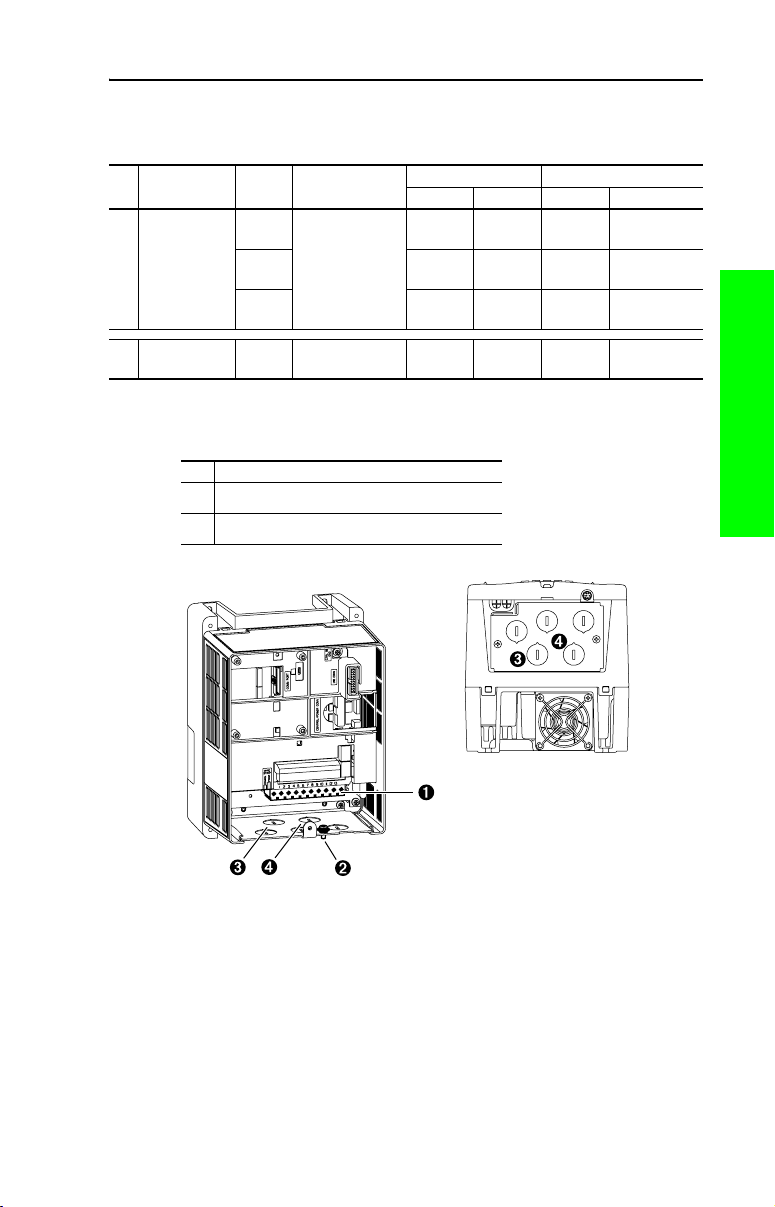
Installation/Wiring 1-11
Power Terminal Block (Frames B…E)
Table 1.B Power Terminal Block Specifications (Frames B…E)
Wire Size Range
No. Name Frame Description
Power Terminal
➊
Block
SHLD terminal B…E Terminating point
➋
(1)
Maximum/minimum sizes that the terminal block will accept - these are not recommendations.
B & C Input power and
motor connections
D 8.4 mm
E 25.0 mm
for wiring shields
Table 1.C Wire Routing Recommendations
No. Description
Suggested entry for incoming line wiring.
➌
Suggested entry for motor wiring.
➍
Figure 1.6 Typical Frame B…E Power Terminal Block Location (B Frame Shown)
Maximum Minimum Maximum Recommended
2
3.5 mm
(12 AWG)
2
(8 AWG)
(3 AWG)
——1.6 N-m
0.3 mm
(22 AWG)
0.8 mm
(18 AWG)
2
2.5 mm
(14 AWG)
(1)
2
2
2
Tor que
0.66 N-m
(5.5 lb.-in.)
1.7 N-m
(15 lb.-in.)
2.71 N-m
(24 lb.-in.)
(14 lb.-in.)
0.6 N-m
(5 lb.-in.)
1.4 N-m
(12 lb.-in.)
2.71 N-m
(24 lb.-in.)
1.6 N-m
(14 lb.-in.)
Cable Entry Plate Removal
If additional wiring access is needed, the Cable Entry Plate on Frames
B…E can be removed. Simply loosen the screws securing the plate to the
heat sink and slide the plate out.
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
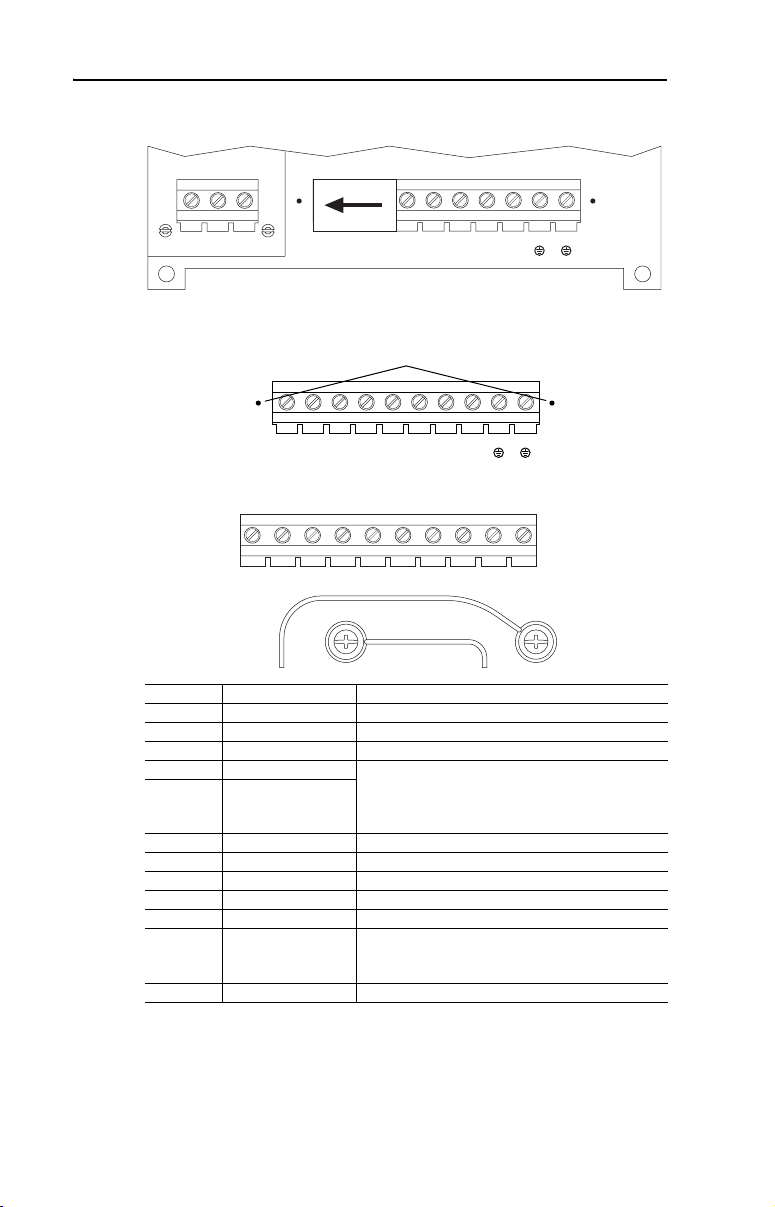
1-12 Installation/Wiring
Figure 1.7 Frame B Power Terminal Blocks
-DC
PE PE
L1RL2SL3
-DC
T
L1RL2SL3TBR1
BR2
+DC
BRKT1UT2VT3W
Figure 1.8 Frames C & D Power Terminal Block and DC Bus Test Points
➊
-DC
L1RL2SL3TBR1
BR2
+DC
BRKT1UT2VT3W
Figure 1.9 Frame E Power Terminal Block
L1RL2SL3T+DC –DC BR1 BR2 T1UT2VT3
M6 M6
Terminal Description Notes
R R (L1) AC Line Input Power
S S (L2) AC Line Input Power
T T (L3) AC Line Input Power
BR1 DC Brake DB Resistor Connection - Important: Do not
connect both an internal and external DB resistor at
BR2 DC Brake
the same time. This may violate the minimum
allowed DB resistance and cause drive damage.
U U (T1) To Motor
V V (T2) To Motor
W W (T3) To Motor
PE PE Ground
PE PE Ground
-DC
PE PE
W
PEPE
➊ Test point on Frames B…D located to the left or
-DC DC Bus (–)
+DC DC Bus (+)
right of the Power Terminal Block. Frame E has a
dedicated terminal.
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
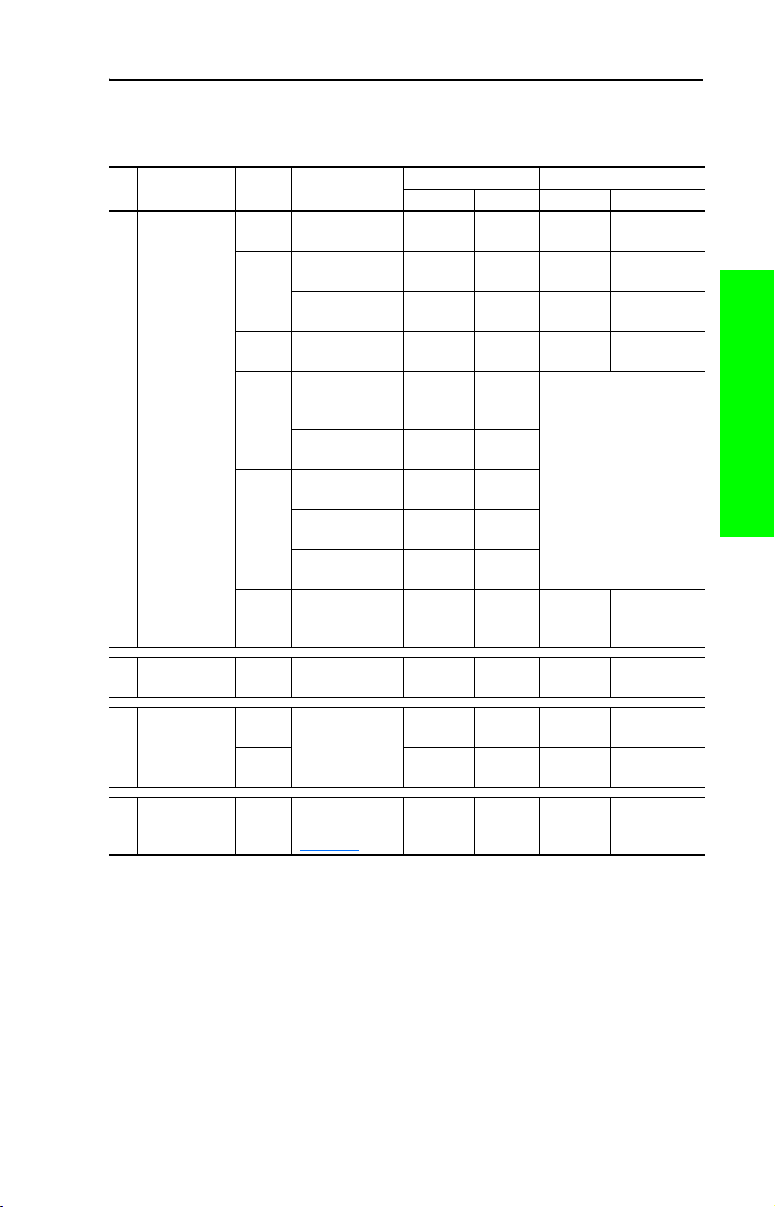
Installation/Wiring 1-13
Power Terminal Block (Frames 2…6)
Table 1.D Power Terminal Block Specifications
(1)
Wire Size Range
No. Name Frame Description
➊ Power Terminal
Block
2 Input power and
motor connections
3 Input power and
motor connections
BR1, 2 terminals 10.0 mm
4 Input power and
motor connections
Input power, BR1,
5
2, DC+, DC– and
40 HP
motor connections
@ 208V,
75 HP
PE 50.0 mm
@ 480V
Input power, DC+,
5
DC– and motor
50 HP
@ 208V,
BR1, 2, terminals 50.0 mm
100 HP
@ 480V
PE 50.0 mm
6 Input power, DC+,
DC–, BR1, 2, PE,
Maximum Minimum Maximum Recommended
2
10.0 mm
(6 AWG)
25.0 mm
(3 AWG)
(6 AWG)
35.0 mm
(1/0 AWG)
50.0 mm
(1/0 AWG)
(1/0 AWG)
70.0 mm
(2/0 AWG)
(1/0 AWG)
(1/0 AWG)
120.0 mm
(4/0 AWG)
0.8 mm
(18 AWG)
2
2.5 mm
(14 AWG)
2
0.8 mm
(18 AWG)
2
10 mm
(8 AWG)
2
2.5 mm
(14 AWG)
2
16.0 mm
(6 AWG)
2
25.0 mm
(4 AWG)
2
2.5 mm
(14 AWG)
2
16.0 mm
(6 AWG)
2
2.5 mm
(14 AWG)
motor connections
SHLD Terminal 2-6 Terminating point
➋
AUX Terminal
➌
Block
Fan Terminal
➍
Block (CB Only)
(1)
Maximum/minimum sizes that the terminal block will accept - these are not recommendations.
(2)
Refer to the terminal block label inside the drive.
(3)
External control power: UL Installation-300V DC, ±10%, Non UL Installation-270-600V DC, ±10%
for wiring shields
2-4 Auxiliary Control
Vol ta ge
(3)
PS+, PS–
5-6 4.0 mm
5-6 User Supplied Fan
Voltage
(page 1-10
)
— — 1.6 N-m
2
1.5 mm
(16 AWG)
(12 AWG)
4.0 mm
(12 AWG)
2
2
0.2 mm
(24 AWG)
0.5 mm
(22 AWG)
0.5 mm
(22 AWG)
2 & 3 Frame - 40 W, 165 mA, 5 Frame - 80 W, 90 mA.
Tor qu e
2
1.7 N-m
(15 lb.-in.)
2
3.6 N-m
(32 lb.-in.)
2
1.7 N-m
(15 lb.-in.)
2
4.0 N-m
(35 lb.-in.)
2
2
2
2
2
2
See Note
6 N-m
(52 lb.-in.)
(14 lb.-in.)
2
——
2
0.6 N-m
(5.3 lb.-in.)
2
0.6 N-m
(5.3 lb.-in.)
1.4 N-m
(12 lb.-in.)
1.8 N-m
(16 lb.-in.)
1.4 N-m
(12 lb.-in.)
4.0 N-m
(35 lb.-in.)
6 N-m
(52 lb.-in.)
1.6 N-m
(14 lb.-in.)
0.6 N-m
(5.3 lb.-in.)
0.6 N-m
(5.3 lb.-in.)
(2)
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
1-14 Installation/Wiring
Figure 1.10 Typical Power Terminal Block Location, Frames 2…6
Communications
➌
BR1 B
AUX IN+ AUX OUT–
SHLD SHLD
Optional
Module
V/T2 W/T3 PE R/L1 S/L2 T/L3
75C Cu Wire
6 AWG [10MM2] Max.
12 IN. LBS.
1.4 N-M
Optional
Communications
Module
WIRE
STRIP
POWER
CONTROL
} TORQUE
PE A
➊
BR1 BR2
75C Cu Wire
6 AWG [10MM2] Max.
12 IN. LBS.
} TORQUE
➌
1.4 N-M
AUX IN
BR1 BR2 DC+ DC- U/T1 V/T2 W/T3 R/L1 S/L2 T/L3
+ –
PE B
WIRE
STRIP
75C Cu Wire
POWER
3 AWG [25MM2] Max.
CONTROL
16 IN. LBS.
} TORQUE
1.8 N-M
➋
➌
➊
➊
POWER TERMINAL RATINGS
WIRE RANGE: 14-1/0 AWG (2.5-35 MM2)
TORQUE: 32 IN-LB (3.6 N-M)
STRIP LENGTH: 0.67 IN (17 MM)
USE 75° C CU WIRE ONLY
GROUND TERMINAL RATINGS (PE)
WIRE RANGE: 6-1/0 AWG (16-35 MM
TORQUE: 44 IN-LB (5 N-M)
STRIP LENGTH: 0.83 IN (21 MM)
17
2
)
21
Frame 2
Optional
Communications
Module
300 VDC EXT PWR SPLY TERM (PS+, PS-)
WIRE RANGE: 22-10 AWG (0.5-4 MM
TORQUE: 5.3 IN-LB (0.6 N-M)
STRIP LENGTH: 0.35 IN (9 MM)
➋
2
)
/
PE
SHLD
Frames 3 & 4
➋
PS–
PS+
22-10
AWG
5.3 IN-LB
WIRE STRIP
BR2
(0.6 N-M)
USE 75°C COPPER WIRE ONLY, TORQUE 52 IN-LB (6 N-M)
USE 75°C
COPPER WIRE
ONLY
TORQUE
52 IN-LB
(6 N-M)
Optional
Communications
Module
BR1 DC+ DC–
➋
9
INPUT ACOUTPUT
➌
➊
INPUTOUTPUT
PE
SHLD
L2L1T3T2T1 L3
Frame 5
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
➍
Common Bus
Drives Only
Frame 6
Terminal Block
Frame
2
Installation/Wiring 1-15
Figure 1.11 Frames 2…6 Power Terminal Block
W
(T3)V(T2)U(T1)
3
+
T
PEDC–DC+BR2BR1
(L3)S(L2)R(L1)
* Note:
Shaded BR1 & BR2 Terminals will only be
present on drives ordered with the Brake Option.
4
DC–DC+BR2BR1
T
(L3)S(L2)R(L1)W(T3)V(T2)U(T1)
208V AC or 480V AC Input 650V DC Input
5 40 HP @ 208V AC
75 HP @ 480V AC
BR1*/
BR2*
DC+
PS–
PS+
50 HP @ 208V AC
100 HP @ 480V AC
BR1*/
BR2*
DC+
PS–
PS+
6 60…100 HP @ 208V AC
W/T3V/T2U/T1DC–DC+
PEPE
75 HP @ 650V DC
PS–
T/L3S/L2R/L1PEPEW/T3V/T2U/T1DC–DC+
PS+
100 HP @ 650V DC
BR2*
PS–
T/L3S/L2R/L1
PS+
125…200 HP @ 650V DC
125…200 HP @ 480V AC
M8 Stud (All Terminals)
PS+
PS–
22-10
AWG
5.3 IN-LB
WIRE STRIP
(0.6 N-M)
USE 75 C COPPER WIRE ONLY, TORQUE 52 IN-LB (6 N-M)
DC–DC+BR1BR2
Max. Lug Width = 25.4 mm (1 in.)
Common Mode Capacitor
& MOV Jumpers
Input Filter Capacitor
PS–
PS+
22-10
AWG
5.3 IN-LB
WIRE STRIP
(0.6 N-M)
BR1*/
BR2*
DC+
BR1*/
DC+
USE 75 C COPPER WIRE ONLY, TORQUE 52 IN-LB (6 N-M)
U/T1DC–DC+
Precharge Resistor Fuse – DCT12-2
(Common Bus Drives w/Precharge Only)
DC–DC+BR1BR2
240
0
PE PEW/T3V/T2
VAC
VAC
120
VAC
240
0
W/T3V/T2U/T1DC–DC+
VAC
VAC
PE
PE
120
Precharge Resistor Fuse – DCT12-2
(Common Bus Drives w/Precharge Only)
VAC
M8 Stud (All Terminals)
Max. Lug Width = 25.4 mm (1 in.)
Precharge Resistor
Fuse
DCT12-2
(Common Bus Drives
w/Precharge Only)
USE 75 C
COPPER WIRE
ONLY
TORQUE
52 IN-LB
(6 N-M)
USE 75 C
COPPER WIRE
ONLY
U
TORQUE
U
T1
VT2W
PE PE
T3
RL1S
L2
INPUTOUTPUT
52 IN-LB
T
L3
(6 N-M)
VT2W
T1
OUTPUT
T3
PE PE
0 VAC
120 VAC
240 VAC
22-10 AWG
5.3 IN-LB
(0.6 N-M)
FAN
1-PHASE
INPUT
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

