Page 1

User’s Guide RIGOL
Publication number DM3-070920
September 2007
DM3000 Series Digital Multimeter
DM3061/2/3/4
DM3051/2/3/4
© Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007
All Rights Reserved
Page 2

Page 3

RIGOL
z Copyright © RIGOL TECHNOLOGIES, INC. 2007 All Rights Reserved.
z RIGOL products are protected by patent law in and outside of P.R. China.
z Information in this publication replaces that in all previously corresponding
material.
z RIGOL Technologies, Inc. reserves the right to modify or change pat of or
all the specifications and pricing policies at company’s sole decision.
NOTE: RIGOL is the registered trademark of RIGOL TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
I
Page 4

RIGOL
Safety Notices
Review the following safety precautions carefully before operate the instrument
to avoid any personal injury or to damage the instrument and any products
connected to it.
To avoid potential hazards use the instrument in a manner only as specified by
this user’s guide.
The instrument should be serviced only by qualified personnel.
To Avoid Fire or Personal Injury.
Use proper power cord. Use only the power cord designed for your
oscilloscope and authorized in your country.
Connect and Disconnect accessories properly. Do not connect or
disconnect probes or test leads while they are connected to a voltage source.
Ground the instrument. This product is grounded through the protective terra
conductor of the power cord. To avoid electric shock the grounding conductor
must be connected to earth ground. Before making connections to the input or
output terminals of the oscilloscope ensure that the instrument is properly
grounded.
Connect the probe properly. The probes’ ground terminals are at the same
voltage level with earth terminal of the instrument. Do not connect the ground
terminals to a high voltage.
Observe All Terminal Ratings. To avoid fire or shock hazard, observe all
ratings and marks on the instrument. Follow the User’s Guide for further ratings
information before making connections to the instrument.
Do not operate without Covers. Do not operate your oscilloscope with covers
or panels removed.
II
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 5

RIGOL
Use Proper Fuse. Use only the fuse type and rating specified for this product.
Avoid Circuit or Wire Exposure. Do not touch exposed connections and
components when power is on.
Do not operate with suspected failures. If you suspect damage with this
product, have it inspected by qualified service personnel who were authorized by
RIGOL before further operations.
Provide Proper Ventilation. Refer to the manual’s installation instructions for
details as to the oscilloscope has proper ventilation.
Do not operate in wet/damp conditions.
Do not operate in an explosive atmosphere.
Keep product surfaces clean and dry.
The disturbance test of all the models can meet the limit values of A in
the standard of EN 61326: 1997+A1+A2+A3, but can't meet the limit
values of B.
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
III
Page 6

RIGOL
Safety Terms and Symbols
Terms in This Guide. These terms may appear in this guide:
!
!
!
Terms on the Product: These terms may appear on the product:
DANGER indicates an injury hazard may happen immediately.
WARNING indicates an injury hazard may not happen immediately.
CAUTION indicates that a potential damage to the instrument or other property
might occur.
Symbols on the Product: These symbols may appear on the Instrument:
Hazardous
Voltage
WARNING: Warning statements identify conditions or practices that
could result in injury or loss of life.
CAUTION: Caution statements identify conditions or practices that
could result in damage to this product or other property.
CAT II (300V): IEC Measurement Category II. Inputs may be
connected to mains (up to 300 VAC) under Category II overvoltage
conditions.
!
Refer to
Instructions
Protective
Earth Terminal
Grounding
Terminal
of Chassis
Test
Grounding
Terminal
IV
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 7
RIGOL
General-Purpose Multimeter
The book covers the following description and eight models DM3000 Series
Digital Multimeter:
DM3061, DM3062, DM3063, DM3064;
DM3051, DM3052, DM3053, DM3054.
DM3000 Series Digital Multimeter desktop naming rules:
DM
30
6 1
Prefix desktop Digital Multimeter
Serial Number
3
4
digit
6-6
1
2
, 5-5
No.
1-Basic; 2-Interface models with expansion board;
3-Inspection plate with the model;
4-Inspection plate with the model and interface extended board.
Application examples:
1
DM3061- 6
2
DM3000 series, Basic type.
1
DM3062- 6
2
DM3000 series, Basic type. Append the interface board with
LAN/GPIB module.
1
DM3063- 6
DM3064- 6
2
DM3000 Series, Basic type. Append the inspection board.
1
2
DM3000 series, Basic type. Append the interface board with
LAN/GPIB and inspection board.
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
V
Page 8

RIGOL
RIGOL DM3000-Series Digital Multimeter is a high-precision, multifunction,
1
multi-automatic measurement for user’s designment of products, including 6
2
digits multimeter, high-speed data acquisition, automatic measurement and
inspection, many mathematical transform, in one of sensor measurements and
other functions. In support RS-232, USB, LAN and GPIB interface. It supports U
disk storage and print.
In performance, the DM3000 has high-resolution monochrome LCD display
system, supports a simple waveform display and data recording waveform
display; clear and easy to operate the button backlight keyboard layout and
operation make it more flexible, user-friendly operating features; 50k/s high data
sampling rate, can be used, such as the rapidly changing high-precision audio
waveform data; depth 2Mbyte of internal storage, external storage can be
arbitrary depth; adopt true RMS AC voltage and current measurement; virtual
terminal display and control, and remote network access.
From the performance and characteristics are given below, you will Understand
how can DM3000 satisfy your measurement requirements.
z 50k/s data sampling rate can be used, such as the rapidly changing
high-precision audio waveform data. Meanwhile waveform can be displayed
on LCD Screen
z Measurement accuracy: more than 6 1/2 and 2,400,000 Count
z 26 measurement functions
DC voltage and current, AC voltage and current, two-wire and four-wire
resistance, capacitance, continuity test, diode test, frequency, cycle
ratio measurements, arbitrary sensor measurement,
And so on.
Upper limit and lower limit on the threshold measurement
Arithmetic include: maximum, minimum, average, dBm, dB
Data acquisition functions include : data records, inspection, automatic
measurement
z True RMS AC voltage and current measurement
z 16- Road inspection functional measurement and control software (optional)
z DC voltage >10GΩ input impedance to achieve the scope of 48V (±24V)
z With data acquisition function,
the maximum sampling rate support to
50kSP/s
z 10 groups measuring set-up storage and embedded PC measuring set up
VI
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 9

RIGOL
unlimited storage
z Saturating responses of 256 x 64 pixel monochrome LCD
z I/O: RS-232, USB, LAN and GPIB
z Built-in USB Host to support USB disk and USB printer
z Simple, convenient, flexible control software: Ultralogger, Supports for
Microsoft® Windows 98/2000/Me/XP
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
VII
Page 10

RIGOL
Content
Safety Notices ......................................................................................................................II
General-Purpose Multimeter ..............................................................................................V
CHAPTER 1 BASIC MULTIMETER OPERATIONS ........................................ 1-1
General Inspection ...........................................................................................................1-2
Handle Adjustment...........................................................................................................1-3
The Front/Rear Panel and User Interface..................................................................... 1-4
To Measure DC Voltage...................................................................................................1-7
To Measure AC Voltage ...................................................................................................1-9
To Measure DC Current.................................................................................................1-11
To Measure AC Current .................................................................................................1-13
To Measure Resistance.................................................................................................. 1-15
To Measure Capacitance ...............................................................................................1-19
To Test Continuity..........................................................................................................1-21
To Check Diodes.............................................................................................................1-23
To Measure Frequency and Period ..............................................................................1-25
To Measure Arbitrary Sensor........................................................................................1-29
To Choice Digits resolving index ..................................................................................1-34
To Choose Data Digit Display.......................................................................................1-35
To Choose Range Options.............................................................................................1-36
To Control Trigger Options ...........................................................................................1-38
CHAPTER 2 OPERATING YOUR MULTIMETER ........................................... 2-1
To Set up Measurement Parameters.............................................................................2-2
Math Functions ...............................................................................................................2-12
To Set Up Triggering Parameter Function..................................................................2-19
Store and Recall..............................................................................................................2-27
To Set Up the Utility.......................................................................................................2-32
High-speed Data Logger ...............................................................................................2-46
Multi-route Scanning......................................................................................................2-53
How to Use the Built-in Help System ..........................................................................2-61
CHAPTER 3 APPLICATION & EXAMPLES .................................................... 3-1
Example 1: Reading Statistic Functions........................................................................3-1
Example 2: Elimination Test Leads Resistance Error...................................................3-3
Example 3: dB Measurement..........................................................................................3-4
Example 4: dBm Measurement ......................................................................................3-5
VIII
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
Page 11

RIGOL
Example 5: Limit Test.......................................................................................................3-6
Example 6: Temperature Sensor ....................................................................................3-7
Example 7: Reading Hold............................................................................................. 3-11
CHAPTER 4 PROMPT MESSAGES& TROUBLESHOOTING .........................4-1
Prompting Message..........................................................................................................4-1
Troubleshooting ................................................................................................................4-3
CHAPTER 5 SUPPORT & SERVICE ................................................................5-4
CHAPTER 6 APPENDIX...................................................................................6-1
Appendix A: Specifications ..............................................................................................6-1
Appendix B: DM3000 Series Accessories ......................................................................6-7
Appendix C: General Care and Cleaning .......................................................................6-8
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
IX
Page 12

Page 13

RIGOL
Chapter 1 Basic Multimeter Operations
This chapter covers the following topics:
General Inspection
Handle Adjustment
The Front Panel and User Interface
To Measure DC Voltage
To Measure AC Voltage
To Measure DC Current
To Measure AC Current
To Measure Resistance
To M ea su re Ca pa c i t an ce
To Test Continuity
To Check Diodes
To Measure Frequency and Period
To Make an Arbitrary Sensor measurement
To Choice Digits resolving index
To Choose Data Digit Display
To Choose Range Options
To Control Trigger Options
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
1-1
Page 14

