Page 1

User’s Manual
QFN Mounting Manual
All information contained in these materials, including products and product specifications,
represents information on the product at the time of publication and is subject to change by
Renesas Electronics Corp. without notice. Please review the latest information published by
Renesas Electronics Corp. through various means, including the Renesas Electronics Corp.
website (http://www.renesas.com).
www.renesas.com
Rev.1.50 Mar2015
Page 2

Notice
1. Descriptions of circuits, software and other related information in this document are provided only to illustrate the operation of
semiconductor products and application examples. You are fully responsible for the incorporation of these circuits, software,
and information in the design of your equipment. Renesas Electronics assumes no responsibility for any losses incurred by you
or third parties arising from the use of these circuits, software, or information.
2. Renesas Electronics has used reasonable care in preparing the information included in this document, but Renesas Electronics
does not warrant that such information is error free. Renesas Electronics assumes no liability whatsoever for any damages
incurred by you resulting from errors in or omissions from the information included herein.
3. Renesas Electronics does not assume any liability for infringement of patents, copyrights, or other intellectual property rights of
third parties by or arising from the use of Renesas Electronics products or technical information described in this document. No
license, express, implied or otherwise, is granted hereby under any patents, copyrights or other intellectual property rights of
Renesas Electronics or others.
4. You should not alter, modify, copy, or otherwise misappropriate any Renesas Electronics product, whether in whole or in part.
Renesas Electronics assumes no responsibility for any losses incurred by you or third parties arising from such alteration,
modification, copy or otherwise misappropriation of Renesas Electronics product.
5. Renesas Electronics products are classified according to the following two quality grades: “Standard” and “High Quality”. The
recommended applications for each Renesas Electronics product depends on the product’s quality grade, as indicated below.
“Standard”: Computers; office equipment; communications equipment; test and measurement equipment; audio and visual
equipment; home electronic appliances; machine tools; personal electronic equipment; and industrial robots etc.
“High Quality”: Transportation equipment (automobiles, trains, ships, etc.); traffic control systems; anti-disaster systems; anti-
crime systems; and safety equipment etc.
Renesas Electronics products are neither intended nor authorized for use in products or systems that may pose a direct threat to
human life or bodily injury (artificial life support devices or systems, surgical implantations etc.), or may cause serious property
damages (nuclear reactor control systems, military equipment etc.). You must check the quality grade of each Renesas
Electronics product before using it in a particular application. You may not use any Renesas Electronics product for any
application for which it is not intended. Renesas Electronics shall not be in any way liable for any damages or losses incurred
by you or third parties arising from the use of any Renesas Electronics product for which the product is not intended by Renesas
Electronics.
6. You should use the Renesas Electronics products described in this document within the range specified by Renesas Electronics,
especially with respect to the maximum rating, operating supply voltage range, movement power voltage range, heat radiation
characteristics, installation and other product characteristics. Renesas Electronics shall have no liability for malfunctions or
damages arising out of the use of Renesas Electronics products beyond such specified ranges.
7. Although Renesas Electronics endeavors to improve the quality and reliability of its products, semiconductor products have
specific characteristics such as the occurrence of failure at a certain rate and malfunctions under certain use conditions. Further,
Renesas Electronics products are not subject to radiation resistance design. Please be sure to implement safety measures to
guard them against the possibility of physical injury, and injury or damage caused by fire in the event of the failure of a Renesas
Electronics product, such as safety design for hardware and software including but not limited to redundancy, fire control and
malfunction prevention, appropriate treatment for aging degradation or any other appropriate measures. Because the evaluation
of microcomputer software alone is very difficult, please evaluate the safety of the final products or systems manufactured by
you.
8. Please contact a Renesas Electronics sales office for details as to environmental matters such as the environmental compatibility
of each Renesas Electronics product. Please use Renesas Electronics products in compliance with all applicable laws and
regulations that regulate the inclusion or use of controlled substances, including without limitation, the EU RoHS Directive.
Renesas Electronics assumes no liability for damages or losses occurring as a result of your noncompliance with applicable laws
and regulations.
9. Renesas Electronics products and technology may not be used for or incorporated into any products or systems whose
manufacture, use, or sale is prohibited under any applicable domestic or foreign laws or regulations. You should not use
Renesas Electronics products or technology described in this document for any purpose relating to military applications or use
by the military, including but not limited to the development of weapons of mass destruction. When exporting the Renesas
Electronics products or technology described in this document, you should comply with the applicable export control laws and
regulations and follow the procedures required by such laws and regulations.
10. It is the responsibility of the buyer or distributor of Renesas Electronics products, who distributes, disposes of, or otherwise
places the product with a third party, to notify such third party in advance of the contents and conditions set forth in this
document, Renesas Electronics assumes no responsibility for any losses incurred by you or third parties as a result of
unauthorized use of Renesas Electronics products.
11. This document may not be reproduced or duplicated in any form, in whole or in part, without prior written consent of Renesas
Electronics.
12. Please contact a Renesas Electronics sales office if you have any questions regarding the information contained in this document
or Renesas Electronics products, or if you have any other inquiries.
(Note 1) “Renesas Electronics” as used in this document means Renesas Electronics Corporation and also includes its majority-
owned subsidiaries.
(Note 2) “Renesas Electronics product(s)” means any product developed or manufactured by or for Renesas Electronics.
(2012.4)
Page 3

