Reznor YDHA060 Service Manual
Y
CQS
C
N
E
E
V
N
G
O
A
C
C
U
S
T
O
M
CQS
E
Q
R
U
A
P
L
I
R
T
Y
O
D
U
C
T
Form O-Y (4-16)
Obsoletes Form O-Y (11-15)
Operation / Maintenance / Service
Applies to: Models YDHA, YDMA, and YDSA
Packaged Rooftop Equipment
Model YDHA High Outside
Air (Conditioned
Ventilation)
P
R
O
C
E
S
R
G
S
E
N
T
P
U
-
T
R
A
T
S
M
Y
E
T
T
S
N
Y
S
A
R
R
A
W
Model YDMA -
Conditioned
Makeup Air
R-410A
Refrigerant
Model YDSA -
Space
Conditioning
DANGER
This unit contains R-410A high pressure refrigerant. Hazards exist that
could result in personal injury or death. Installation, maintenance, and
service should only be performed by an HVAC technician qualied in R-410A
refrigerant and using proper tools and equipment. Due to much higher
pressure of R-410A refrigerant, DO NOT USE service equipment or tools
designed for R22 refrigerant.
IMPORTANT: Do not release refrigerant to the atmosphere! If required
service procedures include the adding or removing of refrigerant, the service
technician must comply with all federal, state and local laws. The procedures
discussed in this manual should only be performed by a qualied HVAC
technician.
Form O-Y P/N 273647R5, Page 1
Table of Contents
1.0 General .......................................................2
2.0 Maintenance Requirements .....................2
2.1 Maintenance Schedule ...........................................3
2.2 Control Locations ....................................................4
2.3 Cabinet Size 1 or 2 by Model & Size Cross-Referenced
to Heat Section Size & Type ...........................5
3.0 Maintenance and Service Procedures -
Unit & Cooling Components ....................6
3.1 Filters ......................................................................6
3.2 Supply Fan and Variable Frequency Drive .............8
3.3 Optional Dampers and Damper Actuator ................9
3.4 Condenser Fans ...................................................10
3.5 Coils and Related Cooling Components ...............10
3.6 Check Refrigerant Pressure and Temperatures
(subcooling and superheat) ...........................17
3.7 Compressor Operation, Maint, and Replacement 19
3.8 Other Controls.......................................................27
4.0 Maintenance/Service Procedures - Power
Exhaust and Energy Recovery ..............27
4.1 Power Exhaust, Option PE ...................................27
4.2 Energy Recovery Wheel,
Option EW .....................................................28
5.0 Maintenance/Service Procedures - Gas
Heat Section ............................................32
5.1 Gas Heat Controls ................................................32
5.2 Combustion Air and Venting .................................37
5.3 Vent Maintenance and Operation .........................40
5.4 Burner and Heat Exchanger .................................41
6.0 Maintenance/Service Procedures - Electric
Heat Section ............................................42
7.0 Troubleshooting ......................................43
7.1 Troubleshooting - Refrigeration ............................43
7.2 Troubleshooting Compressor Digital Controller ...45
7.3 Troubleshooting the Heat Section ........................46
INDEX .............................................................48
1.0 General
Denitions of Hazard
Intensity Levels used
in this Manual
2.0 Maintenance
Requirements
Form O-Y, PN 273647R5, Page 2
This booklet includes operation, maintenance, and service information for Model
YDHA, Model YDMA, and Model YDSA. Before beginning any procedure, carefully
review the information, paying particular attention to the warnings. Handling of refrig-
erant should only be performed by a certied HVAC technician with knowledge of
the requirements of R-410A refrigerant and in compliance with all codes and requirements of authorities having jurisdiction.
There are warning labels on the unit and throughout this manual. For your safety,
comply with all warnings during installation, operation, and service of this system.
See denitions of Hazard Intensity Levels of warnings below.
HAZARD INTENSITY LEVELS
1. DANGER: Failure to comply will result in severe personal injury or death
and/or property damage.
2. WARNING: Failure to comply could result in severe personal injury or
death and/or property damage.
3. CAUTION: Failure to comply could result in minor personal injury and/or
property damage.
To ensure long life and satisfactory performance, a system that is operating under
normal conditions should be inspected according to the Maintenance Schedule in
Paragraph 2.1. If in an area where an unusual amount of dust or soot or other impurities are present in the air, more frequent inspection is recommended.
Refer to the illustration in FIGURE 1, shown on page 4 and follow the instructions in
the paragraphs referenced below to maintain this equipment. Maintenance requirements apply to all Models and Sizes unless noted.
IMPORTANT: Do not release refrigerant to the atmosphere! If
required service procedures include the adding or removing
of refrigerant, the service technician must comply with all
federal, state and local laws. The procedures discussed in
this manual should only be performed by a qualied HVAC
technician familiar with R-410A refrigerant.
WARNING
Lock power OFF before performing any maintenance
procedure (except where power is required such as
checking refrigerant pressure and temperature). Lock
disconnect switch in OFF position. If the system has a gas
heat section, when you turn off the power supply, turn off
the gas. See Hazard Levels on page 2.
If replacement parts are required, use only factory-authorized parts. For
information, contact your local distributor.
2.1 Maintenance
Schedule
Monthly
□ Inspect all lters; clean or replace as needed. See Paragraph 3.1, page 6.
□ Inspect the cooling coil condensate drain; clean as needed. For information, see
Paragraph 3.5, page 10.
Annually
All Models - Beginning of the cooling season or more frequently
in year-round cooling climate:
□ Inspect the wiring for any damaged wire. Replace damaged wiring.
□ Inspect the cooling coil condensate drain pan. Clean the coil cabinet, clean the
drain pan, and ll the trap.
□ Inspect/clean condenser fans. See Paragraph 3.4, page 10.
□ Inspect/clean all coils. See Paragraph 3.5, page 10.
□ Check refrigerant temperatures and pressures (superheat and subcooling).
These checks are done when the unit is operating. See Paragraph 3.6, page 17.
□ Check compressor operation. See Paragraph 3.7, page 19.
Systems with the Optional energy recovery wheel: See Paragraph 4.0, page 27.
□ Inspect the wheel and clean as needed.
□ Check wheel RPM and drive components.
□ Check wheel seals.
Systems with the Optional gas heat section (beginning of the heating
season) - See Paragraph 5.0, page 32:
□ Clean all dirt and grease from the combustion air openings and the venter
assembly.
□ Check the heat exchanger, burner, and venter for scale, dust, or lint
accumulation. Clean as needed.
□ Check the gas valves to ensure that gas ow is being shutoff completely.
Systems with the Optional electric heat section (beginning of the
heating season) - See Paragraph 6.0, page 42:
□ Check wiring connections.
□ Check the heat section and elements for dust or lint accumulation. Clean as
needed.
Form O-Y P/N 273647R5, Page 3
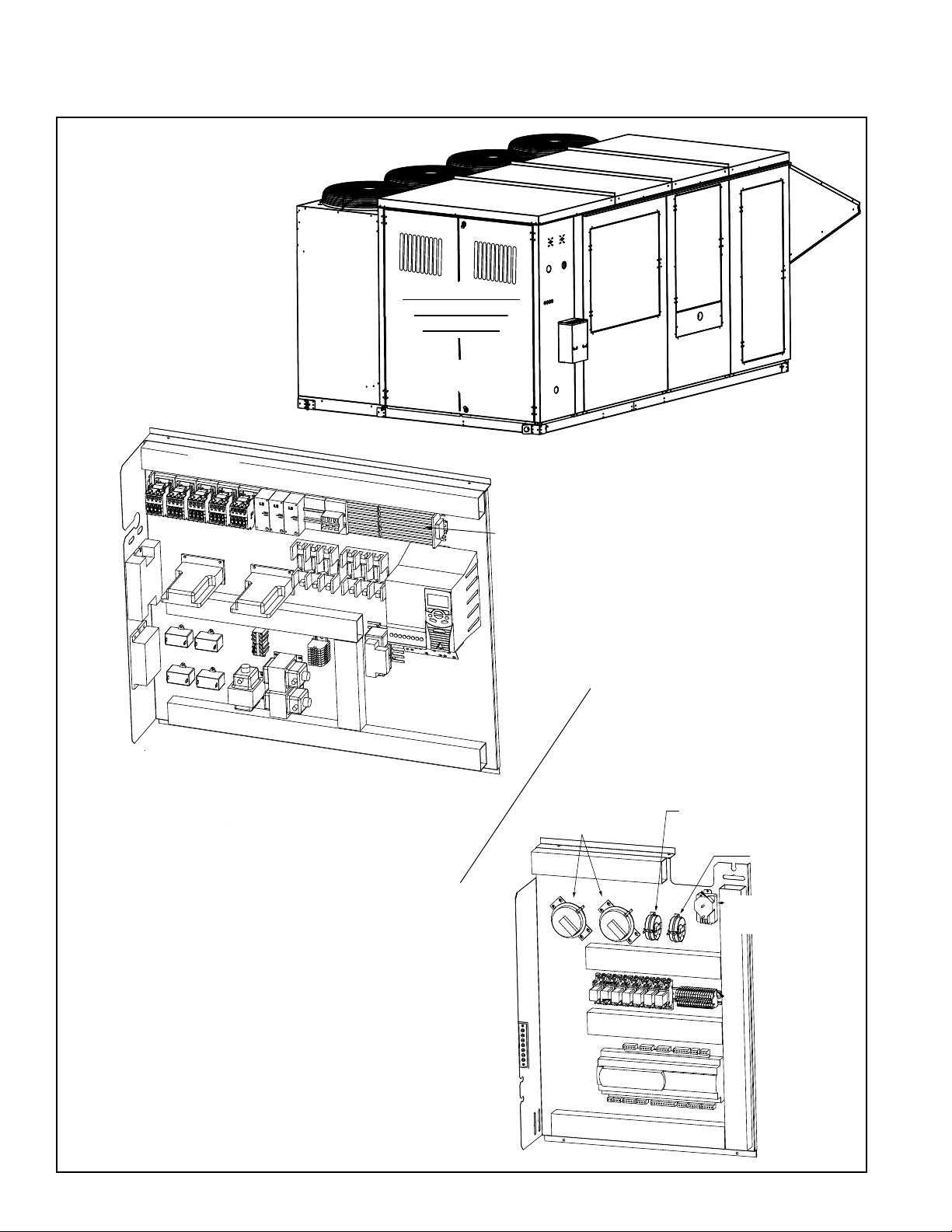
2.0 Maintenance Requirements (cont'd)
2.2 Control Locations
FIGURE 1 Access Doors
and High and
Low Voltage
Control
Locations
A
Comp
Cond
Condenser
Section
HIGH VOLTAGE CONTROL PANEL
Contactors
A
B
B
Cond
DH
Comp
Comp
Condenser Fans
Electrical / Control
Compartments
(See below.)