RIGOL
General Inspection
After you get a new DM3000 Digital Multimeter, you are suggested the following
steps to inspect the instrument.
1. Inspect the shipping container for damage.
Keep a damaged shipping container or cushioning material until the contents of
the shipment have been checked for completeness and the instrument has been
checked mechanically and electrically.
2. Check the accessories.
Accessories supplied with the instrument are listed in "Appendix B" in Chapter 6.
If the contents are incomplete or damaged, please notify your RIGOL Sales
Representative.
3. Inspect the instrument.
In case any mechanical damage or defect, or if the instrument does not operate
properly or pass performance tests, notify your RIGOL Sales Representative.
If the shipping container is damaged, or the cushioning materials show signs of
stress, notify the carrier as well as your RIGOL sales office. Keep the shipping
materials for the carrier’s inspection.
RIGOL offices will arrange for reparation or replacement at RIGOL’s option without
waiting for claim settlement.
1-2
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 15
RIGOL
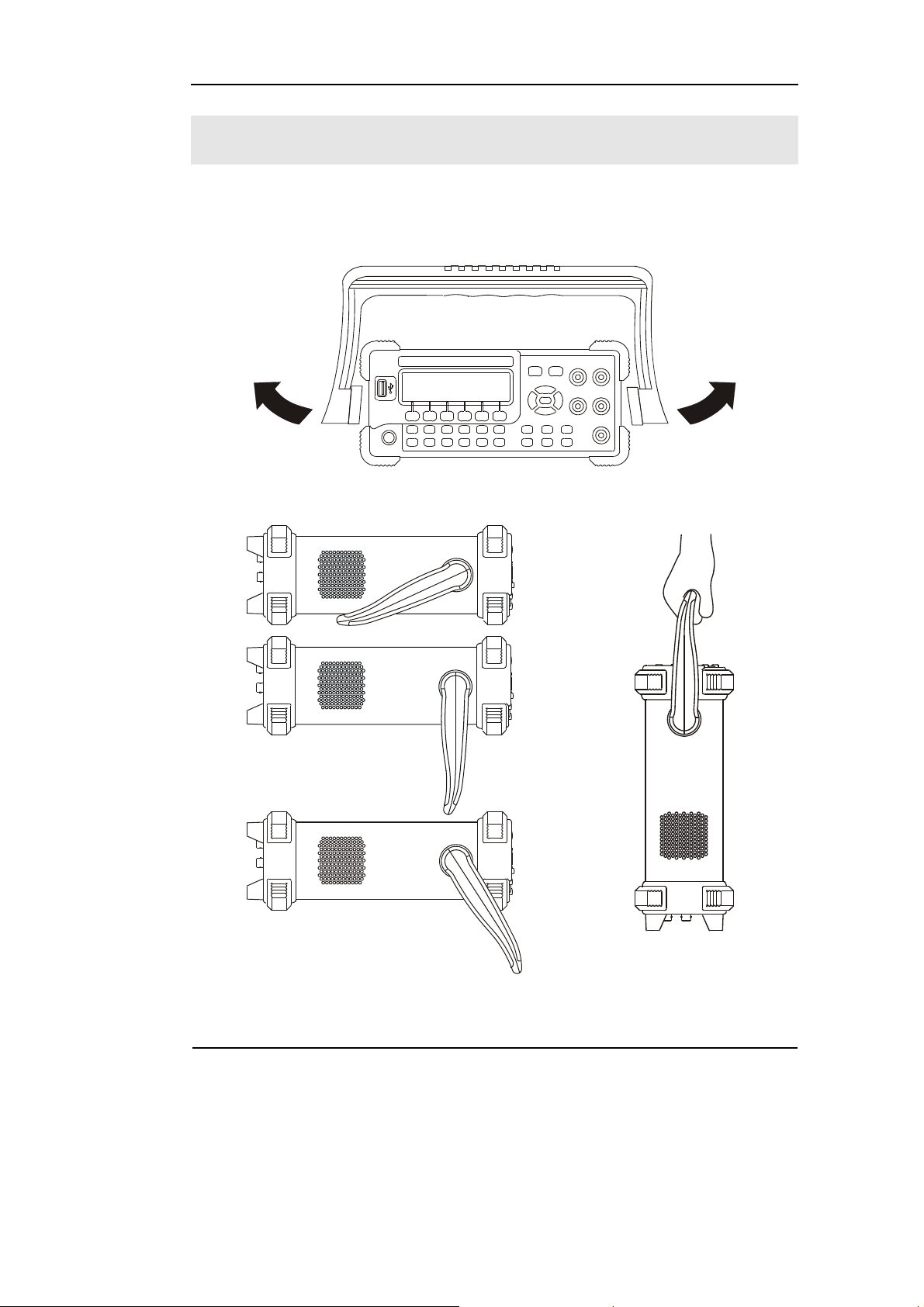
Handle Adjustment
To adjust the handle position of DM3000 Digital Multimeter, please grip the handle by
the sides and pull it outward. Then, make the handle rotate to the desired position.
The operation methods are shown in the graphs 1-1, 1-2, 1-3.
Figure 1-1
Figure 1-2 Figure 1-3
Viewing Positions Carrying Position
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
1-3
Page 16
RIGOL
eys
y
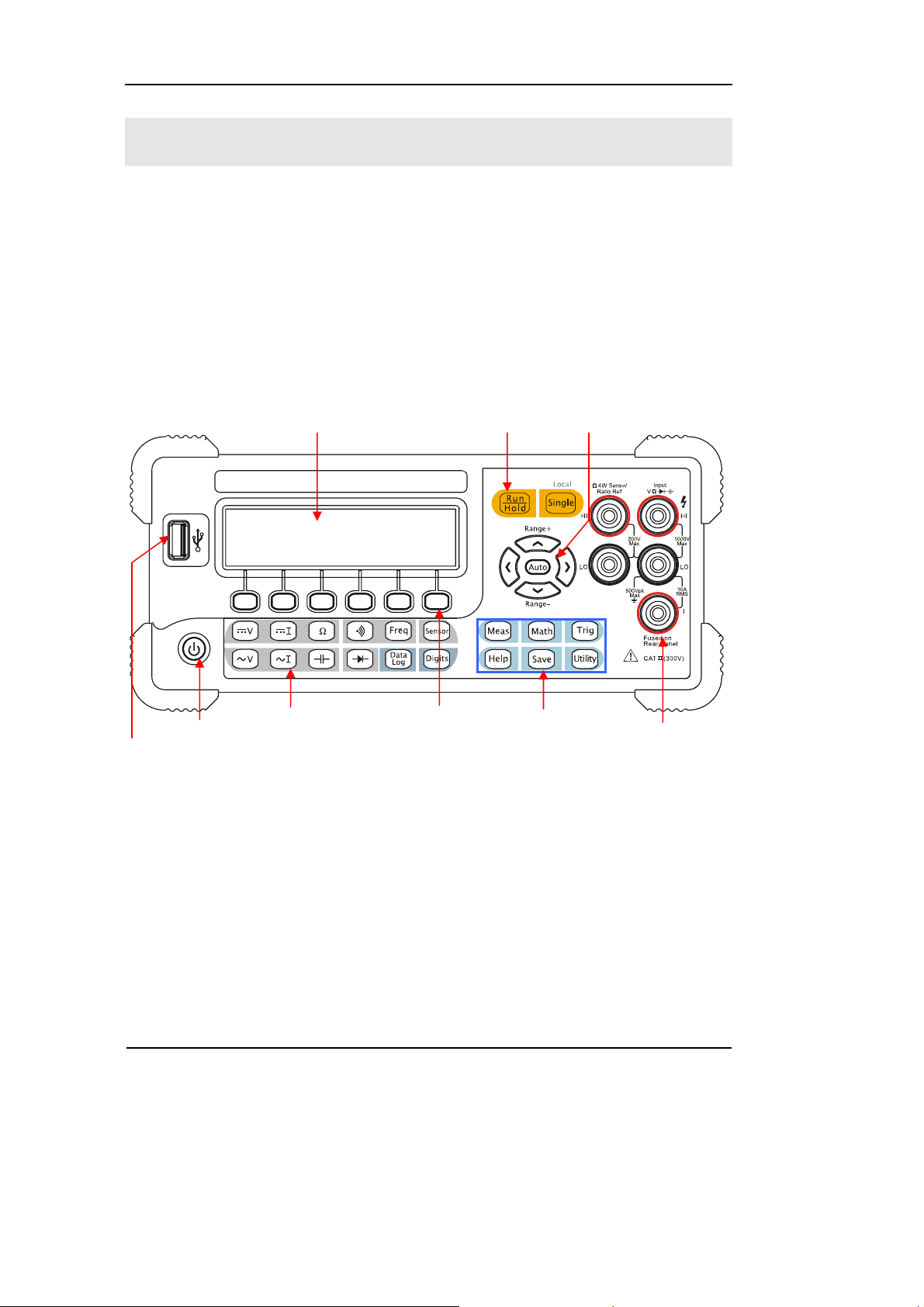
The Front/Rear Panel and User Interface
After you get a new DM3000 Digital Multimeter, first, you need to clear how to
operate the front panel of the DM3000 correctly. This chapter will make a brief
introduction and description for the operation and functions of the Front Panel.
The front panel of the DM3000 is very simple and clear for users operation. The front
panel include direction buttons and functions buttons.
LCD Display
District Yellow:
Trigger Control Keys
Direction Keys
USB Host
1-4
On/Off
District Purple:
Measurement
Function K
Menu Operation
Keys
Blue Direction:
Function Selective
Ke
Figure 1-4
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Current Input Terminal
s
Page 17
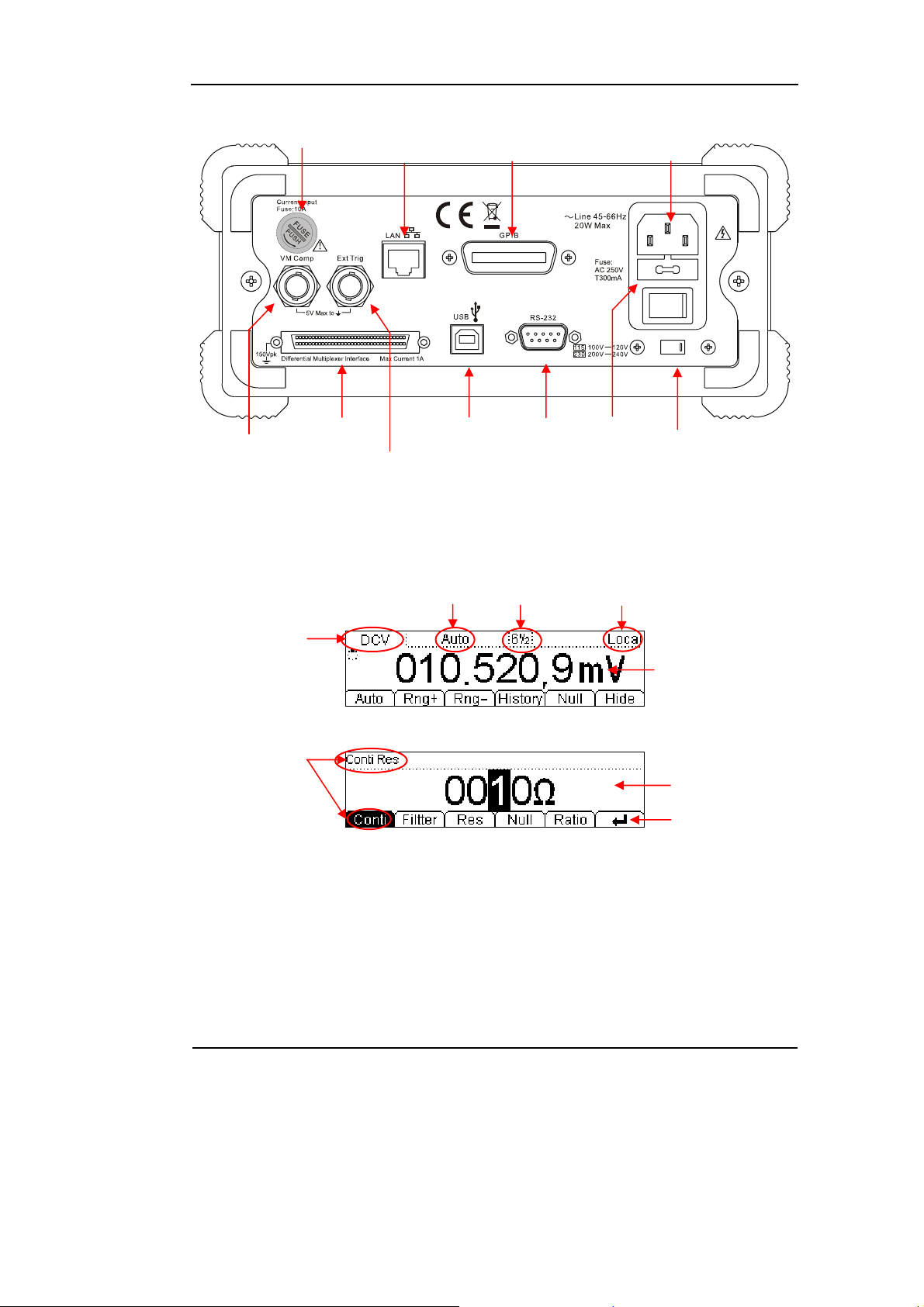
RIGOL
play
Current Input Fuse
10/100
Ethernet
GPIB
(IEEE--488)
Power Socket
VMC
Current
Measurement
Parameters
Differential
Multiplexer Interface
Name
USB Device RS--232
Ext Trigger
Figure 1-5
Range
Figure 1-6
The interface explanation
Digits
resolving
index
Power Fuse
Local/Remote
Operation
AC Voltage
Selector
Measurement
Data Display
Parameters
Dis
Operation
Menu
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
1-5
Page 18

