Page 1

OPE RATORS MAN UAL
AC 23B
ACTIVE CROSSOVER
QUICK START
Labels above the controls refer to the unit being operated in the 2- or 3-Way Stereo mode. Labels below the
controls refer to the unit being operated in the 4- or 5-Way Mono mode.
The AC 23B is a fully balanced version of the popular AC 23 and is equipped with 3-pin (XLR-type) connectors instead
of the standard ¼" TRS jacks. A STEREO/MONO switch has been added to the AC 23B and should be set appropriately.
Switching jacks are not provided. All other specifications and operation are identical.
To operate the unit in Stereo 3-Way mode, be sure the rear panel switches are set for STEREO 3-WAY. Following the
labels above the controls and jacks in logical order, you will find CHANNEL 1 INPUT, LOW OUT, MID OUT, and HIGH
OUT, with the same for CHANNEL 2. The fact that the AC 23B is a multiple function unit means the outputs are switched
around in Mono mode. To use the unit as a Mono 5-Way, first check that the CHANNEL 1 and 2 switches are set to 3WAY, and the other switch is set to MONO. Connect the INPUT source to CHANNEL 1 only. Following the labels below
the jacks, look at SUB OUT, then look over at LOW OUT, now go back to MID OUT, then over to HI MID OUT and then
proceed to the HIGH OUT. An internal jumper determines 4 or 5-Way mode. Our apologies to 4-Way users: We must ship
the units in the 5-Way mode since normal Stereo 3-Way operation demands it: a fact not the least bit obvious, but nevertheless, a fact it remains. Pity. See page Manual-6 for Mono 4-Way configuration.
CAUTION: Never connect anything except an approved Rane Power supply to the thing that looks like a red telephone jack on the rear of the AC 23B. This is an 18 VAC center tapped power input. Consult the Rane factory for a
replacement or substitution.
AC 23B CONNECTION
In agreement with IEC and AES/ANSI standards, AC 23B
wiring convention is pin 2 Positive, pin 3 Negative (return),
pin 1 Signal ground (for unbalanced use), with the connector
case or shell tied to chassis ground.
Balanced Operation
Use only when driving from a true balanced source and
driving to a true balanced destination—either transformer
coupled or active drive. Connect the input to pins 2 and 3 with
pin 2 positive. Do not connect pin 1. Terminate the shield to
the case or shell. Connect the output to pins 2 and 3 with pin
2 positive. Do not connect pin 1. Connect the shield to the
case or shell.
WEAR PARTS: This product contains no wear parts.
Unbalanced Operation
Connect the input between pins 2 and 1 with pin 2
positive and pin 1 Signal ground. Short pin 3 to pin 1.
Terminate the shield to the case or shell. Connect the output
between pins 2 and 1 with pin 2 Positive. Leave pin 3 open—
do not short it to pin 1. Connect the shield to the case or shell.
Combination Operation
For combined balanced and unbalanced operation, use
whichever half of the above instructions apply for each end.
See the “Sound System Interconnection” RaneNote
included with this manual for more information on cabling
and grounding requirements.
Manual-1
Page 2
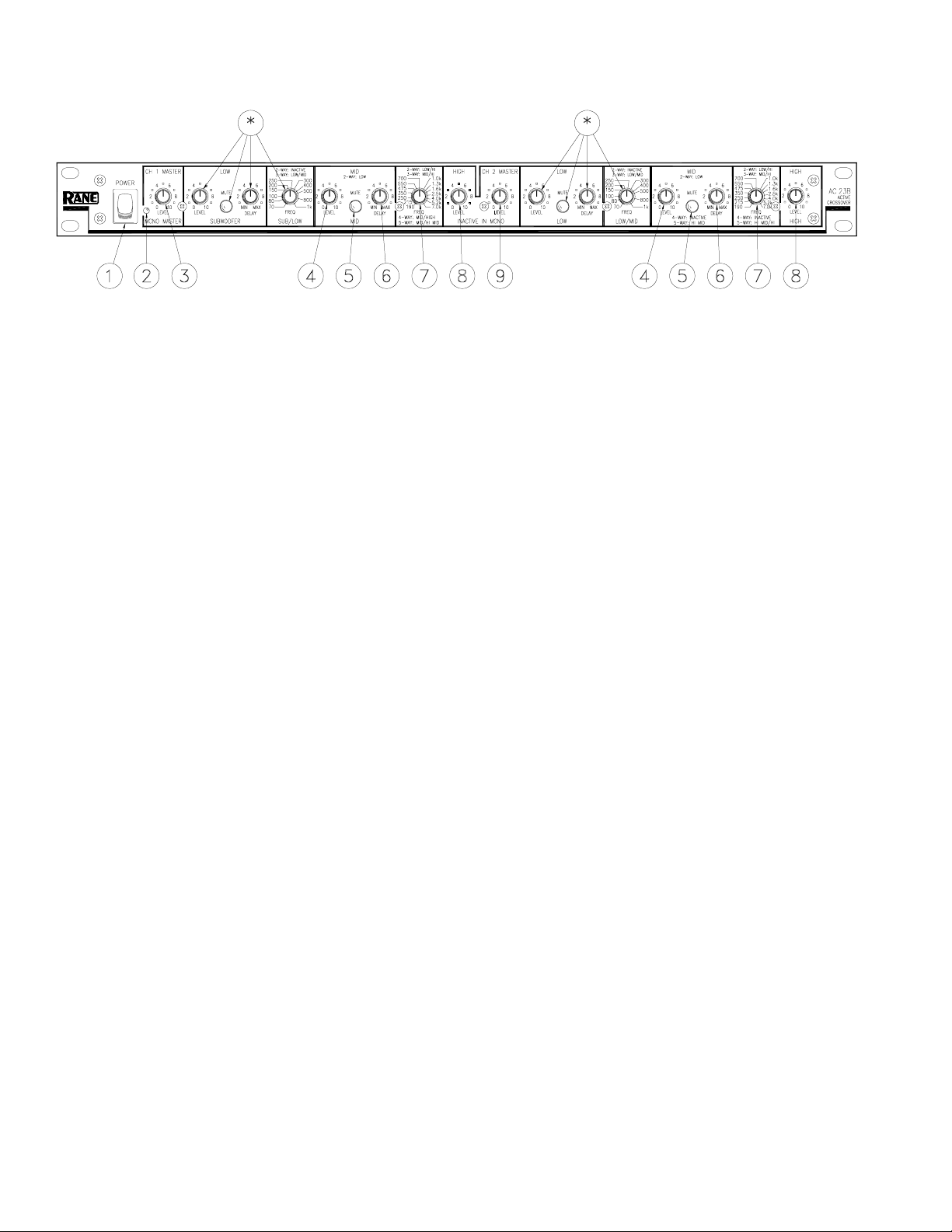
FRONT PANEL: STEREO 2-WAY CONFIGURATION
Observe the labels screened above the controls for stereo operation.
NOTE: In the 2-Way mode, the AC 23B crossover range is from 190 Hz to 7 kHz. The model AC 22 crossover
in stereo 2-Way mode is recommended when the crossover point needs to be outside of this range.
* Not used in 2-Channel 2-Way Mode
햲 POWER switch: Two guesses.
햳 POWER indicator: When this yellow LED is lit the unit is ready to operate.
햴 CHANNEL 1 MASTER LEVEL control: Sets the overall Level of Channel 1 without altering the relative settings of the
Low and High frequency Outputs. Unity gain for all level controls is at “7”.
햵 LOW LEVEL control: Sets the Level of signal going to the Low Frequency output in this channel. Refer to ‘Setting the
Output Level Controls’ on page Manual-15.
햶 LOW MUTE switch: When pressed to the in position, all signal is removed from the Low Frequency Output. This eases
tune-up procedures as described on pages Manual-11-16.
햷 LOW DELAY control: Adds from 0 to 2 ms of time Delay to the Low Frequency Output only. This allows a low fre-
quency driver to be electronically phase-aligned with a mid frequency driver whose diaphragm is situated behind the low
frequency diaphragm. Refer to ‘Time Delay Adjustment Procedure’ on page Manual-10.
햸 LOW/HIGH crossover frequency selector: This 41-detent selector sets the crossover frequency between the Low and
High frequency Outputs. Refer to ‘Selecting Crossover Frequencies’ on page Manual-10.
햹 HIGH LEVEL control: Sets the Level of signal going to the High frequency Output only.
햺 CHANNEL 2 MASTER LEVEL control: Sets the overall Level of Channel 2 without altering the relative settings of the
Low and High Outputs.
