Page 1

INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
ISO 9001:2000
AIR-COOLED CONDENSING UNITS
(-)ARL-JEZ 16 SEER AND (-)ASL-JEZ 18 SEER MODELS
EQUIPPED WITH THE INTEGRATED COMFORT CONTROL SYSTEM™
[ ] INDICATES METRIC CONVERSIONS
Featuring Earth-Friendly
R-410A Refrigerant
92-101691-02-04
SUPERSEDES 92-101691-02-03
Page 2
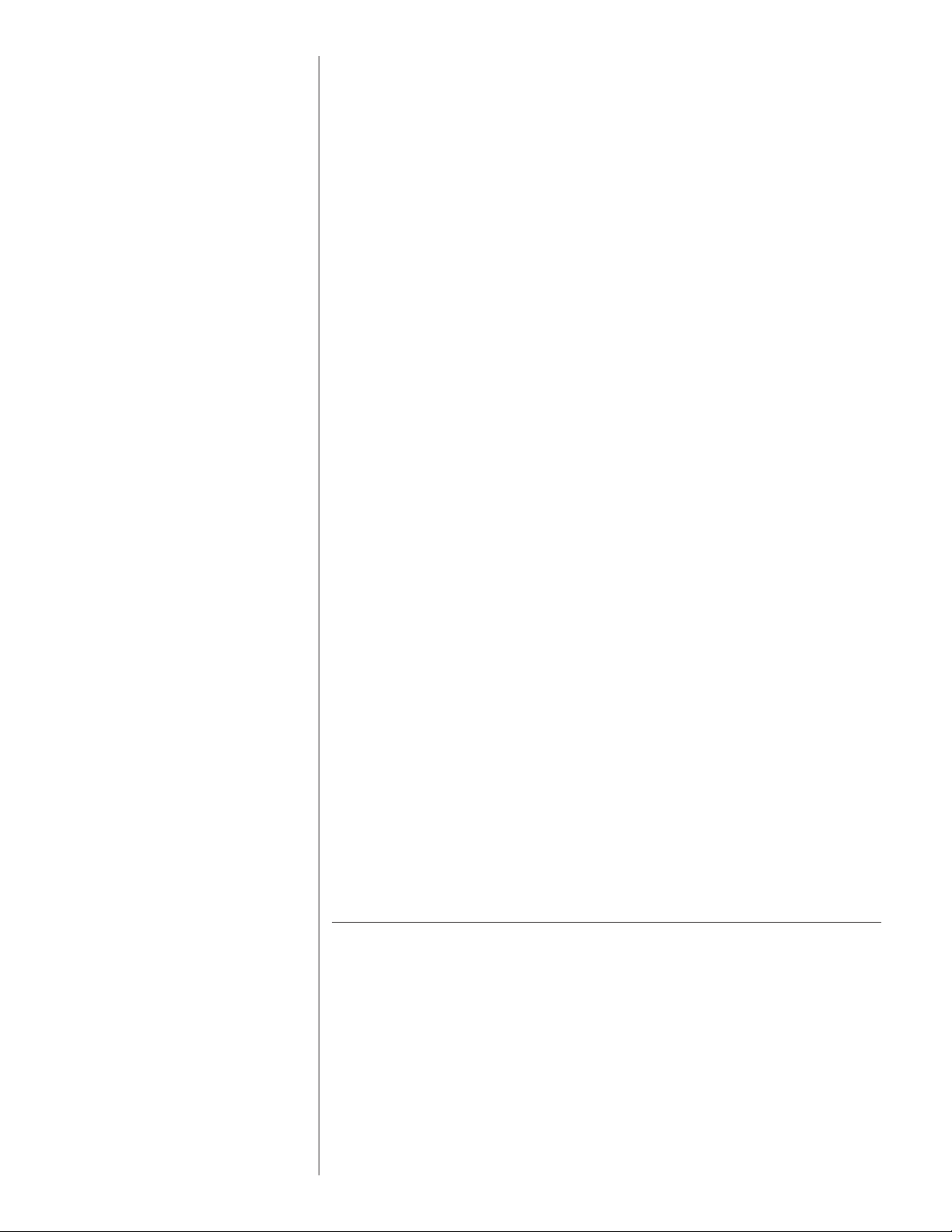
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Checking Product Received . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
Electrical & Physical Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
eneral . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
G
Corrosive Environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Locating Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .5
Unit Mounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
Factory-Preferred Tie-Down Method . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
Refrigerant Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Tools Required for Installing & Serviciing R-410A Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Specification of R-410A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Quick Reference Guide for R-410A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Evaporator Coil . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Interconnecting Tubing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9-11
Liquid Line Size . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Evacuation Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Start-Up and Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Checking Airflow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Checking Refrigerant Charge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Charging by Liquid Pressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Charging Units with R-410A Refrigerant . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
Charging by Weight . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Final Leak Testing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Electrical Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Factory Installed Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Field Installed Accessories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Comfort Control System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Status and Diagnostic Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
Trouble Shooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29-32
Trouble Shooting Chart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Wiring Diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33-34
CHECKING PRODUCT RECEIVED
Upon receiving unit, inspect it for any shipping damage. Claims for damage, either
apparent or concealed, should be filed immediately with the shipping company.
Check condensing unit model number, electrical characteristics and accessories to
determine if they are correct. Check system components (evaporator coil, condensing unit, evaporator blower, etc.) to make sure they are properly matched.
2
Page 3
FIGURE 1
A
IR INLETS
(LOUVERS)
A
LLOW 120 [305 mm]
M
IN. CLEARANCE
3
SIDES
AIR DISCHARGE
ALLOW 600 [1524 mm] CLEARANCE
ALLOW 240 [610 mm]
ACCESS CLEARANCE
ACCESS
PANEL
L
W
H
ALTERNATE HIGH VOLTAGE
CONNECTION (KNOCKOUT)
1
11
/320[34 mm]
SERVICE
FITTINGS
LOW VOLTAGE
CONNECTION
7
/8" [22 mm]
HIGH VOLTAGE
CONNECTION
1
11
/32" [34 mm]
LIQUID LINE
CONNECTION
SERVICE ACCESS
TO ELECTRICAL &
VALVES ALLOW
24" [610 mm]
CLEARANCE
ONE SIDE
2
7
/8" [73 mm] DIA.
ACCESSORY
KNOCKOUTS
VAPOR LINE
CONNECTION
A-00002
DIMENSIONS AND INSTALLATION CLEARANCES
AIR DISCHARGE
ALLOW 60" [1524 mm] CLEARANCE
ACCESS
PANEL
ALLOW 24" [610 mm]
ACCESS CLEARANCE
UNIT MODEL NUMBER EXPLANATION
IR INLETS
A
LOUVERS)
(
LLOW 12" [305 mm]
A
IN. CLEARANCE
M
SIDES
3
ALTERNATE LINE VOLTAGE
ENTRY (KNOCKOUT)
111⁄32" [34 MM]
CONNECT THE LINE
VOLTAGE CONDUIT TO
THE BOTTOM OF THE
CONTROL BOX
-)ARL – 036 JEZ
(
= DESIGN SERIES (R-410A)
L
R = 16 SEER
= 18 SEER
S
A = REMOTE CONDENSING UNIT
TRADE NAME
BASE PAN
Z-SCROLL COMPRESSOR
E = EQUIPPED WITH THE
OMFORT CONTROL SYSTEM™
C
- 208/230-1-60
J
(NOMINAL CAPACITY)
24 = 24000 BTU/HR
0
036 - 36000 BTU/HR
48 = 48000 BTU/HR
0
60 = 60000 BTU/HR
0
LINE VOLTAGE
ENTRY
7
⁄8" [22 MM]
LINE VOLTAGE
ENTRY
111⁄32" [34 MM]
CONNECT THE LINE
VOLTAGE CONDUIT TO
THE BOTTOM OF THE
CONTROL BOX
BOTTOM VIEW SHOWING DRAIN OPENINGS
(\\\\\ SHADED AREAS).
TABLE 1
(-)ARL AND (-)ASL ELECTRICAL DATA
Phase
Model
Number
(-)ARL-024JEZ 1-60-208/230 10.3/10.3 52 0.8 14/14 20/20 20/20 15.8 [1.47] 1 2285 [1078] 117 [3311] 190 [86.2] 200 [90.7] 23 44-3/8 31-1/2
(-)ARL-036JEZ 1-60-208/230 16.7/16.7 82 1.0 22/22 30/30 35/35 15.8 [1.47] 1 3900 [1841] 157 [4445] 236 [107] 246 [111.6] 33 44-3/8 31-1/2
Frequency
(Hz)
Voltage
(Volts)
Compressor
(RLA) (LRA)
(-)ARL-048JEZ 1-60-208/230 21.2/21.2 96 1.0 28/28 35/35 45/45 15.8 [1.47] 1 3900 [1841] 154 [4354] 236 [107] 246 [111.6] 33 44-3/8 31-1/2
(-)ARL-060JEZ 1-60-208/230 25.6/25.6 118 2.8 35/35 45/45 60/60 23.0 [2.14] 2
(-)ASL-024JEZ 1-60-208/230 10.3/10.3 52 0.5 14/14 20/20 20/20 15.8 [1.47] 1
(-)ASL-036JEZ 1-60-208/230 16.7/16.7 82 2.8 24/24 30/30 40/40 23.0 [2.14] 1
*HS = high speed
*LS = low speed
ELECTRICAL PHYSICAL DIMENSIONAL DATA
Fan
Min. Circuit
Motor
Ampacity
(FLA)
Amperes
Fuse or HACR
Circuit Breaker
Min.
Amperes
Amperes
Max.
Outdoor Coil Weight
Face Area
Sq. Ft. [m
2
]
No.
Rows
CFM [L/s}
HS* 3500 [1652]
LS* 2800 [1322]
HS* 2500 [1180]
HS* 2200 [1038]
HS* 3400 [1605]
HS* 2800 [1322]
R-410a
Oz. [g]
224 [6350] 305 [138] 315 [143] 33 44-3/8 31-1/2
144 [4082] 236 [107] 246 [111.6] 33 44-3/8 31-1/2
155 [4394] 236 [107] 246 [111.6] 33 44-3/8 31-1/2
Net
Lbs. [kg]
Shipping
Lbs. [kg]
Height
“H”
(Inches)
Length
“L”
(Inches)
Width
“W”
(Inches)
3
Page 4
WARNING
!
TH E MANUFACT UR ER’S WA RRANTY DOES NOT COVER ANY
DA MAGE OR DEFECT TO THE
AIR CONDITIONER CAUSED BY
THE ATTACHMENT OR USE OF
ANY COM PON ENT S. AC CESSORIES OR DEVICES (OTHER
THAN THOSE AUTHORIZED BY
THE MANU FACTURE R) IN TO,
ONT O OR IN CON JUNCT ION
WI TH THE AIR CON DI TIONER.
YOU SHOULD BE AWARE THAT
THE USE OF UNAUT HOR IZE D
COMPONENTS, ACCESSORIES
OR DEVICES MAY ADVERSELY
AFF ECT TH E OP ERATION
OF THE AIR CONDITIONER AND
MAY ALS O EN DAN GER LIF E
AND PROPERTY. THE MANUFACTUR ER DISCLAIM S ANY
RES PONSIBIL ITY F OR SU CH
LO SS OR INJU RY RESULTING
FRO M T HE USE OF SUC H
UNAUTHORIZED COMPONENTS,
ACCESSORIES OR DEVICES.
MATCH ALL COMPONENTS:
• OUTDOOR UNIT
• INDOOR COIL/METERING DEVICE
• INDOOR AIR HANDLER/FURNACE
• REFRIGERANT LINES
GENERAL
The information contained in this manual has been prepared to assist in the proper
installation, operation and maintenance of the air conditioning system. Improper
installation, or installation not made in accordance with these instructions, can
result in unsatisfactory operation and/or dangerous conditions (noise and component failure), and can cause the related warranty not to apply.
Read this manual and any instructions packaged with separate equipment required
to make up the system prior to installation. Retain this manual for future reference.
To achieve optimum efficiency and capacity, the indoor cooling coils listed in the
condensing unit specification sheet should be used.
APPLICATION
Before specifying any air conditioning equipment, a survey of the structure and a
heat gain calculation must be made. A heat gain calculation begins by measuring
all external surfaces and openings that gain heat from the surrounding air and
quantifying that heat gain. A heat gain calculation also calculates the extra heat
load caused by sunlight and by humidity removal.
Air conditioning systems are sized on the cooling load calculation. There are two
capacities that enable the equipment to provide comfort. The first is sensible capacity.
Sensible heat is the heat energy measured on the dry bulb thermometer as it is
added or removed.
The second form of heat is called latent or hidden heat. This is heat held in the
humidity in the air.
