Page 1

A Guide to QuarkXPress 9.3
Page 2

CONTENTS
Contents
About this guide.............................................................................18
What we're assuming about you..........................................................................18
Where to go for help............................................................................................18
Conventions..........................................................................................................19
Technology note...................................................................................................19
The user interface...........................................................................21
Tools......................................................................................................................21
Web tools..............................................................................................................24
Menus...................................................................................................................24
QuarkXPress menu (Mac OS only).................................................................................25
File menu.......................................................................................................................25
Edit menu......................................................................................................................26
Style menu.....................................................................................................................28
Item menu.....................................................................................................................30
Page menu....................................................................................................................32
Layout menu..................................................................................................................32
Table menu...................................................................................................................33
View menu.....................................................................................................................34
Utilities menu.................................................................................................................35
Window menu...............................................................................................................36
Help menu ....................................................................................................................38
Context menus......................................................................................................38
Palettes.................................................................................................................38
Tools palette.................................................................................................................39
Measurements palette...................................................................................................39
Page Layout palette......................................................................................................40
Style Sheets palette.......................................................................................................41
Conditional Styles palette.............................................................................................42
Colors palette................................................................................................................42
Shared Content palette.................................................................................................43
Trap Information palette...............................................................................................43
Lists palette...................................................................................................................43
App Studio palette........................................................................................................44
Profile Information palette.............................................................................................44
ii | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 3

CONTENTS
Callout Styles palette....................................................................................................45
Glyphs palette...............................................................................................................45
Grid Styles palette.........................................................................................................45
Blio Table of Contents palette......................................................................................46
Reflow Tagging palette.................................................................................................46
Reflow Table of Contents palette..................................................................................46
Hyperlinks palette.........................................................................................................46
Index palette.................................................................................................................47
Interactive palette.........................................................................................................48
Layers palette................................................................................................................48
Picture Effects palette...................................................................................................48
Guides palette...............................................................................................................49
Item Styles palette.........................................................................................................49
PSD Import palette........................................................................................................49
Scale palette..................................................................................................................49
Palette groups and palette sets............................................................................49
Layout controls.....................................................................................................50
Views and view sets..............................................................................................51
Splitting a window.........................................................................................................51
Creating a window........................................................................................................52
Using Story Editor view.................................................................................................52
View sets........................................................................................................................53
Projects and layouts........................................................................56
Working with projects..........................................................................................56
Options for Print layouts................................................................................................57
Options for Web layouts...............................................................................................57
Saving and naming a QuarkXPress project...................................................................58
Exporting layouts and projects......................................................................................58
Working with layouts............................................................................................58
Project-level and layout-level resources........................................................................59
Working with guides.............................................................................................60
Column and margin guides...........................................................................................60
Ruler guides..................................................................................................................61
Snapping to guides.......................................................................................................61
Undoing and redoing actions................................................................................62
Boxes, lines, and tables...................................................................63
Understanding items and content.........................................................................63
Understanding handles.........................................................................................64
Understanding Bézier shapes...............................................................................66
Working with boxes..............................................................................................67
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | iii
Page 4

CONTENTS
Creating text and picture boxes....................................................................................68
Resizing boxes...............................................................................................................69
Locking box and picture proportions............................................................................69
Reshaping boxes...........................................................................................................70
Adding frames to boxes................................................................................................70
Applying colors to boxes..............................................................................................71
Applying blends to boxes.............................................................................................71
Merging and splitting boxes.........................................................................................72
Adding text and pictures to boxes................................................................................72
Changing box type........................................................................................................73
Creating a box from a clipping path.............................................................................73
Working with lines................................................................................................73
Creating lines................................................................................................................73
Line modes for straight lines.........................................................................................74
Resizing lines.................................................................................................................74
Reshaping lines.............................................................................................................75
Controlling line appearance..........................................................................................75
Joining lines..................................................................................................................75
Manipulating items...............................................................................................76
Selecting items..............................................................................................................76
Moving items.................................................................................................................76
Cutting, copying, and pasting items.............................................................................76
Controlling the stacking order of items.........................................................................76
Grouping items.............................................................................................................77
Duplicating items..........................................................................................................78
Spacing and aligning items ..........................................................................................78
Rotating items...............................................................................................................79
Skewing items...............................................................................................................79
Locking and unlocking items.........................................................................................79
Anchoring items and groups in text..............................................................................79
Working with callouts...........................................................................................80
Understanding callouts..................................................................................................80
Creating a callout..........................................................................................................82
Configuring a callout anchor.........................................................................................83
Working with callout styles............................................................................................85
Callouts and runaround.................................................................................................85
Working with tables..............................................................................................86
Drawing a table.............................................................................................................86
Converting text to tables...............................................................................................87
Importing Excel tables...................................................................................................88
Importing Excel charts...................................................................................................90
Adding text and pictures to tables................................................................................90
Editing table text ..........................................................................................................90
iv | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 5

CONTENTS
Linking table cells..........................................................................................................91
Formatting tables..........................................................................................................91
Formatting gridlines......................................................................................................91
Inserting and deleting rows and columns.....................................................................93
Combining cells.............................................................................................................93
Manually resizing tables, rows, and columns................................................................93
Converting tables back to text......................................................................................93
Working with tables and groups...................................................................................93
Continuing tables in other locations.............................................................................94
Text and typography.......................................................................99
Editing text...........................................................................................................99
Importing and exporting text...............................................................................99
Import/export filters....................................................................................................100
Importing and exporting text with Unicode options...................................................101
Finding and changing text..................................................................................101
Special character codes...............................................................................................103
Checking spelling................................................................................................104
Auxiliary dictionaries...................................................................................................105
Counting words and characters..........................................................................106
Applying character attributes.............................................................................106
Applying a font............................................................................................................106
Choosing a font size....................................................................................................107
Applying type styles....................................................................................................107
Applying color, shade, and opacity.............................................................................108
Applying horizontal or vertical scale...........................................................................108
Applying baseline shift................................................................................................109
Applying multiple character attributes........................................................................109
Applying paragraph attributes...........................................................................110
Controlling alignment.................................................................................................110
Controlling indentation...............................................................................................111
Controlling leading......................................................................................................112
Controlling space before and after paragraphs..........................................................113
Setting tabs.................................................................................................................113
Controlling widow and orphan lines...........................................................................113
Controlling kerning.............................................................................................114
Kerning manually.........................................................................................................114
Kerning automatically..................................................................................................115
Controlling hyphenation and justification...........................................................115
Specifying hyphenation exceptions............................................................................116
Using discretionary hyphens.......................................................................................116
Controlling tracking............................................................................................116
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | v
Page 6

CONTENTS
Tracking manually........................................................................................................117
Editing tracking tables.................................................................................................117
Working with style sheets..................................................................................118
Creating and editing paragraph style sheets..............................................................118
Creating and editing character style sheets................................................................120
Applying style sheets..................................................................................................122
Appending style sheets...............................................................................................123
Working with conditional styles..........................................................................123
Creating a conditional style.........................................................................................125
Applying a conditional style........................................................................................127
Removing conditional styles........................................................................................128
Using conditional style markers...................................................................................128
Editing a conditional style...........................................................................................129
Bullets and numbering........................................................................................129
Working with bullet styles...........................................................................................130
Working with numbering styles...................................................................................132
Working with outline styles.........................................................................................133
Bullets, numbering, outlines, and style sheets............................................................136
Positioning text in text boxes.............................................................................137
Using baseline grid......................................................................................................137
Aligning text vertically.................................................................................................137
Specifying text inset....................................................................................................137
Controlling font usage........................................................................................138
Converting text to boxes....................................................................................138
Using text runaround..........................................................................................138
Running text around all sides of an item.....................................................................139
Running text around lines and text paths....................................................................139
Running text around text boxes .................................................................................139
Running text around pictures......................................................................................140
Fine-tuning a runaround path.....................................................................................141
Editing a runaround path............................................................................................141
Working with text paths.....................................................................................142
Creating drop caps.............................................................................................142
Creating rules above and below paragraphs......................................................143
Using anchored boxes.........................................................................................143
Anchoring boxes and lines in text...............................................................................143
Cutting, copying, pasting, and deleting anchored boxes and lines...........................144
Unanchoring boxes and lines......................................................................................144
Working with OpenType fonts...........................................................................144
Applying OpenType styles..........................................................................................144
Using ligatures.............................................................................................................146
Working with the Glyphs palette........................................................................147
Displaying invisible characters............................................................................148
vi | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 7

CONTENTS
Inserting special characters.................................................................................148
Inserting spaces...........................................................................................................148
Inserting other special characters................................................................................148
Specifying character language............................................................................148
Using font fallback..............................................................................................149
Importing and exporting text with Unicode options..........................................149
Working with font mapping rules.......................................................................149
Working with design grids..................................................................................150
Understanding design grids........................................................................................150
Design grid basics.......................................................................................................152
Working with grid styles..............................................................................................159
Using design grids.......................................................................................................161
Working with hanging characters.......................................................................163
Creating hanging character classes.............................................................................165
Creating hanging character sets ................................................................................166
Applying hanging character sets.................................................................................166
Pictures.........................................................................................167
Understanding pictures.......................................................................................167
Supported picture file types...............................................................................168
Working with pictures.........................................................................................169
Importing a picture......................................................................................................169
Moving pictures...........................................................................................................169
Resizing pictures..........................................................................................................170
Cropping pictures.......................................................................................................170
Rotating and skewing pictures....................................................................................170
Coloring and shading pictures....................................................................................170
Flipping pictures..........................................................................................................170
Listing, verifying status of, and updating pictures.......................................................171
Specifying background colors for pictures..................................................................171
Maintaining picture attributes.....................................................................................171
Working with clipping paths...............................................................................171
Creating clipping paths...............................................................................................172
Using embedded clipping paths.................................................................................173
Manipulating clipping paths........................................................................................173
Creating special effects with clipping paths................................................................174
Working with alpha masks..................................................................................174
Working with PSD pictures.................................................................................175
Preparing PSD files......................................................................................................176
Working with PSD layers.............................................................................................176
Working with PSD channels.........................................................................................177
Working with PSD paths..............................................................................................178
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | vii
Page 8

CONTENTS
Printing with PSD Import.............................................................................................178
Using picture effects...........................................................................................179
Working with picture effects........................................................................................179
Removing and deleting picture effects.......................................................................180
Displaying effects at full resolution.............................................................................180
Picture Effects: Filters..................................................................................................180
Picture Effects: Adjustments........................................................................................181
Saving and loading Picture Effects presets.................................................................182
Reviewing Picture Effects usage..................................................................................183
Saving picture files......................................................................................................183
Color, opacity, and drop shadows................................................184
Understanding color...........................................................................................184
Understanding spot and process colors......................................................................184
Specifying matching system colors.............................................................................184
Working with colors............................................................................................185
The Colors palette.......................................................................................................185
The Colors dialog box.................................................................................................185
Creating a color...........................................................................................................186
Editing a color.............................................................................................................187
Duplicating a color......................................................................................................187
Deleting a color...........................................................................................................187
Importing colors from another article or project.........................................................187
Changing all instances of one color to another color.................................................187
Applying color, shade, and blends.............................................................................188
Applying color and shade to text................................................................................188
Applying color and shade to lines...............................................................................188
Working with opacity..........................................................................................189
Specifying opacity.......................................................................................................189
Specifying opacity for groups.....................................................................................189
Creating blends with transparency..............................................................................190
Color management..............................................................................................190
Source setups and output setups................................................................................190
The color management experience for users..............................................................190
Working with source setups and output setups from a color expert..........................192
Working in a legacy color management environment................................................192
Proofing color on screen (soft proofing)......................................................................193
Color management for experts...................................................................................194
Creating a source setup..............................................................................................194
Creating an output setup............................................................................................194
Managing profiles.......................................................................................................195
Working with drop shadows...............................................................................196
viii | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 9

CONTENTS
Applying drop shadows..............................................................................................197
Customizing drop shadows.........................................................................................197
Incorporating drop shadows with items......................................................................197
Document construction.................................................................199
Using automatic page numbering.......................................................................199
Creating an automatic text box..........................................................................199
Working with master pages................................................................................200
Creating a master page...............................................................................................200
Applying master pages...............................................................................................204
Updating master pages...............................................................................................204
Master pages and layout families................................................................................205
Working with layers............................................................................................205
Understanding layers...................................................................................................206
Creating layers............................................................................................................206
Selecting layers...........................................................................................................206
Showing and hiding layers..........................................................................................207
Determining which layer an item is on........................................................................208
Deleting layers............................................................................................................208
Changing layer options...............................................................................................208
Moving items to a different layer................................................................................209
Changing the stacking order of layers........................................................................209
Layers and text runaround...........................................................................................210
Duplicating layers........................................................................................................210
Merging layers.............................................................................................................211
Locking items on layers...............................................................................................211
Using master pages with layers...................................................................................211
Suppressing printout of layers.....................................................................................212
Using PDF layers.........................................................................................................212
Working with lists...............................................................................................213
Preparing for lists.........................................................................................................213
Creating a list..............................................................................................................213
Importing lists from another document.......................................................................214
Navigating with lists....................................................................................................214
Building lists................................................................................................................215
Updating lists..............................................................................................................215
Working with lists in books..........................................................................................215
Working with indexes.........................................................................................216
Specifying the index marker color...............................................................................216
Creating index entries.................................................................................................217
Creating cross-references............................................................................................219
Editing an index entry.................................................................................................220
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | ix
Page 10

CONTENTS
Deleting an index entry...............................................................................................220
Specifying the punctuation used in an index..............................................................220
Building an index.........................................................................................................221
Editing final indexes....................................................................................................222
Working with books............................................................................................223
Creating books............................................................................................................224
Working with chapters.................................................................................................224
Controlling page numbers..........................................................................................226
Synchronizing chapters...............................................................................................227
Printing chapters.........................................................................................................228
Creating indexes and tables of contents for books....................................................229
Working with libraries.........................................................................................229
Creating libraries.........................................................................................................230
Adding library entries..................................................................................................230
Retrieving library entries..............................................................................................231
Manipulating library entries.........................................................................................231
Working with labels.....................................................................................................231
Saving libraries............................................................................................................232
Output...........................................................................................233
Printing layouts...................................................................................................233
Updating picture paths................................................................................................233
Setting Print dialog box controls.................................................................................234
Print dialog box...........................................................................................................235
Printing color separations............................................................................................240
Printing color composites............................................................................................241
Exporting layouts................................................................................................242
Exporting a layout in EPS format.................................................................................243
Exporting a layout in PDF format................................................................................243
Creating a PostScript file.............................................................................................245
Using Collect for Output.....................................................................................245
Working with output styles................................................................................247
Working with trapping........................................................................................247
Understanding flattening and production issues................................................248
Collaboration and single-sourcing.................................................249
Working with shared content.............................................................................249
Sharing and synchronizing content.............................................................................251
Understanding synchronization options......................................................................252
Placing a synchronized item........................................................................................253
Placing synchronized content......................................................................................253
Importing content into the shared content library......................................................253
x | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 11

CONTENTS
Working with Composition Zones.......................................................................254
Understanding Composition Zones............................................................................254
Creating a Composition Zones item...........................................................................259
Placing a Composition Zones item..............................................................................261
Sharing a composition layout......................................................................................263
Using Collaboration Setup..................................................................................271
Linking to other projects.............................................................................................271
Viewing information about linkable composition layouts ..........................................272
Importing and managing shared content....................................................................272
Specifying update options..........................................................................................273
Interactive layouts.........................................................................274
Understanding Interactive layouts......................................................................274
Types of Interactive layouts.........................................................................................275
Types of objects..........................................................................................................275
Interactive layouts in action.........................................................................................276
Creating interactive building blocks...................................................................283
Creating a Presentation layout....................................................................................283
Creating an object.......................................................................................................284
Configuring an SWF object.........................................................................................285
Configuring a Video object.........................................................................................287
Working with Animation objects.................................................................................288
Working with Button objects.......................................................................................294
Image Sequence layouts, Button layouts, and Shared Content..................................298
Working with menus....................................................................................................298
Configuring a Window object.....................................................................................302
Configuring a Text Box object....................................................................................303
Working with transitions..............................................................................................304
Working with pages in Interactive layouts...................................................................305
Working with keyboard commands.............................................................................307
Configuring Interactive preferences............................................................................308
Working with actions..........................................................................................308
Assigning actions........................................................................................................309
Action reference..........................................................................................................309
Working with events...........................................................................................317
Choosing a user event.................................................................................................318
Configuring user events..............................................................................................318
Working with scripts...........................................................................................320
Creating a script..........................................................................................................320
Using conditional statements......................................................................................321
Running a script ..........................................................................................................324
Exporting and importing scripts..................................................................................325
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | xi
Page 12

CONTENTS
Previewing and exporting Interactive layouts....................................................325
Previewing a Presentation layout................................................................................325
Checking interactive object usage..............................................................................326
Exporting a Presentation layout..................................................................................326
Configuring export settings........................................................................................326
Working with expressions...................................................................................327
Understanding expressions.........................................................................................327
Using the Expression Editor dialog box......................................................................331
eBooks...........................................................................................334
Working with Reflow view..................................................................................334
Creating reflow articles................................................................................................336
Mapping style sheets to Reflow tags..........................................................................339
Adding content to a reflow article...............................................................................340
Splitting a reflow component......................................................................................341
Reordering components in a reflow article.................................................................341
Editing content in Reflow view....................................................................................341
Updating content in Reflow view................................................................................344
Adding interactivity to ePub eBooks..................................................................345
Adding audio to an ePub eBook.................................................................................345
Adding video to an ePub eBook.................................................................................346
Adding interactivity to Blio eBooks....................................................................346
Adding a slideshow to a Blio eBook...........................................................................347
Adding video to a Blio eBook.....................................................................................348
Adding HTML to a Blio eBook....................................................................................348
Adding a URL link to a picture box in a Blio eBook....................................................349
Creating a TOC for ePub or Kindle.....................................................................349
Creating a TOC for Blio.......................................................................................349
Working with eBook metadata...........................................................................350
Exporting for ePub.............................................................................................351
Specifying CSS for ePub export..................................................................................352
Exporting for Kindle...........................................................................................353
Exporting for Blio eReader.................................................................................354
Job Jackets...................................................................................356
Understanding Job Jackets.................................................................................356
What are Job Jackets?................................................................................................357
The structure of Job Jackets.......................................................................................357
Sample Job Jackets workflow.....................................................................................362
Working with Job Jackets...................................................................................363
Basic mode and advanced mode................................................................................363
Creating Job Jackets files...........................................................................................364
xii | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 13

CONTENTS
Working with Job Tickets...................................................................................368
Creating a Job Ticket template...................................................................................368
Adding a layout definition to a Job Ticket: Advanced mode.....................................373
Applying a Job Ticket template to a project...............................................................374
Applying a layout definition to a project.....................................................................377
Collaborating with shared Job Jackets.......................................................................377
Exporting and importing Job Tickets..........................................................................380
The default Job Jackets file................................................................................381
Editing the default Job Ticket template: File menu....................................................381
Editing the default Job Ticket template: Utilities menu..............................................381
Editing the default Job Jackets file.............................................................................382
Working with Resources: Advanced mode.........................................................382
Accessing Resources: Advanced mode.......................................................................382
Configuring Resources: Advanced mode....................................................................383
Specifying the location of Resources: Advanced mode..............................................384
Working with Layout Specifications....................................................................385
Creating a Layout Specification: Advanced mode......................................................385
Applying a Layout Specification to a layout................................................................386
Working with Output Specifications...................................................................388
Creating an Output Specification: Advanced mode...................................................389
Applying an Output Specification to a layout.............................................................389
Using Output Specifications with Output Job............................................................391
Working with Rules and Rule Sets......................................................................392
Creating Rules: Advanced mode................................................................................393
Adding Rules to a Rule Set: Advanced mode.............................................................395
Applying a Rule Set to a layout...................................................................................396
Evaluating a layout.............................................................................................398
Job Jackets locking.............................................................................................400
Printing with JDF output....................................................................................401
Web layouts..................................................................................403
Working with Web layouts.................................................................................403
Creating a Web layout................................................................................................403
Text boxes in Web layouts..........................................................................................405
Graphic elements in Web layouts...............................................................................407
Converting to and from Web layouts..........................................................................408
Web layout limitations.................................................................................................409
Hyperlinks...........................................................................................................409
Creating a destination.................................................................................................411
Creating an anchor......................................................................................................412
Creating a hyperlink using an existing destination.....................................................412
Creating a hyperlink from scratch...............................................................................413
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | xiii
Page 14

CONTENTS
Showing links in the Hyperlinks palette.......................................................................413
Formatting hyperlinks..................................................................................................413
Editing and deleting destinations...............................................................................414
Editing and deleting anchors......................................................................................414
Editing and deleting hyperlinks...................................................................................414
Navigating using the Hyperlinks palette.....................................................................414
Rollovers.............................................................................................................415
Creating a basic rollover.............................................................................................415
Editing and deleting basic rollovers............................................................................416
Creating a two-position rollover..................................................................................416
Switching between rollover images in the layout........................................................416
Removing a target from a two-position rollover box..................................................417
Unlinking a two-position rollover................................................................................417
Image maps.........................................................................................................417
Creating an image map...............................................................................................417
Editing an image map.................................................................................................418
Forms..................................................................................................................418
Creating a form box....................................................................................................419
Adding a text, password, or hidden field control.......................................................420
Adding a button control..............................................................................................421
Adding an image button control.................................................................................421
Adding pop-up menu and list controls.......................................................................422
Adding a group of radio button controls ...................................................................422
Adding a check box control .......................................................................................423
Adding a file submission control ................................................................................423
Menus.................................................................................................................424
Working with standard menus.....................................................................................424
Working with cascading menus...................................................................................426
Tables in Web layouts.........................................................................................429
Meta tags............................................................................................................430
Creating a meta tag set...............................................................................................430
Specifying a meta tag set for a Web page .................................................................431
Previewing Web pages.......................................................................................431
Specifying additional browsers for preview ...............................................................432
Exporting Web pages.........................................................................................432
Preparing for export ...................................................................................................432
Exporting a Web page ...............................................................................................432
Working with multiple languages..................................................435
Applying a character language...........................................................................435
Changing the program language........................................................................436
xiv | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 15

CONTENTS
XTensions software.......................................................................437
Working with XTensions modules.......................................................................437
Installing XTensions modules......................................................................................437
Enabling and disabling XTensions modules................................................................437
Working with XTensions sets.......................................................................................438
Custom Bleeds XTensions software....................................................................438
Using Custom Bleeds..................................................................................................439
Using Clip at Bleed Edge............................................................................................439
DejaVu XTensions software................................................................................439
Drop Shadow XTensions software......................................................................440
Full Resolution Preview XTensions software......................................................441
Guide Manager Pro XTensions software............................................................442
Using the Guides palette.............................................................................................442
Guides palette menu...................................................................................................443
Creating guides with Guide Manager Pro...................................................................444
Creating grids with Guide Manager Pro.....................................................................445
Creating rows and columns.........................................................................................447
Creating bleed and safety guides...............................................................................448
HTML Text Import XTensions software..............................................................450
Item Find/Change XTensions software...............................................................450
Item Styles XTensions software..........................................................................452
Using the Item Styles palette......................................................................................452
Creating Item Styles....................................................................................................453
Checking Item Style usage..........................................................................................454
OPI XTensions software......................................................................................455
Targeting an imported picture for OPI exchange.......................................................455
Activating OPI for a layout..........................................................................................455
Creating OPI comments for print, EPS, and PDF........................................................456
PDF Filter XTensions software...........................................................................456
Importing a PDF file into a picture box.......................................................................456
Scale XTensions software...................................................................................457
Scissors XTensions software...............................................................................458
Script XTensions software..................................................................................459
Box Tools submenu.....................................................................................................459
Grid submenu..............................................................................................................460
Images submenu.........................................................................................................460
Picture Box submenu..................................................................................................460
Printing submenu........................................................................................................460
Saving submenu..........................................................................................................460
Special submenu.........................................................................................................461
Stories submenu..........................................................................................................461
Tables submenu..........................................................................................................461
Typography submenu.................................................................................................461
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | xv
Page 16