RIGOL
How the definitions express in this book:
In this book, the regarding keys writing expression has the same log with the
keys on the front panel. It is noteworthy that the menu operates keys, marking with
the belt shadow. For example, Conti indicates the short circuit option in menu .
1-6
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 19
RIGOL
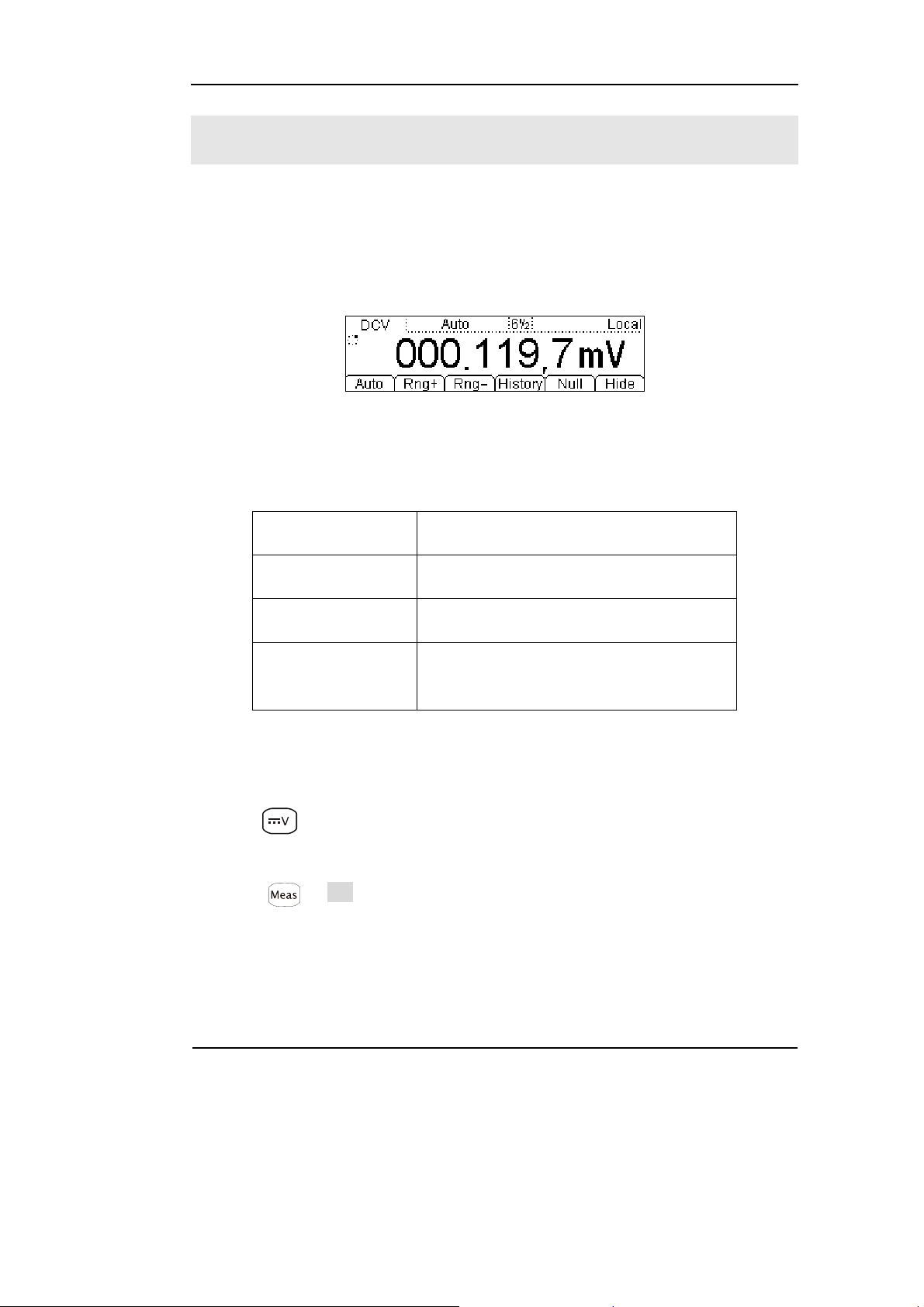
To Measure DC Voltage
In view of DC voltage measurement function, the following part demonstrated how
to link the measurement connection and how to choose measurement functions. The
following practice will gradually guide you to be familiar with the DC Voltage
measurement technique.
Figure 1-7
DC Voltage measurement data interface
Table 1-1 DC Voltage measurement characteristics
Five Range 200mV, 2V, 20V, 200V, 1000V
Max Resolution 100nV
Import Protection 1000V on all ranges (HI Ter mi na l)
Configurable
Parameters
Range, DC impedance, Null value
Basic measurement:
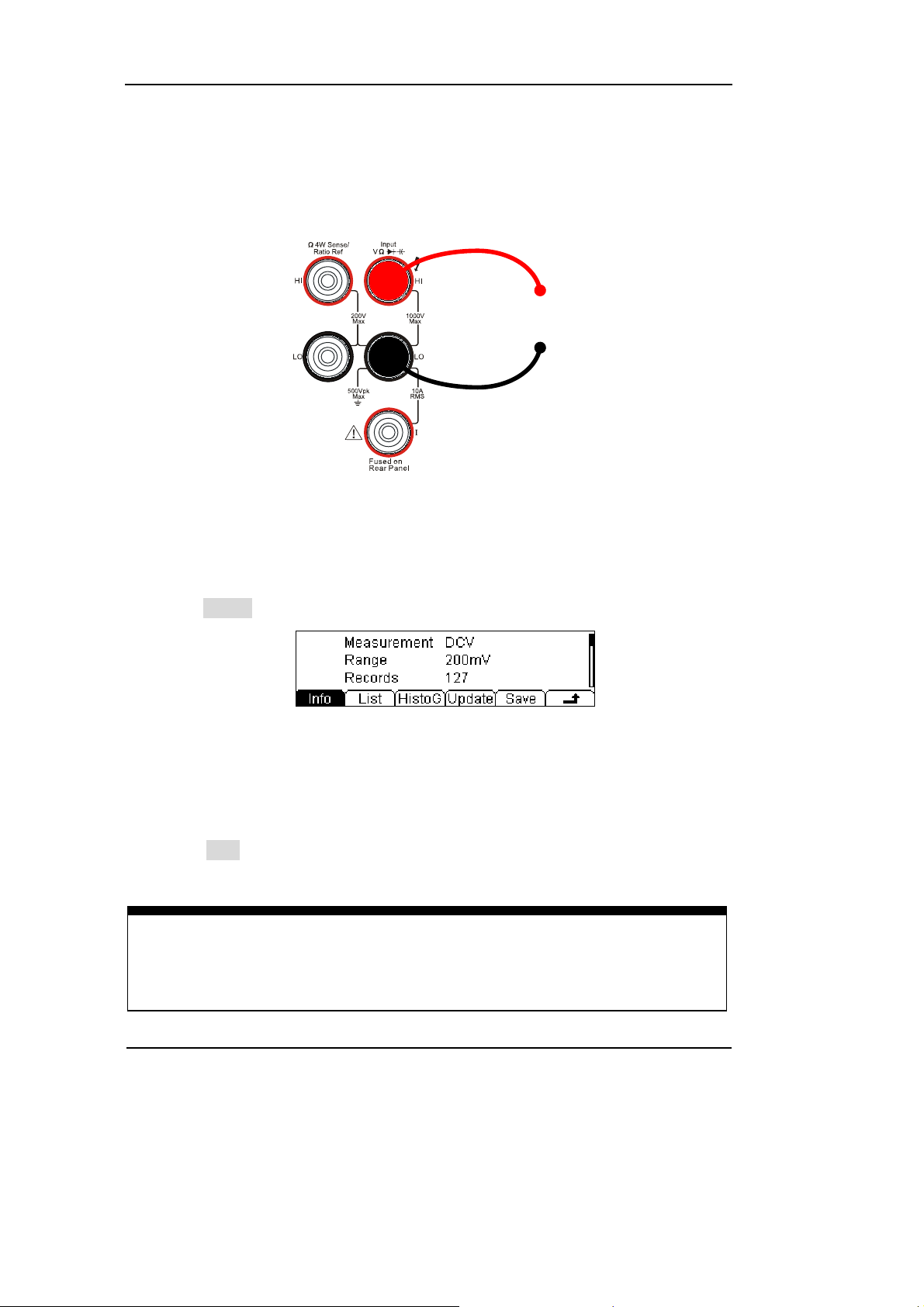
1. Connect test leads as Figure 1-8 shown. Red test lead connects the HI Terminal,
Black test lead connects the LO Terminal.
2. Press to select the DC Voltage measurement function.
3. According to the voltage measuring scope, choose the correct range.
4. Setup the DC impedance.
Press Æ Res, to setup the DC input impedance. Default value of the DC
input impedance will be 10MΩ, this parameter had been setup, and users may carry
on the DC Voltage measurement directly without modification.
5. Set the Null value.
Null computing will be an option operation; it could be setup in accordance with
user demand. If user does not implement Null computing, this parameter is not
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
1-7
Page 20
RIGOL
required, direct implementation of the next step.
(To know the specific setting methods of the Null value setting, please refer to
Chapter 2 “To Set Up Measurement Parameters”, Null computing)
6. Lead test leads into circuit, start to measure.
DC Voltage
Figure 1-8
DC Voltage measurement instruction chart
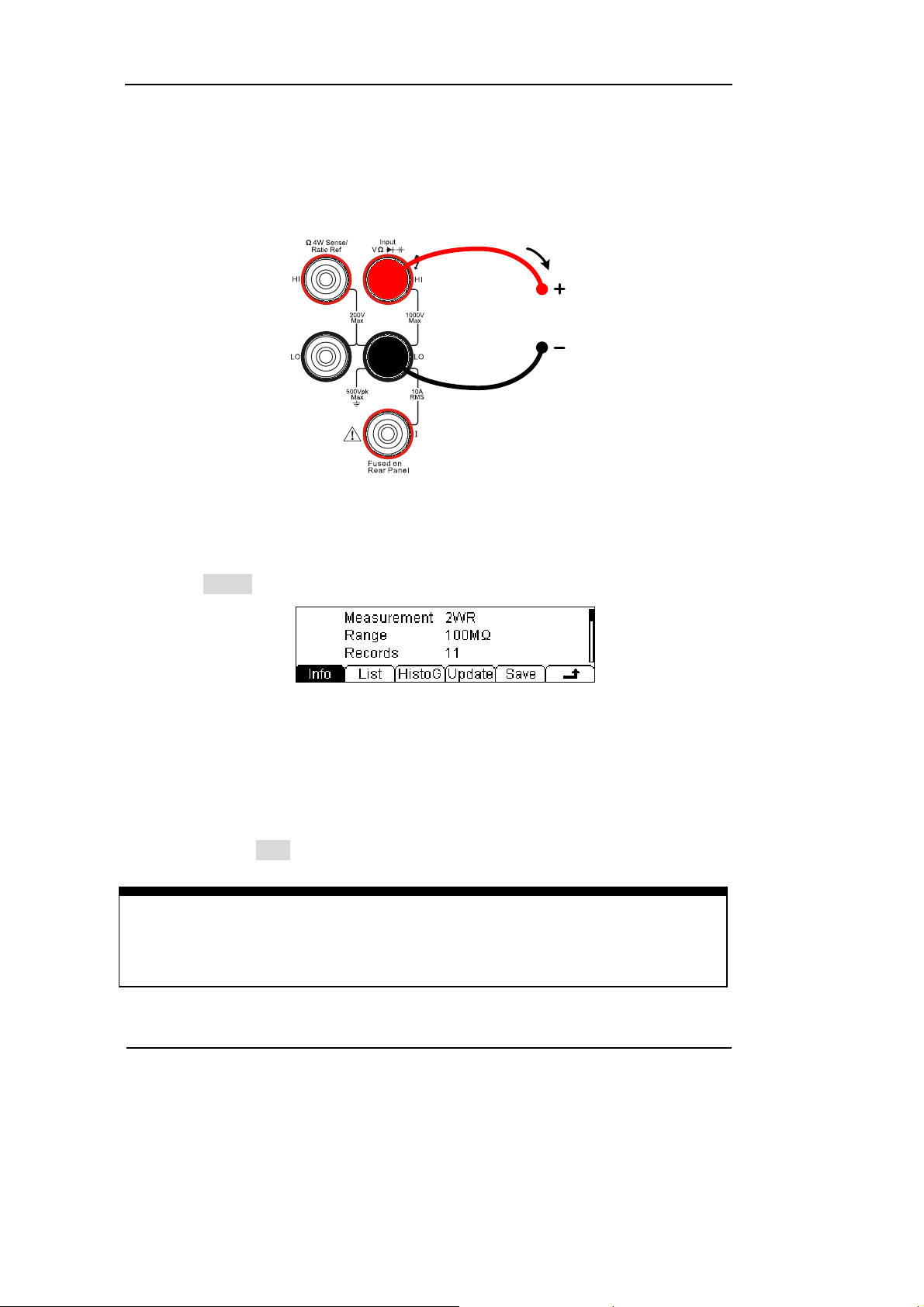
7. Measurement history data processing.
Press History, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 1-9
To check or save the data that has measured by current measurement function, you
can use the history function. In this function you can get the “Info” (information),
“List” and “Graph” of this measurement. Also, you can save this information data
with press Save softkey.
Note
If the users cannot predict the scope of the measurement, please choose Auto
range to obtain more accurate measurement data.
1-8
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
Page 21
RIGOL
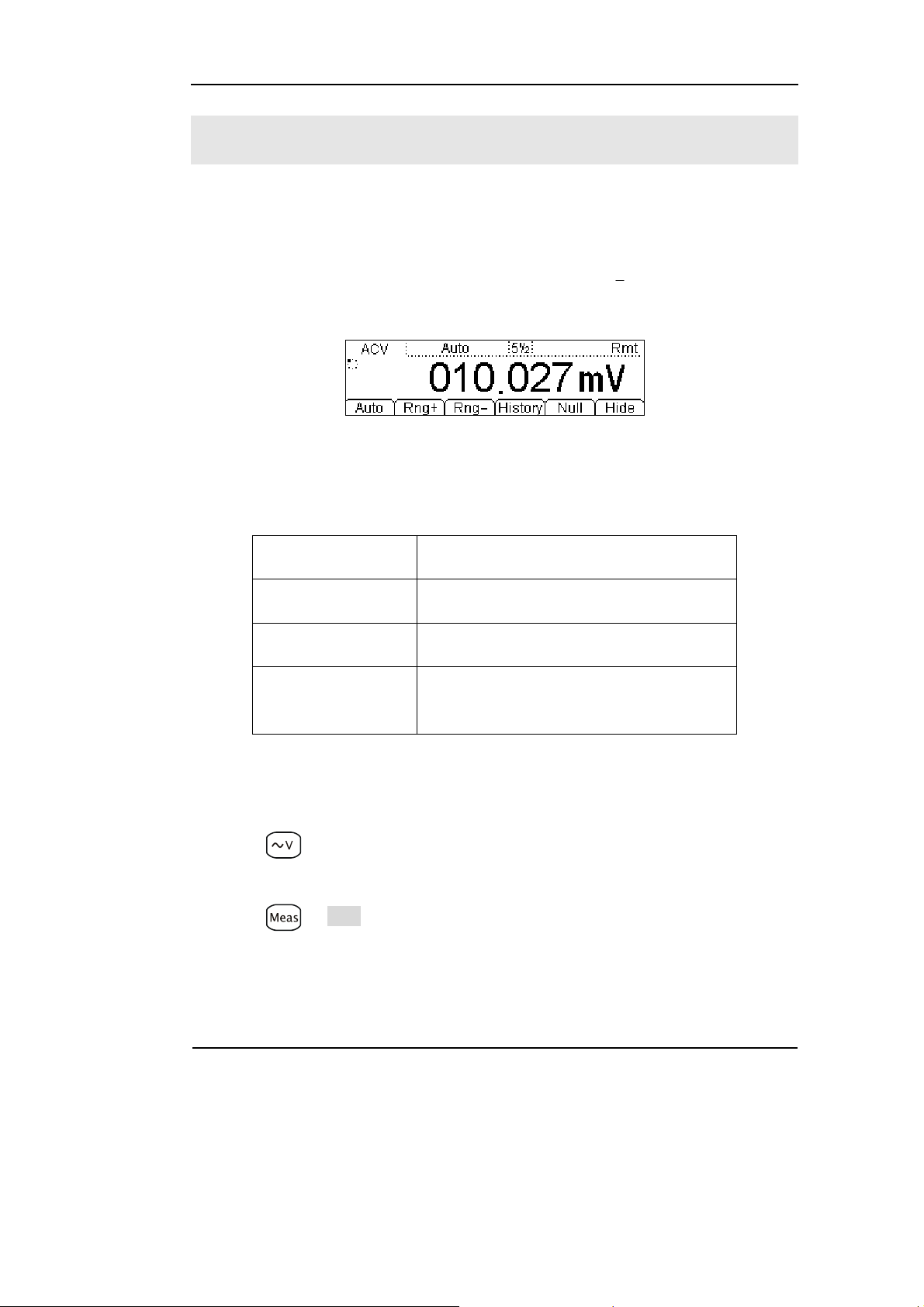
To Measure AC Voltage
In view of AC voltage measurement function, the following part demonstrated how
to link the measurement connection and how to choose measurement functions. The
following practice will gradually guide you to be familiar with the AC Voltage
1
measurement technique. (The AC functions only support 5
Figure 1-10
AC Voltage measurement data interface
Table 1-2 DC Voltage measurement characteristics
2
digits measurement.)
Five Range 200mV, 2V, 20V, 200V, 750V
Max Resolution 100nV
Import Protection 750VRMS on all ranges (HI Ter mi na l)
Configurable
Parameters
Range, DC impedance, Null value
Basic measurement:
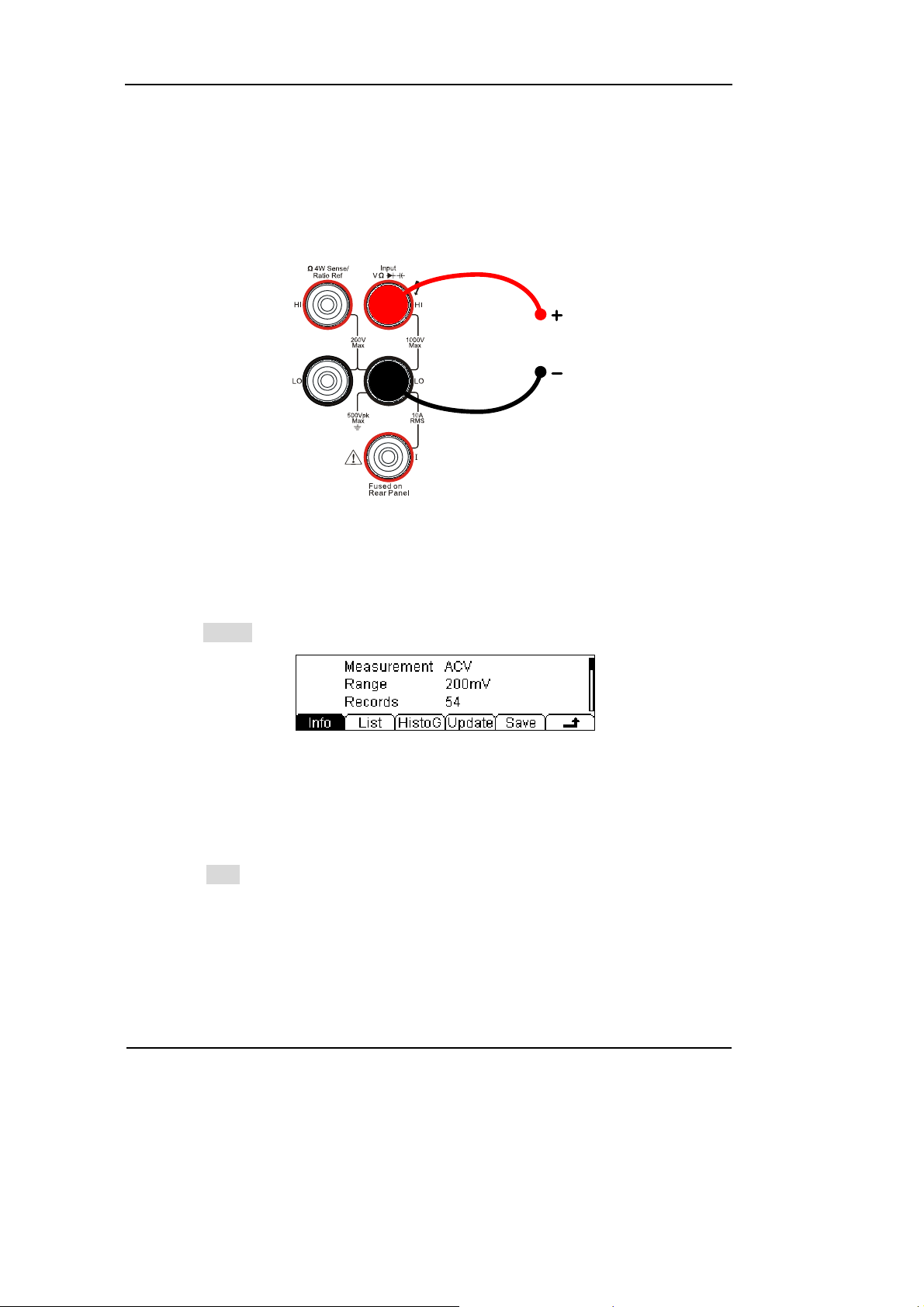
1. Connect test leads as Figure 1-11 shown. Red test lead connects the HI Terminal,
Black test lead connects the LO Terminal.
2. Press to select the AC Voltage measurement function.
3. According to the voltage measuring scope, choose the correct range.
4. Setup the DC impedance.
Press Æ Filter, to setup the AC Filter Bandwidth. Default value of the AC
Filter Bandwidth will be 10MΩ, this parameter had been setup, and users may carry
on the AC Voltage measurement directly without modification.
5. Set the Null value.
Null computing will be an option operation, could be setup in accordance with
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
1-9
Page 22
RIGOL
users’ demand. If user does not implement Null computing, this parameter is not
required, direct implementation of the next step.
(To know the specific setting methods of the Null value setting, please refer to
Chapter 2 “To Set Up Measurement Parameters”, Null computing)
6. Lead test leads into circuit, start to measure.
AC Voltage
Figure 1-11
AC Voltage measurement instruction chart
7. Measurement history data processing.
Press History, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 1-12
To check or save the data that has measured by current measurement function, you
can use the history function. In this function you can get the “Info” (information),
“List” and “Graph” of this measurement. Also, you can save this information data
with press Save softkey.
1-10
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
Page 23
RIGOL
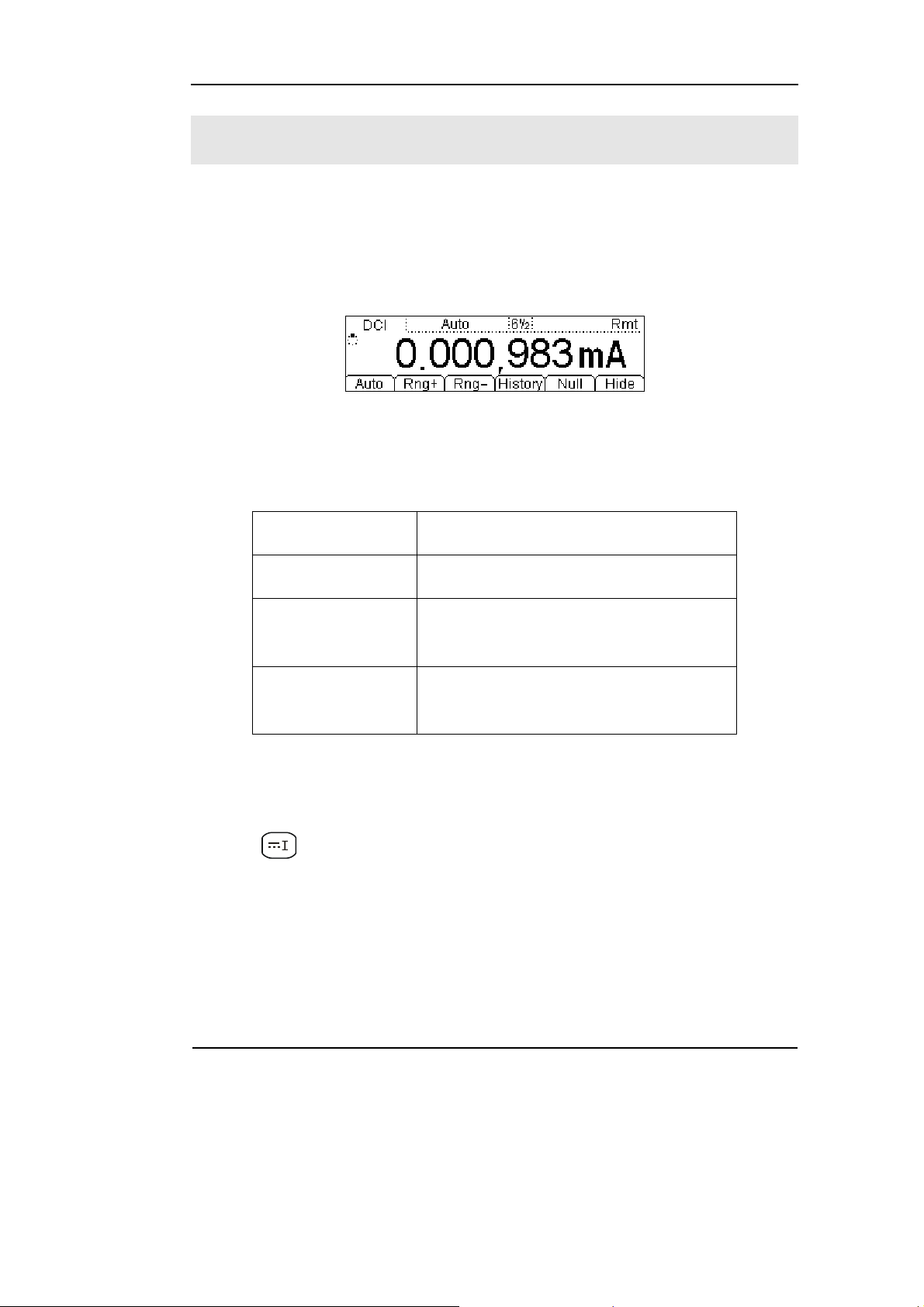
To Measure DC Current
In view of DC current measurement function, the following part demonstrated how
to link the measurement connection and how to choose measurement functions. The
following practice will gradually guide you to be familiar with the DC Current
measurement technique.
Figure 1-13
DC Current measurement data interface
Table 1-3 DC Current measurement characteristics
Five Range 2mA, 20mA, 200mA, 1A, 10A
Max Resolution 10nA
Import Protection
Configurable
Parameters
10A, 250V Current Input Fuse on rear
panel
Range, Null value
Basic measurement:
1. Connect test leads as Figure 1-14 shown. Red test lead connects the HI Terminal,
Black test lead connects the LO terminal.