Manual-2
Page 3

REAR PANEL: STEREO 2-WAY INSTALLATION
Observe the labels above the Inputs and Outputs for Stereo operation.
햲 CHANNEL 1 INPUT: Plug the left output of the mixer, equalizer or other signal source to this Input. See ‘AC 23B
Connection’ on page Manual-1 for wiring details.
햳 CHANNEL 2 INPUT: Plug the right output of the mixer, equalizer or other signal source to this Input..
햴 HIGH FREQUENCY OUTPUTS: Connect the CHANNEL 1 HIGH OUT to the left channel input of the high frequency
amp, and the CHANNEL 2 HIGH OUT to the right channel input of the high frequency amp.
햵 MID FREQUENCY OUTPUTS: Connect the CHANNEL 1 MID OUT to the left channel input of the low frequency
amplifier, and the CHANNEL 2 MID OUT to the right channel input of the low amplifier.
햶 2-WAY/3-WAY switch: Converts the outputs from 3-Way to 2-Way. This switch removes the Low frequency crossover
from the signal path. Low frequencies are now routed to the Mid frequency Output. Be sure to slide the switches to the
2-WAY position. Note: The Low frequency outputs are still active and may be used as additional subwoofer outputs.
햷 STEREO/MONO switch: Set this switch to the STEREO “out” position.
햸 POWER input connector: Use only a model RS 1 or other power supply approved by Rane. This unit is supplied with a
remote power supply suitable for connection to this input jack. This is not a telephone jack. The power requirements call for
an 18-24 VAC center-tapped transformer only. Using any other type of unapproved supply may damage the unit and void
the warranty. Two years parts and labor is worth safeguarding.
햹 Chassis ground point: A #6-32 screw is used for chassis grounding purposes. Always connect crossover chassis ground to
amplifier chassis ground. See ‘Chassis Grounding’ on page Manual-7 for details.
Manual-3
Page 4
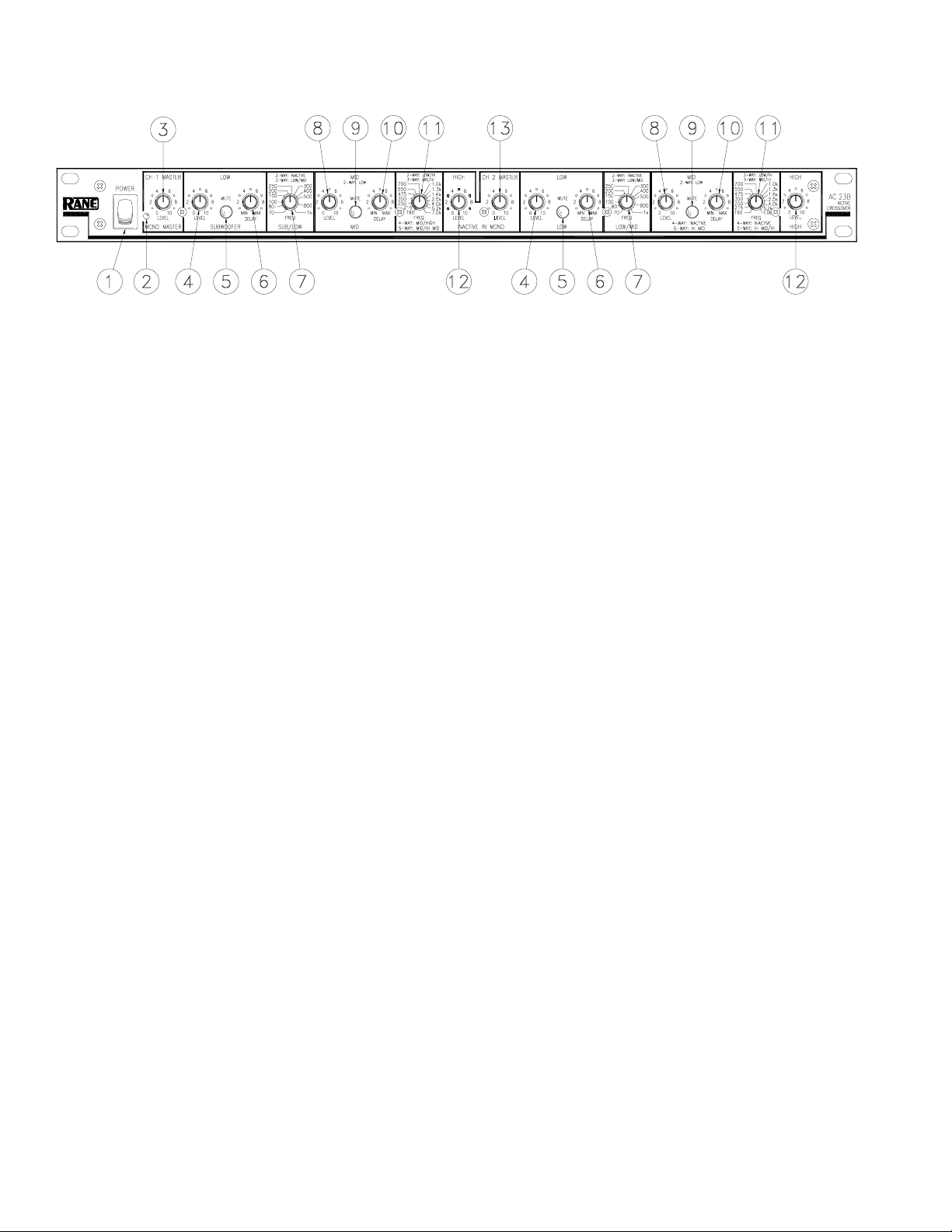
FRONT PANEL: STEREO 3-WAY CONFIGURATION
Observe the labels screened above the controls for stereo operation.
햲 POWER switch: Two guesses.
햳 POWER indicator: When this yellow LED is lit, the unit is ready to operate.
햴 CHANNEL 1 MASTER LEVEL control: Sets the overall Level of Channel 1 without altering the relative settings of the
Low/Mid/High frequency Outputs. Unity gain for all Level controls is at “7”.
햵 LOW FREQUENCY LEVEL control: Sets the Level of signal going to the Low frequency Output only in this Channel.
Refer to page Manual-15 for guidance with the Level control settings.
햶 LOW MUTE switch: When pressed to the in position, all signal is removed from the Low frequency Output. This eases
tune-up procedures as described on pages Manual-11-16.
햷 LOW DELAY control: Adds from 0 to 2 ms of time delay to the Low Frequency Output only. This allows a low frequency
driver to be electronically phase-aligned with a mid frequency driver whose diaphragm is situated behind the low frequency
diaphragm. Refer to page Manual-10.
햸 LOW/MID crossover frequecny selector: This 41-detent selector sets the crossover frequency between the Low and Mid
Outputs. Refer to page Manual-10.
햹 MID LEVEL control: Sets the Level of signal going to the Mid Output in this Channel only.
햺 MID MUTE switch: Removes all signal from the Mid Frequency Output when pressed to the in position.
햻 MID DELAY control: Adds from 0 to 2 ms of time Delay to the Mid Output only.
햽 MID/HIGH crossover frequency selector: Sets the crossover frequency between the Mid and High Outputs in this
Channel.
햾 HIGH LEVEL control: Sets the Level of signal going to the High Output only.
햿 CHANNEL 2 MASTER LEVEL control: Sets the overall Level of Channel 2 without altering the relative settings of the
Low/Mid/High Outputs.