A properly-sized unit removes both forms of heat, producing a comfortable living
space. An oversized system cycles on and off too quickly and does not properly
remove humidity, producing an uncomfortable living space. Select the indoor and
outdoor equipment combination based on the manufacturer’s engineering data.
After the equipment combination has been selected, satisfying both sensible and
latent conditioning requirements, the system must be properly installed. Only then
can the unit provide the comfort the manufacturer intends.
There are several factors that the installers must consider:
• Outdoor unit location • Proper equipment evacuation
• System refrigerant charge • Indoor unit airflow
• Indoor unit blower speed • Supply and return air duct design and sizing
• System air balancing • Diffuser and return air grille location and sizing
CORROSIVE ENVIRONMENT
The metal parts of this unit may be subject to rust or deterioration if exposed to a
corrosive environment. This oxidation could shorten the equipment’s useful life.
Corrosive elements include, but are not limited to, salt spray, fog or mist in seacoast
areas, sulphur or chlorine from lawn watering systems, and various chemical contaminants from industries such as paper mills and petroleum refineries.
If the unit is to be installed in an area where contaminants are likely to be a problem, special attention should be given to the equipment location and exposure.
• Avoid having lawn sprinkler heads spray directly on the unit cabinet.
• In coastal areas, locate the unit on the side of the building away from the waterfront.
• Shielding provided by a fence or shrubs may give some protection, but cannot
violate minimum airflow and service access clearances.
• Elevating the unit off its slab or base enough to allow air circulation will help
avoid holding water against the basepan.
Regular maintenance will reduce the build-up of contaminants and help to protect
the unit’s finish.
WARNING
!
DIS CONNECT ALL POWER TO UNIT BEF ORE S TAR TIN G
MAINTENANCE. FAILURE TO DO SO CAN CAUSE ELECTRICAL SHOCK
RESULTING IN SEVERE PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH.
4
Page 5
• Frequent washing of the cabinet, fan blade and coil with fresh water will remove
most of the salt or other contaminants that build up on the unit.
• Regular cleaning and waxing of the cabinet with a good automobile polish will
provide some protection.
• A good liquid cleaner may be used several times a year to remove matter on
the cabinet that will not wash off with water.
Several different types of protective coatings are offered in some areas. These
coatings may provide some benefit, but the effectiveness of such coating materials
cannot be verified by the equipment manufacturer.
LOCATING UNIT
CONDENSER LOCATION
Consult local and national building codes and ordinances for special installation
requirements. Following location information will provide longer life and simplified
servicing of the outdoor condenser.
NOTE: These units must be installed outdoors. No ductwork can be attached, or
other modifications made, to the discharge grille. Modifications will affect performance or operation.
OPERATIONAL ISSUES
• IMPORTANT: Locate the condenser in a manner that will not prevent, impair or
compromise the performance of other equipment horizontally installed in proximity to the unit. Maintain all required minimum distances to gas and electric
meters, dryer vents, exhaust and inlet openings. In the absence of National
Codes, or manaufacturers’ recommendations, local code recommendations
and requirements will take presidence.
• Refrigerant piping and wiring should be properly sized and kept as short as
possible to avoid capacity losses and increased operating costs.
• Locate the condenser where water run off will not create a problem with the
equipment. Position the unit away from the drip edge of the roof whenever possible. Units are weatherized, but can be affected by the following:
• Water pouring into the unit from the junction of rooflines, without protective
guttering. Large volumes of water entering the condenser while in operation
can impact fan blade or motor life.
• Refer to clearance recommendations on Page 3.
o 24” to the service panel access
o 60” above condenser fan discharge (unit top) to prevent recirculation
o 12” to condenser coil grille air inlets (per condenser).
FOR CONDENSERS WITH SPACE LIMITATIONS
In the event that a space limitation exists, we will permit the following clearances:
Single Unit Applications: One condenser inlet air grille side may be reduced to no
less than an 8-inch clearance. Clearances below 8 inches will reduce unit capacity
and efficiency. Do not reduce the 60-inch discharge, or the 24-inch service clearances.
Multiple Unit Applications: When multiple unit (2 or more condensers) air inlet
grilles are placed side by side, a 12-inch per unit clearance is recommended, for a
total of 24” between two units. When multiple condenser grille sides are aligned, a
4-inch per unit spacing can be used, for a total of 8 inches between multiple units.
Two combined clearances below 8 inches will reduce capacity and efficiency. Do
not reduce the 60-inch discharge, or 24-inch service, clearances.
5
Page 6
CUSTOMER SATISFACTION ISSUES
• The condenser should be located away from the living, sleeping and recreational spaces of the owner and those spaces of adjoining property.
• To prevent noise transmission, the mounting pad for the outdoor unit should
not be connected to the structure, and should be located sufficient distance
above grade to prevent ground water from entering the unit.
NOTE: Tubing installed in walls may cause noise issues.
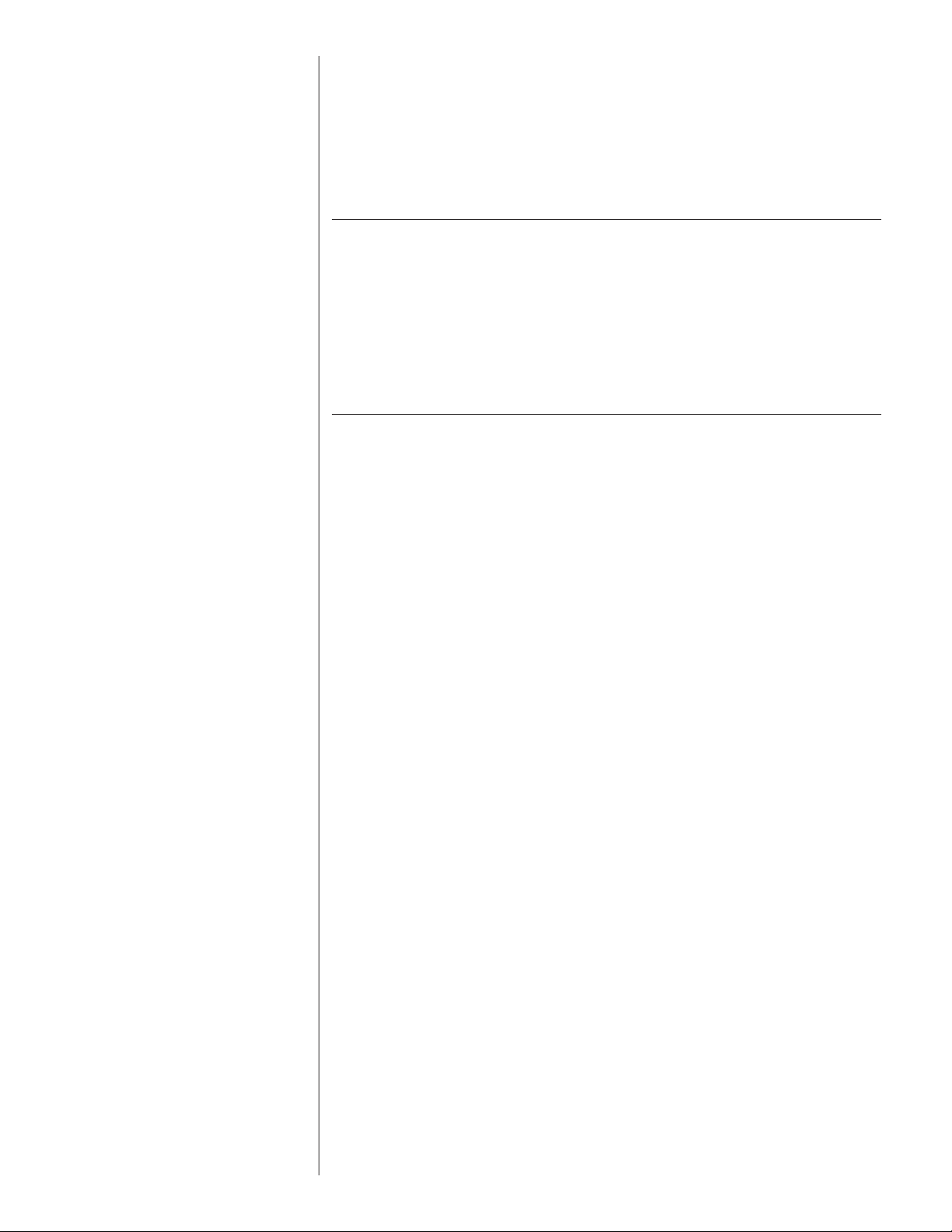
UNIT MOUNTING
If elevating the condensing unit, either on a flat roof or on a slab, observe the
following guidelines.
• The base pan provided elevates the condenser coil 3/4” above the base pad.
• If elevating a unit on a flat roof, use 4” x 4” (or equivalent) stringers positioned
to distribute unit weight evenly and prevent noise and vibration.
NOTE: Do not block drain openings shown in Figure 1.
FACTORY-PREFERRED TIE-DOWN METHOD
FOR CONDENSING UNITS
IMPORTANT: These instructions are intended as a guide to securing equipment for
wind-load ratings of “120 MPH sustained wind load” and “3-second, 150 MPH gust.”
While this procedure is not mandatory, the Manufacturer does recommend that
equipment be properly secured in areas where high wind damage may occur.
STEP 1: Before installing, clear pad of any dirt or debris.
IMPORTANT: The pad must be constructed of industry-approved materials,
and must be thick enough to accommodate the concrete fastener.
STEP 2: Center base pan on pad, ensuring it is level.
STEP 3: Using basepad as a guide, mark spots on concrete where 4 holes will be
drilled (see Figure 2).
STEP 4: Drill four pilot holes in pad, ensuring that the hole is at least 1/4” deeper
than the concrete screw being used.
STEP 5: Center basepan over pre-drilled holes and insert concrete screws.
STEP 6: Tighten concrete screws.
NOTE: Do not over-tighten the concrete screws. Doing so can weaken the
integrity of the concrete screw and cause it to break.
STEP 7: Finish unit assembly per unit’s installation instructions.
6
Page 7
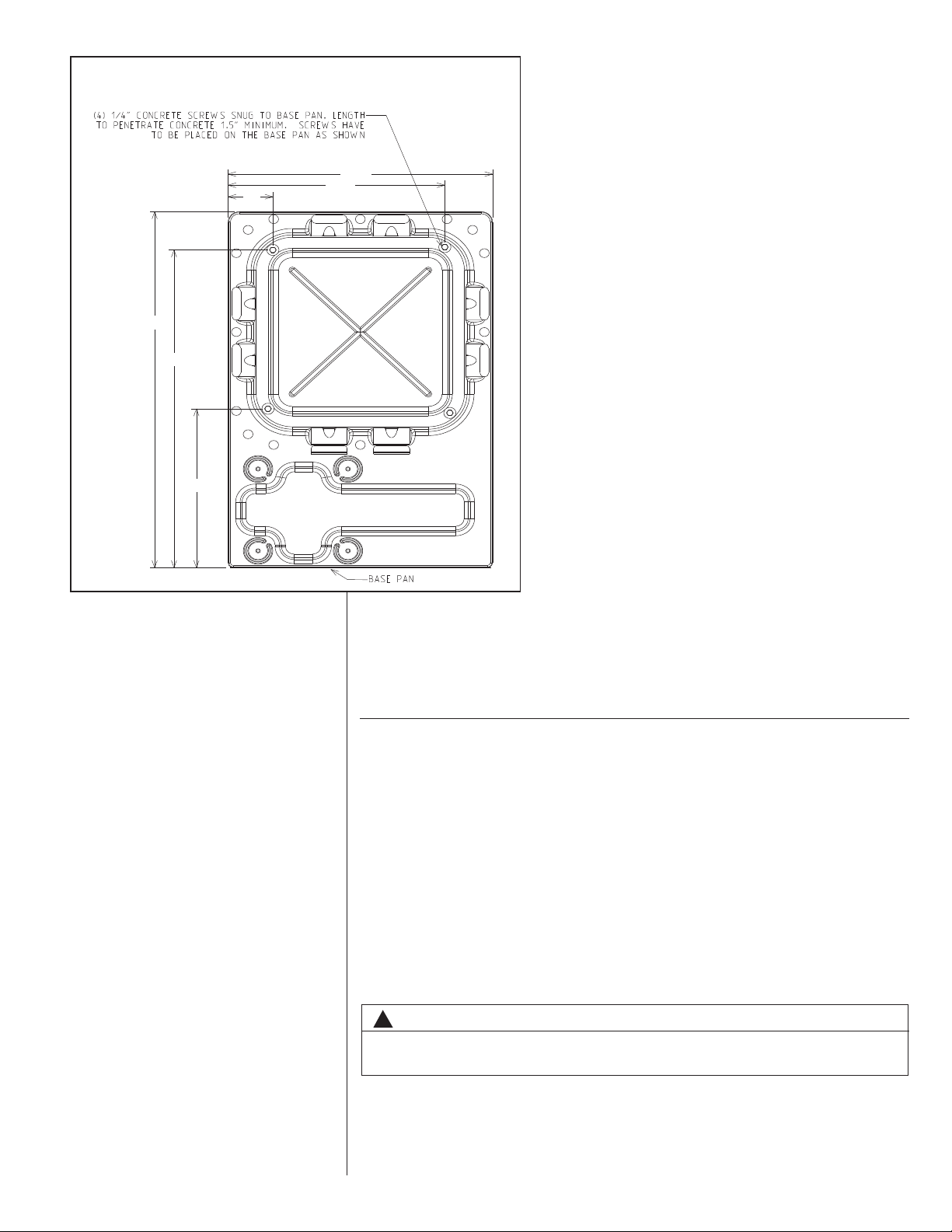
FIGURE 2
SCREW LOCATIONS
411⁄2
38
13
9
2
⁄16
1
6
2
31⁄2
5
1
⁄2
REFRIGERANT CONNECTIONS
All units are factory charged with Refrigerant R-410A. All models are supplied with
service valves. Keep tube ends sealed until connection is to be made to prevent
system contamination.
TOOLS REQUIRED FOR INSTALLING &
SERVICING R-410A MODELS
Manifold Sets:
-Up to 800 PSIG High side
-Up to 250 PSIG Low Side
-550 PSIG Low Side Retard
Manifold Hoses:
-Service Pressure Rating of 800 PSIG
Recovery Cylinders:
-400 PSIG Pressure Rating
-Dept. of Transportation 4BA400 or BW400
!
CAUTION
R-410A systems operate at higher pressures than R-22 systems. Do not use
R-22 service equipment or components on R-410A equipment.
7
Page 8