1-16 Installation/Wiring
Terminal Description Notes
BR1 DC Brake (+) DB Resistor Connection - Important: Only one DB
BR2 DC Brake (–)
DC+ DC Bus (+)
DC– DC Bus (–)
PE PE Ground Refer to Figure 1.10
Motor Ground Refer to Figure 1.10
U U (T1) To motor
V V (T2) To motor
W W (T3) To motor
R R (L1) AC Line Input Power
S S (L2)
T T (L3)
PS+ AUX (+) Auxiliary Control Voltage (see Table 1.D
PS– AUX (–) Auxiliary Control Voltage (see Table 1.D
Using Input/Output Contactors
Input Contactor Precautions
ATTENTION: A contactor or other device that routinely disconnects
and reapplies the AC line to the drive to start and stop the motor can
!
cause drive hardware damage. The drive is designed to use control input
signals that will start and stop the motor. If an input device is used,
operation must not exceed one cycle per minute or drive damage will
occur.
ATTENTION: The drive stop/enable control circuitry includes solid
state components. If hazards due to accidental contact with moving
!
machinery or unintentional flow of liquid, gas or solids exist, an
additional hardwired stop circuit may be required to remove the AC line
to the drive. An auxiliary braking method may be required.
resistor can be used with Frames 2 & 3. Connecting
an internal & external resistor could cause damage.
for location on 3 Frame drives
for location on 3 Frame drives
Three-Phase = R, S & T
Single-Phase = R & S Only
)
)
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

Installation/Wiring 1-17
Output Contactor/Disconnect Precaution
ATTENTION: To guard against drive damage when using output
contactors or disconnects, the following information must be read and
!
understood. One or more output contactors or disconnects may be
installed between the drive and motor(s) for the purpose of
disconnecting or isolating certain motors/loads. If a contactor or
disconnect is opened while the drive is operating, power will be
removed from the respective motor, but the drive will continue to
produce voltage at the output terminals. In addition, reconnecting a
motor to an active drive (by closing the contactor or disconnect) could
produce excessive current that may cause the drive to fault. If any of
these conditions are determined to be undesirable or unsafe, an
auxiliary contact on the output contactor or disconnect should be wired
to a drive digital input that is programmed as “Enable.” This will cause
the drive to execute a coast-to-stop (cease output) whenever an output
contactor or disconnect is opened.
Bypass Contactor Precaution
ATTENTION: An incorrectly applied or installed bypass system can
result in component damage or reduction in product life. The most
!
common causes are:
• Wiring AC line to drive output or control terminals.
• Improper bypass or output circuits not approved by Rockwell
Automation.
• Output circuits which do not connect directly to the motor.
Contact Rockwell Automation for assistance with application or
wiring.
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

1-18 Installation/Wiring
Disconnecting MOVs and Common Mode Capacitors
VTAC 9 drives contain protective MOVs and common mode capacitors
that are referenced to ground. To guard against drive damage, these
devices should be disconnected if the drive is installed on an ungrounded
distribution system where the line-to-ground voltages on any phase
could exceed 125% of the nominal line-to-line voltage. To disconnect
these devices, remove all the jumper(s) shown in the figure and table
below. See Wiring and Grounding Guidelines for PWM AC Drives,
publication DRIVES-IN001 for more information on ungrounded
system installation.
ATTENTION: To avoid an electric shock hazard, verify that the
voltage on the bus capacitors has discharged before removing/installing
!
jumpers. Measure the DC bus voltage at the +DC terminal of the Power
Terminal Block and the -DC test point. The voltage must be zero.
Figure 1.12 Typical Frame B - E Jumper Locations (C Frame Shown)
JP3B
JP3A
Figure 1.13 Phase to Ground MOV Removal (Frame B…E)
R
Three-Phase AC Input
S
T
Jumper
(See Table)
Figure 1.14 Common Mode Capacitors to Ground Removal (Frame B…E)
Converter
Frame Jumper Removes
B JP6 – JP5 Common Mode Capacitors to Ground
C and D JP3B – JP3A Common Mode Capacitors to Ground
E JP3 – JP4 Common Mode Capacitors to Ground
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
123 4
DC+
Common
Mode
Capacitors
DC–
JP3 JP2
Frame Jumper Removes
B, C & D JP3 – JP2 MOV to Ground
E JP2 – JP1 MOV and Line to Line
Capacitors to Ground
Jumper
(See Table)

Installation/Wiring 1-19
Table 1.E Frame 2 - 6 Jumper Removal
Frames Jumper Component Jumper Location No.
2-4 PEA Common Mode Capacitors Jumpers are located above the Power Terminal
PEB MOV’s
5 Wire Common Mode Capacitors Remove the I/O Cassette as described on
MOV’s Note location of the two green/yellow jumper
Input Filter Capacitors
6 Wire Common Mode Capacitors Remove the wire guard from the Power Terminal
MOV’s
Input Filter Capacitors
(1)
Important: Do Not remove jumpers if the distribution system is grounded.
(1)
Block (see Figure 1.15
page 1-28
. The green/yellow jumper is located
on the back of chassis (see Figure 1.15
tion). Disconnect, insulate and secure the wire
to guard against unintentional contact with
chassis or components.
wires next to the Power Terminal Block (Figure
1.15). Disconnect, insulate and secure the wires
to guard against unintentional contact with
chassis or components.
Block. Disconnect the three green/yellow wires
from the two “PE” terminals shown in Figure
1.11. Insulate/secure the wires to guard against
unintentional contact with chassis or components.
).
for loca-
➊
➋
➌
➍
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

1-20 Installation/Wiring
Figure 1.15 Typical Frame 2 - 5 Jumper Locations (see Table 1.E for description)
➋
75C Cu Wire
6 AWG [10MM2] Max.
12 IN. LBS.
} TORQUE
1.4 N-M
PE R/L1 S/L2 T/L3
PE 4
DC FILTER CAP-PE JMPR
BR1 BR2 DC+ DC- U/T1 V/T2 W/T3
AUX IN+ AUX OUT–
➊
PE 3
SHLD SHLD
Frame 2
➊
PE A
BR1 BR2
75C Cu Wire
6 AWG [10MM2] Max.
12 IN. LBS.
} TORQUE
1.4 N-M
AUX IN
BR1 BR2 DC+ DC- U/T1 V/T2 W/T3 R/L1 S/L2 T/L3
+ –
➋
75C Cu Wire
3 AWG [25MM2] Max.
16 IN. LBS.
1.8 N-M
} TORQUE
PE 1
PE 2
MOV-PE JMPR
WIRE
STRIP
POWER
CONTROL
➌
PE B
Optional
Communications
WIRE
STRIP
POWER
CONTROL
Module
PE
SHLD
SHLD
Frames 3 & 4
Important: Do Not discard or replace grounding hardware.
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
➍
POWER TERMINAL RATINGS
WIRE RANGE: 14-1/0 AWG (2.5-35 MM2)
TORQUE: 32 IN-LB (3.6 N-M)
STRIP LENGTH: 0.67 IN (17 MM)
USE 75° C CU WIRE ONLY
GROUND TERMINAL RATINGS (PE)
WIRE RANGE: 6-1/0 AWG (16-35 MM
TORQUE: 44 IN-LB (5 N-M)
STRIP LENGTH: 0.83 IN (21 MM)
17
2
)
21
Frame 5
300 VDC EXT PWR SPLY TERM (PS+, PS-)
WIRE RANGE: 22-10 AWG (0.5-4 MM
TORQUE: 5.3 IN-LB (0.6 N-M)
STRIP LENGTH: 0.35 IN (9 MM)
2
)
9
INPUT ACOUTPUT

Installation/Wiring 1-21
I/O Wiring
Important points to remember about I/O wiring:
• Use copper wire only. Wire gauge requirements and
recommendations are based on 75 degree C. Do not reduce wire
gauge when using higher temperature wire.
• Wire with an insulation rating of 600V or greater is recommended.
• Control and signal wires should be separated from power wires by at
least 0.3 meters (1 foot).
Important: I/O terminals labeled “(–)” or “Common” are
not
referenced to earth ground and are designed to greatly
reduce common mode interference. Grounding these
terminals can cause signal noise.
ATTENTION: Configuring an analog input for 0-20mA operation and
driving it from a voltage source could cause component damage. Verify
!
proper configuration prior to applying input signals.
ATTENTION: Hazard of personal injury or equipment damage exists
when using bipolar input sources. Noise and drift in sensitive input
!
circuits can cause unpredictable changes in motor speed and direction.
Use speed command parameters to help reduce input source sensitivity.
Signal and Control Wire Types
Table 1.F Recommended Signal Wire
Signal Type/
Where Used
Analog I/O & PTC 8760/9460 0.750 mm2(18AWG), twisted pair, 100%
Remote Pot 8770 0.750 mm2(18AWG), 3 cond., shielded
(1)
If the wires are short and contained within a cabinet which has no sensitive circuits, the use of
shielded wire may not be necessary, but is always recommended.
Unshielded Per US NEC or applicable national
Shielded Multi-conductor shielded cable
Belden Wire Type(s)
(or equivalent) Description
shield with drain
Table 1.G Recommended Control Wire for Digital I/O
Wire Type(s) Description
or local code
such as Belden 8770(or equiv.)
0.750 mm
conductor, shielded.
(1)
—300V,
2
(18AWG), 3
Minimum
Insulation Rating
60 degrees C
(140 degrees F)
Min. Insulation
Rating
300V,
75-90° C
(167-194° F)
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

1-22 Installation/Wiring
I/O Terminal Block (Frames B…E)
Figure 1.16 Typical Frame B…E I/O Terminal Block Location (B Frame Shown)
Table 1.H I/O Terminal Block Specifications
Wire Size Range
No. Name Description
I/O Terminal
➊
Block
(1)
Maximum / minimum that the terminal block will accept - these are not recommendations.
Signal & control
connections
Maximum Minimum Maximum Recommended
2
1.5 mm
(16 AWG)
(1)
Torque
0.05 mm
(30 AWG)
2
0.55 N-m
(4.9 lb.-in.)
0.5 N-m
(4.4 lb.-in.)
Table 1.I Wire Routing Recommendations
No. Description
Suggested entry for communication wiring.
➋
Suggested entry for I/O and control wiring.
➌
Figure 1.17 I/O Terminal Positions (Frames B…E)
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
14
1
26
13

Suggested Analog Signal Wiring
Installation/Wiring 1-23
What is your Analog
signal?
Use this Analog Input
(1)
What is your frame size?
Use these terminals for
wiring
(1)
If a different Analog Input selection is required:
Current 4-20 mA Voltage 0-10V
Frame B…E
Analog In 1 Analog In 2
(2)
Frame 2…6
(2)
Frame B…E
(2)
(3)
Frame 2…6
TB 16 & 17 TB 17 & 18 TB 18 & 19 TB 3 & 4
– Parameter 320 bit values will have to be configured
– Parameters 325 and 326 or 322 and 323 will have to be configured
See Chapter 3 for details on programming parameters.
(2)
Frame size can be determined by the number of terminals on the I/O Terminal Block:
– Frames B…E have 26 I/O terminals
– Frames 2…6 have 32 I/O terminals
(3)
If Analog Input 2 is used for speed reference, parameter 90 will have to be programmed to select
option 2 “Analog In 2”.
Bypass Package (Style B) Drives
(2)
Important: If you are intalling a Bypass Package (Style B) Drive, also
refer to VTAC 9 AC Drive Installation Instructions,
publication 9VT-IN001 in addition to this publication.
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

1-24 Installation/Wiring
Interlock Connection Considerations
A “Freeze/Fire Stat” input is typically connected to I/O Terminal 3 on
drives with 26 terminals (Frames B…E) or I/O Terminal 29 on drives
with 32 terminals (Frames 2…6). Factory default parameter settings
cause the drive to fault on an F2 “Function Loss” if the “Freeze/Fire
Stat” input opens or if there is a momentary loss of power to the drive. A
manual reset to restart is required once the input closes or power is
restored.
To restart the drive automatically when the “Freeze/Fire Stat” input
closes or power is restored, the F2 “Function Loss” fault can be
automatically cleared by one of the following methods.
1. Jumper I/O Terminals 2 (Clear Faults) and 3 (Function Loss) on
drives with 26 terminals (Frames B…E) or jumper I/O Terminals 28
(Clear Faults) and 29 (Function Loss) on drives with 32 terminals
(Frames 2…6).
2. Set parameter 363 [Digital In3 Sel] to option 1 “Enable” which will
start the drive on an enable command if the “Freeze/Fire Stat” input
is closed and a Run or Start digital input is present.
If a purge command is intended to follow a “Freeze/Fire Stat” input trip/
reset without requiring a manual reset to restart, the above alternate
customer connections should be used.
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