Manual-4
Page 5
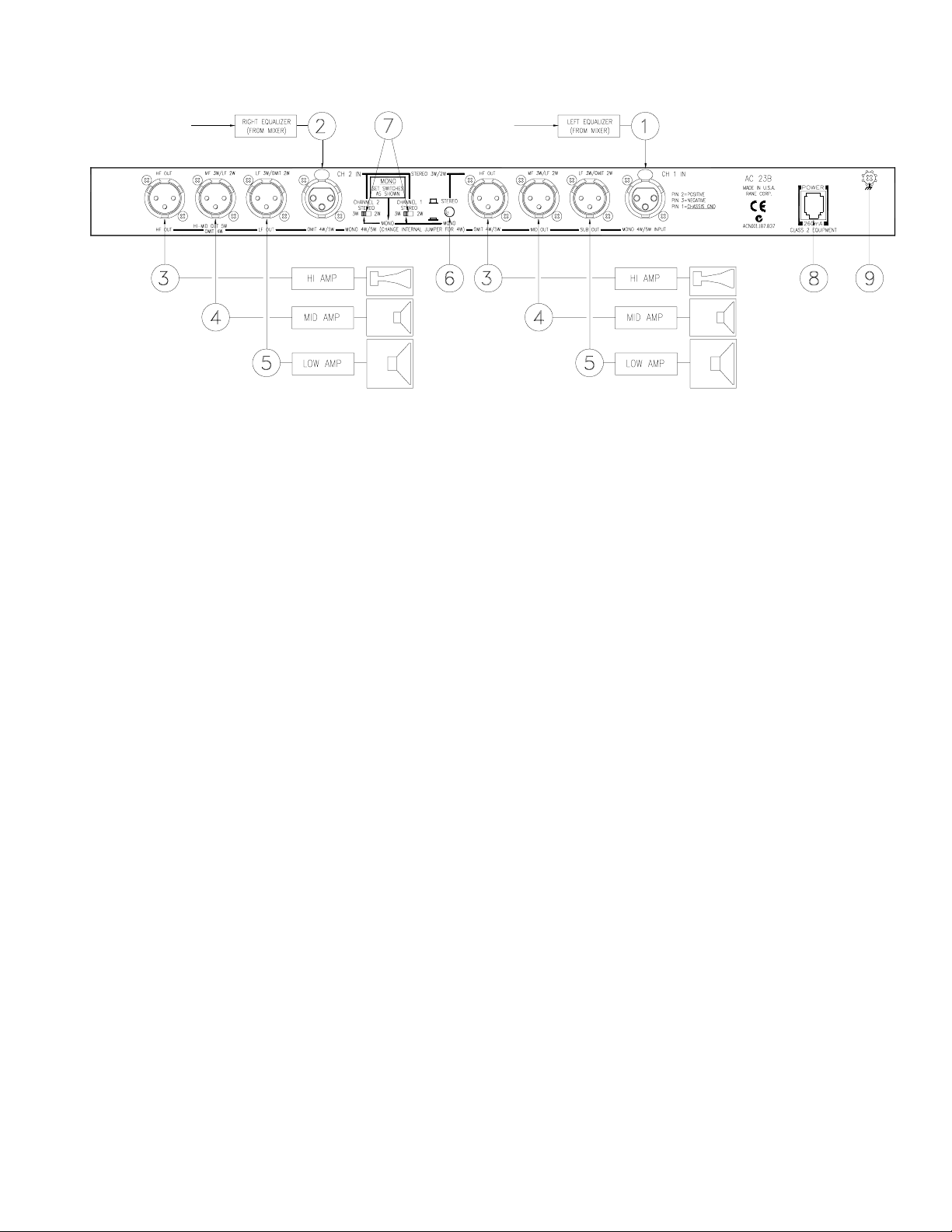
REAR PANEL: STEREO 3-WAY INSTALLATION
Observe the labels above the Inputs and Outputs for Stereo operation.
햲 CHANNEL 1 INPUT: Plug the left output of the mixer, equalizer or other signal source to this Input. Refer to ‘AC 23B
Connection’ on page Manual-1 for wiring details.
햳 CHANNEL 2 INPUT: Plug the right output of the mixer, equalizer or other signal source to this Input.
햴 HIGH FREQUENCY OUTPUTS: Connect the CHANNEL 1 HIGH OUT to the left channel input of the high frequency
amp, and the CHANNEL 2 HIGH OUT to the right channel input of the high frequency amp.
햵 MID FREQUENCY OUTPUT: Connect the CHANNEL 1 MID OUT to the left channel of the mid frequency amp, and
the CHANNEL 2 MID OUT to the right channel of the mid frequency amp.
햶 LOW FREQUENCY OUTPUTS: Connect the CHANNEL 1 and 2 LOW OUTS to the left and right channels of the low
frequency amplifier, respectively.
햷 STEREO/MONO switch: Set this switch to the STEREO position.
햸 2-WAY/3-WAY switch: Converts the outputs from Stereo 3-Way to Stereo 2-Way. Be sure the switches are in the 3-WAY
position.
햹 POWER input connector: Use only a model RS 1 or other power supply approved by Rane. This unit is supplied with a
remote power supply suitable for connection to this input jack. This is not a telephone jack. The power requirements call for
an 18-24 VAC center-tapped transformer only. Using any other type of unapproved supply may damage the unit and void
the warranty. Two years parts and labor is worth safeguarding.
햺 Chassis ground point: A #6-32 screw is used for chassis grounding purposes. Always connect the crossover chassis to the
amplifier chassis. See ‘Chassis Grounding’ on page Manual-7 for details.
Manual-5
Page 6
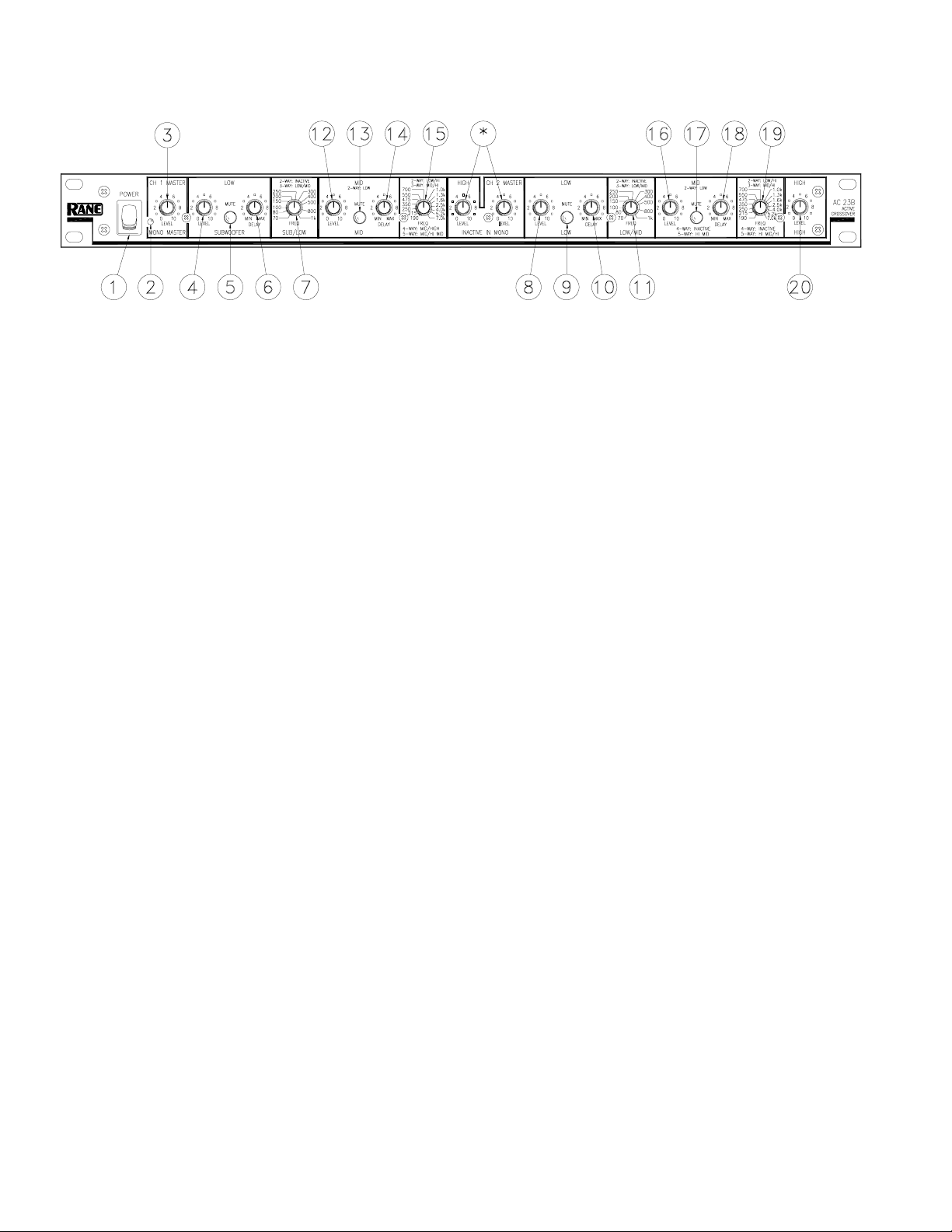
FRONT PANEL: MONO 4-WAY AND 5-WAY CONFIGURATION
Observe the labels screened below the controls for Mono operation.
햲 POWER switch: Two guesses.
햳 POWER indicator: When this yellow LED is lit, the unit is ready to operate.