QFN Mounting Manual
Table of Contents
1. The QFN Package ............................................................................................................................ 1
1.1 Punching Cut Type (anvil singulation) ..................................................................................................................... 1
1.2 Dicing Cut Type (SAW singulation) ......................................................................................................................... 2
1.3 Lead Surface Processing Specifications .................................................................................................................... 2
2. Mounting Pads ................................................................................................................................. 3
2.1 Pad Structure ............................................................................................................................................................. 3
2.2 Mounting Pad Design Parameters ............................................................................................................................. 4
2.3 Notes on Mounting Pad Design (punching cut type) ................................................................................................ 5
2.4 Mounting Pad Design Examples ............................................................................................................................... 5
3. Solder Paste Printing ........................................................................................................................ 6
3.1 Solder Paste ............................................................................................................................................................... 6
3.2 Stencils ...................................................................................................................................................................... 7
4. Package Placement ......................................................................................................................... 10
4.1 Board Mounting Placement Conditions .................................................................................................................. 10
5. Reflow Thermal Resistance ........................................................................................................... 12
5.1 Storage Prior to Opening Moisture-Proof Packing ................................................................................................. 12
5.2 Storage After Opening Moisture-Proof Packing ..................................................................................................... 12
5.3 Baking ..................................................................................................................................................................... 12
5.4 Number of Reflow Operations ................................................................................................................................ 13
5.5 Reflow Thermal Resistance .................................................................................................................................... 13
5.6 Soldering Temperature ............................................................................................................................................ 14
6. Cleaning ......................................................................................................................................... 15
7. Visual Inspection ........................................................................................................................... 16
7.1 Overview of the QFN Package Pin End Surface ..................................................................................................... 16
7.2 Visual Comparison of Air Reflow and Nitrogen Reflow Mounting ....................................................................... 17
8. On Board Mechanical Stress Test Results ..................................................................................... 18
9. On Board Reliability Test Results ................................................................................................. 19
9.1 Board Mounted Thermal Cycle Test Results (punching cut type, 6 × 6 mm, 0.4 mm pitch) ................................. 19
9.2 Board Mounted Thermal Cycle Test Results (dicing cut type, 5 × 5 mm, 0.5 mm pitch)...................................... 19
9.3 Board Mounted Thermal Cycle Test Results (dicing cut type, 7 × 7 mm, 0.5 mm pitch)...................................... 20
9.4 Board Mounted Thermal Cycle Test Results (dicing cut type: package shape dependency) ................................. 20
10. QFN Reworking (removal from the mounting board) ................................................................. 21
R50ZZ0005EJ0150 Rev. 1.50 Contents 1
Mar 25, 2015
Page 4
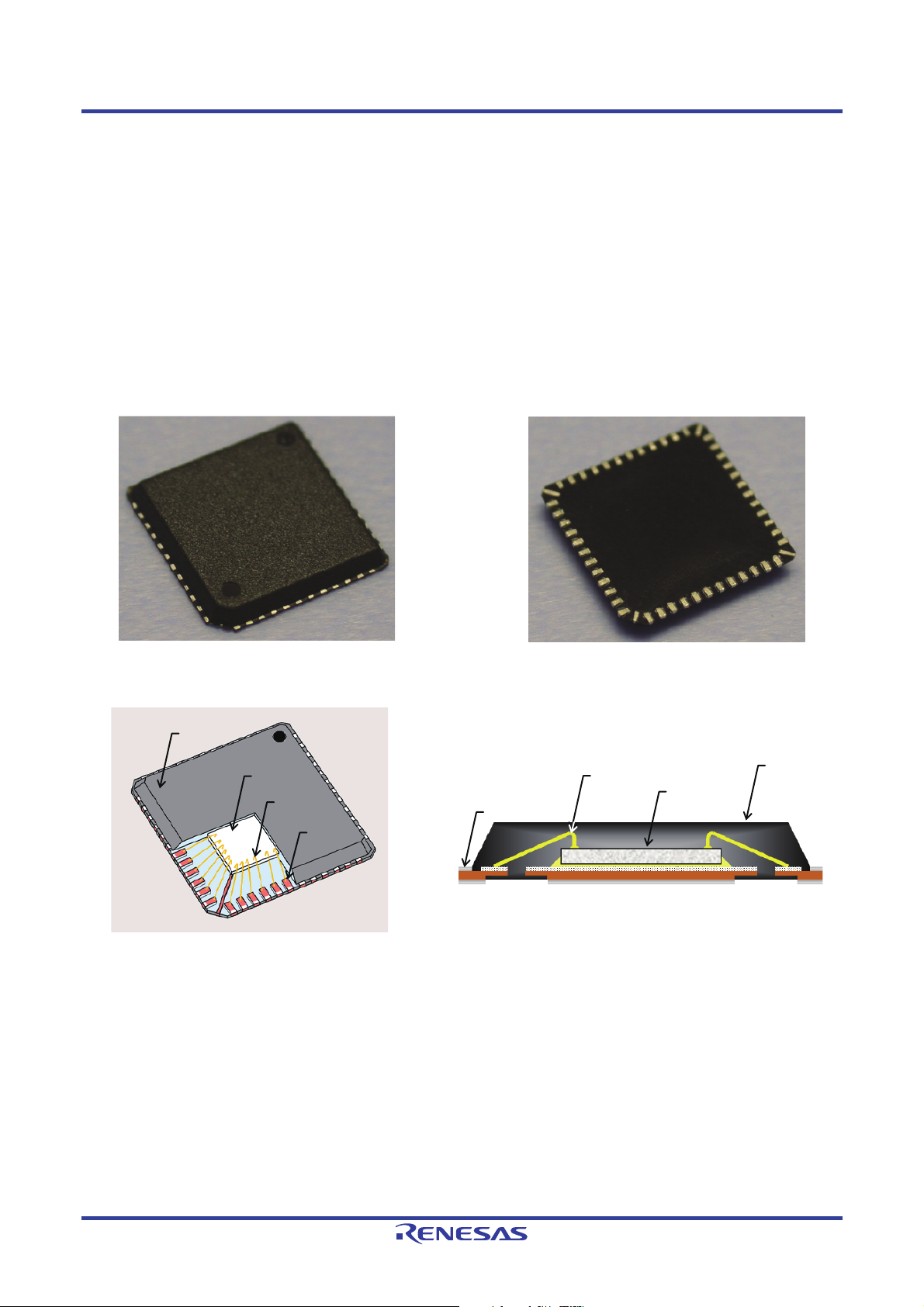
QFN Mounting Manual 1. The QFN Package
n
1. The QFN Package
The QFN (Quad Flat No-lead) package is a low-profile package with a leadless structure. It is appropriate for use in
portable and other equipment that requires miniaturization and reduced weight. QFN packages are classified by their
formation method into the punching cut and dicing cut types. The remainder of this section presents an overview of these
packages.
1.1 Punching Cut Type (anvil singulation)
This type of QFN package is characterized by an individually molded body with punch press excision. Since the external
leads of the package, in which each cavity is sealed with mold resin, are punched with a die, the leads can be made to
protrude for extremely short distances from the package periphery.
Figure 1.1 Package Top Side Figure 1.2 Package Underside
Mold
resin
Chip
Wire bonding
Lead
Figure 1.3 Basic Structure Figure 1.4 Cross-Section View
Wire bonding
Chip
Lead
Mold resi
R50ZZ0005EJ0150 Rev. 1.50 Page 1 of 21
Mar 25, 2015
Page 5