Optional Gas or
Electric Heat Section
Supply
Fan
Access
Inlet Air
Hood
Coil and
Filter Access
Damper Access
Optional Wheel Access
Compressor
Optional
Low
Ambient
Controller
- ECM
Condenser
Fan
Optional
Low
Ambient
Controller
- Std
Condenser
Fan
Controllers (by circuit)
A
1
2
Capacitors
3
4
Transformers 75 VA
Opt
DH
Fuse Blocks
Gas Heat Section Controls
Ignition controller and combustion air pressure
switch are located on the side wall next to the
gas manifold and burner. See FIGURE 23, page
32.
VFD
VFD Line
Reactor
High Voltage Bus Bar
- Compressor & Condenser
Contactors
- 3-Phase Supply Wire
Connections
- Optional Phase
Loss Monitor
- Optional Power
Exhaust Contactor
- Optional Energy
Wheel Contactor
- Optional Energy Wheel
Preheat Contactor
LOW VOLTAGE PANEL
* Optional Dirty Filter
Pressure Switch (1 or 2)
Relays
Optional Exhaust Airflow
Pressure Switch
High Side Tubing - Yellow
Low Side Tubing - Clear
Supply Air
Pressure Switch
High Side Tubing - Blue
Low Side Tubing - Clear
Optional Pressure
Sensor Transducer
(tubing is field supplied)
* Dirty Filter Switch for
System Filters (BE18)
High Side Tubing - Red
Low Side Tubing - Clear
Dirty Filter Switch for
Wheel Filters (BE28)
High Side Tubing - Green
Low Side Tubing - Clear
Form O-Y, PN 273647R5, Page 4
Thermostat Terminal Strip
Carel Controller
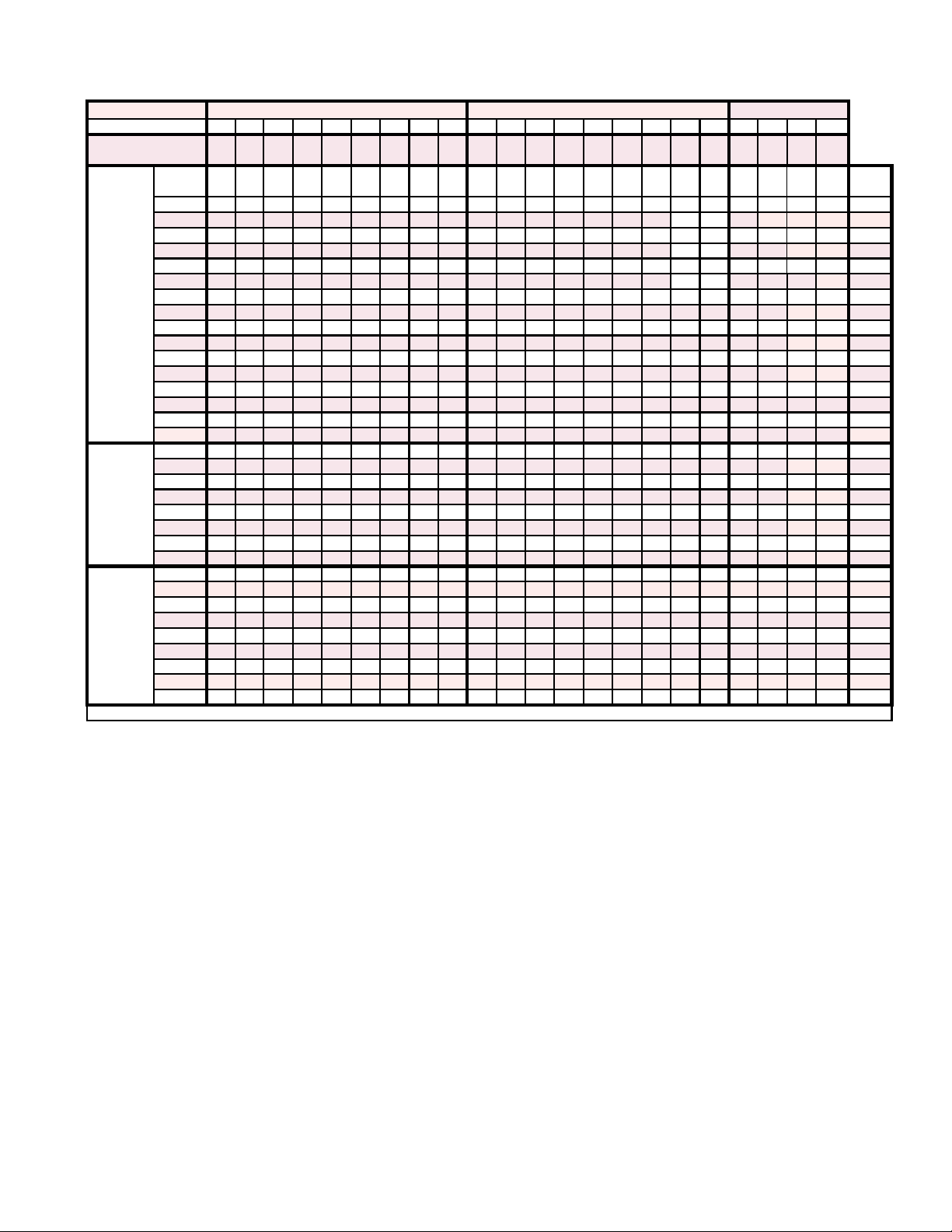
2.3 Cabinet Size 1 or 2 by Model & Size Cross-Referenced to Heat Section Size & Type
Model YDHA YDMA YDSA
Nominal Cooling
Capacity (Tons)
Standard
Efciency
Gas Heat
Section
High
Efciency
Gas Heat
Section
Electric
Heat
Section
* Gas heat sections with dual furnaces.
Size 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 300 360 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 300 360 120 150 180 210
5 7.5 10 12.5 15 17.5 20 25 30 5 7.5 10 12.5 15 17.5 20 25 30 10 12.5 15 17.5
Opt
Code
H50 1 1 1 -- -- -- -- -- -- 1 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- H50
H75 1 1 1 1 2 -- -- -- -- 1 1 1 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- H75
H100 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 -- -- 1 1 1 1 -- -- -- -- -- 2 -- -- -- H100
H102* 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 -- -- 1 1 1 1 -- -- -- -- -- 2 -- -- -- H102*
H125* 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 -- -- 1 1 1 1 2 -- -- -- -- 2 2 -- -- H125*
H150* 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 -- -- 1 1 1 1 2 2 -- -- -- 2 2 3 -- H150*
H175* 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 -- -- 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 -- -- 2 2 3 3 H175*
H200 -- 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 3 3 H200
H202* -- 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 3 3 H202*
H300 -- 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 -- 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 3 3 H300
H400 -- -- 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 -- -- 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 3 3 H400
H402* -- -- 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 -- -- 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 3 3 H402*
H502* -- -- -- -- 2 2 2 3 3 -- -- -- -- 2 2 2 3 3 -- -- 3 3 H502*
H602* -- -- -- -- 2 2 2 3 3 -- -- -- -- 2 2 2 3 3 -- -- --- 3 H602*
H702* -- -- -- -H802* -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 3 3 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 3 3 -- -- -- -- H802*
G150 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 -- -- 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 -- -- 2 2 3 3 G150
G225 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 3 3 G225
G300 -- 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 -- -- 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 3 3 G300
G302* -- 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 -- -- 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 3 3 G302*
G372* -- -- -- -- 2 2 2 3 3 -- -- -- -- 2 2 2 3 3 -- 2 3 3 G372*
G452* -- -- -- -- 2 2 2 3 3 -- -- -- -- 2 2 2 3 3 -- -- 3 3 G452*
G525* -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 3 3 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 3 3 -- -- -- -- G525*
G602* -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 3 3 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 3 3 -- -- -- -- G602*
E20 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 -- -- 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 -- -- 2 2 3 3 E20
E30 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 3 3 E30
E40 -- 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 -- 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 3 3 E40
E50 -- 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 -- 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 3 3 E50
E60 -- 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 -- 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 3 3 E60
E70 -- -- 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 -- -- 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 3 3 E70
E80 -- -- 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 -- -E90 -- -- 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 -- -- 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 3 3 E90
E120 -- -- -- -- 2 2 2 3 3 -- -- -- -- 2 2 2 3 3 -- -- 3 3 E120
-- -- -- 3 3 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 3 3 -- -- -- -- H702*
1 1 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 3 3 E80
Opt
Code
Form O-Y P/N 273647R5, Page 5
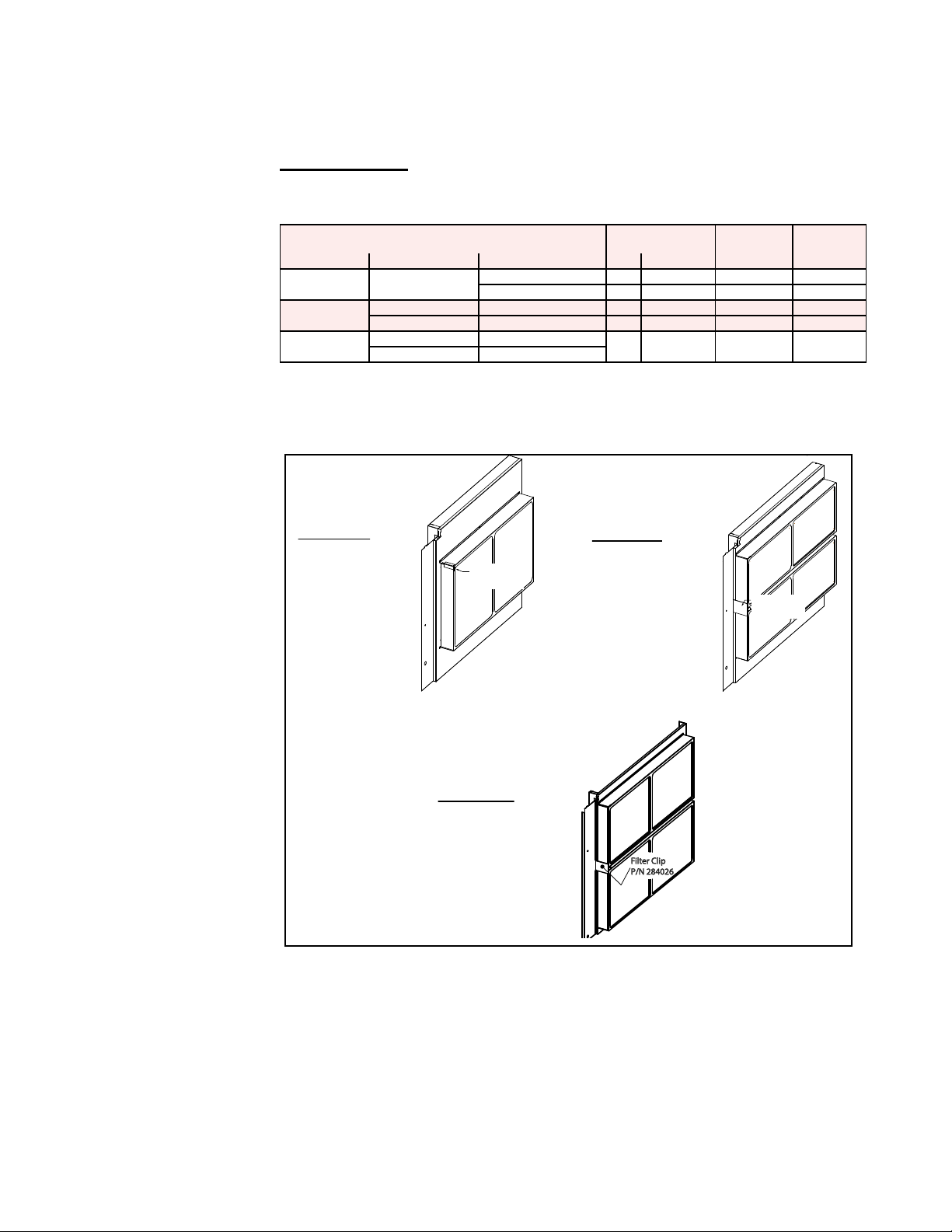
3.0 Maintenance
Filter Clip
P/N 284026
and Service
Procedures Unit & Cooling
Components
3.1 Filters
Systems with disposable lters require more frequent lter inspection. Exposure to
humid makeup air can accelerate lter degradation. Replace lters when needed
using the same type of lters as the original.