햴 MASTER LEVEL control: Sets the overall Level of the entire unit in Mono mode, without changing relative settings of
the individual Sub/Low/Mid/High Outputs. Unity gain for all Level controls is “7”.
햵 SUBWOOFER LEVEL control: Sets the Level of signal going to the Sub Output. See page Manual-15.
햶 SUBWOOFER MUTE switch: Removes all signal from the Sub Output when pressed to the in position. This eases the
system tune-up procedure, as described on pages Manual-11-16.
햷 SUBWOOFER DELAY control: In Subwoofer applications this control has virtually no effect and will normally be set to
minimum (MIN). Refer to page Manual-10.
햸 SUB/LOW crossover frequency selector: This 41-detent selector sets the crossover frequency between the Subwoofer and
Low Outputs. Refer to page Manual-10 to determine the proper setting for your system.
햹 LOW LEVEL control: Sets the Level going to the Low frequency Output.
햺 LOW MUTE switch: Removes all signal from the Low Output when pressed in.
햻 LOW DELAY control: Adds from 0 to 2 ms of time Delay to the Low Frequency Output only. Refer to page Manual-10
for alignment procedure.
햽 LOW/MID crossover frequency selector: Sets the crossover frequency between the Low and Mid frequency Outputs.
햾 MID LEVEL control: Sets the Level of signal going to the Mid Output only.
햿 MID MUTE switch: Removes all signal from the Mid Output when pressed in.
헀 MID DELAY control: Adds from 0 to 2 ms of time Delay to the Mid frequency Output only.
헁 MID/HI MID crossover frequency selector: Sets the crossover frequency between the Mid and Hi Mid Outputs.
* NOTE: Both the CHANNEL 1 HIGH LEVEL control and CHANNEL 2 MASTER LEVEL control are automatically bypassed
when the AC 23B is switched to "MONO" on the back panel. Adjusting these controls has no effect in the Mono mode.
헂 Hl MID LEVEL control: This controls the Level of signal going to the Hi Mid Output only in 5-Way Mode. **NOTE TO
Manual-6
Page 7

4-WAY MONO USERS: An internal jumper determines 4 or 5-Way mode. Our apologies: We must ship the units in the
5-Way mode since normal Stereo 3-Way operation demands it: a fact not the least bit obvious, but nevertheless, a fact it
remains. See the section below for Mono 4-Way Jumper Instructions. The HI MID LEVEL control, HI MID MUTE switch,
HI MID DELAY control and HI MID/HIGH FREQUENCY control are out of circuit and will have no effect regardless of
their settings in 4-Way Mode.
헃 Hl MID MUTE switch: Removes all signal from the Hi Mid Output when pressed to the in position. This control is
disabled in 4-Way mode.
헄 Hl MID DELAY control: This control adds from 0 to 2 ms of time Delay to the Hi Mid Output only. This control is
disabled in 4-Way mode.
헅 Hl MID/HIGH crossover frequency selector: This control sets the crossover Frequency between the Hi Mid and High
Frequency Outputs. This control is disabled in 4-Way mode.
헆 HIGH LEVEL control: This controls the Level of signal to the High Output only.
See the Following Pages for Mono 4- or 5-Way Installation.
Mono 4-Way Jumper Instructions
1. Be sure all power and audio is turned off. Remove the top
cover of the AC 23B.
2. Locate the 4-WAY/5-WAY jumper by the Channel 2 LOW
and MID OUTPUT jacks (see assembly diagram).
3. Remove the jumper from the 5-WAY (Pins 2 & 3) position
and move it to the 4-WAY (Pins 1 & 2) position.
4. Replace the cover. The AC 23B is now set for Mono 4Way Mode. The HI MID OUTPUT will duplicate the MID
OUTPUT frequencies with a different low pass setting as
determined by the HI MID/HI FREQUENCY control, and
is not normally recommended for use since the tweeter
crossover point will be inaccurate.
This operation must be reversed to operate the unit
in either Stereo 3-Way or Mono 5-Way Mode.
IMPORTANT NOTE
CHASSIS GROUNDING
If after hooking up your system it exhibits excessive
hum or buzzing, there is an incompatibility in the grounding configuration between units somewhere. Your
mission, should you accept it, is to discover how your
particular system wants to be grounded. Here are some
things to try:
1. Try combinations of lifting grounds on units that are
supplied with ground lift switches or links.
2. If your equipment is in a rack, verify that all chassis
are tied to a good earth ground, either through the line
cord grounding pin or the rack screws to another
grounded chassis.
3. Units with outboard power supplies do not ground the
chassis through the line cord. Make sure that these
units are grounded either to another chassis which is
earth grounded, or directly to the grounding screw on
an AC outlet cover by means of a wire connected to a
screw on the chassis with a star washer to guarantee
proper contact.
4. Try moving the device away from high magnetic field
sources, such as large transformers used in power
amplifiers.
Please refer to the RaneNote “Sound System
Interconection” for further information on system grounding.
Manual-7
Page 8

REAR PANEL: MONO 4-WAY AND MONO 5-WAY INSTALLATION
**THIS OUTPUT IS NOT USED FOR 4-WAY MONO OPERATION.
4-WAY USERS SEE JUMPER INSTRUCTIONS ON PREVIOUS PAGE.
Observe the labels below the Inputs and Outputs for Mono operation.
햲 MONO INPUT: Connect the output from your mixer or other signal source only to the CHANNEL 1 INPUT for Mono
operation; do not use the Channel 2 Input. See SYSTEM CONNECTION on page Manual-1 for wiring details.
햳 SUBWOOFER OUTPUT: Connect the SUB OUT to the input of the subwoofer (or bass bin) amplifier.
햴 LOW FREQUENCY OUTPUT: Connect the LOW OUT to the input of the low frequency (mid-bass) amp.
햵 MID FREQUENCY OUTPUT: Connect the MID OUT to the input of the mid frequency amplifier.
햶 Hl MID FREQUENCY OUTPUT (FOR MONO 5-WAY ONLY): Use this Output only for Mono 5-Way applications.
Omit this output when using the AC 23B as a Mono 4-Way Crossover. Mono 4-Way Jumper Instructions are on the previous
page. In 4-Way the AC 23 internally bypasses the Hi Mid section and defeats all front panel Hi Mid Controls. For Mono
5-Way connect the HI MID OUT to the input of the hi mid frequency amp.
햷 HIGH FREQUENCY OUTPUT: Connect the HIGH OUT to the input of the high frequency (tweeter) amp.
햸 2-WAY/3-WAY switches: Converts each channels outputs from 3-Way to 2-Way. For Mono 4-or 5-Way, slide these
switches to the 3-WAY position.
햹 MONO-STEREO switch: This should be in the MONO in position.
햺 POWER input connector: Use only a model RS 1 or other power supply approved by Rane. This unit is supplied with a
remote power supply suitable for connection to this input jack.
햻 Chassis ground point: A #6-32 screw is used for chassis grounding purposes. Always connect the crossover chassis to the
amplifier chassis. See the CHASSIS GROUNDING note on page Manual-7 for details.
Manual-8
Page 9

REAR PANEL: ALTERNATE MONO 4-WAY INSTALLATION
Note: The switching in the AC 23B will result in a Mono 4-Way configuration with the crossover ranges SUB,
LOW, MID & HIGH from left to right across the front panel. By connecting a patch cable from the CHANNEL
1 HIGH OUT to the CHANNEL 2 INPUT, the LOW/MID crossover range changes from 70 Hz-1 kHz to a higher
range of 190 Hz-7 kHz. Switch CHANNEL 1 to 3-Way, and CHANNEL 2 to 2-Way.
Note: DO NOT follow the Mono 4-Way Jumper Instructions on page Manual-7.
햲 MONO INPUT: Connect the output from your mixer or other signal source only to the CHANNEL 1 INPUT for Mono
operation; do not use the Channel 2 Input. Note: For this alternate Mono 4-Way installation, connect a patch cord from the
CHANNEL 1 HIGH OUT to the CHANNEL 2 INPUT as shown.
햳 SUBWOOFER OUTPUT: Connect the SUB OUT to the input of the subwoofer amplifier (or bass bin amp).
햴 LOW FREQUENCY OUTPUT: Connect the MID OUT to the input of the low frequency amplifier.
햵 MID FREQUENCY OUTPUT: Connect the HI MID OUT to the input of the mid frequency amplifier. Be sure the
CHANNEL 1 HIGH LEVEL and the CHANNEL 2 MASTER LEVEL controls are set at “7” for unity gain between Channels.