Installation/Wiring 1-25
Table 1.J I/O Terminal Designations (Frames B…E)
Important: Frame B…E drives can be identified by a horizontally oriented I/O
Terminal Block which has 26 terminals. See Figure 1.16
.
No. Signal
1 Digital In 1
Run
2 Digital In 2 Clear Faults
3 D igital In 3 Function Loss
4 Digital In 4 Enable
5 Digital In 5 OIM Control
6 Digital In 6 Purge
Description
Factory
Default
11.2 mA @ 24V DC
19.2V minimum on state
3.2V maximum off state
Important: Use only 24V DC, not suitable for 115V
AC circuitry.
Inputs can be wired as sink or source.
7 24V Common – Drive supplied power for Digital In1-6 inputs.
8 Digital In Common –
9 +24V DC –
See examples on page 1-26
150mA maximum load.
.
10 +10V Pot Reference – 2 k ohm minimum load.
(1)
11 Digital Out 1 – N.O.
12 Digital Out 1 Common
13 Digital Out 1 – N.C.
14 Analog In 1 (– Volts)
15 Analog In 1 (+ Volts)
16 Analog In 1 (– Current) Non-isolated, 4-20mA, 10 bit, 100 ohm input
17 Analog In 1 (+ Current)
18 Analog In 2 (– Volts)
19 Analog In 2 (+ Volts)
20 Analog In 2 (– Current) Isolated, 4-20mA, 10 bit & sign, 100 ohm input
21 Analog In 2 (+ Current)
22 10V Pot Common
Analog Out (– Volts)
23 Analog Out (+ Volts)
NOT Fault Max Resistive Load
250V AC / 30V DC
50 VA / 60 Watts
(1)
Faul t
(2)
Voltage –
Minimum DC Load
10 µA, 10 mV DC
Non-isolated, 0 to +10V, 10 bit, 100k ohm input
impedance.
Reads
value at 14
& 15
(2)
Voltage –
Reads
impedance.
Isolated, bipolar, differential, 0 to +10V unipolar (10
bit) or ±10V bipolar (10 bit & sign), 100k ohm input
impedance.
value at 18
& 19
(2)
Output
Freq
impedance.
0 to +10V, 10 bit, 10k ohm (2k ohm minimum) load.
Referenced to chassis ground.
Common if internal 10V supply (terminal 10) is
Max Inductive Load
250V AC / 30V DC
25 VA / 30 Watts
(3)
(3)
(4)
(4)
used.
24 Digital Out 2 – N.O.
(1)
Run See description at No.s 11-13. 380 -
25 Digital Out 2 Common
(1)
26 Digital Out 2 – N.C.
(1)
Contacts shown in unpowered state. Any relay programmed as Fault or Alarm will energize (pick
NOT Run
up) when power is applied to drive and deenergize (drop out) when fault or alarm exists. Relays
selected for other functions will energize only when that condition exists and will deenergize when
condition is removed.
(2)
These inputs/outputs are dependent on a number of parameters. See “Related Parameters.”
(3)
Differential Isolation - External source must be less than 10V with respect to PE.
(4)
Differential Isolation - External source must be maintained at less than 160V with respect to PE.
Input provides high common mode immunity.
Related
361 366
380 387
320 327
340 344
387
Param.
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

1-26 Installation/Wiring
I/O Wiring Examples (Frames B…E)
Input/Output Connection Example Required Parameter Settings
Potentiometer
Unipolar Speed
Reference
10k Ohm Pot.
Recommended
(2k Ohm minimum)
Analog Input Unipolar
Speed Reference
0 to +10V Input
Analog Input Unipolar
Speed Reference
4-20 mA Input
Analog Output
Unipolar
0 to +10V Output. Can
Drive a 2k Ohm load (25
mA short circuit limit)
2 Wire Control
Non-Reversing
10
Common
+
Common
+
+–
Internal Supply Set Digital Input 1:
1
Stop-Run
7
8
9
Select Speed Reference source:
18
Param. 090 = 2 “Analog In 2”
19
Configure Input for Voltage
Param. 320, Bit #1 = 0 “Voltage”
22
Adjust Scaling:
Param. 091, 092, 325, 326
Check Results:
Param. 017
Select Speed Reference source:
18
Param. 090 = 2 “Analog In 2”
19
Configure Input for Voltage
Param. 320, Bit #1 = 0 “Voltage”
Adjust Scaling:
Param. 091, 092, 325, 326
Check Results:
Param. 017
Select Speed Reference source:
Param. 090 = 1 “Analog In 1”
16
Configure Input for Current:
17
Param. 320, Bit #0 = 1 “Current”
Adjust Scaling:
Param. 091, 092, 322, 323
Check Results:
Param. 016
Select Source Value:
Param. 342
Adjust Scaling:
Param. 343, 344
22
23
Param. 361 = 1 “Run”
3 Wire Control Internal Supply Set Digital Input 1:
Param. 361 = 4 “Stop – CF”
Set Digital Input 2:
Param. 362 = 5 “Start”
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
Stop
Start
1
2
7
8
9

Installation/Wiring 1-27
Input/Output Connection Example Required Parameter Settings
3 Wire Control External Supply Set Digital Input 1:
1
Stop
2
Start
8
+24V Common
Digital Output
Form C Relays
Energized in Normal
State.
or
Power
Source
11
12
13
24
25
26
Enable Input
Shown in enabled state.
4
Param. 361 = 4 “Stop – CF”
Set Digital Input 2:
Param. 362 = 5 “Start”
Select Source:
Param. 380, 384
NOT Fault
Fault
Run
NOT Run
Configure with parameter 364
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

1-28 Installation/Wiring
The I/O Control Cassette (Frames 2…6)
Figure 1.18 shows the I/O Control Cassette and terminal block locations.
The cassette provides a mounting point for the various VTAC 9 I/O
options. To remove the cassette, follow the steps below. Cassette removal
will be similar for all frames (0 Frame drive shown).
Step Description
A
Disconnect the two cable connectors shown in Figure 1.18
B
Loosen the two screw latches shown in Figure 1.18
Slide the cassette out.
C
D
Remove screws securing cassette cover to gain access to the boards.
Figure 1.18 Typical Cassette & I/O Terminal Blocks (Frames 2…6)
.
.
C
➋
B
B
Pin 1
➊
A
D
Detail
BR1
BR
2
D
C
+
DC-
P
E
U
/T
1
V
/T
2
W
/T
3
R
/L
1
L
2
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

Installation/Wiring 1-29
I/O Terminal Blocks
Table 1.K I/O Terminal Block Specifications
Wire Size Range
No. Name Description
I/O Cassette Removable I/O Cassette
➊
I/O Terminal
➋
Block
(1)
Maximum/minimum that the terminal block will accept - these are not recommendations.
Signal & control
connections
Maximum Minimum Maximum Recommended
2
2.1 mm
(14 AWG)
Figure 1.19 I/O Terminal Positions (Frames 2…6)
1
16
32
(1)
0.30 mm
(22 AWG)
Torque
2
0.6 N-m
(5.2 lb.-in.)
0.6 N-m
(5.2 lb.-in.)
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
1-30 Installation/Wiring
Suggested Analog Signal Wiring
What is your Analog
signal?
Use this Analog Input
(1)
What is your frame size?
Use these terminals for
wiring
(1)
If a different Analog Input selection is required:
Current 4-20 mA Voltage 0-10V
Analog In 1 Analog In 2
Frame B…E
(2)
Frame 2…6
(2)
Frame B…E
(2)
Frame 2…6
TB 16 & 17 TB 17 & 18 TB 18 & 19 TB 3 & 4
– Parameter 320 bit values will have to be configured
– Parameters 325 and 326 or 322 and 323 will have to be configured
See Chapter 3 for details on programming parameters.
(2)
Frame size can be determined by the number of terminals on the I/O Terminal Block:
– Frames B…E have 26 I/O terminals
– Frames 2…6 have 32 I/O terminals
(3)
If Analog Input 2 is used for speed reference, parameter 90 will have to be programmed to select
option 2 “Analog In 2”.
Bypass Package (Style B) Drives
(3)
(2)
Important: If you are intalling a Bypass Package (Style B) Drive, also
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
refer to VTAC 9 AC Drive Installation Instructions,
publication 9VT-IN001 in addition to this publication.

Installation/Wiring 1-31
Interlock Connection Considerations
A “Freeze/Fire Stat” input is typically connected to I/O Terminal 3 on
drives with 26 terminals (Frames B…E) or I/O Terminal 29 on drives
with 32 terminals (Frames 2…6). Factory default parameter settings
cause the drive to fault on an F2 “Function Loss” if the “Freeze/Fire
Stat” input opens or if there is a momentary loss of power to the drive. A
manual reset to restart is required once the input closes or power is
restored.
To restart the drive automatically when the “Freeze/Fire Stat” input
closes or power is restored, the F2 “Function Loss” fault can be
automatically cleared by one of the following methods.
1. Jumper I/O Terminals 2 (Clear Faults) and 3 (Function Loss) on
drives with 26 terminals (Frames B…E) or jumper I/O Terminals 28
(Clear Faults) and 29 (Function Loss) on drives with 32 terminals
(Frames 2…6).
2. Set parameter 363 [Digital In3 Sel] to option 1 “Enable” which will
start the drive on an enable command if the “Freeze/Fire Stat” input
is closed and a Run or Start digital input is present.
If a purge command is intended to follow a “Freeze/Fire Stat” input trip/
reset without requiring a manual reset to restart, the above alternate
customer connections should be used.
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

1-32 Installation/Wiring
Table 1.L I/O Terminal Designations (Frames 2…6)
Important: Frame 2…6 drives can be identified by a vertically oriented I/O
Terminal Block which has 32 terminals. See Figure 1.19
.
No. Signal
1 Anlg Volts In 1 (–)
(2)
2 Anlg Volts In 1 (+)
1
3 Anlg Volts In 2 (–)
4 Anlg Volts In 2 (+)
5 Pot Common – For (+) and (–) 10V pot references.
6 Anlg Volts Out 1 (–)
7 Anlg Volts Out 1 (+)
8 Anlg Current Out 1 (–)
(2)
(2)
(2)
9 Anlg Current Out 1 (+)
10
Reserved for Future Use
11 Digital Out 1 – N.C.
6
32
12 Digital Out 1 Common
13 Digital Out 1 – N.O.
14 Digital Out 2 – N.C.
15 Digital Out 2 Common
16 Digital Out 2 – N.O.
17 Anlg Current In 1 (–)
18 Anlg Current In 1 (+)
19 Anlg Current In 2 (–)
(1)
Fault Max. Resistive Load:
(1)
NOT Fault
(1)
NOT Run
(1)
Run
(2)
(2)
20 Anlg Current In 2 (+)
Description
Factory
Default
Isolated
(3)
, bipolar, differential,
±10V, 11 bit & sign, 88k ohm input
impedance.
(4)
Isolated
, bipolar, differential,
±10V, 11 bit & sign, 88k ohm input
impedance.
Bipolar, ±10V, 11 bit & sign, 2k ohm
minimum load.
4-20mA, 11 bit & sign, 400 ohm
maximum load.
240V AC/30V DC – 1200VA, 150W
Max. Current: 5A, Min. Load: 10mA
Max. Inductive Load:
240V AC/30V DC – 840VA, 105W
Max. Current: 3.5A, Min. Load: 10mA
(3)
Isolated
124 ohm input
Isolated
,
4-20mA
impedance.
(4)
, 4-20mA, 11 bit & sign,
124 ohm input impedance.
, 11 bit & sign,
21 –10V Pot Reference – 2k ohm minimum.
22 +10V Pot Reference –
23
Reserved for Future Use
24 +24V DC
25 Digital In Common –
26 24V Common
(5)
– Drive supplied logic input power.
(5)
– Common for internal power supply.
27 Digital In 1 Run Opto isolated
28 Digital In 2 Clear Faults
29 D igital In 3 Function Loss
30 Digital In 4 Enable
Low State: less than 5V AC/DC
High State: greater than 20V AC/DC
11.2 mA DC
31 Digital In 5 OIM Control
32 Digital In 6 Purge
(1)
Contacts in unpowered state. Any relay programmed as Fault or Alarm will energize (pick up) when
power is applied to drive and deenergize (drop out) when a fault or alarm exists. Relays selected
for other functions will energize only when that condition exists and will deenergize when condition
is removed.
(2)
These inputs/outputs are dependant on a number of parameters. See “Related Parameters.”
(3)
Differential Isolation - External source must be maintained at less than 160V with respect to PE.
Input provides high common mode immunity.
(4)
Differential Isolation - External source must be less than 10V with respect to PE.
(5)
150mA maximum Load.
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
Related
Param.
320 327
340 344
380 387
320 327
(5)
361 366

Installation/Wiring 1-33
I/O Wiring Examples (Frames 2…6)
Input/Output Connection Example Required Parameter Changes
Potentiometer
Unipolar Speed
Reference
(1)
10k Ohm Pot.
Recommended
(2k Ohm Minimum)
Analog Voltage
Input Unipolar
Speed Reference
0 to +10V Input
Analog Current
Input Unipolar
Speed Reference
4-20 mA Input
Analog Output
+10V Unipolar
(shown)
4-20 mA Unipolar
(use term. 8 & 9)
2-Wire Control
Non-Reversing
(2)
24V DC internal
supply
Common
+
+–
17
18
24
25
26
27
3
4
5
3
4
6
7
Stop-Run
Common
+
• Select Speed Reference Source:
Parameter 090 = 2 “Analog In 2”
• Configure Input for Voltage:
Parameter 320, Bit 1 = 0 “Voltage”
• Adjust Scaling:
22
Parameters 91/92 and 325/326
• View Results:
Parameter 002
• Select Speed Reference Source:
Parameter 090 = 2 “Analog In 2”
• Configure Input for Voltage:
Parameter 320, Bit 1 = 0 “Voltage”
• Adjust Scaling:
Parameters 91/92 and 325/326
• Check results:
Parameter 017
• Select Speed Reference Source:
Parameter 090 = 1 “Analog In 1”
• Configure Input for Current:
Parameter 320, Bit 0 = 1 “Current”
• Adjust Scaling:
Parameters 91/92 and 325/326
• Check Results:
Parameter 017
• Configure with Parameter 340
• Select Source Value:
Parameter 342, [Analog Out1 Sel]
• Adjust Scaling:
Parameters 343/344
Set Digital Input 1:
Parameter 361 = 1 “Run”
(1)
Refer to the Attention statement on page 1-21 for important bipolar wiring information.
(2)
Important: Programming inputs for 2 wire control deactivates all OIM Start buttons.
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

1-34 Installation/Wiring
/
I/O Wiring Examples (continued)
Input/Output Connection Example Required Parameter Changes
3-Wire Control
Internal supply
3-Wire Control
External supply
(I/O Board dependent).
Requires 3-wire functions
only ([Digital In1 Sel]).
Using 2-wire selections will
cause a type 2 alarm (page
4-10
).
Digital Output
Relays shown in powered
state with drive faulted. See
page 1-32
.
Power
or
Source
11
12
13
14
15
16
24
25
26
Stop
27
28
Start
Neutral/
Common
25
27
28
Stop
Start
115V
+24V
Enable Input • Configure with parameter 364
30
• Set Digital Input #1:
Param. 361 = 4 “Stop – CF”
• Set Digital Input #2:
Param. 362 = 5 “Start”
• Set Digital Input #1:
Param. 361 = 4 “Stop – CF”
• Set Digital Input #2:
Param. 362 = 5 “Start”
• Select Source to Activate:
Parameters 380/384
Fault
NOT Fault
NOT Run
Run
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

Installation/Wiring 1-35
Speed Reference Control
“Auto” Speed Sources
The drive speed command can be obtained from a number of different
sources. The source is determined by drive programming and the
condition of the Speed Select digital inputs, Auto/Manual digital inputs
or reference select bits of a command word.
The default source for a command reference (all speed select inputs open
or not programmed) is the selection programmed in [Speed Ref A Sel].
If any of the speed select inputs are closed, the drive will use other
parameters as the speed command source.
“Manual” Speed Sources
The manual source for speed command to the drive is either the OIM
requesting manual control or the control terminal block (analog input) if
a digital input is programmed to “Auto/Manual”.
Changing Speed Sources
The selection of the active Speed Reference can be made through digital
inputs, DPI command or Hand/Auto OIM operation.
Figure 1.20 Speed Reference Selection Chart
= Default
Auto Speed Ref Options
Speed Ref A Sel, Parameter 090
Preset Speed 1, Parameter 101
Preset Speed 2, Parameter 102
Preset Speed 3, Parameter 103
Preset Speed 4, Parameter 104
Preset Speed 5, Parameter 105
Preset Speed 6, Parameter 106
Purge Speed, Parameter 107
DPI Port Ref 1-6, See Parameter 209 DPI Command
Manual Speed Ref Options
OIM Requesting Auto/Manual
TB Man Ref Sel, Parameter 096
Jog Speed, Parameter 100
Speed Adders [Speed Mode]:
PI Output 2 "Process Pi"
Slip Compensation
None
Tr i m
[Digital Inx Select]:
Speed Sel
321
000
001
010
011
100
101
110
111
Digital Input
Jog Command
1 "Slip Comp"
0 "Open Loop"
PI Exclusive Mode
[PI Configuration]:
Bit 0, Excl Mode = 0
Auto
Man
Drive Ref Rslt
Mod Functions
(Skip, Clamp,
Direction, etc.)
Min/Max Speed
Commanded
Frequency
Acc/Dec Ramp
and
S Curve
Output
Frequency
Pure Reference
to follower drive for
Frequency Reference
Drive Ramp Rslt
to follower drive for
Frequency Reference
Post Ramp
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