Supply Air Filters - The supply air lters are 4-inch pleated disposable lters.
Replacement lters are listed in the table below. Do not use any other type of lters.
FIGURE 2 - Installing
Replacement Supply
Air Filters
Replacement Filters by Model Size and Cabinet Size
Cabinet Size Model(s) Model Sizes Qty Size P/N P/N
1
2
3
YDHA & YDMA
YDHA & YDMA 180, 210, 240 4 16 x 25 211128 256666
YDSA 120, 150 4 16 x 25 211128 256666
YDHA & YDMA 300 & 360
YDSA 180 & 210
060 1 16 x 25 211128 256666
090, 120, 150 2 20 x 24 222480 260828
4" Disposable
Pleated
4 25 x 29 235757 235758
MERV 8 MERV 13
To access supply air lters, open the cooling coil / lter door. Follow the instructions
that apply.
Cabinet Size 0
(see table above)
Instructions:
1) Slide filter clip
left and remove.
2) Slide filters out.
3) Install new filters.
4) Replace filter clip.
Filter Clip,
P/N 272222
Filter
Filter
Cabinet Size 2
(see table above)
Instructions:
1) Slide filter clip tab
from the slot in
the filter support.
Rotate clip slightly
and remove filter
clip.
2) Slide filters out.
3) Install new filters.
4) Replace filter clip.
Filter
Filter Clip,
P/N 272707
Filter
Filter
Filter
Form O-Y, PN 273647R5, Page 6
Cabinet Size 3
(see table above)
Instructions:
1) Slide filter clip tab
from the slot in the
filter support.
Rotate the clip slightly
and remove filter clip.
2) Slide filters out.
3) Install new filters.
4) Replace filter clip.
Filter
Filter
Filter
Filter
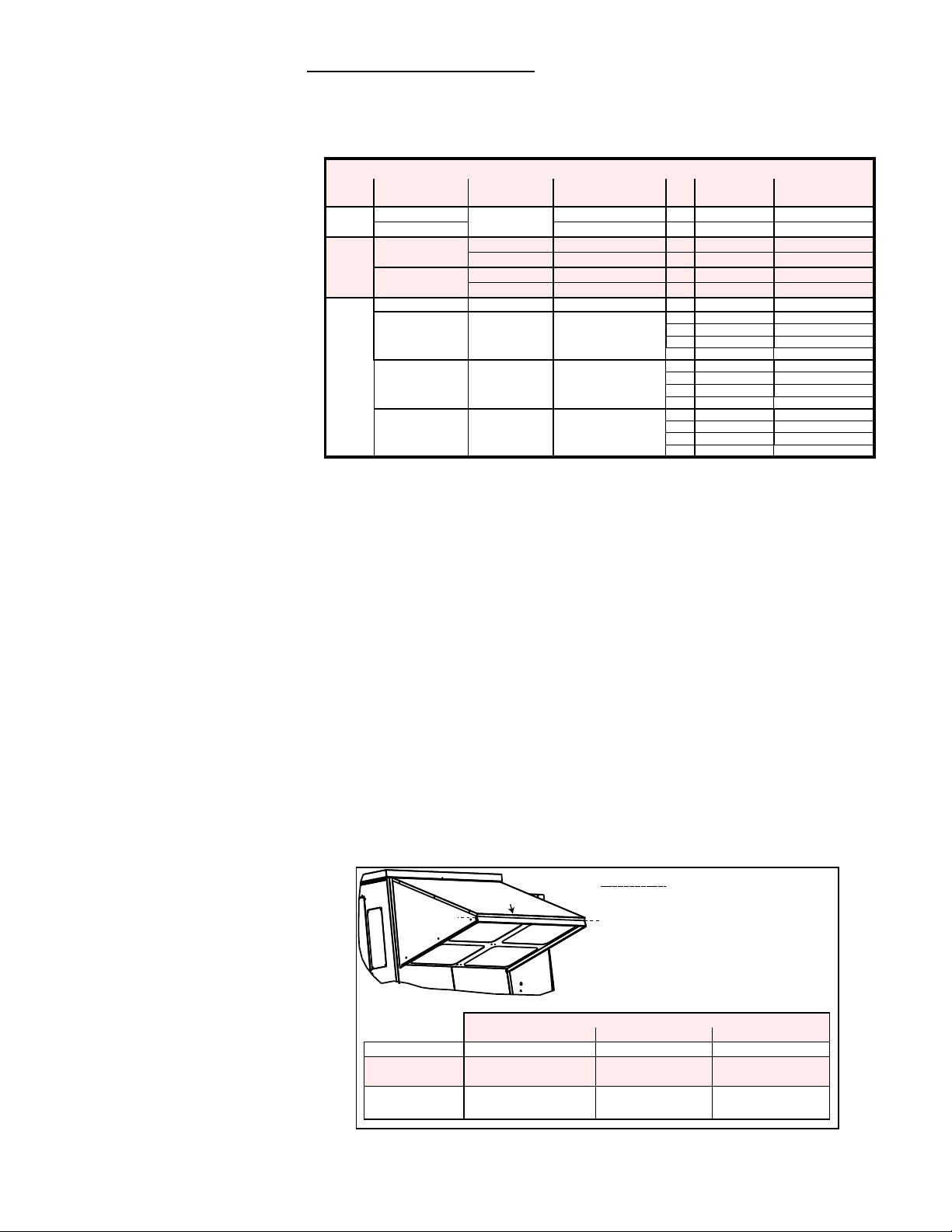
3.1 Filters (cont'd)
Energy Recovery Wheel Filters - The energy recovery wheel has two 1-inch lters
in both the supply and exhaust airstreams. Replacements are listed below. Size of lter is determined by CFM. Permanent lters may be washed and dried and re-used.
To access lters, open the wheel door. Slide the lters out of the lter racks.
Do not operate the system without lters in place.
Filter Application by Cabinet & ER Wheel Sizes
Cabinet
Size
1
2
3
ER Wheel Size Model Model Size Qty Filter Size
30" dia
36" dia
36" dia
46" dia
36" dia
46" dia
52"dia
58"dia
YDHA & YDMA 060, 090, 120, 150
090, 120, 150
YDHA & YDMA 180, 210, 240 4 20 x 25 101610
YDSA 120, 150 4 20 x 25 101610
YDHA & YDMA 180, 210, 240 4 25 x25 119779
YDSA 120, 150 4 25 x 25 119779
YDSA 180, 210
YDSA 180, 210 4 16 x 20 101607
YDHA 300, 360 4 16 x 20 101607
YDHA & YDMA 300, 360 4 16 x 20 101607
4 16 x 16 104102
4 20 x 20 101608
4 20 X 25 101610
4 20 x 20 101608
2 16 x 25 101609
2 20 x 25 101610
4 20 x 20 101608
2 16 x 25 101609
2 20 x 25 101610
4 20 x 20 101608
2 16 x 25 101609
2 20 x 25 101610
1" Permanent
P/N
Dirty Filter Switch (Options BE18 or BE28)
Systems may be equipped with a dirty lter pressure switch (Option BE18) that will
trigger an alarm when the resistance through the inlet air lters indicates that lter
replacement is required. Systems with an energy recovery wheel may be equipped
with two dirty lter pressure switches (Option BE28), one for the inlet air lters and
one for the energy recovery wheel supply lters.
