Page 1

RMX™ Series
▲▲
▲ RMX 850
▲▲
▲▲
▲ RMX 1450
▲▲
▲▲
▲ RMX 2450
▲▲
Technical Service Manual
*TD-000098-00*
TD-000098-00
Rev. B
Page 2

Page 3

RMX Series
Technical Service Manual
RMX 850
RMX 1450
RMX 2450
QSC Audio Products, Inc.
Technical Services Group
Phone: 1-800 QSC AUDIO (1-800-772-2834) USA only
+1 (714) 957-7150
Fax: +1 (714) 754-6173
Postal: 1665 MacArthur Blvd.
Costa Mesa, California 92626 USA
E-mail: tech_support@qscaudio.com
Web: http://www.qscaudio.com (product information and support)
http://www.qscstore.com (parts and accessory sales)
Copyright 2001, 2002 QSC Audio Products, Inc. All rights reserved.
Document # TD-000098-00, Rev. B. Released February 2002.
RMX Series Technical Service Manual 1
Page 4

RMX Series Performance Specifications
RMX 850 RMX 1450 RMX 2450
OUTPUT POWER
in watts
FTC: 20 Hz–20 kHz @ 0.1% THD, both channels driven
8Ω per channel 185 260 450
4Ω per channel 280 400 650
EIA: 1 kHz @ 0.1% THD, both channels driven
8Ω per channel 200 280 500
4Ω per channel 300 450 750
1 kHz @ 1% THD, typical, both channels driven
2Ω per channel 430 700 1200
Bridge Mono:
8Ω, 20 Hz–20 kHz, 0.1% THD 530 800 1300
8Ω, 1 kHz, 0.1% THD 600 900 1500
4Ω, 1 kHz, 1% THD, typical 830 1400 2400
DYNAMIC HEADROOM 2 dB @ 4Ω
DISTORTION
SMPTE-IM < 0.01% < 0.01% < 0.02%
FREQUENCY RESPONSE 20 Hz–20 kHz, +0/-1 dB
(at 10 dB below rated output power) -3 dB points: 5 Hz and 50 kHz
DAMPING FACTOR > 300 @ 8Ω
NOISE (unweighted 20 Hz to 20 kHz, below rated output) 100 dB 100 dB 100 dB
VOLTAGE GAIN 31.6× (30 dB) 40× (32 dB) 50× (34 dB)
INPUT SENSITIVITY, V RMS
full rated power @ 8Ω 1.15v (+3.4 dBu) 1.15v (+3.4 dBu) 1.23v (+4.0 dBu)
INPUT IMPEDANCE 10 KΩ unbalanced
20 KΩ balanced
CONTROLS Front: AC switch, Ch. 1 and Ch. 2 gain
Rear: 10-position DIP switch
INDICATORS POWER: Green LED CLIP: Red LED, 1 per channel
SIGNAL: Yellow LED, 1 per channel
CONNECTORS Input: Active balanced; XLR and ¼" (6.3 mm) TRS, tip and pin 2 positive, and barrier strip
Output: “Touch-Proof” binding posts and Neutrik Speakon™
COOLING Continuously variable speed fan, back-to-front air flow
AMPLIFIER PROTECTION Full short circuit, open circuit, thermal, ultrasonic, and RF protection
Stable into reactive or mismatched loads
LOAD PROTECTION Turn-on/turn-off muting, AC coupling, triac crowbar (on each channel)
OUTPUT CIRCUIT TYPE AB AB H
AB: Class AB complementary linear output
H: Class AB complementary linear output with Class H 2-step high efficiency circuit
DIMENSIONS 19.0" (48.3 cm) wide, 3.5" (8.9 cm) tall (2 rack spaces)
15.9" (40 cm) deep (rack mounting to rear support ears)
WEIGHT Shipping: 41 lb. (18.6 kg) 46 lb. (20.9 kg) 50.5 lb. (23 kg)
Net: 35 lb. (15.9 kg) 40 lb. (18.2 kg) 44.5 lb. (20.2 kg)
POWER REQUIREMENTS Available for 120 or 220–240 VAC, 50/60 Hz
POWER CONSUMPTION
(both channels driven)
Multiply currents by 0.5 for 230V units
@ 120 VAC
eldI
8
ΩΩΩΩΩ
4
ΩΩΩΩΩ
2
ΩΩΩΩΩ
1
2
lacipyT
lluF
A5.0
A3A1.4A4.7
A5.4A6.6A5.11
A5.6*A5.9*A71
3
xaM
8
ΩΩΩΩΩ
4
ΩΩΩΩΩ
2
ΩΩΩΩΩ
eldI
1
2
lacipyT
lluF
A5.0
A7.3A4.5A01
A6A6.9A61
A3.9*A7.41*A52
3
xaM
8
ΩΩΩΩΩ
4
ΩΩΩΩΩ
2
ΩΩΩΩΩ
eldI
1
lacipyT
A6.0
A4A7.9A4.61
A3.6A6.51A72
A2.9*A32*A14
2
3
lluF
xaM
US patents pending
SPECIFICATIONS SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE
2 QSC Audio Products, Inc.
Page 5

Table of Contents
RMX Series Performance Specifications ........................................................................................................................................ 4
1. Introduction ........................................................................................................................................................................................ 6
1.1 Service bulletins ................................................................................................................................................................................ 6
1.2 The well-equipped service bench ..................................................................................................................................................... 6
1.3 Working with surface-mount components ....................................................................................................................................... 6
1.4 Series description ............................................................................................................................................................................. 8
1.5 Technical descriptions and theory of operation ................................................................................................................................ 8
2. Component identification and pinout ........................................................................................................................................... 10
3. Troubleshooting: Symptoms, causes, & remedies ..................................................................................................................... 12
3.1 Excessive current draw ..................................................................................................................................................................... 12
3.2 Protection, muting, and turn-on/turn-off delay problems ................................................................................................................ 12
3.3 Faults with signal present ................................................................................................................................................................. 13
3.4 Instability ........................................................................................................................................................................................... 13
3.5 Power supply & rail balancing problems .......................................................................................................................................... 14
4. RMX calibration procedures .......................................................................................................................................................... 14
4.1 Setting bias ....................................................................................................................................................................................... 14
4.2 Setting positive and negative current limits ..................................................................................................................................... 15
5. Servicing RMX amplifiers ............................................................................................................................................................... 16
5.1 Mechanical disassembly and re-assembly ....................................................................................................................................... 16
6. Replacement parts ............................................................................................................................................................................ 17
6.1 RMX 850 Replacement Parts ............................................................................................................................................................ 17
6.2 RMX 1450 Replacement Parts .......................................................................................................................................................... 20
6.3 RMX 2450 Replacement Parts .......................................................................................................................................................... 23
7. Schematics and diagrams ............................................................................................................................................................... 27
7.1 RMX Assembly/Disassembly Diagram 1 of 2
7.2 RMX Assembly/Disassembly Diagram 2 of 2
7.3 RMX 850 Schematic Diagram 1 of 3
7.4 RMX 850 Schematic Diagram 2 of 3
7.5 RMX 850 Schematic Diagram 3 of 3
7.6 RMX 1450 Schematic Diagram 1 of 3
7.7 RMX 1450 Schematic Diagram 2 of 3
7.8 RMX 1450 Schematic Diagram 3 of 3
7.9 RMX 2450 Schematic Diagram 1 of 3
7.10 RMX 2450 Schematic Diagram 2 of 3
7.11 RMX 2450 Schematic Diagram 3 of 3
7.12 RMX 850 Chassis Wiring Diagram ................................................................................................................................................. 38
7.13 RMX 1450 Chassis Wiring Diagram ............................................................................................................................................... 39
7.14 RMX 2450 Chassis Wiring Diagram ............................................................................................................................................... 40
(All models) ...............................................................................................................
(All models) ...............................................................................................................
Channel 1 ...............................................................................................................................
Channel 2 ...............................................................................................................................
Power Supply .........................................................................................................................
Channel 1 .............................................................................................................................
Channel 2 .............................................................................................................................
Power Supply .......................................................................................................................
Channel 1 .............................................................................................................................
Channel 2 ...........................................................................................................................
Power Supply .....................................................................................................................
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
RMX Series Technical Service Manual 3
Page 6

