Page 1

d
g
W
a
R
0
Us
e
e
l
5
r’s Manua
In
ustri
l Wal
l-mou
of WGR-
nt
00
Gi
abit
GR-5
oute
0
r
1
Page 2

User’s Manual of WGR-500
Trademarks
Copyright © PLANET Technology Corp. 2019.
Contents are subject to revision without prior notice.
PLANET is a registered trademark of PLANET Technology Corp. All other trademarks belong to their respective
owners.
Disclaimer
PLANET Technology does not warrant that the hardware will work properly in all environments and applications,
and makes no warranty and representation, either implied or expressed, with respect to the quality, performance,
merchantability, or fitness for a particular purpose. PLANET has made every effort to ensure that this User's
Manual is accurate; PLANET disclaims liability for any inaccuracies or omissions that may have occurred.
Information in this User's Manual is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the
part of PLANET. PLANET assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies that may be contained in this User's
Manual. PLANET makes no commitment to update or keep current the information in this User's Manual, and
reserves the right to make improvements to this User's Manual and/or to the products described in this User's
Manual, at any time without notice.
If you find information in this manual that is incorrect, misleading, or incomplete, we would appreciate your
comments and suggestions.
FCC Warning
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part
15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference
when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate
radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the Instruction manual, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause
harmful interference in which case the user will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
CE Mark Warning
This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio interference, in which case the
user may be required to take adequate measures.
WEEE Warning
To avoid the potential effects on the environment and human health as a result of the presence of hazardous
substances in electrical and electronic equipment, end users of electrical and electronic
equipment should understand the meaning of the crossed-out wheeled bin symbol. Do not
dispose of WEEE as unsorted municipal waste and have to collect such WEEE separately.
Revision
User's Manual of PLANET WGR-500
Model: WGR-500
Revision: 1.0 (September, 2019)
Part No: EM-WGR-500_v1.0
2
Page 3

User’s Manual of WGR-500
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Chapter 1. Introduction .......................................................................................... 5
1.1. Packet Contents ........................................................................................................ 5
1.2. Product Description ................................................................................................... 6
Compact and Cost-effective for Building Industrial IoT Networks ......................................... 6
Dual Power Input for High Availability Network System .......................................................... 9
1.3. Product Features ..................................................................................................... 10
1.4. Product Specifications ............................................................................................. 11
Chapter 2. Hardware Installation ......................................................................... 13
2.1 Product Outlook ....................................................................................................... 13
2.1.1 Front and Bottom Panel ................................................................................................... 13
2.1.2 LED Indications ................................................................................................................ 16
2.1.3 Wiring the Power Inputs ................................................................................................... 18
2.2 Installing the industrial wall-mount Gigabit router ................................................... 20
2.2.1 Wall-mount Installation ..................................................................................................... 20
2.2.2 Magnet Installation ........................................................................................................... 22
2.2.3 DIN-rail Installation ........................................................................................................... 22
Chapter 3. Router Management .......................................................................... 25
3.1 Requirements .......................................................................................................... 25
3.2 Web Management ................................................................................................... 26
Chapter 4. Configuration in Web UI .................................................................... 28
4.1 Main Web Page ....................................................................................................... 28
4.2 System..................................................................................................................... 31
4.2.1 Dashboard ....................................................................................................................... 32
4.2.2 Setup Wizard ................................................................................................................... 34
4.2.3 Status ............................................................................................................................... 41
4.2.4 Stastics ............................................................................................................................ 41
4.2.5 Operation Mode ............................................................................................................... 4 2
4.2.6 Date and Time .................................................................................................................. 44
4.2.7 User Configuration ........................................................................................................... 4 5
4.2.8 SNMP ............................................................................................................................... 46
4.2.9 Log ................................................................................................................................... 47
4.3 Network ................................................................................................................... 48
4.3.1 WAN Setup ...................................................................................................................... 49
4.3.2 LAN Setup ........................................................................................................................ 52
4.3.3 VLAN................................................................................................................................ 53
4.3.4 Route ............................................................................................................................... 54
4.3.5 DDNS ............................................................................................................................... 56
4.3.6 IPv6 WAN Setting ............................................................................................................ 58
3
Page 4

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.3.7 IPv6 LAN Setting .............................................................................................................. 59
4.3.8 RADVD ............................................................................................................................ 60
4.3.9 Tunnel (6 over 4) .............................................................................................................. 63
4.4 Security.................................................................................................................... 64
4.4.1 QoS .................................................................................................................................. 65
4.4.2 DoS .................................................................................................................................. 67
4.4.3 Port Filtering ..................................................................................................................... 69
4.4.4 IP Filtering ........................................................................................................................ 70
4.4.5 MAC Filtering ................................................................................................................... 71
4.4.6 URL Filtering .................................................................................................................... 72
4.4.7 DMZ ................................................................................................................................. 73
4.4.8 Port Forwarding ............................................................................................................... 74
4.5 Maintenance ............................................................................................................ 75
4.5.1 Connection Test ............................................................................................................... 76
4.5.2 Save/Restore Configuration ............................................................................................. 77
4.5.3 Upgrading Firmware ........................................................................................................ 78
4.5.4 Reboot ............................................................................................................................. 78
Appendix A: Troubleshooting ................................................................................ 79
Appendix B: Planet Smart Discovery Utility ......................................................... 80
Appendix C: Planet DDNS ...................................................................................... 81
Appendix D: Glossary ............................................................................................. 83
4
Page 5
c
0
0
0
0
P
e
o
L
0
o
n
n
n
5
5
5
o
u
t
a
p
m
m
m
m
n
t
t
t
T
s
b
C
t
5
4
4
t
-
4
4
d
r
c
/
t
t
4
p
o
User’s
M
n
C
S
b
m
a
s
W
c
0
e
o
n
t
d
anual of
GR-500
The des
WGR-50
WGR-5
WGR-5
WGR-5
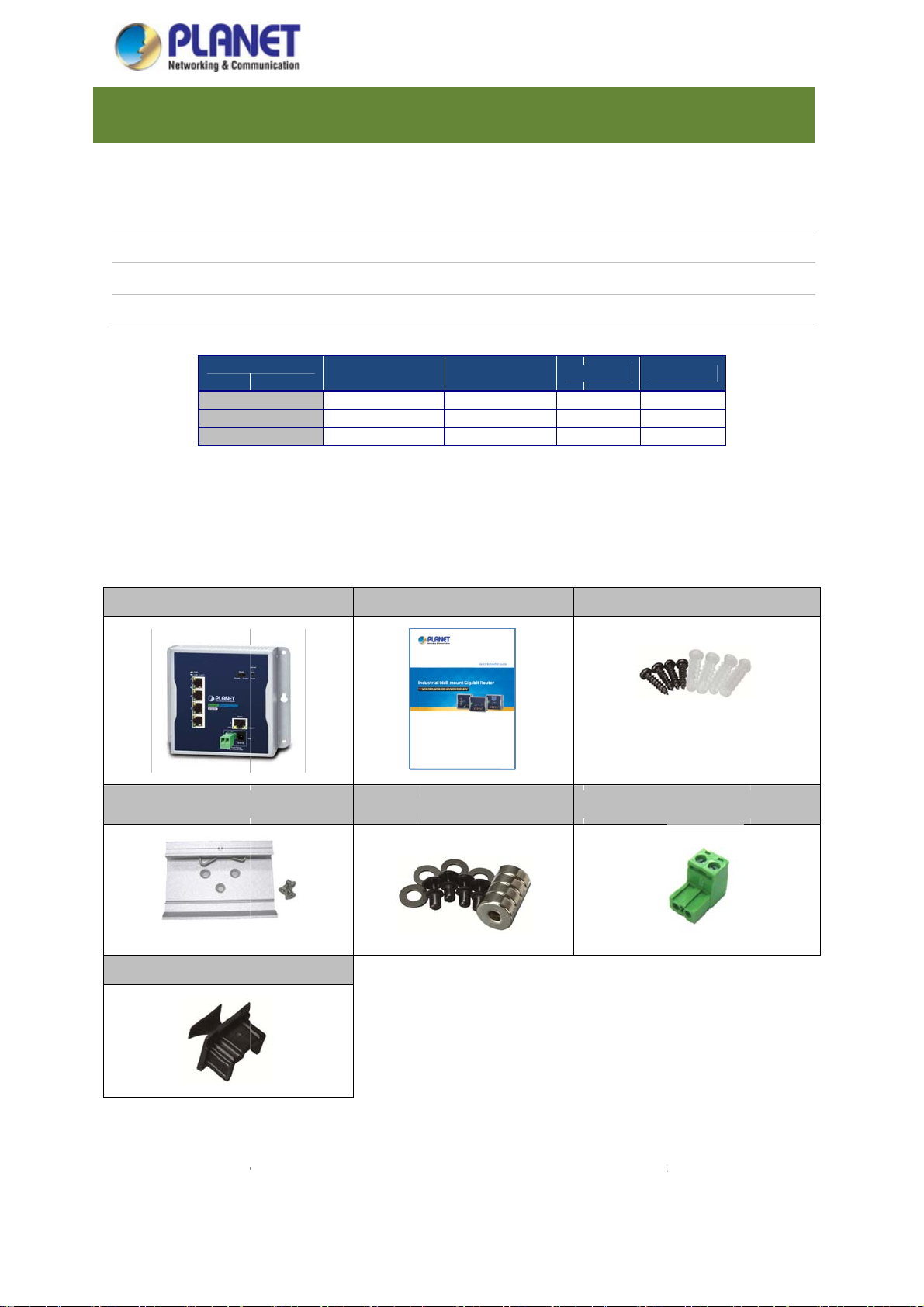
1.1.
Open th
following
riptions of P
-4P, are as f
0
0-4P
0-4PV
Model
WGRWGRWGR-
acket C
box of the
items:
ANET indust
llows:
I
dustrial Wall-
I
dustrial Wall-
I
dustrial Wall-
Name
00
00-4P
00-4PV
ntents
industrial wal
rial wall-mou
ount Gigabi
ount Gigabi
ount Gigabi
10/100/1000
Copper Port
5
5
5
-mount Giga
t Gigabit rou
Router with
Router with
Router with
802.3a
it router an
Po
hapte
er series, su
-Port 10/100
-Port 802.3a
-Port 802.3a
PoE +
rts
carefully un
1. I
h as WGR-5
1000T
PoE+
PoE+ and L
2.
’’ LCD U
-
-
■
ack it. The
trodu
00,WGR-50
D Touch Scr
B Port
-
■
■
ox should c
tion
-4PV and
en
ntain the
Industrial Ro
DIN-rail Ki
RJ45 Dust C
ter x 1
x 1
p x 5
Quick
Installation G
Magnet Kit x
uide x 1
1
Wall-
2-pin Termin
ounted Kit x
l Block Con
1
ector x 1
If any of
including
it to us f
these are mi
the original
r repair.
ssing or da
acking materi
aged, please
al, and use th
contact your
em again to r
5
dealer imme
epack the pr
diately; if po
duct in case t
sible, retain
here is a nee
he carton
to return
Page 6