When performing maintenance, check the condition of the sensing tubes to be sure
that they are not blocked. Check the wiring connections. To set a new dirty lter
switch, see Installation Form I-Y, Paragraph 8.3. Replacement switch is P/N 105507.
FIGURE 3 - Removing
and Installing Filters
in the Outside Air
Hood
Permanent Filters in the Outside Air Hood (Option AS16)
If equipped with an outside air hood, there are 1" permanent, aluminum lters at the
entrance of the hood. The lters act as a moisture eliminator and bird screen. See
FIGURE 3, shown below. When inspecting the inlet air lters, inspect the outside air
hood lters. If cleaning is needed, remove the lters, clean, rinse, dry and re-install.
NOTE: If it is more convenient to keep an extra clean set of lters, lter sizes and part
numbers are listed below.
Instructions:
Front Cover
Filter
Filter
YSDA Models -- 120, 150 180, 210
YDHA, YDMA
Models
Filter No / Size /
(Qty)
060, 090, 120, 150 180, 210, 240 300, 360
Filter
Filter
1 2 3
101607
16x20x1 - (4)
1) Remove two screws,
one on each end of
the front cover.
Remove the cover.
2) Slide filters out.
3) Clean and dry filters.
4) Return filters to hood
and replace cover.
Cabinet Size
101610
20x25x1 - (4)
101609
16x25x1 - (8)
Form O-Y P/N 273647R5, Page 7
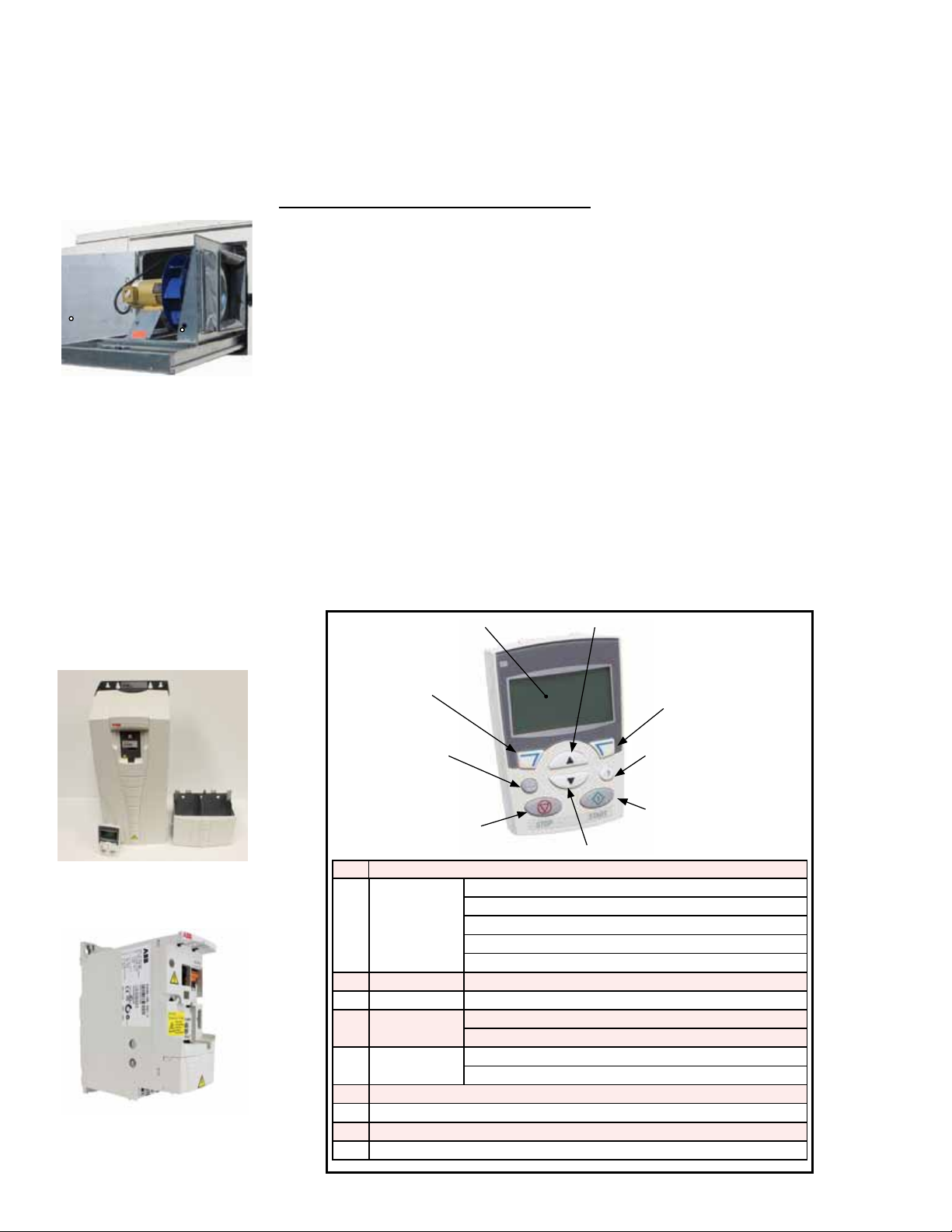
3.0 Maintenance and Service Procedures - Unit & Cooling Components (cont'd)
3.2 Supply Fan
and Variable
Frequency Drive
Supply fan in "slide
out" position
Approx fan sled
screw locations
Variable Frequency
Drive
FIGURE 4 - VFD
Display
Fan motors are permanently lubricated; lubrication is not required, During
maintenance, remove any accumulation of dirt and grease. The fan CFM was
checked and balanced at startup. To recheck, follow the instructions in the installation
manual, Form I-Y, Paragraph 10.3.
If service is required, the supply fan is mounted on a sled that will slide out of the
cabinet.
Instructions for sliding out the supply fan:
1. Turn off the power and lock the disconnect switch.
2. Open the supply fan door and the cooling cabinet door.
3. The exible duct joining the supply fan to the cooling compartment is visible.
Locate the metal ange holding the duct to the cabinet. Remove the two screws
from fan sled (locations shown in picture on the left) and the ange to free the duct
so that it can be slid out with the fan.
4. Open the electrical box on the fan. Mark and disconnect the wires.
5. Carefully slide the complete fan sled out of the cabinet.
6. When service is complete, slide the sled into the cabinet. Re-connect the wires
and re-attach the ange to hold the exible duct in place. If the pressure tube was
removed during service, be sure to re-attach it securely. Reinstall two screws into
the fan sled.
Function: When the main controller calls for supply fan operation, a variable fre-
quency drive (VFD) responds to operate the motor.
The VFD is located on the high voltage electrical panel (See FIGURE 1, page 4).
Control of the variable frequency drive module is dictated by the main controller, and
depending on what was ordered, can function in response to temperature, CO
, or
2
pressure controls. !
Service: Remove any dirt or dust. Check the wire connections. If a VFD needs
to be replaced, use a factory-authorized replacement designed for the application.
1) LCD Display
4) UP
Variable Frequency
Drive Model ACS550
Variable Frequency
Drive Model ACS355
2) RESET / EXIT
6) LOC / REM
8) STOP
5) DOWN
Code Control Panel Display
1 LCD display -
Divided into 5
areas
2 RESET / EXIT Resets faults and exits to higher menus
3 MENU / ENTER Menu selection and saves value
4 UP Scrolls up through menu / list
5 DOWN Scrolls down through menu / list
6 LOC / REM - VFD controlled by main controller
7 DIR - Changes the direction of the motor
8 STOP - Stops the drive
9 START - Starts the drive
Upper left - Control location
Upper right - unit of the displayed value
Center - Parameters and signal values, menus and alarm codes
Lower left and center - Operation state
Lower right - Motor rotation
Increases value of parameters or reference values
Decreases value of parameters or reference values
3) MENU / ENTER
7) DIR
9) START
Form O-Y, PN 273647R5, Page 8
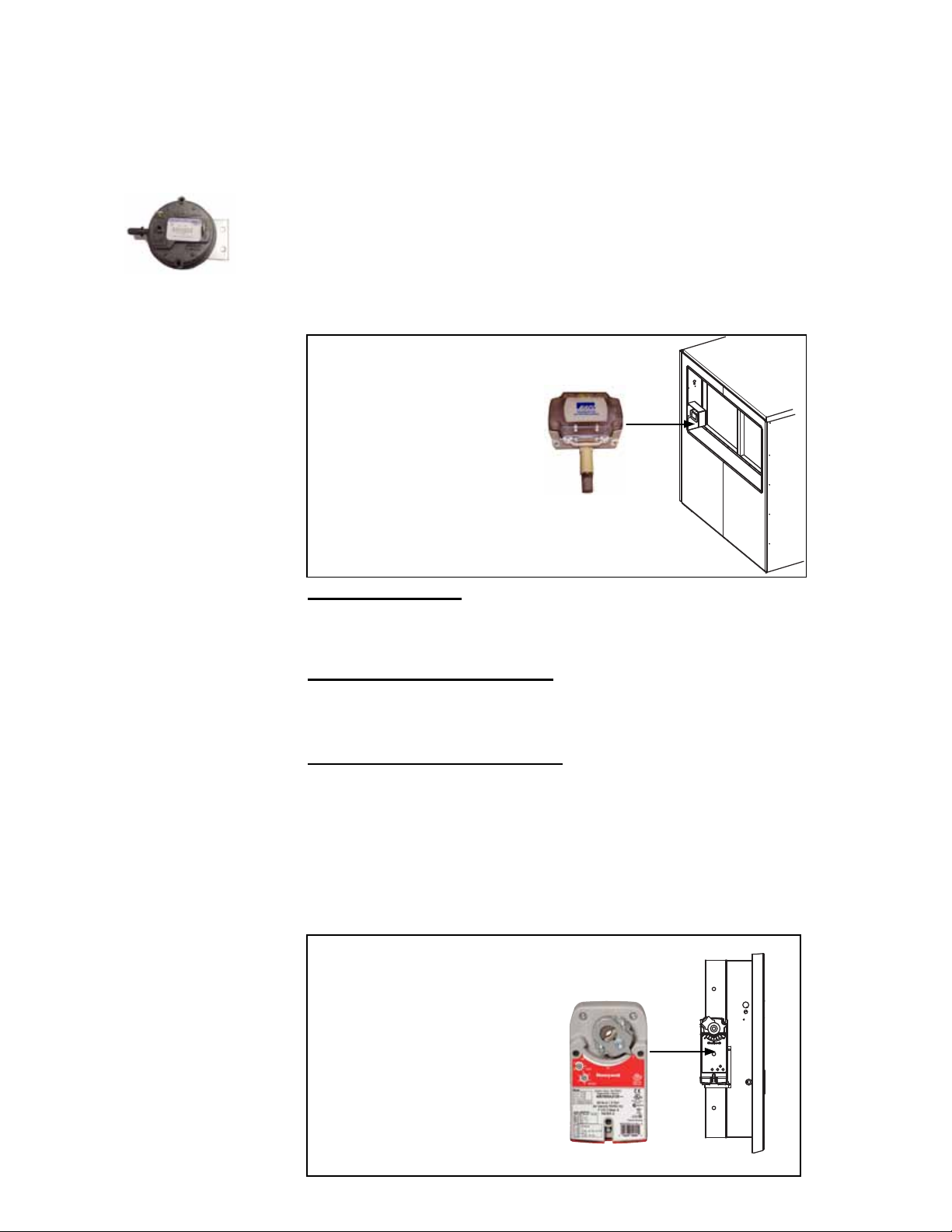
3.0 Maintenance and Service Procedures - Unit & Cooling (cont'd)
3.2 Supply Fan and Variable Frequency Drive (cont'd)
Air Proving Switch
P/N 234712
Set Point 0.10 I.W.C.