1. Introduction
1.1 Service bulletins
Contact QSC Technical Services to make sure you have the most up-to-date service bulletins for RMX Series amplifiers. Service bulletins
may be distributed in hard copy, via fax, and electronically (Adobe Acrobat PDF) via CD-ROMs, FTP from the QSC web site
(www.qscaudio.com), and e-mail.
These service bulletins had been issued at the time this manual was printed: RMX0001, “Q205 Lead Stress” (RMX 2450 only); RMX0002,
“RMX Turn-on Delay” (all RMX models); RMX0003, “RMX 2450 Turn-off Mute” (RMX 2450); RMX0004, “RMX 2450 AC Wire Routing”
(RMX 2450); RMX0005, “RMX 2450 AC Wire Replacement” (RMX 2450); and RMX0006, “RMX 2450 IRFZ44N Field Effect Transistors (RMX 2450).
1.2 The well-equipped service bench
To properly service RMX amplifiers, a technician needs the right tools. The technician’s service bench should have the following equipment:
• Digital multimeter with RMS AC voltage and current
• Digital clamp-on ammeter
• Dual-trace oscilloscope
• Audio distortion analyzer
• Non-inductive load resistors, configurable as 8 ohms (min. 500 watts capacity), as 4 ohms (min. 750 watts capacity), and 2 ohms (min.
1200 watts capacity)
• Variable AC voltage source, such as a Variac or Powerstat variable transformer, with a rated current capacity of up to 25A (for 120V
models) or 12A (for 230V models)
• Low-distortion audio sine wave generator
• Philips and flat screwdrivers
• Soldering iron with a fine tip (25–60W recommended)
• Rosin-core solder (60/40 or 63/37)
• Long-nose pliers
• Diagonal cutters
• Wire strippers
Automated test equipment, such as an Audio Precision workstation, is very useful for servicing RMX amplifiers. Contact QSC Technical
Services to obtain applicable AP test files.
1.3 Working with surface-mount components
RMX amplifiers, like many modern electronic products, use surface-mount technology (SMT) components where appropriate in order to
make high-density circuitry that is reliable and economical to manufacture.
SMT components in the RMX amps are used in the small-signal and control circuits, so they do not handle significant amounts of power;
therefore, they are subject to very little stress and should seldom fail. Sometimes they do fail, or they require replacement for a performance
upgrade or modification. Thus, it is important to know how to work with SMT components.
Specialized tools and equipment exist for soldering, unsoldering, and removing SMT components quickly and
efficiently, but they are often expensive. Most SMT repairs, though, can be handled reasonably well with common
tools and equipment, such as tweezers, solder braid, and fine-tip soldering irons. The original factory components
are tacked to the board with a spot of glue, so you might have to apply some force to break the adhesive.
Two-terminal components (resistors, capacitors, diodes, etc.)
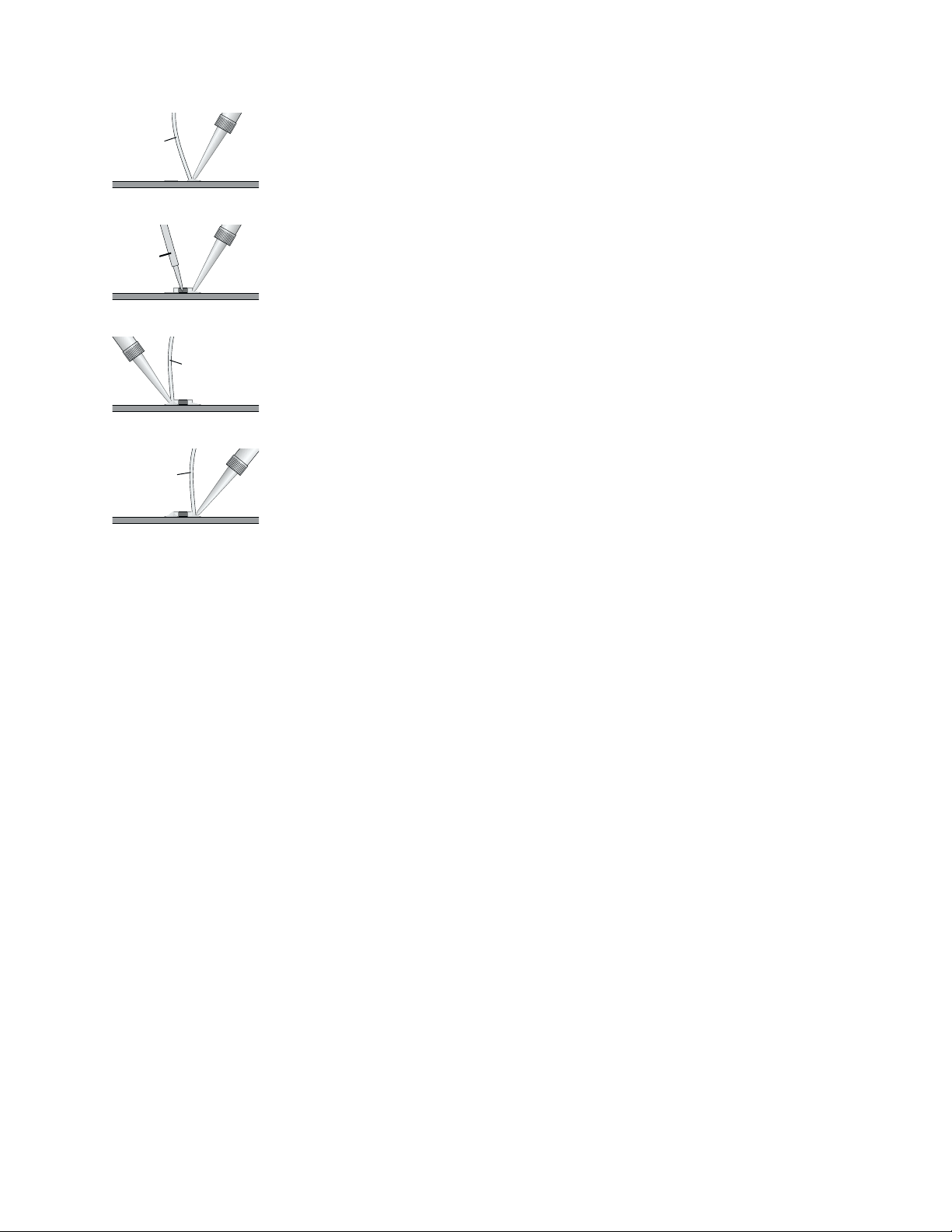
Removal
1 Use two soldering irons, preferably about 25 to 40 watts, with fine tips.
2 With a soldering iron in each hand, hold one tip on the solder at one end of the component and the other
tip on the other end (Figure 1.1).
3 Once the solder melts on both ends, grip the component between the two tips and lift it from the circuit
board.
4 Use solder braid and a soldering iron to remove the solder from the two pads (Figure 1.2).
4 QSC Audio Products, Inc.
Figure 1.1.
Solder braid
Figure 1.2.
Page 7
Solder
Figure 1.3.
Tweezers
Figure 1.4.
Figure 1.5.
Solder
Figure 1.6.
Solder
Insertion
1 With a soldering iron and 60/40 or 63/37 eutectic-type solder, melt just enough solder onto one pad to
create a small mound (Figure 1.3).
2 Grasp the component in the middle with tweezers. Melt the small mound of solder with the iron and
place the component across the two pads (in the correct orientation, if the component is sensitive to
direction) and press it flat against the circuit board, with one end of the component immersed in the
melted solder (Figure 1.4).
3 Hold the component in place and take the soldering iron away. Let the solder harden to tack the
component in place.
4 Fully solder the other end of the component to its pad. Let the solder harden (Figure 1.5).
5 Fully solder the tacked end of the component to its pad (Figure 1.6).
Three-terminal components (transistors, etc.)
Removal
1 With a soldering iron and solder braid, remove as much solder as possible from the middle terminal of
the component.
2 With a soldering iron in each hand, hold one tip on the solder at the terminal at one end of the compo-
nent and the other tip on the terminal at the other end.
3 When the solder on both ends melts, grip the component between the two tips and lift it from the circuit
board. You might need to quickly touch the pad on the middle terminal with a soldering iron to melt any
remaining solder that might be holding the component down.
4 Use solder braid and a soldering iron to remove the solder from the three pads.
Insertion
1 With a soldering iron and 60/40 or 63/37 eutectic-type solder, melt just enough solder onto one pad to create a small mound of solder.
2 Grasp the component with tweezers. Melt the small mound of solder with the iron and place the component in the correct orientation
across the three pads and press it flat against the circuit board, with one terminal of the component pressed into the melted solder.
3 Hold the component in place and take the soldering iron away. Let the solder harden to tack the component in place.
4 Fully solder the other terminals of the component to their pads. Let the solder harden.
5 Fully solder the tacked terminal of the component to its pad.
Multi-pin components (ICs, etc.)
Removal
Removing a multi-pin SMT component is a delicate procedure. Ideally, you should use a soldering iron with an attachment that allows you to
heat all the pins simultaneously.
If such a soldering device is not available, use this procedure:
1 Use a soldering iron and solder braid to remove as much solder as possible from the pins of the component.
2 With fine tweezers, carefully try to lift each pin to see if it’s free. If it’s not, touch it with the tip of the soldering iron and if necessary, use
the solder braid to remove the remaining solder.
3 Repeat the process until all the pins are free and you can remove the component.
Insertion
1 With a soldering iron and 60/40 or 63/37 eutectic-type solder, melt just enough solder onto one pad to create a small mound of solder. It
is usually easiest to use a pad that corresponds to one of the end or corner pins of the component.
2 Grasp the component with tweezers. Melt the small mound of solder with the iron and place the component in the correct orientation
upon its pads and gently press it flat against the circuit board, with the appropriate terminal of the component pressed into the melted
solder.
3 Hold the component in place and take the soldering iron away. Let the solder harden to tack the component in place.
4 Fully solder the other terminals of the component to their pads. Let the solder harden.
5 Fully solder the tacked terminal of the component to its pad.
RMX Series Technical Service Manual 5
Page 8
1.4 Series description
QSC’s RMX Series amplifiers are entry-level professional audio
products, designed for good, basic performance and reliability at
low price. The series comprises three models: the RMX 850, RMX
1450, and RMX 2450. Each one has two audio channels and is two
rack spaces tall. See page 2 for complete specifications.
The RMX 850 and RMX 1450 have single-sided printed circuit
boards. The RMX 2450 uses double-sided boards.
1.5 Technical descriptions and
theory of operation
Note: Some of these descriptions concern circuitry that is duplicated
in the amplifier’s two channels. For the sake of simplicity, the
descriptions are of Channel 1 only. Components in Channel 1 have a
3-digit designation with “1” as
the first digit; their equivalents in
Channel 2 have a “2” as the first
digit, followed by the same two
numerals. For example, R122 and
R222 have identical functions in
their respective channels.
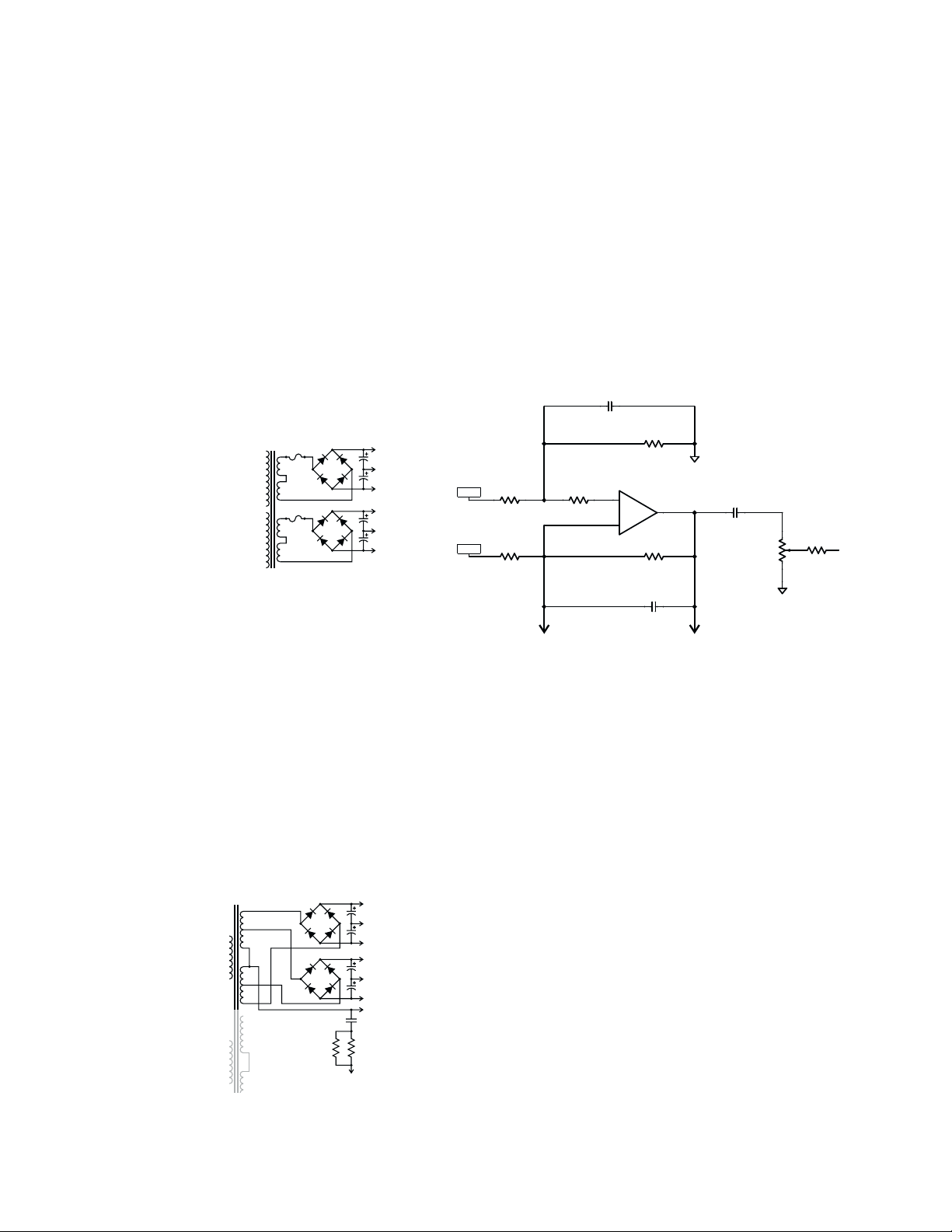
Power supplies
Figure 1.7
Unlike other recent QSC amplifiers,
the RMX line uses strictly conventional power supplies, with large
transformers that operate at the 50 or 60 Hz frequency of the AC
line. The electrical current in the secondary circuitry is converted to
DC through a full-wave bridge rectifier. The resulting 100 or 120 Hz
ripple is filtered out by large capacitors that also serve as current
reservoirs for short-term, transient demands.
The supply provides a bipolar set of supply rails for each channel, with
equal quiescent positive and negative voltages, as shown in Figure 1.7.
Note that unlike many bipolar supplies for complementary transistor
arrangements, the secondary windings are not connected to ground at
the center. This is because the output transistors are directly mounted
to the heat sink, metal-to-metal, to maximize heat transfer; this grounds
the collectors, requiring somewhat different output and power supply
arrangements. The grounded-collector concept is described later in
this chapter.
In the RMX 2450, the
secondaries are tapped to
provide an intermediate set
of bipolar rails for the Class H
output circuitry. Figure 1.8
shows one channel. Class H
operation is described later
in this chapter.
The 24-volt cooling fan is
driven by a separate DC
supply that is powered by a
Figure 1.8
To Channel 2 Center Tap
+Vcc
-Vcc
+Vcc
-Vcc
+110V
-110V
+55V
-55V
Ch. 1 Center Tap
0.047 µF
12 5W×2Ω
Channel 1
Channel 2
Channel 1
20-volt tap on the transformer primary. To minimize fan noise, the
fan speed is controlled by varying its actual DC voltage in response
to the amplifier’s heat sink temperatures. An optocoupler isolates
the fan control circuitry from the thermal sensors.
Audio circuitry
The audio inputs are balanced to offer a reasonably high amount of
common-mode noise rejection. The input balancing is done using a
single op amp (one half of an NE5532 dual op amp) arranged as a
differential amplifier. The degree of common-mode rejection is
dependent on a close match between the input resistors (R100 and
R101 in Figure 1.9) and between the feedback resistor and the shunt
resistor (R105 and R106). The circuitry uses 1% precision resistors
to ensure at least 40 dB of common-mode rejection.
C101
180p-5%
^C_0805
+IN_A
-IN_A
R100
10.0K
^R_0805
R101
10.0K
^R_0805
R102
1K
^R_0805
To LM13600 operational
transconductance amp
Figure 1.9
The feedback and shunt capacitors, C101 and C103, add a first-order
high-frequency roll-off, down 3 dB at 88.4 kHz (over two octaves
above the high end of the audio spectrum). This makes the amplifier
less susceptible to RF interference, high-frequency oscillations, etc.
Also in this stage, the feedback loop contains one half of a 13600 dual
operational transconductance amplifier (Figure 1.10). The OTA is part
of the clip limiter circuitry; when the clip limiter is activated, a control
voltage increases the transconductance of the OTA, which essentially decreases the impedance of the feedback loop and reduces
the gain of the stage in order to reduce the amount of clipping.
The gain control uses a linear potentiometer, but the impedances
loading the wiper to ground make the pot approximate an audio
taper over most of its rotation. After the wiper, RC networks roll off
the low end, if the LF filter is set for that channel, at either 30 or
50 Hz, depending on the DIP switch setting on the rear panel.
The next active device is another 5532 op amp, U101:2. Its output
drives the driver transistors, which in turn drive the output transistors.
The output section has a Class AB+B configuration; the drivers (a
complementary pair, Q105 and Q106, comprising an NPN MJE15032
and a PNP MJE 15033) are class AB. A series network of two diodes
and a 100-ohm trimpot provide the small amount of forward bias on
R105
10.0K
^R_0805
NE5532
U101:1
+
3
-
2
R106
10.0K
^R_0805
C103
180p-5%
A1
C106
1
10-50NP
R112
10K
10K LINEAR 3B
RIGHT ANGLE POT
CW
R113
W
270
^R_0805
CCW
A1
6 QSC Audio Products, Inc.
Page 9
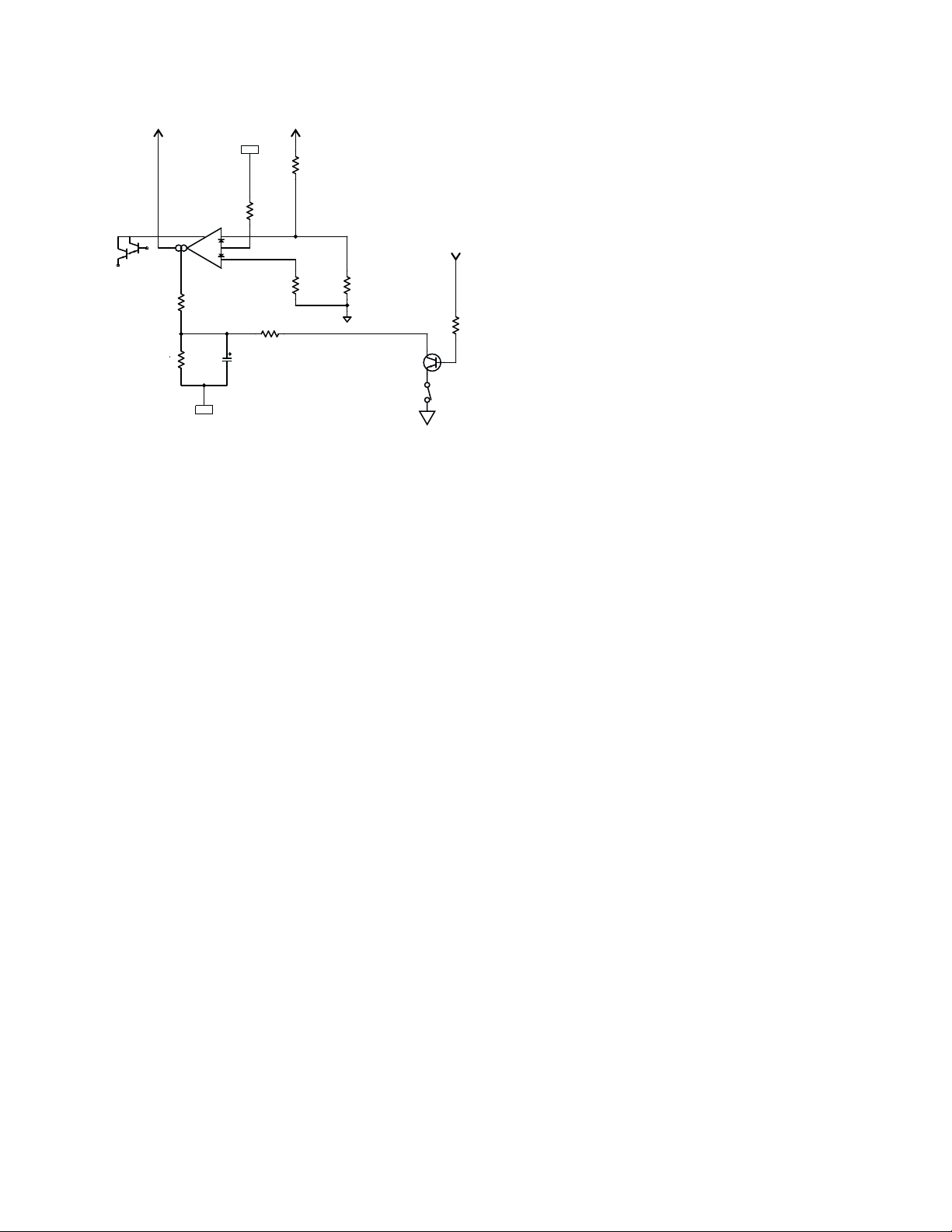
To input op amp U101:1
+14V
R108
7.50K
^R_0805
R107
U10:1
LM13600M
11
5
7
R103
R104
1
10.0K
^R_0805
150K
^R_1206
-14V
8
+
-
C105
39K
^R_0805
3
2
4
^R_0805
100
R111
^R_0805
A1
100-25V
R110
270
^R_0805
R109
100
3906
Q100
From clip
detection
820
R115
CLIP LIMIT
SWITCH
(Open to defeat
clip limiter)
^R_1206
Figure 1.10
the transistor pair to keep crossover distortion minimal. In parallel
with the trimpot is a 50-ohm thermistor with a negative temperature
coefficient; as the circuitry warms, its resistance decreases. This
reduces VBE on both Q105 and Q106, decreasing the bias current to
reduce the threat of thermal runaway. The base of each driver transistor
is tied to ground through a diode and a 2.2K trimpot in series; these set
the current limiting threshold for their respective signal polarities.
The collector of each driver transistor directly drives the bases of its
output transistors, which are the main power-handling signal
devices. If you’re not familiar with the grounded-collector scheme,
the arrangement of the output transistors might look somewhat
strange: the positive voltage swings are handled by PNP transistors,
while the negative swings are handled by NPN devices. The
collectors all connect to ground, which allows them to be mounted
directly to the heat sink—metal-to-metal, without insulators in
between—for the best possible transfer of heat away from the
transistors. The emitters of the PNP and NPN transistors are
coupled through resistors to the positive and negative supply rails,
respectively, forming banks of common-emitter circuits driving the
supply rails. Consequently, the devices drive the rails with the audio
signal, which rides atop the DC. The output to the speaker load is
taken from the point between the positive and negative reservoir
capacitors; this is also where the negative feedback is taken from.
The nature of this arrangement, with audio signal riding on the
supply rails, is why the power supply has no ground reference.
Another unusual characteristic of the grounded-collector output
section is that the signal at the output to the speaker is actually
opposite in polarity to the signal at the op amp output. This is why
the negative feedback resistor, R122, connects to the op amp’s non-
inverting input instead of the inverting input.
The output point of the circuit couples to the output connector
through an RLC network (R160, R161, R162, L100, and C124) that
serves as a high-frequency snubber and also helps keep the amp
circuitry stable when driving capacitive loads.
Clip detection
The output of the op amp also drives a group of four diodes (D102,
D103, D105, and D106) arranged as a full-wave rectifier. Normally,
the op amp’s output signal level is about 1 volt or less, which is all it
takes to drive the driver transistors.
But because this point is within the overall feedback loop, when
clipping occurs, the op amp approcahes full open-loop gain and puts
out a much higher signal voltage to try to make the output signal
track the input. The four diodes rectify the voltage to drive the clip
indicator LED, LD100. The current exiting the full-wave rectifier
passes to ground through R127 and also drives the base of
transistor Q100 through R115. If the clip limiter is switched on,
Q100’s emitter is grounded, and when the voltage across R127 goes
sufficiently negative to forward-bias Q100, which sends current
through R111 and R103 into the amplifier bias input of the operational transconductance amplifier (OTA), U10:1. The OTA is in the
negative feedback loop of U101:1, and increasing its
transconductance essentially reduces the impedance of the
feedback loop, which reduces the gain of the op amp stage. This
reduces the signal level until the amount of clipping is minimal.
When the clipping stops, Q100 is no longer forward-biased, and the
gain returns to normal.
DC protection
The RMX 2450 has a crowbar circuit, based on a triac and two
silicon controlled rectifiers, on the output to protect against DC
faults. If an amp channel puts out a DC voltage, which could be the
result of a component or circuit failure, it will first trigger either
D119 or D120, depending on the polarity of the voltage. The
triggered SCR will in turn trigger triac Q113, shorting the output to
ground through fuse F100. The fuse will blow, safeguarding the
speaker load from the DC fault.
The output sections of the RMX 850 and RMX 1450 are AC coupled.
Class H
The RMX 2450 utilizes a two-step Class H output section. It is
essentially a Class AB+B circuit but with two sets of bipolar supply
rails. On both the positive and the negative sets of rails, a comparator circuit, called a “step driver,” compares the audio signal to the
lower rail voltage. When necessary to fully reproduce the signal’s
voltage swing—just before the signal voltage reaches the lower rail
voltage—the step driver turns on a TMOS power FET to pull the
output transistors’ supply rail up from the lower voltage to the
higher one, and then back down again when the signal allows. By
keeping the transistors’ supply rails low whenever possible, the
devices dissipate less unused power and generate less waste heat,
making the amplifier more efficient than a straight class AB
amplifier with the same power points.
The comparators are 311-type ICs: U170 on the positive step and
U171 on the negative. Each one drives a high-gain complementary
transistor pair (2N3904 + 2N3906), which drive the gate of their
respective MOSFET.
RMX Series Technical Service Manual 7
Page 10
Bridged mono operation and protection
When the amplifier is operated in bridged mono, its two channels
work in tandem to produce up to twice the voltage swing that a
single channel is capable of. To do this, Channel 2 produces a signal
identical to Channel 1’s, but opposite in polarity—in other words, a
mirror image.
Channel 2’s signal feed (bus BR_MONO_FEED) is an attenuated
version of the signal on Channel 1’s speaker bus. Closing DIP switch
#6 (set to “BRIDGE MONO ON”), connects the BR_MONO_FEED bus
on Channel 1 to the BR_RET bus on Channel 2. The BR_RET bus
drives the non-inverting input of op amp U201:2 directly.
With two channels operating as one, but each having its own
feedback and protection circuitry, it is vital to keep both running as
mirror images. A protection circuit monitors the balance between
Channel 1’s and Channel 2’s signals. Resistors R22 and R23 (R22A,
R22B, R23A, and R23B on the RMX 2450) are equal in value and
form a voltage divider between the two channel outputs. If the
output signals are mirror images, the voltage at the junction of the
resistors (bus BR_BAL) will be zero. If the signals are not mirror
images—for example, one channel is defunct, distorting, or reduced
in gain—a voltage will appear on BR_BAL. Through DIP switch 7,
the BR_BAL bus becomes bus BR_CUT and feeds the bases of
transistors Q8 and Q6, which are part of a 4-transistor circuit across
the +15V and -15V rails that supply the op amps and the input
circuitry. If the voltage on BR_CUT goes positive enough to forwardbias Q8, the transistor’s collector will collapse the +15V rail. At the
same time, the emitter current from Q8 will flow through R25 and
into the emitter of Q7, forward-biasing it, too. The collector of Q7
will then collapse the -15V rail.
Similarly, if BR_BAL goes sufficiently negative, it will forward-bias
Q6, in turn forward-biasing Q9, and these will collapse the ±15V rails.
With the rails collapsed, the op amp and the input circuitry will not
function, which will mute the audio.
2. Component identification and pinout
NE5532AN Dual operational amplifier
OUTPUT A
INVERTING
INPUT A
NON-INVERTING
INPUT A
V-
1
2
3
4
AB
V+
8
OUTPUT B
7
INVERTING
6
INPUT B
NON-INVERTING
5
INPUT B
LM311 Voltage comparator
GROUND 1
NON-INVERTING
INPUT
INVERTING
INPUT
1
2
3
V-
4
V+
8
OUTPUT
7
BALANCE/
6
STROBE
BALANCE
5
4N29 Opto-isolator
1
2
3
6
5
4
LM13600 Dual operational transconductance
amplifier
AMP BIAS INPUT A
DIODE BIAS A
NON-INVERTING
INPUT A
INVERTING INPUT A
OUTPUT A
BUFFER INPUT A
BUFFER OUTPUT A
1
2
3
4
5
V-
6
7
8
AB
AMP BIAS INPUT B
16
DIODE BIAS B
15
NON-INVERTING
14
INPUT B
INVERTING INPUT B
13
OUTPUT B
12
V+
11
BUFFER INPUT B
10
BUFFER OUTPUT B
9
2N5064 Sensitive gate thyristor
KAG
8 QSC Audio Products, Inc.
Page 11
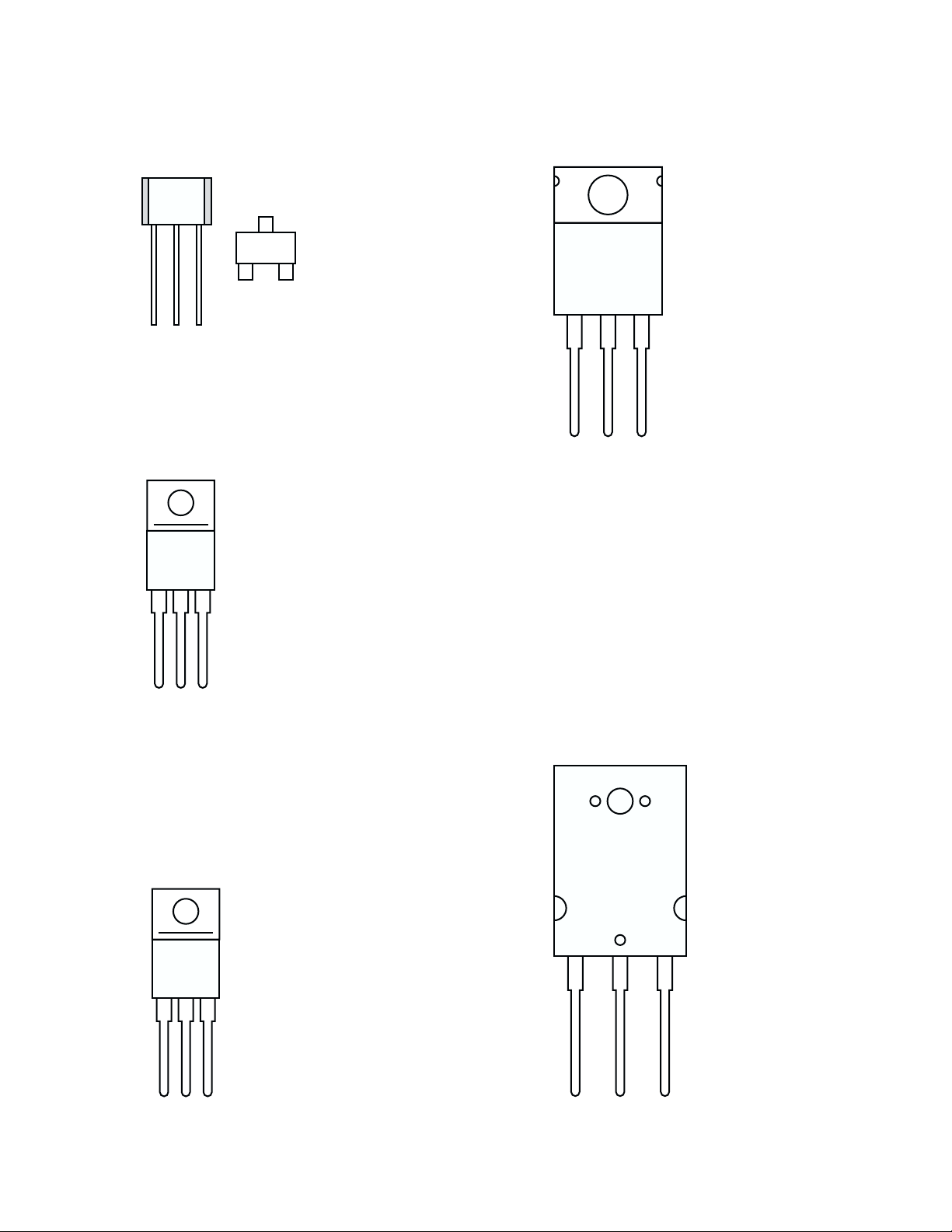
2N3904 (NPN) and 2N3906 (PNP) Small-signal
transistors
C
3
12
BE
BCE
IRFZ44 TMOS power field effect transistor
MAC224 Triac
G
MT1
MT2
MJE15032 (NPN) and MJE15033 (PNP) Driver
transistors
GDS
2SC5200 (PNP) and 2SA1943 (NPN) Power
transistors
TOSHIBA
BCE
RMX Series Technical Service Manual 9
B C E
Page 12

3. Troubleshooting: Symptoms, causes, & remedies
When first checking the operation of an amplifier on the bench,
always turn your variable transformer down to zero before plugging
the amplifier in. After you turn the amplifier on, gradually turn up
the AC voltage as you observe the amplifier’s behavior and its
current draw; this will help you determine what, if anything, is
wrong with it. If you see or smell smoke, flames, or any other signs
of short circuits or excessive current draw, quickly turn the AC back
down to zero. If no such problems occur, it is usually safe to turn the
AC up to the amplifier’s full operating voltage for further testing.
3.1 Excessive current draw
The customer complains of blowing circuit breakers or fuses, or
burning smell or smoke.
Symptoms covered:
• Fuses blow immediately
• The amplifier quickly gets very hot
• Line circuit breakers trip at turn-on
• The amplifier hums loudly and the chassis vibrates
• The amplifier emits smoke
• The amplifier gives off a burning smell
If the symptoms indicate a possible problem in the channel circuits
or output sections, you can isolate either channel module from the
power supply by pulling its fuses from the AC board.
Possible situations:
Excessive current with no signal present
If the amplifier seems to run hot and draws higher-than-normal
current when idling at full AC voltage, the cause could be bias
misadjustments in the output circuitry of one or both channels. See
the calibration procedures in the next section. In the RMX 2450, the
cause might also be blown step FETs; see service bulletin RMX0006.
Fast increase in current draw (current increases rapidly at
only a few volts AC)
• The main bridge rectifiers BR100 and/or BR200 (all models) and
BR101 and/or BR201 (RMX 2450) is reversed or shorted.
• Supply clamp diode pairs D117 and D118 and/or D217 and D218
is reversed or shorted.
• The drivers and/or power transistors is shorted on both polarities
(NPN
and
PNP) on one or both channels.
Moderate increase in current draw (current increases
slowly, doesn’t become excessive until about ¼ of the
amplifier’s full AC operating voltage)
• One polarity’s drivers and/or power transistors (NPN or PNP) is
shorted, on one or both channels.
• Individual supply clamp diodes D117, D118, D217, or D218 is
reversed or shorted.
• Bias diodes D108, D109, D208, or D209 or bias trimpots R131 or
R231 is open.
Slow increase in current draw (current doesn’t become
excessive until about half of the amplifier’s full AC operating
voltage; amplifier may pass signal)
• The bias is severely misadjusted, or bias diodes D108, D109,
D208, or D209 is defective.
• An oscillation is causing excessive current demand.
Runaway current draw (current increases sharply at about
25 to 33% of the amplifier’s full AC operating voltage)
One or more reservoir capacitors is reversed. CAUTION: the gas
buildup in a reversed electrolytic capacitor can cause it to
vent explosively. Immediately turn off power and let the capacitor
cool down before replacing it.
3.2 Protection, muting, and turn-
on/turn-off delay problems
The customer complains of amplifier locking up, or not turning on
and off correctly.
Symptoms covered:
• Both channels do not come out of protect
• Amplifier will not thermally shut down when it should
• Power LED doesn’t light
• Too little or too much muting delay
• No clip limiting
• Fan doesn’t run, or runs always at high speed
Possible situations:
Both channels stay in protect after turn-on
• Q4 or Q5 is shorted base-to-emitter.
• Voltage across D8 should be 14 to 15 volts DC. If it is low, check
D8 and R10; also, C7 and C8 is leaky.
• D9, R4, and/or R7 is open.
The amplifier will not thermally shut down when it overheats
Check for shorted D9, R4, or R7; check also for open LD1 (“POWER”
LED), R2, or R5.
Too much or too little muting delay
• Excessive delay at turn-on: check for open LD1, R2, or R5; check
for incorrect R10 or R15; check for shorted D9; also see service
bulletin RMX0002.
• Too short at turn-on (amplifier unmutes before the circuits stabilize,
causing a thump): check for incorrect or bad C7, C8, or R10.
• Amplifier doesn’t stay muted at turn-off: see service bulletin RMX0003
Power LED doesn’t light
Check for open or shorted LD1; check R2.
No clip limiting
• U10 is defective.
• DIP switches SW1:1 or SW1:10 is defective.
10 QSC Audio Products, Inc.
Page 13