QFN Mounting Manual 1. The QFN Package
1.2 Dicing Cut Type (SAW singulation)
This type of QFN package is characterized by the package being formed by cutting with a rotating blade. Since multiple
packages sealed at the same time are cut apart with a dicing blade (rotating blade), the ends of the leads and the edge of
the package (cut surface) are coplanar.
Figure 1.5 Package Top Side Figure 1.6 Package Underside
Mold resin
Chip
Wire bonding
Chip
Wire bonding
Lead
Lead
Figure 1.7 Basic Structure Figure 1.8 Cross-Section View
1.3 Lead Surface Processing Specifications
See the Renesas web site for the lead surface processing specifications for each QFN package code.
http://www.renesas.com/products/package/information/ic_name_list/index.jsp
Mold resin
R50ZZ0005EJ0150 Rev. 1.50 Page 2 of 21
Mar 25, 2015
Page 6
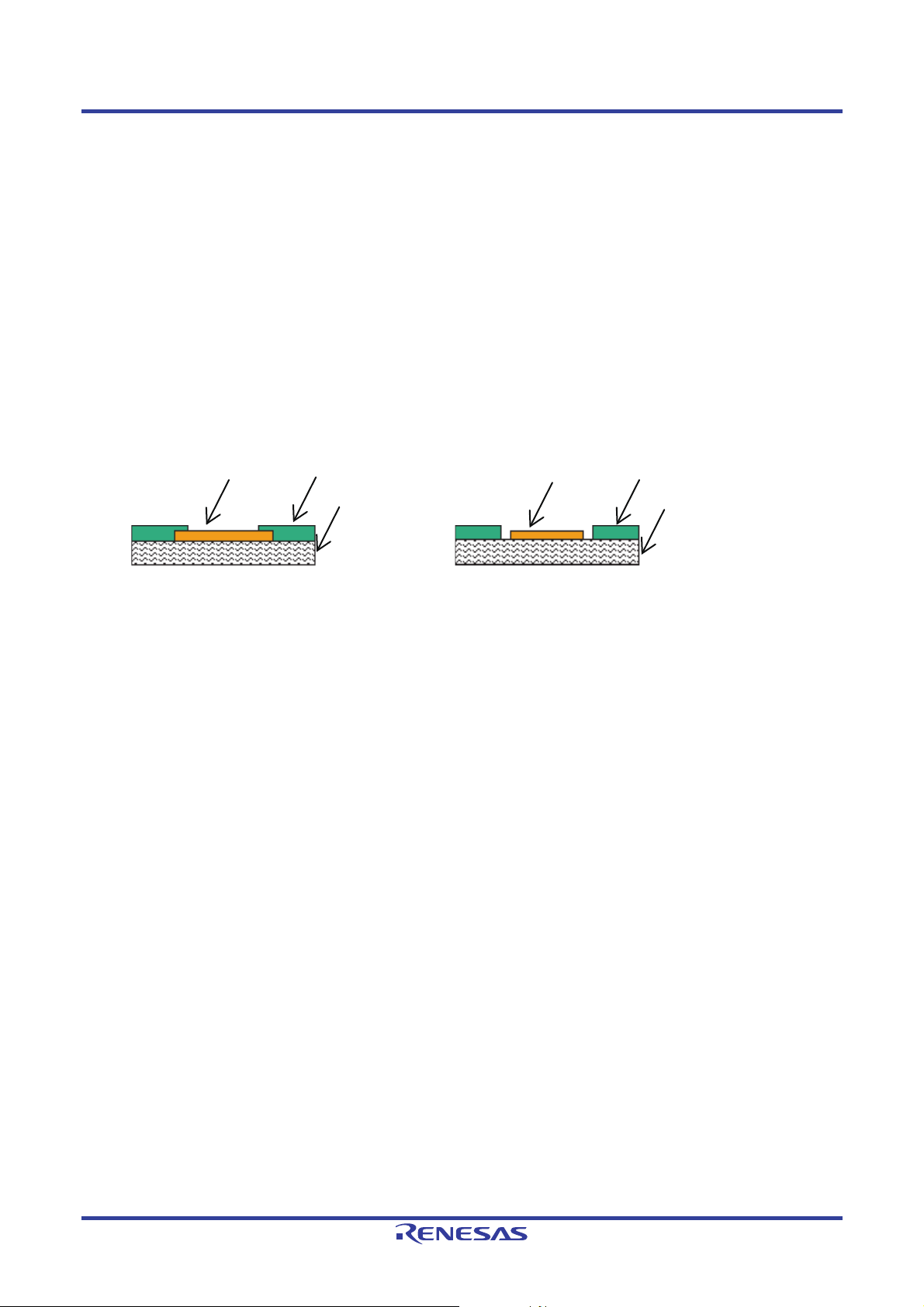
QFN Mounting Manual 2. Mounting Pads
2. Mounting Pads
2.1 Pad Structure
(1) NSMD Type
In this structure, the solder resist does not come over the edges of the mounting pads.
(2) SMD Type
In this structure, the solder resist comes over the edges of the mounting pads.
It is important to consider the characteristics of the lead morphology when designing printed wiring boards. Also, it is
important to be aware that even if the package code is identical, there may be subtle differences in pin dimensions
between individual parts.
Mounting pad
Solder resist
SMD structure
(Solder Masked Defined)
Printed wiring board
(Non Solder Masked Defined)
Figure 2.1 Pad Structures
Mounting pad
NSMD structure
Solder resist
Printed wiring board
R50ZZ0005EJ0150 Rev. 1.50 Page 3 of 21
Mar 25, 2015
Page 7
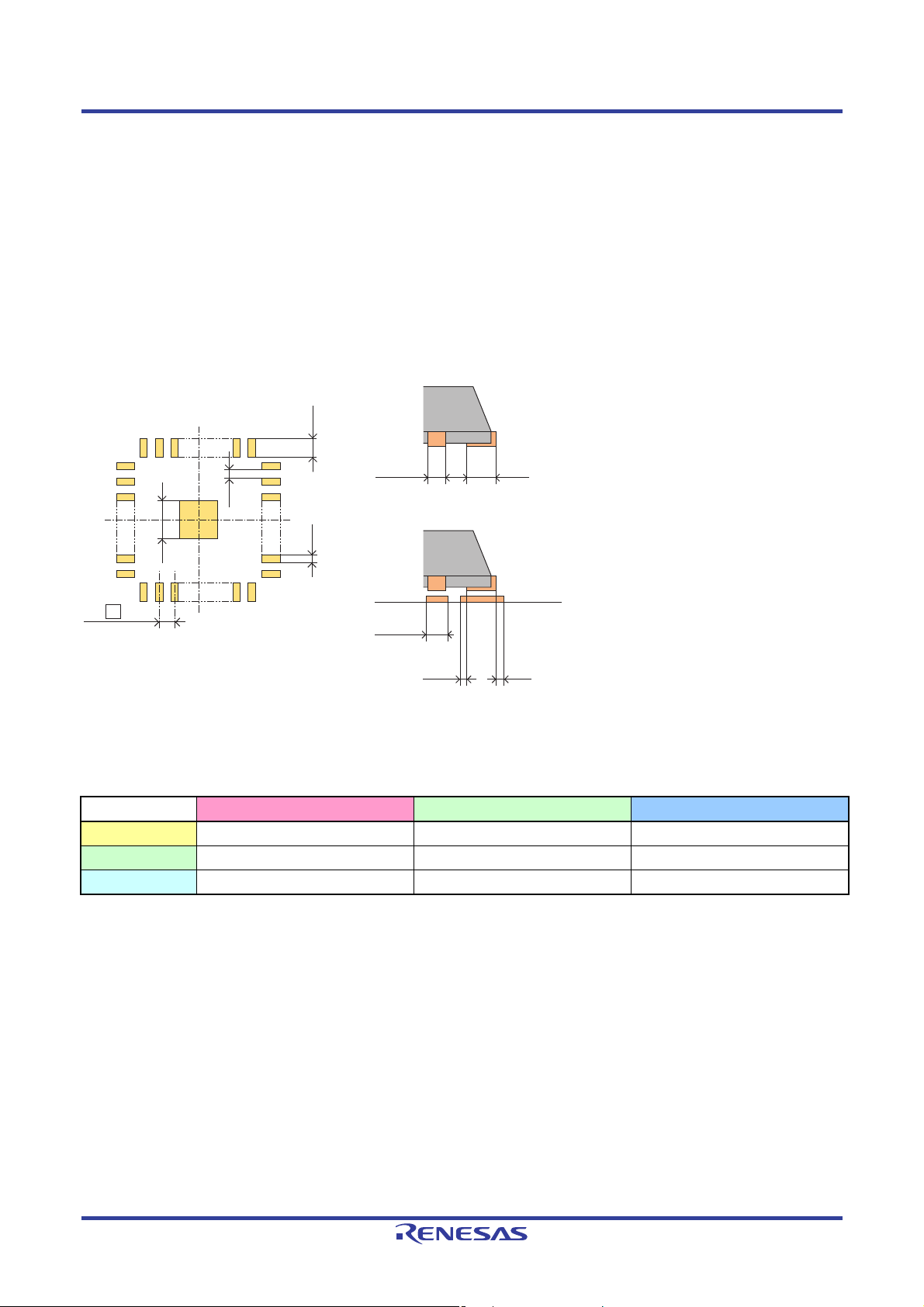
QFN Mounting Manual 2. Mounting Pads
2.2 Mounting Pad Design Parameters
The parameters that determine the mounting pad dimensions include the following.
Soldering strength (1)
Solder mask pattern precision and soldering visual inspectability (2)
Solder bridge tolerance ()
The way the margins for each dimensional area are determined depends on the user’s approach to pattern design and the
application the equipment will be used in. We recommend that users design QFN printed wiring board mounting pads
based on the approach shown below, which is similar to that for QFP packages.
L2b2
b
Lp
Lp = Pin flat section length
b = Pin width
γ
E2
e
b2
β
β
1
2
L2 ≥ Lp + β
b ≤ b2 ≤ e − γ (b2: mounting pad width)
1
+ β2 (L2: mounting pad length)
Figure 2.2 Mounting Pad Design Parameters
Table 2.1 Design Reference Values Unit: mm
e 0.80 0.50 0.40
1 0 to 0.30 0 to 0.30 0 to 0.20
2 0 to 0.30 0 to 0.30 0 to 0.20
0.10 to 0.30 0.10 to 0.30 0.10 to 0.20
Notes: 1. The mounting pad pitch must be the linear pin spacing (pin pitch) for the package being mounted.
2. We do not recommend mounting, on the wiring board, the lead that is exposed at the package corner (die pad
hanging lead) for the punching cut type QFN package.
3. If required, we recommend that users analyze the package end land 1 dimension taking contact with corner
exposed leads into account.
R50ZZ0005EJ0150 Rev. 1.50 Page 4 of 21
Mar 25, 2015
Page 8
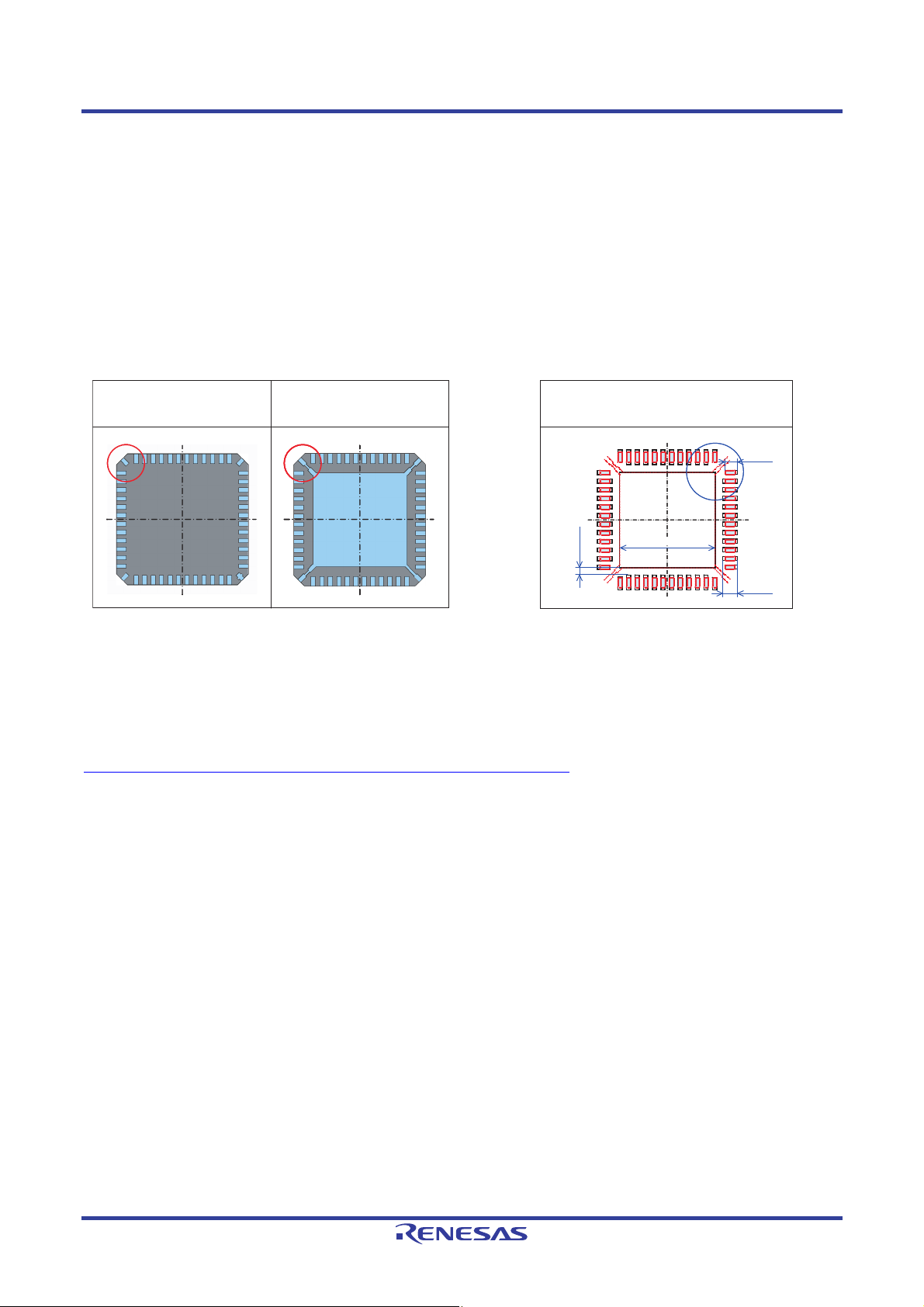
QFN Mounting Manual 2. Mounting Pads
2.3 Notes on Mounting Pad Design (punching cut type)
In the punching cut type QFN package, part, or all, of the lead (hanging lead) that supports the die pad in the corner, is
exposed at the package end. (We do not recommend soldering to this section.)
Since the characteristics of the semiconductor device itself may be affected if electrical contact is made to the corner pin,
we recommend that users consider mounting pad design that takes contact with the corner pin section into account.
A design example for the P-VQFN48-6x6-0.4 package is presented below.
Contact with the die pad hanging lead is avoided by designing 1 to be shorter than that for other pads.
No Exposed Pad Exposed Pad
Die pad hanging lead Die pad hanging lead
Exposed Pad
0.65
>γ
Die pad
Figure 2.3 Die Pad Hanging Lead Example Figure 2.4 Design Example
when a Die Pad is Present
2.4 Mounting Pad Design Examples
See the Renesas web site for mounting pad design examples for each QFN package code.
http://www.renesas.com/products/package/information/ic_name_list/index.jsp
0.85
R50ZZ0005EJ0150 Rev. 1.50 Page 5 of 21
Mar 25, 2015
Page 9
QFN Mounting Manual 3. Solder Paste Printing
3. Solder Paste Printing
3.1 Solder Paste
The main components of solder paste are solder powder and flux. The particular solder paste used should be chosen
based on the usage conditions adopted.
(1) Solder Powder
Due to the desire to eliminate lead from manufacturing processes due to environment considerations, a variety of leadfree metal compositions (mainly Sn-Ag-Cu family compositions) are widely used. The different lead-free alloys are used
according to the type of application and the soldering method used. Furthermore, there is a range of particle sizes in these
powders, and the particle size affects the printability and other characteristics of the paste. Good results can be obtained,
especially for fine-pitch (0.5 mm and under) mounting, if a fine powder with particle diameter of 40 µm or smaller and
also with a narrow distribution of particle sizes is used. Note, however, that for finer powders, there are concerns that
solder balls due to surface oxidation and adverse influence on the wettability may occur. Therefore, extra care is required
when handling solder paste that uses solder powders such as those discussed above.
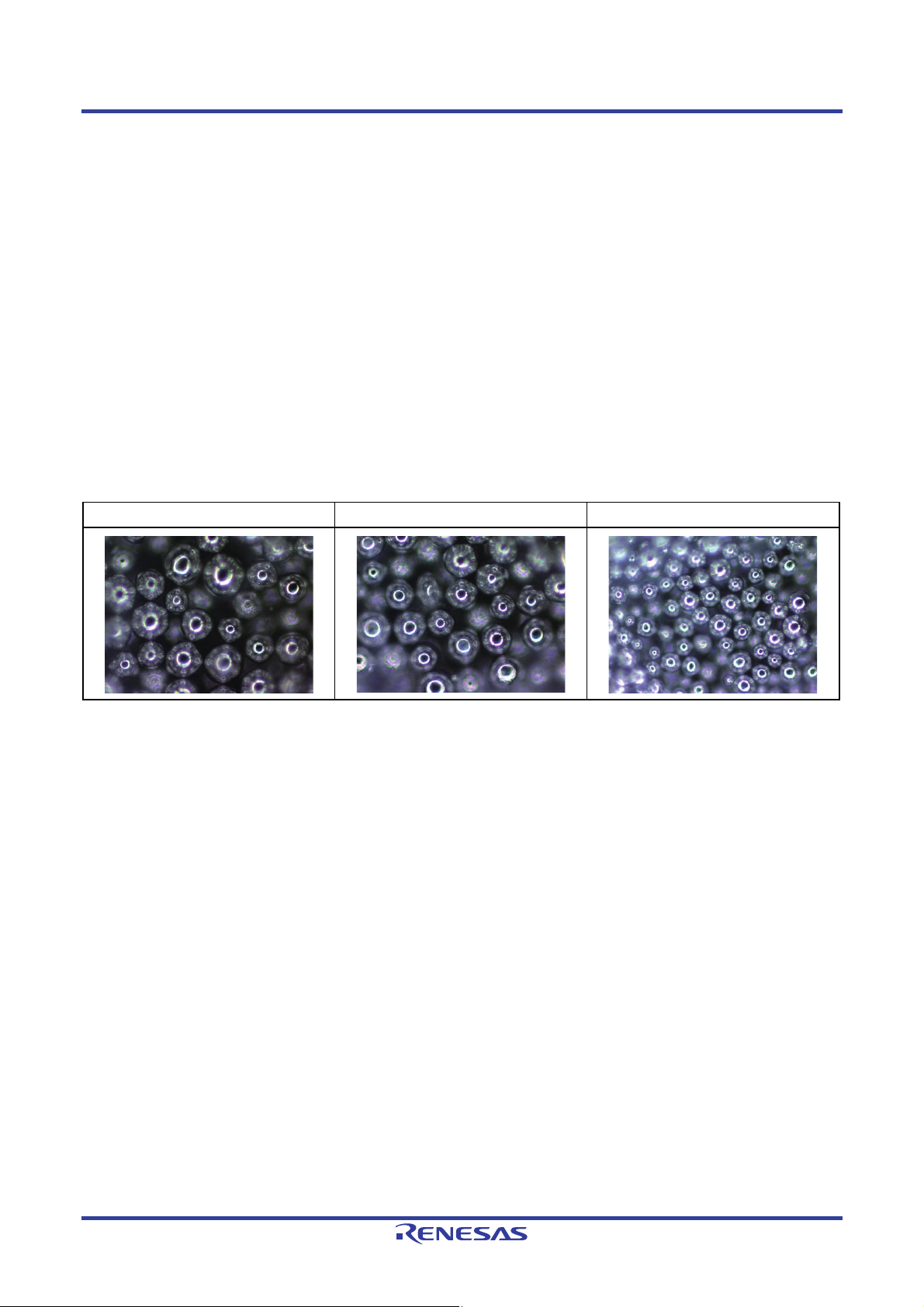
Type 3: 0.045 mm to 0.020 mm Type 4: 0.038 mm to 0.020 mm Type 5: 0.025 mm to 0.010 mm
Figure 3.1 Visual Appearance of Solder Powders
(2) Flux
Flux improves solderability in the soldering process in three ways: (1) it excludes oxides from components and the
pattern surface, (2) it prevents re-oxidation during soldering, and (3) it reduces the surface tension of the melted solder.
Flux includes four components that assist in soldering: tackifiers, thixotropic agents, solvents, and activators. These are
used for the following purposes.
Tackifier resins: Component mountability, metal cleaning, reoxidation prevention
Thixotropic agents: Preventing separation of solder powder and flux, and droop prevention
Activating agents: Metal cleaning
Solvents: Forming the paste
There are three main types of flux: rosin fluxes, alloy resin fluxes, and water soluble fluxes. In addition, rosin fluxes are
classified into three types by their degree of activation: R (rosin flux), RMA (weakly activated flux), and RA (activated
flux). Table 3.1 lists their features.
R50ZZ0005EJ0150 Rev. 1.50 Page 6 of 21
Mar 25, 2015
Page 10