1-36 Installation/Wiring
Auto/Manual Examples
Building Automation Controller = Auto, OIM = Manual
A process is run by a Building Automation Controller when in Auto
mode and requires manual control from the OIM during set-up. The
Auto speed reference is issued by the Building Automation Controller
through a communications module installed in the drive. Since the
internal communications is designated as Network, [Speed Ref A Sel] is
set to “Network” with the drive running from the Auto source.
Attain Manual Control
• Press the Hand button on the OIM.
When the OIM attains manual control, the drive speed command
comes from the OIM speed control keys.
Release to Auto Control
• Press the Auto button on the OIM.
When the OIM releases manual control, the drive speed command
returns to the Building Automation Controller.
Building Automation Controller = Auto, Terminal Block = Manual
A process is run by a Building Automation Controller when in Auto
mode and requires manual control from an analog potentiometer wired
to the drive terminal block. The auto speed reference is issued by the
Building Automation Controller through a communications module
installed in the drive. Since the internal communications is designated as
Network, [Speed Ref A Sel] is set to “Network” with the drive running
from the Auto source. Since the Manual speed reference is issued by an
analog input (“Analog In 1 or 2”), [TB Man Ref Sel] is set to the same
input. To switch between Auto and Manual, [Digital In5 Sel] is set to
“Auto/ Manual”.
Attain Manual Control
• Close the digital input. With the input closed, the speed command
comes from the potentiometer.
Release to Auto Control
• Open the digital input. With the input open, the speed command
returns to the Building Automation Controller.
Auto/Manual Notes
1. Manual control is exclusive. If a OIM or Terminal Block takes
manual control, no other device can take manual control until the
controlling device releases manual control.
2. If a OIM has manual control and power is removed from the drive,
the drive will return to Auto mode when power is reapplied.
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

Installation/Wiring 1-37
EMC Instructions
CE Conformity
Conformity with the Low Voltage (LV) Directive and Electromagnetic
Compatibility (EMC) Directive has been demonstrated using
harmonized European Norm (EN) standards published in the Official
Journal of the European Communities. VTAC 9 Drives comply with the
EN standards listed below when installed according to the User and
Reference Manuals.
CE Declarations of Conformity are available online at:
http://www.ab.com/certification/ce/docs.
Low Voltage Directive (73/23/EEC)
• EN50178 Electronic equipment for use in power installations
EMC Directive (89/336/EEC)
• EN61800-3 Adjustable speed electrical power drive systems Part 3:
EMC product standard including specific test methods.
General Notes
• If the adhesive label is removed from the top of the drive, the drive
must be installed in an enclosure with side openings less than
12.5 mm (0.5 in.) and top openings less than 1.0 mm (0.04 in.) to
maintain compliance with the LV Directive.
• The motor cable should be kept as short as possible in order to avoid
electromagnetic emission as well as capacitive currents.
• Use of line filters in ungrounded systems is not recommended.
• VTAC 9 drives may cause radio interference if used in a residential
or domestic environment. The installer is required to take measures
to prevent interference, in addition to the essential requirements for
CE compliance provided in this section, if necessary.
• Conformity of the drive with CE EMC requirements does not
guarantee an entire machine or installation complies with CE EMC
requirements. Many factors can influence total machine/installation
compliance.
• VTAC 9 drives generate conducted low frequency disturbances
(harmonic emissions) on the AC supply system.
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

1-38 Installation/Wiring
General Notes (continued)
• When operated on a public supply system, it is the responsibility of
the installer or user to ensure, by consultation with the distribution
network operator and Rockwell Automation if necessary, that
applicable requirements have been met.
Essential Requirements for CE Compliance
Conditions 1-6 listed below must be satisfied for VTAC 9 drives to meet
the requirements of EN61800-3.
1. Standard VTAC 9 CE compatible Drive.
2. Review important precautions/attention statements throughout this
manual before installing the drive.
3. Grounding as described on page 1-7
4. Output power, control (I/O) and signal wiring must be braided,
shielded cable with a coverage of 75% or better, metal conduit, or
equivalent attenuation.
5. All shielded cables should terminate with the proper shielded
connector.
.
6. Conditions in Table 1.M
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
.

Installation/Wiring 1-39
Table 1.M VTAC 9 – EN61800-3 EMC Compatibility – Second Environment
Frame HP @ 480V
B 3 40m (131 ft) – –
B 5 40m (131 ft) – –
C 7.5 40m (131 ft) – –
C 10 40m (131 ft) – –
D 15 40m (131 ft) – –
D 20 40m (131 ft) – –
D 25 40m (131 ft) – –
D 30 40m (131 ft) – –
E 40 40m (131 ft) – –
E 50 40m (131 ft) – –
2 25 30m (98 ft) – –
3 30 30m (98 ft) – –
3 40 30m (98 ft) – –
3 50 30m (98 ft) – –
4 60 30m (98 ft) – –
5 75 30m (98 ft) – –
5 100 30m (98 ft) – –
6 125 30m (98 ft) – –
6 150 30m (98 ft) – –
Table 1.N VTAC 9 – EN61800-3 EMC Compatibility – First Environment Restricted
Restrict
HP @
Frame
B 3 12m (40 ft) – – 100m (328 ft) RF3-0006-4 –
B 5 12m (40 ft) – – 100m (328 ft) RF3-0010-4 –
C 7.5 12m (40 ft) – 1321-M048 150m (492 ft) RF3-0018-4 –
C 10 12m (40 ft) – 1321-M048 150m (492 ft) RF3-0018-4 –
D 15 12m (40 ft) – – 150m (492 ft) RF3-0025-4 –
D 20 12m (40 ft) – – 150m (492 ft) 22-RFD036 –
D 25 12m (40 ft) – – 150m (492 ft) 22-RFD050 –
D 30 12m (40 ft) – – 150m (492 ft) 22-RFD050 –
E 40 30m (98 ft) 22-RFD070 – – – –
E 50 30m (98 ft) 22-RFD070 – – – –
2 25 150m (492 ft) 22-RFD036 – – – –
3 30 150m (492 ft) 22-RFD050 – – – –
3 40 150m (492 ft) 22-RFD070 – – – –
3 50 150m (492 ft) 22-RFD070 – – – –
4 60 150m (492 ft) 22-RFD100 – – – –
5 75 150m (492 ft) 22-RFD100 – – – –
5 100 150m (492 ft) 22-RFD150 – – – –
6 125 150m (492 ft) 22-RFD180 – – – –
6 150 150m (492 ft) 22-RFD180 – – – –
480V
Motor Cable
to:
Restrict Motor Cable
to:
External
Filter
Required
External Filter
Required
Common
Mode Core
Required
Restrict
Motor Cable
to:
Common Mode Core
Required
External
Filter
Required
Common
Mode Core
Required
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

1-40 Installation/Wiring
FCC Instructions
FCC Compliance
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a
Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules when
installed according to the User Manual. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the
equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment
generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and if not
installed and used in accordance with the User Manual, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this
equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in
which case the user will be required to correct the interference at their
own expense.
Essential Requirements for FCC Compliance
Conditions 1-4 listed below must be satisfied for VTAC 9 drives to meet
the requirements of FCC Part 15 Subpart B.
1. Grounding as described in Figure 1.4. Refer to page 1-6 for
additional grounding recommendations.
2. Output power, control (I/O) and signal wiring must be braided,
shielded cable with a coverage of 75% or better, metal conduit or
equivalent attenuation.
3. All shielded cables should terminate with the proper shield
connector.
4. Conditions in Table 1.O.
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

Installation/Wiring 1-41
Table 1.O Maximum Motor Cable Length for FCC Compliance Note: Use of these
filters assumes that the drive is mounted in an EMC enclosure.t
Frame
B 3 12m (40 ft) – – 100m (328 ft) RF3-0006-4 –
B 5 12m (40 ft) – – 100m (328 ft) RF3-0010-4 –
C 7.5 12m (40 ft) – 1321-M048 150m (492 ft) RF3-0018-4 –
C 10 12m (40 ft) – 1321-M048 150m (492 ft) RF3-0018-4 –
D 15 12m (40 ft) – – 150m (492 ft) RF3-0025-4 –
D 20 12m (40 ft) – – 150m (492 ft) 22-RFD036 –
D 25 12m (40 ft) – – 150m (492 ft) 22-RFD050 –
D 30 12m (40 ft) – – 150m (492 ft) 22-RFD050 –
E 40 30m (98 ft) 22-RFD070 – – – –
E 50 30m (98 ft) 22-RFD070 – – – –
2 25 150m (492 ft) 22-RFD036 – – – –
3 30 150m (492 ft) 22-RFD050 – – – –
3 40 150m (492 ft) 22-RFD070 – – – –
3 50 150m (492 ft) 22-RFD070 – – – –
4 60 150m (492 ft) 22-RFD100 – – – –
5 75 150m (492 ft) 22-RFD100 – – – –
5 100 150m (492 ft) 22-RFD150 – – – –
6 125 150m (492 ft) 22-RFD180 – – – –
6 150 150m (492 ft) 22-RFD180 – – – –
480V
Motor Cable
to:
Restrict
HP @
External
Filter
Required
Common
Mode Core
Required
Restrict
Motor Cable
to:
External
Filter
Required
Common
Mode Core
Required
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

1-42 Installation/Wiring
Notes:
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

Chapter 2
Start Up
This chapter describes how you start up the VTAC 9 Drive. Refer to
Appendix B for a brief description of the LCD OIM (Operator Interface
Module).
For information on… See page
Prepare For Drive Start-Up
Status Indicators 2-3
Running the Start-Up Routines 2-4
ATTENTION: Power must be applied to the drive to perform the
following start-up procedure. Some of the voltages present are at
!
incoming line potential. To avoid electric shock hazard or damage to
equipment, only qualified service personnel should perform the
following procedure. Thoroughly read and understand the procedure
before beginning. If an event does not occur while performing this
procedure, Do Not Proceed. Remove Power including user supplied
control voltages. User supplied voltages may exist even when main AC
power is not applied to the drive. Correct the malfunction before
continuing.
2-2
ATTENTION: Only qualified electrical personnel familiar with the
construction and operation of this equipment and the hazards involved
should install, adjust, operate, or service this equipment. Read and
understand this chapter in its entirety before proceeding. Failure to
observe this precaution could result in severe bodily injury or loss of
life.
ATTENTION: Incorrect values for some of the parameters in the
Start-Up routines can cause the drive to operate improperly. Verify that
the values of these parameters are appropriate for your application.
Failure to observe this precaution could result in bodily injury.
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

2-2 Start Up
Prepare For Drive Start-Up
Before Applying Power to the Drive
❏ 1. Confirm that all inputs are connected to the correct terminals and are
secure.
❏ 2. Verify that AC line power at the disconnect device is within the rated
value of the drive.
❏ 3. Verify that control power voltage is correct.
The remainder of this procedure requires that a OIM be installed. If
an operator interface is not available, remote devices should be used
to start up the drive.
Important: When power is first applied, the OIM may require
approximately 5 seconds until commands are recognized
(including the Stop key).
Applying Power to the Drive
❏ 4. Apply AC power and control voltages to the drive.
If any of the six digital inputs are configured to “Stop – CF”
(CF = Clear Fault) or “Enable,” verify that signals are present or the
drive will not start. Refer to Alarm Descriptions
list of potential digital input conflicts.
If a fault code appears, refer to Chapter 4.
If the Ready LED is not flashing green at this point, refer to Status
Indicators and their indications below.
❏ 5. Proceed to Running the Start-Up Routines.
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
on page 4-10 for a

Status Indicators
Figure 2.1 Drive Status Indicators (Typical)
Start Up 2-3
➋
➊
➊
➋
Frames B…E
# Name Color State Description
Ready Green Flashing Drive ready, but not running and no faults are present.
➊
Yellow
See page
4-10
Red
See page 4-4
Drive Refer to the Communication
➋
MS Status of communications module (when installed).
NET A Status of network (if connected).
NET B Status of secondary network (if connected).
Adapter User Manual.
Steady Drive running, no faults are present.
Flashing,
Drive Stopped
Flashing,
Drive Running
Steady,
Drive Running
Flashing A fault has occurred.
Steady A non-resetable fault has occurred.
An inhibit condition exists, the drive cannot be started.
Check parameter 214 [Start Inhibits].
An intermittent type 1 alarm condition is occurring.
Check parameter 211 [Drive Alarm 1].
A continuous type 1 alarm condition exists.
Check parameter 211 [Drive Alarm 1].
Status of DPI port internal communications (if present).
Frames 2…6
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

2-4 Start Up
Running the Start-Up Routines
To access the Start-Up routines, select the Start-Up icon from the main
menu as shown in figure Figure 2.2.
Figure 2.2 Accessing the Start-Up Routines
The Start-Up menu screen contains 8 selections. The first 7 menu items
contain the most commonly used parameters associated with each
function. See figure Figure 2.3.
Figure 2.3 Start-Up Menu
Main Menu
Start-Up
Stopped
P0: VTAC 9
Main Menu
Start-Up
Monitor
Highlight Start-Up icon
Select
Auto
Lang
Intro
Press
Quickstart
Set basic
parameters
The Start-Up routine automates the process of entering values of
selected parameters by taking you to the next parameter after you accept
a parameter value. As each item in the list is completed, you are
automatically advanced to the next step.
Important: Parameter values are saved as they are changed.
You do not have to configure all of the parameters in all 7 menus. The
first menu selection, Quickstart, contains the minimum basic parameters
that must be configured before running the drive. These are listed in
table Table 2.A
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
Input
Voltage
Configure for
Alternate
Input Voltage
Pressing or aborting the Start-Up routine will not
Motor
Data
Enter Motor
Nameplate
Data
ESC/
ESC/
PROG
PROG
Motor
Tests
Optimize
Torque and
Verify Direction
Speed
Limits
Set Min/Max
Speed, Stop
Mode, and
Direction Conrol
Ref Setup
Set
Reference
Control
Source
Configure
I/O
Set TB I/O
Functions
undo the changes.
.
Done

Start Up 2-5
Table 2.A Quickstart Parameters
Parameter No. Parameter Name
155 Stop Mode A
42 Motor NP FLA
81 Minimum Speed
82 Maximum Speed
140 Accel Time 1
142 Decel Time 1
90 Speed Ref A Sel
362 Digital In2 Sel
If your application requires adjustment to parameters beyond those listed
in table Table 2.A, you can adjust the parameters in any or all of the next
6 selections in the Start-Up menu, or you can adjust parameters
individually through the Parameters menu.
When you have completed adjusting all of the parameters in the Start-Up
routines that your application requires, select the last item in the menu,
Done.
Important: The drive is shiped with a default configuration of control
from the keypad. For drive control from the terminal block
inputs, parameter 89, Logic Source Sel, must be set to 0.
Exiting Before Completing the Start-Up Routines
To exit the Start-Up routines, press the F4 key (Exit). When you
select the Start-Up icon from the main menu again, you will be
prompted to either continue or restart the Start-Up routines. If
you select “continue,” you will be returned to the point at which
you exited.
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

2-6 Start Up
Notes:
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

Chapter 3
Programming and Parameters
Chapter 3 provides a complete parameter listing and descriptions. The
parameters can be programmed (viewed/edited) using the LCD OIM
(Operator Interface Module).
As an alternative, programming can also be performed using VS Utilities
software and a personal computer. Refer to Appendix
descriptions of the LCD Operator Interface Module.
For information on… See page…
About Parameters
How Parameters are Organized 3-3
Monitor File 3-11
Motor Control File 3-12
Speed Command File 3-18
Dynamic Control File 3-30
Utility File 3-41
Communication File 3-51
Inputs & Outputs File 3-54
Parameter Cross Reference – by Name 3-66
3-1
B for brief
About Parameters
To configure a drive to operate in a specific way, drive parameters may
have to be set. Three types of parameters exist:
• ENUM Parameters
ENUM parameters allow a selection from 2 or more items. The LCD
OIM will display a text message for each item.
• Bit Parameters
Bit parameters have individual bits associated with features or
conditions. If the bit is 0, the feature is off or the condition is false. If
the bit is 1, the feature is on or the condition is true.
• Numeric Parameters
These parameters have a single numerical value (i.e. 0.1 Volts).
The example on the following page shows how each parameter type is
presented in this manual.
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

