Page 1

QNAP Turbo NAS
Software User Manual
(Version: 4.3.x)
This manual is applicable to the following Turbo NAS models: TS-131, TS-131P TS-231,
TS-231+, TS-231P, TS-251, TS-251+, HS-251, HS-251+, TS-251C, TS-251A, TS-253 Pro,
TS-253A, TS-269L, TS-269 Pro, IS-400 Pro, TS-431, TS-431U, TS-431+, TS-431P, TS-451,
TS-451+, TS-451S, TS-451U, TS-451A, TBS-453A, IS-453S, TS-453S Pro, TS-453 Pro,
TS-453A, TS-453U, TS-453U-RP, TS-453mini, TS-453Bmini, TVS-463, TS-463U, TS-463U-RP,
TS-469 Pro, TS-469L, TS-469U-RP, TS-469U-SP, TS-470, TVS-470, TS-470U-RP, TS-470U-SP,
TS-470 Pro, TVS-471, TVS-471U, TVS-471U-RP, TVS-473, TS-531P, TS-531X, TS-563, TS-569
Pro, TS-569L, TS-651, TS-653 Pro, TS-653A, TVS-663, TS-669 Pro, TS-669L, TS-670 Pro,
TS-670, TVS-670, TVS-671, TVS-673, TVS-682, TVS-682T, TS-831X, TS-851, TS-853 Pro,
TS-853S Pro, TS-853U, TS-853U-RP, TS-853A, TS-863U, TVS-863, TVS-863+, TS-863U-RP,
TS-869 Pro, TS-869L, TS-869U-RP, TS-870 Pro, TS-870, TVS-870, TS-870U-RP, TVS-871T,
TVS-871, TVS-871U-RP, TVS-873, TS-879 Pro, TS-879U-RP, TS-EC879U-RP,
TS-EC880U(TS-EC880U-RP), TVS-EC880, TS-EC880 Pro, TS-EC880U R2, TVS-882, TVS-882T,
TVS-882ST, TVS-882S, TS-1079 Pro, TVS-EC1080+, TVS-EC1080, TS-EC1080 Pro, TS-1253U,
TS-1253U-RP, TS-1263U, TS-1263U-RP, TS-1269U-RP, TS-1270U-RP, TVS-1271U-RP,
TS-1279U-RP, TS-EC1279U-RP, TS-EC1279U-SAS-RP, SS-EC1279U-SAS-RP,
TS-EC1280U(TS-EC1280U-RP), TVS-EC1280U-SAS-RP, TS-EC1280U R2,
TVS-EC1280U-SAS-RP R2, TVS-1282, TVS-1282T, TVS-EC1580MU-SAS-RP,
TVS-EC1580MU-SAS-RP R2, TS-1635, TS-1679U-RP, TS-EC1679U-RP, TS-EC1679U-SAS-RP,
TS-EC1680U(TS-EC1680U-RP), TS-EC1680U R2, TVS-EC1680U-SAS-RP,
TVS-EC1680U-SAS-RP R2, SS-EC1879U-SAS-RP, SS-EC2479U-SAS-RP,
TS-EC2480U(TS-EC2480U-RP), TS-EC2480U R2, TVS-EC2480U-SAS-RP,
TVS-EC2480U-SAS-RP R2, TDS-16489U, TES-1885U, TES-3085U.
1
Page 2

Table of Contents
Notice ................................................................................................................................................................................ 6
Legal Notice and Disclaimer .......................................................................................................................................... 7
Regulatory Notice ......................................................................................................................................................... 9
Document Annotation ................................................................................................................................................ 11
Safety Information and Precautions ........................................................................................................................... 12
Getting Started ................................................................................................................................................................ 13
Hardware Installation ................................................................................................................................................. 14
Hard Disk Drive Compatibility List ........................................................................................................................... 15
Checking System Status .......................................................................................................................................... 16
Software Installation ................................................................................................................................................... 19
Smart Installation Guide ......................................................................................................................................... 20
Cloud Installation .................................................................................................................................................... 21
HDMI Installation .................................................................................................................................................... 22
Getting Utilities ........................................................................................................................................................... 23
Connecting to NAS Shared Folders ............................................................................................................................. 24
Windows ................................................................................................................................................................. 25
Mac or Linux ............................................................................................................................................................ 26
Connecting to NAS by Web Browser ........................................................................................................................... 27
Migrating NAS ............................................................................................................................................................. 28
QTS Basics and Desktop .................................................................................................................................................. 32
Introducing QTS .......................................................................................................................................................... 33
Using QTS Desktop ...................................................................................................................................................... 35
System Settings ............................................................................................................................................................... 41
General Settings .......................................................................................................................................................... 42
Storage Manager ......................................................................................................................................................... 45
Dashboard ............................................................................................................................................................... 50
Storage .................................................................................................................................................................... 52
iSCSI ......................................................................................................................................................................... 99
2
Page 3

Virtual Disk ............................................................................................................................................................ 117
Security ..................................................................................................................................................................... 119
Hardware .................................................................................................................................................................. 121
Power ........................................................................................................................................................................ 126
Notification ............................................................................................................................................................... 128
Firmware Update ...................................................................................................................................................... 131
Backup/Restore ......................................................................................................................................................... 133
External Device ......................................................................................................................................................... 135
External Storage .................................................................................................................................................... 136
USB Printer ............................................................................................................................................................ 139
UPS ........................................................................................................................................................................ 146
System Status ............................................................................................................................................................ 149
System Logs ............................................................................................................................................................... 150
Resource Monitor ..................................................................................................................................................... 154
Privilege Settings ........................................................................................................................................................... 156
Users ......................................................................................................................................................................... 157
User Groups .............................................................................................................................................................. 162
Shared Folders .......................................................................................................................................................... 164
Quota ........................................................................................................................................................................ 175
Domain Security ........................................................................................................................................................ 176
Joining NAS to Active Directory (Windows Server 2003/2008/2012) .................................................................. 177
Connecting NAS to an LDAP Directory .................................................................................................................. 180
Domain Controller ..................................................................................................................................................... 183
Network & File Services ................................................................................................................................................ 190
Network & Virtual Switch ......................................................................................................................................... 191
Network Access ......................................................................................................................................................... 208
Win/Mac/NFS ............................................................................................................................................................ 210
Telnet/SSH................................................................................................................................................................. 214
SNMP Settings ........................................................................................................................................................... 215
3
Page 4

Service Discovery ...................................................................................................................................................... 217
FTP ............................................................................................................................................................................. 218
Network Recycle Bin ................................................................................................................................................. 220
Business Applications .................................................................................................................................................... 222
Antivirus .................................................................................................................................................................... 223
Backup Station .......................................................................................................................................................... 227
Backup Server ....................................................................................................................................................... 228
Remote Replication ............................................................................................................................................... 232
Snapshot Replica ................................................................................................................................................... 239
Cloud Backup......................................................................................................................................................... 241
External Backup ..................................................................................................................................................... 242
File Station ................................................................................................................................................................ 248
LDAP Server ............................................................................................................................................................... 262
QVPN Service ............................................................................................................................................................ 264
Qsync Central ............................................................................................................................................................ 274
SQL Server ................................................................................................................................................................. 284
NTP Service ............................................................................................................................................................... 286
RADIUS Server ........................................................................................................................................................... 287
Syslog Server ............................................................................................................................................................. 289
TFTP Server ............................................................................................................................................................... 292
Virtualization ............................................................................................................................................................. 294
Web Server ................................................................................................................................................................ 297
Virtual Host ........................................................................................................................................................... 300
Other Applications ........................................................................................................................................................ 302
App Center ................................................................................................................................................................ 303
DLNA Media Server ................................................................................................................................................... 306
Download Station...................................................................................................................................................... 308
Helpdesk .................................................................................................................................................................... 316
HybridDesk Station ................................................................................................................................................... 319
4
Page 5

iTunes Server ............................................................................................................................................................. 322
Multimedia Management ......................................................................................................................................... 323
Music Station ............................................................................................................................................................ 327
myQNAPcloud Service .............................................................................................................................................. 334
Photo Station ............................................................................................................................................................ 342
Video Station ............................................................................................................................................................. 356
Mobile Apps .................................................................................................................................................................. 366
Computer Utilities ......................................................................................................................................................... 371
NAS Add-ons ................................................................................................................................................................. 373
Use the LCD Panel ......................................................................................................................................................... 379
GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE .................................................................................................................................... 384
5
Page 6

Notice
Legal Notice and Disclaimer
Regulatory Notice
Document Annotation
Safety Information and Precautions
6
Page 7

Legal Notice and Disclaimer
Thank you for choosing QNAP products! This user manual provides detailed instructions of using the Turbo
NAS (network-attached storage). Please read carefully and start to enjoy the powerful functions of the
Turbo NAS!
The Turbo NAS is hereafter referred to as the NAS.
This manual provides the description of all the functions of the NAS. The product you purchased may
not support certain functions dedicated to specific models.
Legal Notices
All the features, functionality, and other product specifications are subject to change without prior notice
or obligation. Information contained herein is subject to change without notice.
QNAP and the QNAP logo are trademarks of QNAP Systems, Inc. All other brands and product names
referred to are trademarks of their respective holders.
Further, the ® or ™ symbols are not used in the text.
Disclaimer
Information in this document is provided in connection with QNAP products. No license, express or implied,
by estoppels or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted by this document. Except as
provided in QNAP's terms and conditions of sale for such products, QNAP Assumes no liability whatsoever,
and QNAP disclaims any express or implied warranty, relating to sale and/or use of QNAP products
including liability or warranties relating to fitness for a particular purpose, merchantability, or
infringement of any patent, copyright or other intellectual property right.
QNAP products are not intended for use in medical, life saving, life sustaining, critical control or safety
systems, or in nuclear facility applications.
In no event shall QNAP Systems, Inc. (QNAP) liability exceed the price paid for the product from direct,
indirect, special, incidental, or consequential damages resulting from the use of the product, its
accompanying software, or its documentation. QNAP makes no warranty or representation, expressed,
implied, or statutory, with respect to its products or the contents or use of this documentation and all
accompanying software, and specifically disclaims its quality, performance, merchantability, or fitness for
any particular purpose. QNAP reserves the right to revise or update its products, software, or
documentation without obligation to notify any individual or entity.
Back up the system periodically to avoid any potential data loss. QNAP disclaims any responsibility of all
sorts of data loss or recovery.
7
Page 8

Should you return any components of the NAS package for refund or maintenance, make sure they are
carefully packed for shipping. Any form of damages due to improper packaging will not be compensated.
QNAP, QNAP logo, QTS, myQNAPcloud and VioStor are trademarks or registered trademarks of QNAP
Systems, Inc. or its subsidiaries. Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
8
Page 9

Regulatory Notice
FCC Notice
QNAP NAS comply with different FCC compliance classes. Please refer the Appendix for details. Once the
class of the device is determined, refer to the following corresponding statement.
FCC Class A Notice
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference.
2. This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired
operation.
Note: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against
harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment
generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy, and if not installed and used in accordance with
the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this
equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference, in which case the user will be
required to correct the interference at his own expense.
Modifications: Any modifications made to this device that are not approved by QNAP Systems, Inc. may
void the authority granted to the user by the FCC to operate this equipment.
FCC Class B Notice
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference.
2. This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired
operation.
Note: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against
harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio
frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in
a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception,
which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
9
Page 10

Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
FCC
CE
NAS Models
Class A
Class A
TS-EC1679U-RP, TS-EC1279U-RP, TS-EC879U-RP, TS-1679U-RP,
TS-1279U-RP, TS-1270U-RP, TS-1263U-RP, TS-1263U,TS-1253U-RP,
TS-1253U, TS-879U-RP, TS-870U-RP, TS-863U-RP, TS-853U-RP,
TS-453U-RP, TS-1079 Pro, TS-879 Pro, TS-863U, TS-853U, TS-463U,
TS-463U-RP, TS-453U-RP, TS-453U, TS-451U, TS-431U, TVS-871U-RP,
TVS-1271U-RP
Class B
Class B
TS-853S Pro, TS-453S Pro, TS-870 Pro, TS-853 Pro, TS-670 Pro, TS-653 Pro,
TS-470 Pro, TS-453 Pro, TS-253 Pro, TS-431+, TS-231+, TS-451S, TS-870,
TS-851, TS-670, TS-651, TS-470, TVS-863+, TVS-863, TVS-663, TVS-463,
TVS-471, TVS-671, TVS-871,TS-451, TS-451+, TS-431, TS-251, TS-251+,
TS-251C, TS-231, TS-131, TS-269H, TS-212P, TS-112P, HS-251, HS-251+,
HS-210, TS-453mini, TS-563, IS-453S, TS-531P, TS-253A, TS-453A,
TS-653A, TS-853A, TS-128, TS-228, TAS-168, TAS-268, TS-831X,
TVS-682T, TVS-882T, TVS-1282T, TVS-682, TVS-882, TVS-1282
connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/television technician for help.
Modifications: Any modifications made to this device that are not approved by QNAP Systems, Inc. may
void the authority granted to the user by the FCC to operate this equipment.
CE Notice
QNAP Turbo NAS models comply with different CE compliance classes. Please refer to the table for details.
10
Page 11

Document Annotation
Annotations in this document
Warning: This indicates the instructions must be strictly followed. Failure to do so could result in
injury to human body or death.
Caution: This indicates the action may lead to disk clearance or loss OR failure to follow the
instructions could result in data damage, disk damage, or product damage.
Important: This indicates the information provided is important or related to legal regulations.
11
Page 12

Warning:
There is the danger of explosion if a battery is incorrectly replaced. Replace only with the same
or equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer. Dispose of used batteries according
to the manufacturer’s instructions.
To avoid serious injuries do NOT touch the fan inside the system.
Safety Information and Precautions
1. The NAS can operate normally in the temperature of 0ºC–40ºC and relative humidity of 0%–95%.
Ensure the environment is well-ventilated.
2. The power cord and devices connected to the NAS must provide correct supply voltage (100W,
90–264V).
3. Do not place the NAS in direct sunlight or near chemicals. Ensure the usage environment's
temperature and humidity is suited for using electronics.
4. Unplug the power cord and all connected cables before cleaning. Wipe the NAS with a dry towel. Do
not use chemicals or aerosols to clean the NAS.
5. Do not place any objects on the NAS during normal system operations and to avoid overheating.
6. Use the flat head screws in the product package to lock the hard disk drives in the NAS when
installing the hard drives for proper operation.
7. Do not place the NAS near any liquid.
8. Do not place the NAS on any uneven surface to avoid falling off and damage.
9. Make sure the voltage is correct in your location when using the NAS. If unsure, contact your
distributor or the local power company.
10. Do not place any object on the power cord.
11. Never attempt to repair the NAS. Improper disassembly of the product may expose you to
electric shock or other risks. For repair-related enquiries, please contact your distributor.
12. Rackmount NAS models should only be installed in server rooms and maintained by authorized
server managers or IT administrators. The server room should be sufficiently locked and only
certified staff allowed to enter.
12
Page 13

Getting Started
New NAS users are advised to follow the below steps to complete their NAS installation. For users who
already own a QNAP NAS and would like to move the data to a new QNAP NAS, refer to Migrating NAS for
detailed instructions.
For New NAS Users:
1. Hardware Installation
2. Software Installation
3. Getting Utilities
4. Connecting to the Shared Folders
5. Connecting to the NAS by Web Browser
For Existing NAS Users:
Migrating NAS
13
Page 14

Note:
The steps above are also illustrated in the Quick Installation Guide (QIG) that can be
found in the product package or QNAP website (http://start.qnap.com).
Hardware Installation
After unpacking the NAS, first follow these instructions to install your hardware:
1. Install the hard drives. Before doing so, ensure the hard drives (HDDs) that you use are compatible
with the NAS. Go to the Hard Disk Drive Compatibility List section for more details.
2. Connect the QNAP NAS to the same network as your PC and power it on. During your installation
process, pay attention to LEDs and alarm buzzers to make sure that the NAS functions properly. Go
to the Checking System Status section for more details.
14
Page 15