QFN Mounting Manual 3. Solder Paste Printing
Table 3.1 Flux Types and Features
Flux Type Features
Type R, ROL Type
(non-activated Rosin, Rosin Low activity levels)
Type RMA, ROM Type
(Rosin Mildly Activated, Rosin Moderate activity
levels)
Type RA, ROH Type
(Rosin Activated, Rosin High activity levels)
These are non-activated fluxes and are noncorrosive.
These are mildly activated fluxes and are noncorrosive. They
have superior solderability compared to the R type fluxes.
These are strongly activated fluxes. While they have superior
solderability compared to the R and RMA type fluxes, they are
strongly corrosive.
3.2 Stencils
In the stencil design, both the pin and the die pad sections must be optimized. The user must design the stencil according
to the conditions under which it will be used.
(1) Pin Section
The pin sections are 100% of the mounting pad area. Also, they must be reduced by a factor of 0.9 in the width direction
to prevent bridging and the amount of paste applied must be about 90% of the mounting pad area.
(2) Die Pad Exposed Sections
When designing a stencil for an exposed die pad type QFN package, the die pad section aperture design should be about
60% of the die pad. This is because if the aperture design was 100%, the package placement load would forcibly spread
the solder and the mountability would be adversely affected. Below, we show evaluations for amount of forced spreading
due to the load when placing packages for 100% printing and for 60% printing (divided). There is concern that, with
100% printing, the solder may be forcibly spread by the placement load and shorting to pins occur. We recommend that
the user verify the results of actual placement evaluations.
Also, since the area of the die pad section is large compared to the pin area, the solder will have a large wetting force, and
the amount of solder applied to this area may adversely influence the mounting height after reflow.
100% Printing 60% Printing (divided)
Printing
Completed
Mounting
Completed
Note: Stencil thickness: 0.1 mm
Figure 3.2 Visual Inspection Photographs of Solder Spreading at Package Placement
(Model package test using glass plates)
R50ZZ0005EJ0150 Rev. 1.50 Page 7 of 21
Mar 25, 2015
Page 11