Fan doesn’t run
• The fan is defective.
• Check the fan connection to the AC board.
• Check R1 and BR1 on the AC board.
Fan runs always on high speed
• Q3 and/or U2 are shorted.
• Check PTC thermistors R4 and R7.
• R130 or R132 (Channel 1) or R230 or R232 (Channel 2) is open.
Excessive hum in loudspeaker when no signal is present
(RMX 850 and RMX 1450)
Check R118, R119, R218, and R219.
Excessive current draw with signal present (RMX 2450)
• Check triacs Q113 and Q213.
• Check D119, D120, D219 and D220.
3.3 Faults with signal present
The customer compains that the amplifier passes a signal but
doesn’t run correctly.
Symptoms covered:
• The output signal breaks up or is distorted
•“Ringing” sound in loudspeaker when no audio signal is present
• The output signal collapses when driving a normal speaker load
• Supply rails OK with no signal, but collapse when a signal passes
• The amplifier gets too hot
• One channel clips prematurely
• Excessive hum in loudspeaker when no audio signal is present
Possible situations:
The output signal breaks up or is distorted
• (RMX 850 and RMX 1450) Check the hum-null resistors R118,
R119, R218, and R219.
• Check the ground traces for continuity among speaker ground,
input ground, and AC ground.
“Ringing” sound in loudspeaker when no audio signal is present
• Check C114, C124, C214 and C224.
• Check or replace dual op amp U101 or U201.
The output signal collapses when driving a normal speaker load
• R139, R140, R239, and/or R240 is misadjusted.
• Check R118, R119, R218, and R219.
The supply rails are OK with no signal but collapse with a signal
• C112, C113, C212, and/or C213 is leaky.
• Check C114, C124, C214, and C224.
The amplifier gets too hot with no load
• Bias trimpots R131 or R231 are misadjusted, burned, or open.
• Bias diodes D108, D109, D208 and/or D209 are incorrect (should
be 1N4934).
• If the amplifier is producing high-frequency oscillations, check
C114, C124, C214, and C224.
• Check resistors R136, R137, R236, and R237.
• Op amp U101 or U201 is unstable.
One channel clips prematurely
• R146 or R147 (Channel 1) or R246 or R247 (Channel 2) are open.
• R139 or R140 (Channel 1) or R239 or R240 (Channel 2) are misadjusted.
• Check R157, R158, R198 (RMX 2450 only), D115, and D116
(Channel 1) or R157, R258, R298 (RMX 2450 only), D215, and
D216 (Channel 2).
• (RMX 850 and RMX 1450) Check R118 and R119 (Channel 1) or
R218 and R219 (Channel 2).
3.4 Instability
The customer complains of gain problems, spurious noises, or oscillations.
Symptoms covered:
• General output distortion
•“Ringing” sound in loudspeaker trailing an audio signal
• Excessive crossover distortion
• The output waveform appears fuzzy on an oscilloscope
Distinguish among the different symptoms of fuzziness (instability),
ringing (momentary instability after a transition), crossover distortion (often causing ringing), or general distortion.
Possible situations:
General distortion in the output signal
• Severe distortion, at any load, often with abnormally high current
draw: check the slew rate capacitors C114, C115, and C116
(Channel 1) or C214, C215, and C216 (Channel 2).
• Moderate distortion, especially with light loading: stability
capacitors C124 and C126 (Channel 1) or C224 and C226 is too
high in capacitance; also check the slew rate capacitors C114,
C115, and C116 (Channel 1) or C214, C215, and C216 (Channel
2), and the output filter resistors R161, R162, R154, and R155
(Channel 1) or R261, R262, R254, or R255 (Channel 2).
• Distortion with low gain: check the feedback shunt components
R120, R138, and C125 (Channel 1) or R220, R238, or C225
(Channel 2); also check for broken circuit traces around the
components; U101 (Channel 1) or U201 (Channel 2) is defective
or its socket is contaminated.
Ringing sound trailing the audio signal
• This usually indicates marginal instability and is usually triggered
by the signal passing through zero volts (the crossover point).
Check the stability components and output filters.
• With a sine wave test signal, use an oscilloscope to check for
excessive crossover notch at the output signal’s zero crossings.
Excessive crossover distortion (unbalanced, asymmetrical,
or excessively large crossover notch)
• Severe crossover discontinuity: bias diodes D108 or D109
(Channel 1) or D208 or D209 (Channel 2) are shorted.
• Moderate discontinuity: bias diodes D108 or D109 (Channel 1) or
D208 or D209 (Channel 2) are out of spec.
• R131 (Channel 1) or R231 (Channel 2) is defective.
• Base resistors R136 or R137 (Channel 1) or R236 or R237
(Channel 2) are open. Also check the NTC thermistors R134
(Channel 1) or R234 (Channel 2).
RMX Series Technical Service Manual 11
Page 14

3.5 Power supply & rail balancing
problems
Symptoms covered:
• Insufficient or excessive current limiting into a shorted load
• Op amp rails too high with a shorted load
• Uneven voltages on supply rails
A channel’s output current should remain unaffected when driving
resistive loads as low as 2 ohms per channel. When driving a short
circuit, the current limiting circuit should collapse the output to a
lower current. This is done by dropping the op amp’s supply rails
from a normal ±14–15 volts down to about ±5–6 volts. Normally, the
output signal helps replenish the op amp supply rails through D115
and D116 (Channel 1) and D215 and D216 (Channel 2), but a short
circuit or excessively low load impedance prevents the replenishment, and the op amp rails collapse because they can’t supply
enough current to let the op amp drive both the clip LED and the
driver transistors. The current limit trimpots R139, R140, R239, and
R240 permit adjustment of the current limit thresholds. See the
RMX calibration section of this manual for adjustment procedures.
Possible situations:
Excessive current into short (insufficient limiting)
• If the op amp rails are dropping to ±5 to 6 volts as they should:
the 5.6V zener diodes D107 and/or D110 (Channel 1) or D207
and/or D210 (Channel 2) are reversed or shorted.
• If high crossover distortion is present: bias diodes D108 or D109
(Channel 1) or D208 or D209 (Channel 2) are shorted.
Excessive current into short (op amp rails are not dropping)
• The op amp U101 (Channel 1) or U201 (Channel 2) is defective,
with insufficient output current.
• Clip LED LD100 (Channel 1) or LD200 (Channel 2) and/or its
rectifying diodes (Channel 1: D102, D103, D105, D106; Channel 2:
D202, D203, D205, D206) are open.
• When driving a short circuit, the output section’s positive and
negative supply rail voltages should be equal, within 3 volts. If
they aren’t, check D107, D110, R146, and R147 (Channel 1) or
D207, D210, R246, and R247 (Channel 2).
Weak current into 2
• Bias resistors R130 and R132 (Channel 1) or R230 and R232
(Channel 2) are too high.
• Driver transistors (Channel 1: Q105, Q106; Channel 2: Q205,
Q206) have very low gain.
• One or more emitter resistors in the output section are open.
Current OK at 2
• LD100, D102, D103, D105, or D106 (Channel 1), or LD200, D202,
D203, D205, or D206 (Channel 2), are shorted.
• Zener voltage of diodes D107 or D110 (Channel 1), or D207 or
D210 (Channel 2), is too high.
Current limits properly into short, but current is weak at 2
• If the op amp rails are low (< 14–15 volts) when driving a 2-ohm
load
without
(Channel 1, all models), R198 (Channel 1, RMX 2450 only) and
diodes D115 and D116 (Channel 1, all models), or R257 and R258
(Channel 2, all models), R298 (Channel 2, RMX 2450 only) and
diodes D215 and D216 (Channel 2, all models).
• If the op amp rails are normal (14–15 volts) when driving a 2-ohm
load
without
driver transistors, open output transistors, or open emitter resistors.
Check the value of the driver transistors’ emitter resistors, too:
R146 and R147 (Channel 1) or R246 and R247 (Channel 2).
Rail voltages unequal
The balance between the positive and negative rail voltages is set
by a voltage divider comprising resistors R118 and R119 (Channel 1)
and R218 and R219 (Channel 2). If the amplifier channel passes a
signal but clips unevenly due to unequal rail voltages, this voltage
divider is the likely culprit.
ΩΩ
Ω or short (excessive or premature limiting)
ΩΩ
ΩΩ
Ω, weak into short
ΩΩ
ΩΩ
Ω
ΩΩ
clipping, check the resistors R157 and R158
clipping, usually the output section gain is too low: weak
4. RMX calibration procedures
4.1 Setting bias
Always set the bias
• after replacing any output or driver transistor.
• after replacing any diode or resistor in the driver/output circuitry.
• if the amplifier seems to run too hot at idle.
• if the amplifier exhibits crossover distortion.
The bias network sets the quiescent base current in the NPN and
PNP driver transistors, which in turn sets the quiescent current in
the output transistors. The driver transistors should both be slightly
“on” at idle so that the transitions of the signal voltage between
positive and negative are smooth and free of gaps or glitches. Too
12 QSC Audio Products, Inc.
much bias current will cause the amplifier to run hotter than it
should, especially at idle, while too little will cause noticeable
crossover distortion, especially at low signal levels.
The amplifier circuitry must be cool, or at least within a couple
degrees of ambient air temperature, and the top cover must be
removed. If the driver and output transistors are significantly
warmer than the ambient air, leave the amplifier off and let it cool
before proceeding.
Before turning the amplifier on to set bias on one or both channels,
familiarize yourself with the locations of the trimpots (R131 and
R231) and the voltage measuring points so you can work quickly but
thoroughly. If the amplifier warms up before you finish setting the
Page 15

bias, you will need to shut the amplifier off and let it cool down
before you resume.
Tools and resources you will need:
• Small flat screwdriver (non-conductive) for adjusting trimpots
• DC voltmeter
• AC power
Procedure
1. Turn the amplifier’s gain controls all the way down. No test
signal is needed.
2. Plug the amplifier into an appropriate AC source. Turn the
amplifier on.
3. Channel 1: While measuring the DC voltage across resistor R146,
adjust trimpot R131 to obtain the voltage listed in Table 1.
4. Channel 2: While measuring the DC voltage across resistor R246,
adjust trimpot R231 to obtain the voltage listed in Table 1.
After setting the bias, calibrate the positive and negative current
limiting; instructions for the procedure follow below.
4.2 Setting positive and negative
current limits
onto one of the brown wires running to the AC switch or onto
the gray output wire from channel 1's module.
4. Turn the gain control all the way up. Adjust trimpots R139 and
R140 equally until the current measured falls within the range
shown in Table 1.
5. Turn the gain control all the way down and remove the short
circuit so the channel drives the 2-ohm load. Turn the gain control
back up until the output clips. The voltage at which the signal
starts to clip should fall within the range shown in Table 1. If the
clipping is asymmetrical, that is, the signal clips on either the
positive or negative side first, adjust R139 to make it symmetrical.
6. Turn the gain control down. If the amp has begun to warm up
shut it off and let it cool a few minutes before proceeding with
Channel 2.
7. Repeat steps 1 through 5 for Channel 2. Use trimpots R239 and
R240 to adjust the current limiting in steps 11 and 12.
8. Turn both channels’ gain controls all the way down. Clamp the
ammeter onto one of the amp’s AC wires and check the amp’s
idle current. If the amplifier is still at about room temperature,
the idle current should match the value shown in Table 1.
Tools and resources you will need
• Oscilloscope
• 2-ohm resistive load (rated for at least 1200 watts)
• Shorting connector for amplifier output
• Variable AC transformer (e.g., Variac, Powerstat, etc.) rated for
25A (120V) or 12A (230V). Make sure the AC supply is appropriate for the amplifier.
• 1 kHz audio sine wave generator
Table 1: Bias and current limit adjustments
• Digital multimeter
• Clamp-on digital current meter
snoitarbilaC tsujdA 058XMR 0541XMR 0542XMR
(e.g., Fluke 30 Clamp Meter)
• Small flat screwdriver (nonconductive) for adjusting trimpots
Procedure
1. Set the audio sine generator to 1
kHz at 1 volt RMS and connect it
to Channel 1's input. Connect a
2-ohm load and the oscilloscope
probe across Channel 1's output.
2. Turn up Channel 1's gain control
partway. On the oscilloscope you
should see the amplitude of the
sine wave increase accordingly.
3. Turn the gain control back down
and apply a short circuit across
the output terminals of Channel
1. Clamp a current probe either
)tohnehwrehgih
641RssorcaegatlovCD:saib1lennahC131RV61.0V41.0V90.0
642RssorcaegatlovCD:saib2lennahC132RV61.0V41.0V90.0
daoldetrohsotnitnerructuptuO
*daoldetrohsgnivirdnehwtnerrucCA
)SMR(smho2otniegatlovgnippilC
)kaep(smho2otniegatlovgnippilC
;erutarepmettneibmata(*dnamedCAeldI
041R&931R:1lennahC
042R&932R:2lennahC
041R&931R:1lennahC
042R&932R:2lennahC
931RtsujdA:1lennahC
yrtemmysrof
932RtsujdA:2lennahC
yrtemmysrof
931RtsujdA:1lennahC
yrtemmysrof
932RtsujdA:2lennahC
yrtemmysrof
.V032rof5.0ybtnerrucylpitlum;sreifilpmaV021roferanwohsserugiF*
A5.4–4A5–4A9–8
A5.4–57.3A5.5–5.4A5.6–5
V92–62V5.73–5.33V94–44
V14–8.63V35–4.74V3.96–2.26
%01±
,A4.0
,A4.0
%01±
A5.0,
%01±
RMX Series Technical Service Manual 13
Page 16

5. Servicing RMX amplifiers
5.1 Mechanical disassembly and re-assembly
Replacing components will usually require removing the channel modules and/or AC board from the amplifier chassis, especially on the RMX 850
and RMX 1450, which have single-side printed circuit boards. The RMX 2450 has double-side boards; many of the through-hole components on
the upper side of the board can be unsoldered and soldered from the top side of the board, so removing modules or boards is not always necessary.
See the fold-out assembly guides on pages 25 and 26 in this manual for assistance.
NOTE: As viewed from the front of the amplifier, the left channel module is Channel 1 and the right is Channel 2
right module is Channel 1, and its left is Channel 2.
Removing the channel modules
1. Disconnect the amplifier from AC power and allow at least 10 minutes for internal voltages to bleed down.
2. Using a Philips screwdriver, remove the screws that fasten the top cover to the chassis. Also remove the top cover’s four recessed
screws that fasten it to the heat sinks. As you remove screws, set them aside, but also make note of where each type is used so you
can properly re-assemble the amplifier.
3. Lift the top cover up at the rear and carefully pull it toward the back, removing the five hooks on the front edge from their slots in the chassis.
4. Pull the gain control knobs straight off from the potentiometer shafts.
5. Tip the amplifier up on its side and remove the four screws that fasten the heat sinks to the chassis.
6. Set the amplifier back down and remove the screws that mount the channel modules to the chassis standoffs. There are six screws in
the left module and five in the right one.
7. Remove the four screws that fasten the fan, fan shroud, and fan guard to the chassis. Lift the fan shroud out from the chassis; this will
give you room to properly remove the modules from the chassis.
8. Disconnect the wire and cable connections to the channel modules. All of the connections are either detachable headers or ¼-inch
quick-connect tabs that are disconnected by pulling them straight up. No unsoldering is necessary.
9. Slide the channel modules toward the back so the potentiometer shafts and front panel LEDs are clear of their holes in the front panel.
Lift the channel modules out from the chassis.
10. Re-assembly is the opposite of disassembly.
except
in the RMX 2450; its
Removing the AC board
The AC board provides AC voltage selection, rectification of the transformer secondary current, and a regulated DC supply for the cooling
fan. It seldom needs to be replaced unless it is physically damaged itself. Most failures involving the AC board can be repaired through
replacement of individual components.
WARNING: Regulatory agencies require that any operating voltage conversions from 120 volts to any other voltage be done
factory service. Any other operating voltage conversions may be done only by a QSC-authorized service center or international distributor.
1. Disconnect the amplifier from AC power and allow at least 10 minutes for internal voltages to bleed down.
2. Remove the four screws that fasten the fan, fan shroud, and fan guard to the chassis. Lift the fan shroud out from the chassis.
3. Disconnect the wires that connect to the channel modules. All of the large single wires attach to the channel modules with ¼-inch
quick-connect tabs that are detached by pulling them straight up. The remaining three black wires disconnect at the left channel
module with a detachable header.
If you are planning to replace the AC board with another, carefully cut each of the transformer wires connecting to the board just above
its solder tab. You must leave enough slack to allow connection to the new AC board. Remove the old heat shrink tubing from the wires
and strip the wire ends about 0.25 inch or 6.3 mm.
4. Remove the five screws that attach the AC board to the chassis standoffs. Lift the board out from the chassis.
5. Re-assembly is the opposite of disassembly. If you’re using a new AC board, slide new pieces of heat shrink tubing over the trans-
former wires before you solder them to the appropriate tabs on the board; after soldering, cover the joints with the tubing and use a
heat gun or other heat source to shrink them tightly.
14 QSC Audio Products, Inc.
only
by QSC’s
Page 17

6. Replacement parts
6.1 RMX 850 Replacement Parts
QSC part # Description Qty. Notes or Component Reference
Misc.
1806-2505-0 POWER TRANSFORMER 700 1
2113-1144-0 AC INLET 1
2444-1001-1 KNOB CONTROL 2
4134-8432-0 RACK-MOUNT BRACKET 2
5200-4717-0 ROCKER POWER SWITCH 1
5200-3532-0 CIRCUIT BREAKER 10A 1 For 120V models
5200-4730-0 CIRCUIT BREAKER 5A 1 For 230V models
7010-9640-0 AC CORD SET 15A 1 For 120V models
7009-8620-0 POWER CORD SET CE 1 For 230V models
8900-9050-1 DC FAN 24V 80X80 (+5V) 1
PCB-QZ010C-PSU AC board
153R-224K-5-Y1 CM 250V 0.22uF 10% RL 2 C127, C227
157Q-108M-5-X9E CE 35V 1000UF 20% RL 1 C6
3130-9270-0 IC 4N29 1 U2
4134-8851-0 FUSE HOLDER (DIA.6.3MM 4 REF: F100, F200
4701-202J-C RCF 1/8W 2K 5% ATS 1 R13
4701-474J-C RCF 1/8W 470K 5% ATS 1 R12
4701-682J-C RCF 1/8W 6.8K 5% ATS 2 R9, R14
4719-121J-1-X RMF 2W 120R 5% AL METAL 1 R17
4840-1760-0 DIODE RECT 1A 200V DB103 1 BR1
4840-2150-0 BRIDGE RECTIFIER 400V 2 BR100, BR200
4860-2620-5 TR TIP31C SAMSUNG 1 Q3
5100-1030-3A FU T10A 125V/250V 2 F100, F200
5400-0831-0 HEATSINK 1 REF: Q3
8910-0273-0 POLYSWITCH 0.15 ohm 1.1A 1 R1
8910-0275-0 THERMAL NTC 30A 1 ohm 1 R21
PCB-QZ010C-PWR1 Channel 1 module (left)
153F-223J-5-LQ CM 50V 0.022UF 5% RL 2 C116, C119
153F-332J-5-KW CM 50V 3300pF 5% RL 6x12 2 C117, C118
153R-683J-5-WWM CM 250V 0.068u 5% RL 1 C124
157F-476M-5-LU CE 50V 47uF 20% RL 1 C8
157R-475M-5-OV CE 250V 4.7u 20% RL 1 C7
1804-1030-0 SPRING COIL 2uH 1 L100
3700-4531-G LED 04mm GREEN W/STAND 1 LD1
4718-220J-2-P RMF 1W 22R 5% AT FP 2 R136, R137
4718-6R8J-1-X RMF 1W 6.8R 5% AL METAL 2 R146, R147
4719-153J-1-X RMF 2W 15K 5% AL METAL 2 R2, R5
4719-5R6J-1-X RMF 2W 5.6R 5% AL METAL 1 R160
471A-022K-5-N RMF 3W 0.22R 10% RL RGC3 6 R142, R148, R149, R152, R153, R159
471B-120J-1-X RMF 5W 12R 5% AL METAL 2 R161, R162
471B-202J-1-X RMF 5W 2K 5% AL METAL 2 R133, R135
471B-821J-1-X RMF 5W 820R 5% AL METAL 2 R157, R158
4756-1016-3-06 SVR H6 100R RH0615C 1 R131
4756-2226-3-06 SVR 2.2K H3 7X7.6 R0615C 2 R139, R140
4804-0040-1 DIODE IN4004 AL 5 D1, D11, D12, D117, D118
4804-9340-2 DIODE IN4934 AT 2 D108, D109
4837-5B10-2 DZ 1/2W 5.5-5.8V AT 2 D107, D110
4838-15V6-2 DZ 1W 15V AT TEMIC 2 D8, D15
4860-5020-5 TR MJE15032 1 Q105
4860-5030-5 TR MJE15033 1 Q106
RMX Series Technical Service Manual 15
Page 18