2. Press to select the DC Current measurement function.
3. According to the current measuring scope, choose the correct range.
4. Set the Null value.
Null computing will be an option operation, could be setup in accordance with
user demand. If user does not implement Null computing, this parameter is not
required, direct implementation of the next step.
(To know the specific setting methods of the Null value setting, please refer to
Chapter 2 “To Set Up Measurement Parameters”, Null computing)
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
1-11
Page 24
RIGOL
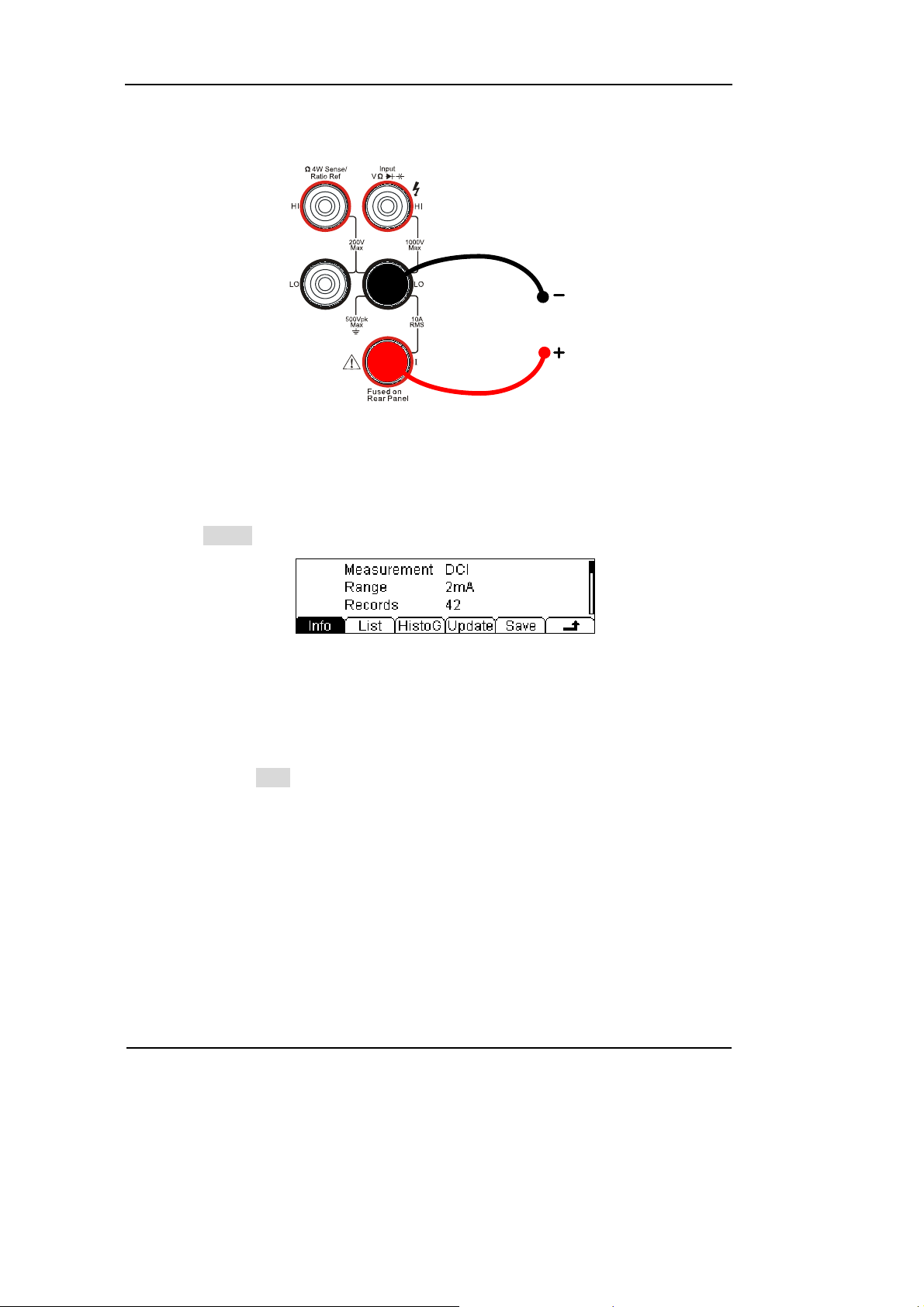
5. Lead test leads into circuit, start to measure.
Figure 1-14
DC Current measurement instruction chart
6. Measurement history data processing.
Press History, enter the menu shown below:
DC Current
Figure 1-15
The history data
To check or save the data that has measured by current measurement function, you
can use the history function. In this function you can get the “Info” (information),
“List” and “Graph” of this measurement. Also, you can save this information data
with pressing the Save softkey.
1-12
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
Page 25
RIGOL
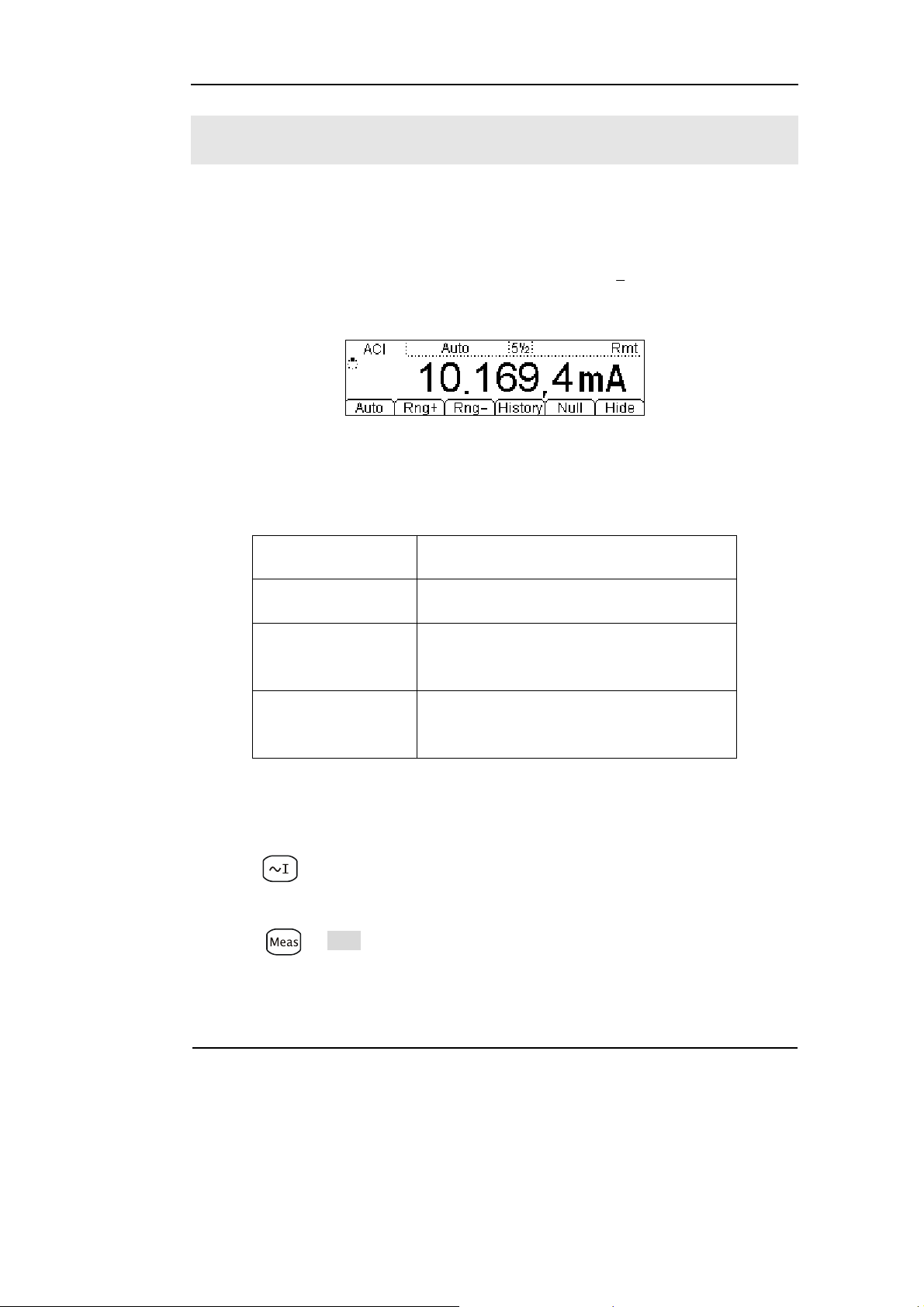
To Measure AC Current
In view of AC current measurement function, the following part demonstrated how to
link the measurement connection and how to choose measurement functions. The
following practice will gradually guide you to be familiar with the AC Current
1
measurement technique. (The AC functions only support 5
Figure 1-16
AC Current measurement data interface
Table 1-4 AC Current measurement characteristics
2
digits measurement.)
Five Range 20mA, 200mA, 1A, 10A
Max Resolution 100nA
Import Protection
Configurable
Parameters
10A, 250V Current Input Fuse on rear
panel
Range, Null value
Basic measurement:
1. Connect test leads as Figure 1-17 shown. Red test lead connects the HI Terminal,
Black test lead connects the LO terminal.
2. Press to select the DC Current measurement function.
3. According to the current measuring scope, choose the correct range.
4. Setup the DC impedance.
Press Æ Filter, to setup the AC Filter Bandwidth. Default value of the AC
Filter Bandwidth will be “Mid”(Middle), this parameter had been setup, and the users
may carry on the AC Voltage measurement directly without modification.
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
1-13
Page 26
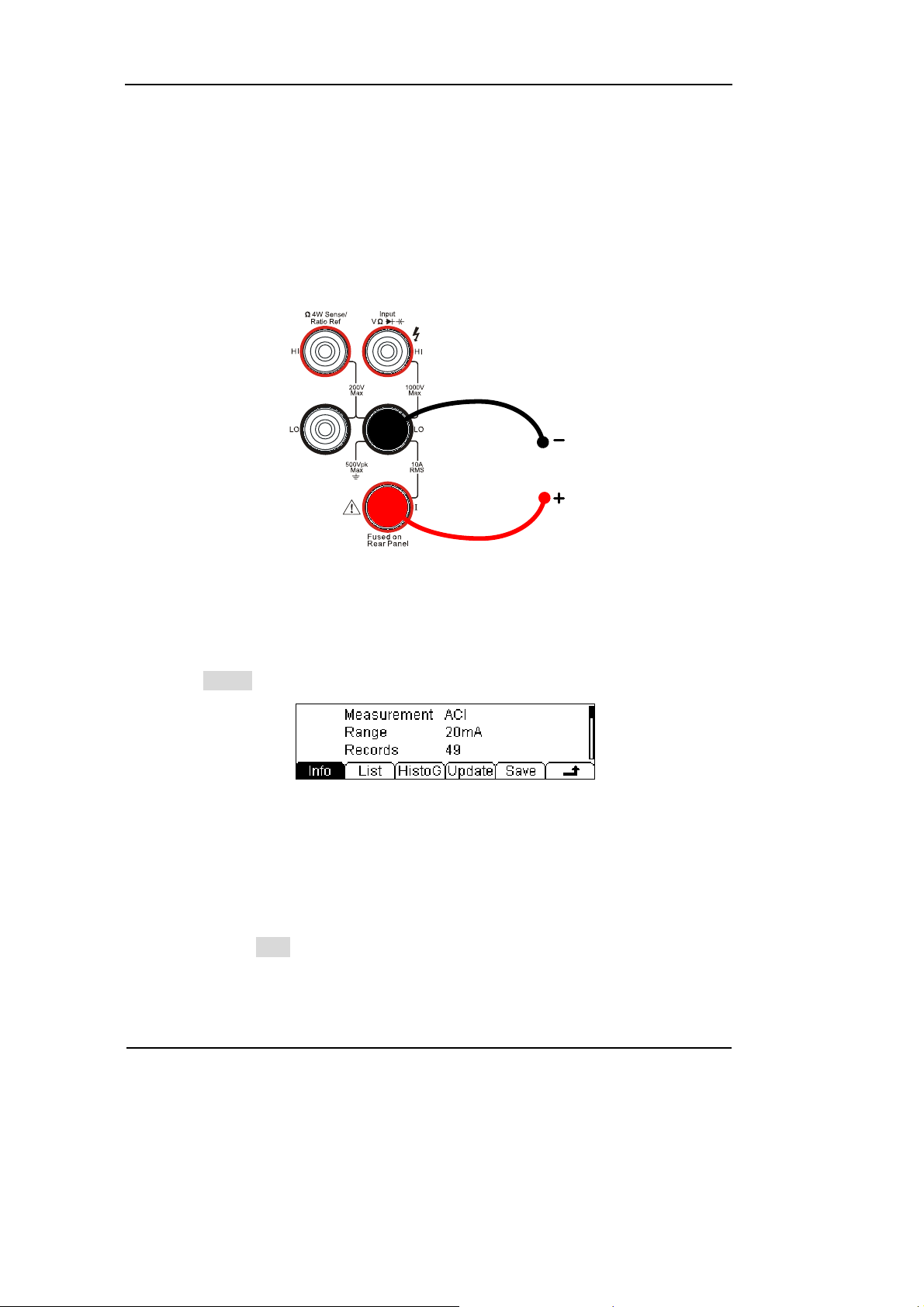
RIGOL
5. Set the Null setting value.
Null computing will be an option operation, could be setup in accordance with
user demand. If user does not implement Null computing, this parameter is not
required, direct implementation of the next step.
(To know the specific setting methods of the Null value setting, please refer to
Chapter 2 “To Set Up Measurement Parameters”, Null computing)
6. Lead test leads into circuit, start to measure.
AC Current
Figure 1-17
AC Current measurement instruction chart
7. Measurement history data processing.
Press History, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 1-18
The history data
To check or save the data that has measured by current measurement function, you
can use the history function. In this function you can get the “Info” (information),
“List” and “Graph” of this measurement. Also, you can save this information data
with pressing the Save softkey.
1-14
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 27
RIGOL
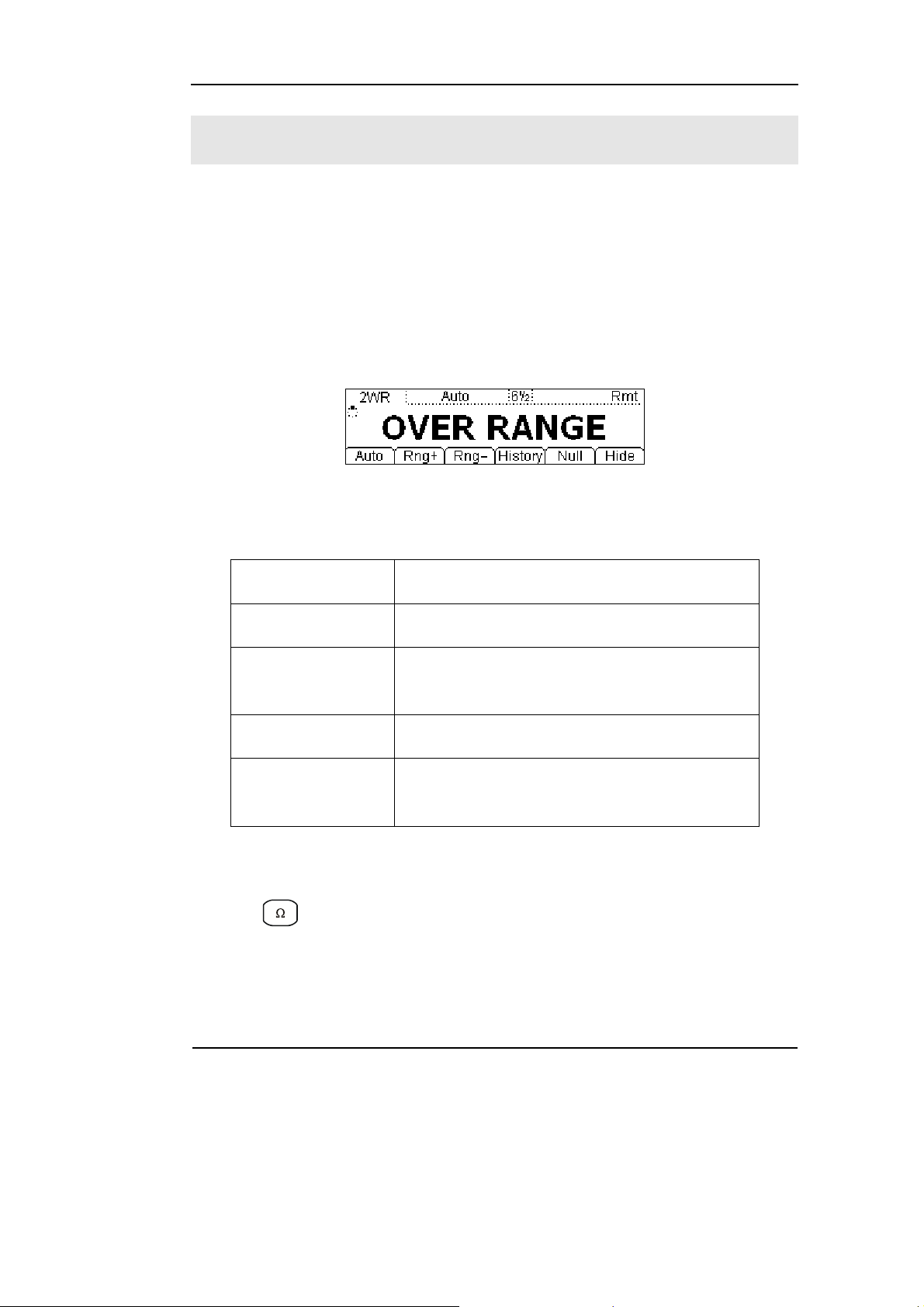
To Measure Resistance
In view of Resistance measurement function, the following part demonstrated how
to link the measurement connection and how to choose measurement functions. The
following practice will gradually guide you to be familiar with the Resistance
measurement technique. Resistance measurement methods include 2-Wire
Resistances Measurement and 4-Wire Resistances Measurement; we will
perform to explain separately.
2-Wire Resistance Measurement
Figure 1-19
Table 1-5 Resistance measurement characteristics
Seven Range 200Ω, 2kΩ, 20kΩ, 200kΩ, 1MΩ, 10MΩ, 100MΩ
Max Resolution 100uΩ
Open-circuit
Voltage
<5V
Import Protection 1000V on all ranges (HI Ter mi na l)
Configurable
Parameters
Range, Null value
Basic measurement:
1. Connect test leads as Figure 1-20 shown. Red test lead connects the HI Terminal,
Black test lead connects the LO Terminal.
2. Press to select the 2-Wire Resistance Measurement.
3. According to the resistance measuring scope, choose the correct range.
4. Set the Null value
Null computing will be an option operation, could be setup in accordance with
user demand. If user does not implement Null computing, this parameter is not
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
1-15
Page 28
RIGOL
required, direct implementation of the next step.
(To know the specific setting methods of the Null value setting, please refer to
Chapter 2 “To Set Up Measurement Parameters”, Null computing)
5. Lead test leads into circuit, start to measure.
Resistance
Figure 1-20
2-Wire Resistance Measurement instruction chart
6. Measurement history data processing.
Press History, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 1-21
The history data
To check or save the data that has measured by current measurement function, you
can use the history function. In this function you can get the “Info” (information),
“List” and “Graph” of this measurement. Also, you can save this information data
with pressing the Save softkey.
NOTE
When measuring small value resistance, Null operation will be recommended, the
test wire impedance error could be eliminated.
1-16
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
Page 29