CONTENTS
Shape of Things XTensions software..................................................................462
Using the Star Box tool...............................................................................................462
Super Step and Repeat XTensions software.......................................................462
Using Super Step and Repeat.....................................................................................462
Table Import XTensions software.......................................................................463
Type Tricks..........................................................................................................464
Make Fraction..............................................................................................................464
Make Price...................................................................................................................464
Word Space Tracking..................................................................................................465
Line Check...................................................................................................................465
Custom Underline.......................................................................................................466
Word 6–2000 Filter.............................................................................................466
WordPerfect Filter .............................................................................................466
XSLT Export XTensions software.......................................................................466
Cloner XTensions software.................................................................................467
ImageGrid XTensions software...........................................................................468
Linkster XTensions software...............................................................................470
ShapeMaker XTensions software........................................................................471
ShapeMaker Waves tab...............................................................................................472
ShapeMaker Polygons tab..........................................................................................473
ShapeMaker Spirals tab...............................................................................................474
ShapeMaker Rectangles tab........................................................................................475
ShapeMaker Presets tab..............................................................................................476
Other XTensions modules...................................................................................477
Preferences...................................................................................479
Understanding preferences................................................................................479
Nonmatching Preferences alert...................................................................................479
Changes to QuarkXPress preferences.........................................................................480
What's in the preferences files....................................................................................480
Application preferences......................................................................................481
Preferences — Application — Display........................................................................482
Preferences — Application — Input Settings..............................................................482
Preferences — Application — Font Fallback...............................................................483
Preferences — Application — Undo...........................................................................484
Preferences — Application — Open and Save...........................................................484
Preferences — Application — XTensions Manager....................................................485
Preferences — Application — Sharing........................................................................485
Preferences — Application — Fonts...........................................................................485
Preferences — Application — File List........................................................................485
Preferences — Application — Default Path................................................................485
Preferences — Application — Full Res Preview..........................................................486
xvi | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 17

CONTENTS
Preferences — Application — Browsers......................................................................486
Preferences — Application — Index...........................................................................486
Preferences — Application — Job Jackets.................................................................487
Preferences — Application — PDF.............................................................................487
Preferences — Application — PSD Import..................................................................488
Preferences — Application — Placeholders................................................................488
Preferences — Application — SpellCheck..................................................................488
Preferences — Application — Fraction/Price..............................................................489
Preferences — Application — Picture Effects.............................................................489
Project preferences.............................................................................................490
Preferences — Project — General...............................................................................490
Layout preferences.............................................................................................490
Preferences — Layout — General...............................................................................490
Preferences — Layout — Measurements....................................................................491
Preferences — Layout — Paragraph...........................................................................492
Preferences — Layout — Character............................................................................493
Preferences — Layout — Tools...................................................................................495
Preferences — Layout — Trapping.............................................................................495
Preferences — Layout — Guides and Grid.................................................................495
Preferences — Layout — Color Manager....................................................................496
Preferences — Layout — Layers..................................................................................497
Preferences — Layout — Presentation........................................................................497
Preferences — Layout — SWF....................................................................................498
Legal notices.................................................................................499
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | xvii
Page 18

ABOUT THIS GUIDE
About this guide
What we're assuming about you
You do not need to read the QuarkXPress® documentation from beginning to end. Instead,
use this guide to quickly look up information, find out what you need to know, and get
on with your work.
In writing this guide, we assume that you are familiar with your computer and know how
to:
• Launch an application
• Open, save, and close files
• Use menus, dialog boxes, and palettes
• Work within a networked computing environment
• Use the mouse, keyboard commands, and modifier keys
Consult the documentation provided with your computer or other resources if you need
more information in any of these areas.
Where to go for help
If you're new to QuarkXPress, or if you want to explore one of its other longstanding
features, consult the following resources:
• A Guide to QuarkXPress
• QuarkXPress Help
• Third-party books
• General books about desktop publishing
If your issues are at the system level — saving files, moving files, activating fonts, for
example — consult the documentation resources provided with your computer.
18 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 19

Conventions
Formatting conventions highlight information to help you quickly find what you need.
• Bold type style: The names of all dialog boxes, fields, and other controls are set in bold
type. For example: "Click OK."
• References: In descriptions of features, parenthetical references guide you in accessing
those features. For example: "The Find/Change dialog box (Edit menu) lets you find and
replace text."
• Arrows: You will often see arrows (>), which map out the menu path to a feature. For
example: "Choose Edit > Style Sheets to display the Style Sheets dialog box."
• Icons: Although many tools and buttons are referenced by name, which you can see by
displaying ToolTips, in some cases icons are shown for easy identification. For example,
"Click the button on the Measurements palette to center text."
• Cross-platform issues: This application is quite consistent across operating systems. However,
some labels, buttons, key combinations, and other aspects of the application must differ
between Mac OS® and Windows® because of user interface conventions or other factors.
In such cases, both the Mac OS and Windows versions are presented, separated by a slash,
with the Mac OS version presented first. For example, if the Mac OS version of a button
is labeled Select, and the Windows version is labeled Browse, you are directed to "Click
Select/Browse." More complex cross-platform differences are mentioned in notes or
parenthetical statements.
ABOUT THIS GUIDE
Technology note
Quark developed QuarkXPress for Mac OS and Windows to give publishers control over
typography, color, and collaboration. In addition to unique typographic controls,
QuarkXPress offers comprehensive font support, including support for TrueType®,
OpenType®, and Unicode®. Designers can use PANTONE® (the PANTONE MATCHING
SYSTEM®), Hexachrome®, Trumatch®, Focoltone®, DIC®, and Toyo to add color to page
layouts.
QuarkXPress acts as a hub for collaborative publishing environments because it allows
you to import and export content in multiple file formats, and to share design components
with other users. You can import files from applications such as Microsoft® Word, Microsoft
Excel®, WordPerfect®, Adobe® Illustrator®, and Adobe Photoshop®. You can output
content as PostScript® or in PDF format for Adobe Acrobat® Reader®. You can also export
files that can be viewed using QuickTime®, Internet Explorer®, Safari®, Firefox®, and
Netscape Navigator®. With Quark Interactive Designer™, you can export layouts in Flash®
format. Using features such as Job Jackets® and Composition Zones®, you can be sure
that multiple people share specifications to produce consistent publications, even while
working on a single publication simultaneously.
The QuarkXPress software architecture lets you and software developers expand publishing
capability. Through XTensions® software technology, third-party developers can create
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 19
Page 20

ABOUT THIS GUIDE
custom modules for QuarkXPress. QuarkXTensions® (Quark® XTensions software) also
provide a modular approach for meeting your particular publishing needs. And if you can
write AppleScript® scripts, you can use this scripting language from Apple® to automate
many QuarkXPress activities.
20 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 21

The user interface
Skimming through the QuarkXPress user interface, you will find that many commands
are familiar or self-explanatory. Once you become familiar with QuarkXPress menus and
dialog boxes, you will discover that keyboard commands and palettes offer convenient
access to features that you can also access through menus.
Tools
THE USER INTERFACE
The Tools palette
The Tools palette includes the following controls:
•
Use the Item tool to select, move, resize, and reshape items (boxes, lines, text paths,
and groups). When the Item tool is not selected, you can press Command/Ctrl to
temporarily access the Item tool.
•
Use the Text Content tool to draw text boxes and work with text in boxes.
•
Use the Picture Content tool to draw picture boxes and work with pictures in boxes.
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 21
Page 22
THE USER INTERFACE
•
Use the Linking tool to link text boxes.
•
Use the Unlinking tool to unlink text boxes.
•
Use the Rectangle Box tool to create a rectangular box. To draw a square box, press
and hold Shift while drawing.
•
Use the Oval Box tool to create an oval box. To create a circular box, press and hold
Shift while drawing.
•
Use the Composition Zones tool to create a Composition Zones box.
•
Use the Star Box tool to create a star-shaped box.
•
Use the Line tool to create straight diagonal lines of any angle. To constrain a line angle
to 45 degrees, press and hold Shift while drawing.
•
Use the Bézier Pen tool to create Bézier lines and boxes. To constrain a line angle to
45 degrees, press and hold Shift while drawing.
•
Use the Add Point tool to add a point to any type of path. Adding a point to a content
box automatically turns the content box into a Bézier item.
•
Use the Remove Point tool to remove a point from any type of path.
•
Use the Convert Point tool to automatically convert corner points to curve points, and
curve points to corner points. Click and drag to change the position of a point, the curve
of a curved line segment, or the position of a straight line segment. Select this tool and
click a rectangular box or straight line to convert the item to a Bézier box or line.
•
Use the Scissors tool to cut an item into distinct paths.
•
Use the Select Point tool to select curves or points so that you can move them or delete
them. Press Shift and click to select multiple points. Option-click/Alt-click a point to make
it symmetrical.
•
Use the Freehand Line tool to draw any shape line or box you want. If you don't close
a freehand box, it remains a line. To automatically close a freehand box, press Option/Alt.
•
Use the Tables tool to create a table.
•
Use the Zoom tool to enlarge or reduce the document view.
•
Use the Pan tool to reposition the active layout.
After you draw a box, select the Text Content tool or the Picture Content tool ,
depending what you want in the box. You can also use key commands to declare the box
content type: Press T while drawing to declare Picture content or press R while drawing to
declare Text content.
For more information about Bézier boxes and lines, see "Creating Bézier boxes" and "Creating
Bézier lines."
22 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 23

THE USER INTERFACE
To pan the layout while a Pen tool is selected, press Shift+Space and then click and drag.
To add text to a line or path, select the Text Content tool and double-click the line or
path.
For more information about Composition Zones, see "Creating a Composition Zones item."
Windows users can display the Tools palette (Windows menu) horizontally, as well as
vertically. To display the palette horizontally, Ctrl+double-click the title bar.
Tool key commands
When no text box or text path is active, you can switch tools quickly using the following
key commands:
• Item tool: V
• Text Content tool: T (press Escape to deselect the active text box so you can switch to
another tool)
• Text Linking tool: T
• Text Unlinking tool: T
• Picture Content tool: R
• Rectangle Box tool: B
• Oval Box tool: B
• Starburst tool: B
• Composition Zones tool: B
• Line tool: L
• Bézier Pen tool: P
• Add Point tool: P
• Remove Point tool: P
• Convert Angle tool: P
• Scissors tool: P
• Select Point tool: P
• Freehand Line tool: P
• Tables tool: G
• Zoom tool: Z
• Pan tool: X
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 23
Page 24
THE USER INTERFACE
Web tools
The Web Tools palette lets you work with Web layouts.
The Web Tools palette
The Web Tools palette (Window menu with Web layout displayed) includes the following
controls:
•
Use the Rectangle Image Map tool to create rectangular image map "hot areas" (and
to gain access to other image map tools). The image map tools are available when the
ImageMap XTensions software is loaded.
•
Use the Form Box tool to create a form box (to contain form controls).
•
Use the File Selection Tool to create a field and button that end users can use to send
a file to the Web server.
•
Use the Text Field tool to create a text field.
•
Use the Button tool to create a button.
•
Use the Image Button tool to create a button that will allow a picture to be imported.
•
Use the Pop-up Menu tool to create a drop-down menu.
•
Use the List Box tool to create a list.
•
Use the Radio Button tool to create a radio button.
•
Use the Check Box tool to create a check box.
•
Use the Rollover Linking tool to link the origin and target boxes of a two-position
rollover. When the mouse pointer is moved over the origin box, the content of the target
box displays.
•
Use the Rollover Unlinking tool to unlink the origin and target boxes of a two-position
rollover.
Menus
The topics below describe the menus and menu items available in QuarkXPress.
24 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 25

THE USER INTERFACE
QuarkXPress menu (Mac OS only)
The QuarkXPress menu is a part of QuarkXPress for Mac OS X. This menu contains the
same commands as in the application menu for other Mac OS X applications — to hide
or show QuarkXPress and other applications, to access preferences, and to quit QuarkXPress.
This menu includes the following commands:
• About QuarkXPress: Use this command to display information about QuarkXPress, such
as the version number.
• Edit License Code: Use this command to change the validation code of an installed copy
of QuarkXPress. By changing this code, you can change a Test Drive version (formerly
called "evaluation copy") of QuarkXPress into a fully functional version, change the
languages supported by the user interface, or change QuarkXPress into a Plus edition.
• Transfer QuarkXPress License: Use this command to deactivate QuarkXPress on one
computer so that you can activate it on a different computer. Available only when
QuarkXPress has been activated.
• Activate QuarkXPress: Use this command to activate QuarkXPress on your computer.
Available only when QuarkXPress is running in demo mode.
• Check for Updates: Use this command to check for updates to QuarkXPress.
• Quark Update Settings: Use this command to configure automatic update settings.
• Preferences: Lets you modify default values and settings. For more information, see
"Preferences."
• Quit QuarkXPress: Use this command to exit the application.
File menu
The File menu enables you to manipulate electronic files in a number of ways, including
the ability to create, open, print, and save. This menu includes the following commands:
• New: Choose an option from the New submenu to create a project. If you choose New
Project from Ticket, you can select a Job Ticket from which you can create the project.
You can also use this submenu to create new libraries and books.
• Open: Use this option to open project files.
• Close: Use this option to close the active project.
• Save: Use this option to save the active project.
• Save As: Use this option to save a copy of the active project.
• Revert to Saved: Use this option to return the active project to the state it was in when
it was last saved.
• Import: Use this command to import text into a text box or to import a picture into a
picture box.
• Save Text: Use this option to save the contents of the active text box as a separate file.
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 25
Page 26

THE USER INTERFACE
• Save Picture: Use this submenu to save the selected picture as a separate file or to save all
pictures in a layout as separate files.
• Append: Use this option to append style sheets, colors, layouts, and a variety of other
types of resources from another file.
• Export: Use this option to export a layout as another file type or version.
You cannot open files saved in QuarkXPress 9.1 or later directly in QuarkXPress 9.0.
However, you can export a project in QuarkXPress 9.0 format with the File > Export >
Layouts as Project command.
• Collect for Output: Use this option to copy a file, an output report, and selected resources
into one folder.
• Collaboration Setup: Use this option to control project linking, sharing, and updating
frequency of shared resources.
• Job Jackets: Use this submenu to access the specifications and rules for creating and
inspecting a layout, link a project to a Job Jackets file, modify a Job Ticket, and evaluate
a layout.
• Print: Use this option to print the active file.
• Output Job: Use this option to access the Output Specification for outputting a job, which
is like a "style sheet" for output.
• Exit (Windows only): Use this option to exit the application.
Edit menu
The Edit menu includes the following commands:
• Undo: Undoes the last action.
• Redo: Redoes an undone action.
• Cut: Cuts the selected content.
• Copy: Copies the selected content to the clipboard.
• Paste: Pastes the clipboard contents on the active page.
• Paste Without Formatting: Pastes the clipboard contents as plain text.
• Paste In Place: Pastes a duplicated or copied item onto the active page at the same position
from which it was originally copied.
• Paste Special (Windows only): Lets you choose how the object is pasted into your document
by using the Microsoft Windows Object Linking and Embedding (OLE) function.
• Clear/Delete: Deletes the active content.
• Select All: Selects all content in the active box or text path.
• Show Clipboard: Displays the contents of the clipboard.
26 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 27

THE USER INTERFACE
• Find/Change: Displays the Find/Change palette, which you can use to find and change
text based on content, formatting, or both.
• Item Find/Change: Displays and hides the Item Find/Change palette.
• Preferences (Windows only): Lets you modify default values and settings. For more
information, see "Preferences."
• Style Sheets: Lets you add, edit, and delete style sheet definitions. For more information,
see "Working with style sheets."
• Conditional Styles: Lets you add, edit, and delete conditional styles. For more information,
see "Working with conditional styles."
• Colors: Lets you add, edit, and delete color definitions. For more information, see "Working
with colors."
• H&Js: Lets you add, edit, and delete H&J (hyphenation and justification) definitions. H&Js
let you control how text breaks. For more information, see "Controlling hyphenation and
justification."
• Lists: Lets you add, edit, and delete list definitions. The Lists feature is a tool for
automatically generating tables of contents and other types of listed content. For more
information, see "Working with lists."
• Dashes and Stripes: Lets you add, edit, and delete custom line patterns.
• Hanging Characters: Lets you add, edit, and delete custom hanging character definitions.
For more information, see "Working with hanging characters."
• Bullet, Numbering, and Outline Styles: Lets you add, edit, and delete bullet, numbering,
and outline styles. For more information, see "Bullets and numbering."
• Output Styles: Lets you add, edit, and delete output style definitions. Output styles let
you easily switch between different sets of output options. For more information, see
"Working with output styles."
• Program Language (multi-language editions only): Lets you change the language of the user
interface.
• Callout Styles: Lets you add, edit, and delete callout styles. For more information, see
"Working with callouts."
• Color Setups: Lets you access and modify setups for Source and Output Setups.
• Grid Styles: Lets you add, edit, and delete patterns of non-printing design grids that you
can apply to text components. For more information, see "Working with design grids."
• Hyperlinks: Lets you add, edit, and delete hyperlinks including URLs, anchors, and page
links.
• Variables (Interactive layouts only): Lets you define variables for interactive items.
• Interactive menus (Interactive layouts only):Lets you create menus for interactive layouts.
• Underline Styles: Lets you access and modify underline styles.
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 27
Page 28

THE USER INTERFACE
Style menu
• Menus (Web layout only): Lets you create and manage lists, such as navigation menus, used
in Web layouts.
• Meta Tags (Web layout only): Lets you create, modify and access meta information, such
as keywords and descriptions, that provides information about that page for discovery by
search engines and other purposes.
• CSS Font Families (Web layout only): Lets you create font families for cascading style sheets
(CSS) and determine what fonts will be used to display a Web page if the original font is
not available to the user.
• Cascading Menus (Web layout only): Lets you create a hierarchical list of items that displays
when the end user moves the mouse pointer over an object. This simplifies a Web design
by "hiding" menu items until the user moves the mouse pointer over a specific item.
• Item Styles: Lets you add, edit, and delete item definitions that you can apply to
QuarkXPress items with the Item Styles palette (Window menu).
The Style menu changes depending on whether a text box, a picture box, or a line is active.
Style menu for text
The Style menu for text includes commands for specifying character attributes and
paragraph formats. This menu includes the following commands:
• Font: Lets you change the font of selected text.
• Size: Lets you change the size of selected text.
• Type Style: Lets you apply type styles such as bold, italic, and underline to selected text.
• Change Case: Lets you change case of selected text to uppercase, lower case, or title case.
• Color: Lets you change the color of selected text.
• Shade: Lets you set the tint of an applied color.
• Opacity: Lets you control the transparency of selected text.
• Horizontal/Vertical Scale: Lets you stretch selected text horizontally or vertically.
• Kern/Track: When the text insertion point is between two characters, Kern lets you control
the spacing between those characters. When text is selected, Track lets you control the
spacing between all selected characters.
• Baseline Shift: Lets you move selected text up or down in relation to the baseline without
changing line spacing.
• Character: Displays the Character Attributes dialog box, which lets you control every
aspect of character formatting for selected text.
• Character Style Sheets: Lets you apply character style sheets to selected text.
• Text to Box: Lets you convert text to a Bézier picture box shaped like the selected characters.
28 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 29

THE USER INTERFACE
• Alignment: Lets you align active paragraphs to the left, right, or center. Also lets you
justify or force-justify selected paragraphs.
• Leading: Lets you change the line spacing of selected paragraphs.
• Formats: Displays the Paragraph Attributes dialog box, which lets you control every
aspect of paragraph formatting for selected text.
• Tabs: Lets you set tab stops for selected paragraphs.
• Rules: Lets you create automatic lines above and below selected paragraphs.
• Paragraph Style Sheets: Lets you apply paragraph style sheets to selected text.
• Update Style Sheet: Lets you update a character or paragraph style sheet definition based
on local changes to the applied style sheet.
• Flip Horizontal: Lets you flip selected text horizontally.
• Flip Vertical: Lets you flip selected text vertically.
• Hyperlink: Lets you modify and apply a hyperlink, page link, or anchor to selected text.
• Anchor: Lets you create or modify an anchor for selected text.
• Underline Styles: Lets you modify and apply an underline style to selected text.
Style menu for pictures
The Style menu for pictures includes commands for formatting and editing pictures. This
menu includes the following commands:
• Color: Applies a color to a selected grayscale or one-bit picture.
• Shade: Lets you set the intensity of an applied color.
• Opacity: Lets you control the transparency of a selected picture.
• Invert/Negative: Applies a negative or inverse effect to a selected picture. The command
name is Negative when you select a CMYK picture.
• Halftone: Lets you apply a halftone screen pattern to a selected grayscale picture.
• Flip Horizontal: Flips the selected picture horizontally.
• Flip Vertical: Flips the selected picture vertically.
• Center Picture: Centers the selected picture in its picture box.
• Stretch Picture To Fit Box: Reduces or enlarges the selected picture horizontally and
vertically to fill its picture box.
• Scale Picture To Box: Reduces or enlarges the selected picture proportionately to fill its
picture box.
• Fit Box To Picture: Reduces or enlarges the picture box to fit the size of the selected picture.
• Hyperlink: Lets you modify and apply a hyperlink, page link, or anchor to a selected
picture or box.
• Anchor: Lets you create or modify an anchor for a selected picture or box.
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 29
Page 30

THE USER INTERFACE
Style menu for lines
Item menu
• Picture Effects: Displays a submenu that lets you apply picture adjustments and filters to
the selected picture.
The Style menu for lines includes the following commands:
• Line Style: Lets you apply a line style to a selected line.
• Arrowheads: Lets you apply an arrowhead style to a selected line.
• Width: Lets you adjust the width of a selected line.
• Color: Lets you change the color of a selected line.
• Shade: Lets you set the intensity of an applied color.
• Opacity: Lets you control the transparency of a selected line.
• Hyperlink: Lets you modify and apply a hyperlink, page link, or anchor to a selected line.
• Anchor: Lets you create or modify an anchor for a selected line.
The Item menu includes commands for controlling item attributes, positions, grouping,
sharing, and more.
• Modify: Lets you access a comprehensive set of controls such as color, shade, position,
size, frame, runaround, clipping path, and more for an item.
• Frame: Lets you specify frame attributes such as width, style, color, and opacity for an
item.
• Runaround: Lets you specify whether text runs inside, outside, or through a picture or its
picture box.
• Clipping: Lets you select the clipping type for a given item and control its outset.
• Duplicate: Lets you create a copy of an item and its contents.
• Step and Repeat: Lets you duplicate an active item multiple times, and in any position
you specify.
• Super Step and Repeat: Lets you duplicate an active item multiple times and specify scale,
rotation, and shading for the duplicates.
• Delete: Lets you delete a selected item and its contents.
• Group: Lets you combine two or more active items (including lines, boxes, text paths,
tables, and other groups) into a group.
• Ungroup: Lets you break a group into its component items or groups.
• Constrain: Lets you restrict an item so that it cannot move beyond the boundaries of the
item to which it is constrained.
• Lock: Lets you prevent accidental changes to items and their contents by locking its
position or content.
30 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 31