P
c
o
R
D
-
s
m
k
e
h
c
d
i
o
a
u
t
n
i
L
t
e
g
p
y
4
o
c
r
s
e
User’s
M
n
n
W
s
d
anual of
GR-500
1.2.
Compa
PLANET
transport
perfect f
The WG
and oper
roduct
t and Cost
WGR-500 i
ation, govern
r any networ
-500, the b
ation function
Setup Wiza
Router and
Firewall wit
HW NAT a
9-48V DC re
escript
effective f
an industri
ent, agricult
environmen
st solution fo
s:
rd design a
switch work
802.1Q V
celerates in
undant pow
on
r Building I
l router desi
re and other
and stable o
any industr
d IPv6 / IPv
ng mode
AN security
ernet NAT r
r design
ndustrial Io
ned for suc
public areas.
eration.
router appli
support
uting perfo
T Networks
h Internet of
Its compact
ation, featur
mance
Things (IoT)
ize and redu
s the followi
networks a
dant power
g special ma
industry,
esign are
nagement
6
Page 7
o
i
e
R
t
n
o
e
r
t
R
g
p
e
T
o
h
h
e
k
e
a
n
t
g
D
a
v
n
y
S
t
m
e
p
t
r
p
s
h
n
u
W
f
v
c
e
v
w
s
u
Y
n
w
e
I
s
d
p
t
User’s
M
s
a
t
e
m
s
6
t
t
a
o
W
n
s
e
d
h
s
t
n
a
D
o
anual of
GR-500
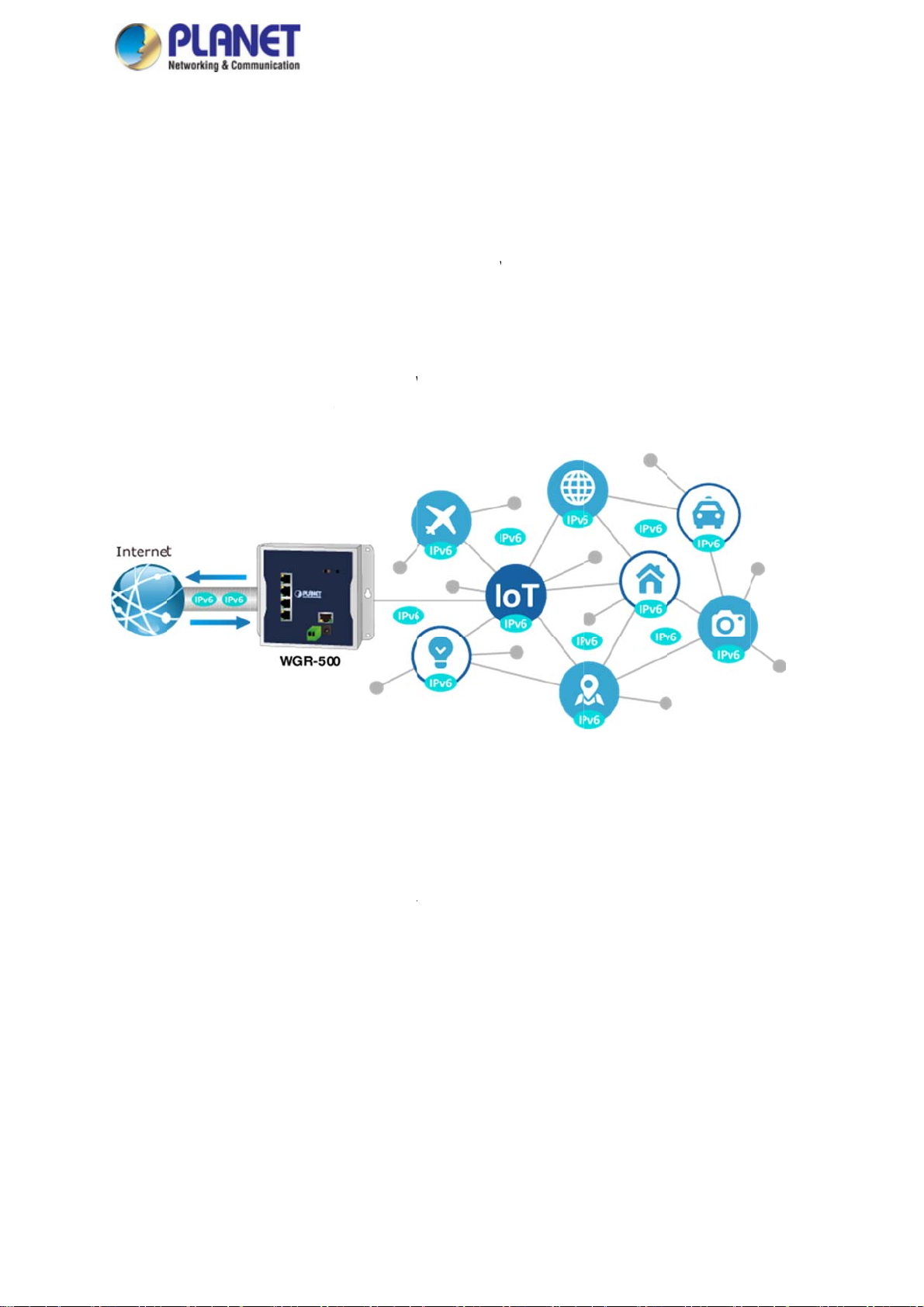
IPv6 Su
With billi
fulfill the
that prov
any pres
without h
The WG
IPv4-bas
traffics
impleme
pport for Io
ns of new Io
requirements
ides a unique
nt and futur
aving to work
-500 suppor
ed networks
hrough the
tations for Io
T Networki
T devices en
of connectin
64-bit host I
communicat
around all of
ts both IPv6
to the full IP
IPv4 enviro
connectivit
g
ering the ma
all the IoT
to every pre
ion device. T
the traditional
nd IPv4 to e
6 infrastruct
ment. The
.
ket each yea
roducts toget
ent and futur
at means IP
NAT and fire
sure industri
re. It assign
GR-500 s
r, IPv4 is fac
her. IPv6 offe
IoT device.
6 allows IoT
all issues.
al Ethernet w
IPv6 addre
pports IPv4
d with the is
s a highly-sc
t is sufficient
products to b
th a smooth
ses to client
tunneling (
ue of not bei
alable addre
o address th
e uniquely a
igration pat
and passe
to4 transitio
g able to
s scheme
needs of
dressable
from the
the IPv6
n tunnel)
Secure
The den
applicati
server r
the othe
bandwid
The WG
emergin
and kee
Firewall Pr
ial-of-service
n access. T
sources, or t
, volume-bas
h of the attac
-500 provid
malicious tr
s networking
tection
attacks (Do
ere are two
ose of inter
d attacks lik
ed site.
s firewall to
ffic before at
more secure.
) attempt to
ypes of DoS
ediate comm
UDP/ICMP
rotect IoT de
acks can oc
consume re
attacks – S
unication equ
floods and ot
ices against
ur. With fire
sources and
N floods an
ipment, such
er spoofed-
etworking at
all protection,
therefore de
ping of dea
as firewalls a
acket floods
ack like deni
it prevents I
ny users ne
h that consu
nd load bala
that would s
l-of-service (
T network fr
work and
e actual
cers, and
turate the
oS), and
m threats
7
Page 8
V
S
A
s
R
w
n
R
w
I
o
n
n
t
r
o
f
r
n
A
a
a
c
e
d
s
t
e
d
p
e
s
t
e
e
o
.
d
e
s
o
M
f
o
A
s
m
-
W
n
a
t
e
n
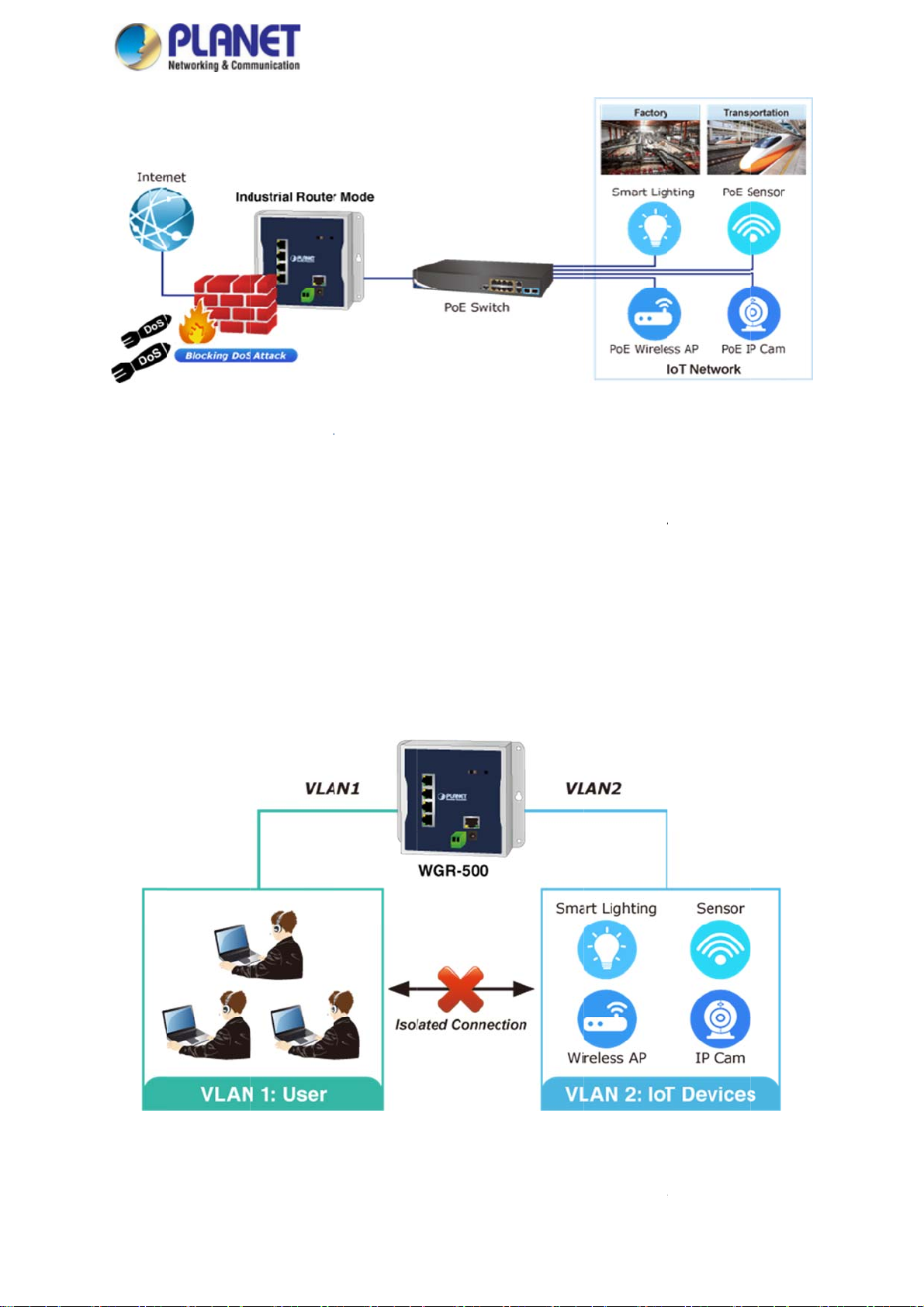
LAN
upport for
solated Tra
fic and Se
urity
User’s
anual of
GR-500
Virtual L
separate
devices i
network
use.
The WG
traffic for
improve
Ns (VLANs)
private netw
n the same
ecurity that
-500 suppor
arder to con
etwork secu
offer the logic
rk into seve
etwork segm
etwork admi
s 802.1Q VL
trol traffic and
ity.
al grouping t
al parts for
ent, it will re
istrators can
N to separa
isolate conn
chnique to s
ifferent user
ult in heavy
control over
e traffic of us
ctions of two
parate the ph
. If there are
raffics locally
each port an
rs and IoT d
groups. It will
ysical ports o
too many c
Besides, VL
whatever re
vices and ca
not only opti
Ethernet swi
mputers or
ANs provide
sources it is
n work as an
ize bandwid
tch. It can
etworking
enhanced
llowed to
intelligent
h but also
Innovat
The WG
flat and
ive Wall-m
-500 is speci
all-mounted
unt Install
ally designed
design fits e
tion
to be installe
sily in any s
in a narrow
ace-limited l
8
nvironment,
cation. It ad
uch as wall e
pts the user
nclosure. Th
friendly “Fro
compact,
t Access”
Page 9

m
c
o
S
t
w
t
o
s
y
f
h
c
t
a
y
e
n
w
t
W
m
4
r
n
n
User’s
M
b
c
m
0
W
anual of
GR-500
design,
magneti
aking the in
wall mountin
stalling and
g or DIN rail,
able wirings
hereby maki
easy. The
g its usability
GR-500 can
more flexible
be installed
y fixed wall
mounting,
Dual P
The WG
network
the hard
power al
wer Input f
-500 feature
o enhance s
are failover
ernatively wit
r High Ava
a strong du
stem reliabilit
unction will b
out any loss
ilability Net
l power input
and uptime.
activated au
of operation.
ork Syste
system (9V~
In the exampl
tomatically to
8V DC) inco
e below, whe
keep poweri
porated into
the 2-pin ter
g the WGS-5
ustomer’s au
minal block fa
0 via the DC
omation
ils to work,
plug
9
Page 10

User’s Manual of WGR-500
1.3. Product Features
Physical Port
Four 10/100/1000BASE-T RJ45 ports
One 10/100/1000BASE-T RJ45 WAN port or LAN port ( router mode / switch mode)
Industrial Case and Installation
Compact size with fixed wall mounting, magnetic wall mounting or DIN-rail design
IP30 metal case
Supports -10 to 60 degrees C operating temperature
Supports ESD 6KV DC Ethernet protection
Dual power input design
- 9V~48V DC wide power input, redundant power with reverse polarity protection
- 2-pin terminal block or DC jack connector
Layer 2 Features
Supports IEEE 802.1Q tagged VLAN
Supports IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
Layer 3 IP Routing Features
IPv6 support
WAN Internet types: Dynamic IP(DHCP Client), static IP, PPPoE, L2TP, PPTP
Static and dynamic (RIP1 and 2) routing
Supports Port Forwarding, DMZ, and UPnP for various networking applications
IP/MAC-based bandwidth control
Supports Dynamic DNS and PLANET DDNS
Security
Port filtering lets you either allow or prevent which applications can access the Internet.
MAC filtering allows you to include or exclude computers and devices based on their MAC address
URL filtering allows you to control access to Internet websites in an URL list
IP source guard prevents IP spoofing attacks
DoS attack prevention
Management
Management Interfaces
- Web GUI management
Static and DHCP for IP address assignment
System Maintenance
- Firmware upload/download via HTTP
- Hardware-based reset button for system reboot or reset to factory default
NTP (Network Time Protocol)
Event message logging to remote syslog server
PLANET Smart Discovery Utility for deployment management
10
Page 11
User’s Manual of WGR-500
1.4. Product Specifications
Product WGR-500
Hardware Specifications
Interface
DIP Switch For router and switch mode
Reset Button
ESD Protection 6KV DC
Enclosure IP30 metal case
Installation DIN-rail or wall mounting
Connector
LED Indicator
Dimensions (W x D x H) 148 x 24.2 x 134 mm
Weight 487 g
Power Requirements Dual 9~48V DC
Power Consumption
Router Features
Internet Connection Type Shares data and Internet access for users, supporting the following internet
Routing Protocol Static routing
Security DOS protection
Protocol / Feature 802.1Q tag-based VLAN
System Management Web-based (HTTP) configuration
LAN 4 x 10/100/1000 BASE-T, auto-negotiation, auto MDI/MDI-X RJ45 port
WAN 1 x 10/100/1000 BASE-T, auto-negotiation, auto MDI/MDI-X RJ45 port
< 5 sec: System reboot
> 5 sec: Factory default
Removable 2-pin terminal block for power input
- Pin 1/2 for Power (Pin 1: V+ / Pin 2: V-)
DC power jack with 2.1mm central pole
System:
Internet (Green)
PWR (Green)
SYS (Green)
Per 10/100/1000T RJ45 Ports:
10/100 LNK/ACT (Green)
1000 LNK/ACT (Amber)
Max. 1.71 watts/5.84 BTU (Power on
without any connection)
Max. 4.32 watts/14.75 BTU (Full loading)
accesses:
PPPoE
Static IP
Dynamic IP
RIPv1/2
MAC/IP/Port/URL filtering
802.1d spanning tree
QoS
NAT and HW NAT
Port Forwarding
DMZ
UPnP and PLANET DDNS
SNTP time synchronization
11
Page 12

System log supports remote log
SNMP v1, v2c
Standards Conformance
Regulatory Compliance FCC Part 15 Class A, CE
IEC60068-2-32 (free fall)
Stability Testing
Standards Compliance
Environment
IEC60068-2-27 (shock)
IEC60068-2-6 (vibration)
IEEE 802.3 10BASE-T
IEEE 802.3u 100BASE-TX/100BASE-FX
IEEE 802.3ab Gigabit 1000T
IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol
IEEE 802.1p Class of Service
IEEE 802.1Q VLAN tagging
RFC 768 UDP
RFC 793 TFTP
RFC 791 IP
RFC 792 ICMP
RFC 2068 HTTP
User’s Manual of WGR-500
Operating Temperature -10 ~ 60 degrees C
Storage Temperature -20 ~ 70 degrees C
Humidity 5 ~ 95% (non-condensing)
12
Page 13

p
i
t
r
t
e
e
m
s
e
t
s
d
e
e
n
e
k
e
u
P
n
w
u
a
t
u
t
b
:
g
.
n
w
z
u
o
o
s
d
h
o
User’s
M
a
F
n
o
-
W
a
e
anual of
GR-500
This cha
different
2.1
This sec
and cont
2.1.1
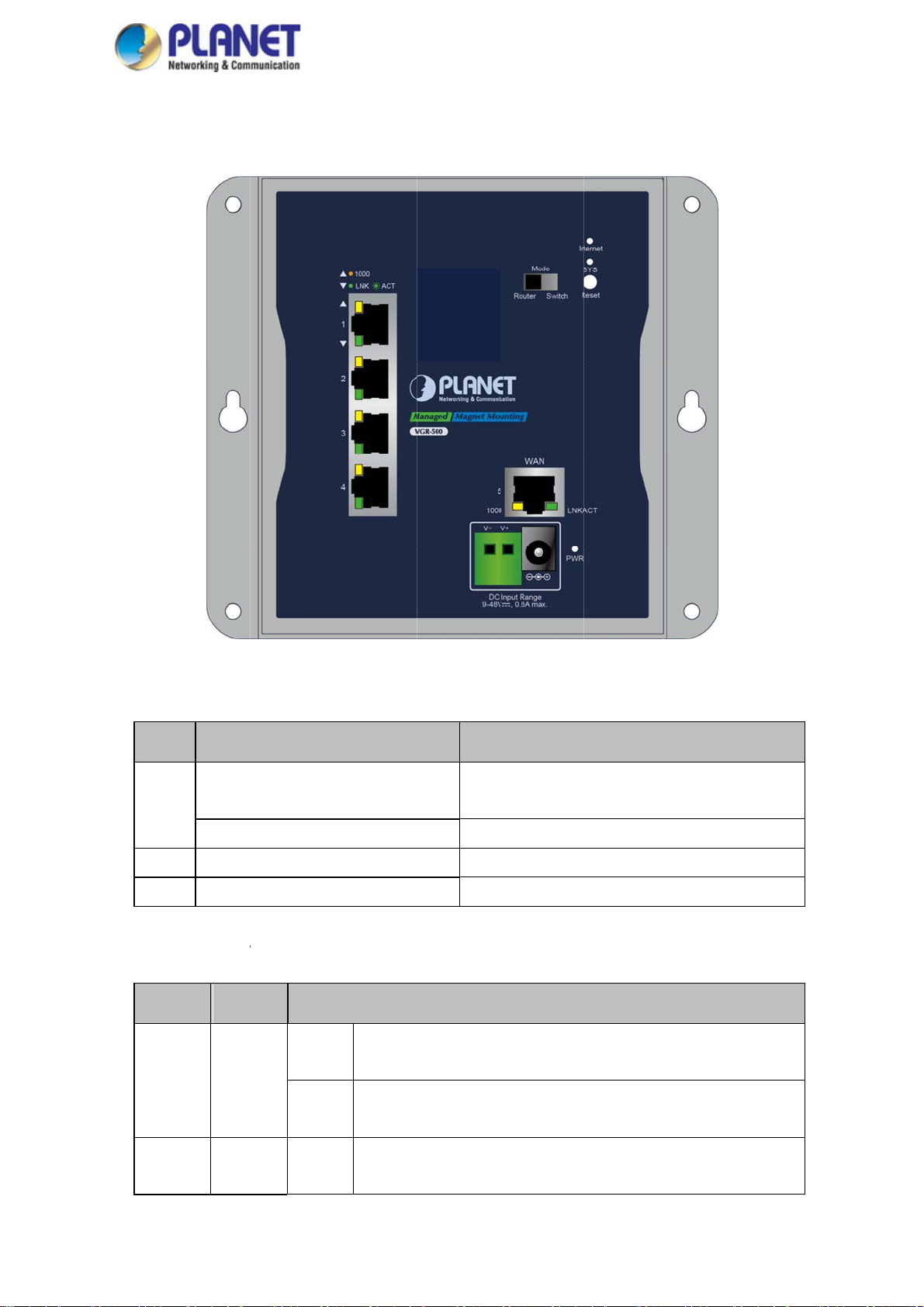
The fron
the front
ter describe
nstallation m
Produc
ion describe
ol of the indu
Front an
panel provid
panels of the
the hardwar
thods.
Outloo
the hardwar
strial wall-mo
Bottom
s a simple i
industrial wall
Ch
of the indus
features of t
nt Gigabit ro
anel
terface moni
-mount Giga
pter 2
rial wall-mou
he industrial
ter, familiari
oring the ind
it routers.
Har
t Gigabit rout
all-mount Gi
e yourself wit
strial wall-m
ware
r and gives
abit router.
its display i
unt Gigabit r
Install
physical ov
or easier ma
dicators and
uter. Figures
tion
rview and
nagement
ports.
2-1 show
Figure 2-1
Front Panel
f WGR-500
■ Res
t Button
The
bottom of th
syst
m or resetti
sum
mary table of
industrial
g to factory
reset button f
all-mount Gi
default. The
nctions:
abit router c
reset button
13
mes with a
are shown
reset button
in Figures 2
designed for
2 and follow
rebooting
ing is the
Page 14