SPECIFICATION OF R-410A:
Application: R-410A is not a drop-in replacement for R-22; equipment designs
must accommodate its higher pressures. It cannot be retrofitted into R-22 condensing units.
Pressure: The pressure of R-410A is approximately 60% (1.6 times) greater
than R-22. Recovery and recycle equipment, pumps, hoses and the like need to
have design pressure ratings appropriate for R-410A. Manifold sets need to range
up to 800 psig high-side and 250 psig low-side with a 550 psig low-side retard.
Hoses need to have a service pressure rating of 800 psig. Recovery cylinders need
to have a 400 psig service pressure rating. DOT 4BA400 or DOT BW400.
Combustibility: At pressures above 1 atmosphere, mixture of R-410A and air can
become combustible. R-410A and air should never be mixed in tanks or supply
lines, or be allowed to accumulate in storage tanks. Leak checking should
never be done with a mixture of R-410A and air. Leak checking can be per-
formed safely with nitrogen or a mixture of R-410A and nitrogen.
QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE FOR R-410A
• R-410A refrigerant operates at approximately 60% higher pressure (1.6 times)
than R-22. Ensure that servicing equipment is designed to operate with R-410A.
• R-410A refrigerant cylinders are pink.
• R-410A, as with other HFC’s is only compatible with POE oils.
• Vacuum pumps will not remove moisture from POE oil.
• R-410A systems are to be charged with liquid refrigerants. Prior to March 1999,
R-410A refrigerant cylinders had a dip tube. These cylinders should be kept
upright for equipment charging. Post March 1999 cylinders do not have a dip
tube and should be inverted to ensure liquid charging of the equipment.
• Do not install a suction line filter drier in the liquid line.
• A liquid line filter drier is standard on every unit.
• Desiccant (drying agent) must be compatible for POE oils and R-410A.
EVAPORATOR COIL
REF ER TO EVA PORATOR C OIL MA NUF ACT URE R’S I NST ALL ATI ON
INSTRUCTIONS.
IMPORTANT: The manufacturer is not responsible for the performance and opera-
tion of a mismatched system, or for a match listed with another manufacturer’s coil.
CAUTION
!
Only use evaporators rated and approved for use on (-)ARL and (-)ASL R-410A
systems.
8
Page 9

The thermostatic expansion valve is specifically designed to operate with R-410A.
DO NOT use an R-22 TXV or evaporator. The existing evaporator must be
replaced with the factory specified TXV evaporator specifically designed for
R-410A.
LOCATION
Do not install the indoor evaporator coil in the return duct system of a gas or oil furnace. Provide a service inlet to the coil for inspection and cleaning. Keep the coil
pitched toward the drain connection.
CAUTION
!
When coil is installed over a finished ceiling and/or living area, it is recommended that a secondary sheet metal condensate pan be constructed and installed
under entire unit. Failure to do so can result in property damage.
INTERCONNECTING TUBING
VAPOR AND LIQUID LINES
Keep all lines sealed until connection is made.
Make connections at the indoor coil first.
Refer to Line Size Information in Tables 2 through 4 for correct size and multipliers to
be used to determine capacity for various vapor line diameters and lengths of run.
The losses due to the lines being exposed to outdoor conditions are not included.
The factory refrigeration charge in the outdoor unit is sufficient for 15 feet of interconnecting lines. The factory refrigeration charge in the outdoor unit is sufficient for
the unit and 15 feet of standard size interconnecting liquid and vapor lines. For different lengths, adjust the charge as indicated below.
1/4” ± .3 oz. per foot
5/16” ± .4 oz. per foot
3/8” ± .6 oz. per foot
1/2” ± 1.2 oz. per foot
OUTDOOR UNIT INSTALLED ABOVE INDOOR COIL
Keep the vertical separation between coils to a minimum. However, the vertical distance can be as great as 120 feet with the condensing unit ABOVE the indoor coil.
Use the following guidelines when installing the unit:
NOTE: If exceeding these measurements, the system must be an engineered system.
OUTDOOR UNIT BELOW INDOOR COIL
Keep the vertical separation to a minimum. Use the following guidelines when
installing the unit:
1. DO NOT exceed the vertical separations as indicated on Table 4.
2. Always use the smallest liquid line size permitted to minimize system charge.
3. Table 4 may be used for sizing horizontal runs.
Vertical separation is limited to the total line length as defined in the liquid line sizing
charts.
Examples:
1. A 2-ton condensing unit with a 1/4" liquid line cannot exceed a total line length
of 25 ft.
2. A 3-ton unit with a 5/16" liquid line cannot exceed a total line length of 125 ft.
3. A 4-ton unit with a 5/16" liquid line cannot exceed a total line length of 50 ft.
IMPORTANT: Do not exceed a total line length of 125 feet in all systems.
9
Page 10