Channel 1 module (continued)
QSC part # Description Qty. Notes or Component Reference
4860-5050-5 TR 2SC5200 T0-3P (L) 3 Q108, Q110, Q112
4860-5060-5 TR 2SA1943 T0-3P (L) 3 Q103, Q107, Q109
4860-8890-0 TR MPS A06 VCE 80V NS 1 Q5
8910-0062-0 CE 80V 4700U 20% RL 25X 2 C120, C121
8910-0274-0 THERMAL PTC 60C 100 ohm 1 R7
8910-0488-0 ROD THERMISTOR NTC 50ohm 1 R134
Channel 1 SMT parts
150F-222K-6-CF CC 50V 2200pF 10% 1206 1 1 C115
150H-102J-6-CF CC 100V 0.001U 5% 1206 1 C114
4720-103J-J RMG 1/10W 10K 5% 0805 1 R128
4720-152J-J RMG 1/10W 1.5K 5% 0805 1 R129
4720-202J-J RMG 1/10W 2K 5% 0805 1 R8
4720-224J-J RMG 1/10W 220K 5% 0805 1 R26
4720-470J-J RMG 1/10W 47R 5% 0805 2 R25, R124
4721-105J-6 RMG 1/8W 1M 5% 1206 2 R3, R6
4721-154J-6 RMG 1/8W 150K 5% 1206 1 R10
4721-224J-6 RMG 1/8W 220K 5% 1206 2 R18, R27
4721-473J-6 RMG 1/8W 47K 5% 1206 1 R125
4721-474J-6 RMG 1/8W 470K 5% 1206 1 R15
4721-682J-6 RMG 1/8W 6.8K 5% 1206 1 R19
4721-821J-6 RMG 1/8W 820R 5% 1206 2 R130, R132
4804-1480-3 DIODE LL4148 SM 15 D2–D7, D9, D14, D104, D111–D116
4853-9060-3 TR 3906 PNP SM 3 Q4, Q6, Q7
4860-0640-3 TR 3904 HFE 100-300 SM 4 Q8, Q9, Q101, Q102
4860-5110-3 TR KST42 1 Q1
PCB-QZ010C-PWR2 Channel 2 module (right)
153F-154J-5-NLM CM 50V 0.15UF 5% RL 4 C108, C109, C208, C209
153F-223J-5-LQ CM 50V 0.022UF 5% RL 2 C216, C219
153F-224J-5-NLM CM 50V 0.22UF 5% RL 2 C107, C207
153F-332J-5-KW CM 50V 3300pF 5% RL 6x12 2 C217, C218
153R-683J-5-WWM CM 250V 0.068u 5% RL 1 C224
157E-107M-5-KW CE 25V 100uF 20% RL 6x12 2 C105, C205
157E-227M-5-PU CE 25V 220uF 20% RL 4 C112, C113, C212, C213
157F-106M-5-LUN CE 50V 10¦F 20% RL 2 C106, C206
1804-1030-0 SPRING COIL 2uH 1 L200
2101-1991-0 8 PIN IC SOCKET DIP 2 REF: U101, U201
3130-2430-0 IC-NE5532 OPER. AMP PHIL 2 U101, U201
3700-4529-R LED 04mm RED W/STAND 2 LD100, LD200
3700-4530-Y LED 04mm YELLOW W/STAND 2 LD101, LD201
471A-022K-5-N RMF 3W 0.22R 10% RL RGC3 6 R242, R248, R249, R252, R253, R259
471B-120J-1-X RMF 5W 12R 5% AL METAL 2 R261, R262
471B-202J-1-X RMF 5W 2K 5% AL METAL 2 R233, R235
471B-821J-1-X RMF 5W 820R 5% AL METAL 2 R257, R258
4717-103A-2 RMF 1/2W 10K 1% AT 2 R122, R222
4717-9091-2 RMF 1/2W 9.09K 1% AT 1 R123
4718-220J-2-P RMF 1W 22R 5% AT FP 2 R236, R237
4750-6200-0 VR V012CPH, D-SHAFT 10K 2 R112, R212
4756-1016-3-06 SVR H6 100R RH0615C 1 R231
4756-2226-3-06 SVR 2.2K H3 7X7.6 R0615C 2 R239, R240
4718-6R8J-1-X RMF 1W 6.8R 5% AL METAL 3 R20, R246, R247
4719-5R6J-1-X RMF 2W 5.6R 5% AL METAL 1 R260
4804-0040-1 DIODE IN4004 AL 4 D10, D13, D217, D218
4804-9340-2 DIODE IN4934 AT 2 D208, D209
4837-5B10-2 DZ 1/2W 5.5-5.8V AT 2 D207, D210
4838-15V6-2 DZ 1W 15V AT TEMIC 4 D100, D101, D200, D201
4860-5020-5 TR MJE15032 1 Q205
16 QSC Audio Products, Inc.
Page 19

Channel 2 module (continued)
QSC part # Description Qty. Notes or Component Reference
4860-5030-5 TR MJE15033 1 Q206
4860-5050-5 TR 2SC5200 T0-3P (L) 3 Q208, Q210, Q212
4860-5060-5 TR 2SA1943 T0-3P (L) 3 Q203, Q207, Q209
8910-0062-0 CE 80V 4700U 20% RL 25X 2 C220, C221
8910-0274-0 THERMAL PTC 60C 100 ohm 1 R4
8910-0488-0 ROD THERMISTOR NTC 50ohm 1 R234
Channel 2 SMT parts
150F-104K-6-CF CER2 1206 X7R 50V 100N 3 C100, C102, C104
150F-181K-J-BD CC 50V 180P 10% 0805 4 C101, C103, C201, C203
150F-222K-6-CF CC 50V 2200pF 10% 1206 1 1 C215
150F-560K-J-BD CC 50V 56pF 10% 0805 1.2 2 C110, C210
150H-102J-6-CF CC 100V 0.001µF 5% 1206 1 C214
15CG-560J-6-CF CTC 0/30 56P 5% 1206 2 C111, C211
3131-9730-0 IC NE5517D 1 U10
4720-101J-J RMG 1/10W 100R 5% 0805 6 R109, R110, R127, R209, R211, R227
4720-102J-J RMG 1/10W 1K 5% 0805 3 R102, R126, R202
4720-103A-J RMG 1/10W 10K 1% 0805 8 R100, R101, R105, R106, R200, R201, R205, R206
4720-103J-J RMG 1/10W 10K 5% 0805 3 R103, R203, R228
4720-152J-J RMG 1/10W 1.5K 5% 0805 1 R229
4720-203A-J RMG 1/10W 20K 1% 0805 4 R117, R121, R217, R221
4720-271J-J RMG 1/10W 270R 5% 0805 6 R111, R113, R120, R210, R213, R220
4720-332J-J RMG 1/10W 3.3K 5% 0805 1 R24
4720-393J-J RMG 1/10W 39K 5% 0805 2 R107, R207
4720-470J-J RMG 1/10W 47R 5% 0805 1 R224
4720-472J-J RMG 1/10W 4.7K 5% 0805 2 R114, R214
4720-752J-J RMG 1/10W 7.5K 5% 0805 2 R108, R208
4721-154A-6 RMG 1/8W 150K 1% 1206 4 R118, R119, R218, R219
4721-154J-6 RMG 1/8W 150K 5% 1206 2 R104, R204
4721-333J-6 RMG 1/8W 33K 5% 1206 2 R22, R23
4721-394J-6 RMG 1/8W 390K 5% 1206 2 R116, R216
4721-473J-6 RMG 1/8W 47K 5% 1206 1 R225
4721-821J-6 RMG 1/8W 820R 5% 1206 4 R115, R215, R230, R232
4804-1480-3 DIODE LL4148 SM 15 D102, D103, D105, D106, D202–D206, D211–D216
4853-9060-3 TR 3906 PNP SM 2 Q100, Q200
4860-0640-3 TR 3904 HFE 100-300 SM 2 Q201, Q202
PCB-QZ010C-INP Input board
150F-471J-5-OF CC 50V 470pF 5% RL 8x3.5 4 C1–C4
7010-9860-0 26 PIN IEC RIBBON CABLE 1 J1
2113-1337-1 XLR FEMALE CONN. 2 J101, J201
2113-1652-0 PHONE JACK 06.4 2 J102, J202
2113-1335-0 5 POLE SPEAKER TERMINAL 1 J5
5200-4713-0 10 POLE DIP SWITCH 1 SW1
PCB-QZ010C-OUT Output board
2113-1336-1 SPEAKON NEUTRIK 4 WIRE 2 J100, J200
2113-1338-0 4-POLE SPEAKER TERMINAL 1 J103
4154-2111-0 OUTPUT POST PLUG FOR CE 2 For European models only
4154-2121-0 OUTPUT POST PLUG FOR CE 2 For European models only
RMX Series Technical Service Manual 17
Page 20

6.2 RMX 1450 Replacement Parts
QSC part # Description Qty. Notes or Component Reference
Misc.
1806-2506-0 POWER TRANSFORMER, 1200 1
2113-1144-0 AC INLET 1
4134-9101-0 METAL WIND GUIDE 1
4154-0361-0 FAN GUIDE 1
5200-4717-0 ROCKER POWER SWITCH 1
5200-3531-0 CIRCUIT BREAKER 15A 1 For 120V models
5200-4731-0 CIRCUIT BREAKER 8A 1 For 230V models
7010-9640-0 AC CORD SET 15A 1 For 120V models
7009-8620-0 POWER CORD SET CE 1 For 230V models
8900-9050-1 DC FAN 24V 80X80 (+5V) 1
PCB-QZ020C-PSU AC Board
153R-224K-5-Y1 CM 250V 0.22uF 10% RL 2 C127, C227
157Q-108M-5-X9E CE 35V 1000UF 20% RL 1 C6
3130-9270-0 IC 4N29 1 U2
4134-8851-0 FUSE HOLDER (DIA.6.3MM 4 REF: F100, F200
4701-202J-C RCF 1/8W 2K 5% ATS 1 R13
4701-474J-C RCF 1/8W 470K 5% ATS 1 R12
4701-682J-C RCF 1/8W 6.8K 5% ATS 2 R9, R14
4719-121J-1-X RMF 2W 120R 5% AL METAL 1 R17
4840-1760-0 DIODE RECT 1A 200V DB103 1 BR1
4840-2150-0 BRIDGE RECTIFIER 400V 2 BR100, BR200
4860-2620-5 TR TIP31C SAMSUNG 1 Q3
5120-0061-0 FUSE T12A/250V 6.3X32MM 2 F100, F200
5400-0831-0 HEATSINK 1 REF: Q3
8910-0273-0 POLYSWITCH 0.15 ohm 1.1A 1 R1
8910-0275-0 THERMAL NTC 30A 1 ohm 1 R21
PCB-QZ020C-PWR1 Channel 1 module (left)
153F-223J-5-LQ CM 50V 0.022UF 5% RL 2 C116, C119
153F-332J-5-KW CM 50V 3300pF 5% RL 6x12 2 C117, C118
153R-683J-5-WWM CM 250V 0.068u 5% RL 1 C124
157F-476M-5-LU CE 50V 47uF 20% RL 1 C8
157R-475M-5-OV CE 250V 4.7u 20% RL 1 C7
1804-1040-0 SPRNG COIL 2uH(14gaWIRE) 1 L100
3700-4531-G LED 04mm GREEN W/STAND 1 LD1
4718-220J-2-P RMF 1W 22R 5% AT FP 2 R136, R137
4718-6R8J-1-X RMF 1W 6.8R 5% AL METAL 2 R146, R147
4719-153J-1-X RMF 2W 15K 5% AL METAL 2 R2, R5
4719-5R6J-1-X RMF 2W 5.6R 5% AL METAL 1 R160
471A-022K-5-N RMF 3W 0.22R 10% RL RGC3 8 R142, R143, R148, R149, R152, R153, R156, R159
471B-102J-1-X RMF 5W 1K 5% AL METAL 2 R157, R158
471B-120J-1-X RMF 5W 12R 5% AL METAL 2 R161, R162
471B-302J-1-X RMF 5W 3K 5% AL METAL 2 R133, R135
4756-1016-3-06 SVR H6 100R RH0615C 1 R131
4756-2226-3-06 SVR 2.2K H3 7X7.6 R0615C 2 R139, R140
4804-0040-1 DIODE IN4004 AL 5 D1, D11, D12, D117, D118
4804-9340-2 DIODE IN4934 AT 2 D108, D109
4837-5B10-2 DZ 1/2W 5.5-5.8V AT 2 D107, D110
4838-15V6-2 DZ 1W 15V AT TEMIC D8, D15
4860-5020-5 TR MJE15032 1 Q105
4860-5030-5 TR MJE15033 1 Q106
4860-5050-5 TR 2SC5200 T0-3P (L) 4 Q104, Q108, Q110, Q112
4860-5060-5 TR 2SA1943 T0-3P (L) 4 Q103, Q107, Q109, Q111
4860-8890-0 TR MPS A06 VCE 80V NS 1 Q5
8910-0272-0 CE 100V 3300u 20% 25X50 4 C120–C123
18 QSC Audio Products, Inc.
Page 21

Channel 2 module (continued)
QSC part # Description Qty. Notes or Component Reference
8910-0274-0 THERMAL PTC 60C 100 ohm 1 R7
8910-0488-0 ROD THERMISTOR NTC 50ohm 1 R134
Channel 1 SMT parts
150F-222K-6-CF CC 50V 2200pF 10% 1206 1 1 C115
150H-102J-6-CF CC 100V 0.001U 5% 1206 1 C114
4720-103J-J RMG 1/10W 10K 5% 0805 1 R128
4720-152J-J RMG 1/10W 1.5K 5% 0805 1 R129
4720-202J-J RMG 1/10W 2K 5% 0805 1 R8
4720-224J-J RMG 1/10W 220K 5% 0805 1 R26
4720-470J-J RMG 1/10W 47R 5% 0805 2 R25, R124
4721-105J-6 RMG 1/8W 1M 5% 1206 2 R3, R6
4721-154J-6 RMG 1/8W 150K 5% 1206 1 R10
4721-224J-6 RMG 1/8W 220K 5% 1206 2 R18, R27
4721-473J-6 RMG 1/8W 47K 5% 1206 1 R125
4721-474J-6 RMG 1/8W 470K 5% 1206 1 R15
4721-682J-6 RMG 1/8W 6.8K 5% 1206 1 R19
4721-821J-6 RMG 1/8W 820R 5% 1206 2 R130, R132
4804-1480-3 DIODE LL4148 SM 15 D2–D7, D9, D14, D104, D111–D116
4853-9060-3 TR 3906 PNP SM 3 Q4, Q6, Q7
4860-0640-3 TR 3904 HFE 100-300 SM 4 Q8, Q9, Q101, Q102
4860-5110-3 TR KST42 1 Q1
PCB-QZ020C-PWR2 Channel 2 module (right)
153F-154J-5-NLM CM 50V 0.15UF 5% RL 4 C108, C109, C208, C209
153F-223J-5-LQ CM 50V 0.022UF 5% RL 2 C216, C219
153F-224J-5-NLM CM 50V 0.22UF 5% RL 2 C107, C207
153F-332J-5-KW CM 50V 3300pF 5% RL 6x12 2 C217, C218
153R-683J-5-WWM CM 250V 0.068u 5% RL 1 C224
157E-107M-5-KW CE 25V 100uF 20% RL 6x12 2 C105, C205
157E-227M-5-PU CE 25V 220uF 20% RL 4 C112, C113, C212, C213
157F-106M-5-LUN CE 50V 10¦F 20% RL 2 C106, C206
1804-1040-0 SPRNG COIL 2uH(14gaWIRE) 1 L200
2101-1991-0 8 PIN IC SOCKET DIP 2 REF: U101, U201
3130-2430-0 IC-NE5532 OPER. AMP PHIL 2 U101, U201
3700-4529-R LED 04mm RED W/STAND 2 LD100, LD200
3700-4530-Y LED 04mm YELLOW W/STAND 2 LD101, LD201
471A-022K-5-N RMF 3W 0.22R 10% RL RGC3 8 R242, R243, R248, R249, R252, R253, R256, R259
471B-102J-1-X RMF 5W 1K 5% AL METAL 2 R257, R258
471B-120J-1-X RMF 5W 12R 5% AL METAL 2 R261, R262
471B-302J-1-X RMF 5W 3K 5% AL METAL 2 R233, R235
4717-1132-2 RMF 1/2W 11.3K 1% AT 1 R123
4717-1332-2 RMF 1/2W 13.3K 1% AT 2 R122, R222
4718-220J-2-P RMF 1W 22R 5% AT FP 2 R236, R237
4718-6R8J-1-X RMF 1W 6.8R 5% AL METAL 3 R20, R246, R247
4719-5R6J-1-X RMF 2W 5.6R 5% AL METAL 1 R260
4750-6200-0 VR V012CPH, D-SHAFT 10K 2 R112, R212
4756-1016-3-06 SVR H6 100R RH0615C 1 R231
4756-2226-3-06 SVR 2.2K H3 7X7.6 R0615C 2 R239, R240
4804-0040-1 DIODE IN4004 AL 4 D10, D13, D217, D218
4804-9340-2 DIODE IN4934 AT 2 D208, D209
4837-5B10-2 DZ 1/2W 5.5-5.8V AT 2 D207, D210
4838-15V6-2 DZ 1W 15V AT TEMIC 4 D100, D101, D200, D201
4860-5020-5 TR MJE15032 1 Q205
4860-5030-5 TR MJE25033 1 Q206
4860-5050-5 TR 2SC5200 T0-3P (L) 4 Q204, Q208, Q210, Q212
4860-5060-5 TR 2SA1943 T0-3P (L) 4 Q203, Q207, Q209, Q211
8910-0272-0 CE 100V 3300u 20% 25X50 4 C220–C223
RMX Series Technical Service Manual 19
Page 22

Channel 2 module (continued)
QSC part # Description Qty. Notes or Component Reference
8910-0274-0 THERMAL PTC 60C 100 ohm 1 R4
8910-0488-0 ROD THERMISTOR NTC 50ohm 1 R234
Channel 2 SMT Parts
150F-104K-6-CF CER2 1206 X7R 50V 100N 3 C100, C102, C104
150F-181K-J-BD CC 50V 180P 10% 0805 4 C101, C103, C201, C203
150F-222K-6-CF CC 50V 2200pF 10% 1206 1 1 C215
150F-560K-J-BD CC 50V 56pF 10% 0805 1.2 2 C110, C210
150H-102J-6-CF CC 100V 0.001U 5% 1206 1 C214
15CG-560J-6-CF CTC 0/30 56P 5% 1206 2 C111, C211
3131-9730-0 IC NE5517D 1 U10
4720-101J-J RMG 1/10W 100R 5% 0805 6 R109, R110, R127, R209, R211, R227
4720-102J-J RMG 1/10W 1K 5% 0805 3 R102, R126, R202
4720-103A-J RMG 1/10W 10K 1% 0805 8 R100, R101, R105, R106, R200, R201, R205, R206
4720-103J-J RMG 1/10W 10K 5% 0805 3 R103, R203, R228
4720-152J-J RMG 1/10W 1.5K 5% 0805 1 R229
4720-203A-J RMG 1/10W 20K 1% 0805 4 R117, R121, R217, R221
4720-271J-J RMG 1/10W 270R 5% 0805 6 R111, R113, R120, R210, R213, R220
4720-332J-J RMG 1/10W 3.3K 5% 0805 1 R24
4720-393J-J RMG 1/10W 39K 5% 0805 2 R107, R207
4720-470J-J RMG 1/10W 47R 5% 0805 1 R224
4720-472J-J RMG 1/10W 4.7K 5% 0805 2 R114, R214
4720-752J-J RMG 1/10W 7.5K 5% 0805 2 R108, R208
4721-154A-6 RMG 1/8W 150K 1% 1206 4 R118, R119, R218, R219
4721-154J-6 RMG 1/8W 150K 5% 1206 2 R104, R204
4721-333J-6 RMG 1/8W 33K 5% 1206 2 R22, R23
4721-473J-6 RMG 1/8W 47K 5% 1206 1 R225
4721-4993-6 RMG 1/8W 499K 1% 1206 2 R116, R216
4721-821J-6 RMG 1/8W 820R 5% 1206 4 R115, R215, R230, R232
4804-1480-3 DIODE LL4148 SM 15 D102, D103, D105, D106, D202–D206, D211–D216
4853-9060-3 TR 3906 PNP SM 2 Q100, Q200
4860-0640-3 TR 3904 HFE 100-300 SM 2 Q201, Q202
PCB-QZ020C-INP Input Board
150F-471J-5-OF CC 50V 470pF 5% RL 8x3.5 4 C1, C2, C3, C4
2113-1337-1 XLR FEMALE CONN. 2 J101, J201
2113-1652-0 PHONE JACK 1/4" 6.4 mm 2 J102, J202
5200-4713-0 10 POLE DIP SWITCH 1 SW1
7010-9860-0 26 PIN IEC RIBBON CABLE 1 J1
PCB-QZ020C-OUT Output Board
2113-1336-1 SPEAKON NEUTRIK 4 WIRE 2 J100, J200
2113-1338-0 4-POLE SPEAKER TERMINAL 1 J103
4154-2111-0 OUTPUT POST PLUG FOR CE 2 For European models only
4154-2121-0 OUTPUT POST PLUG FOR CE 2 For European models only
20 QSC Audio Products, Inc.
Page 23

6.3 RMX 2450 Replacement Parts
QSC part # Description Qty. Notes or Component Reference
Misc.
1806-2507-0 POWER TRANSFORMER, 1800 1
2113-1144-0 AC INLET 1
4134-9101-0 METAL WIND GUIDE 1
4154-0361-0 FAN GUIDE 1
5200-4717-0 ROCKER POWER SWITCH 1
5200-3531-0 CIRCUIT BREAKER 15A 1 For 120V models
5200-4731-0 CIRCUIT BREAKER 8A 1 For 230V models
7010-9640-0 AC CORD SET 15A 1 For 120V models
7009-8620-0 POWER CORD SET CE 1 For 230V models
8900-9050-1 DC FAN 24V 80X80 (+5V) 1
PCB-QZ030C-PSU AC Board
4701-202J-C RCF 1/8W 2K 5% ATS 1 R13
4701-474J-C RCF 1/8W 470K 5% ATS 1 R12
4701-682J-C RCF 1/8W 6.8K 5% ATS 2 R9, R14
153R-224K-5-Y1 CM 250V 0.22uF 10% RL 4 C127, C128, C227, C228
153T-473K-5-WS CM 400V 0.047UF 10% RL 1 C10
157Q-108M-5-X9E CE 35V 1000UF 20% RL 1 C6
3130-9270-0 IC 4N29 1 U2
4719-121J-1-X RMF 2W 120R 5% AL METAL 1 R17
471B-120J-1-X RMF 5W 12R 5% AL METAL 2 R28, R29
4840-1760-0 DIODE RECT 1A 200V DB103 1 BR1
4840-2150-0 BRIDGE RECTIFIER 400V 4 BR100, BR101, BR200, BR201
4860-2620-5 TR TIP31C SAMSUNG 1 Q3
5400-0831-0 HEATSINK 1 REF: Q3
5400-1831-1 HEATSINK FOR RECTIFIER 4 REF: BR100, BR101, BR200, BR201
8910-0273-0 POLYSWITCH 0.15 ohm 1.1A 1 R1
8910-0275-0 THERMAL NTC 30A 1 ohm 1 R21
PCB-QZ030C-PWR2 Channel 1 module (right)
153F-154J-5-NLM CM 50V 0.15UF 5% RL 4 C108, C109, C208, C209
153F-223J-5-LQ CM 50V 0.022UF 5% RL 2 C116, C119
153F-224J-5-NLM CM 50V 0.22UF 5% RL 2 C107, C207
153F-332J-5-KW CM 50V 3300pF 5% RL 6x12 2 C172, C179
153H-102J-5-IQ CM 100V 0.001U 5% RL 5X 2 C131, C231
153R-104J-5-YRM CM 250V 0.1u 5% RL 2 C174, C175
153R-152J-5-XQ CM 250V 0.0015UF 5% RL 1 C114
153R-683J-5-WWM CM 250V 0.068u 5% RL 2 C124, C126
157D-107M-5-OUN CE 16V 100UF 20% RL 8X11 2 C125, C225
157D-476M-5-LUN CE 16V 47u 20% RL 6.5X11 2 C106, C206
157E-107M-5-KW CE 25V 100uF 20% RL 6x12 4 C105, C173, C180, C205
157E-226M-5-IUN CE 25V 22uF 20% RL 5X11 1 C129
157E-227M-5-PU CE 25V 220uF 20% RL 4 C112, C113, C212, C213
157Q-106M-5-IU CE 35V 10uF 20% RL 5x11 1 C171
1804-1040-0 SPRING COIL 2uH (14gaWIRE) 1 L100
2101-1991-0 8 PIN IC SOCKET DIP 2 REF: U101, U201
2101-2081-0 26 PIN DUAL ROW IEC 1 J103
2102-130S-003 13 PIN WAFER P2.0 ST. 1 J104
3130-2430-0 IC-NE5532 OPER. AMP PHIL 2 U101, U201
3700-4529-R LED 04mm RED W/STAND 2 LD100, LD200
3700-4530-Y LED 04mm YELLOW W/STAND 2 LD101, LD201
4134-8851-0 FUSE HOLDER (DIA.6.3MM 2 F100
4715-100J-2 RMF 1/4W 10R 5% AT 1 R163
4715-101J-2 RMF 1/4W 100R 5% AT 1 R164
4717-2322-2 RMF 1/2W 23.2K 1% AT 3 R122, R123, R222
4718-123J-2-X RMF 1W 12K 5% AT METAL 2 R177, R194
RMX Series Technical Service Manual 21
Page 24