S
y
t
y
a
a
P
2
d
h
o
n
h
h
n
e
f
f
f
b
f
n
0
t
w
d
s
5
o
User’s
M
n
.
5
W
Figure 2-
: Reset Butt
n of WGR-5
0
anual of
GR-500
■ DIP
Onl
Figu
Reset But
< 5 sec: S
> 5 sec: F
witch
the WGR-50
re 2-3.
on Pressed
stem Reboot
ctory Default
0 has the DI
nd Release
switch, whic
Functio
Reboot t
Reset t
wall-mou
default s
。 De
。 De
。 De
。 Su
。 De
is for selecti
e system.
e system
t Gigabit ro
ttings as sho
ault Usernam
ault Passwor
ault IP Addre
net Mask: 2
ault Gateway
g an operati
o factory d
ter will the
n below:
e: admin
: admin
s: 192.168.1
5.255.255.0
192.168.1.2
n mode. The
efault. The
reboot and
1
4
DIP switch is
industrial
load the
shown in
14
Page 15

0
User’s
M
anual of WGR-500
Figure 215-3: DIP Switch of WGR-50
Page 16
tLE
r
W
Y
N
KLNK
i
r
/
e
R
e
n
e
e
J
s
sber
s
w
L
r
t
b
e
e
s
n
e
n
s
s
)
h
t
o
0
n
h
h
p
User’s
M
s
d
h
w
i
s
e
W
t
i
o
anual of
GR-500
2.1.2
The
LED Ind
LED indicato
cations
s of the WG
-500 are sho
n in Figures
2-4.
■ Sys
Inte
P
S
■ LA
LN
em
D
net
R
S
Per 10/100
L
ED Co
/ACT Gr
Gre
Bli
Gre
Gre
1000Mbps R
lor
Light
en
Blink
Figure 2-4:
n
k
n
n
45 Port (Po
To indica
:
10/100M
To indicat
:
port.
ED Indicator
Color
Inter
mod
Inter
Light
Light
t-1 to Port-4
e the link t
ps.
that the swi
of WGR-50
et is synchro
.
et data is bei
to indicate t
to indicate t
rough that
ch is actively
ized succes
g transmitte
at the Switc
e system is
Funct
ort is succe
sending or r
Func
fully in the ro
.
has power.
orking.
ion
sfully establ
ceiving data
ion
te
shed at
ver that
To indicat
:
Mbps.
/ACT Am
Light
the link thr
16
ugh that port
is successfull
y established
at 1000
Page 17
User’s Manual of WGR-500
Blinks:
■ WAN Per 10/100/1000Mbps RJ45 Port (Port-5)
LED Color Function
Lights:
LNK/ACT Green
Blinks:
Lights:
LNK/ACT Amber
Blinks:
To indicate that the switch is actively sending or receiving data over that
port.
To indicate the link through that port is successfully established at
10/100Mbps.
To indicate that the switch is actively sending or receiving data over that
port.
To indicate the link through that port is successfully established at 1000
Mbps.
To indicate that the switch is actively sending or receiving data over that
port.
17
Page 18
a
e
u
o
.
n
a
n
i
t
T
9
a
y
s
t
5
User’s
M
i
C
W
d
w
anual of
GR-500
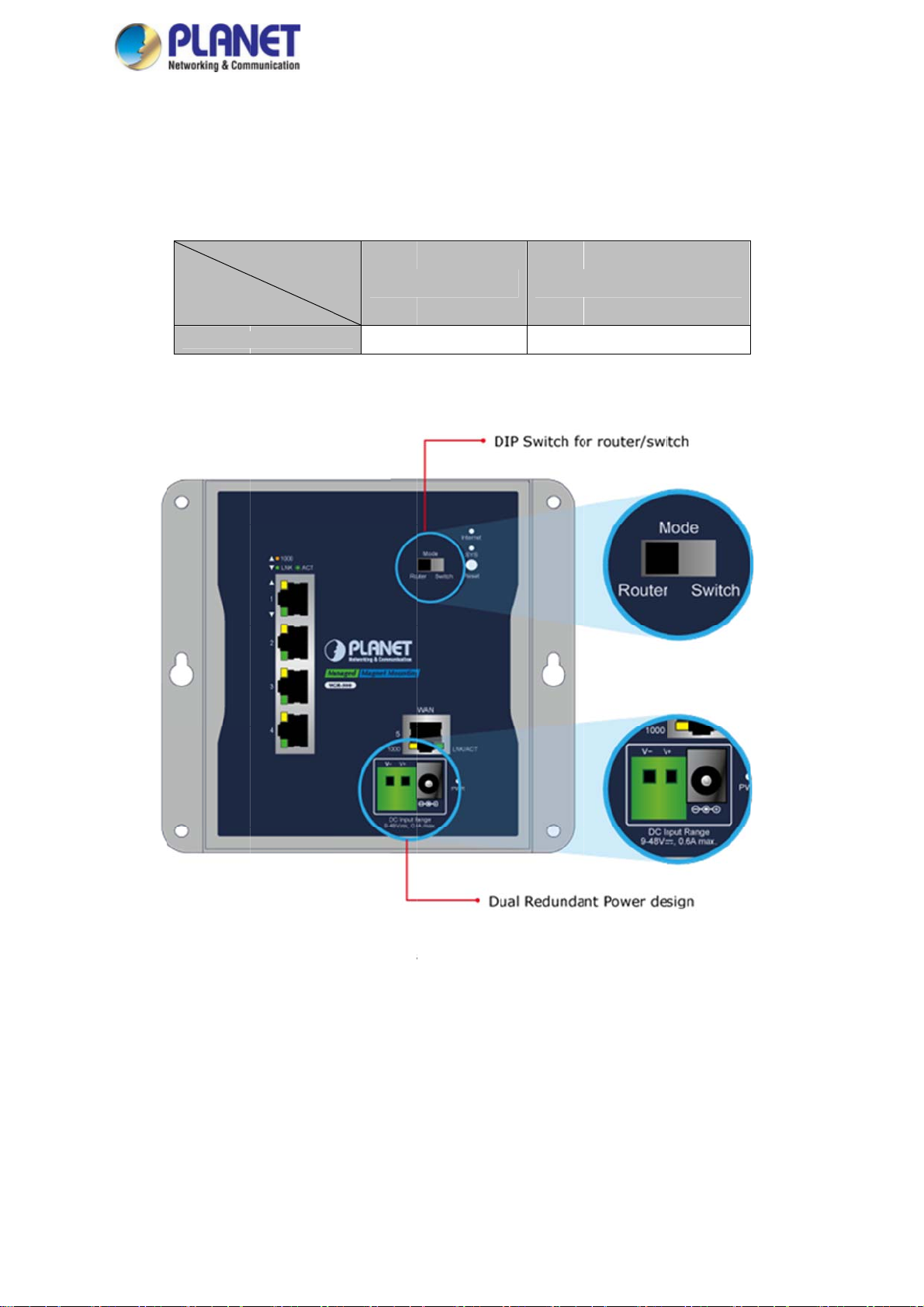
2.1.3
The indu
incorpor
is shown
Wiring th
strial wall-mo
ted into cust
in Figure 2-5
Model
WGR-500
Power I
nt Gigabit ro
mer’s autom
Power In
Ra
puts
uter features
tion network
put
ge 2-pin
a strong dual
o enhance s
erminal Bloc
~48V DC
power input
stem reliabili
k
ystem (Term
and uptime.
DC Jack
9~48V D
inal block an
The dual po
DC jack)
er design
F
gure 2-5: Du
al Power Des
18
ign of WGR-
00
Page 19