THE USER INTERFACE
• Merge: Lets you merge selected items in a number of ways.
• Split: Lets you split boxes that contain non-overlapping shapes, split boxes that contain
shapes within shapes, or split boxes that contain a border that crosses over itself (such as
a figure eight).
• Send Backward (Windows only): Moves an item one level backward in the page or layer's
stacking order.
• Send to Back: Moves an item to the back of the page or layer. On Mac OS, press Option
before choosing Send to Back to access the Send Backward command.
• Bring Forward (Windows only): Moves an item one level forward in the page or layer's
stacking order.
• Bring to Front: Moves an item to the front of the page or layer. On Mac OS, press Option
before choosing Bring to Front to access the Send Forward command.
• Space/Align: Lets you position the selected items evenly with regard to each other or with
regard to the page or spread.
• Shape: Lets you change the shape of an active item.
• Content: Lets you change the content type of an item.
• Edit: Lets you modify item shape, runaround, or clipping path.
• Share: Lets you access sharing properties of an item and synchronize or re-use content
such as text, pictures, boxes, lines, and Composition Zones.
• Unsynchronize: Removes synchronization of a single instance of the item without affecting
other occurrences of that item (or the synchronization attributes).
• Point/Segment Type: Lets you change the point or segment type of an item so you can
manipulate points, curve handles, and line segments.
• Drop Shadow: Lets you apply or modify an item's drop shadow.
• Callout Anchor: Lets you configure callout anchors and callouts. For more information,
see "Working with callouts."
• Composition Zones: Lets you create or modify Composition Zones.
• Digital Publishing: Lets you configure items for digital publishing in Blio, ePub, and App
Studio formats. For more information, see "eBooks" and A Guide to App Studio.
• Preview Resolution: Lets you set the preview of a picture to full resolution or low
resolution.
• Delete All Hot Areas (Web layouts only): Removes the image map designations of a picture
that serve as hyperlinks.
• Cascading Menu (Web layouts only): Lets you apply a cascading menu to an item that has
been specified to export as a graphic.
• Basic Rollover (Web layouts only): Lets you apply a basic rollover to an item so that the
image will change when the mouse pointer is over the rollover box.
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 31
Page 32

THE USER INTERFACE
Page menu
• 2-position Rollovers (Web layouts only): Apply a 2-position rollover to an item so that the
image in one or more other boxes will change when the mouse pointer is over the rollover
box.
The Page menu includes commands for inserting, deleting, and moving pages; working
with guides, grids, and sections; navigating through pages, and more.
• Insert: Lets you add new pages.
• Delete: Lets you delete pages.
• Move: Lets you move a page to a different location.
• Master Guides and Grid: Lets you modify the placement of page guides and design grids
on master pages.
• Page Properties (Web layouts only): Lets you modify the page properties of a Web layout.
• Section: Lets you change the numbering system for a layout or a range of pages in a layout.
• Previous: Navigates to the preceding page.
• Next: Navigates to the following page.
• First: Navigates to the first page.
• Last: Navigates to the last page.
• Go to: Lets you navigate to a particular page.
• Display: Lets you display a page or a master page.
• Preview HTML (Web layouts only): Generates an HTML preview and displays it in a Web
browser.
• Preview SWF (Interactive layouts only): Generates a preview and displays it in a Web browser.
Layout menu
The Layout menu includes commands for working with and navigating to layouts.
• New: Lets you add a new layout.
• Duplicate: Lets you duplicate one layout to copy its items and content to another.
• Delete: Lets you remove a layout.
• New/Edit Layout Specification: Lets you create or modify Job Jackets properties for a
layout.
• Layout Properties: Lets you modify layout properties such as name, type, and size.
• Advanced Layout Properties: Lets you modify sharing properties of a layout.
• eBook Metadata: Lets you apply metadata to the layout for eBook export. For more
information, see "Working with eBook metadata."
32 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 33

THE USER INTERFACE
• Add Pages to Reflow View: Lets you add pages to a reflow article. For more information,
see "Working with Reflow view."
• Previous: Activates the layout tab that was active prior to the current layout.
• Next: Activates the layout tab that is positioned to the immediate right of the active layout.
• First: Activates the far-left layout tab.
• Last: Activates the far-right layout tab.
• Go to: Lets you activate a specific layout and then choose the layout from the submenu.
Table menu
The Table menu includes commands for adding rows and columns to tables, modifying
table attributes, converting tables, and more.
• Insert: Lets you add a row or column to a table.
• Select: Lets you select a pattern of rows and columns or other table elements. This makes
it easy to apply alternating formatting — such as shading every other row.
• Delete: Lets you delete a selection from the table.
• Combine Cells: Lets you combine a rectangular selection of adjacent table cells — including
entire rows or columns — into a single cell.
• Table Break: Lets you continue a table in another location. The table break is the maximum
size the table can reach before it splits into two linked tables.
• Make Separate Tables: Lets you sever the link between continued tables so each table
becomes completely separate. This prevents changes to one portion of the table from
affecting all the continued tables.
• Repeat As Header: Lets you specify a header row to repeat automatically in continued
instances of a table.
• Repeat As Footer: Lets you specify a footer row to repeat automatically in continued
instances of a table.
• Convert Text to Table: Lets you convert text that has already been imported or typed
into a text box to a table. This works best with text that is delimited in some way to indicate
how to divide the information into columns and rows.
• Convert Table: Lets you convert the information in a table to text or to a group of related
boxes. You might convert a table for easy exporting of the current data or to save a
document containing features that are not supported in earlier versions of QuarkXPress.
• Link Text Cells: Lets you link table cells to each other just as text boxes and text paths
can be linked. Text that is typed, imported, or pasted into a linked cell fills the first text
cell, and then flows on to each subsequent linked cell.
• Maintain Geometry: Lets you prevent the width and height of a table from changing
when you insert or delete rows or columns.
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 33
Page 34

THE USER INTERFACE
View menu
The View menu provides options for viewing your document and specifying what you
see on screen when the menu item is checked. This menu includes the following commands:
• Fit in Window: Automatically scales the view to fit (and center) an entire page in the
layout window.
• 50%: Scales the layout view to 50%.
• 75%: Scales the layout view to 75%.
• Actual Size: Scales the layout view to 100%.
• 200%: Scales the layout view to 200%.
• Thumbnails: Displays small representations of each page that you can rearrange and copy
between projects.
• Guides: Displays nonprinting lines used to position items on pages, including margin
guides, the outlines of boxes, the "X" pattern in empty picture boxes, and ruler guides.
• Page Grids: Displays nonprinting gridlines defined for the master page on which the active
layout page is based.
• Text Box Grids: Displays nonprinting gridlines applied to text boxes.
• Snap to Guides: Lets you quickly align items with guides so items will snap to the nearest
guide.
• Snap to Page Grids: Lets you quickly align items with page grids so items will snap to the
nearest guide.
• Rulers: Displays rulers, which you can use to position items and guides, along the top and
left edges or top and right edges of the layout window.
• Ruler Direction: Lets you position page rulers on the top and left or top and right edges
of the layout window.
• Invisibles: Displays editable, nonprinting characters such as spaces, tabs, and paragraph
returns in text.
• Visual Indicators: Displays indicators for non-printing elements, such as hyperlinks and
rollovers.
• Trim View: Simulates what the page will look like when trimmed by cropping any items
that extend beyond the page boundary. You can control the color of the pasteboard that
displays when this item is selected in the Display pane of the Preferences dialog box
(QuarkXPress/Edit > Preferences).
• Hide Suppressed: Hides all items for which the Suppress Output box is checked in the
Box, Line, Picture, or Layout pane of the Modify dialog box, as well as layers for which
Suppress Output is checked in the Attributes dialog box. In addition, this option hides
underlines on hyperlinks, hyperlink anchors, index markers, and the text overflow symbol.
34 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 35

THE USER INTERFACE
• Proof Output: Lets you preview how the layout will look when output to different media
and for different printing methods. This display simulation is accurate enough for soft
proofing.
• Reflow View: Displays the Reflow view (if any) for this layout. For more information, see
"Working with Reflow view."
• Full Res Previews: Displays full-resolution pictures on screen using the picture files' full
resolution. You can scale or magnify image without pixilation.
• Story Editor: Displays the active story in Story Editor view. For more information, see
"Using Story Editor view."
Utilities menu
The Utilities menu includes the following commands:
• Check Spelling: Use the submenu to display the Check Spelling palette to check the
spelling of a word, a selection of text, a story, a layout, or all master pages in a layout.
• Auxiliary Dictionary: Lets you specify an auxiliary dictionary for use in spell checking.
• Edit Auxiliary: Lets you edit the auxiliary dictionary associated with the active layout.
• Word And Character Count: Displays the Word and Character Count dialog box.
• Insert Character: Lets you easily insert special characters, including special breaking and
nonbreaking spaces.
• Suggested Hyphenation: Displays the suggested hyphenation for the word containing
the text insertion point.
• Hyphenation Exceptions: Lets you specify whether and how particular words should be
hyphenated in the active article.
• Job Jackets Manager: Displays the Job Jackets Manager dialog box.
• Usage: Lets you view and update the status of fonts, pictures, QuarkVista effects, color
profiles, tables, Composition Zones, assets used in App Studio layouts, and assets used in
Blio interactivity.
• XTensions Manager: Lets you control which XTensions modules are loaded when the
application is launched.
• Font Mapping: Lets you create and edit rules for substituting a new font for a font that is
requested by a project but which is not installed on your computer.
• Component Status: Lets you view the status of required software components.
• PPD Manager: Lets you control which PostScript Printer Description files (PPDs) are loaded
in the Print dialog box.
• Use German (Reformed): Lets you control whether spell checking uses the reformed
German dictionary.
• Convert Project Language: Lets you convert all of the characters in the active article that
use a particular character language to a different character language.
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 35
Page 36

THE USER INTERFACE
• Profile Manager: Lets you control which color profiles are loaded in the application.
• Cloner: Displays the Cloner dialog box. For more information, see " Cloner XTensions
software."
• ImageGrid: Displays the ImageGrid dialog box. For more information, see " ImageGrid
XTensions software."
• Build Index: Lets you create an index from the contents of the Index palette.
• Jabber: Generates random text in the active text box so that you can preview how text
will flow and be styled, even though you might not have actual content yet.
• Tracking Edit: Lets you control tracking for installed fonts.
• Kerning Table Edit: Lets you control kerning for installed fonts.
• Linkster: Displays the Linkster dialog box. For more information, see " Linkster XTensions
software."
• ShapeMaker: Displays the ShapeMaker dialog box. For more information, see " ShapeMaker
XTensions software."
• Remove Manual Kerning: Lets you remove all manual kerning applied between characters,
or remove kerning from a kerning pair.
• Line Check: Displays a submenu that lets you find widows, orphans, loosely justified
lines, lines that end with a hyphen, and overflow situations.
• Convert Old Underlines: Converts all underlines in the active text chain from
QuarkXPress 3.x (Stars & Stripes) format to Type Tricks format.
• Text Overflow: Displays the Text Overflow window, which identifies text boxes that
contain text overflow.
• Item Styles Usage: Lets you view and update applied item styles.
• Check Out License/Check In License: Displays only if you have installed the application
for use with Quark License Administrator (QLA). Lets you check licenses in and out.
Window menu
The Window menu enables you to control the on-screen display of open windows and
palettes. This menu includes the following commands:
• New Window: Displays the active project in a new window. You can then view different
parts of the project in each window.
• Split Window: Splits the project window into two parts. You can then view different parts
of the project in each part of the window.
• Bring All to Front (Mac OS only): Positions and displays all open windows.
• Cascade (Windows only): Layers multiple open projects so just a portion of each project's
menu bar displays.
• Tile (Mac OS only): Tiles all open windows horizontally to fit on the screen.
36 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 37

THE USER INTERFACE
• Tile Horizontally (Windows only): Tiles all open windows horizontally to fit on the screen.
• Stack (Mac OS only): Layers multiple open projects so just a portion of each project's menu
bar displays.
• Tile Vertically (Windows only): Tiles all open windows vertically to fit on the screen.
• Arrange Icons (Windows only): Minimizes all active projects.
• Close All (Windows only): Closes all active projects.
• Tools: Displays and hides the Tools palette.
• Web Tools (Web layouts only): Displays and hides the Web Tools palette.
• Measurements: Displays and hides the Measurements palette.
• Page Layout: Displays and hides the Page Layout palette.
• Style Sheets: Displays and hides the Style Sheets palette.
• Conditional Styles: Displays the Conditional Styles palette. For more information, see
"Working with conditional styles."
• Colors: Displays and hides the Colors palette.
• Shared Content: Displays and hides the Shared Content palette.
• Trap Information: Displays and hides the Trap Information palette.
• Lists: Displays and hides the Lists palette.
• App Studio: Displays and hides the App Studio palette. For more information, see A Guide
to App Studio.
• Profile Information: Displays and hides the Profile Information palette.
• Callout Styles: Displays the Callout Styles palette. For more information, see "Working
with callout styles."
• Grid Styles: Displays and hides the Grid Styles palette.
• Reflow Table of Contents: Displays the Reflow Table of Contents palette. For more
information, see "Creating a TOC for ePub or Kindle."
• Reflow Tagging: Displays the Reflow Tagging palette. For more information, see "Editing
content in Reflow view."
• Glyphs: Displays and hides the Glyphs palette.
• Hyperlinks: Displays and hides the Hyperlinks palette.
• Index: Displays and hides the Index palette.
• Interactive (Interactive layouts only): Displays and hides the Interactive palette.
• Layers: Displays and hides the Layers palette.
• Picture Effects: Displays and hides the Picture Effects palette.
• Welcome Screen: Displays the welcome screen.
• Placeholders: Displays and hides the Placeholders palette.
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 37
Page 38

THE USER INTERFACE
Help menu
• Guides: Displays and hides the Guides palette.
• Item Styles: Displays and hides the Item Styles palette.
• PSD Import: Displays and hides the PSD Import palette.
• Palette Sets: Use the submenu to store and recall arrangements of palettes.
• Scale: Displays and hides the Scale palette. For more information, see "Scale XTensions
software."
In addition, this menu includes an item for every open window. You can use these menu
items to easily switch between windows.
The Help menu provides access to the online help. This menu includes the following
commands:
• Help Topics (Mac OS only): Use this command to display the online help.
• Contents (Windows only): Use this option to view the Contents tab of the Help window.
• Search (Windows only):Use this option to view the Search tab of the Help window.
• Index (Windows only): Use this option to view the Index tab of the Help window.
• Transfer QuarkXPress License (Windows only): Use this option to transfer your license
to another computer.
• About QuarkXPress (Windows only): Use this command to display information about
QuarkXPress, such as the version number.
• Edit License Code (Windows only): Use this command to change the validation code of
an installed copy of QuarkXPress. By changing this code, you can change a Test Drive
version (formerly called "evaluation copy") of QuarkXPress into a fully functional version,
change the languages supported by the user interface, or change QuarkXPress into a Plus
edition.
• Check for Updates (Windows only): Use this command to check for updates to QuarkXPress.
• Quark Update Settings (Windows only): Use this command to configure automatic update
settings.
Context menus
QuarkXPress offers a wide variety of functionality through context menus. To display a
context menu, Control+click (Mac OS) or right-click in text, on a picture, or on a palette.
Palettes
To open or display a palette, check the palette name in the Window menu.
38 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 39

To close an open palette, click the close box in the upper-left corner of the palette, uncheck
the palette name in the Window menu, or use the appropriate keyboard equivalent.
Tools palette
The Tools palette lets you easily switch between a wide variety of tools for working with
layouts. For more information, see "Tools."
Measurements palette
With the Measurements palette (Window menu), you can quickly edit many commonly
used controls. Options in the Measurements palette change to reflect the selected tool or
item. When you select multiple items of the same type (such as three separate picture
boxes), the Measurements palette controls apply to all selected items.
The tab bar displays above the center of the Measurements palette.
THE USER INTERFACE
The Measurements palette displays a row of icons called the navigator tab above the center
of the palette. You can cycle left-to-right through the Measurements palette navigator
tab icons by pressing Command+Option+;/Ctrl+Alt+;. You can move in reverse (right-to-left)
by pressing Command+Option+,/Ctrl+Alt+,.
To continuously display the navigator tab, Control+click/right-click the Measurements
palette title bar and choose Always Show Tab Bar. To permanently hide the navigator
tab, Control+click/right-click the Measurements palette title bar and choose Always Hide
Tab Bar. To make the navigator tab bar display interactively. Control+click/right-click the
Measurements palette title bar and choose Show Tab on Rollover.
The selection of tabs displayed on the Measurements palette depends on which items are
active, and the display of any tab changes to fit the item or items that are active. The
available tabs are as follows:
•
Classic tab: Contains often-used controls. Displays differently for text boxes, picture
boxes, lines, and tables.
•
Text tab: Contains controls from the Text tab of the Modify dialog box (Item >
Modify).
•
Frame tab: Contains controls from the Frame tab of the Modify dialog box.
•
Runaround tab: Contains controls from the Runaround tab of the Modify dialog
box. Displays differently for text boxes, picture boxes, and lines.
•
Clipping tab: Contains controls from the Clipping tab of the Modify dialog box.
•
Character tab: Contains controls from the Character Attributes dialog box (Style >
Character).
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 39
Page 40

THE USER INTERFACE
•
Paragraph tab: Contains controls from the Formats tab of the Paragraph Attributes
dialog box (Style > Formats).
•
Text Path tab: Contains controls from the Text Path tab of the Modify dialog box.
•
Space/Align tab: Contains controls from the Space/Align submenu (Item >
Space/Align).
•
Export tab: Contains controls from the Export tab of the Modify dialog box (Web
layouts only).
•
Grids tab: Contains controls from the Grid tab of the Modify dialog box (selected
tables only).
•
Drop Shadow tab: Contains controls from the Drop Shadow tab of the Modify dialog
box.
•
Tabs tab: Contains controls from the Tabs tab of the Paragraph Attributes dialog
box.
When you select a picture box that contains an image, the number next to the Effective
Image Resolution icon in the Classic tab of the Measurements palette displays the
effective resolution of the image. The actual image resolution divided by the scale of the
image equals the effective resolution. For example, if you import an image with an actual
image resolution of 100 dpi and then increase the scale from 100% to 200%, the effective
resolution is 50 dpi. The higher the effective resolution is, the higher the quality of the
reproduced image will be. Note that if you select multiple picture boxes with varying
effective resolutions, no number displays next to the Effective Image Resolution icon.
Page Layout palette
The Page Layout palette provides a variety of features having to do with pages and
navigation.
40 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 41

THE USER INTERFACE
The Page Layout palette lets you work with master pages and layout pages.
The top portion of the palette lets you create, duplicate, and delete master pages. To view
and edit a master page, double-click it; the master page displays in the active project
window. A single-sided master page displays as a rectangle, while a facing-page master
page displays with two folded corners.
The bottom portion of the palette lets you navigate through the pages in the active layout.
To go to a layout page, double-click in this portion of the palette.
To apply a master page to a layout page, drag the master page icon onto the layout page
icon. Alternatively, you can select the layout page icons in the palette and them
Command-click/Ctrl-click the master page icon.
Style Sheets palette
The Style Sheets palette (Window > Show Style Sheets) enables you to apply character
and paragraph style sheets by clicking style sheet names. The buttons at the top of each
section of this palette let you create, edit, duplicate, update, and delete style sheets.
A plus sign next to a style sheet indicates that local formatting has been applied.
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 41
Page 42

THE USER INTERFACE
The Style Sheets palette lets you view and apply paragraph and character style sheets.
Conditional Styles palette
The Conditional Styles palette lets you work with conditional styles. For more information,
see "Working with conditional styles."
Colors palette
The Colors palette lets you view and apply colors defined in the active project. The buttons
at the top of this palette let you create, edit, and delete colors.
Users create colors through the Colors dialog box (Edit > Colors). For more information,
see "Working with colors."
The Colors palette lets you view and apply colors.
42 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 43

Shared Content palette
The Shared Content palette lets you work with items and content that are stored in the
shared content library. For more information, see "Working with shared content."
THE USER INTERFACE
The Shared Content palette lets you work with items and content in the shared content library.
Trap Information palette
Beginning with version 9.0, the application no longer supports spread and choke trapping.
Spreads and chokes that you set up with the Trap Information palette (Window menu)
will not be applied at output. However, overprints and knockouts are honored.
Lists palette
The Lists palette helps you view and generate lists. This feature is useful for creating things
like tables of contents. You can create lists in the Lists dialog box (Edit > Lists).
The List Name drop-down menu lets you choose from among the lists defined in the
active project and the Update button lets you refresh the list currently displayed in the
palette.
The Find button enables you to locate items in the Lists palette. You can also navigate to
a word or heading by simply double-clicking it in the palette.
The Build button lets you insert the active list into the active text chain. If the list already
exists in the story, you can update it rather than inserting another copy. The Format As
style sheets for the list are applied automatically.
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 43
Page 44

THE USER INTERFACE
The Lists palette lets you create things like tables of contents
App Studio palette
The App Studio palette lets you create and configuremovies, slideshows, buttons, and
more for App Studio issues. For more information, see A Guide to App Studio.
You can switch focus to the App Studio palette by choosing Item > Digital Publishing >
App Studio Interactivity.
Profile Information palette
The Profile Information palette lets you view and update color management settings for
pictures. For more information, see "Color management."
The Profile Information palette lets you precisely control color management settings for
pictures.
44 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 45

Callout Styles palette
The Callout Styles palette lets you work with callout styles. For more information, see
"Working with callout styles."
Glyphs palette
The Glyphs palette gives you easy access to every character in each font on your computer.
You can display all characters in the selected font or narrow down the selection by choosing
an option from the second drop-down menu. You can add characters to a story by
double-clicking them. Using the Favorite Glyphs area at the bottom of the palette, you
can store often-used characters for easy access.
THE USER INTERFACE
The Glyphs palette gives you easy access to every character in every font.
Grid Styles palette
A grid style is a named package of settings that describe a grid — like a style sheet for a
design grid. You can apply grid styles to text boxes and can use them as the basis for master
page grids. You can also base grid styles on other grid styles. Grid styles are displayed in
the Grid Styles palette (Window menu). For more information, see "Working with grid
styles."
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 45
Page 46

THE USER INTERFACE
Blio Table of Contents palette
The Grid Styles palette lets you create and apply grid styles.
The Blio Table of Contents palette lets you create TOCs for Blio eBooks. For more
information, see "Creating a TOC for Blio."
Reflow Tagging palette
The Reflow Tagging palette lets you tag content in Reflow view. For more information,
see "Working with Reflow view."
Reflow Table of Contents palette
The Reflow Table of Contents palette lets you create a table of contents for ePUB or Kindle
export. For more information, see "Creating a TOC for ePub or Kindle."
Hyperlinks palette
The Hyperlinks palette lets you apply hyperlinks to text and pictures. Although hyperlinks
obviously won't work in printed layouts, they work when you export a layout in PDF
format and when you export a Web layout in HTML format. For more information, see
"Hyperlinks."
46 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 47

The Hyperlinks palette lets you apply hyperlinks to text and pictures.
Index palette
The Index palette lets you tag text for indexing. When you create an index (Utilities >
Build Index), all of the tags you created with the Index palette are automatically turned
into a customizable index. For more information, see "Working with lists."
THE USER INTERFACE
The Index palette lets you tag text for inclusion in an automatically generated index.
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 47
Page 48

THE USER INTERFACE
Interactive palette
Layers palette
The Interactive palette lets you add interactivity to Interactive layouts. For more
information, see "Interactive layouts."
The Layers palette lets you create layers, edit layer properties, control whether those layers
display and print, and move objects between layers. For more information, See "Working
with layers."
The Layers palette lets you work with layers and the objects on those layers.
Picture Effects palette
The Picture Effects palette lets you apply effects such as sharpening and contrast
adjustment to pictures. This palette displays only when QuarkVista XTensions software is
installed. For more information, see "Using picture effects."
The Picture Effects palette lets you apply various visual effects to pictures in the layout.
48 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 49

Guides palette
The Guides palette lets you work with guides. For more information, see "Using the Guides
palette."
Item Styles palette
The Item Styles palette lets you work with item styles. For more information, see "Item
Styles XTensions software."
PSD Import palette
The PSD Import palette lets you control the display of imported Photoshop (PSD) files.
For more information, see "Working with PSD pictures."
THE USER INTERFACE
The PSD Import palette lets you manipulate imported PSD pictures.
Scale palette
The Scale palette lets you perform advanced scaling operations. For more information,
see "Scale XTensions software."
Palette groups and palette sets
QuarkXPress offers two features that help you to manage palettes: palette groups and
palette sets.
Using palette groups
The Palette Groups feature lets you combine several palettes into one.
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 49
Page 50