Note:
If you encounter a "Device not found" message, ensure that:
1.
Your NAS has been powered on;
2.
The network cable is connected to the NAS and the orange and green indicator lights on
its LAN port(s) are blinking; and
3.
The cloud key is correct.
Important:
QNAP disclaims any responsibility for product damage/malfunction or data
loss/recovery due to misuse or improper installation of hard disks in any occasions for any
reasons.
Caution:
Note that
if you install a hard drive (new or used) which has never been
installed on the NAS before, the hard drive will be formatted and partitioned
automatically and all the disk data will be cleared.
Hard Disk Drive Compatibility List
This product works with 2.5-inch and 3.5-inch SATA hard disk drives and/or solid-state drives (SSD) from
major hard drive brands. For a full list of compatible drives, check the compatibility list on the QNAP
website (http://www.qnap.com/compatibility).
15
Page 16

LED
Color
LED Status
Description
System
Status
Red/
Green
Flashes green and
red alternately every
0.5 sec
1) The hard disk drive on the NAS is being formatted.
2) The NAS is being initialized.
3) The system firmware is being updated.
4) RAID rebuilding is in process.
5) Online RAID capacity expansion is in process.
6) Online RAID level migration is in process.
Red
1) The hard disk drive is invalid.
2) The disk volume has reached its full capacity.
3) The disk volume is going to be full.
4) The system fan is out of function (TS-119 does not
support smart fan).
5) An error occurs when accessing (read/write) the
disk data.
6) A bad sector is detected on the hard disk drive.
7) The NAS is in degraded read-only mode (2
member hard drives fail in a RAID 5 or RAID 6
configuration, the disk data can still be read).
8) Hardware self-test error.
Flashes red every 0.5
sec
The NAS is in degraded mode (one member hard drive
fails in RAID 1, RAID 5 or RAID 6 configuration).
Flashes green every
0.5 sec
1) The NAS is starting up.
2) The NAS is not configured.
3) The hard disk drive is not formatted.
Flashes green every 2
sec
The NAS is in S3 Sleep Mode1.
Green
The NAS is ready.
Off
All the hard disk drives on the NAS are in standby
mode.
Power
1
Green
Flashes green
The NAS is booting up.
Green
The NAS is on and ready.
Checking System Status
LED Display & System Status Overview
16
Page 17
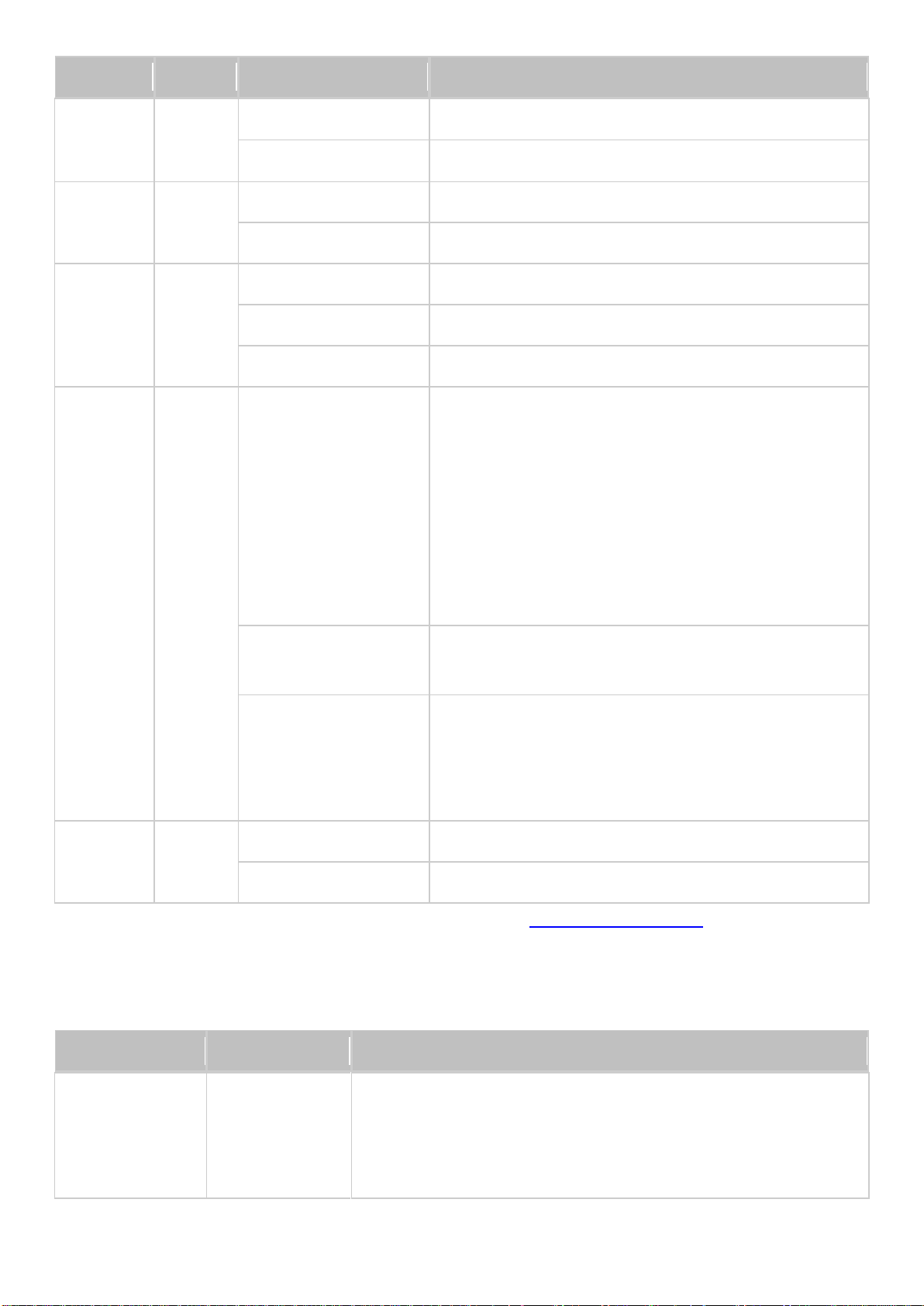
LED
Color
LED Status
Description
LAN
Orange
Orange
The disk data is being accessed from the network.
Flashes orange
The NAS is connected to the network.
10 GbE
Green
Green
The 10GbE network expansion card is installed.
Off
No 10GbE network expansion card is installed.
HDD
Red/
Green
Red
A hard drive read/write error occurs.
Flashes green
The disk data is being accessed.
Green
The hard drive can be accessed.
USB
Blue
Flashes blue every
0.5 sec
1) A USB device (connected to front USB port) is
being detected.
2) A USB device (connected to front USB port) is
being removed from the NAS.
3) The USB device (connected to the front USB port)
is being accessed.
4) The data is being copied to or from the external
USB or eSATA device.
Blue
A front USB device is detected (after the device is
mounted).
Off
1) No USB device is detected.
2) The NAS has finished copying the data to or from
the USB device connected to the front USB port of
the NAS.
eSATA
Orange
Flashes
The eSATA device is being accessed.
Off
No eSATA device can be detected.
1
Beep sound
No. of Times
Description
Short beep
(0.5 sec)
1
1) The NAS is starting up.
2) The NAS is being shut down (software shutdown).
3) The user presses the reset button to reset the NAS.
4) The system firmware has been updated.
This feature is only supported by certain NAS models. Visit http://www.qnap.com for more details.
Alarm Buzzer
The alarm buzzer can be disabled in "Control Panel" > "System Settings" > "Hardware" > "Buzzer
17
".
Page 18

Short beep
(0.5 sec)
3
The NAS data cannot be copied to the external storage device
from the front USB port.
Short beep
(0.5 sec), long
beep (1.5 sec)
3, every 5 min
The system fan is out of function (TS-119 does not support
smart fan).
Long beep
(1.5 sec)
2
1) The disk volume is going to be full.
2) The disk volume has reached its full capacity.
3) The hard disk drives on the NAS are in degraded mode.
4) The user starts hard drive rebuilding.
1
1) The NAS is turned off by force shutdown (hardware
shutdown).
2) The NAS has been turned on and is ready.
18
Page 19

Software Installation
After installing the NAS hardware, proceed to software installation. There are three approaches for
software installation:
1. Smart Installation Guide
2. Cloud Installation
3. HDMI Installation
Online installation and cloud installation are available for all new NAS models. All users are
encouraged to use cloud and online installation if possible. Contact our technical support
department if any problem arises during the installation process
(http://www.qnap.com/support).
19
Page 20

Smart Installation Guide
Follow the steps in this section to complete online installation for your NAS:
1. Go to http://start.qnap.com.
2. Choose the number of HDD bays and the model of your NAS and click "Start Now".
3. Click "Hardware" and follow the on-screen instructions to get hardware ready.
4. Scroll down to "Install firmware" and click "Local Installation".
5. Choose your operating system to download, install and run Qfinder Pro.
6. After installing Qfinder Pro, launch it to search for your NAS. Double click on your NAS in Qfinder Pro
to start the Smart Installation Guide. Follow the on-screen instructions to the built-in Qfinder Pro
Setup Wizard will guide you along the way to complete the firmware installation.
7. Proceed to log into QTS with your account username and password to log in (QTS is the operating
system for the Turbo NAS).
20
Page 21

Note:
If you encounter a "Device not found" message, ensure that:
1. Your NAS has been powered on;
2. the network cable is connected to the NAS and the orange and green indicator lights on its LAN
port(s) are blinking; and
3. The cloud key is correct.
Cloud Installation
Follow the steps in this section to complete cloud installation for your NAS:
1. Connect your NAS to the Internet, and on your PC, go to "install.qnap.com”.
2. Enter the cloud key (cloud key can be found from the sticker on top of your QNAP NAS) and click
"Enter".
3. Login to or register for myQNAPclould account. An activation email will be sent for new accounts.
Click Confirm Registration in email to activate account.
4. Enter a name for your QNAP NAS. This name will be used to remotely access your device. Click Next.
5. Install hard drives on your Turbo NAS if you have not already done so.
6. On the Welcome page, click Start Smart Installation Guide to start the NAS installation process.
7. On the Name / Password page, enter your NAS name and admin password. Click Next.
8. On the Date / Time page, select your preferred time and date settings. Click Next.
9. On the Network page, enter your network settings. Click Next.
10. On the Services page, select which OS features you would like enabled. Multiple selections are
allowed. Click Next.
11. On the Multimedia page, select if you would like to enable multimedia functions immediately after
set up. Multiple selections are allowed. Click Next.
12. On the Disk page, select if you would like to configure disks now or later. Click Next.
13. On the Summary page, review your settings. Click Next if settings are correct. Click Back to make
changes.
21
Page 22

Note:
This installation is restricted to NAS models with an HDMI port.
The default login ID and password of the NAS are both "admin".
HDMI Installation
Follow the steps in this section to complete the HDMI installation for your NAS:
1. Connect the NAS to an HDMI display.
2. Follow the onscreen instructions to complete the firmware installation.
3. Choose to install HD Station or log into QTS with QTS account username and password (QTS is the
operating system for the NAS).
22
Page 23

Getting Utilities
Visit http://www.qnap.com/ and go to "Support" > "Download" > "Utilities" and choose to
download and install the utilities on your PC.
23
Page 24

Connecting to NAS Shared Folders
After installing the hardware and software, it is time to connect to the shared folders on the NAS. Refer to
these links for the connection setup:
Connecting to NAS shared folders in Windows
Connecting to NAS shared folders in Mac or Linux
24
Page 25

Note:
Alternatively, you can use the Storage Plug & Connect Wizard to connect to NAS
shared folders. The steps:
1.
Launch QNAP
Qfinder Pro
;
2.
Select "Storage Plug & Connect" under "Connect";
3.
Check "Login with username and password" and enter the username and password;
4.
Click a NAS shared folder;
5.
Click
"Map the Network Drive"
.
Windows
There are two methods for connecting to shared folders of the NAS when using Windows:
Method 1: Connect to the shared folders of the NAS by using QNAP Qfinder Pro
1. Launch QNAP Qfinder Pro. Select your NAS and then click "Tool" > "Map Network Drive".
2. Select a shared folder on the NAS to be mapped as a network drive and click "Map Network Drive".
3. Enter the username and password to connect to the NAS and click "OK".
4. Select a drive in the OS to map the folder chosen in Step 2 and click "Finish".
5. The mapped folder will appear when opening the File Explorer in Windows.
Method 2: Connect to the shared folders of the NAS by using File Explorer or Run
1. Open the Windows File Explorer, click on "Network" on the left and find the workgroup of the NAS. If
the NAS cannot be found, browse the whole network to search for the NAS. Double click the name of
the NAS to connect to it, or use the Run function in Windows (Windows key + R). Enter \\NAS_name
or \\NAS_IP.
2. Enter the default administrator name and password (the default login ID and password are both
"admin")..
3. Upload files to the shared folders.
25
Page 26

Note: You must login as the "root" user to initiate the above command.
Mac or Linux
Mac Users
There are two methods to connect shared folders on a NAS:
Method 1: Using QNAP Qfinder Pro
1. Launch QNAP Qfinder Pro, select your NAS, and go to "Connect" > "Open in File Explorer".
2. Enter your login ID and password.
3. Select the folder you want to mount and click "OK".
4. The folder is mounted.
Method 2: Connecting to Server
1. Choose "Go" > "Connect to Server".
2. Enter the NAS IP address.
3. Enter your login ID and password.
4. Select the folder you want to mount and click "OK".
5. The folder is mounted.
Linux Users
On Linux, run the following command:
mount -t nfs <NAS IP>:/<Shared Folder Name> <Directory to Mount>
For example, if the IP address of the NAS is 192.168.0.1, to connect to the shared folder "public" under
the /mnt/pub directory, use the following command:
mount -t nfs 192.168.0.1:/public /mnt/pub
Log into the NAS with the specified user ID, use the mounted directory to connect to the shared folders.
26
Page 27
Note: The default NAS IP is 169.254.100.100:8080. If the NAS has been configured to use DHCP, you
can use QNAP Qfinder Pro to check the IP address of the NAS. Make sure the NAS and the computer
that runs QNAP Qfinder Pro are connected to the same subnet. If the NAS cannot be found, connect
the NAS to the computer directly and run QNAP Qfinder Pro again.
Note: If the NAS is behind a NAT gateway, to connect to the NAS by secure login on the Internet, port
443 must be opened on the NAT router and forwarded to the LAN IP of the NAS.
Connecting to NAS by Web Browser
To connect to the NAS by a web browser, follow these steps:
1. Enter http://NAS IP:8080 in the web browser. Or if using QNAP Qfinder Pro, simply double click on
the NAS to open the login page.
2. Enter the administrator's login id and password. Enable "Secure login" (Secure Sockets Layer login) to
allow a secure connection to the NAS. If a user without administration rights logs into the NAS, the
user can only change the login password (the default login ID and password of the NAS are both
"admin").
3. The NAS Desktop will be displayed.
27
Page 28

Destination
Source
HS-210,
TS-x09,
TS-x10,
TS-x12,
TS-x19,
TS-x20,
TS-x21,
TS-x39,
TS-x59
TS-x31
TS-x69
TS-x31+,
TS-x31X,
TS-x31P,
TS-1635
IS-400,
TS-x51,
TBS-x53,
IS-x53,
TS-x53,
TS-x63,
TVS-x63,
TS-x70,
TVS-x70,
TVS-x71,
TVS-x73,
TS-x79,
TS-ECx79,
SS-ECx79,
TS-ECx80,
TVS-ECx82,
TS-x85,
TDS-x89
HS-210,
TS-x09,
TS-x10,
TS-x12,
TS-x19,
TS-x20,
TS-x21,
TS-x39,
Migrating NAS
Users can migrate their existing NAS to another NAS model with all data and configuration retained by
simply installing the hard drives from the original (source) NAS to the new (destination) NAS and
restarting the destination NAS. To determine which NAS models support system migration, see the NAS
Migration Compatibility Table below.
NAS Migration Compatibility Table
The series listed in this table include all models in the series. For example, TS-x51 includes the models
TS-251, TS251+, TS-251C, TS-251A, TS-451, TS-451+, TS-451C, TS-451A, TS-651, TS-851. Note that
x31, x31+, x31X, x31P, and x35 are listed individually.
28
Page 29