TUBING INSTALLATION
Observe the following when installing correctly sized type “L” refrigerant tubing
between the condensing unit and evaporator coil:
• If a portion of the liquid line passes through a hot area where liquid refrigerant
can be heated to form vapor, insulating the liquid line is required.
• Use clean, dehydrated, sealed refrigeration grade tubing.
• Always keep tubing sealed until tubing is in place and connections are to be
made.
• Blow out the liquid and vapor lines with dry nitrogen before connecting to the
outdoor unit and indoor coil. Any debris in the line set will end up plugging the
expansion device.
• Do not allow the vapor line and liquid line to be in contact with each other. This
causes an undesirable heat transfer resulting in capacity loss and increased
power consumption. The vapor line must be insulated.
• If tubing has been cut, make sure ends are deburred while holding in a position
to prevent chips from falling into tubing. Burrs such as those caused by tubing
cutters can affect performance dramatically, particularly on small liquid line
sizes.
• For best operation, keep tubing run as short as possible with a minimum number of elbows or bends.
• Locations where the tubing will be exposed to mechanical damage should be
avoided. If it is necessary to use such locations, the copper tubing should be
housed to prevent damage.
• If tubing is to be run underground, it must be run in a sealed watertight chase.
• Use care in routing tubing and do not kink or twist. Use a tubing bender on the
vapor line to prevent kinking.
• Route the tubing using temporary hangers, then straighten the tubing and
install permanent hangers. Line must be adequately supported.
• The vapor line must be insulated to prevent dripping (sweating) and prevent
performance losses. Armaflex and Rubatex are satisfactory insulations for this
purpose. Use 1/2” minimum insulation thickness, additional insulation may be
required for long runs.
• Check Table 2 for the correct vapor line size. Check Table 3 for the correct liquid line size.
10
TUBING CONNECTIONS
Indoor evaporator coils have only a holding charge of dry nitrogen. Keep all tube
ends sealed until connections are to be made.
• Use type “L” copper refrigeration tubing. Braze the connections with the following alloys:
– copper to copper - 5%
– Silver alloy (no flux)
– copper to steel or brass - 35%
– silver alloy (with flux)
• Be certain both refrigerant shutoff valves at the outdoor unit are closed.
• Clean the inside of the fittings and outside of the tubing with steel wool or sand
cloth before brazing. Always keep chips, steel wool, dirt, etc., out of the inside
when cleaning.
• Assemble tubing part way into fitting. Apply flux all around the outside of the
tubing and push tubing into stop. This procedure will keep the flux from getting
inside the system.
• Remove the cap and schrader core from service port to protect seals from heat
damage.
Page 11
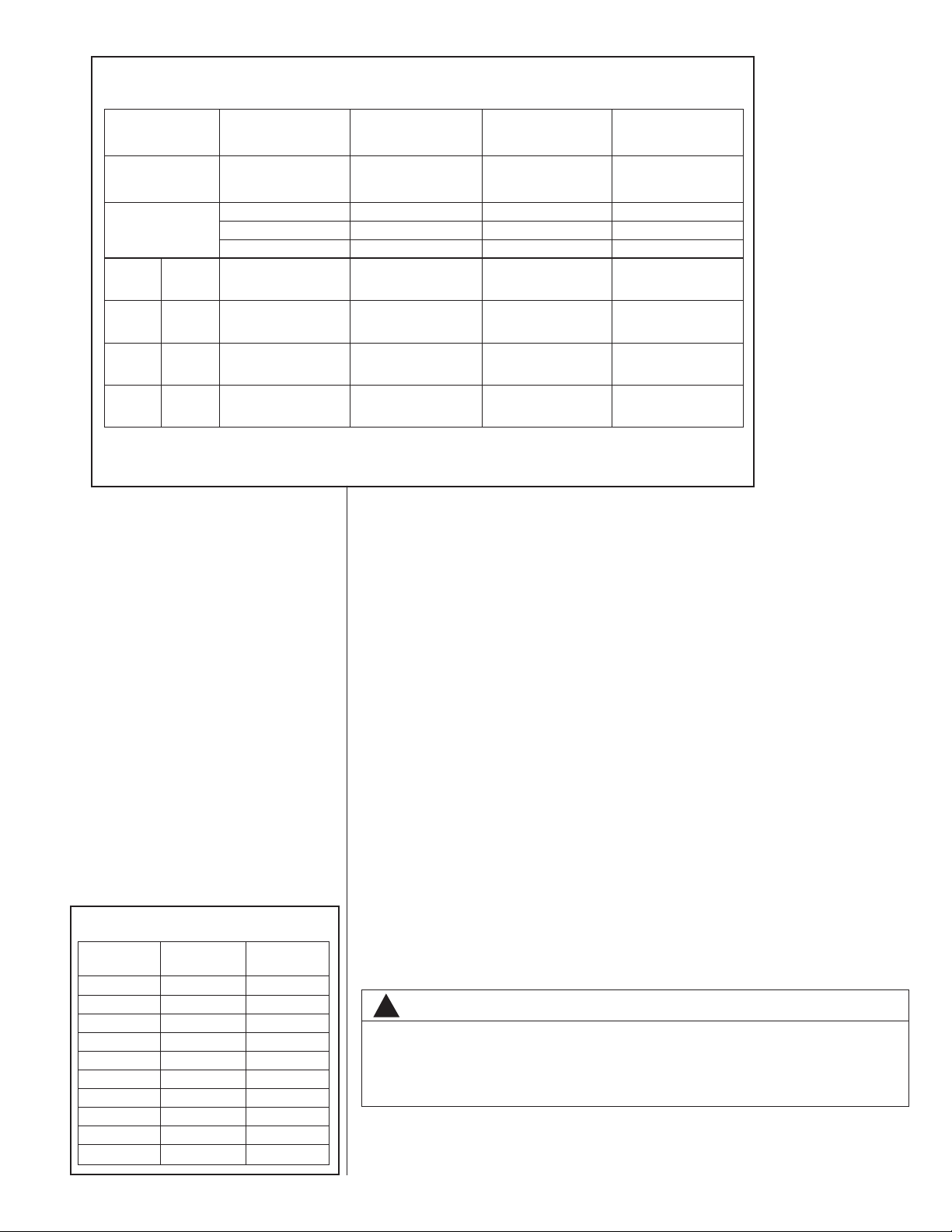
TABLE 2
UCTION LINE LENGTH SIZE VS. CAPACITY MULTIPLIER (2-STAGE R-410A)
S
Unit Size
Suction Line
Connection
Size
Suction Line
Run Feet
Optional
25'
Standard
Optional
Optional
50'
Standard
Optional
Optional
100'
Standard
Optional
Optional
150'
Standard
Optional
*Standard Line Size
Note: Using suction line larger than shown in chart will result in poor oil return.
2 Ton
3/4" I.D. 3/4" I.D. 7/8" I.D. 7/8" I.D.
—
5/8*
3/4
—
1.00
1.00
—
0.99
1.00
—
0.97
0.98
—
0.95
0.97
3 Ton
5/8 3/4 3/4
3/4*
—
0.99
1.00
—
0.98
0.99
—
0.95
0.97
—
0.91
0.95
—
• Use an appropriate heatsink material around the copper stub and the service
valves before applying heat.
• IMPORTANT: Do not braze any fitting with the TEV sensing bulb attached.
• Braze the tubing between the outdoor unit and indoor coil. Flow dry nitrogen
into a service port and through the tubing while brazing.
• After brazing:
• Use an appropriate heatsink material to cool the joint and remove any flux
residue.
• Clamp the TXV bulb securely on the suction line at the 2 o’clock position with
the strap provided in the parts bag.
• Insulate the TXV sensing bulb and suction line with the provided pressure
sensitive insulation (size 4" x 7") and secure with provided wire ties.
• NOTE: TXV SENSING BULB SHOULD BE LOCATED ON A HORIZONTAL
SECTION OF SUCTION LINE, JUST OUTSIDE OF COIL BOX.
• The service valves are not backseating valves. To open the valves, remove the
valve cap with an adjustable wrench. Insert a 3/16” or 5/16” hex wrench into the
stem. Back out counterclockwise.
• Replace the valve cap finger tight then tighten an additional 1/2 hex flat for a
metal-to-metal seal.
4 Ton
7/8* 7/8*
——
1.00
1.00
—
0.98
0.99
—
0.95
0.97
—
0.93
0.95
—
5 Ton
0.99
1.00
—
0.98
0.99
—
0.94
0.97
—
0.91
0.95
—
TABLE 3
ELBOW EQUIVALENT LENGTHS, FT.
Short Long
Size Radius Radius
1/4 0.4 0.2
5/16 0.5 0.3
3/8 0.5 0.3
1/2 0.6 0.4
5/8 0.8 0.6
3/4 0.9 0.8
7/8 1.0 1.0
1-1/8 1.2 1.2
1-3/8 2.1 1.4
1-5/8 2.5 1.5
LEAK TESTING
• Pressurize line set and coil through service fittings with dry nitrogen to 150 psig
maximum. Leak test all joints using liquid detergent. If a leak is found, recover
pressure and repair.
WARNING
!
DO NOT USE OXYGEN TO PURGE LINES OR PRESSURIZE SYSTEM FOR
LEAK T EST. OXYGEN REACTS VIOLEN TLY WI TH OIL, W HICH CAN
CAUSE AN EXPLOSION RESULTING IN SEVERE PERSONAL INJURY OR
DEATH.
11
Page 12

TABLE 4
IQUID LINE SIZING (2-STAGE R-410A)
L
System
Capacity
(2nd Stage)
2 Ton
3 Ton
4 Ton
5 Ton
System
Capacity
(2nd-Stage)
2 Ton 3/8”
3 Ton
4 Ton
5 Ton
Liquid Line
Connection
Size
(Inch I.D.)
/8”
3
/8”
3
3/8”
3/8”
Liquid Line
Connection
Size
(Inch I.D.)
3/8”
3/8”
3/8”
Outdoor unit above Indoor Coil (Cooling Only)
Liquid Line Size
Line Size
(Inch O.D.)
25 50 75 100 125 150
otal Equivalent Length - Feet
T
Minimum Vertical Separation - Feet
1/4 0017 43 70 95
5/16 0 000 00
3/8* 0 000 00
5/16 0 00007
3/8* 000000
5/16 00832 55 80
3/8* 000000
3/8* 000000
1/2 000000
Liquid Line Size
Outdoor unit below Indoor Coil
Line Size
(Inch O.D.)
25 50 75 100 125 150
Total Equivalent Length - Feet
Maximum Vertical Separation - Feet
1/4 25 10 N/A N/A N/A N/A
5/16 25 50 40 35 29 22
3/8* 25 50 45 42 39 37
5/16 25 39 28 16 5 N/A
3/8* 25 50 51 48 44 40
5/16 25 15 N/A N/A N/A N/A
3/8* 25 47 40 32 24 17
3/8* 25 41 30 20 10 0
1/2 25 50 56 54 52 50
*Standard Line Size
N/A - Application not recommended.
12
Page 13

EVACUATION PROCEDURE
Evacuation is the most important part of the entire service procedure. The life and
efficiency of the equipment is dependent upon the thoroughness exercised by the
installing technician when evacuating air and moisture from the system.
Air in the system causes high condensing temperatures and pressure, resulting in
increased power input and non-verifiable performance.
Moisture chemically reacts with the refrigerant and oil to form corrosive hydrofluoric
nd hydrochloric acids. These attack motor windings and parts, causing breakdown.
a
After the system has been leak checked and proven sealed, connect the vacuum
pump and evacuate system to 500 microns. The vacuum pump must be connected
o both the high and low sides of the system through adequate connections. Use
t
the largest size connections available since restrictive service connections may lead
to false readings because of pressure drop through the fittings.
IMPORTANT: Compressors (especially scroll type) should never be used to evacuate the air conditioning system because internal electrical arcing may result in a
damaged or failed compressor.
START UP AND PERFORMANCE
Even though the unit is factory charged with Refrigerant-410A, the charge must be
checked to the charge table attached to the service panel and adjusted, if required.
Allow a minimum of 5 minutes running. Before analyzing charge, see the instructions on the unit service panel rating plate for marking the total charge.
CHECKING AIRFLOW
The air distribution system has the greatest effect. The duct system is totally controlled by the contractor. For this reason, the contractor should use only industryrecognized procedures.
The correct air quantity is critical to air conditioning systems. Proper operation, efficiency, compressor life, and humidity control depend on the correct balance
between indoor load and outdoor unit capacity. Excessive indoor airflow increases
the possibility of high humidity problems. Low indoor airflow reduces total capacity,
and causes coil icing. Serious harm can be done to the compressor by low airflow,
such as that caused by refrigerant flooding.
Air conditioning systems require a specified airflow. Each ton of cooling requires
between 350 and 450 cubic feet of air per minute (CFM), or 400 CFM nominally.
Duct design and construction should be carefully done. System performance can be
lowered dramatically through bad planning or workmanship.
Air supply diffusers must be selected and located carefully. They must be sized and
positioned to deliver treated air along the perimeter of the space. If they are too
small for their intended airflow, they become noisy. If they are not located properly,
they cause drafts. Return air grilles must be properly sized to carry air back to the
blower. If they are too small, they also cause noise.
The installers should balance the air distribution system to ensure proper quiet airflow to all rooms in the home. This ensures a comfortable living space.
These simple mathematical formulas can be used to determine the CFM in a residential or light commercial system.
Electric resistance heaters can use
CFM =
Gas furnaces can use
CFM =
An air velocity meter or airflow hood can give a more accurate reading of the system CFM’s.
volts x amps x 3.414
1.08 x temp rise
BTUH output
∆T x 1.08
13
Page 14