3-2 Programming and Parameters
➊➌➋➏➎➍
File
Parameter Name & Description Values
Group
No.
198 [Load Frm Usr Set]
Loads a previously saved set of
parameter values from a selected user
set location in drive nonvolatile memory
Drive . . .
to active drive memory.
Default:
Options:00
1
2
3
“Ready”
“Ready”
“User Set 1”
“User Set 2”
“User Set 3”
216 [Dig In Status]
Status of the digital
UTILITY (File E)
MOTOR . . .
inputs.
Diagnostics
Bit #
059 [SV Boost Filter]
2…6
Sets the amount of filtering used to boost
voltage during Sensorless Vector
Torq . . .
operation.
10 01234567891112131415
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Digital In5
Digital In4
Digital In6
Nibble 1Nibble 2Nibble 3Nibble 4
500
0/32767
1
Digital In2
Digital In3
Digital In1
000000xxxxxxxxxx
1=Input Present
0=Input Not Present
x=Reserved
No. Description
File – Lists the major parameter file category.
➊
Group – Lists the parameter group within a file.
➋
No. – Parameter number. = Parameter value can not be changed until drive is stopped.
➌
Parameter Name & Description – Parameter name as it appears on an LCD OIM, with a brief
➍
description of the parameters function.
Values – Defines the various operating characteristics of the parameter. Three types exist.
➎
ENUM Default:
Options:
32
= 32 bit parameter.
2…6
= Drive Frames 2, 3, 4, 5 & 6.
Lists the value assigned at the factory. “Read Only” = no default.
Displays the programming selections available.
Bit Bit #: Lists the bit place holder and definition for each bit.
Numeric Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Lists the value assigned at the factory. “Read Only” = no default.
The range (lowest and highest setting) possible for the parameter.
Unit of measure and resolution as shown on the LCD OIM.
Important: Some parameters will have two unit values. For example, analog inputs
can be set for current or voltage with 320 [Anlg In Config].
Important: When sending values through DPI ports, simply remove the decimal
point to arrive at the correct value (i.e. to send “5.00 Hz,” use “500”).
Related – Lists parameters (if any) that interact with the selected parameter. The symbol “ ”
➏
indicates that additional parameter information is available in Appendix C.
Related
199
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
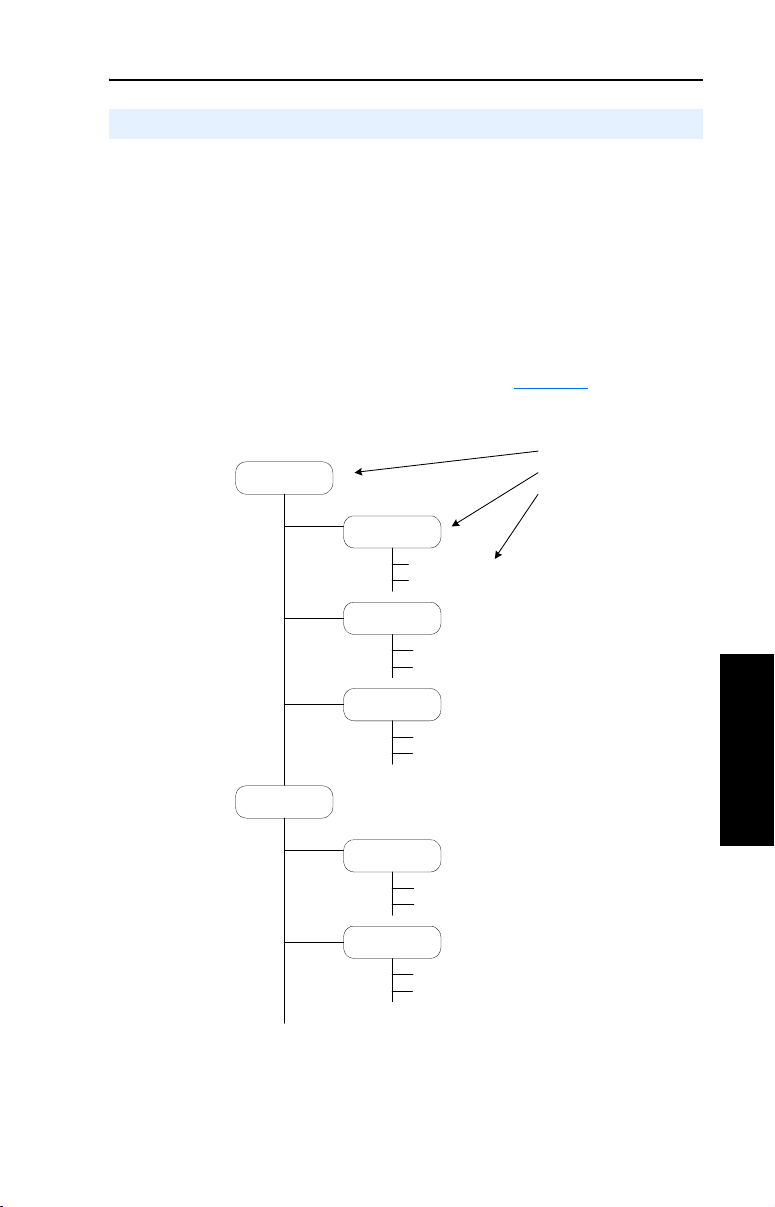
Programming and Parameters 3-3
How Parameters are Organized
Parameters are organized into seven files:
• Monitor
• Motor Control
• Speed Command
• Dynamic Control
• Utility
• Communication
• Inputs & Outputs
Each file contains parameters that are grouped by their function. A file
can contain several groups of parameters. See Figure 3.1
Figure 3.1 Example of Parameter Organization
Motor
Control
Motor Data
Motor Type
Motor NP Volts
Torq
Attributes
Torque Perf Mode
Maximum Voltage
Volts per
Hertz
Start/Acc Boost
Run Boost
.
File
Group
Parameter
Speed
Command
Control Src
Sel
Logic Source Sel
Speed Ref A Sel
Spd Mode &
Lmts
Speed Mode
Minimum Speed
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

3-4 Programming and Parameters
Accessing the Parameters
Parameters are programmed and viewed using the LCD OIM or VS
Utilities software.
The LCD OIM displays parameters by group, by individual parameter
number, and parameters that have changed from their default value.
To access parameters using the LCD OIM, select the Parameters icon
from the main screen. See Figure 3.2
.
See Appendix
B for information on modifying parameters using the
LCD OIM.
Figure 3.2 Accessing the Parameters Using the LCD OIM
Stopped
P0: VTAC 9
Main Menu
Parameters
Monitor Lang
Stopped Auto
P0: VTAC 9
Parameters:
By Group
P Numbers
Changed Params
Stopped Auto
P0: VTAC 9
Parameters:
By Group
P Numbers
Changed Params
Stopped Auto
P0: VTAC 9
Parameters:
By Group
P Numbers
Changed Params
Auto
ESC/
PROG
ESC/
PROG
ESC/
PROG
File:
File 1 Name
File 2 Name
File 3 Name
ESC/
PROG
Parameter #
Parameter Text
+456.78 Unit
Dflt
ESC/
PROG
Parameter #
Parameter Text
+456.78 Unit
Dflt
ESC/
PROG
1234
1234
ESC/
PROG
ESC/
PROG
Group:
Group 1 Name
Group 2 Name
Group 3 Name
Changed: Par
Searching. . .
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

Programming and Parameters 3-5
Selecting the Parameter Access Level
The VTAC 9 drive provides two levels of access to the parameters:
Standard (1) and Advanced (2).
The Advanced level allows access to all of the parameters and is used for
more sophisticated applications.
The Standard level allows access to a subset of the Advanced level and
contains only the most commonly used parameters. See Appendix C for
a list of the parameters available at the Standard level.
The active access level is displayed in Parameter Access Level (196).
To select the parameter access level using the LCD OIM, select the
Password icon from the main menu. See Figure 3.3
Figure 3.3 Selecting the Parameter Access Level
Stopped
P0: VTAC 9
Main Menu
Password
Monitor Lang
Highlight Password icon
Auto
Password:
Set Access Lvl
Set Acc Lvl PW
Set Wrt Prot PW
.
Password:
Standard
Advanced
Highlight option
Select
Restricting Access to the Advanced Parameter Level
ATTENTION: It is the user’s responsibility to determine how to distribute the access level
password. Rockwell Automation is not responsible for unauthorized access violations
!
within the user’s organization. Failure to observe this precaution could result in bodily
injury.
The LCD OIM provides the option to restrict access to the Advanced
parameter level. This feature requires the use of a user-defined password
when an attempt to change the access level is made.
To set the access level password, select the Password icon from the main
menu. See Figure 3.4
value of 0 disables the password (factory default). You must either select
Logout or return to the process display screen to activate the password.
. The password value can range from 1 to 9999. A
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

3-6 Programming and Parameters
Figure 3.4 Setting the Access Level Password
Auto
Stopped
P0: VTAC 9
Main Menu
Password
Monitor Lang
Highlight Password icon
Password:
Set Access Lvl
Set Acc Lvl PW
Set Wrt Prot PW
When you enter the password, you can change access levels until you
select Logout or return to the process display screen, which re-activates
the password. Refer to section B.8 in Appendix B for information about
the process display screen.
Note that once the password is enabled, you will also be prompted to
enter the password to access the Set Acc Lvl PW option.
If There is More Than One OIM Connected to the Drive
Note that setting or changing the access level password on one OIM will
set or change the access level password for all OIMs connected to the
drive.
Highlight option
Set Acc Lvl PW:
New Code:
Increase/decrease
value
Move placeholder
0
Password:
Set Acc Lvl PW
Set Wrt Prot PW
Logout
Highlight Logout
Activate password
Ensuring Program Security
ATTENTION: It is the user’s responsibility to determine how to distribute the write-protect
password. Rockwell Automation is not responsible for unauthorized access violations
!
within the user’s organization. Failure to observe this precaution could result in bodily
injury.
Parameter values can be password-protected using the LCD OIM. When
the password is enabled, parameter values can be displayed. However, if
there is an attempt to change a parameter value, a password pop-up box
will appear on the OIM screen to prompt for the user-defined password.
To set the write-protect password, select the Password icon from the
main menu. See Figure 3.5
9999. A value of 0 disables the password (factory default).
When the password is enabled, the lock symbol on the screen changes
from to .
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
. The password value can range from 1 to

Programming and Parameters 3-7
e
Figure 3.5 Setting the Write-Protect Password
Main Menu
Auto
Password:
Set Access Lvl
Set Acc Lvl PW
Set Wrt Prot PW
Highlight option
Set Wrt Prot PW:
New Code:
0
Increase/decrease valu
Move placeholder
Accept value
Stopped
P0: VTAC 9
Password
Monitor Lang
Highlight Password icon
When you enter the password, you can adjust parameters until you select
Logout or return to the process display screen, which re-activates the
password. Refer to Appendix
B for information about the process
display screen.
If There is More Than One OIM Connected to the Drive
Important: Setting the write-protect password value to zero on one
OIM will disable the write-protect password on all
connected OIMs.
Setting the write-protect password in one OIM will not affect any other
OIM connected to the drive unless a write-protect password has also
been set in the other OIMs. In this case, the last password value entered
becomes the password value for all password-protected OIMs. (Each
OIM cannot have a different password value.)
For example, if the write-protect password has been set to 5555 for the
local OIM, someone using a remote OIM with no write-protect password
set can still program all of the parameters. If the write-protect password
is then set to 6666 on the remote OIM, you will be required to enter 6666
on the local OIM to program the parameters.
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

3-8 Programming and Parameters
Standard Parameter View
Parameter 196 [Param Access Lvl] set to option 1 “Standard.”
File Group Parameters
Monitor Metering Output Freq 001
Monitor
Drive Data Rated kW 026
Motor Control Motor Data Motor NP Volts 041
Motor Control
Torq Attributes Maximum Voltage 054 Maximum Freq 055
Volts per Hertz Run Boost 070
Commanded Freq 002
Output Current 003
Torque Current 004
Rated Volts 027
Motor NP FLA 042
Output Voltage 006
Output Power 007
Elapsed MWh 009
Elapsed Run Time 010
Rated Amps 028
Control SW Ver 029
Motor NP Hertz 043
Motor NP RPM 044
MOP Frequency 011
DC Bus Voltage 012
Analog In1 Value 016
Motor NP Power 045
Mtr NP Pwr Units 046
Speed
Command
Speed Command
Dynamic
Control
Dynamic Control
Spd Mode &
Limits
Speed
References
Discrete
Speeds
Ramp Rates Accel Time 1 140
Load Limits Current Lmt Val 148
Stop/Brake
Modes
Speed Mode 080 Minimum Speed 081
Speed Ref A Sel 090 Speed Ref A Hi 091
Purge Speed 107
Decel Time 1 142
Drive OL Mode 150
Stop Mode A 155
Stop Mode B 156
Restart Modes LevelSense Start 168 Auto Rstr t Tries 174
Utility Drive Memory Param Access Lvl 196
Utility
Inputs &
Outputs
Inputs & Outputs
Analog Inputs Anlg In Config 320
Reset To Defalts 197
Reset Meters 200
Anlg In Sqr Root 321
Analog Outputs Anlg Out Config 340 Analog Out1 Sel 342 Analog Out1 Hi 343
Digital Outputs Digital Out1 Sel 380
Dig Out1 Level 381
Maximum Speed 082
Speed Ref A Lo 092
S Curve % 146
CarrierFrequency 151
Auto Rstrt Delay 175
Analog In1 Hi 322
Analog In1 Lo 323
Analog In 1 Loss 324
Digital Out2 Sel 384
Dig Out2 Level 385
Skip Frequency 1 084
Logic Source Sel 089
Analog Out1 Lo 344
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

Advanced Parameter View
Parameter 196 [Param Access Lvl] set to option 2 “Advanced.”
File Group Parameters
Monitor Metering Output Freq 001
Monitor
Drive Data Rated kW 026
Motor Control Motor Data Motor Type 040
Motor Control
Torq Attributes Torque Perf Mode 053
Volts per Hertz Start/Acc Boost 069
Speed
Command
Speed Command
Dynamic
Control
Dynamic Control
Spd Mode &
Limits
Speed
References
Discrete
Speeds
Speed Trim Trim In Select 117
Slip Comp Slip RPM @ FLA 121
Process PI PI Configuration 124
Ramp Rates Accel Time 1 140
Load Limits Current Lmt Sel 147
Stop/Brake
Modes
Restart Modes LevelSense Start 168
Power Loss Power Loss Mode 184
Commanded Freq 002
Output Current 003
Torque Current 004
Flux Current 005
Rated Volts 027
Motor NP Volts 041
Motor NP FLA 042
Motor NP Hertz 043
Maximum Voltage 054
Maximum Freq 055
Run Boost 070
Speed Mode 080
Minimum Speed 081
Maximum Speed 082
Overspeed Limit 083
Speed Ref A Sel 090
Speed Ref A Hi 091
Speed Ref A Lo 092
Preset Speed 1-6 101-106 Purge Speed 107
Tri m O ut S el ect 118
Slip Comp Gain 122
PI Control 125
PI Reference Sel 126
PI Setpoint 127
PI Feedback Sel 128
Accel Time 2 141
Current Lmt Val 148
Current Lmt Gain 149
Stop Mode A 155
Stop Mode B 156
Flying Start En 169
Flying StartGain 170
Power Loss Time 185
Programming and Parameters 3-9
Output Voltage 006
Output Power 007
Output Powr Fctr 008
Elapsed MWh 009
Elapsed Run Time 010
Rated Amps 028
Control SW Ver 029
Motor NP RPM 044
Motor NP Power 045
Mtr NP Pwr Units 046
Compensation 056
Flux Up Mode 057
Flux Up Time 058
SV Boost Filter 059
Break Voltage 071
Break Frequency 072
Skip Frequency 1 084
Skip Frequency 2 085
Skip Frequency 3 086
TB Man Ref Sel 096
TB Man Ref Hi 097
TB Man Ref Lo 098
Tri m H i 1 19
Tri m L o 1 20
Slip RPM Meter 123
PI Integral Time 129
PI Prop Gain 130
PI Lower Limit 131
PI Upper Limit 132
PI Preload 133
Decel Time 1 142
Decel Time 2 143
Drive OL Mode 150
CarrierFrequency 151
DC Brake Lvl Sel 157
DC Brake Level 158
DC Brake Time 159
Auto Rstrt Tries 174
Auto Rstrt Delay 175
Power Loss Level 186
MOP Frequency 011
DC Bus Voltage 012
DC Bus Memory 013
Analog In1 Value 016
Analog In2 Value 017
Motor OL Hertz 047
Motor OL Factor 048
Autot une 061
IR Voltage Drop 062
Flux Current Ref 063
Ixo Voltage Drop 064
Skip Freq Band 087
Logic Source Sel 089
PI Status 134
PI Ref Meter 135
PI Fdback Meter 136
PI Error Meter 137
PI Output Meter 138
S Curve % 146
Bus Reg Ki 160
Bus Reg Mode A 161
Bus Reg Mode B 162
DB Resistor Type 163
Bus Reg Kp 164
Bus Reg Kd 165
Sleep-Wake Mode 178
Sleep-Wake Ref 179
Wake Level 18 0
Wake Time 18 1
Sleep Level 182
Sleep Time 183
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

3-10 Programming and Parameters
File Group Parameters
Utility Direction Config Direction Mode 190
Utility
Communication Comm Control Drive Logic Rslt 271 Drive Ref Rslt 272 Drive Ramp Rslt 273
Communication
OIM Ref Config Save OIM Ref 192 Man Ref Preload 193
MOP Config Save MOP Ref 194 MOP Rate 195
Drive Memory Param Access Lvl 196
Diagnostics Drive Status 1 209
Faults Fault Config 1 238
Reset To Defalts 197
Load Frm Usr Set 198
Drive Status 2 210
Drive Alarm 1 211
Drive Alarm 2 212
Speed Ref Source 213
Start Inhibits 214
Last Stop Source 215
Fault Clear 240
Save To User Set 199
Reset Meters 200
Language 201
Dig In Status 216
Dig Out Status 217
Drive Temp 218
Drive OL Count 219
Motor OL Count 220
Fault Frequency 224
Fault Amps 225
Fault Bus Volts 226
Fault Clear Mode 241
Power Up Marker 242
Alarms Alarm Config 1 259
Masks &
Owners
Manual Mask 286 Stop Owner 288 Manual Owner 298
Datalinks Data In A1-D2 300-307 Data Out A1-D2 310-317
Voltage Class 202
Drive Checksum 203
Status 1 @ Fault 227
Status 2 @ Fault 228
Alarm 1 @ Fault 229
Alarm 2 @ Fault 230
Testpoint 1 Sel 234
Testpoint 1 Data 235
Testpoint 2 Sel 236
Testpoint 2 Data 237
Inputs &
Outputs
Inputs & Outputs
Analog Inputs Anlg In Config 320
Analog Outputs Anlg Out Config 340
Anlg In Sqr Root 321
Anlg Out Absolut 341
Analog Out1 Sel 342
Digital Inputs Digital In1-6 Sel 361-366
Digital Outputs Digital Out1 Sel 380
Dig Out1 Level 381
Dig Out1 OnTime 382
Dig Out1 OffTime 383
Analog In 1 Hi 322
Analog In 1 Lo 323
Anlg In 1 Loss 324
Analog Out1 Hi 343
Analog Out1 Lo 344
Digital Out2 Sel 384
Dig Out2 Level 385
Dig Out2 OnTime 386
Dig Out2 OffTime 387
Analog In 2 Hi 325
Analog In 2 Lo 326
Anlg In 2 Loss 327
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