RIGOL
4-Wire Resistance Measurement
Figure 1-22
Table 1-6 Resistance measurement characteristics
Seven Range 200Ω, 2kΩ, 20kΩ, 200kΩ, 1MΩ, 10MΩ, 100MΩ
Max Resolution 100uΩ
Open-circuit
Voltage
Import Protection
<5V
(1). 200V
PK
(2). 1000V on all ranges (HI
Ter mi na l)
(3). 200V on all ranges (HI Sense, LO Sense)
Configurable
Parameters
Range, Null value
Basic measurement:
1. Connect test leads as Figure 1-23 shown. Red test leads connect the HI Terminal,
Black test leads connect the LO Terminal.
2. Press twice to select the 4-Wire Resistance Measurement.
3. According to the resistance measuring scope, choose the correct range.
4. Set the Null setting value.
Null computing will be an optional operation, it could be setup in accordance
with users’ demand. If user does not implement Null computing, this parameter is
not required, direct implementation of the next step.
(To know the specific setting methods of the Null value setting, please refer to
Chapter 2 “To Set Up Measurement Parameters”, Null computing)
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
1-17
Page 30
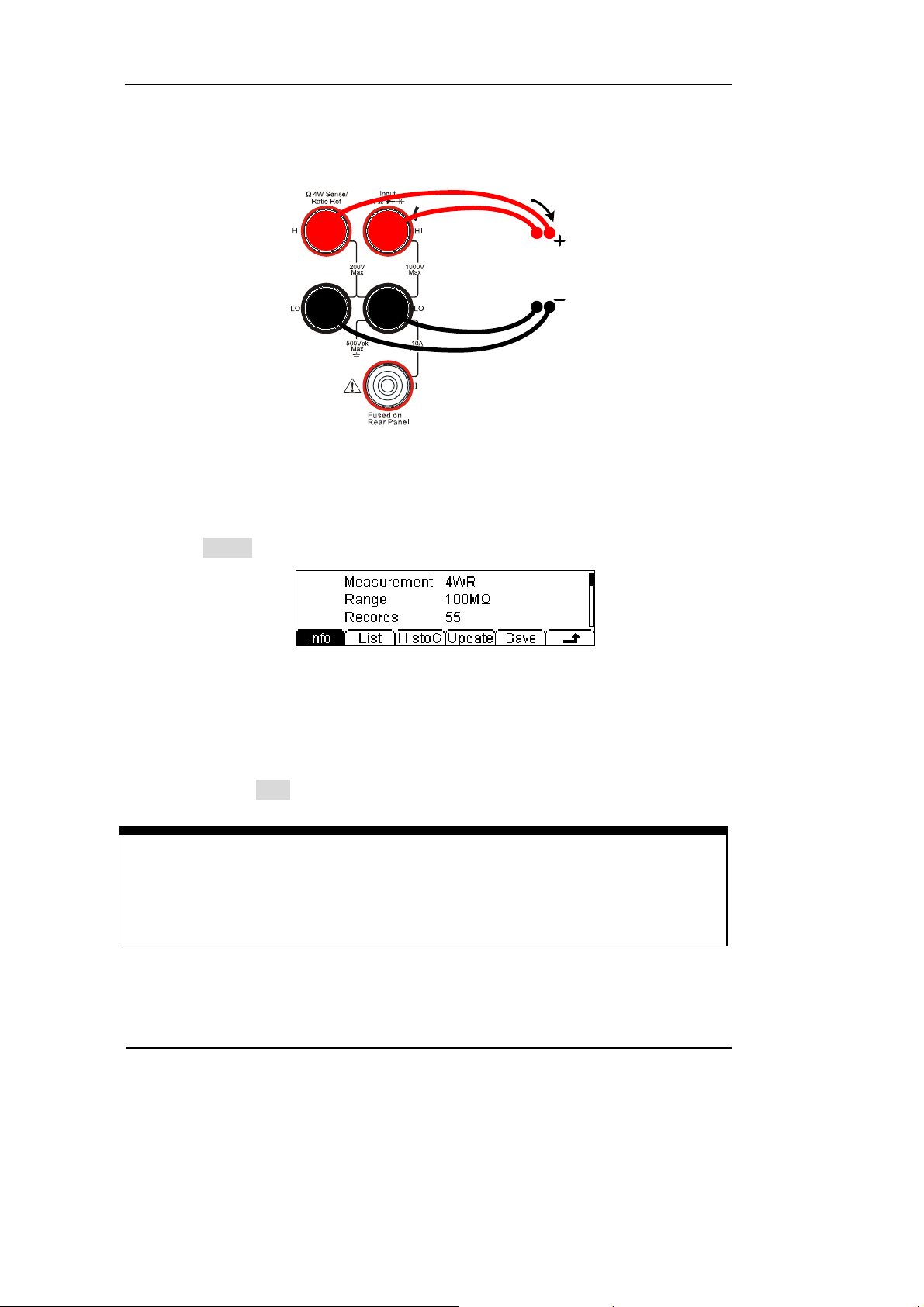
RIGOL
5. Lead test leads into circuit, start to measure.
4-Wire Sense HI
4-Wire Sense LO
Figure 1-23
4-Wire Resistance Measurement instruction chart
6. Measurement history data processing.
Press History, enter the menu shown below:
Resistance
Figure 1-24
To check or save the data that has measured by current measurement function,
you can use the history function. In this function you can get the “Info” (information),
“List” and “Graph” of this measurement. Also, you can save this information data
with pressing the Save softkey.
NOTE
When measuring resistances, you could not touch both ends of the resistance. It
will cause the measurement inaccurate.
1-18
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
Page 31