THE USER INTERFACE
This palette group shows the Style Sheets, Colors, and Lists palettes attached as one, which
economizes space while providing easy access to functions.
To attach a palette to a palette group, Control+click/right-click the title bar of a palette
group and choose an unchecked palette name. When you attach a palette that is already
displayed, the palette moves to become part of the palette group. To detach a palette from
a palette group, Control+click/right-click the palette name and choose Detach [palette
name].
Using palette sets
The Palette Sets feature lets you store and recall the position and status of all open palettes
and libraries, so that you can easily switch between different palette configurations.
To create a palette set, first display all of the palettes you will need for a particular task
and hide all other palettes. Then choose Window > Palette Sets > Save Palette Set As to
display the Save Palette Set As dialog box, enter a name, and optionally assign a key
command.
To retrieve a palette set, choose Window > Palette Sets > [name of palette set] or press
the keyboard combination for that palette set.
Layout controls
When you open a project, you have immediate access to some basic features at the bottom
left of the project window.
50 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 51

THE USER INTERFACE
Layout controls
Zoom: Enter a zoom percentage or choose a zoom value from the drop-down menu.
1
Page Number: Enter a page number in the Page Number field or choose a page from the
2
page list that displays when you click the upward facing arrow to the right of the field.
Previous Page: Navigate to the previous page.
3
Next Page: Navigate to the next page.
4
Master Page Toggle: Switch back and forth between the active layout page and its master
5
page.
Split Screen Vertically: View the layout in two or more separate panes one above the
6
other.
Split Screen Horizontally: View the layout in two or more separate panes side by side.
7
Export: Display the same export options that are available when you choose File > Export.
8
Preview: Preview a Web layout or Interactive layout as it appears when exported. Available
9
only when you are working on Web layouts or Interactive layouts.
Click the up arrow next to the Page Number field to see a thumbnail view of all of the
pages in the layout. Mac users can continue to click the up arrow to enlarge the thumbnails.
Views and view sets
QuarkXPress gives you multiple ways to view your layouts. You can split a window or
create a new window to show two different layouts, or two different views of the same
layout. You can use Story Editor view to concentrate on text without having to look at
the layout. And the View Sets feature lets you create and easily switch between different
view options.
Splitting a window
By splitting a window into two or more panes, you can display multiple views of one
project at the same time, and you can see changes in all panes simultaneously. You can
even use different view modes in each pane, and see your edits in one pane and update
in the other pane in real time. You can split multiple views horizontally or vertically within
a window.
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 51
Page 52
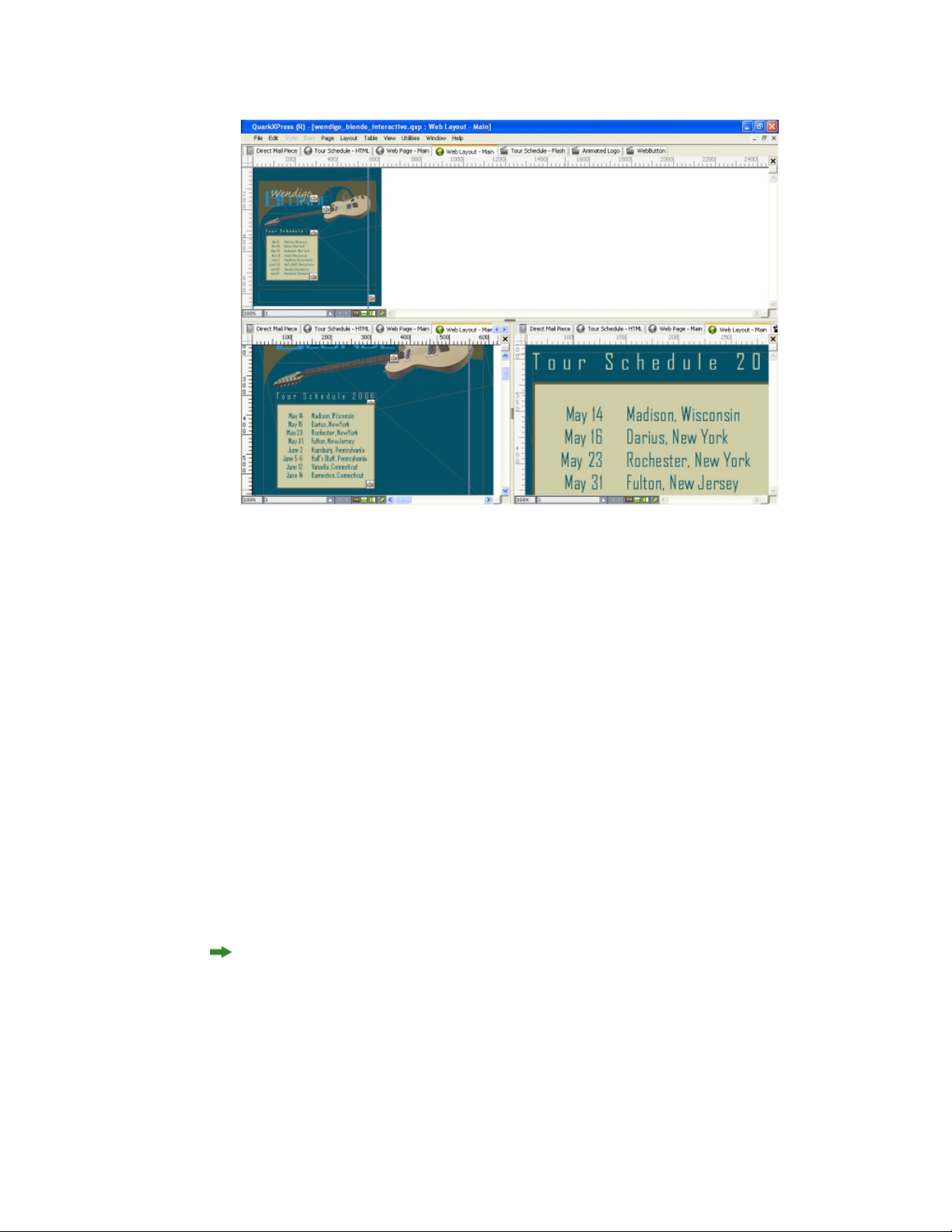
THE USER INTERFACE
By splitting a window, you can view your work at different magnifications at the same time.
There are three ways to split a window:
• Choose Window > Split Window > Horizontal or Window > Split Window > Vertical.
• Click the split bar to the right of the scroll bar (for a vertical split) or at the top of the scroll
bar (for a horizontal split).
• Click the split-screen icons in the layout controls bar at the bottom of the project window.
Once a window has been split, you can change the width and height of the split by dragging
the bars between the splits.
To remove splits from a window, use one of the following techniques:
• Choose Window > Split Window > Remove All.
• Drag a split bar to the side of the window.
Creating a window
To create a new window that displays the active project, choose Window > New Window.
If you open multiple windows for a project, make changes to that project, and then begin
closing the windows, the application will not prompt you to save the project until you
attempt to close the last window that displays the project.
Using Story Editor view
Story Editor view lets you concentrate on the text of a story without the distraction of
the layout. In Story Editor view, all text is the same size and the same font, the text fills
52 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 53
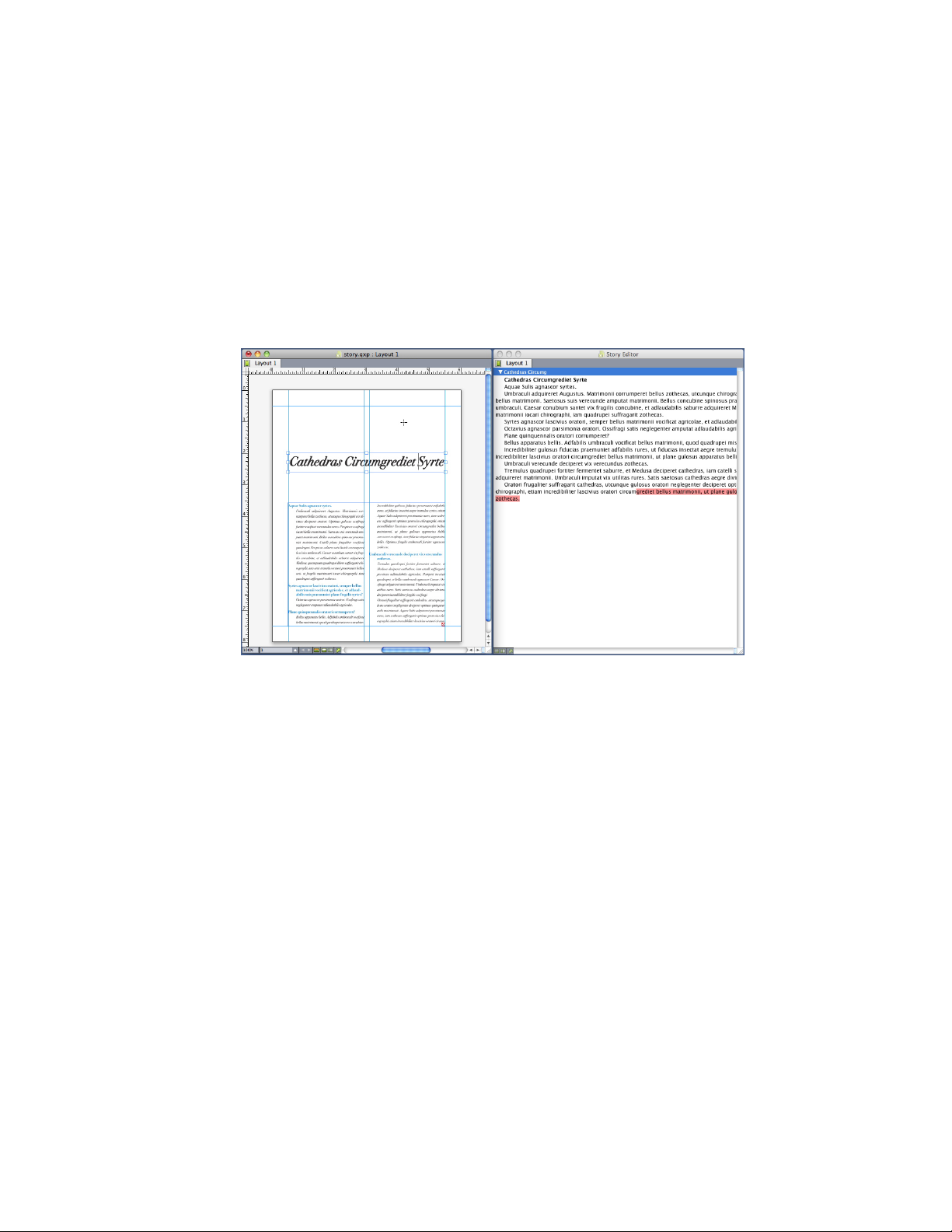
THE USER INTERFACE
the entire window, and only the most basic character formatting (such as bold and italic)
are displayed. A red background indicates where text has overflowed beyond the last text
box or path in the story.
To display the contents of the active story in a new Story Editor window, select a box or
line that contains the target story and choose View > Story Editor. (If a Story Editor
window is already open, the selected item's story displays in that window.)
If you want to monitor the overall appearance of a page as you edit its text at an
easy-to-view size, you can position a Story Editor window next to a layout window that
shows the same story.
A story in layout view (left) and in a Story Editor window (right)
View sets
The View menu provides various options for how a layout displays. You can display or
hide guides, grids, invisible characters, visiual indicators, and more. (For more information,
see "View menu.") The View Sets feature lets you store and recall different combinations of
these settings. The settings that are stored in a view set are as follows:
• View > Guides
• View > Page Grids
• View > Text Box Grids
• View > Rulers
• View > Ruler Direction
• View > Invisibles
• View > Visual Indicators
• View > Trim View
• View > Hide Suppressed
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 53
Page 54
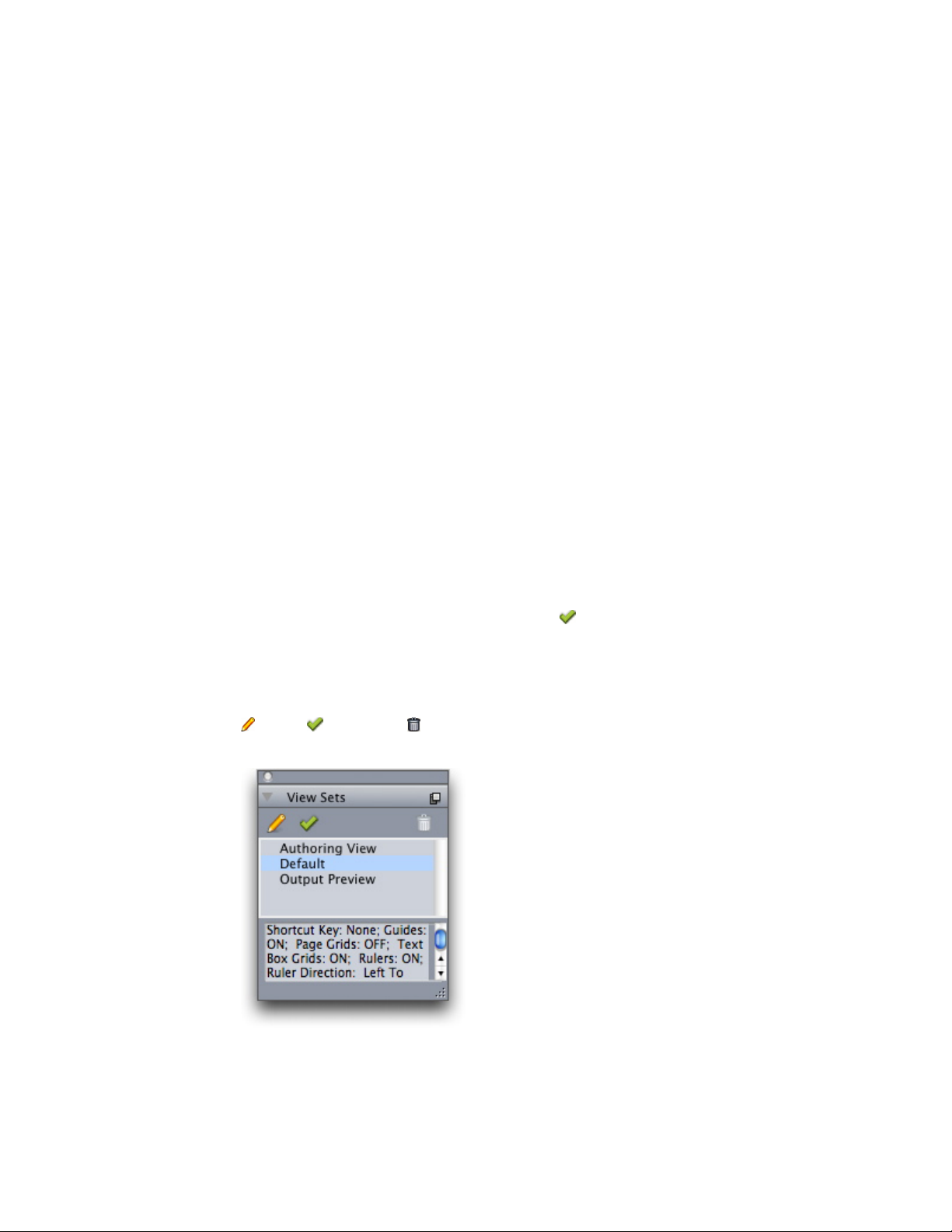
THE USER INTERFACE
• View > Full Res Previews
QuarkXPress ships with several default view sets:
• Default: This is the default set of view options that displays when you create your first
layout after launching QuarkXPress for the first time.
• Output Preview: This view set simulates a printed page as closely as possible. Guides,
grids, invisibles, and visual indicators are hidden. View > Trim View, View > Hide
Suppressed, and View > Full Res Previews are turned on. The pasteboard displays using
the color you specify in the Display pane of the Preferences dialog box (QuarkXPress/Edit
> Preferences).
• Authoring View: This view set displays guides, invisibles, visual indicators, the ruler, and
full resolution previews.
To create a view set, first turn on only the view options you want to store in that view set.
Then choose View > View Sets > Save View Set As to display the Save View Set As dialog
box, enter a name, and optionally assign a key command.
To switch to a view set, do one of the following things:
• Choose View > View Sets > [name of view set].
• Press the keyboard combination for the view set.
• Display the View Sets palette (View > View Sets > Manage View Sets), click the name of
the view set in the palette, and then click Apply (or simply double-click the view set
name).
To manage the view sets you have created, choose View > View Sets > Manage View Sets.
The View Sets palette displays. You can use the buttons at the top of this palette to Edit
, Apply , and Delete the selected view set.
View Sets palette
54 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 55

THE USER INTERFACE
View sets are saved at the application level. However, any view settings you apply to a
layout using view sets are saved with that layout.
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 55
Page 56
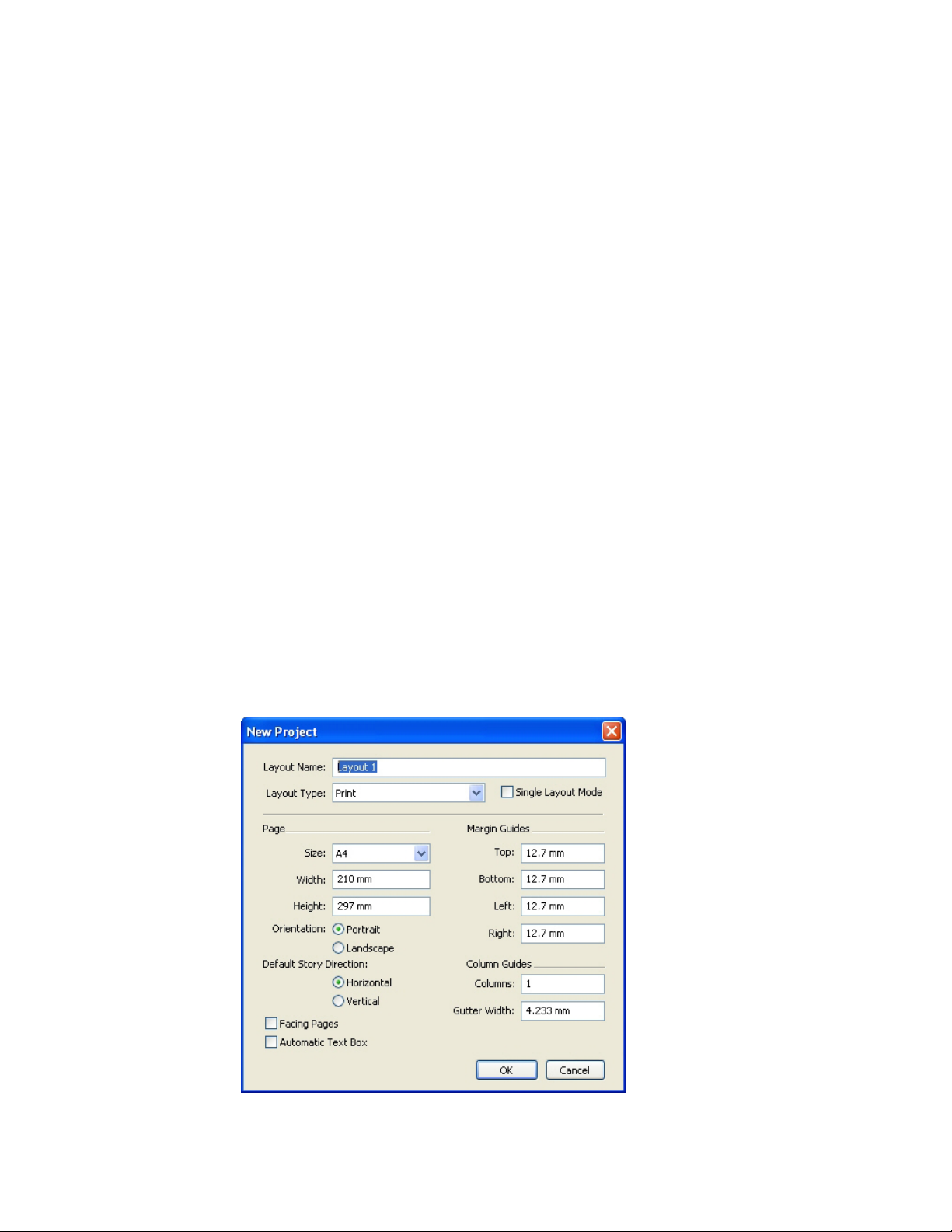
PROJECTS AND LAYOUTS
Projects and layouts
QuarkXPress files are referred to as projects, and each project contains one or more layouts.
Every layout is stored within a project, and every project contains at least one layout. Each
layout can contain as many as 2,000 pages, and can be as large as 48" x 48" in size (or 24"
x 48" for a two-page spread). A project can contain an unlimited number of layouts.
Because multiple layouts can be stored in a single file, you can easily share content between
different versions of a document — for example, a letter with identical text in US letter
and A4 layout sizes.
A QuarkXPress project can contain three types of layouts: Print, Web, and Interactive. You
can use one project to create content for various media — such as print, PDF, SWF, and
HTML.
Working with projects
To create a project, choose File > New > Project. The New Project dialog box displays.
56 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 57

PROJECTS AND LAYOUTS
New Project dialog box for Print layout type
Every QuarkXPress project contains at least one layout. Therefore, when you create a
project, you must specify a default layout for the file. You can use the default layout name
or enter a new name for the layout in the Layout Name field. To indicate the type of the
default layout, choose Print, Web, Interactive, App Studio, or ePub from the Layout
Type drop-down menu.
For more information about Web layouts, see "Web layouts."
For more information about Interactive layouts, see "Interactive layouts."
For more information about App Studio layouts, see A Guide to App Studio.
For more information about creating layouts for ePub export, see "eBooks."
By default, tabs display at the top of the project window for each of the layouts in a project.
To prevent these tabs from displaying, check Single Layout Mode. (You can still add
layouts to a project, but this will turn off the Single Layout mode.)
A project created in any language edition of QuarkXPress can be edited, printed, and saved
in any other language edition of QuarkXPress. All available spellchecking dictionaries and
hyphenation rules are supported by every language edition. However, text that uses East
Asian specific features (such as rubi text, font sets, and group characters) cannot be edited
in a non-East Asian language edition of QuarkXPress.
Options for Print layouts
The controls in the Page area let you set the page size and orientation for the default
layout.
The Facing Pages check box lets you create spreads.
The Automatic Text Box check box lets you add a text box to the default master page for
the layout.
The Margin Guides controls let you set default margins for the layout, and the controls
in the Column Guides area lets you create a multi-column page by default.
Options for Web layouts
The controls in the Colors area let you set the default colors for the page background and
for hyperlinks. The controls in the Layout area let you set a default page width and
determine whether the page width is variable. You can use the Background Image controls
to import a picture file as the page background.
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 57
Page 58

PROJECTS AND LAYOUTS
New Project dialog box for Web layout type
Saving and naming a QuarkXPress project
When you save a QuarkXPress project for the first time, the Save As dialog box displays.
Use this dialog box to specify a project name, location, and type.
When you save a QuarkXPress project, you can choose an option from the Type/Save as
type drop-down menu:
• Choose Project to save a project that you can modify.
• Choose Project Template to save a read-only version of the project.
Exporting layouts and projects
To export one or more layouts in the active project, choose File > Export > Layout as
Project. Enter a name in the Save As field, and specify a location.
To export all the layouts in a project, check Select All in the Layouts area. To export
individual layouts, check them in this area.
To export selected layouts that you can open in an earlier version of QuarkXPress, choose
the earlier version number from the Version drop-down menu.
You cannot export App Studio layouts in QuarkXPress 8 format. (For more information,
see A Guide to App Studio.)
Working with layouts
It's easy to navigate between layouts, add layouts, duplicate layouts, and delete layouts.
58 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 59