Channel 1 module (continued)
QSC part # Description Qty. Notes or Component Reference
4718-153J-2-X RMF 1W 15K 5% AT METAL 1 R165
4718-220J-2-P RMF 1W 22R 5% AT FP 2 R136, R137
4718-3R3J-1-X RMF 1W 3.3R 5% AL 3 R146, R147, R20
4719-1R5J-1-X RMF 2W 1R5 5% AL METAL 2 R181, R182
4719-5R6J-1-X RMF 2W 5.6R 5% AL METAL 1 R160
471A-022K-5-N RMF 3W 0.22R 10% RL RGC3 8 R142, R143, R148, R149, R152, R153, R156, R159
471B-120J-1-X RMF 5W 12R 5% AL METAL 4 R154, R155, R161, R162
471B-222J-1-X RMF 5W 2.2K 5% AL METAL 3 R157, R158, R198
471B-512J-1-X RMF 5W 5.1K 5% AL METAL 2 R180, R188
471B-822J-1-X RMF 5W 8.2K 5% AL METAL 4 R118, R119, R133, R135
4750-6200-0 VR V012CPH, D-SHAFT 10K 2 R112, R212
4756-1016-3-06 SVR H6 100R RH0615C 1 R131
4756-2226-3-06 SVR 2.2K H3 7X7.6 R0615C 2 R139, R140
4804-0040-1 DIODE IN4004 AL 4 D10, D12, D117, D118
4804-9340-2 DIODE IN4934 AT 2 D108, D109
4837-3B20-2 DZ 1/2W 3.8-4.0V AT 1 D170
4837-5B10-2 DZ 1/2W 5.5-5.8V AT 2 D107, D110
4838-10V6-2 DZ 1.3W 10V AT TEMIC 1 D174
4838-12V6-2 DZ 1W 12V AT TEMIC 1 D178
4838-15V6-2 DZ 1W 15V AT TEMIC 4 D100, D101, D200, D201
4840-2190-0 DIODE MUR1520 15A 200V 2 D175, D176
4860-5020-5 TR MJE15032 1 Q105
4860-5030-5 TR MJE15033 1 Q106
4860-5050-5 TR 2SC5200 T0-3P (L) 4 Q104, Q108, Q110, Q112
4860-5060-5 TR 2SA1943 T0-3P (L) 4 Q103, Q107, Q109, Q111
4860-5250-5 TR 2N5064 TRIODE 2 D119, D120
490F-Z440-5 FET IRFZ44 TO-220 60V 2 Q170, Q174
5120-0501-0 FUSE T25A/125V 6.4X32MM 1 F100
8910-0274-0 THERMAL PTC 60C 100 ohm 1 R4
8910-0482-0 TRIAC 600V 40A MAC224A8 1 Q113
8910-0488-0 ROD THERMISTOR NTC 50ohm 1 R134
8910-0494-0 CE 63V 12000uF 20% RL 4 C120–C123
Channel 1 SMT parts
150F-101J-J-BD CC 50V 100pF 5% 0805 1.2 1 C130
150F-101K-J-BD CC 50V 100P 10% 0805 1 C132
150F-103M-J-BD CC 50V 0.01uF 20% 0805 1 1 C181
150F-104M-6-CF CC 50V 0.1uF 20% 1206 1. 2 C104, C178
150F-181K-J-BD CC 50V 180P 10% 0805 4 C101, C103, C201, C203
150F-222K-6-CF CC 50V 2200pF 10% 1206 1 1 C115
150F-470J-J-BD CC 50V 47pF 5% 0805 1.2x 5 C110, C170, C176, C177, C210
15CG-270J-6-CF CTC 0/30 27P 5% 1206 2 C111, C211
3130-9240-0 IC LM311M VOLTAGE 2 U170, U171
3131-9730-0 IC NE5517D 1 U10
4720-101J-J RMG 1/10W 100R 5% 0805 6 R109, R110, R127, R209, R210, R227
4720-102J-J RMG 1/10W 1K 5% 0805 3 R102, R126, R202
4720-103A-J RMG 1/10W 10K 1% 0805 8 R100, R101, R105, R106, R200, R201, R205, R206
4720-103J-J RMG 1/10W 10K 5% 0805 3 R103, R128, R203
4720-123J-J RMG 1/10W 12K 5% 0805 1 R176
4720-152J-J RMG 1/10W 1.5K 5% 0805 1 R129
4720-202J-J RMG 1/10W 2K 5% 0805 2 R190, R195
4720-222J-J RMG 1/10W 2.2K 5% 0805 1 R191
4720-243J-J RMG 1/10W 24K 5% 0805 4 R117, R121, R217, R221
4720-271J-J RMG 1/10W 270R 5% 0805 4 R113, R196, R213, R296
4720-3011-J RMG 1/10W 3.01K 1% 0805 2 R24, R175
4720-391J-J RMG 1/10W 390R 5% 0805 2 R120, R220
4720-393J-J RMG 1/10W 39K 5% 0805 2 R107, R207
4720-470J-J RMG 1/10W 47R 5% 0805 2 R170, R189
22 QSC Audio Products, Inc.
Page 25

Channel 1 module (continued)
QSC part # Description Qty. Notes or Component Reference
4720-472J-J RMG 1/10W 4.7K 5% 0805 8 R114, R138, R174, R179, R187, R193, R214, R238
4720-473J-J RMG 1/10W 47K 5% 0805 1 R183
4720-474J-J RMG 1/10W 470K 5% 0805 2 R172, R185
4720-592A-J RMG 1/10W 5.9K 1% 0805 2 R171, R184
4720-750J-J RMG 1/10W 75R 5% 0805 1 R124
4720-752J-J RMG 1/10W 7.5K 5% 0805 2 R108, R208
4720-821J-J RMG 1/10W 820R 5% 0805 2 R111, R211
4721-101J-6 RMG 1/8W 100R 5% 1206 1 R197
4721-154J-6 RMG 1/8W 150K 5% 1206 6 R104, R173, R178, R186, R192, R204
4721-4643-6 RMG 1/8W 464K 1% 1206 3 R166, R167, R266
4721-473J-6 RMG 1/8W 47K 5% 1206 1 R125
4721-683A-6 RMG 1/8W 68K 1% 1206 4 R22A, R22B, R23A, R23B
4721-821J-6 RMG 1/8W 820R 5% 1206 4 R115, R130, R132, R215
4721-824J-6 RMG 1/8W 820K 5% 1206 2 R116, R216
4804-1480-3 DIODE LL4148 SM 18 D102–D106, D111–D116, D171, D173, D177, D202, D203, D205, D206
4853-9060-3 TR 3906 PNP SM 4 Q100, Q172, Q175, Q200
4860-0640-3 TR 3904 HFE 100-300 SM 4 Q101, Q102, Q171, Q173
PCB-QZ030C-PWR1 Channel 2 module (left)
153F-223J-5-LQ CM 50V 0.022UF 5% RL 2 C216, C219
153F-332J-5-KW CM 50V 3300pF 5% RL 6x12 2 C272, C279
153R-104J-5-YRM CM 250V 0.1u 5% RL 2 C274, C275
153R-152J-5-XQ CM 250V 0.0015UF 5% RL 1 C214
153R-683J-5-WWM CM 250V 0.068u 5% RL 2 C224, C226
157E-107M-5-KW CE 25V 100uF 20% RL 6x12 2 C273, C280
157E-226M-5-IUN CE 25V 22uF 20% RL 5X11 1 C229
157F-476M-5-LU CE 50V 47uF 20% RL 1 C8
157Q-106M-5-IU CE 35V 10uF 20% RL 5x11 1 C271
157R-475M-5-OV CE 250V 4.7u 20% RL 1 C7
1804-1040-0 SPRNG COIL 2uH(14gaWIRE) 1 L200
2102-031S-004 3 PIN ST. WAFER 1 J257
2102-130S-003 13 PIN WAFER P2.0 ST. 1 J204
3700-4531-G LED 04mm GREEN W/STAND 1 LD1
4134-8851-0 FUSE HOLDER (DIA.6.3MM 2 REF: F200
4715-100J-2 RMF 1/4W 10R 5% AT 1 R263
4715-101J-2 RMF 1/4W 100R 5% AT 1 R264
4718-123J-2-X RMF 1W 12K 5% AT METAL 2 R277, R294
4718-153J-2-X RMF 1W 15K 5% AT METAL 1 R265
4718-220J-2-P RMF 1W 22R 5% AT FP 2 R236, R237
4718-3R3J-1-X RMF 1W 3.3R 5% AL 2 R246, R247
4719-1R5J-1-X RMF 2W 1R5 5% AL METAL 2 R281, R282
4719-333J-2-X RMF 2W 33K 5% AT METAL 2 R2, R5
4719-5R6J-1-X RMF 2W 5.6R 5% AL METAL 1 R260
471A-022K-5-N RMF 3W 0.22R 10% RL RGC3 8 R242, R243, R248, R249, R252, R253, R256, R259
471B-120J-1-X RMF 5W 12R 5% AL METAL 4 R254, R255, R261, R262
471B-222J-1-X RMF 5W 2.2K 5% AL METAL 3 R257, R258, R298
471B-512J-1-X RMF 5W 5.1K 5% AL METAL 2 R280, R288
471B-822J-1-X RMF 5W 8.2K 5% AL METAL 4 R218, R219, R233, R235
4756-1016-3-06 SVR H6 100R RH0615C 1 R231
4756-2226-3-06 SVR 2.2K H3 7X7.6 R0615C 2 R239, R240
4804-0040-1 DIODE IN4004 AL 5 D1, D11, D13, D217, D218
4804-9340-2 DIODE IN4934 AT 2 D208, D209
4837-3B20-2 DZ 1/2W 3.8-4.0V AT 1 D270
4837-5B10-2 DZ 1/2W 5.5-5.8V AT 2 D207, D210
4838-10V6-2 DZ 1.3W 10V AT TEMIC 1 D274
4838-12V6-2 DZ 1W 12V AT TEMIC 1 D278
4838-15V6-2 DZ 1W 15V AT TEMIC 2 D8, D15
4840-2190-0 DIODE MUR1520 15A 200V 2 D275, D276
RMX Series Technical Service Manual 23
Page 26

Channel 2 module (continued)
QSC part # Description Qty. Notes or Component Reference
4860-5020-5 TR MJE15032 1 Q205
4860-5030-5 TR MJE15033 1 Q206
4860-5050-5 TR 2SC5200 T0-3P (L) 4 Q204, Q208, Q210, Q212
4860-5060-5 TR 2SA1943 T0-3P (L) 4 Q203, Q207, Q209, Q211
4860-5250-5 TR 2N5064 TRIODE 2 D219, D220
4860-8890-0 TR MPS A06 VCE 80V NS 1 Q5
490F-Z440-5 FET IRFZ44 TO-220 60V 2 Q270, Q274
5120-0501-0 FUSE T25A/125V 6.4X32MM 1 F200
8910-0274-0 THERMAL PTC 60C 100 ohm 1 R7
8910-0482-0 TRIAC 600V 40A MAC224A8 1 Q213
8910-0488-0 ROD THERMISTOR NTC 50ohm 1 R234
8910-0494-0 CE 63V 12000uF 20% RL 4 C220–C223
Channel 2 SMT Parts
150F-101K-J-BD CC 50V 100P 10% 0805 1 C9
150F-103M-J-BD CC 50V 0.01uF 20% 0805 1 1 C281
150F-104M-6-CF CC 50V 0.1uF 20% 1206 1. 1 C278
150F-104M-J-BD CC 50V 0.1uF 20% 0805 1. 1 C11
150F-222K-6-CF CC 50V 2200pF 10% 1206 1 1 C215
150F-470J-J-BD CC 50V 47pF 5% 0805 1.2x 3 C270, C276, C277
3130-9240-0 IC LM311M VOLTAGE 2 U270, U271
4720-103J-J RMG 1/10W 10K 5% 0805 1 R228
4720-123J-J RMG 1/10W 12K 5% 0805 1 R276
4720-152J-J RMG 1/10W 1.5K 5% 0805 1 R229
4720-202J-J RMG 1/10W 2K 5% 0805 3 R8, R290, R295
4720-222J-J RMG 1/10W 2.2K 5% 0805 1 R291
4720-3011-J RMG 1/10W 3.01K 1% 0805 1 R275
4720-470J-J RMG 1/10W 47R 5% 0805 3 R25, R270, R289
4720-472J-J RMG 1/10W 4.7K 5% 0805 4 R274, R279, R287, R293
4720-473J-J RMG 1/10W 47K 5% 0805 1 R283
4720-474J-J RMG 1/10W 470K 5% 0805 2 R272, R285
4720-592A-J RMG 1/10W 5.9K 1% 0805 2 R271, R284
4720-750J-J RMG 1/10W 75R 5% 0805 1 R224
4721-101J-6 RMG 1/8W 100R 5% 1206 1 R30
4721-105J-6 RMG 1/8W 1M 5% 1206 2 R3, R6
4721-154J-6 RMG 1/8W 150K 5% 1206 5 R10, R273, R278, R286, R292
4721-224J-6 RMG 1/8W 220K 5% 1206 2 R18, R26
4721-334J-6 RMG 1/8W 330K 5% 1206 1 R27
4721-4643-6 RMG 1/8W 464K 1% 1206 1 R15
4721-473J-6 RMG 1/8W 47K 5% 1206 1 R225
4721-682J-6 RMG 1/8W 6.8K 5% 1206 1 R19
4721-821J-6 RMG 1/8W 820R 5% 1206 2 R230, R232
4804-1480-3 DIODE LL4148 SM 18 D2–D7, D9, D14, D204, D211–D216, D271, D273, D277
4853-9060-3 TR 3906 PNP SM 5 Q4, Q6, Q7, Q272, Q275
4860-0640-3 TR 3904 HFE 100-300 SM 6 Q8, Q9, Q201, Q202, Q271, Q273
4860-5110-3 TR KST42 1 Q1
PCB-QZ030C-INP Input Board
150F-471J-5-OF CC 50V 470pF 5% RL 8x3.5 4 C1, C2, C3, C4
2113-1337-1 XLR FEMALE CONN. 2 J101, J201
2113-1652-0 PHONE JACK 1/4" 6.4 mm 2 J102, J202
5200-4713-0 10 POLE DIP SWITCH 1 SW1
7010-9860-0 26 PIN IEC RIBBON CABLE 1 J1
PCB-QZ030C-OUT Output Board
2113-1336-1 SPEAKON NEUTRIK 4 WIRE 2 J100, J200
2113-1338-0 4-POLE SPEAKER TERMINAL 1 J103
4154-2111-0 OUTPUT POST PLUG FOR CE 2 For European models only
4154-2121-0 OUTPUT POST PLUG FOR CE 2 For European models only
24 QSC Audio Products, Inc.
Page 27

THIS DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY
INFORMATION WHICH IS THE PROPERTY
OF QSC AUDIO PRODUCTS, THAT MAY NOT
BE DISCLOSED, REPRODUCED OR USED
WITHOUT EXPRESS WRITTEN CONSENT FROM
QSC AUDIO PRODUCTS.
87654321
7. Schematics and diagrams
00
SCREW
4 REQD
REV
AXX
REVISIONS
EFF DATE CHK APPROVED DATEDESCRIPTION
RMX 850: PCB-QZ010C-PSU
D
RMX 850: PCB-QZ010C-INP
INPUT PCB
00
RMX 1450: PCB-QZ020C-PSU
RMX 2450: PCB-QZ030C-PSU
PWR PCB
00
00
SCREW
8 REQD
D
RMX 1450: PCB-QZ020C-INP
RMX 2450: PCB-QZ030C-INP
WASHER
FAN
00
C
CHASSIS
00
00
00
HEX NUT
FLAT WASHER
00
TOROID
SWITCH
C
00
SCREW
00
2 REQD
SCREW
4 REQD
HEX NUT
2 REQD
B
A
00
00
SCREW
4 REQD
00
00
FAN GUARD
THIS DRAWING USED IN CONJUNCTION WITH SCHEMATIC DWGs MAIN PCB SH-002451,
INPUT PCB XO,
WIRING DIAGRAM SH-002450-00 AND FINAL ASSY PF-002450-00.
NOTES: UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED
87654321
SCREW
00
PWR CONNECTOR
00
SCREW
2 REQD
00
SCREW
2 REQD
00
7.1 RMX Assembly/Disassembly Diagram 1 of 2
(All models)
OUTPUT PCB
00
RMX 850: PCB-QZ010C-OUT
RMX 1450: PCB-QZ020C-OUT
RMX 2450: PCB-QZ030C-OUT
NEXT ASSY USED ON
X RMX 2450
APPLICATION
UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED
DIMENSIONS ARE IN INCHES.
TOLERANCES ARE:
DECIMALS DECIMALS ANGLES
.xx ± .02 .xxx ± .010 ±1/2
DEBURR EDGES .XXX R MAX
MATERIAL
SEE TABULATION BLOCK
FINISH
DO NOT SCALE DRAWING
RACK EAR
2 REQD
DRAWN
MILA P. 12-07-2000
CHECKED
ISSUED
00
PARTS LIST
DATEAPPROVALS
D
SCALE
AUDIO PRODUCTS, INC.
COSTA MESA,CALIFORNIA
CHASSIS ASSY
RMX 2450
DWG NO.
PA-002450-00
1/2
SHEET
1 OF 2
B
DWG NO.
PA-002450-00
SH
1
REV
A
REV
RMX Series Technical Service Manual 25
Page 28

THIS DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY
INFORMATION WHICH IS THE PROPERTY
OF QSC AUDIO PRODUCTS, THAT MAY NOT
BE DISCLOSED, REPRODUCED OR USED
WITHOUT EXPRESS WRITTEN CONSENT FROM
QSC AUDIO PRODUCTS.
87654321
CHANNEL MODULES
RMX 850: PCB-QZ010C-PWR1 (left or Channel 1)
RMX 1450: PCB-QZ020C-PWR1 (left or Channel 1)
RMX 2450: PCB-QZ030C-PWR1 (left or Channel 2)
D
CHANNEL MODULES
SCREW
5 REQD
SCREW
6 REQD
D
RMX 850: PCB-QZ010C-PWR2 (right or Channel 2)
RMX 1450: PCB-QZ020C-PWR2 (right or Channel 2)
RMX 2450: PCB-QZ030C-PWR2 (right or Channel 1)
C
C
B
B
DWG NO.
PA-002450-00
KNOB
2 REQD
CHASSIS
NUT
SCREW
A
4 REQD
WIRE ASSY
SH
2
REV
A
7.2 RMX Assembly/Disassembly Diagram 2 of 2
(All models)
87654321
D
SCALE
1/2
DWG NO.
PA-002450-00
SHEET
26 QSC Audio Products, Inc.
REV
2 OF 2
Page 29