Outside Air Humidity
and Temperature
Sensor
Function: The airow proving switch is a pressure switch that veries to the main
controller that the supply fan is operating. If equipped with power exhaust or an
energy recovery wheel, there is a second air proving switch that veries the exhaust
fan is operating. See location in FIGURE 1, page 4.
Service: If a switch needs to be replaced, use a factory-authorized replacement
designed for the application.
Function: All systems have an outside air humidity and temperature sensor in the
outside air inlet. The sensor is wired to the system controller in the electrical compartment.
Service: Check the wiring. If the sensor needs replaced, use a factory-authorized
replacement designed for the application.
FIGURE 5 - Outdoor
Air Sensor, P/N
222754, is mounted
in the outside air
inlet (behind the
hood)
3.3 Optional
Dampers
and Damper
Actuator
Inlet Air Dampers
Location: Dampers and damper motors are located in the inlet air opening.
Function: Dampers operate in response to a variety of controls (GF Options).
Service: Clean dampers and controls of dust and dirt.
2-Position Damper Actuator (Options AR7, AR8, AR2D, AR2L, AR2Y)
Function: The 2-position damper motor opens and closes the dampers in response
to unit operation or a eld-supplied time clock. The motor closes the dampers on
heater shutdown.
Modulating Damper Actuator (Options AR25, AR2G, AR2H, AR2M)
Function: The modulating damper motor actuates the dampers in response to the
selected control with actuation from input switch settings.
The motor closes the inlet dampers on heater shutdown.
Service: Other than external cleaning, there is no service required on the dampers or
the damper motor. If the damper, control, or motor need to be replaced, replace with
a factory-authorized replacement.
For additional information on damper controls (Options GF 1-9), see the system
installation manual Form I-Y.
FIGURE 6 - Damper
Actuator is mounted
on the damper frame
and is accessible
through the Damper
Access Door (See
FIGURE 1, page 4).
Form O-Y P/N 273647R5, Page 9
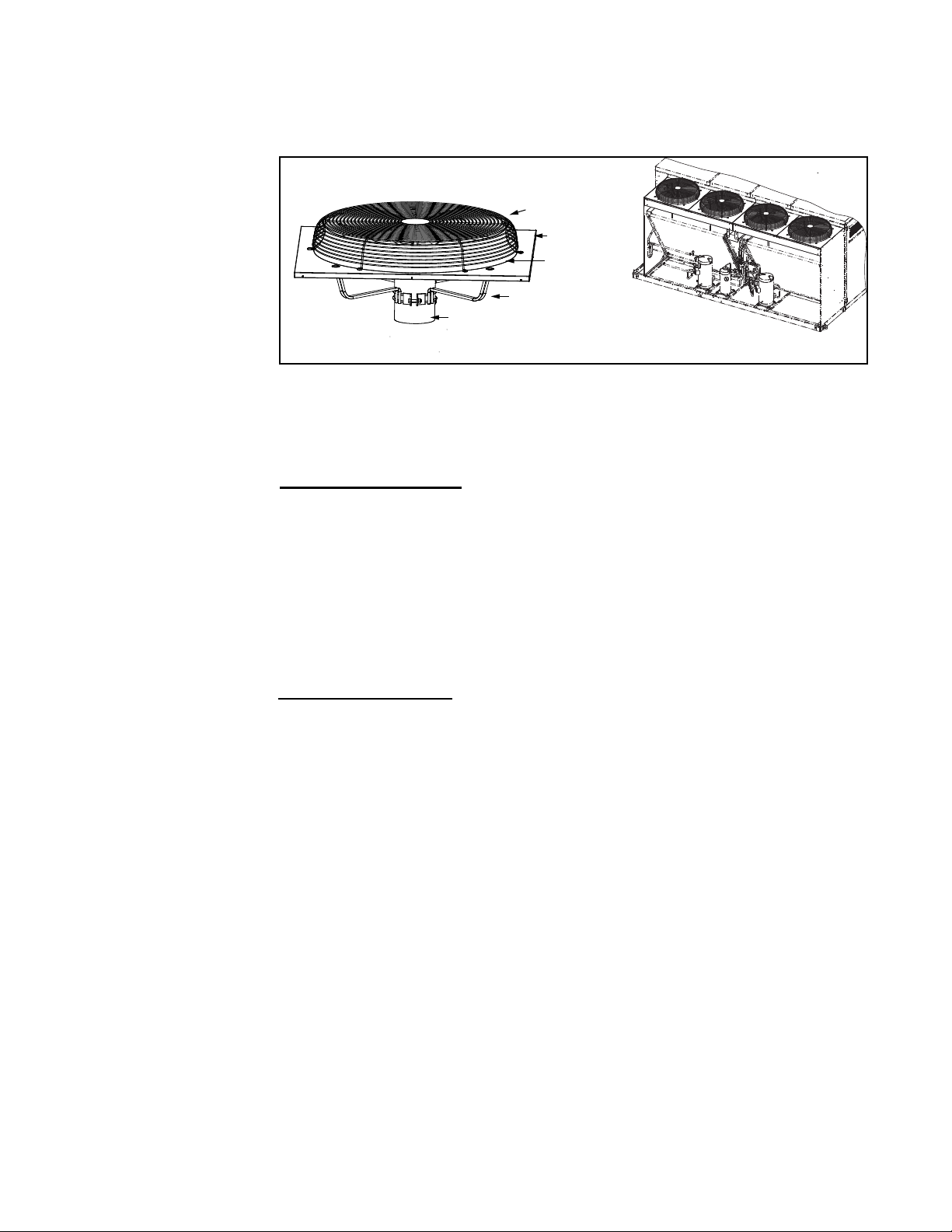
3.0 Maintenance and Service Procedures - Unit & Cooling (cont'd)
3.4 Condenser Fans
3.5 Coils and
Related Cooling
Components
Condenser Coil
Cleaning Instructions
Depending on the model size, there are two or four condenser fans. Fan motors may
be either standard efciency or ECM speed control. If parts need to be replaced, use
only factory authorized replacement parts.
FIGURE 7 - Condenser Fans
Guard
Housing
Propeller Fan
Fan Support
Motor
Condenser Fan Section Assembly
The DX cooling system is equipped with copper nned coils. Inspect all cooling
system coils at the beginning of the cooling season or more often if needed. Follow
the cleaning instructions below. If additional cleaning is required or if a coil must be
removed for any reason, consult the factory. Be prepared to provide rating plate and
specic installation information.
Condensing Coil Access - The condensing coils are visible on the side of the unit
(below the condenser fans).
1. Verify that the electrical power has been turned off and the disconnect switch
locked.
2. Use a soft brush to remove any dirt and debris from the coils.
3. Spray with cold or warm (not hot) water and a cleaning solution (non-acid based
coil cleaner is recommended). Due to possible damage to the coil, DO NOT use
high pressure spray.
4. When clean, rinse with cool, clean water.
Evaporator
Coil Cleaning
Instructions:
Evaporator Coil Access - The evaporative coils can be accessed by opening the coil
cabinet door.
Inspect coils for debris, dirt, grease, lint, pollen, mold, or any element which would
obstruct heat transfer or airow. Inspect coils and tubing for physical damage. Inspect
feeders, piping connections, coil headers, and return bends for signs of fatigue, rubbing, and physical damage.
Clean the coils annually, or more often if needed. Use the proper tools and follow the
instructions carefully to avoid damaging the coil. Use of a non-acid based coil cleaner
is recommended. Due to possible damage to the coil, DO NOT use high pressure
spray.
1. Verify that the electrical power has been turned off and the disconnect switch
locked.
2. Open the cooling coil door.
3. Use a soft brush to remove any dirt and debris from both sides of the coil.
4. Spray with cold or warm (not hot) water and a cleaning solution (non-acid based
coil cleaner is recommended). Due to possible damage to the coil, DO NOT use
high pressure spray. First spray the leaving airow side, then the inlet airow side.
As much as possible, spray the solution perpendicular to the face of the coil.
Follow the instructions on the cleaning solution. When cleaning process is
complete, rinse both sides with cool, clean water.