Monitor File
Parameter Name and Description
File
MONITOR
See page 3-2 for symbol descriptions
Group
No.
001 [Output Freq]
Output frequency present at T1, T2 & T3
(U, V & W). Value includes reference, slip
comp and IR compensation.
002 [Commanded Freq]
Value of the active frequency command.
003 [Output Current]
The total output current present at T1, T2
& T3 (U, V & W). Includes torque and flux
components.
004 [Torque Current]
The amount of current that is in phase
with the fundamental voltage component.
This is the torque producing component of
the output current.
005 [Flux Current]
The amount of current that is out of phase
with the fundamental voltage component.
This is the magnetizing component of the
output current.
Metering
006 [Output Voltage]
Output voltage present at terminals T1,
T2 & T3 (U, V & W).
007 [Output Power]
Output power present at T1, T2 & T3 (U, V
& W).
008 [Output Powr Fctr]
Output power factor.
009 [Elapsed MWh]
32
Accumulated output energy of the drive.
010 [Elapsed Run Time]
32
Accumulated time drive is outputting
power.
011 [MOP Frequency]
Value of the signal at MOP (Motor
Operated Potentiometer).
Programming and Parameters 3-11
Values
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Read Only
–/+400 Hz
0.1 Hz
Read Only
–/+400 Hz
0.1 Hz
Read Only
0.0/Drive Rated Amps × 2
0.1 Amps
Read Only
Drive Rating × –2/+2
0.1 Amps
Read Only
Drive Rating × –2/+2
0.1 Amps
Read Only
0.0/Drive Rated Volts
0.1 VAC
Read Only
0.0/Drive Rated kW × 2
0.1 kW
Read Only
0.00/1.00
0.01
Read Only
0.0/429496729.5 MWh
0.1 MWh
Read Only
0.0/429496729.5 Hrs
0.1 Hrs
Read Only
–/+400 Hz
0.1 Hz
Related
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

3-12 Programming and Parameters
Parameter Name and Description
File
See page 3-2 for symbol descriptions
Group
No.
012 [DC Bus Voltage]
Present DC bus voltage level.
013 [DC Bus Memory]
6 minute average of DC bus voltage level.
016
[Analog In1 Value]
Metering
[Analog In2 Value]
017
Value of the signal at the analog inputs.
Does not include scaling information
programmed by user (e.g. Analog In 1 Hi).
Terminals monitored according to 320
[Analog In Config].
026 [Rated kW]
MONITOR
32
Drive power rating.
027 [Rated Volts]
The drive input voltage class (208, 240,
400 etc.).
028 [Rated Amps]
Drive Data
The drive rated output current.
029 [Control SW Ver]
Main Control Board software version.
Values
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Read Only
0.0/Drive Rating Based
0.1 VDC
Read Only
0.0/Drive Rating Based
0.1 VDC
Read Only
0.000/20.000 mA
10.000V
0.001 mA
0.001 Volt
Read Only
0.37/3000.00 kW
0.01 kW
Read Only
0.0/6553.5 Volt
0.1 VAC
Read Only
0.0/6553.5 Amps
0.1 Amps
Read Only
0.000/65.535
0.001
Related
196
Motor Control File
Parameter Name and Description
File
MOTOR CONTROL
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
See page 3-2 for symbol descriptions
Group
No.
040 [Motor Type]
Set to match the type of motor connected.
041 [Motor NP Volts]
Set to the motor nameplate rated volts.
Motor Data
Motor nameplate base voltage defines the
output voltage when operating at rated
current, rated speed and rated
temperature.
Values
Default:
Options:00
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
“Induction”
“Induction”
1
“Synchr Reluc”
2
“Synchr PM”
Drive Rating Based
0.0/[Rated Volts]
0.1 VAC
Related

Parameter Name and Description
File
See page 3-2 for symbol descriptions
Group
No.
042 [Motor NP FLA]
Set to the motor nameplate rated full load
amps.
Defines the output amps when operating at rated voltage, rated speed, and rated
temperature. It is used in the motor thermal overload and in the calculation of slip.
Set to the motor nameplate rated frequency. The motor nameplate base
frequency defines the output frequency when operating at rated voltage, rated
current, rated speed, and rated temperature.
The motor thermal overload cannot distinguish individual currents in a multimotor
application. Set 238 [Fault Config 1], bit 3 to “0” to disable the motor thermal
overload for applications of this type.
The operation of the overload is based on three parameters: 042 [Motor NP FLA],
048 [Motor OL Factor], and 047 [Motor OL Hertz]. The motor nameplate full load
amps is multiplied by the motor overload factor to define the continuous level of
current allowed by the motor thermal overload.
Parameter 048 [Motor OL Factor] is used to adjust the response of the motor
thermal overload to lower motor speeds (lower output frequencies) where a higher
degree of protection may be required due to decreased motor cooling.
043 [Motor NP Hertz]
Set to the motor nameplate rated
frequency. The motor nameplate base
frequency defines the output frequency
when operating at rated voltage, rated
current, rated speed and rated
Motor Data
MOTOR CONTROL
temperature.
044 [Motor NP RPM]
Set to the motor nameplate rated RPM.
The motor nameplate RPM defines the
rated speed when operating at motor
nameplate base frequency, rated current,
base voltage and rated temperature. This
is used to calculate slip.
045 [Motor NP Power]
Set to the motor nameplate rated power.
32
The motor nameplate rated power is used
with the other nameplate values to
calculate default values for motor
parameters to assist the commissioning
process. This may be entered in
horsepower or in kilowatts as selected in
parameter 046.
046 [Mtr NP Pwr Units]
Selects the motor power units to be used
by parameter 045.
Programming and Parameters 3-13
Values
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Options: 0
Drive Rating Based
0.0/[Rated Amps] × 2
0.1 Amps
60 Hz
5.0/400.0 Hz
0.1 Hz
1740 RPM
60/24000 RPM
1 RPM
Drive Rating Based
0.00/1000.00
0.00/5000.00
(1)
,
(2)
0.01 kW/HP
See [Mtr NP Pwr Units]
(1)
Frame B, C, D, & E
(2)
Frames 2, 3, 4, 5, & 6
Drive Rating Based
“Horsepower”
1
“kiloWatts”
047
048
046
Related
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

3-14 Programming and Parameters
Parameter Name and Description
File
See page 3-2 for symbol descriptions
Group
No.
047 [Motor OL Hertz]
Selects the output frequency below which
the motor operating current is derated.
The motor thermal overload will generate
a fault at lower levels of current. For all
settings of overload Hz other than zero,
the overload capacity is reduced to 70%
when output frequency is zero.
Values
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Motor NP Hz/3
0.0/400.0 Hz
0.1 Hz
Related
042
220
120
100
80
60
40
Continuous Rating
Motor Data
20
MOTOR CONTROL
048 [Motor OL Factor]
Sets the operating level for the motor
overload.
This parameter can be used to raise the
level of current that will cause the motor
thermal overload to trip. The effective
overload factor is a combination of
parameters 047 and 048.
Motor
FLAOLFact or
Changing Overload Hz
0
0102030405060708090100
Hertz
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Operating
=
x
Level
OL Hz = 10
OL Hz = 25
OL Hz = 50
1.00
0.20/2.00
0.01
042
220
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

Parameter Name and Description
File
See page 3-2 for symbol descriptions
Group
No.
053 [Torque Perf Mode]
Sets the method of motor torque
production.
• Sensrls Vect maintains consistent magnetizing current up to base speed, and
voltage increases as a function of load.
• SV Economize allows the drive to automatically adjust output voltage as the
load changes to minimize current supplied to the motor. The voltage is
adjusted by means of flux current adaption.
• Custom V/Hz allows for tailoring the volts/hertz curve by adjusting parameters
054, 055, 070, 071, and 072.
Maximum Voltage
Motor NP Voltage
Break Voltage
Output Voltage
Start Boost
Run Boost
Programming and Parameters 3-15
Values
Default:
Options:30
“Fan/Pmp V/Hz”
“Sensrls Vect”
1
“SV Economize”
2
“Custom V/Hz”
3
“Fan/Pmp V/Hz”
062
063
069
070
Related
Torq Attributes
MOTOR CONTROL
• Fan/Pmp V/Hz mode sets a fan load volts per hertz curve profile exponential to
base frequency and linear from base to maximum frequency). Run boost can
offset the low speed curve point.
Maximum Voltage
Motor NP Voltage
Output Voltage
054 [Maximum Voltage]
Sets the highest voltage the drive will
output.
Run Boost
Frequency
Frequency
Motor NP Hz Break
Frequency
Motor NP Hz
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Maximum
Frequency
Maximum
Frequency
Drive Rated Volts
Rated Volts × 0.25/Rated
Vol ts
0.1 VAC
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
3-16 Programming and Parameters
Parameter Name and Description
File
See page 3-2 for symbol descriptions
Group
No.
055 [Maximum Freq]
Sets the highest frequency the drive will
output. Note that this is not maximum
speed which is set in 083 [Overspeed
Limit].
Refer to Appendix
C.
056 [Compensation]
Enables/disables correction options.
10 01234567891112131415
Bit #
Factory Default Bit Values
Option Descriptions
Reflect Wave Enables/disables reflected wave overvoltage protection for long
cable lengths. Enable this option for cable lengths longer than
300 feet.
Enable Jerk Enables/disables the jerk limit in the current limiter that helps to
eliminate overcurrent trips on fast accelerations. In non-FVC
Vector modes, disabling jerk removes a short S-curve at the
start of the accel/decel ramp. Disable if application requires
acceleration time less than 25 seconds.
MOTOR CONTROL
leakage inductance. See 064 [Ixo Voltage Drop].
Ixo AutoCalc Frame 2, 3, 4, 5, & 6 drives only. Calculates voltage drop due to
Torq Attributes
057 [Flux Up Mode]
Amount of DC current equal to current
limit to establish full motor stator flux
before acceleration.
“Manual” (0) = Flux is established for [Flux
Up Time] before acceleration.
“Automatic” (1) = Flux is established for a
calculated time period based on motor
nameplate data. [Flux Up Time] is not
used.
058 [Flux Up Time]
Sets the amount of time the drive will use
to try and achieve full motor stator flux.
When a Start command is issued, DC
current at current limit level is used to
build stator flux before accelerating.
059 [SV Boost Filter]
2…6
Sets the amount of filtering used to boost
voltage during Sensorless Vector
operation.
Values
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Nibble 1Nibble 2Nibble 3Nibble 4
Default:
Options:00
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
130.0 Hz
5.0/400.0 Hz
0.1 Hz
Wave
AutoCalc
Reflect
Enable Jerk
Ixo
10x 1xxxxxxxxxxxx
1=Enabled
0=Disabled
x=Reserved
“Manual”
“Manual”
1
“Automatic”
0.00 Secs
0.00/5.00 Secs
0.01 Secs
500
0/32767
1
Related
083
053
058
053
058
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
File
Group
061 [Autotune]
Torq Attributes
MOTOR CONTROL
Programming and Parameters 3-17
Parameter Name and Description
See page 3-2 for symbol descriptions
No.
Provides a manual or automatic method
for setting [IR Voltage Drop] and [Flux
Current Ref], which affect sensorless
vector performance. Valid only when
parameter 53 is set to “Sensrls Vect,” “SV
Economize” or “FVC Vector”
“Ready” (0) = Parameter returns to this setting following a “Static Tune” or “Rotate
Tune.” It also permits manually setting [IR Voltage Drop] and [Flux Current Ref].
“Static Tune” (1) = A temporary command that initiates a non-rotational motor
stator resistance test for the best possible automatic setting of [IR Voltage Drop].
A start command is required following initiation of this setting. The parameter
returns to “Ready” (0) following the test, at which time another start transition is
required to operate the drive in normal mode. Used when motor cannot be
rotated.
“Rotate Tune” (2) = A temporary command that initiates a “Static Tune” followed by
a rotational test for the best possible automatic setting of [Flux Current Ref]. A
start command is required following initiation of this setting. The parameter
returns to “Ready” (0) following the test, at which time another start transition is
required to operate the drive in normal mode. Important: Used when motor is
uncoupled from the load. Results may not be valid if a load is coupled to the motor
during this procedure.
ATTENTION: Rotation of the motor in an undesired direction can
occur during this procedure. To guard against possible injury and/or
!
equipment damage, it is recommended that the motor be
disconnected from the load before proceeding.
Values
Default:
Options:30
1
2
3
“Calculate”
“Ready”
“Static Tune”
“Rotate Tune”
“Calculate”
Related
053
062
“Calculate” (3) = This setting uses motor nameplate data to automatically set [IR
Voltage Drop] and [Flux Current Ref].
062 [IR Voltage Drop]
Value of voltage drop across the
resistance of the motor stator at rated
motor current. Used only parameter 53 is
set to “Sensrls Vect”, “SV Economize” or
“FVC Vector.”
063 [Flux Current Ref]
32
Value of amps for full motor flux. Used
only when parameter 53 is set to “Sensrls
Vect”, “SV Economize” or “FVC Vector.”
064 [Ixo Voltage Drop]
Value of voltage drop across the leakage
inductance of the motor at rated motor
2…6
current. Used only when parameter 53 is
set to “FVC Vector.”
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
[Motor NP Volts] × 0.25
0.0/[Motor NP Volts]×0.25
0.1 VAC
Drive Rating Based
0.00/[Motor NP FLA]
0.01 Amps
Drive Rating Based
0.0/Motor NP Volts
0.1 VAC
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
053
061
053
061

3-18 Programming and Parameters
Parameter Name and Description
File
See page 3-2 for symbol descriptions
Group
No.
069 [Start/Acc Boost]
Sets the voltage boost level for starting
and acceleration when “Custom V/Hz”
mode is selected.
Refer to parameter 083 [Overspeed Limit].
070 [Run Boost]
Sets the boost level for steady state or
deceleration when “Fan/Pmp V/Hz” or
“Custom V/Hz” modes are selected.
Refer to the diagram at parameter 083.
071 [Break Voltage]
Volts per Hertz
MOTOR CONTROL
Sets the voltage the drive will output at
[Break Frequency].
Refer to parameter 083 [Overspeed Limit].
072 [Break Frequency]
Sets the frequency the drive will output at
[Break Voltage].
Refer to parameter 083 [Overspeed Limit].
Speed Command File
Values
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
[Motor NP Volts] × 0.25
0.0/[Motor NP Volts] × 0.25
0.1 VAC
[Motor NP Volts] × 0.25
0.0/[Motor NP Volts] × 0.25
0.1 VAC
[Motor NP Volts] × 0.25
0.0/[Motor NP Volts]
0.1 VAC
[Motor NP Hertz] × 0.25
0.0/400.0
0.1 Hz
Related
053
070
053
069
053
072
053
071
Parameter Name and Description
File
See page 3-2 for symbol descriptions
Group
No.
080 [Speed Mode]
Sets the method of speed regulation.
• Open Loop provides no speed
compensation due to load variations.
This is strict volts per hertz output as a
function of the speed reference.
• Slip Comp provides for frequency
output adjustment as a function of
load. The amount of compensation is
defined by the value of 121 [Slip RPM
SPEED COMMAND
Spd Mode & Limits
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
@ FLA].
• Process PI allows for the output motor
speed (frequency) to be adjusted
based on the outer control loop
regulator.
Refer to Appendix
C.
Values
Default:
Options:00
1
2
“Open Loop”
“Open Loop”
“Slip Comp”
“Process PI”
Related
121
thru
138
Parameter Name and Description
File
See page 3-2 for symbol descriptions
Group
No.
081 [Minimum Speed]
Sets the low limit for speed reference after
scaling is applied.
Refer to parameter 083 [Overspeed Limit].
!
Programming and Parameters 3-19
Values
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
ATTENTION: Drive can operate at and maintain zero speed. The
user is responsible for assuring safe conditions for operating
personnel by providing suitable guards, audible or visual alarms, or
other devices to indicate that the drive is operating or may operate
at or near zero speed. Failure to observe this precaution could
result in severe bodily injury or loss of life.
0.0 Hz
0.0/[Maximum Speed]
0.1 Hz
Related
083
092
082 [Maximum Speed]
SPEED COMMAND
Sets the high limit for speed reference
Spd Mode & Limits
after scaling is applied.
Refer to parameter 083 [Overspeed Limit].
!
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
ATTENTION: The user is responsible for ensuring that driven
machinery, all drive-train mechanisms, and application material are
capable of safe operation at the maximum operating speed of the
drive. Overspeed detection in the drive determines when the drive
shuts down. See parameter 083 [Overspeed Limit]. Failure to
observe this precaution could result in bodily injury.
60.0 Hz
5.0/400.0 Hz
0.1 Hz
055
083
091
202
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