햶 Hl FREQUENCY OUTPUT: Connect the HIGH OUT to the input of the high frequency amplifier.
햷 STEREO-MONO switch: Be sure this switch is in the STEREO out position. Yes, STEREO. A Mono circuit is created
when Channel 1 is patched into Channel 2, and the correct signal flow depends on this switch.
햸 2-WAY/3-WAY switches: Converts each channels outputs from 3-Way to 2-Way. For this configuration, set CHANNEL 1
to 3-Way, and CHANNEL 2 to 2-Way.
햹 POWER input connector. Use only a model RS 1 or other power supply approved by Rane. This unit is supplied with a
remote power supply suitable for connection to this input jack.
햺 Chassis ground point. A #6-32 screw is used for chassis grounding purposes. Always connect the crossover chassis to the
amplifier chassis. See the CHASSIS GROUNDING note on page Manual-7 for details.
Manual-9
Page 10

OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Selecting Crossover
Frequencies
Most speaker manufacturers supply low and/or high
frequency cut-off points for each driver, especially if these are
supplied in a system. These cut-off frequencies are based on
each driver’s performance at and beyond this point, with a
certain safety margin to accommodate more gentle filter
roll-offs and resultant higher output beyond the recommended
performance range.
The AC 23B utilizes 41-detent crossover frequency
selectors which are precision potentiometers. The detents will
assure consistent accuracy from Channel to Channel and unit
to unit. This is a distinct advantage over the continuously
variable designs with low-tolerance parts, possible knob
misalignment and panel screening variations. Even with 41
choices it is possible that the exact recommended crossover
frequency may not fall on one of the detents on the selector.
Not to panic, for these sound reasons:
1. The AC 23B possesses 24 dB/octave roll-off, so the
crossover points may be set to the nearest detent above or
below the recommended limit with virtually no hazard to
the driver or degradation in sound quality. If extremely
high power levels are expected, it is safer to defer to the
high frequency drivers and shift the crossover point up in
frequency rather than down.
2. Detents do not rely on knob alignment, silk-screen
accuracy, parallax and other variables which erode the
accuracy of continuously variable designs. Chances are that
even careful visual alignment on these will often yield a
frequency error greater than a full detent on the AC 23B.
3. If it is absolutely critical to obtain the exact crossover
frequency (Mil Spec., P.A., etc.), the selector can be
positioned between detents if necessary. This of course will
require the aid of a precision signal generator and other
equipment to verify the exact setting.
For best overall system results, try to choose the speaker
components so that each operates well within its recommended limits. This will provide valuable leeway so that you
may move crossover points in order to fine-tune the system,
and will also yield higher system reliability. If at all possible,
beg, borrow or best yet always use some kind of realtime
analyzer to tune your crossover and fine-tune the system for
each different location with an equalizer. Refer to the following pages for further alignment details.
Time Delay Adjustment
Procedure
Before jumping feet first into the realm of time delay and
how to adjust it, it might help to spend a moment here to
re-affirm why on earth this delay is really necessary. For a
short course on time delay, Linkwitz-Riley and other
mouth-watering details, we urge you to pick up a free copy of
the “Linkwitz-Riley Crossovers” RaneNote. Ask your dealer,
call us here at the factory, or download it from Rane's web
site.
Problems pop up when two different speakers emit the
same frequency as occurs in the crossover regions of two,
three, four and five way systems. Because the two drivers are
displaced vertically, cancellation occurs somewhere off-axis
because the sound waves have to travel different distances
from the two speakers and hence, will arrive out of phase.
This forms a “lobe” or radiation pattern, bounded on either
side by cancellation lines or axes, which narrow the dispersion pattern or listening area of the speaker.
Fine. So we put up with it. But to make matters worse,
when the two drivers are horizontally displaced – that is, one
is in the front of or behind the other, this “lobe” or dispersion
pattern gets tilted (usually upward) toward the driver that is
further behind. This gets hard to put up with, because the end
result is that your speaker system will have two, three, four or
more tilted radiation patterns and only two or three people in
the house will have decent seats. And we’re not talking trivial
pursuits here—this rampant lobing error can make a sound
system a real headache to listener and operator alike.
The idea, then, is to be sure that all drivers are vertically
aligned and that all components are always in phase. Then all
the main lobes are on-axis, well behaved, and the system
enjoys the widest possible dispersion pattern so that everyone
gets good sound. The one catch is that in many cases it is
physically or otherwise impossible to get all the drivers
vertically lined up at the sound source. This is where time
delay comes in.
By electronically delaying the signal going to the front
driver, enough time allows the sound from the rear driver to
literally catch up to the forward driver’s voice coil, so that
signal from both drivers is emitted in phase—and it works!
Time delay makes an appreciable improvement in overall
sound. The trick is finding the proper time delay amount:
hence the rest of this section.
Unfortunately the amount of time delay is a function of
two factors (life ceased to be simple after age 9, right?): the
amount of horizontal displacement between driver voice coils,
and the actual crossover frequency involved. Setting delay
controls by ear is supposedly possible, but very tricky and
unreliable. The following methods are a couple of (but by no
means all) means of setting time delay.
Manual-10
Page 11

Fig. 1 In-Phase Axis Response Without Time Delay
STEP BY STEP PROCEDURE
A 3-Way mode consisting of High, Mid and Low drivers
is used here as an example. For other configurations, use the
same procedure starting with the highest crossover point and
repeating steps 2 through 5 for each lower crossover point.
NOTE: If you are running two separate channels on the
crossover, tune up only one channel at a time, using the same
procedure for both.
1. Place the analyzer microphone about 15 feet in front of the
speaker stack and at a height about midway between the
high and mid drivers. Turn all crossover LEVEL controls
fully down.
2. Connect the pink noise source to the INPUT of the crossover (or mixer or wherever is convenient). Turn up the
crossover MASTER LEVEL control and the MID OUT
control until noise is heard only from the mid driver at a
comfortable volume.
3. With a healthy but not uncomfortable volume of noise from
the mid driver, set the analyzer DISPLAY LEVEL control
so the LED’s corresponding to the high crossover frequency are reading 0 dB (this would be a green LED at the
crossover frequency with any of the Rane analyzers). For
example, if your high crossover frequency is 2 kHz, set the
RA 27 in the ±1 dB mode and then adjust the RTA
LEVEL control until the green LED is lit in the 2 kHz
band. There...easy.
Fig. 2 Corrected In-Phase Axis Response With Electronic Time Delay on
Low Frequency Driver
Time Delay Adjustment Using
Realtime Analyzer & Pink Noise
This method outlines the use of a realtime analyzer, pink
noise generator and flat response microphone to set crossover
time delay. Some references will be made to the Rane RA 27
realtime analyzer for those with the intelligence and good
taste to use one of these regularly. The procedure applies to
virtually any analyzer system. We recommend using a 1/3 or
2/3 octave analyzer as either of these is more likely to match
your specific crossover points than a one-octave analyzer.
And it is important to match the analyzer to the crossover
point as closely as possible for proper phase alignment,
otherwise the analyzer readings may be misleading.
4. Now press in the MID MUTE switch on the crossover so
that the tone is removed from the mid driver. Without
re-adjusting either the meter or the crossover Input or Mid
Level controls, turn up the HIGH LEVEL control until the
tone coming from only the high driver reads 0 dB (a green
LED at the crossover frequency).
5. Now release the MID MUTE switch on the crossover so
that pink noise is heard from both the high and mid drivers.
Switch the display sensitivity to ±3 dB on Rane analyzers
(not necessary with full scale analyzers) and observe the
display reading at the crossover frequency:
i. If the display shows a +3 dB reading (red LED on with
Rane analyzers in the +3 dB mode), then the drivers are
properly phase aligned and no delay is necessary; leave
the MID DELAY control at minimum.
ii. If the display shows less than +3 dB reading (still in
green or in yellow on Rane analyzers), slowing turn up
the MID DELAY control on the crossover until the
display shows +3 dB (red LED just on with Rane
analyzers). Now the drivers are electronically phase
aligned and the Delay control should be left in this
position at all times unless the speaker system is
physically altered.
iii. If the MID DELAY control is all the way up and you
still do not have a +3 dB (red) reading, you will have to
Manual-11
Page 12

physically move the high driver farther forward until the
display shows +3 dB (red). The amount of displacement
correction available from the Delay depends on the
actual crossover frequency: the higher the frequency, the
less amount of correction capability. If the drivers are
built into a single cabinet and/or it is impossible to
change relative positions, then you will have to obtain
additional external delay to achieve proper phase
alignment. The Rane AD 22B would be suitable.
iv. If turning the MID DELAY control up makes the
display reading decrease instead of increase, this means
that the high driver is actually in front of the mid driver;
adding delay to the mid driver only worsens the situation. There are a couple of ways to deal with this:
a. Try to move the high driver back as far as possible
without losing stability in balancing the speaker stack.