QFN Mounting Manual 3. Solder Paste Printing
The figure below shows a sample stencil design for a QFN package.
Z: Pin section (outer)
E2
b2
G
Z
e
G: Pin section (outer)
b2: Pin section aperture width
E2: Die pad (one divided die pad area)
Figure 3.3 Stencil Design Example (when the die pad is divided into 4 sections)
Table 3.2 Stencil Design Example (punching cut type) Unit: mm
Component Stencil
External
Number
Size
of Pins
z n1 n2 e (b Lp) E1 Z G b2
4 20 5 0.5 (0.22 0.40) — 4.60 3.00 0.25 — — — 0.10
7 48 12 0.5 (0.25 0.35) — 7.60 6.10 — — —
10 64 16 0.5 (0.22 0.60) — 10.60 8.60 — — —
6 48 12 0.4 (0.18 0.45) 4.2 4.2 6.60 4.90 0.20 2 2 1.6 0.33 0.10
8 64 16 0.4 (0.18 0.60) — 8.60 6.60 — — —
Pins/Side
Pin Pitch
(pin size)
Die Pad
Exposure
(100% aperture for the mounting
Pin Section
board Cu pad area)
(60% aperture for the mounting
Number of
Divisions
Die Pad
board Cu pad area)
Size (E2) Gap
Thick-
ness
Table 3.3 Stencil Design Example (dicing cut type: 0.5 mm pitch) Unit: mm
Component Stencil
External
Number
Size
of Pins
z n1 n2 e (b Lp) E1 Z G b2
4 24 6 0.5
5 32 8 3.5 3.5 5.31 3.93 2 2 1.25 0.33
6 40 10 4.5 4.5 6.31 4.93 3 3 1.12 0.28
7 48 12 5.5 5.5 7.31 5.93 3 3 1.38 0.34
8 56 14 6.5 6.5 8.31 6.93 4 4 1.22 0.32
9 64 16 7.5 7.5 9.31 7.93 5 5 1.14 0.27
10 72 18 8.5 8.5 10.31 8.93 5 5 1.29 0.31
Pins/Side Pin Pitch
(pin size)
(0.25 0.40)
Die Pad
Exposure
2.4 2.4 4.31 2.93 0.25
(90% aperture for the mounting
Pin Section
board Cu pad area)
Corner
section:
C0.10
(60% aperture for the mounting
Number of
Divisions
2 2 0.90 0.20 0.12
Die Pad
board Cu pad area)
Size (E2) Gap
Thick-
ness
R50ZZ0005EJ0150 Rev. 1.50 Page 8 of 21
Mar 25, 2015
Page 12