Form O-Y, PN 273647R5, Page 10
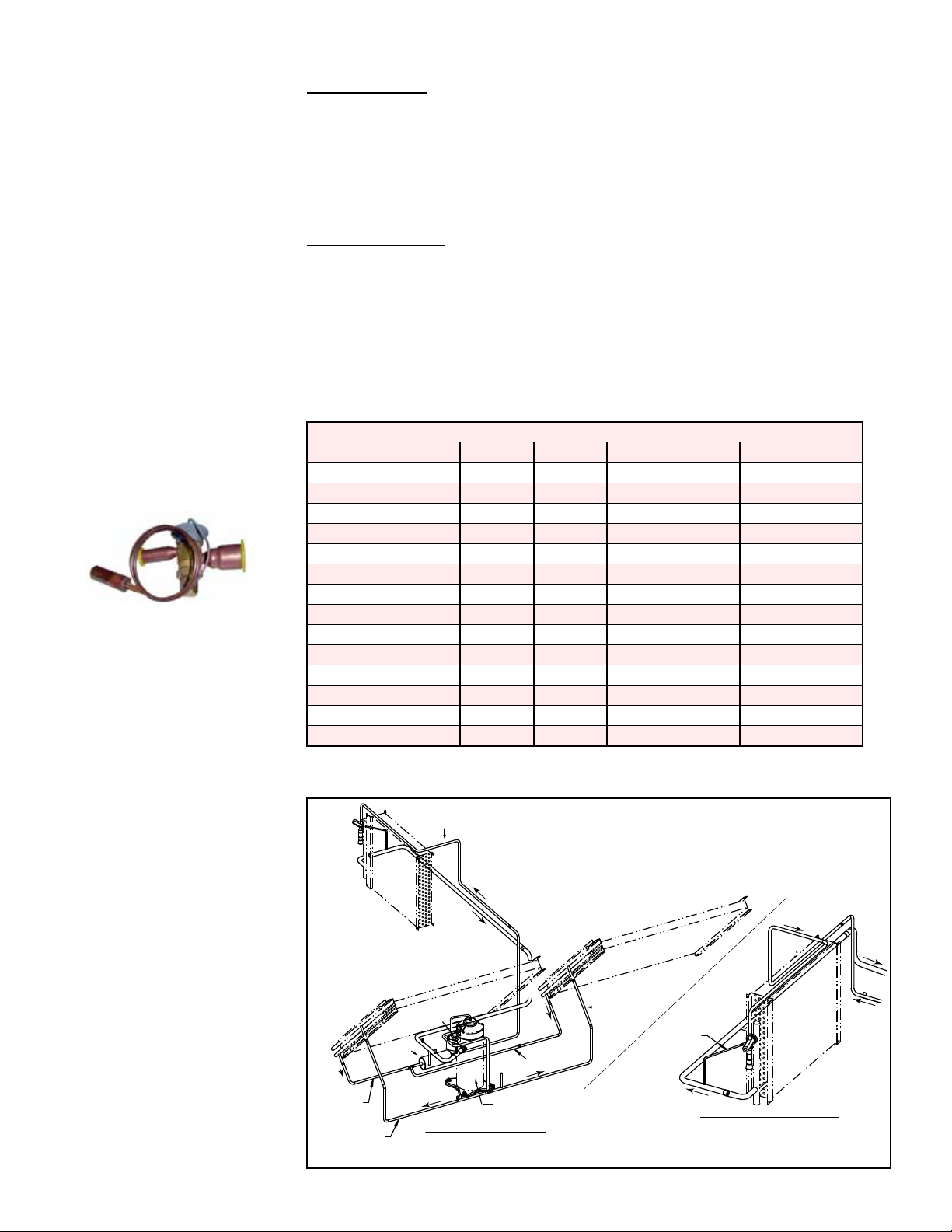
3.5 Coils and Related Components (cont'd)
Condensate Drain
Use and Maintenance
Thermostatic
Expansion Valves
Thermostatic
Expansion Valve
Seasonal Usage - At the beginning of the cooling season, inspect and clean the
entire cooling coil cabinet including the condensate drain pan. Thoroughly clean dirt,
algae, grease, and other contaminants. Inspect condensate drain pan, trap, and pip-
ing; ll trap with water to ensure proper operation. During a wintertime shutdown of
the cooling system, it may be desirable to disconnect and remove all water from the
trap and drain to prevent freeze damage. If local building codes permit, trap may be
lled with an antifreeze solution. Or, piping may be designed with freeze plugs or
other freeze protection methods (such as a heat tape).
Year Round Usage - Climates or applications with cooling requirements year round
require more frequent inspections of the cooling coil cabinet and condensate drains.
Depending on climate, freeze protection of the trap may be required during noncooling days.
All refrigeration circuits have a thermostatic expansion valve. Thermostatic expansion
valves do not have replaceable parts. If a replacement valve is required, it must be for
R-410A refrigerant and must be sized correctly for the application. All refrigerant ser-
vice should be performed by a service technician qualied in R-410A refrigerant.
Replacement valve P/N's by Model, size, and circuit are listed in the table. Locations
are shown in FIGURES 8 through 14, shown on pages 11 through 14.
Thermostat Expansion (TXV) Valves by Circuit and P/N
Model / Size A B DH - Low Enthalpy DH - High Enthalpy
YDHA & YDMA 060 234987 -- 207303 --
YDHA 090 220556 -- -- 207303
YDMA 090 220556 -- 207303 --
YDHA & YDMA 120 234987 234987 -- 207303
YDSA 120 234960 234960 -- --
YDHA & YDMA 150 220555 220555 -- 207303
YDSA 150 220555 220555 -- --
YDHA & YDMA 180 220555 220555 207303 234960
YDSA 180 220555 220555 -- --
YDSA 210 220556 220555 -- --
YDHA & YDMA 210 220556 220556 207303 234960
YDHA & YDMA 240 220556 220556 207303 234960
YDHA & YDMA 300 261175 221175 234960 235729
YDHA & YDMA 360 220558 220558 234960 235729
Refrigerant Circuits - Standard Cooling without Optional Bypass Valve or Reheat
FIGURE 8 - Cooling
Circuit - Models
YDHA and YDMA
Circuit A-1&2
Model JDHA 062 and 092 (Cabinet 0)
Sizes 060 and 090
Evaporator
Circuit A-1
Circuit A-1
Coil with
Single Circuit
Filter
Drier
Condenser Coil
Circuit A-1
Solenoid
Valve
Modulating
View from Compressor and
Condenser Section Side
Compressor
Circuit A-2
Condenser Coil
Circuit A-2
Circuit A-2
Equalizer
Evaporator
Tube
TXV
Valve
View from Cooling Cabinet Door
(Evaporator Coil Side)
Form O-Y P/N 273647R5, Page 11
Coil
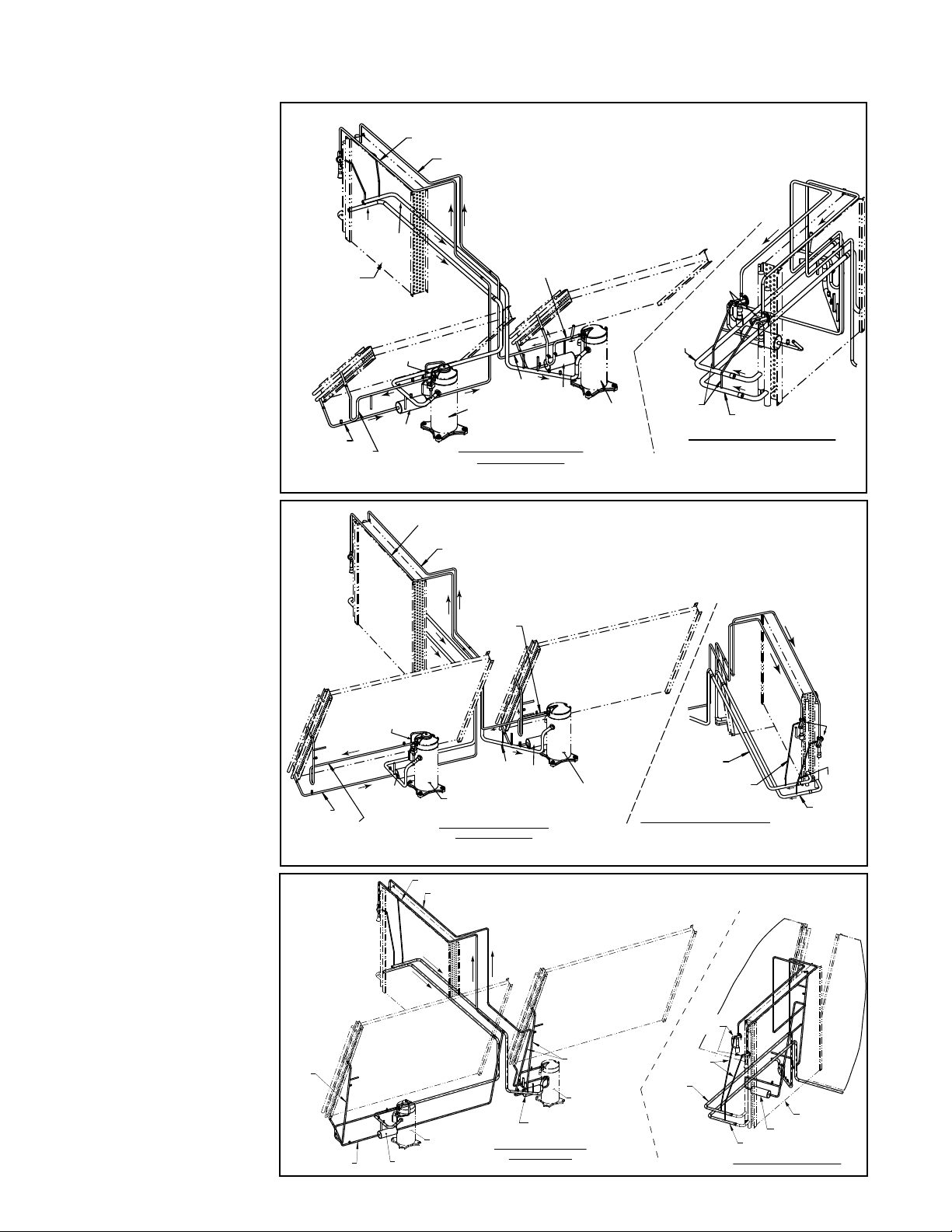
3.0 Maintenance and Service Procedures - Unit & Cooling (cont'd)
3.5 Coils and Related Components (cont'd)
FIGURE 9 - Cooling
Circuits - Models
YDHA and YDMA
Sizes 120 and 150
Evaporator Coil
with intertwined
Circuits A & B
Circuit A
Circuit B
Circuit A
Condenser Coil
Circuit A
Solenoid Valve
Circuit B
Model JDHA 120 and 150 (Cabinet 1)
Condenser Coil
Circuit B
Circuit B
Valves
Circuit B
TXV
FIGURE 10 - Cooling
Circuits - Model YDSA
Sizes 120 and 150;
Models YDHA and
YDMA Sizes 180, 210,
and 240
Circuit A
Circuit A
Evaporator
Coil with
intertwined
Circuits A & B
Circuit A
Circuit A
Filter
Drier
Circuit A
Condenser Coil
Circuit A
Solenoid Valve
Filter
Drier
Circuit B
Modulating
Compressor
(Circuit A)
View from Compressor and
Condenser Section
Circuit B
Modulating
Compressor
(Circuit A)
View from Compressor and
Condenser Section
Model JDHA 180, 210, and 240 (Cabinet 2)
Circuit B
Circuit B
Filter
Drier
Filter
Drier
Compressor
(Circuit B)