You may want to raise it up as well to restore dispersion close to the stack. If you cannot move the high
driver, then you will have to use an additional delay
source to align the high and mid drivers. The built-in
delay system in the AC 23B is designed to accommodate the majority of common speaker configurations;
if you encounter confusion or difficulty with your
particular system, it is best to consult your dealer or
the Rane factory for assistance.
b. If this decrease in the display due to the DELAY
control occurs at a low frequency crossover point
below about 150 Hz, set the DELAY control to
minimum and leave it there. Frequencies below 150
Hz are actually omnidirectional, so that phase
misalignment is virtually inaudible below this point.
Subwoofers will often possess long folded or straight
horns, resulting in the diaphragm being well behind
the rest of the stack. Most authorities agree that phase
alignment of subwoofers is unnecessary.
6. Lower the microphone until it is vertically midway between the mid and low drivers. Repeat steps 2 through 5,
using the crossover LEVEL control, MUTE switch and
next DELAY control. You may start each series of steps 2
through 5 at a different volume as necessary—but once the
Levels are set in step 3 do not alter these until step 5 is
completed. Once all of the crossover DELAY controls are
set, then adjust the output LEVEL controls as outlined on
page Manual-15.
Time Delay Adjustment Using
SPL Meter & Tone Generator
Now that good quality realtime analyzers are becoming
more affordable and easier to use, there are few reasons why
one of these should not be regularly used in any sound
system. If an analyzer is simply not available or for some
reason inappropriate, an accurate delay setting can be obtained by using a straightforward SPL meter (obtainable at
most local electronics and some hi-fi stores) and some kind of
variable tone generator.
In order to exclude the effect of room acoustics and
imperfect driver response, only the crossover frequencies are
to be emitted (one at a time) by the tone generator. First the
highest crossover frequency is run through the crossover and
each of the two speakers sharing the crossover point is set
separately to an arbitrary 0 dB level on the SPL meter. When
both drivers emit the crossover tone simultaneously, the
combined response should read +3 dB higher on the meter. If
the drivers are not phase aligned, some cancellation will occur
on-axis, resulting in a combined response less than +3 dB.
Turning the delay control up causes the lower frequency
driver to electronically move backward until the SPL meter
reads +3 dB; then the two drivers are electronically aligned
and the on-axis cancellation is eliminated. This procedure is
then repeated for the next lower crossover point(s).
STEP BY STEP PROCEDURE
A 3-Way mode consisting of high, mid and low drivers is
used here as an example. For other configurations, use the
same procedure starting with the highest crossover point and
repeating steps 2 through 5 for each lower crossover point.
1. Set the tone generator to the highest crossover frequency
and plug it into the INPUT of the crossover. Turn all
crossover LEVEL controls fully down.
2. Position the SPL meter (microphone) about 15 feet in front
of the speakers and at a height about midway between the
high and mid drivers. It is very important that the meter
remain in exactly the same position throughout the test, so
affix it to a mic stand, small tree or other stable object. Set
the switches on the SPL meter to “C-weighting”, “Slow” if
available. Be sure to minimize background noise (air
conditioners, fans, traffic, wild animals, etc.) as these will
effect the meter reading.
3. Slowly turn up both the crossover MASTER LEVEL
control and the MID LEVEL control until the tone is heard
through the mid driver. Adjust the SPL meter control and/
or the crossover LEVEL controls until you obtain a 0dB
reading on the meter. Verify that no sound is coming from
any other speakers except the mid driver.
Manual-12
Page 13

4. Now press in the MID MUTE switch on the crossover so
that the tone is removed from the mid driver. Without
re-adjusting either the meter or the crossover Input or Mid
frequency Level controls, turn up the HIGH LEVEL
control until the tone coming from only the high driver
reads 0 dB on the SPL meter.
5. Now release the MID MUTE switch so that the tone is
emitted from both the high and mid drivers. Check the
reading on the SPL meter:
i. If the meter reads +3 dB, then the drivers are properly
phase aligned and no delay is necessary; leave the MID
DELAY control at full minimum.
ii. If the meter reads less than +3 dB, slowly turn up the
MID DELAY control until the meter just reads +3 dB.
Now the drivers are electronically phase aligned and the
delay control should be left in this position at all times,
unless the speaker system is physically altered.
iii. If you have turned the MID DELAY control all the way
up and still do not obtain a +3 dB reading, you will have
to physically move the high driver farther forward until
the SPL meter reads +3 dB. The amount of displacement
corrections available from the delay depends on the
actual crossover frequency: the higher the frequency the
less amount of correction capability. If the drivers are
built into a single cabinet and/or it is impossible to
change relative positions, then you will have to obtain
additional delay to achieve proper phase alignment.
control to minimum and leave it there. Frequencies
below 150 Hz are actually omnidirectional, so that
phase misalignment is virtually inaudible below this
point. Subwoofers will often possess long folded or
straight horns, resulting in the diaphragm being well
behind the rest of the stack. Most authorities agree
that phase alignment of subwoofers is unnecessary.
Otherwise you will have to obtain additional delay
equipment to align these to the rest of the system.
6. Tune the tone generator to the next lower crossover
frequency and then repeat steps 2 through 5, using the
appropriate level and delay controls. Once the DELAY
control is set, you may re-adjust any of the crossover
LEVEL controls at the beginning of each alignment
procedure. Once all of the crossover DELAY controls are
set, then re-adjust the output LEVEL controls as outlined
on page Manual-15.
iv. If turning the MID DELAY control up makes the SPL
reading decrease instead of increase, this means that the
high driver is actually in front of the mid driver; adding
delay to the mid driver then only worsens the situation.
There are a couple of ways to deal with this:
a. Try to move the high driver back as far as possible
without losing stability in balancing the speaker stack.
You may want to raise it up as well to restore dispersion close to the stack. If you cannot move the high
driver, then you will have to obtain an additional
external delay source to align the high and mid
drivers. The built-in delay system in the AC 23B is
designed to accommodate the majority of common
speaker configurations; if you encounter confusion or
difficulty with your particular system, it is best to
consult your dealer or the Rane factory for assistance.
b. If this decrease in the display due to the LOW
DELAY control occurs at a low frequency crossover
point below about 150 Hz, set the LOW DELAY
Manual-13
Page 14

Delay vs. Frequency Table
If you do not have the equipment necessary to electronically align the system as described in previous sections, you
may use the table below to obtain a rough and approximate
phase alignment of your drivers. Measure the horizontal
displacement between the voice coils of the two adjacent
drivers sharing the same crossover point, then find the column
in the table nearest your actual displacement. Move down this
column to the proper crossover frequency as indicated on the
left of the table: the corresponding delay knob setting will
then be the closest for your system. For example, if you have
a two-way system crossed over at 800 Hz with the compression driver voice coil located about 9" behind the woofer
voice coil, the delay knob setting corresponding to a 9"
displacement at 800 Hz on the table would be “5” as indicated
on the front panel.
Voice Coil Displacement (Inches)
(Hz) .75" 1.5" 3" 6" 9" 12" 15" 18" 21" 24"
70 11.522.53.55678MAX
80 11.522.53.55678MAX
100 11.522.53.55678MAX
150 1 1.5 2 2.5 3.5 5 6 7 MAX
200 1 1.5 2 2.5 3.5 5 6 7 MAX
250 1 1.5 2 2.5 3.5 5 7 8 MAX
300 1 1.5 2 2.5 3.5 5.5 7 MAX
400 1 1.5 2 2.5 4 6 8 MAX
450 1 1.5 2 2.5 4 6 8 MAX
500 1 1.5 2 2.5 4 6 8 MAX
800 11.52357MAX
lk 1 1.5 2.2 3 6 MAX
1.2k 1 1.5 2.2 3.5 MAX
1.5k 1 1.5 2.3 3.5 MAX
2k 1 1.5 2.3 MAX
2.5k 1 1.5 2.3 MAX
Crossover Frequency
3k 1 1.7 2.4 MAX
3.6k 1 1.7 MAX
4k 1 1.8 MAX
6k 1 2 MAX
7k 1.2 MAX
In order to phase-align two drivers you must observe only
the crossover frequency, which is common to both drivers.