RIGOL
To Measure Capacitance
In view of DC voltage measurement function, the following part demonstrated how
to link the measurement connection and how to choose measurement functions. The
following practice will gradually guide you to be familiar with the DC Voltage
measurement technique.
Figure 1-25
Capacitance measurement data interface
Table 1-7 Capacitance measurement characteristics
Six Range 2nF, 20nF, 200nF, 2uF, 20uF, 200uF
Max Resolution 0.1pF
Import Protection 1000V on all ranges (HI Ter mi na l)
Configurable
Parameters
Range, Null value
Basic measurement:
1. Connect test leads as Figure 1-26 shown. Red test lead connects the HI Terminal,
Black test lead connects the LO Terminal.
2. Press to select the Capacitance measurement function.
3. According to the capacitance measuring scope, choose the correct range.
4. Set the Null value.
Null computing will be an optional operation, could be setup in accordance with
user demand. If user does not implement Null computing, this parameter is not
required, direct implementation of the next step.
(To know the specific setting methods of the Null value setting, please refer to
Chapter 2 “To Set Up Measurement Parameters”, Null computing)
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
1-19
Page 32

RIGOL
5. Lead test leads into circuit, start to measure.
Figure 1-26
Capacitance measurement instruction chart
6. Measurement history data processing.
Press History, enter the menu shown below:
Capacitance
Figure 1-27
To check or save the data that has measured by current measurement function, you
can use the history function. In this function you can get the “Info” (information),
“List” and “Graph” of this measurement. Also, you can save this information data
with pressing the Save softkey.
NOTE
Before measuring the electrolytic capacitance, you should make the two legs of the
electrolytic capacitance short circuit and let it be discharged, and then you can
measure it.
1-20
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
Page 33

RIGOL
To Test Continuity
In view of Continuity measurement function, the following part demonstrated how to
link the measurement connection and how to choose measurement functions. The
following practice will gradually guide you to be familiar with the Continuity
measurement technique.
Figure 1-28
Table 1-8 Continuity measurement characteristics
Tests Current 1mA
Max Resolution Range fixed at 2KΩ
Open-circuit Voltage <5V
Import Protection 1000V (HI Terminal)
0≤R
≤Short-circuit impedance
testing
Configurable Parameters
(0Ω≤Short-circuit impedance≤2kΩ)
Basic measurement:
1. Connect test leads as Figure 1-29 shown. Red test lead connects the HI Terminal,
Black test lead connects the LO Terminal.
2. Press to select the Continuity Measurement.
3. Setup the Short-circuit resistance.
Press Æ Res, to set up the Short-circuit Impedance. Default value of the
Short-circuit Impedance will be 10MΩ, this parameter had been setup, and the user
may carry on the Continuity measurement directly without modification.
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
1-21
Page 34

RIGOL
4. Lead test leads into circuit, start to measure.
Open or Closed Circuit
Figure 1-29
Continuity Measurement instruction chart
I
1-22
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 35

RIGOL
To Check Diodes
In view of Check Diodes function, the following part demonstrated how to link the
measurement connection and how to choose measurement functions. The following
practice will gradually guide you to be familiar with the Check Diodes technique.
Figure 1-30
Table 1-9 Check Diodes characteristics
Tests Current 1mA
Max Resolution Range fixed at 2VDC
Open-circuit Voltage <5V
Import Protection 1000V (HI Terminal)
Configurable Parameters 0.3V≤V
measured
≤2V
Basic measurement:
1. Connect test leads as Figure 1-31 shown. Red test lead connects the HI Terminal,
Black test lead connects the LO Terminal.
2. Press to select the Check Diodes.
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
1-23
Page 36

RIGOL
3. Lead test leads into circuit, start to check.
Figure 1-31
Check Diodes instruction chart
I
Forward Bias
1-24
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 37

RIGOL
To Measure Frequency and Period
In view of Frequency and Period Measurement function, the following part
demonstrated how to link the measurement connection and how to choose
measurement functions. The following practice will gradually guide you to be familiar
with the Frequency and Period Measurement technique.
Frequency Test
Figure 1-32
Table 1-10 Frequency Test characteristics
Range 200mV, 2V, 20V, 200V, 750V
Measurement Range 3Hz~300kHz
Input Signal Range 100mVAC ~ 750VAC
Import Protection 750VRMS on all ranges (HI Te rm in al )
Configurable Parameters Null value
Basic measurement:
1. Connect test leads as Figure 1-33 shown. Red test lead connects the HI Terminal,
Black test lead connects the LO Terminal.
2. Press to select the Frequency Test.
3. Set the Null value.
Null computing will be an option operation, could be setup in accordance with
user demand. If user does not implement Null computing, this parameter is not
required, direct implementation of the next step.
(To know the specific setting methods of the Null value setting, please refer to
Chapter 2 “To Set Up Measurement Parameters”, Null computing)
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
1-25
Page 38

RIGOL
4. Lead test leads into circuit, start to check.
Figure 1-33
Frequency Test instruction chart
5. Measurement history data processing.
Press History, enter the menu shown below:
AC Signal
Figure 1-34
To check or save the data that has measured by current measurement function, you
can use the history function. In this function you can get the “Info” (information),
“List” and “Graph” of this measurement. Also, you can save this information data
with pressing the Save softkey.
1-26
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
Page 39

RIGOL
Period Test
Figure 1-35
Table 1-10 Period Test characteristics
Range 200mV, 2V, 20V, 200V, 750V
Measurement Range 0.33s ~ 3.3us
Input Signal Range 100mVAC~750VAC
Import Protection 750VRMS on all ranges (HI Te rm in al )
Configurable Parameters Null value
Basic measurement:
1. Connect test leads as Figure 1-36 shown. Red test lead connects the HI Terminal,
Black test lead connects the LO Terminal.
2. Press twice to select the Period Test.
3. Set the Null value.
Null computing will be an optional operation, could be setup in accordance with
users’ demand. If user does not implement Null computing, this parameter is not
required, direct implementation of the next step.
(To know the specific setting methods of the Null value setting, please refer to
Chapter 2 “To Set Up Measurement Parameters”, Null computing)
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
1-27
Page 40

RIGOL
4. Lead test leads into circuit, start to check.
Figure 1-36
Period Test instruction chart
5. Measurement history data processing.
Press History, enter the menu shown below:
AC Signal
Figure 1-37
To check or save the data that has measured by current measurement function, you
can use the history function. In this function you can get the “Info” (information),
“List” and “Graph” of this measurement. Also, you can save this information data
with pressing the Save softkey.
1-28
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
Page 41

RIGOL
To Measure Arbitrary Sensor
To set an arbitrary sensor, you will need to set the sensor name, sensor type, sensor
physical unit, sensor reference data, and arithmetic.
Figure 1-38
Table 1-11 Period Test characteristics
New Newly built sensor reference data file
Edit Edit a sensor reference data file
Load Load a sensor reference data file
Display Set display mode
Basic measurement:
1. Connect test leads as Figure 1-54, 1-55 shown. Red test leads connect the HI
Terminal, Black test leads connect the LO Terminal.
2. Press to select the Sensor function.
3. Press New, enter the newly- built sensor reference data file interface.
Figure 1-39
(1). In New function interface, you are allowed to edit the sensor Name, sensor Type
and physical value Unit of the sensor.
Figure 1-40
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
1-29
Page 42

RIGOL
Press Name button, you are allowed to create a name for the sensor reference value
document.
Figure 1-41
Press Type button, you are allowed to select the sensor type, include: DCV, DCI,
2-Wire resistance, and frequency.
Figure 1-42
Press Unit button, you are allowed to select the physical unit, include: , ℃ Pa, % , °,
and F.
Figure 1-43
In New interface, press Define button to build the reference value table. The
reference value documents for each kind of sensor are different, so you need input
reference value in abundance.
Figure 1-43
Press Add button, you are allowed to input the Measured and Corresponding value to
reference value data. In order be suitable for the different type sensor, the reference
value is able to separate into several SEGment in accordance with the different
algorithms.
1-30
Figure 1-44
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 43

RIGOL
Figure 1-45
Figure 1-46
Press SEG button, you are allowed to segment the reference value with different
arithmetic.
Press Arith button select the algorithms to Line or Curve.
Figure 1-47
Figure 1-48
Press return to New interface then press Done button, you have finished the
input work, then you can use this sensor reference immediately, or you can save it
into the built-in storage space or your U-disk for the future work.
Figure 1-49
Press Apply button, to use this reference value file.
Press Save to save the file.
Figure 1-50
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
1-31
Page 44

RIGOL
Press Save button, to finish the save operation.
Figure 1-51
Press Apply button, to start the sensor measurement.
Figure 1-52
(2). Press Edit button, enter the edit function. With this function you can edit the
sensor reference value file that you had saved.
(3). Press Load button, enter the store function interface, you can load the sensor
reference file you had saved.
(4). Press Disp button, you can choose which value will be shown on the display
interface.
(5). Press History, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 1-53
To check or save the data that has measured by current measurement function, you
can use the history function. In this function you can get the “Info” (information),
“List” of this measurement. Also, you can save this information data with pressing
the Save button.
1-32
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
Page 45

RIGOL
4. Lead test leads into circuit, start to check.
Sensor
Figure 1-54
Voltage, Resistance, and Frequency mode sensor instruction chart
Sensor
Figure 1-55
Current mode sensor instruction chart
Figure 1-56
Choosing interfaces of measure and correspond value
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
1-33
Page 46

RIGOL
To Choose Digits resolving index
The digits resolving index (the accurate of reading) differentiates 4 1/2, 5 1/2, 6 1/2
three kinds. Three kinds of digits resolving index are suitable for all measurement
function.
Reduce the index
Increases the index
Figure 1-57
The digits resolving index Choice Keys
Methods:
In the main interface, use left and right direction key to adjust the digits resolving
index. Press left button to lower accuracy, press right button to upper accuracy.
The digits resolving index Selection
(1). Each precision of the measure function can be set separately without influence.
(2). Choose the reading precision of 6 1/2 bit when measuring AC for the best.
(3). Store the digits resolving index in volatile memory.
1-34
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 47

RIGOL
To Choose Data Digit Display
Function is used to set up data display digit. It has 5, 6, 7 three kinds of data
digit display choice. The default display digit is 5.
Figure 1-58
The data digits is 7
Figure 1-59
The data digits is 6
Figure 1-60
The data digits is 5
NOTE
In high-accuracy measurement, if users need to show less data digit, it can show
fewer digits for user-friendly reading.
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
1-35
Page 48

RIGOL
Choose Range Options
To choose measurement range may complete through the manual choice and the
automatic determination two methods. The automatic determination is user-friendly,
but if you want to obtain a better performance you should choose the range in
manual choice.
Increased range
Automatic
selection range
Reduced range
Figure 1-61
Choice Range Options Keys
Methods 1:
In the main interface, use up and down direction key to adjust the Range. Press Up
to increase the range, press Down to reduce the range.
Press key, start the automatic determination.
Methods 2:
In the main interface, use the menu option keys to adjust the range.
Figure 1-62
Choice Range Options Menu
1-36
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 49

RIGOL
Table 1-12 Choice Range Option Menu
Option Menu Explain
Auto
Manually+
Manually-
Started automatically adjustment range, and
banned manually adjustment range.
Started manually increased range, and banned
automatically adjustment range.
Started manually reduced range, and banned
automatically adjustment range.
Save all changes, end the current operation,
Quit
hidden the menu. When the menu was hidden,
press this key to show the menu.
Operation Explanation:
• When the input signal is beyond the current scope of the measurement range, the
multimeter will show “OVER RANGE”.
• After restarting and remote- replacement, range options will turn back default
option “Automatic choice range”.
• When testing the Continuity and Checking the diodes, the range option are fixed.
The range of Continuity is 2KΩ while the diodes are 2V
DC.
NOTE
Other functions of the direction keys:
In measurement parameters setting menu, press the up and down keys to choose
setting areas.
In data input interface, press up and down keys to change the number.
In data input interface, press left and right keys to change the different digits.
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
1-37
Page 50

RIGOL
To Control Trigger Options
Press or to trigger the multimeter. When you start the multimeter, the
Key will turn light, it means this function is running.
Figure 1-63
Trigger Control Keys
Multimeter triggering options include Automatically, Single and Hold.
Auto Triggering
Press key once, it will takes continuous readings at the fastest rate possible for
the specified measurement configuration.
Single Triggering
Press key, The multimeter takes one reading, or a number of readings specified
by a sample count you enter.
Holding Triggering
Press key. The reading- hold mode allows you to capture and hold a stable
reading on the front panel display.
NOTE
Press key, in Remote Mode, by switching back to the local mode.
1-38
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 51