TS-x59
TS-x31
TS-x69
TS-x31+,
TS-x31X,
TS-x31P,
TS-1635
IS-400,
TS-x51,
TBS-x53,
IS-x53,
TS-x53,
TS-x63,
TVS-x63,
TS-x70,
TVS-x70,
TVS-x71,
TVS-x73,
TS-x79,
TS-ECx79,
SS-ECx79,
TS-ECx80,
TVS-ECx82,
TS-x85,
TDS-x89
Note:
Users are encouraged to use drives that are compatible with the NAS. Non-compatible drives may
lead to system migration failure. For the compatibility list, go to
http://www.qnap.com/compatibility.
The destination NAS must have the drive slots to enclose all of the drives from the source NAS.
It is recommended that drive ordering of the source NAS is maintained in the destination NAS.
The myQNAPcloud account of the source NAS will need to be updated manually to the destination
NAS after system migration.
The McAfee License cannot be migrated to the new NAS. A new license will need to be purchased.
Using System Migration
29
Page 30
The myQNAPCloud SSL certification will have to be manually migrated to the destination NAS.
The camera licenses for QVR Pro will not be migrated automatically. Contact technical support to
migrate the licenses to the new NAS after the migration.
Caution:
For rack mount NAS, the system migration procedure should be performed by an
authorized server manager or IT administrator to avoid system damage or serious injury.
1. Check that the source and destination NAS support system migration using the NAS Migration
Compatibility table.
2. Connect the power supply and network cable(s) to the destination NAS.
3. Boot up the destination NAS.
4. Download the source and destination NAS firmware from
https://www.qnap.com/en/product_x_down/. Make sure that both firmware are the same version and
build (QTS 4.2.0 or later).
5. Upgrading the firmware on the NAS.
a. Update the source firmware on NAS.
i. Reboot the NAS.
ii. Log into to QTS as an administrator. The default username/password is admin/admin.
iii. Go to “Control Panel” > “Firmware Update” > “Firmware Update”.
iv. Click "Browse" and locate source firmware.
v. Click "Update System".
b. Update the destination firmware on the NAS (use Qfinder Pro if not any hard drives are installed).
If the destination NAS has not been initialized:
i. Download Qfinder Pro at https://www.qnap.com/en/utility/ and install.
ii. Launch Qfinder Pro.
iii. Right-click the destination NAS in Qfinder Pro and select "Update Firmware".
iv. Enter username and password of an administrator account. The default username/password is
admin/admin.
v. Click "Browse" and locate source firmware.
vi. Click "Update System".
If the destination NAS already has hard drives installed and has been initialized, the user may use
the steps in either 5a or 5b to upgrade the firmware of the NAS.
6. Shut down both NAS.
7. Remove the hard drives from the source NAS and any hard drives from the destination NAS. Install
drives from the source NAS to destination NAS. It is recommended that drive order is maintained.
Refer to hardware user guides for drive slot numbering.
8. Boot up the destination NAS.
9. If prompted to update the firmware, follow the firmware update instructions to install the newest
firmware.
30
Page 31

10. If the volumes do not appear after the firmware update, reinstalled the firmware using the steps in 5a
and the volumes will be accessible.
11. Optional: Check your NAS settings to determine if all settings were migrated by logging into QTS as
an administrator.
Due to the different specifications of different models, there is a slight chance that the settings may not
be imported to the destination NAS. In this event, manual configuration will be required.
Some new features that are available on the destination NAS, but not on the source NAS, may only be
available on newly created storage pools.
31
Page 32

QTS Basics and Desktop
QTS is a user-friendly NAS operating system designed to enhance every aspect of your NAS experience.
With basic methods such as drag-and-drop or point and click, you can complete most NAS operations.
Check the following links to learn more about QTS:
Introducing QTS
Using QTS Desktop
32
Page 33

Introducing QTS
Built on a Linux foundation, QTS is shaped from an optimized kernel to deliver
high-performance services that satisfy needs for file storage, management, backup,
multimedia applications, surveillance, and more. The intuitive, multi-window and multi-tasking
QTS GUI make it incredibly easy to manage your NAS, use its rich home applications, enjoy
multimedia, and install more applications from an integrated App Center. QTS also adds value
to business applications and effectively increase business efficiency with abundant features,
including file sharing, iSCSI, virtualization, backup, privilege settings, and more. Coupled with
various utilities and smart mobile apps, QTS is the ultimate platform for building a personal or
private cloud, synchronizing data and sharing files.
33
Page 34

NAS for Home - Easily enrich home entertainment and content sharing
Tons of photos, music, videos and documents are often scattered across multiple computers in
modern homes. QNAP NAS feature plenty of handy applications to let you smartly connect and
manage your data and enjoy a truly digital life in a well-secured home network. No boundaries
for multimedia sharing at home, and no boundaries for sharing content with family, and friends.
Learn more about the exciting features that a QNAP NAS offers you:
Intuitive GUI with Multi-Windows, Multi-Tasking, Multi-Application, Multi-Device access support
Cross platform data storage, backup and sharing center
Revolutionary music, photo and home video center
Personal cloud storage
Free and large capacity for Dropbox-style data sync
Hundreds of install-on-demand applications from the App Center
Energy-efficient & eco-friendly
NAS for Business - Efficiently optimize business IT infrastructure
IT efficiency, coupled with low total cost of ownership (TCO) is an essential factor for business
competitiveness. QNAP NAS features advanced capabilities for keeping businesses running at maximum
efficiency including business-critical applications, seamless file sharing, easy integration into existing
networks, flexible virtualized IT environments, and more. Learn more about the compelling features that
a QNAP NAS offers your business:
Large data storage, backup and file sharing center
Supports both scale-up and scale-out solutions for growing data needs
Advanced storage management with dynamic thin-provisioning, SSD caching and JBOD expansion
functions
Trustworthy data security and data encryption
Reliable IP SAN storage (iSCSI) as primary and secondary storage for virtualization environments
Private cloud storage
Free and large capacity for Dropbox-style data sync
Hundreds of install-on-demand applications from the App Center
Development Center for third-party partners to build apps for the NAS
34
Page 35

No.
Name
Description
1
Show Desktop
Minimize or restore all open windows.
2
Main Menu
Show the Main Menu. It includes two parts:
1) SYSTEMS: Key system features and options designed to help you manage or
optimize your NAS.
2) APPLICATIONS: Applications developed by QNAP to enhance your NAS
experience.
Using QTS Desktop
After you finish the basic setup and login to the NAS, the desktop will appear. Each main desktop feature
is introduced in the following sections.
Topics covered in this chapter:
QTS Desktop
2-step Verification
QTS Desktop
35
Page 36

Please note that the default Internet browser, instead of a new window on the
NAS Desktop, will be launched once you click a third-party application.
3
Search
Enter keywords in the search bar to find an application or function and related
instructions. Click the search result to launch an application or function or
consult its online QTS help.
4
Background
Task
Review or control (such as pause or postpone) all the tasks running in the
background. For example, HDD S.M.A.R.T. scanning, anti-virus scanning, file
backup, or multimedia conversion.
5
External
Device
List all external storage devices and USB printers that are connected to the NAS
via its USB or SATA ports. Click a listed device to open File Station to view this
device. Click "More>>" to open the External Device page for relevant settings
and operations (for more information about File Station, refer to the File Station
chapter). Click the eject icon (up-arrow icon) to eject the external device.
6
Notification
and Alert
You can check recent errors, warnings, and notifications here. Click “Clear All”
to clear the list. To view all historical events, click “More>>” to open System
Logs. For more information about System Logs, refer to the System Logs
chapter.
7
Options
Profile: Specify your email address and change your profile picture. You can
also check System Logs and edit the Login Screen here.
Wallpaper: Change the default wallpaper or upload your own photo and set
it as the wallpaper.
2-step Verification: Enable 2-step Verification to enhance the security of
user accounts. For more information, refer to the 2-step Verification
section.
Change Password: Change your login password.
E-mail Account: Set up the email address you use when sharing files via
email in Music Station, Photo Station, Video Station, or File Station.
Miscellaneous:
o Auto log-out after an idle period of: Specify the idle period after which
the user will be automatically logged out.
o Warn me when leaving QTS: Users will be prompted for confirmation
every time they try to leave the QTS Desktop (such as closing the
browser or clicking the “back” button of the browser). It is recommended
to enable this option.
o Reopen windows when logging back into QTS: If you enable this option,
all the current desktop settings (such as “the windows opened when your
log out") will be retained until your next login.
36
Page 37

o Show the desktop switching button: Check this option to hide the next
desktop button (No. 12) and only display them when you move your
mouse cursor close to the buttons.
o Show the desktop switching button: Enable this option to show the “next
desktop” button (No. 12). If you disable this option, the “next desktop”
button will only appear when you move the mouse cursor near it.
o Show the link bar on the desktop: Enable this option to show the link bar
(No. 13, No. 14, No. 15, and no.16).
o Show the Dashboard button: Enable this option to show the Dashboard
button (NO. 10).
o Show the NAS time on the desktop: Enable this option to display the NAS
time in the bottom-right corner of the desktop.
o Keep Main Menu open after selection: Keep the Main Menu
pinned/unpinned on the desktop.
o Show a list of actions when external storage devices are detected:
Enable this option and the Autoplay dialog box will appear after you plug
in an external device.
8
Admin Options
Configure user-specific settings, change your user password, restart/shut down
the NAS or log out.
Last login time: The last time when you logged in to the system.
Options: Refer to the previous section.
Sleep: Put your NAS into sleep. There are three ways to wake up the NAS:
1) Press the power button until you hear a beep; 2) Use the Wake-on-LAN
(WOL) feature with QNAP Qfinder Pro or Qmanager. Note that to use this
method, WOL must be enabled in "Control Panel" > "Power" >
"Wake-on-LAN(WOL)"; 3) Press the power button on a RM-IR002 or MCE
remote control.
o Note: This feature is only available on certain models.
Restart: Restart your NAS.
Shutdown: Shut down your NAS.
o Note: To power off a NAS, you can also:
Press and hold the power button on your NAS for 1.5 seconds.
Run Qfinder Pro and click "Tools" > "Shut down Server".
Logout: Log yourself out
9
More
Help: Show NAS references, including Quick Start, Virtualization Guide,
Help Center, and Tutorials.
Language: Choose your preferred language.
Desktop Preference: Applications can be opened in Tab Mode, Window
37
Page 38

Mode, or Frameless Mode. Only Tab Mode is available if you log in to the
NAS using a mobile device.
o Tab Mode: In this mode, the application window will be expanded to fit
the entire NAS Desktop, and only one application window can be
displayed at a time.
o Window mode: In this mode, the application window can be resized to
your preferred shape.
o Frameless Mode: In this mode, applications will be opened without their
frames.
Help Request: Send a help request to QNAP.
About: Check the NAS model, firmware version, numbers of hard drives
already installed and empty bays, used and unused storage space.
10
Dashboard
Check important NAS statistics, including system and hard drive health,
resources, storage usage, online users, scheduled tasks, etc. Click the header in
each widget to open its own page.
11
Desktop Area
Arrange or remove the applications on the desktop.
12
Next Desktop/
Last Desktop
Switch between different desktop pages.
13
myQNAPcloud
Go to the myQNAPcloud website.
14
QNAP Utility
Check and download NAS utilities and mobile apps.
15
Feedback
Go to QNAP Wiki or QNAP Forum, or seek Customer Service.
16
Help Request
Send a help request to QNAP.
17
Network
Recycle Bin
All of the deleted items can be found here. Right click on this icon to open the
Network Recycle Bin, empty it (delete files permanently), or configure it (refer
to the Network Recycle Bin chapter for more information).
2-step Verification
2-step Verification enhances the security of user accounts. Once enabled, you will need to enter a
one-time security code (6 digits) in addition to your password whenever you sign in to the NAS. 2-step
verification requires a mobile device with an authenticator app which supports the Time-based One-Time
password (TOTP) protocol. Supported apps include Google Authenticator (Android/iPhone/BlackBerry) or
Authenticator (Windows Phone).
38
Page 39

Start 2-step verification
Tip:
All of the Dashboard widgets can be dragged onto the desktop for monitoring specific details.
The Dashboard will be presented differently on different screen resolutions.
The color of the Dashboard button will change based on the status of system health for quick
recognition.
1. Install the authenticator App on your mobile device: For Android and iOS devices, install the Google
Authenticator App from their respective App stores. For Windows Phone, install the Authenticator
from its Store.
2. The system times of your mobile device and NAS must be synchronized. It is recommended to use
the time provided from the Internet.
3. Go to "Options" > "2-step Verification" and click "Get Started". Complete the steps in the wizard to
set up the NAS and your mobile device.
4. Configure your authenticator App by scanning the QR code or by entering the Secret Key into the
App.
5. Enter the code generated from the app to the NAS to verify the correct configuration.
6. Select an alternative verification method by emailing you a security code or by answering a security
question if you cannot use your mobile device. To email a security code, the SMTP server must be
properly configured in "Control Panel" > "Notification" > "E-mail".
Sign in QTS with 2-step verification
After your username and password are verified, you will be promoted to enter a security code. Enter the
code currently provided from the authenticator app to sign in to QTS. If you cannot use your mobile device
or your device is lost, you can select "Verify another way" to sign in with your chosen alternative
verification method.
Stop 2-step verification
If you want to disable 2-step verification, go to "Options" > "2-step Verification" and click "Stop".
Administrators can disable 2-step verification for other NAS account users if they are locked out by going
to "Control Panel" > "Users" > "Edit Account Profile"
If an administrator cannot use a mobile device to sign in to QTS and no other administrators are available
to disable 2-step verification for the locked-out administrator, the NAS must be restored to factory
settings by physically pressing the "RESET" button on the NAS.
39
Page 40

Note:
The recommended minimum screen resolution for QTS 4.x is 1024x768.
The sleep function will automatically be disabled if the NAS has QNAP expansion
enclosure(s) connected to it.
40
Page 41

System Settings
Go to
"Control Panel" > "System Settings" to set up your NAS.
For details on the settings, refer to the following links:
General Settings
Storage Manager
Network
Security
Hardware
Power
Notification
Firmware Update
Backup/Restore
External Device
System Status
System Logs
41
Page 42

General Settings
Go to "Control Panel" > "System Settings" > "General Settings" to configure basic settings of the
NAS.
Topics covered in this chapter:
System Administration
Time
Daylight Saving Time
Codepage
Login Screen
System Administration
Basic Settings:
characters and can be a combination of letters (a-z, A-Z), numbers (0-9), and dash (-),
Space ( ), period ()., or pure numbers are not allowed. Enter a port number for system
management. The default port is 8080. The services which use this port include: System
Management, Photo Station, Music Station, File Station and Download Station. If you are
not sure about this setting, use the default port number.
Enter the name of the NAS. The NAS name supports maximum 14
Enable Secure Connection (HTTPS):
Enable secure connection (HTTPS) and enter the port number. If the option "Force secure
Allows users to connect to the NAS by HTTPS.
42
Page 43

connection (HTTPS) only" is enabled, users can only connect to the web administration
Note:
First time synchronization may take several minutes to complete.
page by HTTPS.
Force Secure Connection (HTTPS):
log into the NAS using HTTPS.
Disable and hide the home/multimedia features such as Photo Station, Music
Station, Surveillance Station, Download Station, iTunes server, and DLNA media
server:
2.0 and 1.0.5), Surveillance Station, Download Station, DJ Station, iTunes server, Media
Library and DLNA media server, may be hidden or disabled by default on the following NAS
models: x70U, x79 Pro, x79U, TS-x51,TS-x31+, TS-x31,TS-269H and HS-210. To enable
the multimedia features for those models, uncheck this option.
Time
Basic time settings:
location of the NAS. If the settings are incorrect, the following problems may occur:
o
Multimedia features, including Photo Station, Music Station, Video Station (both
When using a web browser to connect to the NAS or save a file, the displayed time of the
After enabling this option, you can only connect and
Adjust the date and time format and time zone according to the
action will be incorrect.
o
The time of event logs will be inconsistent with the actual time when an action occurs.
o
All scheduled jobs will be run at an incorrect time.
Manual Setting:
Synchronize with an Internet time server automatically:
automatically synchronize the date and time of the NAS with an NTP (Network Time
Protocol) server. Enter the IP address/domain name of the NTP server (for example:
time.nist.gov, time.windows.com) then enter the time interval for synchronization. This
option can only be used when the NAS is connected to the Internet.
Set the server time the same as your computer time:
NAS with your computer's time, click "Update" next to this option.
Daylight Saving Time
Select this option to manually set the time of the NAS.
Enable this option to
To synchronize the time of the
If your region uses daylight saving time (DST), enable "Adjust system clock automatically for
daylight saving time" and click "Apply". The latest DST schedule of the time zone specified in the
"Time" section will be shown. The system time will be adjusted automatically according to the
DST. Note that if your region does not adopt DST, the options on this page will not be available.
To manually enter the DST table, select the option "Enable customized daylight saving time
table". Click "Add Daylight Saving Time Data", enter the daylight saving time schedule, and click
"Apply" to save the settings.
43
Page 44