3-20 Programming and Parameters
Parameter Name and Description
File
See page 3-2 for symbol descriptions
Group
No.
083 [Overspeed Limit]
Sets the incremental amount of the output
frequency (above [Maximum Speed])
allowable for functions such as slip
compensation.
[Maximum Speed] + [Overspeed Limit]
must be ≤
SPEED COMMAND
Spd Mode & Limits
[Skip Frequency 1]
084
[Skip Frequency 2]
085
[Skip Frequency 3]
086
Max Volts
Motor Volts
Voltage
Break Volts
Start Boost
[Maximum Freq]
Frequency Trim due to
Speed Control Mode
Run
0 Min
Speed
Allowable Reference Frequency Range
Frequency
Sets a frequency at which the drive will
not operate.
087 [Skip Freq Band]
Determines the bandwidth around a skip
frequency. [Skip Freq Band] is split,
applying 1/2 above and 1/2 below the
actual skip frequency. The same
bandwidth applies to all skip frequencies.
Values
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Allowable Output Frequency Range
Bus Regulation or Current Limit
Allowable Output Frequency Range
Normal Operation
Overspeed
Break
Motor
Hz
Frequency
Default:
Default:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
10.0 Hz
0.0/20.0 Hz
0.1 Hz
Limit
Max
Speed
0.0 Hz
0.0 Hz
0.0 Hz
–/+400.0 Hz
0.1 Hz
1.0 Hz
0.0/30.0 Hz
0.1 Hz
Output
Freq Limit
Max
Freq
Related
055
082
087
084
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

Parameter Name and Description
File
See page 3-2 for symbol descriptions
Group
No.
089 [Logic Source Sel]
Selects the control source for the following
logic commands:
• Start (Run)
• Clear Faults
• Stop
The All Ports selection allows ports to
control the logic command
simultaneously.
Important: The drive is shipped with a default configuration of control from the
keypad. For drive control from the terminal block inputs, set this parameter to
option 0 “Terminal Blk”.
Important: Asserting the terminal block input OIM Control overrides parameter
089.
Important: Asserting the Purge input overrides OIM Control and parameter 089.
!
SPEED COMMAND
Spd Mode & Limits
Programming and Parameters 3-21
Values
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
“Local OIM”
“Terminal Blk”
“Local OIM”
“DPI Port 2”
“DPI Port 3”
“Reserved”
“Network”
“Reserved”
“All Ports”
Default:
Options:10
ATTENTION: Setting parameter 089 to “Terminal Blk” or “Network”
while 168 [LevelSense Start] is enabled may start the drive if a start
command is on from the newly selected logic source.
ATTENTION: When 168 [LevelSense Start] is enabled, the user
must ensure that automatic start up of the driven equipment will not
cause injury to operating personnel or damage to the driven
equipment. In addition, the user is responsible for providing suitable
audible or visual alarms or other devices to indicate that this
function is enabled and the drive may start at any moment. Failure
to observe this precaution could result in severe bodily injury or
loss of life.
ATTENTION: Removing and replacing the LCD OIM while the
drive is running may cause an abrupt speed change if the LCD OIM
is the selected reference source, but is not the selected control
source. The drive will ramp to the reference level provided by the
OIM at the rate specified in 140 [Accel Time 1], 141 [Accel Time 2],
142 [Decel Time 1] and 143 [Decel Time 2]. Be aware that an
abrupt speed change may occur depending upon the new
reference level and the rate specified in these parameters. Failure
to observe this precaution could result in bodily injury.
ATTENTION: Note the following about stop commands:
• A stop command from any attached OIM will always be enabled
regardless of the value of [Logic Source Sel].
• Network stop commands are effective only when [Logic Source
Sel] is set to option 5 “Network” or 7 “All Ports”.
• Terminal block stop commands are effective only when [Logic
Source Sel] is set to 0 “Terminal Blk” or 7 “All Ports”.
Failure to observe this precaution could result in severe bodily
injury or loss of life.
Related
090
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

3-22 Programming and Parameters
Parameter Name and Description
File
See page 3-2 for symbol descriptions
Group
No.
090 [Speed Ref A Sel]
Selects the source of the speed reference
to the drive unless [Speed Ref B Sel] or
[Preset Speed 1-7] is selected.
Note that the manual reference command
and inputs OIM Control and Purge can
override the reference control source.
For more information on selecting a speed
reference source, see Figure 1.20 on
page 1-35.
ATTENTION: Removing and replacing the LCD OIM while the
Speed References
SPEED COMMAND
drive is running may cause an abrupt speed change if the LCD OIM
!
is the selected reference source, but is not the selected control
source. The drive will ramp to the reference level provided by the
OIM at the rate specified in 140 [Accel Time 1], 141 [Accel Time 2],
142 [Decel Time 1] and 143 [Decel Time 2]. Be aware that an
abrupt speed change may occur depending upon the new
reference level and the rate specified in these parameters. Failure
to observe this precaution could result in bodily injury.
Values
Default:
Options:11
2
3-8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
“Analog In 1”
“Analog In 1”
“Analog In 2”
“Reserved”
“MOP Level”
“Reserved”
“Preset Spd1”
“Preset Spd2”
“Preset Spd3”
“Preset Spd4”
“Preset Spd5”
“Preset Spd6”
“Purge”
“Local OIM
“DPI Port 2”
“DPI Port 3”
“Reserved”
“Network”
“Reserved”
Related
002
091
092
101
thru
106
117
thru
120
192
thru
194
213
272
273
320
361
thru
366
091 [Speed Ref A Hi]
Scales the upper value of the [Speed Ref
A Sel] selection when the source is an
analog input.
092 [Speed Ref A Lo]
Scales the lower value of the [Speed Ref
A Sel] selection when the source is an
analog input.
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
[Maximum Speed]
–/+[Maximum Speed]
0.1 Hz
0.0 Hz
–/+[Maximum Speed]
0.1 Hz
082
092
081

Parameter Name and Description
File
See page 3-2 for symbol descriptions
Group
No.
096 [TB Man Ref Sel]
Sets the manual speed reference source
when a digital input is configured for
“Auto/Manual.”
(1)
“Analog In 2” is not a valid selection if it
was selected for any of the following:
- [Trim In Select]
- [PI Feedback Sel]
- [PI Reference Sel]
- [Current Lmt Sel]
097 [TB Man Ref Hi]
Speed Reference
Scales the upper value of the [TB Man
Ref Sel] selection when the source is an
analog input.
098 [TB Man Ref Lo]
Scales the lower value of the [TB Man Ref
Sel] selection when the source is an
analog input.
[Preset Speed 1]
101
SPEED COMMAND
[Preset Speed 2]
102
[Preset Speed 3]
103
[Preset Speed 4]
104
[Preset Speed 5]
105
[Preset Speed 6]
106
Provides an internal fixed speed
command value. In bipolar mode direction
is commanded by the sign of the
reference.
Discrete Speeds
107 [Purge Speed]
Provides a fixed internal speed similar to
[Preset Speed x]. It is also the frequency
the drive uses when the Purge digital
input is closed.
Programming and Parameters 3-23
Values
Default:
Options:11
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
“Analog In 1”
“Analog In 1”
2
“Analog In 2”
3-8
“Reserved”
9
“MOP Level”
[Maximum Speed]
–/+[Maximum Speed]
0.1 Hz
0.0 Hz
–/+[Maximum Speed]
0.1 Hz
5.0 Hz
10.0 Hz
20.0 Hz
30.0 Hz
40.0 Hz
50.0 Hz
–/+[Maximum Speed]
0.1 Hz
5.0 Hz
–/+[Maximum Speed]
0.1 Hz
097
098
(1)
096
096
090
Related
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

3-24 Programming and Parameters
Parameter Name and Description
File
See page 3-2 for symbol descriptions
Group
No.
117 [Trim In Select]
Specifies which analog input signal is
being used as a trim input. The trim input
signal is added to the Reference A signal.
If an analog input is used as the trim
signal, two scaling parameters are
provided.
[Trim In Select]
[Trim Out Select]
Reference A
+
+
118 [Trim Out Select]
Specifies which speed references are to be trimmed.
Speed Trim
SPEED COMMAND
10 01234567891112131415
Bit #
Trimmed
Reference A
* Enhanced Control Option Only.Factory Default Bit Values
Values
Default:
Options:21
Add or % *
Nibble 1Nibble 2Nibble 3Nibble 4
00x 0xxxxxxxxxxxx
2
3-8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
Tr im
Ref B
Trim Ref A
“Analog In 2”
“Analog In 1”
“Analog In 2”
“Reserved”
“MOP Level”
“Reserved”
“Preset Spd1”
“Preset Spd2”
“Preset Spd3”
“Preset Spd4”
“Preset Spd5”
“Preset Spd6”
“Purge”
“Local OIM
“DPI Port 2”
“DPI Port 3”
“Reserved”
“Network”
“Reserved”
1 = Trimmed
0 = Not Trimmed
x = Reserved
Related
090
117
119
120
119 [Trim Hi]
Scales the upper value of the [Trim In
Select] selection when the source is an
analog input.
120 [Trim Lo]
Scales the lower value of the [Trim In
Select] selection when the source is an
analog input.
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
60.0 Hz
–/+[Maximum Speed]
0.1 Hz
0.0 Hz
–/+[Maximum Speed]
0.1 Hz
082
117
117

Programming and Parameters 3-25
Parameter Name and Description
File
See page 3-2 for symbol descriptions
Group
No.
Important: Parameters in the Slip Comp Group are used to enable and tune the
Slip Compensation Regulator. In order to allow the Slip Compensation Regulator
to control drive operation, parameter 080 must be set to 1 “Slip Comp”.
Values
Related
121 [Slip RPM @ FLA]
Sets the amount of compensation to drive
output at motor FLA.
If the value of parameter 061 [Autotune] =
3 “Calculate” changes made to this
parameter will not be accepted.
Slip Comp
122 [Slip Comp Gain]
SPEED COMMAND
Sets the response time of slip
compensation.
123 [Slip RPM Meter]
Displays the present amount of
adjustment being applied as slip
compensation.
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Based on [Motor NP RPM]
0.0/1200.0 RPM
0.1 RPM
40.0
1.0/100.0
0.1
Read Only
–/+300.0 RPM
0.1 RPM
061
080
122
123
080
121
122
080
121
122
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

3-26 Programming and Parameters
Parameter Name and Description
File
See page 3-2 for symbol descriptions
Group
No.
Important: Parameters in the Process PI Group are used to enable and tune the
PI Loop. To allow the PI Loop to control drive operation, parameter 080 must be
set to 2 “Process PI”.
Values
Related
124 [PI Configuration]
Sets configuration of the PI regulator.
Option Descriptions
Excl Mode Enabled: Selects speed regulation (PI output used as speed
Invert Error Enables/disables the option to invert the sign of the PI error
Preload Mode Enabled: Initializes the PI integrator to the commanded speed
Process PI
SPEED COMMAND
Ramp Ref Enables/disables ramping the PI reference using PI Feedback
Zero Clamp Enables/disables option to limit operation so that the output
Feedback Sqrt Enables/disables the option of using the square root of the
Stop Mode Enabled: PI loop continues to operate during the decel ramp
Anti Wind Up Enabled: The PI loop automatically prevents the integrator from
Bit #
Factory Default Bit Values
command).
Disabled: Selects trim regulation (PI output summed with speed
command).
signal. Enabling creates a decrease in output for an increasing
error and an increase in output for a decreasing error.
while the PI is disabled.
Disabled: The PI integrator is loaded with the PI Pre-load (133)
while PI is disabled.
as the starting point and ramping to the selected PI Reference
after PI is enabled. The active accel time is used for the PI ramp
reference slew rate. The ramping is bypassed when the
reference equals the setpoint. The ramp used is set by the
active ramps (parameters 140 to 143).
frequency at the PI regulator always has the same sign as the
master speed reference. This limits the possible drive action to
one direction only. Output from the drive will be from zero to
maximum frequency forward or zero to maximum frequency
reverse.
feedback signal as the PI feedback.
after a stop command is issued. (Frame 2, 3, 4, 5, & 6)
Disabled: Drive performs a normal stop.
creating an excessive error that could cause instability. The
integrator will be controlled without the need for PI Reset or PI
Hold inputs. (Frame 2, 3, 4, 5, & 6)
124
thru
138
Sqrt
Mode
Ref
Mode
Ramp
Zero Clamp
Stop
Feedbak
Anti-Wind Up
10 01234567891112131415
Nibble 1Nibble 2Nibble 3Nibble 4
Excl
Invert Error
Preload
00000000xxxxxxxx
Mode
1=Enabled
0=Disabled
x=Reserved
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

File
Group
No.
125 [PI Control]
Programming and Parameters 3-27
Parameter Name and Description
See page 3-2 for symbol descriptions
Controls the PI regulator. You can use a Datalink parameter or an assigned digital
input to write to this parameter.
PI control allows the drive to take a reference signal (setpoint) and an actual
signal (feedback) and automatically adjust the speed of the drive to match the
actual signal to the reference.
Proportional control (P) adjusts the output based on the size of the error (larger
error = proportionally larger correction).
Integral control (I) adjusts the output based on the duration of the error. The
integral control by itself is a ramp output correction. This type of control gives a
smoothing effect to the output and will continue to integrate until zero error is
achieved.
By itself, integral control is slower than many applications require, and, therefore,
is combined with proportional control (PI).
The purpose of the PI regulator is to regulate a process variable such as position,
pressure, temperature, or flow rate, by controlling speed.
There are two ways the PI regulator can be configured to operate (see parameter
124):
• Process trim, which takes the output of the PI regulator and sums it with a
master speed reference to control the process.
• Process control, which takes the output of the PI regulator as the speed
command. No master speed reference exists, and the PI output directly
controls the drive output.
Values
Related
080
Process PI
SPEED COMMAND
PI Enable
PI Hold
PI Reset
00x 0xxxxxxxxxxxx
1=Enabled
10 01234567891112131415
Bit #
Factory Default Bit Values
Nibble 1Nibble 2Nibble 3Nibble 4
0=Disabled
x=Reserved
Option Descriptions
PI Enable Enables/disables operation of the PI loop.
PI Hold Enabled: Integrator for the outer control loop is held at the current
level (will not increase).
PI Reset Enabled: Integrator for the outer control loop is reset to zero.
Disabled: Integrator for the outer control loop integrates normally.
PI PosLmt
(132)
(131)
PI NegLmt
(130)
PI Kp
(126)
(128)
PI Ref
PI FB
(129)
+
–
PI Ki
PI_Status
Hold
(125)
+
+
PI Output
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
(138)
In Limit
(134)

3-28 Programming and Parameters
Parameter Name and Description
File
See page 3-2 for symbol descriptions
Group
No.
126 [PI Reference Sel]
Selects the source of the PI reference.
127 [PI Setpoint]
Provides an internal fixed value for
process setpoint when [PI Reference Sel]
is set to “PI Setpoint.”
Process PI
128 [PI Feedback Sel]
SPEED COMMAND
Selects the source of the PI feedback.
129 [PI Integral Time]
Time required for the integral component
to reach 100% of [PI Error Meter]. Not
functional when the PI Hold bit of [PI
Control] = “1” (enabled). A value of zero
disables this parameter
130 [PI Prop Gain]
Sets the value for the PI proportional
component.
PI Error × PI Prop Gain = PI Output
131 [PI Lower Limit]
Sets the lower limit of the PI output.
132 [PI Upper Limit]
Sets the upper limit of the PI output.
Values
Default:
Options:00
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Options:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
“PI Setpoint”
“PI Setpoint”
“Analog In 1”
1
“Analog In 2”
2
“Reserved”
3-8
“MOP Level”
9
“Master Ref”
10
“Preset Spd1”
11
“Preset Spd2”
12
“Preset Spd3”
13
“Preset Spd4”
14
“Preset Spd5”
15
“Preset Spd6”
16
“Purge”
17
“Local OIM”
18
“DPI Port 2”
19
“DPI Port 3”
20
“Reserved”
21
“Network”
22
“Reserved”
23
50.00%
–/+100.00% of Maximum
Process Value
0.01%
2 “Analog In 2”
See
[PI Reference Sel]
2.00 Secs
0.00/100.00 Secs
0.01 Secs
1.00
0.00/100.00
0.01
–[Maximum Freq]
–/+400.0 Hz
0.1 Hz
+[Maximum Freq]
–/+400.0 Hz
0.1 Hz
Related
124
thru
138
124
thru
138
124
thru
138
.
124
thru
138
124
thru
138
124
thru
138
124
thru
138
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