RIGOL
Chapter 2 Operating Your Multimeter
By now you have got a brief understanding of DM3000 series with the front/rear
panel, every function control area and keys. You should also know how to determine
the setup of the multimeters by viewing the status bar.
This chapter takes you through all groups of front-panel buttons and menus. You will
also further your knowledge of the operation instruction by reading this guide.
We recommend you perform all of the following exercises, so that you could get the
most of the powerful measurement capabilities of your multimeters.
This chapter covers the following topics:
To Set up Measurement Parameters ( )
To Make Mathematics Operation ( )
To Set up Trigger System ( )
To Save and Recall ( )
To Set up Utility ( )
To Set up High-speed data acquisition ( )
Use the built-in help system ( )
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
2-1
Page 52

RIGOL
To Set up Measurement Parameters
Press key to operate the Measurement Parameters Menu. Use the measurement
parameters menu to set up the measurement parameters. The default parameters
had been set up by RIGOL, users may carry on any measurement operation directly,
and users also can set up any measurement parameters as their wish.
The measurement parameters menu include: Conti, Filter, Res, Null, and Ratio. To
change these parameters, satisfy the dissimilar condition of the measurement
request.
Figure 2-1
Table 2-1 Menu Explanation
Function
Menu
Explanation
Conti Set up the resistance value in short test.
Filter Choose the AC filter bandwidth.
Res Choose the DC voltage input resistance.
Null Set up null value.
Ratio Measured the ratio of two DC voltage signal.
Freq Measured the frequency of AC signal.
Save all changes, and end the current operation.
2-2
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 53

RIGOL
Continue Resistance
To set up the continue resistance value in the short test, when the test resistance
below the continue resistance value, the DM3000 will judge whether the circuit is
connected or not. The continue resistance is only using at Continue Test.
Press Æ Conti, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 2-2
Use direction keys to change the parameter values:
Press left and right key to choose different digits. Press up and down key to change
the current digital value.
Continue Resistance
The range of continue resistance is 1Ω~1000Ω. The default value is 10Ω.
The continue resistance stored in the easy-lost memorizer, the resistance still keep
when the power is off.
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
2-3
Page 54

RIGOL
AC Filter
There are three kinds of AC Filter. Choose correct filter may make the measurement
more accuracy. This function could only be used in AC Voltage and AC Current
measurement.
Press Æ Filter, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 2-3
Table 2-2 AC Filter Menu Explanation
Table 2-3 AC Filter Parameters Characteristics
AC Filter
Function
Menu
Explanation
Slow Set up the filter with low speed.
Mid Set up the filter with to middle speed.
Fast
Set up the filter with high speed.
Save all changes, back to a higher level menu.
AC Filter Options Input Frequency Setting Timer
Slow
Mid
Fast
3Hz~300kHz
20Hz~300kHz
200Hz~300kHz
1.2 reading/s
0.5 reading/s
0.3 reading/s
The AC Filter Parameters are saved in the volatile memory, the data will lose when
the power is off.
The default value of AC Filter Parameters is “Mid” (middle).
2-4
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
Page 55

RIGOL
DC Input Resistance
To choose DC voltage current measuring input resistance value. The parameters
include 10MΩ and >10GΩ. The default resistance is 10MΩ, but for 200mV, 2V, 20V
measuring ranges may choose >10MΩ for getting a greater measurement value.
Press Æ Res, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 2-4
Table 2-4 DC Input Resistance Menu Explanation
Function
Menu
10MΩ Set up the DC Input Resistance to 10MΩ.
>10GΩ Set up the DC Input Resistance to >10GΩ.
Save all changes, back to a higher level menu.
DC input resistance selection:
(1). While the DC input resistance is selected to 10MΩ, the input resistance of all
measurement range is 10MΩ;
(2). While the DC input resistance is selected to >10GΩ, the input resistance of
200mV, 2V and 20V measurement range is >10GΩ; 200V and 1000V
measurement range will be still keep 10MΩ input resistance.
Explanation
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
2-5
Page 56

RIGOL
Null Measurement
The DM3000 allows separate null settings to be saved for each of the following
measurement functions: dc voltage, ac voltage, dc current, ac current, resistance,
frequency/period, and capacitance.
When making null measurements, each reading is different between a stored
(selected or measured) null value and the input signal. One possible application is to
increase the accuracy of two–wire resistance measurements by nulling the test lead
resistance. Null the leads are particularly important prior to making capacitance
measurements. The formula used for calculating null measurements is:
Result = reading - null value
The null value is adjustable, and you can set it to any value between 0 and
the highest range, for the present function.
Press Æ Null, enter the menu shown below:
±120% of
2-6
Figure 2-5
Table 2-5 Null Measurement Menu Explanation
Function
Menu
Explanation
Current The current measured value will be the setting value.
Clear Set the value to be zero.
On/Off Turn the Null function on or off.
Save all changes, back to a higher level menu.
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 57

RIGOL
Null measurement parameters setting methods:
(1). In operation interface press Null button, use the current value to Null value;
(2). To select Zero function. Start null function, the multimeter will use the current
value to Null value.
(3). In Null setting display interface, it uses the Direction Keys to input the setting
null value.
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
2-7
Page 58

RIGOL
Ratio Measurement
Ratio measurement is used to measure the ratio of 2 directions DC voltage signal.
Ratio measurement is only for measuring DC voltage.
Press Æ Ratio, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 2-6
Table 2-6 Ratio Measurement Menu Explanation
Function
Menu
ON Open the Ratio Measurement Function.
OFF Close the Ratio Measurement Function.
Save all changes, back to a higher level menu.
The method of the radio measurement:
DC Voltage
VoltageDC
Ratio=
DC Reference Voltage
(1). Measuring Sense Terminal, for measuring reference DC voltage. Default range
option is auto.
(2). Measuring Input Terminal, for measuring DC voltage. The measuring voltage
scope is 0V~1000V.
(3). Input LO Terminal and Sense LO Terminal must have a common reference
value, and the voltage difference cannot surpass ±2V.
Re
⋅
tagefrenceVaolDC
Explanation
2-8
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 59

RIGOL
V
Basic measurement:
1. Connect test leads as Figure 2-7 shown. Red test leads connect the HI Terminal,
Black test leads connect the LO Terminal.
2. Press to select the DC Voltage measurement function.
3. According to the voltage measuring scope, choose the correct range.
4. Set up the DC Ratio Measurement.
Press Æ Ratio Æ On, to start the DC Ratio Measurement.
Press
to save all changes, back to a higher level menu.
5. Lead test leads into circuit, start to measure.
Signal
oltage
Reference
Voltage
Figure 2-7
Ratio Measurement instruction chart
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
2-9
Page 60

RIGOL
Frequency Measurement
Frequency measurement function is only used for measuring the frequency of an AC
signal (AC voltage and AC current).
Press Æ Freq, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 2-8
Table 2-7 Ratio Measurement Menu Explanation
Function
Menu
Explanation
ON Open the Frequency Measurement Function
OFF Close the Frequency Measurement Function
Save all changes, back to a higher level menu.
Basic measurement:
1. Connect test leads as Figure 2-9 shown. Red test lead connects the HI Terminal,
Black test lead connects the LO Terminal.
2. Press or to select the AC voltage or current measurement function.
3. According to the voltage measuring scope, choose the correct range.
4. Set up the DC Ratio Measurement.
Press Æ Freq Æ On, to start the AC Frequency Measurement.
Press
to save all changes, back to a higher level menu.
2-10
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 61

RIGOL
5. Lead test leads into circuit, start to measure.
AC Voltage
Figure 2-9
AC Current
Figure 2-10
Figure 2-11
Frequency measurement display interface
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
2-11
Page 62

RIGOL
Math Functions
Press key, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 2-12
The DM3000 provides five math functions: Null, statistic, dB, dBm and Limit testing.
Only one of these math functions can be enabled at a time and remains in effect until
you turn it off or change it.
In Math function interface, you could choose the math function that you want to use.
Then press On to start the Math function that you have chosen.
Math functions are used by union basic measurement function. However, not all
combinations are effective. If the math function you selected does not support the
measurement function you have just choose, the math function will automatic turn
off.
Table 2-8 Math Function Menu Explanation
Function
Menu
Statistic
dB
Settings Explanation
Reading statistic functions, including: Max, Min,
Average, and Reading Count.
The dB measurement is the difference between
the input signal and a stored relative value.
The dBm function is logarithmic, and is based on
dBm
a calculation of power delivered to a reference
resistance.
The limit test function enables you to perform
Limit
pass/fail testing to upper and lower limits that
you specify.
2-12
ON/OFF
ON
OFF
Turn on Math function.
Turn off Math function.
Save all changes, back to a higher level menu.
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 63

RIGOL
The Math function does not used for all basic measurement function. The table
2-9 showed the effective functions combination.
Table 2-9 Math Functions is used for basic measuring function applicable scope
Measurement
DC Voltage Support Support Support Support
AC Voltage Support Support Support Support
DC Current Support Support
AC Current Support Support
Resistance
Resistance
Frequency Support Support
Continuity
Capacitance Support Support
Supported the Math function
Function
2-Wire
4-Wire
Total dB dBm Limit
Support Support
Support Support
Period Support Support
Diodes
Ratio Support Support
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
2-13
Page 64

RIGOL
Math Functions Selective
The DM3000 provides five math functions: Null measurements, Total
measurements, dB measurements, dBm measurements, and Limit testing. Only one
of these math functions can be enabled at the same time, and remains in effect until
you turn it off or change it.
Press key, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 2-13
Table 2-10 Math Functions Menu Function Explanation
Function
Menu
Statistic
dB
dBm
Limit
ON/OFF
Settings Explanation
Reading statistic functions, including: Max, Min,
Average, and Reading Count.
The dB measurement is the difference between
the input signal and a stored relative value.
The dBm function is logarithmic, and is based on
a calculation of power delivered to a reference
resistance.
The limit test function enables you to perform
pass/fail testing to upper and lower limits that
you specify.
ON
OFF
Turn on Math function.
Turn off Math function.
Save all changes, back to a higher level menu.
2-14
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 65

RIGOL
1. Statistic Measurement
The Statistic function allows to measure the following measurement functions: dc
voltage, ac voltage, dc current, ac current, resistance, frequency/period, and
capacitance.
From the front panel, you can view the following statistical data for any set of
readings: average (Ave), maximum (Max), minimum (Min), and you can read all of
these with All functions
Press Æ Stats, enter the menu shown below:
and the number of samples taken (Count).
Figure 2-14
Table 2-11 Statistic Measurement Menu Function Explanation
Function Menu Explanation
Max (Maximum) Statistical measurement all reading Max value.
Min (Minimum) Statistical measurement all reading Min value.
Ave (Average) Statistical measurement all reading Average value.
All Statistical measurement all the number of readings.
Save all changes, back to a higher level menu.
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
2-15
Page 66

RIGOL
2. Limit Measurement
The Limit test function enables you to perform pass/fail testing to upper and lower
limits that you specify. You can set the upper and lower limits to any value between
0 and ±120% of the highest range, for the present function. The upper limit you
select must be a more positive number than the lower limit.
Press Æ Limit, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 2-15
Table 2-12 Limit Measurement Menu Function Explanation
Function
Menu
Settings Explanation
High Set the desired Upper limit.
Low Set the desired Lower limit.
Save all changes, back to a higher level menu.
The parameters value scope of Limit function:
(1). The limit value scope is 0%~±120% of the current measurement range.
(2). The upper limit value should be always bigger than the lower limit value.
2-16
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 67

RIGOL
3. dB Measurement
The dB function applies to AC voltage and DC voltage measurements only.
Each dB measurement is different between the input signal and a stored relative
value, with both values converted to dBm.
Press Æ dB, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 2-16
Table 2-13 dB Measurement Function Menu Function Explanation
Function
Menu
Explanation
Default Use the default value.
Save all changes, back to a higher level menu.
dB =10xLog
[ (Reading2 / R
10
) / 0.001W ] – (dB setting value)
REF
The relative value can take any value between 0 dBm and ±200.0 dBm.
The default relative value is 10 dBm. You can either let the instrument automatically
measure this value, or you can enter a specified value.
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
2-17
Page 68

RIGOL
4. dBm Measurement
This function applies to AC voltage and DC voltage measurements only.
The dBm function is logarithmic, and is based on a calculation of power delivered to
a reference resistance, relative to 1 milliwatt.
Press Æ dBm, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 2-17
Table 2-14 dB Measurement Function Menu Function Explanation
Function
Menu
Explanation
Default Use the default value.
Save all changes, back to a higher level menu.
The computation method of the dBm:
dBm = 10 x Log
R
expressed measuring the resistance value in the actual electric circuit.
REF
[ (Reading2 / R
10
) / 0.001W ]
REF
2-18
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 69

RIGOL
To Set Up Triggering Parameter Function
The DM3000 triggering system allows you to generate triggers either manually or
automatically, take multiple readings per trigger. The DM3000 also allows you to set
a level for internal triggering, and to set up pre-triggering.
Selecting a Trigger Source
Specify the source from which the multimeter will accept a trigger. The power–on
default is auto triggering from the front panel. Several types of triggering are
described in the sections that follow.
The power–on trigger default mode was auto trigger (RUN) mode. Press to go
to the hold trigger mode. Press to go to the single trigger mode. A single
reading is taken, and another reading is taken each time you press , or when a
hardware trigger is received on the Ext Trig connector.
Figure 2-18
Table 2-15 Trigger Parameters Setting Menu Function Explanation
Function
Menu
Auto
Setting system fixed time Auto trigger and reading
Hold scope parameters.
Explanation
Single Setting Single manual trigger parameter.
Ext Setting the reading Hold scope.
VMC Setting the pulse width of sampling ending signal.
Save all changes, back to a higher level menu.
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
2-19
Page 70

RIGOL
Auto Triggering
Auto triggering takes continuous readings at the fastest rate possible for the
specified measurement configuration (function, range, resolution, and so forth).
Auto trigger is a default trigger mode when the multimeter power-on.
Press Æ Auto, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 2-19
Table 2-16 Auto Trigger Function Menu Explanation
Function
Menu
Interval
Setting Explanation
Set interval time in 400~2000ms.
Hold
Save all changes, back to a higher level menu.
Interval time:
You can manually specify a delay between the trigger signal and the first sample
that follows. This may be useful in applications where you want to allow the input
signal to settle before taking a reading, or for pacing a burst of readings.
• The trigger delay may be set from 400 to 2000 ms.
• The continuity and diode test functions ignore the trigger delay segment.
• If a trigger delay is not manually set, the default trigger delay is automatically set.
• If you manually specify a trigger delay, that delay is used for all measurement
functions (except continuity and diode test).
2-20
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 71