Compressor
(Circuit B)
Condenser Coil
Circuit B
Equalizer
Tubes
View from Cooling Cabinet Door
Circuit B
View from Cooling Cabinet Door
(Evaporator Coil Side)
Circuit A
(Evaporator Coil Side)
Equalizer
Tube
Evaporator
Coil
Evaporator
Coil
TXV
Valves
Equalizer
Tube
Circuit A
FIGURE 11 - Cooling
Circuits - Model YDSA
Sizes 180 and 210
Form O-Y, PN 273647R5, Page 12
Circuit A
Evaporator Coil
with Intertwined
Circuits A & B
Circuit A
Circuit A
Condenser Coil
Circuit A
Filter Drier
Circuit B
Compressor
(Circuit A)
Model YDSA 180 and 210 (Cabinet 3)
Condenser Coil
Circuit B
Circuit B
Compressor
(Circuit B)
Filter Drier
View from Compressor and
Condenser Section
Equilizer Tube
Circuit B
TXV
Valves
Circuit A
View from Cooling Cabinet Door
(Evaporator Coil Side)
Evaporator Coil
Filter Drier
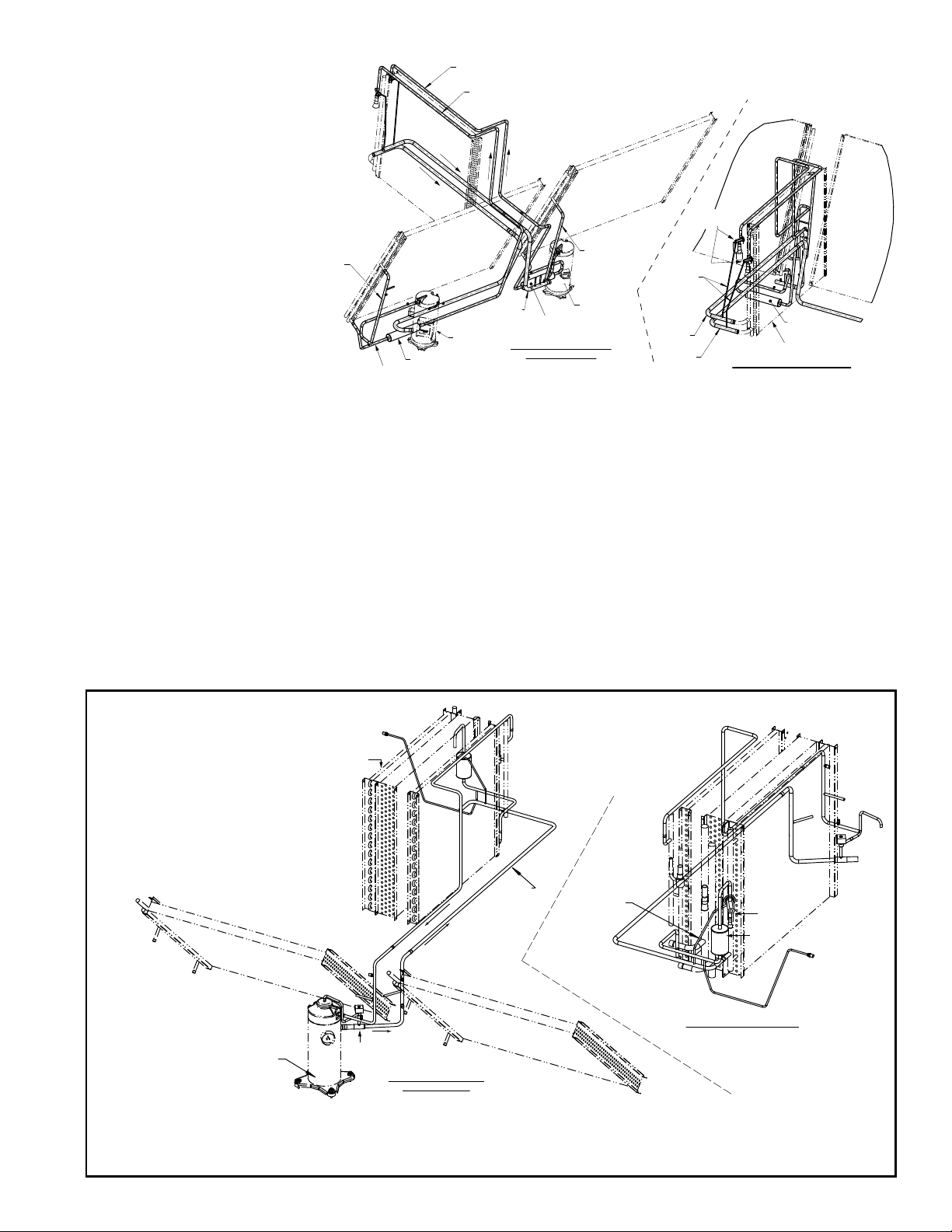
FIGURE 12 - Cooling
Circuits - Models
YDHA and YDMA
Sizes 300 and 360
Circuit B
Circuit A
Model JDHA 300 and 360 (Cabinet 3)
Condenser Coil
Circuit B
TXV
Valves
Optional Modulating
Reheat (High
Enthalpy Option
RPLE or Low
Enthalpy Option
RPHE)
Circuit A
Circuit A
Condenser Coil
Circuit A
Filter Drier
Compressor
(Circuit A)
Circuit B
Filter Drier
View from Compressor and
Condenser Section
Circuit B
Compressor
(Circuit B)
Equilizer Tube
Circuit B
Circuit A
Filter Drier
Evaporator Coil
View from Cooling Cabinet Door
(Evaporator Coil Side)
Function: Units equipped with optional reheat have a dedicated refrigerant system
(DH circuit) that precools the incoming air then directly uses the condenser waste
heat to reheat the air after it passes through the DX cooling coil. The reheat system
precooling evaporator coil is upstream of the main evaporator coil and the reheat
condenser coil is downstream. The upstream "precool" coil tempers outside air and
lowers the wet bulb depression of the air entering the main evaporator coil. The heat
removed at the precool coil is rejected to the downstream "reheat" coil.
Operation of the DH circuit is controlled by the digital controller in the electrical
compartment. See FIGURE 1(shown on page 4) and Figures 13 and 14 (shown on
pages 13 & 14). The digital controller interfaces with the system controller and provides protection and diagnostics for compressor operation.
Service: See Troubleshooting Chart in Paragraph 7.2 on page 45 for identication of
alarm codes. Use only factory-authorized replacement parts.
FIGURE 13 - Optional
DH Circuit (Option
RPLE Low Enthalpy
Reheat Pump or
Option RPHE Low
Enthalpy Reheat Pump
Condenser Coil
Circuit A
Modulating
Compressor
(Optinal DH Circuit)
DH
Coil
Solenoid
Valve
View from Compressor and
DH
Coil
Condenser Section
Circuit DH
Condenser Coil
Circuit B
Model JDHA 060, 090, 120, and 150 (Cabinet 1)
Model JDHA 180, 210, and 240 (Cabinet 2)
Equalizer
Tube
View from Cooling Cabinet Door
(Evaporator Coil Side)
TXV Valve
Filter
Drier
Form O-Y P/N 273647R5, Page 13
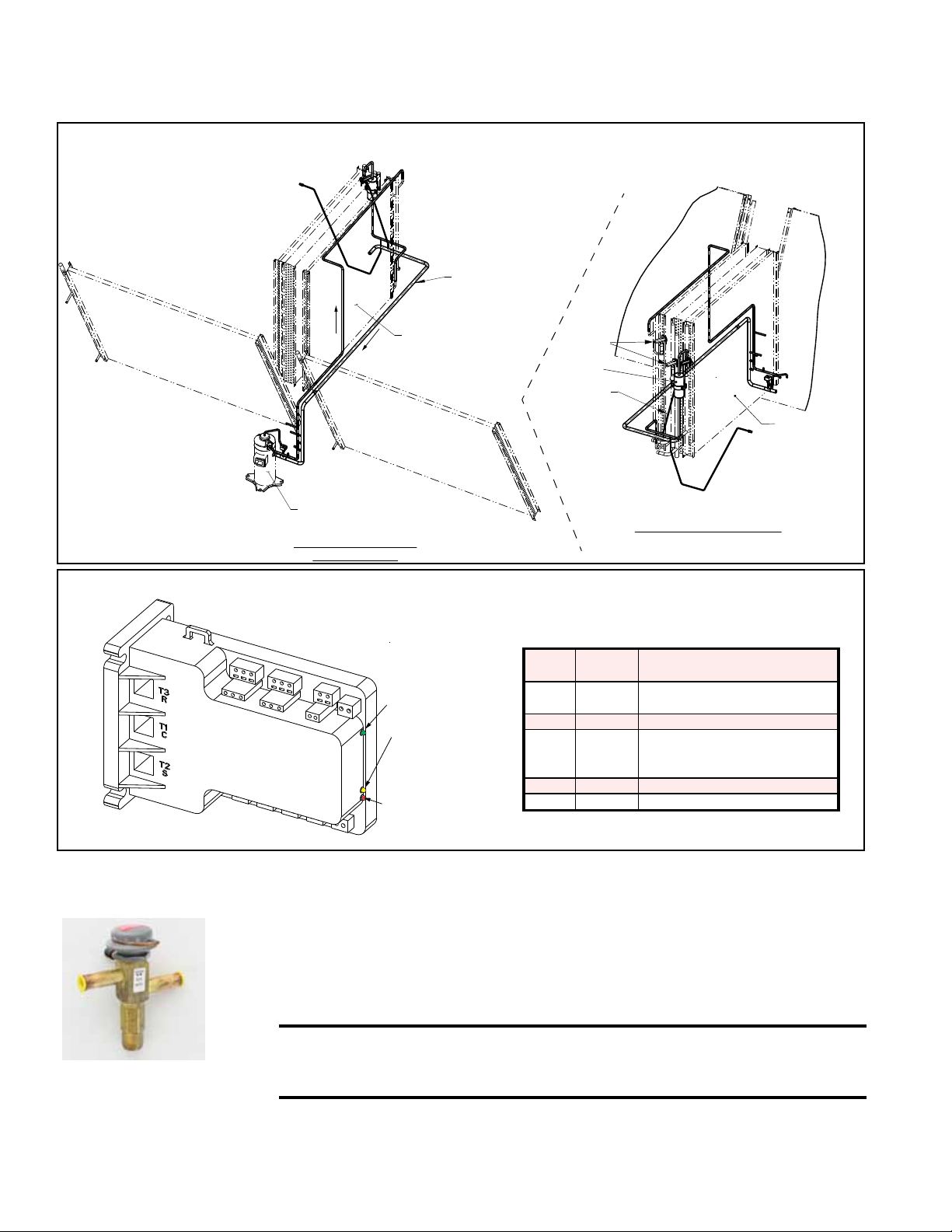
3.0 Maintenance and Service Procedures - Unit & Cooling (cont'd)
3.5 Coils and Related Components (cont'd)
Optional Modulating Reheat (cont'd)
FIGURE 14 - Optional
DH Circuit (Option
RPLE High Enthalpy
Reheat Pump or
Option RPHE Low
Enthalpy Reheat Pump
Model JDHA 300 & 360 (Cabinet 3)
Circuit A & B
Condenser Coil
Circuit A
Modulating
Compressor
View from Compressor and
Condenser Section
Evaporator Coil
with Intertwined
Circuits A & B
Condenser Coil
Circuit B
TXV Valves
Filter Drier
Equilizer Tube
View from Cooling Cabinet Door
FIGURE 15 - Digital Controller for DH Circuit Compressor, P/N 266067
Compressor Digital
Modulating Operation
Optional Hot Gas
Bypass Valve
(Option AUC8)
T6
T4
T2
T5
T3
P6
T1
P5
Controller for
A1
A2
L1
LED
Color
Power Light
24
COM
Alarm Light
(Red LED) - See
Paragraph 7.2
shown on page 45.