Pink noise can be used if all other frequencies are disregarded, since room acoustics and imperfect driver response
will cause erroneous alignment attempts. Using pink noise as
a source, each driver is individually tuned to an arbitrary 0 dB
level on the analyzer display only at the crossover frequency.
When both are turned on simultaneously, the combined
response of the two drivers should read +3 dB higher at the
crossover frequency on the display. If the drivers are not
phase-aligned, some cancellation will occur on-axis, resulting
in a combined response less than +3 dB. Turning up the
DELAY control causes the lower driver to electronically
move backward until the analyzer reads +3 dB; then the two
drivers are electronically aligned and the on-axis cancellation
is eliminated.
Displacement
Manual-14
Figure 3. Front-to-Back Displacement Distance
Page 15

Setting the Output Level Controls
Choosing the crossover frequencies was the easy part.
Now it gets real fun. The idea is to set the output Level
controls on the crossover so that the entire speaker system has
a uniform, flat response. Unfortunately, the room in which
the speakers are placed has a habit of always getting into the
act, so things get messy. As a result there seems to be two
schools of thought regarding the use of active crossovers.
The Set-lt-Once-And-Glue-lt School
The philosophy here is to use the crossover to flatten
system response as much as possible without room acoustics
involved. This means setting up the system outside (unless
you happen to have a very large anechoic chamber handy) and
with the aid of a realtime analyzer and pink noise source (ala
RA 27), adjust all of the crossover outputs so that the system
is as flat as possible. Once the system is tuned, the crossover
is then locked behind a security cover (posted guard is
optional) and never again touched. It is then the job of the
system equalizer(s) to normalize or flatten the system to each
different room.
The Fix-lt-With-The-Crossover School
Here the crossover knobs get a good workout, for the
crossover is used at each location to help flatten the system
along with the equalizer. Some even maintain that a good
active crossover can work alone like a parametric equalizer in
the hands of an expert. This does require experience, skill,
and the right equipment to back it up (not to mention a
licensed set of ears).
Regardless of which school you profess, the absolute
importance and effectiveness of some kind of realtime
analyzer in your system cannot be overstressed! No, this is
not a callous plug for our other products; analyzers in general
have come a long way. They’re out of the lab (i.e. closet) and
into the hands of every smart working musician and sound
technician. An analyzer will save tremendous amounts of time
and provide the absolute consistency, accuracy, and plain old
good sound that very few ears on this earth can deliver. They
are affordable, easy to use and amazingly effective. You owe
it to yourself and your audience to at least look into one of
these analyzers—you’ll wonder how you managed at all
without one.
Whether by analyzer or ear, here are a few recommended
methods of setting the crossover output Levels.
Setting Levels Using a Realtime
Analyzer
NOTE: If you are running two Channels, tune up only one
Channel at a time.
1. Set all LEVEL controls on the crossover to minimum;
leave Delay and Frequency controls as set previously.
2. Place the analyzer microphone at least 15 feet away from
the speaker stack, on axis (dead ahead) and about chest
level. Minimize any background noise (fans, air conditioners, traffic, etc.) that could affect the readings.
3. Run pink noise through the system, either through a mixer
channel or directly into the crossover. Turn all amplifier
controls at least half way up.
4. We will use the 3-Way mode here as an example—the
procedure applies to all configurations. Turn up the INPUT
LEVEL control(s) on the crossover about half way.
5. Slowly turn up the LOW LEVEL control on the crossover,
until you hear a healthy level of noise through the low
frequency drivers (it should sound like rumble at this
point).
6. Adjust the display controls on the analyzer so that it shows
the greatest number of 0 dB LED’s (green on Rane
equipment) below the crossover point.
7. Now slowly turn up the MID LEVEL on the crossover until
the display shows the same output level average as the Low
frequency section.
8. Repeat this procedure for all crossover frequency sections,
lowest to highest, so that the end result is as flat response
as possible on the analyzer display.
IMPORTANT: Compression driver or horn roll-off, bass
roll-off, and room acoustics usually cannot be corrected by
the crossover. If you are using constant directivity horns, see
page 18. If, for example, you are adjusting the High frequency
controls and observe a decline in frequency response somewhat above the crossover point, then set the crossover LEVEL
control for equal display level near the crossover point and
leave it there. Then use an equalizer or bank of tweeters to
correct the roll-off problem. If you are tuning the system in a
room, the room acoustics will greatly influence the system
response, as shown by the analyzer.
Check the system response on an analyzer at several other
locations and adjust the crossover as necessary to reach a
fixed compromise setting if desired. If you plan to use the
analyzer only once to set the crossover, set up the speaker
system in a quiet place outside or in a very large concert
theater, and run pink noise at low levels with closer microphone placement to keep the room acoustics out of the picture
as much as possible.
Manual-15
Page 16

Setting Levels Using an SPL
Meter & Pink Noise Generator
The MUTE switches on the AC 23B make using an SPL
meter an easy and relatively accurate means of tuning a
system. First, obtain a good SPL meter from a local electronics or hi-fi store. Second, and perhaps a little trickier, get a
hold of a pink noise generator—again try electronics stores.
You may also use a sweep or tone generator in place of a pink
noise source. If so, be sure to look at several different tones
within each crossover section to get a good average driver
response.
1. Run pink noise into the crossover Inputs (through the mixer
or directly, as is convenient).
2. Make sure all crossover output LEVEL controls are turned
all the way down and all amplifier level controls are at
least half way up to start with.
3. Turn the crossover MASTER LEVEL(s) half way up. Place
the SPL meter at least 15 feet from the speaker stack and
about chest high. Once positioned, make sure that the SPL
meter remains in the exact same location for the rest of the
procedure. Minimize all background noise (fans, air
conditioners, traffic, wild animals, etc.) to get accurate
readings. Set the SPL meter to “C-weighting” “Slow” if
switches are present.
8. Repeat this process for each frequency section of the
crossover, ending with the highest frequency. NOTE: It is
possible that you may turn one of the frequency section
output LEVEL controls all the way up and still not have
enough volume for a 0 dB reading (as determined by
previous section levels). This is probably due to different
sensitivities of amps, speakers and other level controls in
the system. When this happens, re-set the SPL meter so that
it reads 0 dB on this frequency section (you may have to
“down range” the meter and re-adjust the crossover level
control). Now go back and re-adjust the previous crossover
level controls, turning these down to get a 0 dB reading on
the meter.
9. Once the HIGH LEVEL control is set for 0 dB on the
meter, disengage all of the MUTE switches on the crossover, and check that noise is emitting from all the speaker
components. The crossover should now be aligned. Make
any overall level adjustments with the MASTER LEVEL
controls and leave the output level controls unchanged.
4. Slowly turn the LOW LEVEL of the crossover up until
there is a healthy rumble coming from the bass speakers
(For this example the 3-Way configuration is used—the
same procedure applies to all configurations, starting with
the lowest frequency and ending with the highest). Adjust
the SPL meter and/or crossover output until you get a 0 dB
reading on the meter. After this point do not change the
controls on the SPL meter.
5. While leaving the LOW LEVEL control at the 0dB
adjustment just obtained, press the LOW MUTE switch on
the crossover so that the pink noise disappears from the
bass speakers (revel in the silence...).
6. Now slowly turn up the MID LEVEL control so that pink
noise is heard from the mid frequency speakers. Without
changing any settings on the SPL meter, adjust the crossover MID LEVEL control until you obtain a 0 dB reading
on the SPL meter. Now the low and mid speakers are set at
the same level.
7. Now press the MID MUTE switch on the crossover so that
the pink noise again disappears.
Fig. 4 Configuration with Long
Throw Horn
Fig. 5 Configuration with Constant
Directivity Horn
Manual-16
Page 17

Time Delay Transplant
Modification
There are modification jumpers inside the AC 23B. These
jumpers permit the transplanting of the Delay circuits from
one output to another. As the units are shipped, the Delay
circuit is not installed on the High Frequency outputs. When
the AC 23 was first designed, long throw horns were more
common than Constant Directivity horns (CD horns). The
long throw horn's diaphragm was the farthest sound emitter
from the front of the speaker enclosure, (see Fig. 4) so no
delay was needed. The mid frequency and low frequency
drivers were always in front of the high frequency drivers,
therefore, the mid and low frequency drivers needed the
Delay circuits for proper time alignment.