Note:
All of the files and directories on the NAS use Unicode encoding. If your FTP clients or
PC OS does not support Unicode, select the language which is the same as the OS language
in order to properly view files and directories on the NAS.
Codepage
Select the language the NAS uses to display files and directories.
Login Screen
The administrator can customize the login screen by going to “Control Panel” > “General
Settings” > “Login Screen”. There are two templates to choose from: classic and photo wall.
Classic login page settings:
Show firmware version: Display QTS firmware verion on bottom right of login page.
Show the link bar: Display links to myQNAPCloud, QNAP Utility, and Feedback links to the
bottom of the login page.
Background: Select a photo to use as login screen background, then select center, fill, fit,
stretch, or tile as the display mode. Click remove to set background to default image.
Logo: Select image to use as a logo on login screen. Click remove to remove logo.
Message: Enter a personal login message. You may select font color and size.
Photo Wall page settings:
Show firmware version: Display QTS firmware verion on bottom right of login page.
Show the link bar: Display links to myQNAPCloud, QNAP Utility, and Feedback links at the
bottom of the login page.
Message Title: Enter a personal message title for the login page.
Message: Enter a personal message for the login page.
Randomly select 100 photos: Use 100 random photos stores on the NAS for login page
background.
Display the most recently shared 100 photos: Use 100 most recently shared photos on NAS
for login page background.
Change Picture: Select an image to use as a logo on login screen. Click remove to remove
logo.
Use my profile picture: Use user account profile picture as login screen logo.
After you finish the above settings, click "Preview" to preview your settings or "Apply" to save
changes.
44
Page 45

Note: Some features listed above are only applicable to certain NAS models.
Storage Manager
Based on QNAP's Flexible Volume Architecture, the Storage Manager provides a secure, flexible and
comprehensive approach to managing data on your NAS and offers useful features such as:
Storage pools & multiple RAID groups
Thin-provisioned volumes & space reclamation
Snapshot & Snapshot Replica
Online capacity expansion
These features provide a complete storage solution for your valuable data.
QNAP Flexible Volume Architecture
The QNAP Flexible Volume Architecture consists of the following four layers: Disk Management, Storage
Pool Management, Volume Management and Shared Folder Management, as shown below:
45
Page 46

Basic Storage Management Architecture
Each layer is designed to cover an aspect of the storage system. The four layers combine to offer you a
comprehensive range of options to store and protect your data on your QNAP NAS.
RAID Group: RAID groups combine multiple physical disk drives into a single logical unit to provide
data redundancy, performance improvements, or both.
46
Page 47

Storage pool: Storage pools aggregate physical hard drives or RAID groups into large storage
spaces. A storage pool can be expanded by adding new RAID groups into it or by adding new disks
to an existing RAID group.
Hot Spare: A hot spare is a backup hard drive in the NAS that is used only when a disk in a RAID
group fails. The hot spare will automatically replace the faulty disk and the data will be rebuilt to the
hot spare.
Volume: Volumes are storage spaces on your NAS. A volume is formatted by the file system to store
shared folders and files. There are three types of volumes: thick, thin and static. Thick/thin volumes
must be created in a storage pool, and a storage pool can contain multiple thick/thin volumes. A
thick/thin volume can be resized to a greater capacity if there is available space in the storage pool.
Static volumes, on the other hand, are created from a RAID group instead of a storage pool. A static
volume can be expanded by adding new RAID groups into it or by adding new disks to an existing
RAID group. More information on volumes can be found here.
iSCSI LUN: iSCSI LUNs are logical volumes mapped to iSCSI targets. There are two types of LUNs:
block-based and file-based. Block-based LUNs are usually preferred to File-based LUNs. The
difference between block-based LUN and file-based LUN can be found here.
Shared folder: Shared folders are created in volumes and are used to store and share files with
users or groups that have access privileges.
For more information on Storage Manager, please refer to the links below:
Creating new storage pools.
Creating new volumes.
Creating new shared folders.
Creating iSCSI LUNs.
Advanced Storage Architecture
Qtier - Auto-tiering storage management architecture
47
Page 48

Qtier storage pool: Qtier is an automated-tiering storage solution that consists of different types of
disks to form a multiple-drive volume that during low-load times or based on your schedule:
o Moves frequently used data onto high-performance disks (ie. SSDs) for high-availability or high
I/O cache throughput.
o Moves less frequently used data onto low-cost, high-capacity disks (ie. SATA drives) for better
cost efficiency.
There are three speed tiers of disks:
o Ultra-High speed tier: Ultra-high speed tier is a RAID group that consists of SSD for hot data.
o High speed tier: High speed tier is a RAID group that consists of SAS disks for the data that is
between hot data and cold data.
o Capacity tier: Capacity tier is a RAID group that consists of SATA disks for cold data.
Cache Acceleration: The Cache Acceleration feature is designed to boost access performance of the
NAS by the use of SSD(s). More information on cache acceleration can be found here.
Click here for more information on setting up Qtier.
Disaster-recovery storage management architecture
Snapshot: Take a snapshot to record the state of a volume/LUN. After snapshots are taken, they can
be used to restore the volume/LUN’s state to the time the snapshot was taken. Users may also
choose to only restore particular folders/files in the volume from the Snapshot.
Snapshot Replica: The Snapshot Replica allows you to replicate the volume/LUNs between different
remote servers using snapshot technology, which provides a flexible and efficient backup service for
IT professionals.
Snapshot Vault: Snapshot Vault stores snapshots sent from remote NAS via Snapshot Replica.
Snapshot Vault also lets you manage and restore remote snapshots.
48
Page 49

Features
Legacy
Volume
Static
Volume
QTS 4.1 Storage
Pool Flexible
Volume
QTS 4.2 Storage
Pool Flexible
Volume
Performance level
High
High
Medium
Medium
Online RAID
migration
● ● ●
●
Online RAID
expansion
● ● ●
●
File-based LUN
● ● ●
●
Block-based LUN
●
●
Thin provisioning
●
●
SSD cache
● ● ●
JBOD RAID
expansion
● ● ●
JBOD expansion
roaming
● ● ●
Snapshot
●
Snapshot Replica
●
Snapshot Vault
●
Click here for more information on creating replication jobs.
This architecture supports four distinct types of volumes adapted by QNAP over the years, and each
volume type supports different storage features:
49
Page 50

Note:
It is strongly recommended that each JBOD has its own storage pool. Do not create storage pools
that include hard drives outside the JBOD. Only add new disks to the JBOD (or replace the existing
disks in the JBOD) when expanding the storage pool. Otherwise, data stored on the JBOD will
become inaccessible when connected to a different NAS host.
To migrate storage pools from a previous firmware version to QTS 4.2, please check the migration
tutorial: https://www.qnap.com/i/au/trade_teach/con_show.php?op=showone&cid=139
For specific setup of the Storage Manager, please refer to the following links:
Dashboard
Storage
iSCSI
Virtual Disk
Dashboard
The Storage Manager dashboard provides an overview for IT administrators to easily monitor and
manage storage allocations.
Overview
There are three sections on the page: Disk, Volume/LUN and Storage Pool. They are described below:
Disk: The physical hard disk drives and their associated storage hosts (including both the NAS and its
connected expansion enclosures) are shown in this section. Click the hard disk drive icon to bring up
the Disk Health window. For details on the Disk Health window, please refer to the Disks chapter.
50
Page 51

Volume/LUN: All available logical volumes, their capacity and type (Volume, LUN and Unused) are
Note: Utilization only applies to certain NAS models. To check for applicable models, please refer to the
product comparison table on the QNAP website.
listed in this section. For details on volumes and LUN, please refer to the Volumes chapter.
Storage Pool: This section provides a space usage overview on the storage pool created on the NAS.
You can check the space distribution on the pie chart for each storage pool (including the size of
reserved system space, thick volume and free space) and its subscription. Subscription is the ratio
between claimed space and available space in the storage pool. If a user creates a thin-provisioned
volume with 10TB claimed space, while the available space is only 1TB, the "Subscription" value in
the "Overview" page will be 10:1, meaning that the thin-provisioned space is oversubscribed and
users must note that the available space in storage pool is too low. You can also click on the down
arrow next to the storage pool to switch between storage pools. For details on storage pools, please
refer to the Storage Pools chapter.
Utilization
This page is designed for users to monitor storage utilization of their NAS. With volume and storage pool
usage information presented on this page, users can manage their storage system more effectively and
spot potential issues based on trends over a period of time (from the last hour to the last year).
Select to view the storage usage rate of a particular volume or storage pool and specify the period. Click
"Clear Record" to reset the utilization graph.
51
Page 52

Note:
Some of the features listed above are applicable to certain models. Please check for
applicable models first as you review descriptions of the features.
Storage
Manage volumes, storage pools, hard disk drives, snapshots, encrypt and decrypt file systems, and
configure cache acceleration with Storage Manager.
For details on the features, refer to the following links:
Disks/JBOD
Storage Space
Cache Acceleration
Snapshot
Qtier (Auto Tiering)
52
Page 53

Disks/VJBOD
This page is designed for users to monitor and manage hard disk drives installed on the NAS and its
connected expansion units (both expansion enclosures and VJBOD (also known as Virtual JBOD)). Users
can quickly isolate and identify hard drives for relevant maintenance tasks.
In this chapter, the following topics are covered:
Disks
o Managing NAS Hosts
o Managing Disks
o HDD S.M.A.R.T. Information
o Disk Health Global Settings
Expansion Enclosures
o Managing Physical Expansion Enclosures
o Recovering Physical Expansion Enclosures
o Managing Virtual Expansion Enclosures (VJBOD)
Introducing VJBODs
Creating VJBODs with new iSCSI LUN (using Create Virtual JBOD’s Disk Wizard)
Creating VJBODs with existing iSCSI LUN (using Create Virtual JBOD’s Disk Wizard)
Using VJBODs
Managing and Monitoring VJBODs
Detaching and Reconnecting VJBODs
Data Roaming
Automatic Reconnection
53
Page 54

Disks
Note:
Hot-plugging is not supported for M.2, PCIe, and mSATA drives.
Action
Description
Enclosure
Info
Click this button to check details of an enclosure, including the model, serial number,
firmware version, BUS type, BIOS version, CPU temperature, system temperature,
power status, system fan speed and power fan speed.
Locate
(under
"Action")
Click this button and the chassis LEDs of the selected NAS host will blink for easy
identification.
RAID Group
Click this button and select a RAID group to check its details, including capacity, RAID
group name, RAID type and disk member.
Note:
You can click "NAS Host" in the system component panel and click "Action" > "Port
Table" to check the port speeds.
Action
Description
Disk Info
Click this button to check details of a disk, including the model, model number,
serial number, capacity, firmware version, ATA version and ATA standard.
Managing NAS Hosts
Click a NAS under "NAS Host" in the system component panel to check its general information. Refer to
the following table for actions available to manage a NAS host:
Managing Disks
Click "+" beside the NAS host in the system component panel and select a disk to check its general
information. The legend shown under the system component panel is provided to indicate the types of
hard disk drives:
Cache: A disk drive configured as cache.
Data: A disk drive that contains data.
Free: An empty disk drive that does not have any data on it.
Spare: A disk drive configured as spare drive for a RAID group.
Error: A disk drive detected with errors (could be bad sectors or I/O errors) and it is recommended
that this disk drive is to be replaced immediately.
Warning: A disk drive is approaching failure.
Refer to the following table for actions available to manage a disk:
54
Page 55

Disk Health
Click this button to check disk S.M.A.R.T information. More details about S.M.A.R.T
information will be provided in the next table.
Scan Now
(under
"Action")
Click this button to scan the disk for bad blocks. If bad blocks are found, the
number of bad blocks will be displayed in the "Status" field. Check the bad block
sectors by clicking on the "bad blocks" message so long as the disk is not busy.
You can also use this function if a drive is in an error state. In this case, if no bad
blocks found after a complete scan, the error state of drive will be changed back to
normal.
Locate (under
"Action")
Click this button to locate drives using LED lights for easy identification of physical
hard drives.
Set as
Enclosure
Spare (under
"Action")
Click this button to set the chosen hard disk drive as an enclosure spare drive in
RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6, or RAID 10. In case a spare drive is shared by multiple
RAID groups, that spare drive will be used to replace the first failed drive across all
RAID groups. Please note that the capacity of the enclosure spare drive must be
equal to or larger than that of the member drive in a RAID group and this option is
only available for an empty disks. Note that an enclosure spare can only be used
within an enclosure.
Disable Spare
(under
"Action")
Click this button to cancel the chosen hard disk drive as an enclosure spare drive.
New Volume
(under
"Action")
Click this button to create a new volume. For details, please refer to the chapter on
Volumes.
RAID Group
Click this button and select a RAID group and check its details, including capacity,
RAID group name, RAID type and disk member.
View Mode
(located above
the system
component
panel)
Switch to list view using the list view icon on top-left of the page. In the list view,
you can show or filter for disks. Set the filter from the drop down list to only show
hard disks based on the device (enclosure or NAS they belong to), model, type
(HDD or SSD), BUS type, capacity, used type (data, free, error, spare, cache, or
none) and status. Click "Refresh" to refresh the list.
You can also perform sequential read and IOPS read tests (under "Performance
test"), schedule weekly sequential read tests, and check the test results to gauge
the performance of the tested disks.
55
Page 56

HDD S.M.A.R.T Information
Field
Description
Summary
This page provides an overview on hard disk S.M.A.R.T details and the result of the
latest test.
Hard Disk
Information
This page shows hard disk details, including disk model, model number, serial
number, disk capacity, firmware version, ATA version and ATA standard.
SMART
Information
This page shows the results of the latest S.M.A.R.T test.
Test
Click on this tab to choose a rapid or complete S.M.A.R.T testing method for the hard
disks. The test result will be shown.
Settings
Configure the following settings on this page: 1) Enable Temperature Alarm: enable
this option to set the temperature alarm. When the hard disk temperature exceeds
the specified threshold level, the system will record an error message; and 2) Rapid
and complete test schedules: schedule a rapid or complete test here. The result of the
latest test can be viewed on the "Summary" page.
Click "APPLY to Selected HDD" to apply the settings configured on this page only to
the selected hard disk drive or "APPLY to All HDDs" to all hard disk drives.
Switch to the icon view (or tree view) and click the "Disk Health" button to bring up the Disk Health
window.
First select the NAS Host or an expansion enclosure and one of its disks to check for S.M.A.R.T
information. Refer to the below table for descriptions of each field:
Disk Health Global Settings
You can enable the following Disk Health settings in the Global Setting dialog window (the "setting" icon
next to "?" on top right side of the screen):
Activate Predictive SMART Migration: With Predictive SMART Migration, a warning message will pop
up when an S.M.A.R.T error is detected on a hard disk drive (indicating that the RAID group that the
hard drive disk belongs to is likely to fail very soon). The migration sequence will be initiated for that
RAID group to ensure the availability of that RAID group. The data from the disk with errors will be
migrated to a healthy spare drive. The migration process is much faster than the standard rebuilding
process.
Disk S.M.A.R.T polling time (minutes): This value is the interval the hard drive disks are scanned for
S.M.A.R.T errors and the default is 10 minutes.
TLER/ERC timer (seconds): This option allows system administrators to configure the hard disk drive
R/W response time. If you are not sure about the interval to set for the timer, please leave it as is.
56
Page 57