(Green LED)
Compressor
Modulating
Solenoid Valve
Energized Light
(Yellow LED)
P4
P2
P3
P1
L2
M1
24
VAC
C4
C2
C3
C1
M2
U1
U2
V1
V2
Green Solid
Green Flashing Anti-short cycle timer is active
Yellow Solid
Red Not lit No abnormal operation alerts
Red Flashing See Paragraph 7.2 (page 45).
Function: The hot gas bypass valve allows some of the refrigerant gas from the suction line to be re-routed directly to the evaporator coil providing for expanded compressor modulation at low outside air temperatures. Hot gas bypass is only on the
non-modulating compressor circuit (Circuit B). See FIGURE 16 on page 15.
Service: To check the hot gas bypass valve setting, connect a pressure gauge to the
suction line and block the entering air to the evaporator coil. Suction pressure will
drop, and the hot gas bypass valve should begin to open at a approximately 115 psi
and will be fully open at 95 psi. When the valve begins to open it will be hot to the
touch (see caution below).
LED
State
Power (24VAC present at
power terminals)
Unloader (Solenoid valve
is energized; compressor
capacity is 0.)
Evaporator Coil
(Evaporator Coil Side)
Indicates
Hot Gas Bypass
Valve
Form O-Y, PN 273647R5, Page 14
CAUTION: Touching the operating hot gas bypass valve can cause
a burn. Use caution when checking and adjusting the valve. See
Hazard Levels, page 2.
If a hot gas bypass valve needs to be replaced, use only a factory-authorized
replacement for R-410A refrigerant. All refrigerant service should be done by a
qualied R-410A service technician.
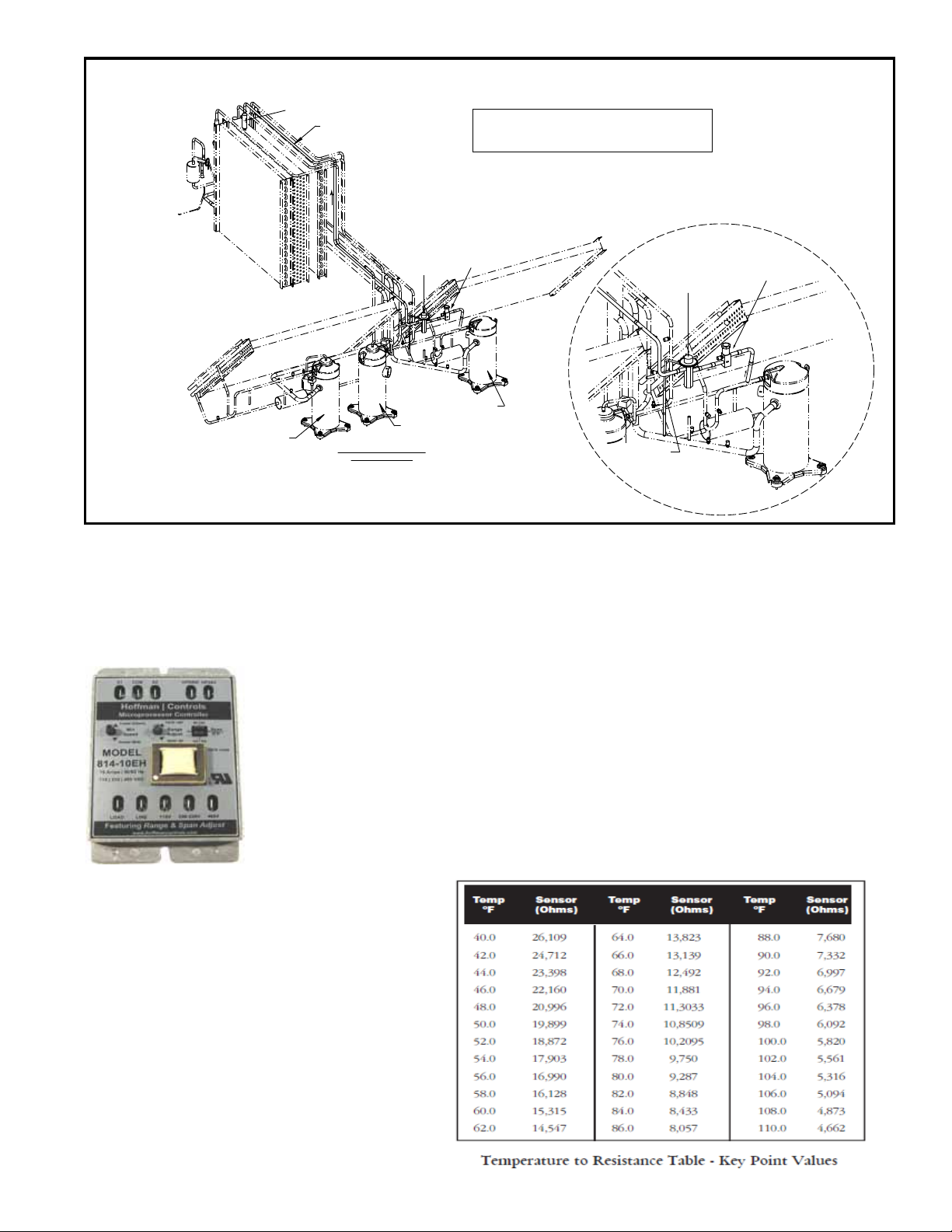
FIGURE 16 - Cooling Circuit B with Optional Bypass Valve (Option AUC8)
Hot Gas Bypass Check Valve at the Evaporator Coil
Circuit B with Optional Hot Gas Bypass
Model JDHA 120 and 150 (Cabinet 1) with Option AUC8
Model JDHA 180, 210, and 240 (Cabinet 2) with Option AUC8
Model JDHA 300 and 360 (Cabinet 3) with Option AUC8
Modulating
Compressor
(Circuit A)
Low Ambient Control,
Option BE8
Option BE Pressure
Controller with Fan
Option CUF3,
P/N 261041
Shutoff
Valve
Compressor
(Circuit B)
Condenser Coil
Circuit B
Equalizer
Tube
Hot Gas
Bypass Valve
Shutoff
Valve
Condenser
Coil - Circuit B
Condenser Coil
Circuit A
Hot Gas
Bypass Valve
Compressor
(Optional Circuit DH)
View from Compressor and
Condenser Section
If equipped with low ambient control, cooling is allowed to operate with an outside air tempera-
ture as low as 35°F (1.7°C).
Low Ambient Control for standard condenser fans (Option BE8
with Fan Option CUF3)
The electronic head pressure control modulates condenser fan motor speed in
low temperatures, varying the air volume through the condenser to regulate head
pressure. This model’s dual sensor input allows for the control of one or two
independent refrigerant circuits sharing the same fan motor(s). Only open, drip
proof, PSC or Shaded Pole motors are applicable for motor speed regulation. The
Controller monitors the liquid line temperature(degrees of excessive sub-cooling)
which is directly proportional to the head pressure. Speed modulation begins at 80°F
liquid line and proportionally reduces the fan to minimum speed once the liquid line
temperature reaches 50°F. Motor is turned off at liquid temperatures below or equal to
50°F. At 53°F the fan restarts at full speed; then modulates to minimum speed. When
the liquid temperature is 50°F and below the condenser fan motor will cycle between
minimum RPM and off to maintain proper condenser temperature (head pressure).
The above describes a 30ºF span (80ºF to 50ºF) function; a 25ºF span is also
available. The 25ºF span is recommended for High Efciency systems; 30ºF span for
typical systems. Variable condenser airow is modulated from full to minimum speed
over the selected span.
Temperature to
Resistance Table
Use Temperature
to Resistance table
shown on right to
verify proper sensor
operation.
Form O-Y P/N 273647R5, Page 15
 Loading...
Loading...