QFN Mounting Manual 3. Solder Paste Printing
Table 3.4 Stencil Design Example (dicing cut type: 0.4 mm pitch) Unit: mm
Component Stencil
External
Number
Size
of Pins
z n1 n2 e (b Lp) E1 Z G b2
4 24 6 0.4
5 32 8 3.5 3.5 5.31 3.94 2 2 1.25 0.33
6 40 10 4.5 4.5 6.31 4.94 3 3 1.12 0.28
7 48 12 5.5 5.5 7.31 5.94 3 3 1.38 0.34
8 56 14 6.5 6.5 8.31 6.94 4 4 1.22 0.32
9 72 18 7.5 7.5 9.31 7.94 5 5 1.14 0.27
10 80 20 8.5 8.5 10.31 8.94 5 5 1.29 0.31
Pins/Side
Pin Pitch
(pin size)
(0.20 0.40)
Die Pad
Exposure
2.4 2.4 4.31 2.94 0.20
(100% aperture for the mounting
Pin Section
board Cu pad area)
Corner
section:
C0.10
(60% aperture for the mounting
Number of
Divisions
2 2 0.90 0.20 0.10
Die Pad
board Cu pad area)
Size (E2) Gap
Thick-
ness
R50ZZ0005EJ0150 Rev. 1.50 Page 9 of 21
Mar 25, 2015
Page 13

QFN Mounting Manual 4. Package Placement
4. Package Placement
4.1 Board Mounting Placement Conditions
Since the area of the resin-sealed surface and the area of the solder connection pin surface are essentially identical in
QFN packages, there are cases where the solder paste is forcibly spread causing problems when placing a package on the
mounting board. In particular, this phenomenon becomes significant with QFN packages that are 5 5 mm and smaller.
The user must look into the load used during package placement, the distance the package is pressed into the solder, and
other aspects, and determine appropriate mounting conditions. The tables below list results obtained in-house here at
Renesas.
(1) Die pad connection present (100% solder printing of the die pad area)
Package Placement
P-WQFN20-4x4-0.5
(dicing cut type)
Speed
83.3 mm/s 0.2 mm 0.6N OK OK
Press-in
Distance
0.4 mm 2.2N NG NG
1.0 mm 2.5N NG NG
Spring Load
(Placement
Load)
Solder Paste A
(Viscosity:
type 4)
Note: Stencil thickness: 0.1 mm
(2) Die pad connection present (60% solder printing of the die pad area, divided into 4 sections)
Package Placement
P-WQFN20-4x4-0.5
(dicing cut type)
Speed
83.3 mm/s 0.2 mm 0.6N OK OK
Press-in
Distance
0.4 mm 2.2N OK NG
1.0 mm 2.5N OK NG
Placement Conditions Overview
Spring load
(placement
load)
Spring Load
(Placement
Placement
speed
Load)
Solder Paste A
(Viscosity:
type 4)
Note: Stencil thickness: 0.1 mm
Solder Paste B
(Viscosity:
type 5)
Solder Paste B
(Viscosity:
type 5)
Press-in
distance
*: Evaluation standard
OK: No paste bridges occur at package placement
NG: Paste bridges occur at package placement
Figure 4.1 Placement Conditions
From the above, we recommend the following to suppress paste spreading at package placement.
1. Minimize the placement press-in distance.
2. Select a nozzle with a small spring load.
3. Increase the solder paste viscosity.
These are effective at achieving good results.
R50ZZ0005EJ0150 Rev. 1.50 Page 10 of 21
Mar 25, 2015
Page 14

QFN Mounting Manual 4. Package Placement
r
We recommend that the user look into the package placement conditions used based on the paste materials and package
placement equipment used.
14
12
10
8
6
Solder Area (mm²)
4
2
6
5
Type5
Printing area
100%
Type4
4
3
2
Printing area
1
60%*
Spring load
(placement load)
1
0
00.20.4
Placement Press-in Distance (mm)
Note: 1. Type 4: Solder particle diamete
(Type 4 > Type 5)
Figure 4.2 Relationship Between Placement Load and Solder Spreading
Placement Load (Spring load) (N)
R50ZZ0005EJ0150 Rev. 1.50 Page 11 of 21
Mar 25, 2015
Page 15

QFN Mounting Manual 5. Reflow Thermal Resistance
5. Reflow Thermal Resistance
5.1 Storage Prior to Opening Moisture-Proof Packing
Before opening moisture-proof packing, semiconductor devices must be stored at a temperature in the range 5 to 35°C
and at a humidity under 85%RH. Note, however, that individual products may have product-specific stipulations. Thus
all products must be stored only after verifying the conditions stipulated in the delivery specifications document.
5.2 Storage After Opening Moisture-Proof Packing
After opening moisture-proof packing, semiconductor devices must be stored under the following conditions to prevent
moisture absorption by the packages.
Table 5.1 Sample Storage Conditions
Item Condition Remarks
Temperature 5 to 30°C
Humidity Under 70% RH
Time 168 hours The time from the point the packaging is opened until mounting
the last device has completed.
Note, however, that individual products may have product-specific stipulations. Thus all products must be stored only
after verifying the conditions stipulated in the delivery specifications documents.
5.3 Baking
Before soldering, perform the baking operation described below.
(1) Cases When Baking Is Required
If the 30% spot on the indicator card packed with the products has changed to pink when the moisture-proof packing
was opened.
If the stipulated storage condition after opening the moisture-proof packing were exceeded.
(2) Baking Conditions
Use the following conditions for baking. Note, however, that some products have individual stipulations, and the baking
(drying) processing should be performed after verifying the conditions stipulated in the delivery specifications.
During baking, use trays or other containers with adequate thermal resistance. Note that trays that are heat proof will be
marker “Heat Proof” or with their thermal resistance temperature. Check this marking before performing this processing.
Table 5.2 Sample Baking Conditions
Baking Temperature Baking Time Repeated Baking
125°C 4 to 24 hours No more than 96 hours total
10 to 72 hours No more than 96 hours total
R50ZZ0005EJ0150 Rev. 1.50 Page 12 of 21
Mar 25, 2015
Page 16

QFN Mounting Manual 5. Reflow Thermal Resistance
5.4 Number of Reflow Operations
The number of reflow operations should be limited to three or fewer. Note, however, that some products have individual
stipulations, and the content of the delivery specifications for the products used should be verified. Furthermore, users
should verify that multiple reflow operations will not result in other problems when designing the mounting process.
After products have been mounted on dual-sided boards or by repairs, when heating for soldering for reflow or a repeated
reflow, problems such as solder shorting or solder peeling may occur. The following points should be observed when
setting mounting conditions.
If moisture has been absorbed, the warping characteristics of QFN package products and the wiring board itself may
change.
The user should manage moisture absorption during reflow operations.
The use of flux and optimization of the reflow atmosphere should be considered to assure solder coverage when
remelting solder.
The mounting process must be optimized so that the temperatures of the package electrical contacts do not greatly exceed
the melting point of the solder.
Furthermore, users should look into setting the temperature to be at or below the melting point of the solder.
5.5 Reflow Thermal Resistance
Although QFN package products have a thermal resistance of 260°C (maximum) to support lead-free solders as
stipulated in JEDEC J-STD 020D, individual products may have a different thermal resistance temperature. Contact your
Renesas sales representative for details on individual products.
260°C Max
30s Max
6°C/s Max3°C/s Max
Time (seconds)
150°C
Package Surface Temperature (°C)
255°C
217°C
200°C
60 to 120 s
60 to 150 s
Figure 5.1 Reflow thermal Resistance Profile
R50ZZ0005EJ0150 Rev. 1.50 Page 13 of 21
Mar 25, 2015
Page 17