m
T
w
P
R
p
C
m
r
g
T
W
m
c
n
o
r
w
g
m
e
4
o
h
g
t
m
e
F
p
c
e
w
w
c
o
i
r
p
w
a
V
n
h
n
User’s
M
m
n
h
c
u
W
e
n
i
u
e
anual of
GR-500
■ Ter
To install
steps:
Step 1: I
Step 2:
inal Block
the 2-pin Ter
nsert positive
ighten the wi
all-mount Gi
1.
2.
onnector Pi
inal Block C
DC power wi
e-clamp scre
abit router
he wire gau
hen perfor
ake sure th
out
nnector on t
e into V+, ne
Figure 2-6:
s for preven
e for the ter
ing any of th
power is OF
e industrial
ative DC po
Terminal Blo
ting the wires
inal block sh
procedures l
F to prevent f
all-mount Gig
er wire into
k Connector
from looseni
uld be in the
ke inserting t
om getting a
bit router, si
-, as shown i
g and plug th
ange of 12 ~
e wires or tig
electric sho
ply follow th
Figure 2-6.
em into the i
24 AWG.
htening the w
k.
following
dustrial
re-clamp scr
ws,
■ DC
The WG
issue of
ower Jack
-500 comes
ower conne
with DC 9V~
tion, please c
8V power in
ntact your lo
Figur
ut. The DC
cal sales repr
2-7: DC Po
ower jack is
sentative.
er Jack
shown in Fig
re 2-7. If yo
have the
19
Page 20
n
t
w
T
ath
a
u
o
h
u
l
h
l
G
e
F
a
a
s
o
t
t
e
n
b
m
h
r
e
m
e
User’s
M
o
e
a
0
W
a
n
anual of
GR-500
2.2 I
This sec
the follo
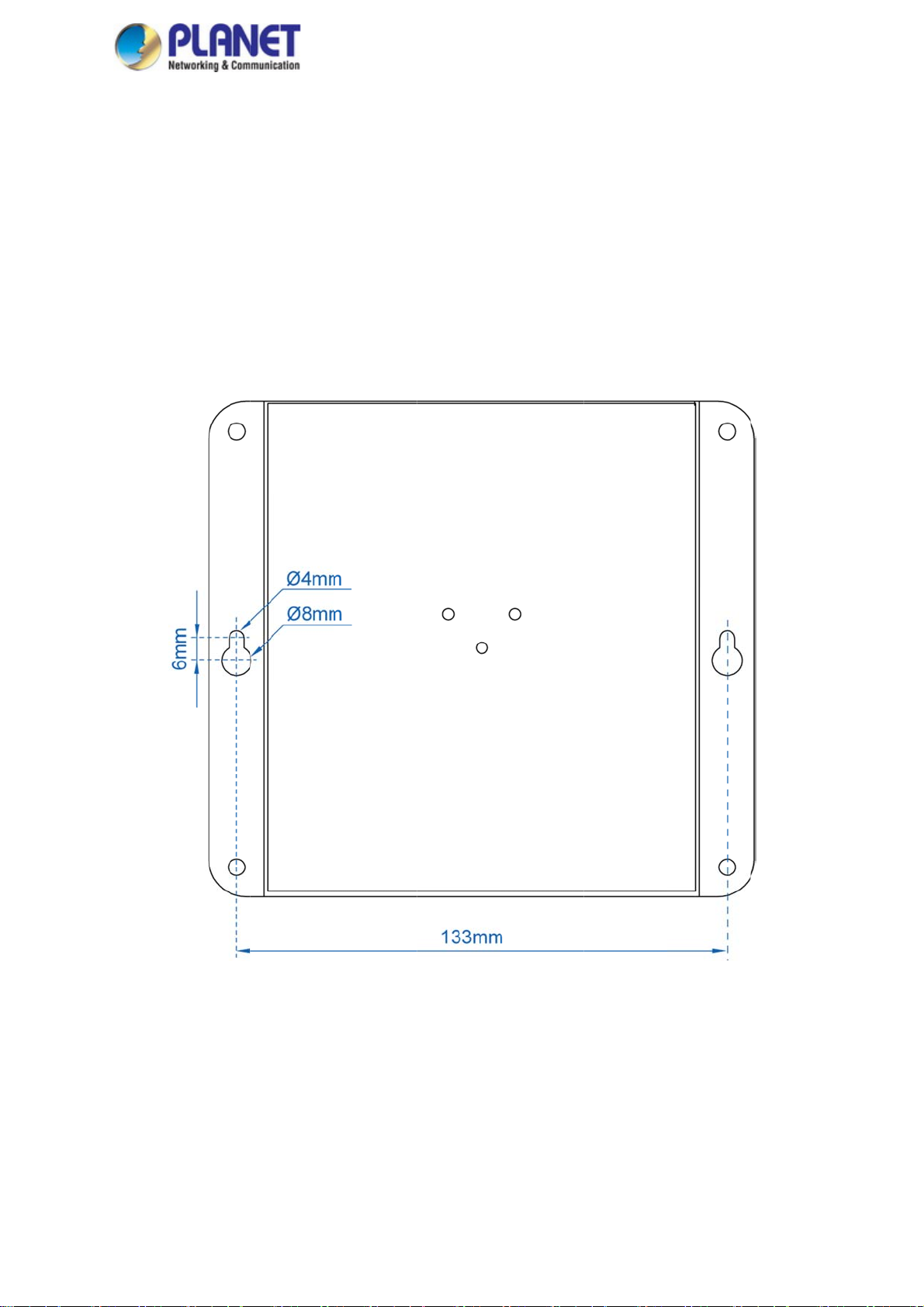
2.2.1
To install
Step 1:
stalling
ion describes
ing sections
Wall-mo
the industrial
here are 4 h
s shown in F
em must be
the ind
how to instal
nd perform t
nt Instal
wall-mount
les with 8mm
igure 2-8. Th
orizontal.
strial w
your industri
e procedure
ation
igabit router
diameter on
distance be
ll-mou
l wall-mount
in the order
n the wall, si
he wall moun
ween the 2
t Gigabi
Gigabit route
eing present
ply follow th
t bracket of th
oles is 133m
t router
and make c
d.
following st
e Industrial w
of WGR-5
nnections. Pl
ps:
all-mount Gig
0, and the li
ase read
bit router
e through
igure 2-8: G
tting Mountin
20
g Holes Align
d
Page 21
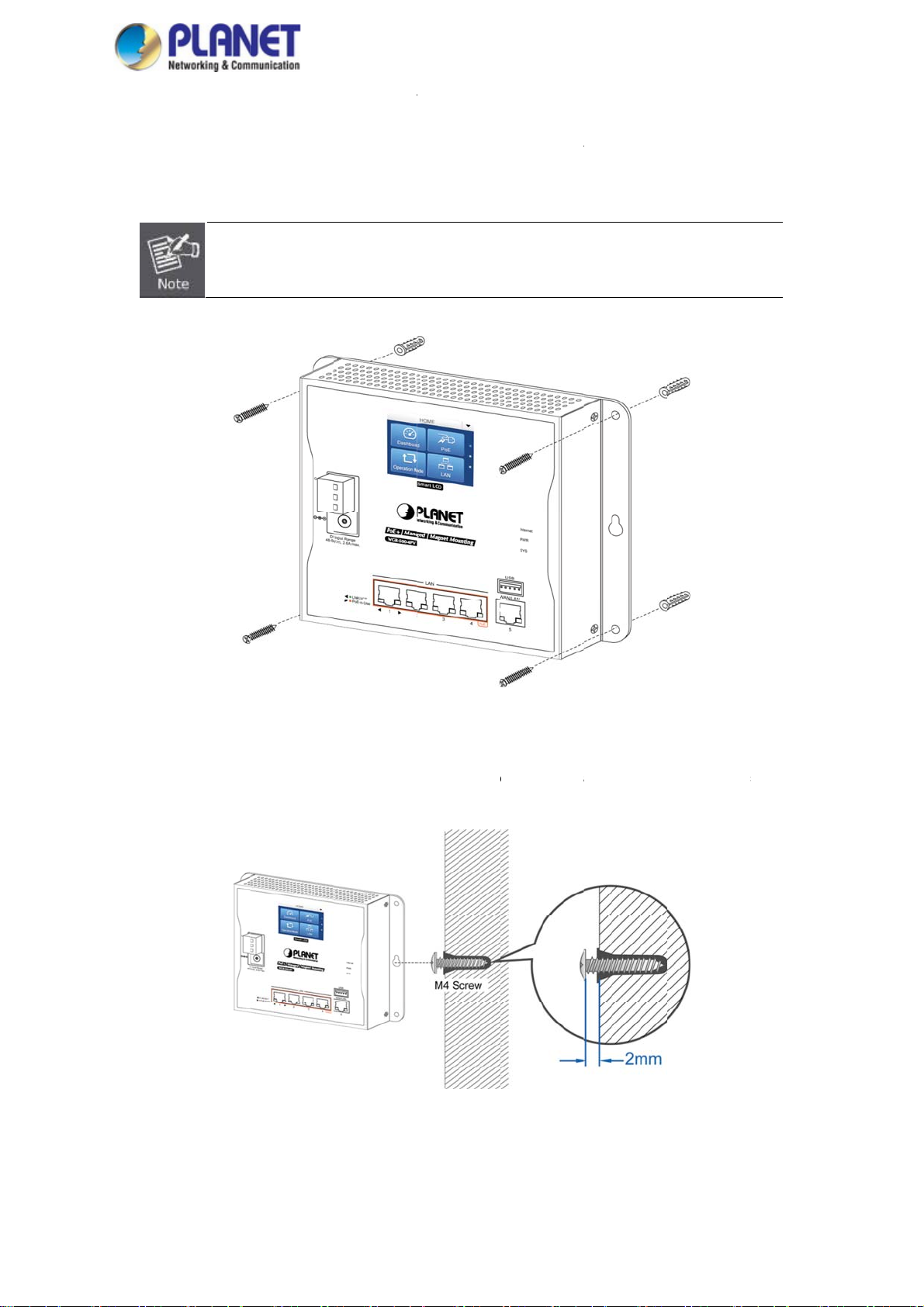
s
d
b
o
5
w
r
s
c
a
n
e
e
R
a
0
u
r
w
f
e
t
t
l
s
User’s
M
u
e
c
e
W
h
s
s
anual of
GR-500
Step 2:
Step 3-1
Install a con
urface.
: Screw the
conductor p
This f
WGR-
uctor pipe in
olts into the
ipe as shown
llowing pictu
00.
ide the boar
onductor pip
in Figure 2-9.
res show th
d hole and fl
. The indust
user how t
sh the edge
ial wall-moun
o install the
of the cond
Gigabit rout
device, and
ctor pipe wit
r is between
the device i
the wall
bolts and
not
Step 3-2
: Insert scre
over the sc
industry rou
s into the w
ews and slid
ter can be hu
Figure 2-9:
ll anchors, le
e the device
g on the wall
Figure 2-1
outer is scre
ving 2mm o
down until th
as shown in
: Wall moun
ed to the wa
each screw
screws fit
Figure 2-10.
ing of router
l
exposed. Pla
nugly into th
e the wall-m
wall-mount
ount slots
lots. The
21
Page 22
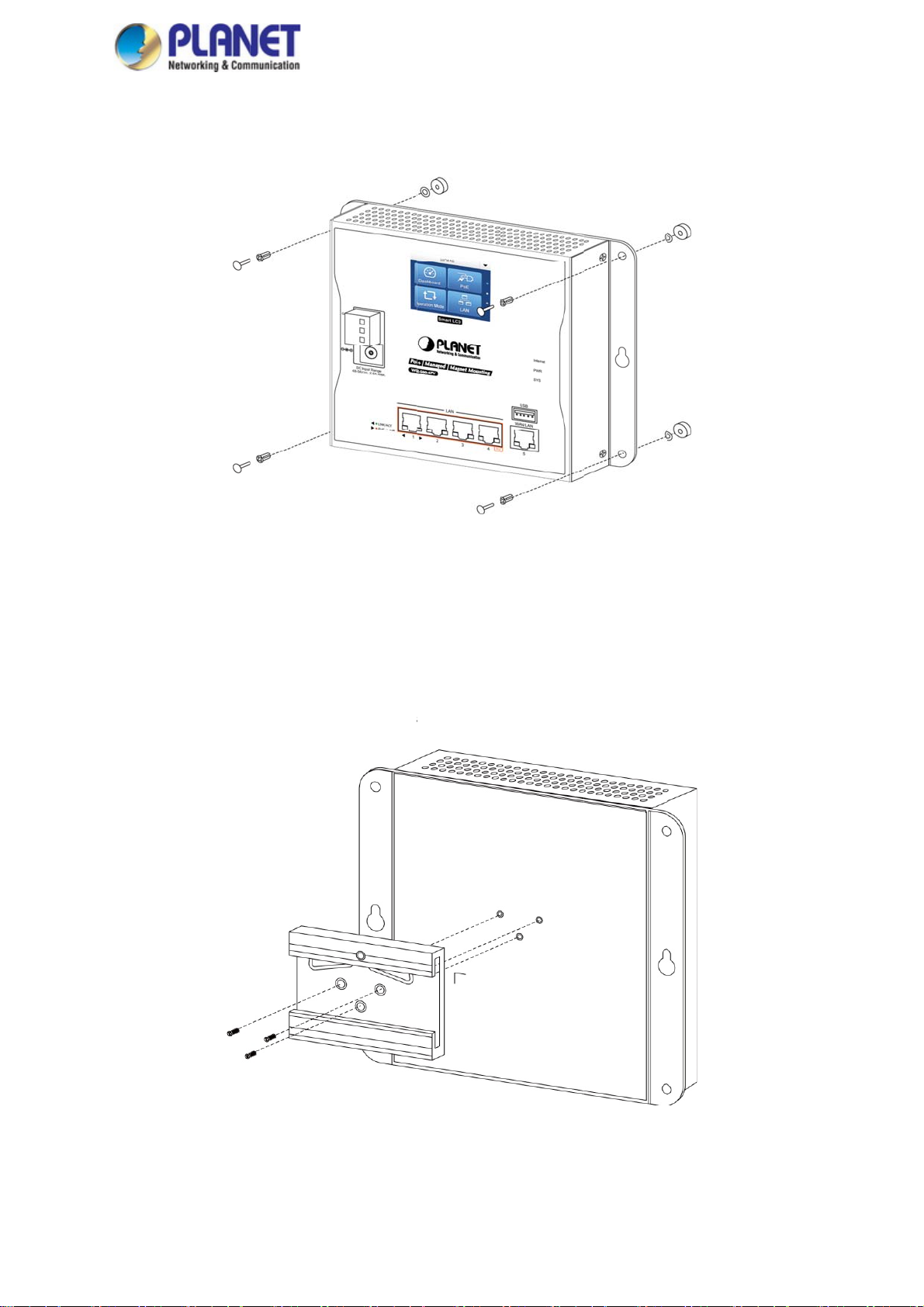
-
e
s
S
I
I
u
N
G
o
a
N
t
o
o
n
i
a
a
c
u
a
s
i
p
e
n
o
G
r
o
User’s
M
s
t
W
w
u
D
e
anual of
GR-500
2.2.2
To install
Magnet
the industrial
nstallatio
wall-mount
n
igabit router
Figure 2-11:
n a magneti
Magnetically i
surface, sim
nstalled rout
ly follow Figu
r
re 2-11 belo
:
2.2.3
The DIN
router n
the indu
Step 1:
DIN-rail
rail kit is incl
eds to be rep
trial wall-mou
crew the DI
nstallati
ded in the p
laced with DI
nt Gigabit rou
-rail bracket
n
ckage. Whe
-rail applicat
er. To hang u
n the Industri
the wall-mo
ion, please re
p the industri
al Router as
nt applicatio
fer to the foll
l wall-mount
hown in Figu
for the indu
wing figures
igabit router,
e 2-12.
trial wall-mo
o screw the
follow the st
nt Gigabit
IN-rail on
ps below:
Fig
ure 2-12: Att
ching DIN-ra
22
l bracket to r
uter
Page 23
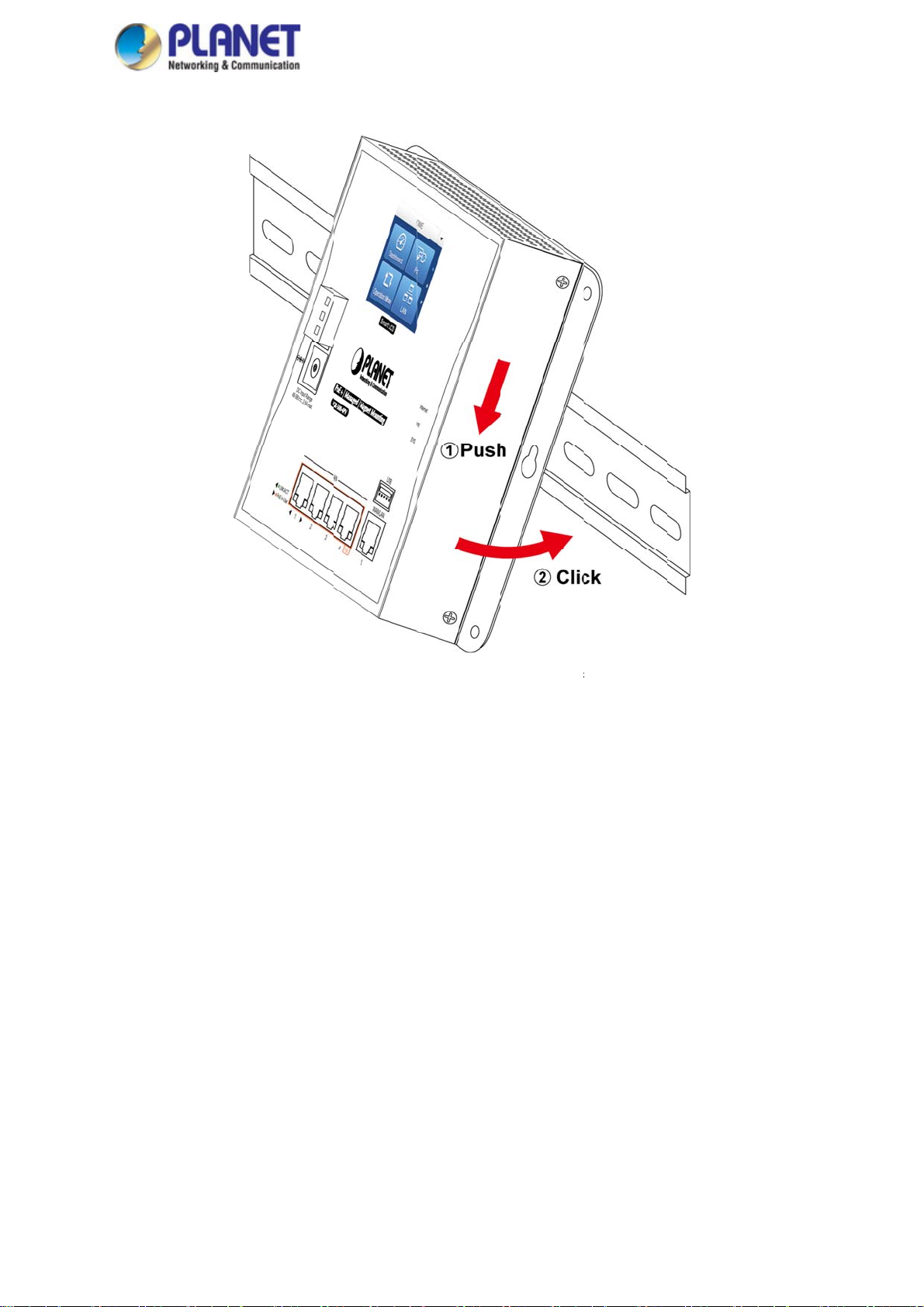
L
R
h
e
a
F
k
R
w
-
c
User’s
M
W
anual of
GR-500
Step 2:
ightly insert t
e DIN-rail br
cket into the
track as sho
n in Figure 2
13.
Step 3:
outer is plac
d on the trac
igure 2-13:
as shown in
outer is plac
Figure 2-14
d on the tra
k
23
Page 24
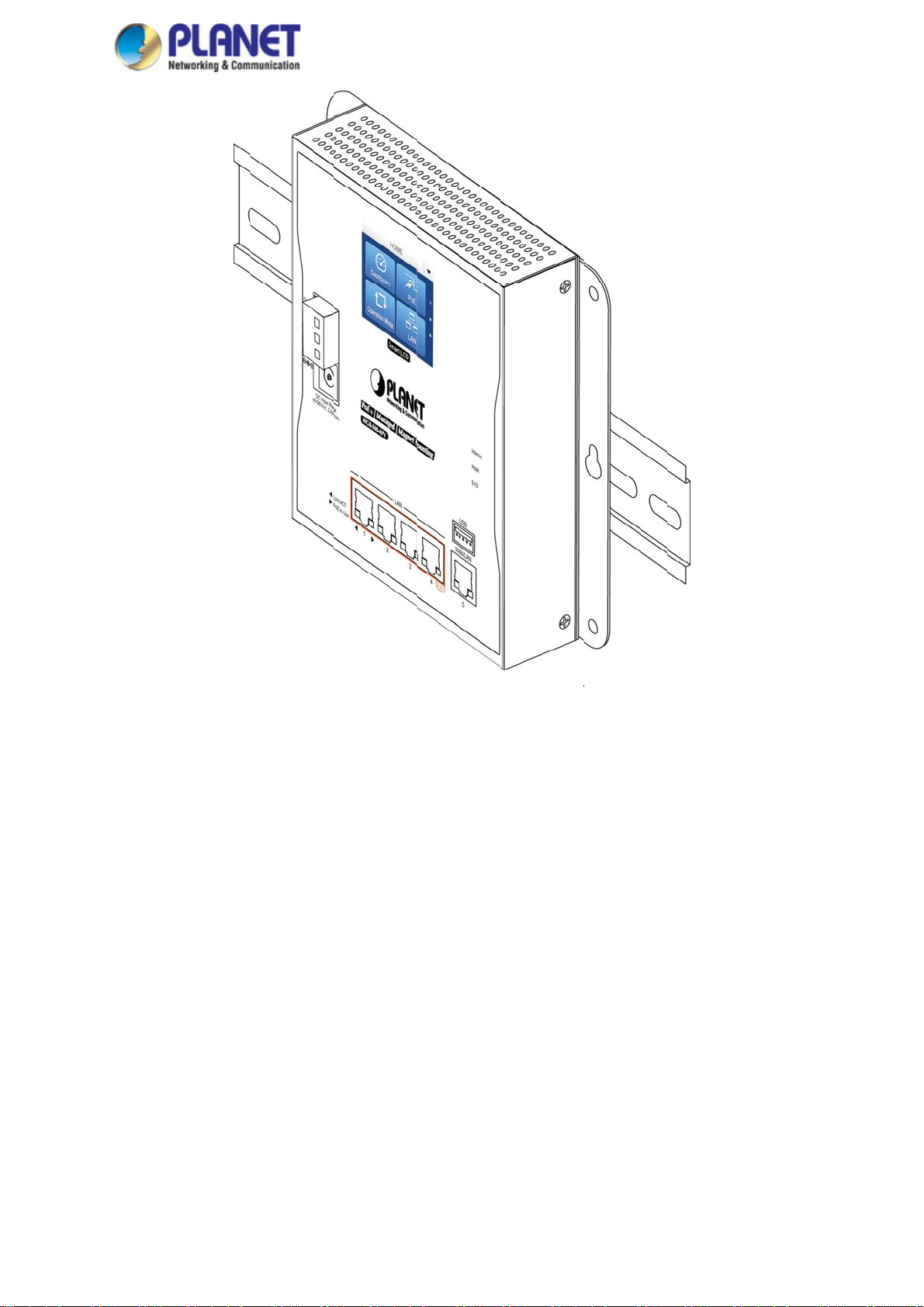
o
r
User’s
M
W
anual of
GR-500
Figure 2-14: R
uter is tightly
ixed on the t
ack
24
Page 25
User’s Manual of WGR-500
Chapter 3. Router Management
This chapter explains the methods that you can use to configure management access to the industrial
wall-mount Gigabit router. It describes the types of management applications and the communication and
management protocols that deliver data between your management device (workstation or personal computer)
and the system. It also contains information about port connection options.
This chapter covers the following topics:
Requirements
Web Management Access
3.1 Requirements
Workstation running Windows XP/2003, Vista, Windows 7/8/10, MAC OS X, Linux, Fedora, Ubuntu or
other platform is compatible with TCP/IP protocols.
Workstation is installed with Ethernet NIC (Network Interface Card)
Ethernet Port
Network cables -- Use standard network (UTP) cables with RJ45 connectors.
The above workstation is installed with Web browser and JAVA runtime environment Plug-in
It is recommended to use Internet Explorer 8.0 or above to access industrial wall-mount
Gigabit router.
25
Page 26
User’s Manual of WGR-500
3.2 Web Management
The industrial wall-mount Gigabit router offers management features that allow users to manage the industrial
wall-mount Gigabit router from anywhere on the network through a standard browser such as Microsoft Internet
Explorer. After you set up your IP address for the industrial wall-mount Gigabit router, you can access the
industrial wall-mount Gigabit router’s Web interface applications directly in your Web browser by entering the IP
address of the industrial wall-mount Gigabit router.
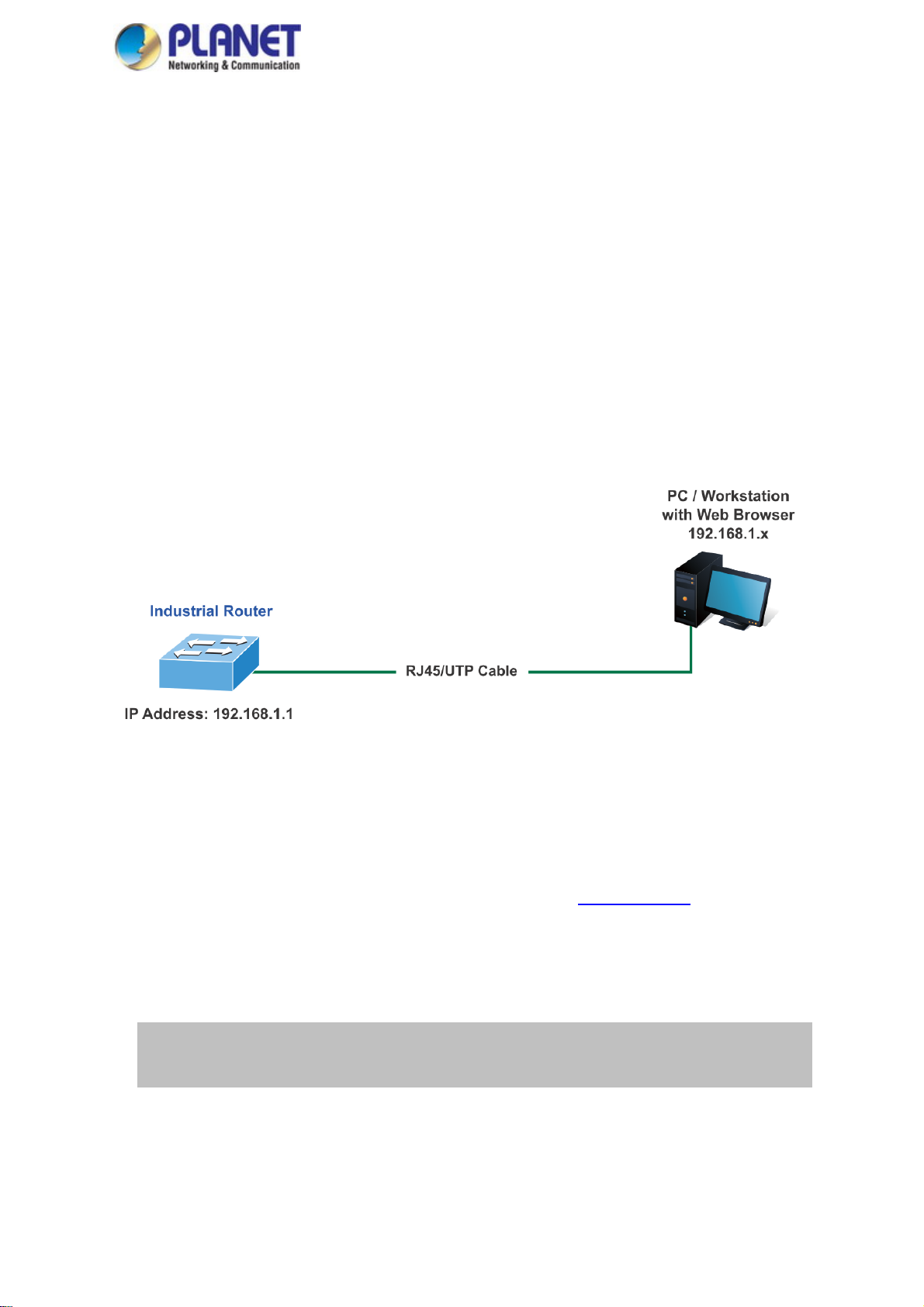
The following shows how to start up the Web Management of the Industrial wall-mount Gigabit router. Note the
Industrial Router is configured through an Ethernet connection. Please make sure the manager PC must be set to
the same IP subnet address. For example, the default IP address of the Industrial Router is 192.168.1.1, then the
manager PC should be set to 192.168.1.x (where x is a number between 1 and 254) and the default subnet mask
is 255.255.255.0 as shown in Figure 3-1.
Figure 3-1: Web Management
You can then use your Web browser to list and manage the industrial wall-mount Gigabit router configuration
parameters from one central location; the Web Management requires Microsoft Internet Explorer 8.0 or later.
1. Use Internet Explorer 8.0 or above Web browser and enter IP address http://192.168.1.1 to access the Web
interface.
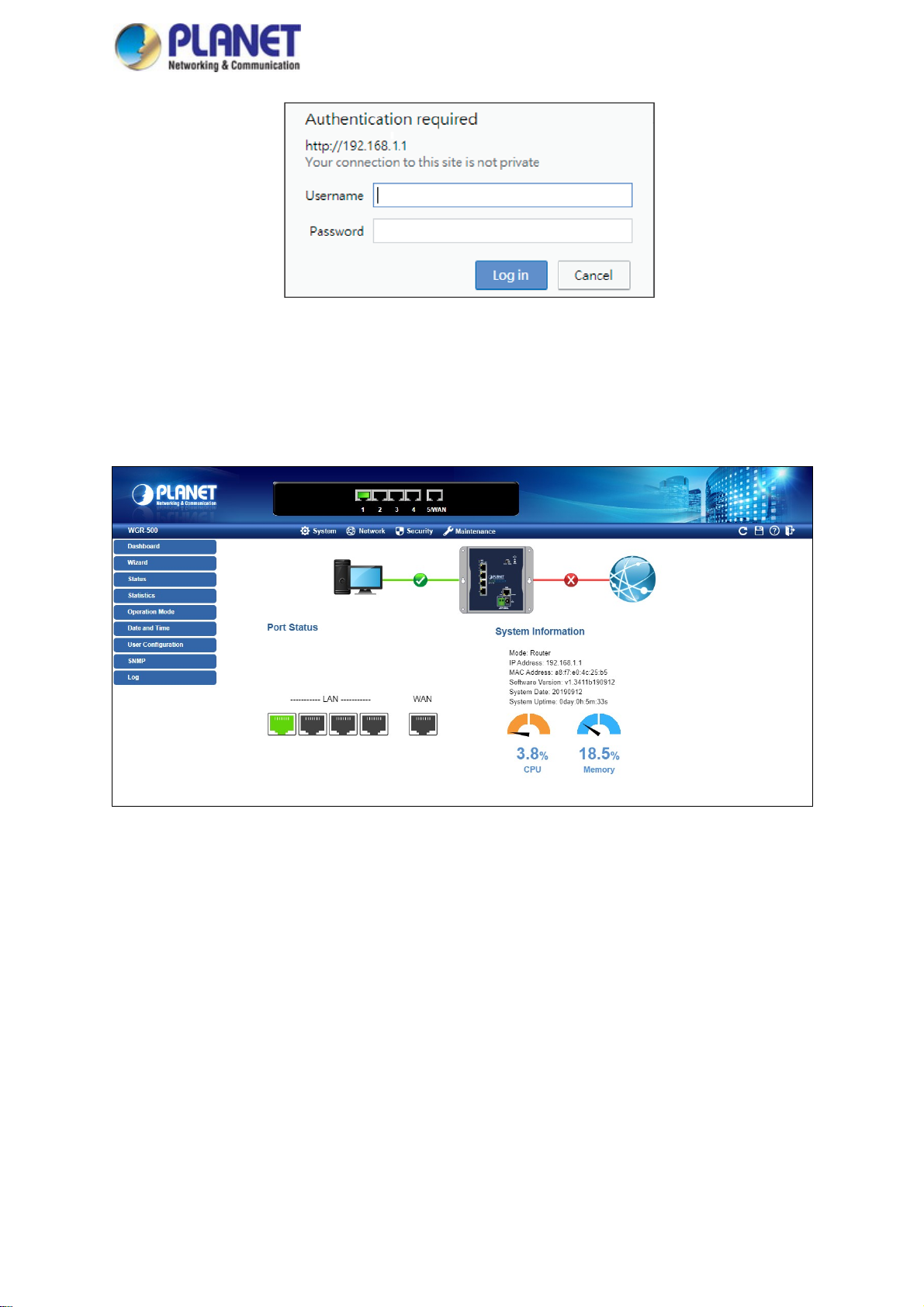
2. When the following dialog box appears, please enter “admin” in both the default user name and password
fields. The login screen shown in Figure 3-2 appears.
Default IP Address: 192.168.1.1
Default Username: admin
Default Password: admin
26
Page 27
User’s Manual of WGR-500
Figure 3-2: Web login Screen
After successfully logging into the web UI of the WGR-500 Series, you will see the main menus on the menu bar
and sub menus on the left side. The Figure 3-3 is the web main page of the WGR-500.
Figure 3-3: Web Main Page of WGR-500
27
Page 28