THIS DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY
INFORMATION WHICH IS THE PROPERTY
OF QSC AUDIO PRODUCTS, THAT MAYNOT
BE DISCLOSED, REPRODUCED OR USED
WITHOUT EXPRESS WRITTEN CONSENT FROM
QSC AUDIO PRODUCTS.
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
REV
1
PROTOTYPE RELEASE
2
CLEAN UP BY AA3
DESCRIPTION
REVISION
3-01-00
3-10-00
1
APPROVED / DATEEFF.DATE CHK
D
C
CLIP LIM A (1)
FILTER 30 HZ (2)
FILTER BYPASSA (3)
B
FILTER BYPASSB (8)
FILTER 30 HZ (9)
CLIP LIM B (10)
J101
J102
J202
J201
PARALLEL
INPUTS
(4, 5)
BRIDGE
MONO
(6, 7)
CH1_+IN
CH1_-IN
CHASSIS_GND
CH2_-IN
FIVE POSITION BARRIER STRIP
CH2_+IN
BR-POS
BR-NEG
D
C
B
DWGNO.
SH-000850-00
SH
1
1
REV
4
+15V_A
15V-1W
8
U101:2
4
NE5532
15V-1W
CHANNEL-1
C112
220-25V
D101
P1
7
D100
P1
C113
220-25V
4
J204:4
C114
R124
CLIP CH 1
J104:4
R125
^R_1206
0.001u, 100V 5%
47
LD100
RED
47K
^C_1206
^R_0805
D102
1N4148
D103
1N4148
4
Q101
R127
3904
1N4148
D104
P1
7
7
R130
^R_1206
D105
1N4148
D106
1N4148
100
^R_0805
R128
10K
^R_0805
820
J104:7
J204:7
P1
R129
1.5K
^R_0805
Q102
3904
D107
5.6V-.25W
R131
BIAS
R135
2.0K-5W
^C_1206
R134
50
NTC
J104:5
J204:5
J204:6
J104:6
R137
22-1W
FP
R136
22-1W
FP
R139
R140
Q103
2SA1943
R142
0.22-3W
Q107
2SA1943
R148
0.22-3W
Q109
2SA1943
R152
D116
Q105
MJE15032
D113
1N4148
C117
CW
.0033
W
NEG
2.2K
CURRENT
LIMIT
CCW
CCW
POS
CURRENT
2.2K
LIMIT
W
C118
.0033
CW
D114
1N4148
R146
6.8-1W
R147
6.8-1W
Q106
MJE15033
1N4148
C119
P1
.022
D115
1N4148
Q104
2SC5200
R143
0.22-3W
Q108
2SC5200
R149
0.22-3W
Q110
2SC5200
R153
D112
1N4148
5
5
LD101
YELLOW
SIGCH1
6
6
D108
1N4934
C115
0.0022u, 10%
D109
1N4934
CW
W
100
C116
.022
CCW
D110
5.6V-.25W
820
R132
^R_1206
D111
1N4148
R133
2.0K-5W
+67V
0.22-3W
P1
4700-80V
R157
820-5W
R158
820-5W
4700-80V
0.22-3W
+VCC_A
D117
1N4004
C120
SPEAKER CONNECTORS
ON BREAK-AWAYPCB.
JP14
5-WAY
BINDING
POST
CH A
JP13
J104:11
J204:11
CONTINUED, SHEET 2
CHANNEL 1
SPEAKER OUTPUT PCB
J103 +
1+
J100
1-
J103 -
2+
2-
SPEAKON
R160
5.6-2W
C124
.068-5%
250V
R161
BR_BAL
12-5W
33K
R22
33K
R23
^R_1206
SP_B
C121
P1
D118
1N4004
-VCC_A
-67V
L100
2uH
^R_1206
R24
3.3K
^R_0805
P1
R162
12-5W
WIRES TO
BREAK-AWAY
SPEAKER
OUTPUT PCB
11
11
P1
E100
E101
SP_A
26-LINE RIBBON CABLE
CONNECTS BREAKAWAY
INPUT PCB TO MAIN PCB
^R_0805
C102
0.1-50V
10%
^C_1206
U10:1
LM13600M
5
1
R103
R102
C101
180p-5%
^C_0805
R105
10.0K
^R_0805
NE5532
U101:1
+
3
1K
-
2
R106
10.0K
^R_0805
C103
180p-5%
^C_0805
SEE SH 3
+14V
11
3
+
2
4
-
6
C104
.1-50V-10%
^C_1206
10.0K
^R_0805
150K
R104
^R_1206
-14V
SEE SH 3
2
3
1
RING
R
TIP
T
S
J5:5
5
J5:4
4
J5:3
J5:2
J5:1
RING
TIP
C1
470p 5%
GND
SW1:1
SW1:2
SW1:3
SW1:4
SW1:5
SW1:6
SW1:7
SW1:8
SW1:9
SW1:10
^C_1206
C2
470p 5%
^C_1206
11
12
13
14
15
BR M SEND (HI-SIG A)
BR MONO FEED
16
17
18
19
20
FILTSEND B (POT)
3
2
1
R
T
S
2
3
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
C3
C4
CLIP-LIM A
FILT-CAPA
FILT-SENDA
FILT-BYPA
FILTBYP B
FILTCAP B
CLIP LIM B
-IN B
+IN B
J1:1
J203:1
1
GND
J1:2
2
+IN A
J1:3
3
-IN A
470p 5%
^C_1206
J1:4
4
470p 5%
^C_1206
J1:5
5
J1:6
6
GND
J1:7
7
J1:8
8
J1:9
9
J1:10
10
GND
J1:11
11
J1:12
12
GND
J1:13
13
J1:14
14
GND
J1:15
15
J1:16
16
J1:17
17
J1:18
18
J1:19
19
J1:20
20
J1:21
21
GND
J1:22
22
J1:23
23
GND
J1:24
24
J1:25
25
J1:26
26
GND
J203:2
J203:3
J203:4
J203:5
J203:6
J203:7
J203:8
J203:9
J203:10
J203:11
J203:12
J203:13
J203:14
J203:15
J203:16
J203:17
J203:18
J203:19
J203:20
J203:21
J203:22
J203:23
J203:24
J203:25
J203:26
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
A1
FILT-CAPA
FILT-SENDA
SW TO GND FOR CLIP LIM
BR MONO FEED
BR_RET
BR_BAL
BR_CUT
F_BYP_B
F_SND_B
F_30_B
CLIP_B
-IN_B
+IN_B
FILT-BYPA
R100
10.0K
^R_0805
R101
10.0K
^R_0805
8
^U_LM13600
P1
7
R107
1
C105
A1
R108
39K
^R_0805
R109
100-25V
C100
0.1-50V 10%
^C_1206
ROUTE THIS GROUND
TO "A" GND AT
JI-2 INPUT CABLE
A1 P1
C106
10-50NP
CW
R112
10K
CCW
A1
10K LINEAR 3B
RIGHT ANGLE POT
7.50K
^R_0805
^R_0805
100
100
R110
A1
^R_0805
P1
R111
R20
6.8-1W
CHANNEL 1 GAIN
R113
W
270
^R_0805
R114
^R_0805
270
A1
ROUTE THIS GROUND
TO "P" GND AT
HEATSINK COMMON
BETWEEN CH A AND CH B
12
NC
12
NC
13
NC
13
C107
.22-5%
C108
.15-5%
4.7K
^R_0805
A1
Q100
3906
J104:10
J204:10
R126
1K
^R_0805
J204:12
J104:12
J104:13
J204:13
R116
R117
390K
.15-5%
20.0K
+VCC_A
10
10
TH_A
SEE SH 3
SP_A
MODEL R116
700 383K
1200 499K
^R_1206
C109
^R_0805
A1
R121
R115
820
^R_1206
R118
R119
R120
270
^R_0805
150K
150K
^C_0805
20.0K
^R_1206
^R_1206
C110
56p
6
5
^R_0805
-15V_A
56p-200V-COG
10.0K-1%-1/2W
R123
9.09K-1%-1/2W
-
+
C111
^C_1206
R122
Gray shading indicates
A
5. J104, J204 ARE CONNECTED PIN TO PIN BY 13-LINE RIBBON CABLE.
4. PART NUMBERING SCHEME
PARTS IN COMMON TO BOTH CH: 1-99. CH 1 PARTS 101-199, CH 2 PARTS 201-299.
3. COMPONENTS MARKED WITH ARE SAFETY CRITICAL PARTS.
2. COMPONENTS WITH VALUE PREFIXED WITH A "^" REPRESENT SMT COMPONENTS.
1. THIS DRAWING USED IN CONJUNCTION WITH ASSEMBLY WP-000851-00
NOTES: UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED
signal path
!
8
7.3 RMX 850 Schematic Diagram 1 of 3
Channel 1
7
6
5
4
WP-000850-00 RMX850
NEXT ASSY USED ON
APPLICATION
3
ITEM NO.QTY PART NO.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED
DIMENSIONS ARE IN INCHES.
DIMENSIONS PER ANSI Y14.5-1982
TOLERANCES ARE:
DECIMALS
DECIMALS
+
.XX
DEBURR EDGES .XXX R MAX
MATERIAL
FINISH
+
.XXX
-
-
DO NOT SCALE DRAWING
ANGLES
CONTRACT NO.
O
DRAWN
CHECKED
ISSUED
CAD SEED FILE NO.
APPROVALS
PATQUILTER
DATE
2-25-00
DESCRIPTION
PARTS LIST
AUDIO PRODUCTS, INC.
COSTA MESA, CALIFORNIA
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
VENDOR
A
RMX 850
SIZE FSCM NO. DWG NO.
D
PLOT DATE:
SCALE CADFILE NO. SHEET
Thu Sep 07, 2000
2
NONE
P:RMXQSCRMX850
SH-000850-00
RMX850-3.sch
1
PLOT DATE:
Thu Sep 07, 2000
REV
3
3OF1
RMX Series Technical Service Manual 27
Page 30

THIS DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY
INFORMATION WHICH IS THE PROPERTY
OF QSC AUDIO PRODUCTS, THAT MAYNOT
BE DISCLOSED, REPRODUCED OR USED
WITHOUT EXPRESS WRITTEN CONSENT FROM
QSC AUDIO PRODUCTS.
8
67 5
1432
D
D
CHANNEL-2
C201
180p-5%
^C_0805
R205
P1
C214
R224
P1
CLIP CH 2
R226
^R_1206
0.001u, 100V 5%
47
LD200
RED
47K
^C_1206
^R_0805
D202
1N4148
D203
1N4148
A1
10.0K
^R_0805
NE5532
R200
+IN_B
10.0K
^R_0805
SEE SH 1
R201
-IN_B
10.0K
^R_0805
C
SEE SH 1
F_30_B
F_SND_B
F_BYP_B
9
10
^R_0805
U10:2
LM13600M
12
16
R202
R203
B
SEE SH 1
CLIP_B
SW-GND FOR CLIP LIM
SEE SH 1
BR MONO RETURN -- CAUTION, SENSITIVE NODE
BR_RET
R204
1K
10.0K
150K
SEE SH 3
^R_0805
^R_1206
-14V
U201:1
+
3
1
-
2
R206
10.0K
^R_0805
C203
180p-5%
^C_0805
C206
10-50NP
R212
10K
10K LINEAR 3B
RIGHT ANGLE POT
CW
R213
W
270
^R_0805
CCW
A1
R216
390K
^R_1206
C207
.22-5%
+15V_B
C212
220-25V
D201
15V-1W
C210
56p
^C_0805
^R_0805
R215
820
R217
^R_1206
20.0K
C209
.15-5%
^R_0805
+VCC_B
-VCC_B
A1
R218
R219
R221
150K
150K
R220
^R_0805
^R_1206
^R_1206
270
20.0K
^R_0805
8
6
-
5
+
4
-15V_B
C211
56p-200V-COG
^C_1206
R222
10.0K-1%-1/2W
U201:2
NE5532
D200
15V-1W
220-25V
7
C213
3906
Q200
R214
C208
.15-5%
4.75K
A1
SEE SH 3
+14V
R208
7.50K
^R_0805
R207
39K
^R_0805
14
+
15
13
-
^R_0805
100
100
R211
C205
100-25V
R210
270
^R_0805
R209
^R_0805
A1
Q201
R227
3904
D204
1N4148
P1
100
^R_0805
D205
1N4148
D206
1N4148
^R_0805
R228
R229
10K
1.5K
^R_0805
Q202
P1
3904
R230
D208
D209
CW
R231
100
BIAS
CCW
R232
820
D207
5.6V-.25W
1N4934
1N4934
W
C216
.022
D210
5.6V-.25W
820
D212
YELLOW
^R_1206
C215
^R_1206
1N4148
LD201
SIGCH2
0.0022u, 10%
R235
2.0K-5W
^C_1206
R234
50
NTC
R236
22-1W
R239
2.2K
R240
2.2K
+67V
R242
0.22-3W
R248
0.22-3W
R252
0.22-3W
FP
Q203
2SA1943
Q207
2SA1943
Q209
2SA1943
P1
D216
1N4148
4700-80V
R257
C219
P1
.022
820-5W
R258
820-5W
D215
4700-80V
1N4148
CW
CCW
CCW
CW
1N4148
D213
W
W
D214
NEG
CURRENT
LIMIT
POS
CURRENT
LIMIT
C217
.0033
C218
.0033
Q205
MJE15032
R246
6.8-1W
R247
6.8-1W
Q206
MJE15033
1N4148
Q204
2SC5200
Q208
2SC5200
Q210
2SC5200
D211
R233
2.0K-5W
1N4148
R237
22-1W
FP
R243
0.22-3W
R249
0.22-3W
R253
0.22-3W
C220
C221
+VCC_B
D217
1N4004
C
R260
5.6-2W
WIRES TO
SPEAKER
OUTPUT PCB
R261
12-5W
L200
2uH
C224
.068-5%
250V
R262
12-5W
E200
E201
P1
P1
D218
1N4004
-VCC_B
-67V
SP_B
JP15
5-WAY
BINDING
POST
CH B
JP16
CHANNEL B
SPEAKER OUTPUT
J203 +
J200
J203 -
SPEAKER CONNECTORS
ON BREAKAWAYPCB
FROM SHEET ONE
BR-POS
TO CH A
SHEET 1
2+
1+
2-
1-
SPEAKON
BR-NEG
B
DWGNO.
SH-000850-00
SH
2
REV
3
A
A
Gray shading indicates
signal path
7.4 RMX 850 Schematic Diagram 2 of 3
Channel 2
NOTES: UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
SIZE FSCM NO. DWG NO.
D
SCALE CADFILE NO. SHEET
NONE
PLOT DATE:
Thu Sep 07, 2000
SH-000850-00
RMX850-3.sch
1
28 QSC Audio Products, Inc.
REV
3
OF
32
Page 31

THIS DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY
INFORMATION WHICH IS THE PROPERTY OF
QSC AUDIO PRODUCTS, THAT MAY NOT BE
DISCLOSED, REPRODUCED OR USED WITHOUT
EXPRESS WRITTEN CONSENT FROM QSC
AUDIO PRODUCTS.
D
C
IEC AC INLET
B
8 67 5
RECTIFIERS BR100, 200 AND C127–227 ARE
LOCATED OFF THE MAIN PCB, MOUNTED
AC VOLTAGE
PROGRAMMING
TERMINALS
AC INPUT,HIGH (ALL)
100V 120V 240V
TRANSFORMER PRI LEADS
BRN
BRN
GRY
GRY
BLK
BLU BLU
-
-
--
WHT
RED
BLU
BLK
RED
WHT
AC INPUT,LOW (ALL)
!
CIRCUIT BREAKER
USA: 10A-125V
EUROPE: 5A-250V
1
LINE
2
NEUT
3
GND
BRN
-
BLK
GRY
RED
-
WHT
!
JSW
JP12
TO POWER SWITCH
JP10
!
R21
1 OHM 30A
QUICK
CONNECT
PC-MTD
TABS
J2A
J3A
J4A
J5A
J6A
J7A
J8A
J9A
20 VAC TO FANPOWER RECTIFIER
U-I CORE POWER TRANSFORMER
NOTE SPLIT SECONDARY WIRING
FROM EACH LEG TO EACH CHANNEL
120V
BRN
20V
BLU
0V
BLK
COIL ONE
COIL TWO
120V
GRY
20V
RED
0V
WHT
TO CHASSIS.
E1
E2
E3
E4
E5
E6
E7
E8
F100
10A-125V
F200
10A-125V
C127
0.22-200V
C227
0.22-200V
MAINTAIN FULL
PRI-SEC CREEPAGE
J21:3
3
BR100
3
400V-25A
AC2
1
4
+
-
AC1
2
BR200
2
400V-25A
AC1
1
4
+
-
AC2
3
E13
E14
E15
E16
R1
1.1 AMP
J157:3
3
E9
E10
E11
E12
+VCC_A
-VCC_A
+VCC_B
-VCC_B
1
BR1
+
200V-1A
3
4
AC2
AC1
-
2
C6
1000-35V
D1
1N4004
LD1
GRN
PILOT
LED
R2
15K-2W
R3
1.0M
^R_1206
D2
1N4148
8
8
R4
60C 100 OHM
ATTACHTO HS-2
SEE SH 1
28V PRI-SIDE DC FAN SUPPLY
ATTACHTO HS-1
TH_A
9
9
MUTING AND THERMAL PROTECTION.
R27
220K
^R_1206
D15
^R_1206
R5
15K-2W
D3
1N4148
60C 100 OHM
J204:9
J104:9
R6
1.0M
J104:8
J204:8
R7
1N4148
D5
1N4148
1N4148
1N4148
15V
R26
220K
^R_0805
2500V
HI-POT
J21:1
J157:1
1
Q1
300V-.2A
R8
2.0K
^R_0805
J157:2
2
J21:2
2
!
1
5
4
263
1
D4
D7
D6
R10
150K
^R_1206
C7
4.7-250V
MAINTAIN FULL
PRI-SEC CREEPAGE
U2
4N29
R12
470K
^R_1206
^R_1206
R15
470K
P1
D14
1N4148
C8
47-50V
R9
R13
+14V
1N4004
D12
1N4004
D11
1N4004
D10
1N4004
+
-
D13
2
2
J104:1
J204:1
+15V_B
J204:2
J104:2
-15V_B
C11
.1-5OV
+15V_A
-15V_A
BR_CUT
R25
47
^R_0805
3904
3906
Q8
Q6
J104:3
3
J204:3
3
BR_CUT
Q9
3904
P1
Q7
3906
D8
15V
6.81K
^R_1206
2.0K
^R_0805
1N4148
R14
R18
220K
^R_1206
P1
Q4
3906
R19
D9
P1
6.81K
^R_1206
Q3
TIP31C
6.8K
R17
120-2W
^R_1206
-14V
Q5
MPSW05
1
1
J18:1
1
TO DC FAN
J18:2
2
D1432
C
B
DWGNO.
SH-000850-00
SH
3
REV
3
A
A
7.5 RMX 850 Schematic Diagram 3 of 3
SIZE FSCM NO. DWG NO.
D
SCALE CADFILE NO. SHEET
NONE
PLOT DATE:
Thu Sep 07, 2000
SH-000850-00
RMX850-3.sch
1
NOTES: UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED
8
Power Supply
7
6
5
4
3
2
RMX Series Technical Service Manual 29
REV
3
OF
33
Page 32

THIS DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY
INFORMATION WHICH IS THE PROPERTY
OF QSC AUDIO PRODUCTS, THAT MAYNOT
BE DISCLOSED, REPRODUCED OR USED
WITHOUT EXPRESS WRITTEN CONSENT FROM
QSC AUDIO PRODUCTS.
8
3-01-00
3-02-00
3-10-00
1
APPROVED / DATEEFF.DATE CHK
7
6
5
4
3
2
REV
1
PROTOTYPE RELEASE
2 CLEAN UP BY PHQ
3
4 CLEAN UP BY AA
DESCRIPTION
REVISION
D
C
CLIP LIM A (1)
FILTER 30 HZ (2)
FILTER BYPASSA (3)
B
FILTER BYPASSB (8)
FILTER 30 HZ (9)
CLIP LIM B (10)
J101
J102
J202
J201
PARALLEL
INPUTS
(4, 5)
BRIDGE
MONO
(6, 7)
CH1_+IN
CH1_-IN
CHASSIS_GND
CH2_-IN
FIVE POSITION BARRIER STRIP
CH2_+IN
BR-POS
BR-NEG
D
C
B
DWGNO.
SH-001451-00
SH
1
1
REV
4
+15V_A
220-25V
15V-1W
8
U101:2
4
NE5532
15V-1W
220-25V
CHANNEL-1
C112
D101
P1
7
D100
P1
C113
4
J204:4
C114
R124
R125
47K
^R_1206
0.001u, 100V 5%
47
1N4148
1N4148
LD100
RED
CLIP CH 1
J104:4
^C_1206
^R_0805
D102
D103
4
R127
Q101
3904
D104
1N4148
7
7
P1
R130
^R_1206
D105
1N4148
D106
1N4148
100
^R_0805
R128
10K
^R_0805
820
J104:7
J204:7
P1
R129
1.5K
^R_0805
Q102
3904
D107
5.6V-.25W
R131
BIAS
R135
3.0K-5W
^C_1206
R134
50
NTC
J104:5
J204:5
J204:6
J104:6
R137
22-1W
FP
R136
22-1W
FP
R139
R140
Q103
2SA1943
R142
0.22-3W
Q107
2SA1943
R148
0.22-3W
Q109
2SA1943
R152
D116
Q105
MJE15032
D113
1N4148
C117
CW
.0033
W
NEG
2.2K
CURRENT
LIMIT
CCW
CCW
POS
CURRENT
2.2K
LIMIT
W
C118
.0033
CW
D114
1N4148
R146
6.8-1W
R147
6.8-1W
Q106
MJE15033
1N4148
C119
P1
.022
D115
1N4148
Q104
2SC5200
R143
0.22-3W
Q108
2SC5200
R149
0.22-3W
Q110
2SC5200
R153
D112
1N4148
5
5
LD101
YELLOW
SIG CH 1
6
6
D108
1N4934
C115
0.0022u, 10%
D109
1N4934
CW
W
100
C116
.022
CCW
D110
5.6V-.25W
820
R132
^R_1206
D111
1N4148
R133
3.0K-5W
0.22-3W
0.22-3W
Q111
2SA1943
2SC5200
+78V
3300-100V
R157
1K-5W
R158
1K-5W
3300-100V
Q112
+VCC_A
D117
R156
0.22-3W
1N4004
P1
C120
C121
R159
-78V
0.22-3W
D118
1N4004
3300-100V
3300-100V
P1
-VCC_A
C122
C123
BR_BAL
SPEAKER CONNECTORS
ON BREAK-AWAYPCB.
JP14
5-WAY
BINDING
POST
CH 1
JP13
J104:11
J204:11
CONTINUED, SHEET 2
CHANNEL 1
SPEAKER OUTPUT PCB
J103 +
1+
J100
1-
J103 -
2+
2-
SPEAKON
R160
5.6-2W
250V
R161
12-5W
C124
.068-5%
L100
WIRES TO
BREAK-AWAY
SPEAKER
OUTPUT PCB
R162
12-5W
E100
2uH
E101
P1
11
11
33K
R22
^R_1206
^R_0805
33K
R23
^R_1206
SP_B
SP_A
R24
3.3K
P1
26-LINE RIBBON CABLE
CONNECTS BREAKAWAY
INPUT PCB TO MAIN PCB
^R_0805
C102
0.1-50V
10%
^C_1206
U10:1
LM13600M
5
1
R103
R102
C101
180p-5%
^C_0805
R105
10.0K
^R_0805
NE5532
U101:1
+
3
1K
-
2
R106
10.0K
^R_0805
C103
180p-5%
^C_0805
SEE SH 3
+14V
11
3
+
2
4
-
6
C104
.1-50V-10%
^C_1206
10.0K
^R_0805
150K
R104
^R_1206
-14V
SEE SH 3
2
3
1
RING
R
TIP
T
S
J5:5
5
J5:4
4
J5:3
J5:2
J5:1
RING
TIP
C1
470p 5%
GND
SW1:1
SW1:2
SW1:3
SW1:4
SW1:5
SW1:6
SW1:7
SW1:8
SW1:9
SW1:10
^C_1206
C2
470p 5%
^C_1206
11
12
13
14
15
BR M SEND (HI-SIG A)
BR MONO FEED
16
17
18
19
20
FILTSEND B (POT)
3
2
1
R
T
S
2
3
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
C3
C4
CLIP-LIM A
FILT-CAPA
FILT-SENDA
FILT-BYPA
FILTBYP B
FILTCAP B
CLIP LIM B
-IN B
+IN B
J1:1
J203:1
1
GND
2
+IN A
3
-IN A
470p 5%
^C_1206
4
470p 5%
^C_1206
5
6
GND
7
8
9
J1:10
10
GND
J1:11
11
J1:12
12
GND
J1:13
13
J1:14
14
GND
J1:15
15
J1:16
16
J1:17
17
J1:18
18
J1:19
19
J1:20
20
J1:21
21
GND
J1:22
22
J1:23
23
GND
J1:24
24
J1:25
25
J1:26
26
GND
1
J1:2
J203:2
2
J1:3
J203:3
3
J1:4
J203:4
4
J1:5
J203:5
5
J1:6
J203:6
6
J1:7
J203:7
7
J1:8
J203:8
8
J1:9
J203:9
9
J203:10
10
J203:11
BR MONO FEED
11
J203:12
12
J203:13
BR_RET
13
J203:14
14
J203:15
15
J203:16
16
J203:17
17
J203:18
18
J203:19
19
J203:20
20
J203:21
21
J203:22
22
J203:23
23
J203:24
24
J203:25
25
J203:26
26
A1
FILT-CAPA
FILT-SENDA
FILT-BYPA
SW TO GND FOR CLIP LIM
BR_BAL
BR_CUT
F_BYP_B
F_SND_B
F_30_B
CLIP_B
-IN_B
+IN_B
R100
10.0K
^R_0805
R101
10.0K
^R_0805
8
^U_LM13600
P1
7
R107
1
C105
A1
R108
39K
^R_0805
R109
100-25V
C100
0.1-50V 10%
^C_1206
ROUTE THIS GROUND
TO "A" GND AT
JI-2 INPUT CABLE
C106
10-50NP
CW
R112
10K
CCW
A1
10K LINEAR 3B
RIGHT ANGLE POT
7.50K
^R_0805
^R_0805
100
100
R110
A1
^R_0805
P1
^R_0805
R111
270
R20
6.8-1W
CHANNEL 1 GAIN
R113
W
270
^R_0805
R114
A1
ROUTE THIS GROUND
TO "P" GND AT
HEATSINK COMMON
BETWEEN CH A AND CH B
12
P1A1
NC
12
NC
13
NC
13
C107
.22-5%
C108
.15-5%
4.7K
^R_0805
A1
Q100
3906
J104:10
J204:10
R126
1K
^R_0805
J204:12
J104:12
J104:13
J204:13
R116
R117
+VCC_A
500K
.15-5%
20.0K
10
10
TH_A
SEE SH 3
^R_1206
C109
^R_0805
A1
SP_A
MODEL R116
700 383K
1200 499K
R121
R115
^R_1206
R118
R119
^R_0805
820
R120
270
150K
150K
^C_0805
20.0K
^R_1206
^R_1206
C110
56p
^R_0805
-15V_A
56p-200V-COG
13.3K-1%-1/2W
R123
11.3K-1%-1/2W
6
-
5
+
^C_1206
C111
R122
A
5. J104, J204 ARE CONNECTED PIN TO PIN BY 13-LINE RIBBON CABLE.
4. PART NUMBERING SCHEME
PARTS IN COMMON TO BOTH CH: 1-99. CH 1 PARTS 101-199, CH 2 PARTS 201-299.
3. COMPONENTS MARKED WITH ARE SAFETY CRITICAL PARTS.
2. COMPONENTS WITH VALUE PREFIXED WITH A "^" REPRESENT SMT COMPONENTS.
1. THIS DRAWING USED IN CONJUNCTION WITH ASSEMBLY WP-001451-00
NOTES: UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED
signal path
!
8
Gray shading indicates
7.6 RMX 1450 Schematic Diagram 1 of 3
Channel 1
7
6
5
4
NEXT ASSY USED ON
RMX 1450WP-001451-00
APPLICATION
3
ITEM NO.QTY PART NO.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED
DIMENSIONS ARE IN INCHES.
DIMENSIONS PER ANSI Y14.5-1982
TOLERANCES ARE:
DECIMALS
DECIMALS
+
+
.XXX
.XX
-
DEBURR EDGES .XXX R MAX
MATERIAL
FINISH
-
DO NOT SCALE DRAWING
ANGLES
CONTRACT NO.
O
DRAWN
CHECKED
ISSUED
CAD SEED FILE NO.
APPROVALS
PATQUILTER
DATE
2-25-00
DESCRIPTION
PARTS LIST
AUDIO PRODUCTS, INC.
COSTA MESA, CALIFORNIA
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
VENDOR
A
RMX 1450
SIZE FSCM NO. DWG NO.
PLOT DATE:
2
D
SCALE CADFILE NO. SHEET
Thu Sep 07, 2000
NONE
P:GPE
PRODUCTS\PRMX-SERIESQSC145
0
SH-001451-00
RMX1450-4.sch
1
PLOT DATE:
Thu Sep 07, 2000
REV
4
3OF1
30 QSC Audio Products, Inc.
Page 33