QFN Mounting Manual 5. Reflow Thermal Resistance
5.6 Soldering Temperature
The reflow soldering temperature must be managed so that the package body temperature remains under its heat
resistance temperature. The ideal temperature conditions are those such that the package contacts and pins enter the
recommended temperature range for the solder paste used. Since the preheating temperature and time and the main
soldering temperature and time will differ depending on the composition of the solder used and the characteristics of the
flux, these must be verified in advance.
Also note that the soldering atmosphere (nitrogen atmosphere) is an item that has a large effect and influence on the
soldering time and temperature and must be taken into consideration when analyzing the process condition settings.
Up to the package heat resistance temperature
(surface temperature) (Renesas)
Recommended temperature range
for the solder paste (soldering position
temperature)
(Solder manufacturer)
Temperature (°C)
Preheating Main heating
Time (seconds)
Above the fusing temperature for
the solder and the package’s ball
metal or lead plating metal.
Figure 5.2 Soldering Temperature
260
240
220
)
200
180
°C
160
140
120
100
80
Temperature (
60
40
20
0
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 220
Peak temperature, Tpk: 240.5°C
Over 220°C:
40.0 seconds
160 to 180°C: 83.0 seconds
pkg
lead
board
Time (seconds)
Figure 5.3 Sample Reflow Temperature Profile for Sn-Ag-Cu Solder Paste (P-WQFN32-5x5-0.5)
R50ZZ0005EJ0150 Rev. 1.50 Page 14 of 21
Mar 25, 2015
Page 18

QFN Mounting Manual 6. Cleaning
6. Cleaning
Previously, a wide variety of cleaning agents have been used in the flux cleaning performed after components are
mounted on the printed wiring board. However there have been increasing desires for selective use of cleaning agents in
consideration of environmental pollution problems, and for support of mounting without a cleaning step. Since the
standoff height of mounted QFN packages is comparatively low, it is difficult to remove flux residues that remain
between the QFN package and the mounting board. We recommend that users look into the types of solder paste that due
not require cleaning, or consulting with the solder paste and cleaning agent manufacturers.
R50ZZ0005EJ0150 Rev. 1.50 Page 15 of 21
Mar 25, 2015
Page 19

QFN Mounting Manual 7. Visual Inspection
7. Visual Inspection
With the earlier lead type SMD packages, the solder defects that occurred included solder balls, wicking, solder not
connected, and shorting. These defects could be detected with either visual inspection or inspection using some sort of
optical system. QFN package soldering defects include solder not connected and shorts. However, since the solder
connections are made underneath the package, they cannot be detected with inspection methods that use an optical
system. Although shorting defects can be detected with transmission X-ray units, solder not connected defects cannot be
detected. There are now three-dimensional detection methods that have been developed for inspection of locations, such
as the areas under the packages, that cannot be seen visually. These include tomosynthesis methods and laminography
methods that use a scanning X-ray beam. Currently, the equipment listed in the table below is available commercially as
equipment for performing post-soldering visual inspections. However, there are products whose operation can be
influenced by exposure to X-rays, so adoption of these methods requires careful verification in advance.
Table 7.1 Visual Inspection Equipment
Inspection Method Details of the Inspection Method
Optical systems
X-ray methods
Integrated laser/sensor rotating scan method
Color highlight method
Combined laser and multi-camera method
Laser scanning method
Methods in which X-ray transmission images are converted to 3D data showing the
object’s actual shape
Methods in which X-ray slice images are converted to 3D data showing the object’s
actual shape
7.1 Overview of the QFN Package Pin End Surface
Since, like the QFP and other packages, the QFN pin end surface is created by cutting processing performed after pin
plating, QFN packages have a structure in which the pin material, without plating, is exposed. In particular, in dicing cut
type QFN packages, since there is no flow-around of plating material, the exposed surface of the pin material (Cu) is
large. The following shows the results of studying the wettability of these pin ends.
Punching Cut Type Dicing Cut Type
Pin End Surface Pin End Surface Package Back Surface
Pin End Visual
Appearance
Features of the
Machining
As is the case with QFP and
similar packages, the pin ends
are cut by punching (with a die).
The pin end surface (pin
material) is exposed and some
of the plating material flows
around the edges. These,
however, are not subject to this
management.
Figure 7.1 QFN Pin End Surface Overview
Dicing cut is performed by
cutting with a dicer (a rotating
blade).
The pin end surface (pin
material) is exposed.
Plated surface
Cu
R50ZZ0005EJ0150 Rev. 1.50 Page 16 of 21
Mar 25, 2015
Page 20

QFN Mounting Manual 7. Visual Inspection
7.2 Visual Comparison of Air Reflow and Nitrogen Reflow Mounting
The table below shows the results of evaluating the effects and influence of the reflow atmosphere. This shows that a
nitrogen atmosphere can be more effective than air for reflow soldering and also that we can see an effect on pin end
surface wetting by soldering the die pad. We recommend die pad soldering, which has an effect on pin end wetting, and
nitrogen atmosphere reflow soldering.
Preprocessing None 30°C / 70% RH 168h
Die Pad No Connection No Connection Connection
Air Reflow
Nitrogen
Reflow
Figure 7.2 Comparison of Effects and Influence of the Reflow Atmosphere
R50ZZ0005EJ0150 Rev. 1.50 Page 17 of 21
Mar 25, 2015
Page 21

QFN Mounting Manual 8. On Board Mechanical Stress Test Results
8. On Board Mechanical Stress Test Results
After mounting, solder may be peeled away by mechanical shock. The user should design products and manufacturing
processes based on thorough verification of stresses applied during manufacturing, such as when cutting boards apart, the
possibility of accidentally dropping boards, and the environment in which the product will be handled in the market.
Since they don’t have leads, QFN packages mounted on a printed wiring board cannot follow bending of the wiring
board, and we have identified cases when, due to their not being able to follow the wiring board, the packages crack
when extremely large bending is applied to the wiring board. We recommend that users look into board mounting layouts
that avoid mounting in sections to which large bending forces may be applied.
90
90°
Bending depth
Load
Evaluation method of maximum bending:
Load from back side center of board.
To measure depth when package crack
occurred.
Figure 8.1 Evaluation Method of Maximum
Figure 8.2 Package Crack
Bending
Table 8.1 The Evaluation Results of Maximum Bending (Reference)
Measurement Span for Bending Max Bending Depth Bending Load
JEITA stipulated span
90 mm
90 mm
60 mm
60 mm
Package crack
17.18 mm 3.23 kg
8.81 mm 6.60 kg
30 mm
30 mm
R50ZZ0005EJ0150 Rev. 1.50 Page 18 of 21
Mar 25, 2015
2.08 mm 13.72 kg
Page 22

QFN Mounting Manual 9. On Board Reliability Test Results
9. On Board Reliability Test Results
9.1 Board Mounted Thermal Cycle Test Results
(punching cut type, 6 × 6 mm, 0.4 mm pitch)
The results of an evaluation of the effects of whether or not die pad soldering was used are shown below. This testing
showed that die pad soldering has an effect on solder connection reliability.
Table 9.1 Evaluation Specs
F(t)
99%
95%
90%
60%
50%
40%
10%
0.1%
Weibull Plot
Solder paste: Sn-Ag-Cu, without E-Pad soldering
Solder paste: Sn-Ag-Cu, with E-Pad soldering
5%
1%
1
10
100
1000
-55 to 125°C (10 min to 10 min) cycle
Figure 9.1 Weibull Plot
(Eevaluation results of temp. cycle on board)
10000 100000
Test
temperature
Package
Printed wiring
board
Stencil Thickness: 0.10 mm (die pad
Reflow soldering
temperature
(leads)
Failure definition Failure recognized when not
-55 to 125°C: 10 minutes dwell
P-VQFN48-6x6-0.4
Lead material: Cu
Lead plating: Sn-Bi
Size: 50 × 100 × t0.8 mm
Material: FR-4/4 layers
Pad surface processing:
Cu + OSP
aperture: 1.6 mm square × 4)
Sn-3Ag-0.5Cu paste: 245°C max
conducting
9.2 Board Mounted Thermal Cycle Test Results
(dicing cut type, 5 × 5 mm, 0.5 mm pitch)
The results of an evaluation of the effects of whether or not die pad soldering was used are shown below. This testing
showed that die pad soldering has an effect on solder connection reliability.
F(t)
99%
95%
90%
60%
50%
40%
10%
0.1%
Solder paste: Sn-Ag-Cu, without E-Pad soldering
Solder paste: Sn-Ag-Cu, with E-Pad soldering
5%
1%
1
10
Weibull Plot
100
1000
-40 to 125°C (10 min to 10 min) cycle
Figure 9.2 Weibull Plot
(Eevaluation results of temp. cycle on board)
10000
100000
Table 9.2 Evaluation Specs
Test temperature -40 to 125°C: 10 minutes dwell
Package
Printed wiring
board
Stencil Thickness: 0.12 mm (die pad
Reflow soldering
temperature
(leads)
Failure definition 20% nominal resistance increase
P-WQFN32-5x5-0.5
Lead material: Cu
Lead plating: Ni/Pd/Au
Size: 124 × 130 × t0.8 mm
Material: FR-4/4 layers
Pad surface processing:
Cu + OSP
aperture: 1.25 mm square × 4)
Sn-3Ag-0.5Cu paste: 240°C max
R50ZZ0005EJ0150 Rev. 1.50 Page 19 of 21
Mar 25, 2015
Page 23