User’s Manual of WGR-500
Chapter 4. Configuration in Web UI
This chapter describes how to use Web-based browser interface for configuring and managing industrial
wall-mount Gigabit router.
4.1 Main Web Page
After a successful login, the main web page appears. The web main page shown in Figure 4-1 displays the web
panel, main menu, function menu, and the main information in the center.
Figure 4-1: Web Main Page
28
Page 29

User’s Manual of WGR-500
■ Web Panel
The web panel displays an image of the industrial wall-mount Gigabit router’s ports as shown in Figure 4-2.
Figure 4-2: Web Panel
Object Icon Function
To indicate the LAN with the RJ45 plug-in.
LAN
■ Main Menu
To indicates network data is sending or receiving
The main menu displays the product name, function menu, and main information in the center. Via the Web
management, the administrator can set up the industrial wall-mount Gigabit router by selecting the functions those
listed in the function menu and button as shown in Figures 4-3 and 4-4.
Figure 4-3: Function Menu
Object Description
System
Network
Security
Maintenance
Provides System information of industrial wall-mount Gigabit router.
Provides WAN, LAN and network configuration of industrial wall-mount
Gigabit router.
Provides QoS and security configuration of industrial wall-mount Gigabit
router.
Provides firmware upgrade and setting file restore/backup configuration
of industrial wall-mount Gigabit router
Figure 4-4: Function Button
29
Page 30

Object Description
User’s Manual of WGR-500
Click the "Refresh button" to refresh the current Web page.
Click the " Save/Restore configuration button" to go to Save/Restore configuration page.
Click the "Help button" to show the function descriptions of the current pages.
Click the "Logout button" to log out the web UI of the industrial wall-mount Gigabit router.
30
Page 31

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.2 System
Use the System menu items to display and configure basic administrative details of the industrial wall-mount
Gigabit router. The System menu shown in Figure 4-5 provides the following features to configure and monitor
system.
Object Description
Dashboard
Wizard
Status
Statistics
Operation Mode
Date and Time
User Configuration
Figure 4-5: System Menu
The overview of system information includes connection, port, and
system status
The Wizard will guide the user to configuring the router easily and
quickly.
Display the status of the system, LAN and WAN.
Display statistics information of network traffic of LAN and WAN
Display the current operation mode, and users can set different modes
to LAN interface.
Allow to set system time by manual or synchronize system time from
Internet NTP server.
Allow to change the username and password of industrial wall-mount
SNMP
Log
Gigabit router.
Display SNMP system information.
Provides the system log setting and information display of industrial
wall-mount Gigabit router
31
Page 32

h
t
r
e
n
O
w
W
W
n
u
n
n
l
b
m
m
d
m
e
c
D
s
s
s
User’s
M
d
o
d
o
W
u
a
d
anual of
GR-500
4.2.1
The das
shown in
Dashboa
board provid
Figure 4-6.
d
s an overvie
of system i
formation inc
uding conne
tion, port, an
system stat
s as
WAN/LA
Port Sta
N Connectio
us
Status
bject
Fig
re 4-6: Dash
The status
connected.
The status
is connecte
The status
disconnect
oard
eans WAN i
eans WAN i
.
eans WAN i
d.
escription
connected t
disconnecte
connected t
Internet and
d to Internet
Internet an
LAN is
nd LAN
LAN is
Object
LAN or
LAN or
AN port is i
AN port is
use.
ot in use.
32
Description
Page 33

System Information
Object Description
User’s Manual of WGR-500
Mode
IP Address
MAC Address
Software Version Display the current firmware version of industrial wall-mount Gigabit
System Date Display the current system date of Industrial wall-mount Gigabit router.
System Uptime
CPU
Memory
Display the current operation mode.
Display the current IP address of industrial wall-mount Gigabit router.
Display the LAN MAC address of industrial wall-mount Gigabit router.
router.
The system date will be correct if NTP function is enabled and the Hub
is connected to Internet.
Display the period of time the device has been operational.
Display the CPU loading
Display the memory usage
33
Page 34

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.2.2 Setup Wizard
The Wizard will guide the user to configuring industrial wall-mount Gigabit router easily and quickly. There are
different procedures in different operation modes. According to the operation mode you switch to, please follow the
instructions below to configure industrial wall-mount Gigabit router via Setup Wizard as shown in Figure 4-7.
Figure 4-7: Setup Wizard
Step 1: Operation Mode
The router supports two operation modes, Router and Switch, as shown in Figure 4-8.
Figure 4-8: Setup Wizard – Operation Mode
Router
Object Description
In this mode, the device is supposed to connect to internet via
xDSL/Cable/xPON/Fiber modem. The NAT is enabled and PCs in LAN ports
share the same IP with ISP through WAN port. The connection type can be
set up in WAN page by using PPPOE, DHCP client, PPTP client , L2TP
client or static IP.
34
Page 35

User’s Manual of WGR-500
Object Description
In this mode, all Ethernet ports are bridged together and NAT function is
Switch
disabled. All the WAN-related functions and firewall are not supported.
Step 3: Time Zone Setting
The Time Configuration option allows you to configure, update, and maintain the correct time on the internal
system clock. Daylight Saving can also be configured to automatically adjust the time when needed.
The setup is shown in Figure 4-9
Figure 4-9: Setup Wizard – Time Zone Configuration
Object Description
Enable NTP client update
Automatically Adjust Daylight
Savings
Time Zone Select
NTP Server
Check this box to connect NTP server and synchronize internet time.
Check this box to adjust the daylight savings automatically.
Select the Time Zone from the drop-down menu.
Select the NTP server from the drop-down menu.
Step 4: LAN Interface Setting
Set up the IP Address and Subnet Mask for the LAN interface as shown in Figure 4-10.
35
Page 36

User’s Manual of WGR-500
Figure 4-10: Setup Wizard – LAN Configuration
Object Description
IP Address Enter the IP address of your Router. The default: 192.168.1.1
Subnet Mask
An address code that determines the size of the network. Normally use
255.255.255.0 as the subnet mask.
Step 5 WAN Interface Setting
The industrial wall-mount Gigabit Router supports five access modes in the WAN side as shown in Figure 4-11.
Please choose the correct mode according to your ISP.
Figure 4-11: Setup Wizard – WAN Configuration
Mode 1 - Static IP
Select Static IP Address if all the Internet port’s IP information is provided to you by your ISP. You will need to
enter the IP address, subnet mask, gateway address, and DNS address provided to you by your ISP. Each IP
address entered in the fields must be in the appropriate IP form, which are four octets separated by a dot (x.x.x.x).
The Router will not accept the IP address if it is not in this format. The setup is shown in Figure 4-12.
36
Page 37

User’s Manual of WGR-500
Figure 4-12: WAN Interface Setup – Static IP Setup
Object Description
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Default Gateway
DNS
Mode 2 DHCP Client
Select DHCP Client to obtain IP Address information automatically from your ISP. The setup is shown in Figure
4-13.
Figure 4-13: WAN Interface Setup – DHCP Setup
Enter the IP address assigned by your ISP.
Enter the Subnet Mask assigned by your ISP.
Enter the Gateway assigned by your ISP.
The DNS server information will be supplied by your ISP.
Mode 3 PPPoE
Choose PPPoE (Point to Point Protocol over Ethernet) if your ISP uses a PPPoE connection. Your ISP will
provide you with a username and password. This option is typically used for DSL services. The setup is shown in
Figure 4-14.
37
Page 38

User’s Manual of WGR-500
Figure 4-14: WAN Interface Setup – PPPoE Setup
Object Description
User Name
Password
Enter your PPPoE user name.
Enter your PPPoE password.
38
Page 39

User’s Manual of WGR-500
Mode 4 PPTP
Choose PPTP (Point-to-Point-Tunneling Protocol) if your ISP uses a PPTP connection. Your ISP will provide
you with IP information and PPTP Server IP Address; of course, it also includes a username and password. This
mode is typically used for DSL services. The setup is shown in Figure 4-15.
Object Description
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Server IP Address
User Name
Password
Figure 4-15: WAN Interface Setup – PPTP Setup
Enter the IP address.
Enter the subnet Mask.
Enter the PPTP Server IP address provided by your ISP.
Enter your PPTP username.
Enter your PPTP password.
39
Page 40

User’s Manual of WGR-500
Mode 5 L2TP
Choose L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol) if your ISP uses an L2TP connection. Your ISP will provide you with a
username and password. The setup is shown in Figure 4-16.
Figure 4-16: WAN Interface Setup – L2TP Setup
Object Description
IP Address Enter the IP address.
Subnet Mask Enter the subnet Mask.
Server IP Address Enter the L2TP Server IP address provided by your ISP.
User Name Enter your L2TP username.
Password Enter your L2TP password.
40
Page 41

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.2.3 Status
This page displays system information of Industrial wall-mount Gigabit router as shown in Figure 4-17.
Figure 4-17: System Information
4.2.4 Stastics
This page displays the number of packet that pass through the router on the WAN and LAN. The statistics are
shown in Figure 4-18.
Figure 4-18: Statistics
41
Page 42