Expansion Enclosures
Note:
The function or its content is only applicable on some models. To check for applicable
models, please refer to the product comparison table on the QNAP website.
Action
Description
Enclosure Info
Click this button to check on details of the chosen enclosure,
including the enclosure model, serial number, firmware version,
BUS type, CPU temperature, system temperature, power
status, system fan speed and power fan speed.
Locate (under "Action")
Click this button and the chassis LEDs of the selected expansion
enclosure will blink for easy identification.
Safely Detach (under "Action")
Click this button to safely remove the enclosure from its host.
Update firmware (under "Action")
Click this button to update firmware for the chosen enclosure.
Rename enclosure (under
"Action")
Click this button to rename the chosen enclosure.
RAID Group
Click this button and select a RAID group to check its details,
including capacity, RAID group name, RAID type and disk
member.
Note:
The function or its content is only applicable on some models. To check for applicable
models, please refer to the product comparison table on the QNAP website.
Expansion enclosures are designed for expanding the storage capacity of a QNAP NAS. This is achieved
either through a direct, physical connection between a NAS and expansion enclosures (via USB or
mini-SAS cables) or a network connection between two NAS (using a LAN connection).
Managing Physical Expansion Enclosures
First click an expansion enclosure (REXP) in the system component panel to check its general
information. Refer to the following table for actions available to manage an expansion enclosure:
Recovering Physical Expansion Enclosures
Click "Recover" on the top-right side of the window, and there are three options available:
1. Recover Enclosure: Recover volumes on an enclosure that was accidentally disconnected (e.g.
unscheduled shutdown or unplugged SAS cable) from the NAS host. When this occurs, a broken
chain symbol will be shown in the Chassis View and the status of the affected storage pool will be
shown as "Error" and RAID group as "Not active".
57
Page 58

2. Reinitialize enclosure ID: This is only used to reorder ID for expansion enclosures in a numerical
Note:
The "Recover" button is only available if the disconnected expansion enclosure
contains volumes.
manner.
3. Scan All Free Drives: Scan drives in a free state in the NAS and attached enclosures for existing
volumes or storage pools.
Managing Virtual Expansion Enclosures (VJBOD)
Introducing VJBODs
Virtual JBOD allows you to allocate the free space of a QNAP NAS to another NAS in order to maximize the
total available storage capacity for that NAS. The following figure illustrates how Virtual JBOD works. An
iSCSI LUN on a remote NAS is created and added to a local host (host NAS in this example) as a hard drive
to expand the Storage Space on the host NAS.
58
Page 59

Note:
This function or its content is only applicable to some models (refer to the software
specification page on the QNAP website for further details) and requires firmware 4.2.2
(or newer).
Any QNAP NAS that supports iSCSI and storage pools can be used as a remote NAS, but
it is recommended that they use firmware 4.2.1 (or newer) and have at least 154GB free
space.
For greater connection stability and to automatically recover from connection failure, it is
recommended that both the remote and local NAS be on the same local network and that
the remote NAS uses a static IP address. For other network related optimization settings
(such as Port Trunking or Link Aggregation), please refer to the Network chapter.
Note:
Before you start this process, please ensure that the remote NAS has a storage pool
with at least 154GB of free space.
Creating VJBODs with new iSCSI LUN (using Create Virtual JBOD’s Disk Wizard)
Follow these steps to create a VJBOD:
1. Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Disks/VJBOD".
2. Click "VJBOD" > "Create Virtual JBOD".
3. The Create Virtual JBOD’s Disk Wizard will appear. Read the introductions and click "Next".
4. Establish a connection to a remote NAS:
o Enter the remote NAS’ IP address (or click "Detect" and select the NAS using its hostname or IP
from the dropdown list). Or click "Local Host" to mount a LUN from the local host itself.
o Enter the username and password used to log into the remote NAS (or the credentials of the local
host if you select it in the last step).
59
Page 60

o Specify the system port and enable "Secure Connection (HTTP)" for a secure connection to the
Note:
The purpose of mounting a LUN from a local host itself is to ensure that the LUN will still
be accessible if the original local host becomes unavailable.
After ticking "Host Binding" in Step 5, the LUN can only be accessed by the bound host,
even if the connection between the local host and remote NAS is lost (in this case, only the
administrator of the remote NAS can access it).
VJBOD currently only supports "Single" RAID configuration and cannot be used to create
a system volume or expand other storage pools unless the pool also consists of VJBODs
that come from the same remote NAS and same pool. The expanded capacity of the LUN
on the remote NAS will not be reflected on the local host. Therefore, to expand a VJBOD
pool, you can only create a new VJBOD on the same storage pool and join the disk into the
pool as a new RAID.
The LUN created here is a block-level iSCSI LUN.
Note:
Before you start this process, please ensure that the remote NAS has an idle target,
storage pool with an instantly-allocated LUN and the capacity of the LUN is at least 154GB.
remote NAS.
o Use "Test" to test the connection settings.
o Click "Next".
5. Select "Create a new iSCSI LUN on the selected NAS".
o You can click "NAS Detail" in the top-right corner to check the storage status of the selected NAS.
o Tick "Host Binding" if the LUN will be used to store sensitive information.
o Click "Next".
6. Select a storage pool and click "Next".
7. Choose to set up CHAP authentication and enter the required information. Click "Next".
8. Set up the capacity for creating a new LUN and choose whether to enable 4K byte sector size and
SSD cache in "Advanced Settings". Click "Next".
9. Review the configuration summary and click "Next".
10. Click "Finish" (you can also choose to create a new storage pool, new static volume, or recover
existing data in this step).
11. The new VJBOD Disk will be created.
Creating VJBODs with existing iSCSI LUN (using Create Virtual JBOD’s Disk Wizard)
Follow these steps to create a VJBOD:
1. Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Disks/VJBOD".
2. Click "VJBOD Beta" > "Create Virtual JBOD".
3. The Create Virtual JBOD’s Disk Wizard will appear. Read the introduction and click "Next".
60
Page 61

4. Establish a connection to a remote NAS:
Action
Description
Disk Info
Check details of the chosen VJBOD, including the remote NAS
model, disk name, disk type, disk location, remote disk
configuration, remote LUN name, remote iSCSI name, target
IQN and disk capacity.
New Volume (under "Action")
Create a volume using the chosen VJBOD. Please refer to the
chapter on Volumes for more information. Note that this action
is only available for VJBODs without any volumes.
NAS Detail (under "Action")
Check details of the remote NAS where the LUN is located. The
details include the hardware information, storage configuration,
shared folders and installed applications.
o Enter the remote NAS’ IP address (or click "Detect" and select the NAS using its hostname or IP
from the dropdown list). Or click "Local Host" to mount a LUN from the local host itself.
o Enter the username and password used to log into the remote NAS (or the credentials of the local
host if you select it in the last step).
o Specify the system port and enable "Secure Connection (HTTP)" for a secure connection to the
remote NAS.
o Click "Test" to test the connection settings.
o Click "Next".
5. Select "Choose an existing iSCSI LUN on the selected NAS". Click "Next".
6. Select a storage pool and click "Next".
7. Choose to set up CHAP authentication and select to use "Data Digest" and "Header Digest" (under
"CRC/Checksum"). Click "Next".
8. Review the configuration summary and click "Next".
9. Click "Finish" (you can also choose to create a new storage pool, new static volume, or recover
existing data in this step).
10. The new JBOD is created.
Using VJBODs
The VJBOD is essentially a space mapped from a LUN on a remote NAS. Before a VJBOD can be used to
store data, a storage pool or volume must be created first. For volume or storage pool creation
instructions, please check the relevant chapters (refer to the Volumes chapter for volume creation
instructions and the Storage Pools chapter for storage pool creation instructions).
Managing and Monitoring VJBODs
Click a disk under "Virtual JBOD" in the system component panel to check its general information. Refer
to the following table for actions available for managing a VJBOD:
61
Page 62

Remote Log (under "Action")
Review logs (including information, warnings and errors) of the
storage pool or NAS where the VJBOD disk is located. This will
allow you to identify issues on the remote pool if the VJBOD
becomes abnormal. You can click on the down arrow button on
the "Log" page for advanced log search functionality.
Date Recovery (under "Action")
Recover the Volume or Storage Pool in VJBODs (if it exists). This
action is only available when the VJBOD is idle.
Edit Disk (under "Action")
Edit the name of the chosen VJBOD.
Disconnect (under "Action")
Disconnect a VJBOD. Note that this action is only available for
VJBODs that are in an abnormal status.
Connect (under "Action")
Reconnect a VJBOD. Note that this action is only available for
VJBODs that are Disconnected.
Edit Target (under "Action")
Edit the VJBOD iSCSI connection and Remote NAS IP. Note that
this action is only available for VJBODs that are Disconnected.
Delete (under "Action")
Delete a VJBOD connection configuration. Note that this action
is only available for VJBODs that are Disconnected.
Alternatively, click on "Virtual JBOD" > "Virtual JBOD Overview" and check the following for each VJBOD
disk:
Disk details associated with the local host: The disk name, status, total size, storage pool and
volume/LUN.
Disk details associated with the remote host: The NAS name, storage pool, disk configuration, target
& LUN name and CHAP.
62
Page 63

Tip:
If the firmware of the remote NAS is 4.2.2 (or newer), you can monitor what NAS has
connected to an iSCSI LUN, as well as receive warnings if the iSCSI connection is lost on
the "iSCSI Storage" page ("Storage Manager" > "iSCSI" > "iSCSI Storage").
If more detailed monitoring is required for multiple NAS, you can use Q'center to monitor
both host and remote NAS.
Detaching and Reconnecting VJBODs
If a VJBOD has been used to create a virtual volume or storage pool, that volume or storage pool must be
detached first before the VJBOD can be detached. Refer to the Volumes chapter for volume removal
instructions and Storage Pools chapter for storage pool removal instructions. To detach a VJBOD disk,
follow these steps:
1. Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Disks/VJBOD".
2. Select a VJBOD in the system component panel.
3. Click "Action" > "Disconnect".
4. Click "OK" and the VJBOD will enter "Disconnected" status.
5. Click "Action" > "Delete".
6. Check to remove the LUN and unused iSCSI target from the remote NAS and click "OK". The VJBOD
will be deleted.
To reconnect disconnected VJBODs (there will be an error symbol in front of such disks), follow these
steps:
1. Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Disks/VJBOD".
2. Select a disconnected Virtual JBOD in the system component panel.
63
Page 64

3. Click "Action" > "Connect".
Note:
To protect the data and file system of VJBODs, always detach them before shutting
down the remote NAS.
Note:
If the remote NAS system port is changed, some information regarding the remote
NAS may be incorrectly displayed on the host NAS. If this occurs, you can enter the updated
information in the "Re-login" page (select the disk in "Disks/VJBOD" and click "Action" >
"Re-login").
4. Click "OK" and the VJBOD will enter the "Ready" status.
You can detach all of the VJBOD disks at once. To do so, go to the "Virtual JBOD Overview" page (click
the "Virtual JBOD Overview" button in the top-right corner of the "Storage Manager" window) and click
"Safely Detach all". Detached VJBODs can be re-attached by selecting "Recover" > "Scan All Free Disks"
in the "Disks/VJBOD" page.
Data Roaming
You can move VJBODs from one NAS to another without needing to physically disconnect and reconnect
drives. To do so, follow these steps:
1. Safely detach a VJBOD (refer to the Detaching and Reconnecting Virtual JBOD Disks section for
instructions).
2. Open the Create Virtual JBOD’s Disk Wizard on the NAS that you want to move the JBOD to and
choose the existing iSCSI LUN on the remote NAS (refer to the Creating VJBOD with existing iSCSI
LUN section for instructions).
Automatic Reconnection
The system will attempt to reconnect and recover a storage pool on a remote NAS for VJBODs after they
become inaccessible for 30 seconds. However, the reconnection and recovery process may take longer if
the remote NAS uses a dynamic IP (or it will fail if the two NAS are not on the same LAN). Therefore, we
recommend using a static IP for the remote NAS.
64
Page 65

Symbol
Name
Description
Volume
Users may change the volume name. System volume
names are appended with "(System)".
LUN
Users may change the LUN name.
Snapshot
The number to the right of the camera icon indicates
how many Snapshots are currently saved.
Storage
Pool Usage
Gray: Unallocated
Green: Allocated
Dark blue: Snapshot used
Light blue: Snapshot reserved
Red line: Alert threshold
Volume
Usage
Dark blue: Used
Red line: Alert threshold
Storage Space
The Storage Space features Storage Pools and Volumes. This page lists available storage pools and the
volumes, iSCSI LUNs, and snapshots from remote NAS on each of these storage pools. It displays these
storage entities’ capacity and/or usage to give a complete view of storage allocation. Users can create or
manage storage pools/volumes/RAID groups, or take/view snapshots of the volumes on this page.
Below is a chart of what the icons and bars indicate.
65
Page 66

LUN Usage
Light blue: Allocated
Red line: Alert threshold
For details on Storage Pools, Volumes, and RAID Groups, refer to the following links:
Storage Pools
Volumes
RAID Groups
66
Page 67

Note:
Storage Pools are not supported by some NAS models. Please refer to the QNAP website,
product information, and software specifications for more details.
For RAID groups that contain 16 hard drives, up to 512MB RAM will be used for them. 1GB
RAM is recommended for 24-32 hard drives.
Storage Pools
A storage pool is designed to aggregate physical hard disk drives into a large storage space and to
provide enhanced RAID protection for it. You can perform the following actions to manage storage pools:
Creating New Storage Pools
Removing Storage Pools
Safely Detaching Storage Pools
Expanding Storage Pools
Setting a Threshold
Setting Snapshot Reservation
Creating New Volumes for Storage Pools
Creating New iSCSI LUNs for Storage Pools
Creating New Storage Pools
Follow these steps to create a new storage pool:
1. Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Storage Space".
2. Click "Create" > "New Storage Pool".
3. Select the enclosure unit, hard disk drive(s), RAID type and hot spare disk and click "Create".
4. Set the percentage of storage spool space that is reserved to store snapshots.
5. Please note that all data on the selected hard disk drive(s) will be erased. Click "OK" if you are certain
about this.
6. A new storage pool will be created.
Removing Storage Pools
Follow these steps to remove a storage pool:
Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Storage Space".
Double click a storage pool to be removed to bring up the Storage Pool Management page.
Click "Remove" > "Remove Pool".
Click "Apply".
The selected storage pool will be removed.
67
Page 68

Note:
Before you remove a storage pool, be sure to remove all volumes and LUNs on that
storage pool.
Note:
After a storage pool is reattached, the configurations of iSCSI LUNs mapped in the
storage pool or Apps installed before the detachment will not be automatically recovered.
Note:
New disks cannot be inserted into existing RAID groups of storage pools for specific
RAID types (such as RAID 0, RAID 10, Single or JBOD). You must create an additional RAID
group to expand those storage pools.
Safely Detaching Storage Pools
Follow these steps to safely detach a storage pool:
1. Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Storage Space".
2. Double click a storage pool to be removed to bring up the Storage Pool Management page.
3. Click "Remove" > "Safely Detach Pool".
4. Click "Apply".
5. The selected storage pool will be removed.
Expanding Storage Pools
Follow these steps to expand a storage pool:
1. Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Storage Space".
2. Double click a storage pool to be expanded to bring up the Storage Pool Management page.
3. Click "Expand Pool".
4. Select to create and add a new RAID group. Select "Adding new hard drive(s) to an existing RAID
group"(the option "Create new RAID groups" will be covered in the following section), choose an
existing RAID group from the drop-down list and click "Next".
5. Select the hard drive(s) to expand the storage pool and click "Next".
6. Click "Expand".
7. Please note that all data on the selected hard disk drive(s) will be erased. Click "OK" if you are certain
about this.
8. The chosen storage pool will be expanded.
Expanding storage pools by creating new RAID groups
Follow these steps to create a RAID group for storage pool expansion:
1. Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Storage Space".
2. Double click a storage pool to be expanded to bring up the Storage Pool Management page.
3. Click "Expand Pool", select "Create and add a new RAID group" and click "Next".
68
Page 69