QFN Mounting Manual 9. On Board Reliability Test Results
9.3 Board Mounted Thermal Cycle Test Results
(dicing cut type, 7 × 7 mm, 0.5 mm pitch)
The results of an evaluation of the effects of whether or not die pad soldering was used are shown below. This testing
showed almost no effect of die pad soldering on solder connection reliability.
Table 9.3 Evaluation Specs
Weibull Plot
Solder paste: Sn-Ag-Cu, without E-Pad soldering
Solder paste: Sn-Ag-Cu, with E-Pad soldering
5%
1%
1
10
100
1000
-40 to 125°C (10 min to 10 min) cycle
Figure 9.3 Weibull Plot
(Eevaluation results of temp. cycle on board)
10000
100000
Test
-40 to 125°C: 10 minutes dwell
temperature
Package
P-WQFN48-7x7-0.5
Lead material: Cu
Lead plating: Ni/Pd/Au
Printed wiring
board
Size: 124 × 130 × t0.8 mm
Material: FR-4/4 layers
Pad surface processing: Cu + OSP
Stencil Thickness: 0.12 mm (die pad aperture:
1.38 mm square 9)
Reflow soldering
Sn-3Ag-0.5Cu paste: 240°C max
temperature
(leads)
Failure definition 20% nominal resistance increase
9.4 Board Mounted Thermal Cycle Test Results
(dicing cut type: package shape dependency)
This testing showed that the smaller the package the greater the effect on connection lifetime.
Table 9.4 Evaluation Specs
F(t)
99%
95%
90%
60%
50%
40%
10%
0.1%
5x5mm
5 x 5 mm
7x7mm
7 x 7 mm
9x9mm
9 x 9 mm
5%
1%
1
10
Weibull Plot
100
1000
-40 to 125°C (10 min to 10 min) cycle
Figure 9.4 Weibull Plot
(Eevaluation results of temp. cycle on board)
10000
100000
Test
temperature
Package
Printed wiring
board
Stencil Thickness: 0.12 mm
Reflow soldering
temperature
(leads)
Failure definition 20% nominal resistance increase
-40 to 125°C: 10 minutes dwell
5 × 5 mm, 32 pins, 0.5 mm pitch
7 × 7 mm, 48 pins, 0.5 mm pitch
9 × 9 mm, 64 pins, 0.5 mm pitch
Cu + Ni/Pd/Au plating
Size: 124 × 130 × t1.6 mm
Material: FR-4/4 layers
Pad surface processing: Cu + OSP
Sn-3Ag-0.5Cu paste: 240°C max
R50ZZ0005EJ0150 Rev. 1.50 Page 20 of 21
Mar 25, 2015
Page 24

QFN Mounting Manual 10. QFN Reworking (removal from the mounting board)
10. QFN Reworking (removal from the mounting board)
Although it is not possible to repair boards with a soldering iron after QFN package devices have been mounted, it is
possible using special-purpose equipment. The following points must be observed in the reworking method used.
The influence of the heating on adjacent pins must be minimized.
Since the heating conditions will differ due to differences in the heat capacities of the printed wiring board (board
thickness, number of layers) and mounted components used. Therefore the conditions must be set to correspond to the
actual product and its mounted components.
Consult the manufacturer of each component to determine if mounted components can be reused after reworking.
Note: Renesas quality guarantees do not apply to components that have been removed during package reworking
(component replacement). Therefore we strongly recommend that component reuse be avoided if at all possible.
Chip capacitor
SOP
Hot air
Figure 10.1 QFN Reworking Method
BGA
Heated stageQFNMounting board
R50ZZ0005EJ0150 Rev. 1.50 Page 21 of 21
Mar 25, 2015
Page 25

QFN Mounting Manual
Publication Date: Rev.1.00 Sep 26, 2013
Rev.1.50 Mar 25, 2015
Published by: Renesas Electronics Corporation
Page 26

SALES OFFICES
Refer to "h ttp:// www.renesas.com/" for the latest and detailed information.
Renesas Electronics America Inc.
2801 Scott Boulevard Santa Clara, CA 95050-2549, U.S.A.
Tel: +1-408-588-6000, Fax: +1-408-588-6130
Renesas Electronics Canada Limited
9251 Yonge Street, Suite 8309 Richmond Hill, Ontario Canada L4C 9T3
Tel: +1-905-237-2004
Renesas Electronics Europe Limited
Dukes Meadow, Millboard Road, Bourne End, Buckinghamshire, SL8 5FH, U.K
Tel: +44-1628-585-100, Fax: +44-1628-585-900
Renesas Electronics Europe GmbH
Arcadiastrasse 10, 40472 Düsseldorf, Germany
Tel: +49-211-6503-0, Fax: +49-211-6503-1327
Renesas Electronics (China) Co., Ltd.
Room 1709, Quantum Plaza, No.27 ZhiChunLu Haidian District, Beijing 100191, P.R.China
Tel: +86-10-8235-1155, Fax: +86-10-8235-7679
Renesas Electronics (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
Unit 301, Tower A, Central Towers, 555 Langao Road, Putuo District, Shanghai, P. R. China 200333
Tel: +86-21-2226-0888, Fax: +86-21-2226-0999
Renesas Electronics Hong Kong Limited
Unit 1601-1611, 16/F., Tower 2, Grand Century Place, 193 Prince Edward Road West, Mongkok, Kowloon, Hong Kong
Tel: +852-2265-6688, Fax: +852 2886-9022
Renesas Electronics Taiwan Co., Ltd.
13F, No. 363, Fu Shing North Road, Taipei 10543, Taiwan
Tel: +886-2-8175-9600, Fax: +886 2-8175-9670
Renesas Electronics Singapore Pte. Ltd.
80 Bendemeer Road, Unit #06-02 Hyflux Innovation Centre, Singapore 339949
Tel: +65-6213-0200, Fax: +65-6213-0300
Renesas Electronics Malaysia Sdn.Bhd.
Unit 1207, Block B, Menara Amcorp, Amcorp Trade Centre, No. 18, Jln Persiaran Barat, 46050 Petaling Jaya, Selangor Darul Ehsan, Ma laysia
Tel: +60-3-7955-9390, Fax: +60-3-7955-9510
Renesas Electronics India Pvt. Ltd.
No.777C, 100 Feet Road, HAL II Stage, Indiranagar, Bangalore, India
Tel: +91-80-67208700, Fax: +91-80-67208777
Renesas Electronics Korea Co., Ltd.
12F., 234 Teheran-ro, Gangnam-Gu, Seoul, 135-080, Korea
Tel: +82-2-558-3737, Fax: +82-2-558-5141
http://www.renesas.com
© 2015 Renesas Electronics Corporation. All rights reserved.
Colophon 4.0
Page 27

QFN Mounting Manual
R50ZZ0005EJ0150
Page 28

QFN Mounting Manual
R50ZZ0005EJ0150
 Loading...
Loading...