CHECKING REFRIGERANT CHARGE
Charge for all systems should be checked against the Charging Chart inside the
access panel cover. Before using the chart, the indoor conditions must be within
2°F of desired comfort conditions and system must be run until operating conditions
stabilize (15 min. to 30 min.)
CAUTION
!
THE TOP OF THE SCROLL COMPRESSOR SHELL IS HOT. TOUCHING THE
COMPRESSOR TOP MAY RESULT IN SERIOUS PERSONAL INJURY.
IMPORTANT: Do not operate the compressor without charge in system.
Addition of R-410A will raise pressures (vapor, liquid and discharge) and lower
vapor temperature.
If adding R-410A raises both vapor pressure and temperature, the unit is overcharged.
IMPORTANT: Use industry-approved charging methods to ensure proper system
charge.
CHARGING BY LIQUID PRESSURE
Liquid pressure method is used for charging systems in the cooling mode when an
expansion valve is used on the evaporator. The service port on the liquid service
valve (small valve) is used for this purpose.
Read and record the outdoor ambient temperature entering the condensing unit,
and the liquid line pressure at the service valve (the small valve). Locate the charging chart attached to the unit. The correct liquid line pressure will by found by finding the intersection of the unit model size and the outdoor ambient temperature.
Adjust the liquid line pressure by either adding refrigerant to raise pressure or
removing refrigerant to lower pressure.
CHARGING UNITS WITH R-410A REFRIGERANT
Checking the charge, or charging units using R-410A refrigerant, differs from those
with R-22. The following procedures apply to units with R-410A refrigerant. These
procedures require outdoor ambient temperature, liquid line pressure and indoor
wet bulb temperature be used.
IMPORTANT: ONLY ADD LIQUID REFRIGERANT CHARGE INTO THE SUCTION
LINE WITH R-410A UNITS. USE A COMMERCIAL METERING DEVICE TO ADD
CHARGE INTO THE SUCTION LINE WITHOUT DAMAGE TO THE COMPRESSOR.
1. Read and record the outdoor ambient temperature entering the condensing
unit.
2. Read and record the liquid line pressure at the small service valve.
3. Read and record the indoor ambient wet bulb temperature entering the indoor
coil.
4. Use the appropriate charging chart to compare the actual liquid pressure to the
correct pressure as listed on the chart.
5. R-410A charging charts are listed on the unit.
CAUTION
!
R-410A PRESSURES ARE APPROXIMATELY 60% HIGHER THAN R-22
PRESSURES. USE APPROPRIATE CARE WHEN USING THIS REFRIGERANT. FAILURE TO EXERCISE CARE MAY RESULT IN EQUIPMENT DAMAGE, OR PERSONAL INJURY.
14
Page 15

CHARGING BY WEIGHT
For a new installation, evacuation of interconnecting tubing and evaporator coil is
adequate; otherwise, evacuate the entire system. Use the factory charge shown in
Table 1 of these instructions or unit data plate. Note that charge value includes
charge volume required for 15 ft. of standard size interconnecting liquid line.
Calculate actual charge required with installed liquid line size and length using:
1/4” O.D. = 0.20 oz./ft.
5/16” O.D. = 0.3 oz./ft.
3/8” O.D. = 0.50 oz./ft.
1/2” O.D. = 1.0 oz./ft.
With an accurate scale (+/– 1 oz.) or volumetric charging device, adjust charge difference between that shown on the unit data plate and that calculated for the new
system installation. If the entire system has been evacuated, add the total calculated charge.
NOTE: When the total refrigerant charge volume exceeds 10 pounds, the manufacturer recommends installing a crankcase heater and start kit.
FINAL LEAK TESTING
After the unit has been properly evacuated and charged, a leak detector should be
used to detect leaks in the system. All piping within the condensing unit, evaporator,
and interconnecting tubing should be checked for leaks. If a leak is detected, the
refrigerant should be recovered before repairing the leak. The Clean Air Act prohibits releasing refrigerant into the atmosphere.
WARNING
!
TURN OFF ELECTRIC POWER AT
THE FUS E B OX OR S ERVIC E
PA NEL BEFORE MAKING ANY
ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS.
ALSO, THE GROUND CONNECTIO N MU ST BE COM PLETE D
BEFORE MAKING LINE VOLTAGE
CONNECTIONS. FAILURE TO DO
SO CAN RESULT IN ELECTRICAL
SHO CK, SE VER E PERS ONA L
INJURY OR DEATH.
TABLE 5
VOLTAGE RANGES (60 HZ)
ELECTRICAL WIRING
Field wiring must comply with the National Electric Code (C.E.C. in Canada) and
any applicable local code.
POWER WIRING
It is important that proper electrical power from a commercial utility is available at
the condensing unit contactor. Voltage ranges for operation are shown in Table 5.
Power wiring must be run in a rain-tight conduit. Conduit must be run through the
connector panel below the access cover (see Figure 1) and attached to the bottom
of the control box.
Connect power wiring to control located in outdoor condensing unit electrical box.
(See wiring diagram attached to unit access panel.)
Check all electrical connections, including factory wiring within the unit and make
sure all connections are tight.
IMPORTANT: DO NOT connect aluminum field wire to the contactor terminals.
Operating Voltage Range at Copeland
Nameplate Voltage Maximum Load Design Conditions for
Compressors
208/230 (1 Phase) 197 - 253
GROUNDING
A grounding lug is provided near the control for a ground wire.
15
Page 16

FIGURE 3
ONTROL WIRING FOR GAS OR ELECTRIC HEAT
C
CONTROL WIRING
(See Figure 3)
If the low voltage control wiring is run in conduit with the power supply, Class I insulation is required. Class II insulation is required if run separate. Low voltage wiring
may be run through the insulated bushing provided in the 7/8 hole in the base
panel, up to and attached to the pigtails from the bottom of the control box. Conduit
can be run to the base panel if desired by removing the insulated bushing.
NOTE: Use No. 18 AWG solid copper wire at a minimum. If the wire length between
the thermostat and the unit is more than 100 ft., use 16 AWG solid copper wire to
avoid excessive voltage drop.
A thermostat and a 24 volt, 40 VA minimum transformer are required for the control
circuit of the condensing unit. The furnace or the air handler transformer may be
used if sufficient. Verify the correct primary voltage tap is used on the transformer.
NOTE: Reference unit wiring diagram for detailed wiring instructions.
FOR TYPICAL GAS OR OIL HEAT
R – BROWN WIRE
B
L – YELLOW WIRE
Y
– WIRE CONNECTION
X
/RD – WHITE/RED
W
D – RED WIRE
R
TYPICAL CONDENSING
UNIT
W/RD
L
RD
R
YL
Y
BR
C
YL/BL
Y2
TYPICAL THERMOSTAT
SUBBASE
LYGWR
TYPICAL GAS OR
OIL FURNACE
Y2
R
X
X
X
X
X
W
G
Y
C
Y2
FOR TYPICAL ELECTRIC HEAT
W/RD – WHITE/RED
BR – BROWN WIRE
D – RED WIRE
R
YL – YELLOW WIRE
W/BK – WHITE WIRE WITH BLACK STRIPE
/BK – GREEN WIRE WITH BLACK STRIPE
G
PU – PURPLE WIRE (NOT USED)
X–WIRE CONNECTION
TYPICAL CONDENSING
UNIT
W/RD
L
RD
R
YL
Y
BR
C
YL/BL
Y2
X
X
X
X
X
TYPICAL THERMOSTAT
SUBBASE
LYGWR Y2
TYPICAL ELECTRIC HEAT
LOW VOLTAGE JUNCTION BOX
X
X
X
X
X
X
•
R
W/BK
G/BK
YL
BR
PU
YL/BL
16
Page 17

FACTORY INSTALLED ACCESSORIES
HARD START COMPONENTS
tart components are factory installed.
S
HIGH AND LOW PRESSURE CONTROLS
(HPC OR LPC)
Pressure controls are factory installed.
These controls keep the compressor from operating in pressure ranges which can cause
damage to the compressor. Both controls are in the low voltage control circuit.
High pressure control (HPC) is an automatic reset which opens near 610 PSIG and closes near 420 PSIG.
The low pressure control (LPC) is an automatic reset which opens near 50 PSIG and
closes near 95 PSIG.
COMPRESSOR SOUND WRAP
All (-)ARL and (-)ASL units are factory equipped with compressor sound wraps to
reduce operating noise levels.
COMPRESSOR CRANKCASE HEATER (CCH)
The 5-ton (-)ARL is factory equipped with a crankcase heater. Refrigerant migration
during the off cycle can result in a noisy start up. The crankcase heater minimizes
refrigeration migration and helps reduce start up noise or bearing “wash out.”
The heater is located on the lower half of the compressor shell. Its purpose is to
drive refrigerant from the compressor shell during low outdoor ambient conditions
(below 75°F), thus preventing damage to the compressor during start-up. At initial
start-up or after extended shutdown periods during low outdoor ambient conditions
(below 75°F), make sure the heater is energized for at least 12 hours before the
compressor is started. (Disconnect switch on and wall thermostat off.)
CONTROL BOX COVER
The control box cover allows access to the Comfort Control System™ diagnostic
chart is provided on the control box cover.
17
Page 18

FIELD INSTALLED ACCESSORIES
COMPRESSOR CRANKCASE HEAT (CCH)
While scroll compressors usually do not require crankcase heaters, there are
instances when a heater should be added. Refrigerant migration during the off cycle
can result in a noisy start up. Add a crankcase heater to minimize refrigeration
migration, and to help eliminate any start up noise or bearing “wash out.”
NOTE: A crankcase heater should be installed if: the charge of the system exceeds
the values in Table 1, if the system is subject to voltage variations or when a low
ambient control is used for system operation below 55°F.
All heaters are located on the lower half of the compressor shell. Its purpose is to
drive refrigerant from the compressor shell during long off cycles, thus preventing
damage to the compressor during start-up.
At initial start-up or after extended shutdown periods, make sure the heater is energized for at least 12 hours before the compressor is started. (Disconnect switch on
and wall thermostat off.)
NOTE: Reference unit wiring diagram for detailed wiring instructions.
IMPORTANT: (-)ARL & (-)ASL unit sound wraps are not compatible with field
installed crankcase heaters. Sound wraps must be removed unless the unit was
factory-equipped with a crankcase heater or a field installed insulating strip (PROSTOCK part no. 686033) is used. This strip insulates the field installed crankcase
heater from the soundwrap.
LOW AMBIENT CONTROL (LAC) – RXAD-A03
This component senses compressor head pressure and shuts the condenser fan off
when the head pressure drops to approximately 220 PSIG. This allows the unit to build a
sufficient head pressure at lower ambient in order to maintain system balance and
obtain improved capacity. Low ambient control should be used on all equipment operated below 70°F [21°C] ambient.
OUTDOOR UNIT COVERS
Outdoor condensing unit covers are available if the homeowner requests a cover for
their unit. With the complete model number for the unit, the correct cover can be
obtained through an authorized distributor.
CAUTION
!
FAILURE TO REMOVE CONDENSING UNIT COVER BEFORE OPERATING
OUTDOOR UNIT CAN CAUSE COMPONENTS TO FAIL.
COMFORT CONTROL SYSTEM
The Integrated Compressor Control (ICC) is an integral part of the Comfort Control
System and has the following features:
- Independent compressor and outdoor fan control
- Anti-short cycle protection (3 minute)
- Minimum unit run time (30 seconds)
- 7-segment LED to display status and diagnostics for faster service and accuracy
- High and low pressure switch monitoring
- Power and control voltage monitoring
- Active compressor protection integrated into the control
- Fault Recall capability with power loss memory
- Test Button allows unit operation for start-up diagnostics
- Can be used with a standard thermostat
- Flash diagnostic codes to room thermostat with L terminal
- Sealed compressor relay
- Compressor Solenoid Control
18
Page 19