4. Select the enclosure unit, hard disk drive(s), RAID type and hot spare disk and click "Next".
Note:
RAID 0, JBOD or Single RAID Group cannot be added to a storage pool if that storage pool
already contains RAID 1, 5, 6, or 10.
It is recommended to set an independent storage pool on a JBOD and only add new disks
to that JBOD (or replace the existing disks in that JBOD) when expanding the storage
pool. Otherwise, data stored on that JBOD will become inaccessible when connecting that
JBOD to a different NAS host.
Note:
Available RAID management operations are detailed in the chapter on RAID Groups.
5. Please note that if the type of the newly-created RAID group is different from that of the existing
RAID group(s), the performance of the entire storage pool may be affected. To continue, click "OK".
6. Click "Expand".
7. Please note that all data on the selected hard drive(s) will be erased. Click "OK" if you are certain
about this.
8. The chosen storage pool will be expanded.
Expanding storage pools by replacing hard disk drives in a RAID array
With this function, RAID group capacity can be expanded by replacing hard disk drives in an array one
by one. This option is supported for the following RAID types: RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6 and RAID 10.
Follow these steps to expand a RAID group:
1. Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Storage Space".
2. Double click a storage pool to be expanded to bring up the Storage Pool Management page.
3. Select a RAID group and click "Manage" > "Replace Disks One by One".
4. Select at least one hard disk drive and click "Change". After the description displays "Please remove
this drive", remove the hard disk drive from the NAS or expansion enclosure.
5. After the description displays "You can replace this drive", plug in the new hard disk drive to the drive
slot.
6. Repeat steps 4 and 5 until all hard drives have been replaced.
7. Click "Expand Capacity" to continue. Click "Yes".
8. The chosen RAID group is expanded.
Setting a Threshold
The system will generate a warning message in system logs when the storage pool used size hits the
threshold. To set a threshold value for a storage pool, follow these steps:
1. Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Storage Space".
2. Double click a storage pool to set a threshold to bring up the Storage Pool Management page.
3. Click "Actions" > "Set Threshold".
69
Page 70

4. Enter a value for alert threshold and click "Apply".
Note:
For more Snapshot details, refer to the Snapshot section in the Volumes chapter.
The function or its content is only applicable on some models. To check for applicable
models, please refer to the product comparison table on the QNAP website.
o
A minimum of 4 GB RAM is required to use snapshots.
o
x51 series models only support up to 256 snapshots instead of 1024. The HS-251 does
not support snapshots.
Setting Snapshot Reservation
You can set snapshot reservation space to ensure enough space for saving snapshots. Snapshot
reservation is set as a percentage of total storage pool space and there are two scenarios:
When the snapshot reserve is set to 0%, new snapshots taken will all be saved to a storage pool until
that storage pool runs out of its space. When that happens, the system will start recycling older
snapshots regardless the snapshot limitation set in Snapshot Global Settings.
When the snapshot reserve is set to a value greater than 0%, this reserved space will be dedicated
entirely to snapshots. The free space in a storage pool will be lower after the value is set and the
snapshots will only use the space reserved. When the space used for snapshots exceeds the
snapshot reserve, the system will start recycling older snapshots regardless the snapshot limitation
set in Snapshot Global Settings.
To set snapshot reservation, follow these steps:
1. Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Storage Space".
2. Double click a storage pool to set reserved space for snapshots and to bring up the Storage Pool
Management page.
3. Click "Actions" > "Set Snapshot Reserved", enter a value for snapshot reserved space, and click
"Apply".
Creating New Volumes for Storage Pools
To create a new volume for a storage pool, follow these steps:
1. Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Storage Space".
2. Double click a storage pool.
3. Click "Create"> "New Volume". Follow the onscreen instructions to finish the creation process. For
more details, please refer to the Volumes section.
70
Page 71

Creating New iSCSI LUNs for Storage Pools
To create a new iSCSI LUN for a storage pool, follow these steps:
1. Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Storage Space".
2. Double click a storage pool.
3. Click "Create"> "New iSCSI LUN". Follow the onscreen instructions to finish the creation process. For
more details, please refer to the iSCSI Storage section.
71
Page 72

Bytes
per
Inode
Max. Size of Volume
Max. Number of Files/Folders
4096
15.99 TB
Volume Size/Bytes per Inode
8192
31.99 TB
16384
(Default)
63.99 TB
32768
127.99 TB
65536
250 TB
Volumes
A volume is formatted by the file system to store share folders and files. Users can manage, monitor,
create, or delete a logical volume on this page. The following topics are covered in this chapter:
Creating New Volumes
Removing Volumes
Expanding Volumes
Available Volume operations
Configuring Alert Threshold
Creating New Shared Folders
Snapshot
Managing Previous Versions in Windows
Encryption
Setting Thin Provisioning Space Reclamation and SSD Trim
Creating New Volumes
1. Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Storage Space".
2. Click "Create" > "New Volume" to launch the volume creation wizard.
3. Configure the mode for the volume from static single, thick multiple, and thin multiple according to
your needs (learn more about "Thick or Thin Volumes" in the following section) and click "Next".
4. Select the enclosure unit, hard disk drive(s), RAID type and hot spare disk for the volume to be
created and click "Next".
5. Set the alert threshold and volume alias. You can also click "File system option" to specify bytes per
inode, check the maximum volume size and number of files/folders, enable volume encryption, and
create share folders. Click "Next".
72
Page 73

6. Confirm your settings and click "Finish".
Note:
The hot spare disk feature is only available for RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6 and RAID 10.
For other RAID types, the hot spare disk field will be grayed out.
Note:
Static Single Volume:
This mode offers the best performance but does not support thin
provisioning, space reclamation and snapshots. For this option, the RAID group itself is a
volume.
Thick Multiple Volumes:
This method can create multiple volumes on the same storage
pool and instantly allocate physical storage space for the volume. It has better
performance than thin volumes while also offering flexibility.
Thin Multiple Volumes:
Thin Multiple Volumes: This method can over-allocate the
volume capacity for each volume regardless of the physical storage limit. Disk space is
only used when files are written to the volume. After files are deleted, this space can be
reclaimed for increasing the free space of the storage pool. The maximum size of thin
multiple volumes is 20 times that of the storage pool's free space. With thin provisioning,
volume space is fully utilized.
A thick volume is usually more efficient for high frequency read/write activities. Because
the space has been allocated for the volume, the predicament of insufficient physical
space can be avoided, but the use of space is relatively inefficient.
NAS models that do not support Storage Pools can only create Static Single Volumes.
Please refer to the QNAP website, product information, and software specifications for
more details.
7. Please note that all data on the selected hard drive(s) will be erased. Click "OK" if you are certain
about this.
8. The new volume will be created.
Follow these steps to create a new, thick or thin volume:
1. Select "Thick Multiple Volume" or "Thin Multiple Volume". Select to create a new storage pool or from
an existing storage pool and click "Next".
2. Configure the mode for the volume from static single, thick multiple, and thin multiple according to
your needs.
3. Configure the volume capacity, alert threshold, volume alias, Bytes per inode, encryption and shared
folder settings and click "Next".
4. Click "Finish".
5. A new volume will be created.
73
Page 74

Removing Volumes
Note:
All the data on a disk will be erased if it is formatted. Please use the "Format" feature with
caution.
For encryption related options (Change, Download, Save, Lock this Volume), refer to
Encryption.
The function or its content is only applicable on some models. To check for applicable
models, please refer to the product comparison table on the QNAP website.
o
A minimum of 4 GB RAM is required to use snapshots.
o
x51 series models only support up to 256 snapshots instead of 1024. The HS-251 does
not support snapshots.
1. Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Storage Space".
2. Double click a volume to be removed to bring up the Volume Management page.
3. Click "Remove". Click "Apply" and the selected volume is removed.
Expanding Volumes
1. Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Storage Space".
2. Double click a volume to be expanded to bring up the Volume Management page.
3. Click "Expand Volume".
4. Enter the desired capacity or click "Set to Max" to allocate the maximum available space for the
volume and click "Apply". ("Set to Max" is only available for thick provisioned volumes).
5. The capacity of the volume will be expanded.
Available Volume Operations
After you go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Storage Space", click "Actions" and choose to
configure the threshold and cache settings, check the file system of a volume, rename volume alias,
reclaim volume space, create a new share folder, format a volume, or manage snapshots.
Configuring Alert Threshold
The alert threshold is used to remind users when the capacity of a chosen volume is used up to the
specified threshold level. A warning message will pop up when the specified threshold is reached.
To set an alert threshold, select a volume in "Storage Space" to bring up the Volume Management page,
click "Actions" > "Set Threshold", enter the threshold level and click "Apply". The alert threshold is set.
74
Page 75

Creating New Shared Folders
Note:
Snapshot Replica (or volumes/LUNs replication between remote servers) is covered in
Backup Station. For details, please refer to the Snapshot Replica chapter in Backup
Station.
The function or its content is only applicable on some models. To check for applicable
models, please refer to the product comparison table on the QNAP website.
o
A minimum of 4 GB RAM is required to use snapshots.
o
x51 series models only support up to 256 snapshots instead of 1024. The HS-251 does
not support snapshots.
1. Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Storage Space".
2. Double click a volume to bring up the Volume Management page.
3. Click "Actions" > "Create New Shared Folder".
4. Specify the folder name and description of the new shared folder and select the disk volume for the
shared folder.
5. Click "Edit" to the right of "Configure access privileges for users" in Step 4 and specify user
privileges.
6. Click "Edit" to the right of "Advanced settings" in Step 4 and configure the guest access right, hidden
folder, Oplocks, recycle bin and path. Click "Create".
7. A new shared folder will be created.
Snapshot
Users can take a snapshot, manage snapshots (revert, delete, and clone a snapshot, set up snapshot
schedules, or restore snapshot files for LUNs or volumes), or replicate volumes/LUNs between different
remote servers using snapshot technology.
Taking a Snapshot
After reserved space is set, you can proceed to take snapshots. To create a snapshot, follow these steps:
1. Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Storage Space".
2. Select a volume or LUN and click "Snapshot" > "Take a Snapshot".
3. Specify the snapshot name and duration to retain the snapshot.
4. Click "OK".
Managing Snapshots with Snapshot Manager
The Snapshot Manager allows you to take, revert, delete, and clone a snapshot, set up snapshot
schedules, or restore snapshot files.
To launch Snapshot Manager, select a volume or LUN in "Storage Space" and click "Snapshot" >
"Snapshot Manager" (or click the camera icon of a volume or LUN).
75
Page 76

In Snapshot Manager, you can perform the following actions:
Note:
The "When reaching snapshot limitation" setting uses the number of snapshots, not
the space used for snapshots. For more details, please refer to the Setting Snapshot
Reservation section.
Restore files: Click a desired snapshot and select the folder(s) or file(s) that you want to restore,
right click and select "Restore" to replace the existing folder/file with the one in the snapshot or
"Restore to" to restore your data to a different location. Or choose "Download" to download the
selection to your computer.
Revert a snapshot: Select a snapshot and click "Revert", and the entire snapshot will be restored to
its original path. Be cautious that the volume reverted to the selected snapshot will be in the previous
state when the snapshot was taken.
Delete: Select a snapshot and click "Delete" to delete that snapshot.
Clone a snapshot: This action allows you to clone a snapshot into a new volume or LUN. To clone a
snapshot, first select a snapshot, click "Clone", enter an alias for the new volume, and select the
folders to share after cloning. If the snapshot cloned is a LUN snapshot, you can map it to an iSCSI
target.
Set up snapshot schedules: Click "Schedule", select "Enable schedule", specify the time, frequency,
and retention period. The system will take the chosen volume’s snapshot by schedule. For Smart
Snapshot, the system will only take a new snapshot if there are new changes made in the selected
volume.
Snapshot Global Settings
Click "Global Settings" in the top-right of the Snapshot Manager window, and there is one global
setting:
Make snapshot directory (@Recently-Snapshot) visible: Mount a snapshot volume as a directory of
a shared folder and set the snapshot volumes to be read-only in File Station. The snapshot directory
will appear as "@Recently-Snapshot".
Click "Global Settings" in the top-right of the Storage Manager window, and there is one global setting:
When reaching snapshot limitation: Choose the policy to handle snapshots when the snapshot
limitation is reached. There are two choices.
o Overwrite the oldest snapshot: When the number of snapshots reaches the limitation (256 per
LUN, 1024 total) the oldest snapshot will be deleted in order to continue taking new snapshots for
data protection.
o Stop making snapshot: When the number of snapshots reaches the limitation (256 per LUN, 1024
total), no more new and scheduled snapshots will be taken until older snapshot are deleted. This
option will prevent the deletion of older snapshots without administrators’ consent.
76
Page 77

Managing Previous Versions in Windows
Note:
This feature is only applicable to files that have been changed between snapshots.
Otherwise, there will be no previous versions listed in "File Explorer" > "Properties" >
"Previous Versions".
Note:
The AES volume-based encryption is applicable only to specific NAS models. Please
refer to the product comparison table for details.
Starting in QTS 4.2.1, snapshots can be used with the Previous Versions feature in Windows, allowing
you to instantly revert to a previous version of a file in case of an accident (e.g. file deletion, corruption,
or accidental changes).
To use this feature, follow these steps:
1. In Windows, connect to a shared folder on the NAS (the shared folder must be located in a storage
pool that you can take a snapshot).
2. Take a snapshot of the storage pool where the shared folder is located.
3. In Windows, right click on the shared folder (or a file in that shared folder) in "File Explorer" >
"Properties" > "Previous Versions".
4. Select a version and choose to open, copy, or restore that version.
5. Click "OK".
Encryption
The disk volumes on the NAS can be encrypted with 256-bit AES encryption to protect against data
breaches. Encrypted disk volumes can only be mounted for normal read/write access with an authorized
password. The encryption feature protects confidential data from unauthorized access even if the hard
drives or the entire NAS were stolen.
Data encryption on QNAP NAS
Users can manage encrypted disk volumes on the NAS. Each encrypted disk volume is locked by a
particular key. The encrypted volume can be unlocked using the following methods:
Encryption password: Enter the encryption password to unlock the disk volume. The password must
be 8-32 characters long. Symbols (! @ # $ % ^ & * ( )_+ = ? ") are supported.
Encryption key file: Upload the encryption key file to the NAS to unlock the disk volume. The key can
be downloaded from the "Encryption" page after the disk volume is successfully unlocked.
Before you start
Please remember the following before using the data encryption feature of the NAS.
77
Page 78