THIS DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY
INFORMATION WHICH IS THE PROPERTY
OF QSC AUDIO PRODUCTS, THAT MAYNOT
BE DISCLOSED, REPRODUCED OR USED
WITHOUT EXPRESS WRITTEN CONSENT FROM
QSC AUDIO PRODUCTS.
8 67 5
1432
D
D
CHANNEL-2
C201
180p-5%
^C_0805
R205
A1
10.0K
^R_0805
NE5532
1K
10.0K
150K
SEE SH 3
^R_0805
^R_1206
-14V
U201:1
+
3
1
-
2
R206
10.0K
^R_0805
C203
180p-5%
^C_0805
C206
10-50NP
R212
10K
10K LINEAR 3B
RIGHT ANGLE POT
CW
R213
W
270
^R_0805
CCW
A1
R216
500K
^R_1206
C207
.22-5%
+15V_B
C212
220-25V
D201
15V-1W
P1
C210
56p
C209
.15-5%
^R_0805
+VCC_B
-VCC_B
A1
R218
R219
R221
150K
^R_1206
150K
^R_1206
R220
270
^R_0805
20.0K
^C_0805
^R_0805
8
6
-
5
+
4
-15V_B
C211
56p-200V-COG
^C_1206
R222
13.3K-1%-1/2W
U201:2
NE5532
D200
15V-1W
220-25V
7
P1
C213
CLIP CH 2
3906
Q200
R214
C208
.15-5%
R217
^R_0805
R215
820
20.0K
^R_1206
4.75K
A1
SEESH3
+14V
R208
7.50K
^R_0805
R207
39K
^R_0805
14
+
15
13
-
^R_0805
100
100
R211
C205
100-25V
R210
270
^R_0805
R209
^R_0805
A1
10
^R_0805
U10:2
LM13600M
12
16
R202
R200
+IN_B
10.0K
^R_0805
SEE SH 1
R201
-IN_B
10.0K
^R_0805
C
SEE SH 1
F_30_B
F_SND_B
F_BYP_B
9
R203
B
SEE SH 1
CLIP_B
SW-GND FOR CLIP LIM
SEE SH 1
BR MONO RETURN -- CAUTION, SENSITIVE NODE
BR_RET
R204
C214
R224
^R_1206
0.001u, 100V 5%
47
LD200
RED
R226
47K
^R_0805
D202
1N4148
D203
1N4148
^C_1206
Q201
R227
3904
D204
1N4148
100
P1
^R_0805
D205
1N4148
D206
1N4148
^R_0805
R228
R229
1.5K
10K
^R_0805
Q202
P1
3904
R230
D208
D209
CW
R231
100
BIAS
CCW
R232
820
^R_1206
D207
5.6V-.25W
1N4934
C215
1N4934
W
C216
.022
D210
5.6V-.25W
820
^R_1206
D212
1N4148
LD201
YELLOW
SIG CH 2
0.0022u, 10%
R235
3.0K-5W
^C_1206
R234
50
NTC
R236
22-1W
R239
R240
+78V
R242
0.22-3W
R248
0.22-3W
R252
0.22-3W
FP
Q203
2SA1943
Q207
2SA1943
Q209
2SA1943
Q211
2SA1943
P1
D216
Q205
MJE15032
D213
C217
1N4148
.0033
CW
W
NEG
2.2K
CURRENT
LIMIT
CCW
CCW
POS
CURRENT
2.2K
LIMIT
W
C218
CW
.0033
D214
1N4148
R246
6.8-1W
R247
6.8-1W
Q206
MJE15033
1N4148
3300-100V
R257
C219
P1
.022
1.0K-5W
R258
1.0K-5W
D215
3300-100V
1N4148
Q204
2SC5200
Q208
2SC5200
Q210
2SC5200
Q212
2SC5200
D211
R233
3.0K-5W
1N4148
R237
22-1W
FP
R243
0.22-3W
R249
0.22-3W
R253
0.22-3W
R256
C220
C221
R259
0.22-3W
0.22-3W
-78V
D217
1N4004
D218
1N4004
+VCC_B
3300-100V
3300-100V
P1
-VCC_B
C222
C223
R260
5.6-2W
C224
250V
R261
12-5W
L200
2uH
.068-5%
C
JP15
5-WAY
BINDING
POST
CH 2
JP16
CHANNEL 2
SPEAKER OUTPUT
J203 +
J200
J203 -
SPEAKER CONNECTORS
ON BREAKAWAYPCB
FROM SHEET ONE
BR-POS
TO CH 1
SHEET 1
2+
1+
2-
1-
SPEAKON
BR-NEG
WIRES TO
SPEAKER
OUTPUT PCB
R262
12-5W
P1
E200
E201
B
DWGNO.
SP_B
SH-001451-00
SH
2
REV
4
A
Gray shading indicates
signal path
A
7.7 RMX 1450 Schematic Diagram 2 of 3
Channel 2
NOTES: UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
SIZE FSCM NO. DWG NO.
D
SCALE CADFILE NO. SHEET
NONE
PLOT DATE:
Thu Sep 07, 2000
SH-001451-00
RMX1450-4.sch
1
RMX Series Technical Service Manual 31
OF
23
REV
4
Page 34

THIS DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY
INFORMATION WHICH IS THE PROPERTY
OF QSC AUDIO PRODUCTS, THAT MAYNOT
BE DISCLOSED, REPRODUCED OR USED
WITHOUT EXPRESS WRITTEN CONSENT FROM
QSC AUDIO PRODUCTS.
D
C
IEC AC INLET
B
8 67 5
RECTIFIERS BR100, 200 AND C127-227 ARE
LOCATED OFF THE MAIN PCB, MOUNTED
TO CHASSIS.
E1
E2
E3
E4
E5
E6
E7
E8
!
F100
12A-125V
!
F200
12A-125V
C127
0.22-200V
C227
0.22-200V
MAINTAIN FULL
PRI-SEC CREEPAGE
J21:3
3
BR100
3
400V-25A
AC2
1
4
+
-
AC1
2
BR200
2
400V-25A
AC1
1
4
-
+
AC2
3
AC VOLTAGE
PROGRAMMING
TERMINALS
AC INPUT,HIGH (ALL)
100V 120V 240V
TRANSFORMER PRI LEADS
BRN
GRY
BLU BLU
-
--
RED
BLK
WHT
BRN
BLK
GRY
RED
WHT
BRN
GRY
BLK
-
WHT
BLU
RED
AC INPUT,LOW (ALL)
!
CIRCUIT BREAKER
USA: 15A-125V
EUROPE: 7.5A-250V
1
LINE
2
NEUT
3
GND
-
-
JSW
TO POWER SWITCH
!
R21
1 OHM 30A
!
JP12
JP10
U-I CORE POWER TRANSFORMER
NOTE SPLIT SECONDARY WIRING
FROM EACH LEG TO EACH CHANNEL
BRN
QUICK
CONNECT
PC-MTD
TABS
BLU
J2A
BLK
J3A
J4A
J5A
GRY
J6A
J7A
RED
WHT
J8A
J9A
20 VAC TO FANPOWER RECTIFIER
!
120V
20V
0V
COIL ONE
COIL TWO
120V
20V
0V
E13
E14
E15
E16
R1
1.1 AMP
J157:3
3
E9
+VCC_A
E10
-VCC_A
E11
+VCC_B
1N4004
R2
15K-2W
1.0M
^R_1206
D1
LD1
GRN
PILOT
LED
R3
E12
-VCC_B
MUTING AND THERMAL PROTECTION.
^R_1206
R27
220K
^R_1206
D15
^R_1206
R5
15K-2W
1.0M
R6
1N4148
D5
1N4148
15V
D4
Q1
300V-.2A
C7
4.7-250V
R26
220K
^R_0805
D7
MAINTAIN FULL
R8
PRI-SEC CREEPAGE
2.0K
^R_0805
150K
+14V
D12
1N4004
D11
1N4004
D10
1N4004
D13
1N4004
2
2
J104:1
J204:1
+15V_B
J204:2
J104:2
-15V_B
C11
.1-5OV
+15V_A
-15V_A
BR_CUT
R25
47
^R_0805
3904
3906
Q8
J104:3
3
J204:3
3
BR_CUT
Q6
Q9
3904
P1
Q7
3906
1N4148
R15
470K
^R_1206
D8
15V
C8
47-50V
P1
D14
R18
220K
^R_1206
3906
P1
Q4
R19
6.81K
^R_1206
Q5
MPSW05
1
1
D9
1N4148
P1
-14V
R10
1N4148
D6
1N4148
8
8
60C 100 OHM
ATTACHTO HS-1
9
9
D3
J104:8
J204:8
R7
J204:9
J104:9
1N4148
2500V
HI-POT
D2
1N4148
R4
60C 100 OHM
ATTACHTO HS-2
TH_A
1
BR1
+
200V-1A
3
4
AC2
AC1
-
2
C6
1000-35V
SEE SH 1
28V PRI-SIDE DC FAN SUPPLY
J157:2
2
J21:2
2
!
1
5
U2
4
263
4N29
R12
J21:1
1
J157:1
1
470K
^R_1206
R9
R13
6.81K
2.0K
^R_1206
^R_0805
R14
6.81K
^R_1206
Q3
TIP31C
R17
120-2W
J18:1
1
TO DC FAN
J18:2
2
+
-
D1432
C
B
DWGNO.
SH-001451-00
SH
3
REV
4
A
A
7.8 RMX 1450 Schematic Diagram 3 of 3
SIZE FSCM NO. DWG NO.
D
SCALE CADFILE NO. SHEET
NONE
PLOT DATE:
Thu Sep 07, 2000
SH-001451-00
RMX1450-4.sch
1
NOTES: UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED
8
Power Supply
7
6
5
4
3
2
32 QSC Audio Products, Inc.
OF
33
REV
4
Page 35

THIS DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY
INFORMATION WHICH IS THE PROPERTY
OF QSC AUDIO PRODUCTS, THAT MAYNOT
BE DISCLOSED, REPRODUCED OR USED
WITHOUT EXPRESS WRITTEN CONSENT FROM
QSC AUDIO PRODUCTS.
D
2
3
1
RING
R
TIP
T
S
J5:5
CH1_+IN
J5:4
CH1_-IN
J5:3
CHASSIS_GND
J5:2
CH2_-IN
FIVE POSITION BARRIER STRIP
J5:1
CH2_+IN
RING
R
TIP
T
S
2
3
1
Gray shading indicates
signal path
C
CLIP LIM A (1)
FILTER 30 HZ (2)
FILTER BYPASSA (3)
B
FILTER BYPASSB (8)
FILTER 30 HZ (9)
CLIP LIM B (10)
A
J101
J102
J202
J201
PARALLEL
INPUTS
(4, 5)
BRIDGE
MONO
(6, 7)
R162
12-5W
R155
12-5W
E100
E101
R22B
R23B
2N5064
68K
68K
D120
5-WAY
BINDING
POST
CH 1
1
R163
10-1/4W
R164
100-1/4W
SPEAKER CONNECTORS
ON BREAK-AWAYPCB.
CONTINUED, SHEET 2
CHANNEL 1
SPEAKER OUTPUT PCB
JP14
J103 +
J100
J103 -
JP13
WIRES TO
BREAK-AWAY
SPEAKER
OUTPUT PCB
68K
R22A
^R_1206
^R_1206
68K
R23A
^R_1206
^R_1206
SP_B
G
P1
1+
1-
R24
3.01K
^R_0805
D
MT2
Q113
MAC224
MT1
C
BR-POS
2+
2-
SPEAKON
BR-NEG
B
P1
DWGNO.
SH-002451-00
SH
2
REV
4
C173
100-25V
P1
1N4148
R156
0.22-3W
R159
0.22-3W
100-25V
Q170
RFZ44
^D_SOT-23
TO -VMED
R181
1.5-2W
D117
1N4004
D118
1N4004
R182
1.5-2W
C180
2
P1
MUR1520
R188
D178
R180
5.1K-5W
D175
MUR1520
D176
5.1K-5W
C120
12000-63V
C174
0.1-250V
C121
12000-63V
SEE SH 3
CT_A
C122
12000-63V
C175
.1-250V
C123
12000-63V
12V-1W-1N4742A
F100
25A-125V
+110_A
+55_A
R165
15K-1W
R160
5.6-2W
0.068-250V
R161
12-5W
R154
12-5W
0.068-250V
-55_A
-110_A
DC FAULT
PROTECTION
D119
2N5064
C129
22-25NP
L100
2uH
C124
P1
C126
BR_BAL
8
7
6
CHANNEL-1
26-LINE RIBBON CABLE
CONNECTS BREAKAWAY
INPUT PCB TO MAIN PCB
C101
180p-5%
LM13600M
A1
U10:1
5
R102
1K
^R_0805
P1
1
R103
-14V
10.0K
^R_0805
^C_0805
C103
180p-5%
^C_0805
C102
.1-50V-10%
^C_1206
11
+
-
6
3
2
R104
^R_0805
NE5532
U101:1
+
-
^R_0805
+14V
3
2
4
C104
150K
J1:1
J2:1
1
GND
J1:2
2
+IN A
5
4
C1
470p 5%
GND
SW1:1
SW1:2
SW1:3
SW1:4
SW1:5
SW1:6
SW1:7
SW1:8
SW1:9
SW1:10
^C_1206
C2
470p 5%
^C_1206
11
12
13
14
15
BR M SEND (HI-SIG A)
BR MONO FEED
16
17
18
19
20
FILTSEND B (POT)
3
2
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
C3
C4
CLIP-LIM A
FILT-CAPA
FILT-SENDA
FILT-BYPA
FILTBYP B
FILTCAP B
CLIP LIM B
-IN B
+IN B
J1:3
3
-IN A
470p 5%
^C_1206
J1:4
4
470p 5%
^C_1206
J1:5
5
J1:6
6
GND
J1:7
7
J1:8
8
J1:9
9
J1:10
10
GND
J1:11
11
J1:12
12
GND
J1:13
13
J1:14
14
GND
J1:15
15
J1:16
16
J1:17
17
J1:18
18
J1:19
19
J1:20
20
J1:21
21
GND
J1:22
22
J1:23
23
GND
J1:24
24
J1:25
25
J1:26
26
GND
J2:2
J2:3
J2:4
J2:5
J2:6
J2:7
J2:8
J2:9
J2:10
J2:11
J2:12
J2:13
J2:14
J2:15
J2:16
J2:17
J2:18
J2:19
J2:20
J2:21
J2:22
J2:23
J2:24
J2:25
J2:26
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
A1
FILT-CAPA
FILT-SENDA
SW TO GND FOR CLIP LIM
BR MONO FEED
BR_RET
C132
47P-50V
^C_1206
A1
BR_BAL
BR_CUT
C130
100p-50V
^C_1206
F_BYP_B
F_SND_B
F_30_B
CLIP_B
-IN_B
+IN_B
FILT-BYPA
R100
10.0K
^R_0805
R101
10.0K
^R_0805
8
R197
100
^R_0805
7
R105
10.0K
R106
10.0K
.1-50V-10%
^R_1206
1
R107
C105
39K
^C_1206
ROUTE THIS GROUND
TO "A" GND AT
JI-2 INPUT CABLE
A1
10K LINEAR 3B
RIGHT ANGLE POT
R108
7.50K
^R_0805
100
R109
100-25V
C106
47-10NP
R112
10K
^R_0805
^R_0805
R111
820
^R_0805
CW
CCW
100
R110
A1
R20
3.3-1W
A1 P1
R_RES1W
CHANNEL 1 GAIN
R113
W
274
^R_0805
A1
270
R196
^R_0805
C131
.001-5%
R114
A1
^R_0805
Q100
3906
^Q_BJTP_SOT-23
ROUTE THIS GROUND
TO "P" GND AT
HEATSINK COMMON
BETWEEN CH A AND CH B
C107
.22-5%
C108
.15-5%
4.7K
^R_0805
A1
R115
A1
A1
^R_0805
SPEAKER BUS -- BEFORE FUSE
27p-200V-COG
820K
R116
^R_1206
C109
.15-5%
24K
R117
^R_0805
820
^R_1206
C125
100-16NP
R138
4.7K
^R_0805
R126
1K
R166
464K
^R_1206
C111
^C_1206
R121
R120
^R_0805
24K
390
5
6
5
^R_0805
23.2K-1%-1/2W
R123
23.2K-1%-1/2W
R167
464K
^R_1206
R122
4
C172
.0033
R190
2.00K
^R_0805
+15V_A
220-25V
D101
15V-1W
C110
27p
^C_0805
8
-
7
+
U101:2
4
NE5532
D100
15V-1W
C113
-15V_A
R173
150K
^R_1206
R177
12K-1W
R178
150K
^R_1206
^Q_BJTN_SOT-23
R125
47K
^R_1206
C114
C112
0.0015u, 250V
P1
75
R124
1N4148
^D_SOT-23
1N4148
^D_SOT-23
LD100
RED
220-25V
CLIP CH 1
SPEAKER BUS -- AFTER FUSE
R194
12K-1W
R195
2.00K
^R_0805
C179
.0033
^C_1206
^R_0805
D102
D103
Q101
3904
D104
1N4148
^D_SOT-23
^D_SOT-23
^D_SOT-23
100
R127
P1
R174
4.7K
^R_0805
R179
4.7K
^R_0805
^R_0805
D105
1N4148
D106
1N4148
^R_0805
R186
150K
^R_1206
R192
150K
^R_1206
.36W at full clip
R128
10K
P1
^Q_BJTN_SOT-23
POS STEP DRIVER
3.9V
D170
R172
470K
^R_0805
1
2
3
4
D174
10V-1N4740A
R129
1.5K
^R_0805
C181
D112
0.01
Q102
3904
R130
820
^R_1206
D107
5.6V-.25W
D108
1N4934
C115
D109
1N4934
CW
R131
W
100
C116
BIAS
.022
CCW
D110
5.6V-.25W
820
R132
^R_1206
D111
1N4148
^D_SOT-23
R183
47K
^R_0805
R185
470K
R187
^R_0805
4.7K
^R_0805
R193
4.7K
^R_0805
R171
U170
8
^U_LM311
GND
V+
7
6
BAL/STR
^LM311-SMT
^D_SOT-23
LD101
^C_1206
0.0022u, 10%
R134
50
NTC
R133
8.2K-5W
R135
8.2K-5W
R118
8.2K-5W
R119
8.2K-5W
5
BAL
+110_A
R136
22-1W
1N4148
^D_SOT-23
R139
2.2K
R140
2.2K
1N4148
^D_SOT-23
R137
22-1W
FP
-110_A
V-
1N4148
YELLOW
SIG CH 1
C176
47pF-50V-5%
^C_0805
U171
1
GND
2
3
4
V-
^U_LM311
^LM311-SMT
BAL/STR
8
V+
C178
7
6
5
BAL
NEG STEP DRIVER
5.90K
R175
3.01K
^R_0805
FP
CW
CCW
CCW
CW
^R_0805
D113
W
NEG
CURRENT
LIMIT
POS
CURRENT
LIMIT
W
D114
R184
^C_1206
.1-50V-10%
D171
1N4148
^D_SOT-23
Q103
2SA1943
Q104
2SC5200
5.90K
1N4148
^D_SOT-23
^R_0805
3
^Q_BJTP_SOT-23
R142
R_RES1W
R_RES1W
R143
^R_0805
D177
R191
2.2K
^Q_BJTN_SOT-23
Q171
3904
Q172
3906
0.22-3W
Q107
2SA1943
Q105
MJE15032
R146
3.3-1W
R147
3.3-1W
Q106
MJE15033
Q108
2SC5200
0.22-3W
Q173
3904
Q175
3906
C170
47pF-50V-5%
^C_0805
10-35V
R148
0.22-3W
Q109
2SA1943
D116
1N4148
^D_SOT-23
C119
P1
.022
D115
1N4148
^D_SOT-23
Q110
2SC5200
R149
0.22-3W
C177
47pF-50V-5%
^C_0805
^Q_BJTN_SOT-23
R189
47
^R_0805
^Q_BJTP_SOT-23
C171
R176
R152
R153
12K
0.22-3W
Q111
2SA1943
2.2K-5W
2.2K-5W
2.2K-5W
2SC5200
0.22-3W
R170
47
^R_0805
^R_0805
R198
R157
R158
Q112
Q174
RFZ44
D173
A
7.9 RMX 2450 Schematic Diagram 1 of 3
SIZE FSCM NO. DWG NO.
D
SCALE CADFILE NO. SHEET
NONE
P:GPE
PRODUCTS\PRMX-SERIESQSC245
0
SH-002451-00
PLOT DATE:
Thu Sep 07, 2000
1
NOTES: UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED
8
Channel 1
7
6
5
4
3
2
RMX Series Technical Service Manual 33
REV
4
OF
42
Page 36