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.2.5 Operation Mode
If you want to set a different mode between router and switch, it can only be configured by DIP switch instead of
web GUI.
The industrial wall-mount Gigabit router supports two modes for your application, select the Router mode to act as
a Gateway which provides the firewall function to protect your private network. To select the Switch mode,
industrial wall-mount Gigabit router will act as a pure 5-Port Ethernet Switch.
The setup is shown in Figure 4-19 and default mode is Router mode.
Figure 4-19: Operation Mode
Object Description
In this mode, the device is supposed to connect to internet via
xDSL/Cable/xPON/Fiber modem. The NAT is enabled and PCs in LAN ports
Router
Switch
share the same IP with ISP through WAN port. The connection type can be
set up in WAN page by using PPPOE, DHCP client, PPTP client , L2TP
client or static IP.
In this mode, all Ethernet ports are bridged together and NAT function is
disabled. All the WAN related function and firewall are not supported.
42
Page 43

User’s Manual of WGR-500
■ The Function Menu of Router Mode
System Network Security Maintenance
Dashboard WAN Setup QoS Connection Test
Wizard LAN Setup DoS Save/Restore Configuration
Status VLAN Port Filtering Firmware
Statistics Route IP Filtering Reboot
Operation Mode DDNS MAC Filtering
Date and Time IPv6 WAN Setting URL Filtering
User Configuration IPv6 LAN Setting DMZ
SNMP Radvd Port Forwarding
Log Tunnel (6 over 4)
■ The Function Menu of Switch Mode
System Network Maintenance
Dashboard LAN Setup Connection Test
Wizard VLAN Save/Restore Configuration
Status IPv6 LAN Setting Firmware
Statistics Reboot
Operation Mode
Date and Time
User Configuration
SNMP
Log
43
Page 44

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.2.6 Date and Time
This section assists you in setting the system time of industrial wall-mount Gigabit router. You can either select to
set the time and date manually or automatically obtain the GMT time from Internet as shown in Figure 4-20.
Object Description
Time Zone Select
Time Zone Select
Enable NTP Client
Update
NTP Server
Save
Save & Apply
Reset
Refresh
Figure 4-20: Date and Time
Input current time manually.
Select the time zone of the country you are currently in. The router will set its time
based on your selection.
Check to enable NTP update. Once this function is enabled, router will
automatically update current time from NTP server.
User may select NTP sever or input address of NTP server manually.
Press this button to save changes.
Press this button to save and apply changes.
Press this button to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously
saved values.
Press this button to refresh the page
44
Page 45

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.2.7 User Configuration
To ensure the industrial wall-mount Gigabit router's security is secure, you will be asked for your password when
you access the industrial wall-mount Gigabit router's Web-based utility. The default user name and password are
"admin". This page will allow you to modify the user name and passwords as shown in Figure 4-21.
Figure 4-21: User Configuration
Object Description
User Name
New Password
Confirmed Password
Save
Save & Apply
Reset
Enter user name.
Input password for this user.
Confirm password again.
Press this button to save changes.
Press this button to save and apply changes.
Press this button to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously
saved values.
45
Page 46

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.2.8 SNMP
This section provides SNMP setting of industrial wall-mount Gigabit router as shown in Figure 4-22.
Object Description
Enable SNMP
Name
Location
Contact
Read/Write Community
Read-Only Community
Save
Save & Apply
Figure 4-22: SNMP
Disable or enable the SNMP function.
Allows to enter characters for Name of industrial wall-mount Gigabit router.
Allows to enter characters for Location of industrial wall-mount Gigabit router.
Allows to enter characters for contact of industrial wall-mount Gigabit router.
Allows to enter characters for SNMP Read/Write Community of industrial
wall-mount Gigabit router.
Allow to enter characters for SNMP Read-Only Community of industrial
wall-mount Gigabit router.
Press this button to save changes.
Press this button to save and apply changes.
Reset
Press this button to undo any changes made locally and revert to previously
saved values.
46
Page 47

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.2.9 Log
This section will help you to configure the settings of system log as shown in Figure 4-24. You can check the box
of the items you want to record it in the log.
Figure 4-24: Log
Object Description
Enable Log
System all/DoS
Enable Remote Log
Log Server IP Address
Apply Changes
Refresh
Clear
Check to enable log function.
Select which log you want to check. Related information will be shown
below.
Check to enable remote log functionality.
Enter Log Server IP Address for remote log.
Press this button to save and apply changes.
Press this button to refresh the current Web page.
Press this button to clear log information.
47
Page 48

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.3 Network
The Network function provides WAN, LAN and network configuration of industrial wall-mount Gigabit router as
shown in Figure 4-25.
Figure 4-25: Network Menu
Object Description
WAN Setup
LAN Setup
VLAN
Route
DDNS
IPv6 WAN Setting
IPv6 LAN Setting
Radvd
Tunnel (6 over 4)
Allows to set WAN interface.
Allows to set LAN interface.
Allows to set VLAN interface.
Allows to set Route interface.
Allows to set DDNS and PLANET DDNS
Allows to set IPv6 WAN interface.
Allows to set IPv6 LAN interface.
Allows to set RADVD
Allows to set Tunnel (6 over 4)
48
Page 49

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.3.1 WAN Setup
This page is used to configure the parameters for Internet network which connects to the WAN port of industrial
wall-mount Gigabit router as shown in Figure 4-26. Here you may change the access method to static IP, DHCP,
PPPoE, PPTP or L2TP by clicking the item value of WAN Access type.
WAN Access Type
Figure 4-26: WAN Setup
Object Description
Please select the corresponding WAN Access Type for the Internet, and fill
out the correct parameters from your local ISP in the fields which appear
below.
Select Static IP Address if all the Internet ports’ IP information
is provided to you by your ISP (Internet Service Provider). You
will need to enter the IP address, subnet mask, gateway
address, and DNS address provided to you by your ISP.
Static IP
Each IP address entered in the fields must be in the
appropriate IP form, which are four octets separated by a dot
(x.x.x.x). The Router will not accept the IP address if it is not
in this format.
IP Address
49
Page 50

User’s Manual of WGR-500
Object Description
Enter the IP address assigned by your ISP.
Subnet Mask
Enter the Subnet Mask assigned by your ISP.
Default Gateway
Enter the Gateway assigned by your ISP.
DNS
The DNS server information will be supplied by your ISP.
DHCP
Client
PPPoE
Select DHCP Client to obtain IP Address information
automatically from your ISP.
Choose PPPoE (Point to Point Protocol over Ethernet) if your
ISP uses a PPPoE connection. Your ISP will provide you with
a username and password. This option is typically used for
DSL services.
User Name
Enter your PPPoE user name.
Password
Enter your PPPoE password.
Choose PPTP (Point-to-Point-Tunneling Protocol) if your ISP
uses a PPTP connection. Your ISP will provide you with IP
information and PPTP Server IP Address; of course, it also
includes a username and password. This mode is typically
used for DSL services.
IP Address
Enter the IP address.
PPTP
L2TP
Subnet Mask
Enter the Subnet Mask.
Server IP Address
Enter the PPTP Server IP address provided by your ISP.
User Name
Enter your PPTP user name.
Password
Enter your PPTP password.
Choose L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol) if your ISP uses a
L2TP connection. Your ISP will provide you with a username
and password.
IP Address
Enter the IP address.
Subnet Mask
Enter the Subnet Mask.
Server IP Address
50
Page 51

User’s Manual of WGR-500
Object Description
Enter the L2TP Server IP address provided by your ISP.
User Name
Enter your L2TP user name.
Password
Enter your L2TP password.
Host Name
MTU Size
Attain DNS Automatically
Set DNS Manually
Enable uPnP
Enable IGMP Proxy
Enable Ping Access on
WAN
Enable Web Server
Access on WAN
Enable IPSec pass
This option specifies the Host Name of the industrial wall-mount Gigabit
router.
The normal MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) value for most Ethernet
networks is 1492 Bytes. It is not recommended that you change the default
MTU Size unless required by your ISP.
Select “Attain DNS Automatically”, the DNS servers will be assigned
dynamically from your ISP.
If your ISP gives you one or two DNS addresses, select Set DNS Manually
and enter the primary and secondary addresses into the correct fields.
Check the box to enable the uPnP function.
Check the box to enable the IGMP Proxy function.
Check the box to enable Ping access from the Internet Network.
Check the box to enable the web server access of the Industrial wall-mount
Gigabit router from the Internet network.
Check the box to enable IPSec passthrough function on VPN connection.
through on VPN
connection
Enable PPTP passthrough
on VPN connection
Enable L2TP passthrough
on VPN connection
Enable IPv6 passthrough
on VPN connection
If you get Address found to be in error when you access a Web site, it is likely that your
DNS servers are set up improperly. You should contact your ISP to get DNS server
addresses.
WAN IP, whether obtained automatically or specified manually, should NOT be on the same
IP net segment as the LAN IP; otherwise, the router will not work properly. In case of
emergency, press the hardware-based "Reset" button.
Check the box to enable PPTP passthrough function on VPN connection.
Check the box to enable L2TP passthrough function on VPN connection.
Check the box to enable IPv6 passthrough function on VPN connection.
51
Page 52

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.3.2 LAN Setup
This page is used to configure the parameters for local area network which connects to the LAN port of your
industrial wall-mount Gigabit router as shown in Figure 4-27. Here you may change the setting for IP address,
subnet mask, DHCP, etc.
Figure 4-27: LAN Setup
Object Description
IP Address
Subnet Mask Default is 255.255.255.0. You can change it according to your request.
DHCP
DHCP Client Range
Domain Name
802.1d Spanning Tree
Clone MAC Address
The LAN IP address of the Industrial wall-mount Gigabit router and default is
192.168.1.1. You can change it according to your request.
You can select one of them -- Disable, Client, or Server. Default is Server,
where the industrial wall-mount Gigabit router can assign IP addresses to
the computers automatically.
For the Server mode, you must enter the DHCP client IP address range in
the field. And you can click the “Show Client” button to show the Active
DHCP Client Table.
Default is Planet.
You can enable or disable the spanning tree function.
You can input an MAC address here for using clone function.
If you change the device’s LAN IP address, you must enter the new one in your browser to
get back to the web-based configuration utility. And LAN PCs’ gateway must be set to this
new IP for successful Internet connection.
52
Page 53

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.3.3 VLAN
VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) allows a physical network to be partitioned into multiple logical networks.
Devices on a logical network belong to one group. A device can belong to more than one group. With VLAN, a
device cannot directly talk to or hear from devices that are not in the same group. Please refer to the following
sections for the details as shown in Figure 4-28.
Object Description
Enable 802.1Q VLAN
VLAN ID
Forwarding Rule
Hardware NAT
Member
Tagged
Change PVID setting
Figure 4-28: VLAN Setup
Check this box to enable 802.1Q VLAN function.
Set VLAN ID (1-4095)
Select Bridge or NAT mode
Check this box to enable Hardware NAT function.
Add VLAN without tag to packet
Add VLAN tag to packet
Check this box to enable change PVID (default vlan id)
53
Page 54

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.3.4 Route
There are two route types -- Dynamic Route and Static Route. Please refer to the following sections for the
details as shown in Figure 4-29.
Figure 4-29: Routing setup
■ Dynamic routing
Dynamic routing is a networking technique that provides optimal data routing. Unlike static routing, dynamic
routing enables routers to select paths according to real-time logical network layout changes. RIPng exchanges
routing information used to compute routes and is intended for IP version 6 (IPv6)-based networks while RIPv1
and RIPv2 is intended for IP version 4 (IPv4)-based networks.
Object Description
Enable Dynamic Route
NAT
RIP Send
Click this box to enable Dynamic Route.
Enable or Disable NAT function
Disable:do not send any RIP packet out
RIP1: Send RIP1 packet out
RIP2. Send RIP2 packet out
54
Page 55

User’s Manual of WGR-500
Object Description
Disable:do not receive any RIP packet
RIP Recv
RIPng
■ Static routing
Static routing is a special type of routing that can be applied in a network to reduce the problem of routing
selection and data flow overload caused by routing selection so as to improve the packets forwarding speed. You
can set the destination IP address, subnet mask, and gateway to specify a routing rule. The destination IP address
and subnet mask determine a destination network or host to which the router sends packets through the gateway.
Object Description
Enable Static Route
IP Address
Subnet Mask
RIP1: Only receive RIP1 packet
RIP2: Only receive RIP2 packet
Enable or Disable RIPng function
Click this box to enable Static Route.
The network or host IP address desired to access.
The subnet mask of destination IP.
Gateway
Metric
Interface
Show Routing Table
Static Routing table
The gateway is the router or host’s IP address to which packet was sent. It
must be the same network segment with the WAN or LAN port.
The route metric is a value from 1 to 16 that indicates the cost of using this
route.
Select the interface that the IP packet must use to transmit out of the router
when this route is used.
Press the button to show all the routing tables of the system.
It only shows the static routing table and you can delete one or all.
55
Page 56

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.3.5 DDNS
The industrial wall-mount Gigabit router offers the DDNS (Dynamic Domain Name System) feature, which allows
the hosting of a website, FTP server, or e-mail server with a fixed domain name (named by yourself) and a
dynamic IP address, and then your friends can connect to your server by entering your domain name no matter
what your IP address is. Before using this feature, you need to sign up for DDNS service providers such as
PLANET DDNS or www.dyndns.org. The Dynamic DNS client service provider will give you a password or key.
■ Planet DDNS
PLANET DDNS website provides a free DDNS (Dynamic Domain Name Server) service for PLANET devices.
Whether the IP address used on your PLANET device supporting DDNS service is fixed or dynamic, you can
easily connect the devices anywhere on the Internet with a meaningful or easy-to-remember name you
gave.PLANET DDNS provides two types of DDNS services -- Dynamic DDNS and Easy DDNS -- as shown in
Figure 4-30.
PLANET Dynamic DDNS
For example, you've just installed a PLANET IP camera with dynamic IP like 210.66.155.93 in the network. You
can name this device as “Mycam1” and get the URL link as Mycam1.planetddns.com. Thus, you don't need to
memorize the exact IP address but just the URL link: Mycam1.planetddns.com.
PLANET Easy DDNS
PLANET Easy DDNS is an easy way to help user to get your Domain Name with just one click. You can just log in
to the Web Management Interface of your devices, say, your IP Camera, check the DDNS menu and just enable it.
Once you enabled the Easy DDNS, your PLANET Network Device will use the format PLxxxxxx where xxxxxx is
the last 6 characters of your MAC address that can be found on the Web page or bottom label of the device. (For
example, A8-F7-E0-81-96-C9 will be converted into pt8196c9.planetddns.com)
Figure 4-30: PLANET DDNS
56
Page 57

User’s Manual of WGR-500
Object Description
Disable: do not activate PLANET DDNS function
DDNS Option
Account
Password
DDNS
Comment
Status
■ Dynamic DNS
The industrial wall-mount Gigabit router supports DynDNS and TZO DDNS service providers for Dynamic DNS as
shown in Figure 4-31.
Enable Easy DDNS: activate Easy DDNS service
Enable Dynamic DDNS: activate Easy Dynamic DDNS service
The User Name for PLANET DDNS account.
The Password for PLANET DDNS account.
The DDNS name of PLANET device
Add some comment for this item.
Connection staus for PLANET DDNS
Object Description
Enable DDNS
Service Provider
Domain Name
User Name/Email
Password/Key
Figure 4-31: Dynamic DNS
Check the box to enable the Dynamic DNS function.
Select the DDNS service provider from the drop-down menu, such as
DynDNS or TZO.
Enter the domain name you have registered from the DDNS service
provider.
Enter the user name or email you have registered from the DDNS service
provider.
Enter the password you have registered from the DDNS service provider.
57
Page 58

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.3.6 IPv6 WAN Setting
This page is used to configure parameter for IPv6 internet network which connects to WAN port of your industrial
wall-mount Gigabit router as shown in Figure 4-32. It allows you to enable IPv6 function and set up the parameters
of the router’s WAN. In this setting, you may change WAN original type and WAN link type.
Enable IPv6
Original Type
WAN Link Type
Figure 4-32: IPv6 WAN setup
Object Description
Click this box to enable IPv6 configuration.
Select either Auto or Static. In Auto you could choose the DHCP type for
Stateless Address Auto or Stateful Address Auto Configuration. In Static you
need to fill in the Static IP address table.
Select IPv6 WAN type either by using Ethernet or PPPoE.
58
Page 59

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.3.7 IPv6 LAN Setting
IPv6 LAN Setting will be only available if you enable IPv6 WAN. Make sure IPv6 WAN is enabled before you could
configure the IPv6 LAN. The setup is shown in Figure 4-33.
Object Description
Enable IPv6 LAN
DNS Address
Interface Name
From
To
Figure 4-33: IPv6 LAN Setup
Click this box to enable IPv6 LAN configuration.
Enter IPv6 DNS Address assigned by your ISP.
Enter assigned Interface name of the IPv6 LAN port.
Enter assigned starting Address pool.
Enter assigned ending Address pool.
59
Page 60