The volume encryption feature of the NAS is volume-based. A volume can be a single disk a JBOD
Note:
Data encryption functions may be unavailable in accordance to the legislative
restrictions of some countries (ex. Russia, Belarus, Ukraine, Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan).
configuration, or a RAID array. To only encrypt a shared folder, please refer to the Shared Folder
chapter.
Select whether or not to encrypt a disk volume before it is created on the NAS. A volume cannot be
encrypted after it is created unless the disk volume is initialized. Note that initializing a disk volume
will clear all data on the disks.
Disk volume encryption cannot be removed without initialization. To remove encryption on the disk
volume, the disk volume must be initialized and all the data will be cleared.
Keep the encryption password or key safe. If the password is forgotten or the encryption key is lost,
the data cannot be accessed and cannot be recovered.
Before starting, read the instructions carefully and strictly adhere to them.
Creating new encrypted disk volumes
1. Log into the NAS as an administrator. Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Storage Space" and
click "Create" > "New Volume".
2. Select a volume type based on your needs and click "Next".
3. Specify the volume details (including the volume capacity, alert threshold and volume alias,) tick
"Encryption", fill out the encryption password and choose whether to save the encryption key, select
to create a shared folder automatically after new volume initialization and fill out the name of the
shared folder for the intended volume. Click "Next".
4. Confirm the settings and click "Finish".
5. Note that all the data on the selected drives will be DELETED! Please back up the data before creating
the encrypted volume. Click "Yes" after data backup.
6. Double click the newly-created volume to bring up the Volume Management page.
7. Click "Actions" > "Encryption" > "Lock this Volume". Click "Yes".
8. An encrypted disk volume will be created on the NAS.
Encryption key management
To manage the encryption key settings, log into the NAS as an administrator and go to "Storage
Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Storage Space". Double click a volume to bring up the Volume Management
page and click "Actions" > "Encryption".
There are three options to manage the encryption key:
Change the encryption key: Enter your old encryption password and the new password. (Please note
that after the password is changed, any previously exported keys will not work anymore. The new
encryption key needs to be downloaded if necessary, see below).
78
Page 79

Download the encryption key file: Enter the encryption password to download the encryption key file.
Note:
For details on enabling or disabling the "Save Encryption Key" option, please refer to
the section on Encryption Key Management above.
With this option, the encryption key can be saved as a file. The file is also encrypted and can be used
to unlock a volume, without knowing the real password (see "Locking and unlocking disk volumes
manually" below). Please save the encryption key file in a secure place!
Save the encryption key: Save the encryption key on the NAS to automatically unlock and mount the
encrypted disk volume after the NAS restarts. Note that saving the encryption key alone is not
completely safe, as if the NAS is stolen, the volume will be automatically unlocked after it
restarts.
Locking and unlocking disk volumes manually
To lock a volume, log into the NAS as an administrator. Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" >
"Storage Space". Double click a volume to be locked to bring up the Volume Management page and click
"Actions" > "Encryption" > "Lock this Volume". Click "Yes".
To unlock a volume, log into the NAS as an administrator. Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" >
"Storage Space". Select a volume to be unlocked and click "Manage" > " Unlock this volume". Choose
either to enter the encryption password, or use the encryption key file exported previously. Click "Apply".
If the encryption password or the key file is correct, the volume will be unlocked and become available.
Verifying encrypted disk volumes
To verify that a disk volume is encrypted, log into the NAS as an administrator. Go to "Storage Manager"
> "STORAGE" > "Storage Space". The encrypted disk volume will be shown on this page, with a lock icon
under "Status". The lock will be shown as opened if the encrypted volume is unlocked. A disk volume
without the lock icon under "Status" is not encrypted.
Behaviors of encrypted volumes upon system reboot
An example is provided to illustrate the behavior of encrypted volumes upon system reboot. In this
example, there are two encrypted disk volumes on the NAS:
DataVol1 is created with the option "Save Encryption Key" disabled.
DataVol2 is created with the option "Save Encryption Key" enabled.
79
Page 80

After restarting the NAS, check the volume status. DataVol1 is locked, but DataVol2 is unlocked and
mounted. Since the encryption key is not saved on DataVol1, the encryption password needs to be
manually entered to unlock DataVol1. Please remember that by saving the key on the NAS, data will only
be protected in case of stolen hard disk drives. However, there is still a risk of data breach if the entire
NAS is stolen as the data is accessible after the NAS is restarted. If the encryption key is not saved on
the NAS, the NAS will be protected against data breach even if the entire NAS were stolen. The
disadvantage is that the disk volume needs to be manually unlocked each time the system restarts.
Setting Thin Provisioning Space Reclamation and SSD Trim
Thin Provisioning Space Reclamation allows you to increase free space on thin-provisioned storage pools
by reclaiming space from deleted files. SSD Trim enables garbage collection on SSDs, which wipes out
blocks of data that are no longer in use, and increases future write performance.
To enable Space Reclamation and SSD Trim, log into QTS, launch Storage Manager and click on the
"Global Settings" icon located at the top right of the Storage Manager window. The Global Settings
window will open, then click on "Edit" beside Space Reclamation and SSD Trim. There are two settings
for Space Reclamation and SSD Trim:
Auto reclaim and SSD trim schedule: Check this checkbox to enable space reclamation and SSD
trim.
Schedule: Set the schedule for thin provisioning space reclamation and SSD TRIM in order to
reclaim space and increase free space for storage pools.
80
Page 81

Field
Description
Single Disk
A single, stand-alone RAID group can be set up for your NAS. However, this setup
does not provide any redundancy protection. So, in the event that a disk is corrupted
or otherwise damaged, all data on that disk will be lost.
RAID 0
Striping
A striping RAID group combines two or more disks into one large, logical disk. It
offers the fastest disk access performance but no data redundancy protection in the
event of disk failure or damage. The disk capacity is the sum of all disks. Disk striping
is usually used to maximize disk capacity or to accelerate disk access speed. Please
note that RAID 0 configuration is not recommended for storing sensitive data.
RAID 1
Mirroring
Disk Mirroring protects your data by automatically mirroring the contents of one disk
to the second disk in the mirrored pair. It provides protection in the event of a single
disk failure. The storage capacity is equal to the capacity of the smallest single disk,
as the second disk drive is used to back up the first disk drive. RAID 1 configuration
is suitable for storing sensitive data on a corporate or personal level.
RAID 5
RAID 5 configurations are ideal for organizations running databases and other
transaction-based applications that require storage efficiency and data protection. A
minimum of 3 hard disks are required to create a RAID 5 group. The total capacity of
the RAID 5 group is equal to the size of the disk with the smallest capacity in the array
times the number of (hard disk – 1). It is recommended (though not required) that
RAID Groups
Users can expand a RAID group, add hard drive(s) to a RAID group, migrate a RAID group, configure a
spare drive, enable a bitmap and recover a RAID group for a chosen volume, while the data contained in
the RAID group remains intact. In this chapter, the following topics are covered:
RAID Group Introduction
Expanding RAID Group Capacity
Adding Hard Disk Drives
Migrating RAID Configuration
Configuring Spare Drives
Enabling/Disabling Bitmap
Recovering Failed RAID Disk Volumes
RAID Group Introduction
RAID group types
Refer to the table below for explanations on RAID types:
81
Page 82

only hard drives of the same brand and capacity are used to establish the most
efficient hard drive capacity.
In addition, if your system contains four disk drives, it is possible to use three drives
to implement a RAID 5 data array with the fourth drive kept as a spare disk. In this
configuration, the system will automatically use the spare disk to rebuild the array in
the event of a physical disk failure. A RAID 5 configuration can survive one disk failure
without losing any system functionality. When a disk fails in RAID 5, the disk volume
will operate in the "degraded mode". There is no more data protection at this stage,
and all the data will be lost if the unit suffers a second disk failure. A failed disk should
be immediately replaced. Users can choose to install a new disk after turning off the
server or hot-swap the new disk while the server is running. The status of the disk
volume will change to "rebuilding" after installing a new disk. Your disk volume will
return to a normal status once the volume rebuilding process is complete.
Note: To install a new disk when the server is running, first ensure the disk volume
is in "degraded" mode. Or, wait to hear two long beeps after the disk crashes and
then insert the new disk in place of the failed disk.
RAID 6
RAID 6 is ideal for critical data protection needs. To create a RAID 6 group, a
minimum of 4 hard disks are required. The total capacity of a RAID 6 group is equal
to the size of the disk with the smallest capacity in the array times the number of
(hard disks – 2). It is recommended (though not required) to use identical hard drives
to establish the most efficient hard drive capacity. RAID 6 can survive 2 disk failures
and the system can still operate properly.
Note: To install a new disk when the server is running, first ensure the disk volume
is in "degraded" mode. Or, wait to hear two long beeps after the disk crash and then
insert the new disk in place of the failed disk.
RAID 10
RAID 10 is a combination of RAID 1 (mirroring) and RAID 0 (striping), without parity.
RAID 10 is a stripe across a number of disks to provide fault tolerance and high speed
data transfer. The storage capacity of a RAID 10 group is equal to the size of the disk
with the smallest capacity in the array times (the number of hard disks in the
array/2). It is recommended that only hard disk drives of the same brand and
capacity are used to create a RAID 10 group. RAID 10 is suitable for high volume
transaction applications, such as a database, that require high performance and fault
tolerance. A maximum of 1 failed disk from each disk pair is allowed in RAID 10.
Note: To install a new disk when the server is running, first be sure the disk volume
is in the "degraded" mode. Or, wait to hear two long beeps after the disk crashes and
82
Page 83

then insert the new disk in place of the failed disk.
JBOD
Two or more disks can be combined into one larger volume. Files are sequentially
saved on physical disks. The overall capacity of the linear disk is the sum of the
capacity of all disks. This configuration does not provide disk failure protection;
failure of one drive will cause the entire array to be lost. A JBOD group is generally
used for storing a large amount of data. It is not appropriate for storing sensitive
data.
Note:
BBM support is only available for RAID 5 and RAID 6.
Bad Block Management (BBM)
BBM uses the bad block list (log) for each drive and uses it to allow the system to fail single blocks rather
than entire drives. This feature is especially useful for RAID arrays and is automatically enabled if your
disks support BBM. Bad blocks in different sections on different drives can cause a RAID array to fail.
With BBM, the RAID array can be functional even when encountering bad blocks.
Expanding RAID Group Capacity
With this function, RAID group capacity can be expanded by replacing hard disk drives in a RAID group
array one by one. This option is supported for the following RAID types: RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6 and
RAID 10. Follow these steps to expand a RAID group:
1. Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Storage Space".
2. Double click a storage pool to bring up the Storage Pool Management page.
3. Select a RAID group and click "Manage" > "Replace Disks One by One".
4. Select at least one hard disk drive. After the description displays "Please remove this drive", remove
the hard disk drive from the NAS or expansion enclosure.
5. After the description displays "You can replace this drive", plug in the new hard disk drive to the drive
slot. Repeat the same process for all hard drives to be replaced. Click "Expand Capacity" to continue.
6. Click "Yes".
7. The chosen RAID group is expanded.
Adding Hard Disk Drives
With this function, new drive members can be added to a RAID group. This option is supported for RAID
5 and RAID 6 drive configurations.
Follow these steps to add the hard disk drive(s) to a RAID group:
1. Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Storage Space".
2. Double click a storage pool to bring up the Storage Pool Management page.
3. Select a RAID group and click "Manage" > "Add Hard Drive".
83
Page 84

4. Select hard disk drive(s) from the list to add to the chosen RAID group and click "Apply".
Note:
New disks cannot be inserted into existing RAID groups for specific RAID types, such
as, RAID 0, RAID 10, Single, or JBOD. You must create additional RAID groups to expand
these storage pools.
5. Please note that all data on the selected hard drive(s) will be erased. Click "Yes" if you are certain
about this.
6. The chosen hard disk drive(s) are added to the selected RAID group.
Migrating RAID Configuration
With this function, a RAID configuration can be migrated to a different RAID configuration. This option is
supported for the following drive configurations: Migrating single drives to RAID 1; Migrating RAID 1 to
RAID 5; Migrating RAID 5 to RAID 6. Follow these steps to migrate a RAID configuration:
1. Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Storage Space".
2. Double click a storage pool to bring up the Storage Pool Management page.
3. Select a RAID group and click "Manage" > "Migrate".
4. Select the hard disk drive(s) from the list and click "Apply".
5. Please note that all data on the selected hard disk drive(s) will be erased. Click "Yes" if you are
certain about this.
6. The chosen RAID configuration is migrated to the new one.
Configuring Spare Drives
84
Page 85

With this function, a spare drive can be added to or removed from a RAID 1, RAID, 5, RAID 6, or RAID
Note:
Bitmap support is only available for RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6 and RAID 10.
10 configuration. Unlike a global spare drive, the drive in this case will be dedicated to the RAID group.
Follow these steps to configure a spare drive:
1. Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Storage Space".
2. Double click a storage pool to bring up the Storage Pool Management page.
3. Select a RAID group and click "Manage" > "Configure Spare Drive".
4. Select the hard disk drive(s) to be configured as spare drive and click "Apply".
5. Please note that all data on the selected hard disk drive(s) will be erased. Click "Yes" if you are
certain about this.
6. The chosen disk drives are added as spare drive.
Enabling/Disabling Bitmap
This function can reduce the rebuild time after a crash, or the time length required to remove/re-add a
hard disk. This feature does not improve disk read/write performance and may even cause slight
performance degradation. However, if an array has a bitmap, a hard disk can be removed and re-added,
and only changes in blocks need to be made since the removal (as recorded in the bitmap) can be
re-synced. To enable a bitmap, follow these steps:
1. Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Storage Space".
2. Double click a storage pool to bring up the Storage Pool Management page.
3. Select a RAID group and click "Manage" > "Enable Bitmap" and then "OK".
To disable a bitmap,
1. Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Storage Space".
2. Double click a storage pool to bring up the Storage Pool Management page.
3. Select a RAID group and click "Manage" > "Disable Bitmap" (only available after a bitmap has been
enabled) and then "OK".
Recovering Failed RAID Disk Volumes
This can recover failed RAID disk volumes from the "Inactive" status to a normal state (RAID 1, RAID 5,
RAID 6 and RAID 10 will be recovered to the degraded mode; RAID 0 and JBOD will be recovered to the
normal state). Before recovering a failed disk volume, please confirm that all hard disks of that disk
volume are properly seated in the NAS drive bays. Once recovery is completed, immediately back up
your data on the disk(s) in case the disk volume fails again.
85
Page 86

Inactive RAID disk volumes can only be recovered if the minimal number of healthy disks required for
RAID
group
Minimal number of hard disks required for recovery
RAID 1
1
RAID 5
Number of disks - 1
RAID 6
Number of disks - 2
RAID 10
Number of disks / 2; (1 hard drive per RAID 1)
the RAID configuration is available on the NAS. For example, in a RAID 5 configuration with three disks
in the array, at least two healthy hard disk drives are required available in the NAS for volume recovery.
If not, this RAID volume cannot be recovered. Refer to the following table for the minimal number of
hard disks required to recover a RAID group:
Follow these steps to recover a failed RAID group:
1. Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Storage Space".
2. Double click a storage pool to bring up the Storage Pool Management page.
3. Select a failed RAID group.
4. Click "Manage" > "Recover".
5. The chosen RAID group will be recovered.
86
Page 87

Cache Capacity
RAM Requirement*
512 GB
from 1 GB to 4 GB
1 TB
from 4 GB to 8 GB
2 TB
from 8 GB to 16 GB
4 TB
Above 16 GB
Note:
You can toggle this feature by clicking the switch button right above "Usage".
Cache Acceleration
Based on SSD technology, the Cache Acceleration feature is designed to boost access performance of
the NAS. On this page, you can both monitor SSD performance and manage cache acceleration for your
NAS. This chapter covers the following topics:
Feature Requirements
Creating SSD Volumes
Removing SSD Volumes
Expanding SSD Volumes
Configuring Volumes for SSD Cache
Feature Requirements
SSD drives must be installed to enable this function and this feature is only available for certain NAS
models, with memory requirements. Refer to the following link for details:
https://www.qnap.com/i/en/enterprise_apply_v2/con_show.php?op=showone&cid=7
Refer to the table below for memory requirements:
*For example, for 1 TB of SSD capacity, at least 4GB RAMs are required for the NAS.
On this page, users can choose to create, remove and expand a SSD volume and configure the SSD
cache.
Creating SSD Volumes
Follow the steps below to create a SSD volume:
1. Click "Create".
2. Select the SSD drive(s) and cache algorithm to create a SSD cache volume.
3. Select the cache type: Read-Only or Read/Write. Click "Next".
4. Choose the SSD Cache Mode:
87
Page 88

o Accelerate random I/O: Only small random I/O will be stored in SSD cache. This mode is
Note:
If SSD Cache is enabled with the Read-Write type, the SSD MUST NOT be removed
while it is being used, as this will cause data loss.
recommended for virtualization and database applications. Also, select the bypass block size
under this mode (block sizes that are larger than the specified one will not be cached).
o Accelerate sequential I/O: All I/O will be stored in SSD cache. This mode is recommended for
video streaming or large file access operations.
5. Select (or deselect) from the list to enable (or disable) the SSD cache for each iSCSI LUN and
Volume.
6. Click "Create".
7. Please note that all of the data on the selected hard drive(s) will be erased. Click "OK" to confirm.
8. An SSD cache volume will be created.
Removing SSD Volumes
Follow the steps below to remove a SSD volume:
1. Click "Remove".
2. Please note that all data on the selected hard drive(s) will be erased. Click "Yes" if you are certain
about this.
3. The SSD volume will be removed. This operation can take a prolonged period if the SSD Cache is in
Read/Write mode, as all the data in the cache must be flushed to the hard drive first.
Expanding SSD Volumes
Follow the steps below to expand a SSD volume:
1. Click "Add SSD Drive".
2. Select the SSD drive(s) from the list and click "Expand".
3. Please note that all data on the selected hard drive(s) will be erased. Click "Yes" if you are certain
about this.
4. The SSD volume will be expanded.
Configuring Volumes for SSD Cache
Follow the steps below to configure volumes for a SSD cache:
1. Click "Cache Setting".
2. Select or deselect a volume to enable/disable the SSD cache, choose whether or not to record large
block, sequential I/O operations in the cache space, and click "Finish".
3. The settings will be applied to the chosen volume.
88
Page 89