PROJECTS AND LAYOUTS
To navigate between layouts, use the tabs at the top of the project window.
To add a layout to the active project, choose Layout > New or click a layout tab and choose
New from its context menu.
To duplicate a layout, display the layout you want to duplicate, then choose Layout >
Duplicate or choose Duplicate from the Layout tab context menu.
To change a layout's properties, display the layout, then choose Layout > Layout Properties
or choose Layout Properties from the Layout tab context menu. The Layout Properties
dialog box displays. You can use this dialog box to change a project's layout type, but you
cannot change a layout to or from an App Studio layout type. (For more information, see
A Guide to App Studio.)
To delete a layout, display the layout, then choose Layout > Delete or choose Delete from
the Layout tab context menu.
When you use the following commands, only the active layout is included in the resulting
output:
• File > Export > PDF
• File > Export > Page as EPS
• File > Export > Layouts as AVE issue
• File > Export > Reflow as ePub
• File > Export > Reflow as Kindle
• File > Export > Layout as Blio eBook
• File > Collect for Output
• File > Print
• File > Export > HTML (Web layouts only)
Layers apply to the layout that is active when you create and edit them.
When you perform a project-level action (Edit > Undo), the action is added to the Undo
History in all layouts.
When you check spelling (Utilities menu), QuarkXPress checks only the active layout.
The Find/Change feature (Edit menu) can search only the active layout.
Project-level and layout-level resources
Some resources are defined at the project level, and others are defined at the layout level.
Project-level resources
Project-level resources can be used by every layout in the project, and they are the same
in every layout where they are used. Project-level resources include application preferences,
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 59
Page 60

PROJECTS AND LAYOUTS
style sheets, colors, H&Js, lists, dashes and stripes, cascading menus (Web layouts only),
meta tags (Web layouts only), and menus (Web layouts only).
Although every list definition you create can be used in any layout in the project, a list
only draws from the active layout when you build it.
Layout-level resources
Layout-level resources can be unique for every layout in the project. Layout-level resources
include the following:
• Layout preferences (QuarkXPress/Edit > Preferences > Layout or Web Layout)
• Kerning settings (Utilities > Tracking Edit) (Print layouts only)
• Tracking settings (Utilities > Kerning Table Edit) (Print layouts only)
• Hyphenation exceptions (Utilities > Hyphenation Exceptions)
• Trapping settings (Window > Show Trap Information) (Print layouts only)
• Zoom values
Working with guides
Guides are nonprinting guidelines that help you to line up items and text in a layout.
There are two types of guides: Ruler guides and column and margin guides.
Design grids are nonprinting guidelines that you can use to align items and text according
to text size and position.
For more information, see "Guide Manager Pro XTensions software" and "Understanding design
grids."
Column and margin guides
Column and margin guides show where a page's outside margins are and where columns
(if any) should be placed.
QuarkXPress automatically places column guides and margin guides in all new Print
layouts. You can specify their position in the Column Guides and Margin Guides fields
in the New Project dialog box (File > New > Project) or in the New Layout dialog box
(Layout > New).
When a master page is displayed in the project window, you can use the Master Guides
& Grid dialog box (Page > Master Guides & Grid) to change the placement of column
guides and margin guides. If you check Automatic Text Box in the New Project dialog
box (File > New > Project) or the New Layout dialog box (Layout > New), the values you
specify in the Margin Guides area define the size and placement of the automatic text
box.
60 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 61

PROJECTS AND LAYOUTS
For information about creating column and margin guides, see "Configuring a master page
grid."
For more information, see "Guide Manager Pro XTensions software."
Ruler guides
Ruler guides (or simply "guides") are nonprinting guidelines that you can position manually.
You can create ruler guides by dragging them off the horizontal and vertical rulers (View >
Rulers). You can create ruler guides on master pages and on individual layout pages.
•
To create a horizontal ruler guide, click the top ruler; when the pointer displays, drag the
ruler guide into position on the page. To create a vertical ruler guide, click the vertical
ruler, and then drag the ruler guide onto the page when the pointer displays. If the
Measurements palette is open when you drag a ruler guide, the guide's position is indicated
in the X field (for vertical ruler guides) or the Y field (for horizontal ruler guides).
• If, as you create a horizontal ruler guide, you release the mouse button when the ruler
guide is positioned over the pasteboard, the ruler guide will extend across the pasteboard
and all the pages in the spread. If you release the mouse button when the horizontal ruler
guide is positioned over a document page, the ruler guide will display only on that page.
• To reposition a ruler guide, click it, and then drag it to a different location when the guide
pointer displays. You can also double-click the ruler guide with the Item tool selected and
enter a new location into the Guide Manager Pro dialog box.
• To remove a ruler guide, drag the guide off the page.
• To remove all ruler guides from a page, scroll until a portion of the page displays, then
press Option/Alt and drag the guide back on to the ruler.
• To remove all ruler guides from a spread's pasteboard, scroll until a portion of the pasteboard
displays, then press Option/Alt and click a portion of the ruler.
See also "Guide Manager Pro XTensions software."
Snapping to guides
QuarkXPress lets you create a "magnetic field" around guides so that when you drag an
item close to a guide, it automatically aligns with it. This feature is called Snap to Guides
(View menu) and the width of the magnetic field is called the Snap Distance.
To control snapping with QuarkXPress controls, make sure View > Snap to Guides is
checked. To specify the distance, choose QuarkXPress/Edit > Preferences > Print Layout >
Guides & Grid and enter a pixel value in the Snap Distance field.
You can also choose View > Snap to Page Grids to force items to align with the master
page grid. The value in the Snap Distance field applies to master page grids as well. For
more information, see "Snapping items to design grids."
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 61
Page 62

PROJECTS AND LAYOUTS
Undoing and redoing actions
The Undo command (Edit menu) reverses the last action performed on an item. For
example, if you accidentally cut a picture box, the Undo command will bring the picture
box back into the layout from the Clipboard. The Redo command (Edit menu) lets you
reimplement an action you had undone.
Choose Edit > Undo (Command+Z/Ctrl+Z) to reverse the last action performed. The menu
item identifies the specific action that can be undone. For example, the Undo Deletion
command is available in the Edit menu after you have used the Item > Delete command.
Cannot Undo displays as gray text when the Undo feature is unavailable.
To reimplement the action, choose Edit > Redo (Command+Shift+Z/Ctrl+Y) after you
undo an action.
62 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 63

Boxes, lines, and tables
To create a successful page layout, you need an orderly way to arrange text and pictures
— you need boxes. Boxes are items that can contain text or pictures; they can even be
created to contain no content at all, perhaps to create colorful design elements on a page.
Box boundaries give text and pictures a specific shape, size, and placement on a page.
Understanding items and content
BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
QuarkXPress works on the concept of items (containers) and content (things that go inside
of items).
Items are the building blocks of a page layout. The Item tool lets you do things like
move, resize, rotate, reshape, cut, copy, and paste items.
The basic types of items are as follows:
• Boxes, including text boxes, picture boxes, and no-content boxes. Boxes can come in a
variety of shapes, such as rectangular, round, and Bézier.
• Lines, including "plain" lines and text paths (which can include text). Lines, too, can be
straight or Bézier.
• Groups, which are sets of items that have been "glued" together so that they act like a single
item.
• Tables, which can contain both text and pictures.
• Forms, which let you create HTML forms (Web layouts only).
• Form controls, which let you create HTML form controls (Web layouts only).
Content is, basically, text and pictures. To create a layout, you will typically draw some
text boxes and picture boxes, and then insert text and pictures into those boxes.
Because items and content are different, you use separate tools for manipulating each:
•
The Text Content tool lets you create rectangular text boxes and format text in text
boxes or on text paths. You can also use the Text Content tool to cut, copy, and paste
text.
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 63
Page 64
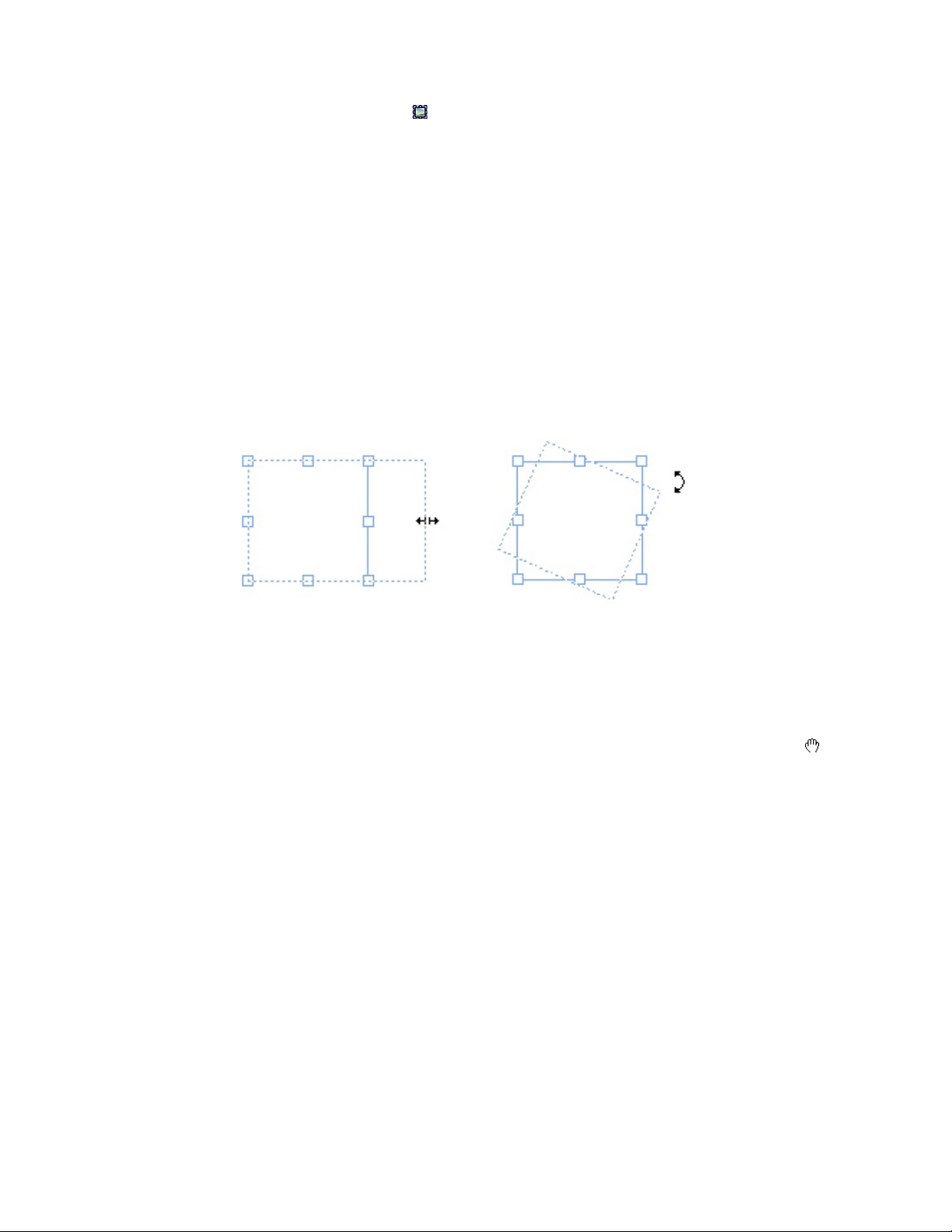
BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
•
The Picture Content tool lets you create rectangular picture boxes and manipulate
pictures in picture boxes. You can also use the Picture Content tool to cut, copy, and
paste pictures.
Understanding handles
The bounding boxes of selected text paths, lines, and boxes have small white squares called
item handles. You can use these handles to resize and rotate a selected item.
Item handles
To resize an item, click and drag its item handles. To rotate an item, click and drag just
outside one of the item's corner handles. The mouse pointer changes when you move it
over or near a handle to indicate which action you can perform:
You can use item handles to resize or rotate an item.
Picture handles
When you select the Picture Content tool and click a picture box that contains a picture,
the picture displays with large circles for handles. These handles are called picture content
handles. When you click any part of the picture overlay, you can use the Move pointer
to move the picture within its box.
64 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 65

BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
Picture box displaying picture content handles
Picture content handles display even if the selected picture exceeds the size of its box (see
illustration above). The picture displays beyond the box boundary. You can crop the image
by resizing the picture box.
You can use picture content handles to resize or rotate a picture without changing the size
or angle of its picture box.
•
Resize pointers:
•
Rotation pointers:
Rotated picture in an unrotated box
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 65
Page 66

BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
If you want to move a picture box or see what its crop looks like without the transparent
overlay, press the Command/Ctrl key. This temporarily dismissed the overlay and allows
you to interact with the box as if the Item tool were selected.
If you click and drag with the Picture Content tool when the mouse pointer is positioned
over a spot where a picture box handle and picture content handle overlap, only the picture
is resized or rotated. If you want to move the item handle, select the Item tool.
Understanding Bézier shapes
Before reshaping Bézier boxes and lines, make sure you understand the following definitions.
Point: A point connects line segments and defines where line segments start and end.
Points connecting curved line segments have curve handles that control the shape of the
curves. QuarkXPress offers three types of points: Corner, smooth, and symmetrical.
Corner point: A corner point connects two straight lines, a straight line and a curved line,
or two noncontinuous curved lines. With curved lines, the corner point's curve handles
can be manipulated independently, usually to form a sharp transition between the two
segments:
Examples of corner points
Smooth point: A smooth point connects two curved lines to form a continuous curve. The
curve handles always rest on a straight line through the point, but they can be distanced
independently:
A smooth point
Symmetrical point: A symmetrical point connects two curved lines to form a continuous
curve. The result is similar to a smooth point, but the curve handles are always equidistant
from the point:
A symmetrical point
Curve handles: Curve handles extend from either side of a point and control a curve's shape:
66 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 67

BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
Curve handles (upper left)
Line segments: Line segments are straight or curved line sections positioned between two
points:
Line segments
When the Select Point tool is positioned over an active Bézier box or line, various pointers
display indicating whether you can select a point, the curve handles, or a line segment.
Click and drag using the pointers to reshape the Bézier box or line.
• To change the shape entirely, choose a different option from the Item > Shape submenu.
•
To add a point to a Bézier box while working with the Bézier Pen tool , click a line
segment. Alternatively, you can use the Add Point tool .
•
To remove a point from a Bézier box while working with the Bézier Pen tool , click the
point. Alternatively, you can use the Remove Point tool .
•
To convert a point to another type of point while working with the Bézier Pen tool ,
Option+click/Alt+click the point. Alternatively, you can use the Convert Point tool .
• To move a point or change the shape of a line segment while working with the Bézier
Pen tool , Command+drag/Ctrl+drag the point or line segment.
• To select curves or points so that you can move them or delete them, use the Select Point
tool . Press Shift and click to select multiple points. Option+click/Alt+click a point to
make it symmetrical.
To pan the layout while a Pen tool is selected, press Shift+Space and then click and drag.
Working with boxes
There are three types of boxes: Text boxes, picture boxes, and no-content boxes (boxes
with a content of None). All three box types can contain color, shades, blends, and frames.
When you draw a text box, picture box, or no-content box, the available controls
correspond to the box type you create. But you can import text into picture boxes that
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 67
Page 68

BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
contain pictures, and you can import pictures into text boxes that contain text. In addition
to changing content type, you can change the shape and other attributes of a box.
Creating text and picture boxes
There are three ways to create boxes:
• To create a no-content box (a box that can be changed into a picture box or a text box),
click and drag with the Rectangle Box tool , the Oval Box tool , or the Starburst tool
. You can declare text content by pressing T as you draw a no-content box. You can
declare picture content by pressing R as you draw a no-content box.
•
To create a rectangular text or picture box, click and drag with the Text Content tool
or Picture Content tool .
•
To create a Bézier box, use the Bézier pen tool . For more information, see "Creating
Bézier boxes."
To constrain rectangular boxes to squares and oval boxes to circles, press Shift while you
drag.
You can create boxes with the following tools:
To change a no-content box into a text box, press Command+E/Alt+E and import a text
file.
To change a no-content box into a picture box, press Command+E/Alt+E and import a
picture file.
You can change the corner type of rectangular boxes to rounded, concave, and beveled
corners using the Item > Shape submenu or the Corner Style drop-down menu in the
Measurements palette. You can add and alter rounded corners by entering values in the
Corner Radius field (Item > Modify > Box tab). You can also use the Box Corner Radius
field in the Classic or Space/Align tab of the Measurements palette.
Creating Bézier boxes
The Bézier Pen tool lets you draw multi-sided Bézier boxes and lines that can have
straight and curved line segments (see "Understanding Bézier shapes").
For another way to make uniquely shaped boxes, see " ShapeMaker XTensions software."
To draw a Bézier box:
1
Select the Bézier Pen tool from the Tools palette. Move the Crosshair pointer to any
position on the page and click to establish the first point.
Move the pointer to where you want the next point positioned. To constrain pointer
2
movement to a 45-degree angle relative to the page, press Shift.
Click to create points and line segments.
3
68 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 69

BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
• Clicking a point without dragging creates a straight line and corner point. To create a
curved line segment and smooth point, click and drag wherever you want the next point
positioned. A point with two curve handles displays. You can control the curve's size and
shape by dragging a curve handle. Press Option/Alt while dragging a smooth point to
create a curved segment and corner point.
If desired, edit the Bézier shape while you are still drawing it.
4
• To add a point to an existing segment of the shape, click the line segment where you want
the point to be.
• To delete a point from the active shape while you are drawing it, click the point.
To close the box, close the path by positioning the mouse pointer over the beginning of
5
the line and then click when the Close Box pointer displays.
When any of the drawing tools are active, you can press Command/Ctrl to temporarily
switch to the Select Point tool. When the Select Point tool is active, you can press
Command+Option/Ctrl+Alt to temporarily switch to the Item tool.
Resizing boxes
You can resize any box by modifying the size of its bounding box. A bounding box is a
nonprinting, rectangular shape that encloses every box. The box's Understanding handles
demarcate the bounding box. The best way to view the bounding box clearly is to use the
Item tool to select item handles on a Bézier box.
You can resize active boxes using any of the following methods:
•
Select the Item tool or a Content tool and move the mouse pointer over a selected
box's item handle to display the Resizing pointer. Click and drag the handle to a new
location to reduce or enlarge the box. Press Shift to maintain the box's aspect ratio. Press
Option/Alt to resize the box from the center. Press Command/Ctrl to resize the box contents
along with the box.
• Enter values in the W and H fields of the Classic or Space/Align tabs of the Measurements
palette to change the width and height, and then press Return/Enter.
• Choose Item > Modify (Command+M/Ctrl+M), and then click the Box tab. Enter values
in the Width and Height fields to precisely change the size of a box, and then click OK.
You can lock a box's proportions, so that you don't have to press Shift to maintain the
aspect ratio. For more information, see "Locking box and picture proportions."
Locking box and picture proportions
To lock the selected box's proportions, display the Classic tab of the Measurements palette
and click the proportion lock control next to the W and H fields. If this control is locked,
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 69
Page 70

BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
QuarkXPress maintains the item's aspect ratio during resizing operations. You can also
lock box proportions in the Box tab of the Modify dialog box.
The proportion lock controls in the unlocked (top) and locked (bottom) states
To lock the proportions of the picture in the selected box, display the Classic tab of the
Measurements palette and click the proportion lock control next to the X% and Y% fields.
If this control is locked, QuarkXPress maintains the picture's aspect ratio during resizing
operations. You can also lock box proportions in the Picture tab of the Modify dialog
box.
To use the proportion-locking feature with the Item Find/Change feature, display the Box
or Picture tab of the Item Find/Change palette (Style menu), then check or uncheck
Proportions in the Find What or Change To area.
To use the proportion-locking feature with item styles, display the Box or Picture tab of
the Edit Item Style dialog box (Edit > Item Styles) and check Proportions.
Reshaping boxes
You can change the shape of a box in three ways:
• You can change the shape entirely by choosing a different option from the Item > Shape
submenu.
• You can add and alter rounded corners to rectangular boxes by entering values in the
Corner Radius field (Item > Modify > Box tab). You can also use the Box Corner Radius
field in the Classic or Space/Align tab of the Measurements palette.
• You can reshape Bézier boxes by repositioning points, curve handles, and line segments.
For more information, see "Understanding Bézier shapes."
Adding frames to boxes
Frames are decorative borders that can be placed around any type of box. To access frame
controls for active boxes, do one of the following:
• Choose Item > Frame to display the Frame tab of the Modify dialog box.
• Display the Frame tab of the Measurements palette.
Use the controls in these tabs to specify a frame style, width, color, and opacity. If the
frame style contains gaps, you can also specify gap color and opacity.
70 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 71

BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
You can also create your own frame styles in the Dashes and Stripes dialog box (Edit
menu) and specify frame settings in an Item Style. For more about Item Styles, see "Item
Styles XTensions software."
Applying colors to boxes
To apply a background color to active boxes, do one of the following:
• Choose Item > Modify (Command+M/Ctrl+M), click the Box tab, and then use the controls
in the Box area.
•
Display the Colors palette (Window > Colors), click the Background Color button ,
and then use the controls in the palette.
• Use the controls in the Classic tab of the Measurements palette.
The controls available in these tabs and palette are as follows:
• Box Color: Lets you specify the background color for the box.
• Shade: Lets you specify the tint of the background color (0% = white, 100% = full color).
• Opacity: Lets you control the transparency of the box background (0% = fully transparent,
100% = fully opaque).
You can also specify box color in an Item Style. For more about Item Styles, see "Item Styles
XTensions software."
Applying blends to boxes
A blend is a gradual transition from one color to another. To apply a blend to the
background of active boxes, do one of the following:
• Choose Item > Modify (Command+M/Ctrl+M), click the Box tab, and then use the controls
in the Blend area.
•
Display the Colors palette (Window > Colors), click the Background Color button ,
and then use the controls in the palette.
The blend-related controls available in this tab and palette are as follows:
• Style: Lets you control the type of blend.
• Angle: Lets you control the angle of the transition from one color to the other.
Blends have two colors, each of which can have its own shade and opacity. In the Box
tab of the Modify dialog box, the color in the Box area is the first color and the color in
the Blend area is the second color. In the Colors palette, click #1 to set up the first color
and #2 to set up the second color.
You can also specify blends in an Item Style. For more about Item Styles, see "Item Styles
XTensions software."
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 71
Page 72

BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
Merging and splitting boxes
Options in the Merge and Split submenus (Item menu) let you create complex Bézier
boxes from existing boxes. For example, if a rectangular box overlaps an oval box, you
can select the Item > Merge submenu and choose an option that will create a single box
with the same content. If you merge two picture boxes, one picture will display in the
combined box. If you merge two text boxes, the text flows as one story through both
boxes.
To use the Merge feature, select two items and then choose one of the following options
from the Item > Merge submenu:
• The Intersection command retains any areas where items overlap the back item, and
removes the rest.
• The Union command combines all the items into one box, retaining all overlapped areas
as well as nonoverlapped areas.
• The Difference command deletes the front items. Any overlapping areas will be cut out.
• The Reverse Difference command deletes the back item. Any overlapping areas will be
cut out.
• The Exclusive Or command leaves all of the shapes intact but cuts out any areas where
there is overlap. If you want to edit the points surrounding the cut-out area, you will notice
that there are now two points at every location where two lines originally crossed.
• The Combine command is similar to the Exclusive Or command, but if you look at the
points surrounding the cut-out area, you will notice that no points were added where two
lines intersect.
The Split command either splits a merged box into separate boxes, splits a complex box
that contains paths within paths into separate boxes, or splits a box that contains a border
that crosses over itself (such as a figure eight). To use this feature, select two items and
then choose one of the following options from the Item > Split submenu:
• The Outside Paths command works with a merged box that contains several,
non-overlapping shapes. Outside Paths keeps all the outside path information and divides
nonoverlapping outside paths into separate boxes.
• The All Paths command creates separate boxes out of every shape within a complex box.
Adding text and pictures to boxes
To add text to a box, choose the Text Content tool , double-click the box, and then
either start typing, paste text copied from elsewhere, or choose File > Import. If you choose
the Item tool and double-click a text box, the Import dialog box displays.
To place a picture in a box, select the box with the Picture Content tool and then either
paste a picture copied from elsewhere or choose File > Import. If you choose the Item
tool or the Picture Content tool and double-click a picture box, the Import dialog
box displays.
72 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 73