FIGURE 4
CC BOARD
I
IELD LINE VOLTAGE
F
ONNECTION (ST1)
C
COMPRESSOR
WIRING
CONNECTOR (ST2)
.D. FAN (OFM) RELAY
O
{
OMPRESSOR
C
OLENOID
S
UTPUT
O
LOW PRESSURE CONTROL INPUT
IGH PRESSURE CONTROL INPUT
H
TEST BUTTON
RED LED (Y1)
OW VOLT FUSE
L
HERMOSTAT
T
ONNECTION
C
E2)
(
SW2 BUTTON
MBIENT SENSOR
A
COMPRESSOR
CONTROL (K2)
ICC (INTEGRATED
COMPRESSOR CONTROL)
7-SEGMENT LED
CONTROL DESCRIPTION (SEE FIGURE 4)
7-Segment LED
• Displays status and diagnostic codes (See Status and Diagnostic Description)
• Displays diagnostic/fault recall (See Test Mode/Fault Recall)
Red LED (Y1)
• Y1 red LED (solid on) indicates Y1 call from thermostat is present
CAUTION
!
UNIT MAY START SUDDENLY AND WITHOUT WARNING
Solid red light indicates a thermostat call for unit operation is present at
the ICC control. ICC control will attempt to start unit after short cycle timer
expires or when in Active Protection mode will attempt to restart unit prior
to Lockout mode.
Line Voltage Connector (ST1)
• Line voltage is connected to control board at Connector ST1
• Maximum wire size accepted is 6 AWG copper wire
• Torque terminals up to 20 in. lbs. max (Check wire terminations annually)
Compressor Wiring Connectors (ST2)
• Compressor wiring assembly is factory installed (Red – Run, Yellow – Start,
Black – Common)
Compressor Control (K2)
• Sealed single pole compressor relay switch with optical feedback feature (arc
detection)
Thermostat Connector (E2)
• R – 24VAC from the indoor unit 24VAC transformer (40 VA minimum)
• C – 24VAC Common from the indoor unit 24VAC transformer
• Y1 – Call for unit operation (cooling)
• L – Communicate/flash diagnostic codes to an indoor thermostat that is enabled
with an ‘L’ terminal, ‘check service light’, or similar function
• Y2 – Call for unit second stage operation (cooling)
19
Page 20

Low Volt Fuse
• If required replace with 3 A automotive ATC style blade fuse
Low Pressure Control (LPC Input – E14)
• Low-pressure control is factory installed
• Low pressure control is an automatic resetting device
High Pressure Control (HPC Input – E14)
• High-pressure control is factory installed
• High pressure control is an automatic resetting device
Compressor Solenoid Output (E14)
• Compressor solenoid output is controlled by the control for second stage cooling
operation.
Ambient Temperature Sensor
• Included on control but not required in the cooling only condenser application
TEST and SW2 Buttons
• TEST and SW2 buttons used to enter Test and Fault Recall Mode
ICC CONTROL OPERATION
Installation Verification
• 24V AC power on R and C must be present at the ICC for it to operate
• Line voltage must be present at the ICC for the compressor and the outdoor fan
to operate
• When line and 24VAC control voltage is present and there is no Y1 call, or other
diagnostics displayed, the control will display an “O” for standby mode
• If a Y1 call is initiated within 3 minutes of unit power-up or last compressor activation the control will display a flashing “c” and the red Led will activate to solid on
Call for Operation (Y1 Call)
• The ICC has an on/off fan delay of one (1) second.
• The ICC ignores state of LPC for 90 seconds upon compressor start
• The ICC will cause the compressor to be energized for 30 seconds minimum run
time except when TEST button is pushed without a Y1 call
Call for Operation (Y2 Call)
• 5 sec delay from Y1 to Y2
• 1 minute recycle when Y2 call ends
• The control will not allow the 2 stage solenoid to be energized for 1 minute after
the solenoid has been deenergized.
3-minute Anti-short Cycle Timer
• The ICC has a built in 3-minute time delay between compressor operations to
protect the compressor against short cycling (Status flashing c).
• The 3-minute time delay can be bypassed when a Y1 call is present by pressing
the TEST button for 1 second and releasing (Status solid on c).
30 Second Minimum Run Timer
• The ICC has a built in 30 second minimum unit run time (Status flashing c).
1 Second Compressor/Fan Delay
• The ICC starts/stops the outdoor fan 1 second after the start/stop of the compressor upon a Y1 call to minimize current inrush and/or voltage droop.
Low Pressure Control (LPC)
• Upon a Y1 call, if the ICC senses an open LPC it will not allow the compressor to
be energized (diagnostic code 21).
20
Page 21

7 -Segment
Display
Code
Diagnostic Description Status / Possible Cause -Troubleshooting
Information
0 Standby Standby - No call for operation
c Y1 First Stage or Single Stage Unit Operation
Status and Diagnostic Description
c or
C Flashing
Anti-Short Cycle Timer (3 minutes) or
Minimum Run Timer (30 seconds)
Waiting for anti-short cycle timer to expire
Waiting for minimum run timer to expire
F 1. Low voltage wiring damage or miswired
1 (*) Compressor Running Extremely Long Run
Cycle (Cooling mode only)
1. Low refrigerant charge
2. Air ducts have substantial leakage
3. Check thermostat operation
4. Dirty filter
5. Dirty outdoor coil
2 (*) Pressure Control Trip (L terminal output only) 1. (See faults 21, L21, 23, L23)
21 (***) Low Pressure Control Trip
Note: Low-pressure control is ignored for 90
seconds after call for unit operation.
restart the unit after the pressure control
automatically re-closes.
Unit will try to restart 3 times in the same
thermostat call for operation (Y1) before
lockout (fault L21).
1. Unit is low on refrigerant charge
2. Indoor coil is frozen (cooling mode)
3. Dirty indoor coil or filter (cooling mode)
4. Indoor blower is not running (cooling mode)
5. TEV is not operating correctly
L21 (**) Lockout - Low Pressure Control Trip (**) LPC tripped three consecutive times in same
thermostat call
23 (***)
High Pressure Control Trip
restart the unit after the pressure control
automatically re-closes.
Unit will try to restart 3 times in the same
thermostat call for operation (Y1) before
lockout (fault L23)
1. Outdoor coil is dirty (cooling mode)
2. Outdoor fan is not running (cooling mode)
3. Dirty indoor coil or filter (heat pump mode)
4. Liquid line restriction (filter drier blocked, etc.)
5. Excessive refrigerant charge
L23 (**) Lockout - High Pressure Control Trip (**) HPC tripped three consecutive times in same
thermostat call
25 Outdoor Ambient Temperature Sensor
27 Abnormal Low Line or No Line Voltage
(See unit nameplate for operating voltage)
1. Check incoming line voltage to the disconnect
and unit
2. Check wiring connections
28 Abnormal High Line Voltage 1. Check line voltage
3 (*) Short Cycling 1. Check thermostat for intermittent demand
signal
2. Check thermostat location in zone (too close to
discharge grill)
Active Protection – The ICC will try to
Active Protection – The ICC will try to
1. ICC board sensor damaged (ICC
will continue to operate)
ICC Board Fuse Open
C Y2 Second stage unit operation
(2-stage unit only)
21
Page 22

(*) – Indicates flash code will be an output on the ICC “L” terminal to the indoor
5 (*) (***) Compressor will not run
A
ctive Protection
– After detecting compressor
w
ill not run the ICC control will shut the unit
down. The control will try to restart the unit
every 5 minutes for 4 tries. After that, the ICC
will attempt a restart every 20 minutes up to 6
hours.
1
. Check for damaged, miswired, or wrong run
capacitor
2. Check for damaged or miswired start capacitor
a
nd relay
compressor
4. Check for broken wires, loose connectors, or
miswired
5. Check compressor motor windings for
continuity
6. Check for open compressor internal protector
7. Check for excessive liquid refrigerant in
compressor
L5 (**) Lockout – Check Compressor (**) After 6 hours of attempted unit restart ICC
control
8 (*)
output only)
9 (*)
(Less than 18V)
1. Check transformer for miswiring or
overloading.
3. Check voltage levels at ICC board and
ICC Board Mis-operation
ICC Board Mis-operation (L terminal
1. Check ICC board compressor relay
1. Check ICC board compressor relay
ICC Secondary Voltage Low
thermostat “L” terminal. Unless a diagnostic/fault is manually cleared by cycling
power or pressing the TEST button the flash code will continue at the L terminal for
up to 20 seconds after the start of a successful call for unit operation.
L Terminal Output
• Flash 1 – Compressor running extremely long run cycle
• Flash 2 – Low or High pressure control trip
• Flash 3 – Unit short cycling
• Flash 5 – Compressor will not run
• Flash 8 – Control mis-operation
• Flash 9 – Low control voltage
(**) – Lockout modes are reset by either cycling line voltage, low voltage, or by
pressing control TEST button for 1 second. The control will attempt to start the unit
when the TEST button is pressed and released (See TEST button label)
(***) – Caution: Indicates Active Protection. Unit will attempt to restart automatically.
CAUTION
!
UNIT MAY START SUDDENLY AND WITHOUT WARNING
Solid red light indicates a thermostat call for unit operation is present at the ICC.
ICC will attempt to start unit after short cycle timer expires or when in Active
Protection mode will attempt to restart unit prior to Lockout mode.
NOTE: For Additional Questions or Comments concerning the ICC, call 1-888923-2323.
SERVICE
SINGLE-POLE COMPRESSOR RELAY
Integrated Compressor Control Relay is a single-pole relay used on all single phase
22
units up through 5 tons. Caution must be exercised when servicing as only one leg
of the power supply is broken with the relay.
Page 23

GENERAL SERVICE ANALYZER CHARTS
COMPRESSOR OVERHEATING
SYMPTOMS POSSIBLE CAUSE CHECK/REMEDIES
High superheat Low charge Check system charge
Faulty metering device Restricted cap tube, TEV (TXV)
Power element superheat
adjustment
Foreign matter stopping flow
High internal load Hot air (attic) entering return
eat source on; mis-wired or
H
faulty control
Restriction in liquid line Drier plugged
Line kinked
Low head pressure Low charge
Operating in low ambient
temperatures
Suction or liquid line subjected Hot attic
to high heat source
Low voltage Loose wire connections Check wiring
Power company problem, Have problem corrected before
transformer diagnosis continues
Undersized wire feeding unit Correct and complete diagnosis
High voltage Power company problem Have problem corrected
High head pressure Overcharge Check system charge
Dirty heat pump coil Clean coil
Faulty or wrong size Replace fan motor
heat pump fan motor
Faulty fan blade Replace fan blade
or wrong rotation
Recirculation of air Correct installation
Additional Heat Source Check for dryer vent near unit
Non-condensibles Recover refrigerant, Evacuate and
Equipment not matched Correct mis-match
Short cycling of compressor Faulty pressure control Replace pressure control
Loose wiring Check unit wiring
Thermostat Located in supply air stream
TEV Internal foreign matter
Hot water line
Replace with correct rotation motor
Check for recirculation from
other equipment
recharge system
Differential setting too close
Customer misuse
Power element failure
Valve too small
Distributor tube/tubes restricted
CONTINUED
23
Page 24