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.3.8 RADVD
The RADVD configuration is responsible for defining interface setting, prefixes, routers and RDNSS
announcements. The setup is shown in Figures 4-34 to 4-35.
Object Description
Enable
Radvdinterfacename
MaxRtrAdvInterval
MinRtrAdvInterval
MinDelayBetwennRAs
AdvManagedFlag
Figure 4-34: IPv6 RADVD
Click this box to enable RADVD configuration.
Assigned interface name of RADVD.
Enter the maximum time allowed between sending unsolicited multicast
router advertisements from the interface in seconds. By default the value is
600.
Enter the minimum time allowed between sending unsolicited multicast
router advertisements from the interface in seconds. By default the value is
198.
Enter the minimum time allowed between sending multicast router
advertisements from the interface in seconds By default the value is 3
To enables and disable the additional stateful administered
auto-configuration protocol.
AdvOtherConfigFlag
To enable and disable the auto-configuration of additional, non address
information.
60
Page 61

AdvLinkMTU
User’s Manual of WGR-500
Object Description
Enter value of Advertises the given link MTU in the RA if specified. 0 value
disables MTU advertisements.
Enter value of Advertises assumed reach-ability time in milliseconds of
AdvReachable Time
AdvRetransTime
AdvCurHopLimit
AdvDefaultLifetime
AdvDefaultPreference
AdvSourceLLAddress
UnicastOnly
neighbors in the RA if specified. 0 value disables reach-ability
advertisements.
Enter value of Advertises wait time in milliseconds between Neighbor
Solicitation messages in the RA if specified. 0 value is disables re-transmit
advertisements
Enter value of Advertises the default Hop Count value for outgoing unicast
packets in the RA. 0 value is disables hopcount advertisements. By default
value is set to 64.
Enter value of Advertises the lifetime of the default router in seconds. 0
value is indicates that the node is no default router. By default it is set to
1800.
Select the advertises default router preference. By default it is set to
medium.
To include the link-layer address of the outgoing interface in the RA.
To enable the indication that the underlying link is not broadcast capable,
prevents unsolicited advertisements from being sent.
61
Page 62

User’s Manual of WGR-500
Object Description
Enable RADVD prefix
Prefix
AdvOnLinkFlag
AdvAutonomousFlag
AdvValidLifetime
AdvPreferredLifeTime
AdvRouterAddr
Figure 4-35: IPv6 RADVD Prefix
Click this box to enable RADVD prefix.
Assigned the advertised IPv6 route prefix.
To enable indication that this prefix can be used for on-link determination.
To enable indication that this prefix can be used for autonomous address
configuration.
Enter the advertising length of time in seconds that the prefix is valid for
purpose of on-link determination.
Enter the advertising length of time in seconds that addresses generated
from the prefix via stateless address autoconfiguration remain preferred.
The special value infinity means forever
Enable indication of the address of interface that is sent instead of network
prefix.
if6to4
Specifies a logical interface name to derive a 6to4 prefix origin.
62
Page 63

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.3.9 Tunnel (6 over 4)
6 to 4 is an IPv6 address assignment and automatic tunneling technology that is used to provide unicast IPv6
connectivity between IPv6 sites and hosts across the IPv4 Internet. The setup is shown in Figure 4-36.
Figure 4-36: IPv6 Tunnel (6 over 4)
Object Description
Enable Tunnel (6 to 4)
Click this box to enable Tunnel (6 to 4).
63
Page 64

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.4 Security
The Security menu provides QoS, firewall and access filtering as shown in Figure 4-37. Please refer to the
following sections for the details.
Figure 4-37: Secuirty menu
Object Description
QoS
DoS
Port Filtering
IP Filtering
MAC Filtering
URL Filtering
DMZ
Port Forwarding
Allows to set QoS (Quality of Service).
Allows to set DoS (Denial of Service).
Allows to set Port Filtering.
Allows to set IP Filtering.
Allows to set MAC Filtering
Allow to set MAC Filtering.
Allow to set DMZ.
Allow to set Port Forwarding
64
Page 65

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.4.1 QoS
The QoS (Quality of Service) helps improve your network gaming performance by prioritizing applications as
shown in Figure 4-38. By default the bandwidth control is disabled and application priority is not classified
automatically. In order to complete this settings, please follow the steps below.
Figure 4-38: QoS
65
Page 66

User’s Manual of WGR-500
Object Description
Enable QoS
Automatic Uplink Speed
Automatic Downlink Speed
Name
QoS Type
Protocol
Select IP
Local IP Address
Local Port
Check the box to enable the QoS function.
Check the box to adjust the uplink speed automatically by the Industrial
wall-mount Gigabit router. Or enter the uplink data rate manually in the field
below.
Check the box to adjust the downlink speed automatically by the Industrial
wall-mount Gigabit router. Or enter the downlink data rate manually in the
field below.
Add a QoS rule name.
Choose type of QoS either by IPv4, MAC Address, IPv6, PHYPORT or
DSCP.
Select type of protocol to use for QoS. It can be either TCP, UDP or both.
Select connected client IP Address.
Enter local IP Address range of client or device (if QoS type is IPv4).
Enter local port range of client or device (if QoS type is IPv4).
Remote IP Address
Remote Port
IPv6 Address
MAC Address
PHYPORT
DSCP
Mode
Uplink Bandwidth
Downlink Bandwidth
remark dscp
Comment
Enter remote IP Address range of client or device (if QoS type is IPv4).
Enter remote port range of client or device (if QoS type is IPv4).
Enter IPv6 Address of client or device (if QoS type is IPv6).
Enter MAC Address of client or device (if QoS type is MAC).
Enter Physical Ethernet port of connected client or device (if QoS type is
PHYPORT).
Enter DSCP number of client or device (if QoS type is DSCP).
Select QoS mode for “Guaranteed minimum bandwidth” or “Restricted
maximum bandwidth”.
Enter value of upload limitation value according to the QoS mode.
Enter value of download limitation value according to the QoS mode.
Insert a remark on DSCP configuration.
Insert comment of the DSCP configuration as references.
66
Page 67

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.4.2 DoS
A "Denial-of-Service" (DoS) attack is characterized by an explicit attempt by hackers to prevent legitimate users of
a service from using that service. The industrial wall-mount Gigabit router can prevent specific DoS attacks as
shown in Figure 4-39.
Object Description
Enable DoS Prevention
Whole System Flood SYN
Whole System Flood FIN
Whole System Flood UDP
Whole System Flood ICMP
Figure 4-39: DoS
Check to enable DoS function.
User may set other related configurations about DoS below.
Check the box to enable. If enabled, when the number of the current SYN
packets is beyond the set value, the router will startup the blocking function
immediately.
Check the box to enable. If enabled, when the number of the current FIN
packets is beyond the set value, the router will startup the blocking function
immediately.
Check the box to enable. If enabled, when the number of the current
UPD-FLOOD packets is beyond the set value, the router will startup the
blocking function immediately.
Check the box to enable. If enabled, when the number of the current
ICMP-FLOOD packets is beyond the set value, the router will startup the
blocking function immediately.
67
Page 68

User’s Manual of WGR-500
Check the box to enable. When the IP Flood SYN Detection is enabled, the
Per-Source IP Flood SYN
Per-Source IP Flood FIN
Per-Source IP Flood UDP
Per-Source IP Flood ICMP
TCP/UDP PortScan
ICMP Smurf
IP Land
IP Spoof
router has the ability to block malicious devices that are attempting to flood
devices.
Check the box to enable. When the IP Flood FIN Detection is enabled, the
router has the ability to block malicious devices that are attempting to flood
devices.
Check the box to enable. When the IP Flood UDP Detection is enabled, the
router has the ability to block malicious devices that are attempting to flood
devices.
Check the box to enable. When the IP Flood IGMP Detection is enabled, the
router has the ability to block malicious devices that are attempting to flood
devices.
Check the box wil l block against hackers from probe to router system
remotely and determine what TCP/UDP port are open.
Check box to enable protection against ICMP Smurf attack.
Check the box to enable the protection against LAND attack.
Check box to enable protection against IP Spoofing attack on device within
network.
IP TearDrop
PingOfDeath
TCP Scan
TCP SynWithData
UDP Bomb
UDP EchoChargen
Select All
Enable Source IP Blocking
Check box to enable protection against Teardrop attack that targeting on
TCP/IP fragmentation reassembly codes.
Check box to enable protection against Ping of Death attack that aims to
disrupt a targeted machine by sending a packet larger that maximum
allowable size causing the target machine to freeze or crash.
Check the box to enable protection against TCP Scan. TCP Scan is
technique use to identify listening TCP Port.
Check the box to block TCP Syn With Data evasion technique.
Check the box to enable protection against UDP Bomb or called as UDP
Flood or packet storm.
Check the box to enable protection against CharGEN attack. CharGEN
attack is carried out by sending small packets carrying a spoofed IP of the
target to the internet enabled devices running CharGEN.
Select to enable all the DoS protection method.
Enter value of time duration for IP Blocking.
68
Page 69

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.4.3 Port Filtering
Entries in this table are used to restrict certain types of data packets from your local network to Internet through
the Gateway. Use of such filters can be helpful in securing or restricting your local network as shown in Figure
4-40
Object Description
Enable Port Filtering
Enable IPv4
Enable IPv6
Port Range
Protocol
Comment
Figure 4-40: Port Filtering
Check box to enable Port Filtering function.
Check box to enable Port filtering method using IPv4.
Check box to enable Port filtering method using IPv6.
Add ports you want to control.
Select the port number protocol type (TCP, UDP or both). If you are unsure,
then leave it to the default both protocols.
Enter the description for this setting.
69
Page 70

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.4.4 IP Filtering
IP Filtering is used to block internet or network access to specific IP addresses on your local network as shown in
Figure 4-41. The restricted user may still be able to log in to the network but will not be able to access the internet.
To begin blocking access to an IP address, enable IP Filtering and enter the IP address of the user you wish to
block.
Object Description
Enable IP Filtering
Enable IPv4
Enable IPv6
Local IP Address
Protocol
Comment
Figure 4-41: IP Filtering
Check this box to enable IP Filter function
Check this box to enable IP filtering method using IPv4.
Check this box to enable IP filtering method using IPv6.
Add LAN IP address you want to control
Select the port number protocol type (TCP, UDP or both).
If you are unsure, then leave it to the default both protocol
Enter the description for this setting.
70
Page 71

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.4.5 MAC Filtering
Entries in this table are used to restrict certain types of data packets from your local network to Internet through
the Industrial wall-mount Gigabit router. Use of such filters can be helpful in securing or restricting your local
network as shown in Figure 4-42.
Figure 4-42: MAC Filtering
Object Description
Enable MAC Filtering
MAC Address
Comment
Check this box to enable MAC filtering.
Add MAC address you want to control.
Enter the description for this setting.
71
Page 72

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.4.6 URL Filtering
URL filter is used to deny LAN users from accessing the internet as shown in Figure 4-43. Block those URLs which
contain keywords listed below.
Figure 4-43: URL Filtering
Object Description
Enable URL Filtering
deny url address (black list)
allow url address (white list)
URL Address
Check this box to enable URL Filter function.
deny access listed URL in the Current URL Filtering table and allow other
URLs which are not in the list.
allow access listed URL in the Current URL Filtering table and deny other
URLs which are not in the list.
The URL Address that you want to filter.
72
Page 73

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.4.7 DMZ
A Demilitarized Zone is used to provide Internet services without sacrificing unauthorized access to its local private
network as shown in Figure 4-44.Typically, the DMZ host contains devices accessible to Internet traffic, such as
Web (HTTP) servers, FTP servers, SMTP (e-mail) servers and DNS servers.
Figure 4-44: DMZ
Object Description
Enable DMZ
DMZ Host IP Address
Check the box to enable DMZ function. If the DMZ Host Function is enabled,
it means that you set up DMZ host at a particular computer to be exposed to
the Internet so that some applications/software, especially Internet / online
game can have two way connections.
Enter the IP address of a particular host in your LAN which will receive all
the packets originally going to the WAN port / Public IP address above.
73
Page 74

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.4.8 Port Forwarding
Entries in this table allow you to automatically redirect common network services to a specific machine behind the
NAT firewall as shown in Figure 4-45. These settings are only necessary if you wish to host some sort of server
like a web server or mail server on the private local network behind your Router's NAT firewall.
Object Description
Enable Port Forwarding
Local IP Address
Protocol
Local Port Range
Remote IP Address
Remote Port Range
Figure 4-45: Port Forwarding
Check the box to enable Port Forwarding function
Enter Local IP address of specified host or server on the private local
network.
Select the port number protocol type (TCP, UDP or both). If you are unsure,
then leave it to the default both protocols.
Enter local ports you want to control. For TCP and UDP Services, enter the
beginning of the range of port numbers used by the service. If the service
uses a single port number, enter it in both the start and finish fields.
Enter remote IP address of external IP Address. You could set to 0.0.0.0 for
any IP address.
Enter remote ports you want to control. For TCP and UDP Services, enter
the beginning of the range of port numbers used by the service. If the
service uses a single port number, enter it in both the start and finish fields.
Comment
Enter the description for this setting.
74
Page 75

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.5 Maintenance
The Maintenance menu provides the following features for managing the system as Figure 4-52 is shown below:
Figure 4-52: Maintenance Menu
Object Description
Connection Test
Allows you to issue ICMP PING packets to troubleshoot IP.
Save/Restore Configuration
Firmware
Reboot
Backup and restore setting file via USB HDD or PC.
Firmware upgrade.
Reboot the system
75
Page 76

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.5.1 Connection Test
The page allows you to issue ICMP PING packets to troubleshoot IP connectivity issues. After you press “Ping”, 5
ICMP packets are transmitted, and the sequence number and roundtrip time are displayed upon reception of a
reply. The Page refreshes automatically until responses to all packets are received, or until a timeout occurs. The
ICMP Ping is shown in Figure 4-53.
Figure 4-53: Ping
Object Description
IP Address
Counts
Be sure the target IP address is within the same network subnet of the industrial wall-mount
Gigabit router, or you have to set up the correct gateway IP address.
The destination IP Address.
The time of ping.
76
Page 77

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.5.2 Save/Restore Configuration
This page shows the status of the configuration. You may save the setting file to the PC as Figure 4-54 is shown
below:
Figure 4-54: Save/Restore Configuration
Object Description
Save Settings to File
Load Settings from File
Reset Setting to Default
Press the button to save setting file to PC.
Press the button to select the setting file, and then press
the button to upload setting file from PC.
Press the button to reset to factory default.
77
Page 78

User’s Manual of WGR-500
4.5.3 Upgrading Firmware
This page provides the firmware upgrade of industrial wall-mount Gigabit router as shown in Figure 4-55.
Figure 4-55: Firmware upgrade
Object
Choose File
Upload
Reset
Description
Press the button to select the firmware.
Press the button to upgrade firmware to system.
Press this button to cancel the file.
4.5.4 Reboot
This page enables the device to be rebooted from a remote location. Once the Reboot button is pressed, users
have to re-log in the Web interface for about 60 seconds later as Figure 4-56 is shown below:
Object
Reboot
You can also check the SYS LED on the front panel to identify whether the System is loaded
completely or not. If the SYS LED is blinking, then it is in the firmware load stage; if the SYS
LED light is on, you can use the Web browser to log in the industrial wall-mount Gigabit router.
Description
Press the button to reboot system.
Figure 4-56: Reboot
78
Page 79

User’s Manual of WGR-500
Appendix A: Troubleshooting
This chapter contains information to help you solve issues. If the industrial wall-mount Gigabit router is not
functioning properly, make sure the industrial wall-mount Gigabit router was set up according to instructions in this
manual.
■ The Link LED is not lit
Solution:
Check the cable connection and remove duplex mode of the industrial wall-mount Gigabit router
■ Some stations cannot talk to other stations located on the other port
Solution:
Please check the VLAN settings.
■ Performance is bad
Solution:
Check the full duplex status of the industrial wall-mount Gigabit router. If the industrial wall-mount Gigabit router
is set to full duplex and the partner is set to half duplex, then the performance will be poor. Please also check the
in/out rate of the port.
■ Why the Router doesn't connect to the network
Solution:
1. Check the LNK/ACT LED on the router
2. Try another port on the router
3. Make sure the cable is installed properly
4. Make sure the cable is the right type
5. Turn off the power. After a while, turn on power again
■ 1000BASE-T port link LED is lit, but the traffic is irregular
Solution:
Make sure the attached device is not set to dedicated full duplex. Some devices use a physical or software
switch to change duplex modes. Auto-negotiation may not recognize this type of full-duplex setting.
■ Router does not power up
Solution:
1. Terminal block or DC jack is not inserted or faulty
2. Check whether the terminal block or DC jack is inserted correctly
3. If the terminal block or DC jack is inserted correctly; check that the power source is working by
connecting a different device in place of the router.
4. If that device works, refer to the next step.
5. If that device does not work, check the power source
79
Page 80