THIS DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY
INFORMATION WHICH IS THE PROPERTY
OF QSC AUDIO PRODUCTS, THAT MAYNOT
BE DISCLOSED, REPRODUCED OR USED
WITHOUT EXPRESS WRITTEN CONSENT FROM
QSC AUDIO PRODUCTS.
D
C
B
A
Gray shading indicates
signal path
8 67 5
+IN_B
SEE SH 1
-IN_B
SEE SH 1
F_30_B
F_BYP_B
F_BYP_B
SEE SH 1
CLIP_B
SEE SH 1
BR_RET
R200
10.0K
^R_0805
R201
10.0K
^R_0805
9
C201
180p-5%
^C_0805
R202
3
1K
^R_0805
2
SW-30 HZ
SW-FILTBYPASS
U10:2
LM13600M
10
-14V
+
12
16
-
R203
10.0K
^R_0805
150K
R204
C205
^R_1206
SW-GND FOR CLIP LIM
BR MONO RETURN -- CAUTION, SENSITIVE NODE
C272
.0033
R290
CHANNEL-2
2.00K
^R_0805
12K-1W
5
J204:5
5
J104:5
R205
A1
10.0K
^R_0805
NE5532
U201:1
+
1
-
R206
10.0K
^R_0805
C204
180p-5%
^C_0805
C206
47-10NP
R212
10K
10K LINEAR 3B
RIGHT ANGLE POT
J204:10
J104:10
CW
R213
W
274
^R_0805
CCW
A1
.22-5%
C207
SPEAKER BUS -- BEFORE FUSE
10
10
27p-200V-COG
820K
R216
^R_1206
R266
464K
^R_1206
C211
^C_1206
+15V_B
LD201
YELLOW
6
6
C212
220-25V
D201
15V-1W
J204:6
J104:6
C210
27p
-15V_B
^C_0805
8
6
-
7
5
+
U201:2
4
NE5532
D200
15V-1W
C213
220-25V
4
4
^R_0805
R214
A1
R215
4.7K
C208
.15-5%
^R_0805
.001
^R_0805
^R_0805
R210
C231
270
R296
A1
100
^R_0805
A1
+14V-A
R208
7.50K
R207
39K
^R_0805
14
15
13
100
R209
820
^R_1206
R217
24K
C209
.15-5%
^R_0805
R221
24K
^R_0805
R211
820K
^R_0805
100-25V
4-5 MA CHARGE CURRENT
1 MA DISCHARGE.
Q200
3906
^Q_BJTP_SOT-23
A1
C225
100-16NP
R238
4.7K
^R_0805
R220
390
^R_0805
R222
23.21K-1%-1/2W
R277
J104:4
J204:4
P1
P1
^R_0805
C_MYL2_AI
R295
2.00K
C279
.0033
C214
^R_0805
LD200
RED
CLIP CH 2
R273
150K
^R_1206
R278
150K
^R_1206
Q201
3904
^Q_BJTN_SOT-23
R225
4.7K
^R_1206
1N4148
^D_SOT-23
^C_1206
0.0015u, 250V 5%
R224
75
D202
1N4148
^D_SOT-23
D203
1N4148
^D_SOT-23
R227
R294
12K-1W
D204
R274
4.7K
^R_0805
R279
4.7K
^R_0805
7
7
^D_SOT-23
^D_SOT-23
100
P1
R228
10K
^R_0805
D205
1N4148
D206
1N4148
^R_0805
R_RES1W
^R_1206
^R_1206
R286
150K
R292
150K
POS STEP DRIVER
3.9V
D270
R272
^R_0805
D274
10V-1N4740A
R229
1.5K
^D_SOT-23
^R_0805
C281
0.01
Q202
3904
R231
BIAS
100
^R_0805
^Q_BJTN_SOT-23
R230
D208
1N4934
D209
1N4934
CW
W
C216
.022
CCW
R232
D211
1N4148
R283
47K
R287
4.7K
^R_0805
R293
4.7K
^R_0805
820
D207
5.6V-.25W
D210
5.6V-.25W
820
^D_SOT-23
P1
J204:7
J104:7
R271
470K
U270
1
2
3
4
D212
1N4148
GND
V-
^LM311-SMT
BAL/STR
R218
8.2K-5W
R219
8
V+
7
6
5
BAL
8.2K-5W
FP
SIG CH 2
^R_1206
^D_SOT-23
C215
0.0022u, 10%
^C_1206
R234
50
NTC
R239
R240
2.2K
2.2K
^D_SOT-23
^R_1206
R233
8.2K-5W
22-1W
R235
8.2K-5W
-110_B
C276
47pF-50V-5%
^C_0805
R285
470K
^R_0805
U271
1
GND
V-
^LM311-SMT
BAL/STR
V+
BAL
2
3
4
NEG STEP DRIVER
+110_B
R236
22-1W
1N4148
1N4148
R237
FP
8
7
6
5
5.90K
R275
3.01K
^R_0805
FP
CW
CCW
CCW
CW
^R_0805
D213
W
NEG
CURRENT
LIMIT
POS
CURRENT
LIMIT
W
D214
C278
D271
1N4148
^D_SOT-23
Q203
2SA1943
Q204
2SC5200
R284
^C_1206
.1-50V-10%
^Q_BJTP_SOT-23
R242
R246
3.3-1W
R247
3.3-1W
R243
5.90K
^R_0805
D277
1N4148
^D_SOT-23
R291
2.2K
^R_0805
^Q_BJTN_SOT-23
Q271
3904
Q272
3906
0.22-3W
Q207
2SA1943
Q205
MJE15032
R_RES1W
R_RES1W
Q206
MJE15033
Q208
2SC5200
0.22-3W
Q273
3904
Q275
3906
47pF-50V-5%
R248
0.22-3W
Q209
2SA1943
^D_SOT-23
P1
^D_SOT-23
2SC5200
R249
0.22-3W
^Q_BJTN_SOT-23
^Q_BJTP_SOT-23
C270
^C_0805
10-35V
D216
1N4148
C219
.022
D215
1N4148
Q210
C277
47pF-50V-5%
^C_0805
^R_0805
C271
R289
R276
47
R252
R253
12K
0.22-3W
Q211
2SA1943
2SC5200
0.22-3W
R270
^R_0805
^R_0805
R298
2.2K-5W
R257
2.2K-5W
R258
2.2K-5W
Q212
47
D273
C273
100-25V
P1
Q274
RFZ44
1N4148
R256
R259
0.22-3W
0.22-3W
Q270
RFZ44
^D_SOT-23
TO -VMED
D217
1N4004
D218
1N4004
P1
R282
1.5-2W
R288
100-25V
R281
1.5-2W
MUR1520
5.1K-5W
C280
R280
5.1K-5W
D275
MUR1520
D276
12000-63V
C274
.1-250V
12000-63V
SEE SH 3
CT_B
12000-63V
C275
.1-250V
12000-63V
D278
12V-1W-1N4742A
C220
C221
C222
C223
+110_B
+55_B
F200
25A-125V
-55_B
-110_B
R265
15K-1W
R260
5.6-2W
L200
2uH
C224
.068-250V
R261
12-5W
P1
R254
12-5W
C226
0.068-250V
11
11
C229
J204:11
J104:11
SP_B
DC FAULT
PROTECTION
D219
E200
E201
2N5064
JP15
5-WAY
BINDING
POST
CH 2
JP16
D220
J203 +
J203 -
22-25NP
WIRES TO
SPEAKER
OUTPUT PCB
R262
12-5W
R255
12-5W
2N5064
R263
10-1/4W
R264
100-1/4W
CHANNEL 2
SPEAKER OUTPUT
1+
J200
1-
SPEAKER CONNECTORS
ON BREAKAWAYPCB
FROM SHEET ONE
1432
D
MT2
G
Q213
MAC224
MT1
C
P1
BR-POS
TO CH 1
SHEET 1
2+
2-
SPEAKON
BR-NEG
B
DWGNO.
SH-002451-00
SH
3
REV
4
A
7.10 RMX 2450 Schematic Diagram 2 of 3
SIZE FSCM NO. DWG NO.
D
SCALE CADFILE NO. SHEET
NONE
PLOT DATE:
Thu Sep 07, 2000
SH-002451-00
RMX2450-4.sch
1
NOTES: UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED
8
Channel 2
7
6
5
4
3
2
34 QSC Audio Products, Inc.
REV
4
OF
43
Page 37

D
THIS DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY
INFORMATION WHICH IS THE PROPERTY
OF QSC AUDIO PRODUCTS, THAT MAYNOT
BE DISCLOSED, REPRODUCED OR USED
WITHOUT EXPRESS WRITTEN CONSENT FROM
QSC AUDIO PRODUCTS.
AC VOLTAGE
PROGRAMMING
TERMINALS
C
B
AC INPUT,HIGH (ALL)
100V 120V 240V
TRANSFORMER PRI LEADS
BRN
GRY
BLK
-
--
WHT
BLU
RED
AC INPUT,LOW (ALL)
CIRCUIT BREAKER
USA: 15A-125V
EUROPE: 7.5A-250V
IEC AC INLET
LINE
NEUT
GND
BRN
GRY
-
RED
BLK
WHT
1
2
3
8 67 5
RECTIFIER BR100-201 CIRCUIT
BRN
-
BLUBLU
BLK
GRY
RED
-
WHT
!
!
JP12
JSW
TO POWER SWITCH
JP10
!
R21
1 OHM 30A
QUICK
CONNECT
PC-MTD
TABS
J4A
J5A
J6A
J8A
J9A
J7A
J2A
J3A
20 VAC TO FANPOWER RECTIFIER
U-I CORE POWER TRANSFORMER
NOTE SPLIT SECONDARY WIRING
FROM EACH LEG TO EACH CHANNEL
BRN
120V
20V
BLU
0V
BLK
COIL ONE
COIL TWO
GRY
120V
20V
RED
0V
WHT
E1
E2
E3
E4
E5
E6
E7
E8
E9
E10
E11
E12
IS DRAWN FOR CHASSIS MTG
OF RECTIFIERS. E-POINTS ARE
WIRE CONNECTIONS.
0.22-250V
3
AC2
1
+
C128
0.22-250V
C228
0.22-250V
AC1
400V-25A
2
BR201
2
400V-25A
AC1
1
+
AC2
3
C127
4
-
BR101
4
-
0.22-250V
MAINTAIN FULL
PRI-SEC CREEPAGE
BR100 400V-25A
1
+
1
+
C227
R1
1.1 AMP
R29
12-5W
E112
E13
E114
E14
3
AC2
AC1
AC1
AC2
2
BR200
2
3
4
-
400V-25A
4
-
E113
E15
E115
E16
E212
E17
E214
E18
E213
E19
E215
E20
C10
0.047-400V
R28
12-5W
1
BR1
+
200V-1A
3
4
AC1
AC2
-
2
C6
1000-35V
CT_A
SEE SH 1
+110_A
+55_A
-55_A
-110_A
+110_B
+55_B
-110_B
-55_B
CT_A
SEE SH 2
CT_B
J21:1
1
J157:1
1
D1
1N4004
LD1
GRN
PILOT
LED
R2
33K-2W
R3
1.0M
D2
1N4148
^D_SOT-23
60C 100 OHM
ATTACHTO HS-2
8
8
R4
ATTACHTO HS-1
9
9
28V PRI-SIDE DC FAN SUPPLY
MUTING AND THERMAL PROTECTION.
R27
330K
^R_1206
^R_1206
R5
33K-2W
D3
1N4148
^D_SOT-23
J204:8
J104:8
R7
60C 100 OHM
J104:9
J204:9
1.0M
R6
^R_1206
1N4148
^D_SOT-23
D5
1N4148
^D_SOT-23
1N4148
^D_SOT-23
1N4148
^D_SOT-23
D15
15V
D4
Q1
300V-.2A
^Q_BJTN_SOT-23
R26
220K
^R_0805
D7
R8
D6
2500V HI-POT
J21:3
J157:3
3
3
2.0K
J157:2
2
2
!
^R_0805
J21:2
1
263
MAINTAIN FULL
PRI-SEC CREEPAGE
D1432
J104:12
J104:2
J204:2
+15_B
C11
.1-5OV
13
13
12
12
J204:12
+15V_A
^Q_BJTN_SOT-23
P1
3906
^Q_BJTP_SOT-23
-15V_A
J204:13
J104:13
Q9
3904
Q7
R25
47
^R_0805
Q8
3904
^Q_BJTN_SOT-23
Q6
3906
^Q_BJTP_SOT-23
BR_CUT
A1
3
3
C9
100pF
^C_1206
R30
100
^R_0805
J204:3
J104:3
BR_CUT-A
C
B
DWGNO.
+14V
+15V_A
Q5
MPSA06
1
1
-14V
2 PIN HEADER
1
2
1N4004
D13
1N4004
D11
1N4004
D10
1N4004
J18:1
TO DC FAN
J18:2
D12
2
2
J204:1
J104:1
+
-
-15V_B
-15V_A
1N4148
^D_SOT-23
R15
464K
^R_1206
R12
D8
15V
C8
47-50V
P1
D14
470K
^R_1206
^Q_BJTP_SOT-23
D9
1N4148
^D_SOT-23
R9
6.81K
^R_1206
R13
2.0K
^R_0805
R18
220K
^R_1206
3906
R14
P1
Q4
R19
6.8K
^R_1206
P1
6.81K
^R_1206
Q3
TIP31C
R17
120-2W
R10
150K
^R_1206
C7
4.7-250V
5
U2
4
4N29
SH-002451-00
SH
4
REV
4
A
A
7.11 RMX 2450 Schematic Diagram 3 of 3
SIZE FSCM NO. DWG NO.
D
SCALE CADFILE NO. SHEET
NONE
PLOT DATE:
Thu Sep 07, 2000
SH-002451-00
RMX2450-4.sch
1
NOTES: UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED
8
Power Supply
7
6
5
4
3
2
RMX Series Technical Service Manual 35
REV
4
OF
44
Page 38

THIS DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY
INFORMATION WHICH IS THE PROPERTY
OF QSC AUDIO PRODUCTS, THAT MAY NOT
BE DISCLOSED, REPRODUCED OR USED
WITHOUT EXPRESS WRITTEN CONSENT FROM
QSC AUDIO PRODUCTS.
D
8 7654321
REVISIONS
D
INPUT PCB
OUTPUT PCB
1724-340C-0102
E100
WHI
E101
E200
E201
GRY
WHI
GRY
26 CONDUCTOR RIBBON CABLE
WITH PIN-TO-PIN INTERCONNECTS
J1
1
J203
1
MAIN PCB
1724-330A-0001
JP14
JP13
JP15
JP16
J103
CH 1 SPKR OUTPUT
CH 1 SPKR COMMON
CH 2 SPKR OUTPUT
CH 2 SPKR COMMON
J203
REV DESCRIPTION EFF. DATE APPROVED/DATECHK
E9
E10
INPUT PCB
1724-340B-0102
26
WIRE ASSY
C
12
26
E112
GRN
E212
E11
E12
RED
BLK
RED
BLK
C
FAN ASSY
1
2
J128
3
3-PIN CABLE ASSY
J18
1
2
B
E1
E2
E3
E4
E5
E6
E7
E8
J21
-VCC_B
+_BVCC
1
2
3
B
DWG NO.
SH-0025000
TRANSFORMER
(1806-2505-0)
AC POWER CORD
A
HOT
GND
NEUT
BRN
GRN
BLU
CIRCUIT-
BREAKER
AC POWER
SWITCH
BRNBRN
RED •
BRN
BLU
GRN
BLK
BLU •
WHT
VIO
RED
GRY
120V 230V 100V
J3A J6A J3A
J7A J7A J9A
J9A J9A J7A
J8A J5A J4A
J4A J4A J8A
J2A J2A J2A
JP12
JP10
1724-340A-0102
PWR PCB
-VCC_A
+VCC_A
AUDIO PRODUCTS, INC.
COSTA MESA, CALIFORNIA
SH
1
REV
A
A
WIRING DIAGRAM,
RMX 850
1 OF 1
REV
A
NOTES: UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED
876 54321
36 QSC Audio Products, Inc.
SCALE
NONE
SHEET
7.12 RMX 850 Chassis Wiring Diagram
Page 39

THIS DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY
INFORMATION WHICH IS THE PROPERTY
OF QSC AUDIO PRODUCTS, THAT MAY NOT
BE DISCLOSED, REPRODUCED OR USED
WITHOUT EXPRESS WRITTEN CONSENT FROM
QSC AUDIO PRODUCTS.
D
8 7654321
REVISIONS
D
INPUT PCB
OUTPUT PCB
1724-340C-0102
E100
WHI
E101
E200
E201
GRY
WHI
GRY
26 CONDUCTOR RIBBON CABLE
WITH PIN-TO-PIN INTERCONNECTS
J1
1
J203
1
MAIN PCB
1724-330A-0001
JP14
JP13
JP15
JP16
J103
CH 1 SPKR OUTPUT
CH 1 SPKR COMMON
CH 2 SPKR OUTPUT
CH 2 SPKR COMMON
J203
REV DESCRIPTION EFF. DATE APPROVED/DATECHK
E9
E10
INPUT PCB
1724-340B-0102
26
WIRE ASSY
C
12
26
E112
GRN
E212
E11
E12
RED
BLK
RED
BLK
C
FAN ASSY
1
2
J128
3
3-PIN CABLE ASSY
J18
1
2
B
E1
E2
E3
E4
E5
E6
E7
E8
J21
-VCC_B
+_BVCC
1
2
3
B
DWG NO.
SH-0025000
TRANSFORMER
1806-2506-0
RED •
RED
GRN •
BRN
AC POWER CORD
A
HOT
GND
NEUT
BRN
GRN
BLU
CIRCUIT-
BREAKER
AC POWER
SWITCH
BRNBRN
BLU
GRN
BLK
BLU •
WHT
BLU
RED
VIO •
GRY
VIO
120V 230V 100V
J3A J6A J3A
J7A J7A J9A
J9A J9A J7A
J8A J5A J4A
J4A J4A J8A
J2A J2A J2A
JP12
JP10
PWR PCB
1724-340A-0102
-VCC_A
+VCC_A
AUDIO PRODUCTS, INC.
COSTA MESA, CALIFORNIA
SH
1
REV
A
A
WIRING DIAGRAM,
RMX 1450
1 OF 1
REV
A
NOTES: UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED
876 54321
RMX Series Technical Service Manual 37
SCALE
NONE
SHEET
7.13 RMX 1450 Chassis Wiring Diagram
Page 40

THIS DOCUMENT CONTAINS PROPRIETARY
INFORMATION WHICH IS THE PROPERTY
OF QSC AUDIO PRODUCTS, THAT MAY NOT
BE DISCLOSED, REPRODUCED OR USED
WITHOUT EXPRESS WRITTEN CONSENT FROM
QSC AUDIO PRODUCTS.
D
8 7654321
REVISIONS
D
INPUT PCB
REV DESCRIPTION EFF. DATE APPROVED/DATECHK
OUTPUT PCB
1724-342A-0102
E100
WHI
E101
E200
E201
GRY
WHI
GRY
26 CONDUCTOR RIBBON CABLE
WITH PIN-TO-PIN INTERCONNECTS
J1
1
J203
1
MAIN PCB
1724-332A-0003
JP14
JP13
JP15
JP16
J103
CH 1 SPKR OUTPUT
CH 1 SPKR COMMON
CH 2 SPKR OUTPUT
CH 2 SPKR COMMON
J203
PRODUCTION RELEASE PER ECO X MPA
C
B
A
NOTES: UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED
876 54321
AC POWER CORD
HOT
GND
NEUT
BRN
GRN
BLU
INPUT PCB
1724-342A-0102
CIRCUITBREAKER
26
TRANSFORMER
1806-2507-0
RED
RED(2)
AC POWER
SWITCH
RED 5
RED 4
BLK 3
BLK 2
BLK 1
RED 5
RED 4
BLK 3
BLK 2
BLK 1
1
2
3
WIRE ASSY
FAN ASSY
12
E112
E114
E113
26
E117
GRN
E115
E116
E217
E212
E214
E213
E215
E216
J257
3-PIN CABLE ASSY
J18
CT_B
-55V_B
-110V_B
+55V_B
+110V_B
CT_A
-55V_A
-110V_A
+55V_A
+110V_A
1
2
3
BRN
1
2
E1
E2
E3
E7
E8
E9
E4
E5
E6
E10
E11
E12
VIO
BLU
GRY
BLU(2)
GRN
ORG
GRN(2)
RED
WHT
BLU
BLK
BRN
BRNBRN
VIO(2)
GRY
YEL
120V 230V 100V
J5A J9A J5A
J7A J7A J3A
J3A J3A J7A
J2A J8A J6A
J6A J6A J2A
J4A J4A J4A
JP12
JP10
PWR PCB
1724-342A-0102
7.14 RMX 2450 Chassis Wiring Diagram
FG-002450-00 RMX 2450
NEXT ASSY USED ON
FIRST APPLICATION
UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED
DIMENSIONS ARE IN INCHES
DO NOT SCALE DRAWING
DRAWN
CHECKED
ISSUED
APPROVALS
MILA P.
PARTS LIST
DATE
12-12-00
SCALE
AUDIO PRODUCTS, INC.
COSTA MESA, CALIFORNIA
WIRING DIAGRAM,
RMX 2450
DWG NO.
NONE
SH-002450-00
SHEET
1 OF 1
C
B
DWG NO.
SH-0025000
SH
1
REV
A
A
REV
A
38 QSC Audio Products, Inc.
Page 41

Page 42

“QSC” and the QSC logo are registered trademarks of QSC Audio Products, Inc. 1675 MacArthur Blvd. Costa Mesa, CA 92626
(800) 772-2834 FAX (714)754-6173
www.qscaudio.com
 Loading...
Loading...