Note:
For larger block, sequential I/O operations such as video streaming, the hit rate is lower,
and by default, they are not recorded in the cache space. If you need to record such
operations, please cancel this setting, but please remember that after this setting is
cancelled, more cache space and computing resources will be consumed for such
operations.
Not all applications can benefit from a SSD cache. Please make sure that the SSD cache
is supported by your applications.
89
Page 90

Note:
Snapshot Replica (or volumes/LUNs replication between remote servers) is covered in
Backup Station. For more details, please refer to the Snapshot Replica chapter in Backup
Station.
Snapshots and related features are currently only available for the following NAS series:
x51*, x53, x63, x70, x71, x79, x80, x82, x89.
o
* The NAS must have minimum of 4 GB RAM to use snapshots.
Snapshot
Snapshot Vault stores snapshots created remotely from remote NAS via Snapshot Replica in Backup
Station. It also lets you manage and restore remote snapshots.
In this chapter, the following topics are covered:
Snapshot
o
Taking a Snapshot
o
Managing Snapshots with Snapshot Manager
o
Snapshot Global Settings
o
Managing Previous Versions in Windows
Snapshot Vault
o
Filtering Snapshots
o
Displaying Snapshot Content
o
Removing Snapshots
o
Cloning Snapshots
90
Page 91

o
* x51 series models only support up to 256 snapshots instead of 1024. The HS-251
does not support snapshots.
Action
Description
View snapshot details
Select one of the following views:
Table view: Displays a chronological list of all snapshots
Timeline view: Displays a timeline containing all snapshots
created within a specific period and other information, including
the following:
o Snapshot details: Name, date and time of creation, status, file
size, and description
o Volume details: Shared folders and files
Restore and download files
1. Click a snapshot and select the folders and files that you want to
restore.
2. Right-click one of the following:
o "Restore": Replaces the existing folder/file with the one in the
snapshot
o "Restore to": Restores data to a different location
o "Download": Downloads the selection to your computer
Revert snapshots
Select a snapshot and click "Revert" to restore the snapshot to its
original path.
Snapshot
Taking a Snapshot
After a reserved space is set, you can proceed to take snapshots. To create a snapshot, follow
these steps:
1.
Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Snapshot".
2.
Switch between "Volume" or "LUN" depending on your needs, select a volume/LUN, and
click "Take a Snapshot".
3.
Specify the snapshot name, duration to retain the snapshot and snapshot type (the
snapshot type is only available for LUN snapshots).
4.
Click "OK".
Managing Snapshots with Snapshot Manager
To open Snapshot Manager, select a volume or LUN in "Storage Space" and click "Snapshot"
> "Snapshot Manager". Alternately, you can click the camera icon of a volume or LUN.
Snapshot Manager enables you to perform the following actions:
91
Page 92

Warning:
The volume reverted to the selected snapshot will
be in the previous state when the snapshot was taken.
Clone snapshots to new
volumes or LUNs
1. Select a snapshot and click "Clone".
2. Type an alias for the new volume, and select the folders to share
after cloning.
Note:
You can map cloned LUN snapshots to iSCSI targets.
Delete snapshots
Select a snapshot and click "Delete" to delete that snapshot.
Configure snapshot schedules
1. Click "Schedule".
2. Select "Enable schedule" and specify the time, frequency, and
retention period.
Note:
For Smart Snapshot, the system takes a new
snapshot only if new changes are made in the selected
volume.
Note:
The "When reaching snapshot limitation" setting uses the number of snapshots, not
Snapshot Global Settings
There are two global snapshot settings:
In the Snapshot Manager window: Click "Snapshot global settings" (the gear icon) in the
top-right corner of the Snapshot Manager window. There is one global setting:
Make snapshot directory (@Recently-Snapshot) visible: Mount a snapshot volume as a
directory of a shared folder and set the snapshot volumes to be accessed (read-only) in File
Station. The snapshot directory will appear as "@Recently-Snapshot".
In the Storage Manager window: Click "Global Settings" (the gear icon) in the top-right corner
of the Storage Manager window, and there is one global setting:
When reaching snapshot limitation: Choose the policy to handle snapshots when the
snapshot limitation is reached. There are two choices.
o
Overwrite the oldest snapshot: When the number of snapshots reaches the limitation
(256 per LUN, 1024 total) the oldest snapshot will be deleted in order to make space for
new snapshots.
o
Stop making snapshot: When the number of snapshots reaches the limitation (256 per
LUN, 1024 total), no more new and scheduled snapshots will be taken until existing
snapshots are deleted. This option will prevent the deletion of older snapshots without
administrators’ consent.
92
Page 93

the space used for snapshots. For more details, please refer to the Setting Snapshot
Reservation section.
Note:
This feature is only applicable to files that have been changed between snapshots.
Otherwise, there will be no previous versions listed in "File Explorer" > "Properties" >
"Previous Versions".
Note:
If this is the first time using this feature, please configure Snapshot Replica in Backup
Station on the source NAS first.
Snapshots and related features are currently only available for the following NAS series:
x51*, x53, x63, x70, x71, x79, x80, x82, x89.
o
* The NAS must have minimum of 4 GB RAM to use snapshots.
o
* x51 series models only support up to 256 snapshots instead of 1024. The HS-251
does not support snapshots.
Managing Previous Versions in Windows
Starting with QTS 4.2.1, snapshots can be used with the Previous Versions feature in Windows,
allowing you to instantly revert to a previous version of a file in the event of an accident (e.g. file
deletion, corruption, or accidental changes).
To use this feature, follow these steps:
1.
In Windows, connect to a shared folder on the NAS (the shared folder must be located in a
storage pool where snapshots can be taken).
2.
Take a snapshot of the storage pool where the shared folder is located.
3.
In Windows, right click on a shared folder (or a file in that shared folder) in "File Explorer"
> "Properties" > "Previous Versions".
4.
Select a version and choose to open, copy, or restore that version.
5.
Click "OK".
Snapshot Vault
Snapshot Vault stores snapshots that are created by remote NAS devices and sent through
Snapshot Replica in Backup Station. Snapshot Vault also allows you manage and restore remote
snapshots, and replicate entire vaults to remote NAS devices.
Snapshot Vault enables you to perform the following actions:
93
Page 94

Action
Description
Filter snapshots
Go to "Storage Manager" > "Snapshot" > "Snapshot Vault" to see a
list of available snapshots. You can filter snapshots using the
following criteria:
Source: Source NAS IP address
Volume/LUN: Replicated volume or LUN
Location: Storage pool that contains the snapshot
Status: Snapshot status
Note:
If the status of a snapshot is not "Ready", you will not
be able to view or access that snapshot.
Display content
1. Go "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Snapshot" > "Snapshot
Vault".
2. Select a snapshot from the list and click "Show Snapshots”.
The screen displays the following information:
Left panel: Overview of snapshots
Right panel: Folders and files in the snapshots
Note:
To review advanced information in an expanded
window, click "Hide snapshot content" next to the search
box.
Download content
1. Go "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Snapshot" > "Snapshot
Vault".
2. Select a snapshot from the list and click "Show Snapshots”.
3. Click "Show snapshot content".
4. Select the files that you want to download, right-click, and then
select "Download".
Remove snapshots
1. Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Snapshot" >
"Snapshot Vault".
2. Select a snapshot in the list and click "Remove".
Filtering Snapshots
Navigate to Snapshot Vault in "Storage Manager" > "Snapshot" > "Snapshot Vault" and you will
see a list of available snapshots. You can click the filter drop down list to filter snapshots with a
set of criteria:
Source: Source NAS IP address
Volume/LUN: The volume/LUN that has been replicated
Location: The storage pool where the snapshot has been stored
Status: The snapshot status
94
Page 95

Note:
If the status of a snapshot is not "Ready", you will not be able to view or access that
snapshot.
Displaying Snapshot Content
Navigate to Snapshot Vault in "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Snapshot", choose the
desired snapshot replication from the list, and click "Show Snapshots" to display its content. You
can see an overview of snapshots in the left panel or browse through folders and see files in the
snapshots on the right panel.
Click the "Hide snapshot content" button next to the search box to review advanced information
regarding snapshots in an expanded window.
To download files in a snapshot, click the "Show snapshot content" button, select the files, right
click your mouse and click "Download".
Removing Snapshots
1.
Navigate to Snapshot Vault in "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Snapshot".
2.
Select a snapshot replication in the list and click "Remove".
3.
The snapshot replication is removed.
Cloning Snapshots
1.
Navigate to Snapshot Vault in "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Snapshot".
2.
Select a snapshot replication in the list and click "Show Snapshots".
3.
Select a snapshot on the left panel and click "Clone".
4.
Enter a name for the volume to mount the snapshot.
5.
Choose the folders/files to clone.
6.
Select "OK" and the task will start immediately.
7.
Go to "Storage Manager" > "STORAGE" > "Storage Space" and you will see the new volume
that has been cloned from Snapshot Vault.
8.
You can now also use File Station to manage the files in the new volume.
95
Page 96

Note:
This function or its content is only applicable on some models. To check for applicable
models, please refer to the product comparison table on the QNAP website.
Qtier
Qtier is an automated-tiering storage solutions that moves hot data to high-performance storage tiers
and cold data to lower-cost, higher-capacity drives, allowing users to enjoy exceptional application
performance and lower TCO of storage at the same time. This chapter covers the following topics:
Creating Storage Space with Qtier
Managing Auto Tiering
Monitoring Auto-Tiering Performance
Creating Storage Space with Qtier
1. Install at least two different types of drives (SSD, SAS, or SSD) in the NAS. One of the types of drives
must be SSDs.
2. Create a new storage pool in "Storage Manager" > "Storage Space" > "Create” > “New Storage Pool"
or "Storage Manager" > "Storage Space" > or "Storage Manager" > "Storage Space" > “New Storage
Pool”.
3. The storage pool creation wizard will appear, check "Enable Qtier" and click "Next".
4. Select the SSD drives to be used to build the ultra-high speed tier in the storage pool. Select RAID
type and Hot Spare Disk. Click “Next”.
5. Configure the Snapshot settings in the “Snapshot Protection Settings” section, then click “Create”. A
confirmation box will appear informing you that the data on the selected disks will be erased if you
continue. To continue, click “OK”.
6. The “Expandable Qtier Tiered Storage Pool” window will appear, click “OK” to create other tiers. At
least two tiers must be created.
7. Proceed to create different tiers. Select the drives to build other tiers. Select RAID type and Hot
Spare Disk. Review summary and click “Expand” to continue. A confirmation box will appear
informing you that the data on the selected disks will be erased if you continue. To continue, click
“OK”.
8. The “Expandable Qtier Tiered Storage Pool” window will appear.
o To continue expanding the Qtier tiered storage pool, click “OK”. Select the drives to expand the
storage pool. Select RAID type and Hot Spare Disk. Review summary and click “Expand” to
continue.
o If you are done expanding this storage pool, click “Cancel”.
9. The “Qtier Auto Tiering Schedule Settings” window will appear. Choose to reallocate data
automatically during system idle time or during a specified schedule. Select “Apply”.
96
Page 97

Note:
As relocation may affect the storage I/O performance, it is recommended to schedule this
action during off-peak hours or when the storage is not frequently used.
Auto Tiering cannot be started immediately after a storage pool is created, as it will need
time to retrieve information on when data is accessed. It also cannot be scheduled for full
time, otherwise the data access pattern may not be accurate.
Action
Description
Relocation Schedule
Automatically reallocate data when the system is idle.
The system will attempt to reduce the performance impact by
only reallocating data to different tiers when the system is idle.
Enable Qtier Auto Tiering Schedule.
The administrator can manually set the data relocation schedule
to low load times to reduce performance impact.
Statistics
Review the general information for each tier and history report.
Manage > Stop Relocations
Stop allocation.
Manage > Set Allocation Level
Set the default data allocation tier and data reservation ratio for
ultra-high speed tier.
Default data allocation tier: Set which tier new data will be
stored in.
Data reservation ratio for the ultra-high speed tier: Choose the
amount of data to retain in the ultra high-speed tier (even
though they are cold data).
Managing Auto Tiering
Go to "Storage Manager" > "Storage Space" and double click on a Qtier Auto Tiering Storage Pool to
bring up the “Storage Pool Management” window. Select “Qtier Auto Tiering”. The following actions are
available:
Monitoring Auto-Tiering Performance
On the Storage Pool Management dialog (bottom of the dialog), the current auto-tiering settings and
performance will be listed:
Relocation status: Indicates if auto-tiering is active (or idle).
Enable schedule: Indicates if the schedule is enabled.
Data reservation ratio for ultra-high speed tier: Indicates the amount of data currently set to be
retained in the ultra-high speed tier.
97
Page 98

Amount of data optimized for performance: Shows the amount of data that has been allocated to
high-speed tiers (or the "Move Down" or "Move Up" columns in "Manage" > "Statistics") in the last
auto tiering schedule.
Amount of data optimized for capacity: Shows the amount of data that have been allocated to high
speed tiers (or the "Move Down" or "Move Up" columns in "Manage" > "Statistics") in the last auto
tiering schedule.
Data allocation priority: Indicates whether data will be written on the SSD tier if the "ultra-high
speed" is set in "Manage" or first written on the SATA tier and then the SSD if "Capacity" is set in
"Manage"
Additionally, you can check the history report ("Manage" > “Qtier Auto Tiering” > "Statistics") for further
details on auto-tiering performance, including data moved up/down in a task, total used space after task
completion and the current tasks with a trend chart.
98
Page 99

iSCSI
Manage the iSCSI storage, create advanced ACLs and back up LUNs with the iSCSI management
features.
For details on the features, please refer to the following links:
iSCSI Storage
LUN Backup
99
Page 100

Note:
In the context of your network, your computer (an initiator) connects to the NAS and retrieves
the following:
o List of available targets
o List of available LUNs in each target
Note:
The NAS supports multiple iSCSI targets and multiple LUNs per target.
iSCSI Storage
The NAS supports a built-in Internet Small Computer System Interface (iSCSI) service for clustered and
virtualized environments.
An iSCSI storage network includes the following nodes:
Target: Storage device that contains one or more LUNs, which are logical units of storage
Initiator: Client that initiates connections (through SCSI commands) to the storage device, which is
called a target
In addition to enabling and disabling the service, users can perform the following tasks:
Configure the port of the iSCSI portal
Enable or disable the Internet Storage Name Service (iSNS) service
Manage all iSCSI targets and LUNs, including mapping and unmapping of LUNs to specific targets
In this chapter, these topics are covered:
100
 Loading...
Loading...