SYMPTOMS POSSIBLE CAUSE CHECK OR REMEDIES
Short cycling of compressor (cont.) Low charge Check system charge
ow evaporator air flow Dirty coil
L
Dirty filter
Duct too small or restricted
Faulty run capacitor Replace
Faulty internal overload Replace compressor
ELECTRICAL
SYMPTOMS POSSIBLE CAUSE CHECK OR REMEDIES
No voltage on line side Blown fuses or tripped circuit breaker Check for short in wiring or unit
of control board
Improper voltage High voltage Wrong unit
(See Control Diagnostics)
mproper wiring Re-check wiring diagram
I
Power supply problem
Low voltage Wrong unit
Power supply problem
Wiring undersized
Loose connections
CONTAMINATION
SYMPTOMS POSSIBLE CAUSE CHECK OR REMEDIES
Moisture Poor evacuation on installation In each case, the cure is the same.
High head pressure Non-condensibles air
Unusual head and suction readings Wrong refrigerant
Foreign Mattercopper filings Copper tubing cuttings
Copper oxide Dirty copper piping
Welding scale Nitrogen not used
Soldering flux Adding flux before seating
Excess soft solder Wrong solder material
or during service Recover refrigerant. Add filter drier,
evacuate and re-charge
copper part way
24
CONTINUED
Page 25

LOSS OF LUBRICATION
SYMPTOMS POSSIBLE CAUSE CHECK OR REMEDIES
Compressor failures Line tubing too long Add oil to the recommended level
ine tubing too large Reduce pipe size to improve
L
Low suction pressure Low charge Check system charge
Refrigerant leaks Repair and recharge
Cold, Noisy compressor - Slugging Dilution of Oil with Refrigerant Observe piping guidelines
Noisy compressor Migration Check crankcase heater
Cold, sweating compressor Flooding Check system charge
Low Load Reduced air flow Dirty filter
Thermostat setting Advise customer
Short cycling of compressor Faulty pressure control Replace control
Loose wiring Check all control wires
Thermostat In supply air stream,
oil return
irty coil
D
Wrong duct size
Restricted duct
out of calibration,
Customer misuse
FLOODED STARTS
SYMPTOMS POSSIBLE CAUSES CHECK OR REMEDIES
Liquid in the compressor shell Faulty or missing crankcase heater Replace crankcase heater
Too much liquid in system Incorrect piping Check Piping guidelines
Overcharge Check and adjust charge
SLUGGING
SYMPTOMS POSSIBLE CAUSES CHECK OR REMEDIES
On start up Incorrect piping Review pipe size guidelines
TEV hunting when running Oversized TEV Check TEV application
FLOODING
SYMPTOMS POSSIBLE CAUSES CHECK OR REMEDIES
Poor system control Loose sensing bulb Secure the bulb and insulate
using a TEV
Bulb in wrong location Relocate bulb
Wrong size TEV Use correct replacement
Improper superheat setting Adjust, if possible;
Replace, if not
CONTINUED
25
Page 26

THERMOSTATIC EXPANSION VALVES
SYMPTOMS POSSIBLE CAUSE CHECK OR REMEDIES
High Superheat, Low Suction Pressure Moisture freezing and blocking valve Recover charge, install filter-drier,
Dirt or foreign material blocking valve Recover charge, install filter-drier,
Low refrigerant charge Correct the charge
Vapor bubbles in liquid line Remove restriction in liquid line
Misapplication of internally equalized Use correct TEV
valve
Plugged external equalizer line Remove external equalizer line
Undersized TEV Replace with correct valve
Loss of charge from power Replace power head or complete
head sensing bulb TEV
Charge migration from sensing bulb Ensure TEV is warmer than
to power head (Warm power head sensing bulb
with warm, wet cloth. Does valve
operate correctly now?)
Improper superheat adjustment Adjust superheat setting counter(Only applicable to TEV with adjustable clockwise
superheat settings)
Valve feeds too much refrigerant, Moisture causing valve to stick open. Recover refrigerant, replace filterwith low superheat and higher than drier, evacuate system and then normal suction pressure recharge
Dirt or foreign material causing Recover refrigerant, replace filtervalve to stick open drier, evacuate system and
TEV seat leak (A gurgling or hissing Replace the TEV
sound is heard AT THE TEV during
the off cycle, if this is the cause.)
NOT APPLICABLE TO BLEED
PORT VALVES.
Oversized TEV Install correct TEV
Incorrect sensing bulb location Install bulb with two mounting
Low superheat adjustment Turn superheat adjustment
(only applicable to TEV with clockwise
adjustable superheat setting)
Incorrectly installed, or restricted Remove restriction, or relocate
external equalizer line external equalizer
Compressor flood back upon start up Refrigerant drainage from flooded Install trap riser to the top of the
evaporator evaporator coil
Compressor in cold location Install crankcase heater on
evacuate system, recharge
evacuate system, recharge
Correct the refrigerant charge
emove non-condensible gases
R
Size liquid line correctly
restriction
recharge
straps, in 2:00 or 4:00 position on
suction line, with insulation
compressor
26
CONTINUED
Page 27

THERMOSTATIC EXPANSION VALVES
SYMPTOMS POSSIBLE CAUSE CHECK OR REMEDIES
Superheat is low to normal Unequal evaporator circuit loading Ensure air flow is equally distributed
with low suction pressure through evaporator
Check for blocked distributor
tubes
Low load or airflow entering Ensure blower is moving proper air
evaporator coil CFM
Remove/Correct any air flow
restriction
Superheat and suction Expansion valve is oversized Install correct TEV
pressure fluctuate (valve is hunting)
Sensing bulb is affected by liquid Relocate sensing bulb in another
refrigerant or refrigerant oil flowing position around the circumference of
through suction line the suction line
Unequal refrigerant flow through Ensure proper distributor piston is
evaporator circuits inserted in RCBA or RCHA coil
Ensure sensing bulb is located
properly
Check for blocked distributor
tubes
Improper superheat adjustment Replace TEV or adjust superheat
(only possible with TEV having
superheat adjustment)
Moisture freezing and partially Recover refrigerant, change filterblocking TEV drier, evacuate system and
Valve does not regulate at all External equalizer line not connected Connect equalizer line in proper
or line plugged location, or remove any blockage
Sensing bulb lost its operating charge Replace TEV
Valve body damaged during soldering Replace TEV
or by improper installation
recharge
CONTINUED
27
Page 28

Caution – UNIT MAY START SUDDENLY AND WITHOUT WARNING
S ol id r ed L E D li ght i ndicates a thermo stat c all f or unit operation i s present at the I CC.
I C C wil l attempt to start unit after s hort cy cle timer ex pires or when in A ctiv e
Pr otection mode will attempt to restart uni t prior to Lockout mode.
ICC – Integrated Compressor Control
(*) – I ndicates the display code will be flashed as an output on the ICC “L ” terminal. For example 2 flashes (blinks) from the “L” terminal output
indicates a pressure control trip.
(**) – L ockout modes are reset by removi ng li ne voltage, low voltage, or by pressing control TEST button f or 1 sec ond.
T he control wil l attempt to start the unit when the TEST button is pressed and released ( See TEST button label)
(***) – I ndicates Active Pr otection. Unit will attempt to restar t automatically.
Red LED
Display Code
Diagnostic Description Status Information
S oli d On Call for U nit O peration Y 1 call i s present from the room thermostat at the control
F or A ddi ti onal Q uesti ons or C omments concer ni n
g
the ICC call 1-888-923-2323
7 - S egmen t
Display Code
Diagnostic Description Status / Possible Cause -Troubleshooting I nformation
0
S
tandby S tandby - N o call for operation
c
Y 1 First Stage or Single Stage Unit Operation
C
Y 2 S econd S tage U nit Oper ati on ( 2- stage unit only)
c or C
Flashing
Anti-Short Cycle Timer (3 minutes) or
Minimum Run Timer (30 seconds)
Waiting for anti-short cycle timer to expire
W aiti ng for minimum run timer to ex pi re
d
D efr ost H eat P ump D efrost Oper ati on
d Flashing
A bnormal Defrost C ondition
( Defr ost c ontrol exceeds maxi mum def rost time)
1. Defrost control miswired
2. Faulty defr ost control
F
I
C C Fuse Open 1 . Low vol tage wiring damage or miswi red
1 (*)
C ompressor R unning E xtremel y L ong Run Cycle
(Cooling mode only)
1. L ow ref ri gerant charge
2. A ir ducts have substanti al l eakage
3. C heck thermostat operati on
4. Y 2 ther mostat signal may not be connected ( 2- stage uni ts onl y)
5. Di rty outdoor coi l
2 (*)
Pressure Control T rip (L terminal output only) 1. ( See faults 21, L 21, 23, L 23)
21 (***)
L ow Pressur e Control Tr ip
Note: L ow-pressure control is ignored for 90 seconds after call
for unit operati on.
Active Protection – T he ICC wil l tr y to restart the unit after the
pressure control automaticall y re-closes.
U ni t wi ll try to restart 3 ti mes i n the s ame ther mostat call for
operation (Y1) before lockout (fault L21).
1. Unit i s low on refrigerant charge
2. I ndoor coil i s frozen ( cooli ng mode)
3. Dirty indoor coil or filter (cooling mode)
4. I ndoor blower is not runni ng (cooli ng mode)
5. Outdoo r coil i s f rozen ( heat pump mode)
6. Outdoor fan i s not running (heat pump mode)
7. T EV is not operating correctl y
L21 (**)
Lockout - Low Pressure Control Trip (** ) L PC tripped three consecutive times in same thermostat call
23 (***)
High Pressure Control Trip
Active Protection – T he ICC wil l tr y to restart the unit after the
pressure control automaticall y re-closes.
Unit will try to restart 3 times in the same thermostat call for
operation (Y1) before lockout (fault L23)
1. Outdoor coil is dirty (cooling mode)
2. Outdoor fan is not running ( cool ing mode)
3. Dirty indoor coil or filter (heat pump mode)
4. Indoor blower is not runni ng ( heat pump mode)
5. L iquid line restriction (filter drier blocked, etc.)
6. E xcessive refrigerant charge
L23 (**)
L ockout - High Pr essure C ontrol T ri p ( * * ) H PC tri pped thr ee consecutive ti mes in s ame ther mostat cal l
25
Outdoor Ambi ent Temperature S ensor 1. ICC sensor damaged (I CC wil l continue to operate)
27
A bnormal Low L ine or N o L ine V oltage
(See uni t nameplate for operati ng vol tage)
1. Check incomi ng l ine vol tage to the disconnect and unit
2. C heck wir ing connections
28
A bnormal High L ine V ol tage 1. C heck li ne vol tage
3 (*)
Short C ycl ing 1. C heck thermostat for intermittent demand signal
2. C heck thermostat location in zone (too cl ose to discharge gri ll)
5 (*) (***)
C ompressor wi l l not run
Active Protection – A fter detecting compressor wil l not run the
I CC wil l shut the unit down. T he control will try to restart the
uni t every 5 mi nutes for 4 tries. A fter that, the ICC will attempt
a restart every 20 minutes up to 6 hours.
1. Check for damaged, miswired, or wrong run capacitor
2. C heck for damaged or mi swi red s tart capaci tor and relay
3. C heck voltage levels at I CC and compress or
4. C heck f or brok en wir es, loose connectors, or miswired
5. Check compressor motor windings for continuity
6. Check f or open compressor internal protector
7. Check for excessive liquid refrigerant in compressor
L5 (**)
L ock out – C heck C ompressor ( **) L ockout after 6 hours of attempted restart
-
ICC Mis-operation 1. Check ICC compressor relay
8 (*)
ICC Mis-operation (L terminal output only) 1. Check ICC compressor relay
9 (*)
ICC Secondary V oltage L ow (< 18V ) 1. Check transformer for miswiring or overloading.
92-102221-01-02
FIGURE 5
-SERIES DIAGNOSTIC LABEL
E
28
Page 29