File
Group
No.
133 [PI Preload]
Parameter Name and Description
See page 3-2 for symbol descriptions
Sets the value used to preload the integral
component on start or enable.
(133)
Preload Value PI Integrator
(133)
Preload Value
Programming and Parameters 3-29
Values
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
0.0 Hz
–/+400.0 Hz
0.1 Hz
124
thru
138
Related
134 [PI Status]
Status of the Process PI regulator.
Option Descriptions
PI Enabled Indicates whether or not the PI loop is enabled.
Process PI
PI Hold Set to 1 to indicate when a digital input is configured for PI Hold
SPEED COMMAND
PI Reset Set to 1 to indicate when the PI Integrator is being set to zero.
PI InLimit Set to 1 to indicate when the PI output equals positive limit or
135 [PI Ref Meter]
Present value of the PI reference signal.
136 [PI Fdback Meter]
Present value of the PI feedback signal.
137 [PI Error Meter]
Present value of the PI error.
138 [PI Output Meter]
Present value of the PI output.
Bit #
Read Only 124
PI Enabled
PI Hold
PI Reset
PI InLimit
0000xxxxxxxxxxxx
1=Condition True
10 01234567891112131415
Nibble 1Nibble 2Nibble 3Nibble 4
0=Condition False
x=Reserved
and is turned on, or the PI Hold bit is set in 125 [PI Control].
negative limit.
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Read Only
–/+100.00%
0.01%
Read Only
–/+100.00%
0.01%
Read Only
–/+100.00%
0.01%
Read Only
–/+100.0 Hz
0.1 Hz
thru
138
124
thru
138
124
thru
138
124
thru
138
124
thru
138
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

3-30 Programming and Parameters
Dynamic Control File
Parameter Name and Description
File
DYNAMIC CONTROL
See page 3-2 for symbol descriptions
Group
No.
140
[Accel Time 1]
[Accel Time 2]
141
Sets the rate the drive ramps to its output
frequency after a start command or during
a speed change.
Max Speed
Accel Time
Two accel times are provided to allow
acceleration rate changes “on the fly”
using a building automation system
command, digital input, or F-Key if
configured (see Appendix
142
[Decel Time 1]
[Decel Time 2]
143
Sets the rate of decel for all speed
decreases.
Ramp Rates
Max Speed
Decel Time
Two decel times are provided to allow
acceleration rate changes “on the fly”
using a building automation system
command, digital input, or F-Key if
configured (see Appendix
=
Accel Rate
=
Decel Rate
146 [S Curve %]
Sets the percentage of accel or decel time
that is applied to the ramp as S Curve.
Time is added, 1/2 at the beginning and
1/2 at the end of the ramp.
147 [Current Lmt Sel]
Selects the source for the adjustment of
current limit (i.e. parameter, analog input,
etc.).
148 [Current Lmt Val]
Defines the current limit value when
[Current Lmt Sel] = “Cur Lim Val.”
149 [Current Lmt Gain]
Load Limits
Sets the responsiveness of the current
limit.
150 [Drive OL Mode]
Selects the drive’s response to increasing
drive temperature.
B).
B).
Values
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Options:00
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Options:30
20.0 Secs
20.0 Secs
0.1/3600.0 Secs
0.1 Secs
20.0 Secs
20.0 Secs
0.1/3600.0 Secs
0.1 Secs
20%
0/100%
1%
“Cur Lim Val”
“Cur Lim Val”
1
“Analog In 1”
2
“Analog In 2”
[Rated Amps] × 1.5
(Equation approximates
default value.)
Drive Rating Based
0.1 Amps
200
0/5000
1
“Both–PWM 1st”
“Disabled”
1
“Reduce CLim”
2
“Reduce PWM”
3
“Both–PWM 1st”
Related
142
143
146
361
thru
366
140
141
146
361
thru
366
140
thru
143
146
149
147
149
147
148
219
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
Parameter Name and Description
File
See page 3-2 for symbol descriptions
Group
No.
151 [CarrierFrequency]
Sets the carrier frequency for the PWM
output. Drive derating may occur at higher
carrier frequencies. For derating
information, refer to Appendix A
155
[Stop Mode A]
[Stop Mode B]
156
Active stop mode. [Stop Mode A] is active
unless [Stop Mode B] is selected by
inputs. Allows switching between two stop
modes using external logic.
(1)
When using options 1 or 2, refer to the
Attention statements at [DC Brake
Load Limits
DYNAMIC CONTROL
Level].
!
Programming and Parameters 3-31
Values
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
.
Default:
Default:
Options:
ATTENTION: If a hazard of injury do to movement of equipment or
material exists, an auxiliary mechanical braking device must be
used.
ATTENTION: The user must provide an external, hard wired
emergency stop circuit outside of the drive circuitry. This circuit
must disable the system in case of improper operation.
Uncontrolled machine operation may result if this procedure is not
followed. Failure to observe this precaution could result in bodily
injury.
4 kHz
2/10 kHz
1 kHz
“Coast”
0
“Ramp”
1
“Coast”
0
“Ramp”
1
2
“Ramp to Hold”
3
“DC Brake”
(1)
(1)
Related
157
158
159
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

3-32 Programming and Parameters
Parameter Name and Description
File
See page 3-2 for symbol descriptions
Group
No.
157 [DC Brake Lvl Sel]
Selects the source for [DC Brake Level].
158 [DC Brake Level]
Defines the DC brake current level
injected into the motor when “DC Brake”
is selected as a stop mode.
The DC braking voltage used in this
function is created by a PWM algorithm
and may not generate the smooth holding
force needed for some applications.
ATTENTION: If a hazard of injury due to movement of equipment
or material exists, an auxiliary mechanical braking device must be
!
used. Failure to observe this precaution could result in severe
bodily injury or loss of life.
DYNAMIC CONTROL
Stop/Brake Modes
ATTENTION: This feature should not be used with synchronous or
permanent magnet motors. Motors may be demagnetized during
braking. Failure to observe this precaution could result in damage
to, or destruction of, equipment.
Values
Default:
Options:00
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
“DC Brake Lvl”
“DC Brake Lvl”
1
“Analog In 1”
2
“Analog In 2”
[Rated Amps]
0/[Rated Amps] × 1.5
(Equation yields
approximate maximum
value.)
0.1 Amps
Related
155
156
158
159
159 [DC Brake Time]
Sets the amount of time DC brake current
is “injected” into the motor.
160 [Bus Reg Ki]
(Bus Reg Gain)
Sets the responsiveness of the bus
regulator.
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
0.0 Secs
0.0/90.0 Secs
0.1 Secs
450
0/5000
1
155
thru
158
161
162

Programming and Parameters 3-33
Parameter Name and Description
File
DYNAMIC CONTROL
See page 3-2 for symbol descriptions
Group
No.
161
[Bus Reg Mode A]
[Bus Reg Mode B]
162
Sets the method and sequence of the DC
bus regulator voltage. Choices are
dynamic brake, frequency adjust or both.
Sequence is determined by programming
or digital input to the terminal block.
Dynamic Brake Setup
If a dynamic brake resistor is connected to
the drive, both these parameters must be
set to either option 2, 3 or 4.
ATTENTION: The drive does not offer protection for externally
mounted brake resistors. A risk of fire exists if external braking
!
resistors are not protected. External resistor packages must be
self-protected from over temperature or the protective circuit shown
in Figure C.1 on page C-1
ATTENTION: The adjust freq portion of the bus regulator function
is extremely useful for preventing nuisance overvoltage faults
resulting from aggressive decelerations, overhauling loads, and
eccentric loads. It forces the output frequency to be greater than
commanded frequency while the drive’s bus voltage is increasing
towards levels that would otherwise cause a fault. However, it can
Stop/Brake Modes
also cause either of the following two conditions to occur:
• Fast positive changes in input voltage (more than a 10%
increase within 6 minutes) can cause uncommanded positive
speed changes; however, an OverSpeed Limit fault will occur if
the speed reaches Max Speed + Overspeed Limit. If this
condition is unacceptable, action should be taken to 1) limit
supply voltages within the specification of the drive, and 2) limit
fast positive input voltage changes to less than 10%. Without
taking such actions, if this operation is unacceptable, the adjust
freq portion of the bus regulator function must be disabled (see
parameters 161 and 162).
• Actual deceleration times can be longer than commanded
deceleration times; however, a Decel Inhibit fault is generated if
the drive stops decelerating altogether. If this condition is
unacceptable, the adjust freq portion of the bus regulator must
be disabled (see parameters 161 and 162). In addition,
installing a properly sized dynamic brake resistor will provide
equal or better performance in most cases.
Note that these faults are not instantaneous and have shown test
results that take between 2 and 12 seconds to occur.
Values
Default:
Options:
(or equivalent) must be supplied.
“Adjust Freq”
1
“Disabled”
0
“Disabled”
0
“Adjust Freq”
1
“Dynamic Brak”
2
“Both-DB 1st”
3
“Both-Frq 1st”
4
Related
160
163
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

3-34 Programming and Parameters
Parameter Name and Description
File
See page 3-2 for symbol descriptions
Group
No.
163 [DB Resistor Type]
Selects whether the internal or an
external DB resistor will be used.
If a dynamic brake resistor is connected to
the drive, [Bus Reg Mode x], A, B or Both
(if used), must be set to either option 2, 3
or 4.
ATTENTION: The drive does not offer protection for externally
mounted brake resistors. A risk of fire exists if external braking
!
resistors are not protected. External resistor packages must be
self-protected from over temperature or the protective circuit shown
in Figure C.1 on page C-1
Stop/Brake Modes
DYNAMIC CONTROL
ATTENTION: Equipment damage may result if a drive mounted
(internal) resistor is installed and this parameter is set to “External
Res.” Thermal protection for the internal resistor will be disabled,
resulting in possible device damage.
Values
Default:
Options:00
, or equivalent, must be supplied.
1
2
“Internal Res”
“Internal Res”
“External Res”
“None”
Related
161
162
164 [Bus Reg Kp]
2…6
Proportional gain for the bus regulator.
Used to adjust regulator response.
165 [Bus Reg Kd]
2…6
Derivative gain for the bus regulator. Used
to control regulator overshoot.
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
1200
0/10000
1
1000
0/10000
1
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

Parameter Name and Description
File
See page 3-2 for symbol descriptions
Group
No.
168 [LevelSense Start]
Enables/disables a feature to issue a Start
or Run command and automatically
resume running at commanded speed
after drive input power is restored.
Requires a digital input configured for Run
or Start and a valid start contact.
Enables/disables a feature to issue a start or run command and automatically run
at the commanded speed when drive input power is applied.
Disabled: The drive starts on the open-to-closed transition of the control source
start input when no start inhibit conditions are present (edge-sensitive detection).
Enabled: The drive starts when the control source start input is closed, no start
inhibit conditions are present, and power is applied (level-sensitive detection).
Note that this feature (LevelSense Start) requires a digital input configured for run
or start and a valid start contact.
!
Restart Modes
DYNAMIC CONTROL
Programming and Parameters 3-35
Values
Default:
Options:10
ATTENTION: Equipment damage and/or personal injury may
result if this parameter is used in an inappropriate application. Do
not use this function without considering applicable local, national
and international codes, standards, regulations or industry
guidelines.
ATTENTION: Be aware of the following:
• Setting parameter 168 to 1 (Enabled) immediately applies
output power to the motor when all start conditions are met.
• If the drive is running from the terminal block, LevelSense Start
is enabled, and a fault occurs, the drive coasts to rest and
generates a fault. In this case, resetting and clearing the fault
immediately restarts the drive without any change to the start or
stop input states.
When this function is enabled, the user must ensure that automatic
start up of the driven equipment will not cause injury to operating
personnel or damage to the driven equipment. In addition, the user
is responsible for providing suitable audible or visual alarms or
other devices to indicate that this function is enabled and the drive
may start at any moment. Failure to observe this precaution could
result in severe bodily injury or loss of life.
ATTENTION: Disabling this function will alter the operation of the
drive or, for drives with the bypass option, inhibit the drive from
starting. Do not disable this function. Failure to observe this
precaution could result in severe bodily injury or loss of life.
1
“Enabled”
“Disabled”
“Enabled”
Related
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

3-36 Programming and Parameters
Parameter Name and Description
File
See page 3-2 for symbol descriptions
Group
No.
169 [Flying Start En]
Enables/disables the function which
reconnects to a spinning motor at actual
RPM when a start command is issued.
When a drive is started in its normal mode, it initially applies a frequency of 0 Hz
and ramps to the desired frequency. If the drive is started into an already spinning
motor in this manner, without Flying Start enabled, large currents will be
generated and an overcurrent trip may result.
In Flying Start mode, the drive's response to a start command will be to identify
the motor's speed and apply a voltage that is synchronized in frequency,
Restart Modes
DYNAMIC CONTROL
amplitude and phase to the counter emf of the spinning motor. The motor will then
accelerate to the desired frequency.
170 [Flying StartGain]
Sets the response of the flying start
function.
Values
Default:
Options:10
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
“Enabled”
“Disabled”
1
“Enabled”
4000
20/32767
1
Related
170
169
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P

Parameter Name and Description
File
See page 3-2 for symbol descriptions
Group
No.
174 [Auto Rstrt Tries]
Sets the maximum number of times the
drive attempts to reset a fault and restart.
Important: The drive will re-start after a reset if the start input is still asserted.
Specifies the maximum number of times the drive attempts to reset a fault and
restart when the auto restart feature is enabled.
The auto restart feature provides the ability for the drive to automatically perform a
fault reset followed by a start attempt without user or application intervention. Only
certain faults are permitted to be reset, see chapter 12 for more information.
When the auto restart feature is enabled (that is, Auto Rstrt Tries is set to a value
Restart Modes
DYNAMIC CONTROL
greater than zero), and an auto-resettable fault occurs, the drive will stop. After the
number of seconds in [Auto Restrt Delay] has elapsed, the drive will automatically
reset the faulted condition. The drive will then issue an internal start command to
start the drive.
If another auto-resettable fault occurs, the cycle will repeat up to the number of
attempts specified in Auto Rstrt Tries.
If the drive faults repeatedly for more than the number of attempts specified in
Auto Rstrt Tries with less than five minutes between each fault, the drive will
remain in the faulted state. The fault Auto Rstrt Tries will be logged in the fault
queue.
The auto restart feature is disabled when the drive is stopping and during
autotuning. Note that a DC Hold state is considered stopping.
The following conditions will abort the reset/run process:
• Issuing a stop command from any control source. (Note that removal of a
2-wire run-fwd or run-rev command is considered a stop command.)
• Issuing a fault reset command from any active source.
• Removing the enable input signal.
• Setting Auto Restrt Tries to zero.
• Occurrence of a fault that is not auto-resettable.
• Removing power from the drive.
• Exhausting an auto-reset/run cycle.
Note that two autotuning status bits are provided in [Drive Status 2]: an active
status bit and a countdown status bit.
Programming and Parameters 3-37
Values
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
ATTENTION: Equipment damage and/or personal injury may
result if this parameter is used in an inappropriate application. Do
!
not use this function without considering applicable local, national
and international codes, standards, regulations or industry
guidelines.
ATTENTION: The drive may start immediately after a fault is
auto-reset when 168 [LevelSense Start] is enabled.
When LevelSense Start is enabled, the user must ensure that
automatic start up of the driven equipment will not cause injury to
operating personnel or damage to the driven equipment. In
addition, the user is responsible for providing suitable audible or
visual alarms or other devices to indicate that this function is
enabled and the drive may start at any moment. Failure to observe
this precaution could result in severe bodily injury or loss of life.
0
0/9
1
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
Related
175

3-38 Programming and Parameters
Parameter Name and Description
File
See page 3-2 for symbol descriptions
Group
No.
175 [Auto Rstrt Delay]
Sets the time between restart attempts
when [Auto Rstrt Tries] is set to a value
other than zero.
178 [Sleep Wake Mode]
Enables/disables the Sleep/Wake
function. Important: When enabled, the
following conditions must be met:
• A proper value must be programmed
for [Sleep Level] & [Wake Level].
• A speed reference must be selected in
[Speed Ref A Sel].
• At least one of the following must be
programmed (and input closed) in
[Digital Inx Sel]; “Enable,” “Stop=CF,”
“Run,” “Run Forward,” “Run Reverse.”
ATTENTION: Enabling the Sleep-Wake function can cause
unexpected machine operation during the Wake mode. Equipment
damage and/or personal injury can result if this parameter is used in
!
Restart Modes
DYNAMIC CONTROL
an inappropriate application. Do Not use this function without
considering the information below. Failure to observe this precaution
could result in personal injury or damage to equipment.
Values
Default:
Min/Max:
Units:
Default:
Options:00
30.0 Secs
0.5/30.0 Secs
0.1 Secs
“Disabled”
“Disabled”
1
“Direct”
Related
174
Conditions Required to Start Drive
Important: P089 [Logic Source Sel] = 0 “Terminal Blk”
After Power-Up After a Drive Fault After a Stop Command
Input
Stop Stop Closed
Wake Signal
Enable Enable Closed
Wake Signal
Run Closed
Run
Wake Signal
Run For.
Run Rev.
Publication 9VT-UM001D-EN-P
Reset by Stop-CF,
OIM or TB
Stop Closed
Wake Signal
New Start or Run Cmd.
Enable Closed
Wake Signal
New Start or Run Cmd.
New Run Cmd.
Wake Signal
Reset by Clear
Faul ts (TB) OIM or TB
Stop Closed
Wake Signal
Enable Closed
Wake Signal
Run Closed
Wake Signal
Stop Closed
Direct Mode
Analog Sig. > Wake Level
Enable Closed
Direct Mode
Analog Sig. > Wake Level
New Run Cmd.
Wake Signal
 Loading...
Loading...