RIGOL
Reading Hold
The reading hold mode allows you to capture and hold a stable reading on the front
panel display. This is useful in situations when you want to take a reading, remove
the test probes, and have the reading remain on the display. When a stable reading
is detected the reading will hold on the display. Hold scope include 0.01%, 0.1%, 1%,
and 10%.
Press Æ Auto Æ Hold, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 2-20
Table 2-17 Reading Hold Function Menu Explanation
Function
Menu
On/Off
Turn on/off the reading hold function.
Explanation
0.01% Set the hold scope is 0.01%.
0.1% Set the hold scope is 0.1%.
1%
10%
Set the hold scope is 1%.
Set the hold scope is 10%.
Save all changes, back to a higher level menu.
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
2-21
Page 72

RIGOL
Reading Hold Function
Start the Reading Hold Function, the hold measurement use the following rules
judge the reading count:
When Max() - Min() ≤ hold scope x ReadingN, the multimeter hold ReadingN on the
display.
The display update a new reading was based on the current value of reading and the
following three readings before the reading was hold:
Max (ReadingN, ReadingN-1, ReadingN-2, ReadingN-3)
Min (ReadingN, ReadingN-1, ReadingN-2, ReadingN-3)
NOTE
When reading hold started, the input resistance was automatism set to 10MΩ for all
DC voltage range. This set-up is conducive to reducing noise arising from the
open-loop testing.
2-22
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 73

RIGOL
Single Triggering
The multimeter takes one reading, or a number of readings specified by a sample
count you enter, each time you press.
Press Æ Single, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 2-21
Table 2-18 Single Trigger Function Menu Explanation
Function
Menu
Single Set a sample count, the default sample count is 1.
Save all changes, back to a higher level menu.
Sample Count
While the multimeter receives a single trigger single, the multimeter takes one
reading or a number of readings.
The number of sample count scope from 1 to 50,000. The factory default is 1.
Explanation
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
2-23
Page 74

RIGOL
External Triggering
is used to set the parameter which accomplish the triggering function, the
external triggering function needs to set the following parameter: the Rise edge, the
Fall edge, HiLev (high level) and LoLev (low level). After ensuring the setting is
correct, press Done to startup the external triggering, the key and on the
front panel will wink out, it means that the instrument has been working in the
external triggering mode.
Press Æ Ext, enter the following menu.
Figure 2-22
The interface of the external triggering
Users could set the triggering mod as the following: the rise edge, the fall edge, high
level and low level.
2-24
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 75

RIGOL
To start up the triggering function
Auto, hold and Single trigger can switch by using and , press on the
triggering interface to startup the external triggering.
Figure 2-23
The interface of the external triggering
After the external triggering start, the key and on the front panel both will
wink out.
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
2-25
Page 76

RIGOL
To Set up the VMC
Once in the external triggering mode, when the data sampling is over, the instrument
outputs a pulse signal pass the signal over-put port (VM Comp) on the rear panel. By
setting the output, the pulse width can be intercalated.
Press Æ VMC, enter the following menu. Output the export Terminal.
Figure 2-24
Table 2-19 The interface of the external triggering(polarity: positive)
Function
Menu
Polar
Setting Explanation
Pos
Neg
Setting the pulse signal’s polarity.
PWidth Setting the pulse width.
Store the changing and return.
Export the VMC function setting range
(1). Once in the external triggering mode, when the data sampling is over, the
instrument will export a pulse signal and hint over.
(2). Once in the external triggering mode, when operate the math limited value,
the instrument will export a pulse signal and hint it has over pass.
2-26
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 77

RIGOL
Store and Recall
To use the Storage and Recall function, you can save, load, and delete the
measurement data, parameters and sensor documents in the local storage. And also
you can do the same operation in USB storage.
Press key, and enter the menu shown below:
Figure 2-25
Table 2-20 Storage and Recall Function Menu Explanation
Function
Menu
Setting Explanation
C:\ (Local)
Disk
A:\ (U-Disk)
Choose Local or U-Disk storage.
Data/
Parameters/
Typ e
Sensor
Choose the type of the files shown.
…
Read
Save
Load the documents you have selected.
Save the document to the location which you
have selected.
Erase Delete the document which you have selected.
Save all changes, back to a higher level menu.
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
2-27
Page 78

RIGOL
Local/U-Disk Storage
Local storage block is built-in the multimeter. The U-Disk storage will be a USB flash
disk.
Press key, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 2-26
Table 2-21 Storage and Recall Function Menu Explanation
Function
Menu
Explore
Setting Explanation
Choose Local storage or U-Disk rout.
Sys Setting/
Meas Data/
Data log/
Typ e
Sensor/
Choose the type of the files shown.
Sensor Data/
Scan Task
Read
Save
Load the document you have selected.
Save the document to the location which you
have selected.
Erase Delete the document which you have selected.
Save all changes, back to a higher level menu.
2-28
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 79

RIGOL
Document Storage
In local/U-disk storage area, you allowed to save, load and delete parameter, data
and sensor documents.
Choose the storage area of the files
Press Æ Disk, choose Local storage or U-Disk rout. Choose C:\, and the default
fype is “SysSetting”.
Figure 2-27
Choose the storage type of the files
Press Æ Type, choose the type “MeasData” of the files, into the menu shown
below:
Figure 2-28
Press Æ Type, choose the type “Datalog” of the files, into the menu shown
below:
Figure 2-29
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
2-29
Page 80

RIGOL
Press Æ Type, choose the type “Sensor”, “SensorData”, “ScanTask” of the files,
into the menu shown below:
Figure 2-30
NOTE
Store, recall and delete use the same interface.
1) When choose different storage locations, Press Disk, to switch the store
location (C:\(Local) and A:\(U-Disk)).
2) When choose different files types, Press Type, to switch the file type (Data,
Parameter, and Sensor).
3) When operating the A disk, do not take off the U disk.
2-30
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 81

RIGOL
Document Operation
Use the up and down buttons select the right document, then press U-Disk Read,
Save and Erase soft keys to do corresponding operation.
Figure 2-31
To save the document, you are allowed to name the document with letters and
numeral.
Figure 2-32
NOTE
1) Use the up/down key to choose the cursor position: for switching the area of
filename and input method.
2) The cursor will wink at the position of the current operation area.
3) The delete function can only delete the letter on which the cursor taking place.
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
2-31
Page 82

RIGOL
To Set Up the Utility
In utility function set up menu, the function of various parameters related system set
up, include: system parameters, interface parameters, self-test, and calibration.
Figure 2-33
Table 2-22 Utility Function Menu Explanation
Function
Menu
Explanation
I/O To set up I/O parameters.
Sys To set up system information configuration.
T/C Test function.
2-32
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 83

RIGOL
System settings
Press Æ System, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 2-34
The interface of setting the system function
Table 2-23 System Settings Function Menu Explanation
Function
Menu
Explanation
Lang Select the display interface languages.
Disp Set up the display.
Sound Switch beeper sound On/Off.
Clock Set up the benchmark clock.
Format Set up digit display format.
Cfg Set up or resume the system values.
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
2-33
Page 84

RIGOL
Select languages
DM3000 supports two kinds of languages for users.
Press Æ Sys Æ Lang, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 2-35
Table 2-24 System Settings Function Menu Explanation
Function
Menu
中文简
Select the Chinese Simplified.
Explanation
English Select the English.
Save all changes, back to a higher level menu.
2-34
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 85

RIGOL
Set Up the Display
Press Æ Sys Æ Disp, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 2-36
Table 2-25 Display Settings Function Menu Explanation
Function
Menu
Bright
Contr
Increase or decrease the display light with left and
right keys.
Increase or decrease the display contrast with left
and right keys.
Explanation
Invert Set to invert display mode.
Save all changes, back to a higher level menu.
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
2-35
Page 86

RIGOL
Switch Beeper Sound
Press Æ Sys Æ Sound, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 2-37
Sound On
Figure 2-38
Sound Off
2-36
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 87

RIGOL
Set Up the Benchmark Clock
Press Æ Sys Æ Clock, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 2-39
Data set interface
Figure 2-40
Time set interface
Table 2-26 Clock Settings Function Menu Explanation
Function
Menu
Explanation
Data Set up the data.
Time Set up the time.
Hide Hide data and time display.
Done Save all changes, back to a higher level menu.
Back to a higher level menu, without save.
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
2-37
Page 88

RIGOL
Set Up Digit Format
Press Æ Sys Æ Format, and enter the menu shown below:
Figure 2-41
Table 2-27 Digit Format Function Menu Explanation
Function
Menu
Radix
Point
Expresses radix point with
Explanation
or .
Separator Expresses separator with , space or none.
Save all changes, back to a higher level menu.
Figure 2-42
“
” express radix point, “ ” express separator
2-38
Figure 2-43
“
” express radix point, “ ” express separator
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 89

RIGOL
Figure 2-44
“
” express radix point, none express separator
Figure 2-45
“
” express radix point, “space” express separator
Figure 2-46
“
” express radix point, “space” express separator
Notice:
The decimal and the separator cannot be the same mode, if the decimal is , then
the separator can only be
the separator can only be
, none of space; in contrarily, if the decimal is , then
, none of space.
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
2-39
Page 90

RIGOL
Set Up the I/O System
Press Æ I/O, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 2-47
Tab le 2-28 I/O Setting Function Menu Explanation
Function
Menu
Explanation
LAN Set up LAN interface.
GPIB Set up GPIB I/O interface.
USB Check USB interface ID.
RS232 Set up RS-232 I/O interface.
Save all changes, back to a higher level menu.
2-40
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 91

RIGOL
Set Up LAN I/O Parameter
LAN Parameters You may choose to manually set the following parameters, as
described in the subsections that follow. Following these descriptions are procedures
for setting up a LAN configuration from the front panel and the remote interface.
• IP Address
• Subnet Mask
• Default Gateway
• DNS Server
• Host Name
Press Æ I/O Æ LAN, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 2-48
Table 2-29 LAN Parameter Function Menu Explanation
Function
Menu
Setting Explanation
IP Set IP address and others information.
Host Name/
DNS
Domain Name/
DNS address
Info
Set the host name.
Set the domain name.
Set DNS address.
Examines the current LAN connection
information.
Save all changes, back to a higher level
menu.
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
2-41
Page 92

RIGOL
IP Settings
Press Æ I/O Æ LAN Æ IP, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 2-49
DHCP On
Figure 2-50
DHCP Off
Table 2-30 IP Setting Menu Explanation
Function
Menu
DHCP
Done
Setting Explanation
ON/
OFF
Automatically assigns the IP address
Manual assigns the IP address
Save all changes, back to a higher level
menu.
2-42
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 93

RIGOL
DNS Setting
Press Æ I/O Æ LAN Æ DNS, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 2-51
Table 2-31 DNS Setting Menu Explanation
Function
Menu
Setting Explanation
Host Set the host name.
DN Set the domain name.
DNS Set the DNS address.
Done
Save all changes, back to a higher
level menu.
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
2-43
Page 94

RIGOL
Set Up GPIB I/O Parameter
Each device on the GPIB (IEEE–488) interface must have a unique address. You can
set the address of multimeter to any integral value between 0 and 30. The default
address is “1” when the instrument is shipped from the factory.
Press Æ I/O Æ GPIB, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 2-52
Table 2-32 GPIB I/O Setting Function Menu Explanation
Function
Menu
Save all changes, back to a higher level menu.
Explanation
2-44
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 95

RIGOL
Set Up RS-232 I/O Parameters
Press Æ I/O Æ RS232, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 2-53
Table 2-33 RS-232 Parameter Function Menu Explanation
Function
Menu
Display Explanation
300
Set RS-232 baud rate as 300,
2400, 4800, 9600, 19200 or
38400.
Baud
.
.
38400
None
Parity
Odd
Even
The parity check include: None,
Odd check, and Even check.
Save all changes, back to a higher
level menu.
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
2-45
Page 96

RIGOL
High-speed Data Logger
High-speed data logger displaying areas include: display mode settings, start acquire
mode settings, and end acquire mode settings. When finish all settings, press
button to begin the high-speed data logger.
Setting high-speed data logger parameters
Press button, enter the menu shown below:
Figure 2-54
The main interface of DataLog
Table 2-34 Data Logger Parameter Setting Function Menu Explanation
Function
Menu
Log
Scan
Setting Explanation
Gather the data of DCV, DCI, 2WR or 4WR
continuously.
Use the scanning mode to test the
16-roads signals continuously.
Save all changes, back to a higher level
menu.
Notice: Once in the DataLog mod, do not use the Auto range option function but
choose the appropriate range option, thus the Log rates can be guaranteed.
Press Log, enter the data logger interface shown below.
Figure 2-55
The DataLog setting interface
2-46
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 97

RIGOL
Table 2-35 Datalog menu Explanation
Function
Menu
Setting Explanation
1/10m
1/5m
Sa/s
.
.
To set the sample rate with 13 values from
1/10m to 50k/s.
.
50k/s
Start
Stop
Trig
Delay
Timer
REC#
To set the sample manner to be Trig or delay.
To set the data measurement stop manner to
be timer or counter.
Run Start logger the data.
Save all the changes, back to a higher level
menu.
Press Æ Log Æ Sa/s, enter the interface shows below.
Figure 2-56
The DataLog rate setting interface
Press Æ Log Æ Start, enter the interface shows below.
Figure 2-57
The DataLog start manner setting interface
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
2-47
Page 98

RIGOL
Press Æ Log Æ Stop, enter the interface shows below.
Figure 2-58
The DataLog Stop manner setting interface
2-48
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
Page 99

RIGOL
1.DataLog rate
To set the DataLog sample rate.
Press Æ Log Æ Sa/s, enter the interface shows below.
Figure 2-59
The Datalog rate setting interface
Table 2-36 The DataLog rate setting menu explanation
Function
Menu
Setting Explanation
1/10m
1/5m
.
.
To set the sample rate with 13 values from
1/10m to 50k/s.
50k/s
Save all the changes, back to a higher level
menu.
The system has set 13 DataLog rates; it is convenient for the user.
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
2-49
Page 100

RIGOL
T
2.The start manner
To set a manner of the start condition and delay time of DataLog function.
Press Æ Log Æ Start, enter the interface shows below.
Figure 2-60
The start condition setting interface
Table 2-37 The start condition setting menu explanation
Function
Menu
Trig
Setting Explanation
Manu
Ext
To set the DataLog start manner to be
manual trigger.
o set the DataLog start manner to be
external trigger.
Delay
The latency time from trigger start to
beginning DataLog.
Save all the changes, back to a higher
level menu.
2-50
User’s Guide for DM3000 Series
©Copyright RIGOL Technologies, Inc. 2007.
 Loading...
Loading...