Now, with the use of CD horns becoming more common,
occasionally there is a need to delay the CD horn as its
diaphragm is usually in front of the other drivers in the
enclosure (see Fig. 5). If you are using CD horns, you should
also read the CD horn EQ modification as described on page
18.With the AC 23 it is a little difficult to figure out which
Delay to move to the High Frequency Output. The normal
configuration for a speaker enclosure is shown in Fig. 3. The
long throw horn’s driver is the farthest back in the enclosure,
so no Delay is needed for this driver. Some Delay is needed
on the Low and Mid drivers. The enclosure with the CD
Horn, shown in Fig. 5, needs the Delay circuit transplanted
from the Low to the High frequencies Outputs. As can be seen
from the dashed line in the drawing, the CD Horn’s driver is
in front of the mid and low drivers. Of the three drivers, the
low frequency driver will need no Delay, the mid frequency
driver will need some Delay, and the CD Horn will need the
most Delay. Soldering is required. This modification should
only be attempted by an experienced technician.
STEP BY STEP PROCEDURE
Transplanting the Low Frequency Delay to the High
Frequency Output.
CHANNEL ONE:
1. Refer to the board assembly layout on page Schematics-1.
2. Behind the Channel 1 LF DELAY pot find the jumper
labeled W8. Behind the Channel 1 LF LEVEL pot find the
jumper labeled W4.
3. To remove the Delay 1 circuit from the Low Frequency
output, remove both the W8 and W4 jumpers.
4. To get the Low Frequency output to work again, install a
long jumper from W8 Pin 1 to W4 Pin 2.
5. The Delay 1 circuit is now removed from all circuits.
6. To install the Delay 1 circuit into the Channel 1 High
Frequency Output, find the jumper W19 behind the
Channel 1 MF MUTE switch and remove it.
7. Install a long jumper from W4 Pin 1 to W19 Pin 2, and
install a long jumper from W8 Pin 2 to W19 Pin 1.
The Delay 1 circuit is now installed into Channel 1 High
Frequency Output.
CHANNEL TWO:
1. Refer to the board layout on page Schematics-1.
2. Behind the Channel 2 LF DELAY pot find the jumper
labeled W44. Behind the Channel 1 LF LEVEL pot find
the jumper labeled W42.
3. To remove the Delay 3 circuit from the Low Frequency
output, remove both the W42 and W44 jumpers.
4. To get the Low Frequency output to work again, install a
long jumper from W44 Pin 1 to W42 Pin 2.
5. The Delay 3 circuit is now removed from all circuits.
6. To install the Delay 3 circuit into the Channel 2, High
Frequency Output, find the jumper W51 behind the
Channel 2 MF MUTE and remove it.
7. Install a long jumper from W42 Pin 1 to W51 Pin 2, and
install a long jumper from W44 Pin 2 to W51 Pin 1.
The Delay 3 circuit is now installed into Channel 2 High
Frequency Output.
STEP BY STEP PROCEUDURE
Transplanting the Mid Frequency Delay to the High
Frequency Output
CHANNEL ONE:
1. Refer to the board layout on page Schematics-1.
2. Behind the Channel 1 MF DELAY pot find the jumper
labeled W26. Behind the Channel 1 MF LEVEL pot find
the jumper labeled W18.
3. To remove the Delay 2 circuit from the Mid Frequency
output, remove both the W26 and W18 jumpers.
4. To get the Mid Frequency output to work again, install a
long jumper from W26 Pin 1 to W18 Pin 2.
5. The Delay 2 circuit is now removed from all circuits.
6. To install the Delay 2 circuit into the Channel 1, High
Frequency output, find the jumper W19 behind the Channel
1 MF MUTE switch and remove it.
7. Install a long jumper from W26 Pin 2 to W19 Pin 1, and
install a long jumper from W18 Pin 1 to W19 Pin 2.
The Delay 2 circuit is now installed into Channel 1 High
Frequency Output.
CHANNEL TWO:
1. Refer to the board layout on page Schematics-1.
2. Behind the Channel 2 MF DELAY pot find the jumper
labeled W55. Behind the Channel 2 MF LEVEL locate the
jumper labeled W50.
3. To remove the Delay 4 circuit from the Mid Frequency
output, remove both the W50 and W55 jumpers.
4. To get the Mid Frequency output to work again, install a
long jumper from W55 Pin 1 to W50 Pin 2.
5. The Delay 4 circuit is now removed from all circuits.
6. To install the Delay 4 circuit into the Channel 2 High
Frequency output, find the jumper W51 behind the Channel
2 MF MUTE switch and remove it.
7. Install a long jumper from W55 Pin 2 to W51 Pin 1, and
install a long jumper from W50 Pin 1 to W51 Pin 2.
The Delay 4 circuit is now installed into Channel 2 High
Frequency Output.
Manual-17
Page 18

Constant Directivity Horn
Equalization Modification
Constant Directivity (or CD) horns need additional
equalization to help cover the same area a long throw horn
can cover. Additional circuitry has been added to the AC 23B
for the additional equalization of the High Frequency outputs
for the CD Horns. This modification should only be attempted
by an experienced technician.
It is important to know the 3 dB down point of the CD
driver's frequency response. The manufacturer of your driver
should be able to supply you with a chart showing a frequency response curve. Find the point where the high end
starts to roll off, and look for the point on the chart that is 3
dB down from that point (toward the right, as the higher
frequencies roll off). Find the frequency at the bottom of the
chart of this point—an approximate is fine, you don't have to
be exact. Find the closest frequency in the table below to
determine the correct value capacitor to install in the AC 23B
to correct for this high frequency roll off.
STEP BY STEP PROCEDURE
The following procedure is for CD horn EQ on the High
output in Stereo 3-Way mode. For a Mono 4- or 5-Way
system with a CD horn on the high output, only place C16 in
Channel 2.
1. Remove the top and bottom covers of the AC 23B.
2. Locate the positions for C15 and C16 on page Schematics-
1 and on the circuit board. C15 (for Channel 1) is located
behind the CH 1 MF MUTE switch. C16 (for Channel 2) is
located behind the CH 2 MF MUTE switch.
3. Clean the solder pad on the underside of the board so that
the appropriate capacitor can be inserted. Install the
capacitor, and solder the leads from the underside using
fresh solder. Clip the excess leads.
4. Replace the top and bottom covers.
3 dB Down
Frequency
Capacitor
2.0 kHz .0015 µf
2.5 kHz .0012 µf
3.0 kHz .001 µf
Monoing the Low Frequency
Outputs
It is possible to mono the Low Frequency Outputs of the
AC 23B by an internal jumper modification. This requires
that the Delay 1 and Delay 3 circuits be removed from the
signal path, and that R33 be removed. The following procedure will assist you through the modification. Soldering is
required. This modification should only be attempted by an
experienced technician.
DELAY ONE REMOVAL
1. Refer to the board layout on page Schematics-1 and on the
circuit board.
2. Behind the Channel 1 LF LEVEL pot find the jumper
labeled W4. Behind the Channel 1 LF DELAY pot find the
jumper labeled W8.
3. To remove the Delay 1 circuit from the Low Frequency
output, remove both the W4 and W8 jumpers.
4. To get the Low Frequency output to work again, install a
long jumper from W8 Pin 1 to W4 Pin 2.
The Delay 1 circuit is now removed from all circuits.
DELAY THREE REMOVAL
1. Refer to the board layout on page Schematics-1 and on the
circuit board.
2. Behind the Channel 2 LF DELAY pot find the jumper
labeled W44. Behind the Channel 1 LF LEVEL pot find
the jumper labeled W42.
3. To remove the Delay 3 circuit from the Low Frequency
output, remove both the W42 and W44 jumpers.
4. To get the Low Frequency output to work again, install a
long jumper from W44 Pin 1 to W42 Pin 2.
The Delay 3 circuit is now removed from all circuits.
REMOVING R33 AND SUMMING THE LOW FREQUENCY OUTPUTS
1. Refer to the board layout on page Schematics-1 and on the
circuit board.
2. Behind the Channel 2 LF LEVEL pot find the resistor R33,
and remove it, in any way your heart desires, though
violence will void your warranty.
3. Behind the Channel 1 HF LEVEL pot find the jumper W29.
4. Install a short jumper wire from W29 Pin 1 to W29 Pin 2.
Solder in place.
The Low Frequency Outputs are now summed.
3.7 kHz 820 pf
4.0 kHz 750 pf
5.0 kHz 620 pf
6.4 kHz 470 pf
©Rane Corporation 10802 47th Ave. W., Mukilteo WA 98275-5098 TEL (425)355-6000 FAX (425)347-7757 WEB http://www.rane.com
Manual-18
103045
 Loading...
Loading...