TROUBLE SHOOTING
In diagnosing common faults in the air conditioning system, it is useful to present
the logical pattern of thought that is used by experienced technicians. The charts
which follow are not intended to be an answer to all problems, but only to guide
your thinking as you attempt to decide on your course of action. Through a series of
yes and no answers, you will follow the logical path to a likely conclusion.
Use these charts as you would a road map, if you are a beginning technician. As
you gain experience, you will learn where to establish the shortcuts. Remember
that the chart will help clarify the logical path to the problem.
ELECTRICAL CHECKS FLOW CHART
Unit Running?
YES
Repair and Recheck
YES
Repair and Recheck
YES
Run Capacitor
Start Capacitor
Potential Relay
Compressor Internal
Overload Open
NO
Thermostat Problem?
NO
Transformer Problem?
NO
Voltage on Compressor
Side of Contactor?
NO
Circuit Breakers
or Fuses Open
YES
YES
Go to
Mechanical Checks
NO
Voltage on Line
Side of Contactor?
YES
Compressor Contactor
Hi Pressure Control
Compressor Winding Open
Unit Wiring and
Connections
Compressor Winding
Grounded
Condenser Fan
Grounded
Grounded Capacitor
Replace Fuses
or Reset Breakers and Recheck
Lo Pressure Control
Compressor Time-Delay
Unit Wiring and
Connections
29
Page 30

MECHANICAL CHECKS FLOW CHART
Unit Running?
YES
Pressure problems?
High Head Pressure
Inoperative Outdoor Fan
Overcharge Low Ambient Temperature
Recirculation of
Condenser Air
Non-condensibles
Low Head Pressure
Low on Charge Dirty FiltersDirty Condenser Coil
Open IPR Valve Dirty Evaporator
Inoperative Compressor
Valves
Restricted Filter-drier
NO
Go to Electrical
Checks Flow Chart
Low Suction Pressure
Inadequate Airflow
Inoperative Indoor Blower
Low on Charge
Higher than Ambient
Air Entering Condenser
Wrong Condenser Fan Rotation
Indoor Metering Device
Stuck Open
Faulty Metering Device
Restriction in System
Restriction in System
Indoor Metering
Device Stuck
Closed
Restricted Filter-drier
Recirculation of
Evaporator Air
Wrong Evaporator
Blower Rotation
Inadequate Ducts
30
Page 31

TABLE 6
TEMPERATURE PRESSURE CHART
TEMP R-410A
(Deg. F) PSIG
-150 —
-140 —
-130 —
-120 —
-110 —
-100 —
-90 —
80 —
-
-70 —
-60 0.4
-50 5.1
-40 10.9
-35 14.2
-30 17.9
-25 22.0
-20 26.4
-15 31.3
-10 36.5
-5 42.2
0 48.4
5 55.1
10 62.4
15 70.2
20 78.5
25 87.5
30 97.2
35 107.5
40 118.5
45 130.2
50 142.7
55 156.0
60 170.1
65 185.1
70 201.0
75 217.8
80 235.6
85 254.5
90 274.3
95 295.3
100 317.4
105 340.6
110 365.1
115 390.9
120 418.0
125 446.5
130 476.5
135 508.0
140 541.2
145 576.0
150 612.8
SYSTEM CHARGE TROUBLESHOOTING
SUPERHEAT CALCULATION
1. Measure the suction pressure at the suction line service valve.
2. Convert the suction pressure to saturated temperature. See Table 6.
3. Measure the temperature of the suction line at the suction line service valve.
4. Compare the temperature of the suction line to the saturated temperature.
5. The difference between saturated temperature and suction line temperature is
the superheat. Superheat normal range 9° to 16°.
SUBCOOLING CALCULATION
1. Measure the liquid pressure at the liquid line service valve.
2. Convert the liquid line pressure to saturated temperature. See Table 6.
3. Measure the liquid line temperature at the liquid line service valve.
4. Compare the liquid line temperature to the saturated temperature.
5. The difference between saturated temperature and liquid line temperature is the
subcooling. Subcooling normal range 5° to 14°.
TABLE 7
AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM TROUBLESHOOTING TIPS
AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM
ROUBLESHOOTING TIPS
T
SYSTEM PROBLEM
Overcharge High High Low High High
Undercharge Low Low High Low Low
Liquid Restriction (Drier) Low Low High High Low
Low Evaporator Airflow Low Low Low Low Low
Dirty Condenser High High Low Low High
Low Outside Ambient Temperature Low Low High High Low
Inefficient Compressor Low High High High Low
TXV Sensing Bulb Charge Lost Low Low High High Low
Poorly Insulated Sensing Bulb High High Low Low High
DISCHARGE SUCTION
PRESSURE PRESSURE AMPS
LOW VOLTAGE SOLENOID TROUBLESHOOTING
Recommended troubleshooting process
1. Begin diagnosis at the ICC:
Check for flashing codes at the ICC.
2. Check compressor amperage:
Operate the system and measure compressor amperage. Cycle the solenoid on
and off at ten plus second intervals by applying and removing the molded plug
(make certain the ICC is in 2nd stage; large C on the 7-segment LED). Wait five
seconds after power is applied via the molded plug before taking a reading. The
compressor amperage should go up or down at least 25 percent (a saturated
condensing temperature below 80°F may not produce as wide a change in
amperage).
3. Check the voltage supplied to the solenoid:
Remove the solenoid plug from the compressor. With the unit running and the
thermostat calling for Y2 (24VAC at the yellow/blue wire; large C on the 7-segment LED), test the voltage output at the plug with a DC voltmeter. The reading
should be 4 to 18 volts. If not, unplug the harness from the ICC harness and
check voltage at the pins of the ICC harness. The ICC will not power the solenoid if the compressor is not running or fault code 1 or 9 is active.
4. Check solenoid resistance:
Measure the solenoid resistance at the pins on the compressor. The resistance
should be 32 to 60 ohms depending on compressor temperature. If the coil resistance is infinity, much lower than 32 ohms, or is grounded the compressor must
be replaced.
INDICATORS
SUPERHEAT SUBCOOLING
COMPRESSOR
31
Page 32

How do I know if the low voltage solenoid is switching?
Go through the four standard troubleshooting steps. If inconclusive do the following:
1. Make sure the compressor is OFF.
2. Apply 18 to 28V AC to the solenoid pins at the pump.
3. The solenoid should make an audible click as it is energized.
4. Remove the AC signal to the solenoid pins.
5. The solenoid should make an audible click as it de-energizes.
IMPORTANT: Do not operate the compressor with 24VAC applied to the low volt-
age solenoid pins. Applying 24VAC to the solenoid pins can overheat it over time
and cause solenoid failure.
Use the above steps for troubleshooting only!
TROUBLE SHOOTING CHART
!
WARNING
DISCONNECT ALL POWER TO UNIT BEFORE SERVICING. CONTACTOR MAY BREAK ONLY ONE SIDE. FAILURE
TO SHUT OFF POWER CAN CAUSE ELECTRICAL SHOCK RESULTING IN PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH.
SYMPTOM POSSIBLE CAUSE REMEDY
Unit will not run • Power off or loose electrical connection • Check for correct voltage at contactor in condensing unit
Outdoor fan runs, compressor • Run or start capacitor defective • Replace
doesn’t • Start relay defective • Replace
Insufficient cooling • Improperly sized unit • Recalculate load
Compressor short cycles • Incorrect voltage • At compressor terminals, voltage must be ± 10% of
Registers sweat • Low indoor airflow • Increase speed of blower or reduce restriction - replace air
High head-low vapor pressures • Restriction in liquid line, expansion device or filter drier • Remove or replace defective component
High head-high or normal vapor • Dirty outdoor coil • Clean coil
pressure - Cooling mode • Refrigerant overcharge • Correct system charge
Low head-high vapor pressures • Flowcheck piston size too large • Change to correct size piston
Low vapor - cool compressor - • Low indoor airflow • Increase speed of blower or reduce restriction - replace air
iced indoor coil filter
High vapor pressure • Excessive load • Recheck load calculation
Fluctuating head & vapor • TXV hunting • Check TXV bulb clamp - check air distribution on coil - replace
pressures TXV
Gurgle or pulsing noise at • Air or non-condensibles in system • Recover refrigerant, evacuate & recharge
expansion device or liquid line
Compressor runs, ECM • 24VAC signal not present at yellow fan wire • Check for correct thermostat connections
outdoor fan doesn't • Common signal not present at blue fan wire • Verify blue fan wire is connected to the common side
• Thermostat out of calibration-set too high • Reset
• Defective contactor • Check for 24 volts at contactor coil - replace if contacts are
open
• Blown fuses / tripped breaker • Replace fuses / reset breaker
• Transformer defective • Check wiring-replace transformer
• High pressure control open (if provided) • Reset-also see high head pressure remedy-The high pressure
control opens at 450 PSIG
• Loose connection • Check for correct voltage at compressor check & tighten all connections
• Compressor stuck, grounded or open motor winding, • Wait at least 2 hours for overload to reset.
open internal overload. If still open, replace the compressor.
• Low voltage condition • Add start kit components
• Improper indoor airflow • Check - should be approximately 400 CFM per ton.
• Incorrect refrigerant charge • Charge per procedure attached to unit service panel
• Air, non-condensibles or moisture in system • Recover refrigerant, evacuate & recharge, add filter drier
nameplate marking when unit is operating.
• Defective overload protector • Replace - check for correct voltage
• Refrigerant undercharge • Add refrigerant
filter
• Flowcheck piston size too small • Change to correct size piston
• Incorrect capillary tubes • Change coil assembly
• Outdoor fan not running • Repair or replace
• Air or non-condensibles in system • Recover refrigerant, evacuate & recharge
• Defective Compressor valves • Replace compressor
• Incorrect capillary tubes • Replace coil assembly
• Operating below 65°F outdoors • Add Low Ambient Kit
• Moisture in system • Recover refrigerant - evacuate & recharge - add filter drier
• Defective compressor • Replace
• Air or non-condensibles in system • Recover refrigerant, evacuate & recharge
32
Page 33

FIGURE 6
-)ARL, -024, -036, -048 WIRING DIAGRAM
(
33
Page 34

FIGURE 7
-)ARL-060 JEZ, (-)ASL-024 JEZ, (-)ASL-036 JEZ WIRING DIAGRAM
(
34
Page 35

35
Page 36

36
CM 0409
 Loading...
Loading...