User’s Manual of WGR-500
Appendix B: Planet Smart Discovery Utility
For easily listing the industrial wall-mount Gigabit router in your Ethernet environment, Planet Smart Discovery
Utility from PLANET download center is an ideal solution.
The following installation instructions guide you to running the Planet Smart Discovery Utility.
Step 1: Download the Planet Smart Discovery Utility to the administrator PC.
Step 2: Run this utility and the following screen appears.
Step 3: Press the “Refresh” button for the currently connected devices in the discovery list as shown in the
following screen:
Step 3: Press the “Connect to Device” button and then the Web login screen appears.
The fields in the white background can be modified directly, and then you can apply the new setting
by clicking the “Update Device” button.
80
Page 81

User’s Manual of WGR-500
Appendix C: Planet DDNS
First of all, please go to http://www.planetddns.com to register a Planet DDNS account, and refer to the FAQs
(http://www.planetddns.com/index.php/faq) for how to register a free account.
When you finish your DDNS account, please return to WAN Setup -> WAN Setup to set up your WAN type which
can be connected to external network.
Step 1. Enable PLANET Dynamic DDNS, and enter account, password, and DDNS.
81
Page 82

c
o
c
M
D
e
e
g
a
e
n
D
a
h
W
t
w
e
User’s
M
s
e
W
c
anual of
GR-500
Step 2.
Step 3.
Go to Netw
Apply the se
rk-> WAN s
ttings, and en
tup page to
sure you hav
llow remote
connected t
ccess from
e WAN port
AN port.
o the internet
by Ethernet
able.
Step 4.
Lastly yo
This indi
In a remote
u can go to
ates your D
omputer, ent
y Devices pa
NS service is
r the Domai
e of Planet
working prop
Name to the
DNS website
erly.
internet bro
to check if th
ser’s addres
“Last Conn
bar.
ction IP” is di
splayed.
82
Page 83

A
ARP
ARP is an acronym for Address Resolution Protocol. It is a protocol that used to convert an IP address
into a physical address, such as an Ethernet address. ARP allows a host to communicate with other
hosts when only the Internet address of its neighbors is known. Before using IP, the host sends a
broadcast ARP request containing the Internet address of the desired destination system.
ARP Inspection
ARP Inspection is a secure feature. Several types of attacks can be launched against a host or devices
connected to Layer 2 networks by "poisoning" the ARP caches. This feature is used to block such attacks.
Only valid ARP requests and responses can go through the switch device.
User’s Manual of WGR-500
Appendix D: Glossary
Auto-Negotiation
Auto-negotiation is the process where two different devices establish the mode of operation and the
speed settings that can be shared by those devices for a link.
D
Default Gateway (Router)
Every non-router IP device needs to configure a default gateway’s IP address. When the device sends
out an IP packet, if the destination is not on the same network, the device has to send the packet to its
default gateway, which will then send it out towards the destination.
DHCP
DHCP is an acronym for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. It is a protocol used for assigning
dynamic IP addresses to devices on a network.
DHCP used by networked computers (clients) to obtain IP addresses and other parameters such as the
default gateway, subnet mask, and IP addresses of DNS servers from a DHCP server.
The DHCP server ensures that all IP addresses are unique, for example, no IP address is assigned to a
second client while the first client's assignment is valid (its lease has not expired). Therefore, IP address
pool management is done by the server and not by a human network administrator.
Dynamic addressing simplifies network administration because the software keeps track of IP addresses
rather than requiring an administrator to manage the task. This means that a new computer can be
added to a network without the hassle of manually assigning it a unique IP address.
DHCP Relay
DHCP Relay is used to forward and to transfer DHCP messages between the clients and the server
when they are not on the same subnet domain.
83
Page 84

DNS
User’s Manual of WGR-500
The DHCP option 82 enables a DHCP relay agent to insert specific information into a DHCP request
packets when forwarding client DHCP packets to a DHCP server and remove the specific information
from a DHCP reply packets when forwarding server DHCP packets to a DHCP client. The DHCP server
can use this information to implement IP address or other assignment policies. Specifically the option
works by setting two sub-options: Circuit ID (option 1) and Remote ID (option2). The Circuit ID sub-option
is supposed to include information specific to which circuit the request came in on. The Remote ID
sub-option was designed to carry information relating to the remote host end of the circuit.
The definition of Circuit ID in the switch is 4 bytes in length and the format is "vlan_id" "module_id"
"port_no". The parameter of "vlan_id" is the first two bytes represent the VLAN ID. The parameter of
"module_id" is the third byte for the module ID (in standalone switch it always equal 0, in stackable switch
it means switch ID). The parameter of "port_no" is the fourth byte and it means the port number.
The Remote ID is 6 bytes in length, and the value is equal the DHCP relay agents MAC address.
DNS is an acronym for Domain Name System. It stores and associates many types of information with
domain names. Most importantly, DNS translates human-friendly domain names and computer
hostnames into computer-friendly IP addresses. For example, the domain name www.example.com
might translate to 192.168.0.1.
DoS
DoS is an acronym for Denial of Service. In a denial-of-service (DoS) attack, an attacker attempts to
prevent legitimate users from accessing information or services. By targeting at network sites or network
connection, an attacker may be able to prevent network users from accessing email, web sites, online
accounts (banking, etc.), or other services that rely on the affected computer.
E
Ethernet Type
Ethernet Type, or EtherType, is a field in the Ethernet MAC header, defined by the Ethernet networking
standard. It is used to indicate which protocol is being transported in an Ethernet frame.
F
FTP
H
HTTP
FTP is an acronym for File Transfer Protocol. It is a transfer protocol that uses the Transmission Control
Protocol (TCP) and provides file writing and reading. It also provides directory service and security
features.
HTTP is an acronym for Hypertext Transfer Protocol. It is a protocol that used to transfer or convey
information on the World Wide Web (WWW).
84
Page 85

HTTPS
User’s Manual of WGR-500
HTTP defines how messages are formatted and transmitted, and what actions Web servers and
browsers should take in response to various commands. For example, when you enter a URL in your
browser, this actually sends an HTTP command to the Web server directing it to fetch and transmit the
requested Web Page. The other main standard that controls how the World Wide Web works is HTML,
which covers how Web Pages are formatted and displayed.
Any Web server machine contains, in addition to the Web Page files it can serve, an HTTP daemon, a
program that is designed to wait for HTTP requests and handle them when they arrive. The Web browser
is an HTTP client, sending requests to server machines. An HTTP client initiates a request by
establishing a Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) connection to a particular port on a remote host (port
80 by default). An HTTP server listening on that port waits for the client to send a request message.
HTTPS is an acronym for Hypertext Transfer Protocol over Secure Socket Layer. It is used to indicate a
secure HTTP connection.
HTTPS provide authentication and encrypted communication and is widely used on the World Wide Web
I
ICMP
IGMP
for security-sensitive communication such as payment transactions and corporate logons.
HTTPS is really just the use of Netscape's Secure Socket Layer (SSL) as a sublayer under its regular
HTTP application layering. (HTTPS uses port 443 instead of HTTP port 80 in its interactions with the
lower layer, TCP/IP.) SSL uses a 40-bit key size for the RC4 stream encryption algorithm, which is
considered an adequate degree of encryption for commercial exchange.
ICMP is an acronym for Internet Control Message Protocol. It is a protocol that generated the error
response, diagnostic or routing purposes. ICMP messages generally contain information about routing
difficulties or simple exchanges such as time-stamp or echo transactions. For example, the PING
command uses ICMP to test an Internet connection.
IGMP is an acronym for Internet Group Management Protocol. It is a communications protocol used to
manage the membership of Internet Protocol multicast groups. IGMP is used by IP hosts and adjacent
IP
multicast routers to establish multicast group memberships. It is an integral part of the IP multicast
specification, like ICMP for unicast connections. IGMP can be used for online video and gaming, and
allows more efficient use of resources when supporting these uses.
IP is an acronym for Internet Protocol. It is a protocol used for communicating data across a internet
network.
IP is a "best effort" system, which means that no packet of information sent over it is assured to reach its
destination in the same condition it was sent. Each device connected to a Local Area Network (LAN) or
Wide Area Network (WAN) is given an Internet Protocol address, and this IP address is used to identify
85
Page 86

the device uniquely among all other devices connected to the extended network.
The current version of the Internet protocol is IPv4, which has 32-bits Internet Protocol addresses
allowing for in excess of four billion unique addresses. This number is reduced drastically by the practice
of webmasters taking addresses in large blocks, the bulk of which remain unused. There is a rather
substantial movement to adopt a new version of the Internet Protocol, IPv6, which would have 128-bits
Internet Protocol addresses. This number can be represented roughly by a three with thirty-nine zeroes
after it. However, IPv4 is still the protocol of choice for most of the Internet.
IP Source Guard
IP Source Guard is a secure feature used to restrict IP traffic on DHCP snooping untrusted ports by
filtering traffic based on the DHCP Snooping Table or manually configured IP Source Bindings. It helps
prevent IP spoofing attacks when a host tries to spoof and use the IP address of another host.
L
LAN
User’s Manual of WGR-500
N
NAT
NetBIOS
Local Area Network. A LAN is a group of computers and devices connected together in a relatively small
area (such as a house or an office). Your network is considered a LAN.
Network Address Translation. NAT technology translates IP addresses of a local area network to a
different IP address for the Internet Using the NAT capability of WGR-500 Series , you can access the
Internet from any computer on your network without having to purchase more IP addresses from your
ISP.
NetBIOS is an acronym for Network Basic Input/Output System. It is a program that allows applications
on separate computers to communicate within a Local Area Network (LAN), and it is not supported on a
Wide Area Network (WAN).
The NetBIOS giving each computer in the network both a NetBIOS name and an IP address
NTP
PD
corresponding to a different host name, provides the session and transport services described in the
Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model.
NTP is an acronym for Network Time Protocol, a network protocol for synchronizing the clocks of
computer systems. NTP uses UDP (datagrams) as transport layer.
PD is an acronym for Powered Device. In a PoE> system the power is delivered from a PSE ( power
sourcing equipment ) to a remote device. The remote device is called a PD.
86
Page 87

PHY
PING
POP3
User’s Manual of WGR-500
PHY is an abbreviation for Physical Interface Transceiver and is the device that implement the Ethernet
physical layer (IEEE-802.3).
ping is a program that sends a series of packets over a network or the Internet to a specific computer in
order to generate a response from that computer. The other computer responds with an acknowledgment
that it received the packets. Ping was created to verify whether a specific computer on a network or the
Internet exists and is connected.
ping uses Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) packets. The PING Request is the packet from the
origin computer, and the PING Reply is the packet response from the target.
POP3 is an acronym for Post Office Protocol version 3. It is a protocol for email clients to retrieve email
PPPoE
messages from a mail server.
POP3 is designed to delete mail on the server as soon as the user has downloaded it. However, some
implementations allow users or an administrator to specify that mail be saved for some period of time.
POP can be thought of as a "store-and-forward" service.
An alternative protocol is Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP). IMAP provides the user with more
capabilities for retaining e-mail on the server and for organizing it in folders on the server. IMAP can be
thought of as a remote file server.
POP and IMAP deal with the receiving of e-mail and are not to be confused with the Simple Mail Transfer
Protocol (SMTP). You send e-mail with SMTP, and a mail handler receives it on your recipient's behalf.
Then the mail is read using POP or IMAP. IMAP4 and POP3 are the two most prevalent Internet standard
protocols for e-mail retrieval. Virtually all modern e-mail clients and servers support both.
PPPoE is an acronym for Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet.
It is a network protocol for encapsulating Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) frames inside Ethernet frames. It
is used mainly with ADSL services where individual users connect to the ADSL transceiver (modem) over
Ethernet and in plain Metro Ethernet networks (Wikipedia).
Q
QoS
QoS is an acronym for Quality of Service. It is a method to guarantee a bandwidth relationship between
individual applications or protocols.
A communications network transports a multitude of applications and data, including high-quality video
and delay-sensitive data such as real-time voice. Networks must provide secure, predictable,
measurable, and sometimes guaranteed services.
Achieving the required QoS becomes the secret to a successful end-to-end business solution. Therefore,
87
Page 88

QoS is the set of techniques to manage network resources.
QoS class
Every incoming frame is classified to a QoS class, which is used throughout the device for providing
queuing, scheduling and congestion control guarantees to the frame according to what was configured
for that specific QoS class. There is a one to one mapping between QoS class, queue and priority. A QoS
class of 0 (zero) has the lowest priority.
R
RADIUS
RADIUS is an acronym for Remote Authentication Dial In User Service. It is a networking protocol that
provides centralized access, authorization and accounting management for people or computers to
connect and use a network service.
S
User’s Manual of WGR-500
SHA
SMTP
SNMP
SHA is an acronym for Secure Hash Algorithm. It designed by the National Security Agency (NSA) and
published by the NIST as a U.S. Federal Information Processing Standard. Hash algorithms compute a
fixed-length digital representation (known as a message digest) of an input data sequence (the message)
of any length.
SMTP is an acronym for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. It is a text-based protocol that uses the
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and provides a mail service modeled on the FTP file transfer
service. SMTP transfers mail messages between systems and notifications regarding incoming mail.
SNMP is an acronym for Simple Network Management Protocol. It is part of the Transmission Control
Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) protocol for network management. SNMP allow diverse network
objects to participate in a network management architecture. It enables network management systems to
learn network problems by receiving traps or change notices from network devices implementing SNMP.
T
Tag Pri orit y
Tag Priority is a 3-bit field storing the priority level for the 802.1Q frame.
TCP
TCP is an acronym for Transmission Control Protocol. It is a communications protocol that uses the
88
Page 89

TELNET
User’s Manual of WGR-500
Internet Protocol (IP) to exchange the messages between computers.
The TCP protocol guarantees reliable and in-order delivery of data from sender to receiver and
distinguishes data for multiple connections by concurrent applications (for example, Web server and
e-mail server) running on the same host.
The applications on networked hosts can use TCP to create connections to one another. It is known as a
connection-oriented protocol, which means that a connection is established and maintained until such
time as the message or messages to be exchanged by the application programs at each end have been
exchanged. TCP is responsible for ensuring that a message is divided into the packets that IP manages
and for reassembling the packets back into the complete message at the other end.
Common network applications that use TCP include the World Wide Web (WWW), e-mail, and File
Transfer Protocol (FTP).
TELNET is an acronym for TELetype NETwork. It is a terminal emulation protocol that uses the
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and provides a virtual connection between TELNET server and
U
UDP
TELNET client.
TELNET enables the client to control the server and communicate with other servers on the network. To
start a Telnet session, the client user must log in to a server by entering a valid username and password.
Then, the client user can enter commands through the Telnet program just as if they were entering
commands directly on the server console.
UDP is an acronym for User Datagram Protocol. It is a communications protocol that uses the Internet
Protocol (IP) to exchange the messages between computers.
UDP is an alternative to the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) that uses the Internet Protocol (IP).
Unlike TCP, UDP does not provide the service of dividing a message into packet datagrams, and UDP
doesn't provide reassembling and sequencing of the packets. This means that the application program
that uses UDP must be able to make sure that the entire message has arrived and is in the right order.
Network applications that want to save processing time because they have very small data units to
exchange may prefer UDP to TCP.
UDP provides two services not provided by the IP layer. It provides port numbers to help distinguish
different user requests and, optionally, a checksum capability to verify that the data arrived intact.
Common network applications that use UDP include the Domain Name System (DNS), streaming media
applications such as IPTV, Voice over IP (VoIP), and Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP).
UPnP
UPnP is an acronym for Universal Plug and Play. The goals of UPnP are to allow devices to connect
seamlessly and to simplify the implementation of networks in the home (data sharing, communications,
and entertainment) and in corporate environments for simplified installation of computer components
89
Page 90

User Priority
User Priority is a 3-bit field storing the priority level for the 802.1Q frame.
V
VLAN
Virtual LAN. A method to restrict communication between switch ports. VLANs can be used for the
following applications:
VLAN unaware switching: This is the default configuration. All ports are VLAN unaware with Port VLAN
ID 1 and members of VLAN 1. This means that MAC addresses are learned in VLAN 1, and the switch
does not remove or insert VLAN tags.
VLAN aware switching: This is based on the IEEE 802.1Q standard. All ports are VLAN aware. Ports
connected to VLAN aware switches are members of multiple VLANs and transmit tagged frames. Other
User’s Manual of WGR-500
ports are members of one VLAN, set up with this Port VLAN ID, and transmit untagged frames.
Provider switching: This is also known as Q-in-Q switching. Ports connected to subscribers are VLAN
unaware, members of one VLAN, and set up with this unique Port VLAN ID. Ports connected to the
service provider are VLAN aware, members of multiple VLANs, and set up to tag all frames. Untagged
frames received on a subscriber port are forwarded to the provider port with a single VLAN tag. Tagged
frames received on a subscriber port are forwarded to the provider port with a double VLAN tag.
VLAN ID
VLAN ID is a 12-bit field specifying the VLAN to which the frame belongs.
W
WAN
Wide Area Network. A network that connects computers located in geographically separate areas (e.g.
different buildings, cities, countries). The Internet is a wide area network.
90
 Loading...
Loading...