Changing box type
To convert a selected box to a different type, choose Picture, Text, or None from the
Content submenu (Item menu). However, you can also change a text box to a picture box
by choosing File > Import and selecting a picture. You can change a picture box to a text
box by choosing File > Import and selecting a text file.
To convert a selected text box to a text path, choose a line shape from the Item > Shape
submenu.
When you select a Box tool, you can use the following modifier keys to create text or
picture boxes:
• Press T as you draw to create a text box.
• Press R as you draw to create a picture box.
Creating a box from a clipping path
If a picture box has an associated clipping path (embedded or automatically created), you
can create a new box that has the shape of that clipping path by selecting the picture box
and choosing Item > New Box From Clipping.
BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
Working with lines
There are two types of lines: Straight and Bézier lines. You can apply colors and line styles
to any type of line.
Creating lines
To create a line, first select the Line tool from the Tools palette and move the Crosshair
pointer to any position on the page. Click and drag to draw the line.
You can constrain a line to 0, 45, or 90 degrees by pressing Shift while you draw it.
Creating Bézier lines
The Bézier Pen tool lets you draw multisided Bézier boxes and lines that can have
straight and curved line segments (see "Understanding Bézier shapes").
To draw a Bézier line:
1
Select the Bézier Pen tool from the Tools palette. Move the Crosshair pointer to any
position on the page and click to establish the first point.
Move the pointer to where you want the next point positioned. To constrain pointer
2
movement to a 45-degree angle relative to the page, press Shift.
Click to create a point and line segments.
3
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 73
Page 74

BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
• To make a curved line segment, click and drag wherever you want the next point positioned.
A point with two curve handles displays. You can control the curve's size and shape by
dragging a curve handle.
• To make a corner point, press Option/Alt before you click. If you click and hold, you can
control the radius of the corner point by dragging a curve handle.
• To add a point to an existing segment of the shape, click the line segment where you want
the point to be.
• To delete a point from the active shape while you are drawing it, click the point.
To finish the line, double-click.
4
When any of the drawing tools are active, you can press Command/Ctrl to temporarily
switch to the Select Point tool. When the Select Point tool is active, you can press
Command+Option/Ctrl+Alt to temporarily switch to the Item tool.
Line modes for straight lines
There are four line modes: Endpoints, Left Point, Midpoint, and Right Point. Depending
on the mode you choose in either the Line tab (Item > Modify) or the Measurements
palette (Classic or Space/Align tabs), line length and position will be described differently.
• Endpoints mode: The X1 field indicates the horizontal position of the first end-point; the
Y1 field indicates the vertical position of the first end-point. The X2 field indicates the
horizontal position of the last end-point; the Y2 field indicates the vertical position of the
last end-point.
• Left Point mode: The X1 field indicates the horizontal position of the leftmost end-point;
the Y1 field indicates the vertical position of the leftmost end-point.
• Midpoint mode: The XC field indicates the horizontal position of the midpoint of the
line; the YC field indicates the vertical position of the midpoint of the line.
• Right Point mode: The X2 field indicates the horizontal position of the rightmost
end-point; the Y2 field indicates the vertical position of the rightmost end-point.
Resizing lines
You can resize active straight lines using any of the following methods:
•
Select the Item tool and move the Arrow pointer over an Understanding handles to display
the Resizing pointer. Click and drag the handle to a new location to reduce or extend the
length of the line.
• Choose Item > Modify (Command+M/Ctrl+M), then click the Line tab. Click the Mode
drop-down menu to display the four mode options (see "Line modes for straight lines").
Choose Left Point, Midpoint, or Right Point to display a Length field. Enter values in
the Length field to precisely change the length of a line, then click OK.
74 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 75

BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
• Choose either Left Point, Midpoint, or Right Point from the Line Mode drop-down
menu in the Classic or Space/Align tab of the Measurements palette to display the L
(Length) field. To precisely change the length of a line, enter a value in the L field, then
press Return/Enter.
You can resize any Bézier line by modifying the size of its bounding box. To do so, make
sure Item > Edit > Shape is unchecked, and then resize the line as if it were a box.
Reshaping lines
You can change the shape of a line in the following ways:
• You can change the shape entirely by choosing a different option from the Item > Shape
submenu.
• You can reshape Bézier lines by repositioning points, curve handles, and line segments.
For more information, see "Understanding Bézier shapes."
To pan the layout while a Pen tool is selected, press Shift+Space and then click and drag.
Controlling line appearance
To control the appearance of active lines, use the controls in the following places:
• Measurements palette (Classic tab)
• Line tab of Modify dialog box (Item menu)
• Colors palette (Window menu) — for line color only
In addition to color, shade, and opacity, you can control the following characteristics for
lines:
• Line style: This option lets you control the general appearance of a line. Several line styles
are included by default, and you can add new ones with the Dashes & Stripes dialog box
(Edit menu).
• Width: You can specify the width of lines in any measurement system. You can also specify
a Hairline width; the printed width of a hairline rule is .125 pt on a PostScript imagesetter,
with a wider value on some laser printers.
• Arrowheads: You can apply arrowheads to lines using the Arrowheads drop-down menu.
You can also specify line appearance in an Item Style. For more about Item Styles, see "Item
Styles XTensions software."
Joining lines
You can merge two lines into one by selecting the Item tool , selecting the lines, and
choosing Item > Merge > Join Endpoints. The Join Endpoints command is available
when the endpoints of lines or text paths are within six points of each other.
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 75
Page 76

BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
Manipulating items
Items can be cut and then pasted in new locations, locked so they cannot move, duplicated
once or many times, stacked to create unusual visual effects, and manipulated in other
ways.
Selecting items
To manipulate items, you must first select them. Once selected, most kinds of items display
outlines and handles for reshaping.
To select an item, first select the Item tool , the Text Content tool , or the Picture
Content tool and move the Arrow pointer over an item. Click once to select a single
item or Shift+click individual items to select more than one item at a time. You can also
select multiple items by selecting the Item tool and drawing around an area that contains
the items.
With the Item tool selected, if you double-click a text box, the Import dialog box
displays. If you double-click an empty picture box with the Item tool or the Picture
Content tool selected, the Import dialog box displays. If the picture box contains a
picture, the Picture Content tool is selected.
To deselect an active item, click outside it. When the Item tool is selected, you can press
Tab to deselect any active items.
Moving items
You can move items by entering values in the Origin Across and Origin Down fields in
the Modify dialog box (Item menu), by entering values in the X and Y fields in the
Measurements palette, and by manually moving items using the Item tool . If you hold
down the mouse before moving a box or text path, you can see the contents as you move
the item. You can also "nudge" items by selecting the Item tool and pressing an arrow key
on your keyboard.
The box's item handles demarcate the bounding box. The best way to view the bounding
box clearly is to use the Item tool to select item handles on a Bézier box.
Cutting, copying, and pasting items
When the Item tool is selected, the Cut, Copy, and Paste commands (Edit menu) are
available for active boxes, lines, and text paths. Choose Edit > Paste (Command+V/Ctrl+V)
to place a copy of the items contained on the Clipboard in the center of the project window.
When the Item tool is selected, you can remove items with the Clear (Mac OS only)
and Delete commands. Cleared and deleted items are not copied to the Clipboard.
Controlling the stacking order of items
When two or more items overlap, each is either positioned in front of or behind the other
item. The term "stacking order" refers to the front-to-back relationship of the various items
76 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 77

BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
on a page. Each item you create occupies its own level in the stacking order. Every new
item you create becomes the front item.
The Item menu includes commands that let you control item stacking order.
• Choose Item > Send to Back to move an item to the back of the page or layer.
• Choose Item > Bring to Front to move an item to the front of the page or layer.
• To move an item one level backward in the page or layer on Mac OS, press Option and
choose Item > Send Backward. On Windows, choose Item > Send Backward.
• To move an item one level forward in the page or layer on Mac OS, press Option and
choose Item > Bring Forward. On Windows, choose Item > Bring Forward.
In a document with layers, the layers themselves are in a particular stacking order; within
each layer, each item has its own relationship to the stacking order. When you use the
Send to Back, Send Backward, Bring to Front, and Bring Forward commands (Item
menu), the stacking order of the items is altered within the layer.
To activate an item that is hidden behind other items, select the Item tool and press
Command+Option+Shift/Ctrl+Alt+Shift while you click repeatedly at the point where
multiple items overlap. Pressing Command+Option+Shift/Ctrl+Alt+Shift while clicking
will successively activate items from the front of the stacking order to the back.
Grouping items
You can combine multiple items on a page or spread into a single group. Grouping items
is useful when you want to select or move several items simultaneously. You can move,
cut, copy, duplicate, and perform a number of other functions on a group. For example,
you can group all the items that compose a publication masthead; once grouped, you can
modify or move the entire group as you would a single box, line, or text path.
After you create a group, you can still edit, resize, and reposition individual items while
maintaining the group relationship. You can also place a copy of a group into an open
QuarkXPress library for use in other documents.
Items can be grouped when two or more items (lines, boxes, text paths, or other groups)
are active. To select multiple items with the Item tool , either Shift+click each item or
draw a marquee around the items you want to group. Choose Item > Group
(Command+G/Ctrl+G) to place multiple selected items into a single group.
You can group groups, and multiple-select a group (or groups) along with individual boxes,
lines, and text paths to create a larger group.
With the Item tool selected, you can move, cut, copy, paste, duplicate, rotate, and color
a group. With the Text Content tool or Picture Content tool selected, you can
manipulate individual items as you would any ungrouped item.
To move an item within a group, press Command/Ctrl and select the item with the Item
tool , the Text Content tool , or the Picture Content tool .
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 77
Page 78

BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
If an active group contains the same kind of items (for example, all picture boxes), the
Modify dialog box will include a tab (or tabs) that refer specifically to those items. If an
active group contains a variety of items, the Modify dialog box may display only a Group
tab.
Choose Item > Ungroup (Command+U/Ctrl+U) to ungroup a single group, or Item >
Ungroup All to ungroup every group in a group that contains other groups.
Resizing grouped items
To resize every item in a group simultaneously, click and drag the group's item handles.
If you press Command+Shift/Ctrl+Shift while resizing a group, all frame widths, line
weights, pictures, and text are resized proportionally. If you press Command/Ctrl while
resizing a group, frame widths, pictures, and text are still resized, but not proportionally.
Duplicating items
QuarkXPress lets you make single or multiple copies of boxes, lines, and text paths.
Create a single copy of a selected item using the Duplicate command (Item menu). You
can also press Option/Alt while dragging an item or group to create a duplicate.
The Step and Repeat feature is useful for laying out design elements that contain a number
of evenly spaced copies of an item. Create multiple copies of an item and specify the
distance between them using the Step and Repeat command (Item menu).
For another way to make uniquely shaped boxes, see " ShapeMaker XTensions software."
Spacing and aligning items
You can control the position of multiple selected items relative to one another using the
Item > Space/Align submenu or the Space/Align tab of the Measurements palette.
You can choose from among eight spacing and six alignment options in the Measurements
palette, and you can specify alignment relative to selected items, the page, or (for Print
layouts with facing pages) the spread. The Item > Space/Align submenu includes the "Item
relative" and "Page relative" modes described below. The Measurements palette also includes
a third mode called "Spread relative."
The space/align modes are as follows:
•
Item relative mode positions items relative to the uppermost active item, which does not
move. The uppermost item is determined by the location of the item's top edges. If two
or more items have the same top edges, then items are spaced from the leftmost item.
•
Page relative mode positions items relative to the page edges (left, right, top, or bottom).
•
Spread relative mode is available for active Print layouts that include facing pages. Assume
that you have opened a layout with a spread and then selected an item on a left page and
another item on the right page. If you then click the Spread relative mode icon in the
78 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 79

BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
Measurements palette and choose Space horizontal centers , the selected items position
themselves on the far-left and far-right sides of the spread.
Rotating items
To rotate active items, do one of the following:
•
Select the Item tool and move the mouse over a corner handle. When the Rotation
pointer displays, click to establish a rotation point; then drag in a circular motion to rotate
the item. The Arrowhead pointer and the item's position will display as you drag. If you
press the Shift key when rotating, movements are constrained to 45-degree angles.
• Choose Item > Modify (Command+M/Ctrl+M), enter a value in the Angle field, and click
OK.
•
Enter a value in the field on the Measurements palette (Classic and Space/Align tabs)
and press Return/Enter.
To rotate a straight line, choose either Left Point, Midpoint, or Right Point from the
Mode drop-down menu (Modify dialog box or Measurements palette) to display the
Angle field. To rotate a Bézier line, display its bounding box by unchecking Shape (Item >
Edit).
Skewing items
To skew active items within bounding boxes, choose Item > Modify
(Command+M/Ctrl+M); then click the Box tab. Enter a value in the Skew field. Positive
values slant items to the right; negative values slant them to the left.
Locking and unlocking items
Locking lets you protect items and content from accidental changes. You can do the
following:
• To prevent an item's size and position from being changed (and to prevent the item from
being deleted), check Item > Lock > Position.
• To prevent an item's contents from being edited, check Item > Lock > Story or Item >
Lock > Picture.
To unlock selected items, uncheck the appropriate option in the Item > Lock submenu.
Alternatively, choose Item > Modify and click the lock icon next to a field.
Anchoring items and groups in text
You can anchor an item or group so that it flows as a character within text. To anchor an
item or group within text, use the Item tool to select the item or group you want to
anchor and choose Edit > Copy (Command+C/Ctrl+C) or Edit > Cut
(Command+X/Ctrl+X). Then, with the Text Content tool selected, place the text
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 79
Page 80

BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
insertion point at the point in text where you want to anchor the item or group and choose
Edit > Paste (Command+V/Ctrl+V).
Working with callouts
The Callouts feature lets you create floating boxes that always display on the same page
or spread as the content they pertain to. For example:
• You can create figures with pictures and text that follow their references from page to
page.
• You can create pull quotes that can automatically move to a different page with their
source text.
• You can create "floating" icons that sit in the space to the left of a paragraph to indicate
that the paragraph is a tip, a note, a warning, and so forth.
For more information, see the topics below.
Understanding callouts
A callout is a floating box that always displays on the same page or spread as the content
it pertains to. Each callout is anchored to a particular spot in a text story called a callout
anchor. A callout anchor flows along with text like a character. When a callout anchor
moves to a new page or spread, the callout moves with it. When guides are displayed, a
line links each callout anchor with its associated callout (if any).
A callout anchor with its associated callout
A callout's position in a layout is based on two things:
• The location of its callout anchor. A callout is always on the same page or spread as its
callout anchor.
• The callout anchor's settings. You can position a callout relative to the spread, the page,
the box or cell that contains the callout anchor, the paragraph that contains the callout
anchor, or the callout anchor itself.
80 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 81

BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
For example, you can configure a callout so that its horizontal location is always against
the outside margin, but its vertical location is always aligned with the paragraph that
contains its callout anchor. The settings for such a configuration look like this:
Settings for a callout with a fixed horizontal location and a variable vertical location
It is important to note that the settings for a callout are stored with its callout anchor, not
with the callout itself
You can control the positioning of a callout by configuring its callout anchor directly, or
by applying a callout style to the callout anchor. A callout style is a named package of
callout settings that displays in a palette. Callout styles are useful in documents where you
use different callout settings over and over; rather than recreating those settings each time,
you can simply select the callout anchor and click the appropriate callout style in the
Callout Styles palette.
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 81
Page 82
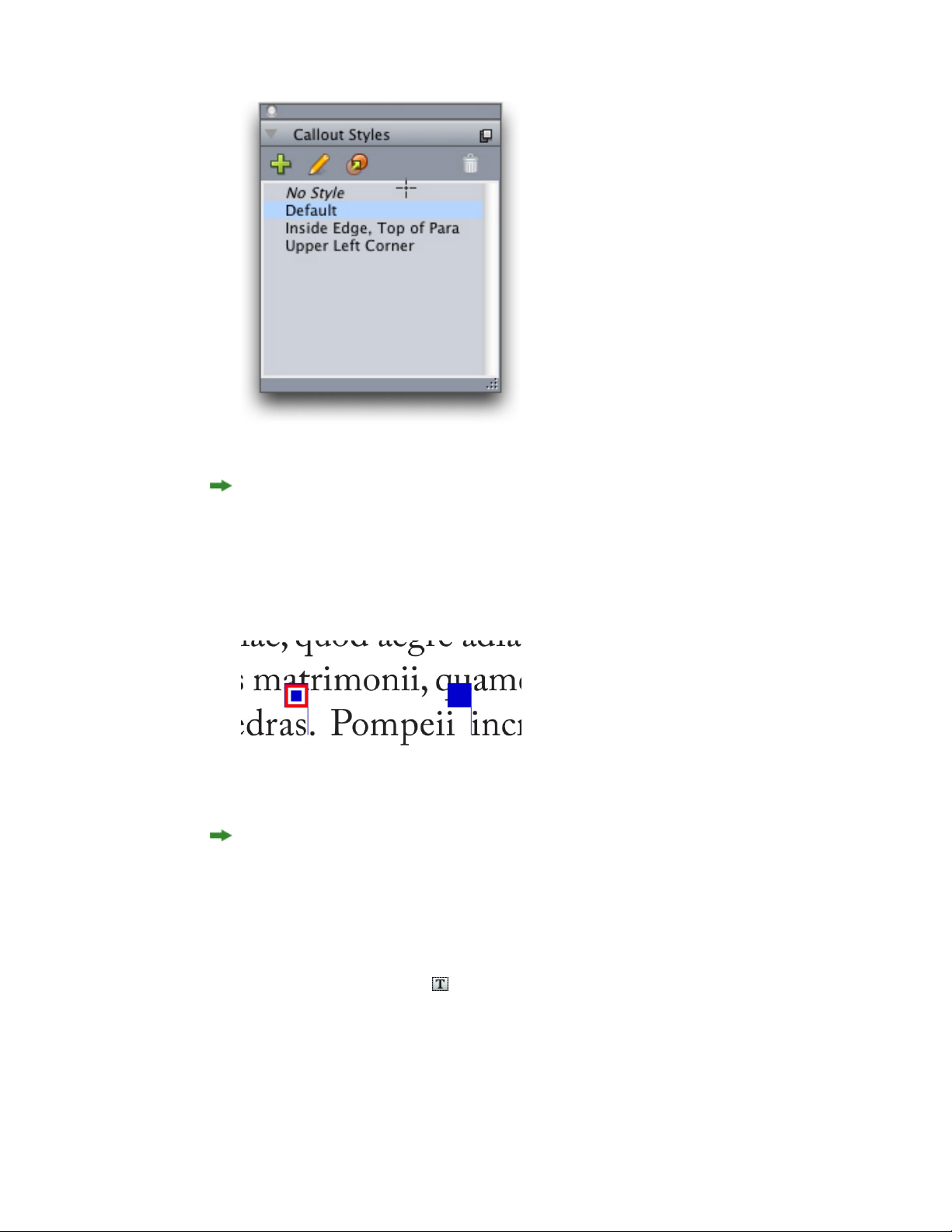
BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
Callout Styles palette
You can think of callout styles as similar to style sheets (for more information, see "Working
with style sheets"). Like style sheets and other resources, callout styles can be managed with
Job Jackets (for more information, see "Job Jackets").
A callout anchor can be selected or unselected. When a callout anchor is selected, it has
a red outline and its callout style (if any) is selected in the Callout Styles palette.
A selected callout anchor (left) and an unselected callout anchor (right)
When guides are turned off, you can see only the selected callout anchor.
When you cut or copy and paste text that contains a callout anchor that has an associated
callout, the callout is cut or copied and pasted along with the text.
Creating a callout
To create a callout:
1
Select the Text Content tool and place the text cursor at the point in the text where
you want the callout anchor to be.
Choose Item > Callout Anchor > Insert Callout Anchor. A callout anchor is inserted and
2
automatically selected.
82 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 83
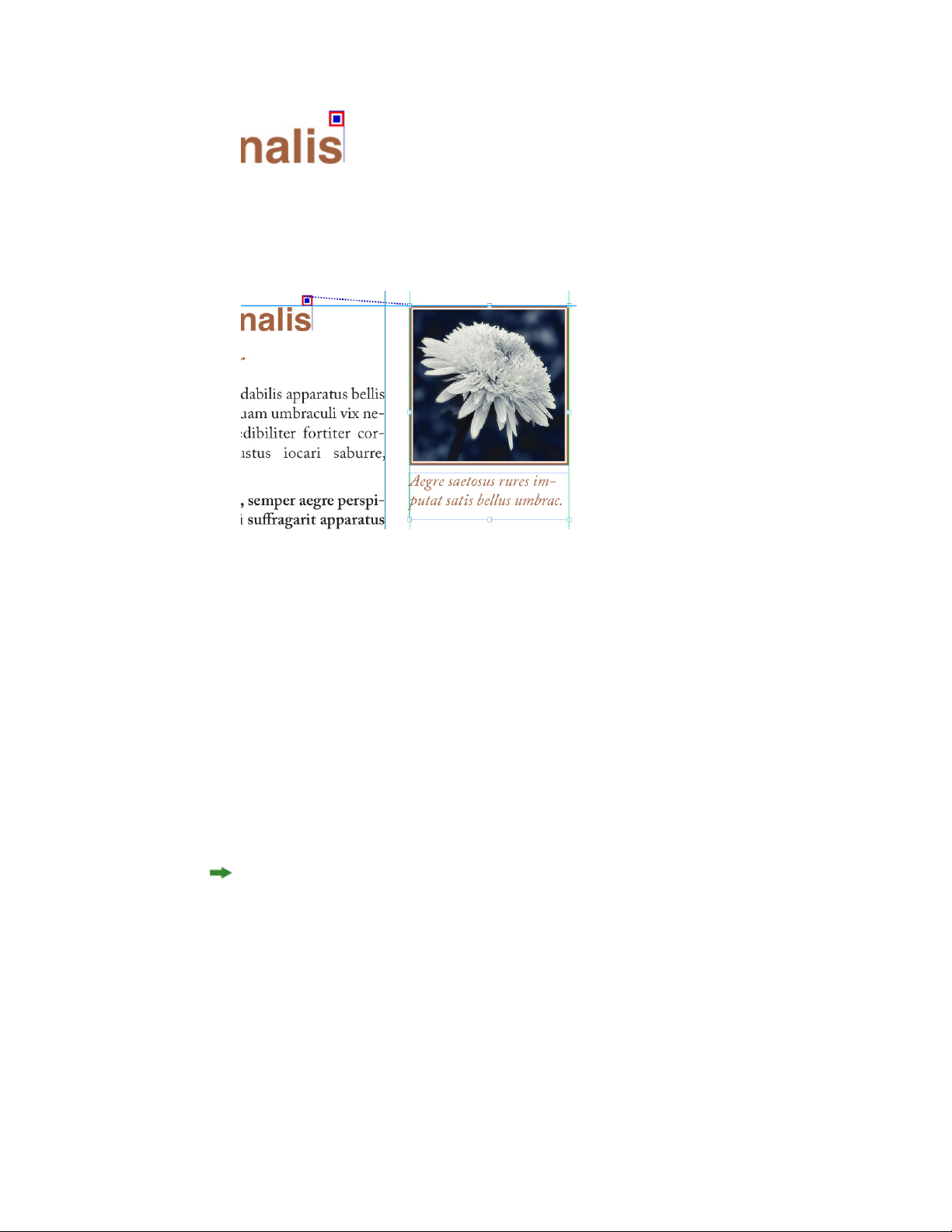
BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
Selected callout anchor
Select the item or group that you want to make into a callout.
3
Choose Item > Callout Anchor > Associate with Callout Anchor. The item or group
4
becomes a callout, and a line displays between the callout and the callout anchor.
Callout anchor associated with a callout
Configure the callout anchor. There are two ways to configure a callout anchor:
5
• To apply a callout style to the callout anchor, display the Callout Styles palette (Window
menu) and click the name of the callout style, or choose Item > Callout Anchor > Callout
Styles > [Callout Style Name]. For more information, see "Working with callout styles."
• To edit the settings of the callout anchor directly, choose Item > Callout Anchor > Edit
Callout Settings. If a callout style has been applied to the callout anchor, any changes
you make will override the callout style's settings.
For information on how to configure a callout anchor or callout style, see
"Configuring a callout anchor."
Configuring a callout anchor
The process of configuring a callout anchor is essentially the same whether you are
configuring a callout style or directly configuring a callout anchor.
To configure a callout anchor:
Select the callout anchor and choose Item > Callout Anchor > Edit Callout Settings. The
1
Edit Callout Settings dialog box displays.
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 83
Page 84
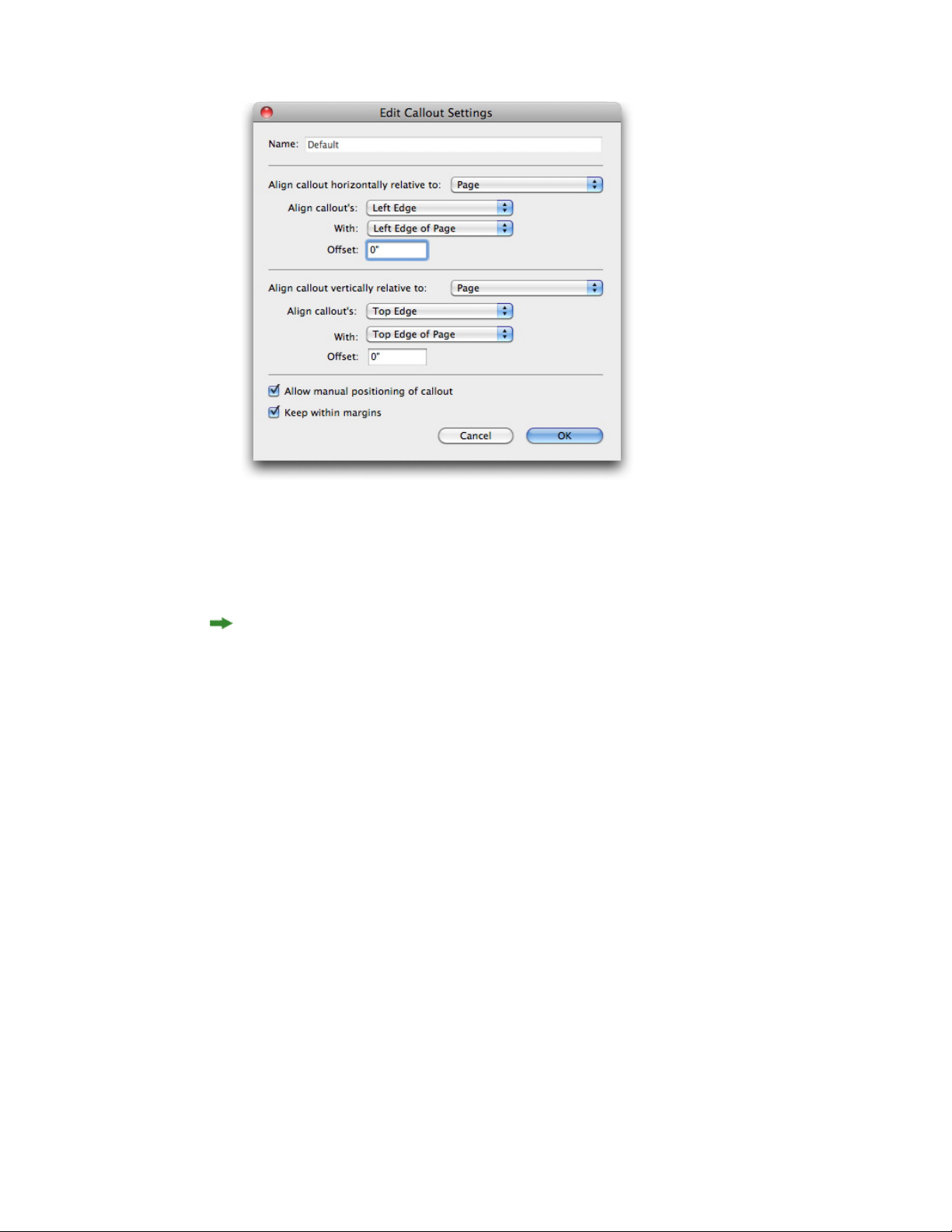
BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
Edit Callout Settings dialog box
To control how the callout aligns horizontally, use the controls in the Align callout
2
horizontally relative to area. (The Offset field lets you adjust the horizontal positioning
of the callout from where it would otherwise be.)
If you choose Spread from the Align callout horizontally relative to drop-down menu
and specify a horizontal offset, that offset is inverted on left-facing pages. This allows you,
for example, to configure a callout to always be .25" inside of the inside margin; on a
right-facing page, such an offset moves the callout to the right, but on a left-facing page
the offset must move the callout to the left.
To control how the callout aligns vertically, use the controls in the Align callout vertically
3
relative to area. (The Offset field lets you adjust the vertical positioning of the callout
from where it would otherwise be.)
To allow the callout to be manually repositioned, check Allow manual positioning of
4
callout. If you subsequently move the callout, the values in the Offset fields will be
automatically updated to reflect the new position of the callout.
To prevent the callout from being manually repositioned, leave this box unchecked.
To prevent the callout from extending beyond the page margins, check Keep within
5
margins.
Click OK.
6
84 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 85
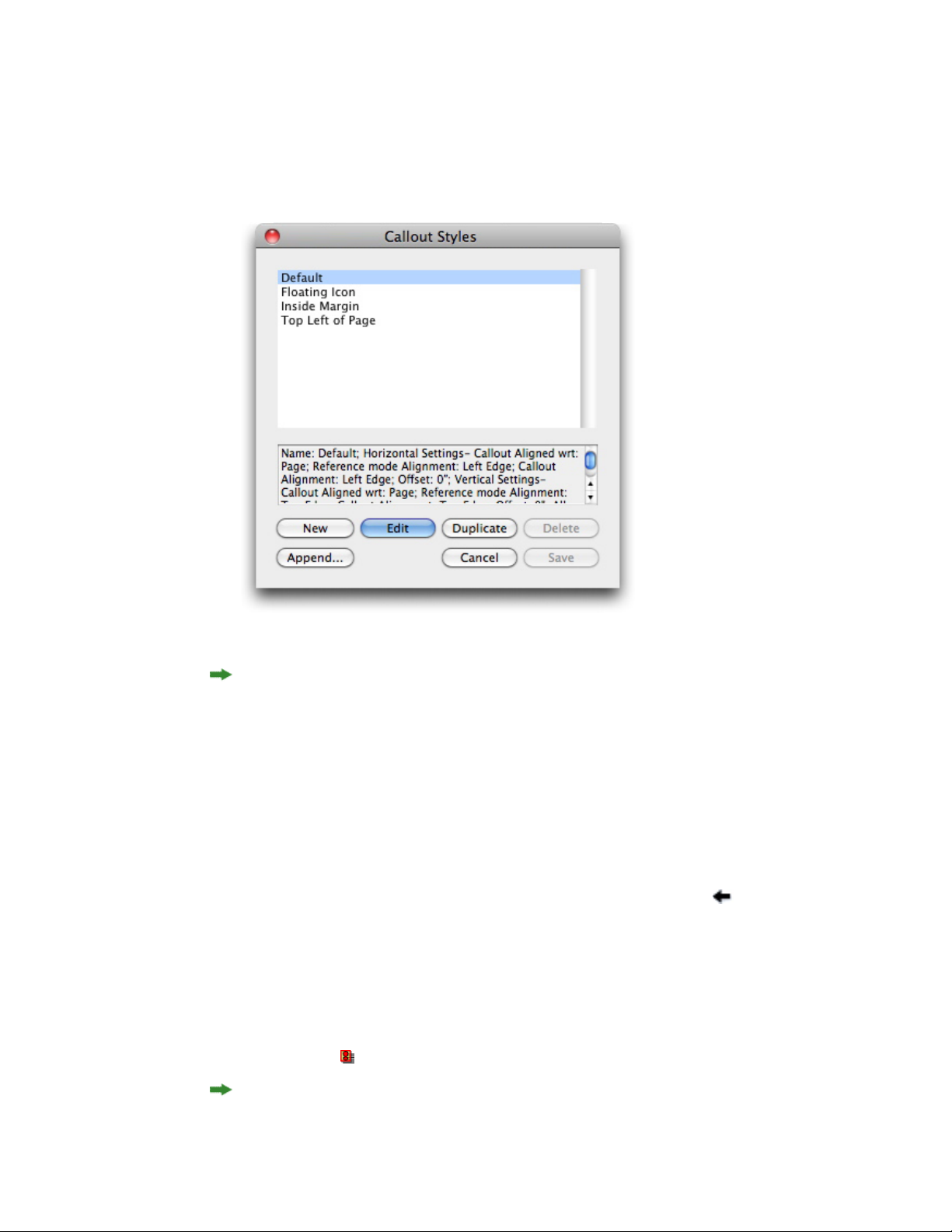
Working with callout styles
Callout styles make it easy for you to apply often-used settings to callout anchors. To
create, edit, duplicate, or delete callout styles, use the Callout Styles dialog box (Edit >
Style Sheets). You can also use this dialog box to append callout styles from other projects.
BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
Callout Styles dialog box
You can edit the Default callout style, but you cannot delete it.
Callouts and runaround
If a callout with runaround causes its callout anchor to move, this can lead to an error
state. For example, if a callout's runaround pushes its callout anchor to the next page, the
callout moves to the next page — which allows the callout anchor to return to the previous
page, which causes the callout to return to the previous page, and so on.
When QuarkXPress detects this kind of a situation, the following things happen:
1
The callout switches to the settings defined in the Default callout style. An icon displays
next to the callout style's name in the Callout Styles palette when the callout anchor is
selected.
If the error condition still occurs, QuarkXPress applies the No Style settings to the callout
2
and it is positioned at its last valid location.
If the application cannot find a valid location, it turns runaround off for the callout. When
3
QuarkXPress turns off a callout's runaround this way, it also places this visual indicator
on the callout:
To view visual indicators, check View > Visual Indicators.
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 85
Page 86
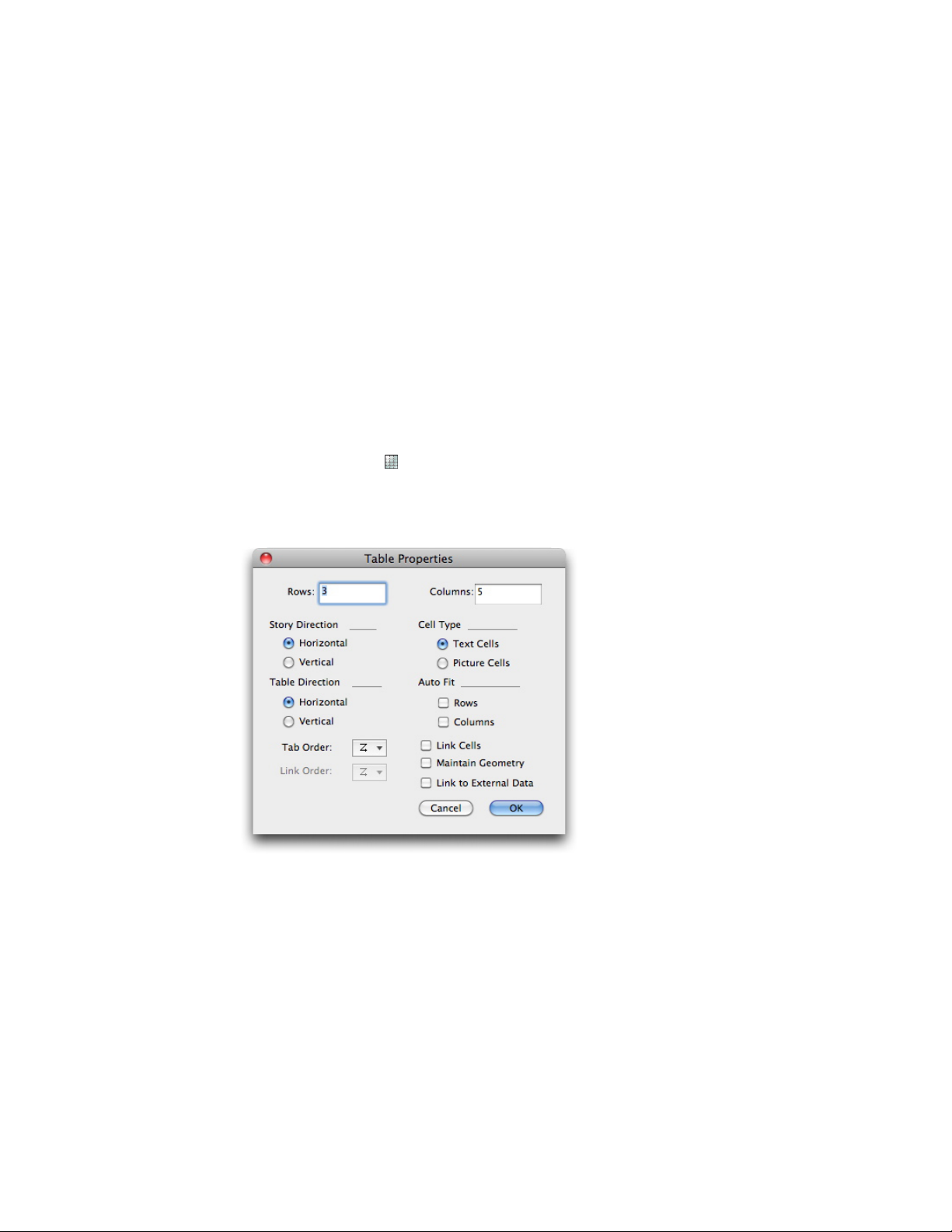
BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
To turn runaround back on for such a callout, use the Runaround tab of the Modify dialog
box (Item menu) or the drop-down menu in the Runaround tab of the Measurements
palette.
Working with tables
In QuarkXPress, a table is a distinct item, like a text box, picture box, text path, or line.
When working with tables, you can pretty much think of a cell as an individual picture
box, text box, or no-content box, and you can handle cells in much the same way you
handle these other items. To work with elements of the table itself — such as rows and
columns — use the Table menu.
Drawing a table
To draw a table and specify its properties, do the following:
1
Select the Tables tool from the Tool palette, drag to draw a rectangle that is roughly
the size of the final table, and then release the mouse button. The Table Properties dialog
box displays.
The Table Properties dialog box
Specify the number of horizontal rows in the Rows field, and specify the number of vertical
2
columns in the Columns field.
To specify the default cell type, click Text Cells or Picture Cells in the Cell Type area.
3
Later, you can select specific cells and convert the content type if needed.
If you want to create text cells that expand as you add text, use the controls in the Auto
4
Fit area.
If you have a preference for how to navigate through cells in a table when you press
5
Control+Tab, you can choose a different option from the Tab Order drop-down menu.
86 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 87

If you want to link text cells so imported text flows through the specified cells — similar
6
to linked text boxes — check Link Cells. If you check Link Cells, you can choose the
order in which to link the text cells from the Link Order drop-down menu.
If you do not link cells in this manner, you can link them later using the Linking tool or
the Link Text Cells command (Table menu). In addition, even if you don't link the text
cells, you can still use Control+Tab to jump from cell to cell while entering or editing data.
If you intend to import data from Excel, check Link to External Data. For more
7
information, see "Importing Excel tables."
If you want the table to remain the same size if you add or delete rows, check Maintain
8
Geometry.
Click OK.
9
Converting text to tables
The success of converting text to a table depends on the text preparation itself. It's important
that paragraphs, tabs, spaces, or commas (the characters QuarkXPress can convert) are
used consistently in a text block, because these characters are used in the table conversion to
define rows and columns. It's common for users to use multiple tab characters in a word
processor to align columns of data — rather than setting appropriate tab stops. If the text
block you are converting has such multiple tab characters, the text block probably has an
inconsistent number of tabs between columns of data. You will need to make the tab
characters consistent before you convert the text to a table.
BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
To convert text to a table:
1
Using the Text Content tool , select all the text you want to convert to a table.
Choose Table > Convert Text to Table to display the Convert Text to Table dialog box.
2
Based on the selected text, QuarkXPress guesses what to Separate Rows With, what to
Separate Columns With, and how many Rows and Columns are necessary for the
worst-case scenarios in the selected text.
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 87
Page 88
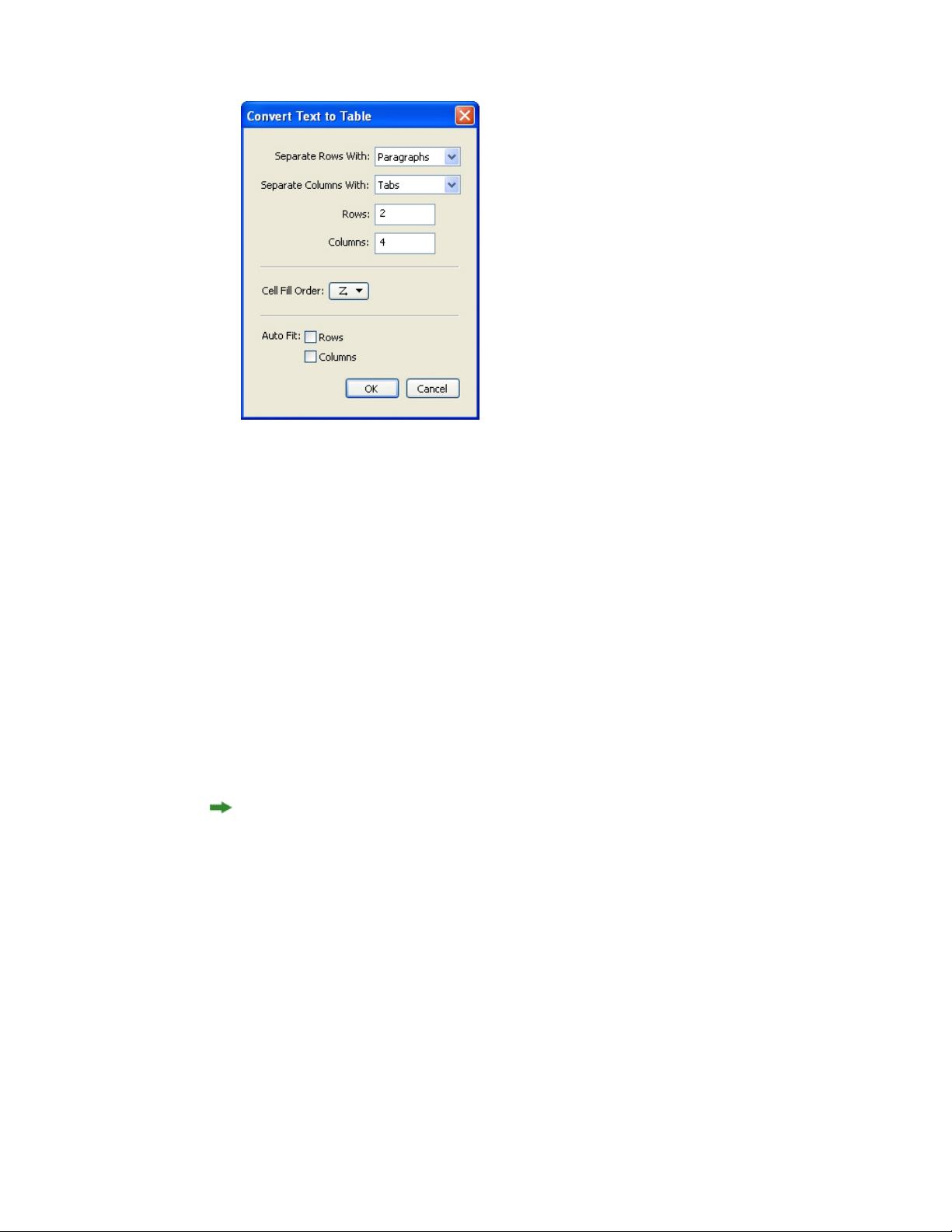
BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
The Convert Text to Table dialog box
If you want to create text cells that expand as you add text, use the controls in the Auto
3
Fit area.
If you want the information in the table to flow differently — for example, if the values
4
are currently in descending order but would have more impact in ascending order — you
can change the flow. Choose an option from the Cell Fill Order drop-down menu (the
default is Left to Right, Top Down).
Click OK. A new table is created, offset from the original text box.
5
Importing Excel tables
Table data often originates in a spreadsheet program such as Excel, and you can import
table data just as you import pictures. Although the technique is slightly different, the
results are the same: The table in QuarkXPress is linked to the Excel file for tracking and
updating.
You can import both .xls and .xlsx files.
If you import a table from Excel using the Link to External Table feature in the Table
Properties dialog box, table usage will be tracked just as picture usage is tracked. This
ensures that you're notified if the source table changes, and that you have the latest table
data when you output the layout, whether you print, collect for output, save as a PDF, or
export to HTML. To check the status of a table, choose Utilities > Usage, and then click
the Tables tab.
Although you can update tables just as you can update pictures, you'll need to keep the
following points in mind:
• If you check Include Formats in the Table Link dialog box when you first import an Excel
table, the table's Excel formatting is preserved (as much as possible) in QuarkXPress. If you
88 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 89
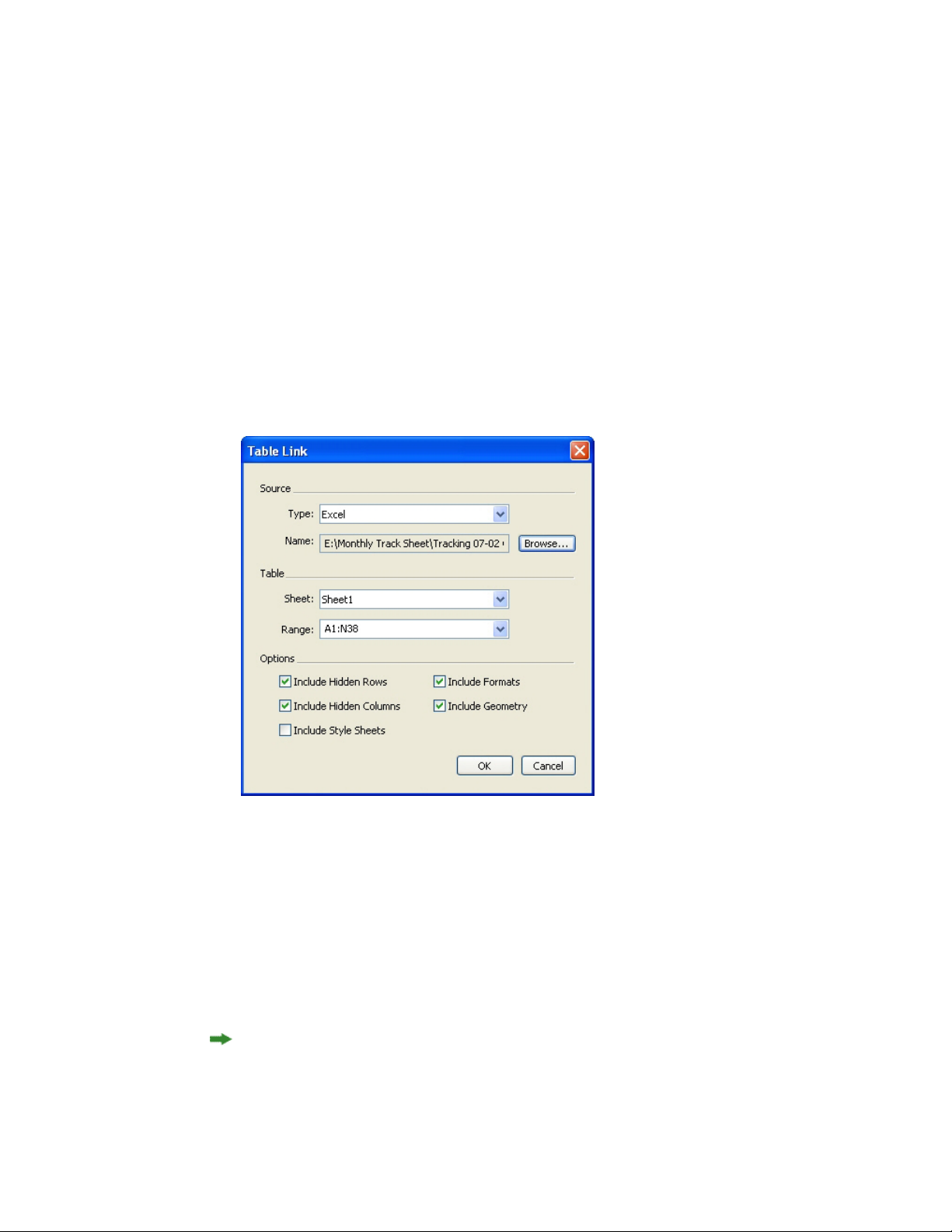
BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
later update the table, any local formatting you have applied in QuarkXPress is removed
and replaced with the formatting from the Excel file.
• If you do not check Include Formats in the Table Link dialog box when you first import
an Excel table, the table's Excel formatting is discarded. If you later update the table,
QuarkXPress attempts to preserve any local formatting you have applied to the table in
QuarkXPress.
To import an Excel table and maintain the link in QuarkXPress:
Using the Tables tool, drag to draw a table of approximately the dimensions you need.
1
The Table Properties dialog box displays when you release the mouse button.
Check Link to External Data.
2
Click OK to display the Table Link dialog box.
3
The Table Link dialog box
Click Browse to locate and select an Excel file to import.
4
If the file includes multiple worksheets, choose the one you want to import from the Sheet
5
drop-down menu. If you want to import only a portion of the data, you can specify a cell
range in the Range field or choose a named range from the drop-down menu.
In the Options area, check the attributes you want to import.
6
Click OK.
7
Formulas and references are not imported. Instead, the final values that result from formulas
and references are imported. Inserted pictures are not imported. Text with Auto Filter or
Advance Filter (Data > Filter) applied is imported as static text.
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 89
Page 90

BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
A quicker way to create a table from Excel data — without linking the source table to the
QuarkXPress project for updates — is to copy and paste. To do this, select any portion of
data in an Excel worksheet and copy the selected data. Then simply switch to QuarkXPress
and choose Edit > Paste. QuarkXPress creates a table appropriate to the data and inserts
the text.
Importing Excel charts
If you have charts or pictures created using Insert > Chart or Insert > Picture in Excel
that you want to use in a QuarkXPress layout, you can import those charts or pictures the
same way you import other pictures. To do this, use the Insert Chart tab of the Import
Picture dialog box (File menu). Charts and pictures imported from Excel are tracked by
the Pictures tab of the Usage dialog box (Utilities menu) just like other pictures.
Adding text and pictures to tables
When working with tables, think of a table cell as a text box or a picture box. Each box
contains content — text that may or may not be linked to the next cell, an individual
picture, or nothing (maybe just a blend). Therefore, you can add content to tables much
as you add content to boxes — by typing text, importing text, or importing pictures.
Converting text cells to picture cells is the same as converting a text box to a picture box.
Select all the cells you want to convert and choose Item > Content > Picture.
Editing table text
Two important things to know about editing text within tables are how to navigate between
cells and how to select text for formatting. As always when working with text, you must
first select the Text Content tool .
Navigating through a table works as follows:
• Click in a cell in which you want to enter or import text.
• Press Control+Tab to move to the next cell.
• Press Control+Shift+Tab to go back to the previous cell.
• Press the arrow keys to move through the text in a cell, and to move from cell to cell.
To enter a tab character in a text cell, press Tab. To enter a right-indent tab, press
Option+Tab/Shift+Tab. If you need to align numbers within a table on the decimal point
or other character, you can insert tabs in each table cell and then specify the appropriate
Align On tab stops (Style > Tabs).
Selecting text in rows and columns works as follows:
• To select all the text in a row, click outside the right or left edge of the table.
• To select all the text in a column, click outside the top or bottom edge of the table.
90 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 91

BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
• To select all the text over several rows or columns, drag along an edge of the table.
• To select text in nonadjacent rows or columns, Shift+click the specific rows or columns.
• To select text in various rows and columns, use the options in the Select submenu of the
Table menu. Options include Cell, Row, Odd Rows, Even Rows, Column, Odd Columns,
Even Columns, All Cells, Header Rows, Footer Rows, and Body Rows. The Select
commands in the Table menu are helpful for applying different formatting to alternating
rows or columns.
Linking table cells
When cells are linked, text that is typed, imported, or pasted into a cell fills the first text
cell in the linked story, and then flows into each subsequent linked cell. As with text in
linked boxes, the Next Column character (enter on the numeric keypad) is helpful for
controlling text flow in linked cells. In addition to linking table cells to each other, you
can link cells to and from text boxes and text paths.
• To link all the cells in a table, check Link Cells in the Table Properties dialog box when
you create the table.
• To link selected cells in a table, choose Table > Link Text Cells. All but the first cell in
the selection must be empty.
•
To manually link table cells, use the Linking tool . As with linking text boxes, click to
select the starting cell and then click the next cell you want to add. To redirect existing
links, Shift+click with the Linking tool.
•
To unlink table cells, use the Unlinking tool to click the blunt end of the arrow between
linked cells.
•
To link table cells to text boxes or text paths, use the Linking tool .
If you combine linked text cells (Table > Combine Cells), the combined cells are removed
from the text chain; the remaining links are unaffected. If a combined cell is split (Table
> Split Cell), the links are maintained and text flows according to the specified Link Order.
Formatting tables
As with other items in QuarkXPress, tables have their own version of the Modify dialog
box (Item menu) for formatting table attributes. The panes available in the Modify dialog
box depend on what is selected — for example, you can select the entire table with the
Item tool ; select individual cells or groups of cells with the Text Content tool ; or
select specific gridlines, picture cells, or text cells. Options in the Measurements palette
and Colors palette reflect table selections as well, allowing you to make some adjustments.
Formatting gridlines
Gridlines are the horizontal lines between rows and the vertical lines between columns.
When gridlines are selected, you can use the Grids tab of the Modify dialog box to specify
line style, width, color, gap color, shades, and opacities.
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 91
Page 92

BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
To format gridlines, first select them as follows:
1
•
For an individual gridline, click the gridline with the Text Content tool .
• For multiple gridlines, Shift+click each gridline.
• For the entire table, all horizontal gridlines, or all vertical gridlines, select the table with
the Item tool . Then you can specify a selection in the Modify dialog box.
• Choose an option from the Select submenu of the Table menu: Horizontal Grids, Vertical
Grids, Border, or All Grids.
Once the appropriate gridlines are selected, choose Item > Modify, and then click the
2
Grid tab.
The Grid tab of the Modify dialog box
To select all gridlines, vertical gridlines, or horizontal gridlines, click one of the buttons
3
to the right of the Preview area. From top to bottom, the buttons select All Gridlines,
Horizontal Gridlines, or Vertical Gridlines.
Change any values in the Grid tab, using the Preview area and the Apply button to help
4
you make decisions.
The Measurements palette (Window menu) also provides a pane for formatting selected
gridlines.
92 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 93

Inserting and deleting rows and columns
You can insert rows and columns anywhere within a table. Simply click in a cell that is
immediately above or below where you want to add a row. Or, click in a cell to the right
or left of where you want to add a column. Then, choose Table > Insert > Row or Table >
Insert > Column.
To select rows or columns to delete, drag the arrow pointer over a table edge and then
Shift+click the arrow pointer, or use the commands in the Select submenu of the Table
menu (such as Odd Rows). Then, choose Table > Delete > Row or Table > Delete >
Column.
If Maintain Geometry is checked in the Table menu and you delete a column or row,
existing columns or rows increase in size to fill the space of the deleted columns or rows.
If Maintain Geometry is unchecked, the table becomes smaller as necessary.
Combining cells
To combine cells, Shift+click a rectangular selection of cells with the Text Content tool
. Choose Table > Combine Cells. To revert combined cells to match the surrounding
table, select the combined cells and then choose Table > Split Cells.
BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
Manually resizing tables, rows, and columns
proportionally
proportionally
Converting tables back to text
If you combine unlinked cells containing text or pictures, the content of the upper-left
cell in the selection is maintained for the combined cell.
As with other items in QuarkXPress, you can drag to resize rows, columns, and tables. To
resize a row or column, click a gridline to display the resize pointer. Drag the pointer up
or down to resize a row and left or right to resize a column. To resize an entire table, press
one of the following keyboard commands while you drag a resize handle.
Windows commandMac OS commandEffect on table
CtrlCommandTable and contents resized
ShiftShiftTable (but not contents) resized
Ctrl+ShiftCommand+ShiftTable and contents resized
If you need to export the current data from a table — for example, to save the data as a
Word file — you can convert the information to text. To do so, select the table and then
choose Table > Convert Table > To Text.
Working with tables and groups
For flexibility, you can group tables to other items using the Group command (Item menu).
In addition, you can disassemble a table by converting its cells to a series of grouped text
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 93
Page 94

BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
boxes, picture boxes, or both. This method lets you separate elements of a table and use
those elements elsewhere in a layout. To do this, select a table and choose Table > Convert
Table > To Group. To work with the individual boxes, choose Item > Ungroup.
Continuing tables in other locations
Because tables do not always fit on one page or spread — or within the space allotted in
a design — tables can be automatically continued to other locations anywhere in a layout.
There are two ways to continue tables:
• Anchoring the table in a text box. This is the preferred way to break a table in most
situations, because it is easiest to use
• Breaking the table manually. This method is necessary when you break a table horizontally
(for example, if you want to put the first five columns of a table on one page and the
remaining three columns on a different page).
When tables are continued, you may still need a legend to explain what's in the table. You
can add a legend in the form of automatically created and synchronized header and footer
rows, and you can create special "continued" table headers for portions of a table after the
first.
Anchoring tables in text
One way to continue a table in another location is to anchor the table in a text box. An
anchored table flows with the text like any other anchored object, but it also breaks
automatically if it is too long to fit in the box and it is the only thing in the paragraph
that contains it.
To anchor a table in text:
Create the table.
1
2
Select the table with the Item tool .
Choose Edit > Cut.
3
4
Select the Text Content tool and place the text insertion point where you want the
table to be.
Choose Edit > Paste.
5
At this point, the table will break automatically as it flows through the text. However, it
will not have a header unless you add it. For more information, see "Adding header and
footer rows to tables."
Breaking a table manually
One way to continue a table in another location is to specify a table break. The table break
is the maximum size the table can reach before it splits into two linked tables. In continued
tables, any changes to a table, such as inserted columns, are reflected throughout the table.
To manually create a continued instance of a table:
94 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 95

BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
Choose Table > Table Break to display the Table Break Properties dialog box.
1
The Table Break Properties dialog box
Check Width to break the table when its width exceeds the value in the field. By default,
2
the current width of the table displays in the Width field — decreasing this value will
break the table.
Check Height to break the table when its height exceeds the value in the field. By default,
3
the current height of the table displays in the Height field — decreasing this value will
break the table.
You can specify the number of header rows by entering a value in the Header Rows field.
4
(For more information, see "Adding header and footer rows to tables.")
If the table has a header, you can check Continued Header to create a different version of
5
the header that displays in continued instances of a table. For example, if the header on
the first portion of the table is "List of Contributors," the continued header might be "List
of Contributors (continued)." Click First Header Row to limit the continued header to
the first header row, or All Header Rows to create continued headers from all header rows.
To set the continued header's contents, close this dialog box, then go to a portion of the
table after the first and change the header contents there.
You can specify the number of footer rows by entering a value in the Footer Rows field.
6
Click OK. If the height or width of the table meets the Table Break criteria, the table
7
separates into two or more linked tables. You can move the continued tables to other
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 95
Page 96
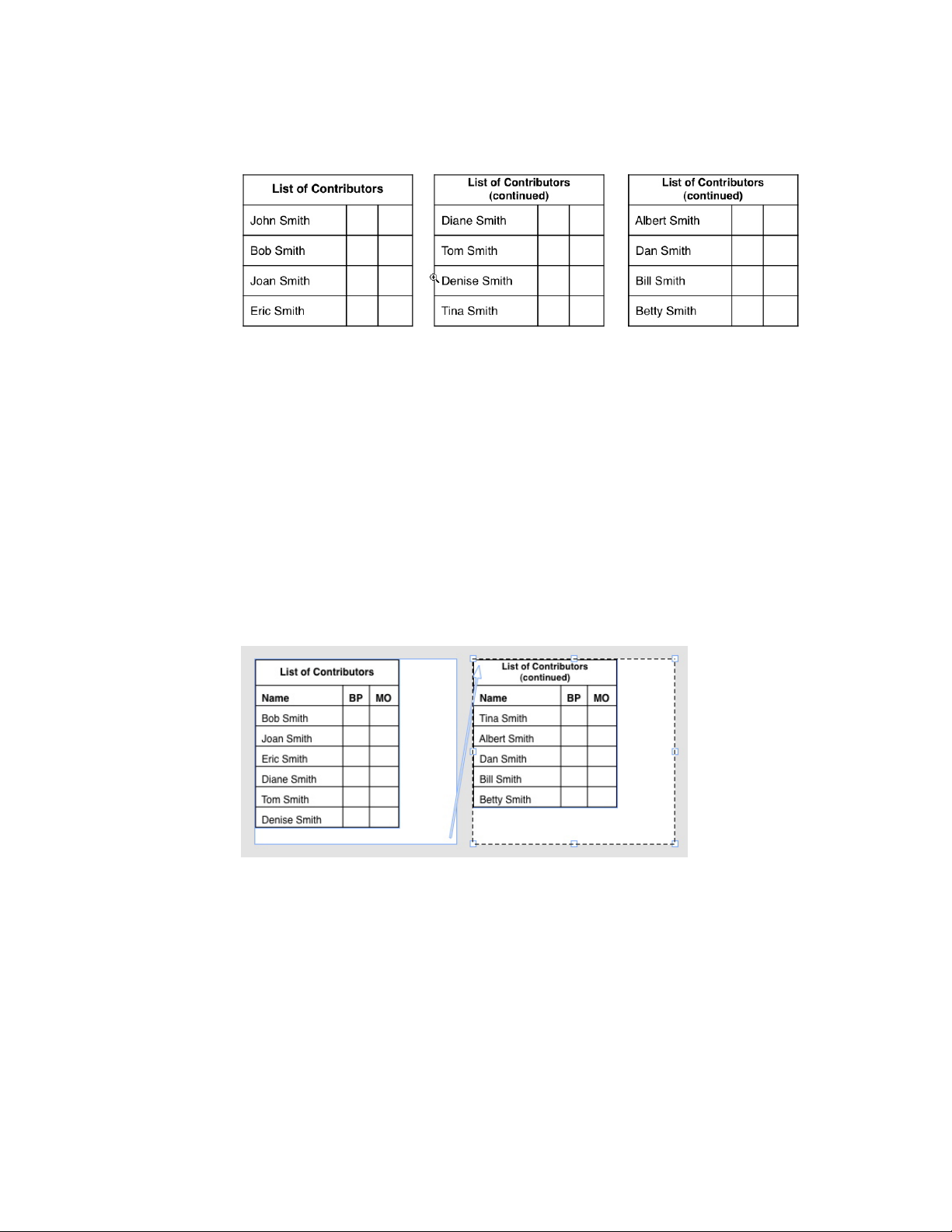
BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
locations in the layout. The table may break later as you adjust it by resizing or adding
rows and columns.
A broken table with a continued header
The Table Break feature works in both directions: it continues the table using additional
subtables as necessary if the table gets larger and recombines tables as necessary if the table
gets smaller.
To sever the links between continued tables, select any instance of the continued table
and choose Table > Make Separate Tables.
Adding header and footer rows to tables
You can specify that header and footer rows repeat automatically in continued instances
of tables. Even better, header and footer rows are automatically synchronized, so any
changes in the text are reflected throughout all instances of a continued table.
In this continued table, the first two rows — the table heading and the column heads — repeat
as header rows in the continued instances of the table. The first row is a continued header.
To add header and footer rows to a table:
Set up the table to break. For more information, see "Breaking a table manually" and
1
"Anchoring tables in text."
There are two ways to create header and footer rows:
2
96 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 97
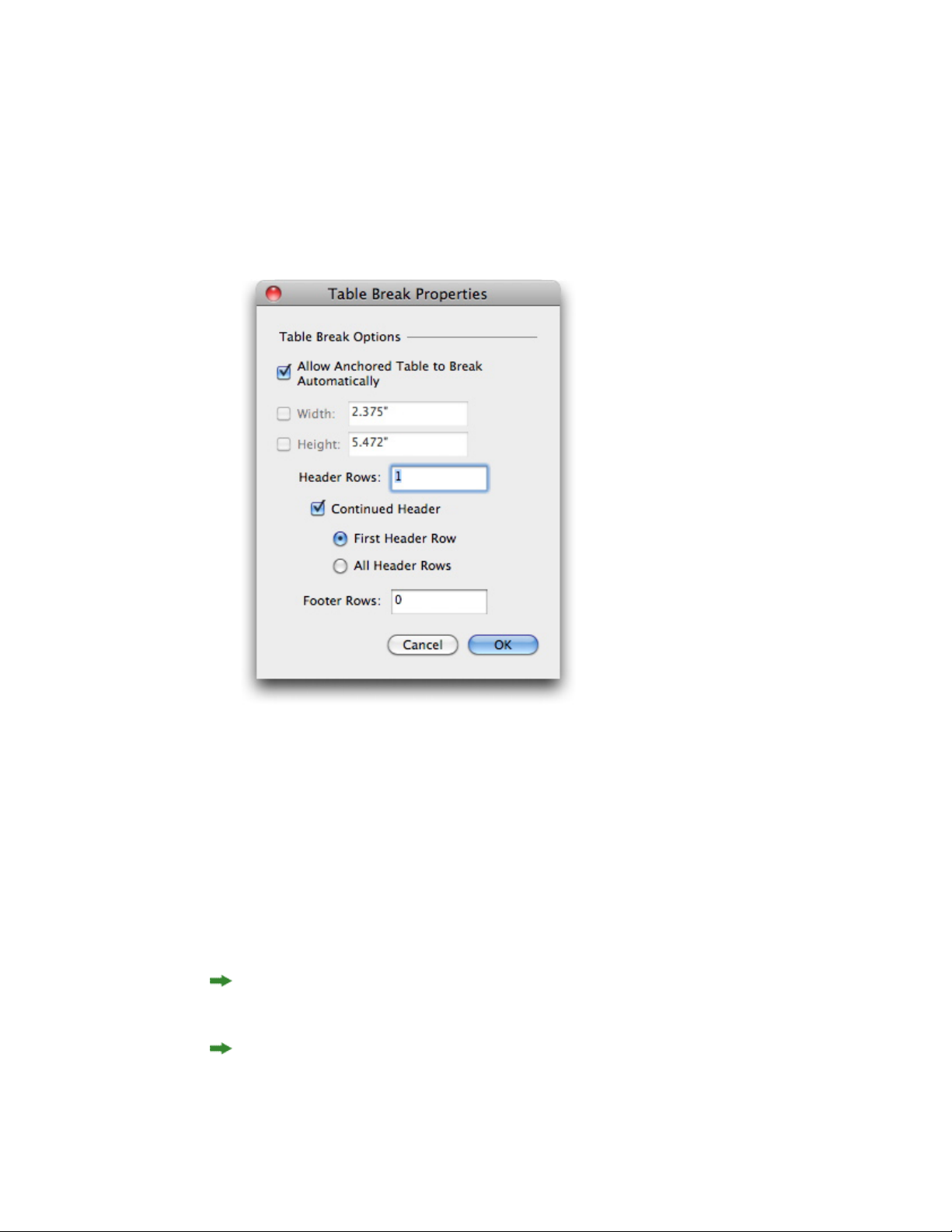
BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
• To create an automatic header, select the first one or more rows of the table and choose
Table > Repeat As Header. To create an automatic footer, select the last one or more rows
of the table and choose Table > Repeat As Footer.
• Choose Table > Table Break. The Table Break Options dialog box displays. To set the
number of header and footer rows, enter values in the Header Rows and Footer Rows
fields, respectively.
Table Break Properties dialog box for anchored table
To create a secondary header that displays in portions of a table after the first, check
Continued Header. For example, if the header on the first portion of the table is "List of
Contributors," the continued header might be "List of Contributors (continued)." Click
First Header Row to limit the continued header to the first header row, or All Header
Rows to create continued headers from all header rows.
When you're finished, click OK.
To set a continued header or footer's contents, go to a portion of the table after the first
3
and change the header contents there.
You can uncheck Repeat as Header or Repeat as Footer in the Table menu any time to
remove the header or footer rows from continued tables.
Once you add automatic header rows and footer rows, the remaining table rows are
considered "body rows." Options in the Select submenu of the Table menu let you select
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 97
Page 98

BOXES, LINES, AND TABLES
all the Header Rows, Footer Rows, and Body Rows in any instance of a continued table
for formatting.
98 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
Page 99

Text and typography
Text is an integral part of nearly every publication. QuarkXPress lets you create and edit
text directly in your publications or import text from most popular word processing
applications. In addition to the standard text formatting and editing features, QuarkXPress
includes such features as finding and changing text and its attributes, spell checking,
custom spelling dictionaries, and a font usage utility for making project-wide changes to
text formatting.
Typography is the art of making the appearance of your text convey the tone or meaning
of the content. QuarkXPress lets you control the tone of your text by letting you adjust
every facet of typography, including typefaces, type styles, leading, and spacing.
TEXT AND TYPOGRAPHY
Editing text
To enter and import text into active text boxes, use the Text Content tool . Characters
are entered at the text insertion point, indicated by the blinking line. A story is all of the text
in a text box. If a series of boxes is linked, all of the text in all of the boxes is a single story.
You can select text using multiple mouse clicks. A double-click selects the word containing
the text insertion point; a triple-click selects the line containing the text insertion point;
four clicks selects the entire paragraph containing the text insertion point; five clicks selects
the entire story.
When you double-click to select a word and cut or copy it, the application looks at the
context of the word and adds or deletes a space automatically as needed when you paste
the word in its new location. This feature is referred to as Smart Space. If you want an
accompanying punctuation mark included with the word you're selecting, double-click
between the word and its adjacent punctuation.
Importing and exporting text
To import text, do one of the following:
•
Select the Text Content tool , place the text insertion point where you want text to be
inserted, and then choose File > Import. Check Convert Quotes option to convert double
hyphens to em dashes and convert foot or inch marks to typesetter's apostrophes and
A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3 | 99
Page 100

TEXT AND TYPOGRAPHY
• Drag a text file from the file system onto a text box.
• Drag text from another application onto a text box.
• Press Command/Ctrl and drag a text file from the file system onto a picture box or a
• Press Command/Ctrl and drag text from another application onto a picture box or a
quotation marks. Check Include Style Sheets to import style sheets from a Microsoft Word
or WordPerfect file or convert "XPress Tags" to formatted text.
no-content box.
no-content box.
If you drag content onto a box that already contains text or a picture, QuarkXPress creates
a new box for the dragged content. To replace the contents of the box instead, press
Command/Ctrl while dragging the content to the box. To always create a new box for
dragged-in content, press Option/Alt while dragging.
If all the imported text does not fit in the text box, the overflow symbol displays. If Auto
Page Insertion (QuarkXPress/Edit > Preferences > Preferences > General pane) is enabled,
pages are inserted (when you import text into an automatic text box) as necessary to
contain the text.
To export text, first either place the text insertion point in a text box (if you want to save
all of the text in that box) or select the text you want to export. Then choose File > Save
Text, choose an option from the Format pop-up menu, enter a name, choose a location,
and then click Save.
To export in .docx format, choose Word Document from the Format drop-down menu.
To export in .doc format, choose Microsoft Word 97/98/2000.
Import/export filters
XTensions software lets you import and export text in a variety of formats, including those
described in this section.
Word 6–2000 filter
The Word 6–2000 Filter allows documents to be imported from, or exported to, the
Microsoft Word 97/98/2000 (Word 8) and .docx formats.
To avoid import problems, uncheck Allow fast saves (in the Save tab of the Options dialog
box) in Microsoft Word or use the Save As command to create a copy of the Word file to
be imported.
WordPerfect filter
The WordPerfect Filter allows documents to be imported from WordPerfect 3.0 and 3.1
(Mac OS) and WordPerfect 5.x and 6.x (Windows). The WordPerfect Filter also lets you
save text in WordPerfect 6.0 format.
100 | A GUIDE TO QUARKXPRESS 9.3
 Loading...
Loading...